RU2319310C2 - Method for dynamic distribution of bandwidth of communication line on dynamic packet ring - Google Patents
Method for dynamic distribution of bandwidth of communication line on dynamic packet ringDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2319310C2 RU2319310C2RU2005124510/09ARU2005124510ARU2319310C2RU 2319310 C2RU2319310 C2RU 2319310C2RU 2005124510/09 ARU2005124510/09 ARU 2005124510/09ARU 2005124510 ARU2005124510 ARU 2005124510ARU 2319310 C2RU2319310 C2RU 2319310C2
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- rate
- local
- idle
- fair
- acc
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Small-Scale Networks (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromRussianОбласть техники, к которой относится изобретениеFIELD OF THE INVENTION
Изобретение относится к технологии передачи данных, используемой в Глобальной сети связи (ГС, WAN) или в локальной сети связи (ЛС, LAN), более конкретно к способу динамического распределения полосы пропускания линии связи на Динамическом Пакетном Кольце (ДПК, RPR).The invention relates to data transmission technology used in a global communication network (WAN, WAN) or in a local area network (LAN), and more particularly, to a method for dynamically allocating bandwidth of a communication line on a Dynamic Packet Ring (DPR, RPR).
Уровень техникиState of the art
RPR является региональной сетью связи (РСС, MAN) с совершенно новой кольцевой структурой, которая поддерживает трафик данных для трех уровней обслуживания и имеет преимущества большего использования полосы пропускания, высокой надежности и так далее. В одном из ключевых способов для реализации RPR полосу пропускания линии связи распределяют узлам, конкурирующим за ресурсы на кольце. В настоящем изобретении раскрыт способ, в котором полосу пропускания на динамическом пакетном кольце распределяют динамически. По сравнению с решением, предложенным существующей рабочей группой PRP (рабочей группой IEEE 802.17), указанный способ является более простым и обладает бóльшим использованием полосы пропускания. Задачей рабочей группы IEEE 802.17 является установление технического стандарта для RPR. Технология RPR используется при передаче данных в WAN или LAN и имеет два очевидных преимущества по сравнению с существующей технологией передачи данных, используемой в WAN или LAN:RPR is a regional communications network (RCC, MAN) with a completely new ring structure that supports data traffic for three levels of service and has the advantages of more bandwidth, high reliability and so on. In one of the key ways to implement RPR, the bandwidth of the communication line is allocated to nodes competing for resources on the ring. The present invention discloses a method in which the bandwidth on a dynamic packet ring is dynamically allocated. Compared to the solution proposed by the existing PRP working group (IEEE 802.17 working group), this method is simpler and has more bandwidth. The task of the IEEE 802.17 working group is to establish a technical standard for RPR. RPR technology is used when transferring data to a WAN or LAN and has two obvious advantages over the existing data transfer technology used in a WAN or LAN:
1) большее использование полосы пропускания;1) greater use of bandwidth;
2) высокоскоростной механизм защиты. Защита срабатывает в пределах 50 мс, что соответствует уровню обнаружения сбоя.2) high speed protection mechanism. Protection is triggered within 50 ms, which corresponds to the level of failure detection.
Каждый узел на кольце RPR может ввести на кольцо некоторый пакет, имеющий право на равноправие (равноправный пакет). При добавлении пакета данных на кольцо он будет передаваться узлами нижнего уровня. В продолжение этого процесса узел верхнего уровня может передавать слишком большой трафик, "подавляя" узлы нижнего уровня. Следовательно, требуется механизм для обеспечения каждому узлу на кольце одинаковой возможности передавать пакеты данных пользователя.Each node on the RPR ring can introduce a packet that has the right to equality (equal packet) onto the ring. When a data packet is added to a ring, it will be transmitted by lower-level nodes. During this process, the top-level node may transmit too much traffic, "suppressing" the lower-level nodes. Therefore, a mechanism is required to provide each node on the ring with the same ability to transmit user data packets.
В механизме, предложенном рабочей группой IEEE 802.17, каждый узел должен передавать специальный пакет, называемый пакетом равноправия, который используется для передачи предложенной извещаемой интенсивности потока в узел верхнего уровня.In the mechanism proposed by the IEEE 802.17 working group, each node must transmit a special packet, called an equality packet, which is used to transmit the proposed notified flow rate to the upper level node.
Для обеспечения каждому узлу на кольце определенной возможности передавать свои пакеты каждый узел должен удостовериться, что количество равноправных пакетов, добавляемых на кольцо, не превышает дозволенной интенсивности, которая является наименьшей из принятой извещаемой интенсивности и локальной справедливой интенсивности.In order to provide each node on the ring with a certain opportunity to transmit its packets, each node must make sure that the number of peer packets added to the ring does not exceed the allowed intensity, which is the smallest of the received notified intensity and local fair intensity.
Ключевой момент обеспечения эффективности сети основан на том, как определить извещаемую интенсивность на основе извещаемой интенсивности, принятой из узла нижнего уровня, и локальной справедливой интенсивности. Кратко будет описан механизм, предложенный рабочей группой IEEE 802.17.The key to ensuring network efficiency is based on how to determine the notified intensity based on the notified intensity received from the lower level node and local fair intensity. The mechanism proposed by the IEEE 802.17 working group will be briefly described.
В настоящее время существует два режима равноправия (справедливого распределения ресурсов), предложенных рабочей группой IEEE 802.17, один называется агрессивным режимом, другой называется консервативным режимом.Currently, there are two modes of equality (equitable distribution of resources) proposed by the IEEE 802.17 working group, one is called aggressive mode, the other is called conservative mode.
Здесь обсуждается только вариант без взвешивания существующего алгоритма равноправия, предложенного IEEE 802.17. Следует отметить, что способ динамического распределения полосы пропускания линии связи на динамическом пакетном кольце, предложенный в данной заявке на патент, является алгоритмом равноправия с взвешиванием.Here, only the option without weighting the existing equality algorithm proposed by IEEE 802.17 is discussed. It should be noted that the method for dynamically allocating the bandwidth of a communication line on a dynamic packet ring, proposed in this patent application, is an equal weighting algorithm.
Существующий алгоритм равноправия описывается:The existing equality algorithm is described:
добавочной интенсивностью (add_rate): это количество байтов в интервал извещения для локальных пакетов, добавленных на кольцо узлом, для равноправных (Р, FE) пакетов;additional intensity (add_rate): this is the number of bytes in the notification interval for local packets added to the ring by the node, for peer (P, FE) packets;
локальной справедливой интенсивностью (local_fair_rate): добавочная интенсивность, фильтрованная фильтром нижних частот, различные режимы используют различные алгоритмы для получения local_fair_rate;local fair intensity (local_fair_rate): incremental intensity filtered by low-pass filter; different modes use different algorithms to get local_fair_rate;
принимаемой извещаемой интенсивностью (received_advertising_rate): извещаемая интенсивность, переносимая в пакете равноправия типа A, извещается узлом нижнего уровня;Received Noticeable Intensity (received_advertising_rate): Noticeable intensity carried in the Type A equal package is notified by a lower level node;
интервалом извещения: на каждом интервале извещения станциям верхнего уровня должен передаваться пакет равноправия типа A с advertising_rate внутри сообщения равноправия типа A;notification interval: at each notification interval, top-level stations should receive a type A equality packet with advertising_rate inside the type A equality message;
извещаемой интенсивностью: интенсивность определяетсяNotified Intensity: Intensity is determined
Если (локальный узел перегружен и local_fair_rate<received_advertising_rate), то advertising_rate будет local_fair_rate, которая является фильтрованным вариантом add_rate. Add_rate является количеством байтов внутри Интервала извещения для пакетов с установленным битом FE (битом наличия права на равноправность). Received_advertising_rate является интенсивностью, которая переносится внутри сообщения равноправия типа A.If (the local node is overloaded and local_fair_rate <received_advertising_rate), then advertising_rate will be local_fair_rate, which is a filtered version of add_rate. Add_rate is the number of bytes within the Notification Interval for packets with the FE bit set (the bit of the presence of an equal right). Received_advertising_rate is the intensity that is carried inside the type A equality message.
Если (локальный узел перегружен и local_fair_rate>=received_advertising_rate) имеет место перегрузка, то advertising_rate будет принятая извещаемая интенсивность с нижнего уровня (received_advertising_rate).If (the local node is overloaded and local_fair_rate> = received_advertising_rate) there is congestion, then advertising_rate will be the received notified intensity from the lower level (received_advertising_rate).
Если (локальный узел не перегружен), то advertising_rate будет принятая с нижнего уровня или нуль при приеме нулевой интенсивности, которая указывает максимальную интенсивность линии связи.If (the local node is not overloaded), then advertising_rate will be received from the lower level or zero when receiving zero intensity, which indicates the maximum intensity of the communication line.
Наряду с некоторыми незначительными различиями, основное различие между агрессивным режимом и консервативным режимом основано на том, как определять local_fair_rate. В агрессивном режиме local_fair_rate является вариантом add_rate, фильтрованным фильтром нижних частот. В консервативном режиме local_fair_rate является вариантом add_rate, фильтрованным фильтром нижних частот, что подобно агрессивному режиму, иAlong with some minor differences, the main difference between aggressive mode and conservative mode is based on how to define local_fair_rate. In aggressive mode, local_fair_rate is an add_rate option, filtered by a low-pass filter. In conservative mode, local_fair_rate is an add_rate option, filtered by a low-pass filter, which is similar to aggressive mode, and
- плюс часть фильтрованного варианта add_rate, если использование линии связи составляет менее 85% (ниже low_threshold)- plus part of the filtered add_rate option if the link utilization is less than 85% (below low_threshold)
- минус часть фильтрованного варианта add_rate, если использование линии связи составляет более 95% (выше high_threshold)- minus part of the filtered add_rate option if the use of the communication line is more than 95% (higher than high_threshold)
По сравнению с алгоритмом равноправия в агрессивном режиме алгоритм равноправия в консервативном режиме предлагает более высокую эффективность при изменяющихся условиях за счет максимум 95%-ного использования полосы пропускания, что в некоторых ситуациях является худшим.Compared to the Equal Algorithm in aggressive mode, the Equal Algorithm in the conservative mode offers higher efficiency under changing conditions due to a maximum of 95% bandwidth utilization, which is worse in some situations.
Основная проблема в отношении агрессивного режима возникает, когда точкой перегрузки не является поглощающий (жадный) источник, как иллюстрируется фиг.1, при этом невозможно корректно распределить полосу пропускания среди всех источников, и это приводит к неэффективному использованию ресурса, как иллюстрируется моделированием фиг.2.The main problem with respect to the aggressive mode occurs when the overload point is not an absorbing (greedy) source, as illustrated in FIG. 1, while it is not possible to correctly allocate the bandwidth among all sources, and this leads to inefficient use of the resource, as illustrated by the modeling of FIG. 2 .
Раскрытие изобретенияDisclosure of invention
Согласно раскрытию изобретения, основной проблемой в отношении алгоритма равноправия в агрессивном режиме является устойчивость распределения полосы пропускания, когда не поглощающий источник смешивается с поглощающим источником, что ведет к потерям в полосе пропускания. Основной проблемой в отношении алгоритма равноправия в консервативном режиме является максимум 95% использование полосы пропускания, что ведет к худшей эффективности, когда все источники являются поглощающими источниками.According to the disclosure of the invention, the main problem with respect to the aggressive equality algorithm is the stability of the bandwidth allocation when the non-absorbing source is mixed with the absorbing source, which leads to losses in the passband. The main problem with the conservative equality algorithm is a maximum of 95% bandwidth utilization, which leads to worse efficiency when all sources are absorbing sources.
Задачей настоящего изобретения является обеспечение способа динамического распределения полосы пропускания линии связи на динамическом пакетном кольце, которое может обеспечить равноправие в распределении полосы пропускания. Он должен быть более простым и давать большее использование полосы пропускания, чем существующий алгоритм равноправия в проектах стандарта 802.17.An object of the present invention is to provide a method for dynamically allocating a bandwidth of a communication line on a dynamic packet ring, which can ensure equal distribution of bandwidth. It should be simpler and give greater use of bandwidth than the existing equal rights algorithm in 802.17 standard projects.
Способ динамического распределения полосы пропускания линии связи на динамическом пакетном кольце для согласованности поддерживает базовую структуру и тип сообщения, определенные рабочей группой IEEE 802.17. Используется концепция интервала извещения. Внутри одного интервала извещения выполняются этапы, на которыхA method for dynamically allocating link bandwidth on a dynamic packet ring for consistency supports the basic structure and message type defined by the IEEE 802.17 working group. The concept of a notification interval is used. Within the same notification interval, the steps are performed in which
a. Измеряют значения для переменныхa. Measures Values for Variables
1) add_rate: является количеством байтов для локальных пакетов, добавленных на кольцо узлом, для равноправных пакетов;1) add_rate: is the number of bytes for local packets added to the ring by the node, for peer packets;
2) total_add_rate: является общим количеством байтов для локальных пакетов, добавленных на кольцо узлом;2) total_add_rate: is the total number of bytes for local packets added to the ring by the node;
3) fw_rate: является количеством байтов для транзитных пакетов на кольце, для равноправных пакетов;3) fw_rate: is the number of bytes for transit packets on the ring, for peer packets;
4) total_fw_rate: является общим количеством байтов для транзитных пакетов на кольце.4) total_fw_rate: is the total number of bytes for transit packets on the ring.
b. Задачей способа динамического распределения полосы пропускания связи на динамическом пакетном кольце является обеспечение полного использования линии связи наряду с корректным распределением полосы пропускания между всеми конкурирующими станциями. Для достижения этого local_fair_rate всегда вычисляют согласно этапам, на которыхb. The objective of the method of dynamic allocation of communication bandwidth on a dynamic packet ring is to ensure full use of the communication line along with the correct distribution of bandwidth between all competing stations. To achieve this, local_fair_rate is always calculated according to the steps in which
b1. Вычисляют свободную интенсивность (idle_rate) уравнением:b1. The free intensity (idle_rate) is calculated by the equation:
idle_rate=link_rate-total_add_rate-total_fw_rate,idle_rate = link_rate-total_add_rate-total_fw_rate,
где link_rate является количеством байтов на один интервал извещения при полной интенсивности линии связи.where link_rate is the number of bytes per notification interval at full link intensity.
b2. Если idle_rate<idle_rate_threshold (idle_rate_threshold могут установить в 0,01 или даже ниже):b2. If idle_rate <idle_rate_threshold (idle_rate_threshold can be set to 0.01 or even lower):
acc_idle=(α-1)*acc_idle/α,acc_idle = (α-1) * acc_idle / α,
иначеotherwise
acc_idle=acc_idle+idle_rate/βacc_idle = acc_idle + idle_rate / β
acc_idle=min(acc_idle, unreserved_rate),acc_idle = min (acc_idle, unreserved_rate),
где acc_idle, в основном, является интегралом свободной интенсивности и его значение не превышает незарезервированную интенсивность (unreserved_rate).where acc_idle is basically an integral of free intensity and its value does not exceed unreserved intensity (unreserved_rate).
b3. Вычисляют локальную справедливую интенсивность (local_fair_rate) по формуле:b3. The local fair intensity (local_fair_rate) is calculated by the formula:
local_fair_rate=(δ-1)*local_fair_rate/δ+add_rate(δ* weight)+acc_idle/δ,local_fair_rate = (δ-1) * local_fair_rate / δ + add_rate (δ * weight) + acc_idle / δ,
где weight является весом станции для алгоритма равноправия с взвешиванием.where weight is the station weight for the weighting algorithm.
c. Определение извещаемой интенсивности (advertising_rate) включает этапы, на которыхc. The definition of the advertised intensity (advertising_rate) includes the steps in which
с1. Если значение принятой извещаемой интенсивности меньше значения локальной справедливой интенсивности (то есть received_advertising_rate<local_fair_rate), то значение извещаемой интенсивности (advertising_rate) устанавливают в значение принятой извещаемой интенсивности (received_advertising_rate).c1. If the value of the received notified intensity is less than the value of the local fair intensity (i.e., received_advertising_rate <local_fair_rate), then the value of the notified intensity (advertising_rate) is set to the value of the received notified intensity (received_advertising_rate).
с2. Если (fw_rate<local_fair_rate), то извещаемую интенсивность (advertising_rate) устанавливают в локальную справедливую интенсивность (local_fair_rate). Это подобно существующему алгоритму для обработки разделения точек затора алгоритмом единственной точки затора.c2. If (fw_rate <local_fair_rate), then the advertised intensity (advertising_rate) is set to the local fair intensity (local_fair_rate). This is similar to the existing algorithm for handling mash point separation by a single mash point algorithm.
с3. Если (add_rate>минимального размера пакета) или в очереди с более низким приоритетом существуют пакеты для передачи, то извещаемую интенсивность (advertising_rate) устанавливают в локальную справедливую интенсивность (local_fair_rate).c3. If (add_rate> minimum packet size) or in a queue with a lower priority there are packets for transmission, then the advertised intensity (advertising_rate) is set to local fair intensity (local_fair_rate).
с4. Иначе извещаемую интенсивность (advertising_rate) устанавливают в принятую извещаемую интенсивность (received_advertising_rate).c4. Otherwise, the notified intensity (advertising_rate) is set to the received notified intensity (received_advertising_rate).
d. Для обеспечения справедливого совместного использования кольца полосы пропускания каждый узел на кольце RPR передает пакеты данных с интенсивностью, не большей, чем извещаемая интенсивность, определенная на третьем этапе.d. To ensure fair sharing of the bandwidth ring, each node on the RPR ring transmits data packets with an intensity not greater than the notified intensity determined in the third stage.
По сравнению с существующим алгоритмом равноправия в проекте стандарта 802.17 способ динамического распределения полосы пропускания линии связи на динамическом пакетном кольце в этом изобретении вводит интеграл для свободной интенсивности, чтобы получить 100%-ное использование полосы пропускания. (В большинстве случаев из-за правил извещения для local_fair_rate при практическом осуществлении только одна линия связи может достигнуть указанных 100%.) Новый алгоритм также исключает концепцию "состояния перегрузки", имеющуюся в существующих алгоритмах равноправия. Новый алгоритм в этом изобретении имеет следующие преимущества:Compared to the existing fairness algorithm in the draft 802.17 standard, the method for dynamically allocating a link bandwidth on a dynamic packet ring in this invention introduces an integral for the free intensity to obtain 100% bandwidth utilization. (In most cases, due to the notification rules for local_fair_rate, in practice, only one communication line can reach the indicated 100%.) The new algorithm also eliminates the concept of "congestion state" that exists in existing equality algorithms. The new algorithm in this invention has the following advantages:
Философское преимущество:Philosophical advantage:
1. В существующем алгоритме равноправия делается попытка получить справедливое распределение полосы пропускания между всеми конкурирующими станциями, только когда некоторые узлы находятся в "состоянии перегрузки".1. In the existing equal rights algorithm, an attempt is made to obtain a fair distribution of bandwidth between all competing stations only when some nodes are in an "overload state".
2. В способе динамического распределения полосы пропускания линии связи на динамическом пакетном кольце делается попытка обеспечить 100%-ное использование линии связи на каждом сегменте. В большинстве случаев для алгоритма равноправия единственной точки затора только одна линия связи может достигнуть такого использования линии связи, что также является одной из задач алгоритма равноправия.2. In the method of dynamically allocating bandwidth of a communication line on a dynamic packet ring, an attempt is made to ensure 100% utilization of the communication line on each segment. In most cases, for a single point congestion equality algorithm, only one communication line can achieve such use of the communication line, which is also one of the tasks of the equality algorithm.
Алгоритмическое преимущество:Algorithmic advantage:
1. Состояние перегрузки: В существующем подходе каждая станция извещает "нуль", указывающий максимальную полосу пропускания, если на кольце отсутствуют точки перегрузки. Станция извещает ненулевое значение, только если она находится в состоянии перегрузки или принимает извещение с ненулевым значением. В новом подходе концепция "состояния перегрузки" отсутствует и каждая станция должна осуществлять извещение согласно алгоритму, приведенному выше, что существенно уменьшает сложность алгоритма.1. Congestion status: In the existing approach, each station announces a “zero” indicating the maximum bandwidth if there are no congestion points on the ring. A station notifies a nonzero value only if it is in an overload condition or receives a notification with a nonzero value. In the new approach, the concept of an “overload state” is absent and each station should carry out a notification according to the algorithm given above, which significantly reduces the complexity of the algorithm.
2. Измерение свободной интенсивности: Задача такого измерения состоит в обеспечении 100%-ного использования полосы пропускания линии связи. Интегральный (подобный функции И контроллера PID (Пропорционального, Интегрального, Дифференциального) в теории управления) вариант свободной интенсивности способствует local_fair_rate. При существующем подходе требуется осуществлять измерение большого количества другой информации, которая не будет требоваться при новом подходе.2. Measurement of free intensity: The objective of this measurement is to ensure 100% utilization of the bandwidth of the communication line. Integral (similar to the function AND controller PID (Proportional, Integral, Differential) in control theory) the free-intensity option contributes to local_fair_rate. With the existing approach, it is necessary to measure a large amount of other information that would not be required with the new approach.
3. Извещаемая интенсивность: Определение advertising_rate является различным. При новом подходе станция RPR должна извещать свою local_fair_rate, если станция передает какой-либо пакет или если существует какой-либо пакет, ожидающий передачи, ограничения на local_fair_rate, меньшую,чем received_advertising_rate (правило c3 выше).3. Notified intensity: The definition of advertising_rate is different. With the new approach RPR station should notify its local_fair_rate, if the station transmits a packet, or if there is a packet awaiting transmission, restriction on local_fair_rate, lessthan received_advertising_rate (typically c3 above).
4. Локальная справедливая интенсивность (local_fair_rate): Механизм вычисления для получения local_fair_rate полностью различен в существующем алгоритме равноправия и в настоящем изобретении.4. Local fair intensity (local_fair_rate): The calculation mechanism for obtaining local_fair_rate is completely different in the existing equality algorithm and in the present invention.
Краткое описание чертежейBrief Description of the Drawings
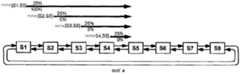
Фиг.1 изображает сценарий равноправия не поглощающего и поглощающего источников, совместно использующих полосу пропускания линии связи. (Подробный возможный вариант, как и затора пар высокой/низкой полосы пропускания в Приложении I.3.7 к проекту 2.4 IEEE 802.17.)Figure 1 depicts a scenario of equality of non-absorbing and absorbing sources sharing bandwidth of the communication line. (A detailed possible option, as well as congestion of high / low bandwidth pairs in Appendix I.3.7 to IEEE 802.17 draft 2.4.)
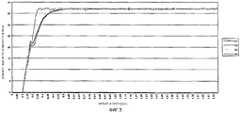
Фиг.2 - результат моделирования возможного варианта фиг.1 при использовании агрессивного режима существующего алгоритма равноправия.FIG. 2 is a simulation result of a possible embodiment of FIG. 1 when using the aggressive mode of the existing equality algorithm.
Фиг.3 - результат моделирования возможного варианта фиг.1 при использовании консервативного режима существующего алгоритма равноправия.FIG. 3 is a simulation result of a possible embodiment of FIG. 1 when using the conservative mode of the existing equality algorithm.
Фиг.4 изображает сценарий равноправия с четырьмя источниками, запрашивающими передачу пакетов FE (см. возможный вариант автостоянки, подробно описанный в Приложении I.3.1 к проекту 2.4 IEEE 802.17).FIG. 4 depicts an equality scenario with four sources requesting the transmission of FE packets (see a possible parking option described in detail in Appendix I.3.1 to IEEE 802.17 Project 2.4).
Фиг.5 - результат моделирования сценария равноправия фиг.4 при агрессивном режиме существующего алгоритма равноправия.Figure 5 - the simulation result of the equality scenario of figure 4 in the aggressive mode of the existing equality algorithm.
Фиг.6 - результат моделирования сценария равноправия Фиг.4 при консервативном режиме существующего алгоритма равноправия.Fig.6 is the result of modeling the scenario of equality of Fig.4 with the conservative mode of the existing algorithm of equality.
Фиг.7 - результат моделирования сценария равноправия фиг.4 при использовании способа этого изобретения.FIG. 7 is a simulation result of the equality scenario of FIG. 4 using the method of this invention.
Фиг.8 - результат моделирования сценария равноправия фиг.1 при использовании способа этого изобретения.Fig. 8 is a result of modeling the equality scenario of Fig. 1 using the method of this invention.
Фиг.9 - блок-схема для определения local_fair_rate в способе настоящего изобретения.9 is a flowchart for determining local_fair_rate in the method of the present invention.
Фиг.10 - блок-схема для определения advertising_rate в способе настоящего изобретения.10 is a flowchart for determining advertising_rate in the method of the present invention.
Осуществление изобретенияThe implementation of the invention
Детальная реализация технического решения будет описана согласно чертежам. В этом изобретении раскрывается способ динамического распределения полосы пропускания линии связи на динамическом пакетном кольце. Способ включает в одном интервале извещения этапы, на которыхA detailed implementation of the technical solution will be described according to the drawings. This invention discloses a method for dynamically allocating communication channel bandwidth on a dynamic packet ring. The method includes, in one notification interval, the steps of
a. Измеряют значения для переменныхa. Measures Values for Variables
1) add_rate: является количеством байтов для локальных пакетов, добавленных на кольцо узлом, для равноправных пакетов;1) add_rate: is the number of bytes for local packets added to the ring by the node, for peer packets;
2) total_add_rate: является общим количеством байтов для локальных пакетов, добавленных на кольцо узлом;2) total_add_rate: is the total number of bytes for local packets added to the ring by the node;
3) fw_rate: является количеством байтов для транзитных пакетов на кольце, для равноправных пакетов;3) fw_rate: is the number of bytes for transit packets on the ring, for peer packets;
4) total_fw_rate: является общим количеством байтов для транзитных пакетов на кольце.4) total_fw_rate: is the total number of bytes for transit packets on the ring.
b. Задачей настоящего изобретения является обеспечение полного использования линии связи наряду с корректным распределением полосы пропускания между всеми конкурирующими станциями. Для достижения этого local_fair_rate всегда вычисляется согласно этапам (см. фиг.9), на которыхb. The objective of the present invention is to ensure full use of the communication line along with the correct allocation of bandwidth between all competing stations. To achieve this, local_fair_rate is always calculated according to the steps (see Fig. 9), in which
b1. Вычисляют свободную интенсивность (idle_rate) уравнениемb1. The free intensity (idle_rate) is calculated by the equation
idle_rate=link_rate-total_add_rate-total_fw_rate,idle_rate = link_rate-total_add_rate-total_fw_rate,
где link_rate является количеством байтов на один интервал извещения при полной интенсивности линии связи.where link_rate is the number of bytes per notification interval at full link intensity.
b2. Если idle_rate<idle_rate_threshold (idle_rate_threshold могут установить в 0,01 или даже ниже):b2. If idle_rate <idle_rate_threshold (idle_rate_threshold can be set to 0.01 or even lower):
acc_idle=(α-1)*acc_idle/α,acc_idle = (α-1) * acc_idle / α,
иначеotherwise
acc_idle=acc_idle+idle_rate/βacc_idle = acc_idle + idle_rate / β
acc_idle=min(acc_idle, unreserved_rate),acc_idle = min (acc_idle, unreserved_rate),
где acc_idle, в основном, является интегралом свободной интенсивности и его значение не превышает незарезервированную интенсивность (unreserved_rate).where acc_idle is basically an integral of free intensity and its value does not exceed unreserved intensity (unreserved_rate).
b3. Вычисляют локальную справедливую интенсивность (local_fair_rate) по формуле:b3. The local fair intensity (local_fair_rate) is calculated by the formula:
local_fair_rate=(δ-1)*local_fair_rate/δ+add_rate(δ*weight)+ acc_idle/δ,local_fair_rate = (δ-1) * local_fair_rate / δ + add_rate (δ * weight) + acc_idle / δ,
где weight является весом станции для алгоритма равноправия с взвешиванием.where weight is the station weight for the weighting algorithm.
c. Определение извещаемой интенсивности (advertising_rate) включает этапы (см. фиг.10), на которыхc. The determination of the advertised intensity (advertising_rate) includes the steps (see FIG. 10) in which
с1. Если значение принятой извещаемой интенсивности меньше значения локальной справедливой интенсивности (то есть received_advertising_rate<local_fair_rate), то значение извещаемой интенсивности (advertising_rate) устанавливают в значение принятой извещаемой интенсивности (received_advertising_rate).c1. If the value of the received notified intensity is less than the value of the local fair intensity (i.e., received_advertising_rate <local_fair_rate), then the value of the notified intensity (advertising_rate) is set to the value of the received notified intensity (received_advertising_rate).
с2. Если (fw_rate<local_fair_rate), то извещаемую интенсивность (advertising_rate) устанавливают в локальную справедливую интенсивность (local_fair_rate). Это подобно существующему алгоритму для обработки разделения точек затора алгоритмом единственной точки затора.c2. If (fw_rate <local_fair_rate), then the advertised intensity (advertising_rate) is set to the local fair intensity (local_fair_rate). This is similar to the existing algorithm for handling mash point separation by a single mash point algorithm.
с3. Если (add_rate>минимального размера пакета) или в очереди с более низким приоритетом существуют пакеты для передачи, то извещаемую интенсивность (advertising_rate) устанавливают в локальную справедливую интенсивность (local_fair_rate).c3. If (add_rate> minimum packet size) or in a queue with a lower priority there are packets for transmission, then the advertised intensity (advertising_rate) is set to local fair intensity (local_fair_rate).
с4. Иначе извещаемую интенсивность (advertising_rate) устанавливают в принятую извещаемую интенсивность (received_advertising_rate).c4. Otherwise, the notified intensity (advertising_rate) is set to the received notified intensity (received_advertising_rate).
d. Для обеспечения справедливого совместного использования кольца полосы пропускания каждый узел на кольце RPR передает пакеты данных с интенсивностью, не большей, чем извещаемая интенсивность, определенная на третьем этапе.d. To ensure fair sharing of the bandwidth ring, each node on the RPR ring transmits data packets with an intensity not greater than the notified intensity determined in the third stage.
По этому изобретению были выполнены исследования моделирования. Исследования моделирования охватывают все 8 случаев, предложенных рабочей группой IEEE 802.17 для оценки алгоритма равноправия, и межоперационное тестирование между существующим алгоритмом равноправия и этим изобретением. Здесь будет предложен выбранный результат, при этом остальная часть результатов доступна по запросу.According to this invention, simulation studies have been performed. Simulation studies cover all 8 cases proposed by the IEEE 802.17 working group for evaluating the equality algorithm, and inter-operational testing between the existing equality algorithm and this invention. The selected result will be offered here, with the rest of the results available upon request.
Сценарий (1) равноправия представляет высокую - низкую полосу пропускания:Scenario (1) of equal rights represents a high - low bandwidth:
Установку высокой - низкой полосы пропускания иллюстрирует фиг.1. Идеальным распределением полосы пропускания для узла S5 является 12.5M (более 5% из-за определенных параметров моделирования), а для узла S1 137.5M. Результат моделирования при агрессивном режиме изображен на фиг.2. При агрессивном режиме полоса пропускания, распределенная узлу S1, колеблется между 46M и 130M. Это является основной причиной введения консервативного режима существующего алгоритма равноправия. Основной проблемой в отношении консервативного режима является максимум 95%-е использование полосы пропускания, что ведет к худшей эффективности, когда все источники являются поглощающими источниками.The setting of high - low bandwidth is illustrated in figure 1. The ideal bandwidth allocation for the S5 node is 12.5M (more than 5% due to certain modeling parameters), and for the S1 node it is 137.5M. The simulation result in aggressive mode is shown in figure 2. In aggressive mode, the bandwidth allocated to S1 is between 46M and 130M. This is the main reason for introducing the conservative regime of the existing equality algorithm. The main problem with the conservative regime is the maximum 95% bandwidth utilization, which leads to worse efficiency when all sources are absorbing sources.
Фиг.3 изображает результат моделирования при консервативном режиме.Figure 3 depicts the simulation result in a conservative mode.
Фиг.8 изображает результат моделирования способа динамического распределения полосы пропускания линии связи на динамическом пакетном кольце.Fig. 8 depicts a simulation result of a method for dynamically allocating a link bandwidth on a dynamic packet ring.
Результаты моделирования показывают, что, как изображено на фиг.8, настоящее изобретение дает большое использование полосы пропускания. Настоящее изобретение достигает почти 100%-ного использования полосы пропускания. При сравнении с агрессивным режимом, изображенным на фиг.2, оно может исключить потери полосы пропускания.The simulation results show that, as depicted in FIG. 8, the present invention provides great bandwidth utilization. The present invention achieves nearly 100% bandwidth utilization. When compared with the aggressive mode depicted in FIG. 2, it can eliminate bandwidth loss.
Сценарий (2) равноправия представляет "автостоянку":Scenario (2) of Equality represents a "parking lot":
Фиг.4 изображает размещение станций и требования на трафик.Figure 4 depicts the location of stations and traffic requirements.
Фиг.5 - результат моделирования сценария равноправия фиг.4 при агрессивном режиме существующего алгоритма равноправия.Figure 5 - the simulation result of the equality scenario of figure 4 in the aggressive mode of the existing equality algorithm.
Фиг.6 - результат моделирования сценария равноправия фиг.4 при консервативном режиме существующего алгоритма равноправия.6 is the result of modeling the scenario of equality of figure 4 with the conservative mode of the existing algorithm of equality.
Фиг.7 - результат моделирования сценария равноправия фиг.4 при использовании способа этого изобретения.FIG. 7 is a simulation result of the equality scenario of FIG. 4 using the method of this invention.
Фундаментальным требованием на распределение полосы пропускания является равноправие. По указанным результатам моделирования можно заметить, что новый алгоритм может обеспечить справедливое распределение полосы пропускания. Это могут все существующие алгоритмы равноправия. Новый алгоритм достигает использования полосы пропускания, идентичного достигаемому агрессивным режимом. Использование полосы пропускания при консервативном режиме составляет только около 90%.The fundamental requirement for bandwidth allocation is equality. From the indicated simulation results, it can be noted that the new algorithm can provide a fair distribution of bandwidth. These can be all existing equality algorithms. The new algorithm achieves the use of a bandwidth identical to that achieved by the aggressive mode. Conservative bandwidth usage is only about 90%.
Claims (4)
Translated fromRussianPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2005124510/09ARU2319310C2 (en) | 2003-01-02 | 2003-01-02 | Method for dynamic distribution of bandwidth of communication line on dynamic packet ring |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2005124510/09ARU2319310C2 (en) | 2003-01-02 | 2003-01-02 | Method for dynamic distribution of bandwidth of communication line on dynamic packet ring |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2005124510A RU2005124510A (en) | 2006-01-27 |
| RU2319310C2true RU2319310C2 (en) | 2008-03-10 |
Family
ID=36047754
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2005124510/09ARU2319310C2 (en) | 2003-01-02 | 2003-01-02 | Method for dynamic distribution of bandwidth of communication line on dynamic packet ring |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2319310C2 (en) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5546377A (en)* | 1995-10-31 | 1996-08-13 | Digital Equipment Corporation | Efficient distributed method for computing max-min fair rates of a limited resource in ATM networks |
| RU2123237C1 (en)* | 1994-10-28 | 1998-12-10 | ЛГ Инфомейшн энд Коммюникейшнс, Лтд. | Virtual cellular network and method for communication used in said virtual cellular network |
| US6002667A (en)* | 1995-07-19 | 1999-12-14 | Fujitsu Network Communications, Inc. | Minimum guaranteed cell rate method and apparatus |
| US6324184B1 (en)* | 1996-03-18 | 2001-11-27 | General Instrument Corporation | Dynamic bandwidth allocation for a communication network |
- 2003
- 2003-01-02RURU2005124510/09Apatent/RU2319310C2/enactive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2123237C1 (en)* | 1994-10-28 | 1998-12-10 | ЛГ Инфомейшн энд Коммюникейшнс, Лтд. | Virtual cellular network and method for communication used in said virtual cellular network |
| US6002667A (en)* | 1995-07-19 | 1999-12-14 | Fujitsu Network Communications, Inc. | Minimum guaranteed cell rate method and apparatus |
| US5546377A (en)* | 1995-10-31 | 1996-08-13 | Digital Equipment Corporation | Efficient distributed method for computing max-min fair rates of a limited resource in ATM networks |
| US6324184B1 (en)* | 1996-03-18 | 2001-11-27 | General Instrument Corporation | Dynamic bandwidth allocation for a communication network |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| RU2005124510A (en) | 2006-01-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100560748B1 (en) | Bandwidth Allocation Method Using Alpial Fairness Mechanism | |
| JP5400109B2 (en) | Repeater | |
| KR980007251A (en) | Method and apparatus for improved dynamic bandwidth prediction and adaptation in high speed packet switching network | |
| US9014156B2 (en) | Traffic forwarding in mesh networks | |
| US11929911B2 (en) | Shaping outgoing traffic of network packets in a network management system | |
| RU2012155863A (en) | METHOD AND MANAGEMENT SYSTEM OF THE BANDBAND | |
| WO2021057659A1 (en) | Traffic allocation method for path, network device, and network system | |
| CN103327542B (en) | A kind of QoS support method and device that is applied to MANET network | |
| CN100539523C (en) | Dynamic link bandwidth allocation method for resilient packet ring | |
| RU2598293C1 (en) | Method and apparatus for transmitting standard configuration data of improved system of selecting a transmitting protocol | |
| CN115413041B (en) | Centralized wireless ad hoc network resource allocation method and system | |
| CN106453121A (en) | A link dynamic load configuration method, system and server | |
| CN114650603B (en) | Dynamic allocation method of time slot resources in UAV swarm self-organizing communication network | |
| RU2319310C2 (en) | Method for dynamic distribution of bandwidth of communication line on dynamic packet ring | |
| EP1947810B1 (en) | A method and equipment for admitting and controlling the integration service model | |
| CN100521809C (en) | Method for allocating resources in communication system | |
| JP2008219722A (en) | Node, communication system and program for node | |
| EP3251450B1 (en) | Method and rate controlling node for providing data rate for data communication | |
| RU2547631C2 (en) | Method for efficient use of communication resources of multiservice network in congestion conditions | |
| CN109804693B (en) | A scheduling method, device and system | |
| WO2021074999A1 (en) | Signal transfer control device and signal transfer control method | |
| Lehrieder et al. | Marking conversion for pre-congestion notification | |
| Sadeghi | Congestion Control in Wireless mesh networks | |
| JP2004282387A (en) | Shared resource distribution controller | |
| Zhang et al. | A QoS guarantee mechanism based on multi-priority bionic competition model in vehicular edge etwork |