RU2350361C2 - Method of left-sided additional pathways mapping - Google Patents
Method of left-sided additional pathways mappingDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2350361C2 RU2350361C2RU2006128023/14ARU2006128023ARU2350361C2RU 2350361 C2RU2350361 C2RU 2350361C2RU 2006128023/14 ARU2006128023/14 ARU 2006128023/14ARU 2006128023 ARU2006128023 ARU 2006128023ARU 2350361 C2RU2350361 C2RU 2350361C2
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- potential
- mapping
- during
- electrical stimulation
- electrode
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement And Recording Of Electrical Phenomena And Electrical Characteristics Of The Living Body (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromRussianИзобретение относится к медицине, а именно к аритмологии, кардиологии и кардиохирургии и предназначено для инвазивного лечения синдрома Вольфа-Паркинсона-Уайта (синдрома WPW).The invention relates to medicine, namely to arrhythmology, cardiology and cardiac surgery and is intended for invasive treatment of Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW syndrome).
Синдром WPW является причиной более 60% случаев пароксизмальных суправентрикулярных тахикардий у лиц молодого возраста и связан с функционированием дополнительных проводящих путей (ДПП), связывающих предсердный и желудочковый миокард на уровне правого (правосторонние ДПП) или левого (левосторонние ДПП) атриовентрикулярного кольца. Лечение данного заболевания направлено на устранение указанного пути в процессе катетерной внутрисердечной процедуры (катетерной аблации). Ее наиболее важным этапом является процесс картирования (обнаружения локализации) ДПП.WPW syndrome is the cause of more than 60% of cases of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in young people and is associated with the functioning of additional conduction pathways (DPP) connecting the atrial and ventricular myocardium at the level of the right (right-sided BPP) or left (left-sided BPP) atrioventricular ring. The treatment of this disease is aimed at eliminating the indicated path during the catheter intracardiac procedure (catheter ablation). Its most important stage is the process of mapping (locating) the DFS.
Известен способ картирования левосторонних дополнительных проводящих путей при помощи многополюсного электрода, введенного в просвет коронарного синуса, на основе обнаружения непрерывной электрической активности на уровне митрального кольца во время синусового ритма или суправентрикулярной тахикардии [1]. Через подключичную вену проводят многополюсный электрод, который устанавливают в коронарный синус. Для определения локализации ДПП одновременно регистрируют электрограмму со всех пар электрода во время предсердной и желудочковой электростимуляции с частотой, превышающей спонтанную, а также во время ортодромной тахикардии. При этом измеряют следующие интервалы:A known method of mapping left-side additional conductive paths using a multipolar electrode inserted into the lumen of the coronary sinus, based on the detection of continuous electrical activity at the level of the mitral ring during sinus rhythm or supraventricular tachycardia [1]. Through the subclavian vein, a multipolar electrode is inserted, which is installed in the coronary sinus. To determine the localization of the DPP, the electrogram from all pairs of the electrode is simultaneously recorded during atrial and ventricular electrical stimulation with a frequency exceeding spontaneous, as well as during orthodromic tachycardia. The following intervals are measured:
St-V - от спайка электростимулятора во время предсердной электростимуляции до начала желудочкового потенциала;St-V - from the adhesion of the electrical stimulator during atrial electrical stimulation to the onset of ventricular potential;
St-A - от спайка электростимулятора во время желудочковой электростимуляции до начала предсердного потенциала;St-A - from the spike of an electrical stimulator during ventricular electrical stimulation to the onset of atrial potential;
V-A - от начала желудочкового потенциала до начала предсердного потенциала во время ортодромной тахикардии.V-A - from the onset of ventricular potential to the onset of atrial potential during orthodromic tachycardia.
Электрограмма с наименьшим значением данных интервалов указывает пару полюсов электрода, где расположен ДПП и где необходимо выполнить аблацию.The electrogram with the smallest value of these intervals indicates the pair of poles of the electrode, where the DPP is located and where ablation is necessary.
Однако способ не лишен недостатков. В частности, наименьшие значения указанных интервалов могут быть обнаружены на нескольких парах. А феномен «непрерывной электрической активности» в области ДПП также затрудняет измерение интервалов до начала второго потенциала. Все это снижает точность определения левосторонних ДПП, а значит и его последующего хирургического устранения.However, the method is not without drawbacks. In particular, the smallest values of these intervals can be detected on several pairs. And the phenomenon of “continuous electrical activity” in the field of DFS also makes it difficult to measure the intervals to the beginning of the second potential. All this reduces the accuracy of determination of left-sided DPP, and hence its subsequent surgical elimination.
Целью данного изобретения является повышение точности картирования левосторонних дополнительных проводящих путей у пациентов с синдромом WPW, а значит повышение качества лечения данного заболевания.The aim of this invention is to improve the accuracy of mapping of left-side additional pathways in patients with WPW syndrome, and therefore improving the quality of treatment of this disease.
Поставленная цель достигается тем, что при картировании левосторонних ДПП при помощи многополюсного электрода, введенного в коронарный синус, ориентируются не на значения интервалов St-V, St-A, V-A, а на полярность второго потенциала каждого интервала.This goal is achieved by the fact that when mapping left-sided DCFs using a multipolar electrode inserted into the coronary sinus, they are oriented not on the values of the intervals St-V, St-A, V-A, but on the polarity of the second potential of each interval.
Способ осуществляется следующим образом:The method is as follows:
через подключичную вену проводят многополюсный электрод (не менее 6 полюсов) и устанавливают его в коронарный синус;through the subclavian vein conduct a multipolar electrode (at least 6 poles) and install it in the coronary sinus;
для определения локализации ДПП одновременно регистрируют биполярные электрограммы со всех пар электрода во время предсердной и желудочковой электростимуляции с частотой, превышающей спонтанную, а также во время ортодромной тахикардии;to determine the localization of the DPP, bipolar electrograms are simultaneously recorded from all electrode pairs during atrial and ventricular electrical stimulation with a frequency exceeding spontaneous, as well as during orthodromic tachycardia;
при этом анализируют форму и полярность следующих потенциалов:while analyzing the shape and polarity of the following potentials:
V - потенциал левого желудочка, анализируют во время предсердной электростимуляции и во время ортодромной тахикардии;V is the potential of the left ventricle, analyzed during atrial electrical stimulation and during orthodromic tachycardia;
А - потенциал левого предсердия, анализируют во время желудочковой электростимуляции;And - the potential of the left atrium, analyzed during ventricular electrical stimulation;
устанавливают две электрограммы, где произошла смена полярности указанных потенциалов (с «+» на «-», или наоборот);establish two electrograms where the polarity of the indicated potentials has changed (from “+” to “-”, or vice versa);
участок между полюсами, с которых регистрируют данные электрограммы, считают местом нахождения ДПП, где и производят радиочастотную аблацию.the area between the poles from which the electrogram data are recorded is considered the location of the DPP, where they perform radio frequency ablation.
Физиологическая сущность способа.The physiological essence of the method.
Коронарный (венечный) синус проходит в венечной борозде, огибая митральный клапан. Регистрируя электрограммы по его ходу, можно, таким образом, судить о возбуждении левопредсердного и левожелудочкового миокарда по периметру фиброзного кольца, где и располагаются ДПП. Дополнительный проводящий путь является электрическим «шунтом» между предсердным и желудочковым миокардом. При его функционировании происходит прорыв возбуждения из предсердия на желудочек или обратно, что проявляется в локальном возбуждении миокарда, которое затем распространяется по всей сердечной камере и по периметру митрального кольца в обе стороны от ДПП. Таким образом, образом произойдет изменение полярности потенциала, вызванного проведением по ДПП, на той паре электрода, которая соответствует расположению ДПП. И по одну сторону от этой пары полюса электрода будут возбуждаться с «+» на «-», а по другую - с «-» на «+».The coronary (coronary) sinus passes in the coronary sulcus, circling the mitral valve. By registering electrograms along its course, one can thus judge the excitation of the left atrial and left ventricular myocardium along the perimeter of the fibrous ring, where the DPP is located. The additional pathway is an electrical “shunt” between the atrial and ventricular myocardium. During its functioning, a breakthrough of excitation from the atrium to the ventricle or vice versa occurs, which manifests itself in local excitation of the myocardium, which then spreads throughout the cardiac chamber and along the perimeter of the mitral ring on both sides of the DPP. Thus, a change in the polarity of the potential caused by conducting along the DPP will occur on that pair of electrode that corresponds to the location of the DPP. And on one side of this pair of poles of the electrode will be excited from "+" to "-", and on the other - from "-" to "+".
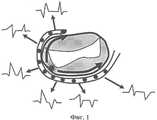
На фиг.1 схематично изображен митральный клапан и 12-полюсный электрод в коронарном синусе, огибающий клапан по его периметру. Схематично представлены шесть биполярных электрограмм с данного электрода, зарегистрированных во время ортодромной тахикардии (интервал V-A). Звездочкой указана область расположения ДПП, а стрелками в проекции клапана - направление распространения возбуждения вдоль электрода. Можно видеть, что потенциал А (второй потенциал исследуемого интервала) имеет положительную полярность на парах 1-3, начиная с кончика электрода, а затем меняет полярность на отрицательную в парах 4-6, начиная с кончика электрода. Это, в свою очередь, говорит о входе возбуждения в левое предсердие между 3 и 4 парами, то есть между 6 и 7 полюсом, начиная с кончика электрода, где и необходимо проводить аблацию.Figure 1 schematically shows the mitral valve and a 12-pole electrode in the coronary sinus, the envelope of the valve around its perimeter. Six bipolar electrograms from this electrode recorded during orthodromic tachycardia (interval V-A) are schematically presented. The asterisk indicates the location of the DPP, and the arrows in the projection of the valve indicate the direction of excitation propagation along the electrode. It can be seen that potential A (the second potential of the studied interval) has a positive polarity at pairs 1-3, starting at the tip of the electrode, and then changes polarity to negative at pairs 4-6, starting at the tip of the electrode. This, in turn, indicates the entry of excitation into the left atrium between 3 and 4 pairs, that is, between the 6 and 7 poles, starting from the tip of the electrode, where ablation is necessary.
С целью оценки эффективности указанного способа проведено сравнение двух групп пациентов с синдромом WPW, у которых картирование во время операции осуществлялось «стандартным» (группа I; n=34) или описанным нами (группа II; n=30) способом. Интраоперационный эффект получен у всех пациентов, однако для достижения эффекта были нанесены 2,9±0,5 аппликаций у больных первой группы и 1,6±0,3 аппликации у больных второй группы (p<0,01). Первая аппликация была эффективной у 12 пациентов (35,3%) первой группы и у 23 пациентов (76,7%) второй группы. Все это свидетельствует о большей точности картирования при использовании предложенного нами способа.In order to evaluate the effectiveness of this method, a comparison was made of two groups of patients with WPW syndrome, in whom the mapping during the operation was carried out using the “standard” (group I; n = 34) or the method described by us (group II; n = 30). An intraoperative effect was obtained in all patients, however, to achieve the effect, 2.9 ± 0.5 applications were applied in patients of the first group and 1.6 ± 0.3 applications in patients of the second group (p <0.01). The first application was effective in 12 patients (35.3%) of the first group and in 23 patients (76.7%) of the second group. All this indicates a greater accuracy of the mapping when using our proposed method.
Применение способа иллюстрируется следующим примером.The application of the method is illustrated by the following example.
Пример. Больной Щ-ко, 22 лет. В возрасте 15 лет появились приступы учащенного сердцебиения. По данным электрокардиограммы, зарегистрированной во время приступа, установлена пароксизмальная суправентрикулярная тахикардия, связанная с синдромом WPW, что стало показанием к проведению внутрисердечного электрофизиологического исследования (ЭФИ) и радиочастотной аблации. В процессе ЭФИ по стандартной методике подтвержден диагноз скрытого синдрома WPW, установлена левосторонняя локализация ДПП. Для картирования ДПП проведен анализ электрограмм коронарного синуса во время ортодромной тахикардии.Example. Patient Shchko, 22 years old. At the age of 15 years, attacks of rapid heartbeat appeared. According to the electrocardiogram recorded during the attack, a paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia associated with WPW syndrome was established, which became an indication for an intracardiac electrophysiological study (EPI) and radiofrequency ablation. In the process of EFI, the diagnosis of latent WPW syndrome was confirmed by a standard method, and left-sided localization of DPP was established. For the mapping of DPP, an analysis was made of the electrograms of the coronary sinus during orthodromic tachycardia.
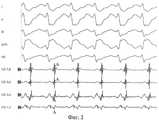
На фиг.2 представлен фрагмент картирования, где I, II, III, aVR, V6 - отведения поверхностной электрокардиограммы, CS - электрограммы с 8-полюсного электрода в коронарном синусе. Буквой «А» обозначен потенциал левого предсердия как второй потенциал интервала V-A. При анализе электрограмм по ходу коронарного синуса обращает на себя внимание, что в отведениях CS7-8 и CS5-6 данный потенциал преимущественно положительный, а в отведениях CS3-4 и CS1-2 - преимущественно отрицательный. То есть смена полярности произошла на участке между 4 и 5 полюсом, где аблация и была эффективна с первой аппликации. В то же время наименьший интервал V-A наблюдался в отведениях CS3-4 и CS1-2, где он составил соответственно по 86 мс. Однако аблация на этих парах, согласно способу-прототипу, не принесла эффекта.Figure 2 presents a fragment of the mapping, where I, II, III, aVR, V6 are the leads of the surface electrocardiogram, CS is the electrogram from the 8-pole electrode in the coronary sinus. The letter “A” designates the potential of the left atrium as the second potential of the V-A interval. When analyzing electrograms along the coronary sinus, it is noteworthy that in potentials CS7-8 and CS5-6 this potential is mostly positive, and in leads CS3-4 and CS1-2 it is mostly negative. That is, a change in polarity occurred in the area between the 4th and 5th poles, where ablation was effective from the first application. At the same time, the smallest V-A interval was observed in leads CS3-4 and CS1-2, where it was 86 ms, respectively. However, ablation on these pairs, according to the prototype method, did not bring effect.
Таким образом, предложенный нами способ позволил уточнить местонахождение ДПП в ситуации, когда «классический» способ картирования указывал неверное местоположение ДПП.Thus, our proposed method made it possible to clarify the location of the DPP in a situation where the “classic” mapping method indicated the incorrect location of the DPP.
Предложенный способ прост в применении, характеризуется высокой точностью картирования ДПП. Способ может быть использован в любом Центре, выполняющем катетерные аблации.The proposed method is easy to use, characterized by high accuracy mapping of the DPP. The method can be used in any Center performing catheter ablation.
ЛитератураLiterature
1. Л.А.Бокерия, А.Ш.Ревишвили «Катетерная аблация аритмий у пациентов детского и юношеского возраста». М.: Изд-во НЦССХ им. А.Н.Бакулева РАМН, 1999, с.15-17, 34-37.1. L.A. Bokeria, A.Sh. Revishvili "Catheter ablation of arrhythmias in patients of childhood and adolescence." M.: Publishing House of the National Center for Contemporary Arts named after A.N. Bakuleva RAMS, 1999, p. 15-17, 34-37.
Claims (1)
Translated fromRussianPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2006128023/14ARU2350361C2 (en) | 2006-08-01 | 2006-08-01 | Method of left-sided additional pathways mapping |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2006128023/14ARU2350361C2 (en) | 2006-08-01 | 2006-08-01 | Method of left-sided additional pathways mapping |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2006128023A RU2006128023A (en) | 2008-02-10 |
| RU2350361C2true RU2350361C2 (en) | 2009-03-27 |
Family
ID=39265878
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2006128023/14ARU2350361C2 (en) | 2006-08-01 | 2006-08-01 | Method of left-sided additional pathways mapping |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2350361C2 (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2397718C1 (en)* | 2009-04-22 | 2010-08-27 | Учреждение Российской академии медицинских наук Научно-исследовательский институт кардиологии Сибирского отделения РАМН | Method of preparation patients with coronary heart disease with postinfarction left ventricular aneurysm and ventricular tachycardias for surgery of aneurysmectomy with endocardectomy |
| RU2414176C1 (en)* | 2009-11-05 | 2011-03-20 | Государственное образовательное учреждение Высшего профессионального образования "Омская государственная медицинская академия Федерального агентства по здравоохранению и социальному развитию Росздрава" | Method of bipolar radio-frequency ablation in left auricle during operations on open heart |
| RU2417732C2 (en)* | 2006-10-10 | 2011-05-10 | Байосенс Уэбстер, Инк. | Oesophageal mapping catheter |
| RU2438569C1 (en)* | 2010-06-30 | 2012-01-10 | Учреждение Российской академии медицинских наук Научно-исследовательский институт комплексных проблем сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний Сибирского отделения Российской академии медицинских наук (УРАМН НИИ КПССЗ СО РАМН) | Method of radiofrequency catheter ablation of left-side additional paths of atrioventricular passage |
| RU2538177C2 (en)* | 2009-04-08 | 2015-01-10 | Конинклейке Филипс Электроникс Н.В. | Pulmonary congestion control system and method |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2092104C1 (en)* | 1995-01-13 | 1997-10-10 | Научный центр сердечно-сосудистой хирургии РАМН | Method of noninvasive diagnosis of arhythmogenic zone at wolff-parkinson-white syndrome |
| US5722416A (en)* | 1995-02-17 | 1998-03-03 | Ep Technologies, Inc. | Systems and methods for analyzing biopotential morphologies in heart tissue to locate potential ablation sites |
| RU2268640C2 (en)* | 2004-02-24 | 2006-01-27 | Валерий Николаевич Бакуцкий | Method for localizing additional conducting paths in wolff-parkinson-white syndrome cases using vector electrocardiograms |
- 2006
- 2006-08-01RURU2006128023/14Apatent/RU2350361C2/ennot_activeIP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2092104C1 (en)* | 1995-01-13 | 1997-10-10 | Научный центр сердечно-сосудистой хирургии РАМН | Method of noninvasive diagnosis of arhythmogenic zone at wolff-parkinson-white syndrome |
| US5722416A (en)* | 1995-02-17 | 1998-03-03 | Ep Technologies, Inc. | Systems and methods for analyzing biopotential morphologies in heart tissue to locate potential ablation sites |
| RU2268640C2 (en)* | 2004-02-24 | 2006-01-27 | Валерий Николаевич Бакуцкий | Method for localizing additional conducting paths in wolff-parkinson-white syndrome cases using vector electrocardiograms |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| БОКЕРИЯ Л.А. РЕВИШВИЛИ А.Ш. Катетерная аблация аритмий у пациентов детского и юношеского возраста. - М.: издательство НЦССХ им. А.Н.Бакулева, 1999, с.15-17, 34-37.* |
| САЙГАНОВ С.А., ГРИШИН Ю.Н. Роль дополнительных проводящих путей в развитии фибрилляции предсердий у больных с синдромом Вольфа-Паркинсона-Уайта. Вестник аритмологии, 1998, №9, с.32-34.* |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2417732C2 (en)* | 2006-10-10 | 2011-05-10 | Байосенс Уэбстер, Инк. | Oesophageal mapping catheter |
| RU2538177C2 (en)* | 2009-04-08 | 2015-01-10 | Конинклейке Филипс Электроникс Н.В. | Pulmonary congestion control system and method |
| RU2397718C1 (en)* | 2009-04-22 | 2010-08-27 | Учреждение Российской академии медицинских наук Научно-исследовательский институт кардиологии Сибирского отделения РАМН | Method of preparation patients with coronary heart disease with postinfarction left ventricular aneurysm and ventricular tachycardias for surgery of aneurysmectomy with endocardectomy |
| RU2414176C1 (en)* | 2009-11-05 | 2011-03-20 | Государственное образовательное учреждение Высшего профессионального образования "Омская государственная медицинская академия Федерального агентства по здравоохранению и социальному развитию Росздрава" | Method of bipolar radio-frequency ablation in left auricle during operations on open heart |
| RU2438569C1 (en)* | 2010-06-30 | 2012-01-10 | Учреждение Российской академии медицинских наук Научно-исследовательский институт комплексных проблем сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний Сибирского отделения Российской академии медицинских наук (УРАМН НИИ КПССЗ СО РАМН) | Method of radiofrequency catheter ablation of left-side additional paths of atrioventricular passage |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| RU2006128023A (en) | 2008-02-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Guo et al. | Short‐term and intermediate‐term performance and safety of left bundle branch pacing | |
| US8239019B2 (en) | Implantable device for cardiac vector determination | |
| Nogami et al. | Changes in the isolated delayed component as an endpoint of catheter ablation in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: predictor for long‐term success | |
| Dunbar et al. | Intracavitary electrode catheter cardioversion of atrial tachyarrhythmias in the dog | |
| RU2350361C2 (en) | Method of left-sided additional pathways mapping | |
| Refaat et al. | Electrocardiographic characteristics in right ventricular vs biventricular pacing in patients with paced right bundle-branch block QRS pattern | |
| Pang et al. | Capturing the His‐Purkinje system is not possible from conventional right ventricular apical and nonapical pacing sites | |
| Silka et al. | Assessment and follow-up of pediatric survivors of sudden cardiac death. | |
| Gula et al. | Reduction in atrial flutter ablation time by targeting maximum voltage: results of a prospective randomized clinical trial | |
| Bashir et al. | Radiofrequency ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways: predictive value of local electrogram characteristics for the identification of successful target sites. | |
| Bashir et al. | Radiofrequency current delivery by way of a bipolar tricuspid annuls-mitral annulus electrode configuration for ablation of posteroseptal accessory pathways | |
| Da Costa et al. | Anatomic and electrophysiological differences between chronic and paroxysmal forms of common atrial flutter and comparison with controls: an observational study | |
| Zhang et al. | Common and distinctive electrocardiographic characteristics and effective catheter ablation of idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias originating from different areas of ventricular septum adjacent to atrioventricular annulus | |
| Tokuda et al. | Characteristics of clinical and induced ventricular tachycardia throughout multiple ablation procedures | |
| US8880160B2 (en) | Optimization of LV and RV lead placement based on electrical delays | |
| Wiles et al. | Contemporary management of complex ventricular arrhythmias | |
| US10350419B2 (en) | Supraventricular tachy sensing vector | |
| Chen et al. | Serial electrophysiological studies in the late outcome of radiofrequency ablation for accessory atrioventricular pathway-mediated tachyarrhythmias | |
| Wang et al. | Reflections on the early invasive clinical cardiac electrophysiology era through fifty manuscripts: 1967–1992 | |
| Miyauchi et al. | Successful radiofrequency catheter ablation of an anteroseptal (superoparaseptal) atrioventricular accessory pathway from the left ventricular outflow tract | |
| RU2438569C1 (en) | Method of radiofrequency catheter ablation of left-side additional paths of atrioventricular passage | |
| RU2354421C2 (en) | Method of additional conducting tracts mapping | |
| Kawamura et al. | Characteristics of ventricular intracardiac electrograms of ventricular tachycardias originating from the epicardia in patients with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator | |
| Marenco et al. | Testing of a New T‐Wave Subtraction Algorithm as an Aid to Localizing Ectopic Atrial Beats | |
| Verbeet et al. | Transesophageal pacing: a versatile diagnostic and therapeutic tool |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees | Effective date:20090802 |