US8092374B2 - Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device - Google Patents
Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US8092374B2 US8092374B2US11/367,607US36760706AUS8092374B2US 8092374 B2US8092374 B2US 8092374B2US 36760706 AUS36760706 AUS 36760706AUS 8092374 B2US8092374 B2US 8092374B2
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- hollow body
- tendons
- space
- handle
- flexible
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related, expires
Links
- 0C1C2=**C*12Chemical compoundC1C2=**C*120.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M29/00—Dilators with or without means for introducing media, e.g. remedies
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/00064—Constructional details of the endoscope body
- A61B1/00071—Insertion part of the endoscope body
- A61B1/00078—Insertion part of the endoscope body with stiffening means
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/005—Flexible endoscopes
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/005—Flexible endoscopes
- A61B1/0051—Flexible endoscopes with controlled bending of insertion part
- A61B1/0055—Constructional details of insertion parts, e.g. vertebral elements
Definitions
- the inventionrelates to a variably flexible insertion device and to a method for variably flexing an insertion device.
- the insertion devicemay be used to insert an instrument, in particular a scope, such as an endoscope or a colonoscope, into a patient.
- U.S. Pat. No. 6,942,613 to Ewers et al.discloses a shape lockable apparatus and method, in which nestable elements of an overtube are linked by elastic tension wires connected to an actuator to selectively stiffen the overtube for advancing an instrument.
- U.S. Pat. No. 5,759,151 to Sturgesuses a spine having cylindrical segments interconnected by a flexible cable. The cable is secured to a controller for selectively stiffening and relaxing the spine.
- the Ewers et al. and Sturges devicesare complicated and have only elastic tension wires or a flexible cable to maintain stiffness.
- U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,984,203 and 6,800,056 to Tartaglia et al.teach a guide which advances in a distal portion of a steerable endoscope having a segmented body.
- Related U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,468,203 and 6,610,007 to Belson et al.disclose a steerable endoscope with a body, a steering control for a distal portion of the body which selects a path within the patients body and a motion controller for a proximal end of the body which assumes the selected curve.
- a fiber optic imaging bundle or a video cameraare disposed in the body.
- the Tartaglia et al. and Belson et al. devicesprovide no mechanism for variably stiffening the guide.
- U.S. Pat. No. 5,337,733 to Bauerfeind et al.relates to a tubular inserting device with variable rigidity, in which a flexible insertion part has outer and inner walls defining an intermediate space therebetween. Application of a vacuum to the intermediate space causes the inner wall to lie against the outer wall to render the insertion part rigid.
- the Bauerfeind et al. devicerelies merely upon contact between the outer and inner walls for rigidity, with no additional stiffening aid.
- ASGE Abstract 136 submitted in 1983discloses a soft-plastic, split, stiffening overtube to be placed over a colonoscope at any point during the examination.
- a variably flexible insertion devicecomprising a hollow body having a proximal end with an entrance for receiving an instrument, such as a scope, and a distal end with a tip for protrusion of the instrument.
- a deviceis provided for transitioning the hollow body between a relatively flexible condition and a relatively stiff condition.
- Tendonsare disposed within the hollow body for maintaining the hollow body in the relatively flexible and relatively stiff conditions.
- a method for variably flexing an insertion device for receiving an instrumentcomprises providing a hollow body having inner and outer sleeves defining a space therebetween and providing tendons in the space. Suction is applied to create a vacuum in the space for frictionally locking the tendons in place between the inner and outer sleeves in a relatively stiff condition of the hollow body. The vacuum is relieved to release the tendons in a relatively flexible condition of the hollow body.
- the hollow bodyhas an inner sleeve and an outer sleeve defining a space therebetween at least partly surrounding the tendons, and the transitioning device, such as a vacuum port communicating with said space, applies suction to the space for frictionally locking the tendons in place.
- Vertebraemay be disposed within the hollow body for guiding the tendons.
- the hollow bodyhas a handle and a flexible section with a given length.
- the tendonsextend substantially entirely over said given length.
- the tendonsfloat in said handle when said hollow body is in said relatively flexible condition, but are rigidly attached at said distal end.
- the tendonsare not under tension both in said relatively flexible and in the relatively stiff conditions.
- vertebraeare disposed within said hollow body for guiding said tendons.
- the vertebraeinclude a distal-most vertebra at which said tendons are attached.
- the hollow bodymay have a longitudinal slit formed therein for radially loading the hollow body onto the instrument.
- the slitmay be sealed by a closure, such as a slide or press zipper used for plastic storage bags, permitting the device to be resealed after the hollow body has been loaded.
- the hollow bodyhas a coil for maintaining a circular cross section.
- the coilmay be a bookbinding-type coil to permit loading of the hollow body on the instrument.
- a bookbinding-type coilis known as a ring wire, double wire, double loop or twin loop binding.
- the hollow bodyhas a handle, a distal end cap to accommodate differently sized instruments, and a flexible portion having a predetermined length in a longitudinal direction between said handle and said distal end cap.
- the hollow body and said tendonsextend entirely along said predetermined length.
- locking padsencircle said tendons in a friction lock area transversely to said longitudinal direction for frictionally locking said tendons in place in addition to said friction locking by said inner and outer sleeves.
- the handleis an outer handle and the hollow body has an inner handle within said outer handle.
- the inner handlehas channel grooves permitting movement of said tendons.
- the inner handlehas a groove formed therein receiving an O-ring for sealing a space between said outer handle and said inner handle.
- both a transitioning device using a vacuum to cause contact between the inner and outer sleeves and tendons supporting the stiffening but being free of tensionare combined to enhance the reliability of the device.
- the capability of loading the hollow body onto the instrument at any time during a procedurealso exists by virtue of the slit in the hollow body.
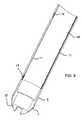
- FIG. 1is a diagrammatic, side-elevational view of a variably flexible insertion device according to the invention
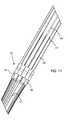
- FIG. 2is a view similar to FIG. 1 showing details of the interior of the insertion device of the invention
- FIG. 3is an enlarged, fragmentary, perspective view showing inner and outer handles, locking pads and tendons of the insertion device of the invention
- FIG. 4is a view similar to FIG. 3 , showing the inner and outer handles and a friction surface and grooves for the tendons;
- FIG. 5is a perspective view of a portion of the insertion device of the invention, showing details of the inner and outer handles;
- FIG. 6is an enlarged, fragmentary, side-elevational view of a nose tip and tendons of the insertion device of the invention
- FIG. 7is a fragmentary, perspective view of the nose tip showing details of the tendons and vertebrae;
- FIG. 8is a fragmentary, longitudinal-sectional view of the nose tip and vertebrae
- FIG. 9is an enlarged, fragmentary, perspective view of the tendons over a friction zone
- FIG. 10is a fragmentary, perspective view illustrating the tendons in transition and locking
- FIG. 11is a fragmentary, perspective view showing the locking pads for the tendons
- FIG. 12is a fragmentary, longitudinal-sectional view of the handle
- FIG. 13is a fragmentary, longitudinal-sectional view of a handle locking area
- FIG. 14is a cross-sectional view taken along a line XIV-XIV of FIG. 3 , through the handle assembly during transition;
- FIG. 15is a cross-sectional view taken along a line XV-XV of
- FIG. 10through the vertebrae with the tendons
- FIG. 16is a cross-sectional view taken along a line XVI-XVI of FIG. 3 , through the vertebrae with the tendons;
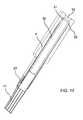
- FIG. 17is a fragmentary, side-elevational view of the device in a flexed condition, showing the nose tip, the vertebrae and the effect of bending on the tendons;
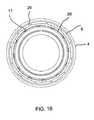
- FIG. 18is a view similar to FIG. 1 , showing a slit hollow body with a zipper closure;
- FIG. 19is a perspective view of a coil used with the embodiment of FIG. 18 .
- the insertion device 1has a hollow body with a proximal end 2 for manipulation by an operator and for receiving an instrument 32 such as an endoscope or colonoscope seen in FIG. 5 .
- the insertion device 1also has a distal end 3 for insertion into a patient and for protrusion of the instrument 32 .
- An outer handle 4 of the hollow body for the operatoris disposed at the proximal end 2 .
- the handle 4has a vacuum port 5 formed therein.
- An outer sleeve 6 of the hollow bodyis disposed between the outer handle 4 and a nose tip 7 of the hollow body at the distal end 3 .
- the outer sleeve 6provides a flexible section with a given length extending beyond the handle 4 .
- FIG. 2shows that the outer handle 4 contains an inner handle 30 of the hollow body having channel grooves 10 which permit movement of tendons 11 .
- the tendons 11extend substantially entirely over the given length of the flexible section provided by the outer sleeve 6 .
- the tendons 11may have a rounded or flattened cross section or a flattened cross section twisted along its length.
- a friction lock area 12is disposed within the outer sleeve 6 for locking the tendons 11 in a manner to be discussed below.
- Vertebrae 13 - 17are distributed along a flexible area 20 which is approximately 30 inches long. Whereas the vertebrae 14 - 17 allow movement of the tendons 11 , the first vertebra 13 closest to the distal end 3 is fixed to the tendons 11 .
- six vertebraeare shown, it is understood that more or fewer vertebrae may be provided, for example eight vertebrae, depending on the length of the device 1 .
- the number of tendons 11is also variable, although twelve is used as an example
- a ring of locking pads 25encircles the friction lock area 12 .
- Each tendon 11is assigned a respective locking pad 25 , which is clearly shown in FIG. 16 .
- the tendons 11are disposed between the locking pads 25 and a friction surface 26 shown in FIGS. 4 and 16 .
- the friction surface 26is part of the inner handle 30 having the grooves 10 in which the tendons 11 move.
- FIG. 5illustrates the outer handle 4 as well as the inner handle 30 with the channel grooves 10 for the tendons 11 .
- the outer handle 4is shown as being transparent in FIG. 5 , so as to be able to illustrate an entrance 32 for the surgical instrument 38 , such as an endoscope or colonoscope, a groove 33 for receiving an O-ring and the vacuum port 5 .
- FIG. 6shows the region of the nose tip 7 .
- the tendons 11are fixed and welded to the first vertebra 13 .
- FIG. 7also shows the tendons 11 fixed to the first vertebra 13 as well as the second vertebra 14 under which the tendons are free to move in the channel grooves 10 formed in the inner handle 30 .
- FIG. 8illustrates the outer sleeve 6 , the nose tip 7 , two tendons 11 , as well as the tendons being welded to the first vertebra 13 and being freely movable in the second vertebra 14 .
- An inner sleeve 35 of the hollow bodyis also shown in FIG. 8 .
- FIG. 8additionally shows an end cap 37 to be snapped-on at the distal end to accommodate different sized instruments or scopes 38 .
- FIG. 9shows how the tendons 11 are freely movable in the channel grooves 10 in the inner handle 30 and pass over the friction surface 26 .
- FIG. 10also shows the friction locking pads 25 , the inner handle 30 with the grooves 10 and the tendons 11 passing through the grooves 10 and under the fifth vertebra 17 .
- the cross section of the vertebra 17 illustrated in FIG. 15additionally shows a coil 36 of the hollow body disposed within and supporting the inner sleeve 35 .
- the coilmay be a wire which is TEFLON- or hydrophilic-coated to ease insertion of an endoscope or colonoscope.
- the stiffness or spring constant k of the coil 36tends to maintain the device 1 in a straight condition. However, as will be explained in detail below, the device 1 does not remain straight when held horizontal in its flexible state.
- the coil 36is used to maintain the round cross section of the device 1 while it is flexed.
- FIG. 11shows the tendons 11 passing through the channel grooves 10 formed in the inner handle 30 and under the friction locking pads 25 .
- the tendons 11are freely movable in the channel grooves 10 , except when pinched between the friction locking pads 25 and the friction surface 26 in the friction lock area 12 .
- FIG. 12shows an O-ring 31 disposed in the groove 33 .
- FIG. 14shows a space 34 between the outer handle 4 and the inner handle 30 .
- the space 34is sealed by the O-ring 31 and communicates with the vacuum port 5 for applying positive and negative pressure (vacuum) to the space.
- FIG. 13is a cross-sectional view illustrating details of the friction lock area 12 . It may be seen that the tendons 11 which pass below the vertebrae 16 , 17 are pinched between the friction locking pads 25 and the friction surface 26 in the friction area 12 .
- the hollow body 4 , 6 , 7 , 30 , 35 , 36has a longitudinal slit 39 formed therein for radially loading the hollow body onto the instrument 38 .
- the slithas a closure 40 , such as a slide or press zipper used for plastic storage bags, permitting the device to be resealed after the hollow body has been loaded.
- the coilin this case is a ring wire, double wire, double loop or twin loop binding 41 seen in FIG. 19 , such as is used for notebooks.
- the operation of the variably flexible insertion device 1is best understood by making reference to FIG. 17 in conjunction with the above-described figures.
- vacuumis applied to the space 34 through the vacuum port 5 .
- suctionis applied to create the vacuum, it causes the inner sleeve 35 and the outer sleeve 6 to firmly contact each other with the tendons 11 sandwiched and frictionally locked therebetween.
- the vacuum port 5acts as a device for transitioning the hollow body 4 , 6 , 7 , 30 , 35 , 36 between the relatively flexible condition and the relatively stiff condition through the application of a vacuum.
- Most of the stiffness causing the device 1 to maintain its flexed conditionis accomplished by this interaction of the inner and outer sleeves and the tendons.
- additional stiffnessmay optionally be accomplished by providing the friction locking pads 25 which contract and hold the tendons 11 against the friction surface 26 in the friction area 12 .
- the device 1therefore maintains its flexed condition.
- FIG. 17shows that in the flexed condition, the tendons 11 at the outer periphery of the bend become shorter and the tendons 11 at the inner periphery of the bend become longer, since they are all fixed in place at the first vertebra 13 .
- the tendons or wires 11are passive elements which are not in tension at any time.
- the tendonsfloat within the hollow body when it is in the flexible condition, except at the distal end.
- the tendonsare frictionally locked by the inner sleeve 35 and the outer sleeve 6 when the hollow body is in the stiff condition.
- the tendonshave no active control imposed on them and are not pulled or constrained.
- the vacuum in the space 34is replaced by air at ambient or positive pressure. This causes the inner sleeve 35 and the outer sleeve 6 to release the tendons 11 and allows the stiffness or spring constant k of the coil 36 to place the device 1 into its normally flexible condition. If friction locking pads 25 are used, they also relax and expand, which in turn releases the tendons 11 .
- the deviceis intended to be used in a manner similar to prior art devices. Therefore, the device will be placed over the endoscope. The endoscope will then be inserted into the rectum. The device will then be pushed in its flexible condition, to follow the curvature of the scope. The device will then be stiffened, allowing the scope to be pushed forward with less pressure exerted on the colon of the patient. This procedure can be repeated until the scope reaches the cecum.
- the deviceis placed over the endoscope.
- the endoscopeis inserted into the patient transorally, through the stomach and then partially into the small bowel.
- the deviceis then pushed in its flexible condition, to follow the curvature of the scope.
- the deviceis then stiffened, allowing the scope to be pushed forward without the scope looping in the stomach.
- Another use of the deviceis for aiding in access to internal body parts, such as the gallbladder, through an opening of an internal body cavity, such as the stomach.
- the deviceis placed over the endoscope.
- the endoscopeis inserted into the patient transorally, through the stomach and then up against the internal surface of the stomach.
- the deviceis then pushed in its flexible condition, to follow the curvature of the scope.
- the deviceis then stiffened, allowing the surgeon to create an opening in the stomach wall without the scope looping in the stomach. Once the opening is created, the device and the scope can be advanced outside the stomach.
- the devicecan then be stiffened to create a stable platform to perform surgical procedures outside of the stomach.
- the devicecould contain one or more features (i.e. balloons) for sealing the outer periphery of the device to the stomach wall to prevent gastric fluids from exiting the stomach.
- the deviceis capable of being loaded on the instrument or scope after the scope is inserted into the patient.
- the slit down the length of the deviceallows it to be loaded on the scope so that the scope is inserted radially into the hollow body.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Anesthesiology (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Prostheses (AREA)
- Endoscopes (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims (47)
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US11/367,607US8092374B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2006-03-02 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
| PCT/US2007/005478WO2007103239A2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2007-03-02 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
| US13/311,145US8696639B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2011-12-05 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
| US14/021,266US9155451B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2013-09-09 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
| US14/837,328US10123683B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2015-08-27 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
| US16/150,328US10835112B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2018-10-03 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US11/367,607US8092374B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2006-03-02 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US11/502,322Continuation-In-PartUS7988621B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2006-08-10 | Torque-transmitting, variably-flexible, corrugated insertion device and method for transmitting torque and variably flexing a corrugated insertion device |
Related Child Applications (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/311,145DivisionUS8696639B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2011-12-05 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
| US14/021,266Continuation-In-PartUS9155451B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2013-09-09 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
| US14/837,328Continuation-In-PartUS10123683B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2015-08-27 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US20070208364A1 US20070208364A1 (en) | 2007-09-06 |
| US8092374B2true US8092374B2 (en) | 2012-01-10 |
Family
ID=38472354
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US11/367,607Expired - Fee RelatedUS8092374B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2006-03-02 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
| US13/311,145Expired - Fee RelatedUS8696639B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2011-12-05 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/311,145Expired - Fee RelatedUS8696639B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2011-12-05 | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US8092374B2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2007103239A2 (en) |
Cited By (46)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110040282A1 (en)* | 2006-02-15 | 2011-02-17 | Epflex Feinwerktechnik Gmbh | Controllably Stiffenable Tube |
| US20120095491A1 (en)* | 2006-03-02 | 2012-04-19 | Smith Kevin W | Variably Flexible Insertion Device and Method for Variably Flexing an Insertion Device |
| US20140364766A1 (en)* | 2011-04-26 | 2014-12-11 | Creative Vascular, Llc | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral iv catheter |
| US20150025320A1 (en)* | 2008-05-27 | 2015-01-22 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Stiffening Assembly |
| USD731652S1 (en) | 2014-02-19 | 2015-06-09 | Tidi Products, Llc | Dental curing light sleeve |
| US20150306353A1 (en)* | 2014-04-28 | 2015-10-29 | Mark Edman Idstrom | Guidewires With Variable Rigidity |
| US20150306355A1 (en)* | 2014-04-28 | 2015-10-29 | Mark Edman Idstrom | Guidewires with variable rigidity |
| US9186049B2 (en) | 2012-10-25 | 2015-11-17 | Choon Kee Lee | Extensible and guidable apparatus |
| US9186100B2 (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2015-11-17 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral IV catheter |
| US9433468B2 (en) | 2013-10-04 | 2016-09-06 | Tidi Products, Llc | Sheath for a medical or dental instrument |
| US9744344B1 (en) | 2016-06-30 | 2017-08-29 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Devices and methods for catheter placement within a vein |
| US9750446B2 (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2017-09-05 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral IV catheter |
| US20180064311A1 (en)* | 2007-06-27 | 2018-03-08 | Syntheon, Llc | Torque-Transmitting, Variably-Flexible, Locking Insertion Device and Method for Operating the Insertion Device |
| US10004558B2 (en) | 2009-01-12 | 2018-06-26 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Electrical ablation devices |
| US10105141B2 (en) | 2008-07-14 | 2018-10-23 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Tissue apposition clip application methods |
| US10123683B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2018-11-13 | Syntheon, Llc | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
| US10143411B2 (en) | 2009-07-21 | 2018-12-04 | The General Hospital Corporation | Peripheral blood sampling methods and devices |
| US10159527B2 (en) | 2004-09-24 | 2018-12-25 | Syntheon, Llc | Selective stiffening catheter and methods for operating a selective stiffening catheter |
| US10206709B2 (en) | 2012-05-14 | 2019-02-19 | Ethicon Llc | Apparatus for introducing an object into a patient |
| US10258406B2 (en) | 2011-02-28 | 2019-04-16 | Ethicon Llc | Electrical ablation devices and methods |
| US10278761B2 (en) | 2011-02-28 | 2019-05-07 | Ethicon Llc | Electrical ablation devices and methods |
| US10300247B2 (en) | 2016-02-03 | 2019-05-28 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Devices and methods for fluid transfer through a placed peripheral intravenous catheter |
| US10314603B2 (en) | 2008-11-25 | 2019-06-11 | Ethicon Llc | Rotational coupling device for surgical instrument with flexible actuators |
| US10342598B2 (en) | 2012-08-15 | 2019-07-09 | Ethicon Llc | Electrosurgical system for delivering a biphasic waveform |
| US10478248B2 (en) | 2007-02-15 | 2019-11-19 | Ethicon Llc | Electroporation ablation apparatus, system, and method |
| US10492880B2 (en) | 2012-07-30 | 2019-12-03 | Ethicon Llc | Needle probe guide |
| US10751507B2 (en) | 2017-04-10 | 2020-08-25 | Syn Variflex, Llc | Thermally controlled variable-flexibility catheters and methods of manufacturing same |
| US10773056B2 (en) | 2017-03-21 | 2020-09-15 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for controlling catheter device size |
| US10779882B2 (en) | 2009-10-28 | 2020-09-22 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Electrical ablation devices |
| US11090461B2 (en) | 2017-03-21 | 2021-08-17 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Devices and methods for fluid transfer through a placed peripheral intravenous catheter |
| US11122971B2 (en) | 2016-08-18 | 2021-09-21 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Device and method for enhanced visualization of the small intestine |
| US11135398B2 (en) | 2018-07-19 | 2021-10-05 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Dynamically rigidizing composite medical structures |
| US11197977B2 (en) | 2017-12-15 | 2021-12-14 | Perfuze Limited | Catheters and devices and systems incorporating such catheters |
| US11207498B2 (en) | 2019-08-20 | 2021-12-28 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Fluid transfer devices with extended length catheters and methods of using the same |
| US11219351B2 (en) | 2015-09-03 | 2022-01-11 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Device for endoscopic advancement through the small intestine |
| US11389624B2 (en) | 2020-11-26 | 2022-07-19 | Avia Vascular, Llc | Blood collection devices, systems, and methods |
| US11446469B2 (en) | 2016-07-13 | 2022-09-20 | Perfuze Limited | High flexibility, kink resistant catheter shaft |
| US11484191B2 (en) | 2013-02-27 | 2022-11-01 | Cilag Gmbh International | System for performing a minimally invasive surgical procedure |
| US11744443B2 (en) | 2020-03-30 | 2023-09-05 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Layered walls for rigidizing devices |
| US11793392B2 (en) | 2019-04-17 | 2023-10-24 | Neptune Medical Inc. | External working channels |
| US11937778B2 (en) | 2022-04-27 | 2024-03-26 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Apparatuses and methods for determining if an endoscope is contaminated |
| US12059128B2 (en) | 2018-05-31 | 2024-08-13 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Device and method for enhanced visualization of the small intestine |
| US12121677B2 (en) | 2021-01-29 | 2024-10-22 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Devices and methods to prevent inadvertent motion of dynamically rigidizing apparatuses |
| US12295550B2 (en) | 2017-07-20 | 2025-05-13 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Dynamically rigidizing overtube |
| US12329473B2 (en) | 2019-04-17 | 2025-06-17 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Dynamically rigidizing composite medical structures |
| US12330292B2 (en) | 2023-09-28 | 2025-06-17 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Telescoping robot |
Families Citing this family (56)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8075572B2 (en) | 2007-04-26 | 2011-12-13 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical suturing apparatus |
| US8100922B2 (en) | 2007-04-27 | 2012-01-24 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Curved needle suturing tool |
| US8262655B2 (en) | 2007-11-21 | 2012-09-11 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Bipolar forceps |
| US8579897B2 (en) | 2007-11-21 | 2013-11-12 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Bipolar forceps |
| US8568410B2 (en) | 2007-08-31 | 2013-10-29 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Electrical ablation surgical instruments |
| US8480657B2 (en) | 2007-10-31 | 2013-07-09 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Detachable distal overtube section and methods for forming a sealable opening in the wall of an organ |
| US20090112059A1 (en) | 2007-10-31 | 2009-04-30 | Nobis Rudolph H | Apparatus and methods for closing a gastrotomy |
| US8287469B2 (en)* | 2008-01-09 | 2012-10-16 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Articulating surgical device and method of use |
| US8262680B2 (en) | 2008-03-10 | 2012-09-11 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Anastomotic device |
| US8652150B2 (en) | 2008-05-30 | 2014-02-18 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Multifunction surgical device |
| US8114072B2 (en) | 2008-05-30 | 2012-02-14 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Electrical ablation device |
| US8070759B2 (en) | 2008-05-30 | 2011-12-06 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical fastening device |
| US8679003B2 (en) | 2008-05-30 | 2014-03-25 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical device and endoscope including same |
| US8771260B2 (en) | 2008-05-30 | 2014-07-08 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Actuating and articulating surgical device |
| US8317806B2 (en) | 2008-05-30 | 2012-11-27 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Endoscopic suturing tension controlling and indication devices |
| US8906035B2 (en) | 2008-06-04 | 2014-12-09 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Endoscopic drop off bag |
| US8403926B2 (en) | 2008-06-05 | 2013-03-26 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Manually articulating devices |
| US8361112B2 (en) | 2008-06-27 | 2013-01-29 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical suture arrangement |
| US8262563B2 (en) | 2008-07-14 | 2012-09-11 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Endoscopic translumenal articulatable steerable overtube |
| US8211125B2 (en) | 2008-08-15 | 2012-07-03 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Sterile appliance delivery device for endoscopic procedures |
| US8529563B2 (en) | 2008-08-25 | 2013-09-10 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Electrical ablation devices |
| US8241204B2 (en) | 2008-08-29 | 2012-08-14 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Articulating end cap |
| US8480689B2 (en) | 2008-09-02 | 2013-07-09 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Suturing device |
| US8409200B2 (en) | 2008-09-03 | 2013-04-02 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical grasping device |
| US8114119B2 (en) | 2008-09-09 | 2012-02-14 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical grasping device |
| US20100076451A1 (en)* | 2008-09-19 | 2010-03-25 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Rigidizable surgical instrument |
| US8337394B2 (en) | 2008-10-01 | 2012-12-25 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Overtube with expandable tip |
| US8172772B2 (en) | 2008-12-11 | 2012-05-08 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Specimen retrieval device |
| US8828031B2 (en) | 2009-01-12 | 2014-09-09 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Apparatus for forming an anastomosis |
| US9226772B2 (en) | 2009-01-30 | 2016-01-05 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical device |
| US8252057B2 (en) | 2009-01-30 | 2012-08-28 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical access device |
| US8037591B2 (en) | 2009-02-02 | 2011-10-18 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical scissors |
| US20100249700A1 (en)* | 2009-03-27 | 2010-09-30 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical instruments for in vivo assembly |
| DE102009037827A1 (en)* | 2009-08-10 | 2011-02-17 | Epflex Feinwerktechnik Gmbh | Medical catheter instrument |
| DE102009037047A1 (en)* | 2009-08-13 | 2011-02-17 | Olympus Winter & Ibe Gmbh | Tubular shaft of a surgical instrument |
| JP5448637B2 (en)* | 2009-08-18 | 2014-03-19 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Insertion path securing device |
| US8608652B2 (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2013-12-17 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Vaginal entry surgical devices, kit, system, and method |
| US8496574B2 (en) | 2009-12-17 | 2013-07-30 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Selectively positionable camera for surgical guide tube assembly |
| US8353487B2 (en) | 2009-12-17 | 2013-01-15 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | User interface support devices for endoscopic surgical instruments |
| US8506564B2 (en) | 2009-12-18 | 2013-08-13 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical instrument comprising an electrode |
| US9028483B2 (en) | 2009-12-18 | 2015-05-12 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical instrument comprising an electrode |
| US9005198B2 (en) | 2010-01-29 | 2015-04-14 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical instrument comprising an electrode |
| DE102010022430A1 (en)* | 2010-06-01 | 2011-12-01 | Karl Storz Gmbh & Co. Kg | Field of view device for an endoscope |
| US10092291B2 (en) | 2011-01-25 | 2018-10-09 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Surgical instrument with selectively rigidizable features |
| US9314620B2 (en) | 2011-02-28 | 2016-04-19 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Electrical ablation devices and methods |
| US9049987B2 (en) | 2011-03-17 | 2015-06-09 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Hand held surgical device for manipulating an internal magnet assembly within a patient |
| EP3326558B1 (en)* | 2011-11-14 | 2025-04-30 | The University of British Columbia | Intramedullary fixation system for management of pelvic and acetabular fractures |
| US8986199B2 (en) | 2012-02-17 | 2015-03-24 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Apparatus and methods for cleaning the lens of an endoscope |
| US9078662B2 (en) | 2012-07-03 | 2015-07-14 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Endoscopic cap electrode and method for using the same |
| US9572623B2 (en) | 2012-08-02 | 2017-02-21 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Reusable electrode and disposable sheath |
| US10314649B2 (en) | 2012-08-02 | 2019-06-11 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Flexible expandable electrode and method of intraluminal delivery of pulsed power |
| WO2015134750A1 (en) | 2014-03-06 | 2015-09-11 | University Of British Columbia | Shape adaptable intramedullary fixation device |
| JP6389002B2 (en) | 2014-10-14 | 2018-09-12 | ザ ユニヴァーシティ オブ ブリティッシュ コロンビア | System and method for intramedullary bone fixation |
| EP3522803A4 (en) | 2016-10-05 | 2020-05-27 | The University of British Columbia | Intramedullary fixation device with shape locking interface |
| CN112912022A (en) | 2018-10-17 | 2021-06-04 | 不列颠哥伦比亚大学 | Bone fixation device and system |
| CN111928037A (en)* | 2020-08-06 | 2020-11-13 | 重庆橙壹科技有限公司 | Rotary buckle type telescopic sleeve assembly |
Citations (60)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3557780A (en)* | 1967-04-20 | 1971-01-26 | Olympus Optical Co | Mechanism for controlling flexure of endoscope |
| US3998216A (en) | 1973-10-04 | 1976-12-21 | Olympus Optical Co., Ltd. | Bending tube for endoscope |
| US4176662A (en) | 1977-06-17 | 1979-12-04 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Administrator Of The National Aeronautics And Space Administration | Apparatus for endoscopic examination |
| US4575185A (en) | 1983-08-01 | 1986-03-11 | Combustion Engineering, Inc. | System for a fiber optic cable for remote inspection of internal structure of a nuclear steam generator |
| US4753223A (en) | 1986-11-07 | 1988-06-28 | Bremer Paul W | System for controlling shape and direction of a catheter, cannula, electrode, endoscope or similar article |
| US4762118A (en)* | 1987-07-28 | 1988-08-09 | Welch Allyn, Inc. | Self-adjusting steering mechanism for borescope, endoscope, or guide tube |
| US4815450A (en) | 1988-02-01 | 1989-03-28 | Patel Jayendra I | Endoscope having variable flexibility |
| US4817613A (en) | 1987-07-13 | 1989-04-04 | Devices For Vascular Intervention, Inc. | Guiding catheter |
| US4838859A (en)* | 1987-05-19 | 1989-06-13 | Steve Strassmann | Steerable catheter |
| US4890602A (en) | 1987-11-25 | 1990-01-02 | Hake Lawrence W | Endoscope construction with means for controlling rigidity and curvature of flexible endoscope tube |
| US4893613A (en)* | 1987-11-25 | 1990-01-16 | Hake Lawrence W | Endoscope construction with means for controlling rigidity and curvature of flexible endoscope tube |
| US4998282A (en) | 1987-12-09 | 1991-03-05 | Olympus Optical Co., Ltd. | Lifesaving borescope system |
| US5211633A (en) | 1992-06-24 | 1993-05-18 | Stouder Jr Albert E | Selectable seal cannula |
| USD337733S (en) | 1991-10-31 | 1993-07-27 | Novitas, Inc. | Housing for a one-way ultrasonic ceiling sensor |
| US5259366A (en)* | 1992-11-03 | 1993-11-09 | Boris Reydel | Method of using a catheter-sleeve assembly for an endoscope |
| US5271382A (en)* | 1991-07-24 | 1993-12-21 | Kabushiki Kaisha Machida Seisakusho | Bending device |
| US5337733A (en)* | 1989-10-23 | 1994-08-16 | Peter Bauerfeind | Tubular inserting device with variable rigidity |
| US5386817A (en)* | 1991-06-10 | 1995-02-07 | Endomedical Technologies, Inc. | Endoscope sheath and valve system |
| US5577992A (en)* | 1993-10-05 | 1996-11-26 | Asahi Kogaku Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Bendable portion of endoscope |
| US5759151A (en) | 1995-06-07 | 1998-06-02 | Carnegie Mellon University | Flexible steerable device for conducting exploratory procedures |
| US5807237A (en) | 1997-03-31 | 1998-09-15 | Tindel; Nathaniel L. | Endoscopic device |
| US5873816A (en) | 1994-11-02 | 1999-02-23 | Olympus Optical Co., Ltd. | Electronic endoscope having an insertional portion a part of which is a conductive armor |
| US6117068A (en) | 1995-10-19 | 2000-09-12 | Elite Genetics, Inc | Artificial insemination system |
| US6196967B1 (en) | 1998-03-18 | 2001-03-06 | Linvatec Corporation | Arthroscopic component joining system |
| US20020002323A1 (en) | 2000-06-30 | 2002-01-03 | Olympus Optical Co., Ltd. | Endoscope characterized by soft section thereof through which built-in components lie |
| US6346077B1 (en)* | 1996-02-20 | 2002-02-12 | Cardiothoracic Systems, Inc. | Surgical instrument for stabilizing the beating heart during coronary artery bypass graft surgery |
| US6375654B1 (en) | 2000-05-19 | 2002-04-23 | Cardiofocus, Inc. | Catheter system with working portion radially expandable upon rotation |
| US6387044B1 (en) | 1998-12-02 | 2002-05-14 | J. Morita Manufacturing Corporation | Laparoscope apparatus |
| US6468203B2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2002-10-22 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Steerable endoscope and improved method of insertion |
| US6478731B2 (en) | 2001-02-23 | 2002-11-12 | Linvatec Corporation | Endoscope-sheath interface using scope light post |
| US20020177750A1 (en) | 2001-01-09 | 2002-11-28 | Tonis Pilvisto | Endoscope-type device, particularly for emergency intubation |
| US6506150B1 (en)* | 1999-04-13 | 2003-01-14 | Pentax Corporation | Self-retaining endoscope |
| US6517477B1 (en)* | 2000-01-27 | 2003-02-11 | Scimed Life Systems, Inc. | Catheter introducer system for exploration of body cavities |
| US20030135198A1 (en) | 1999-07-23 | 2003-07-17 | Tfx Medical Extrusion Products | Catheter device having multi-lumen reinforced shaft and method of manufacture for same |
| US6610007B2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2003-08-26 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Steerable segmented endoscope and method of insertion |
| US6645223B2 (en)* | 2001-04-30 | 2003-11-11 | Advanced Cardiovascular Systems, Inc. | Deployment and recovery control systems for embolic protection devices |
| US20040044350A1 (en) | 1999-04-09 | 2004-03-04 | Evalve, Inc. | Steerable access sheath and methods of use |
| US20040138529A1 (en) | 2003-01-15 | 2004-07-15 | Usgi Medical Corp. | Endoluminal tool deployment system |
| US20040186350A1 (en)* | 2003-01-13 | 2004-09-23 | Usgi Medical Corp. | Apparatus and methods for guiding an endoscope via a rigidizable wire guide |
| US20040182393A1 (en) | 2003-02-27 | 2004-09-23 | Macmillan Nicholas Paul | Valves and suction catheter assemblies |
| US6800056B2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2004-10-05 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Endoscope with guiding apparatus |
| US6802809B2 (en) | 2001-06-29 | 2004-10-12 | Olympus Corporation | Endoscope |
| US6858005B2 (en)* | 2000-04-03 | 2005-02-22 | Neo Guide Systems, Inc. | Tendon-driven endoscope and methods of insertion |
| US20050075538A1 (en) | 2003-04-01 | 2005-04-07 | Banik Michael S. | Single use endoscopic imaging system |
| WO2005048814A2 (en) | 2003-11-12 | 2005-06-02 | Van Lue Stephen J | Magnetic devices and apparatus for medical/surgical procedures and methods for using same |
| US20050131279A1 (en) | 2003-04-01 | 2005-06-16 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Articulation joint for video endoscope |
| US6942613B2 (en)* | 2002-06-13 | 2005-09-13 | Usgi Medical Inc. | Shape lockable apparatus and method for advancing an instrument through unsupported anatomy |
| US6974411B2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2005-12-13 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Endoscope with single step guiding apparatus |
| US6984203B2 (en)* | 2000-04-03 | 2006-01-10 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Endoscope with adjacently positioned guiding apparatus |
| US20060025652A1 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2006-02-02 | Vargas Jaime S | Cannula system and method of use |
| US20060069346A1 (en) | 2004-09-24 | 2006-03-30 | Kms Medical, Llc | Catheter with controllable stiffness and method for operating a selective stiffening catheter |
| US7104951B2 (en) | 2000-03-15 | 2006-09-12 | Olympus Corporation | Endoscope apparatus with drum part to wind insertion part therearound |
| US20070088367A1 (en) | 2004-10-22 | 2007-04-19 | Alexander Von Weymarn-Scharli | Device, especially tube or catheter, for at least partially introducing into a body passage |
| US20070179339A1 (en) | 2005-11-30 | 2007-08-02 | Era Endoscopy S.R.L. | Self-propelled endoscopic device |
| US20070208300A1 (en) | 2006-03-01 | 2007-09-06 | Applied Medical Resources Corporation | Gas insufflation and suction/irrigation tubing |
| US20070270648A1 (en) | 2006-05-22 | 2007-11-22 | Kms Medical Llc | Torque-transmitting, variably flexible insertion device and method for transmitting torque and variably flexing an insertion device |
| US20080091170A1 (en) | 2003-09-12 | 2008-04-17 | Vargas Jaime S | Cannula system for free-space navigation and method of use |
| US7435214B2 (en) | 2004-01-29 | 2008-10-14 | Cannuflow, Inc. | Atraumatic arthroscopic instrument sheath |
| US20090149710A1 (en) | 2007-12-07 | 2009-06-11 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Selective stiffening devices and methods |
| US7811228B2 (en) | 2004-07-26 | 2010-10-12 | Medtronic Xomed, Inc. | Disposable endoscope sheath having adjustable length |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6890329B2 (en)* | 1999-06-15 | 2005-05-10 | Cryocath Technologies Inc. | Defined deflection structure |
| US8092374B2 (en)* | 2006-03-02 | 2012-01-10 | Kevin Smith | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
- 2006
- 2006-03-02USUS11/367,607patent/US8092374B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
- 2007
- 2007-03-02WOPCT/US2007/005478patent/WO2007103239A2/enactiveApplication Filing
- 2011
- 2011-12-05USUS13/311,145patent/US8696639B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (61)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3557780A (en)* | 1967-04-20 | 1971-01-26 | Olympus Optical Co | Mechanism for controlling flexure of endoscope |
| US3998216A (en) | 1973-10-04 | 1976-12-21 | Olympus Optical Co., Ltd. | Bending tube for endoscope |
| US4176662A (en) | 1977-06-17 | 1979-12-04 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Administrator Of The National Aeronautics And Space Administration | Apparatus for endoscopic examination |
| US4575185A (en) | 1983-08-01 | 1986-03-11 | Combustion Engineering, Inc. | System for a fiber optic cable for remote inspection of internal structure of a nuclear steam generator |
| US4753223A (en) | 1986-11-07 | 1988-06-28 | Bremer Paul W | System for controlling shape and direction of a catheter, cannula, electrode, endoscope or similar article |
| US4838859A (en)* | 1987-05-19 | 1989-06-13 | Steve Strassmann | Steerable catheter |
| US4817613A (en) | 1987-07-13 | 1989-04-04 | Devices For Vascular Intervention, Inc. | Guiding catheter |
| US4762118A (en)* | 1987-07-28 | 1988-08-09 | Welch Allyn, Inc. | Self-adjusting steering mechanism for borescope, endoscope, or guide tube |
| US4893613A (en)* | 1987-11-25 | 1990-01-16 | Hake Lawrence W | Endoscope construction with means for controlling rigidity and curvature of flexible endoscope tube |
| US4890602A (en) | 1987-11-25 | 1990-01-02 | Hake Lawrence W | Endoscope construction with means for controlling rigidity and curvature of flexible endoscope tube |
| US4998282A (en) | 1987-12-09 | 1991-03-05 | Olympus Optical Co., Ltd. | Lifesaving borescope system |
| US4815450A (en) | 1988-02-01 | 1989-03-28 | Patel Jayendra I | Endoscope having variable flexibility |
| US5337733A (en)* | 1989-10-23 | 1994-08-16 | Peter Bauerfeind | Tubular inserting device with variable rigidity |
| US5386817A (en)* | 1991-06-10 | 1995-02-07 | Endomedical Technologies, Inc. | Endoscope sheath and valve system |
| US5271382A (en)* | 1991-07-24 | 1993-12-21 | Kabushiki Kaisha Machida Seisakusho | Bending device |
| USD337733S (en) | 1991-10-31 | 1993-07-27 | Novitas, Inc. | Housing for a one-way ultrasonic ceiling sensor |
| US5211633A (en) | 1992-06-24 | 1993-05-18 | Stouder Jr Albert E | Selectable seal cannula |
| US5259366A (en)* | 1992-11-03 | 1993-11-09 | Boris Reydel | Method of using a catheter-sleeve assembly for an endoscope |
| US5577992A (en)* | 1993-10-05 | 1996-11-26 | Asahi Kogaku Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Bendable portion of endoscope |
| US5873816A (en) | 1994-11-02 | 1999-02-23 | Olympus Optical Co., Ltd. | Electronic endoscope having an insertional portion a part of which is a conductive armor |
| US5759151A (en) | 1995-06-07 | 1998-06-02 | Carnegie Mellon University | Flexible steerable device for conducting exploratory procedures |
| US6117068A (en) | 1995-10-19 | 2000-09-12 | Elite Genetics, Inc | Artificial insemination system |
| US6346077B1 (en)* | 1996-02-20 | 2002-02-12 | Cardiothoracic Systems, Inc. | Surgical instrument for stabilizing the beating heart during coronary artery bypass graft surgery |
| US5807237A (en) | 1997-03-31 | 1998-09-15 | Tindel; Nathaniel L. | Endoscopic device |
| US6196967B1 (en) | 1998-03-18 | 2001-03-06 | Linvatec Corporation | Arthroscopic component joining system |
| US6387044B1 (en) | 1998-12-02 | 2002-05-14 | J. Morita Manufacturing Corporation | Laparoscope apparatus |
| US20040044350A1 (en) | 1999-04-09 | 2004-03-04 | Evalve, Inc. | Steerable access sheath and methods of use |
| US6506150B1 (en)* | 1999-04-13 | 2003-01-14 | Pentax Corporation | Self-retaining endoscope |
| US20030135198A1 (en) | 1999-07-23 | 2003-07-17 | Tfx Medical Extrusion Products | Catheter device having multi-lumen reinforced shaft and method of manufacture for same |
| US6517477B1 (en)* | 2000-01-27 | 2003-02-11 | Scimed Life Systems, Inc. | Catheter introducer system for exploration of body cavities |
| US7066880B2 (en) | 2000-01-27 | 2006-06-27 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Catheter introducer system for exploration of body cavities |
| US7104951B2 (en) | 2000-03-15 | 2006-09-12 | Olympus Corporation | Endoscope apparatus with drum part to wind insertion part therearound |
| US6468203B2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2002-10-22 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Steerable endoscope and improved method of insertion |
| US6800056B2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2004-10-05 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Endoscope with guiding apparatus |
| US6610007B2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2003-08-26 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Steerable segmented endoscope and method of insertion |
| US6984203B2 (en)* | 2000-04-03 | 2006-01-10 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Endoscope with adjacently positioned guiding apparatus |
| US6974411B2 (en) | 2000-04-03 | 2005-12-13 | Neoguide Systems, Inc. | Endoscope with single step guiding apparatus |
| US6858005B2 (en)* | 2000-04-03 | 2005-02-22 | Neo Guide Systems, Inc. | Tendon-driven endoscope and methods of insertion |
| US6375654B1 (en) | 2000-05-19 | 2002-04-23 | Cardiofocus, Inc. | Catheter system with working portion radially expandable upon rotation |
| US20020002323A1 (en) | 2000-06-30 | 2002-01-03 | Olympus Optical Co., Ltd. | Endoscope characterized by soft section thereof through which built-in components lie |
| US20020177750A1 (en) | 2001-01-09 | 2002-11-28 | Tonis Pilvisto | Endoscope-type device, particularly for emergency intubation |
| US6478731B2 (en) | 2001-02-23 | 2002-11-12 | Linvatec Corporation | Endoscope-sheath interface using scope light post |
| US6645223B2 (en)* | 2001-04-30 | 2003-11-11 | Advanced Cardiovascular Systems, Inc. | Deployment and recovery control systems for embolic protection devices |
| US6802809B2 (en) | 2001-06-29 | 2004-10-12 | Olympus Corporation | Endoscope |
| US6942613B2 (en)* | 2002-06-13 | 2005-09-13 | Usgi Medical Inc. | Shape lockable apparatus and method for advancing an instrument through unsupported anatomy |
| US20040186350A1 (en)* | 2003-01-13 | 2004-09-23 | Usgi Medical Corp. | Apparatus and methods for guiding an endoscope via a rigidizable wire guide |
| US20040138529A1 (en) | 2003-01-15 | 2004-07-15 | Usgi Medical Corp. | Endoluminal tool deployment system |
| US20040182393A1 (en) | 2003-02-27 | 2004-09-23 | Macmillan Nicholas Paul | Valves and suction catheter assemblies |
| US20050131279A1 (en) | 2003-04-01 | 2005-06-16 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Articulation joint for video endoscope |
| US20050075538A1 (en) | 2003-04-01 | 2005-04-07 | Banik Michael S. | Single use endoscopic imaging system |
| US20080091170A1 (en) | 2003-09-12 | 2008-04-17 | Vargas Jaime S | Cannula system for free-space navigation and method of use |
| WO2005048814A2 (en) | 2003-11-12 | 2005-06-02 | Van Lue Stephen J | Magnetic devices and apparatus for medical/surgical procedures and methods for using same |
| US7435214B2 (en) | 2004-01-29 | 2008-10-14 | Cannuflow, Inc. | Atraumatic arthroscopic instrument sheath |
| US7811228B2 (en) | 2004-07-26 | 2010-10-12 | Medtronic Xomed, Inc. | Disposable endoscope sheath having adjustable length |
| US20060025652A1 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2006-02-02 | Vargas Jaime S | Cannula system and method of use |
| US20060069346A1 (en) | 2004-09-24 | 2006-03-30 | Kms Medical, Llc | Catheter with controllable stiffness and method for operating a selective stiffening catheter |
| US20070088367A1 (en) | 2004-10-22 | 2007-04-19 | Alexander Von Weymarn-Scharli | Device, especially tube or catheter, for at least partially introducing into a body passage |
| US20070179339A1 (en) | 2005-11-30 | 2007-08-02 | Era Endoscopy S.R.L. | Self-propelled endoscopic device |
| US20070208300A1 (en) | 2006-03-01 | 2007-09-06 | Applied Medical Resources Corporation | Gas insufflation and suction/irrigation tubing |
| US20070270648A1 (en) | 2006-05-22 | 2007-11-22 | Kms Medical Llc | Torque-transmitting, variably flexible insertion device and method for transmitting torque and variably flexing an insertion device |
| US20090149710A1 (en) | 2007-12-07 | 2009-06-11 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Selective stiffening devices and methods |
Non-Patent Citations (10)
| Title |
|---|
| ASGE Abstract 136, "A Split Overture for Easier Colonoscopy", (author not named) (1983). |
| International Search Report dated Dec. 17, 2007. |
| International Search Report for PCT/US/068348 dated Oct. 30, 2008. |
| International Search Report for PCT/US07/012179 dated Sep. 12, 2008. |
| International Search Report for PCT/US07/05478 dated Dec. 17, 2007. |
| International Search Report for PCT/US07/075701 dated Aug. 29, 2008. |
| International Search Report for PCT/US07/12179 dated Sep. 12, 2008. |
| International Search Report for PCT/US07/75701 dated Aug. 29, 2008. |
| International Search Report for PCT/US08/064084 dated Dec. 9, 2008. |
| International Search Report for PCT/US08/068348 dated Oct. 30, 2008. |
Cited By (87)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10463427B2 (en) | 2004-09-24 | 2019-11-05 | Syn Variflex, Llc | Selective stiffening catheter |
| US11376065B2 (en) | 2004-09-24 | 2022-07-05 | Syn Variflex, Llc | Selective stiffening catheter |
| US10159527B2 (en) | 2004-09-24 | 2018-12-25 | Syntheon, Llc | Selective stiffening catheter and methods for operating a selective stiffening catheter |
| US20110040282A1 (en)* | 2006-02-15 | 2011-02-17 | Epflex Feinwerktechnik Gmbh | Controllably Stiffenable Tube |
| US10835112B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2020-11-17 | Syntheon, Llc | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
| US20120095491A1 (en)* | 2006-03-02 | 2012-04-19 | Smith Kevin W | Variably Flexible Insertion Device and Method for Variably Flexing an Insertion Device |
| US8696639B2 (en)* | 2006-03-02 | 2014-04-15 | Syntheon, Llc | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
| US10123683B2 (en) | 2006-03-02 | 2018-11-13 | Syntheon, Llc | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device |
| US10478248B2 (en) | 2007-02-15 | 2019-11-19 | Ethicon Llc | Electroporation ablation apparatus, system, and method |
| US10806331B2 (en)* | 2007-06-27 | 2020-10-20 | Syntheon, Llc | Torque-transmitting, variably-flexible, locking insertion device and method for operating the insertion device |
| US20180064311A1 (en)* | 2007-06-27 | 2018-03-08 | Syntheon, Llc | Torque-Transmitting, Variably-Flexible, Locking Insertion Device and Method for Operating the Insertion Device |
| US10874829B2 (en) | 2008-05-27 | 2020-12-29 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Stiffening assembly |
| US10307568B2 (en)* | 2008-05-27 | 2019-06-04 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Stiffening assembly |
| US20150025320A1 (en)* | 2008-05-27 | 2015-01-22 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Stiffening Assembly |
| US11684243B2 (en) | 2008-05-27 | 2023-06-27 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Stiffening assembly |
| US11399834B2 (en) | 2008-07-14 | 2022-08-02 | Cilag Gmbh International | Tissue apposition clip application methods |
| US10105141B2 (en) | 2008-07-14 | 2018-10-23 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Tissue apposition clip application methods |
| US10314603B2 (en) | 2008-11-25 | 2019-06-11 | Ethicon Llc | Rotational coupling device for surgical instrument with flexible actuators |
| US10004558B2 (en) | 2009-01-12 | 2018-06-26 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Electrical ablation devices |
| US10143411B2 (en) | 2009-07-21 | 2018-12-04 | The General Hospital Corporation | Peripheral blood sampling methods and devices |
| US10779882B2 (en) | 2009-10-28 | 2020-09-22 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Electrical ablation devices |
| US10278761B2 (en) | 2011-02-28 | 2019-05-07 | Ethicon Llc | Electrical ablation devices and methods |
| US10258406B2 (en) | 2011-02-28 | 2019-04-16 | Ethicon Llc | Electrical ablation devices and methods |
| US10799167B1 (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2020-10-13 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral IV catheter |
| US10076272B2 (en)* | 2011-04-26 | 2018-09-18 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral IV catheter |
| US11957466B2 (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2024-04-16 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral IV catheter |
| US10064576B2 (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2018-09-04 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral IV catheter |
| US9750446B2 (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2017-09-05 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral IV catheter |
| US9186100B2 (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2015-11-17 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral IV catheter |
| US11191465B2 (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2021-12-07 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral IV catheter |
| US11331023B2 (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2022-05-17 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral IV catheter |
| US20140364766A1 (en)* | 2011-04-26 | 2014-12-11 | Creative Vascular, Llc | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral iv catheter |
| US10674950B2 (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2020-06-09 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral IV catheter |
| US10729367B1 (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2020-08-04 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for phlebotomy through a peripheral IV catheter |
| US10206709B2 (en) | 2012-05-14 | 2019-02-19 | Ethicon Llc | Apparatus for introducing an object into a patient |
| US11284918B2 (en) | 2012-05-14 | 2022-03-29 | Cilag GmbH Inlernational | Apparatus for introducing a steerable camera assembly into a patient |
| US10492880B2 (en) | 2012-07-30 | 2019-12-03 | Ethicon Llc | Needle probe guide |
| US10342598B2 (en) | 2012-08-15 | 2019-07-09 | Ethicon Llc | Electrosurgical system for delivering a biphasic waveform |
| US9186049B2 (en) | 2012-10-25 | 2015-11-17 | Choon Kee Lee | Extensible and guidable apparatus |
| US11484191B2 (en) | 2013-02-27 | 2022-11-01 | Cilag Gmbh International | System for performing a minimally invasive surgical procedure |
| US9433468B2 (en) | 2013-10-04 | 2016-09-06 | Tidi Products, Llc | Sheath for a medical or dental instrument |
| USD731652S1 (en) | 2014-02-19 | 2015-06-09 | Tidi Products, Llc | Dental curing light sleeve |
| US9993623B2 (en)* | 2014-04-28 | 2018-06-12 | Mark Edman Idstrom | Guidewires with variable rigidity |
| US20150306355A1 (en)* | 2014-04-28 | 2015-10-29 | Mark Edman Idstrom | Guidewires with variable rigidity |
| US20150306353A1 (en)* | 2014-04-28 | 2015-10-29 | Mark Edman Idstrom | Guidewires With Variable Rigidity |
| US11219351B2 (en) | 2015-09-03 | 2022-01-11 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Device for endoscopic advancement through the small intestine |
| US12082776B2 (en) | 2015-09-03 | 2024-09-10 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Methods for advancing a device through a gastrointestinal tract |
| US11717649B2 (en) | 2016-02-03 | 2023-08-08 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Devices and methods for fluid transfer through a placed peripheral intravenous catheter |
| US12161821B2 (en) | 2016-02-03 | 2024-12-10 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Devices and methods for fluid transfer through a placed peripheral intravenous catheter |
| US10300247B2 (en) | 2016-02-03 | 2019-05-28 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Devices and methods for fluid transfer through a placed peripheral intravenous catheter |
| US11400259B2 (en) | 2016-02-03 | 2022-08-02 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Devices and methods for fluid transfer through a placed peripheral intravenous catheter |
| US9744344B1 (en) | 2016-06-30 | 2017-08-29 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Devices and methods for catheter placement within a vein |
| US11446469B2 (en) | 2016-07-13 | 2022-09-20 | Perfuze Limited | High flexibility, kink resistant catheter shaft |
| US12336695B2 (en) | 2016-08-18 | 2025-06-24 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Device and method for enhanced visualization of the small intestine |
| US11944277B2 (en) | 2016-08-18 | 2024-04-02 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Device and method for enhanced visualization of the small intestine |
| US11122971B2 (en) | 2016-08-18 | 2021-09-21 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Device and method for enhanced visualization of the small intestine |
| US11090461B2 (en) | 2017-03-21 | 2021-08-17 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Devices and methods for fluid transfer through a placed peripheral intravenous catheter |
| US12194250B2 (en) | 2017-03-21 | 2025-01-14 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for controlling catheter device size |
| US12138402B2 (en) | 2017-03-21 | 2024-11-12 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Devices and methods for fluid transfer through a placed peripheral intravenous catheter |
| US11583661B2 (en) | 2017-03-21 | 2023-02-21 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Devices and methods for fluid transfer through a placed peripheral intravenous catheter |
| US11351340B2 (en) | 2017-03-21 | 2022-06-07 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for controlling catheter device size |
| US10773056B2 (en) | 2017-03-21 | 2020-09-15 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for controlling catheter device size |
| US12017016B2 (en) | 2017-03-21 | 2024-06-25 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Devices and methods for fluid transfer through a placed peripheral intravenous catheter |
| US11744990B2 (en) | 2017-03-21 | 2023-09-05 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Systems and methods for controlling catheter device size |
| US10751507B2 (en) | 2017-04-10 | 2020-08-25 | Syn Variflex, Llc | Thermally controlled variable-flexibility catheters and methods of manufacturing same |
| US12295550B2 (en) | 2017-07-20 | 2025-05-13 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Dynamically rigidizing overtube |
| US11197977B2 (en) | 2017-12-15 | 2021-12-14 | Perfuze Limited | Catheters and devices and systems incorporating such catheters |
| US12059128B2 (en) | 2018-05-31 | 2024-08-13 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Device and method for enhanced visualization of the small intestine |
| US11478608B2 (en) | 2018-07-19 | 2022-10-25 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Dynamically rigidizing composite medical structures |
| US11724065B2 (en) | 2018-07-19 | 2023-08-15 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Nested rigidizing devices |
| US11135398B2 (en) | 2018-07-19 | 2021-10-05 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Dynamically rigidizing composite medical structures |
| US12311122B2 (en) | 2018-07-19 | 2025-05-27 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Rigidizing overtube with hemostasis valve |
| US11554248B1 (en) | 2018-07-19 | 2023-01-17 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Rigidizing devices |
| US12285571B2 (en) | 2018-07-19 | 2025-04-29 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Methods of performing vascular procedures using a rigidizing device |
| US12193637B2 (en) | 2019-04-17 | 2025-01-14 | Neptune Medical Inc. | External working channels |
| US11793392B2 (en) | 2019-04-17 | 2023-10-24 | Neptune Medical Inc. | External working channels |
| US12329473B2 (en) | 2019-04-17 | 2025-06-17 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Dynamically rigidizing composite medical structures |
| US11207498B2 (en) | 2019-08-20 | 2021-12-28 | Velano Vascular, Inc. | Fluid transfer devices with extended length catheters and methods of using the same |
| US11744443B2 (en) | 2020-03-30 | 2023-09-05 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Layered walls for rigidizing devices |
| US11638806B2 (en) | 2020-11-26 | 2023-05-02 | Avia Vascular, Llc | Blood collection devices, systems, and methods |
| US11452847B1 (en) | 2020-11-26 | 2022-09-27 | Avia Vascular, Llc | Blood collection devices, systems, and methods |
| US11389624B2 (en) | 2020-11-26 | 2022-07-19 | Avia Vascular, Llc | Blood collection devices, systems, and methods |
| US12121677B2 (en) | 2021-01-29 | 2024-10-22 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Devices and methods to prevent inadvertent motion of dynamically rigidizing apparatuses |
| US12324565B2 (en) | 2022-04-27 | 2025-06-10 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Methods of attaching a rigidizing sheath to an endoscope |
| US12102289B2 (en) | 2022-04-27 | 2024-10-01 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Methods of attaching a rigidizing sheath to an endoscope |
| US11937778B2 (en) | 2022-04-27 | 2024-03-26 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Apparatuses and methods for determining if an endoscope is contaminated |
| US12330292B2 (en) | 2023-09-28 | 2025-06-17 | Neptune Medical Inc. | Telescoping robot |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20120095491A1 (en) | 2012-04-19 |
| US8696639B2 (en) | 2014-04-15 |
| WO2007103239A3 (en) | 2008-03-20 |
| US20070208364A1 (en) | 2007-09-06 |
| WO2007103239A2 (en) | 2007-09-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8092374B2 (en) | Variably flexible insertion device and method for variably flexing an insertion device | |
| US9820634B2 (en) | Integrated steering device | |
| US10682041B2 (en) | Extendible flexible sheath | |
| US6960162B2 (en) | Shape lockable apparatus and method for advancing an instrument through unsupported anatomy | |
| AU2006213225B2 (en) | Flexible tube for endoscope, and endoscope device | |
| US7837615B2 (en) | Shape lockable apparatus and method for advancing an instrument through unsupported anatomy | |
| US8277375B2 (en) | Flexible segment system | |
| JP7560133B2 (en) | Insertion unit for medical instrument and intubation system thereof | |
| US20080091073A1 (en) | Inflatable actuation device | |
| JP2007289703A (en) | Medical cannula and medical cannula system | |
| AU2007201563B2 (en) | Medical tubular assembly | |
| JP2008220972A (en) | Treatment instrument | |
| JP2009056054A (en) | Endoscope guiding tube device | |
| TR201808839T4 (en) | Flexible and extendable tubular guide and manufacturing process. | |
| KR20250073161A (en) | Systems and methods for medical device intubation |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:KMS DEVELOPMENT LLC, FLORIDA Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:SMITH, KEVIN;DEVILLE, DEREK;KLINE, KOREY;AND OTHERS;REEL/FRAME:017651/0589 Effective date:20060227 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:SYNTHEON, LLC, FLORIDA Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:KMS DEVELOPMENT, LLC;REEL/FRAME:023176/0343 Effective date:20090828 | |
| STCF | Information on status: patent grant | Free format text:PATENTED CASE | |
| FPAY | Fee payment | Year of fee payment:4 | |
| FEPP | Fee payment procedure | Free format text:MAINTENANCE FEE REMINDER MAILED (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: REM.); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: SMALL ENTITY | |
| LAPS | Lapse for failure to pay maintenance fees | Free format text:PATENT EXPIRED FOR FAILURE TO PAY MAINTENANCE FEES (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: EXP.); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: SMALL ENTITY | |
| STCH | Information on status: patent discontinuation | Free format text:PATENT EXPIRED DUE TO NONPAYMENT OF MAINTENANCE FEES UNDER 37 CFR 1.362 | |
| FP | Lapsed due to failure to pay maintenance fee | Effective date:20200110 |