TW202114595A - Dynamic plantar pressure sensing system including a pressure sensing insole, a signal processing device and a cloud server - Google Patents
Dynamic plantar pressure sensing system including a pressure sensing insole, a signal processing device and a cloud serverDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- TW202114595A TW202114595ATW108136668ATW108136668ATW202114595ATW 202114595 ATW202114595 ATW 202114595ATW 108136668 ATW108136668 ATW 108136668ATW 108136668 ATW108136668 ATW 108136668ATW 202114595 ATW202114595 ATW 202114595A
- Authority
- TW
- Taiwan
- Prior art keywords
- pressure
- signal
- pressure sensing
- plantar
- foot
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement Of The Respiration, Hearing Ability, Form, And Blood Characteristics Of Living Organisms (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese本發明係關於一種足底壓力量測系統,尤其是一種具有動態足底壓力量測的系統。The invention relates to a plantar pressure measurement system, in particular to a system with dynamic plantar pressure measurement.
隨著現代科技和醫療領域的不斷發展,人們越來越加重視自身的身體健康,而足部健康是全身健康中不可或缺的一環,現代生活中大部分的人一整天有許多時間必須穿著鞋子進行活動,而鞋子的鞋墊版型針對每個人不同的腳型便有可能造成相關的足部健康問題。舉例來說,不適合的腳墊版型可能造成足底特定區域壓力峰值長期過高,造成腳部的疼痛不適問題,並且有可能因此養成錯誤的行走姿勢或步態。如同血壓量測可以得知身體健康問題,透過測量雙腳足底壓力可以得知長短腳、骨盆傾斜等健康問題之情形。With the continuous development of modern technology and medical field, people are paying more and more attention to their own physical health, and foot health is an indispensable part of the whole body health. In modern life, most people have a lot of time throughout the day. Wearing shoes for activities, and the insole version of shoes for each person's different foot shape may cause related foot health problems. For example, an unsuitable foot pad pattern may cause long-term high pressure peaks in specific areas of the sole, causing pain and discomfort in the feet, and may therefore develop the wrong walking posture or gait. Just like blood pressure measurement, you can learn about physical health problems. By measuring the pressure on the soles of your feet, you can learn about health problems such as length of feet, pelvic tilt, and so on.
因此各種可測量人體足底壓力的裝置也應運而生。透過這類裝置可以測量一受測者的足底壓力分佈,以用來分析判斷該受測者的足部或身體軀幹的健康情況。然而,現有的測量足底壓力裝置大多是以測量靜態的測量數據為主,該靜態測量的測量數據分析並不能反映受測者完整的足部相關健康情況,因為人體實際走路時的足底壓力情況不一定會和人體靜止站立時的足底壓力情況相同,而且人體的病痛傷害大多都是在動態的行為中衍生出來的;一般人雙腳在每天的動作型態中,除了睡覺是呈現赤腳放鬆狀態之外,其他過半的時間都是雙腳穿著鞋子的狀態,可能是拖鞋、涼鞋、皮鞋、運動鞋…等,所以以雙腳穿入鞋子中行走的動態情境來取得真實數據是較貼切且具說服力的。故如何針對現有量測分析技術進行改進是現在相關領域的重要研究方向。Therefore, various devices that can measure the pressure of the foot of the human body have also emerged. Through this type of device, the plantar pressure distribution of a subject can be measured to analyze and judge the health of the subject's foot or torso. However, most of the existing plantar pressure measurement devices are mainly based on measuring static measurement data. The measurement data analysis of the static measurement cannot reflect the complete foot-related health of the subject, because the plantar pressure when the human body is actually walking The situation is not necessarily the same as the plantar pressure when the human body is standing still, and most of the human body’s pain and injury are derived from dynamic behaviors; in the daily movement patterns of ordinary people, except for sleeping, they are barefoot and relaxed. In addition to the state, the other half of the time is the state of both feet wearing shoes, which may be slippers, sandals, leather shoes, sports shoes... etc. Therefore, it is more appropriate and appropriate to obtain real data in the dynamic context of walking in the shoes. Persuasive. Therefore, how to improve the existing measurement and analysis technology is an important research direction in related fields.
有鑑於上述問題,本發明提供一種足底動態壓力感測系統,讓一使用者穿上該鞋子系統進行足底之動態壓力量測,以用來提供該使用者評估自身足部健康情況的相關參考。In view of the above problems, the present invention provides a plantar dynamic pressure sensing system that allows a user to wear the shoe system to measure the plantar dynamic pressure, so as to provide relevant information for the user to assess his own foot health. reference.
為完成上述目的,本發明提出一種足底動態壓力感測系統,其包含:一壓力感測墊,係放置於一鞋子之內部空間的底部,該壓力感測墊包含:複數個壓力感測器,該複數個壓力感測器平均分布且分別感測一使用者的足部踩壓該壓力感測墊時所產生之壓力訊號;一傳輸線,連接各該壓力感測器;以及一訊號收集器,係透過該傳輸線電性連接於該壓力感測墊,接收該壓力感測墊感測到之壓力訊號;一訊號處理裝置,係無線連接該訊號收集器,接收該訊號收集器發送的該壓力感測墊感測到之壓力訊號,並將該壓力感測墊感測到之壓力訊號整合成一足底壓力訊號;以及一雲端伺服器,係連接該訊號處理裝置,以接收該足底壓力訊號,並根據該足底壓力訊號分析出使用者的足部狀態後,產生一足部狀態訊號,且回傳該足部狀態訊號至該訊號處理裝置。To accomplish the above objective, the present invention proposes a plantar dynamic pressure sensing system, which includes:A pressure sensing pad is placed at the bottom of the inner space of a shoe. The pressure sensing pad includes:A plurality of pressure sensors, the plurality of pressure sensors are evenly distributed and respectively sense a pressure signal generated when a user's foot presses on the pressure sensing pad;A transmission line to connect each of the pressure sensors; andA signal collector is electrically connected to the pressure sensing pad through the transmission line, and receives the pressure signal sensed by the pressure sensing pad;A signal processing device is wirelessly connected to the signal collector, receives the pressure signal sensed by the pressure sensing pad sent by the signal collector, and integrates the pressure signal sensed by the pressure sensing pad into a plantar pressure Signal; andA cloud server connected to the signal processing device to receive the plantar pressure signal and analyze the user's foot state based on the plantar pressure signal, generate a foot state signal, and return the foot state Signal to the signal processing device.
本發明藉由測量該使用者之動態或靜態足部壓力量測,並藉由量測資料進一步分析評估該使用者的相關足部健康問題。本發明改進先前技術中缺乏的相關動態之足部壓力感測技術,讓該使用者在使用該發明知系統進行足部健康檢查時可以得到比先前相關檢查技術更深入的足部健康分析成效。The present invention measures the user's dynamic or static foot pressure, and further analyzes and evaluates the user's related foot health problems by using the measurement data. The present invention improves the related dynamic foot pressure sensing technology that is lacking in the prior art, so that the user can obtain a more in-depth foot health analysis effect than the prior related inspection technology when performing a foot health check using the known system of the invention.
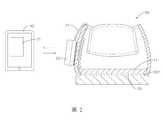
請參閱圖1,本發明的足底動態壓力感測系統包含一壓力感測墊20、一訊號處理裝置30以及一雲端伺服器40。如圖2和圖3所示,該壓力感測墊20是設置在一鞋子50內部,較佳地該壓力感測墊20放置在一鞋墊51之下。Please refer to FIG. 1, the foot dynamic pressure sensing system of the present invention includes a
請進一步參考圖3,該壓力感測墊20包含複數個壓力感測器21、一傳輸線22以及一訊號收集器23,該壓力感測器21可在受壓時產生一壓力訊號。如圖2所示,該壓力感測墊20固定於該鞋子50的內部空間之內底面501和該鞋墊51之間。在較佳之實施例中,該壓力感測墊20厚度極薄,因此使用者在行走時並不會感受到有凸起之異物感,讓使用者可以在不被干擾的情況下用平常的走路習慣來進行動態足底壓力資訊的量測,以取得最貼切實際情況的壓力數據資料。該複數個壓力感測器21較佳的分布位置是設置於對應足部的腳趾、足前、足中及足跟區域,以取得該不同區域的壓力訊號。該訊號收集器23透過傳輸線22電性連接於壓力感測墊20,該訊號收集器23包含一儲存單元231和一無線單元232。該訊號收集器23將感測的壓力訊號儲存到內部的儲存單元231,並且將儲存的壓力訊號透過該無線單元232用無線傳輸方式傳送到外部的一訊號接收裝置30,這裡的無線傳輸方式可包括藍芽、WIFI、RFID等無線傳輸技術。另外該訊號接收裝置30可為一個人手持行動裝置,例如智慧型手機、平板電腦、筆記型電腦等等。同時該訊號接收裝置30可安裝一個人終端應用程式31,其可將接收的壓力訊號轉換成實際壓力之數值,以整合成一足底壓力訊號,並上傳該足底壓力訊號至該雲端伺服器40,且由該雲端伺服器40根據該足底壓力訊號分析出使用者的足部狀態後,產生一足部狀態訊號,再由該雲端伺服器40回傳該足部狀態訊號至該訊號處理裝置30,由該訊號處理裝置30根據該足部狀態訊號呈現相關的數據資訊供使用者參考。較佳地,該訊號處理裝置30係藉由一網路與該雲端伺服器40連線。Please further refer to FIG. 3, the
該訊號收集器23透過傳輸線22電性連接於壓力感測墊20,該訊號收集器23包含一儲存單元231和一無線單元232。該訊號收集器23將感測的壓力訊號儲存到內部的儲存單元231,並且將儲存的壓力訊號透過該無線單元232用無線傳輸方式傳送到該訊號處理裝置30,這裡的無線傳輸方式可包括藍芽、WIFI、RFID等無線傳輸技術,在較佳之實施例之中,該訊號收集器23內建一電池座以用來提供電能和供該使用者在有需求時更換電池。The
請參考圖4,當使用者穿上一搭載該足底動態壓力感測的鞋子系統之鞋子並且開始走動,該壓力感測墊20透過壓力感測器21偵測所承受到的足部所施加壓力並將該偵測到的壓力訊號透過傳輸線22傳送給訊號收集器23。訊號收集器23透過藍芽、WIFI、RFID等無線通訊方式傳送該壓力訊號資訊給該訊號處理裝置30。該訊號處理裝置30接收前述壓力訊號資訊並且使用該個人終端應用程式31進行處理,將接收的壓力訊號轉換成實際壓力之數值,以整合成該足底壓力訊號,並將該足底壓力訊號上傳至該雲端伺服器40。Please refer to FIG. 4, when the user puts on a shoe equipped with the footwear system for dynamic foot pressure sensing and starts to walk, the
接著,由該雲端伺服器40根據該足底壓力訊號分析出使用者的足部狀態後,產生一足部狀態訊號,再回傳該足部狀態訊號至該訊號處理裝置30,由該訊號處理裝置30根據該足部狀態訊號呈現一分析結果顯示在一顯示螢幕上以用來提供該使用者相關評估。此外,該訊號處理裝置30可以藉由網路向該雲端伺服器40進行該個人終端應用程式31的下載和版本更新,且該雲端伺服器40可將分析結果保留,以用來保存資料提供日後參考。Then, the
以下舉例說明如何將上述量測到的該足底動態壓力資料經過處理運算,以用來提供客觀的足底或身體之健康情況評估。當一使用者穿上一搭載該足底動態壓力感測的鞋子系統之鞋子並且開始走動。測量該使用者走一趟一直線步道,並得出該使用者的該趟走動過程中的一平均步幅(平均每一步跨出的距離,計算方法為該直線步道的總距離除上該使用者的總步數);並且得出該使用者的該趟走動過程中一平均步頻(平均一分鐘走幾步)。藉由該使用者的該平均步幅和該平均步頻,可以供相關人員評估該使用者的可能足部健康情況,例如當該使用者的平均步幅低某一數值時,該使用者被評估為有足部相關肌力不足的問題,因此建議攝取乳清蛋白之類的蛋白質營養補給品並配合相關足部肌群的訓練。並且在較佳實施例之中,一使用者的該平均步幅和該平均步頻數據資料經由該個人終端程式31上傳並儲存在該雲端伺服器40,以提供長期的連續足步情況之追蹤,藉由該兩項數據的變化趨勢進一步來評估該使用者足部情況,並由相關人員給予該使用者相應的建議對策。The following examples illustrate how to process the measured plantar dynamic pressure data to provide an objective assessment of the plantar or physical health. When a user puts on a shoe equipped with the footwear system for dynamic pressure sensing on the sole and starts walking. Measure the user's walk along a straight line, and obtain an average stride length (average the distance stepped by each step) during the walking process of the user. The calculation method is the total distance of the straight line divided by the user The total number of steps); and obtain an average step frequency during the walking process of the user (an average of a few steps per minute). With the average stride length and the average stride frequency of the user, relevant personnel can assess the user’s possible foot health. For example, when the user’s average stride length is lower by a certain value, the user is It is assessed that there is a problem of insufficient muscle strength related to the foot, so it is recommended to take protein supplements such as whey protein and cooperate with the training of the relevant foot muscles. And in the preferred embodiment, the average stride length and the average stride frequency data of a user are uploaded via the
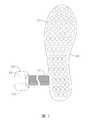
以下舉例說明如何將上述量測到的該足底動態壓力資料經過處理運算,以用來提供客觀的足底或身體之健康情況評估。請參閱圖5,該壓力感測鞋墊的感測區域包含一足跟區域A、一足中區域B、一足前區域C,測量該足跟區域A之內的所有壓力感測器之壓力總和得到一足跟區域壓力總和,測量該足中區域B之內的所有壓力感測器之壓力總和得到一足中區域壓力總和,另外再測量該足前區域C之內的所有壓力感測器之壓力總和得到一足前區域壓力總和,根據可以得到一足弓指標,該足弓指標為該足中區域壓力總和除以所有壓力感測器之壓力總和,亦即該足弓指標等於:The following examples illustrate how to process the measured plantar dynamic pressure data to provide an objective assessment of plantar or physical health. Please refer to FIG. 5, the sensing area of the pressure sensing insole includes a heel area A, a midfoot area B, and a forefoot area C. The total pressure of all pressure sensors in the heel area A is measured to obtain a heel Sum of regional pressure , Measure the total pressure of all pressure sensors in the mid-foot area B to get the total pressure in the mid-foot area , And then measure the total pressure of all pressure sensors in the forefoot area C to get the total pressure of the forefoot area ,according to An arch index can be obtained, the arch index is the total pressure in the area of the foot Divide by the total pressure of all pressure sensors, that is, the arch index is equal to:
若該足弓指標數值大於0.26,則該受測者足部有可能為扁平足;若該足弓指標數值小於0.21,則該受測者足部有可能為高弓足;若該足弓指標數值介於0.21至0.26之間,則該受測者足部有可能為正常狀況。上述判斷結果僅是一種風險評估結果,僅供使用者參考,並不能斷定受測者必然有該問題。If the arch index value is greater than 0.26, the subject’s foot may have flat feet; if the arch index value is less than 0.21, the subject’s foot may be high arch; if the arch index value Between 0.21 and 0.26, the subject's feet may be in a normal condition. The above judgment result is only a risk assessment result, which is for the user's reference only, and it cannot be concluded that the subject must have the problem.
該足底壓力數據也可以用於評估該受測者的下肢整體、骨盆及軀幹的平衡性。例如該壓力感測鞋墊係供設置於一右腳鞋身內部,供感測該受測者右腳踩壓該右腳壓力感測鞋墊時所產生的右腳壓力訊號,且該足底動態壓力感測系統還進一步包含有一左腳壓力感測鞋墊,供設置於一左腳鞋身內部,而該左腳壓力感測鞋墊的結構與該壓力感測鞋墊相同,故不再贅述。該雲端伺服器40可將該受測者右腳透過該壓力感測鞋墊所測得之全部壓力相加得到一右腳足部壓力總和,再將該受測者左腳透過左腳壓力感測鞋墊所測得之全部壓力相加得到一左腳足部壓力總和,進一步取得一右腳足部壓力總和之佔重比例,亦即該右腳足部壓力總和之佔重比例等於:The plantar pressure data can also be used to evaluate the balance of the subject's overall lower limbs, pelvis, and trunk. For example, the pressure sensing insole is provided inside a right shoe body for sensing the right foot pressure signal generated when the subject's right foot presses the right foot pressure sensing insole, and the sole dynamic pressure The sensing system further includes a left foot pressure sensing insole for setting inside a left foot shoe body, and the left foot pressure sensing insole has the same structure as the pressure sensing insole, so it will not be repeated. The
同樣的取得一左腳足部壓力總和之佔重比例,亦即該左腳足部壓力總和之佔重比例等於:Get the total pressure of the left foot in the same way The weight ratio, that is, the total pressure of the left foot The weighting ratio is equal to:
若該左右腳之足部壓力總和之佔重比例相差10%以上,則該受測者有可能為具有骨盆傾斜的風險;若該左右腳之足部壓力總和之佔重比例相差範圍落在5%至10%,則該受測者有可能有長短腳的狀況;若該左右腳之足部壓力總和之佔重比例相差落在5%之內,則該受測者被應為沒有相關骨盆傾斜或是長短腳的問題。在本較佳實施例中,該足弓指標、該右腳足部壓力總和之佔重比例、以及該左腳足部壓力總和之佔重比例是由該雲端伺服器40計算的。If the weight ratio of the total foot pressure of the left and right feet differs by more than 10%, the subject may be at risk of pelvic tilt; if the weight ratio of the total foot pressure of the left and right feet is within 5 % To 10%, the subject may have long and short feet; if the weight ratio of the total foot pressure of the left and right feet is within 5%, the subject should be considered as having no related pelvis Tilting or long and short feet. In this preferred embodiment, the arch index and the total pressure of the right foot The weight ratio and the total pressure of the left foot The weighting ratio is calculated by the
以下另外舉例如何使用該動態壓力感測系統進行步態穩定性測試:測量該使用者來回走一趟一直線步道,並測量該趟來回走動過程中右腳(或左腳)每一步的壓力數據,並將去程的相對應回程的該步伐之重心座標進行比對以用來評估該使用者的步態穩定性。The following is another example of how to use the dynamic pressure sensing system to perform a gait stability test: measure the user walking a straight line back and forth, and measure the pressure data of each step of the right foot (or left foot) during the walking back and forth, The center of gravity coordinates of the step corresponding to the return journey of the outbound journey are compared to evaluate the user's gait stability.
在一較佳實施例中,該使用者來回走一給定的直線L米步道,經過壓力數據測量後,總共走了N步,評估去程走了N/2步,回程走了N/2步,扣除去程前兩步(開始加速)及停止前兩步(開始減速),只提取穩定速度的步數之計算而得的去程中的第n步的重心座標為,以及回程中的第n步的重心座標為,分別為一平面之二維座標,可得一步計算得一步態穩定性評估指標為:In a preferred embodiment, the user walks a given straight L-meter trail back and forth. After pressure data measurement, he walks a total of N steps. It is estimated that the forward journey has taken N/2 steps, and the return journey has taken N/2. Step, deduct the first two steps of the outgoing journey (start to accelerate) and stop the first two steps (start to decelerate), and only extract the number of stable speed steps, and the center of gravity coordinates of the nth step in the outgoing journey are , And the coordinate of the center of gravity of the nth step in the return journey is , They are the two-dimensional coordinates of a plane, and the one-step stability evaluation index can be calculated as:
若該步態穩定指標數值越趨近於0則越穩定;若該步態穩定指標數值大於0.2~0.4,則該受測者步態穩定性不佳;若該步態穩定指標數值高於0.4以上,則該受測者步態則為較不穩定狀況建議就診。If the gait stability index value is closer to 0, the more stable; if the gait stability index value is greater than 0.2~0.4, the gait stability of the subject is not good; if the gait stability index value is higher than 0.4 Above, the gait of the subject is more unstable and it is recommended to see a doctor.
舉例來說,在給定的6米步道上該使用者走了12步,因此評估去程走了6步,回程走了6步,將第3步(即去程的第3步)的壓力資訊計算而得的去程第3步之重心座標和第9步(即回程的第3步)的壓力資訊計算而得的回程第3步之重心座標取距離平方;另外將第4步(即去程的第4步)和第10步(回程的第4步)的壓力資訊計算而得的重心座標取距離平方。如下表所示:
當中先去掉前兩步與後兩步後的穩定速度的步數,且經計算後,去程中的第3步的重心座標為:Among them, the number of stable speed steps after the first two steps and the last two steps are removed first, and after calculation, the center of gravity coordinates of the third step in the going journey are:
回程中的第3步(即第9步)的重心座標為:The coordinates of the center of gravity of the third step (i.e., step 9) in the return journey are:
去程中的第4步的重心座標為:The coordinates of the center of gravity of the fourth step in the outbound journey are:
回程中的第4步(即第10步)的重心座標為:The coordinates of the center of gravity of the 4th step (that is, the 10th step) in the return journey are:
因此,該步態穩定性評估指標為:Therefore, the gait stability evaluation index is:
在另一較佳實施例中,該使用者來回走一給定的直線L米步道,經過壓力數據測量後,總共走了N步,扣除去程前兩步(開始加速)及停止前兩步(開始減速),只提取穩定速度的步數之計算而得的去程中的第n步的重心座標為,以及回程中的第n步的重心座標為,分別為一平面之二維座標,可得一步計算得一步態穩定性評估參數為:In another preferred embodiment, the user walks a given straight L-meter trail back and forth, and after pressure data measurement, a total of N steps are taken, deducting the first two steps of the outgoing journey (starting to accelerate) and the first two steps of stopping (Start deceleration), the center of gravity coordinates of the n-th step in the forward journey calculated by extracting only the number of steps of stable speed , And the coordinate of the center of gravity of the nth step in the return journey is , They are the two-dimensional coordinates of a plane, and the one-step stability evaluation parameters that can be calculated in one step are:
當中:among:
舉例來說,該使用者來回走一給定的直線12米步道,經過壓力數據測量後,總共走了12步,扣除去程前兩步(開始加速)及停止前兩步(開始減速),只提取穩定速度的步數,如下表所示:
將全部有效之步伐之壓力值帶入,估算該使用者之步態穩定性評估參數為:Bring in the pressure value of all effective steps , To estimate the user’s gait stability evaluation parameters for:
當中:among:
綜上所述,若該使用者在一給定L米步道上另外進一步透過該動態壓力感測系統量測該使用者的足底壓力之重心,量測方法為將使用者左腳和右腳的足底壓力訊號個別進行重心座標的計算,若該使用者的足底重心為內偏(也就是足底的重心座標比較靠近腳底內側),則相關人員再結合其他數據量測結果(例如有無扁平足之類問題)提出該使用者的鞋子選購方針,舉例來說,對於足底重心內偏的使用者建議選擇有支撐功能的鞋子,以用來減少足部或身體軀幹區域因為重心內偏而受傷的機率;對於足底重心外偏的使用者,建議選擇有避震功能的鞋子,以用來減少足部或身體軀幹區域因為重心外偏而受傷的機率。In summary, if the user further measures the center of gravity of the user’s plantar pressure through the dynamic pressure sensing system on a given L-meter trail, the measurement method is to measure the user’s left foot and right foot The plantar pressure signal is calculated separately. If the user’s plantar center of gravity is inward (that is, the plantar’s center of gravity is closer to the inner side of the foot), the relevant personnel will then combine the measurement results with other data (such as whether there is Flat feet and other issues) propose the user’s shoe purchase policy. For example, for users who have a deviated plantar center of gravity, it is recommended to choose supportive shoes to reduce the foot or body trunk area due to the deviated center of gravity. And the chance of injury; for users who have a deviated plantar center of gravity, it is recommended to choose shoes with shock-absorbing function to reduce the chance of injury to the foot or body trunk area due to the deviated center of gravity.
100:足底動態壓力感測系統20:壓力感測鞋墊21:壓力感測器22:傳輸線23:訊號收集器231:儲存單元232:無線單元30:訊號處理裝置31:個人終端應用程式40:雲端伺服器A:足跟區域B:足中區域C:足前區域:足跟區域壓力總和:足中區域壓力總和:足前區域壓力總和:右腳足部壓力總和:左腳足部壓力總和100: Plantar dynamic pressure sensing system 20: Pressure sensing insole 21: Pressure sensor 22: Transmission line 23: Signal collector 231: Storage unit 232: Wireless unit 30: Signal processing device 31: Personal terminal application 40: Cloud server A: heel area B: midfoot area C: forefoot area : Total pressure in the heel area : Sum of pressure in the midfoot area : The total pressure in the forefoot area : The total pressure of the right foot : The total pressure of the left foot
圖1:足底動態壓力感測系統架構圖。圖2:結合該足底動態壓力感測系統應用之鞋子的剖面示意圖。圖3:壓力感測墊結構圖。圖4:足底動態壓力感測系統運作示意圖。圖5:壓力感測墊之區域定義示意圖。Figure 1: Architecture diagram of the plantar dynamic pressure sensing system.Figure 2: A schematic cross-sectional view of a shoe combined with the sole dynamic pressure sensing system.Figure 3: Structure diagram of pressure sensing pad.Figure 4: Schematic diagram of the operation of the plantar dynamic pressure sensing system.Figure 5: Schematic diagram of the area definition of the pressure sensing pad.
100:足底動態壓力感測系統100: Plantar dynamic pressure sensing system
20:壓力感測墊20: Pressure sensing pad
21:壓力感測器21: Pressure sensor
22:傳輸線22: Transmission line
23:訊號收集器23: Signal Collector
30:訊號處理裝置30: Signal processing device
31:個人終端應用程式31: Personal terminal application
40:雲端伺服器40: Cloud server
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| TW108136668ATW202114595A (en) | 2019-10-09 | 2019-10-09 | Dynamic plantar pressure sensing system including a pressure sensing insole, a signal processing device and a cloud server |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| TW108136668ATW202114595A (en) | 2019-10-09 | 2019-10-09 | Dynamic plantar pressure sensing system including a pressure sensing insole, a signal processing device and a cloud server |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| TW202114595Atrue TW202114595A (en) | 2021-04-16 |
Family
ID=76604423
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| TW108136668ATW202114595A (en) | 2019-10-09 | 2019-10-09 | Dynamic plantar pressure sensing system including a pressure sensing insole, a signal processing device and a cloud server |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| TW (1) | TW202114595A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113907745A (en)* | 2021-10-15 | 2022-01-11 | 成都识康堂医疗科技有限公司 | System for resistance value conversion plantar pressure value |
| CN114010181A (en)* | 2021-10-15 | 2022-02-08 | 成都识康堂医疗科技有限公司 | Method and system for converting plantar pressure value through resistance value |
- 2019
- 2019-10-09TWTW108136668Apatent/TW202114595A/enunknown
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113907745A (en)* | 2021-10-15 | 2022-01-11 | 成都识康堂医疗科技有限公司 | System for resistance value conversion plantar pressure value |
| CN114010181A (en)* | 2021-10-15 | 2022-02-08 | 成都识康堂医疗科技有限公司 | Method and system for converting plantar pressure value through resistance value |
| CN113907745B (en)* | 2021-10-15 | 2024-01-16 | 成都识康堂医疗科技有限公司 | System for converting resistance value into plantar pressure value |
| CN114010181B (en)* | 2021-10-15 | 2024-01-16 | 成都识康堂医疗科技有限公司 | Method and system for converting resistance value into plantar pressure value |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US12230395B2 (en) | Sensor-equipped smartphone configured for connection to its user's footwear soles with sensors and structures configurable by the smartphone and for connection to a big data artificial intelligence computer system connected to millions of other smartphones controlling users' configurable footwear soles | |
| US10473483B2 (en) | Smart shoes, method of providing sensor information to smart shoes, smart device and method of providing guidance program via smart device | |
| US20170038747A1 (en) | Bladders, compartments, chambers or internal sipes controlled by a web-based cloud computer system using a smartphone device | |
| US11154243B2 (en) | Sensor systems for user-specific evaluation of gait, footwear and garment fitting; monitoring of contact, force, pressure and/or shear at or near body surfaces | |
| US20210145318A1 (en) | System for detecting a gait disorder of a user and associated methods | |
| TWI438018B (en) | Human lower limb mechanical behavior assessment system and method | |
| US9877523B2 (en) | Bladders, compartments, chambers or internal sipes controlled by a computer system using big data techniques and a smartphone device | |
| US20160349076A1 (en) | Nanopedometer | |
| KR102235926B1 (en) | Gait Analysis System Using Smart Insole | |
| CN102283467A (en) | Method and apparatus for customizing insoles for footwear | |
| KR101856077B1 (en) | Walking Calibrator Using Smart Insole | |
| US12029277B2 (en) | Insole with embedded sensing system | |
| Mann et al. | Reliability and validity of pressure and temporal parameters recorded using a pressure-sensitive insole during running | |
| JP2025063230A (en) | Multimodal Sensor Fusion Platform | |
| KR20220040967A (en) | Recording medium | |
| US11901072B2 (en) | Big data artificial intelligence computer system used for medical care connected to millions of sensor-equipped smartphones connected to their users' configurable footwear soles with sensors and to body sensors | |
| TW202114595A (en) | Dynamic plantar pressure sensing system including a pressure sensing insole, a signal processing device and a cloud server | |
| Buchecker et al. | The effect of different Masai Barefoot Technology (MBT) shoe models on postural balance, lower limb muscle activity and instability assessment | |
| US11567463B2 (en) | Smartphone-controlled active configuration of footwear, including with concavely rounded soles | |
| KR20220040337A (en) | System for providing foot health care service | |
| Zhang et al. | Automatic detection of fatigued gait patterns in older adults: an intelligent portable device integrating force and inertial measurements with machine learning | |
| TWM588789U (en) | Plantar dynamic pressure sensing system | |
| Penny et al. | Can an off-the-rack orthotic stiletto alter pressure and comfort scores in the forefoot, arch and heel? | |
| KR20220145130A (en) | Device and its operation method for providing foot health care O2O service | |
| US20240324714A1 (en) | Insole with Wireless Charging System |