US3754555A - Controllable barbed intracardial electrode - Google Patents
Controllable barbed intracardial electrodeDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US3754555A US3754555AUS00186654AUS3754555DAUS3754555AUS 3754555 AUS3754555 AUS 3754555AUS 00186654 AUS00186654 AUS 00186654AUS 3754555D AUS3754555D AUS 3754555DAUS 3754555 AUS3754555 AUS 3754555A
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- piston
- cavity
- electrode
- insulating member
- prongs
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000002513implantationMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 230000000638stimulationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription8
- 210000005003heart tissueAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription7
- 239000004020conductorSubstances0.000claimsdescription18
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000claimsdescription6
- 230000002035prolonged effectEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 210000004165myocardiumAnatomy0.000description4
- 102100026827Protein associated with UVRAG as autophagy enhancerHuman genes0.000description2
- 101710102978Protein associated with UVRAG as autophagy enhancerProteins0.000description2
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000description2
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000description2
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000description2
- 210000003205muscleAnatomy0.000description2
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-NplatinumChemical compound[Pt]BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 238000003466weldingMethods0.000description2
- 101100536354Drosophila melanogaster tant geneProteins0.000description1
- 239000004677NylonSubstances0.000description1
- 210000001015abdomenAnatomy0.000description1
- 150000001408amidesChemical class0.000description1
- 210000000038chestAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 210000003709heart valveAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000000314lubricantSubstances0.000description1
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description1
- 229920001778nylonPolymers0.000description1
- 229910052697platinumInorganic materials0.000description1
- 230000000717retained effectEffects0.000description1
- 229920002379silicone rubberPolymers0.000description1
- 239000004945silicone rubberSubstances0.000description1
- 210000003462veinAnatomy0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/02—Details
- A61N1/04—Electrodes
- A61N1/05—Electrodes for implantation or insertion into the body, e.g. heart electrode
- A61N1/056—Transvascular endocardial electrode systems
- A61N1/057—Anchoring means; Means for fixing the head inside the heart
- A61N1/0573—Anchoring means; Means for fixing the head inside the heart chacterised by means penetrating the heart tissue, e.g. helix needle or hook
Definitions
- a heart stimulation deviceprovides a piston mov- 419 p 4 9 R able axially within a cavity in the electrode body.
- the 1 pistoncarries resilient prongs which move through ⁇ 56] Ra cm channels in the electrode body to engage the heart tis- UNITED STATES PATENTS sue for implantation of the electrode.
- the prongsare 3 348.548 10/1967 chum, 128/418 retracted when tension is exerted on the piston, and are 665,916 5/1972 xobs uhi2:111:11: 128/2 R advanged by 3,631,848 1/1972 Muller 128/205 R 2 Cllllns, 1 Drawing Fllll't lllllllllllilll l 1. CONTROLLABLE' BARBED "INTRACARDIAL ELECTRODE lar isopened; and theelectrodeisthen pushed through the vein, metal head foremost; until it reaches the auricle of the heart;
- stimulation of either the auricle or theventriclemaybe desired.- In the case of stimulation of the amide, .the
- the electrodeis fed through the heart valve and'is pressed againstthe wall of the ventricle. It is-desirable to dispose th'ehelical conductorina bowed position, so that the head is pressed against'thelwall of the heart 'by'the resilience of'ithe conductor.
- measuring and testingapparatusis connected to the end bf the conductorthat remains'outside the-patients body, in orde'r'to measure the stimulation threshold of the heart.
- cardiacstimulation deviceheart'pacer
- a support orbedfor the stimulator-isprovided in the thorax or abdomen and thenconnected to the neck by means of tubingthat is led through the body.
- the external 'end' of the helical conductor(remote from-the heart) is the wall of the heart,rather than within'the wall tissue,
- ltis therefore an object of the invention to provide an improvedimplantable intracardial electrode, which substantially reduces the likelihood of dislocation of the electrode, and.thus increases the safety of the patie'ntusing it.
- a number of resilientprongs or barbsare attached to the cylinder.
- Channelsare provided in the tip of the head, at an angle to the. cavity axis; and the resilient prongs are extendable through these channels to the outside of the electrode.
- the prongsbe placed at a suitable angle with respect to the axis of the piston, and that the diameter of the prongs be suitably chosen. Good results may be obtained when the channels in the head of the electrode are-placed at an angle of about 40 with respect to the axis of the piston.
- the prongs he preferred embodimentmay be advantageously made of nylon of 0.3 mm diameter.
- metalprongs covered with insulating'materialmay be advantageously made of nylon of 0.3 mm diameter.
- the use of metal prongshas the advert tage that the placement of the prongs in the wall of the heart may be observed with the aid of X-rays.
- the prongsmay be'freed from the heart wail tissue by means of a thin flexible wire attached to the piston, and led through the inside of the insulating member. Tension on the wire retracts the piston .and"
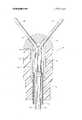
- FIG. lis a cross-sectional view of the electrode.
- electrode 10is connected to a helical conductor 12, carried within an insulating member 14, such as a tube of silicone rubber.
- Conductor 12may be externally connected at its remote; end to a heart stimulation device.
- Conductor 12is electri cally connected with a head 16, which may be made,
- a narrowed portion 18 of 7 head 16is inserted into insulating member 14, so that portion 18 lies between conductor 12 and insulating member 14.
- head 16the end of I ton axis.
- prongsare a desirable number.
- Prongs 24are finnly attached at 28, as by welding, to the end of piston 22 nearest conductor 12. At the forward end of the piston the prongs are retained by a ring 30, to prevent their spreading.
- a force-transmitting memberis provided in the form of a stiff wire 32, carried within insulating member 14, by which piston 22 can be moved forward, causing prongs 24 to protrude through channels 26 to the exterior of electrode 10, enabling them to engage the tissue of the myocardium.
- a thin wire 34may be attached to cylinder 22,'for instance .by welding, to provide a tension- 7 transmitting member by means of which piston .22 together with attached prongs 24 can be retracted if the first attempt at implantation in the myocardium is unsatisfactory.
- Prongs 24may be of varying-length, depending on whether the electrode is to be attached to the auricle or the ventricle.
- the lengthshould be such that when piston 22 is in'its extreme forward position (shown in the drawing), a length of about 3 mm "protrudes from head 16, if the head is to beattached to the auricle, or a length of 4 to 5' mm if it is to be attached to the ventrimoved back and forth several times, after which the superfluous lubricant may be'removed.
- the electrodeis secured'in place by pushing on stiff wire 32 to force prongs 24 outwardly into the heart wall tissue.
- Wire 32may then be removed through insulating member 14, leaving only the coiled conductor 12 and thin wire 34, which are relatively flexible.
- the end of insulating member 14 remote from electrode 10,:with conductor 12,may then be connected to a suitable heart stimulation device internal or external to the patient. in the event that electrode 10 is unsatisfactorily placed or must be removed, prongs 24 are retracted by tension on thin wire 34, and stiff wire 32 may be'reinserted through-the'remote end of insulating member 14 to exert the desired force on cylinder 22 to cause reimplantation.
- a controllable repeatably implantable electrodecomprising I a conducting head, a conductor electrically connected to said head, said head having a front portion and elongated body portion defining an axially oriented cavity, g a tubular insulating member connected to said body portion and aligned'with sa'id cavityJaid conductor being carried away from insulating member,
- said headwithin said a plurality of channels extending from said cavity through said front portion to the exterior of said head, and each disposed at an angle to the axis of said cavity,
- a rigid cylindrical pistonmovable axially within said cavity between a forward implantation position and a retracted position, carrying a plurality of resilient prongs each extending into a said channel,
- a removable force-transmitting membercarried within said insulating member, having one end bearing-against said piston and the other end re- I mote from said piston,
- a flexible tension-transmitting membercarried within said-'insulating'member, having one end attached to said piston and the other end remote from said pistOll,
- said pistonbeing moved within said cavity to said forward implantation position by force applied to said remote end of said force-transmitting member, said prongs being thereby moved through said channels to engage the heart tissue for implantation of said electrode, and said piston being moved to saidretractedpos'ition by tension exerted on said remote end of .said tension-transmitting member, said prongs being thereby retracted and freed from said heart tissue for removal of said electrode.
- An intracardial electrodefor use in artificial stimu- I lation of a patients heart, suitable for prolonged implantation within a patients body,
- said electrodecomprising an elongated body defining an axially oriented cavity
- said bodyhaving at least one channel extending from said cavity to the exterior of said body and disposed at an angle to the axis of said cavity, a rigid piston movable axially within said cavity, and at least one resilient prong longer than a said channel, attached to said piston and extending into a said channel,
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Electrotherapy Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
United States Patent 1191 Schmitt Aug. 28,, 1973 CONTROLLABLE BARBED INTRACARDIAL 3,120,227 2/1964 Hunter, Jr. =1 a1. 128/418 ELECTRODE 3,347,224 10/1967 Adams 12812.05 F 3,523,538 8/1970 Shimizo 128/404 [76] inventor: Gel-Inn Sclunltt, Vredenweg 8, 44
Mum", Germany FOREIGN PATENTS OR APPLICATIONS [22] Filed: Oct. 5" 1971 246,004 11/1969 U.S.S.R. 128/419 P [211 Appl. No.: 186,654 Primary Examiner-William E. Kamm I Attorney-Martin Kirkpatrick [52] US. Cl. 128/418 128/419 P 51 in. C1. A6ln 1/04 [57] ABSTRACT [581 r1614 6: Search 128/2 A, 2 R, 2.05 n, A repeatably implantable intracardisl electrodefor 128/105 1:, 295 105 2 1 E, 404' 418. with a heart stimulation device provides a piston mov- 419 p 4 9 R able axially within a cavity in the electrode body. The 1 piston carries resilient prongs which move through {56] Ra cm channels in the electrode body to engage the heart tis- UNITED STATES PATENTS sue for implantation of the electrode. The prongs are 3 348.548 10/1967 chum, 128/418 retracted when tension is exerted on the piston, and are 665,916 5/1972 xobs uhi2:111:11: 128/2 R advanged by 3,631,848 1/1972 Muller 128/205 R 2 Cllllns, 1 Drawing Fllll't lllllllllllllilll l 1. CONTROLLABLE' BARBED "INTRACARDIAL ELECTRODE lar isopened; and theelectrodeisthen pushed through the vein, metal head foremost; until it reaches the auricle of the heart;
Depending. on the clinical situation of the patient, stimulation of either the auricle or theventricle maybe desired.- In the case of stimulation of the amide, .the
head of the electrode ispressed against the auriclewall;v
24 thetcase"ofstim'ulation of the ventricle; the electrode is fed through the heart valve and'is pressed againstthe wall of the ventricle. It is-desirable to dispose th'ehelical conductorina bowed position, so that the head is pressed against'thelwall of the heart 'by'the resilience of'ithe conductor.
' After the electrode has reached the desired position, measuring and testingapparatus is connected to the end bf the conductorthat remains'outside the-patients body, in orde'r'to measure the stimulation threshold of the heart.
Afterthese measurements have been" completed, the conductor is connected to a cardiacstimulation device (heart'pacer), which-may be'either external to thebody or=implanted 'withinthe patient.
When' th'eheart pacer is to be-implanted, a support orbedfor the stimulator-is provided in the thorax or abdomen and thenconnected to the neck by means of tubingthat is led through the body. The external 'end' of the helical conductor (remote from-the heart) is the wall of the heart,rather than within'the wall tissue,
provides a most important advantage, in that the surgical procedureforimplantationis much lessextensive. However, such an exterior electrode has previously in volved the disadvantage: that after a period of 'use the electrode sometimes becomes dislodged, separating the operative tip of the electrode fro'mthe heart wall. Such dislocation'is generally-the result of movements of the heart wall. As aresult, the patient must undergo a'further surgical operation in order to replant the electrode, withobvious undesirable stress on the patient.
To prevent such dislocation, it has been attempted to placethe tip of the electrode between trabecular muscles: but such muscles are not common in "the heart wall. "has also been suggested that a portion ofthe head of the electrode might be formed as a truncated cone, so that the head can operate as abarb. At present, no useful measurements canbe expected using such a-device.
lt is therefore an object of the invention to provide an improvedimplantable intracardial electrode, which substantially reduces the likelihood of dislocation of the electrode, and.thus increases the safety of the patie'ntusing it.
'and connected to the conductor. A number of resilientprongs or barbs are attached to the cylinder. Channels are provided in the tip of the head, at an angle to the. cavity axis; and the resilient prongs are extendable through these channels to the outside of the electrode.
Motion of the cylinder towards the heart wall pushes these resilient prongsinto the myocardium, securing the'electrode in place. To obtain this effect, it is impor tant thatthe prongs be placed at a suitable angle with respect to the axis of the piston, and that the diameter of the prongs be suitably chosen. Good results may be obtained when the channels in the head of the electrode are-placed at an angle of about 40 with respect to the axis of the piston.
The prongs he preferred embodiment may be advantageously made of nylon of 0.3 mm diameter. Alternatively, one may use metalprongs covered with insulating'material. The use of metal prongs has the advert tage that the placement of the prongs in the wall of the heart may be observed with the aid of X-rays. h
If on the first attempt the electrode is not satisfactorily implanted, the prongs may be'freed from the heart wail tissue by means of a thin flexible wire attached to the piston, and led through the inside of the insulating member. Tension on the wire retracts the piston .and"
thereby the prongs.
Forward motion of the piston, to force the prongs' into the myocardium, is accomplished by means of a stiff wire, also led through the inside of the insulating member. To obtain good operating contact of this wire with the piston, the end of the piston nearest the,con ductor may be covered with a metallic cap..
Other objects, features and advantages will appear from the following description of a preferred embodiment of the invention, taken together with the attached drawing thereof, in which:
FIG. lis a cross-sectional view of the electrode. Referring to the drawing,electrode 10 is connected to ahelical conductor 12, carried within aninsulating member 14, such as a tube of silicone rubber.Conductor 12 may be externally connected at its remote; end to a heart stimulation device.Conductor 12 is electri cally connected with ahead 16, which may be made,
for example, of platinum; a narrowedportion 18 of 7head 16 is inserted into insulatingmember 14, so thatportion 18 lies betweenconductor 12 andinsulating member 14. In the construction ofhead 16, the end of I ton axis. Four prongs are a desirable number.
A force-transmitting member is provided in the form of astiff wire 32, carried within insulatingmember 14, by whichpiston 22 can be moved forward, causingprongs 24 to protrude throughchannels 26 to the exterior ofelectrode 10, enabling them to engage the tissue of the myocardium.
In addition, athin wire 34 may be attached tocylinder 22,'for instance .by welding, to provide a tension- 7 transmitting member by means of which piston .22 together with attachedprongs 24 can be retracted if the first attempt at implantation in the myocardium is unsatisfactory.
ln use, the electrode is secured'in place by pushing onstiff wire 32 to forceprongs 24 outwardly into the heart wall tissue.Wire 32 may then be removed through insulatingmember 14, leaving only thecoiled conductor 12 andthin wire 34, which are relatively flexible. The end of insulatingmember 14 remote fromelectrode 10,:withconductor 12, may then be connected to a suitable heart stimulation device internal or external to the patient. in the event thatelectrode 10 is unsatisfactorily placed or must be removed,prongs 24 are retracted by tension onthin wire 34, andstiff wire 32 may be'reinserted through-the'remote end of insulatingmember 14 to exert the desired force oncylinder 22 to cause reimplantation.
What is claimed is: l. A controllable repeatably implantable electrode comprising I a conducting head, a conductor electrically connected to said head, said head having a front portion and elongated body portion defining an axially oriented cavity, g a tubular insulating member connected to said body portion and aligned'with sa'id cavityJaid conductor being carried away from insulating member,
said head. within said a plurality of channels extending from said cavity through said front portion to the exterior of said head, and each disposed at an angle to the axis of said cavity,
a rigid cylindrical piston movable axially within said cavity between a forward implantation position and a retracted position, carrying a plurality of resilient prongs each extending into a said channel,
a removable force-transmitting member carried within said insulating member, having one end bearing-against said piston and the other end re- I mote from said piston,
a flexible tension-transmitting member carried within said-'insulating'member, having one end attached to said piston and the other end remote from said pistOll,
said piston being moved within said cavity to said forward implantation position by force applied to said remote end of said force-transmitting member, said prongs being thereby moved through said channels to engage the heart tissue for implantation of said electrode, and said piston being moved to saidretractedpos'ition by tension exerted on said remote end of .said tension-transmitting member, said prongs being thereby retracted and freed from said heart tissue for removal of said electrode.
2. An intracardial electrode for use in artificial stimu- I lation of a patients heart, suitable for prolonged implantation within a patients body,
said electrode comprising an elongated body defining an axially oriented cavity,
a tubular flexible insulating member connected to said body and aligned with said cavity,
a flexible electrical conductor connected to said body and carried away therefrom within said flexible insulating member,
said body having at least one channel extending from said cavity to the exterior of said body and disposed at an angle to the axis of said cavity, a rigid piston movable axially within said cavity, and at least one resilient prong longer than a said channel, attached to said piston and extending into a said channel,
a substantially rigid force-transmitting member carried within said insulating member, having one end bearing against said piston and the other end remote from said piston and protruding from said insulating member, and
a generally flexible retracting member attached to said piston and carried away therefrom within said conducting member,
whereby force exerted on said remote end of said force-transmitting member is transmitted by said bearing end to said piston, causing said prong to extend through said channel to engage the tissue of the said patients heart, and tension exerted on said retracting member is transmitted to said piston and retracts it, freeing said prongs from the heart tissue.
I t i l i UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE CERTIFICATE OF CORRECTION Patent No. 3,75 h555 Dated AugustZB, 197 3 Inventor (5) German Schmitt It is certified that error appears in the above-identified patent .and that said Letters Patent are hereby corrected as shown below:
Column l, line 20, delete "2L; and insert in Column Lt,line 32, delete "tubular".
Signed and sealed this Ltth day of June 197M.
(SEAL) Attestz' EDWARD PLFIETCHEKJR. C. MARSHALL DA'NN Attesting Officer j Commissioner of Patients F ORM PO-1 050 (10-69) USCOMM-DC B0376-P69 .5. GOVERNMENT PRINTING OFFICE l9! 0J6-38|,
Claims (2)
1. A controllable repeatably implantable electrode comprising a conducting head, a conductor electrically connected to said head, said head having a front portion and elongated body portion defining an axially oriented cavity, a tubular insulating member connected to said body portion and aligned with said cavity, said conductor being carried away from said head within said insulating member, a plurality of channels extending from said cavity through said front portion to the exterior of said head, and each disposed at an angle to the axis of said cavity, a rigid cylindrical piston movable axially within said cavity between a forward implantation position and a retracted position, carrying a plurality of resilient prongs each extending into a said channel, a removable force-transmitting member carried within said insulating member, having one end bearing against said piston and the other end remote from said piston, a flexible tension-transmitting member carried within said insulating member, having one end attached to said piston and the other end remote from said piston, said piston being moved within said cavity to said forward implantation position by force applied to said remote end of said force-transmitting member, said prongs being thereby moved through said channels to engage the heart tissue for implantation of said electrode, and said piston being moved to said retracted position by tension exerted on said remote end of said tension-transmitting member, said prongs being thereby retracted and freed from said heart tissue for removal of said electrode.
2. An intracardial electrode for use in artificial stimulation of a patient''s heart, suitable for prolonged implantation within a patient''s body, said electrode comprising an elongated body defining an axially oriented cavity, a tubular flexible insulating member connected to said body and aligned with said cavity, a flexible electrical conductor connected to said body and carried away therefrom within said flexible insulating member, said body having at least one channel extending from said cavity to the exterior of said body and disposed at an angle to the axis of said cavity, a rigid piston movable axially within said cavity, and at least one resilient prong longer than a said channel, attached to said piston and extending into a said channel, a substantially rigid force-transmitting member carried within said insulating member, having one end bearing against said piston and the other end remote from said piston and protruding from said insulating member, and a generally flexible retracting member attached to said piston and carried away therefrom within said conducting member, whereby force exerted on said remote end of said force-transmitting member is transmitted by said bearing end to said piston, causing said prong to extend through said channel to engage the tissue of the said patient''s heart, and tension exerted on said retracting member is transmitted to said piston and retracts it, freeing said prongs from the heart tissue.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US18665471A | 1971-10-05 | 1971-10-05 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US3754555Atrue US3754555A (en) | 1973-08-28 |
Family
ID=22685787
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US00186654AExpired - LifetimeUS3754555A (en) | 1971-10-05 | 1971-10-05 | Controllable barbed intracardial electrode |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US3754555A (en) |
Cited By (86)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3814104A (en)* | 1971-07-05 | 1974-06-04 | W Irnich | Pacemaker-electrode |
| US3865118A (en)* | 1973-12-27 | 1975-02-11 | Univ California | Transvenous coaxial catheter |
| DE2506694A1 (en)* | 1974-03-04 | 1975-09-11 | Medtronic Inc | IMPLANTABLE ELECTRODE ARRANGEMENT |
| US3937225A (en)* | 1973-02-02 | 1976-02-10 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Electrode adapted for implantation |
| US3976082A (en)* | 1974-02-25 | 1976-08-24 | German Schmitt | Intracardial stimulation electrode |
| FR2302107A1 (en)* | 1973-06-21 | 1976-09-24 | Medtronic Inc | INTRACARDIAC ELECTRODE |
| US4010757A (en)* | 1974-02-19 | 1977-03-08 | Jula James L | Auxiliary tool for removing electrode from holder |
| US4103690A (en)* | 1977-03-21 | 1978-08-01 | Cordis Corporation | Self-suturing cardiac pacer lead |
| US4136701A (en)* | 1977-12-09 | 1979-01-30 | Barton Steven A | Retractable stimulation electrode apparatus |
| US4142530A (en)* | 1978-03-06 | 1979-03-06 | Vitatron Medical B. V. | Epicardial lead |
| US4144890A (en)* | 1975-01-14 | 1979-03-20 | Cordis Corporation | Contact device for muscle stimulation |
| US4146035A (en)* | 1977-09-23 | 1979-03-27 | Edward Basta | Endocardial electrode and applicator therefor |
| US4146036A (en)* | 1977-10-06 | 1979-03-27 | Medtronic, Inc. | Body-implantable lead with protector for tissue securing means |
| FR2446001A1 (en)* | 1979-01-03 | 1980-08-01 | Cardiofrance Co | Electrical conductor for cardiac pacemaker - has inner conducting sleeve surrounded by carbon fibres inside outer flexible insulating sleeve |
| US4235246A (en)* | 1979-02-05 | 1980-11-25 | Arco Medical Products Company | Epicardial heart lead and assembly and method for optimal fixation of same for cardiac pacing |
| FR2462171A1 (en)* | 1979-07-26 | 1981-02-13 | Cardiofrance Co | DEVICE FOR INTRODUCING AND PLACING A PROBE OR ELECTRODE, IMPROVEMENTS IN THE PROBES OR ELECTRODES AND TOOL COMPRISING THE DEVICE |
| US4258724A (en)* | 1978-04-19 | 1981-03-31 | Synthelabo | Endocavitary cardiac stimulation probe |
| US4269198A (en)* | 1979-12-26 | 1981-05-26 | Medtronic, Inc. | Body implantable lead |
| DE2949782A1 (en)* | 1979-12-11 | 1981-06-19 | Vsesojuznyj kardiologičeskij naučnyj centr Akademii medicinskich Nauk SSSR,, Moskva | Attachment of electrode inside heart - remotely screwing electrode into inner tissue at selected position for min. trauma |
| US4280512A (en)* | 1978-09-30 | 1981-07-28 | Biotronik Mess-und Therapiegerate G.m.b.H. & Co. | Cardiac pacemaker electrode for transvenous application |
| US4282885A (en)* | 1978-08-21 | 1981-08-11 | Bisping Hans Juergen | Electrode for implantation in the heart |
| US4301815A (en)* | 1980-01-23 | 1981-11-24 | Telectronics Pty. Limited | Trailing tine electrode lead |
| US4408604A (en)* | 1981-04-06 | 1983-10-11 | Teletronics Pty, Limited | Porous pacemaker electrode tip |
| US4475560A (en)* | 1982-04-29 | 1984-10-09 | Cordis Corporation | Temporary pacing lead assembly |
| US4501276A (en)* | 1982-07-16 | 1985-02-26 | Illinois Tool Works Inc. | Fetal electrode apparatus |
| FR2560052A1 (en)* | 1984-02-29 | 1985-08-30 | Benhaim Jean | Improvement to a lead for vascular catheterisation |
| US4590949A (en)* | 1984-11-01 | 1986-05-27 | Cordis Corporation | Neural stimulating lead with stabilizing mechanism and method for using same |
| US4862887A (en)* | 1987-05-29 | 1989-09-05 | Gesellschaft Fuer Strahlen Und Umweltforschung (Gsf) | Heart catheter |
| US4924881A (en)* | 1989-05-12 | 1990-05-15 | Intermedics, Inc. | Implantable endocardial lead with fixation device retractable by threaded stylet |
| DE4018681A1 (en)* | 1990-06-11 | 1991-12-12 | Vasco Med Inst Fuer Katheterte | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR EXTRACING ELECTRODE SPIRALS GROWN IN A BODY ORGAN |
| WO1993000130A1 (en)* | 1991-06-20 | 1993-01-07 | Possis Medical, Inc. | Cardiac lead with retractable fixators |
| US5246014A (en)* | 1991-11-08 | 1993-09-21 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable lead system |
| US5324327A (en)* | 1991-12-17 | 1994-06-28 | Cohen Donald M | Low threshold cardiac pacing lead |
| WO1994027670A1 (en)* | 1993-06-02 | 1994-12-08 | Cardiac Pathways Corporation | Catheter having tip with fixation means |
| EP0646389A1 (en)* | 1993-09-24 | 1995-04-05 | Pacesetter AB | Device for explantation of an electrode |
| US5549615A (en)* | 1989-11-11 | 1996-08-27 | Vascomed Institut Fur Kathetertechnologie Gmbh | Method and apparatus for extracting pacemaker electrodes embedded in the heart |
| US5601568A (en)* | 1994-04-11 | 1997-02-11 | B. Braun Celsa (Societe Anonyme) | Handle for the controlled relative sliding of a sheath and of a stem; apparatus comprising such a handle and method for implanting a blood filter using a handle |
| US5609623A (en)* | 1994-08-19 | 1997-03-11 | Pacesetter Ab | Electrode device for intracardiac stimulation of heart tissue and/or sensing heart signals having conductive surfaces relatively positionable with respect to each other by a control element |
| US5914115A (en)* | 1994-10-17 | 1999-06-22 | Surface Genesis, Inc. | Biocompatible coating, medical device using the same and methods |
| US20020062143A1 (en)* | 1999-04-30 | 2002-05-23 | Medtronic, Inc. | Techniques for selective activation of neurons in the brain, spinal cord parenchyma or peripheral nerve |
| US20030018364A1 (en)* | 2001-07-17 | 2003-01-23 | Medtronic, Inc. | Enhanced method and apparatus to identify and connect a small diameter lead with a low profile lead connector |
| WO2003008037A2 (en) | 2001-07-17 | 2003-01-30 | Medtronic,Inc. | Automatic implantable medical lead recognition and configuration |
| US20030187459A1 (en)* | 2002-03-26 | 2003-10-02 | Image-Guided Neurologics, Inc. | Placement of chronic micro-catheter device and method |
| US20030233037A1 (en)* | 2002-06-14 | 2003-12-18 | Scimed Life Systems, Inc. | Medical probe with variable tip length and shape |
| US20040225194A1 (en)* | 2002-09-20 | 2004-11-11 | Kevin Smith | Tissue retractor and method for using the retractor |
| US20050080435A1 (en)* | 2002-09-20 | 2005-04-14 | Kevin Smith | Tissue retractor and method for using the retractor |
| US20050085886A1 (en)* | 2003-10-17 | 2005-04-21 | Medtronic, Inc. | Medical lead fixation |
| US20080208303A1 (en)* | 2007-02-28 | 2008-08-28 | Rutten Jean J G | Implantable medical device system with fixation member |
| WO2012094058A1 (en) | 2010-11-12 | 2012-07-12 | Medtronic, Inc. | Connectivity detection and type identification of an implanted lead for an implantable medical device |
| US20160001060A1 (en)* | 2014-07-07 | 2016-01-07 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Electrical stimulation leads and systems with elongate anchoring elements and methods of making and using |
| US9393427B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2016-07-19 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker with delivery and/or retrieval features |
| US9480850B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2016-11-01 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker and retrieval device |
| US9492674B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2016-11-15 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker with delivery and/or retrieval features |
| US9610435B2 (en) | 2009-04-07 | 2017-04-04 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Anchoring units for implantable electrical stimulation systems and methods of making and using |
| US9649489B2 (en) | 2014-06-02 | 2017-05-16 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Electrical stimulation leads and systems with anchoring units having struts and methods of making and using |
| US9669210B2 (en) | 2014-04-22 | 2017-06-06 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Electrical stimulation leads and systems with folding anchoring units and methods of making and using |
| US9700732B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2017-07-11 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker and retrieval device |
| US9775982B2 (en) | 2010-12-29 | 2017-10-03 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device fixation |
| US9795781B2 (en) | 2014-04-29 | 2017-10-24 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker with retrieval features |
| US10080887B2 (en) | 2014-04-29 | 2018-09-25 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacing devices including tissue engagement verification |
| US10112045B2 (en) | 2010-12-29 | 2018-10-30 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device fixation |
| US10179236B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2019-01-15 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacing devices |
| US10195419B2 (en) | 2012-06-13 | 2019-02-05 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Electrode leads for use with implantable neuromuscular electrical stimulator |
| US10265503B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2019-04-23 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Delivery devices and methods for leadless cardiac devices |
| US10327810B2 (en) | 2016-07-05 | 2019-06-25 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for enhanced implantation of electrode leads between tissue layers |
| US10406353B2 (en) | 2013-05-14 | 2019-09-10 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Electrical stimulation leads with anchoring unit and electrode arrangement and methods of making and using |
| US10449355B2 (en) | 2012-06-13 | 2019-10-22 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for restoring muscle function to the lumbar spine and kits for implanting the same |
| US10463853B2 (en) | 2016-01-21 | 2019-11-05 | Medtronic, Inc. | Interventional medical systems |
| US10471268B2 (en) | 2014-10-16 | 2019-11-12 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for monitoring muscle rehabilitation |
| US10485435B2 (en) | 2012-03-26 | 2019-11-26 | Medtronic, Inc. | Pass-through implantable medical device delivery catheter with removeable distal tip |
| US10518084B2 (en) | 2013-07-31 | 2019-12-31 | Medtronic, Inc. | Fixation for implantable medical devices |
| US10661078B2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2020-05-26 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Modular stimulator for treatment of back pain, implantable RF ablation system and methods of use |
| US10722723B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2020-07-28 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Delivery devices and methods for leadless cardiac devices |
| US10828490B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2020-11-10 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for restoring muscle function to the lumbar spine |
| US10842993B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2020-11-24 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacing devices |
| US10925637B2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2021-02-23 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Methods of implanting electrode leads for use with implantable neuromuscular electrical stimulator |
| US11027125B2 (en) | 2016-01-21 | 2021-06-08 | Medtronic, Inc. | Interventional medical devices, device systems, and fixation components thereof |
| US11103706B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2021-08-31 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for enhancing function of spine stabilization muscles associated with a spine surgery intervention |
| US11331488B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2022-05-17 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for enhancing function of spine stabilization muscles associated with a spine surgery intervention |
| US11679261B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2023-06-20 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for enhancing function of spine stabilization muscles associated with a spine surgery intervention |
| US11679262B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2023-06-20 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for restoring muscle function to the lumbar spine |
| US11684774B2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2023-06-27 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Electrical stimulator for treatment of back pain and methods of use |
| US20230256237A1 (en)* | 2020-08-21 | 2023-08-17 | Korea University Research And Business Foundation | Electrical Stimulation System |
| US11759632B2 (en) | 2019-03-28 | 2023-09-19 | Medtronic, Inc. | Fixation components for implantable medical devices |
| US11786725B2 (en) | 2012-06-13 | 2023-10-17 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for restoring muscle function to the lumbar spine and kits for implanting the same |
| US12097365B2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2024-09-24 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Electrical stimulator for the treatment of back pain and methods of use |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU246004A1 (en)* | Л. И. Архипова, С. Б. Вавилов, А. Э. Радзевич, С. Н. Филиппов | INTRAVASCULAR BIOACTIVE TOOL FOR ELECTRIC HEART STIMULATION | ||
| US3120227A (en)* | 1960-07-08 | 1964-02-04 | Jr Charles A Hunter | Method for obtaining a fetal electrocardiogram |
| US3347224A (en)* | 1964-05-26 | 1967-10-17 | Brandon L Adams | Apparatus and method for measuring cardiac output |
| US3348548A (en)* | 1965-04-26 | 1967-10-24 | William M Chardack | Implantable electrode with stiffening stylet |
| US3523538A (en)* | 1965-12-06 | 1970-08-11 | Kunio Shimizu | Arrest device |
| US3631848A (en)* | 1968-09-04 | 1972-01-04 | Us Catheter & Instr Corp | Extensible catheter |
| US3665916A (en)* | 1968-09-30 | 1972-05-30 | Tokyo Shibaura Electric Co | Catheter type semiconductor radiation detector |
- 1971
- 1971-10-05USUS00186654Apatent/US3754555A/ennot_activeExpired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU246004A1 (en)* | Л. И. Архипова, С. Б. Вавилов, А. Э. Радзевич, С. Н. Филиппов | INTRAVASCULAR BIOACTIVE TOOL FOR ELECTRIC HEART STIMULATION | ||
| US3120227A (en)* | 1960-07-08 | 1964-02-04 | Jr Charles A Hunter | Method for obtaining a fetal electrocardiogram |
| US3347224A (en)* | 1964-05-26 | 1967-10-17 | Brandon L Adams | Apparatus and method for measuring cardiac output |
| US3348548A (en)* | 1965-04-26 | 1967-10-24 | William M Chardack | Implantable electrode with stiffening stylet |
| US3523538A (en)* | 1965-12-06 | 1970-08-11 | Kunio Shimizu | Arrest device |
| US3631848A (en)* | 1968-09-04 | 1972-01-04 | Us Catheter & Instr Corp | Extensible catheter |
| US3665916A (en)* | 1968-09-30 | 1972-05-30 | Tokyo Shibaura Electric Co | Catheter type semiconductor radiation detector |
Cited By (138)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3814104A (en)* | 1971-07-05 | 1974-06-04 | W Irnich | Pacemaker-electrode |
| US3937225A (en)* | 1973-02-02 | 1976-02-10 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Electrode adapted for implantation |
| FR2302107A1 (en)* | 1973-06-21 | 1976-09-24 | Medtronic Inc | INTRACARDIAC ELECTRODE |
| US3865118A (en)* | 1973-12-27 | 1975-02-11 | Univ California | Transvenous coaxial catheter |
| US4010757A (en)* | 1974-02-19 | 1977-03-08 | Jula James L | Auxiliary tool for removing electrode from holder |
| US3976082A (en)* | 1974-02-25 | 1976-08-24 | German Schmitt | Intracardial stimulation electrode |
| DE2506694A1 (en)* | 1974-03-04 | 1975-09-11 | Medtronic Inc | IMPLANTABLE ELECTRODE ARRANGEMENT |
| US3939843A (en)* | 1974-03-04 | 1976-02-24 | Medtronic, Inc. | Transvenous electrode |
| US4144890A (en)* | 1975-01-14 | 1979-03-20 | Cordis Corporation | Contact device for muscle stimulation |
| US4103690A (en)* | 1977-03-21 | 1978-08-01 | Cordis Corporation | Self-suturing cardiac pacer lead |
| US4146035A (en)* | 1977-09-23 | 1979-03-27 | Edward Basta | Endocardial electrode and applicator therefor |
| US4146036A (en)* | 1977-10-06 | 1979-03-27 | Medtronic, Inc. | Body-implantable lead with protector for tissue securing means |
| US4136701A (en)* | 1977-12-09 | 1979-01-30 | Barton Steven A | Retractable stimulation electrode apparatus |
| US4142530A (en)* | 1978-03-06 | 1979-03-06 | Vitatron Medical B. V. | Epicardial lead |
| US4258724A (en)* | 1978-04-19 | 1981-03-31 | Synthelabo | Endocavitary cardiac stimulation probe |
| US4282885A (en)* | 1978-08-21 | 1981-08-11 | Bisping Hans Juergen | Electrode for implantation in the heart |
| US4280512A (en)* | 1978-09-30 | 1981-07-28 | Biotronik Mess-und Therapiegerate G.m.b.H. & Co. | Cardiac pacemaker electrode for transvenous application |
| FR2446001A1 (en)* | 1979-01-03 | 1980-08-01 | Cardiofrance Co | Electrical conductor for cardiac pacemaker - has inner conducting sleeve surrounded by carbon fibres inside outer flexible insulating sleeve |
| US4235246A (en)* | 1979-02-05 | 1980-11-25 | Arco Medical Products Company | Epicardial heart lead and assembly and method for optimal fixation of same for cardiac pacing |
| EP0024963A1 (en)* | 1979-07-26 | 1981-03-11 | Cardiofrance - Compagnie Francaise D'electrocardiologie | Device for introducing and positioning a cardiac probe or electrode and probes or electrodes used with this device |
| FR2462171A1 (en)* | 1979-07-26 | 1981-02-13 | Cardiofrance Co | DEVICE FOR INTRODUCING AND PLACING A PROBE OR ELECTRODE, IMPROVEMENTS IN THE PROBES OR ELECTRODES AND TOOL COMPRISING THE DEVICE |
| DE2949782A1 (en)* | 1979-12-11 | 1981-06-19 | Vsesojuznyj kardiologičeskij naučnyj centr Akademii medicinskich Nauk SSSR,, Moskva | Attachment of electrode inside heart - remotely screwing electrode into inner tissue at selected position for min. trauma |
| US4269198A (en)* | 1979-12-26 | 1981-05-26 | Medtronic, Inc. | Body implantable lead |
| US4301815A (en)* | 1980-01-23 | 1981-11-24 | Telectronics Pty. Limited | Trailing tine electrode lead |
| US4408604A (en)* | 1981-04-06 | 1983-10-11 | Teletronics Pty, Limited | Porous pacemaker electrode tip |
| US4475560A (en)* | 1982-04-29 | 1984-10-09 | Cordis Corporation | Temporary pacing lead assembly |
| US4501276A (en)* | 1982-07-16 | 1985-02-26 | Illinois Tool Works Inc. | Fetal electrode apparatus |
| FR2560052A1 (en)* | 1984-02-29 | 1985-08-30 | Benhaim Jean | Improvement to a lead for vascular catheterisation |
| US4590949A (en)* | 1984-11-01 | 1986-05-27 | Cordis Corporation | Neural stimulating lead with stabilizing mechanism and method for using same |
| US4862887A (en)* | 1987-05-29 | 1989-09-05 | Gesellschaft Fuer Strahlen Und Umweltforschung (Gsf) | Heart catheter |
| US4924881A (en)* | 1989-05-12 | 1990-05-15 | Intermedics, Inc. | Implantable endocardial lead with fixation device retractable by threaded stylet |
| US5549615A (en)* | 1989-11-11 | 1996-08-27 | Vascomed Institut Fur Kathetertechnologie Gmbh | Method and apparatus for extracting pacemaker electrodes embedded in the heart |
| DE4018681A1 (en)* | 1990-06-11 | 1991-12-12 | Vasco Med Inst Fuer Katheterte | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR EXTRACING ELECTRODE SPIRALS GROWN IN A BODY ORGAN |
| DE4018681C2 (en)* | 1990-06-11 | 2000-09-21 | Vasco Med Inst Fuer Katheterte | Device for extracting a pacemaker electrode |
| WO1993000130A1 (en)* | 1991-06-20 | 1993-01-07 | Possis Medical, Inc. | Cardiac lead with retractable fixators |
| US5179962A (en)* | 1991-06-20 | 1993-01-19 | Possis Medical, Inc. | Cardiac lead with retractible fixators |
| US5246014A (en)* | 1991-11-08 | 1993-09-21 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable lead system |
| US5324327A (en)* | 1991-12-17 | 1994-06-28 | Cohen Donald M | Low threshold cardiac pacing lead |
| WO1994027670A1 (en)* | 1993-06-02 | 1994-12-08 | Cardiac Pathways Corporation | Catheter having tip with fixation means |
| US5507802A (en)* | 1993-06-02 | 1996-04-16 | Cardiac Pathways Corporation | Method of mapping and/or ablation using a catheter having a tip with fixation means |
| EP0646389A1 (en)* | 1993-09-24 | 1995-04-05 | Pacesetter AB | Device for explantation of an electrode |
| US5601568A (en)* | 1994-04-11 | 1997-02-11 | B. Braun Celsa (Societe Anonyme) | Handle for the controlled relative sliding of a sheath and of a stem; apparatus comprising such a handle and method for implanting a blood filter using a handle |
| US5609623A (en)* | 1994-08-19 | 1997-03-11 | Pacesetter Ab | Electrode device for intracardiac stimulation of heart tissue and/or sensing heart signals having conductive surfaces relatively positionable with respect to each other by a control element |
| US5914115A (en)* | 1994-10-17 | 1999-06-22 | Surface Genesis, Inc. | Biocompatible coating, medical device using the same and methods |
| US20020062143A1 (en)* | 1999-04-30 | 2002-05-23 | Medtronic, Inc. | Techniques for selective activation of neurons in the brain, spinal cord parenchyma or peripheral nerve |
| US7442183B2 (en) | 1999-04-30 | 2008-10-28 | Medtronic, Inc. | Techniques for selective activation of neurons in the brain, spinal cord parenchyma or peripheral nerve |
| US20030018364A1 (en)* | 2001-07-17 | 2003-01-23 | Medtronic, Inc. | Enhanced method and apparatus to identify and connect a small diameter lead with a low profile lead connector |
| WO2003008037A2 (en) | 2001-07-17 | 2003-01-30 | Medtronic,Inc. | Automatic implantable medical lead recognition and configuration |
| US6968235B2 (en) | 2001-07-17 | 2005-11-22 | Medtronic, Inc. | Enhanced method and apparatus to identify and connect a small diameter lead with a low profile lead connector |
| US6675049B2 (en) | 2001-07-17 | 2004-01-06 | Medtronic, Inc. | Method and apparatus for automatic implantable medical lead recognition and configuration |
| US20040078067A1 (en)* | 2001-07-17 | 2004-04-22 | Medtronic, Inc. | Method and apparatus for automatic implantable medical lead recognition and configuration |
| US20040176822A1 (en)* | 2001-07-17 | 2004-09-09 | Medtronic, Inc. | Method and apparatus for automatic implantable medical lead recognition and configuration |
| US7239916B2 (en) | 2001-07-17 | 2007-07-03 | Medtronic, Inc. | Method and apparatus for automatic implantable medical lead recognition and configuration |
| US20030187459A1 (en)* | 2002-03-26 | 2003-10-02 | Image-Guided Neurologics, Inc. | Placement of chronic micro-catheter device and method |
| US7588581B2 (en) | 2002-03-26 | 2009-09-15 | Medtronic, Inc. | Placement of chronic micro-catheter device and method |
| US6925318B2 (en)* | 2002-06-14 | 2005-08-02 | Scimed Life Systems, Inc. | Medical probe with variable tip length and shape |
| US20030233037A1 (en)* | 2002-06-14 | 2003-12-18 | Scimed Life Systems, Inc. | Medical probe with variable tip length and shape |
| US20050080435A1 (en)* | 2002-09-20 | 2005-04-14 | Kevin Smith | Tissue retractor and method for using the retractor |
| US20040225194A1 (en)* | 2002-09-20 | 2004-11-11 | Kevin Smith | Tissue retractor and method for using the retractor |
| US7731655B2 (en)* | 2002-09-20 | 2010-06-08 | Id, Llc | Tissue retractor and method for using the retractor |
| US20050085886A1 (en)* | 2003-10-17 | 2005-04-21 | Medtronic, Inc. | Medical lead fixation |
| WO2005037368A1 (en)* | 2003-10-17 | 2005-04-28 | Medtronic, Inc. | Medical lead fixation |
| US7251532B2 (en) | 2003-10-17 | 2007-07-31 | Medtronic, Inc. | Medical lead fixation |
| US7904179B2 (en) | 2007-02-28 | 2011-03-08 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device system with fixation member |
| US20080208247A1 (en)* | 2007-02-28 | 2008-08-28 | Rutten Jean J G | Implantable medical device system with fixation member |
| US20080208248A1 (en)* | 2007-02-28 | 2008-08-28 | Rutten Jean J G | Implantable medical device system with fixation member |
| US20080208339A1 (en)* | 2007-02-28 | 2008-08-28 | Rutten Jean J G | Implantable medical device system with fixation member |
| US7890191B2 (en) | 2007-02-28 | 2011-02-15 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device system with fixation member |
| US20080208303A1 (en)* | 2007-02-28 | 2008-08-28 | Rutten Jean J G | Implantable medical device system with fixation member |
| US20110125163A1 (en)* | 2007-02-28 | 2011-05-26 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device system with fixation member |
| US11679262B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2023-06-20 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for restoring muscle function to the lumbar spine |
| US12285612B1 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2025-04-29 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for restoring muscle function to the lumbar spine |
| US11103706B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2021-08-31 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for enhancing function of spine stabilization muscles associated with a spine surgery intervention |
| US11331488B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2022-05-17 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for enhancing function of spine stabilization muscles associated with a spine surgery intervention |
| US11679261B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2023-06-20 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for enhancing function of spine stabilization muscles associated with a spine surgery intervention |
| US12168130B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2024-12-17 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for restoring muscle function to the lumbar spine |
| US10828490B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2020-11-10 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for restoring muscle function to the lumbar spine |
| US12121728B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2024-10-22 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for enhancing function of spine stabilization muscles associated with a spine surgery intervention |
| US11951310B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2024-04-09 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for restoring muscle function to the lumbar spine |
| US9610435B2 (en) | 2009-04-07 | 2017-04-04 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Anchoring units for implantable electrical stimulation systems and methods of making and using |
| US11471670B2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2022-10-18 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Electrical stimulator for treatment of back pain and methods of use |
| US12048844B2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2024-07-30 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Modular stimulator for treatment of back pain, implantable RF ablation system and methods of use |
| US11684774B2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2023-06-27 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Electrical stimulator for treatment of back pain and methods of use |
| US12097365B2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2024-09-24 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Electrical stimulator for the treatment of back pain and methods of use |
| US10926083B2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2021-02-23 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Stimulator for treatment of back pain utilizing feedback |
| US10925637B2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2021-02-23 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Methods of implanting electrode leads for use with implantable neuromuscular electrical stimulator |
| US10661078B2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2020-05-26 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Modular stimulator for treatment of back pain, implantable RF ablation system and methods of use |
| WO2012094058A1 (en) | 2010-11-12 | 2012-07-12 | Medtronic, Inc. | Connectivity detection and type identification of an implanted lead for an implantable medical device |
| US9775982B2 (en) | 2010-12-29 | 2017-10-03 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device fixation |
| US10835737B2 (en) | 2010-12-29 | 2020-11-17 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device fixation |
| US10173050B2 (en) | 2010-12-29 | 2019-01-08 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device fixation |
| US10118026B2 (en) | 2010-12-29 | 2018-11-06 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device fixation |
| US10112045B2 (en) | 2010-12-29 | 2018-10-30 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device fixation |
| US9844659B2 (en) | 2010-12-29 | 2017-12-19 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device fixation |
| US12157003B2 (en) | 2010-12-29 | 2024-12-03 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device fixation |
| US12268867B2 (en) | 2010-12-29 | 2025-04-08 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device fixation |
| US12268868B2 (en) | 2010-12-29 | 2025-04-08 | Medtronic, Inc. | Implantable medical device fixation |
| US10485435B2 (en) | 2012-03-26 | 2019-11-26 | Medtronic, Inc. | Pass-through implantable medical device delivery catheter with removeable distal tip |
| US10449355B2 (en) | 2012-06-13 | 2019-10-22 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for restoring muscle function to the lumbar spine and kits for implanting the same |
| US11376427B2 (en) | 2012-06-13 | 2022-07-05 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for restoring muscle function to the lumbar spine and kits for implanting the same |
| US10195419B2 (en) | 2012-06-13 | 2019-02-05 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Electrode leads for use with implantable neuromuscular electrical stimulator |
| US11786725B2 (en) | 2012-06-13 | 2023-10-17 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for restoring muscle function to the lumbar spine and kits for implanting the same |
| US10406353B2 (en) | 2013-05-14 | 2019-09-10 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Electrical stimulation leads with anchoring unit and electrode arrangement and methods of making and using |
| US10518084B2 (en) | 2013-07-31 | 2019-12-31 | Medtronic, Inc. | Fixation for implantable medical devices |
| US11400281B2 (en) | 2013-07-31 | 2022-08-02 | Medtronic, Inc. | Fixation for implantable medical devices |
| US12208259B2 (en) | 2013-07-31 | 2025-01-28 | Medtronic, Inc. | Fixation for implantable medical devices |
| US10625085B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2020-04-21 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker with delivery and/or retrieval features |
| US9492674B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2016-11-15 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker with delivery and/or retrieval features |
| US10981008B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2021-04-20 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Delivery devices and methods for leadless cardiac devices |
| US9393427B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2016-07-19 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker with delivery and/or retrieval features |
| US10842993B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2020-11-24 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacing devices |
| US10722723B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2020-07-28 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Delivery devices and methods for leadless cardiac devices |
| US9480850B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2016-11-01 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker and retrieval device |
| US10179236B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2019-01-15 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacing devices |
| US12161863B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2024-12-10 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacing devices |
| US11446511B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2022-09-20 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker with delivery and/or retrieval features |
| US10857353B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2020-12-08 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacing devices |
| US11666752B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2023-06-06 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacing devices |
| US9700732B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2017-07-11 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker and retrieval device |
| US10286220B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2019-05-14 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker with delivery and/or retrieval features |
| US10265503B2 (en) | 2013-08-16 | 2019-04-23 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Delivery devices and methods for leadless cardiac devices |
| US9669210B2 (en) | 2014-04-22 | 2017-06-06 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Electrical stimulation leads and systems with folding anchoring units and methods of making and using |
| US11717677B2 (en) | 2014-04-29 | 2023-08-08 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker with retrieval features |
| US10420932B2 (en) | 2014-04-29 | 2019-09-24 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker with retrieval features |
| US9795781B2 (en) | 2014-04-29 | 2017-10-24 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacemaker with retrieval features |
| US10080887B2 (en) | 2014-04-29 | 2018-09-25 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Leadless cardiac pacing devices including tissue engagement verification |
| US9649489B2 (en) | 2014-06-02 | 2017-05-16 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Electrical stimulation leads and systems with anchoring units having struts and methods of making and using |
| US9533141B2 (en)* | 2014-07-07 | 2017-01-03 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Electrical stimulation leads and systems with elongate anchoring elements |
| US20160001060A1 (en)* | 2014-07-07 | 2016-01-07 | Boston Scientific Neuromodulation Corporation | Electrical stimulation leads and systems with elongate anchoring elements and methods of making and using |
| US10471268B2 (en) | 2014-10-16 | 2019-11-12 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for monitoring muscle rehabilitation |
| US10463853B2 (en) | 2016-01-21 | 2019-11-05 | Medtronic, Inc. | Interventional medical systems |
| US12251559B2 (en) | 2016-01-21 | 2025-03-18 | Medtronic, Inc. | Interventional medical devices, device systems, and fixation components thereof |
| US11027125B2 (en) | 2016-01-21 | 2021-06-08 | Medtronic, Inc. | Interventional medical devices, device systems, and fixation components thereof |
| US11937847B2 (en) | 2016-07-05 | 2024-03-26 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for enhanced implantation of electrode leads between tissue layers |
| US10327810B2 (en) | 2016-07-05 | 2019-06-25 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for enhanced implantation of electrode leads between tissue layers |
| US11406421B2 (en) | 2016-07-05 | 2022-08-09 | Mainstay Medical Limited | Systems and methods for enhanced implantation of electrode leads between tissue layers |
| US11759632B2 (en) | 2019-03-28 | 2023-09-19 | Medtronic, Inc. | Fixation components for implantable medical devices |
| US20230256237A1 (en)* | 2020-08-21 | 2023-08-17 | Korea University Research And Business Foundation | Electrical Stimulation System |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US3754555A (en) | Controllable barbed intracardial electrode | |
| US3978865A (en) | Implantable pacemaker and electrode member therefor | |
| US4475560A (en) | Temporary pacing lead assembly | |
| US3844292A (en) | Intravascular lead assembly | |
| US4233992A (en) | Implantable electrode | |
| US3087486A (en) | Cardiac electrode means | |
| US4236529A (en) | Tined lead | |
| US5179962A (en) | Cardiac lead with retractible fixators | |
| US3835864A (en) | Intra-cardiac stimulator | |
| US4217913A (en) | Body-implantable lead with protected, extendable tissue securing means | |
| USRE30366E (en) | Organ stimulator | |
| US3974834A (en) | Body-implantable lead | |
| US3788329A (en) | Body implantable lead | |
| US3057356A (en) | Medical cardiac pacemaker | |
| US3875947A (en) | Device for screwing body tissue electrode into body tissue | |
| US4414986A (en) | Biomedical stimulation lead | |
| US5584874A (en) | Medical electrical lead having improved anchoring sleeve | |
| US4624266A (en) | Introducer tool for screw-in lead | |
| US3976082A (en) | Intracardial stimulation electrode | |
| US3939843A (en) | Transvenous electrode | |
| US4967766A (en) | Implantable endocardial lead with fixation apparatus retractable by a lanyard | |
| US4280510A (en) | Sutureless myocardial lead introducer | |
| US4146037A (en) | Cardiac pacer electrode and lead insertion tool | |
| EP0571985B1 (en) | Positive fixation device | |
| US5003992A (en) | Atraumatic screw-in lead |