RU2258496C2 - Method for treating patients with traumatic and degenerative lesions of vertebral column and spinal cord - Google Patents
Method for treating patients with traumatic and degenerative lesions of vertebral column and spinal cordDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2258496C2 RU2258496C2RU2003122104/14ARU2003122104ARU2258496C2RU 2258496 C2RU2258496 C2RU 2258496C2RU 2003122104/14 ARU2003122104/14 ARU 2003122104/14ARU 2003122104 ARU2003122104 ARU 2003122104ARU 2258496 C2RU2258496 C2RU 2258496C2
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- spinal cord
- traction
- level
- enmg
- affected
- Prior art date
Links
- 210000000278spinal cordAnatomy0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription68
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription40
- 230000003902lesionEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription10
- 230000003412degenerative effectEffects0.000titleclaimsdescription4
- 230000000472traumatic effectEffects0.000titleclaimsdescription4
- 230000000638stimulationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription46
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription29
- 210000002161motor neuronAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription25
- 210000000578peripheral nerveAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription15
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000claimsdescription10
- 230000006378damageEffects0.000claimsdescription6
- 230000036770blood supplyEffects0.000claimsdescription5
- 230000002792vascularEffects0.000claimsdescription5
- 210000003205muscleAnatomy0.000abstractdescription25
- 230000008569processEffects0.000abstractdescription10
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000abstractdescription9
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000abstractdescription7
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000abstractdescription4
- 208000035475disorderDiseases0.000abstractdescription3
- 208000014306Trophic diseaseDiseases0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000004087circulationEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000000399orthopedic effectEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000abstract1
- 238000002560therapeutic procedureMethods0.000abstract1
- 208000019553vascular diseaseDiseases0.000abstract1
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description22
- 230000004936stimulating effectEffects0.000description17
- 208000002193PainDiseases0.000description13
- 230000001537neural effectEffects0.000description13
- 230000001965increasing effectEffects0.000description11
- 230000036407painEffects0.000description11
- 210000005036nerveAnatomy0.000description10
- 230000017531blood circulationEffects0.000description9
- 208000011580syndromic diseaseDiseases0.000description9
- 238000002591computed tomographyMethods0.000description8
- 210000004705lumbosacral regionAnatomy0.000description7
- 231100000862numbnessToxicity0.000description7
- 210000001617median nerveAnatomy0.000description6
- 230000007433nerve pathwayEffects0.000description6
- 206010060860Neurological symptomDiseases0.000description5
- 206010019909HerniaDiseases0.000description4
- 201000009859OsteochondrosisDiseases0.000description4
- 229920006926PFCPolymers0.000description4
- 102100038567ProperdinHuman genes0.000description4
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description4
- 230000006835compressionEffects0.000description4
- 238000007906compressionMethods0.000description4
- 230000003247decreasing effectEffects0.000description4
- 208000002173dizzinessDiseases0.000description4
- 230000000763evoking effectEffects0.000description4
- 210000003414extremityAnatomy0.000description4
- 210000002683footAnatomy0.000description4
- 210000002414legAnatomy0.000description4
- 210000002569neuronAnatomy0.000description4
- 239000013598vectorSubstances0.000description4
- 206010001497AgitationDiseases0.000description3
- 208000003618Intervertebral Disc DisplacementDiseases0.000description3
- 206010028570MyelopathyDiseases0.000description3
- 230000004913activationEffects0.000description3
- 210000003050axonAnatomy0.000description3
- 210000000245forearmAnatomy0.000description3
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description3
- 210000003141lower extremityAnatomy0.000description3
- 210000001699lower legAnatomy0.000description3
- 238000002595magnetic resonance imagingMethods0.000description3
- 210000000944nerve tissueAnatomy0.000description3
- 230000002085persistent effectEffects0.000description3
- 210000001364upper extremityAnatomy0.000description3
- 206010010214Compression fractureDiseases0.000description2
- 208000012902Nervous system diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 208000008457Neurologic ManifestationsDiseases0.000description2
- 208000025966Neurological diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 208000007542ParesisDiseases0.000description2
- 230000006978adaptationEffects0.000description2
- 230000008033biological extinctionEffects0.000description2
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description2
- 244000309466calfSpecies0.000description2
- 230000001684chronic effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000000875corresponding effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000002405diagnostic procedureMethods0.000description2
- 210000001951dura materAnatomy0.000description2
- 238000002347injectionMethods0.000description2
- 239000007924injectionSubstances0.000description2
- 208000028867ischemiaDiseases0.000description2
- 230000004060metabolic processEffects0.000description2
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000description2
- 238000009608myelographyMethods0.000description2
- 210000004126nerve fiberAnatomy0.000description2
- 238000005457optimizationMethods0.000description2
- 230000008533pain sensitivityEffects0.000description2
- 210000004345peroneal nerveAnatomy0.000description2
- 230000009467reductionEffects0.000description2
- 230000011514reflexEffects0.000description2
- 210000000273spinal nerve rootAnatomy0.000description2
- 230000008925spontaneous activityEffects0.000description2
- 238000001356surgical procedureMethods0.000description2
- 210000003371toeAnatomy0.000description2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 206010003694AtrophyDiseases0.000description1
- 208000010392Bone FracturesDiseases0.000description1
- 206010017076FractureDiseases0.000description1
- 206010021639IncontinenceDiseases0.000description1
- 206010050296Intervertebral disc protrusionDiseases0.000description1
- 208000034819Mobility LimitationDiseases0.000description1
- 206010030113OedemaDiseases0.000description1
- 235000010830Prunus insititiaNutrition0.000description1
- 244000039376Prunus insititiaSpecies0.000description1
- 206010059604Radicular painDiseases0.000description1
- 208000008765SciaticaDiseases0.000description1
- 201000006559Vertebrobasilar insufficiencyDiseases0.000description1
- 208000027418Wounds and injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 210000001015abdomenAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000003213activating effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000003044adaptive effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000003459anti-dromic effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000013459approachMethods0.000description1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-Natomic oxygenChemical compound[O]QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000037444atrophyEffects0.000description1
- 210000004369bloodAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000008280bloodSubstances0.000description1
- 244000309464bullSpecies0.000description1
- 206010061592cardiac fibrillationDiseases0.000description1
- 210000004027cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000001413cellular effectEffects0.000description1
- 210000003169central nervous systemAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000002490cerebral effectEffects0.000description1
- 210000001175cerebrospinal fluidAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000008602contractionEffects0.000description1
- 230000002596correlated effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007812deficiencyEffects0.000description1
- 230000007850degenerationEffects0.000description1
- 230000002638denervationEffects0.000description1
- 230000006866deteriorationEffects0.000description1
- 238000003745diagnosisMethods0.000description1
- 201000010099diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 230000009189divingEffects0.000description1
- 238000002567electromyographyMethods0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 230000005284excitationEffects0.000description1
- 238000001125extrusionMethods0.000description1
- 238000005562fadingMethods0.000description1
- 230000002600fibrillogenic effectEffects0.000description1
- 210000002082fibulaAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000007789gasSubstances0.000description1
- 238000013101initial testMethods0.000description1
- 208000014674injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 230000030214innervationEffects0.000description1
- 238000009434installationMethods0.000description1
- 230000002427irreversible effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000002690local anesthesiaMethods0.000description1
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000description1
- 230000032630lymph circulationEffects0.000description1
- 230000007246mechanismEffects0.000description1
- 230000001095motoneuron effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000003387muscularEffects0.000description1
- 210000002346musculoskeletal systemAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000001087myotubuleAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000007383nerve stimulationEffects0.000description1
- 230000000926neurological effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000010984neurological examinationMethods0.000description1
- 230000008906neuronal responseEffects0.000description1
- 235000015097nutrientsNutrition0.000description1
- 230000001191orthodromic effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000001301oxygenSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052760oxygenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 230000037325pain toleranceEffects0.000description1
- 230000001575pathological effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000000737periodic effectEffects0.000description1
- 210000005259peripheral bloodAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000011886peripheral bloodSubstances0.000description1
- 210000001428peripheral nervous systemAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000002980postoperative effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000003389potentiating effectEffects0.000description1
- 102000004169proteins and genesHuman genes0.000description1
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000description1
- 238000002601radiographyMethods0.000description1
- 230000008707rearrangementEffects0.000description1
- 230000001172regenerating effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007832reinnervationEffects0.000description1
- 230000008439repair processEffects0.000description1
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description1
- 230000035807sensationEffects0.000description1
- 208000020431spinal cord injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 210000001032spinal nerveAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000000021stimulantSubstances0.000description1
- 210000002330subarachnoid spaceAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000000725suspensionSubstances0.000description1
- 208000024891symptomDiseases0.000description1
- 238000003786synthesis reactionMethods0.000description1
- 210000002435tendonAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000002303tibiaAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000002972tibial nerveAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000002385vertebral arteryAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000000007visual effectEffects0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Electrotherapy Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromRussianИзобретение относится к медицине, а именно к вертебрологии, и предназначено для лечения позвоночника и спинного мозга, и может быть применено в ортопедии, нейрохирургии и травматологии.The invention relates to medicine, namely to vertebrology, and is intended for the treatment of the spine and spinal cord, and can be used in orthopedics, neurosurgery and traumatology.
Известен способ лечения больных с заболеваниями позвоночника, имеющих мышечно-тонические, вегетативно-трофические, вегетативно-сосудистые, рефлекторные и чувствительные нарушения (а.с. SU №831124, А 61 Н 1/02//А 61 Н 23/00 от 05.07.79, опубл. в БИ №19 за 1981 г. от 23.05.81), включающий одновременное проведение вытяжения позвоночника приложением нагрузки грузами весом от 5 кг до 15-25 кг и наложение продольной вибрации позвоночника частотой 50-100 Гц и амплитудой 0,1-0,3 мм для стабилизации кровообращения в тканях над позвоночником.A known method of treating patients with diseases of the spine, having muscle-tonic, autonomic-trophic, autonomic-vascular, reflex and sensitive disorders (a.s. SU No. 831124, A 61 N 1/02 // A 61 N 23/00 from 05.07 .79, published in BI No. 19 for 1981 from 05.23.81), including simultaneous spinal traction by applying loads of 5 kg to 15-25 kg and applying longitudinal vibration of the spine with a frequency of 50-100 Hz and an amplitude of 0, 1-0.3 mm to stabilize blood circulation in the tissues above the spine.
Недостатками данного способа являются:The disadvantages of this method are:
- отсутствие объективного контроля за состоянием сегментарного аппарата спинного мозга и динамикой кровообращения, не позволяющее точно определить параметры механического воздействия на ткани позвоночника, спинного мозга, корешки, оценить степень восстановления проводимости спинного мозга при вертеброгенной недостаточности;- the lack of objective monitoring of the state of the segmental apparatus of the spinal cord and the dynamics of blood circulation, which does not allow to accurately determine the parameters of the mechanical effect on the tissue of the spine, spinal cord, root, to evaluate the degree of restoration of spinal cord conductivity in vertebral insufficiency;
- невозможность оптимизации параметров воздействия;- the impossibility of optimizing exposure parameters;
- отсутствие направленного воздействия на репаративно-пластические процессы и перестройку нервного волокна спинного мозга.- the absence of directed influence on the repair-plastic processes and the restructuring of the nerve fiber of the spinal cord.
Известен способ лечения больных с остеохондрозом позвоночника с неврологическими проявлениями (а.с. №1304822, А 61 N 1/36, от 07.01.85, опубл. в Бюл. №15 за 1987 г. от 23.04.87), включающий проведение электроимпульсной стимуляции (ЭИС) путем воздействия на проекцию патологического очага, зоны поражения и мышцы, иннервируемые пораженным нервом, импульсным электрическим током, параметры модуляции которого изменяют для полного исключения адаптации организма даже к самым незначительным величинам токов и напряжений, а также управляют режимами тока, подбирая его силу по порогу начала ощущений на каждом стимулируемом сегменте для создания и сохранения необходимого уровня электрораздражения зон воздействия, до и после лечения проводится биомеханический и биоэлектрический контроль: силовых характеристик стимулируемых мышц - методами тензодинамометрии и биоэлектрической активности мышц электромиографией (ЭМГ).There is a method of treating patients with osteochondrosis of the spine with neurological manifestations (and.with. No. 1304822, A 61 N 1/36, from 07.01.85, publ. In Bull. No. 15 for 1987 from 04.23.87), including conducting an electrical pulse stimulation (EIS) by acting on the projection of the pathological focus, the affected area and the muscles innervated by the affected nerve, pulsed electric current, the modulation parameters of which are changed to completely eliminate the body’s adaptation to even the smallest amounts of currents and voltages, and also control the current modes, selecting it force on the threshold of the onset of sensations on each stimulated segment to create and maintain the necessary level of electroirritation of the exposure zones, before and after treatment, biomechanical and bioelectric control is performed: the strength characteristics of the stimulated muscles are determined by the methods of tensodynamometry and muscle bioelectrical activity by electromyography (EMG).
Недостатками данного способа являются:The disadvantages of this method are:
- отсутствие объективного контроля за состоянием сегментарного аппарата спинного мозга и динамикой кровообращения;- lack of objective control over the state of the segmental apparatus of the spinal cord and the dynamics of blood circulation;
- невозможность оптимизации параметров воздействия;- the impossibility of optimizing exposure parameters;
- отсутствие возможности точного определения параметров воздействия из-за проведения контроля по косвенным параметрам;- the lack of the ability to accurately determine exposure parameters due to the control of indirect parameters;
- частичное восстановление нейрональных связей и проводимости в пораженных участках спинного мозга, неполная приостановка дистрофических процессов в спинно-мозговых тканях.- partial restoration of neuronal connections and conduction in the affected areas of the spinal cord, incomplete suspension of dystrophic processes in the spinal cord tissues.
Известен способ Великанова И.И. лечения вертеброгенной недостаточности мозгового кровообращения (Пат. RU №2194485, А 61 Н 1/02, приор. 19.09.2000, опубл. 20.12.2002) путем увеличения пульсового притока крови в сосудах вертебрально-базилярного бассейна, включающий проведение вытяжения шейного отдела позвоночника приложением нагрузки величиной от 0,5 кг при угле наклона тяги вперед от 0° до 20° с интервалом в 5°, при этом изменяют вектор тяги во фронтальной плоскости при наличии асимметрии пульсового притока крови по позвоночным артериям и по достижении максимального притока крови при оптимальных векторах тяги в 2-х плоскостях - сагиттальной и фронтальной, продолжают тракцию при установленных параметрах силы и вектора тяги.The known method of Velikanov II for treating vertebrogenic insufficiency of cerebral circulation (Pat. RU No. 2194485, A 61 N 1/02, prior. September 19, 2000, publ. December 20, 2002) by increasing the pulse blood flow in the vessels of the vertebral-basilar basin, including the application of traction of the cervical spine loads from 0.5 kg at an angle of forward draft from 0 ° to 20 ° with an interval of 5 °, while changing the thrust vector in the frontal plane in the presence of asymmetry of the pulse blood flow through the vertebral arteries and when the maximum blood flow is reached at the optimum tal traction vectors in 2 planes - sagittal and frontal, continue traction with the set parameters of force and traction vector.
Недостатками данного способа являются:The disadvantages of this method are:
- отсутствие контроля за изменением функционирования мотонейронов спинного мозга во время вытяжения и определение параметров воздействия только по параметрам тока крови, что часто приводит к неврологическим расстройствам;- lack of control over changes in the functioning of spinal cord motor neurons during traction and determination of exposure parameters only by blood flow parameters, which often leads to neurological disorders;
- невозможность оптимизации параметров воздействия;- the impossibility of optimizing exposure parameters;
- определение параметров воздействия только по параметрам тока крови, без учета состояния нейрональных связей и проводимости спинного мозга, что часто приводит к неврологическим расстройствам;- determination of exposure parameters only by parameters of blood flow, without taking into account the state of neuronal connections and spinal cord conductivity, which often leads to neurological disorders;
- отсутствие направленного влияния и воздействия на дегенеративно-дистрофические процессы в спинном мозге, обычно возникающие при ишемии и вертеброгенной недостаточности, а также на репаративно-пластические изменения и перестройку структур спинного мозга.- the absence of directed influence and impact on degenerative-dystrophic processes in the spinal cord, usually arising from ischemia and vertebrogenic insufficiency, as well as on reparative plastic changes and rearrangement of the structures of the spinal cord.
Наиболее близким по назначению и совокупности совпадающих существенных признаков является способ лечения дискогенных радикулитов (А.с. № SU 1242160, A 61 F 5/04, от 25.05.82, опубл. БИ №25 за 1986 г., 07.07.86), включающий горизонтальное и вертикальное вытяжение позвоночника, проведение электродиагностики до и после вытяжения путем воздействия электрическим током на болевые зоны позвоночника и зоны, иннервируемые соответствующими нервами, для определения порога болевой чувствительности и порога переносимости боли к электрическому воздействию, по результатам которой изменяют величину нагрузок на позвоночник.The closest in purpose and combination of essential features is the method of treatment of discogenic sciatica (A.S. No. SU 1242160, A 61 F 5/04, 05.25.82, publ. BI No. 25 for 1986, 07.07.86), including horizontal and vertical traction of the spine, conducting electrodiagnostics before and after traction by applying an electric current to the pain zones of the spine and areas innervated by the corresponding nerves to determine the threshold of pain sensitivity and the threshold of pain tolerance to electrical exposure, as a result It is which alter the magnitude of load on the spine.
Недостатками данного способа являются:The disadvantages of this method are:
- неудовлетворительная точность определения параметров воздействия из-за проведение контроля по косвенным параметрам и зависимости от субъективных факторов;- unsatisfactory accuracy of determination of exposure parameters due to the control of indirect parameters and dependence on subjective factors;
- отсутствие контроля во время вытяжения за состоянием спинного мозга, пораженных корешков и периферических нервов;- lack of control during traction over the condition of the spinal cord, affected roots and peripheral nerves;
- невозможность проведения динамического контроля и отимизации параметров воздействия во время вытяжения;- the impossibility of carrying out dynamic control and optimization of exposure parameters during traction;
- косвенное влияние на дегенеративно-дистрофические процессы в нервных тканях, отсутствие направленного влияния и воздействия на репаративно-пластические изменения и перестройку структур спинного мозга.- indirect effect on degenerative-dystrophic processes in nerve tissues, lack of directed influence and impact on reparative-plastic changes and restructuring of the structures of the spinal cord.
Задачи, решаемые изобретением:The tasks solved by the invention:
- повышение точности определения параметров воздействия;- improving the accuracy of determining exposure parameters;
- повышение управляемости вытяжением и электростимуляцией для ускорения восстановления проводимости нервных тканей и трофики спинного мозга и его корешков;- increased controllability by traction and electrical stimulation to accelerate the restoration of conduction of nerve tissues and trophism of the spinal cord and its roots;
- стимуляция репаративно-пластических процессов в зонах поражения спинного мозга, корешков и периферических нервов.- stimulation of reparative plastic processes in the areas of damage to the spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves.
Для решения поставленных задач в предлагаемом способе лечения больных с травматическими и дегенеративными поражениями позвоночника и спинного мозга (СМ)To solve the problems in the proposed method for the treatment of patients with traumatic and degenerative lesions of the spine and spinal cord (SM)
- выполняют электродиагностику методом электронейромиографии (ЭНМГ) путем определения активности мотонейронов для определения степени воздействия,- perform electrodiagnostics by the method of electroneuromyography (ENMG) by determining the activity of motor neurons to determine the degree of exposure,
- проводят горизонтальное и вертикальное вытяжения позвоночника путем дозированного дистракционного асимметричного и/или симметричного воздействия на уровнях пораженных сегментов позвоночника и/или спинного мозга и его корешков,- carry out horizontal and vertical traction of the spine by dosed distraction asymmetric and / or symmetric exposure at the levels of the affected segments of the spine and / or spinal cord and its roots,
- при этом характер, степень и время тракции определяют по положительному результату показателей (уровню и характеру изменения) активности мотонейронов,- the nature, degree and time of traction is determined by a positive result of indicators (level and nature of change) of motor neuron activity,
- дополнительно проводят электростимуляцию: эпидуральную - спинного мозга на уровне его поражения или накожную - в проекции пораженных зон спинного мозга и/или пораженных корешков и периферических нервов,- additionally conduct electrical stimulation: epidural - of the spinal cord at the level of its lesion or cutaneous - in the projection of the affected areas of the spinal cord and / or the affected roots and peripheral nerves,
- при этом характер электростимуляционного воздействия определяют по изменению активности мотонейронов, которую определяют во время стимуляции и после нее.- the nature of the electrostimulation effect is determined by the change in the activity of motor neurons, which is determined during and after stimulation.
При этом электростимуляцию возможно проводить одновременно с вытяжением.In this case, electrical stimulation can be carried out simultaneously with traction.
Степень вытяжения позвоночника и/или режимов электростимуляции возможно дополнительно контролировать по изменению уровня кровенаполнения и тонуса сосудистой стенки путем проведения реовазографии и доплерографии.The degree of spinal traction and / or electrical stimulation modes can be additionally controlled by changing the level of blood supply and vascular wall tone by conducting rheovasography and dopplerography.
Электростимуляцию возможно проводить дифференцированно: вначале накожную - в проекции пораженных зон спинного мозга, пораженных корешков и периферических нервов, а при ее неэффективности - эпидуральную на уровне пораженных зон спинного мозга.It is possible to carry out electrical stimulation differentially: first, the cutaneous - in the projection of the affected areas of the spinal cord, the affected roots and peripheral nerves, and if it is ineffective - epidural at the level of the affected areas of the spinal cord.
Предлагаемый способ лечения отличается от прототипа:The proposed method of treatment differs from the prototype:
- проведением электродиагностики до и во время вытяжения, а также во время электростимуляции и после нее;- conducting electrodiagnostics before and during traction, as well as during electrical stimulation and after it;
- измерением активности мотонейронов при проведении ЭНМГ-исследования для управления степенью, характером вытяжения и временем экспозиции и/или характером электростимуляции;- measuring the activity of motoneurons during an ENMG study to control the degree, nature of the traction and exposure time and / or the nature of electrical stimulation;
- проведением электростимуляции: эпидуральной - на уровне поражения спинного мозга или накожной - в проекции зон поражения спинного мозга, пораженных корешков и периферических нервов;- conducting electrical stimulation: epidural - at the level of damage to the spinal cord or cutaneous - in the projection of the areas of damage to the spinal cord, the affected roots and peripheral nerves;
- возможностью проведения электростимуляции одновременно с вытяжением;- the possibility of electrical stimulation simultaneously with traction;
- возможностью коррекции параметров вытяжения и электростимуляции по изменению возможностью проведения уровня кровенаполнения и тонус (реакцию) сосудистой стенки.- the ability to correct the parameters of traction and electrical stimulation by changing the ability to conduct the level of blood supply and tone (reaction) of the vascular wall.
Предлагаемый способ лечения позволяет перейти на качественно новый уровень лечения больных за счет более точного определения параметров механо- и электростимуляционного воздействия, позволяющего проводить оптимизацию лечебных режимов, при этом в качестве управляющего параметра используются показания активности мотонейронов (уровень и характер изменения), получаемые при проведении ЭНМГ-исследования. По изменению активности мотонейронов, измеряемому до и во время вытяжения, определяют степень и характер (симметричное и/или асимметричное) последнего и время экспозиции. Динамический контроль нейрональных параметров и управление режимами вытяжением позволяет активизировать репаративно-пластические изменения и перестройку в нервных тканях спинного мозга, пораженных корешках и периферических нервах. Дополнительное проведение управляемой по параметрам активности мотонейронов локальной электростимуляции пораженных зон позволяет ликвидировать дистрофические процессы в позвоночнике, спинном мозге, в спинно-мозговых корешках, периферических нервах и иннервируемых ими тканях, перераспределять нагрузку в спазмированных мышцах, тем самым увеличить возбуждение нервной ткани и активизировать кровоток в пораженных зона. Это позволяет восстанавливать мышечно-тонические нарушения в позвоночно-двигательном сегменте, уменьшить его вегетососудистые и трофические расстройства.The proposed method of treatment allows you to switch to a qualitatively new level of treatment of patients due to a more accurate determination of the parameters of mechanical and electrical stimulation, allowing optimization of treatment regimes, while the motoneuron activity (level and nature of change) obtained by conducting ENMG is used as a control parameter - research. By the change in the activity of motoneurons, measured before and during traction, the degree and nature (symmetric and / or asymmetric) of the latter and the exposure time are determined. Dynamic control of neuronal parameters and control of traction regimes make it possible to activate reparative plastic changes and restructuring in the nerve tissues of the spinal cord, the affected roots and peripheral nerves. The additional conduct of local electrical stimulation of the affected areas, controlled by the parameters of motor neuron activity, allows eliminating dystrophic processes in the spine, spinal cord, spinal roots, peripheral nerves and tissues innervated by them, redistributing the load in spasmodic muscles, thereby increasing nervous tissue excitation and activating blood flow in affected area. This allows you to restore muscle-tonic disorders in the spinal-motor segment, to reduce its vegetovascular and trophic disorders.
Вытяжение, управляемое по показателям состояния спинного мозга, не только восстанавливает нарушенную статодинамику позвоночника и улучшает функцию сегментарного аппарата, но и активизирует систему «гипофиз-кора надпочечников», влияющую на выделение адренокортико-стероидов, что способствует ускорению обменных процессов на клеточном уровне, активизации репаративно-пластических процессов в нервных и мышечных тканях и запусканию адаптационного механизма организма. Электростимуляция приводит к повышению возбудимости нейронов спинного мозга, центральной и периферической нервных систем, ускорению синтеза в нервных клетках белка и РНК, используемых самими нейронами и их аксонами. В активизированном участке нервной ткани происходит перераспределение крови, восполняющее потребность клеток в кислороде, ускоряются обменные процессы.Traction, controlled by indicators of the state of the spinal cord, not only restores the disturbed statodynamics of the spine and improves the function of the segmental apparatus, but also activates the “pituitary-adrenal cortex” system, which affects the release of adrenocorticosteroids, which helps to accelerate metabolic processes at the cellular level, and activates reparatively -plastic processes in nerve and muscle tissues and triggering the body's adaptive mechanism. Electrical stimulation increases the excitability of neurons of the spinal cord, central and peripheral nervous systems, accelerates the synthesis of protein and RNA in nerve cells used by the neurons themselves and their axons. In the activated area of the nervous tissue, redistribution of blood occurs, replenishing the oxygen demand of the cells, metabolic processes are accelerated.
Это позволяет активизировать центральное и периферическое крово- и лимфообращение, создать условия для увеличения площади транскапилярного обмена газов и питательных веществ, тем самым стимулирует репаративно-пластические процессы в спинном мозге, пораженных корешках и периферических нервах, что, в конечном счете, приводит к повышению жизнеспособности нервных клеток и работоспособности мышечных тканей.This allows you to activate the central and peripheral blood and lymph circulation, create conditions for increasing the area of transcapillary exchange of gases and nutrients, thereby stimulating the repair and plastic processes in the spinal cord, the affected roots and peripheral nerves, which ultimately leads to increased vitality nerve cells and muscle performance.
Способ осуществляют в следующей последовательности.The method is carried out in the following sequence.
Проводят электродиагностику, для чего в зависимости от пораженного сегмента позвоночника размещают электроды для ЭНМГ-исследования на шейный, грудопоясничный, поясничный отделы. Выбирают рациональный метод их введения - накожный или эпидуральный. Активный регистрирущий электрод накладывают на мышцу, а референтный - на ее сухожилие. При подаче прямоугольных электрических импульсов на нервные стволы импульс распространяется в 2-х направлениях: ортодромно к мышце, вызывая ее сокращение и антидромно к спинному мозгу, вызывая активацию тел мотонейронов. Ток увеличивают до тех пор, пока амплитуда мышечного ответа не станет максимальной. При этой величине тока происходит возбуждение всех аксонов нерва и всех мотонейронов.They conduct electrodiagnostics, for which, depending on the affected segment of the spine, electrodes are placed for ENMG studies on the cervical, thoracolumbar, lumbar regions. Choose a rational method of their introduction - cutaneous or epidural. An active recording electrode is applied to the muscle, and a reference electrode to its tendon. When rectangular electrical impulses are applied to the nerve trunks, the impulse propagates in 2 directions: orthodromic to the muscle, causing its contraction and antidromic to the spinal cord, causing activation of the bodies of motor neurons. The current is increased until the amplitude of the muscular response becomes maximum. At this current magnitude, all axons of the nerve and all motor neurons are excited.
При данной силе тока определяют уровень и характер изменения активности мотонейронов, для этого регистрируют 20 таких ответов. Определяют количество зарегистрированых F-волн в % и отношение амплитуды F-волны к амплитуде М-ответа и соотносят с показателями нормы (В норме на каждый стимул нерва, регистрируется нейрональный ответ, показатель амплитуды F-волны не должен быть меньше 40 мкВ и превышать 5% показателя амплитуды М-ответа).At a given current strength, the level and nature of changes in the activity of motor neurons are determined, for this 20 such responses are recorded. The number of registered F-waves in% and the ratio of the amplitude of the F-wave to the amplitude of the M-response are determined and correlated with normal indicators (Normally, for each nerve stimulus, a neuronal response is recorded, the F-wave amplitude should not be less than 40 μV and exceed 5 % of the amplitude of the M-response).
Для подбора степени и характера вытяжения проводят предварительное тестовое ЭНМГ-исследование: определяют характер изменения активности мотонейронов в пораженной зоне по регистрации сдвигов показателей F-волн (наличие блока F-волн (активности мотонейронов)), показателей СРВ по моторным стволам, амплитуду вызванного мышечного ответа, потенциалов двигательных единиц (ПДЕ) и т.д.To select the degree and nature of the traction, a preliminary ENMG test is carried out: the nature of changes in the activity of motor neurons in the affected area is determined by recording the shifts of F-wave indices (the presence of a block of F-waves (activity of motor neurons)), SRV indices for motor trunks, amplitude of the evoked muscle response potentials of motor units (PDE), etc.
По результатам тестирования определяют дальнейшую тактику лечения: консервативный или оперативный подход, инвазивный или неинвазивный метод установки электродов для электростимуляции, а также степень и характер (симметричное или асимметричное) вытяжения и время экспозиции, а также режимы и характер электростимуляции.Based on the test results, further treatment tactics are determined: a conservative or operative approach, an invasive or non-invasive method of installing electrodes for electrical stimulation, as well as the degree and nature of (symmetrical or asymmetric) traction and exposure time, as well as the modes and nature of electrical stimulation.
При консервативном лечении проводят вытяжение пораженной зоны позвоночника в корсете, управляемое по показателям состояния спинного мозга и проводящих нервных путей в сочетании с накожной элетростимуляцией проекции соответствующих зон поражения спинного мозга, пораженных корешков и периферических нервов.With conservative treatment, an extension of the affected area of the spine in the corset is carried out, controlled by indicators of the condition of the spinal cord and the conduction of the nerve pathways in combination with cutaneous electrostimulation of the projection of the corresponding zones of damage to the spinal cord, affected roots and peripheral nerves.
При оперативном лечении проводят вытяжение в дистрагирующем корсете, управляемое по показателям состояния спинного мозга и нервных путей в сочетании с эпидуральной элетростимуляцией спинного мозга при помощи игольчатых электродов, вводимых (интраоперационно или инъекционным путем) в эпидуральное пространство на твердую мозговую оболочку на уровне его поражения.During surgical treatment, an extension is carried out in a distracting corset, controlled by indicators of the condition of the spinal cord and nerve pathways in combination with epidural electrostimulation of the spinal cord using needle electrodes inserted (intraoperatively or by injection) into the epidural space on the dura mater at the level of its lesion.
Для проведения вытяжения больному одевается один из видов дистрагирующих корсетов (в зависимости от пораженного сегмента позвоночника): шейный, грудопоясничный, поясничный, имеющий телескопические стержни, обеспечивающие плавное изменение нагрузок на позвоночник от десятков - сотен грамм до нескольких килограмм в миллиметровом эквиваленте.To carry out the traction, the patient wears one of the types of distracting corsets (depending on the affected segment of the spine): cervical, thoracolumbar, lumbar, having telescopic rods that provide a smooth change in the load on the spine from tens - hundreds of grams to several kilograms in millimeter equivalent.
Вытяжение позвоночника осуществляют медленным вращением нагрузочных гаек, выдвигая телескопические стержни. Степень вытяжения (величины нагружающего усилия) контролируется по показаниям состояния спинного мозга путем активного ЭНМГ-исследования: по уровню и характеру изменения активности мотонейронов.Traction of the spine is carried out by slow rotation of the load nuts, pushing the telescopic rods. The degree of traction (the magnitude of the loading effort) is controlled by indications of the state of the spinal cord by means of an active ENMG study: by the level and nature of changes in the activity of motor neurons.
При необходимости проводят реовазографию и доплерографию: определяют показания изменения уровня кровенаполнения и тонуса (реакции) сосудистой стенки.If necessary, rheovasography and dopplerography are performed: the indications of changes in the level of blood supply and the tone (reaction) of the vascular wall are determined.
В соответствии с выбранной тактикой лечения проводят электростимуляцию: эпидуральную - на уровне поражения спинного мозга или накожную - проекции зон поражения спинного мозга, пораженных корешков и периферических нервов. Для электростимуляции используют стимуляторы, выпускаемые отечественной промышленностью, стационарные (УЭИ-1, ЭНС-01, ЭСУ-2, Дельта-102, Элиман-101) и портативные (Дельта-101, Элиман-206, Мирабель, Нейрон-02).In accordance with the chosen tactics of treatment, electrical stimulation is carried out: epidural - at the level of spinal cord lesion or cutaneous - projection of the spinal cord lesion zones, affected roots and peripheral nerves. For electrical stimulation, stimulants produced by the domestic industry are used, stationary (UEI-1, ENS-01, ESU-2, Delta-102, Eliman-101) and portable (Delta-101, Eliman-206, Mirabel, Neuron-02).
При применении накожной (транскутанной) электростимуляции стимулирующие электроды располагают на дистальных точках по ходу периферического нерва (на его проксимальные и дистальные стволы) для восполнения дефицита афферентной и эфферентной импульсации. Величина стимулирующего тока соответствует пороговому значению, т.е. при данном токе регистрируется минимальный М-ответ, длительность импульса от 0,1 до 0,5 мс, частота 50-60 Гц (так как ее увеличение можно вызвать необратимые изменения мотонейронов).When applying cutaneous (transcutaneous) electrical stimulation, the stimulating electrodes are located at distal points along the peripheral nerve (on its proximal and distal trunks) to compensate for the deficiency of afferent and efferent impulse. The magnitude of the stimulating current corresponds to the threshold value, i.e. at this current, the minimum M-response is recorded, the pulse duration is from 0.1 to 0.5 ms, the frequency is 50-60 Hz (since its increase can cause irreversible changes in motor neurons).
При применении эпидуральной или корешковой электростимуляции игольчатые электроды вводят (интраоперационно или инъекционным путем) в эпидуральное пространство на твердую мозговую оболочку на уровне его поражения.When using epidural or radicular electrostimulation, needle electrodes are inserted (intraoperatively or by injection) into the epidural space on the dura mater at the level of its lesion.
После стихания послеоперационного отека больному проводят электростимуляцию пораженных отделов спинного мозга или нервных стволов. Каждому больному индивидуально подбираются оптимальные параметры: сила тока и длительность стимулирующего импульса. Проводят регистрацию и анализ вызванного М-ответа, полученного при подаче стимулирующих импульсов на имплантированные во время операции электроды. Регистрирующие (отводящие) электроды располагают на иннервируемой данным нервом мышце. Начальное значение длительности подаваемого электрического импульса - 0,1 мс, частота - 1-2 Гц.After the subsidence of postoperative edema, the patient undergoes electrical stimulation of the affected parts of the spinal cord or nerve trunks. The optimal parameters are individually selected for each patient: current strength and duration of the stimulating impulse. The evoked M-response obtained by applying stimulating pulses to the electrodes implanted during the operation is recorded and analyzed. The recording (discharge) electrodes are located on the muscle innervated by this nerve. The initial value of the duration of the supplied electric pulse is 0.1 ms, the frequency is 1-2 Hz.
Амплитуду тока постепенно увеличивают от нулевого значения и отмечают ее минимальную величину, при которой наблюдается появление вызванного М-ответа. При достижении силы стимулирующего тока величины 25 мА и отсутствии М-ответа длительность импульса увеличивают (для нервов верхней конечности максимально до 0,5 мс и для нервов нижней конечности до 1 мс) и вновь производят регистрацию вызванного мышечного ответа. Полученные показатели длительности импульса и амплитуды тока в каждом конкретном случае используют при проведении тестового сеанса электростимуляции.The current amplitude is gradually increased from a zero value and its minimum value is noted at which the appearance of an induced M-response is observed. When the stimulating current strength reaches 25 mA and the absence of an M-response, the pulse duration is increased (for nerves of the upper limb to a maximum of 0.5 ms and for nerves of the lower limb to 1 ms) and the evoked muscle response is recorded again. The obtained indicators of the pulse duration and the amplitude of the current in each case are used when conducting a test session of electrical stimulation.
Для контроля оптимального уровня параметров стимуляции сразу же после сеанса электростимуляции проводили контрольное исследование М-ответа. Если при этом отмечалось уменьшение его амплитуды более чем на 10% от исходного значения до сеанса электростимуляции, то величину стимулирующего тока снижали на 10-20%. После подбора параметров проводят сеансы прямой электростимуляции.To control the optimal level of stimulation parameters, immediately after the electrostimulation session, a control study of the M-response was performed. If at the same time a decrease in its amplitude was noted by more than 10% from the initial value before the electrostimulation session, then the value of the stimulating current was reduced by 10-20%. After selecting the parameters, direct electrical stimulation sessions are performed.
Ввиду изменения порога возбудимости нервных волокон 2 раза в неделю проводят коррекцию параметров электроимпульсного воздействия, ориентируясь на показатели контрольного ЭНМГ-исследования (вызванного М-ответа (аналогично первичному подбору параметров электростимуляции)).In view of the change in the threshold of excitability of nerve fibers 2 times a week, the parameters of the electropulse effect are corrected, focusing on the indicators of the control ENMG study (induced M-response (similar to the initial selection of parameters of electrical stimulation)).
Стимулирующие вытяжение и электровоздействие проводят в течение назначенного срока.Stimulating traction and electrical exposure are carried out within the prescribed period.
По результатам проведенного лечения проводят клинические исследования: изменение болевого синдрома, регресс неврологической симптоматики (купирование онемение в конечностей, рост мышечной силы, снижение головокружения и т.д.).According to the results of the treatment, clinical studies are carried out: a change in the pain syndrome, regression of neurological symptoms (relief of numbness in the limbs, increase in muscle strength, decrease in dizziness, etc.).
Для объективации результатов лечения проводят итоговое ЭНМГ-обследование: определяют уровень и характер изменения активности мотонейронов (по ЭНМГ), спонтанной активности, СРВ (скорости распространения возбудимости), показатели изменения уровня кровенаполнения и тонуса (реакции) сосудистой стенки.To objectify the results of treatment, a final ENMG examination is performed: the level and nature of changes in motor neuron activity (according to ENMG), spontaneous activity, SRV (excitability propagation velocity), indicators of changes in the level of blood supply and tone (reaction) of the vascular wall are determined.
Применение предлагаемого способа поясняется следующими чертежами, гдеThe application of the proposed method is illustrated by the following drawings, where
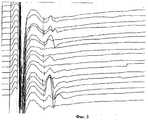
- фиг.1 - Иллюстрация к примеру 1: ЭНМГ-протокол до лечения (динамика нейрональной активности (F-волн) спинного мозга на уровне С7): при подаче 20 стимулов зарегистрировано 5 F-волн (75% блок проводимости);- figure 1 - Illustration for example 1: ENMG protocol before treatment (dynamics of neuronal activity (F-waves) of the spinal cord at C7 level): when 20 stimuli were applied, 5 F-waves were registered (75% conduction block);
- фиг.2 - Иллюстрация к примеру 1: ЭНМГ-протокол во время лечения после приложения нагрузки в течение 10 мин и при проведении накожной электростимуляции срединного нерва (динамика нейрональной активности (F-волн) спинного мозга на уровне С7): при подаче 20 стимулов зарегистрировано 15 F-волн (25% блок проводимости);- figure 2 - Illustration for example 1: ENMG protocol during treatment after application of the load for 10 min and during the cutaneous electrostimulation of the median nerve (dynamics of neuronal activity (F-waves) of the spinal cord at C7 level): when applying 20 stimuli 15 F waves (25% conduction block) were detected;
- фиг.3 - Иллюстрация к примеру 1: ЭНМГ-протокол после проведения стимулирующего вытяжения и накожной электростимуляции (динамика нейрональной активности (F-волн) спинного мозга на уровне С7): при подаче 20 стимулов зарегистрировано 19 F-волн (5% блок проводимости);- figure 3 - Illustration for example 1: ENMG protocol after stimulating traction and cutaneous electrostimulation (dynamics of neuronal activity (F-waves) of the spinal cord at the C7 level): when 20 stimuli were applied, 19 F-waves were recorded (5% conduction block );
- фиг.4 - Иллюстрация к примеру 2: Снимок компьютерной томограммы (КТ) поясничного отдела позвоночника с контрастом в положении больной на животе - стрелкой отмечена парамедианная грыжа 8×12×12 мм диска LV-S1 до лечения. Снимок для наглядного сравнения повернут на 180;- figure 4 - Illustration for example 2: Computed tomography (CT) scan of the lumbar spine with contrast in the position of the patient on the abdomen - the arrow marks a paramedian hernia of 8 × 12 × 12 mm LV-S1 disk before treatment. Image for visual comparison rotated 180;
- фиг.5 - Иллюстрация к примеру 2: Снимок компьютерной томограммы (КТ) после лечения - стимулирующего вытяжения и накожной электростимуляции поясничного отдела позвоночника - стрелкой отмечена парамедианная грыжа диска LV-S1, уменьшившаяся до размера 4×10×8 мм;- Fig. 5 - Illustration for example 2: A computed tomography (CT) scan after treatment - stimulating traction and cutaneous electrical stimulation of the lumbar spine - the arrow marks the paramedian hernia of the LV-S1 disc, reduced to a size of 4 × 10 × 8 mm;
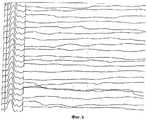
- фиг.6 - Иллюстрация к примеру 3: ЭНМГ-протокол до лечения (динамика нейрональной активности (F-волн) спинного мозга на уровне С7): при подаче 20 стимулов ответных F-волн не зарегистрировано (полный блок проводимости);- 6 - Illustration for example 3: ENMG protocol before treatment (dynamics of neuronal activity (F-waves) of the spinal cord at C7 level): when 20 stimuli were applied, no response F-waves were recorded (full block of conductivity);
- фиг.7 - Иллюстрация к примеру 3: ЭНМГ-протокол после проведения стимулирующего вытяжения и эпидуральной электростимуляции спинного мозга (динамика нейрональной активности (F-волн) спинного мозга на уровне С7): при подаче 20 стимулов зарегистрировано 10 F-волн (50% блок проводимости).- Fig. 7 - Illustration for example 3: ENMG protocol after stimulating traction and epidural electrical stimulation of the spinal cord (dynamics of neuronal activity (F-waves) of the spinal cord at the C7 level): when applying 20 stimuli, 10 F-waves were recorded (50% conduction block).
Пример 1. Больная С. в возрасте 47 лет, поступила СарНИИТО с жалобами на боли в шейном отделе позвоночника, слабость в кистях, онемение в I-III пальцах, головокружение, усиливающееся при поворотах головы и наклонах. Больна на протяжении 6 лет. Боли в шейном отделе позвоночника, в начале непродолжительные и проходившие самостоятельно, постепенно усиливались. Последние три года стали отмечаться неврологические проявления в виде онемения в пальцах кистей, головокружение. Проводившееся в последние время медикаментозное лечение давало незначительный и непродолжительный эффект.Example 1. Patient S., aged 47, received SARNIIITO with complaints of pain in the cervical spine, weakness in the hands, numbness in the I-III fingers, dizziness, aggravated by turning the head and tilting. Sick for 6 years. Pain in the cervical spine, at the beginning short-lived and passing on its own, gradually intensified. The last three years, neurological manifestations began in the form of numbness in the fingers, dizziness. The recent medical treatment has given an insignificant and short-lasting effect.
В СарНИИТО проведены обследования: рентгенографическое (Rg) исследование, магнитно-резонансная (МРГ) и компьютерная томография (КТ) шейного отдела позвоночника, электронейромиография (ЭНМГ) верхних конечностей. При МРТ-исследовании выявлено: снижение межпозвонкового промежутка CVI-CVII, грыжа диска на этом уровне, компрессия дурального мешка со сдавлением переднего субарахноидального пространства и оттеснением корешков спинного мозга. Размеры грыжевого выпячивания 6×10×10 мм.Surveys were conducted at SarNIIITO: X-ray (Rg) examination, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) of the cervical spine, electroneuromyography (ENMG) of the upper extremities. An MRI scan revealed: CVI-CVII intervertebral space reduction, disc herniation at this level, dural sac compression with compression of the anterior subarachnoid space and extrusion of the spinal cord roots. Dimensions of hernial protrusion 6 × 10 × 10 mm.
При ЭНМГ-исследовании выявлено: наибольшее изменение показателей срединного нерва справа: снижение показателей СРВ по моторным стволам на плече до 45 м/с, предплечье - до 43 м/с, снижение амплитуды вызванного мышечного ответа (М-ответа, мышцы тенара) - 3,7 мВ, 75% блок появления F-волн (активности мотонейронов) {на фиг.1 приведен ЭНМГ-протокол до лечения - динамика нейрональной активности уровня С7 при стимуляции срединного нерва: при подаче 20 стимулов зарегестрировано 19 F-волн (5% блок проводимости)), регистрация в мышце, отводящей первый палец, потенциалов фасцикулляций (ПФЦ), фибрилляций (ПФ), появление «укрупненных» потенциалов двигательных единиц (ПДЕ) с длительностью, превышающей показатели нормы на 36%, амплитуда в 35% более 1 мВ. Слева СРВ на уровне плеча - 59 м/с (норма), предплечья 52 м/с -норма, амплитуда М-ответа 5.2 мВ (снижена), блок появления F-волн составил 15%. В мышцах тенара регистрировались ПФЦ, из 20 исследуемых единиц 2 ПДЕ имели размеры, превышающие норму.An ENMG study revealed: the greatest change in the indices of the median nerve on the right: a decrease in the SRV of the motor trunks on the shoulder to 45 m / s, the forearm to 43 m / s, a decrease in the amplitude of the evoked muscle response (M-response, tenar muscles) - 3 , 7 mV, 75% block of the appearance of F-waves (activity of motor neurons) {Fig. 1 shows the ENMG protocol before treatment - dynamics of neuronal activity of level C7 during stimulation of the median nerve: when 20 stimuli are applied, 19 F-waves are registered (5% block conduction)), registration in the muscle that removes the first finger, potent als fastsikullyatsy (PFC) fibrillations (PD), the appearance of "enlarged" motor unit potentials (MUP) with a duration exceeding the norm indicators 36%, 35% amplitude greater than 1 mV. On the left, the SRV at the shoulder level is 59 m / s (normal), the forearm is 52 m / s normal, the amplitude of the M-response is 5.2 mV (reduced), the F-wave appearance block is 15%. PFCs were recorded in the muscles of the tenar; of the 20 units studied, 2 PDEs were larger than normal.
Поставлен диагноз: остеохондроз шейного отдела позвоночника, грыжа диска CVI-CVII с компрессией дурального мешка и CVII корешка), миелорадикулопатия уровня CV-CVII сегмента.Diagnosed with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, herniated disc CVI-CVII with compression of the dural sac and CVII root), myeloradiculopathy of the level of CV-CVII segment.
Для подбора степени вытяжения и направления его вектора провели предварительное тестовое ЭНМГ-исследование и определили изменение активности мотонейронов срединного нерва справа: при исходном тестировании сохранялся 75% блок активности, а изменения ЭНМГ-показателей носили 2- сторонний характер. Поэтому вначале было решено провести тракцию сзади симметрично. Регистрация F-волн не выявила существенных сдвигов показателей - 75% блока F-волн.To select the degree of traction and the direction of its vector, a preliminary ENMG test was carried out and the change in the activity of the median nerve motor neurons on the right was determined: during the initial testing, a 75% block of activity was preserved, and changes in the ENMG indices were 2-sided. Therefore, at first it was decided to traction back symmetrically. Registration of F-waves did not reveal significant changes in indicators - 75% of the block of F-waves.
Более интенсивное вытяжение справа и сзади привело к появлению еще 5 F-волн (25%), что свидетельствовало о дополнительной активации мотонейронов С7 уровня спинного мозга. При исследовании через 15 мин вытяжения, блок снизился с 75% до 45%.A more intense traction on the right and behind led to the appearance of another 5 F-waves (25%), which indicated the additional activation of C7 spinal cord motor neurons. When examining after 15 minutes of traction, the block decreased from 75% to 45%.
По результатам тестирования проведено консервативное лечение по предлагаемому способу: вытяжение в шейном корсете, управляемое по показателям состояния спинного мозга и проводящих нервных путей в сочетании с накожной элетростимуляцией шейного отдела.According to the test results, conservative treatment was carried out according to the proposed method: traction in the cervical corset, controlled by indicators of the condition of the spinal cord and conduction of the nerve pathways in combination with cutaneous electrostimulation of the cervical spine.
При вытяжении медленным вращением нагрузочных гаек, выдвигали передние телескопические стержни, увеличивая тем самым степень вытяжения, при этом проводили ЭНМГ-контроль: регистрировали амплитуды F-волн и М-ответов. Величина суммарного вытяжения составила: на передние - 6 см и на задние - 7 см. Получили положительный результат при ЭНМГ-контроле. На фиг.2 приведен ЭНМГ-протокол после сеанса вытяжения - приложения нагрузки в течение 10 мин - динамика нейрональной активности уровня С7 при стимуляции срединного нерва: при подаче 20 стимулов зарегистрировано 15 F-волн (25% блок проводимости).When stretching by slow rotation of the load nuts, the front telescopic rods were extended, thereby increasing the degree of traction, while the ENMG control was performed: the amplitudes of the F waves and M responses were recorded. The magnitude of the total traction was: on the front - 6 cm and on the rear - 7 cm. A positive result was obtained with ENMG control. Figure 2 shows the ENMG protocol after a traction session - applying a load for 10 min - the dynamics of the neuronal activity of level C7 during stimulation of the median nerve: when 20 stimuli were applied, 15 F-waves were registered (25% conduction block).
При экспозиции 12 мин отмечено угасание регистрируемых результатов ЭНМГ-исследования. При повторном вытяжении с 10 мин перерывом вновь получен положительный результат, однако период экспозиции составил всего 9 мин.When the exposure was 12 min, the fading of the recorded results of the ENMG study was noted. Upon repeated stretching with a 10 min break, a positive result was again obtained, however, the exposure period was only 9 min.
Для проведения электростимуляции три стимулирующих электрода расположили в следующем порядке: 1 - в зоне Эрба, 2- на проксимальные стволы срединного нерва (верхняя треть внутренней поверхности плеча) и 3 - на дистальную точку стимуляции нерва. Амплитуда тока составляла 25-30 мкВ, длительность 0,1 мс, частота 50 Гц. Сеанс электростимуляции - 25 мин. После сеанса электростимуляции при контрольном ЭНМГ-обследовании не выявило отрицательной динамики показателей. Стимулирующие вытяжение и электровоздействие проводили в течение трех недель.To conduct electrical stimulation, three stimulating electrodes were arranged in the following order: 1 - in the Erb zone, 2 - on the proximal trunks of the median nerve (upper third of the inner surface of the shoulder) and 3 - on the distal nerve stimulation point. The current amplitude was 25-30 μV, duration 0.1 ms, frequency 50 Hz. Electrical stimulation session - 25 min. After a session of electrical stimulation during the control ENMG examination, no negative dynamics of the indicators were revealed. Stimulating traction and electrical exposure were performed for three weeks.
В результате проведенного лечения болевой синдром купировался уже на 8 день, а к концу второй недели отмечен значительный регресс неврологической симптоматики: купировалось онемение в пальцах, наросла мышечная сила, отмечено значительное уменьшение головокружения при поворотах головы.As a result of the treatment, the pain syndrome stopped already on the 8th day, and by the end of the second week a significant regression of neurological symptoms was noted: numbness in the fingers stopped, muscle strength increased, a significant decrease in dizziness during head turns was noted.
При итоговом ЭНМГ обследовании выявлено повышение СРВ на плече до 57 м/с, на предплечье до 52 м/с, увеличение амплитуды М-ответа до 7,6 мВ, на 20 стимулов регистрировалось 19 F-волн. Значительно снизилось количество регистрируемых ПФЦ. Данное состояние иллюстрируется фиг.3, где приведен ЭНМГ-протокол после проведения стимулирующего вытяжения и накожной электростимуляции (динамика нейрональной активности (F-волн) спинного мозга на уровне С7): при подаче 20 стимулов зарегестрировано 19 F-волн (5% блок проводимости).The final ENMG examination revealed an increase in SRV on the shoulder to 57 m / s, on the forearm to 52 m / s, an increase in the amplitude of the M-response to 7.6 mV, 19 F-waves were recorded for 20 stimuli. The number of registered PFCs has significantly decreased. This state is illustrated in Fig. 3, where the ENMG protocol is shown after stimulating traction and cutaneous electrostimulation (dynamics of neuronal activity (F-waves) of the spinal cord at level C7): when 20 stimuli are applied, 19 F-waves are registered (5% conduction block) .
Пример 2. Больной М. 43 лет, №640 карты дневного стационара. Болен около 8 лет, вначале появились периодические боли в поясничном отделе позвоночника, которые стали постоянными с иррадировнием в правую ногу. За последние три месяца боли стали беспокоить и в левой ноге, а справа стал отмечать слабость мышц-разгибателей стопы, больше III-V пальцев, появилось онемение и снижение болевой чувствительности в области наружной поверхности голени и стопы.Example 2. Patient M., 43 years old, No. 640 cards of the day hospital. Sick for about 8 years, at first there were periodic pains in the lumbar spine, which became permanent with irradiation in the right leg. Over the past three months, pain in the left leg began to bother, and on the right began to notice weakness of the extensor muscles of the foot, more than III-V fingers, numbness and a decrease in pain sensitivity in the outer surface of the lower leg and foot appeared.
Клинике-неврологическое исследование: у больного имеется гипотрофия правой голени, особенно икроножной. Сила мышц-разгибателей снижена до 2 баллов. Имеется гиперстезия по наружной поверхности правой голени и стопы, включая V палец. Отмечается снижение левого и отсутствие правого ахилловых рефлексов.Clinic-neurological examination: the patient has hypotrophy of the right lower leg, especially the calf. The strength of the extensor muscles is reduced to 2 points. There is hypersthesia on the outer surface of the right lower leg and foot, including the V toe. There is a decrease in left and the absence of right Achilles reflexes.
Проведены обследования: рентгенография (Rg) и КТ-миелография поясничного отдела позвоночника, ЭНМГ нижних конечностей. При рентгенографическом Rg-исследовании выявлены признаки остеохондроза 2-3 степени, со снижением высоты межтелового промежутка LV-SI, являющееся косвенным признаком грыжи диска. При КТ-миелография выявлена парамедианная грыжа диска 8×12×12 мм, компремирующая левый SI-корешок и умеренно деформирующая дуральный мешок.. Данное состояние иллюстрируется фиг.4.Examinations: radiography (Rg) and CT myelography of the lumbar spine, ENMG of the lower extremities. An X-ray Rg study revealed signs of osteochondrosis of the 2nd to 3rd degree, with a decrease in the height of the interbody gap LV-SI, which is an indirect sign of a disc herniation. When CT-myelography revealed a paramedian hernia of the disc 8 × 12 × 12 mm, compressing the left SI-root and moderately deforming the dural sac .. This condition is illustrated in figure 4.
При ЭНМГ-обследовании выявлено: выраженное снижение всех показателей с 2-х сторон;An ENMG examination revealed: a pronounced decrease in all indicators from 2 sides;
- снижение СРВ по малоберцовому нерву справа до 32 м/с, амплитуда М-ответа составила всего 2,1 мВ; слева - до 41 м/с, М-ответ - 3.6 мВ; F-волны не регистрируются;- reduction of SRV along the peroneal nerve on the right to 32 m / s, the amplitude of the M-response was only 2.1 mV; on the left - up to 41 m / s, M-response - 3.6 mV; F-waves are not recorded;
- по большеберцовому нерву - справа СРВ снижена до 26 м/с, слева - до 37 м/с, 45% выпадение F-волн;- along the tibial nerve - on the right the SRV is reduced to 26 m / s, on the left - to 37 m / s, 45% loss of F-waves;
- снижены амплитуды М-ответов до 2,4 мВ и 3,2 мВ соответственно.- reduced the amplitude of the M-responses to 2.4 mV and 3.2 mV, respectively.
В мышцах голени (особенно в зоне иннервации малоберцового нерва) при произвольной активности регистрировалась спонтанная активность, свидетельствовавшая о более глубоких денервационных процессах в мышцах.In the muscles of the leg (especially in the area of the innervation of the peroneal nerve), spontaneous activity was recorded with arbitrary activity, indicating a deeper denervation in the muscles.
Диагностировано: остеохондроз поясничного отдела позвоночника, парамедианная грыжа диска LV-SI, хроническая компрессия SI-корешка справа, миелорадикулопатия уровня LV, парез разгибателей III-V пальцев правой стопы, хроническое прогродиентное течение.Diagnosed with osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, paramedian hernia of the LV-SI disc, chronic compression of the SI root on the right, myeloradiculopathy of the LV level, paresis of extensor III-V of the toes of the right foot, chronic progrodient course.
Для выбора тактики лечения больному выполнен диагностический тест с наложением дистрагирующего поясничного корсета и последующим вытяжением под ЭНМГ-контролем. При вытяжении с установкой передних телескопических стержней на 8 см и задних - на 6 см получен положительный результат по ЭНМГ-контроле: появление дополнительных F-волн с уровня S1 и снижение блока до 35% свидетельствовало о положительной реакции мотонейронов на вытяжение. При экспозиции 12 мин отмечено угасание ЭНМГ-результатов. При повторном вытяжении с 10 мин перерывом вновь получен положительный результат, однако период экспозиции составил всего 10 мин.To select treatment tactics, a diagnostic test was performed on the patient with the application of a distracting lumbar corset and subsequent stretching under ENMG control. When stretching with the front telescopic rods installed at 8 cm and the rear ones at 6 cm, a positive result was obtained by the ENMG control: the appearance of additional F waves from level S1 and a decrease in the block to 35% indicated a positive reaction of motoneurons to traction. At an exposure of 12 min, the extinction of the ENMG results was noted. Upon repeated stretching with a 10 min break, a positive result was again obtained, however, the exposure period was only 10 min.
По результатам тестирования проведено консервативное лечение по предлагаемому способу: вытяжение в поясничном корсете, управляемое по показателям состояния спинного мозга и нервных путей в сочетании с накожной электростимуляцией поясничного отдела позвоночника. Общая продолжительность курса составила три недели.According to the test results, conservative treatment was carried out according to the proposed method: traction in the lumbar corset, controlled by indicators of the condition of the spinal cord and nerve pathways in combination with cutaneous electrical stimulation of the lumbar spine. The total duration of the course was three weeks.
При вытяжении больного в горизонтальном положении помещали в поясничный корсет и медленным вращением нагрузочных гаек, выдвигали передние телескопические стержни, увеличивая тем самым степень вытяжения, при этом проводили ЭНМГ-контроль: регистрировали амплитуды F-волн и М-ответов. Величина суммарного вытяжения составила: на передние - 8 см и на задние - 9 см. По данным ЭНМГ-контроля оптимальное время сеанса вытяжения составило 25-30 мин.When the patient was stretched in a horizontal position, they were placed in the lumbar corset and the load nuts were slowly rotated, the front telescopic rods were extended, thereby increasing the degree of traction, while the ENMG control was performed: the amplitudes of the F waves and M responses were recorded. The total traction was: to the front - 8 cm and to the rear - 9 cm. According to the ENMG control, the optimal traction session time was 25-30 minutes.
Электростимуляцию поясничного отдела осуществляли тремя стимулирующими электродами. Амплитуда тока составляла 25-30 мкВ, длительность 0,1 мс, частота 50 Гц. Каждый сеанс продолжался 25 мин.Electrical stimulation of the lumbar was carried out by three stimulating electrodes. The current amplitude was 25-30 μV, duration 0.1 ms, frequency 50 Hz. Each session lasted 25 minutes.
Болевой синдром купирован на 12 день, а к концу третьей недели отмечен полный регресс неврологической симптоматики.The pain syndrome was stopped on day 12, and by the end of the third week a complete regression of neurological symptoms was noted.
При повторном КТ-исследовании выявлено, что объем грыжевого выпячивания уменьшился до 4×10×8 мм. SI-корешок принял округлую форму, не деформирован, дуральный мешок интактен. Данное состояние иллюстрируется фиг.5.A repeat CT scan revealed that the hernial protrusion volume decreased to 4 × 10 × 8 mm. SI-root took a rounded shape, not deformed, dural sac intact. This state is illustrated in FIG.
При контрольном ЭНМГ-обследовании зафиксирована существенная положительная динамика показателей: повышение СРВ по всем нервам: по малоберцовому справа до 40 м/с, по большеберцовому до 48 м/с, на уровне S1 блок появления F-волн отсутствовал, на уровне L5 снизился до 50%. В мышцах голени исчезли ПОВ, ПФЦ, появились низкоамплитудные полифазные ПДЕ - характерные признаки реинервации мышечных волокон регенерирующими аксонами.During the control ENMG examination, there was a significant positive dynamics of the indicators: an increase in SRV in all nerves: in the fibula on the right to 40 m / s, in the tibia to 48 m / s, at the S1 level, the F-wave block was absent, at the L5 level it decreased to 50 % POV and PFC disappeared in the calf muscles, low-amplitude polyphase PDEs appeared - characteristic signs of muscle fiber reinnervation by regenerating axons.
Наблюдение за больным в течение года выявило стойкую ремиссию.Observation of the patient during the year revealed persistent remission.
Пример 3. Больной К-й, 52 лет, в 1997 г. находился на лечении в клинике нейрохирургии СарНИИТО по поводу последствий позвоночно-спинномозговой травмы с диагнозом: консолидированный перелом тела CVI позвонка с незначительной клиновидной его деформацией, миелорадикулопатия с уровня CV сегмента с синдромом частичного нарушения проводимости спинного мозга, тетрапарез, корешковый болевой синдром, синдром вертебробазилярной недостаточности.Example 3. Patient K-52, in 1997, was treated at the SarNIIITO neurosurgery clinic for the consequences of a spinal cord injury with a diagnosis of consolidated vertebral body fracture with a slight wedge-shaped deformity, myeloradiculopathy from the level of the CV segment with the syndrome partial conduction disturbance of the spinal cord, tetraparesis, radicular pain syndrome, vertebrobasilar insufficiency syndrome.
Травму получил в 1997 г. при нырянии в воду на мелководье: сразу же после травмирующего события ощутил слабость в конечностях, онемение в кистях со жгучими болями в них. Сразу же после получения травмы был доставлен в стационар, где при рентгенологическом обследовании был выявлен компрессионный перелом тела CVI позвонка, уточненный при пункционном исследовании: компрессионный перелом без нарушения ликвородинамики.He was injured in 1997 when diving into the water in shallow water: immediately after the traumatic event, he felt weakness in the limbs, numbness in the hands with burning pains in them. Immediately after the injury, he was taken to a hospital, where, during an X-ray examination, a compression fracture of the CVI vertebral body was revealed, specified in a puncture study: compression fracture without disturbing cerebrospinal fluid dynamics.
В 1997 г. в СарНИИТО больному было назначено консервативное лечение - вытяжением на петле Глиссона.In 1997, a conservative treatment was prescribed to the patient at SarNIIIT - traction on the Glisson loop.
В результате проведенного лечения неврологическая симптоматика значительно регрессировала. Мышечная сила в конечностях была снижена до 3-4 баллов. Больной смог приступить к работе. Однако впоследствии больной стал отмечать медленное ухудшение состояния в виде нарастания слабости в верхних конечностях.As a result of the treatment, neurological symptoms significantly regressed. Muscle strength in the limbs was reduced to 3-4 points. The patient was able to get to work. However, later the patient began to notice a slow deterioration in the form of an increase in weakness in the upper limbs.
После резкого запрокидывания головы появились резкие боли в шее, отдающие по наружной поверхности рук, онемение в руках, слабость в кистях рук, наростающая слабость в ногах.After a sharp tipping of the head, sharp pains appeared in the neck, extending along the outer surface of the hands, numbness in the hands, weakness in the hands, growing weakness in the legs.
При поступлении в СарНИИТО у больного выявлено: гиперстезия в CVI-CVII дерматома с двух сторон. Глубокий вялый парез кистей рук, больше слева, атрофия мышц тенара, межкостных промежутков левой кисти, выраженная слабость в проксимальных отделах нижних конечностей. Неудержание предметов в руках, трудности при ходьбе.Upon admission to SarnIIITO, the patient revealed: hypersthesia in the CVI-CVII dermatome from two sides. Deep flaccid paresis of the hands, more on the left, atrophy of the muscles of the tenar, interosseous spaces of the left hand, severe weakness in the proximal lower extremities. Incontinence of objects in hands, difficulty walking.
По данным миелорадикулографии (МРГ) и электронейромиографии (ЭНМГ) - признаки миелоишемии на уровне CVI-CVII сегмента. Ликвородинамика сохранена. Имеется незначительная клиновидная деформация тела CI-позвонка. Снижение межтелового промежутка на уровне дисков CV-CVI и CVI-CVII. Межпозвонковый диск CV-CVI практически не определяется, CVI-CVII значительно уменьшен в размерах за счет дегенеративного перерождения. Данное состояние иллюстрируется фиг.6, где приведен ЭНМГ-протокол до лечения (динамика нейрональной активности (F-волн) спинного мозга на уровне С7): при подаче 20 стимулов не зарегистрировано ответных F-волн (полный блок проводимости).According to myeloradiculography (MRH) and electroneuromyography (ENMG), there are signs of myeloid ischemia at the level of the CVI-CVII segment. Liquorodynamics saved. There is a slight wedge-shaped deformation of the body of the CI vertebra. Reduced interbody gap at CV-CVI and CVI-CVII. The CV-CVI intervertebral disc is practically undetectable, CVI-CVII is significantly reduced in size due to degenerative degeneration. This condition is illustrated in Fig.6, which shows the ENMG protocol before treatment (dynamics of neuronal activity (F-waves) of the spinal cord at the C7 level): when 20 stimuli were applied, no response F-waves were recorded (full block of conduction).
На основании сопоставления результатов клинико-неврологического и электрофизиологического исследования намечено провести оперативное лечение по предлагаемому способу: вытяжение в шейном дистрагирующем корсете, управляемое по показателям состояния спинного мозга и нервных путей в сочетании эпидуральной элетростимуляцией шейного отдела позвоночника.Based on a comparison of the results of clinical, neurological and electrophysiological studies, it is planned to carry out surgical treatment according to the proposed method: traction in the cervical distracting corset, controlled by indicators of the condition of the spinal cord and nerve pathways in combination with epidural electrostimulation of the cervical spine.
Для осуществления эпидуральной элетростимуляции шейного отдела позвоночника в СарНИИТО 22.12.97 проведена операция: под местным обезболиванием пункционным путем в эпидуральное пространство введены две пары игольчатых электродов на двух уровнях.To carry out epidural electrostimulation of the cervical spine in SarNIIITO on December 22, 1997, an operation was performed: two pairs of needle electrodes at two levels were introduced into the epidural space under local anesthesia by puncture.
Через неделю после установки эпидуральных электродов больному выполнен диагностический тест, заключающийся в наложении дистрагирующего шейного корсета с последующей дистракцией и ЭНМГ-контролем. При установке передних телескопических стержней на 4 см и задних - на 6 получена положительная динамика ЭНМГ-результатов. При экспозиции 8 мин отмечено угасание показателей ЭНМГ исследования. При повторном вытяжении с 10 мин перерывом вновь получен положительный результат, однако период экспозиции составил всего 5 мин.A week after the installation of epidural electrodes, the patient underwent a diagnostic test consisting in the application of a distracting cervical corset with subsequent distraction and ENMG control. When installing the front telescopic rods at 4 cm and the rear ones at 6, positive dynamics of the ENMG results was obtained. When the exposure was 8 min, the extinction of the ENMG study was noted. Upon repeated stretching with a 10-minute break, a positive result was again obtained, however, the exposure period was only 5 minutes.
На аппарате «Элиман» проводили электростимуляцию 3 раза в сутки по 25-30 мин. После сеанса электростимуляции при контрольном ЭНМГ-обследовании не выявило отрицательной динамики показателей.On the apparatus "Eliman" conducted electrical stimulation 3 times a day for 25-30 minutes. After a session of electrical stimulation during the control ENMG examination, no negative dynamics of the indicators were revealed.
Общий курс вытяжения в шейном дистрагирующем корсете и эпидуральной элетростимуляции составил три недели.The general course of traction in the cervical distracting corset and epidural electrostimulation was three weeks.
Болевой синдром купирован уже на 7 день, а к концу третьей недели отмечен значительный регресс неврологической симптоматики.The pain syndrome was stopped already on the 7th day, and by the end of the third week a significant regression of neurological symptoms was noted.
При повторных МРТ и ЭНМГ-исследованиях признаки миелоишемии не наросли, отмечается тенденция к ее уменьшению. Данное состояние иллюстрируется фиг.7: ЭНМГ-протокол после проведения стимулирующего вытяжения и эпидуральной электростимуляции спинного мозга (динамика нейроналъной активности (F-волн) спинного мозга на уровне С7): при подаче 20 стимулов зарегистрировано 10 F-волн (50% блок проводимости).With repeated MRI and ENMG studies, the symptoms of myelosemia did not increase, there is a tendency to decrease it. This state is illustrated in Fig. 7: ENMG protocol after stimulating traction and epidural electrical stimulation of the spinal cord (dynamics of neuronal activity (F-waves) of the spinal cord at C7 level): when 20 stimuli were applied, 10 F-waves were recorded (50% conduction block) .
Наблюдение за больным в течение года выявило стойкую ремиссию: при контроле отдаленного результата, через 12 месяцев, функции конечностей полностью восстановлены, а имевшийся до лечения по данному способу болевой синдром отсутствовал.Observation of the patient during the year revealed persistent remission: when monitoring the long-term result, after 12 months, the functions of the limbs were fully restored, and there was no pain syndrome before treatment with this method.
Медико-социальная эффективность способа заключается:Medical and social effectiveness of the method is:
- в создании новой наукоемкой технологии лечения больных данной категории, основанной на сочетании вытяжения позвоночника и элетростимуляции пораженных зон, управляемых по показателям состояния спинного мозга и проводящих нервных путей;- in the creation of a new high-tech technology for the treatment of patients of this category, based on a combination of spinal traction and electrostimulation of the affected areas, controlled by indicators of the condition of the spinal cord and conduction of the nerve pathways;
- в создании метода стимуляции репаративно-пластических процессов нервной ткани и спинного мозга и формирования стойкой ремиссии;- in the creation of a method for stimulating the repair-plastic processes of the nervous tissue and spinal cord and the formation of persistent remission;
- в повышении качества жизни больных данной категории: восстановление или активизации утраченных функций опорно-двигательного аппарата и избавлении от спастико-болевого синдрома;- in improving the quality of life of patients in this category: restoration or activation of lost functions of the musculoskeletal system and getting rid of spastic-pain syndrome;
- в быстрой социальной и трудовой адаптации больных данной категории, сокращении сроков нетрудоспособности-инвалидизации.- in the rapid social and labor adaptation of patients in this category, reducing the time of disability, disability.
Claims (4)
Translated fromRussianPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2003122104/14ARU2258496C2 (en) | 2003-07-15 | 2003-07-15 | Method for treating patients with traumatic and degenerative lesions of vertebral column and spinal cord |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2003122104/14ARU2258496C2 (en) | 2003-07-15 | 2003-07-15 | Method for treating patients with traumatic and degenerative lesions of vertebral column and spinal cord |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2003122104A RU2003122104A (en) | 2004-02-10 |
| RU2258496C2true RU2258496C2 (en) | 2005-08-20 |
Family
ID=35846231
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2003122104/14ARU2258496C2 (en) | 2003-07-15 | 2003-07-15 | Method for treating patients with traumatic and degenerative lesions of vertebral column and spinal cord |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2258496C2 (en) |
Cited By (31)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2389435C1 (en)* | 2009-04-01 | 2010-05-20 | Федеральное государственное учреждение "Саратовский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии Федерального агентства по высокотехнологичной медицинской помощи" | Method of choosing modality in patients with traumatic rachiopathy |
| RU2392907C1 (en)* | 2009-04-01 | 2010-06-27 | Федеральное государственное учреждение "Саратовский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии Федерального агентства по высокотехнологичной медицинской помощи" | Method of treating patients with degenerative rachiopathy |
| RU2393756C1 (en)* | 2009-04-01 | 2010-07-10 | Федеральное государственное учреждение "Саратовский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии Федерального агентства по высокотехнологичной медицинской помощи" | Method of selecting tactics of treating patients with degenerative affection of spine |
| RU2432920C1 (en)* | 2010-05-25 | 2011-11-10 | Государственное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования Первый Московский государственный медицинский университет имени И.М.Сеченова Министерства здравоохранения и социального развития Российской Федерации (ГОУВПО Первый МГМУ им.И.М.Сеченова Минздравсоцразвития России) | Method of patients' management in postoperative regimen after posterior stabilisation of lumbar spine |
| RU2441679C1 (en)* | 2010-07-13 | 2012-02-10 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение "Российский научный центр "Восстановительная травматология и ортопедия" имени академика Г.А.Илизарова" Министерства здравоохранения и социального развития Российской Федерации (ФГБУ "РНЦ "ВТО" им. акад. Г.А.Илизарова" Минздравсоцразвития России) | Medullary electric stimulation |
| RU2452528C1 (en)* | 2010-12-21 | 2012-06-10 | Александр Ильич Тома | Method of anterior spinal cord electrostimulation in surgical management of thoracic spinal-cerebrospinal injury |
| RU2481868C1 (en)* | 2011-12-05 | 2013-05-20 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение "Саратовский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии" Министерства здравоохранения и социального развития Российской Федерации (ФГБУ "СарНИИТО" Минздравсоцразвития России) | Method of treating spastic and spastic pain syndromes in patients with vertebral-spinal trauma impact and spinal diseases |
| RU2506970C1 (en)* | 2012-10-08 | 2014-02-20 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение "Российский научный центр "Восстановительная травматология и ортопедия" имени академика Г.А. Илизарова" Министерства здравоохранения и социального развития Российской Федерации | Method for rehabilitation treatment of patients with lower mono- and paraparesis with involved peripheral nerve |
| US9101769B2 (en) | 2011-01-03 | 2015-08-11 | The Regents Of The University Of California | High density epidural stimulation for facilitation of locomotion, posture, voluntary movement, and recovery of autonomic, sexual, vasomotor, and cognitive function after neurological injury |
| RU2572298C1 (en)* | 2014-07-10 | 2016-01-10 | Оксана Владимировна Кузина | Method for integrated treatment of spinal diseases |
| US9393409B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2016-07-19 | Neuroenabling Technologies, Inc. | Non invasive neuromodulation device for enabling recovery of motor, sensory, autonomic, sexual, vasomotor and cognitive function |
| US9409023B2 (en) | 2011-03-24 | 2016-08-09 | California Institute Of Technology | Spinal stimulator systems for restoration of function |
| US9409011B2 (en) | 2011-01-21 | 2016-08-09 | California Institute Of Technology | Method of constructing an implantable microelectrode array |
| US9415218B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2016-08-16 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation: noninvasive tool for activation of locomotor circuitry |
| US9993642B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2018-06-12 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Multi-site transcutaneous electrical stimulation of the spinal cord for facilitation of locomotion |
| US10092750B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2018-10-09 | Neuroenabling Technologies, Inc. | Transcutaneous neuromodulation system and methods of using same |
| US10137299B2 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2018-11-27 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Engaging the cervical spinal cord circuitry to re-enable volitional control of hand function in tetraplegic subjects |
| US10751533B2 (en) | 2014-08-21 | 2020-08-25 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Regulation of autonomic control of bladder voiding after a complete spinal cord injury |
| US10773074B2 (en) | 2014-08-27 | 2020-09-15 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Multi-electrode array for spinal cord epidural stimulation |
| US10786673B2 (en) | 2014-01-13 | 2020-09-29 | California Institute Of Technology | Neuromodulation systems and methods of using same |
| US11097122B2 (en) | 2015-11-04 | 2021-08-24 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Magnetic stimulation of the spinal cord to restore control of bladder and/or bowel |
| US11298533B2 (en) | 2015-08-26 | 2022-04-12 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Concerted use of noninvasive neuromodulation device with exoskeleton to enable voluntary movement and greater muscle activation when stepping in a chronically paralyzed subject |
| US11672983B2 (en) | 2018-11-13 | 2023-06-13 | Onward Medical N.V. | Sensor in clothing of limbs or footwear |
| US11691015B2 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2023-07-04 | Onward Medical N.V. | System for neuromodulation |
| US11752342B2 (en) | 2019-02-12 | 2023-09-12 | Onward Medical N.V. | System for neuromodulation |
| US11839766B2 (en) | 2019-11-27 | 2023-12-12 | Onward Medical N.V. | Neuromodulation system |
| US11992684B2 (en) | 2017-12-05 | 2024-05-28 | Ecole Polytechnique Federale De Lausanne (Epfl) | System for planning and/or providing neuromodulation |
| US12268878B2 (en) | 2017-02-17 | 2025-04-08 | The University Of British Columbia | Apparatus and methods for maintaining physiological functions |
| US12357828B2 (en) | 2017-12-05 | 2025-07-15 | Ecole Polytechnique Federale De Lausanne (Epfl) | System for planning and/or providing neuromodulation |
| US12415079B2 (en) | 2019-11-27 | 2025-09-16 | Onward Medical N.V. | Neuromodulation system |
| US12434068B2 (en) | 2017-05-23 | 2025-10-07 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Accessing spinal networks to address sexual dysfunction |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2329834C2 (en)* | 2006-09-12 | 2008-07-27 | Государственное учреждение здравоохранения Свердловской области "Центр организации специализированных видов медицинской помощи "Институт медицинских клеточных технологий" (ГУЗ СО "Институт медицинских клеточных технологий) | Method of spinal diseases treatment |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU1242160A1 (en)* | 1982-05-25 | 1986-07-07 | Донецкий медицинский институт им.А.М.Горького | Method of treatment of discogenous radiculitis |
| SU1304822A1 (en)* | 1985-01-07 | 1987-04-23 | Харьковский политехнический институт им.В.И.Ленина | Method of treatment of patients ill with osteochondrosis of the spine with neurologic symptoms |
| RU2038099C1 (en)* | 1992-08-18 | 1995-06-27 | Саратовский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии | Method for alleviating spastic syndrome caused by spinal cord segmental disorder |
- 2003
- 2003-07-15RURU2003122104/14Apatent/RU2258496C2/ennot_activeIP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU1242160A1 (en)* | 1982-05-25 | 1986-07-07 | Донецкий медицинский институт им.А.М.Горького | Method of treatment of discogenous radiculitis |
| SU1304822A1 (en)* | 1985-01-07 | 1987-04-23 | Харьковский политехнический институт им.В.И.Ленина | Method of treatment of patients ill with osteochondrosis of the spine with neurologic symptoms |
| RU2038099C1 (en)* | 1992-08-18 | 1995-06-27 | Саратовский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии | Method for alleviating spastic syndrome caused by spinal cord segmental disorder |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| ЗЕНКОВ Л.Р., РОНКИН М.Д. Функциональная диагностика нервных болезней. М.: Медицина, 1991, с.576-587.* |
Cited By (48)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2389435C1 (en)* | 2009-04-01 | 2010-05-20 | Федеральное государственное учреждение "Саратовский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии Федерального агентства по высокотехнологичной медицинской помощи" | Method of choosing modality in patients with traumatic rachiopathy |
| RU2392907C1 (en)* | 2009-04-01 | 2010-06-27 | Федеральное государственное учреждение "Саратовский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии Федерального агентства по высокотехнологичной медицинской помощи" | Method of treating patients with degenerative rachiopathy |
| RU2393756C1 (en)* | 2009-04-01 | 2010-07-10 | Федеральное государственное учреждение "Саратовский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии Федерального агентства по высокотехнологичной медицинской помощи" | Method of selecting tactics of treating patients with degenerative affection of spine |
| RU2432920C1 (en)* | 2010-05-25 | 2011-11-10 | Государственное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования Первый Московский государственный медицинский университет имени И.М.Сеченова Министерства здравоохранения и социального развития Российской Федерации (ГОУВПО Первый МГМУ им.И.М.Сеченова Минздравсоцразвития России) | Method of patients' management in postoperative regimen after posterior stabilisation of lumbar spine |
| RU2441679C1 (en)* | 2010-07-13 | 2012-02-10 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение "Российский научный центр "Восстановительная травматология и ортопедия" имени академика Г.А.Илизарова" Министерства здравоохранения и социального развития Российской Федерации (ФГБУ "РНЦ "ВТО" им. акад. Г.А.Илизарова" Минздравсоцразвития России) | Medullary electric stimulation |
| RU2452528C1 (en)* | 2010-12-21 | 2012-06-10 | Александр Ильич Тома | Method of anterior spinal cord electrostimulation in surgical management of thoracic spinal-cerebrospinal injury |
| US11957910B2 (en) | 2011-01-03 | 2024-04-16 | California Institute Of Technology | High density epidural stimulation for facilitation of locomotion, posture, voluntary movement, and recovery of autonomic, sexual, vasomotor, and cognitive function after neurological injury |
| US11116976B2 (en) | 2011-01-03 | 2021-09-14 | The Regents Of The University Of California | High density epidural stimulation for facilitation of locomotion, posture, voluntary movement, and recovery of autonomic, sexual, vasomotor, and cognitive function after neurological injury |
| US9101769B2 (en) | 2011-01-03 | 2015-08-11 | The Regents Of The University Of California | High density epidural stimulation for facilitation of locomotion, posture, voluntary movement, and recovery of autonomic, sexual, vasomotor, and cognitive function after neurological injury |
| US9907958B2 (en) | 2011-01-03 | 2018-03-06 | The Regents Of The University Of California | High density epidural stimulation for facilitation of locomotion, posture, voluntary movement, and recovery of autonomic, sexual, vasomotor, and cognitive function after neurological injury |
| US9409011B2 (en) | 2011-01-21 | 2016-08-09 | California Institute Of Technology | Method of constructing an implantable microelectrode array |
| US10737095B2 (en) | 2011-03-24 | 2020-08-11 | Californina Institute of Technology | Neurostimulator |
| US9409023B2 (en) | 2011-03-24 | 2016-08-09 | California Institute Of Technology | Spinal stimulator systems for restoration of function |
| US9931508B2 (en) | 2011-03-24 | 2018-04-03 | California Institute Of Technology | Neurostimulator devices using a machine learning method implementing a gaussian process optimization |
| US10806927B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2020-10-20 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation: noninvasive tool for activation of locomotor circuitry |
| US12226631B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2025-02-18 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Non invasive neuromodulation device for enabling recovery of motor, sensory, autonomic, sexual, vasomotor and cognitive function |
| US10092750B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2018-10-09 | Neuroenabling Technologies, Inc. | Transcutaneous neuromodulation system and methods of using same |
| US10124166B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2018-11-13 | Neuroenabling Technologies, Inc. | Non invasive neuromodulation device for enabling recovery of motor, sensory, autonomic, sexual, vasomotor and cognitive function |
| US12201833B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2025-01-21 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Transcutaneous neuromodulation system and methods of using same |
| US9393409B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2016-07-19 | Neuroenabling Technologies, Inc. | Non invasive neuromodulation device for enabling recovery of motor, sensory, autonomic, sexual, vasomotor and cognitive function |
| US12023492B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2024-07-02 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Non invasive neuromodulation device for enabling recovery of motor, sensory, autonomic, sexual, vasomotor and cognitive function |
| US11638820B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2023-05-02 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Transcutaneous neuromodulation system and methods of using same |
| US9415218B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2016-08-16 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation: noninvasive tool for activation of locomotor circuitry |
| US10881853B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2021-01-05 | The Regents Of The University Of California, A California Corporation | Transcutaneous neuromodulation system and methods of using same |
| US11033736B2 (en) | 2011-11-11 | 2021-06-15 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Non invasive neuromodulation device for enabling recovery of motor, sensory, autonomic, sexual, vasomotor and cognitive function |
| RU2481868C1 (en)* | 2011-12-05 | 2013-05-20 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение "Саратовский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии" Министерства здравоохранения и социального развития Российской Федерации (ФГБУ "СарНИИТО" Минздравсоцразвития России) | Method of treating spastic and spastic pain syndromes in patients with vertebral-spinal trauma impact and spinal diseases |
| RU2506970C1 (en)* | 2012-10-08 | 2014-02-20 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение "Российский научный центр "Восстановительная травматология и ортопедия" имени академика Г.А. Илизарова" Министерства здравоохранения и социального развития Российской Федерации | Method for rehabilitation treatment of patients with lower mono- and paraparesis with involved peripheral nerve |
| US11400284B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2022-08-02 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Method of transcutaneous electrical spinal cord stimulation for facilitation of locomotion |
| US9993642B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2018-06-12 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Multi-site transcutaneous electrical stimulation of the spinal cord for facilitation of locomotion |
| US12311169B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2025-05-27 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Multi-site transcutaneous electrical stimulation of the spinal cord for facilitation of locomotion |
| US11123312B2 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2021-09-21 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Engaging the cervical spinal cord circuitry to re-enable volitional control of hand function in tetraplegic subjects |
| US10137299B2 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2018-11-27 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Engaging the cervical spinal cord circuitry to re-enable volitional control of hand function in tetraplegic subjects |
| US12076301B2 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2024-09-03 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Engaging the cervical spinal cord circuitry to re-enable volitional control of hand function in tetraplegic subjects |
| US10786673B2 (en) | 2014-01-13 | 2020-09-29 | California Institute Of Technology | Neuromodulation systems and methods of using same |
| RU2572298C1 (en)* | 2014-07-10 | 2016-01-10 | Оксана Владимировна Кузина | Method for integrated treatment of spinal diseases |
| US10751533B2 (en) | 2014-08-21 | 2020-08-25 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Regulation of autonomic control of bladder voiding after a complete spinal cord injury |
| US10773074B2 (en) | 2014-08-27 | 2020-09-15 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Multi-electrode array for spinal cord epidural stimulation |
| US11298533B2 (en) | 2015-08-26 | 2022-04-12 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Concerted use of noninvasive neuromodulation device with exoskeleton to enable voluntary movement and greater muscle activation when stepping in a chronically paralyzed subject |
| US11097122B2 (en) | 2015-11-04 | 2021-08-24 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Magnetic stimulation of the spinal cord to restore control of bladder and/or bowel |
| US12268878B2 (en) | 2017-02-17 | 2025-04-08 | The University Of British Columbia | Apparatus and methods for maintaining physiological functions |
| US12434068B2 (en) | 2017-05-23 | 2025-10-07 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Accessing spinal networks to address sexual dysfunction |
| US11691015B2 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2023-07-04 | Onward Medical N.V. | System for neuromodulation |
| US11992684B2 (en) | 2017-12-05 | 2024-05-28 | Ecole Polytechnique Federale De Lausanne (Epfl) | System for planning and/or providing neuromodulation |
| US12357828B2 (en) | 2017-12-05 | 2025-07-15 | Ecole Polytechnique Federale De Lausanne (Epfl) | System for planning and/or providing neuromodulation |
| US11672983B2 (en) | 2018-11-13 | 2023-06-13 | Onward Medical N.V. | Sensor in clothing of limbs or footwear |
| US11752342B2 (en) | 2019-02-12 | 2023-09-12 | Onward Medical N.V. | System for neuromodulation |
| US11839766B2 (en) | 2019-11-27 | 2023-12-12 | Onward Medical N.V. | Neuromodulation system |
| US12415079B2 (en) | 2019-11-27 | 2025-09-16 | Onward Medical N.V. | Neuromodulation system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| RU2003122104A (en) | 2004-02-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| RU2258496C2 (en) | Method for treating patients with traumatic and degenerative lesions of vertebral column and spinal cord | |
| Gerrits et al. | Contractile properties of the quadriceps muscle in individuals with spinal cord injury | |
| Daly et al. | Therapeutic neural effects of electrical stimulation | |
| Baek et al. | Effects of repetitive peripheral magnetic stimulation over vastus lateralis in patients after hip replacement surgery | |
| RU2499614C1 (en) | Method for electromagnetic stimulation of central and peripheral nerve system | |
| RU2159606C2 (en) | Method for treating the cases of lumbar osteochondrosis | |
| RU2180830C2 (en) | Method for treating the cases of diskogenic manifestations of vertebral column osteochondrosis | |
| Ahmad et al. | Transspinal stimulation preceding assisted step training reorganizes neuronal excitability and function of inhibitory networks in spinal cord injury: A randomized controlled trial | |
| RU2062124C1 (en) | Method for treating vertebral osteochondrosis with radiculoischemic syndrome | |
| RU2481869C1 (en) | Method of treating neurogenic bladder in patients with traumatic spinal disease | |
| RU2164128C2 (en) | Method of complex rehabilitation of patients pathology of locomotor system | |
| RU2267337C1 (en) | Method for treating patients for cervical or lumbar vertebral column segment osteochondrosis | |
| RU2662657C1 (en) | Nerve function recovery method | |
| RU2411025C1 (en) | Method of treating lumbar osteochondrosis with accompanying osteoarthrosis | |
| RU2229279C1 (en) | Method for treating hernias of intervertebral disks | |
| RU2004265C1 (en) | Method of treating compression affections of neural pipes | |
| RU2843424C1 (en) | Method of combined treatment of degenerative-dystrophic changes of spine | |
| RU2817633C1 (en) | Method for rehabilitation of patients after microsurgical removal of intervertebral disc herniation of lumbosacral spine | |
| RU2804751C1 (en) | Method for rehabilitation of patients after surgical treatment of herniated intervertebral disc of the lumbosacral department of the spine | |
| RU2265460C2 (en) | Multi-channel electroneurostimulation method for treating lumbar osteochondrosis patients after replacing intervertebral disks with prostheses | |
| Atteya | Biofeedback traction versus conventional traction in cervical radiculopathy | |
| RU2280478C1 (en) | Method for reconstructing sensitive and motor function and, also, the function of pelvic organs at affected spinal cord | |
| RU2286132C2 (en) | Method for treating lumbar osteochondrosis cases accompanied by subcutaneous leg nerve syndrome | |
| RU2684178C1 (en) | Method of rehabilitation after total knee endoprosthesis replacementin patients with sarcopenia | |
| RU2147897C1 (en) | Method for treating neurological manifestations in patients possessing postlaminectomy syndrome |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees | Effective date:20050716 |