US20010055608A1 - Treating traumatic burns or blisters of the skin - Google Patents
Treating traumatic burns or blisters of the skinDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US20010055608A1 US20010055608A1US09/314,271US31427199AUS2001055608A1US 20010055608 A1US20010055608 A1US 20010055608A1US 31427199 AUS31427199 AUS 31427199AUS 2001055608 A1US2001055608 A1US 2001055608A1
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- skin
- patch
- blister
- adhesive
- layer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 230000000472traumatic effectEffects0.000titledescription2
- 210000003491skinAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription90
- 239000000017hydrogelSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription59
- 230000003204osmotic effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription45
- 239000000853adhesiveSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription43
- 230000001070adhesive effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription43
- 239000012530fluidSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription41
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription35
- 239000000499gelSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription23
- 150000003839saltsChemical class0.000claimsabstractdescription16
- 239000004744fabricSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription15
- -1karayaChemical class0.000claimsabstractdescription12
- 210000000434stratum corneumAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription12
- 229920001477hydrophilic polymerPolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription8
- 229920002401polyacrylamidePolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription8
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical compoundCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription7
- 102000004169proteins and genesHuman genes0.000claimsabstractdescription7
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000claimsabstractdescription7
- 235000015125Sterculia urensNutrition0.000claimsabstractdescription6
- 240000001058Sterculia urensSpecies0.000claimsabstractdescription6
- 150000004677hydratesChemical class0.000claimsabstractdescription6
- 229920001059synthetic polymerPolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription6
- 229920005615natural polymerPolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription5
- 235000000346sugarNutrition0.000claimsabstractdescription5
- 241000512259Ascophyllum nodosumSpecies0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 239000010410layerSubstances0.000claimsdescription53
- 239000012790adhesive layerSubstances0.000claimsdescription26
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsdescription23
- 239000011347resinSubstances0.000claimsdescription15
- 229920005989resinPolymers0.000claimsdescription15
- 239000000839emulsionSubstances0.000claimsdescription12
- 239000004820Pressure-sensitive adhesiveSubstances0.000claimsdescription10
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-NAcetic acidChemical compoundCC(O)=OQTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription9
- 208000024891symptomDiseases0.000claimsdescription9
- YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-Nsalicylic acidChemical compoundOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1OYGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- 206010061218InflammationDiseases0.000claimsdescription7
- 230000004054inflammatory processEffects0.000claimsdescription7
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription7
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000claimsdescription7
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-NIsopropanolChemical compoundCC(C)OKFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000004599antimicrobialSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000003795chemical substances by applicationSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 206010006802Burns second degreeDiseases0.000claimsdescription5
- 210000003722extracellular fluidAnatomy0.000claimsdescription5
- ULGZDMOVFRHVEP-RWJQBGPGSA-NErythromycinChemical compoundO([C@@H]1[C@@H](C)C(=O)O[C@@H]([C@@]([C@H](O)[C@@H](C)C(=O)[C@H](C)C[C@@](C)(O)[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H](C[C@@H](C)O2)N(C)C)O)[C@H]1C)(C)O)CC)[C@H]1C[C@@](C)(OC)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)O1ULGZDMOVFRHVEP-RWJQBGPGSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-NHydrogen peroxideChemical compoundOOMHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- 229920002678cellulosePolymers0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000001913celluloseSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 231100000252nontoxicToxicity0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000003000nontoxic effectEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-Npapa-hydroxy-benzoic acidNatural productsOC(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- 229920001296polysiloxanePolymers0.000claimsdescription4
- 229960004889salicylic acidDrugs0.000claimsdescription4
- SQGYOTSLMSWVJD-UHFFFAOYSA-Nsilver(1+) nitrateChemical compound[Ag+].[O-]N(=O)=OSQGYOTSLMSWVJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000002344surface layerSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N2-Propenoic acidNatural productsOC(=O)C=CNIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- 206010006797Burns first degreeDiseases0.000claimsdescription3
- 229920002134Carboxymethyl cellulosePolymers0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000002253acidSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 150000001412aminesChemical group0.000claimsdescription3
- 150000001413amino acidsChemical class0.000claimsdescription3
- 229920000831ionic polymerPolymers0.000claimsdescription3
- 229920001495poly(sodium acrylate) polymerPolymers0.000claimsdescription3
- 229920000573polyethylenePolymers0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000002904solventSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- CPKVUHPKYQGHMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N1-ethenylpyrrolidin-2-one;molecular iodineChemical compoundII.C=CN1CCCC1=OCPKVUHPKYQGHMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004342Benzoyl peroxideSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- OMPJBNCRMGITSC-UHFFFAOYSA-NBenzoylperoxideChemical compoundC=1C=CC=CC=1C(=O)OOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1OMPJBNCRMGITSC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- GHXZTYHSJHQHIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-NChlorhexidineChemical compoundC=1C=C(Cl)C=CC=1NC(N)=NC(N)=NCCCCCCN=C(N)N=C(N)NC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1GHXZTYHSJHQHIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-MD-gluconateChemical compoundOC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C([O-])=ORGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-M0.000claimsdescription2
- 241000196324EmbryophytaSpecies0.000claimsdescription2
- SHGAZHPCJJPHSC-NUEINMDLSA-NIsotretinoinChemical compoundOC(=O)C=C(C)/C=C/C=C(C)C=CC1=C(C)CCCC1(C)CSHGAZHPCJJPHSC-NUEINMDLSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- BYBLEWFAAKGYCD-UHFFFAOYSA-NMiconazoleChemical compoundClC1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1COC(C=1C(=CC(Cl)=CC=1)Cl)CN1C=NC=C1BYBLEWFAAKGYCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920000153Povidone-iodinePolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920002472StarchPolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004098TetracyclineSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960000583acetic acidDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960004150aciclovirDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- MKUXAQIIEYXACX-UHFFFAOYSA-NaciclovirChemical compoundN1C(N)=NC(=O)C2=C1N(COCCO)C=N2MKUXAQIIEYXACX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- SHGAZHPCJJPHSC-YCNIQYBTSA-Nall-trans-retinoic acidChemical compoundOC(=O)\C=C(/C)\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)CSHGAZHPCJJPHSC-YCNIQYBTSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960003328benzoyl peroxideDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 235000019400benzoyl peroxideNutrition0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960003260chlorhexidineDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960003276erythromycinDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 229940050410gluconateDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- ACGUYXCXAPNIKK-UHFFFAOYSA-NhexachloropheneChemical compoundOC1=C(Cl)C=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C1CC1=C(O)C(Cl)=CC(Cl)=C1ClACGUYXCXAPNIKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960004068hexachloropheneDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960002163hydrogen peroxideDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960004592isopropanolDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960005280isotretinoinDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- SQFDQLBYJKFDDO-UHFFFAOYSA-KmerbrominChemical compound[Na+].[Na+].C=12C=C(Br)C(=O)C=C2OC=2C([Hg]O)=C([O-])C(Br)=CC=2C=1C1=CC=CC=C1C([O-])=OSQFDQLBYJKFDDO-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000claimsdescription2
- 229940008716mercurochromeDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960002509miconazoleDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920001343polytetrafluoroethylenePolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004810polytetrafluoroethyleneSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960001621povidone-iodineDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 229930002330retinoic acidNatural products0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960001516silver nitrateDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910001961silver nitrateInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000008107starchSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 235000019698starchNutrition0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960002180tetracyclineDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 229930101283tetracyclineNatural products0.000claimsdescription2
- 235000019364tetracyclineNutrition0.000claimsdescription2
- 150000003522tetracyclinesChemical class0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000001225therapeutic effectEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960001727tretinoinDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 241001465754MetazoaSpecies0.000claims3
- 230000008961swellingEffects0.000claims3
- 238000002560therapeutic procedureMethods0.000claims3
- 230000005660hydrophilic surfaceEffects0.000claims2
- SMZOUWXMTYCWNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N2-(2-methoxy-5-methylphenyl)ethanamineChemical compoundCOC1=CC=C(C)C=C1CCNSMZOUWXMTYCWNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claims1
- 239000004372Polyvinyl alcoholSubstances0.000claims1
- 239000001768carboxy methyl celluloseSubstances0.000claims1
- 235000010948carboxy methyl celluloseNutrition0.000claims1
- 239000008112carboxymethyl-celluloseSubstances0.000claims1
- 229920002451polyvinyl alcoholPolymers0.000claims1
- 230000001737promoting effectEffects0.000claims1
- 239000002562thickening agentSubstances0.000claims1
- 125000000391vinyl groupChemical group[H]C([*])=C([H])[H]0.000claims1
- 229920002554vinyl polymerPolymers0.000claims1
- 229920002125Sokalan®Polymers0.000abstractdescription4
- 239000000123paperSubstances0.000abstractdescription4
- 239000004584polyacrylic acidSubstances0.000abstractdescription4
- 150000001720carbohydratesChemical class0.000abstractdescription3
- 235000014633carbohydratesNutrition0.000abstractdescription3
- 229920003023plasticPolymers0.000abstractdescription3
- 239000004033plasticSubstances0.000abstractdescription3
- 229920000642polymerPolymers0.000abstractdescription3
- 150000005846sugar alcoholsPolymers0.000abstractdescription3
- 229920002261Corn starchPolymers0.000abstractdescription2
- 239000008120corn starchSubstances0.000abstractdescription2
- 229940099112cornstarchDrugs0.000abstractdescription2
- 239000003906humectantSubstances0.000abstractdescription2
- 231100000075skin burnToxicity0.000abstract1
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-NPropylene glycolChemical compoundCC(O)CODNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description18
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium chlorideChemical compound[Na+].[Cl-]FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description16
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthylene glycolChemical compoundOCCOLYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description13
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-NGlycerineChemical compoundOCC(O)COPEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description13
- 239000004615ingredientSubstances0.000description10
- 210000002615epidermisAnatomy0.000description8
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description8
- 239000011780sodium chlorideSubstances0.000description8
- CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-NSucroseChemical compoundO[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N0.000description7
- 229930006000SucroseNatural products0.000description7
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000description7
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000description7
- 239000004745nonwoven fabricSubstances0.000description7
- 239000005720sucroseSubstances0.000description7
- 229920002774MaltodextrinPolymers0.000description6
- 239000005913MaltodextrinSubstances0.000description6
- 235000011187glycerolNutrition0.000description6
- 229940035034maltodextrinDrugs0.000description6
- 238000004513sizingMethods0.000description6
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description6
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description6
- XTXRWKRVRITETP-UHFFFAOYSA-NVinyl acetateChemical compoundCC(=O)OC=CXTXRWKRVRITETP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description5
- 229920001577copolymerPolymers0.000description5
- 239000000835fiberSubstances0.000description5
- 210000002683footAnatomy0.000description5
- 235000018102proteinsNutrition0.000description5
- 230000001154acute effectEffects0.000description4
- 230000008901benefitEffects0.000description4
- 231100000344non-irritatingToxicity0.000description4
- 229920000728polyesterPolymers0.000description4
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-NMethanolChemical compoundOCOKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 230000009471actionEffects0.000description3
- 239000002390adhesive tapeSubstances0.000description3
- 239000002826coolantSubstances0.000description3
- 210000004207dermisAnatomy0.000description3
- 208000014674injuryDiseases0.000description3
- 239000004816latexSubstances0.000description3
- 229920000126latexPolymers0.000description3
- 230000000750progressive effectEffects0.000description3
- 230000008719thickeningEffects0.000description3
- 102000009027AlbuminsHuman genes0.000description2
- 108010088751AlbuminsProteins0.000description2
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-LCalcium carbonateChemical compound[Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=OVTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description2
- UXVMQQNJUSDDNG-UHFFFAOYSA-LCalcium chlorideChemical compound[Cl-].[Cl-].[Ca+2]UXVMQQNJUSDDNG-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description2
- 229920003043Cellulose fiberPolymers0.000description2
- 229920000742CottonPolymers0.000description2
- DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-NGlycineChemical compoundNCC(O)=ODHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 239000004698PolyethyleneSubstances0.000description2
- WCUXLLCKKVVCTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-MPotassium chlorideChemical compound[Cl-].[K+]WCUXLLCKKVVCTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description2
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium bicarbonateChemical compound[Na+].OC([O-])=OUIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description2
- 150000007513acidsChemical class0.000description2
- WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-Nadipic acidChemical compoundOC(=O)CCCCC(O)=OWNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 235000001014amino acidNutrition0.000description2
- 230000001580bacterial effectEffects0.000description2
- 210000004369bloodAnatomy0.000description2
- 239000008280bloodSubstances0.000description2
- 239000001110calcium chlorideSubstances0.000description2
- 229910001628calcium chlorideInorganic materials0.000description2
- 238000001816coolingMethods0.000description2
- 239000008367deionised waterSubstances0.000description2
- 229910021641deionized waterInorganic materials0.000description2
- 230000002500effect on skinEffects0.000description2
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description2
- 239000003792electrolyteSubstances0.000description2
- 238000001704evaporationMethods0.000description2
- WGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-NhydroxyacetaldehydeNatural productsOCC=OWGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 230000006872improvementEffects0.000description2
- 208000015181infectious diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 230000008595infiltrationEffects0.000description2
- 238000001764infiltrationMethods0.000description2
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000description2
- 239000012528membraneSubstances0.000description2
- 239000001814pectinSubstances0.000description2
- 235000010987pectinNutrition0.000description2
- 229920001277pectinPolymers0.000description2
- 230000035515penetrationEffects0.000description2
- 239000002985plastic filmSubstances0.000description2
- 229920006255plastic filmPolymers0.000description2
- 230000001681protective effectEffects0.000description2
- 210000002966serumAnatomy0.000description2
- 239000007787solidSubstances0.000description2
- 150000008163sugarsChemical class0.000description2
- 230000008733traumaEffects0.000description2
- BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-REOHCLBHSA-N(S)-malic acidChemical compoundOC(=O)[C@@H](O)CC(O)=OBJEPYKJPYRNKOW-REOHCLBHSA-N0.000description1
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-MAcetateChemical compoundCC([O-])=OQTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description1
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-XLOQQCSPSA-NAlpha-LactoseChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1OGUBGYTABKSRVRQ-XLOQQCSPSA-N0.000description1
- 206010013786Dry skinDiseases0.000description1
- RFSUNEUAIZKAJO-ARQDHWQXSA-NFructoseChemical compoundOC[C@H]1O[C@](O)(CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1ORFSUNEUAIZKAJO-ARQDHWQXSA-N0.000description1
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-NGlucoseNatural productsOC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1OWQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N0.000description1
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-UHFFFAOYSA-NGlutamic acidNatural productsOC(=O)C(N)CCC(O)=OWHUUTDBJXJRKMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000004471GlycineSubstances0.000description1
- 229920013646HycarPolymers0.000description1
- XUJNEKJLAYXESH-REOHCLBHSA-NL-CysteineChemical compoundSC[C@H](N)C(O)=OXUJNEKJLAYXESH-REOHCLBHSA-N0.000description1
- QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-NL-alanineChemical compoundC[C@H](N)C(O)=OQNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-N0.000description1
- CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-NL-aspartic acidChemical compoundOC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(O)=OCKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N0.000description1
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-NL-glutamic acidChemical compoundOC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(O)=OWHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N0.000description1
- ROHFNLRQFUQHCH-YFKPBYRVSA-NL-leucineChemical compoundCC(C)C[C@H](N)C(O)=OROHFNLRQFUQHCH-YFKPBYRVSA-N0.000description1
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-NLactoseNatural productsOC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@@H]2CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1OGUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N0.000description1
- ROHFNLRQFUQHCH-UHFFFAOYSA-NLeucineNatural productsCC(C)CC(N)C(O)=OROHFNLRQFUQHCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000004677NylonSubstances0.000description1
- 239000004743PolypropyleneSubstances0.000description1
- 229920005830Polyurethane FoamPolymers0.000description1
- 229920001131Pulp (paper)Polymers0.000description1
- 206010040880Skin irritationDiseases0.000description1
- 229920006362Teflon®Polymers0.000description1
- 208000027418Wounds and injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 238000010521absorption reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000009825accumulationMethods0.000description1
- 235000011054acetic acidNutrition0.000description1
- 150000001252acrylic acid derivativesChemical class0.000description1
- 208000038016acute inflammationDiseases0.000description1
- 230000006022acute inflammationEffects0.000description1
- 239000001361adipic acidSubstances0.000description1
- 235000011037adipic acidNutrition0.000description1
- 230000002411adverseEffects0.000description1
- 235000004279alanineNutrition0.000description1
- 150000001298alcoholsChemical class0.000description1
- BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-Nalpha-hydroxysuccinic acidNatural productsOC(=O)C(O)CC(O)=OBJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 235000003704aspartic acidNutrition0.000description1
- 230000003385bacteriostatic effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-Nbeta-D-glucoseChemical compoundOC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1OWQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N0.000description1
- OQFSQFPPLPISGP-UHFFFAOYSA-Nbeta-carboxyaspartic acidNatural productsOC(=O)C(N)C(C(O)=O)C(O)=OOQFSQFPPLPISGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 210000004204blood vesselAnatomy0.000description1
- 229910000019calcium carbonateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 229940077731carbohydrate nutrientsDrugs0.000description1
- 239000005018caseinSubstances0.000description1
- BECPQYXYKAMYBN-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncasein, tech.Chemical compoundNCCCCC(C(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(CC(C)C)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(C(C)O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(COP(O)(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(N)CC1=CC=CC=C1BECPQYXYKAMYBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 235000021240caseinsNutrition0.000description1
- 239000000470constituentSubstances0.000description1
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000description1
- 230000001276controlling effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000005520cutting processMethods0.000description1
- 235000018417cysteineNutrition0.000description1
- XUJNEKJLAYXESH-UHFFFAOYSA-NcysteineNatural productsSCC(N)C(O)=OXUJNEKJLAYXESH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000006378damageEffects0.000description1
- 230000007812deficiencyEffects0.000description1
- 230000010339dilationEffects0.000description1
- 238000010790dilutionMethods0.000description1
- 239000012895dilutionSubstances0.000description1
- TVWTZAGVNBPXHU-FOCLMDBBSA-Ndioctyl (e)-but-2-enedioateChemical compoundCCCCCCCCOC(=O)\C=C\C(=O)OCCCCCCCCTVWTZAGVNBPXHU-FOCLMDBBSA-N0.000description1
- 238000009826distributionMethods0.000description1
- 230000037336dry skinEffects0.000description1
- 238000010894electron beam technologyMethods0.000description1
- 239000003623enhancerSubstances0.000description1
- 230000008020evaporationEffects0.000description1
- 210000001723extracellular spaceAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000000416exudates and transudateAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000006260foamSubstances0.000description1
- 238000009472formulationMethods0.000description1
- 229960002737fructoseDrugs0.000description1
- 239000007789gasSubstances0.000description1
- 239000008103glucoseSubstances0.000description1
- 235000013922glutamic acidNutrition0.000description1
- 239000004220glutamic acidSubstances0.000description1
- 230000035876healingEffects0.000description1
- 230000036541healthEffects0.000description1
- 230000036571hydrationEffects0.000description1
- 238000006703hydration reactionMethods0.000description1
- 125000002887hydroxy groupChemical group[H]O*0.000description1
- 230000007794irritationEffects0.000description1
- 239000008101lactoseSubstances0.000description1
- 235000005772leucineNutrition0.000description1
- 210000000265leukocyteAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000description1
- 229920001684low density polyethylenePolymers0.000description1
- 239000004702low-density polyethyleneSubstances0.000description1
- 239000001630malic acidSubstances0.000description1
- 235000011090malic acidNutrition0.000description1
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001338necrotic effectEffects0.000description1
- 229920001778nylonPolymers0.000description1
- 238000002559palpationMethods0.000description1
- 230000007170pathologyEffects0.000description1
- 230000035699permeabilityEffects0.000description1
- 239000002984plastic foamSubstances0.000description1
- 229920006267polyester filmPolymers0.000description1
- 229920001155polypropylenePolymers0.000description1
- 239000011496polyurethane foamSubstances0.000description1
- 229940075065polyvinyl acetateDrugs0.000description1
- 239000011118polyvinyl acetateSubstances0.000description1
- 235000015497potassium bicarbonateNutrition0.000description1
- 229910000028potassium bicarbonateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000011736potassium bicarbonateSubstances0.000description1
- 239000001103potassium chlorideSubstances0.000description1
- 235000011164potassium chlorideNutrition0.000description1
- TYJJADVDDVDEDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-Mpotassium hydrogencarbonateChemical compound[K+].OC([O-])=OTYJJADVDDVDEDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description1
- 230000000306recurrent effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000009467reductionEffects0.000description1
- 230000001105regulatory effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000036556skin irritationEffects0.000description1
- 231100000475skin irritationToxicity0.000description1
- 235000017557sodium bicarbonateNutrition0.000description1
- 229910000030sodium bicarbonateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000003860storageMethods0.000description1
- 239000000758substrateSubstances0.000description1
- 229920002994synthetic fiberPolymers0.000description1
- 210000003371toeAnatomy0.000description1
- 231100000331toxicToxicity0.000description1
- 230000002588toxic effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000009736wettingMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/70—Web, sheet or filament bases ; Films; Fibres of the matrix type containing drug
- A61K9/7023—Transdermal patches and similar drug-containing composite devices, e.g. cataplasms
- A61K9/703—Transdermal patches and similar drug-containing composite devices, e.g. cataplasms characterised by shape or structure; Details concerning release liner or backing; Refillable patches; User-activated patches
- A61K9/7038—Transdermal patches of the drug-in-adhesive type, i.e. comprising drug in the skin-adhesive layer
- A61K9/7046—Transdermal patches of the drug-in-adhesive type, i.e. comprising drug in the skin-adhesive layer the adhesive comprising macromolecular compounds
- A61K9/7053—Transdermal patches of the drug-in-adhesive type, i.e. comprising drug in the skin-adhesive layer the adhesive comprising macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions only involving carbon to carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl, polyisobutylene, polystyrene
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/02—Adhesive bandages or dressings
- A61F13/0203—Adhesive bandages or dressings with fluid retention members
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/70—Web, sheet or filament bases ; Films; Fibres of the matrix type containing drug
- A61K9/7023—Transdermal patches and similar drug-containing composite devices, e.g. cataplasms
- A61K9/703—Transdermal patches and similar drug-containing composite devices, e.g. cataplasms characterised by shape or structure; Details concerning release liner or backing; Refillable patches; User-activated patches
- A61K9/7038—Transdermal patches of the drug-in-adhesive type, i.e. comprising drug in the skin-adhesive layer
- A61K9/7046—Transdermal patches of the drug-in-adhesive type, i.e. comprising drug in the skin-adhesive layer the adhesive comprising macromolecular compounds
- A61K9/7053—Transdermal patches of the drug-in-adhesive type, i.e. comprising drug in the skin-adhesive layer the adhesive comprising macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions only involving carbon to carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyvinyl, polyisobutylene, polystyrene
- A61K9/7061—Polyacrylates
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L15/00—Chemical aspects of, or use of materials for, bandages, dressings or absorbent pads
- A61L15/16—Bandages, dressings or absorbent pads for physiological fluids such as urine or blood, e.g. sanitary towels, tampons
- A61L15/42—Use of materials characterised by their function or physical properties
- A61L15/58—Adhesives
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L15/00—Chemical aspects of, or use of materials for, bandages, dressings or absorbent pads
- A61L15/16—Bandages, dressings or absorbent pads for physiological fluids such as urine or blood, e.g. sanitary towels, tampons
- A61L15/42—Use of materials characterised by their function or physical properties
- A61L15/60—Liquid-swellable gel-forming materials, e.g. super-absorbents
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F2013/00361—Plasters
- A61F2013/00365—Plasters use
- A61F2013/00519—Plasters use for treating burn
- A61F2013/00523—Plasters use for treating burn with hydrogel
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F2013/00361—Plasters
- A61F2013/00655—Plasters adhesive
- A61F2013/00676—Plasters adhesive hydrogel
Definitions
- This inventionrelates to a method and therapeutic adhesive patch product for treating trauma blisters, burns or exposure to chemicals.
- Blisters of the skincan be caused by repeated trauma due to chafing against the skin, most commonly experienced on the hands and feet or from other causes. Further, some first and second degree burns of the skin or exposure to chemicals can also cause blisters. These blisters all have a common pathology regardless of the traumatic causation.
- Another objectis to provide an adhesive patch for treating blisters.
- This inventionprovides a moist and flexible hydrogel, most preferably in the form of a flexible but dimensionably stable patch for covering the blister by which the fluid volume within the skin blister is significantly reduced.
- This reductionresults from placing a hypertonic hydrogel layer in direct contact with the blister so as to produce an osmotic imbalance between the liquid within the blister and the hydrogel.
- the fluidis drawn out of the blister by osmotic force through the raised epidermis which, upon being hydrated externally by the gel, can then act as a semi-permeable membrane.
- the structural integrity of the epidermisremains intact due to the protection provided by the patch. Following this, the epidermis will lay down on the dermis.
- the present inventionprovides a means of reducing accumulated extracellular fluid contained in the blister.
- the osmotic imbalancepersists while the patch is in place and continues to draw fluid from the low concentration in the blistered skin to the high concentration in the hypertonic hydrogel.
- This inventiontherefore concerns a method for treating blistered skin by applying directly to the blistered area a moist, flexible, hypertonic hydrophilic gel patch.
- the gelpreferably has a tacky, i.e., pressure-sensitive adhesive, surface enabling the patch to be self-bonding to the skin. This bond enhances hydration of the skin and the transfer of fluids.
- the patchalso includes a backing such as paper, cloth or plastic that acts as a support for the patch and a water-based hypertonic hydrogel layer applied to the backing.
- a backingsuch as paper, cloth or plastic that acts as a support for the patch
- a water-based hypertonic hydrogel layerapplied to the backing.
- the tacky pressure-sensitive adhesive surface of the gel layerwhen present, bonds the hydrogel and the patch itself to the skin.
- the hydrogel layerforms a water bridge between itself and the outer surface of the skin that makes up the top of the blister. This hydro bridge allows the flow of fluid from within the blister, which has a lower osmotic pressure than the osmotic pressure in the hydrogel layer.
- the hydrogel layercomprises water and, as a thickening or gel forming agent, a hydrophilic natural or synthetic polymer dispersed in the water.
- the polymercan comprise a high molecular weight hydrophilic carbohydrate such as karaya, cornstarch, or kelp gel and/or a synthetic hydrophilic polymer such as polyacrylamide, a polyionic gel, or polyacrylic acid.
- a humectantsuch as an alcohol containing two or more hydroxyl groups, i.e., a polyhydric alcohol, is preferably employed to keep the adhesive layer moist.
- any water soluble solutesuch as salt or an alcohol is dissolved in the water in a quantity sufficient to raise the osmotic pressure above that within the blister; namely, to a value over about 308 mOsmol/L so as to maintain the adhesive hydrogel layer in a hypertonic state with respect to the interior of the blister.
- the adhesivehydrates the outermost layer of skin above the blister. Consequently, the hydrogel adhesive, when applied to a patient, forms a hydrophilic bridge with the patient's normally dry outer skin layer, the stratum corneum, which allows fluid transport between the skin and the patch across the hydrophilic bridge.
- the fluid in the blisteris then transported to the hydrogel layer by osmotic pressure to thereby improve or entirely relieve the blistered condition.
- the epidermiswill then heal to the dermis, much like a split thickness skin graft and without pain. It was also found that the invention provides substantial and sometimes complete removal of pain as soon as it is applied, probably because of its cooling effect since the patch acts somewhat like a heat sink in very good thermal contact with the skin with moisture evaporating from its upper surface.
- the patchas noted above contains a flexible backing and a lower hydrophilic, pressure-sensitive adhesive layer containing water, a hydrophilic polymer dispersed in the water, and a dissolved substance.
- the relative amounts of the solute and solventare adjusted such that the osmotic pressure of the patch is above that of the underlying tissue of the patient so as to maintain the adhesive hydrogel layer in a hypertonic state with respect to the fluid in the blister.
- the tacky surface of the adhesive layerwets the normally dry skin surface and creates the hydrophilic bridge with the patient's elevated skin layer. This allows the free transport of fluid from the blister.
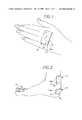
- FIG. 1is a perspective view of the back of the hand showing a patch according to the present invention that has been applied to cover a blister and the surrounding skin.
- FIG. 2is a side perspective view of the foot of a patient that has four blisters which are covered by rectangular hypertonic adhesive patches in accordance with the invention.
- FIG. 3is a top perspective top view of the patch of FIG. 2 showing a portion of the removable liner that covers the adhesive before the patch is used.
- FIG. 4is a greatly enlarged partial cross-sectional view of the patch taken on line 4 - 4 of FIG. 3 showing the patch as it appears when applied to the patient's skin over a blister.
- FIG. 4Ais a still further enlarged microscopic view showing the lower portion of the patch in contact with the skin over a blister.
- FIG. 5is a perspective bottom view of the patch of FIG. 3 showing the exposed pressure-sensitive surface after the liner sheet has been removed and before the patch has been applied to the skin.
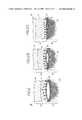
- FIGS. 6A, 6B and 6 Cshow sequential microscopic vertical cross-sectional views of the patch and underlying skin to illustrate the progressive improvement of a blister as an increasing amount of fluid diffuses from the blister and surrounding tissue into the hydrogel matrix of the patch.
- FIG. 1a patient's hand having a blister 8 to which a patch 10 in accordance with the invention has been applied.
- the patch 10which in this case is rectangular, has a water-based hydrogel adhesive layer 14 with a pressure-sensitive surface 14 a and a backing layer 16 that provides structural support for the patch and is composed, for example, of cloth, nonwoven fabric, or plastic film.
- the adhesive layer 14contains moisture and a dissolved material in sufficient quantity to maintain the osmotic pressure within the patch 10 above that of blister beneath the upper layer of skin (the stratum corneum).
- the patch 10is bonded to the skin of the patient by the hydrogel adhesive layer 14 directly over the blister 8 being treated.
- the hydrogel layer 14contains enough moisture to hydrate the skin, and the tacky surface 14 a of the patch 10 forms hydrophilic bridge with the patient's skin by wetting the normally dry stratum corneum 24 (FIG. 4A) enough to allow the progressive transfer of fluid into the adhesive layer 14 through the stratum corneum which acts as a semi-permeable membrane when hydrated.
- the patch 10is left in place for as long as needed, e.g., a day or more, and is replaced whenever necessary.
- One preferred protocolis to replace the patch 10 twice a day.
- FIG. 2shows four more patches 10 which are similar to the patch of FIG. 1.
- the patches 10 of FIG. 2are applied to the patient's foot over blisters (not shown) above the heel and on the tops of the toes.
- FIGS. 3 - 4 Aillustrate the structural features of the patch in more detail.
- the patch 10in this case is provided with an underlying layer of medical grade, non-irritating, hydrated pressure-sensitive adhesive 14 of any suitable type known to those skilled in the art, for example as described in U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,536,263; 4,675,009; 2,498,338; 3,645,835; 4,427,737 and 4,867,150 (which are incorporated herein by reference) except that the osmotic pressure of the adhesive gel is controlled as already described by regulating the ratio of solvent (water) to dissolved solutes.
- the lower surface 14 a of adhesive 14is protected during shipment and storage by a removable liner sheet 18 (FIG.
- the liner sheet 18can be a 2 mil. sheet of polyester film. Before use, the liner sheet 18 is removed to expose the lower surface of the pressure-sensitive adhesive 14 . The patch 10 is then applied to the skin 15 and is held in place by the pressure-sensitive adhesive surface 14 a , for example, on the hand or foot of the patient as shown in FIGS. 1, 2, 4 and 4 A. While it is preferred that the hydrogel layer have a pressure-sensitive adhesive surface 14 a that will hold the patch in contact with the skin 15 , the patch 10 can also be held in place if desired by wrapping it with a cloth bandage or by taping down the edges with any suitable commercially available medical adhesive tape (not shown).
- the patch 10is typically about one inch long by one or two inches wide and has rounded corners. It can also be circular with a diameter of from about 1 ⁇ 2 inch to 11 ⁇ 2 inches.
- the backing sheet 16typically has a thickness of about 3-8 mils and has applied to it about 0.012 ounces per square inch of the adhesive.
- the backing sheet 16is typically a flexible sheet of open-cell polyurethane foam, open-cell polyethylene foam, nonwoven fabric or cloth.
- the hydrogel layer 14comprises a base or matrix composed of water and a water-dispersible hydrophilic polymer.
- the hydrophilic polymer contained in the adhesive layer 14acts as a thickening or gel forming agent that helps the adhesive layer set up once applied to the backing 16 .
- a high molecular weight natural or synthetic polymer and optionally a polymeric tackifieris included as a part of the hydrophilic hydrogel adhesive layer.
- the hydrophilic polymercan be any natural or synthetic polymer, for example a gum, i.e., a natural plant exudate such as karaya as described in U.S. Pat. No.
- the adhesive hydrogel layer 14In order to create the desired osmotic pressure within the patch 10 , at least one substance is dissolved in the adhesive hydrogel layer 14 . Increasing amounts of this solute will create higher osmotic pressures, since the osmotic pressure of a solution is proportional to the fraction of solute molecules in the solution. Enough solute is used to produce an osmotic pressure greater than that of human tissue, namely over about 308 mOsmol/L.
- Various solutescan be employed.
- the most suitable for the present inventioncomprise soluble carbohydrates including sugar, soluble salts, weak acids and bases, mono- and polyhydric alcohols, soluble amino acids or proteins, and other water soluble molecules. Those proteins that are soluble in water form colloidal solutions.
- saltsare generally the most effective osmotic enhancers since, at the same temperature, equal volumes of solutions showing the same osmotic pressure contain equal numbers of molecules of the solute. If sucrose which has a molecular weight of 342.3 is used, for example, the osmotic pressure of a molal solution is 24.8 atmospheres at 0° C. Sodium chloride, however, with a molecular weight of 58 is almost six times as effective in increasing the osmotic pressure as the same quantity of sucrose by weight.
- the saltsthat can be employed are sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, and calcium carbonate.
- sugars that can be usedare sucrose, glucose, levulose, and lactose.
- weak acids that can be employedare acetic acid, adipic acid, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and malic acid.
- weak basesare potassium bicarbonate and sodium bicarbonate.
- proteinsare albumin and casein.
- amino acidsare glycine, alanine, cysteine and leucine.
- alcoholsare ethanol, methanol, glycerin, ethylene glycol, and propylene glycol.
- solutes that can be usedwill be apparent to those skilled in the art. Naturally, the solute should be non-irritating and unlikely to produce toxic reactions or skin irritation at the concentration used.
- saltsare typically present for example at concentrations of about 0.1% to 15% by weight or more, and preferably from about 0.5% to about 7% by weight, to produce an osmotic pressure greater than the fluid within the infected skin.
- Sugars and proteinsare typically used in an amount, for example, from about 1% to 25% by weight.
- Solutescan be used in combination.
- the osmotic pressure increase produced by glycerincan be further increased by the addition of any nontoxic electrolyte, e.g., the addition of 1% sodium chloride.
- a solution of about 0.9% sodium chlorideis isotonic with serum or blood. Accordingly, anything with a higher osmotic pressure than the equivalent of 0.9% sodium chloride is sufficient to be at a greater osmotic pressure than blood or serum.
- it is desirable to have a much higher osmotic pressure in the hydrophilic layer than in the blistersince the higher the osmotic pressure of the hydrophilic layer, the greater will be the absorption of moisture from the blister.
- the permeability of any particular skin areacannot be precisely predicted, it is desirable to keep the osmotic pressure in the adhesive substantially higher than that of the blister to maintain a high osmotic differential and to provide a margin of error.
- the pressure-sensitive hydrocolloidal adhesive layer 14can be prepared by admixing the constituents just prior to applying the adhesive to the backing 16 .
- Mixingcan be accomplished by providing a processing mixer with a cooling jacket through which a coolant such as a chilled mixture of water and ethylene glycol is passed during operation.
- the components of the hydrogelare continuously added to the mixer during operation. While any suitable mixer can be used, one suitable mixer is a five-inch continuous processing mixer manufactured by Teledyne Readco Company of York, Penn.
- the coolant passed through the processing mixercan be maintained at about 0° C.
- the temperature of the moisture-containing hydrogel 14 as it flows onto the exposed surface of the backing sheet 16is important for controlling the infiltration of the coating into the backing sheet 16 .
- the coolantwill, under typical operating conditions, keep the extruded hydrogel 14 at a temperature of about 9° C. to 14° C. as it comes into contact with the backing 16 . If deeper penetration is desired, the temperature of the hydrogel is lowered to about 9° C. for a typical hydrogel formulation. If less penetration is wanted, the temperature is raised closer to 15° C.
- hydrogel adhesive produced by the processing mixerwhich is in a chilled fluid condition, is expelled onto backing sheet 16 and is spread out, e.g., by means of a knife coater of suitable known construction.
- the backing 16can be a porous or non-porous self-supporting sheet of water insoluble polymeric material that provides strength and integrity for the adhesive patch 10 , and when porous can act as a substrate for receiving and retaining a portion of the adhesive hydrogel 14 .
- One preferred backing sheet 16is a lightweight, pliable strip composed, for example, from a nonwoven fabric which consists of polymeric fibers such as polyester, cotton or cellulose fibers bonded together with a sizing resin.
- the backing sheet 16should be nonirritating to human skin.
- the backing sheet 16can be coated on its back surface with a release coating such as a silicone release coating as described in U.S. Pat. No. 4,696,854 which is incorporated herein by reference.
- One suitable release coatingis a 100% solids electron beam curable silicone such as TEGO® Resin Acrylates/RC-Series RC 705 and RC 726 by Goldschmidt Chemical Corporation of Hopewell, Virginia.
- the preferred backing sheet 16is a porous polymeric water insoluble nonwoven fibrous fabric.
- a suitable sizing material for bonding the fibers togetheris a latex resin.
- the backing sheet 16can comprise other stable, water insoluble flexible sheet materials.
- Another preferred backingcomprises a 5.5 mil. strip of nonwoven fabric formed from a mixture of cellulose fibers derived from wood pulp and polyester fibers. The fibers are assembled loosely into the backing to maintain porosity.
- a sizing resinis applied to hold the fibers together.
- the sizing resincan comprise a nonirritating resin applied as a latex emulsion.
- HYCAR® 26477a resin produced by B.F. Goodrich Co. of Brecksville, Ohio.
- Another suitable backing sheetis a nonwoven fabric comprising a wetlay cellulose and polyester nonwoven fabric containing as a sizing an acrylic latex emulsion resin, e.g., product number N7601 by Dexter Corporation of Windsor Locks, Connecticut.
- the backing sheet 16comprises a porous woven 5 mil. acetate polymer cloth sometimes known as “silk cloth.”
- Another form of backing sheet 16is an open-cell plastic foam strip of low density polyethylene or poly-vinyl acetate resin.
- Other backing sheets that can be usedinclude woven cotton cloth or other cloth formed from a synthetic polymer. Suitable synthetic cloths include nylon, polyester, polyacetate.
- the backing sheet 16is a woven cloth, no sizing resin is needed.
- the backing sheet 16is pervious to air, the patch is non-occlusive to the skin. However, an occlusive backing can be used if desired.
- the backing 16is covered by a slippery friction-reducing layer 17 which has been broken away for clarity of illustration (FIG. 3), such as a sheet of slippery polyethylene, polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon®), polypropylene, waxed parchment or any other slippery sheet material known to the art to reduce surface friction above the blister 8 .
- a slippery friction-reducing layer 17such as a sheet of slippery polyethylene, polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon®), polypropylene, waxed parchment or any other slippery sheet material known to the art to reduce surface friction above the blister 8 .
- a slippery coatingsuch as a silicone or wax-containing coating well known to those skilled in the adhesive tape art, which in ordinary adhesive tape serves as a release coating. If, for example, the slippery layer 17 is applied on the outer surface of the patches 10 shown in FIG.
- the slippery surface characteristicwill help reduce friction between the patch 10 and the stocking and shoe that are placed on the foot over the patch.
- the low friction outer surface layer 17 of the patch 10helps promote sliding contact and eliminate chafing between the patch 10 and a material such as an article of clothing that is placed over the patch 10 .
- the patchescan be formed by die-cutting, for example as described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,536,263.
- FIGS. 4 and 4Aillustrate a cross-sectional view of the patch after application to the skin 15 following removal of the liner sheet 18 .
- the patch 10has been applied over a blister 8 .
- the blister 8is covered by the stratum corneum 24 which may have, or may eventually develop, an opening 26 just above the center of the blister 8 .
- the opening 26appears, fluid and necrotic tissue debris will flow out at an increasing rate to be absorbed into the hydrophilic adhesive layer 14 of the patch 10 .
- the moisture within the adhesive layer 14soon hydrates the normally dry stratum corneum 24 (FIG. 4A), causing it to swell and to become more flexible.
- FIGS. 6 A- 6 Cshow in timed sequence three microscopic vertical cross-sectional views of the same patch 10 and the underlying skin 15 to illustrate how an increasing amount of interstitial fluid from the blister 8 is progressively carried by osmotic pressure upwardly into the adhesive layer 14 of the patch 10 , causing it to swell.
- FIGS. 6A- 6 Cshow the progressive improvement of the blister 8 over time proceeding from FIG. 6A to 6 C as fluid is removed from the blister 8 .
- the upward flow of fluid from the blister 8 into the adhesive layer 14is indicated by vertical arrows in the figures.
- the blister 8is much reduced as even more fluid is carried by osmotic pressure from the blister into the hydrophilic gel layer 14 , thereby expanding the hydrophilic gel layer.
- saltis used to create the hypertonic pressure within the adhesive 14 , it provides an additional benefit in helping to keep the patch 10 sterile or at least helps to reduce the bacterial count to a safe level.
- the patchesare prepared by providing a porous nonwoven flexible fabric backing, e.g., nonwoven fabric having a thickness of 5 mils.
- a hydrophilic adhesive composition shown in each exampleto a thickness of about 3 mils.
- the hydrophilic adhesive compositionsare given in the following examples:
- the hypertonic gel layerremoved the fluid within the blisters and some of the increased extracellular fluid in the surrounding areas as a result of the burn.
- the result of this actionreduced the inflammation which apparently never returned, either by clinical action or by the subjective observation of the absence of pain.
- the immediate effect of the hydrophilic gelalmost immediately removed the pain by covering the burned surface with a moist layer of hydrogel, thereby reducing or eliminating the irritation to the pain sensors in the burned skin. As the fluid was removed and the acute inflammation subsided, the pain also clinically abated without the presence of the hydrogel patch.
- the adhesive gels described aboveare applied to the backing 16 to provide a thin adhesive layer which is covered by a removable slip sheet or liner sheet 18 of any suitable commercially available composition.
- the patches 10are then packaged in protective paper or plastic wrappers, pouches or envelopes for distribution. Also contained in the package, e.g., by being printed on the pouch or envelope, are directions for treating blisters by removing the liner sheet 18 and applying the patch to the skin directly over the blister.
- the user or health care workercan easily remove the patches from the envelope, remove the protective liner sheet, and apply the patch directly to the blister.
- the contact between the gel and the blistered skinconsequently results in an osmotic gradient, pulling the fluid from the blister through the hydrated stratum corneum into the patch, thereby reducing fluid within the blister.
- the patch 10 in accordance with the inventioncan be either non-sterile or, if desired, sterilized as described for example in U.S. Pat. No. 4,307,717 which is incorporated herein by reference.
- any of the hydrophilic hydrogel adhesive compositions in accordance with the present inventioncan have dispersed therein one or more antimicrobial agents including but not limited to any of the following: isopropyl alcohol, povidone iodine, mercurochrome, hydrogen peroxide, benzoyl peroxide, retinoic acid, tetracycline, chlorohexidine gluconate, erythromycin, miconazole, acyclovir, isotretinoin, hexachlorophene, silver nitrate, acetic acid, salicylic acid and the like.
- antimicrobial agentsincluding but not limited to any of the following: isopropyl alcohol, povidone iodine, mercurochrome, hydrogen peroxide, benzoyl peroxide, retinoic acid, tetracycline, chlorohexidine gluconate, erythromycin, miconazole, acyclovir, isotretinoin, hexachloroph
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Dermatology (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Medicinal Preparation (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- This invention relates to a method and therapeutic adhesive patch product for treating trauma blisters, burns or exposure to chemicals.[0001]
- Blisters of the skin can be caused by repeated trauma due to chafing against the skin, most commonly experienced on the hands and feet or from other causes. Further, some first and second degree burns of the skin or exposure to chemicals can also cause blisters. These blisters all have a common pathology regardless of the traumatic causation.[0002]
- When the epidermal layer of the skin is traumatized, an acute accumulation of clear extracellular fluid develops very rapidly between the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin. Secondary inflammation then occurs as part of the healing process. If the epidermal layer opens, the secondary inflammation also may be associated with infection and, as a result, may develop purulent fluid with an infiltration of white blood cells. Moreover, the actual exposure of the dermal layer of skin often results in pain. The present invention takes advantage of the finding that all of these symptoms can be alleviated in whole or in part by significantly reducing the fluid in the acute stage of the blister while maintaining the integrity of the epidermis.[0003]
- Immediately following a burn to the skin which results in a first or second degree burn, there is an acute inflammatory reaction in the burned skin consisting of acute dilation of blood vessels with leakage of fluid into the extravascular and extracellular space in the burned skin. In addition, in second degree burns there is characteristically a blister filled with clear fluid on the skin surface. Further, there is a great deal of pain in the injured area which may last up to seven days or more.[0004]
- In view of the deficiencies in prior treatment, it is an important object of the present invention to provide a treatment for blisters that is safe and can be used by the patient for effectively relieving adverse symptoms or improving the blistered skin and in reducing or eliminating the associated pain.[0005]
- Another object is to provide an adhesive patch for treating blisters.[0006]
- These and other more detailed and specific objects of the present invention will be better understood by reference to the following figures and detailed description which illustrate by way of example of but a few of the various forms of the invention within the scope of the appended claims.[0007]
- This invention provides a moist and flexible hydrogel, most preferably in the form of a flexible but dimensionably stable patch for covering the blister by which the fluid volume within the skin blister is significantly reduced. This reduction results from placing a hypertonic hydrogel layer in direct contact with the blister so as to produce an osmotic imbalance between the liquid within the blister and the hydrogel. After the patch has been applied, the fluid is drawn out of the blister by osmotic force through the raised epidermis which, upon being hydrated externally by the gel, can then act as a semi-permeable membrane. The structural integrity of the epidermis remains intact due to the protection provided by the patch. Following this, the epidermis will lay down on the dermis. It was found that the epidermis will then heal to the dermis without pain like a split thickness skin graft. Thus, the present invention provides a means of reducing accumulated extracellular fluid contained in the blister. The osmotic imbalance persists while the patch is in place and continues to draw fluid from the low concentration in the blistered skin to the high concentration in the hypertonic hydrogel. This invention therefore concerns a method for treating blistered skin by applying directly to the blistered area a moist, flexible, hypertonic hydrophilic gel patch. While not essential, the gel preferably has a tacky, i.e., pressure-sensitive adhesive, surface enabling the patch to be self-bonding to the skin. This bond enhances hydration of the skin and the transfer of fluids. The patch also includes a backing such as paper, cloth or plastic that acts as a support for the patch and a water-based hypertonic hydrogel layer applied to the backing. The tacky pressure-sensitive adhesive surface of the gel layer, when present, bonds the hydrogel and the patch itself to the skin. The hydrogel layer forms a water bridge between itself and the outer surface of the skin that makes up the top of the blister. This hydro bridge allows the flow of fluid from within the blister, which has a lower osmotic pressure than the osmotic pressure in the hydrogel layer.[0008]
- The hydrogel layer comprises water and, as a thickening or gel forming agent, a hydrophilic natural or synthetic polymer dispersed in the water. The polymer can comprise a high molecular weight hydrophilic carbohydrate such as karaya, cornstarch, or kelp gel and/or a synthetic hydrophilic polymer such as polyacrylamide, a polyionic gel, or polyacrylic acid. A humectant such as an alcohol containing two or more hydroxyl groups, i.e., a polyhydric alcohol, is preferably employed to keep the adhesive layer moist. Any water soluble solute such as salt or an alcohol is dissolved in the water in a quantity sufficient to raise the osmotic pressure above that within the blister; namely, to a value over about 308 mOsmol/L so as to maintain the adhesive hydrogel layer in a hypertonic state with respect to the interior of the blister. As already noted, the adhesive hydrates the outermost layer of skin above the blister. Consequently, the hydrogel adhesive, when applied to a patient, forms a hydrophilic bridge with the patient's normally dry outer skin layer, the stratum corneum, which allows fluid transport between the skin and the patch across the hydrophilic bridge. With the patch in place on the skin, the fluid in the blister is then transported to the hydrogel layer by osmotic pressure to thereby improve or entirely relieve the blistered condition. After the fluid is gone, the epidermis will then heal to the dermis, much like a split thickness skin graft and without pain. It was also found that the invention provides substantial and sometimes complete removal of pain as soon as it is applied, probably because of its cooling effect since the patch acts somewhat like a heat sink in very good thermal contact with the skin with moisture evaporating from its upper surface.[0009]
- Another aspect of the invention is the hypertonic moisture-containing adhesive patch itself. The patch as noted above contains a flexible backing and a lower hydrophilic, pressure-sensitive adhesive layer containing water, a hydrophilic polymer dispersed in the water, and a dissolved substance. The relative amounts of the solute and solvent are adjusted such that the osmotic pressure of the patch is above that of the underlying tissue of the patient so as to maintain the adhesive hydrogel layer in a hypertonic state with respect to the fluid in the blister. The tacky surface of the adhesive layer wets the normally dry skin surface and creates the hydrophilic bridge with the patient's elevated skin layer. This allows the free transport of fluid from the blister.[0010]
- FIG. 1 is a perspective view of the back of the hand showing a patch according to the present invention that has been applied to cover a blister and the surrounding skin.[0011]
- FIG. 2 is a side perspective view of the foot of a patient that has four blisters which are covered by rectangular hypertonic adhesive patches in accordance with the invention.[0012]
- FIG. 3 is a top perspective top view of the patch of FIG. 2 showing a portion of the removable liner that covers the adhesive before the patch is used.[0013]
- FIG. 4 is a greatly enlarged partial cross-sectional view of the patch taken on line[0014]4-4 of FIG. 3 showing the patch as it appears when applied to the patient's skin over a blister.
- FIG. 4A is a still further enlarged microscopic view showing the lower portion of the patch in contact with the skin over a blister.[0015]
- FIG. 5 is a perspective bottom view of the patch of FIG. 3 showing the exposed pressure-sensitive surface after the liner sheet has been removed and before the patch has been applied to the skin.[0016]
- FIGS. 6A, 6B and[0017]6C show sequential microscopic vertical cross-sectional views of the patch and underlying skin to illustrate the progressive improvement of a blister as an increasing amount of fluid diffuses from the blister and surrounding tissue into the hydrogel matrix of the patch.
- In FIG. 1 is shown a patient's hand having a[0018]
blister 8 to which apatch 10 in accordance with the invention has been applied. Thepatch 10, which in this case is rectangular, has a water-based hydrogeladhesive layer 14 with a pressure-sensitive surface 14aand abacking layer 16 that provides structural support for the patch and is composed, for example, of cloth, nonwoven fabric, or plastic film. Theadhesive layer 14 contains moisture and a dissolved material in sufficient quantity to maintain the osmotic pressure within thepatch 10 above that of blister beneath the upper layer of skin (the stratum corneum). During use, thepatch 10 is bonded to the skin of the patient by the hydrogeladhesive layer 14 directly over theblister 8 being treated. Thehydrogel layer 14 contains enough moisture to hydrate the skin, and thetacky surface 14aof thepatch 10 forms hydrophilic bridge with the patient's skin by wetting the normally dry stratum corneum24 (FIG. 4A) enough to allow the progressive transfer of fluid into theadhesive layer 14 through the stratum corneum which acts as a semi-permeable membrane when hydrated. Thepatch 10 is left in place for as long as needed, e.g., a day or more, and is replaced whenever necessary. One preferred protocol is to replace thepatch 10 twice a day. - FIG. 2 shows four[0019]
more patches 10 which are similar to the patch of FIG. 1. Thepatches 10 of FIG. 2 are applied to the patient's foot over blisters (not shown) above the heel and on the tops of the toes. - Refer now to FIGS.[0020]3-4A which illustrate the structural features of the patch in more detail. The
patch 10 in this case is provided with an underlying layer of medical grade, non-irritating, hydrated pressure-sensitive adhesive 14 of any suitable type known to those skilled in the art, for example as described in U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,536,263; 4,675,009; 2,498,338; 3,645,835; 4,427,737 and 4,867,150 (which are incorporated herein by reference) except that the osmotic pressure of the adhesive gel is controlled as already described by regulating the ratio of solvent (water) to dissolved solutes. Thelower surface 14aof adhesive14 is protected during shipment and storage by a removable liner sheet18 (FIG. 3) that can comprise any suitable commercially available release paper or plastic film. The liner sheet18 can be a 2 mil. sheet of polyester film. Before use, the liner sheet18 is removed to expose the lower surface of the pressure-sensitive adhesive 14. Thepatch 10 is then applied to theskin 15 and is held in place by the pressure-sensitive adhesive surface 14a, for example, on the hand or foot of the patient as shown in FIGS. 1, 2,4 and4A. While it is preferred that the hydrogel layer have a pressure-sensitive adhesive surface 14athat will hold the patch in contact with theskin 15, thepatch 10 can also be held in place if desired by wrapping it with a cloth bandage or by taping down the edges with any suitable commercially available medical adhesive tape (not shown). - The[0021]
patch 10 is typically about one inch long by one or two inches wide and has rounded corners. It can also be circular with a diameter of from about ½ inch to 1½ inches. Thebacking sheet 16 typically has a thickness of about 3-8 mils and has applied to it about 0.012 ounces per square inch of the adhesive. Thebacking sheet 16 is typically a flexible sheet of open-cell polyurethane foam, open-cell polyethylene foam, nonwoven fabric or cloth. - The composition of a[0022]
preferred hydrogel adhesive 14 will now be described in more detail. Thehydrogel layer 14 comprises a base or matrix composed of water and a water-dispersible hydrophilic polymer. The hydrophilic polymer contained in theadhesive layer 14 acts as a thickening or gel forming agent that helps the adhesive layer set up once applied to thebacking 16. For this purpose, a high molecular weight natural or synthetic polymer and optionally a polymeric tackifier is included as a part of the hydrophilic hydrogel adhesive layer. The hydrophilic polymer can be any natural or synthetic polymer, for example a gum, i.e., a natural plant exudate such as karaya as described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,536,263 which is incorporated herein by reference, starch, kelp, gum or a synthetic hydrophilic polymer such as polyacrylamide, polyacrylic acid or a polyionic gel, e.g., polysodium acrylate, a polyquaternary amine, a polysulfonate, carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), carboxypropyl cellulose (CPC), and the like as described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,547,681 which is also incorporated herein by reference. When karaya is used as a thickening or gel forming agent for thehydrogel adhesive layer 14, it has the advantage of providing a bacteriostatic action and thereby reduces bacterial counts. Another advantage of the invention is its ability to prevent infections. - In order to create the desired osmotic pressure within the[0023]
patch 10, at least one substance is dissolved in theadhesive hydrogel layer 14. Increasing amounts of this solute will create higher osmotic pressures, since the osmotic pressure of a solution is proportional to the fraction of solute molecules in the solution. Enough solute is used to produce an osmotic pressure greater than that of human tissue, namely over about 308 mOsmol/L. Various solutes can be employed. The most suitable for the present invention comprise soluble carbohydrates including sugar, soluble salts, weak acids and bases, mono- and polyhydric alcohols, soluble amino acids or proteins, and other water soluble molecules. Those proteins that are soluble in water form colloidal solutions. On a weight basis, salts are generally the most effective osmotic enhancers since, at the same temperature, equal volumes of solutions showing the same osmotic pressure contain equal numbers of molecules of the solute. If sucrose which has a molecular weight of 342.3 is used, for example, the osmotic pressure of a molal solution is 24.8 atmospheres at 0° C. Sodium chloride, however, with a molecular weight of 58 is almost six times as effective in increasing the osmotic pressure as the same quantity of sucrose by weight. A few examples of the salts that can be employed are sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, and calcium carbonate. Among the sugars that can be used are sucrose, glucose, levulose, and lactose. Among the weak acids that can be employed are acetic acid, adipic acid, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and malic acid. Among the weak bases are potassium bicarbonate and sodium bicarbonate. Among the proteins are albumin and casein. Among the amino acids are glycine, alanine, cysteine and leucine. Among the alcohols are ethanol, methanol, glycerin, ethylene glycol, and propylene glycol. Other solutes that can be used will be apparent to those skilled in the art. Naturally, the solute should be non-irritating and unlikely to produce toxic reactions or skin irritation at the concentration used. While amounts will vary depending upon the desired osmotic pressure, salts, if used, are typically present for example at concentrations of about 0.1% to 15% by weight or more, and preferably from about 0.5% to about 7% by weight, to produce an osmotic pressure greater than the fluid within the infected skin. Sugars and proteins are typically used in an amount, for example, from about 1% to 25% by weight. - Solutes can be used in combination. For example, the osmotic pressure increase produced by glycerin can be further increased by the addition of any nontoxic electrolyte, e.g., the addition of 1% sodium chloride. A solution of about 0.9% sodium chloride is isotonic with serum or blood. Accordingly, anything with a higher osmotic pressure than the equivalent of 0.9% sodium chloride is sufficient to be at a greater osmotic pressure than blood or serum. However, in practice it is desirable to have a much higher osmotic pressure in the hydrophilic layer than in the blister, since the higher the osmotic pressure of the hydrophilic layer, the greater will be the absorption of moisture from the blister. Moreover, since the permeability of any particular skin area cannot be precisely predicted, it is desirable to keep the osmotic pressure in the adhesive substantially higher than that of the blister to maintain a high osmotic differential and to provide a margin of error. During use, as water is transported from the blister into the hydrophilic adhesive layer of the patch, some electrolytes are carried with it, as well as other substances such as small amounts of simple proteins. The water that thus passes through the stratum corneum, which has been hydrated by the patch, dilutes the salt present in the overlying adhesive layer. As the[0024]
patch 10 is used, dilution of the solute causes the patch to lose effectiveness over time. Consequently, thepatch 10 should be removed periodically and replaced with a fresh patch. - The pressure-sensitive hydrocolloidal[0025]
adhesive layer 14 can be prepared by admixing the constituents just prior to applying the adhesive to thebacking 16. Mixing can be accomplished by providing a processing mixer with a cooling jacket through which a coolant such as a chilled mixture of water and ethylene glycol is passed during operation. The components of the hydrogel are continuously added to the mixer during operation. While any suitable mixer can be used, one suitable mixer is a five-inch continuous processing mixer manufactured by Teledyne Readco Company of York, Penn. The coolant passed through the processing mixer can be maintained at about 0° C. The temperature of the moisture-containinghydrogel 14 as it flows onto the exposed surface of thebacking sheet 16 is important for controlling the infiltration of the coating into thebacking sheet 16. The coolant will, under typical operating conditions, keep theextruded hydrogel 14 at a temperature of about 9° C. to 14° C. as it comes into contact with thebacking 16. If deeper penetration is desired, the temperature of the hydrogel is lowered to about 9° C. for a typical hydrogel formulation. If less penetration is wanted, the temperature is raised closer to 15° C. - The hydrogel adhesive produced by the processing mixer, which is in a chilled fluid condition, is expelled onto[0026]
backing sheet 16 and is spread out, e.g., by means of a knife coater of suitable known construction. - The[0027]
backing 16 can be a porous or non-porous self-supporting sheet of water insoluble polymeric material that provides strength and integrity for theadhesive patch 10, and when porous can act as a substrate for receiving and retaining a portion of theadhesive hydrogel 14. - One[0028]
preferred backing sheet 16 is a lightweight, pliable strip composed, for example, from a nonwoven fabric which consists of polymeric fibers such as polyester, cotton or cellulose fibers bonded together with a sizing resin. Thebacking sheet 16 should be nonirritating to human skin. If desired, thebacking sheet 16 can be coated on its back surface with a release coating such as a silicone release coating as described in U.S. Pat. No. 4,696,854 which is incorporated herein by reference. One suitable release coating is a 100% solids electron beam curable silicone such as TEGO® Resin Acrylates/RC-Series RC 705 and RC 726 by Goldschmidt Chemical Corporation of Hopewell, Virginia. Thepreferred backing sheet 16 is a porous polymeric water insoluble nonwoven fibrous fabric. A suitable sizing material for bonding the fibers together is a latex resin. - The[0029]
backing sheet 16 can comprise other stable, water insoluble flexible sheet materials. Another preferred backing comprises a 5.5 mil. strip of nonwoven fabric formed from a mixture of cellulose fibers derived from wood pulp and polyester fibers. The fibers are assembled loosely into the backing to maintain porosity. A sizing resin is applied to hold the fibers together. The sizing resin can comprise a nonirritating resin applied as a latex emulsion. One example is HYCAR® 26477, a resin produced by B.F. Goodrich Co. of Brecksville, Ohio. Another suitable backing sheet is a nonwoven fabric comprising a wetlay cellulose and polyester nonwoven fabric containing as a sizing an acrylic latex emulsion resin, e.g., product number N7601 by Dexter Corporation of Windsor Locks, Connecticut. - In another embodiment of the invention, the[0030]
backing sheet 16 comprises a porous woven 5 mil. acetate polymer cloth sometimes known as “silk cloth.” Another form ofbacking sheet 16 is an open-cell plastic foam strip of low density polyethylene or poly-vinyl acetate resin. Other backing sheets that can be used include woven cotton cloth or other cloth formed from a synthetic polymer. Suitable synthetic cloths include nylon, polyester, polyacetate. When thebacking sheet 16 is a woven cloth, no sizing resin is needed. When thebacking sheet 16 is pervious to air, the patch is non-occlusive to the skin. However, an occlusive backing can be used if desired. - In accordance with another optional form of the invention, the[0031]
backing 16 is covered by a slippery friction-reducinglayer 17 which has been broken away for clarity of illustration (FIG. 3), such as a sheet of slippery polyethylene, polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon®), polypropylene, waxed parchment or any other slippery sheet material known to the art to reduce surface friction above theblister 8. Another alternative is to product thelayer 17 by applying a slippery coating such as a silicone or wax-containing coating well known to those skilled in the adhesive tape art, which in ordinary adhesive tape serves as a release coating. If, for example, theslippery layer 17 is applied on the outer surface of thepatches 10 shown in FIG. 2, the slippery surface characteristic will help reduce friction between thepatch 10 and the stocking and shoe that are placed on the foot over the patch. In this way the low frictionouter surface layer 17 of thepatch 10 helps promote sliding contact and eliminate chafing between thepatch 10 and a material such as an article of clothing that is placed over thepatch 10. - After the[0032]
hydrogel adhesive layer 14 has been applied to thebacking 16, the patches can be formed by die-cutting, for example as described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,536,263. - Refer now to FIGS. 4 and 4A which illustrate a cross-sectional view of the patch after application to the[0033]
skin 15 following removal of the liner sheet18. As shown in the figures, thepatch 10 has been applied over ablister 8. Theblister 8 is covered by thestratum corneum 24 which may have, or may eventually develop, an opening26 just above the center of theblister 8. When the opening26 appears, fluid and necrotic tissue debris will flow out at an increasing rate to be absorbed into thehydrophilic adhesive layer 14 of thepatch 10. If should also be noted that the moisture within theadhesive layer 14 soon hydrates the normally dry stratum corneum24 (FIG. 4A), causing it to swell and to become more flexible. In addition, because of the added moisture, the free transport of fluids from theblister 8 upwardly into the hydrophilicadhesive gel 14 will be possible over an extended period of time as indicated by the vertical arrows in FIG. 4A. This osmotic effect is beneficial since it enhances drainage of the inflamed nodules. The evaporation of moisture through theporous backing 16 helps to maintain the osmotic differential and thus facilitates continued fluid transport out of the skin. - FIGS.[0034]6A-6C show in timed sequence three microscopic vertical cross-sectional views of the
same patch 10 and theunderlying skin 15 to illustrate how an increasing amount of interstitial fluid from theblister 8 is progressively carried by osmotic pressure upwardly into theadhesive layer 14 of thepatch 10, causing it to swell. These figures show the progressive improvement of theblister 8 over time proceeding from FIG. 6A to6C as fluid is removed from theblister 8. The upward flow of fluid from theblister 8 into theadhesive layer 14 is indicated by vertical arrows in the figures. Finally, as shown in FIG. 6C, theblister 8 is much reduced as even more fluid is carried by osmotic pressure from the blister into thehydrophilic gel layer 14, thereby expanding the hydrophilic gel layer. When salt is used to create the hypertonic pressure within the adhesive14, it provides an additional benefit in helping to keep thepatch 10 sterile or at least helps to reduce the bacterial count to a safe level. - The invention will be better understood by reference to the examples. The patches are prepared by providing a porous nonwoven flexible fabric backing, e.g., nonwoven fabric having a thickness of 5 mils. To the flexible backing is applied a hydrophilic adhesive composition shown in each example to a thickness of about 3 mils. The hydrophilic adhesive compositions are given in the following examples:[0035]
- [0036]
Ingredient % by Weight Glycerin 22.0 Water 10.0 Propylene Glycol 20.0 Sodium Chloride 1.0 Polyquaternary amine 37.0 - [0037]
Ingredient % by Weight Propylene Glycol 33.0 Water 20.0 Polyacrylamide 15.0 Sucrose 11.0 Maltodextrin 12.0 Tackifier comprising a vinyl acetate resin emulsion 9.0 - [0038]
Ingredient % by Weight Water 14.0 Karaya 10.0 Albumin solids 45.0 Tackifier comprising an acrylic ester copolymer 31.0 emulsion adhesive (B.F. Goodrich 26415) - [0039]
Ingredient % by Weight Water 16.0 Ethylene Glycol 12.0 Acrylic ester copolymer emulsion tackifier 25.0 Tackifier comprising vinyl acetate/dioctyl maleate 38.0 copolymer emulsion Polysodium acrylate 9.0 - [0040]
Ingredient % by Weight Glycerol 58.0 Water 10.0 Polyacrylamide 15.0 Polyacrylic acid 15.0 Calcium chloride 2.0 - [0041]
Ingredient % by Weight Propylene Glycol 33.0 Water 20.0 Polysulfonate 15.0 Sucrose 11.0 Maltodextrin 12.0 Tackifier comprising a vinyl acetate resin emulsion 9.0 - [0042]
Ingredient % by Weight Propylene Glycol 33.0 Water 20.0 Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) 15.0 Sucrose 11.0 Maltodextrin 12.0 Tackifier comprising a vinyl acetate resin emulsion 9.0 - [0043]
Ingredient % by Weight Propylene Glycol 33.0 Water 20.0 Carboxypropyl cellulose (CPC) 15.0 Sucrose 11.0 Maltodextrin 12.0 Tackifier comprising a vinyl acetate resin emulsion 9.0 - [0044]
Ingredient % by Weight Glycerin 49 Nonionic and/or ionic polyacrylamide 16 Acrylic ester copolymer adhesive 8 Malto dextrin 6 Pectin 4 Deionized water 6.6 Proplylene glycol 6.45 Salicylic acid 2 Sodium chloride 1.95 - [0045]
Ingredient % by Weight Glycerin 49 Nonionic and/or ionic polyacrylamide 16 Acrylic ester copolymer adhesive 8 Malto dextrin 6.25 Pectin 4 Deionized water 7 Proplylene glycol 7 Salicylic acid 2 Sodium chloride 0.75 - A 48-year-old woman burned the distal palmer surface of the distal first four digits of the right hand by trying to move the metal grate on a gas stove which had unknowingly just been turned off. She suffered second degree burns on all of the four digits which all measured one centimeter across and one-half centimeter wide. All burned digits had fluid-filled blisters and the largest blister was on the index finger. All fingers were extremely painful. About one hour after the injury, one patch of Example 1 above was placed on each finger. Within five minutes the patient reported that the pain was completely gone. The patches were replaced about three hours after they were first placed. Examination of the fingers revealed there was no clinical fluid within the blisters, including the first digit. Further, with the blistered areas exposed, there was no recurrent pain to the air or gentle palpation. The examination of the patches revealed that all of the hydrophilic layers contained fluid and the layer on the index finger contained the most fluid. New patches were applied. The next day the patches were removed. There was minimal added fluid in the patches and no clinical blisters. The skin on the surface of the blistered areas was somewhat thickened but not painful to air or touch. The patches were not reapplied. When the burned areas were examined four days later, there were only minimal findings in the wounded areas. Further, the patient had never had any recurrence of pain or limitations of motion and use of the fingers. The probable action of the hypertonic hydrophilic gel layer of the patch on first and second degree burns is two-fold. First, the hypertonic gel layer removed the fluid within the blisters and some of the increased extracellular fluid in the surrounding areas as a result of the burn. The result of this action reduced the inflammation which apparently never returned, either by clinical action or by the subjective observation of the absence of pain. Second, the immediate effect of the hydrophilic gel almost immediately removed the pain by covering the burned surface with a moist layer of hydrogel, thereby reducing or eliminating the irritation to the pain sensors in the burned skin. As the fluid was removed and the acute inflammation subsided, the pain also clinically abated without the presence of the hydrogel patch.[0046]
- The adhesive gels described above are applied to the[0047]
backing 16 to provide a thin adhesive layer which is covered by a removable slip sheet or liner sheet18 of any suitable commercially available composition. Thepatches 10 are then packaged in protective paper or plastic wrappers, pouches or envelopes for distribution. Also contained in the package, e.g., by being printed on the pouch or envelope, are directions for treating blisters by removing the liner sheet 18 and applying the patch to the skin directly over the blister. The user or health care worker can easily remove the patches from the envelope, remove the protective liner sheet, and apply the patch directly to the blister. The contact between the gel and the blistered skin consequently results in an osmotic gradient, pulling the fluid from the blister through the hydrated stratum corneum into the patch, thereby reducing fluid within the blister. - The[0048]
patch 10 in accordance with the invention can be either non-sterile or, if desired, sterilized as described for example in U.S. Pat. No. 4,307,717 which is incorporated herein by reference. - If desired, any of the hydrophilic hydrogel adhesive compositions in accordance with the present invention can have dispersed therein one or more antimicrobial agents including but not limited to any of the following: isopropyl alcohol, povidone iodine, mercurochrome, hydrogen peroxide, benzoyl peroxide, retinoic acid, tetracycline, chlorohexidine gluconate, erythromycin, miconazole, acyclovir, isotretinoin, hexachlorophene, silver nitrate, acetic acid, salicylic acid and the like.[0049]
- Many variations of the present invention within the scope of the appended claims will be apparent to those skilled in the art once the principles described herein are understood.[0050]
Claims (29)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/314,271US6348212B2 (en) | 1999-05-18 | 1999-05-18 | Treating traumatic burns or blisters of the skin |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/314,271US6348212B2 (en) | 1999-05-18 | 1999-05-18 | Treating traumatic burns or blisters of the skin |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US20010055608A1true US20010055608A1 (en) | 2001-12-27 |
| US6348212B2 US6348212B2 (en) | 2002-02-19 |
Family
ID=23219289
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/314,271Expired - Fee RelatedUS6348212B2 (en) | 1999-05-18 | 1999-05-18 | Treating traumatic burns or blisters of the skin |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6348212B2 (en) |
Cited By (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20030170296A1 (en)* | 2000-07-27 | 2003-09-11 | Amnon Sintov | Transdermal drug delivery system |
| US7005556B1 (en) | 1995-09-05 | 2006-02-28 | Argentum Medical | Multilayer wound dressing |
| FR2891463A1 (en)* | 2005-10-03 | 2007-04-06 | Sabine Vercamer | Wound protecting dressing, also keeping wounds sterile and moisturized, comprises adhesive part of elastic non-woven fabric, hydrocolloid piece and plastics protective film |
| US7214847B1 (en) | 1997-09-22 | 2007-05-08 | Argentum Medical, L.L.C. | Multilayer conductive appliance having wound healing and analgesic properties |
| WO2007007115A3 (en)* | 2005-07-14 | 2007-06-07 | First Water Ltd | Treatment of chronic ulcerous skin lesions |
| US7230153B2 (en) | 1997-09-22 | 2007-06-12 | Argentum International, Llc | Multilayer conductive appliance having wound healing and analgesic properties |
| US20070208130A1 (en)* | 2004-04-22 | 2007-09-06 | Shuichi Sasahara | Gel Adhesive Compositions |
| US7291762B2 (en) | 1997-09-22 | 2007-11-06 | Argentum International, Llc | Multilayer conductive appliance having wound healing and analgesic properties |
| US20080021358A1 (en)* | 2005-05-23 | 2008-01-24 | Tucker Kenneth H | Blister inhibiting cover dressing and method of using same |
| US7334321B2 (en) | 2001-11-24 | 2008-02-26 | Delphi Technologies, Inc. | Wire loader |
| WO2008023237A3 (en)* | 2006-08-23 | 2008-04-17 | Martin Wenckens | Patch for the expulsion of insect poison from the skin after stings from membranous insects (hymenoptera) |
| US20090148394A1 (en)* | 2005-07-14 | 2009-06-11 | Hugh Semple Munro | Treatment of chronic ulcerous skin lesions |
| US20110243882A1 (en)* | 2010-03-31 | 2011-10-06 | Xiangting Dong | Antibacterial polymer emulsion and coating composition |
| US8118791B2 (en) | 1995-09-05 | 2012-02-21 | Argentum Medical, Llc | Medical device |
| US8449514B2 (en) | 1997-09-22 | 2013-05-28 | Argentum Medical, Llc | Conductive wound dressings and methods of use |
| US20150150908A1 (en)* | 2013-12-03 | 2015-06-04 | Team Unlimited, LLC | Compositions and methods for treating skin wounds |
| CN109316621A (en)* | 2018-10-15 | 2019-02-12 | 苏州汇涵医用科技发展有限公司 | A kind of preparation method of aerogel dressing |
| CN114246976A (en)* | 2021-12-09 | 2022-03-29 | 上海纳米技术及应用国家工程研究中心有限公司 | Hydrogel dressing for wound inflammation diminishing and preparation method thereof |
| GB2596842B (en)* | 2020-07-08 | 2025-03-05 | Jaques Stephen | Medical dressing |
Families Citing this family (24)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20060002949A1 (en)* | 1996-11-14 | 2006-01-05 | Army Govt. Of The Usa, As Rep. By Secretary Of The Office Of The Command Judge Advocate, Hq Usamrmc. | Transcutaneous immunization without heterologous adjuvant |
| US6797276B1 (en) | 1996-11-14 | 2004-09-28 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Army | Use of penetration enhancers and barrier disruption agents to enhance the transcutaneous immune response |
| US5980898A (en) | 1996-11-14 | 1999-11-09 | The United States Of America As Represented By The U.S. Army Medical Research & Material Command | Adjuvant for transcutaneous immunization |
| US20060002959A1 (en)* | 1996-11-14 | 2006-01-05 | Government Of The United States | Skin-sctive adjuvants for transcutaneous immuization |
| US20040258703A1 (en)* | 1997-11-14 | 2004-12-23 | The Government Of The Us, As Represented By The Secretary Of The Army | Skin-active adjuvants for transcutaneous immunization |
| CA2323382C (en)* | 2000-10-17 | 2004-04-13 | Pharma Mag Inc. | Wound dressing |
| EP1372708B1 (en)* | 2001-02-13 | 2008-06-18 | GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, as represented by THE SECRETARY OF THE ARMY | Vaccine for transcutaneous immunization against travellers' diarrhoea |
| WO2002074325A1 (en)* | 2001-03-19 | 2002-09-26 | Iomai Corporation | Patch for transcutaneous immunization |
| US6830758B2 (en)* | 2001-04-02 | 2004-12-14 | Lectec Corporation | Psoriasis patch |
| US6666836B1 (en)* | 2001-04-06 | 2003-12-23 | Sti Medical Products, Inc. | Thermal treatment system |
| US20040137004A1 (en)* | 2002-03-19 | 2004-07-15 | Glenn Gregory M | Patch for transcutaneous immunization |
| KR100433363B1 (en)* | 2002-04-15 | 2004-05-28 | 주식회사 동구제약 | Epidermal hydrogel formulation containing acyclovir |
| US7175897B2 (en)* | 2002-12-17 | 2007-02-13 | Avery Dennison Corporation | Adhesive articles which contain at least one hydrophilic or hydrophobic layer, method for making and uses for same |
| US7887842B2 (en)* | 2003-02-07 | 2011-02-15 | Teikoku Pharma Usa, Inc. | Methods of administering a dermatological agent to a subject |
| CA2529236A1 (en)* | 2004-12-07 | 2006-06-07 | Centre Des Technologies Textiles | New antimicrobial material |
| WO2006105661A1 (en)* | 2005-04-04 | 2006-10-12 | Bioartificial Gel Technologies Inc. | Prevention and treatment of radiation dermatitis |
| JP5128483B2 (en) | 2005-10-24 | 2013-01-23 | テイコク ファーマ ユーエスエー インコーポレーテッド | N, 2,3-trimethyl-2-isopropylbutanamide topical pain relieving composition and use thereof |
| RU2317305C2 (en)* | 2006-03-29 | 2008-02-20 | ООО "Гель-тех" | Method for preparing supermolecular gel |
| US8501214B2 (en)* | 2007-11-26 | 2013-08-06 | Modetex Biomedical Materials & Technology Industrial Corp. | Hydrophilic foam and pharmaceutical dosage form employing the same |
| AU2010314992B2 (en) | 2009-11-09 | 2016-09-15 | Spotlight Technology Partners Llc | Polysaccharide based hydrogels |
| CN107033368A (en) | 2009-11-09 | 2017-08-11 | 聚光灯技术合伙有限责任公司 | fragmentation hydrogel |
| CN101926833B (en)* | 2010-08-06 | 2012-01-04 | 云南白药集团无锡药业有限公司 | Hydrogel patch and preparation method thereof |
| MX2017005046A (en) | 2014-10-31 | 2017-07-04 | Avent Inc | Method and articles for inhibiting bladder contractions. |
| US9326881B1 (en) | 2015-02-23 | 2016-05-03 | Roberta Press | Multi-layer torso wrap for back pain relief having elasticity and water-retaining capacity |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4675009A (en) | 1977-11-07 | 1987-06-23 | Lec Tec Corporation | Drug dispensing device for transdermal delivery of medicaments |
| US4307717A (en) | 1977-11-07 | 1981-12-29 | Lectec Corporation | Sterile improved bandage containing a medicament |
| US4306551A (en) | 1980-07-28 | 1981-12-22 | Lectec Corporation | Sterile improved bandage and sealant |
| US4622089A (en) | 1983-02-28 | 1986-11-11 | Johnson & Johnson Products, Inc. | Method of making blister pad adhesive bandage |
| US4671266A (en) | 1986-02-05 | 1987-06-09 | The Kendall Company | Blister bandage |
| US5643589A (en) | 1992-12-04 | 1997-07-01 | Chalmers; Susanna Elizabeth | Desiccant formulated for treating wounds or lesions |
| US5423737A (en) | 1993-05-27 | 1995-06-13 | New Dimensions In Medicine, Inc. | Transparent hydrogel wound dressing with release tab |
| AU667766B2 (en) | 1993-05-27 | 1996-04-04 | Paul Hartmann Ag | Hydrogel wound dressing product |
| US5536263A (en) | 1994-03-30 | 1996-07-16 | Lectec Corporation | Non-occulusive adhesive patch for applying medication to the skin |
| US5547681A (en) | 1994-07-14 | 1996-08-20 | Union Carbide Chemicals & Plastics Technology Corporation | Dermal patch |
| GR1002807B (en) | 1996-06-20 | 1997-11-13 | Lavipharm A.E. | Device for topical treatment of acne and method of manufacture. |
| US6039940A (en)* | 1996-10-28 | 2000-03-21 | Ballard Medical Products | Inherently antimicrobial quaternary amine hydrogel wound dressings |
- 1999
- 1999-05-18USUS09/314,271patent/US6348212B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Cited By (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8118791B2 (en) | 1995-09-05 | 2012-02-21 | Argentum Medical, Llc | Medical device |
| US7005556B1 (en) | 1995-09-05 | 2006-02-28 | Argentum Medical | Multilayer wound dressing |
| US8801681B2 (en) | 1995-09-05 | 2014-08-12 | Argentum Medical, Llc | Medical device |
| US8293964B2 (en) | 1995-09-05 | 2012-10-23 | Argentum Medical, Llc | Multilayer laminate wound dressing |
| US8283513B2 (en) | 1995-09-05 | 2012-10-09 | Argentum Medical, Llc | Multilayer wound dressing |
| US8449514B2 (en) | 1997-09-22 | 2013-05-28 | Argentum Medical, Llc | Conductive wound dressings and methods of use |
| US7989674B2 (en) | 1997-09-22 | 2011-08-02 | Argentum Medical, Llc | Multilayer conductive appliance having wound healing and analgesic properties |
| US7291762B2 (en) | 1997-09-22 | 2007-11-06 | Argentum International, Llc | Multilayer conductive appliance having wound healing and analgesic properties |
| US8455710B2 (en) | 1997-09-22 | 2013-06-04 | Argentum Medical, Llc | Conductive wound dressings and methods of use |
| US7214847B1 (en) | 1997-09-22 | 2007-05-08 | Argentum Medical, L.L.C. | Multilayer conductive appliance having wound healing and analgesic properties |
| US7230153B2 (en) | 1997-09-22 | 2007-06-12 | Argentum International, Llc | Multilayer conductive appliance having wound healing and analgesic properties |
| US8093444B2 (en) | 1997-09-22 | 2012-01-10 | Argentum Medical, Llc | Multilayer conductive appliance having wound healing and analgesic properties |
| US20030170296A1 (en)* | 2000-07-27 | 2003-09-11 | Amnon Sintov | Transdermal drug delivery system |
| US7334321B2 (en) | 2001-11-24 | 2008-02-26 | Delphi Technologies, Inc. | Wire loader |
| US20070208130A1 (en)* | 2004-04-22 | 2007-09-06 | Shuichi Sasahara | Gel Adhesive Compositions |
| US7868072B2 (en)* | 2004-04-22 | 2011-01-11 | Sekisui Plastics Co., Ltd. | Gel adhesive compositions, method of making, and use thereof |
| CN101862462B (en)* | 2004-04-22 | 2013-04-17 | 积水化成品工业株式会社 | Electrode |
| US20080021358A1 (en)* | 2005-05-23 | 2008-01-24 | Tucker Kenneth H | Blister inhibiting cover dressing and method of using same |
| US20090148394A1 (en)* | 2005-07-14 | 2009-06-11 | Hugh Semple Munro | Treatment of chronic ulcerous skin lesions |
| WO2007007115A3 (en)* | 2005-07-14 | 2007-06-07 | First Water Ltd | Treatment of chronic ulcerous skin lesions |
| FR2891463A1 (en)* | 2005-10-03 | 2007-04-06 | Sabine Vercamer | Wound protecting dressing, also keeping wounds sterile and moisturized, comprises adhesive part of elastic non-woven fabric, hydrocolloid piece and plastics protective film |
| US8241660B2 (en) | 2006-08-23 | 2012-08-14 | Martin Wenckens | Patch for the expulsion of insect poison from the skin after stings from membranous insects (hymenoptera) |
| WO2008023237A3 (en)* | 2006-08-23 | 2008-04-17 | Martin Wenckens | Patch for the expulsion of insect poison from the skin after stings from membranous insects (hymenoptera) |
| US20110243882A1 (en)* | 2010-03-31 | 2011-10-06 | Xiangting Dong | Antibacterial polymer emulsion and coating composition |
| US8858926B2 (en)* | 2010-03-31 | 2014-10-14 | Rohm And Haas Company | Antibacterial polymer emulsion and coating composition |
| US20150150908A1 (en)* | 2013-12-03 | 2015-06-04 | Team Unlimited, LLC | Compositions and methods for treating skin wounds |
| CN109316621A (en)* | 2018-10-15 | 2019-02-12 | 苏州汇涵医用科技发展有限公司 | A kind of preparation method of aerogel dressing |
| GB2596842B (en)* | 2020-07-08 | 2025-03-05 | Jaques Stephen | Medical dressing |
| CN114246976A (en)* | 2021-12-09 | 2022-03-29 | 上海纳米技术及应用国家工程研究中心有限公司 | Hydrogel dressing for wound inflammation diminishing and preparation method thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US6348212B2 (en) | 2002-02-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6348212B2 (en) | Treating traumatic burns or blisters of the skin | |
| US6455065B1 (en) | Therapeutic method for treating acne or isolated pimples and adhesive patch therefor | |
| US8058499B2 (en) | Absorbent wound dressing containing a hydrogel layer | |
| US4759354A (en) | Wound dressing | |
| US7619130B2 (en) | Multi-layer wound dressing formed as a single unit | |
| US4909244A (en) | Hydrogel wound dressing | |
| US5780048A (en) | First aid bandage dressing system and method of application thereof | |
| KR101651709B1 (en) | Water-soluble pressure sensitive adhesives | |
| WO2009107189A1 (en) | Wound-covering hydrogel material | |
| RU2715718C2 (en) | Wound dressing | |
| JP2004520096A (en) | Hydrogel wound dressing | |
| US6033684A (en) | Compositions and methods for wound management | |
| JPH09502367A (en) | Surgical dressing | |
| US20110098620A1 (en) | Medical device for skin with ultra-hydrophilic pressure-sensitive adhesive | |
| US20030152612A1 (en) | Method and article to control cellulite | |
| JP5147207B2 (en) | Hydrogel wound dressing | |
| AU649475B2 (en) | Bilayer wound dressing | |
| JPH07308339A (en) | Aseptic wound packing | |
| JP7552066B2 (en) | Film and transfer sheet for attaching to biological tissue | |
| US8951599B2 (en) | Wound dressing | |
| JP2781016B2 (en) | Transdermal formulation | |
| KR20080006960A (en) | Transdermal Dosages Containing Hydrophobic Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs | |
| US20020039590A1 (en) | Nontoxic vernix compositions and method of producing | |
| JP2927785B1 (en) | Cooling sheet agent | |
| JP2002200111A (en) | Poultice |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:WELLS FARGO BUSINESS CREDIT, INC., MINNESOTA Free format text:SECURITY INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:LECTEC CORPORATION;REEL/FRAME:010822/0294 Effective date:19991122 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:LECTEC CORPORATION, MINNESOTA Free format text:ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:HYMES, ALAN C.;NICHOLS, JANE;REEL/FRAME:011785/0074;SIGNING DATES FROM 20010306 TO 20010321 | |
| CC | Certificate of correction | ||
| FPAY | Fee payment | Year of fee payment:4 | |
| FPAY | Fee payment | Year of fee payment:8 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:LECTEC CORPORATION, MINNESOTA Free format text:RELEASE;ASSIGNOR:WELLS FARGO BANK MINNESOTA, N A.;REEL/FRAME:026578/0652 Effective date:20110421 Owner name:WELLS FARGO BANK MINNESOTA, N.A., MINNESOTA Free format text:RELEASE;ASSIGNOR:LECTEC CORPORATION;REEL/FRAME:026272/0219 Effective date:19991122 | |
| XAS | Not any more in us assignment database | Free format text:RELEASE;ASSIGNOR:LECTEC CORPORATION;REEL/FRAME:026272/0219 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:MIDCAP FINANCIAL SBIC, LP, MARYLAND Free format text:SECURITY AGREEMENT;ASSIGNORS:AXOGEN, INC.;AXOGEN CORPORATION;REEL/FRAME:027000/0770 Effective date:20110930 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:AXOGEN CORPORATION, FLORIDA Free format text:RELEASE OF SECURITY AGREEMENT;ASSIGNOR:MIDCAP FINANCIAL SBIC, LP;REEL/FRAME:029087/0774 Effective date:20121005 Owner name:AXOGEN, INC., FLORIDA Free format text:RELEASE OF SECURITY AGREEMENT;ASSIGNOR:MIDCAP FINANCIAL SBIC, LP;REEL/FRAME:029087/0774 Effective date:20121005 | |
| REMI | Maintenance fee reminder mailed | ||
| LAPS | Lapse for failure to pay maintenance fees | ||
| STCH | Information on status: patent discontinuation | Free format text:PATENT EXPIRED DUE TO NONPAYMENT OF MAINTENANCE FEES UNDER 37 CFR 1.362 | |
| FP | Lapsed due to failure to pay maintenance fee | Effective date:20140219 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:THREE PEAKS CAPITAL S.A.R.L., NEW YORK Free format text:SECURITY INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:AXOGEN, INC.;REEL/FRAME:034173/0091 Effective date:20141112 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:AXOGEN CORPORATION, FLORIDA Free format text:RELEASE OF SECURITY INTEREST OF REEL/FRAME 034173/0091;ASSIGNOR:THREE PEAKS CAPITAL S.A.R.L.;REEL/FRAME:040502/0007 Effective date:20161025 Owner name:AXOGEN, INC. (FORMERLY KNOWN AS LECTEC CORPORATION Free format text:RELEASE OF SECURITY INTEREST OF REEL/FRAME 034173/0091;ASSIGNOR:THREE PEAKS CAPITAL S.A.R.L.;REEL/FRAME:040502/0007 Effective date:20161025 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST, AS AGENT, MARYLAND Free format text:SECURITY INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:AXOGEN, INC. FORMERLY KNOWN AS LECTEC CORPORATION;AXOGEN CORPORATION;REEL/FRAME:040189/0049 Effective date:20161025 Owner name:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST, AS AGENT, MARYLAND Free format text:SECURITY INTEREST;ASSIGNORS:AXOGEN, INC. FORMERLY KNOWN AS LECTEC CORPORATION;AXOGEN CORPORATION;REEL/FRAME:040189/0429 Effective date:20161025 | |
| AS | Assignment | Owner name:AXOGEN, INC. FORMERLY KNOWN AS LECTEC CORPORATION, FLORIDA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNORS:MIDCAP FUNDING IV TRUST;MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST;REEL/FRAME:045952/0283 Effective date:20180522 Owner name:AXOGEN CORPORATION, FLORIDA Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNORS:MIDCAP FUNDING IV TRUST;MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST;REEL/FRAME:045952/0283 Effective date:20180522 Owner name:AXOGEN, INC. FORMERLY KNOWN AS LECTEC CORPORATION, Free format text:RELEASE BY SECURED PARTY;ASSIGNORS:MIDCAP FUNDING IV TRUST;MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST;REEL/FRAME:045952/0283 Effective date:20180522 |