US8038700B2 - System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization - Google Patents
System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilizationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US8038700B2 US8038700B2US12/044,810US4481008AUS8038700B2US 8038700 B2US8038700 B2US 8038700B2US 4481008 AUS4481008 AUS 4481008AUS 8038700 B2US8038700 B2US 8038700B2
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- coupled
- brace
- end portion
- dynamic
- pedicle screw
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active, expires
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods
- A61B17/56—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor
- A61B17/58—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor for osteosynthesis, e.g. bone plates, screws or setting implements
- A61B17/68—Internal fixation devices, including fasteners and spinal fixators, even if a part thereof projects from the skin
- A61B17/70—Spinal positioners or stabilisers, e.g. stabilisers comprising fluid filler in an implant
- A61B17/7001—Screws or hooks combined with longitudinal elements which do not contact vertebrae
- A61B17/7002—Longitudinal elements, e.g. rods
- A61B17/7019—Longitudinal elements having flexible parts, or parts connected together, such that after implantation the elements can move relative to each other
- A61B17/7025—Longitudinal elements having flexible parts, or parts connected together, such that after implantation the elements can move relative to each other with a sliding joint
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods
- A61B17/56—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor
- A61B17/58—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor for osteosynthesis, e.g. bone plates, screws or setting implements
- A61B17/68—Internal fixation devices, including fasteners and spinal fixators, even if a part thereof projects from the skin
- A61B17/70—Spinal positioners or stabilisers, e.g. stabilisers comprising fluid filler in an implant
- A61B17/7001—Screws or hooks combined with longitudinal elements which do not contact vertebrae
- A61B17/7002—Longitudinal elements, e.g. rods
- A61B17/7019—Longitudinal elements having flexible parts, or parts connected together, such that after implantation the elements can move relative to each other
- A61B17/7026—Longitudinal elements having flexible parts, or parts connected together, such that after implantation the elements can move relative to each other with a part that is flexible due to its form
- A61B17/7028—Longitudinal elements having flexible parts, or parts connected together, such that after implantation the elements can move relative to each other with a part that is flexible due to its form the flexible part being a coil spring
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods
- A61B17/56—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor
- A61B17/58—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor for osteosynthesis, e.g. bone plates, screws or setting implements
- A61B17/68—Internal fixation devices, including fasteners and spinal fixators, even if a part thereof projects from the skin
- A61B17/70—Spinal positioners or stabilisers, e.g. stabilisers comprising fluid filler in an implant
- A61B17/7062—Devices acting on, attached to, or simulating the effect of, vertebral processes, vertebral facets or ribs ; Tools for such devices
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods
- A61B17/56—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor
- A61B17/58—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor for osteosynthesis, e.g. bone plates, screws or setting implements
- A61B17/68—Internal fixation devices, including fasteners and spinal fixators, even if a part thereof projects from the skin
- A61B17/70—Spinal positioners or stabilisers, e.g. stabilisers comprising fluid filler in an implant
- A61B17/7074—Tools specially adapted for spinal fixation operations other than for bone removal or filler handling
- A61B17/7083—Tools for guidance or insertion of tethers, rod-to-anchor connectors, rod-to-rod connectors, or longitudinal elements
- A61B17/7085—Tools for guidance or insertion of tethers, rod-to-anchor connectors, rod-to-rod connectors, or longitudinal elements for insertion of a longitudinal element down one or more hollow screw or hook extensions, i.e. at least a part of the element within an extension has a component of movement parallel to the extension's axis
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods
- A61B17/56—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor
- A61B17/58—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor for osteosynthesis, e.g. bone plates, screws or setting implements
- A61B17/68—Internal fixation devices, including fasteners and spinal fixators, even if a part thereof projects from the skin
- A61B17/70—Spinal positioners or stabilisers, e.g. stabilisers comprising fluid filler in an implant
- A61B17/7001—Screws or hooks combined with longitudinal elements which do not contact vertebrae
- A61B17/7002—Longitudinal elements, e.g. rods
- A61B17/7019—Longitudinal elements having flexible parts, or parts connected together, such that after implantation the elements can move relative to each other
- A61B17/7023—Longitudinal elements having flexible parts, or parts connected together, such that after implantation the elements can move relative to each other with a pivot joint
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods
- A61B17/56—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor
- A61B17/58—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor for osteosynthesis, e.g. bone plates, screws or setting implements
- A61B17/68—Internal fixation devices, including fasteners and spinal fixators, even if a part thereof projects from the skin
- A61B17/70—Spinal positioners or stabilisers, e.g. stabilisers comprising fluid filler in an implant
- A61B17/7001—Screws or hooks combined with longitudinal elements which do not contact vertebrae
- A61B17/7044—Screws or hooks combined with longitudinal elements which do not contact vertebrae also having plates, staples or washers bearing on the vertebrae
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods
- A61B17/56—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor
- A61B17/58—Surgical instruments or methods for treatment of bones or joints; Devices specially adapted therefor for osteosynthesis, e.g. bone plates, screws or setting implements
- A61B17/68—Internal fixation devices, including fasteners and spinal fixators, even if a part thereof projects from the skin
- A61B17/70—Spinal positioners or stabilisers, e.g. stabilisers comprising fluid filler in an implant
- A61B17/7049—Connectors, not bearing on the vertebrae, for linking longitudinal elements together
Definitions
- This disclosurerelates to skeletal stabilization and more particularly to systems and methods for stabilization of human spines and even more particularly to dynamic stabilization techniques.
- the skeletal systemis a complex structure designed to achieve a myriad of tasks, many of them of a complex kinematic nature. While performing its function, the spine must move into flexion (bending forward) and extension (bending backward). For example, the vertebrae that make up the lumbar region of the human spine move through roughly an arc of 15° relative to its neighbor vertebrae. Vertebrae of other regions of the human spine (e.g., the thoracic and cervical regions) have different ranges of movement.
- a healthy vertebraeif one were to view the posterior edge of a healthy vertebrae one would observe that the edge moves through an arc of some degree (e.g., of about 15° if in the lumbar region) centered around an elliptical center of rotation.
- the inter-vertebral spacing in a healthy spineis maintained by a compressible disc which serves to allow the spine to move through this arc.
- the inter-vertebral disctends to compress, and in doing so pressure is exerted on nerves extending from the spinal cord by this reduced inter-vertebral spacing.
- Various other types of nerve problemsmay be experienced in the spine, such as exiting nerve root compression in neural foramen, passing nerve root compression, and enervated annulus (where nerves grow into a cracked/compromised annulus, causing pain every time the disc/annulus is compressed), as examples.
- Many medical procedureshave been devised to alleviate such nerve compression and the pain that results from nerve pressure. Many of these procedures revolve around attempts to prevent the vertebrae from moving too close to each other thereby maintaining space for the nerves to exit without being impinged upon by movements of the spine.
- United States Patent Application Publication No. US/2004/002708A1(hereafter “the '708 publication”) with a Publication Date of Jan. 1, 2004 is entitled, “DYNAMIC FIXATION DEVICE AND METHOD OF USE” shows a dynamic fixation device that allows flexion.
- the device and method of the '708 publicationuses a geometric shape to allow flexion but makes no provision for preventing or reducing disc compression during such flexion.
- an inter-vertebral dynamic braceis used to maintain proper distraction.
- the dynamic braceis designed to allow the vertebrae to which it is attached to move through its natural arc.
- An adjustable compression deviceis used to maintain the proper distraction force while allowing the dynamic brace to move through an arc centered with respect to the center of rotation of the portion of the spine between the distracted vertebrae. Accordingly, such dynamic brace aids in permitting a substantial range of motion in flexion, extension, and/or other desired types of spinal motion.
- a methodfor adjusting the dynamic brace, both with respect to the center of rotation of the distracted vertebrae in both the flexion/extension axis and in the superior/inferior axis.
- the spring tensionis adjustable on a patient by patient basis to take into account body weight and strength as well as physical characteristics of the patient's skeletal system. Also, provisions may be made to convert the dynamic brace to a static brace while the device remains in situ.
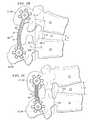
- FIG. 1shows one embodiment of a dynamic brace fitted between a pair of bone anchors
- FIGS. 2A , 2 B and 2 Cshow one embodiment of a dynamic brace fitted between adjacent spinous processes
- FIGS. 3A , 3 B and 3 Cshow one embodiment of a dynamic brace used for spinous process stabilization
- FIGS. 4A , 4 B and 4 Cshow one embodiment of a dynamic brace used for pedicle screw stabilization
- FIGS. 5A and 5Billustrate the movement of the center of rotation between a pair of adjacent vertebrae
- FIGS. 6A , 6 B, 6 C, 6 D, 6 E and 6 Fshow one embodiment of a procedure for implanting a dynamic brace to implanted pedicle screws
- FIG. 7shows one embodiment of a dynamic stabilization device having a cover thereon
- FIGS. 8A and 8Bshow one embodiment of a cross-connector between a pair of dynamic braces.
- FIG. 1shows dynamic brace (or “rod”) 40 positioned with respect to pedicle screws 101 and 102 in system 10 .
- a dynamic stabilization devicecan be employed to partially off-load (or un-weight) the disc between vertebrae (to reduce compression forces) so that as the spine moves through its normal range of motion pressure on the disc is reduced throughout the entire range of motion.
- the pedicle screwsare positioned in the pedicles of the spine as discussed and shown in the above-identified co-pending U.S. patent application entitled “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR STABILIZING INTERNAL STRUCTURES.”
- FIGS. 6A through 6F discussed belowshow in more detail how and where the pedicle screws are implanted for a dynamic brace in accordance with one procedure.
- one of the purposes of the dynamic braceis so that as adjacent pedicles move with respect to each other they are free to follow their natural motion around a center of rotation. In certain embodiments, some amount of translation is permitted such that the center of rotation need not be a fixed point.
- brace portions 41 and 43 of dynamic brace 40are free to move with respect to each other along their longitude axis in a telescoping manner. This motion is controlled, in part, by spring 44 .
- Stop 46working in conjunction with stop 45 , serves to allow spring 44 (or springs) to be effectively lengthened or shortened thereby changing the force the spring exerts which, in turn, changes the force between brace portions 41 and 43 .
- brace portions 41 and 43which could be a tube within a tube, allows for 5° to 20° flexion of the vertebrae to which it is attached in certain embodiments.
- brace 40may be adapted to allow for any desired range of flexion in alternative embodiments.
- dynamic brace 40as it bends, will maintain a correct biomechanical center of rotation, which is not necessarily limited to a fixed center of rotation, with respect to the vertebrae while also reducing or eliminating pressure on the disc between the vertebrae. This partial off-loading of the disc is accomplished by the rigid nature of the rod and spring assembly.
- the telescoping portionscan be designed, for example, using an interlocking groove or using matched longitudinal channels, one in each tube, to prevent relative rotation.
- Dynamic brace 40can be adjusted to create a proper distraction height prior to being implanted and thereafter can be adjusted to the desired distraction force in situ. Because the spine is free (subject to constrained motion) to bend, multiple dynamic braces can be used along the spine while still allowing the spine to move into flexion and, if desired, extension. In certain procedures, the dynamic brace 40 may be, for example, be positioned and correctly tensioned/adjusted in communication with a device that determines a patient's spinal neutral zone.
- FIGS. 2A to 2Cshow a dynamic stabilization device being used across adjacent spinous processes 21 -SP- 22 -SP as opposed to being in the pedicles, such as in pedicle 22 -P and pedicle 21 -P.
- FIG. 2Ashows two vertebrae 21 and 22 (which could, for example, be L4, L5 or any other vertebrae) separated by disc 23 . Space 204 between vertebrae 21 and 22 is where nerves would typically emerge from the spinal column.
- FIG. 2Ashows the skeletal system in the neutral position. In this position, the angle between the generally horizontal planes defined by end-plates of the adjacent vertebrae could be, for example, 8°.
- an extension(or a stabilization device 30 ) could extend to a next adjacent spinous process if multiple vertebrae are to be stabilized.
- the center of rotation for this vertebral pairis 210 .
- this embodimentis shown as a mated pair, it can be used unilaterally.
- the attachment to the spinous processshould be as anterior on the spinous process as practical.
- the junction of the lamina and the spinous processwould be a strong fixation point.
- FIG. 2Bshows the dynamic stabilization device 30 with vertebrae 21 and 22 in the flexed position.
- spinous process 21 -SPhas moved up and into the right (anterior) as the spine is bent forward (flexion).
- a typical movement distance for the posterior of the spinous processis patient specific and would be approximately 4-16 mm.
- Spring 34has expanded along with the dynamic brace to allow spinous process 21 -SP to move upward and forward rotating about center of rotation 210 .
- the center of rotationis not a constant point but will move in an ellipse or centroid as the vertebrae move from extension to flexion.
- the front surfaces of vertebrae 21 and 22form an angle of, for example, ⁇ 4°, which is a change of 12° from the neutral position. Assuming the vertebrae goes into extension by, for example, 3°, the total range of motion is about 15° as shown in FIG. 2C . Ideally, the center of rotation would be around the location shown as 210 . The center of rotation of the spine does not change from flexion to extension or with side bending. However, the “Instantaneous Axis of Rotation” (IAR) changes throughout the rotation arc. The sum of all of the IARs is therefore one point which is called the Center of Rotation “COR).
- IARIntelligent Axis of Rotation
- the dynamic bracecan be adjusted to move the center of rotation 210 forward-backward (X axis) and upward-downward (Y axis), as will be discussed.
- spring 34serves to pull the spinous process back together thereby limiting the compression applied to nerves extending from 204 .
- the respective pedicleshave separated by approximately 8 mm.
- the range shown (31 mm to 39 mm)is but one example.
- Other patientswould have other starting and ending points depending upon their particular physical structure and medical condition. The important point being that the pedicles (vertebrae) and facets can move through their natural range of motion and thus separate during flexion.
- spring 34serves to stabilize the spine when in extension. In both cases, the limit of movement is controlled by the limits of brace portions 31 and 33 along their longitudinal length.
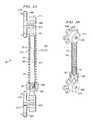
- FIG. 3Ashows a cross-section of the one embodiment of spinous process dynamic device 30 having an external spring and a pair of expandable brace portions 31 and 33 .
- Portion 31which can be a solid rod, if desired, (or any other suitable structure, such as a tube, a plurality of parallel-arranged rods or tubes, etc.) moves inside portion 33 which can be a hollow tube.
- spring 34External of both of these portions is spring 34 , the tension of which is controlled by stop 36 tightening (or loosening) under control of openings 301 ( FIG. 3B ).
- Stop 36in this embodiment works in cooperation with threads 306 . Note that any type of stop can be used, thread or threadless and the stop(s) can be inside the rod or outside.
- Dynamic stabilization device (or “brace” or “rod”) 30can be attached to either side of the spinous process or could be used in pairs interconnected by rod 312 ( FIG. 3C ).
- brace portion 33moves upward. Brace portion 31 remain relatively stationary and thus rod end 31 - 2 moves down (relatively) inside portion 33 . This expansion and contraction along the lateral length of device 30 allows the spine to follow a normal physiologic motion during bending of the spine.
- spherical bearing 311which is free to move in three planes or axis around spherical end support 312 .
- Stop 36is moved to adjust tension or spring 34 —as it is moved upward (toward stop 35 ) force increases and as it moves downward force decreases.
- Force markse.g., triangles and squares 307 shown in this example
- embossed (or otherwise marked) on shaft 31aid the surgeon in adjustment of the spring force.
- the triangles are showing the spring forcecould be, for example, 30 pounds and if the squares are showing the spring force is known to be, for example, 60 pounds. This pre-calibration helps the installation process. Note that the spacing between these force marks in the drawing are arbitrarily drawn in this example, but may be implemented so as to represent the difference between forces.
- Load transfer plates 304help distribute the forces between the respective vertebrae.
- Spikes 310can be used for better load distribution to the spinous process.
- FIG. 3Bshows device 30 from a perspective view.
- Bearings 311of dynamic stabilization device 30 , revolve around rod end bearings 312 and allow rotation of the brace for flexion/extension; lateral bending and trunk rotation.
- Fastener 305serves to hold the brace to the end support.
- FIG. 3Cshows one embodiment of a pair of dynamic stabilization devices connected on either side of spinous process 21 -SP ( 22 -SP).
- Device 30is installed by creating a hole (by drilling or other means) in each spinous process and screwing (or otherwise connecting) rod 312 through the created hole to interconnect the two internally separated devices, as shown.
- FIG. 4Ashows another example embodiment of a dynamic stabilization device 40 for use between bone anchors, such as, for example, pedicle screws.
- Device 40is constructed similar to device 30 except that the ends are held in position by pedicle screws.
- Portion 47is attached to one pedicle screw while portion 41 is held by a second pedicle screw.
- Adjustment along the Y-axisis achieved by moving the position along portion 41 where the pedicle anchor is clamped to device 40 . This effectively changes the neutral length of device 40 .
- FIG. 4Bshows device 40 extended when the spine is in flexion.
- Device 40extends around a curvilinear path (as will be detailed with respect to FIG. 4C ) and the spring length increases, in this example, from approximately 0.745 to 0.900 inches.
- Spring deflectionis 0.155 inches.
- End 48 of device 41is assumed in a fixed position while end 47 moves superior (right) and exterior (down) with respect to end 48 .
- other dimensions of increase in length and deflectionmay be achieved in other uses. That is, different amounts of flexion and extension may be permitted in certain patients.
- FIG. 4Cshows device 40 attached to pedicle screws 101 and 102 .
- One end of portion 41is held captive by head 12 positioned at the top of pedicle screw 102 by a polyaxial connection.
- Portion 43 of dynamic stabilization device 40slides over curved guide portion 41 - 1 of portion 41 .
- portion 41 (and 41 - 1 )can be hollow or solid and portion 43 will be hollow.
- End 43 - 1 of portion 43is held captive by head 11 polyaxially mounted to pedicle screw (or other type of bone anchor) 101 .
- end 43 - 1may be adjusted to extend beyond head 11 prior to being clamped into head 11 if it is necessary to allow for a greater range of travel of end 41 - 1 within tube 43 . For example, this may be necessary for closely placed bone anchors.
- spring 44is positioned around the outside of portion 43 between stops 45 and 46 . Spring 44 is held in compression and adjusted by rotatable stop 45 moving under control of threads 406 .
- guide 41 - 1fits inside of portion 43 and is curved. It is this curve that allows pedicle screw 101 to move in an arc (as shown) when the pedicle to which screw 101 is attached rotates in flexion. This allows dynamic stabilization device 40 to rotate about center of rotation 210 with a natural motion. Natural meaning how the spine would have moved had it been working properly. Note that the X-axis center of rotation of device 40 is controlled by the bend of guide 41 - 1 relative to portion 43 . As discussed above, the center of rotation in the superior/inferior axis (Y-axis) is controlled by the position of end 48 with respect to the pedicle screw 102 .
- Positions 101 - 1 and 101 - 2 of pedicel screw 101shows pedicle screw kinematic analysis as the spine moves into flexion. As shown, pedicle screw 101 goes through a range of arc motion around center of rotation 210 . It is this range of arc motion that the stabilization device tries to maintain.
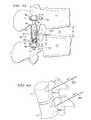
- FIG. 5Ashows dynamic stabilization device 40 positioned in pedicles 21 -P, 22 -P of vertebrae 21 , 22 , respectively.
- the length of the device between heads 11 and 12is adjusted during implantation such that dimension H positions the length by tightening locks 66 when the H dimension is as desired.
- This, as discussed,is the (Y) axis (or superior/inferior) of adjustment.
- the curvilinear motionis set with respect to the R dimension and this is the (X) axis (or flexion/extension) of adjustment.
- the (X) and (Y) dimensionsare set with reference to the desired center of rotation 210 .
- the force provided by spring 44 in combination with portions 41 and 43keep vertebrae 21 from pressing too heavily on disc 23 thereby partially off-loading the intervertebral disc.
- FIG. 5Bshows that by applying a moment about extensions 55 and then locking down the length of device 40 there can be created an anterior distraction force on vertebral bodies 21 , 22 . This will more evenly distribute the loading on disc 23 thereby creating a more optimal environment for the disc when compared to only a posterior distracting implant system. Extensions 55 are removed after the proper length of device 40 is achieved.
- FIGS. 6A-6Fshow one procedure to insert the dynamic brace between vertebrae, such as vertebrae L5 ( 21 ) and L4 ( 22 ).
- This procedureis detailed in the above-identified patent application and is repeated herein for convenience.
- the surgeonidentifies the desired vertebral levels and pedicle positions via standard techniques. Once the target vertebrae are identified, a small incision is made through the skin and a tracking needle (or other device) is inserted to pinpoint exactly where each anchor is to be placed. A fluoroscope, or other x-ray technique, is used to properly position the tracking needle. Once the proper position is located, guide wire (K wire) 622 ( FIG.
- a guide wire 623may be similarly positioned with its distal end against/within pedicle 637 - 1 of vertebrae L4.
- the surgeonthen slides a series of continuing larger sized dilators 612 , 612 a , 612 b , 612 c down guide wire 622 , and slides a series of continuing larger sized dilators 613 , 613 a , 613 b , 613 c down wire 623 .
- a tapis inserted over the K wire to tap a hole into the pedicle in preparation for receiving the anchor, which in this case is a pedicle screw.
- This tapwill usually be a size slightly smaller than the pedicle screw thread size selected for that patient and that level.
- dynamic brace 40is attached to screw 101 to form a brace-screw assembly.
- This assemblyis then positioned at the distal end of cannula 65 and a screwdriver or wrench is inserted into cannula 65 and attached to proximal end 61 of dynamic brace 40 .
- the entire assemblyis then inserted into dilator 613 C.
- the screwdriverengages with proximal end 61 of dynamic brace 40 so as to allow the surgeon to screw pedicle screw 101 into the pre-tapped hole in vertebrae L4. Pressure on the screwdriver forces the screw to be in-line with the dynamic brace, which, in turn, is in-line with the screwdriver.
- the screwdrivercan be removeably attached to end 61 of dynamic brace 40 by engaging, for example, a flat and/or hole in the brace end.
- dilators 612 C and 613 Care removed and, the surgeon slides a blunt dissection tool into the incision and gently parts the muscle bundle below the skin (or cuts a slit in the skin if necessary) between vertebrae.
- the blunt dissection toolcould go down the second cannula and, starting at the bottom of the second cannula work open the muscle bundle between the cannula working upward as far as is necessary.
- the muscles (and other tissue)only need be separated to a point where the dynamic brace 40 must pass. Thus, the separation need not go to the skin level. This reduces trauma even further.
- dynamic brace 40is then positioned, by pivoting, as shown in FIG. 6D , by sliding a tool down cannula 65 to engage proximal end 61 of dynamic brace 40 .
- the toolcould have a force fit with end 61 or a handle for controlling removable attachment with dynamic brace 40 .
- end 61 of dynamic brace 40the surgeon can pull the tool slightly outward to disengage brace end 43 - 1 from screw 101 .
- Brace end 61is forced out of cannula 65 (through opening 65 - 1 thereof) and through the prepared muscle opening and into opening 64 - 1 of cannula 64 .
- brace end 61down cannula 64 and into a mating relationship with screw 102 . Once this mating relationship is achieved, the tool is released from brace end 61 and the tool is removed from both cannulas.
- the surgeonreceives positive feedback (a sensory event), either by feel (for example, a snap action) or by sound (for example, a click), or both when dynamic brace 40 is properly mated with assembly 12 .
- positive feedbacka sensory event
- one or both of assembly 12 or 11 mounted to the respective pedicle screws 102 and 101can be angularity adjusted to accommodate the patient's body structure.
- the polyaxial nature of assemblies 102 and 101 with respect to the anchorsallows for such adjustments which are necessary for a variety of reasons, one of which is that the angulation between adjacent vertebral pedicles varies.
- set screws 66are introduced down cannulas 64 and 65 to lock each end of dynamic brace 40 to its respective pedicle screw. As discussed above, this establishes the y-axis adjustment of the dynamic brace.
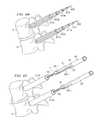
- FIG. 7shows alternative embodiment 70 of a dynamic stabilization device having cover 77 surrounding spring 74 .
- cover 77can be constructed from fabric and/or polyester, as examples.
- FIG. 8Ashows a pair of devices 40 interconnect with one or more cross-connectors 81 .
- the cross-connectorscan be fixed or adjustable, and straight or curved as desired, and could be a bar or plate or a tube as shown.
- the cross-connectoracts to combine individual dynamic stability, has devices into a single assembly and will serve to provide a more fluid motion.
- the cross-connectscan be individual, as shown in FIG. 8B with openings to ends 82 and 83 to go around members 41 , 42 or device 40 or the entire unit can be constructed as a unit, if desired
- the spring forcecan be increased to a point where the device effectively becomes static in order to achieve fusion.
- one or more holescould be positioned through the slide portions such that when a pin is inserted through the holes, the pin effectively prevents the brace from further expansion or contracting.
- pin 330could be pushed through holes 331 and 332 , in portions 31 and 33 .
- the pincould, for example, have spring loaded balls (or any other mechanism) that serve to prevent the pin from easily pulling out of device 30 once inserted.
- the spacing stop 36could be tightened, either permanently or on a temporary basis, to a point where spring tension effectively places the device in a static condition in order to promote fusion of the treated vertebrae in situations where motion preservation fails to meet surgical end-goals.
- a dynamic stabilization systemshould be sensitive to proper placement of the device to restore proper kinematics and full range of motion, and avoid causal deleterious effects of increasing rate of degeneration on adjacent segments.
- a neutral zone deviceis a device that can aid in the placement of the dynamic stabilization device by determining the center of rotation in flexion/extension. Once this center of rotation has been determined, the device can be located to best reproduce that center of rotation. The neutral zone device will cycle the spine through a range of motion measuring forces throughout the range of motion. Also, the device can be used after device implantation to confirm proper implant placement.
- curvilinear guides discussed hereinreproduce the natural motion of the spine while still.
- a pair of curvilinear guides(one female and one male) is used to create a curvilinear path of the pedicles which creates, restores and controls the normal center of rotation.
- Other embodiments that would produce the proper motioncould include; for example:
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Surgical Instruments (AREA)
- Prostheses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- a) a guide bar comprising a pair of pins articulating in a matching pair slots where the slots would diverge to produce a curvilinear motion of a point on the guide bar;
- b) a pair of curvilinear plates with attachment means for bone anchors;
- c) any type of curvilinear guides made up of male and female shapes following a curvilinear path with a geometric cross section (i.e. dovetail, T-slot, round, square, rectangle, etc. cross section geometry);
- d) a four or five bar mechanism that would produce a curvilinear path of the pedicle screw.
Claims (19)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/044,810US8038700B2 (en) | 2004-08-09 | 2008-03-07 | System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/914,751US7854752B2 (en) | 2004-08-09 | 2004-08-09 | System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization |
| US12/044,810US8038700B2 (en) | 2004-08-09 | 2008-03-07 | System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/914,751ContinuationUS7854752B2 (en) | 2004-08-09 | 2004-08-09 | System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US20080154307A1 US20080154307A1 (en) | 2008-06-26 |
| US8038700B2true US8038700B2 (en) | 2011-10-18 |
Family
ID=35800958
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/914,751Expired - Fee RelatedUS7854752B2 (en) | 2004-08-09 | 2004-08-09 | System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization |
| US12/044,810Active2026-09-18US8038700B2 (en) | 2004-08-09 | 2008-03-07 | System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/914,751Expired - Fee RelatedUS7854752B2 (en) | 2004-08-09 | 2004-08-09 | System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US7854752B2 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9907582B1 (en) | 2011-04-25 | 2018-03-06 | Nuvasive, Inc. | Minimally invasive spinal fixation system and related methods |
| US10419753B2 (en)* | 2016-09-12 | 2019-09-17 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | Semiconductor device, moving image processing system, method of controlling semiconductor device |
| US11583318B2 (en) | 2018-12-21 | 2023-02-21 | Paradigm Spine, Llc | Modular spine stabilization system and associated instruments |
Families Citing this family (325)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2812185B1 (en)* | 2000-07-25 | 2003-02-28 | Spine Next Sa | SEMI-RIGID CONNECTION PIECE FOR RACHIS STABILIZATION |
| US7833250B2 (en) | 2004-11-10 | 2010-11-16 | Jackson Roger P | Polyaxial bone screw with helically wound capture connection |
| US7862587B2 (en) | 2004-02-27 | 2011-01-04 | Jackson Roger P | Dynamic stabilization assemblies, tool set and method |
| US8353932B2 (en)* | 2005-09-30 | 2013-01-15 | Jackson Roger P | Polyaxial bone anchor assembly with one-piece closure, pressure insert and plastic elongate member |
| US20160242816A9 (en) | 2001-05-09 | 2016-08-25 | Roger P. Jackson | Dynamic spinal stabilization assembly with elastic bumpers and locking limited travel closure mechanisms |
| US8292926B2 (en) | 2005-09-30 | 2012-10-23 | Jackson Roger P | Dynamic stabilization connecting member with elastic core and outer sleeve |
| US10729469B2 (en)* | 2006-01-09 | 2020-08-04 | Roger P. Jackson | Flexible spinal stabilization assembly with spacer having off-axis core member |
| US10258382B2 (en) | 2007-01-18 | 2019-04-16 | Roger P. Jackson | Rod-cord dynamic connection assemblies with slidable bone anchor attachment members along the cord |
| WO2006052796A2 (en) | 2004-11-10 | 2006-05-18 | Jackson Roger P | Helical guide and advancement flange with break-off extensions |
| US8876868B2 (en) | 2002-09-06 | 2014-11-04 | Roger P. Jackson | Helical guide and advancement flange with radially loaded lip |
| US8172885B2 (en) | 2003-02-05 | 2012-05-08 | Pioneer Surgical Technology, Inc. | Bone plate system |
| US8540753B2 (en) | 2003-04-09 | 2013-09-24 | Roger P. Jackson | Polyaxial bone screw with uploaded threaded shank and method of assembly and use |
| US7621918B2 (en) | 2004-11-23 | 2009-11-24 | Jackson Roger P | Spinal fixation tool set and method |
| US8652175B2 (en)* | 2003-05-02 | 2014-02-18 | Rachiotek, Llc | Surgical implant devices and systems including a sheath member |
| US7713287B2 (en)* | 2003-05-02 | 2010-05-11 | Applied Spine Technologies, Inc. | Dynamic spine stabilizer |
| CA2524145A1 (en) | 2003-05-02 | 2004-11-18 | Yale University | Dynamic spine stabilizer |
| US7377923B2 (en) | 2003-05-22 | 2008-05-27 | Alphatec Spine, Inc. | Variable angle spinal screw assembly |
| DE10327358A1 (en)* | 2003-06-16 | 2005-01-05 | Ulrich Gmbh & Co. Kg | Implant for correction and stabilization of the spine |
| US7967850B2 (en) | 2003-06-18 | 2011-06-28 | Jackson Roger P | Polyaxial bone anchor with helical capture connection, insert and dual locking assembly |
| US8366753B2 (en) | 2003-06-18 | 2013-02-05 | Jackson Roger P | Polyaxial bone screw assembly with fixed retaining structure |
| US7766915B2 (en) | 2004-02-27 | 2010-08-03 | Jackson Roger P | Dynamic fixation assemblies with inner core and outer coil-like member |
| US8092500B2 (en)* | 2007-05-01 | 2012-01-10 | Jackson Roger P | Dynamic stabilization connecting member with floating core, compression spacer and over-mold |
| US8926670B2 (en) | 2003-06-18 | 2015-01-06 | Roger P. Jackson | Polyaxial bone screw assembly |
| US7776067B2 (en) | 2005-05-27 | 2010-08-17 | Jackson Roger P | Polyaxial bone screw with shank articulation pressure insert and method |
| US7799082B2 (en) | 2003-08-05 | 2010-09-21 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Artificial functional spinal unit system and method for use |
| US7753958B2 (en)* | 2003-08-05 | 2010-07-13 | Gordon Charles R | Expandable intervertebral implant |
| US7909869B2 (en) | 2003-08-05 | 2011-03-22 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Artificial spinal unit assemblies |
| US20050203513A1 (en)* | 2003-09-24 | 2005-09-15 | Tae-Ahn Jahng | Spinal stabilization device |
| US8979900B2 (en) | 2003-09-24 | 2015-03-17 | DePuy Synthes Products, LLC | Spinal stabilization device |
| US7137985B2 (en)* | 2003-09-24 | 2006-11-21 | N Spine, Inc. | Marking and guidance method and system for flexible fixation of a spine |
| US7815665B2 (en)* | 2003-09-24 | 2010-10-19 | N Spine, Inc. | Adjustable spinal stabilization system |
| US7763052B2 (en)* | 2003-12-05 | 2010-07-27 | N Spine, Inc. | Method and apparatus for flexible fixation of a spine |
| US7967826B2 (en)* | 2003-10-21 | 2011-06-28 | Theken Spine, Llc | Connector transfer tool for internal structure stabilization systems |
| US7527638B2 (en) | 2003-12-16 | 2009-05-05 | Depuy Spine, Inc. | Methods and devices for minimally invasive spinal fixation element placement |
| US11419642B2 (en) | 2003-12-16 | 2022-08-23 | Medos International Sarl | Percutaneous access devices and bone anchor assemblies |
| US7179261B2 (en) | 2003-12-16 | 2007-02-20 | Depuy Spine, Inc. | Percutaneous access devices and bone anchor assemblies |
| US11241261B2 (en)* | 2005-09-30 | 2022-02-08 | Roger P Jackson | Apparatus and method for soft spinal stabilization using a tensionable cord and releasable end structure |
| US7160300B2 (en) | 2004-02-27 | 2007-01-09 | Jackson Roger P | Orthopedic implant rod reduction tool set and method |
| US8152810B2 (en) | 2004-11-23 | 2012-04-10 | Jackson Roger P | Spinal fixation tool set and method |
| JP2007525274A (en) | 2004-02-27 | 2007-09-06 | ロジャー・ピー・ジャクソン | Orthopedic implant rod reduction instrument set and method |
| DE102004011685A1 (en)* | 2004-03-09 | 2005-09-29 | Biedermann Motech Gmbh | Spine supporting element, comprising spiraled grooves at outer surface and three plain areas |
| FR2870718B1 (en)* | 2004-05-25 | 2006-09-22 | Spine Next Sa | TREATMENT ASSEMBLY FOR THE DEGENERATION OF AN INTERVERTEBRAL DISC |
| US7931675B2 (en)* | 2004-06-23 | 2011-04-26 | Yale University | Dynamic stabilization device including overhanging stabilizing member |
| US7637914B2 (en)* | 2004-08-04 | 2009-12-29 | Leslie Stern | Surgical base unit and retractor support mechanism |
| US8460310B2 (en) | 2004-08-04 | 2013-06-11 | Leslie Stern | Surgical base unit and retractor support mechanism |
| US7854752B2 (en) | 2004-08-09 | 2010-12-21 | Theken Spine, Llc | System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization |
| CA2574277A1 (en)* | 2004-08-09 | 2006-02-23 | Innovative Spinal Technologies, Inc. | System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization |
| US7959653B2 (en)* | 2004-09-03 | 2011-06-14 | Lanx, Inc. | Spinal rod cross connector |
| US7887566B2 (en)* | 2004-09-16 | 2011-02-15 | Hynes Richard A | Intervertebral support device with bias adjustment and related methods |
| US7651502B2 (en) | 2004-09-24 | 2010-01-26 | Jackson Roger P | Spinal fixation tool set and method for rod reduction and fastener insertion |
| US7766940B2 (en) | 2004-12-30 | 2010-08-03 | Depuy Spine, Inc. | Posterior stabilization system |
| US7896906B2 (en)* | 2004-12-30 | 2011-03-01 | Depuy Spine, Inc. | Artificial facet joint |
| US20060084976A1 (en)* | 2004-09-30 | 2006-04-20 | Depuy Spine, Inc. | Posterior stabilization systems and methods |
| US8092496B2 (en) | 2004-09-30 | 2012-01-10 | Depuy Spine, Inc. | Methods and devices for posterior stabilization |
| WO2006041963A2 (en)* | 2004-10-05 | 2006-04-20 | Abdou M S | Devices and methods for inter-vertebral orthopedic device placement |
| DE102004048938B4 (en)* | 2004-10-07 | 2015-04-02 | Synthes Gmbh | Device for the dynamic stabilization of vertebral bodies |
| US20060085076A1 (en)* | 2004-10-15 | 2006-04-20 | Manoj Krishna | Posterior spinal arthroplasty-development of a new posteriorly inserted artificial disc and an artificial facet joint |
| US8162985B2 (en)* | 2004-10-20 | 2012-04-24 | The Board Of Trustees Of The Leland Stanford Junior University | Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US8025680B2 (en) | 2004-10-20 | 2011-09-27 | Exactech, Inc. | Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US20090030465A1 (en)* | 2004-10-20 | 2009-01-29 | Moti Altarac | Dynamic rod |
| US20070239159A1 (en)* | 2005-07-22 | 2007-10-11 | Vertiflex, Inc. | Systems and methods for stabilization of bone structures |
| US7935134B2 (en) | 2004-10-20 | 2011-05-03 | Exactech, Inc. | Systems and methods for stabilization of bone structures |
| US8226690B2 (en)* | 2005-07-22 | 2012-07-24 | The Board Of Trustees Of The Leland Stanford Junior University | Systems and methods for stabilization of bone structures |
| US8267969B2 (en) | 2004-10-20 | 2012-09-18 | Exactech, Inc. | Screw systems and methods for use in stabilization of bone structures |
| US20060265074A1 (en)* | 2004-10-21 | 2006-11-23 | Manoj Krishna | Posterior spinal arthroplasty-development of a new posteriorly inserted artificial disc, a new anteriorly inserted artifical disc and an artificial facet joint |
| US8926672B2 (en) | 2004-11-10 | 2015-01-06 | Roger P. Jackson | Splay control closure for open bone anchor |
| US8444681B2 (en) | 2009-06-15 | 2013-05-21 | Roger P. Jackson | Polyaxial bone anchor with pop-on shank, friction fit retainer and winged insert |
| US9980753B2 (en) | 2009-06-15 | 2018-05-29 | Roger P Jackson | pivotal anchor with snap-in-place insert having rotation blocking extensions |
| WO2006057837A1 (en) | 2004-11-23 | 2006-06-01 | Jackson Roger P | Spinal fixation tool attachment structure |
| US9216041B2 (en) | 2009-06-15 | 2015-12-22 | Roger P. Jackson | Spinal connecting members with tensioned cords and rigid sleeves for engaging compression inserts |
| US9168069B2 (en) | 2009-06-15 | 2015-10-27 | Roger P. Jackson | Polyaxial bone anchor with pop-on shank and winged insert with lower skirt for engaging a friction fit retainer |
| WO2006058221A2 (en) | 2004-11-24 | 2006-06-01 | Abdou Samy M | Devices and methods for inter-vertebral orthopedic device placement |
| US9339301B2 (en) | 2004-12-30 | 2016-05-17 | Mark A. Barry | System and method for aligning vertebrae in the amelioration of aberrant spinal column deviation conditions |
| US20060229613A1 (en)* | 2004-12-31 | 2006-10-12 | Timm Jens P | Sheath assembly for spinal stabilization device |
| US20070088359A1 (en)* | 2005-02-07 | 2007-04-19 | Woods Richard W | Universal dynamic spine stabilization device and method of use |
| US10076361B2 (en) | 2005-02-22 | 2018-09-18 | Roger P. Jackson | Polyaxial bone screw with spherical capture, compression and alignment and retention structures |
| US7604654B2 (en) | 2005-02-22 | 2009-10-20 | Stryker Spine | Apparatus and method for dynamic vertebral stabilization |
| US7901437B2 (en) | 2007-01-26 | 2011-03-08 | Jackson Roger P | Dynamic stabilization member with molded connection |
| CA2614898C (en)* | 2005-04-27 | 2014-04-22 | Trinity Orthopedics, Llc | Mono-planar pedilcle screw method, system, and kit |
| US20060264937A1 (en)* | 2005-05-04 | 2006-11-23 | White Patrick M | Mobile spine stabilization device |
| US20060264935A1 (en)* | 2005-05-04 | 2006-11-23 | White Patrick M | Orthopedic stabilization device |
| FR2886129B1 (en)* | 2005-05-26 | 2007-08-10 | Xavier Renard | ELASTIC EXTERNAL FIXER BETWEEN TWO BONE PORTIONS |
| US7828825B2 (en)* | 2005-06-20 | 2010-11-09 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Multi-level multi-functional spinal stabilization systems and methods |
| US8523865B2 (en) | 2005-07-22 | 2013-09-03 | Exactech, Inc. | Tissue splitter |
| US7811309B2 (en)* | 2005-07-26 | 2010-10-12 | Applied Spine Technologies, Inc. | Dynamic spine stabilization device with travel-limiting functionality |
| US7699875B2 (en)* | 2006-04-17 | 2010-04-20 | Applied Spine Technologies, Inc. | Spinal stabilization device with weld cap |
| US7713288B2 (en)* | 2005-08-03 | 2010-05-11 | Applied Spine Technologies, Inc. | Spring junction and assembly methods for spinal device |
| DE602005007223D1 (en)* | 2005-08-24 | 2008-07-10 | Biedermann Motech Gmbh | Rod-shaped element for use in spine or trauma surgery and stabilization device with such an element |
| EP1942817B1 (en) | 2005-09-27 | 2014-05-07 | Paradigm Spine, LLC | Interspinous vertebral stabilization devices |
| US8105368B2 (en) | 2005-09-30 | 2012-01-31 | Jackson Roger P | Dynamic stabilization connecting member with slitted core and outer sleeve |
| US20070093814A1 (en)* | 2005-10-11 | 2007-04-26 | Callahan Ronald Ii | Dynamic spinal stabilization systems |
| US20070093813A1 (en)* | 2005-10-11 | 2007-04-26 | Callahan Ronald Ii | Dynamic spinal stabilizer |
| US20070093815A1 (en)* | 2005-10-11 | 2007-04-26 | Callahan Ronald Ii | Dynamic spinal stabilizer |
| US8137385B2 (en) | 2005-10-31 | 2012-03-20 | Stryker Spine | System and method for dynamic vertebral stabilization |
| WO2007061960A2 (en)* | 2005-11-18 | 2007-05-31 | Life Spine, Inc. | Dynamic spinal stabilization devices and systems |
| US8034078B2 (en) | 2008-05-30 | 2011-10-11 | Globus Medical, Inc. | System and method for replacement of spinal motion segment |
| FR2894129B1 (en)* | 2005-12-07 | 2008-08-22 | Alain Tornier | DEVICE FOR STABILIZING THE RACHIS |
| US7704271B2 (en)* | 2005-12-19 | 2010-04-27 | Abdou M Samy | Devices and methods for inter-vertebral orthopedic device placement |
| DE602005008265D1 (en)* | 2005-12-23 | 2008-08-28 | Biedermann Motech Gmbh | Flexible stabilization device for the dynamic stabilization of bones or vertebrae |
| US7578849B2 (en)* | 2006-01-27 | 2009-08-25 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Intervertebral implants and methods of use |
| US7682376B2 (en)* | 2006-01-27 | 2010-03-23 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Interspinous devices and methods of use |
| US7815663B2 (en)* | 2006-01-27 | 2010-10-19 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Vertebral rods and methods of use |
| US7776075B2 (en)* | 2006-01-31 | 2010-08-17 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Expandable spinal rods and methods of use |
| USD589147S1 (en)* | 2006-02-02 | 2009-03-24 | Innovative Spinal Technologies | Bone anchor head |
| US20070233090A1 (en)* | 2006-02-23 | 2007-10-04 | Naifeh Bill R | Aligning cross-connector |
| US8118869B2 (en) | 2006-03-08 | 2012-02-21 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Dynamic interbody device |
| US8025681B2 (en)* | 2006-03-29 | 2011-09-27 | Theken Spine, Llc | Dynamic motion spinal stabilization system |
| WO2007117571A2 (en)* | 2006-04-06 | 2007-10-18 | Lotus Medical, Llc | Active compression to facilitate healing of bones |
| EP2012686B1 (en)* | 2006-04-18 | 2013-10-02 | Joseph Nicholas Logan | Spinal rod system |
| US20070288012A1 (en)* | 2006-04-21 | 2007-12-13 | Dennis Colleran | Dynamic motion spinal stabilization system and device |
| US20070270821A1 (en)* | 2006-04-28 | 2007-11-22 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Vertebral stabilizer |
| US8012179B2 (en)* | 2006-05-08 | 2011-09-06 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Dynamic spinal stabilization members and methods |
| US20070270838A1 (en)* | 2006-05-08 | 2007-11-22 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Dynamic spinal stabilization device with dampener |
| US7785350B2 (en)* | 2006-05-08 | 2010-08-31 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Load bearing flexible spinal connecting element |
| US8529626B2 (en)* | 2006-05-09 | 2013-09-10 | Centinel Spine, Inc. | Systems and methods for stabilizing a functional spinal unit |
| US20070288009A1 (en)* | 2006-06-08 | 2007-12-13 | Steven Brown | Dynamic spinal stabilization device |
| US8858600B2 (en)* | 2006-06-08 | 2014-10-14 | Spinadyne, Inc. | Dynamic spinal stabilization device |
| US20080058808A1 (en)* | 2006-06-14 | 2008-03-06 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Implant system and method to treat degenerative disorders of the spine |
| US7666211B2 (en)* | 2006-12-28 | 2010-02-23 | Mi4Spine, Llc | Vertebral disc annular fibrosis tensioning and lengthening device |
| WO2008003047A2 (en)* | 2006-06-28 | 2008-01-03 | Synthes (U.S.A.) | Dynamic fixation system |
| US7927356B2 (en)* | 2006-07-07 | 2011-04-19 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Dynamic constructs for spinal stabilization |
| US8303630B2 (en)* | 2006-07-27 | 2012-11-06 | Samy Abdou | Devices and methods for the minimally invasive treatment of spinal stenosis |
| US20080086128A1 (en)* | 2006-09-07 | 2008-04-10 | David Warren Lewis | Method and apparatus for treatment of scoliosis |
| US20080097431A1 (en)* | 2006-09-22 | 2008-04-24 | Paul Peter Vessa | Flexible spinal stabilization |
| WO2008045914A1 (en)* | 2006-10-10 | 2008-04-17 | Ormco Corporation | Corrector assembly with a telescopable portion, a crimpable portion, and an engaging portion, and a related method |
| US20080147122A1 (en)* | 2006-10-12 | 2008-06-19 | Jackson Roger P | Dynamic stabilization connecting member with molded inner segment and surrounding external elastomer |
| US8096996B2 (en) | 2007-03-20 | 2012-01-17 | Exactech, Inc. | Rod reducer |
| US20080177316A1 (en)* | 2006-11-30 | 2008-07-24 | Bergeron Brian J | Apparatus and methods for spinal implant |
| US9867640B2 (en) | 2006-12-07 | 2018-01-16 | Nexus Spine, LLC | Press-on pedicle screw assembly |
| CA2670988C (en)* | 2006-12-08 | 2014-03-25 | Roger P. Jackson | Tool system for dynamic spinal implants |
| US20080140202A1 (en)* | 2006-12-08 | 2008-06-12 | Randall Noel Allard | Energy-Storing Spinal Implants and Methods of Use |
| CN102525623B (en)* | 2006-12-10 | 2015-04-29 | 帕拉迪格脊骨有限责任公司 | Posterior functionally dynamic stabilization system |
| FR2910267B1 (en)* | 2006-12-21 | 2009-01-23 | Ldr Medical Soc Par Actions Si | VERTEBRAL SUPPORT DEVICE |
| US20080172091A1 (en)* | 2007-01-12 | 2008-07-17 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Spinal Stabilization System |
| US8475498B2 (en) | 2007-01-18 | 2013-07-02 | Roger P. Jackson | Dynamic stabilization connecting member with cord connection |
| US11224463B2 (en) | 2007-01-18 | 2022-01-18 | Roger P. Jackson | Dynamic stabilization connecting member with pre-tensioned flexible core member |
| US8366745B2 (en) | 2007-05-01 | 2013-02-05 | Jackson Roger P | Dynamic stabilization assembly having pre-compressed spacers with differential displacements |
| US8435268B2 (en)* | 2007-01-19 | 2013-05-07 | Reduction Technologies, Inc. | Systems, devices and methods for the correction of spinal deformities |
| US7959677B2 (en) | 2007-01-19 | 2011-06-14 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Artificial functional spinal unit system and method for use |
| US8568453B2 (en)* | 2007-01-29 | 2013-10-29 | Samy Abdou | Spinal stabilization systems and methods of use |
| US8034081B2 (en)* | 2007-02-06 | 2011-10-11 | CollabComl, LLC | Interspinous dynamic stabilization implant and method of implanting |
| US9414861B2 (en) | 2007-02-09 | 2016-08-16 | Transcendental Spine, Llc | Dynamic stabilization device |
| US9314346B2 (en)* | 2007-02-12 | 2016-04-19 | Brigham Young University | Spinal implant |
| US8012177B2 (en)* | 2007-02-12 | 2011-09-06 | Jackson Roger P | Dynamic stabilization assembly with frusto-conical connection |
| US20080208260A1 (en)* | 2007-02-22 | 2008-08-28 | Csaba Truckai | Spine treatment devices and methods |
| US20080255615A1 (en)* | 2007-03-27 | 2008-10-16 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Treatments for Correcting Spinal Deformities |
| US8202302B2 (en)* | 2007-04-19 | 2012-06-19 | Mi4Spine, Llc | Pedicle screw and rod system |
| US8241362B2 (en)* | 2007-04-26 | 2012-08-14 | Voorhies Rand M | Lumbar disc replacement implant for posterior implantation with dynamic spinal stabilization device and method |
| WO2008134703A2 (en)* | 2007-04-30 | 2008-11-06 | Globus Medical, Inc. | Flexible spine stabilization system |
| EP2146656A1 (en)* | 2007-04-30 | 2010-01-27 | Theken Spine, LLC | Implant insertion and alignment system |
| US8979904B2 (en) | 2007-05-01 | 2015-03-17 | Roger P Jackson | Connecting member with tensioned cord, low profile rigid sleeve and spacer with torsion control |
| US10383660B2 (en) | 2007-05-01 | 2019-08-20 | Roger P. Jackson | Soft stabilization assemblies with pretensioned cords |
| US7655041B2 (en)* | 2007-05-01 | 2010-02-02 | Moximed, Inc. | Extra-articular implantable mechanical energy absorbing systems and implantation method |
| US20080275567A1 (en)* | 2007-05-01 | 2008-11-06 | Exploramed Nc4, Inc. | Extra-Articular Implantable Mechanical Energy Absorbing Systems |
| US20080275504A1 (en)* | 2007-05-02 | 2008-11-06 | Bonin Henry K | Constructs for dynamic spinal stabilization |
| EP1994900A1 (en) | 2007-05-22 | 2008-11-26 | Flexismed SA | Interspinous vertebral implant |
| CA2690038C (en)* | 2007-05-31 | 2012-11-27 | Roger P. Jackson | Dynamic stabilization connecting member with pre-tensioned solid core |
| US8070779B2 (en)* | 2007-06-04 | 2011-12-06 | K2M, Inc. | Percutaneous interspinous process device and method |
| US8021396B2 (en) | 2007-06-05 | 2011-09-20 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Configurable dynamic spinal rod and method for dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| WO2008151097A1 (en)* | 2007-06-05 | 2008-12-11 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | A deflection rod system for a dynamic stabilization and motion preservation spinal implantation system and method |
| US8048115B2 (en) | 2007-06-05 | 2011-11-01 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Surgical tool and method for implantation of a dynamic bone anchor |
| US8092501B2 (en) | 2007-06-05 | 2012-01-10 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Dynamic spinal rod and method for dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US8114134B2 (en) | 2007-06-05 | 2012-02-14 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Spinal prosthesis having a three bar linkage for motion preservation and dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US8048128B2 (en) | 2007-06-05 | 2011-11-01 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Revision system and method for a dynamic stabilization and motion preservation spinal implantation system and method |
| US8048123B2 (en)* | 2007-06-05 | 2011-11-01 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Spine implant with a deflection rod system and connecting linkages and method |
| US8083772B2 (en) | 2007-06-05 | 2011-12-27 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Dynamic spinal rod assembly and method for dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US20080312694A1 (en)* | 2007-06-15 | 2008-12-18 | Peterman Marc M | Dynamic stabilization rod for spinal implants and methods for manufacturing the same |
| US20110172708A1 (en)* | 2007-06-22 | 2011-07-14 | Simpirica Spine, Inc. | Methods and systems for increasing the bending stiffness of a spinal segment with elongation limit |
| US8043343B2 (en) | 2007-06-28 | 2011-10-25 | Zimmer Spine, Inc. | Stabilization system and method |
| US8361126B2 (en) | 2007-07-03 | 2013-01-29 | Pioneer Surgical Technology, Inc. | Bone plate system |
| US8623019B2 (en) | 2007-07-03 | 2014-01-07 | Pioneer Surgical Technology, Inc. | Bone plate system |
| US10758283B2 (en) | 2016-08-11 | 2020-09-01 | Mighty Oak Medical, Inc. | Fixation devices having fenestrations and methods for using the same |
| WO2009011845A1 (en)* | 2007-07-13 | 2009-01-22 | George Frey | Systems and methods for spinal stabilization |
| FR2930886A1 (en)* | 2007-07-24 | 2009-11-13 | Henry Graf | EXTRA-DISCAL ASSEMBLY FOR INTERNETEBRAL PROTHERMAL STABILIZATION |
| EP2178451A2 (en)* | 2007-08-07 | 2010-04-28 | Synthes GmbH | Dynamic cable system |
| US8080038B2 (en)* | 2007-08-17 | 2011-12-20 | Jmea Corporation | Dynamic stabilization device for spine |
| US8348976B2 (en) | 2007-08-27 | 2013-01-08 | Kyphon Sarl | Spinous-process implants and methods of using the same |
| US20090093843A1 (en)* | 2007-10-05 | 2009-04-09 | Lemoine Jeremy J | Dynamic spine stabilization system |
| EP2047810B1 (en)* | 2007-10-11 | 2011-09-28 | BIEDERMANN MOTECH GmbH | Modular rod system for spinal stabilization |
| US20090099608A1 (en)* | 2007-10-12 | 2009-04-16 | Aesculap Implant Systems, Inc. | Rod assembly for dynamic posterior stabilization |
| US8267965B2 (en) | 2007-10-22 | 2012-09-18 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Spinal stabilization systems with dynamic interbody devices |
| US8162994B2 (en) | 2007-10-22 | 2012-04-24 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Posterior stabilization system with isolated, dual dampener systems |
| US8182514B2 (en) | 2007-10-22 | 2012-05-22 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Dampener system for a posterior stabilization system with a fixed length elongated member |
| US8157844B2 (en) | 2007-10-22 | 2012-04-17 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Dampener system for a posterior stabilization system with a variable length elongated member |
| US8187330B2 (en) | 2007-10-22 | 2012-05-29 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Dampener system for a posterior stabilization system with a variable length elongated member |
| US8523912B2 (en) | 2007-10-22 | 2013-09-03 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Posterior stabilization systems with shared, dual dampener systems |
| US20090105764A1 (en)* | 2007-10-23 | 2009-04-23 | Jackson Roger P | Dynamic stabilization member with fin support and solid core extension |
| US8911477B2 (en)* | 2007-10-23 | 2014-12-16 | Roger P. Jackson | Dynamic stabilization member with end plate support and cable core extension |
| US20090105756A1 (en) | 2007-10-23 | 2009-04-23 | Marc Richelsoph | Spinal implant |
| US20090131984A1 (en)* | 2007-11-19 | 2009-05-21 | Linares Miguel A | Spine support implant including inter vertebral insertable fluid ballastable insert and inter-vertebral web retaining harnesses |
| US8888850B2 (en)* | 2007-11-19 | 2014-11-18 | Linares Medical Devices, Llc | Combination spacer insert and support for providing inter-cervical vertebral support |
| US8758439B2 (en) | 2007-11-19 | 2014-06-24 | Linares Medical Devices, Llc | Spine support implant including inter vertebral insertable fluid ballastable insert and inter-vertebral web retaining harnesses |
| US8894687B2 (en) | 2011-04-25 | 2014-11-25 | Nexus Spine, L.L.C. | Coupling system for surgical construct |
| US20100318130A1 (en)* | 2007-12-15 | 2010-12-16 | Parlato Brian D | Flexible rod assembly for spinal fixation |
| US8252028B2 (en) | 2007-12-19 | 2012-08-28 | Depuy Spine, Inc. | Posterior dynamic stabilization device |
| US9232968B2 (en)* | 2007-12-19 | 2016-01-12 | DePuy Synthes Products, Inc. | Polymeric pedicle rods and methods of manufacturing |
| CA2781407A1 (en) | 2008-01-14 | 2009-07-23 | Michael P. Brenzel | Apparatus and methods for fracture repair |
| EP2249727A4 (en)* | 2008-02-06 | 2013-01-23 | Exactech Inc | DYNAMIC ROD |
| US8083775B2 (en) | 2008-02-26 | 2011-12-27 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Load-sharing bone anchor having a natural center of rotation and method for dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US8097024B2 (en) | 2008-02-26 | 2012-01-17 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Load-sharing bone anchor having a deflectable post and method for stabilization of the spine |
| US8048125B2 (en) | 2008-02-26 | 2011-11-01 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Versatile offset polyaxial connector and method for dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US8057517B2 (en) | 2008-02-26 | 2011-11-15 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Load-sharing component having a deflectable post and centering spring and method for dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US8337536B2 (en) | 2008-02-26 | 2012-12-25 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Load-sharing bone anchor having a deflectable post with a compliant ring and method for stabilization of the spine |
| US8267979B2 (en) | 2008-02-26 | 2012-09-18 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Load-sharing bone anchor having a deflectable post and axial spring and method for dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US8211155B2 (en) | 2008-02-26 | 2012-07-03 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Load-sharing bone anchor having a durable compliant member and method for dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US8007518B2 (en) | 2008-02-26 | 2011-08-30 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Load-sharing component having a deflectable post and method for dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US8333792B2 (en) | 2008-02-26 | 2012-12-18 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Load-sharing bone anchor having a deflectable post and method for dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US8202299B2 (en)* | 2008-03-19 | 2012-06-19 | Collabcom II, LLC | Interspinous implant, tools and methods of implanting |
| US20090248077A1 (en)* | 2008-03-31 | 2009-10-01 | Derrick William Johns | Hybrid dynamic stabilization |
| US20090275945A1 (en)* | 2008-04-30 | 2009-11-05 | Exploramed Nc4, Inc. | Sheaths for extra-articular implantable systems |
| US20090276044A1 (en)* | 2008-04-30 | 2009-11-05 | Exploramed Nc4, Inc. | Sheaths for extra-articular implantable systems |
| US8034083B2 (en)* | 2008-05-01 | 2011-10-11 | Custom Spine, Inc. | Artificial ligament assembly |
| US8043340B1 (en)* | 2008-06-09 | 2011-10-25 | Melvin Law | Dynamic spinal stabilization system |
| US8784453B1 (en) | 2008-06-09 | 2014-07-22 | Melvin Law | Dynamic spinal stabilization system |
| US20090326583A1 (en)* | 2008-06-25 | 2009-12-31 | Missoum Moumene | Posterior Dynamic Stabilization System With Flexible Ligament |
| US20090326584A1 (en)* | 2008-06-27 | 2009-12-31 | Michael Andrew Slivka | Spinal Dynamic Stabilization Rods Having Interior Bumpers |
| US20100016906A1 (en)* | 2008-07-21 | 2010-01-21 | Abdou M Samy | Device and method to access the anterior column of the spine |
| AU2010260521C1 (en) | 2008-08-01 | 2013-08-01 | Roger P. Jackson | Longitudinal connecting member with sleeved tensioned cords |
| WO2010016949A1 (en)* | 2008-08-08 | 2010-02-11 | Alphatec Spine, Inc. | Spinous process device and method of use |
| US8287571B2 (en) | 2008-08-12 | 2012-10-16 | Blackstone Medical, Inc. | Apparatus for stabilizing vertebral bodies |
| EP2160988B1 (en)* | 2008-09-04 | 2012-12-26 | Biedermann Technologies GmbH & Co. KG | Rod-shaped implant in particular for stabilizing the spinal column and stabilization device including such a rod-shaped implant |
| US9603629B2 (en) | 2008-09-09 | 2017-03-28 | Intelligent Implant Systems Llc | Polyaxial screw assembly |
| ES2394670T3 (en)* | 2008-10-08 | 2013-02-04 | Biedermann Technologies Gmbh & Co. Kg | Elongated implant device and vertebral stabilization device |
| EP2174608B1 (en)* | 2008-10-08 | 2012-08-01 | Biedermann Technologies GmbH & Co. KG | Bone anchoring device and stabilization device for bone parts or vertebrae |
| US20100094344A1 (en)* | 2008-10-14 | 2010-04-15 | Kyphon Sarl | Pedicle-Based Posterior Stabilization Members and Methods of Use |
| WO2010048396A2 (en) | 2008-10-23 | 2010-04-29 | Linares Maedical Devices, Llc | Support insert associated with spinal vertebrae |
| US20100114165A1 (en)* | 2008-11-04 | 2010-05-06 | Abbott Spine, Inc. | Posterior dynamic stabilization system with pivoting collars |
| GB2465156B (en)* | 2008-11-05 | 2012-09-26 | Dalmatic Lystrup As | Bone fixation system |
| EP2346425A4 (en) | 2008-11-12 | 2012-04-18 | Simpirica Spine Inc | Modulated constraining apparatus and methods of use |
| WO2010065795A1 (en) | 2008-12-03 | 2010-06-10 | Eminent Spine Llc | Spinal Cross-Connector and Method for Use of Same |
| WO2010068829A2 (en)* | 2008-12-12 | 2010-06-17 | Spinefrontier, Inc. | Improved spinous process fixation implant |
| WO2010078029A1 (en)* | 2008-12-17 | 2010-07-08 | Synthes Usa, Llc | Posterior spine dynamic stabilizer |
| US8641734B2 (en)* | 2009-02-13 | 2014-02-04 | DePuy Synthes Products, LLC | Dual spring posterior dynamic stabilization device with elongation limiting elastomers |
| CA2743721A1 (en)* | 2009-02-19 | 2010-08-26 | Anton E. Bowden | Compliant dynamic spinal implant |
| WO2010096829A2 (en)* | 2009-02-23 | 2010-08-26 | Crocker Spinal, L.L.C. | Press-on link for surgical screws |
| US8998961B1 (en) | 2009-02-26 | 2015-04-07 | Lanx, Inc. | Spinal rod connector and methods |
| US8118840B2 (en) | 2009-02-27 | 2012-02-21 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Vertebral rod and related method of manufacture |
| AU2015230721B2 (en)* | 2009-03-26 | 2017-11-16 | K2M, Inc. | Semi - constrained anchoring system for correcting a spinal deformity |
| US8357182B2 (en) | 2009-03-26 | 2013-01-22 | Kspine, Inc. | Alignment system with longitudinal support features |
| US20100268119A1 (en)* | 2009-04-15 | 2010-10-21 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc., An Indiana Corporation | Integrated feedback for in-situ surgical device |
| US8202301B2 (en)* | 2009-04-24 | 2012-06-19 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Dynamic spinal rod and implantation method |
| US20110040331A1 (en)* | 2009-05-20 | 2011-02-17 | Jose Fernandez | Posterior stabilizer |
| US8998959B2 (en) | 2009-06-15 | 2015-04-07 | Roger P Jackson | Polyaxial bone anchors with pop-on shank, fully constrained friction fit retainer and lock and release insert |
| US11229457B2 (en) | 2009-06-15 | 2022-01-25 | Roger P. Jackson | Pivotal bone anchor assembly with insert tool deployment |
| CN103826560A (en) | 2009-06-15 | 2014-05-28 | 罗杰.P.杰克逊 | Polyaxial Bone Anchor with Socket Stem and Winged Inserts with Friction Fit Compression Collars |
| US9668771B2 (en) | 2009-06-15 | 2017-06-06 | Roger P Jackson | Soft stabilization assemblies with off-set connector |
| US8876867B2 (en) | 2009-06-24 | 2014-11-04 | Zimmer Spine, Inc. | Spinal correction tensioning system |
| US9320543B2 (en)* | 2009-06-25 | 2016-04-26 | DePuy Synthes Products, Inc. | Posterior dynamic stabilization device having a mobile anchor |
| US8105360B1 (en) | 2009-07-16 | 2012-01-31 | Orthonex LLC | Device for dynamic stabilization of the spine |
| US9011494B2 (en)* | 2009-09-24 | 2015-04-21 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Composite vertebral rod system and methods of use |
| EP2485654B1 (en) | 2009-10-05 | 2021-05-05 | Jackson P. Roger | Polyaxial bone anchor with non-pivotable retainer and pop-on shank, some with friction fit |
| US9157497B1 (en) | 2009-10-30 | 2015-10-13 | Brigham Young University | Lamina emergent torsional joint and related methods |
| US8328849B2 (en)* | 2009-12-01 | 2012-12-11 | Zimmer Gmbh | Cord for vertebral stabilization system |
| CN102695465A (en) | 2009-12-02 | 2012-09-26 | 斯帕泰克医疗股份有限公司 | Low profile spinal prosthesis incorporating a bone anchor having a deflectable post and a compound spinal rod |
| US8764806B2 (en) | 2009-12-07 | 2014-07-01 | Samy Abdou | Devices and methods for minimally invasive spinal stabilization and instrumentation |
| US8114132B2 (en)* | 2010-01-13 | 2012-02-14 | Kyphon Sarl | Dynamic interspinous process device |
| US20110178520A1 (en) | 2010-01-15 | 2011-07-21 | Kyle Taylor | Rotary-rigid orthopaedic rod |
| WO2011091052A1 (en) | 2010-01-20 | 2011-07-28 | Kyle Taylor | Apparatus and methods for bone access and cavity preparation |
| CA2829196A1 (en)* | 2010-03-08 | 2011-09-15 | Conventus Orthopaedics, Inc. | Apparatus and methods for bone repair |
| WO2011112615A1 (en) | 2010-03-08 | 2011-09-15 | Krinke Todd A | Apparatus and methods for securing a bone implant |
| US8758347B2 (en)* | 2010-03-19 | 2014-06-24 | Nextremity Solutions, Inc. | Dynamic bone plate |
| US9445844B2 (en)* | 2010-03-24 | 2016-09-20 | DePuy Synthes Products, Inc. | Composite material posterior dynamic stabilization spring rod |
| US8641723B2 (en) | 2010-06-03 | 2014-02-04 | Orthonex LLC | Skeletal adjustment device |
| US20110307015A1 (en) | 2010-06-10 | 2011-12-15 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Adaptive spinal rod and methods for stabilization of the spine |
| US20120271353A1 (en)* | 2010-08-16 | 2012-10-25 | Mark Barry | System and method for aligning vertebrae in the amelioration of aberrant spinal column deviation conditions in patients requiring the accomodation of spinal column growth or elongation |
| US10531897B2 (en)* | 2010-08-26 | 2020-01-14 | Moximed, Inc. | Implantable device for relieving ankle pain |
| AU2011299558A1 (en) | 2010-09-08 | 2013-05-02 | Roger P. Jackson | Dynamic stabilization members with elastic and inelastic sections |
| US8282671B2 (en) | 2010-10-25 | 2012-10-09 | Orthonex | Smart device for non-invasive skeletal adjustment |
| AU2011324058A1 (en) | 2010-11-02 | 2013-06-20 | Roger P. Jackson | Polyaxial bone anchor with pop-on shank and pivotable retainer |
| US8721566B2 (en)* | 2010-11-12 | 2014-05-13 | Robert A. Connor | Spinal motion measurement device |
| JP5865479B2 (en) | 2011-03-24 | 2016-02-17 | ロジャー・ピー・ジャクソン | Multiaxial bone anchor with compound joint and pop-mounted shank |
| US8388687B2 (en) | 2011-03-25 | 2013-03-05 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Interbody device insertion systems and methods |
| US20120277798A1 (en)* | 2011-04-28 | 2012-11-01 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Spinal Rod Construct to Limit Facet Impingement |
| WO2012177412A2 (en)* | 2011-06-07 | 2012-12-27 | Brigham Young University | Serpentine spinal stability device and associated methods |
| US8845728B1 (en) | 2011-09-23 | 2014-09-30 | Samy Abdou | Spinal fixation devices and methods of use |
| US8657855B2 (en)* | 2011-10-17 | 2014-02-25 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Spinal fixation implant for mounting to spinous processes and related method |
| US9451987B2 (en) | 2011-11-16 | 2016-09-27 | K2M, Inc. | System and method for spinal correction |
| US8920472B2 (en) | 2011-11-16 | 2014-12-30 | Kspine, Inc. | Spinal correction and secondary stabilization |
| WO2014172632A2 (en) | 2011-11-16 | 2014-10-23 | Kspine, Inc. | Spinal correction and secondary stabilization |
| US9526627B2 (en) | 2011-11-17 | 2016-12-27 | Exactech, Inc. | Expandable interbody device system and method |
| US8430916B1 (en) | 2012-02-07 | 2013-04-30 | Spartek Medical, Inc. | Spinal rod connectors, methods of use, and spinal prosthesis incorporating spinal rod connectors |
| US20130226240A1 (en) | 2012-02-22 | 2013-08-29 | Samy Abdou | Spinous process fixation devices and methods of use |
| US20130261666A1 (en)* | 2012-03-28 | 2013-10-03 | Spinesmith Partners, L.P. | Interspinous fixation device |
| US9198767B2 (en) | 2012-08-28 | 2015-12-01 | Samy Abdou | Devices and methods for spinal stabilization and instrumentation |
| US9320617B2 (en) | 2012-10-22 | 2016-04-26 | Cogent Spine, LLC | Devices and methods for spinal stabilization and instrumentation |
| US8911478B2 (en) | 2012-11-21 | 2014-12-16 | Roger P. Jackson | Splay control closure for open bone anchor |
| US10058354B2 (en) | 2013-01-28 | 2018-08-28 | Roger P. Jackson | Pivotal bone anchor assembly with frictional shank head seating surfaces |
| US9113968B2 (en) | 2013-01-28 | 2015-08-25 | Nextremity Solutions, Inc. | Dynamic bone plate compression device and method |
| US8852239B2 (en) | 2013-02-15 | 2014-10-07 | Roger P Jackson | Sagittal angle screw with integral shank and receiver |
| US9492288B2 (en) | 2013-02-20 | 2016-11-15 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Expandable fusion device for positioning between adjacent vertebral bodies |
| FR3004919B1 (en)* | 2013-04-30 | 2015-05-08 | Xavier Renard | IMPROVEMENT TO EXTERNAL FIXATORS |
| US9308123B2 (en)* | 2013-09-16 | 2016-04-12 | Neuraxis, Llc | Methods and devices for applying localized thermal therapy |
| US8911486B1 (en) | 2013-09-16 | 2014-12-16 | Neuraxis, Llc | Implantable devices for thermal therapy and related methods |
| US9044273B2 (en) | 2013-10-07 | 2015-06-02 | Intelligent Implant Systems, Llc | Polyaxial plate rod system and surgical procedure |
| US9566092B2 (en) | 2013-10-29 | 2017-02-14 | Roger P. Jackson | Cervical bone anchor with collet retainer and outer locking sleeve |
| CN105939677A (en) | 2013-12-12 | 2016-09-14 | 康文图斯整形外科公司 | Tissue displacement tools and methods |
| US9717533B2 (en) | 2013-12-12 | 2017-08-01 | Roger P. Jackson | Bone anchor closure pivot-splay control flange form guide and advancement structure |
| US9451993B2 (en) | 2014-01-09 | 2016-09-27 | Roger P. Jackson | Bi-radial pop-on cervical bone anchor |
| US10398565B2 (en) | 2014-04-24 | 2019-09-03 | Choice Spine, Llc | Limited profile intervertebral implant with incorporated fastening and locking mechanism |
| US9517144B2 (en) | 2014-04-24 | 2016-12-13 | Exactech, Inc. | Limited profile intervertebral implant with incorporated fastening mechanism |
| US10064658B2 (en) | 2014-06-04 | 2018-09-04 | Roger P. Jackson | Polyaxial bone anchor with insert guides |
| US9597119B2 (en) | 2014-06-04 | 2017-03-21 | Roger P. Jackson | Polyaxial bone anchor with polymer sleeve |
| US9642651B2 (en) | 2014-06-12 | 2017-05-09 | Brigham Young University | Inverted serpentine spinal stability device and associated methods |
| EP3258868B1 (en) | 2015-02-16 | 2019-08-21 | Akros Medical, Inc. | Devices and systems for semi-rigid bone fixation |
| US11547450B2 (en) | 2015-04-17 | 2023-01-10 | Apifix Ltd. | Expandable polyaxial spinal system |
| US10857003B1 (en) | 2015-10-14 | 2020-12-08 | Samy Abdou | Devices and methods for vertebral stabilization |
| WO2017142426A1 (en)* | 2016-02-19 | 2017-08-24 | Gallagher Group Limited | A fence post |
| US20180000522A1 (en)* | 2016-06-30 | 2018-01-04 | Linares Medical Devices, Llc | Vertebral scaffold for supporting a rear of a spinal column along opposite extending rows of lateral processes |
| US12016573B2 (en) | 2016-08-11 | 2024-06-25 | Mighty Oak Medical, Inc. | Drill apparatus and surgical fixation devices and methods for using the same |
| US10743890B2 (en) | 2016-08-11 | 2020-08-18 | Mighty Oak Medical, Inc. | Drill apparatus and surgical fixation devices and methods for using the same |
| US10744000B1 (en) | 2016-10-25 | 2020-08-18 | Samy Abdou | Devices and methods for vertebral bone realignment |
| US10973648B1 (en) | 2016-10-25 | 2021-04-13 | Samy Abdou | Devices and methods for vertebral bone realignment |
| CA3043217A1 (en) | 2016-11-18 | 2018-05-24 | Javier Garcia-Bengochea | Implants and instruments for enhancing vertebral alignment and sagittal balance |
| US10610262B2 (en)* | 2017-05-24 | 2020-04-07 | Umc Utrecht Holding B.V. | Spinal distraction system |
| WO2019010252A2 (en) | 2017-07-04 | 2019-01-10 | Conventus Orthopaedics, Inc. | APPARATUS AND METHODS FOR TREATING BONES |
| US11737793B2 (en)* | 2017-10-20 | 2023-08-29 | Mayo Foundation For Medical Education And Research | Facet joint replacement devices |
| EP3501457A1 (en)* | 2017-12-20 | 2019-06-26 | Materialise N.V. | Flexible porous implant fixation system |
| US11179248B2 (en) | 2018-10-02 | 2021-11-23 | Samy Abdou | Devices and methods for spinal implantation |
| KR102328801B1 (en)* | 2019-12-18 | 2021-11-18 | 인제대학교 산학협력단 | Spine manipulation apparatus |
| US11723691B2 (en)* | 2019-12-25 | 2023-08-15 | Apifix Ltd | Biasing device for spinal device |
| US11877779B2 (en) | 2020-03-26 | 2024-01-23 | Xtant Medical Holdings, Inc. | Bone plate system |
| CN115462886A (en)* | 2022-08-10 | 2022-12-13 | 浙江德康医疗器械有限公司 | Zero-notch nail rod system and implantation method |
| KR102836394B1 (en)* | 2023-02-02 | 2025-07-22 | 박경우 | Bio-flexible spinal fixation apparatus to prevent fatigue fracture |
| CN117442394B (en)* | 2023-12-25 | 2024-03-08 | 北京爱康宜诚医疗器材有限公司 | Linkage type vertebral body prosthesis |
| CN118267069B (en)* | 2024-05-29 | 2024-08-27 | 北京大学人民医院 | Elastic damping bionic assembled pedicle screw rod fixing system |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4488542A (en)* | 1981-11-27 | 1984-12-18 | Per Helland | External setting and correction device for the treatment of bone fractures |
| US5122140A (en)* | 1989-08-23 | 1992-06-16 | Jaquet Orthopedie, S.A. | Dynamic external fixation device |
| US6267764B1 (en)* | 1996-11-15 | 2001-07-31 | Stryker France S.A. | Osteosynthesis system with elastic deformation for spinal column |
| US20060229609A1 (en)* | 2005-03-18 | 2006-10-12 | Chao-Jan Wang | Microadjustment spinal joint fixture |
| USD618349S1 (en)* | 2007-03-23 | 2010-06-22 | Disc Motion Technologies, Inc. | Spinal stabilization device |
| USD618348S1 (en)* | 2007-03-23 | 2010-06-22 | Disc Motion Technologies, Inc. | Spinal stabilization device |
| US7905906B2 (en)* | 2006-06-08 | 2011-03-15 | Disc Motion Technologies, Inc. | System and method for lumbar arthroplasty |
Family Cites Families (276)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1931269A (en) | 1932-11-23 | 1933-10-17 | Lucius Y Randall | Reenforcement device |
| US2689756A (en) | 1953-10-15 | 1954-09-21 | Theodore F Carlson | Coupling means for relatively oscillating members |
| US3499222A (en) | 1965-08-17 | 1970-03-10 | Leonard I Linkow | Intra-osseous pins and posts and their use and techniques thereof |
| US3426364A (en) | 1966-08-25 | 1969-02-11 | Colorado State Univ Research F | Prosthetic appliance for replacing one or more natural vertebrae |
| GB1405091A (en) | 1971-08-19 | 1975-09-03 | Nat Res Dev | Orthopaedic fracutre fixing device |
| US3920060A (en) | 1973-07-11 | 1975-11-18 | Veeder Industries Inc | Cup-point fastener |
| DE2713837C2 (en) | 1977-03-25 | 1978-10-26 | Erhard Dr. 1000 Berlin Westerhoff | Drive device for a distraction device |
| US4643178A (en) | 1984-04-23 | 1987-02-17 | Fabco Medical Products, Inc. | Surgical wire and method for the use thereof |
| US4854311A (en) | 1986-01-09 | 1989-08-08 | Acro Med Corporation | Bone screw |
| US5151103A (en) | 1987-11-03 | 1992-09-29 | Synthes (U.S.A.) | Point contact bone compression plate |
| MX170527B (en) | 1987-11-03 | 1993-08-30 | Synthes Ag | IMPLEMENTATION FOR OSTEOSYNTHESIS |
| FR2623085B1 (en) | 1987-11-16 | 1992-08-14 | Breard Francis | SURGICAL IMPLANT TO LIMIT THE RELATIVE MOVEMENT OF VERTEBRES |
| FR2625097B1 (en) | 1987-12-23 | 1990-05-18 | Cote Sarl | INTER-SPINOUS PROSTHESIS COMPOSED OF SEMI-ELASTIC MATERIAL COMPRISING A TRANSFILING EYE AT ITS END AND INTER-SPINOUS PADS |
| DE3823737A1 (en) | 1988-07-13 | 1990-01-18 | Lutz Biedermann | CORRECTION AND HOLDING DEVICE, ESPECIALLY FOR THE SPINE |
| US5474553A (en) | 1989-04-18 | 1995-12-12 | Rainer Baumgart | System for setting tubular bone fractures |
| DE3936702C2 (en) | 1989-11-03 | 1994-07-28 | Lutz Biedermann | Pedicle screw and correction and holding device with such a pedicle screw |
| US5019080A (en) | 1990-02-13 | 1991-05-28 | Trextron Inc. | Drive system for prosthetic fasteners |
| US5129900B1 (en) | 1990-07-24 | 1998-12-29 | Acromed Corp | Spinal column retaining method and apparatus |
| US6520990B1 (en) | 1990-10-05 | 2003-02-18 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Lateral fixation plates for a spinal system |
| US5300073A (en) | 1990-10-05 | 1994-04-05 | Salut, Ltd. | Sacral implant system |
| US5129899A (en) | 1991-03-27 | 1992-07-14 | Smith & Nephew Richards Inc. | Bone fixation apparatus |
| FR2676911B1 (en)* | 1991-05-30 | 1998-03-06 | Psi Ste Civile Particuliere | INTERVERTEBRAL STABILIZATION DEVICE WITH SHOCK ABSORBERS. |
| PT100685A (en) | 1991-07-15 | 1994-05-31 | Danek Group Inc | SPINAL FIXING SYSTEM |
| DE4124472A1 (en) | 1991-07-24 | 1993-01-28 | Adolf Wuerth Gmbh & Co Kg | SCREW |
| US5584887A (en) | 1991-08-15 | 1996-12-17 | Smith & Nephew Richards, Inc. | Percutaneous screw adapter |
| US5176679A (en) | 1991-09-23 | 1993-01-05 | Lin Chih I | Vertebral locking and retrieving system |
| US5330474A (en) | 1991-09-23 | 1994-07-19 | Lin Chih I | Vertebral locking and retrieving system |
| US5257994A (en) | 1991-09-23 | 1993-11-02 | Lin Chih I | Vertebral locking and retrieving system |
| US5603713A (en) | 1991-09-24 | 1997-02-18 | Aust; Gilbert M. | Anterior lumbar/cervical bicortical compression plate |
| DE9112176U1 (en) | 1991-09-30 | 1991-11-14 | Howmedica GmbH, 2314 Schönkirchen | Vertebral body spacer |
| US5261909A (en) | 1992-02-18 | 1993-11-16 | Danek Medical, Inc. | Variable angle screw for spinal implant system |
| US5171279A (en) | 1992-03-17 | 1992-12-15 | Danek Medical | Method for subcutaneous suprafascial pedicular internal fixation |
| FR2689750B1 (en) | 1992-04-10 | 1997-01-31 | Eurosurgical | BONE ANCHORING ELEMENT AND SPINAL OSTEOSYNTHESIS DEVICE INCORPORATING SUCH ELEMENTS. |
| ATE124238T1 (en) | 1992-05-18 | 1995-07-15 | Pina Vertriebs Ag | IMPLANT FOR THE SPINE. |
| JP3308271B2 (en) | 1992-06-25 | 2002-07-29 | ジンテーズ アクチエンゲゼルシャフト,クール | Osteosynthesis fixation device |
| FR2692952B1 (en)* | 1992-06-25 | 1996-04-05 | Psi | IMPROVED SHOCK ABSORBER WITH MOVEMENT LIMIT. |
| FR2693364B1 (en) | 1992-07-07 | 1995-06-30 | Erpios Snc | INTERVERTEBRAL PROSTHESIS FOR STABILIZING ROTATORY AND FLEXIBLE-EXTENSION CONSTRAINTS. |
| GB9217578D0 (en) | 1992-08-19 | 1992-09-30 | Surgicarft Ltd | Surgical implants,etc |
| FR2697743B1 (en) | 1992-11-09 | 1995-01-27 | Fabrication Mat Orthopedique S | Spinal osteosynthesis device applicable in particular to degenerative vertebrae. |
| US5498262A (en) | 1992-12-31 | 1996-03-12 | Bryan; Donald W. | Spinal fixation apparatus and method |
| US5527314A (en) | 1993-01-04 | 1996-06-18 | Danek Medical, Inc. | Spinal fixation system |
| US5496318A (en) | 1993-01-08 | 1996-03-05 | Advanced Spine Fixation Systems, Inc. | Interspinous segmental spine fixation device |
| US5676701A (en) | 1993-01-14 | 1997-10-14 | Smith & Nephew, Inc. | Low wear artificial spinal disc |
| US5403314A (en) | 1993-02-05 | 1995-04-04 | Acromed Corporation | Apparatus for retaining spinal elements in a desired spatial relationship |
| DE4303770C1 (en) | 1993-02-09 | 1994-05-26 | Plus Endoprothetik Ag Rotkreuz | Stiffening and correction system for spinal vertebrae - comprises screw-ended holders with connecting rod supporting clamped distance pieces. |
| US5413576A (en) | 1993-02-10 | 1995-05-09 | Rivard; Charles-Hilaire | Apparatus for treating spinal disorder |
| FR2701650B1 (en) | 1993-02-17 | 1995-05-24 | Psi | Double shock absorber for intervertebral stabilization. |
| US5415661A (en)* | 1993-03-24 | 1995-05-16 | University Of Miami | Implantable spinal assist device |
| US5487744A (en) | 1993-04-08 | 1996-01-30 | Advanced Spine Fixation Systems, Inc. | Closed connector for spinal fixation systems |
| DE4316794C1 (en) | 1993-05-19 | 1994-10-13 | Joerg Bischof | Device for the distraction of bones |
| US6077262A (en) | 1993-06-04 | 2000-06-20 | Synthes (U.S.A.) | Posterior spinal implant |
| US5304179A (en) | 1993-06-17 | 1994-04-19 | Amei Technologies Inc. | System and method for installing a spinal fixation system at variable angles |
| US5423816A (en) | 1993-07-29 | 1995-06-13 | Lin; Chih I. | Intervertebral locking device |
| FR2709246B1 (en)* | 1993-08-27 | 1995-09-29 | Martin Jean Raymond | Dynamic implanted spinal orthosis. |
| FR2709247B1 (en) | 1993-08-27 | 1995-09-29 | Martin Jean Raymond | Device for anchoring spinal instrumentation on a vertebra. |
| JP3683909B2 (en) | 1993-10-08 | 2005-08-17 | ロゴジンスキ,チェーム | Device for treating spinal conditions |
| US5628740A (en) | 1993-12-23 | 1997-05-13 | Mullane; Thomas S. | Articulating toggle bolt bone screw |
| US5476463A (en) | 1994-01-12 | 1995-12-19 | Acromed Corporation | Spinal column retaining apparatus |
| US5611800A (en) | 1994-02-15 | 1997-03-18 | Alphatec Manufacturing, Inc. | Spinal fixation system |
| ATE180402T1 (en) | 1994-02-28 | 1999-06-15 | Sulzer Orthopaedie Ag | STABILIZATION OF ADJACENT BACK VERTEBRATE |
| FR2718945B1 (en) | 1994-04-25 | 1996-07-05 | Soprane Sa | Device for retaining a connecting rod of a spine fixator on a pedicle screw. |
| SE9402130D0 (en) | 1994-06-17 | 1994-06-17 | Sven Olerud | Device and method for plate fixation of legs |
| US5498263A (en) | 1994-06-28 | 1996-03-12 | Acromed Corporation | Transverse connector for spinal column corrective devices |
| US5520688A (en) | 1994-07-20 | 1996-05-28 | Lin; Chih-I | Vertebral auxiliary fixation device |
| FR2722980B1 (en)* | 1994-07-26 | 1996-09-27 | Samani Jacques | INTERTEPINOUS VERTEBRAL IMPLANT |
| US5575791A (en) | 1994-07-27 | 1996-11-19 | Lin; Chih-I | Universal eccentric fixation mechanism for orthopedic surgery |
| US5474551A (en) | 1994-11-18 | 1995-12-12 | Smith & Nephew Richards, Inc. | Universal coupler for spinal fixation |
| US5620443A (en) | 1995-01-25 | 1997-04-15 | Danek Medical, Inc. | Anterior screw-rod connector |
| DE29501880U1 (en) | 1995-02-06 | 1995-05-24 | Karl Leibinger Medizintechnik GmbH & Co. KG, 78570 Mühlheim | Bone extension device |
| US5562661A (en) | 1995-03-16 | 1996-10-08 | Alphatec Manufacturing Incorporated | Top tightening bone fixation apparatus |
| US5591166A (en) | 1995-03-27 | 1997-01-07 | Smith & Nephew Richards, Inc. | Multi angle bone bolt |
| US5613968A (en) | 1995-05-01 | 1997-03-25 | Lin; Chih-I | Universal pad fixation device for orthopedic surgery |
| US5582612A (en) | 1995-05-01 | 1996-12-10 | Lin; Chih-I | Vertebral fixing and retrieving device having centrally two fixation |
| CA2222247A1 (en) | 1995-06-07 | 1996-12-19 | Innogenetics N.V. | Immunotoxins specific for cd80 and cd86 expressing cells |
| US5643264A (en) | 1995-09-13 | 1997-07-01 | Danek Medical, Inc. | Iliac screw |
| EP0770359A1 (en) | 1995-10-05 | 1997-05-02 | Medicon e.G. Chirurgiemechaniker-Genossenschaft | Distraction device for bone segments |
| US5846245A (en) | 1995-10-20 | 1998-12-08 | New York University | Bone-adjusting device |
| US5649599A (en)* | 1995-11-22 | 1997-07-22 | The Catanese Family Limited Partnership | Fast attack penetrating nozzle which minimizes potential formation of backdraft conditions during fire suppression |
| CA2237811C (en) | 1995-11-30 | 2003-09-02 | Synthes (U.S.A.) | Bone-fixing device |
| EP0865258B1 (en) | 1995-12-01 | 2000-06-21 | David A. Walker | Telescopic bone plate for use in bone lengthening by distraction osteogenesis |
| US5688275A (en) | 1996-02-09 | 1997-11-18 | Koros; Tibor | Spinal column rod fixation system |
| US5951555A (en) | 1996-03-27 | 1999-09-14 | Rehak; Lubos | Device for the correction of spinal deformities |
| FR2747034B1 (en) | 1996-04-03 | 1998-06-19 | Scient X | INTERSOMATIC CONTAINMENT AND MERGER SYSTEM |
| US5741255A (en) | 1996-06-05 | 1998-04-21 | Acromed Corporation | Spinal column retaining apparatus |
| US6835207B2 (en) | 1996-07-22 | 2004-12-28 | Fred Zacouto | Skeletal implant |
| FR2751864B1 (en) | 1996-08-01 | 1999-04-30 | Graf Henry | DEVICE FOR MECHANICALLY CONNECTING AND ASSISTING VERTEBRES BETWEEN THEM |
| US5879350A (en) | 1996-09-24 | 1999-03-09 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Multi-axial bone screw assembly |
| US5725528A (en) | 1997-02-12 | 1998-03-10 | Third Millennium Engineering, Llc | Modular polyaxial locking pedicle screw |
| US5735851A (en) | 1996-10-09 | 1998-04-07 | Third Millennium Engineering, Llc | Modular polyaxial locking pedicle screw |
| US5800435A (en) | 1996-10-09 | 1998-09-01 | Techsys, Llc | Modular spinal plate for use with modular polyaxial locking pedicle screws |
| ES2191775T3 (en) | 1996-12-12 | 2003-09-16 | Synthes Ag | DEVICE FOR CONNECTING A LONGITUDINAL SUPPORT WITH A PEDICULAR SCREW. |
| US6712819B2 (en) | 1998-10-20 | 2004-03-30 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Mating insertion instruments for spinal implants and methods of use |
| US5836948A (en) | 1997-01-02 | 1998-11-17 | Saint Francis Medical Technologies, Llc | Spine distraction implant and method |
| US7201751B2 (en) | 1997-01-02 | 2007-04-10 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Supplemental spine fixation device |
| US6451019B1 (en) | 1998-10-20 | 2002-09-17 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Supplemental spine fixation device and method |
| US6695842B2 (en) | 1997-10-27 | 2004-02-24 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Interspinous process distraction system and method with positionable wing and method |
| US6902566B2 (en) | 1997-01-02 | 2005-06-07 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Spinal implants, insertion instruments, and methods of use |
| US6156038A (en) | 1997-01-02 | 2000-12-05 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Spine distraction implant and method |
| US5860977A (en) | 1997-01-02 | 1999-01-19 | Saint Francis Medical Technologies, Llc | Spine distraction implant and method |
| US6796983B1 (en) | 1997-01-02 | 2004-09-28 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Spine distraction implant and method |
| US6068630A (en) | 1997-01-02 | 2000-05-30 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Spine distraction implant |
| US6514256B2 (en) | 1997-01-02 | 2003-02-04 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Spine distraction implant and method |
| US7101375B2 (en) | 1997-01-02 | 2006-09-05 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Spine distraction implant |
| DE19702201C1 (en) | 1997-01-23 | 1998-08-06 | Aesculap Ag & Co Kg | Pin-shaped holding component for orthopaedic retention system |
| US5827286A (en) | 1997-02-14 | 1998-10-27 | Incavo; Stephen J. | Incrementally adjustable tibial osteotomy fixation device and method |
| US6017345A (en) | 1997-05-09 | 2000-01-25 | Spinal Innovations, L.L.C. | Spinal fixation plate |
| US6413257B1 (en) | 1997-05-15 | 2002-07-02 | Surgical Dynamics, Inc. | Clamping connector for spinal fixation systems |
| IES77331B2 (en) | 1997-06-03 | 1997-12-03 | Tecos Holdings Inc | Pluridirectional and modulable vertebral osteosynthesis device of small overall size |
| US5899902A (en) | 1997-07-03 | 1999-05-04 | Depuy Motech Acromed Corporation | Fastener |
| US6287308B1 (en) | 1997-07-14 | 2001-09-11 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for fusionless treatment of spinal deformities |
| US5951553A (en) | 1997-07-14 | 1999-09-14 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for fusionless treatment of spinal deformities |
| US5891145A (en) | 1997-07-14 | 1999-04-06 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Multi-axial screw |
| US5954722A (en) | 1997-07-29 | 1999-09-21 | Depuy Acromed, Inc. | Polyaxial locking plate |
| AU8768998A (en) | 1997-08-04 | 1999-02-22 | Gordon, Maya, Roberts & Thomas Number 1 Llc | Multiple axis intervertebral prosthesis |
| US6454769B2 (en) | 1997-08-04 | 2002-09-24 | Spinal Concepts, Inc. | System and method for stabilizing the human spine with a bone plate |
| EP1867293A2 (en) | 1997-10-27 | 2007-12-19 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Spine distraction implant |
| FR2771280B1 (en) | 1997-11-26 | 2001-01-26 | Albert P Alby | RESILIENT VERTEBRAL CONNECTION DEVICE |
| US5899941A (en) | 1997-12-09 | 1999-05-04 | Chubu Bearing Kabushiki Kaisha | Artificial intervertebral disk |
| US5976135A (en) | 1997-12-18 | 1999-11-02 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Lateral connector assembly |
| EP0933065A1 (en) | 1998-02-02 | 1999-08-04 | Sulzer Orthopädie AG | Pivotable attachment system for a bone screw |
| FR2774581B1 (en)* | 1998-02-10 | 2000-08-11 | Dimso Sa | INTEREPINOUS STABILIZER TO BE ATTACHED TO SPINOUS APOPHYSIS OF TWO VERTEBRES |
| FR2775183B1 (en) | 1998-02-20 | 2000-08-04 | Jean Taylor | INTER-SPINOUS PROSTHESIS |
| US6045552A (en) | 1998-03-18 | 2000-04-04 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Spine fixation plate system |
| US6019792A (en) | 1998-04-23 | 2000-02-01 | Cauthen Research Group, Inc. | Articulating spinal implant |
| US6679915B1 (en) | 1998-04-23 | 2004-01-20 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Articulating spinal implant |
| ATE256432T1 (en) | 1998-05-19 | 2004-01-15 | Synthes Ag | OSTEOSYNTHETIC IMPLANT WITH EMBEDDED JOINT CONNECTION |
| FR2780631B1 (en) | 1998-07-06 | 2000-09-29 | Dimso Sa | SPINAL OSTEOSYNTHESIS DEVICE FOR ANTERIOR FIXATION WITH PLATE |
| DE19832513A1 (en) | 1998-07-20 | 2000-02-17 | Impag Gmbh Medizintechnik | Fastening arrangement |
| US6241731B1 (en) | 1998-08-11 | 2001-06-05 | Daniel Fiz | Plate and screw assembly for fixing bones |
| US6296644B1 (en) | 1998-08-26 | 2001-10-02 | Jean Saurat | Spinal instrumentation system with articulated modules |
| US6231575B1 (en) | 1998-08-27 | 2001-05-15 | Martin H. Krag | Spinal column retainer |
| WO2000015125A1 (en) | 1998-09-11 | 2000-03-23 | Synthes Ag Chur | Variable angle spinal fixation system |
| US6669697B1 (en) | 1998-09-25 | 2003-12-30 | Perumala Corporation | Self-retaining bolt for internal spinal stabilizers |
| US6355038B1 (en) | 1998-09-25 | 2002-03-12 | Perumala Corporation | Multi-axis internal spinal fixation |
| US5984924A (en) | 1998-10-07 | 1999-11-16 | Isola Implants, Inc. | Bone alignment system having variable orientation bone anchors |
| US7029473B2 (en) | 1998-10-20 | 2006-04-18 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Deflectable spacer for use as an interspinous process implant and method |
| US6652534B2 (en) | 1998-10-20 | 2003-11-25 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Apparatus and method for determining implant size |
| US6652527B2 (en) | 1998-10-20 | 2003-11-25 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Supplemental spine fixation device and method |
| US7189234B2 (en) | 1998-10-20 | 2007-03-13 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Interspinous process implant sizer and distractor with a split head and size indicator and method |
| US5944719A (en) | 1998-11-10 | 1999-08-31 | Millennium Devices, L.L.C. | External fixator |
| US6050997A (en) | 1999-01-25 | 2000-04-18 | Mullane; Thomas S. | Spinal fixation system |
| US6746485B1 (en) | 1999-02-18 | 2004-06-08 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Hair used as a biologic disk, replacement, and/or structure and method |
| US6416776B1 (en) | 1999-02-18 | 2002-07-09 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Biological disk replacement, bone morphogenic protein (BMP) carriers, and anti-adhesion materials |
| US6423069B1 (en) | 1999-03-23 | 2002-07-23 | Synthes (Usa) | Orthopedic system having detachable bone anchors |
| US6315779B1 (en) | 1999-04-16 | 2001-11-13 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Multi-axial bone anchor system |
| US6280445B1 (en) | 1999-04-16 | 2001-08-28 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Multi-axial bone anchor system |
| US6936071B1 (en) | 1999-07-02 | 2005-08-30 | Spine Solutions, Inc. | Intervertebral implant |
| FR2796828B1 (en) | 1999-07-27 | 2001-10-19 | Dev Sed Soc Et | IMPLANTABLE INTERVERTEBRAL CONNECTION DEVICE |
| US6529889B1 (en) | 1999-07-27 | 2003-03-04 | Acappella Software, Inc. | System and method of knowledge architecture |
| FR2799640B1 (en) | 1999-10-15 | 2002-01-25 | Spine Next Sa | IMPLANT INTERVETEBRAL |
| US20050261770A1 (en) | 2004-04-22 | 2005-11-24 | Kuiper Mark K | Crossbar spinal prosthesis having a modular design and related implantation methods |
| US6811567B2 (en)* | 1999-10-22 | 2004-11-02 | Archus Orthopedics Inc. | Facet arthroplasty devices and methods |
| ES2270888T3 (en) | 1999-12-01 | 2007-04-16 | Henry Graf | INTERVERTEBRAL STABILIZATION DEVICE. |
| US7066957B2 (en) | 1999-12-29 | 2006-06-27 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Device and assembly for intervertebral stabilization |
| US6331179B1 (en) | 2000-01-06 | 2001-12-18 | Spinal Concepts, Inc. | System and method for stabilizing the human spine with a bone plate |
| US6261288B1 (en) | 2000-02-08 | 2001-07-17 | Roger P. Jackson | Implant stabilization and locking system |
| US6610062B2 (en) | 2000-02-16 | 2003-08-26 | Ebi, L.P. | Method and system for spinal fixation |
| US20020133155A1 (en) | 2000-02-25 | 2002-09-19 | Ferree Bret A. | Cross-coupled vertebral stabilizers incorporating spinal motion restriction |
| US6309391B1 (en) | 2000-03-15 | 2001-10-30 | Sdgi Holding, Inc. | Multidirectional pivoting bone screw and fixation system |
| US6402750B1 (en) | 2000-04-04 | 2002-06-11 | Spinlabs, Llc | Devices and methods for the treatment of spinal disorders |
| US6471706B1 (en) | 2000-04-18 | 2002-10-29 | Walter Lorenz Surgical, Inc. | Resorbable bone distractor and method |
| US6235033B1 (en) | 2000-04-19 | 2001-05-22 | Synthes (Usa) | Bone fixation assembly |
| US6645207B2 (en) | 2000-05-08 | 2003-11-11 | Robert A. Dixon | Method and apparatus for dynamized spinal stabilization |
| AU2001270720B2 (en) | 2000-06-30 | 2007-02-08 | Henry Graf | Intervertebral linking device |
| FR2811540B1 (en)* | 2000-07-12 | 2003-04-25 | Spine Next Sa | IMPORTING INTERVERTEBRAL IMPLANT |
| FR2812186B1 (en) | 2000-07-25 | 2003-02-28 | Spine Next Sa | FLEXIBLE CONNECTION PIECE FOR SPINAL STABILIZATION |
| FR2812185B1 (en) | 2000-07-25 | 2003-02-28 | Spine Next Sa | SEMI-RIGID CONNECTION PIECE FOR RACHIS STABILIZATION |
| JP2004505745A (en) | 2000-08-24 | 2004-02-26 | ジンテーズ アクチエンゲゼルシャフト クール | Device for connecting a bone anchoring element to a longitudinal rod |
| US6554831B1 (en) | 2000-09-01 | 2003-04-29 | Hopital Sainte-Justine | Mobile dynamic system for treating spinal disorder |
| US6685705B1 (en) | 2000-10-23 | 2004-02-03 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Six-axis and seven-axis adjustable connector |
| US6579319B2 (en) | 2000-11-29 | 2003-06-17 | Medicinelodge, Inc. | Facet joint replacement |
| FR2817461B1 (en) | 2000-12-01 | 2003-08-15 | Henry Graf | INTERVERTEBRAL STABILIZATION DEVICE |
| US7651516B2 (en) | 2000-12-01 | 2010-01-26 | Spinevision S.A. | Connection assembly for the field of spinal osteosynthesis and method for using at least one such assembly |
| US6565605B2 (en) | 2000-12-13 | 2003-05-20 | Medicinelodge, Inc. | Multiple facet joint replacement |
| US6743257B2 (en) | 2000-12-19 | 2004-06-01 | Cortek, Inc. | Dynamic implanted intervertebral spacer |
| FR2818530B1 (en)* | 2000-12-22 | 2003-10-31 | Spine Next Sa | INTERVERTEBRAL IMPLANT WITH DEFORMABLE SHIM |
| NL1017284C2 (en) | 2001-02-05 | 2002-08-06 | Accius Bv | Fixing device for an orthosis or prosthesis. |
| FR2822051B1 (en) | 2001-03-13 | 2004-02-27 | Spine Next Sa | INTERVERTEBRAL IMPLANT WITH SELF-LOCKING ATTACHMENT |
| US6802844B2 (en) | 2001-03-26 | 2004-10-12 | Nuvasive, Inc | Spinal alignment apparatus and methods |
| US6641583B2 (en) | 2001-03-29 | 2003-11-04 | Endius Incorporated | Apparatus for retaining bone portions in a desired spatial relationship |
| US6582433B2 (en) | 2001-04-09 | 2003-06-24 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Spine fixation device and method |
| US6972020B1 (en) | 2001-06-01 | 2005-12-06 | New York University | Multi-directional internal distraction osteogenesis device |
| FR2826861B1 (en) | 2001-07-04 | 2004-06-18 | Materiel Orthopedique En Abreg | SIDE CONNECTOR WITH ADJUSTABLE OFFSET FOR A SPINE CORRECTION AND STABILIZATION DEVICE, FIXING DEVICE ADAPTED TO THIS CONNECTOR AND ASSEMBLY FORMED BY THIS CONNECTOR AND THIS FIXING DEVICE |
| US6926728B2 (en) | 2001-07-18 | 2005-08-09 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Curved dilator and method |
| DE10136162B4 (en) | 2001-07-25 | 2016-05-12 | Biedermann Technologies Gmbh & Co. Kg | Connecting element for connecting two used for bone and spine stabilization rod-shaped elements |
| JP4755781B2 (en) | 2001-08-01 | 2011-08-24 | 昭和医科工業株式会社 | Jointing member for osteosynthesis |
| US6673074B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2004-01-06 | Endius Incorporated | Apparatus for retaining bone portions in a desired spatial relationship |
| US6974460B2 (en) | 2001-09-14 | 2005-12-13 | Stryker Spine | Biased angulation bone fixation assembly |
| DE60238997D1 (en) | 2001-09-28 | 2011-03-03 | Stephen Ritland | CHROME OR HOOKS |
| US6623485B2 (en) | 2001-10-17 | 2003-09-23 | Hammill Manufacturing Company | Split ring bone screw for a spinal fixation system |
| FR2830742B1 (en) | 2001-10-17 | 2004-07-30 | Spinevision Sa | SYSTEM FOR MAINTAINING AT LEAST TWO VERTEBRAINS IN RELATION TO THE OTHER FOR REALIZING A RACHIDIAN OSTEOSYNTHESIS |
| US6887242B2 (en) | 2001-10-17 | 2005-05-03 | Ortho Innovations, Llc | Split ring bone screw for a spinal fixation system |
| US6679883B2 (en) | 2001-10-31 | 2004-01-20 | Ortho Development Corporation | Cervical plate for stabilizing the human spine |
| DE10157814B4 (en) | 2001-11-27 | 2004-12-02 | Biedermann Motech Gmbh | Closure device for securing a rod-shaped element in a holding element connected to a shaft |
| FR2832917B1 (en) | 2001-11-30 | 2004-09-24 | Spine Next Sa | ELASTICALLY DEFORMABLE INTERVERTEBRAL IMPLANT |
| US20030105462A1 (en) | 2001-11-30 | 2003-06-05 | Haider Thomas T. | Poly axial cervical plate system |
| US6852113B2 (en) | 2001-12-14 | 2005-02-08 | Orthopaedic Designs, Llc | Internal osteotomy fixation device |
| US7070599B2 (en) | 2002-07-24 | 2006-07-04 | Paul Kamaljit S | Bone support assembly |
| US6709433B1 (en) | 2001-12-20 | 2004-03-23 | Biomet, Inc. | Bridging/non-bridging external bone fixator |
| DE10164323C1 (en) | 2001-12-28 | 2003-06-18 | Biedermann Motech Gmbh | Bone screw has holder element joined to shaft and possessing two free arms , with inner screw, slot, external nut, cavity and shoulder cooperating with attachment |
| US6740118B2 (en) | 2002-01-09 | 2004-05-25 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Intervertebral prosthetic joint |
| US7011684B2 (en) | 2002-01-17 | 2006-03-14 | Concept Matrix, Llc | Intervertebral disk prosthesis |
| US6733534B2 (en) | 2002-01-29 | 2004-05-11 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | System and method for spine spacing |
| US7335201B2 (en) | 2003-09-26 | 2008-02-26 | Zimmer Spine, Inc. | Polyaxial bone screw with torqueless fastening |
| US7678136B2 (en) | 2002-02-04 | 2010-03-16 | Spinal, Llc | Spinal fixation assembly |
| US20040006342A1 (en) | 2002-02-13 | 2004-01-08 | Moti Altarac | Posterior polyaxial plate system for the spine |
| FR2836368B1 (en) | 2002-02-25 | 2005-01-14 | Spine Next Sa | SEQUENTIAL LINK DEVICE |
| US6626909B2 (en) | 2002-02-27 | 2003-09-30 | Kingsley Richard Chin | Apparatus and method for spine fixation |
| FR2837094B1 (en) | 2002-03-15 | 2004-11-26 | Fixano | INTERVERTEBRAL IMPLANT |
| US6966910B2 (en) | 2002-04-05 | 2005-11-22 | Stephen Ritland | Dynamic fixation device and method of use |
| US20050261682A1 (en) | 2002-04-13 | 2005-11-24 | Ferree Bret A | Vertebral shock absorbers |
| US6706068B2 (en) | 2002-04-23 | 2004-03-16 | Bret A. Ferree | Artificial disc replacements with natural kinematics |
| US20040030391A1 (en) | 2002-04-24 | 2004-02-12 | Bret Ferree | Artificial intervertebral disc spacers |
| ATE552789T1 (en) | 2002-05-08 | 2012-04-15 | Stephen Ritland | DYNAMIC FIXATION DEVICE |
| US7048736B2 (en) | 2002-05-17 | 2006-05-23 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Device for fixation of spinous processes |
| US20030220643A1 (en)* | 2002-05-24 | 2003-11-27 | Ferree Bret A. | Devices to prevent spinal extension |
| US7277946B2 (en) | 2002-06-28 | 2007-10-02 | Microsoft Corporation | Distributed session listing and content discovery |
| US7060066B2 (en) | 2002-06-28 | 2006-06-13 | Mayo Foundation For Medical Education And Research | Spinal fixation support device and methods of using |
| US7001389B1 (en) | 2002-07-05 | 2006-02-21 | Navarro Richard R | Fixed and variable locking fixation assembly |
| DE10236691B4 (en) | 2002-08-09 | 2005-12-01 | Biedermann Motech Gmbh | Dynamic stabilization device for bones, in particular for vertebrae |
| AU2003265597A1 (en) | 2002-08-23 | 2004-03-11 | Paul C. Mcafee | Metal-backed uhmpe rod sleeve system preserving spinal motion |
| US7220263B2 (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2007-05-22 | Seaspine, Inc. | Cervical plate/screw system for immobilizing vertebral bodies |
| DE10247762A1 (en) | 2002-10-14 | 2004-04-22 | Waldemar Link (Gmbh & Co.) | Intervertebral prosthesis |
| FR2845587B1 (en)* | 2002-10-14 | 2005-01-21 | Scient X | DYNAMIC DEVICE FOR INTERVERTEBRAL CONNECTION WITH MULTIDIRECTIONALLY CONTROLLED DEBATMENT |
| US7083649B2 (en) | 2002-10-29 | 2006-08-01 | St. Francis Medical Technologies, Inc. | Artificial vertebral disk replacement implant with translating pivot point |
| US20040147928A1 (en) | 2002-10-30 | 2004-07-29 | Landry Michael E. | Spinal stabilization system using flexible members |
| US20040186577A1 (en) | 2003-01-29 | 2004-09-23 | Ferree Bret A. | In situ artificaial disc replacements and other prosthetic components |
| US20040158254A1 (en) | 2003-02-12 | 2004-08-12 | Sdgi Holdings, Inc. | Instrument and method for milling a path into bone |
| EP1596738A4 (en) | 2003-02-25 | 2010-01-20 | Stephen Ritland | Adjustable rod and connector device and method of use |
| GB2399503B (en)* | 2003-03-20 | 2006-03-29 | Blatchford & Sons Ltd | Prosthetic knee joint mechanism |
| US7060097B2 (en) | 2003-03-31 | 2006-06-13 | Depuy Spine, Inc. | Method and apparatus for implant stability |
| US6964666B2 (en) | 2003-04-09 | 2005-11-15 | Jackson Roger P | Polyaxial bone screw locking mechanism |
| US7291152B2 (en) | 2003-04-18 | 2007-11-06 | Abdou M Samy | Bone fixation system and method of implantation |
| US7473267B2 (en) | 2003-04-25 | 2009-01-06 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | System and method for minimally invasive posterior fixation |
| CA2524145A1 (en) | 2003-05-02 | 2004-11-18 | Yale University | Dynamic spine stabilizer |
| US8652175B2 (en)* | 2003-05-02 | 2014-02-18 | Rachiotek, Llc | Surgical implant devices and systems including a sheath member |
| US7615068B2 (en) | 2003-05-02 | 2009-11-10 | Applied Spine Technologies, Inc. | Mounting mechanisms for pedicle screws and related assemblies |
| US20050171543A1 (en) | 2003-05-02 | 2005-08-04 | Timm Jens P. | Spine stabilization systems and associated devices, assemblies and methods |
| US20050177164A1 (en) | 2003-05-02 | 2005-08-11 | Carmen Walters | Pedicle screw devices, systems and methods having a preloaded set screw |
| US7635379B2 (en) | 2003-05-02 | 2009-12-22 | Applied Spine Technologies, Inc. | Pedicle screw assembly with bearing surfaces |
| DE10320417A1 (en) | 2003-05-07 | 2004-12-02 | Biedermann Motech Gmbh | Dynamic anchoring device and dynamic stabilization device for bones, in particular for vertebrae, with such an anchoring device |
| US6986771B2 (en) | 2003-05-23 | 2006-01-17 | Globus Medical, Inc. | Spine stabilization system |
| DE10326643A1 (en) | 2003-06-11 | 2004-12-30 | Mückter, Helmut, Dr. med. Dipl.-Ing. | Osteosynthesis plate or comparable implant with ball sleeve |
| US6945974B2 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2005-09-20 | Aesculap Inc. | Spinal stabilization implant and method of application |
| US6945975B2 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2005-09-20 | Aesculap, Inc. | Bone fixation assembly and method of securement |
| US7909869B2 (en) | 2003-08-05 | 2011-03-22 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Artificial spinal unit assemblies |
| US7799082B2 (en) | 2003-08-05 | 2010-09-21 | Flexuspine, Inc. | Artificial functional spinal unit system and method for use |
| FR2860138A1 (en) | 2003-09-26 | 2005-04-01 | Stryker Spine | ASSEMBLY AND METHOD OF FIXING BONES |
| US7182782B2 (en) | 2003-09-30 | 2007-02-27 | X-Spine Systems, Inc. | Spinal fusion system and method for fusing spinal bones |
| US20050085814A1 (en) | 2003-10-21 | 2005-04-21 | Sherman Michael C. | Dynamizable orthopedic implants and their use in treating bone defects |
| US7588588B2 (en) | 2003-10-21 | 2009-09-15 | Innovative Spinal Technologies | System and method for stabilizing of internal structures |
| US20050090823A1 (en) | 2003-10-28 | 2005-04-28 | Bartimus Christopher S. | Posterior fixation system |
| TWI243047B (en) | 2003-11-03 | 2005-11-11 | A Spine Holding Group Corp | Spigot vertebra fixing and reposition device |
| DE602004006709T2 (en)* | 2003-11-07 | 2008-02-07 | Impliant Ltd. | SPINE GRAFT |
| US7862586B2 (en) | 2003-11-25 | 2011-01-04 | Life Spine, Inc. | Spinal stabilization systems |
| US7553320B2 (en) | 2003-12-10 | 2009-06-30 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Method and apparatus for replacing the function of facet joints |
| US20050131406A1 (en) | 2003-12-15 | 2005-06-16 | Archus Orthopedics, Inc. | Polyaxial adjustment of facet joint prostheses |
| US20050131407A1 (en) | 2003-12-16 | 2005-06-16 | Sicvol Christopher W. | Flexible spinal fixation elements |
| US20050143737A1 (en) | 2003-12-31 | 2005-06-30 | John Pafford | Dynamic spinal stabilization system |
| US7806914B2 (en) | 2003-12-31 | 2010-10-05 | Spine Wave, Inc. | Dynamic spinal stabilization system |
| US7195633B2 (en) | 2004-01-08 | 2007-03-27 | Robert J. Medoff | Fracture fixation system |
| US20050165398A1 (en)* | 2004-01-26 | 2005-07-28 | Reiley Mark A. | Percutaneous spine distraction implant systems and methods |
| US7597694B2 (en) | 2004-01-30 | 2009-10-06 | Warsaw Orthopedic, Inc. | Instruments and methods for minimally invasive spinal stabilization |
| US7214227B2 (en) | 2004-03-22 | 2007-05-08 | Innovative Spinal Technologies | Closure member for a medical implant device |
| US7942913B2 (en) | 2004-04-08 | 2011-05-17 | Ebi, Llc | Bone fixation device |
| US7524324B2 (en)* | 2004-04-28 | 2009-04-28 | Kyphon Sarl | System and method for an interspinous process implant as a supplement to a spine stabilization implant |
| US7338527B2 (en) | 2004-05-11 | 2008-03-04 | Geoffrey Blatt | Artificial spinal disc, insertion tool, and method of insertion |
| US20050267470A1 (en) | 2004-05-13 | 2005-12-01 | Mcbride Duncan Q | Spinal stabilization system to flexibly connect vertebrae |
| US7931675B2 (en) | 2004-06-23 | 2011-04-26 | Yale University | Dynamic stabilization device including overhanging stabilizing member |
| US7854752B2 (en) | 2004-08-09 | 2010-12-21 | Theken Spine, Llc | System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization |
| US7896906B2 (en) | 2004-12-30 | 2011-03-01 | Depuy Spine, Inc. | Artificial facet joint |
| US20060085076A1 (en) | 2004-10-15 | 2006-04-20 | Manoj Krishna | Posterior spinal arthroplasty-development of a new posteriorly inserted artificial disc and an artificial facet joint |
| US20060265074A1 (en) | 2004-10-21 | 2006-11-23 | Manoj Krishna | Posterior spinal arthroplasty-development of a new posteriorly inserted artificial disc, a new anteriorly inserted artifical disc and an artificial facet joint |
| US20060229613A1 (en) | 2004-12-31 | 2006-10-12 | Timm Jens P | Sheath assembly for spinal stabilization device |
| US7604654B2 (en) | 2005-02-22 | 2009-10-20 | Stryker Spine | Apparatus and method for dynamic vertebral stabilization |
| US7811309B2 (en) | 2005-07-26 | 2010-10-12 | Applied Spine Technologies, Inc. | Dynamic spine stabilization device with travel-limiting functionality |
- 2004
- 2004-08-09USUS10/914,751patent/US7854752B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
- 2008
- 2008-03-07USUS12/044,810patent/US8038700B2/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4488542A (en)* | 1981-11-27 | 1984-12-18 | Per Helland | External setting and correction device for the treatment of bone fractures |
| US5122140A (en)* | 1989-08-23 | 1992-06-16 | Jaquet Orthopedie, S.A. | Dynamic external fixation device |
| US6267764B1 (en)* | 1996-11-15 | 2001-07-31 | Stryker France S.A. | Osteosynthesis system with elastic deformation for spinal column |
| US20060229609A1 (en)* | 2005-03-18 | 2006-10-12 | Chao-Jan Wang | Microadjustment spinal joint fixture |
| US7905906B2 (en)* | 2006-06-08 | 2011-03-15 | Disc Motion Technologies, Inc. | System and method for lumbar arthroplasty |
| USD618349S1 (en)* | 2007-03-23 | 2010-06-22 | Disc Motion Technologies, Inc. | Spinal stabilization device |
| USD618348S1 (en)* | 2007-03-23 | 2010-06-22 | Disc Motion Technologies, Inc. | Spinal stabilization device |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9907582B1 (en) | 2011-04-25 | 2018-03-06 | Nuvasive, Inc. | Minimally invasive spinal fixation system and related methods |
| US10716600B1 (en) | 2011-04-25 | 2020-07-21 | Nuvasive, Inc. | Minimally invasive spinal fixation system |
| US11596453B2 (en) | 2011-04-25 | 2023-03-07 | Nuvasive, Inc. | Minimally invasive spinal fixation system |
| US12357350B2 (en) | 2011-04-25 | 2025-07-15 | Nuvasive, Inc. | Minimally invasive spinal fixation system and related methods |
| US10419753B2 (en)* | 2016-09-12 | 2019-09-17 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | Semiconductor device, moving image processing system, method of controlling semiconductor device |
| US11583318B2 (en) | 2018-12-21 | 2023-02-21 | Paradigm Spine, Llc | Modular spine stabilization system and associated instruments |
| US12114895B2 (en) | 2018-12-21 | 2024-10-15 | Xtant Medical Holdings, Inc. | Modular spine stabilization system and associated instruments |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20060036240A1 (en) | 2006-02-16 |
| US20080154307A1 (en) | 2008-06-26 |
| US7854752B2 (en) | 2010-12-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8038700B2 (en) | System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization | |
| US12396765B2 (en) | Instruments and methods for tensioning a spinal tether | |
| US9907579B2 (en) | Interspinous spacer assembly | |
| US7588588B2 (en) | System and method for stabilizing of internal structures | |
| US8147525B2 (en) | Bone anchor assembly and methods of use | |
| US9480502B2 (en) | Expansion interspinous fixation device and method | |
| US8357181B2 (en) | Intervertebral prosthetic device for spinal stabilization and method of implanting same | |
| CN112312851A (en) | Modular screw system with adjustable length | |
| US20070233090A1 (en) | Aligning cross-connector | |
| US20080065073A1 (en) | Offset dynamic motion spinal stabilization system | |
| US20070233091A1 (en) | Multi-level spherical linkage implant system | |
| US20070288012A1 (en) | Dynamic motion spinal stabilization system and device | |
| US20060247637A1 (en) | System and method for dynamic skeletal stabilization | |
| EP3406212B1 (en) | Spinal distraction system | |
| EP2542168B1 (en) | Dynamic vertebral construct | |
| US11109894B2 (en) | Apparatus, system, and method for spinal vertebrae stabilization | |
| US20230032049A1 (en) | Systems and methods for treatment of spinal deformities |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:SILICON VALLEY BANK, AS AGENT AND AS A LENDER, MAS Free format text:SECURITY AGREEMENT;ASSIGNOR:INNOVATIVE SPINAL TECHNOLOGIES, INC.;REEL/FRAME:021750/0493 Effective date:20080912 Owner name:GE BUSINESS FINANCIAL SERVICES INC., F/K/A MERRILL Free format text:SECURITY AGREEMENT;ASSIGNOR:INNOVATIVE SPINAL TECHNOLOGIES, INC.;REEL/FRAME:021750/0493 Effective date:20080912 Owner name:SILICON VALLEY BANK, AS AGENT AND AS A LENDER,MASS Free format text:SECURITY AGREEMENT;ASSIGNOR:INNOVATIVE SPINAL TECHNOLOGIES, INC.;REEL/FRAME:021750/0493 Effective date:20080912 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:THEKEN SPINE, LLC, OHIO Free format text:TERMINATION AND RELEASE OF SECURITY INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:SILICON VALLEY BANK;GE BUSINESS FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC.;REEL/FRAME:023228/0001 Effective date:20090910 Owner name:THEKEN SPINE, LLC,OHIO Free format text:TERMINATION AND RELEASE OF SECURITY INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:SILICON VALLEY BANK;GE BUSINESS FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC.;REEL/FRAME:023228/0001 Effective date:20090910 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:THEKEN SPINE, LLC, OHIO Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:WARREN E. AGIN, QUALIFIED CHAPTER 7 TRUSTEE IN BANKRUPTCY FOR INNOVATIVE SPINAL TECHNOLOGIES, INC.;REEL/FRAME:023233/0395 Effective date:20090910 Owner name:THEKEN SPINE, LLC,OHIO Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:WARREN E. AGIN, QUALIFIED CHAPTER 7 TRUSTEE IN BANKRUPTCY FOR INNOVATIVE SPINAL TECHNOLOGIES, INC.;REEL/FRAME:023233/0395 Effective date:20090910 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:INNOVATIVE SPINAL TECHNOLOGIES, TEXAS Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:COLLERAN, DENNIS;SCHORER, SCOTT;MCAFEE, PAUL, M.D.;REEL/FRAME:023279/0230;SIGNING DATES FROM 20040809 TO 20041209 Owner name:INNOVATIVE SPINAL TECHNOLOGIES, TEXAS Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:COLLERAN, DENNIS;SCHORER, SCOTT;MCAFEE, PAUL, M.D.;SIGNING DATES FROM 20040809 TO 20041209;REEL/FRAME:023279/0230 | |
| STCF | Information on status: patent grant | Free format text:PATENTED CASE | |
| FPAY | Fee payment | Year of fee payment:4 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:WELLS FARGO BANK, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION, CALIFORNIA Free format text:SECURITY INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:SEASPINE HOLDINGS CORPORATION;SEASPINE ORTHOPEDICS CORPORATION;SEASPINE, INC.;AND OTHERS;REEL/FRAME:037393/0895 Effective date:20151224 | |
| FEPP | Fee payment procedure | Free format text:ENTITY STATUS SET TO SMALL (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: SMAL); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: SMALL ENTITY | |
| MAFP | Maintenance fee payment | Free format text:PAYMENT OF MAINTENANCE FEE, 8TH YR, SMALL ENTITY (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: M2552); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: SMALL ENTITY Year of fee payment:8 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:WELLS FARGO BANK, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION, AS AGENT, CALIFORNIA Free format text:SECOND AMENDMENT TO PATENT SECURITY AGREEMENT;ASSIGNORS:SEASPINE HOLDINGS CORPORATION;SEASPINE ORTHOPEDICS CORPORATION;SEASPINE, INC.;AND OTHERS;REEL/FRAME:060715/0395 Effective date:20220715 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:7D SURGICAL USA INC., CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:WELLS FARGO BANK, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION;REEL/FRAME:062336/0593 Effective date:20230105 Owner name:SEASPINE ORTHOPEDICS INTERMEDIATECO, INC., CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:WELLS FARGO BANK, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION;REEL/FRAME:062336/0593 Effective date:20230105 Owner name:THEKEN SPINE, LLC, CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:WELLS FARGO BANK, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION;REEL/FRAME:062336/0593 Effective date:20230105 Owner name:ISOTIS ORTHOBIOLOGICS, INC., CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:WELLS FARGO BANK, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION;REEL/FRAME:062336/0593 Effective date:20230105 Owner name:SEASPINE SALES LLC, CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:WELLS FARGO BANK, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION;REEL/FRAME:062336/0593 Effective date:20230105 Owner name:ISOTIS, INC., CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:WELLS FARGO BANK, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION;REEL/FRAME:062336/0593 Effective date:20230105 Owner name:SEASPINE, INC., CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:WELLS FARGO BANK, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION;REEL/FRAME:062336/0593 Effective date:20230105 Owner name:SEASPINE ORTHOPEDICS CORPORATION, CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:WELLS FARGO BANK, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION;REEL/FRAME:062336/0593 Effective date:20230105 Owner name:SEASPINE HOLDINGS CORPORATION, CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:WELLS FARGO BANK, NATIONAL ASSOCIATION;REEL/FRAME:062336/0593 Effective date:20230105 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A., AS ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANT, ILLINOIS Free format text:SECURITY INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:SEASPINE ORTHOPEDICS CORPORATION;SEASPINE, INC.;ISOTIS ORTHOBIOLOGICS, INC.;AND OTHERS;REEL/FRAME:062819/0650 Effective date:20230217 | |
| FEPP | Fee payment procedure | Free format text:ENTITY STATUS SET TO UNDISCOUNTED (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: BIG.); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: LARGE ENTITY | |
| MAFP | Maintenance fee payment | Free format text:PAYMENT OF MAINTENANCE FEE, 12TH YEAR, LARGE ENTITY (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: M1553); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: LARGE ENTITY Year of fee payment:12 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:BLUE TORCH FINANCE LLC, AS COLLATERAL AGENT, NEW YORK Free format text:SECURITY INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:THEKEN SPINE, LLC;REEL/FRAME:066257/0388 Effective date:20231106 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:THEKEN SPINE, LLC, CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A.;REEL/FRAME:069323/0561 Effective date:20241107 Owner name:ISOTIS ORTHOBIOLOGICS, INC., CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A.;REEL/FRAME:069323/0561 Effective date:20241107 Owner name:SEASPINE, INC., CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A.;REEL/FRAME:069323/0561 Effective date:20241107 Owner name:SEASPINE ORTHOPEDICS CORPORATION, CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK, N.A.;REEL/FRAME:069323/0561 Effective date:20241107 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:OXFORD FINANCE LLC, AS AGENT, VIRGINIA Free format text:SECURITY INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:ORTHOFIX MEDICAL INC.;ORTHOFIX US LLC;SPINAL KINETICS LLC;AND OTHERS;REEL/FRAME:069332/0761 Effective date:20241107 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:THEKEN SPINE, LLC, CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:BLUE TORCH FINANCE LLC;REEL/FRAME:069358/0110 Effective date:20241111 Owner name:SPINAL KINETICS LLC, CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:BLUE TORCH FINANCE LLC;REEL/FRAME:069358/0110 Effective date:20241111 Owner name:SEASPINE ORTHOPEDICS CORPORATION, CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:BLUE TORCH FINANCE LLC;REEL/FRAME:069358/0110 Effective date:20241111 Owner name:SEASPINE, INC., CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:BLUE TORCH FINANCE LLC;REEL/FRAME:069358/0110 Effective date:20241111 Owner name:ORTHOFIX US, LLC, TEXAS Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:BLUE TORCH FINANCE LLC;REEL/FRAME:069358/0110 Effective date:20241111 Owner name:ISOTIS ORTHOBIOLOGICS, INC., CALIFORNIA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNOR:BLUE TORCH FINANCE LLC;REEL/FRAME:069358/0110 Effective date:20241111 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:SEASPINE ORTHOPEDICS CORPORATION, CALIFORNIA Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:THEKEN SPINE, LLC;REEL/FRAME:069746/0620 Effective date:20241220 |