RU2183480C2 - Method for treating biological tissue with plasma flow - Google Patents
Method for treating biological tissue with plasma flowDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2183480C2 RU2183480C2RU97108750ARU97108750ARU2183480C2RU 2183480 C2RU2183480 C2RU 2183480C2RU 97108750 ARU97108750 ARU 97108750ARU 97108750 ARU97108750 ARU 97108750ARU 2183480 C2RU2183480 C2RU 2183480C2
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- plasma
- air
- area
- biological tissues
- range
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Surgical Instruments (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromRussianИзобретение относится к области медицины, более конкретно к способам воздействия на биологические ткани потоком плазмы, и может быть использовано, например, в абдоминальной и торакальной хирургии, хирургии печени и селезенки, в урологии, в онкохирургии, а также для лечения ожогов, ран, раневой инфекции и т.д. Исключительно эффективно заявляемое изобретение может быть использовано в военно-полевой хирургии и в медицине катастроф. The invention relates to medicine, more specifically to methods of influencing biological tissues with a plasma stream, and can be used, for example, in abdominal and thoracic surgery, surgery of the liver and spleen, in urology, in oncological surgery, and also for the treatment of burns, wounds, wound infections, etc. Extremely effectively claimed invention can be used in field surgery and disaster medicine.
В настоящее время широко известны различные способы воздействия на биологические ткани потоком плазмы. Известен, например, хирургический способ рассечения биологических тканей с помощью потока плазмы (см. патент США 3903891), заключающийся в формировании и поддержании с помощью высокочастотного тока холодной плазмы с поперечным сечением потока достаточно малым (диаметр от 0,13 до 0,38 мм) для получения узкой зоны контакта между плазмой и тканью с последующим введением потока этой плазмы в ткань для получения разреза. Currently, various methods of influencing biological tissues by plasma flow are widely known. Known, for example, is a surgical method for dissecting biological tissues using a plasma stream (see US patent 3903891), which consists in the formation and maintenance of high plasma cold plasma with a cross section of the stream sufficiently small (diameter from 0.13 to 0.38 mm) to obtain a narrow contact zone between the plasma and the tissue, followed by the introduction of a stream of this plasma into the tissue to obtain an incision.
В качестве плазмообразующего рабочего газа используют инертный газ аргон с расходом менее примерно 2,4 л/мин, предпочтительно от 0,05 до 0,95 л/мин. An inert argon gas with a flow rate of less than about 2.4 L / min, preferably from 0.05 to 0.95 L / min, is used as the plasma-forming working gas.
Однако вышеописанный способ в силу заявленных параметров, а именно малого диаметра плазменного потока, не в состоянии обеспечить надежную и быструю коагуляцию достаточно обширных рассеченных раневых поверхностей биологических тканей, а использование холодной плазмы не дает возможности осуществлять эффективную деструкцию, например выпаривание патологически измененных биологических тканей. However, the above method, due to the stated parameters, namely the small diameter of the plasma stream, is not able to provide reliable and fast coagulation of sufficiently extensive dissected wound surfaces of biological tissues, and the use of cold plasma does not allow for effective destruction, for example, evaporation of pathologically altered biological tissues.
Кроме того, существенным недостатком способа является необходимость использования в качестве плазмообразующего рабочего газа аргона. В нормальных условиях содержание аргона в атмосферном воздухе составляет не более 0,9%, поэтому практическая реализация способа подразумевает подачу рабочего газа (аргона) из специального источника, в наиболее доступном и распространенном варианте представляющего собой сосуд высокого давления с устройством редуцирования и регулирования расхода аргона. Использование предложенного способа в практической медицине требует наличия в операционном или предоперационном помещении баллонов с запасом аргона, а также необходимости периодического возобновления запаса расходуемого газа, которым является аргон. Следует отметить, что чем меньше объем сосуда с аргоном, тем чаще требуется его замена. In addition, a significant disadvantage of this method is the need to use argon as a plasma-forming working gas. Under normal conditions, the argon content in atmospheric air is not more than 0.9%, therefore, the practical implementation of the method involves the supply of working gas (argon) from a special source, in the most accessible and common version, which is a high pressure vessel with a device for reducing and regulating the flow of argon. The use of the proposed method in practical medicine requires the presence of cylinders with a supply of argon in the operating or preoperative room, as well as the need for periodic renewal of the supply of consumed gas, which is argon. It should be noted that the smaller the volume of the vessel with argon, the more often it needs to be replaced.
Известен также способ коагуляции биологических тканей в области хирургического разреза (см., например, патент США 3938525), заключающийся в формировании и поддержании с помощью постоянного тока электрически нейтральной холодной плазмы с достаточно малым поперечным сечением потока плазмы (диаметр от 0,127 до 1,27 мм), обеспечивающим узкую область контакта между плазмой и тканью, и далее направлении потока плазмы на биологические ткани в области разреза для их коагуляции. В качестве плазмообразующего газа в вышеописанном способе используют газ, выбранный из группы газов, включающей в себя аргон, гелий, азот либо смеси из двух или трех из перечисленных газов. There is also known a method of coagulation of biological tissues in the field of surgical incision (see, for example, US patent 3938525), which consists in the formation and maintenance of direct electrically neutral cold plasma with a sufficiently small cross section of the plasma flow (diameter from 0.127 to 1.27 mm ), providing a narrow contact area between the plasma and the tissue, and then the direction of the plasma flow to biological tissues in the incision region for their coagulation. As the plasma-forming gas in the above method, a gas selected from the group of gases including argon, helium, nitrogen, or a mixture of two or three of these gases is used.
В вышеописанном способе холодная плазма может использоваться как с позиций ее только кровоостанавливающих свойств, так и в варианте, в котором холодная плазма одновременно обеспечивает получение разреза и коагуляцию ткани в области последнего. In the above method, cold plasma can be used both from the point of view of its hemostatic properties only, and in an embodiment in which cold plasma simultaneously provides an incision and coagulation of tissue in the region of the latter.
Однако и этот способ вследствие малого энергосодержания холодноплазменного потока, формируемого и поддерживаемого постоянным током, не в состоянии обеспечить эффективную деструкцию - разрушение либо выпаривание - патологически измененных биологических тканей. However, this method, due to the low energy content of the cold plasma stream, formed and supported by direct current, is not able to provide effective destruction - destruction or evaporation - of pathologically altered biological tissues.
Кроме того, при использовании в качестве плазмообразующего газа аргона или азота ему присущи все недостатки вышеописанного способа согласно патенту США 3903891, которые лишь усугубляются при выборе в качестве рабочего газа гелия вследствие малой распространенности, ограниченной доступности и большой стоимости последнего. In addition, when using argon or nitrogen as a plasma-forming gas, it has all the disadvantages of the above method according to US patent 3903891, which are only exacerbated when choosing helium as the working gas due to its low prevalence, limited availability and high cost.
Известен также способ воздействия на биологические ткани потоком плазмы (см. , например, патент США 3434476). Этот способ заключается в формировании и поддержании постоянным током электрически нейтральной горячей плазмы с достаточно малым поперечным сечением и далее направлении потока плазмы на биологические ткани для получения разреза, коагуляции или испарения (деструкции). В качестве рабочего газа используется инертный газ, например гелий или аргон. There is also known a method of influencing biological tissues by a plasma stream (see, for example, US patent 3434476). This method consists in the formation and maintenance by direct current of an electrically neutral hot plasma with a sufficiently small cross section and then the direction of plasma flow to biological tissues to obtain an incision, coagulation or evaporation (destruction). An inert gas such as helium or argon is used as the working gas.
Однако и данному способу вследствие использования в качестве плазмообразующего газа аргона или гелия присущи недостатки, аналогичные вышеописанным способам. However, this method, due to the use of argon or helium as a plasma-forming gas, has disadvantages similar to the methods described above.
Таким образом, ни один из известных способов воздействия на биологические ткани потоком плазмы не нашел широкого практического применения в медицине, в основном вследствие использования в качестве плазмообразующих рабочих веществ инертных газов. Кроме того, ни один из известных в настоящее время способов не оказывает стимулирующее воздействие на репаративные процессы при заживлении раневых поверхностей. Thus, none of the known methods of influencing biological tissues by a plasma stream has found wide practical application in medicine, mainly due to the use of inert gases as plasma-forming working substances. In addition, none of the currently known methods has a stimulating effect on reparative processes during the healing of wound surfaces.
Задачей настоящего изобретения является создание такого способа воздействия на биологические ткани потоком плазмы, который за счет выбора рабочего газа обеспечил бы не только возможность хирургического воздействия на биологические ткани, но и терапевтического их лечения. The present invention is the creation of such a method of exposure of biological tissues to a plasma stream, which due to the choice of working gas would provide not only the possibility of surgical exposure to biological tissues, but also their therapeutic treatment.
Эта задача решается тем, что в способе воздействия на биологические ткани потоком плазмы, заключающемся в том, что сначала формируют пучок электрически нейтральной плазмы, затем этот пучок направляют в область локализации биологической ткани, подлежащей воздействию, и вводят их в непосредственное соприкосновение, согласно изобретению пучок электрически нейтральной плазмы представляет собой поток термически равновесной воздушной плазмы. This problem is solved by the fact that in the method of influencing biological tissues with a plasma stream, which consists in first forming a beam of electrically neutral plasma, then this beam is sent to the localization region of the biological tissue to be exposed, and the beam is brought into direct contact, according to the invention An electrically neutral plasma is a stream of thermally equilibrium air plasma.
Это дает возможность осуществлять лечебное терапевтическое воздействие на биологические ткани, а при необходимости и хирургическое. This makes it possible to carry out therapeutic therapeutic effect on biological tissues, and, if necessary, surgical.
Целесообразно при терапевтическом воздействии на биологические ткани длину воздушно-плазменного потока от места истечения до области воздействия выбрать в пределах от 10 до 20 см, объемный расход установить в пределах от 0,5 до 1,0 л/мин, при этом в области воздействия диаметр пучка воздушной плазмы поддерживать в пределах примерно от 10 до 20 мм, а среднемассовую температуру воздушно-плазменного потока - от 40 до 70oС. При таком выборе теплофизических и геометрических параметров воздушно-плазменного потока обеспечивается максимальная эффективность терапевтического воздействия на биологические ткани при достаточно комфортном состоянии пациента.It is advisable to use a therapeutic effect on biological tissues to select the length of the air-plasma stream from the place of discharge to the area of influence from 10 to 20 cm, set the volume flow to be from 0.5 to 1.0 l / min, while the diameter in the area of influence beam of air plasma at between about 10 to 20 mm, and the weight average temperature of the air-plasma flux - from 40 to 70o C. With this choice of the geometric parameters of thermal and air-plasma flow ensures maximum efficiency spine therapeutic effects on biological tissue with sufficient patient comfort.
Рационально при хирургическом воздействии на биологические ткани для их коагуляции длину воздушно-плазменного потока от места истечения до области воздействия установить в пределах от 10 до 30 мм, его объемный расход - примерно от 1,5 до 2,0 л/мин, при этом в области воздействия диаметр пучка воздушной плазмы зафиксировать в пределах от 3,0 до 5,0 мм, а тепловую мощность воздушно-плазменного потока выбрать примерно от 100 до 200 Вт. Это позволяет добиться наилучшего эффекта при коагуляции биологических тканей воздушно-плазменным потоком. It is rational for surgical intervention on biological tissues to coagulate them to establish the length of the air-plasma flow from the place of expiration to the area of influence from 10 to 30 mm, its volumetric flow rate from about 1.5 to 2.0 l / min, In the area of influence, fix the diameter of the air plasma beam in the range from 3.0 to 5.0 mm, and select the thermal power of the air-plasma flow from about 100 to 200 W. This allows you to achieve the best effect when coagulating biological tissues with an air-plasma flow.
При хирургическом воздействии на биологические ткани для их деструкции целесообразно длину воздушно-плазменного потока от места истечения до области воздействия выбрать в пределах примерно от 5 до 10 мм, его объемный расход - примерно от 2,0 до 3,0 л/мин, при этом в области воздействия диаметр пучка воздушной плазмы зафиксировать в пределах примерно от 1,0 до 3,0 мм, а тепловую мощность воздушно-плазменного потока установить примерно от 200 до 300 Вт. При таком выборе параметров воздушно-плазменного потока удается добиться наиболее эффективной деструкции патологически измененных биологических тканей. When surgical impact on biological tissues for their destruction, it is advisable to choose the length of the air-plasma flow from the place of expiration to the area of influence in the range from about 5 to 10 mm, its volumetric flow rate is from about 2.0 to 3.0 l / min, while in the area of influence, fix the diameter of the air plasma beam in the range of about 1.0 to 3.0 mm, and set the thermal power of the air-plasma flow from about 200 to 300 watts. With this choice of parameters of the air-plasma flow, it is possible to achieve the most effective destruction of pathologically altered biological tissues.
Рационально при хирургическом воздействии на биологические ткани для их рассечения установить длину воздушно-плазменного потока от места истечения до области воздействия в пределах примерно от 1,0 до 5,0 мм, его объемный расход выбрать примерно от 1,0 до 1,5 л/мин, при этом в области воздействия диаметр пучка воздушной плазмы зафиксировать в пределах примерно от 0,5 до 1,0 мм, а тепловую мощность воздушно-плазменного потока установить примерно от 50 до 100 Вт. Это дает возможность добиться наилучшего эффекта при рассечении биологических тканей воздушно-плазменным потоком. It is rational for surgical intervention on biological tissues to dissect them to establish the length of the air-plasma flow from the place of expiration to the area of influence in the range of about 1.0 to 5.0 mm, its volumetric flow rate should be selected from about 1.0 to 1.5 l min, while in the area of influence, the diameter of the air plasma beam should be fixed in the range from about 0.5 to 1.0 mm, and the thermal power of the air-plasma flow should be set from about 50 to 100 W. This makes it possible to achieve the best effect when dissecting biological tissues with an air-plasma flow.
В дальнейшем заявленное изобретение поясняется конкретными примерами его выполнения и прилагаемыми чертежами, на которых представлено следующее:
фиг. 1 - общий вид операции стимулирования раневой поверхности при терапевтическом воздействии согласно заявляемому способу;
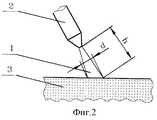
фиг.2 - общий вид процесса коагуляции биологических тканей;
фиг.3. - общий вид процесса деструкции биологических тканей;
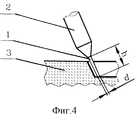
фиг.4. - общий вид процесса рассечения биологических тканей.Further, the claimed invention is illustrated by specific examples of its implementation and the accompanying drawings, which show the following:
FIG. 1 is a General view of the operation of stimulating the wound surface during therapeutic treatment according to the claimed method;
figure 2 - General view of the process of coagulation of biological tissues;
figure 3. - a general view of the process of destruction of biological tissues;
figure 4. - a general view of the process of dissection of biological tissues.
Заявленный способ воздействия на биологические ткани заключается в следующем. Путем пропускания постоянного электрического тока через поток атмосферного воздуха, характеризующийся определенным химическим составом, диаметром и расходом, формируют и поддерживают пучок 1 (фиг.1) электрически нейтральной воздушной плазмы, которая истекает из источника 2 в окружающее пространство в виде светящегося факела, имеющего форму цилиндра или усеченного конуса с вершиной у места истечения. The claimed method of exposure to biological tissue is as follows. By passing a constant electric current through a stream of atmospheric air, characterized by a specific chemical composition, diameter and flow rate, a beam 1 (Fig. 1) of electrically neutral air plasma is formed and supported, which flows from the
Сформированный таким образом пучок 1 воздушной плазмы направляют на локальный участок биологической ткани 3, подлежащий воздействию, и вводят пучок 1 плазмы в непосредственное соприкосновение с биологической тканью 3. Воздушно-плазменный поток 1 с определенными физическими и геометрическими параметрами - длиной h, диаметром d, расходом G, тепловой мощностью Р, температурой Т и т.д., оказывает на биологическую ткань 3 лечебное воздействие - терапевтическое (фиг. 1) или хирургическое: коагуляция (фиг.2), деструкция (фиг.3), рассечение (фиг.4), продолжительность которого зависит от цели конкретного лечения. The
Установлено, что многие из проблем, связанные с воздействием на биологические ткани, решаются использованием пучка термически равновесной воздушной плазмы, формируемой и поддерживаемой пропусканием постоянного тока через поток атмосферного воздуха. It has been established that many of the problems associated with exposure to biological tissues are solved by using a beam of thermally balanced air plasma formed and supported by passing direct current through a stream of atmospheric air.
Во-первых, воздушно-плазменный поток, характеризующийся сложным химическим и спектральным составом, существенно модифицированным по сравнению с исходным составом атмосферного воздуха и тем более по сравнению с плазмой инертных газов, содержит молекулы, атомы, ионы, свободные радикалы и т.д. в определенном соотношении, что при соприкосновении с биологическими тканями обеспечивает терапевтическое лечение этих тканей, стимулируя процессы репаративной регенерации. Firstly, an air-plasma stream, characterized by a complex chemical and spectral composition, significantly modified in comparison with the initial composition of atmospheric air, and even more so in comparison with an inert gas plasma, contains molecules, atoms, ions, free radicals, etc. in a certain ratio, which, in contact with biological tissues, provides therapeutic treatment of these tissues, stimulating the processes of reparative regeneration.
Во-вторых, в зависимости от сочетания таких легко варьируемых физических и геометрических параметров, как расход воздуха, диаметр плазменного пучка 1, его длина h от места истечения до поверхности воздействия и т.д., светящаяся, т. е. наиболее энергоемкая, часть воздушно-плазменного потока обладает свойствами, достаточными для выполнения рассечения биологических тканей, деструкции патологических образований и коагуляции раневых поверхностей с одновременным бактерицидным (санирующим) и аналгезирующим действием. Secondly, depending on the combination of such easily variable physical and geometric parameters as air flow rate,
И, наконец, при использовании в качестве рабочего газа одной из составляющих окружающей среды, а именно атмосферного воздуха, отпадают все проблемы, связанные с хранением и транспортировкой любого иного рабочего вещества. And, finally, when using one of the components of the environment as a working gas, namely atmospheric air, all the problems associated with the storage and transportation of any other working substance disappear.
Терапевтическое воздействие на биологические ткани 3 (фиг.1) потоком термически равновесной воздушной плазмы проводят для немедикаментозного лечения больных с различной раневой патологией - длительно заживающие, вялогранулирующие раны и трофические язвы любого происхождения; пролежни; гнойно-воспалительные заболевания мягких тканей; ожоги различного генеза; патология пересаженных лоскутов в пластической и реконструктивной хирургии и косметологии; радиационные повреждения; бытовые, военные травмы и ранения мягких тканей и т.д. The therapeutic effect on biological tissue 3 (Fig. 1) by a flow of thermally equilibrium air plasma is carried out for non-drug treatment of patients with various wound pathologies - long-term healing, sluggishly granulating wounds and trophic ulcers of any origin; pressure sores; purulent-inflammatory diseases of the soft tissues; burns of various origins; pathology of transplanted flaps in plastic and reconstructive surgery and cosmetology; radiation damage; domestic, military injuries and injuries of soft tissues, etc.
При терапевтическом воздействии на биологические ткани длину h воздушно-плазменного пучка 1 от места истечения до области воздействия следует устанавливать в пределах примерно от 10 до 20 см. Уменьшение длины h воздушно-плазменного потока ниже 10 см приводит к возрастанию теплового потока в области воздействия (на раневой поверхности) и к чрезмерному ожогу биологический ткани 3; увеличение длины h более 20 см приводит к практическому исчезновению лечебного действия. Выход за пределы диапазона от 0,5 до 1,0 л/мин по объемному расходу потока приводит к изменению оптимального химического состава воздействующей плазмы и снижению ее лечебной эффективности. Диапазон изменения диаметра d пучка 1 воздушной плазмы от 10 до 20 мм является наилучшим с точки зрения визуального контроля за состоянием биологической ткани, подвергающейся лечебному воздействию. Снижение температуры Т воздушно-плазменного потока ниже 40oС не приводит к необходимому подсушиванию раневой поверхности, а повышение ее более 70oС ведет к появлению болевых ощущений у пациента.With a therapeutic effect on biological tissues, the length h of the air-
Коагуляцию биологических тканей 3 (фиг.2) обычно проводят при хирургических операциях для остановки кровотечения из обширных раневых поверхностей, например паренхиматозных органов и других диффузно кровоточащих тканей (гемостаз), герметизации легочной ткани (аэростаз), прекращения желчеистечения (холеостаз), лимфоистечения (лимфостаз) и т.д., а также для обработки огнестрельных и гнойных ран с целью снижения микробной обсемененности. Coagulation of biological tissues 3 (Fig. 2) is usually carried out during surgical operations to stop bleeding from extensive wound surfaces, for example, parenchymal organs and other diffusely bleeding tissues (hemostasis), sealing of lung tissue (aerostasis), cessation of bile duct (choleostasis), lymph flow (lymphostasis) ), etc., as well as for the treatment of gunshot and purulent wounds in order to reduce microbial contamination.
Осуществляя коагуляцию биологических тканей, длину h воздушно-плазменного потока от места его истечения до области локализации биологических тканей 3, подлежащих коагуляции, следует устанавливать в пределах примерно от 10 до 30 мм. Уменьшение расстояния h от места истечения плазменного потока до области воздействия ниже 10 мм приводит за счет большого газодинамического напора и скорости потока к разбрызгиванию крови, истекающей из биологической ткани 3, а увеличение расстояния h свыше 30 мм - к уменьшению температуры воздушно-плазменного потока и отсутствию гемостаза. Объемный расход потока менее 1,5 л/мин не обеспечивает удаление крови и других жидкостей с раневой поверхности, что приводит к образованию "плавающего" струпа, а повышение расхода потока более 2,0 л/мин повышает вероятность возникновения газовой эмболии. Диаметр d пучка 1 воздушной плазмы в пределах от 3,0 до 5,0 мм позволяет одномоментно коагулировать достаточно большую площадь раневой поверхности биологический ткани 3 и вместе с тем обеспечивает достаточный контроль за процессом коагуляции. При тепловой мощности воздушно-плазменного потока от 100 до 200 Вт на биологической ткани 3 происходит наиболее эффективное формирование коагуляционной пленки без возникновения деструкции. When coagulating biological tissues, the length h of the air-plasma flow from the place of its expiration to the localization region of the
Деструкцию биологических тканей 3 (фиг.3) обычно проводят при хирургических операциях для ликвидации патологически измененных биотканей - небольших опухолей, метастазов, булл, стенок капсул, нежизнеспособных тканей, а также для выпаривания экссудата и т.д. The destruction of biological tissues 3 (Fig.3) is usually carried out during surgical operations to eliminate pathologically altered biological tissues - small tumors, metastases, bullae, capsule walls, non-viable tissues, as well as for exudate evaporation, etc.
Для осуществления деструкции биологических тканей 3 длину h воздушно-плазменного пучка 1 от места его истечения до области воздействия следует установить в пределах от примерно 5 до 10 мм. При уменьшении длины h воздушно-плазменного потока от места истечения до области воздействия менее 5 мм при осуществлении деструкции возможно повреждение подлежащих здоровых тканей, при увеличении этой длины выше 10 мм скорость деструкции заметно снижается за счет уменьшения температуры плазменного потока. При объемном расходе потока менее 2,0 л/мин его скорости недостаточно для эффективного уноса продуктов деструкции из области воздействия, при расходе потока более 3,0 л/мин, наоборот, возможен перенос продуктов деструкции далеко за пределы операционного поля. При диаметре d пучка 1 воздушной плазмы менее 1,0 мм скорость деструкции может вырасти настолько, что будет затруднен контроль за ее выполнением, а при диаметре d пучка более 3,0 мм возможно повреждение окружающих здоровых тканей. Тепловая мощность воздушно-плазменного потока в пределах от 200 до 300 Вт является оптимальной для быстрого испарения деструктируемых тканей без прогрева близлежащих здоровых тканей. For the destruction of
Рассечение биологических тканей 3 (фиг.4) проводят при хирургических операциях для получения бескровного разреза, например, при вскрытии и пересечении полых органов желудочно-кишечного тракта, стенок кист поджелудочной железы и других органов, а также при рассечении ткани легкого при атипичной резекции, рассечении межреберных мышц, нервных стволов и т.д. Dissection of biological tissues 3 (Fig. 4) is carried out during surgical operations to obtain a bloodless incision, for example, when opening and crossing the hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract, walls of the pancreatic cysts and other organs, as well as when dissecting lung tissue during atypical resection, dissection intercostal muscles, nerve trunks, etc.
Для рассечения биологических тканей расстояние h от места истечения потока 1 воздушной плазмы до области воздействия устанавливают в пределах примерно от 1 до 5 мм. Уменьшение расстояния h от места истечения воздушно-плазменного потока до области воздействия менее 1 мм практически труднореализуемо и нецелесообразно, увеличение длины h воздушно-плазменного потока свыше 5 мм может привести к повреждению подлежащих тканей. Диапазон объемных расходов воздушно-плазменного потока от 1,0 до 1,5 л/мин обеспечивает необходимую для эффективного уноса массы биологической ткани 3 из области разреза скорость потока, а диаметр d пучка в пределах от 0,5 до 1,0 мм обеспечивает достаточно тонкий разрез биологической ткани 3. Тепловой мощности воздушно-плазменного потока менее 50 Вт будет недостаточно для быстрого испарения биологической ткани в области разреза, а мощность потока более 100 Вт приведет к слишком большому тепловому повреждению биологической ткани по краю разреза (боковому некрозу). For dissection of biological tissues, the distance h from the place where the flow of
Патентуемый способ практически осуществляется следующим образом. Для проведения терапевтического воздействия на биологические ткани 3 (фиг.1) потоком воздушной плазмы, например, при раневой патологии, пациента размещают в процедурной или перевязочной комнате стоя, сидя или лежа в зависимости от локализации раневого дефекта и физического состояния больного. Снимают повязку, закрывающую рану. Лечащий врач включает источник 2 воздушно-плазменного потока, находящийся у него в руке, и воздействует на раневую поверхность, ориентируясь на болевые ощущения пациента. Немедикаментозная стимуляция репаративных процессов в ране осуществляется воздействием воздушно-плазменного потока на поверхность раны до появления светло-желтоватой, опалерисцирующей пленки и отсутствия раневого экссудата. Воздействие проводят на очищенную от лекарств, мазей, перевязочного материала поверхность; обязателен захват в зону воздействия воздушно-плазменного потока окружающих, визуально неизмененных тканей; в ране должны отсутствовать кровотечения и массивные некробиотические изменения. После обработки рану закрывают стерильной марлевой повязкой или оставляют открытой. Число сеансов лечения и продолжительность каждого сеанса устанавливают в зависимости от площади раны, ее фазы и других условий. Patented method is practically as follows. To conduct a therapeutic effect on biological tissue 3 (Fig. 1) with an air plasma flow, for example, in case of wound pathology, the patient is placed in a treatment or dressing room while standing, sitting or lying, depending on the location of the wound defect and the physical condition of the patient. Remove the dressing covering the wound. The attending physician includes a source of 2 air-plasma flow, located in his hand, and acts on the wound surface, focusing on the pain of the patient. Non-drug stimulation of reparative processes in the wound is carried out by the action of an air-plasma flow on the surface of the wound until a light yellowish, opalerizing film appears and there is no wound exudate. The impact is carried out on a surface cleared of drugs, ointments, dressings; Mandatory capture in the zone of exposure to the air-plasma flow of surrounding, visually unchanged tissues; the wound should be free of bleeding and massive necrobiotic changes. After treatment, the wound is closed with a sterile gauze dressing or left open. The number of treatment sessions and the duration of each session are set depending on the area of the wound, its phase and other conditions.
Хирургическое воздействие на биологические ткани пучком 1 (фиг.2-4) плазмы осуществляют в операционной комнате. Больного, находящегося, как правило, под общим наркозом, размещают на операционном столе. Наружную поверхность источника 2 воздушно-плазменного потока, находящегося в руке оперирующего хирурга, подвергают стерилизации одним из традиционных способов. Хирург проводит лечебное воздействие - коагуляцию, деструкцию или рассечение - по показаниям на определенных этапах операции, периодически включая источник 2 воздушно-плазменного потока в режимах согласно изобретению. Surgical effects on biological tissue with a beam of 1 (Fig.2-4) plasma are carried out in the operating room. The patient, usually under general anesthesia, is placed on the operating table. The outer surface of the
При воздействии на биологические ткани потоком плазмы специальных мер защиты пациента, хирурга и персонала не требуется. When exposed to biological tissues by a plasma stream, special measures to protect the patient, surgeon and staff are not required.
Клинический пример осуществления заявляемого способа. A clinical example of the implementation of the proposed method.
Больной Дауров П.А., 1924 г.р. Patient Daurov P.A., born in 1924
Д-з: Плоскоклеточный рак кожи передней грудной клетки. Dz: Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin of the anterior chest.
Номер истории болезни ЕА-3442. EA-3442 medical history number.
Анамнез заболевания. Считает себя больным в течение 2-х лет, когда впервые обратил внимание на появление небольшой язвы до 0,5 см. К врачам не обращался, лечился самостоятельно - присыпки, мази, травы (названий не помнит). Medical history. She considers herself ill for 2 years, when for the first time he paid attention to the appearance of a small ulcer up to 0.5 cm. I did not go to the doctors, I was treated on my own - powders, ointments, herbs (I do not remember the names).
В последние 6-8 месяцев отмечает ухудшение состояния - размер язвы увеличился в 2-3 раза, появилась кровоточивость, зуд кожи вокруг. Обратился к онкологу по месту жительства, направлен в МНИОИ им. П.А.Герцена. In the last 6-8 months, the condition has worsened - the size of the ulcer has increased by 2-3 times, bleeding, itching of the skin around. He went to the oncologist at the place of residence, was sent to the Moscow Scientific Research Institute for Medical Sciences. P.A. Herzen.
При обращении (02.12.96 г.) на правой половине грудной стенки на границе с грудиной имеется каллезная язва до 4 см в диаметре, с неровными контурами, избыточными грануляциями. Кожа вокруг гиперемирована, отмечается контактная кровоточивость. Регионарные лимфоузлы не увеличены. Цитология: Базально-клеточный рак кожи с элементами плоскоклеточного. Р-графия легких и костей грудной стенки без патологии. Общий анализ крови, мочи без изменений. When handling (02.12.96 g.), On the right half of the chest wall at the border with the sternum there is a callous ulcer up to 4 cm in diameter, with uneven contours, excessive granulation. The skin around is hyperemic, contact bleeding is noted. Regional lymph nodes are not enlarged. Cytology: Basal cell skin cancer with squamous cells. P-graphy of the lungs and bones of the chest wall without pathology. General analysis of blood, urine unchanged.
Операция 19.12.96 г. - Широкое иссечение опухоли передней грудной стенки с пластикой дефекта тканей перемещенным лоскутом. Operation 12/19/96; - Wide excision of the tumor of the anterior chest wall with plastic tissue defect displaced flap.
Послеоперационный период осложнился краевым некрозом и расхождением краев ран на 5 - 7-е сутки, образовалась рана 6•8 см. The postoperative period was complicated by marginal necrosis and the divergence of the edges of the wounds on the 5-7th day, a wound of 6 • 8 cm was formed.
Ткани раны тусклые, без признаков грануляции с выраженной гиперемией кожи вокруг на протяжении до 2-3 см. Wound tissue is dull, without signs of granulation with severe flushing around for up to 2-3 cm.
Гистологическое исследование И-63658-621 - плоскоклеточный рак кожи. Histological examination of I-63658-621 - squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
Для стимуляции репаративных процессов больному проведен курс терапевтического лечения воздушно-плазменным потоком с помощью аппарата "Плазмер" (12 сеансов). На 3-4 сеансе отмечено появление активной грануляционной ткани, уменьшение размеров раны. В последующем - заполнение раны грануляционной тканью, нарастание краевой и островковой эпителизации, прогрессирующее уменьшение размеров раны и ее закрытие. To stimulate reparative processes, the patient underwent a course of therapeutic treatment with an air-plasma flow using the Plazmer apparatus (12 sessions). At the 3-4 session, the appearance of active granulation tissue, a decrease in the size of the wound was noted. Subsequently, filling the wound with granulation tissue, an increase in marginal and islet epithelization, a progressive reduction in the size of the wound and its closure.
К окончанию курса лечения: размеры раны 1-1,5 см, без отделяемого и наличия некротических тканей, покрыта опалерисцирующей пленкой. Кожа вокруг представлена вновь образованной тканью, без грубого рубцевания. By the end of the course of treatment: the size of the wound is 1-1.5 cm, without detachable and the presence of necrotic tissue, it is covered with an opalescent film. The skin around is represented by a newly formed tissue, without rough scarring.
Осмотрен через 7 дней - рана полностью зажила. Examined after 7 days - the wound healed completely.
Осмотрен через 3 месяца - местно без рецидива. Рубцовая ткань не деформирует кожу вокруг. Болевых и других ощущений не отмечается. Заключение: В результате терапевтического лечения послеоперационной осложненной раны воздушно-плазменным потоком достигнут полный клинический эффект. Examined after 3 months - locally without relapse. Scar tissue does not deform the skin around. Pain and other sensations are not noted. Conclusion: As a result of therapeutic treatment of a postoperative complicated wound with an air-plasma flow, a complete clinical effect was achieved.
Из вышеизложенного следует, что впервые в отечественной и мировой практике создан способ немедикаментозной стимуляции репаративной регенерации, приводящий к ускоренному заживлению осложненных ран практически любого происхождения. Способ позволяет сократить сроки заживления ран по сравнению с лекарственными и другими физическими, например лазерными, методами в 2-3,5 раза, обеспечивает формирование качественного рубца по типу дермального регенерата, дает возможность проведения как стационарного, так и амбулаторного лечения с открытым ведением раневого процесса, обеспечивает значительную (70-85%) экономию лекарственных средств и перевязочного материала. From the above it follows that for the first time in domestic and world practice, a method for non-drug stimulation of reparative regeneration has been created, leading to accelerated healing of complicated wounds of almost any origin. The method allows to reduce the healing time of wounds in comparison with medicinal and other physical, for example laser, methods by 2-3.5 times, provides the formation of a quality scar according to the type of dermal regenerate, makes it possible to carry out both inpatient and outpatient treatment with open wound healing , provides significant (70-85%) savings in medicines and dressings.
Заявленный способ позволяет эффективно осуществлять лечение в области раневой патологии в целом. Следует особо отметить, что лечение, обеспечиваемое использованием заявленного способа, легко сочетается с любыми другими видами терапевтического лечения, например медикаментозными. The claimed method allows effective treatment in the field of wound pathology in general. It should be especially noted that the treatment provided by the use of the claimed method is easily combined with any other types of therapeutic treatment, for example, medication.
Кроме того, достоинством заявленного способа является его универсальность, что позволяет путем использования режимов коагуляции, деструкции и рассечения качественно и быстро проводить органосберегающие хирургические операции. In addition, the advantage of the claimed method is its versatility, which allows using organ-saving surgical operations to be performed efficiently and quickly using coagulation, destruction and dissection modes.
Использование в качестве рабочего газа атмосферного воздуха делает способ особо перспективным для применения в условиях, приближенных к полевым, т. е. в военно-полевой хирургии как на этапах специализированной помощи, так и квалифицированной помощи с элементами специализированной, например в Медицинских отрядах специального назначения (МОСН), а также в медицине катастроф. The use of atmospheric air as a working gas makes the method particularly promising for use in conditions close to field conditions, i.e., in military field surgery both at the stages of specialized care and skilled care with elements of specialized care, for example, in special medical units ( MOSN), as well as in disaster medicine.
Claims (5)
Translated fromRussianPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU97108750ARU2183480C2 (en) | 1997-06-02 | 1997-06-02 | Method for treating biological tissue with plasma flow |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU97108750ARU2183480C2 (en) | 1997-06-02 | 1997-06-02 | Method for treating biological tissue with plasma flow |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU97108750A RU97108750A (en) | 1999-05-27 |
| RU2183480C2true RU2183480C2 (en) | 2002-06-20 |
Family
ID=20193405
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU97108750ARU2183480C2 (en) | 1997-06-02 | 1997-06-02 | Method for treating biological tissue with plasma flow |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2183480C2 (en) |
Cited By (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2252043C1 (en)* | 2003-10-20 | 2005-05-20 | Смоленская государственная медицинская академия | Method for carrying out intraoperational treatment of the abdominal cavity in peritonitis cases |
| RU2314769C2 (en)* | 2005-08-05 | 2008-01-20 | Виктор Петрович Усов | Method and device for contact-free discrete-coherent cold plasma coagulation |
| US7589473B2 (en) | 2007-08-06 | 2009-09-15 | Plasma Surgical Investments, Ltd. | Pulsed plasma device and method for generating pulsed plasma |
| RU2405477C2 (en)* | 2009-02-09 | 2010-12-10 | Государственное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования Смоленская государственная медицинская академия федерального агентства по здравоохранению и социальному развитию | Instrument for plasma resection of pancreas tissue |
| US7928338B2 (en) | 2007-02-02 | 2011-04-19 | Plasma Surgical Investments Ltd. | Plasma spraying device and method |
| RU2434656C1 (en)* | 2010-08-04 | 2011-11-27 | Георгий Цыренович Дамбаев | Method of stopping intra-operation haemorrhage |
| US8105325B2 (en) | 2005-07-08 | 2012-01-31 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Plasma-generating device, plasma surgical device, use of a plasma-generating device and method of generating a plasma |
| US8109928B2 (en) | 2005-07-08 | 2012-02-07 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Plasma-generating device, plasma surgical device and use of plasma surgical device |
| US8613742B2 (en) | 2010-01-29 | 2013-12-24 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Methods of sealing vessels using plasma |
| US8735766B2 (en) | 2007-08-06 | 2014-05-27 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Cathode assembly and method for pulsed plasma generation |
| US9089319B2 (en) | 2010-07-22 | 2015-07-28 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Volumetrically oscillating plasma flows |
| RU2647624C1 (en)* | 2017-07-18 | 2018-03-16 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное научное учреждение "Томский национальный исследовательский медицинский центр Российской академии наук" (Томский НИМЦ) | Method of treatment of infectious complications after cardiac-vascular interventions |
| US10201067B2 (en) | 2005-07-08 | 2019-02-05 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Plasma-generating device, plasma surgical device and use of a plasma surgical device |
| RU2726599C1 (en)* | 2019-10-03 | 2020-07-14 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Санкт-Петербургский государственный педиатрический медицинский университет" Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации (ФГБОУ ВО СПбГПМУ Минздрава России) | Method of treating wounds |
| RU2802710C1 (en)* | 2022-08-08 | 2023-08-31 | Кирилл Александрович Новиков | How to eliminate cicatricial changes in the skin of the face |
| US11882643B2 (en) | 2020-08-28 | 2024-01-23 | Plasma Surgical, Inc. | Systems, methods, and devices for generating predominantly radially expanded plasma flow |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5396882A (en)* | 1992-03-11 | 1995-03-14 | The General Hospital Corporation | Generation of nitric oxide from air for medical uses |
- 1997
- 1997-06-02RURU97108750Apatent/RU2183480C2/enactive
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5396882A (en)* | 1992-03-11 | 1995-03-14 | The General Hospital Corporation | Generation of nitric oxide from air for medical uses |
Cited By (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2252043C1 (en)* | 2003-10-20 | 2005-05-20 | Смоленская государственная медицинская академия | Method for carrying out intraoperational treatment of the abdominal cavity in peritonitis cases |
| US8337494B2 (en) | 2005-07-08 | 2012-12-25 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Plasma-generating device having a plasma chamber |
| US12075552B2 (en) | 2005-07-08 | 2024-08-27 | Plasma Surgical, Inc. | Plasma-generating device, plasma surgical device and use of a plasma surgical device |
| US8105325B2 (en) | 2005-07-08 | 2012-01-31 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Plasma-generating device, plasma surgical device, use of a plasma-generating device and method of generating a plasma |
| US8109928B2 (en) | 2005-07-08 | 2012-02-07 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Plasma-generating device, plasma surgical device and use of plasma surgical device |
| US10201067B2 (en) | 2005-07-08 | 2019-02-05 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Plasma-generating device, plasma surgical device and use of a plasma surgical device |
| US8465487B2 (en) | 2005-07-08 | 2013-06-18 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Plasma-generating device having a throttling portion |
| RU2314769C2 (en)* | 2005-08-05 | 2008-01-20 | Виктор Петрович Усов | Method and device for contact-free discrete-coherent cold plasma coagulation |
| US7928338B2 (en) | 2007-02-02 | 2011-04-19 | Plasma Surgical Investments Ltd. | Plasma spraying device and method |
| US7589473B2 (en) | 2007-08-06 | 2009-09-15 | Plasma Surgical Investments, Ltd. | Pulsed plasma device and method for generating pulsed plasma |
| US8030849B2 (en) | 2007-08-06 | 2011-10-04 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Pulsed plasma device and method for generating pulsed plasma |
| US8735766B2 (en) | 2007-08-06 | 2014-05-27 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Cathode assembly and method for pulsed plasma generation |
| RU2405477C2 (en)* | 2009-02-09 | 2010-12-10 | Государственное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования Смоленская государственная медицинская академия федерального агентства по здравоохранению и социальному развитию | Instrument for plasma resection of pancreas tissue |
| US8613742B2 (en) | 2010-01-29 | 2013-12-24 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Methods of sealing vessels using plasma |
| US10631911B2 (en) | 2010-07-22 | 2020-04-28 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Volumetrically oscillating plasma flows |
| US10463418B2 (en) | 2010-07-22 | 2019-11-05 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Volumetrically oscillating plasma flows |
| US10492845B2 (en) | 2010-07-22 | 2019-12-03 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Volumetrically oscillating plasma flows |
| US9089319B2 (en) | 2010-07-22 | 2015-07-28 | Plasma Surgical Investments Limited | Volumetrically oscillating plasma flows |
| US12023081B2 (en) | 2010-07-22 | 2024-07-02 | Plasma Surgical, Inc. | Volumetrically oscillating plasma flows |
| RU2434656C1 (en)* | 2010-08-04 | 2011-11-27 | Георгий Цыренович Дамбаев | Method of stopping intra-operation haemorrhage |
| RU2647624C1 (en)* | 2017-07-18 | 2018-03-16 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное научное учреждение "Томский национальный исследовательский медицинский центр Российской академии наук" (Томский НИМЦ) | Method of treatment of infectious complications after cardiac-vascular interventions |
| RU2726599C1 (en)* | 2019-10-03 | 2020-07-14 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Санкт-Петербургский государственный педиатрический медицинский университет" Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации (ФГБОУ ВО СПбГПМУ Минздрава России) | Method of treating wounds |
| US11882643B2 (en) | 2020-08-28 | 2024-01-23 | Plasma Surgical, Inc. | Systems, methods, and devices for generating predominantly radially expanded plasma flow |
| US12058801B2 (en) | 2020-08-28 | 2024-08-06 | Plasma Surgical, Inc. | Systems, methods, and devices for generating predominantly radially expanded plasma flow |
| RU2802710C1 (en)* | 2022-08-08 | 2023-08-31 | Кирилл Александрович Новиков | How to eliminate cicatricial changes in the skin of the face |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| RU2183480C2 (en) | Method for treating biological tissue with plasma flow | |
| Meinero et al. | Endoscopic pilonidal sinus treatment (EP Si. T.) | |
| US8876746B2 (en) | Electrosurgical system and method for treating chronic wound tissue | |
| Blok et al. | Skin‐Tissue‐sparing Excision with Electrosurgical Peeling (STEEP): a surgical treatment option for severe hidradenitis suppurativa Hurley stage II/III | |
| Glover et al. | The use of thermal knives in surgery: electrosurgery, lasers, plasma scalpel | |
| Hainer et al. | Electrosurgery for the skin | |
| Redett et al. | Methods and results of rhinophyma treatment | |
| Goh et al. | Needlescopic thoracic sympathectomy: treatment for palmar hyperhidrosis | |
| Kwak et al. | Comparison of surgical outcomes between papillary thyroid cancer patients treated with the Harmonic ACE scalpel and LigaSure Precise instrument during conventional thyroidectomy: a single-blind prospective randomized controlled trial | |
| Butenko et al. | Review of clinical applications of nitric oxide-containing air-plasma gas flow generated by Plason device | |
| Eguiluz et al. | Non-thermal plasma wound healing after removal of a neck tumor in a patient with HIV: A case report | |
| JP2020529257A (en) | Diffuse applicator for cold atmospheric plasma systems | |
| RU2174398C2 (en) | Method of treatment and/or prophylaxis of invaded soft tissues of body | |
| Landscheidt et al. | Use of cold plasma in wound healing: A case report | |
| Vedbhushan et al. | Surgical incision by high frequency cautery | |
| EP3827878A1 (en) | Electromedical device for blood clotting and treatment of ulcers and other skin injuries in human and animal patients | |
| Korpan | Cryosurgery in the 21st Century | |
| RU2414189C2 (en) | Method of cryogenic treatment | |
| Xue et al. | Effect of electrochemical treatment on high-flow vascular malformations in the maxillofacial region | |
| Carneiro et al. | Management of locally aggressive mandibular tumours using a gas combination cryosurgery | |
| RU2186584C1 (en) | Biosynchronization system of physiotherapeutic and destructive impact processes | |
| RU2392875C1 (en) | Non-suture haemorrhoidectomy by using plasma scalpel | |
| RU2791386C1 (en) | Method for surgical treatment of moderate and severe rhinophyma | |
| RU2325198C1 (en) | Face furuncles treatment method | |
| RU2716263C1 (en) | Method of treating wounds and burns |