RU2177278C2 - Interbody fixative for surgical treatment of lumbar intervertebral osteochondrosis - Google Patents
Interbody fixative for surgical treatment of lumbar intervertebral osteochondrosisDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2177278C2 RU2177278C2RU98106515/14ARU98106515ARU2177278C2RU 2177278 C2RU2177278 C2RU 2177278C2RU 98106515/14 ARU98106515/14 ARU 98106515/14ARU 98106515 ARU98106515 ARU 98106515ARU 2177278 C2RU2177278 C2RU 2177278C2
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- interbody
- height
- fixative
- surgical treatment
- lumbar intervertebral
- Prior art date
Links
- 0CC*1*c***1CChemical compoundCC*1*c***1C0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Prostheses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromRussianИзобретение относится к медицине, а именно к травматологии и ортопедии, и может быть использовано при радикальных оперативных вмешательствах - тотальной дискэктомии и расклинивающем межтеловом корпородезе. The invention relates to medicine, namely to traumatology and orthopedics, and can be used for radical surgical interventions - total discectomy and wedging interbody corporodesis.
Известно устройство "Передний внутренний ортопедический фиксатор" Kozak Jeffrey, Boyd Larry, Danec medical Inc. A 61 F 2/44 WO 9510248 AL. Положительными качествами фиксатора является возможность расположения его в межтеловом пространстве с формированием металлического каркаса, являющегося распоркой, удерживающей тела позвонков в положении необходимого удаления друг от друга с опорой конструкции на края тел позвонков, являющихся более прочными механически, а также возможность размещения по центру конструкции костного трансплантата, являющегося пластическим материалом для формирования в последующем вентрального костного блока. Known device "Front internal orthopedic retainer" Kozak Jeffrey, Boyd Larry, Danec medical Inc. A 61
Недостатками данного устройства являются:
1. Конструкция является сборной и собирается непосредственно в межпозвонковом пространстве, это вызывает определенные технические сложности, повышает опасность послеоперационных осложнений.The disadvantages of this device are:
1. The design is a team and is assembled directly in the intervertebral space, this causes certain technical difficulties, increases the risk of postoperative complications.
2. При установке такой конструкции трудно добиться эффекта расклинивания межпозвонкового пространства, необходимого для устранения инклинации суставных отростков и восстановления нормальной высоты межпозвонкового промежутка
3. Конструкция удерживается в межпозвонковом промежутке за счет сохранения стенок фиброзного кольца и ущемления ее между телами позвонков, что является не совсем надежным и не исключается последующая дислокация конструкции в послеоперационном периоде.2. When installing such a design, it is difficult to achieve the effect of wedging of the intervertebral space, necessary to eliminate the inclination of the articular processes and restore the normal height of the intervertebral space
3. The structure is retained in the intervertebral space due to the preservation of the walls of the fibrous ring and its infringement between the vertebral bodies, which is not entirely reliable and subsequent dislocation of the structure in the postoperative period is not ruled out.
4. Элипсная форма конструкции не способна достаточно жестко фиксировать тела позвонков относительно друг друга, особенно в направлении осевой ротации позвоночника. 4. The elliptical shape of the structure is not able to rigidly fix the vertebral bodies relative to each other, especially in the direction of axial rotation of the spine.
5. Костный трансплантат вводится в центральную полость конструкции уже после ее установления, в связи с чем возникают сложности в полном заполнении им межпозвонкового промежутка, а также в обеспечении достаточно плотного контакта костного трансплантата со смежными замыкательными пластинками тел позвонков. 5. The bone graft is inserted into the central cavity of the structure after it has been established, which makes it difficult to completely fill the intervertebral gap, as well as to ensure a sufficiently tight contact between the bone graft and adjacent vertebral body contact plates.
Наиболее близким к предлагаемой конструкции и клинически апробированным является конструкция и метод спинальной межпозвоночной фиксации Stephen D. Kuslich (The Treatment of Chronic Discogenic Low Back Pain by the Bagby and Kuslich Method of interbody Fusion, Stephen D. Kuslich, Instrumented Fusion of the Degenerative Lumbar Spine. State of the ART, Questions, and Controversies, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadellphia, New York, 1996, p. 233-248). Предлагаемая автором конструкция представляет собой цилиндр различной длины и диаметра, который вводится в межпозвонковый промежуток параллельно замыкательным пластинкам тел позвонков как с вентральной поверхности, так и при дорзальных доступах и имеет на своей поверхности расположенные по окружности кромки, исключающие передне-задние смещения конструкции. Преимуществом данной конструкции является простота ее установки (может вводиться как в сформированный специальным инструментом канал, так и самостоятельно (по типу самореза), может вводиться как с вентральной поверхности позвоночника, так и с дорзальной, может вводиться как после субтотальной дискэктомии, так и без радикального удаления межпозвонкового диска, обеспечивает надежную стабилизацию тел позвонков относительно друг друга. Недостатками данной конструкции являются необходимость введения двух цилиндров, для стабилизации позвоночника в боковом направлении, не обеспечивает расклинивание межпозвонкового промежутка и тем самым не восстанавливает как его высоту, так и не нормализует сегментарный угол, в связи с чем часто используется как дополнительный метод вентральной стабилизации после транспедикулярной фиксации позвоночника. Маленькая площадь контакта радиуса самой конструкции с замыкательными пластинками тел позвонков снижает ее надежность фиксации, а также практически исключает использование аутотрансплантатов (возможно введение в полость конструкции незначительного по объему костно-пластического материала) из-за своей формы и суммарной массивности. Closest to the proposed design and clinically tested is the design and method of spinal intervertebral fixation Stephen D. Kuslich (The Treatment of Chronic Discogenic Low Back Pain by the Bagby and Kuslich Method of interbody Fusion, Stephen D. Kuslich, Instrumented Fusion of the Degenerative Lumbar Spine State of the ART, Questions, and Controversies, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadellphia, New York, 1996, p. 233-248). The design proposed by the author is a cylinder of various lengths and diameters, which is inserted into the intervertebral space parallel to the locking plates of the vertebral bodies both from the ventral surface and at the dorsal approaches and has circumferential edges on its surface that exclude the anteroposterior displacement of the structure. The advantage of this design is the simplicity of its installation (it can be inserted either into the canal formed by a special tool or independently (as a self-tapping screw), it can be inserted either from the ventral surface of the spine or from the dorsal, it can be inserted either after subtotal discectomy or without radical removal of the intervertebral disc, provides reliable stabilization of the vertebral bodies relative to each other.The disadvantages of this design are the need for the introduction of two cylinders to stabilize the the lateral direction, does not wedge the intervertebral gap and thereby does not restore both its height and does not normalize the segmental angle, which is why it is often used as an additional method of ventral stabilization after transpedicular fixation of the spine. plates of the vertebral bodies reduces its reliability of fixation, and also virtually eliminates the use of autografts (the introduction of a construct into the cavity is possible ii insignificant in terms of bone-plastic material) because of its shape and overall massiveness.
Задача изобретения: создать конструкцию, обеспечивающую надежную вентральную сегментарную стабилизацию тел поясничных позвонков при операциях субтотальной дискэктомии с восстановлением анатомических взаимоотношений межпозвонковых промежутков (восстановление их высоты, устранение инклинации суставных отростков, восстановление межсегментарного угла) в сочетании с возможностью использования полноценной костной пластики, обеспечивающей в последующем развитие полноценного вентрального костного блока. The objective of the invention: to create a design that provides reliable ventral segmental stabilization of the lumbar vertebral bodies during subtotal discectomy operations with restoration of the anatomical relationships of the intervertebral spaces (restoration of their height, elimination of the articular process inclineation, restoration of the intersegmental angle) in combination with the possibility of using full-fledged bone grafting, providing subsequently development of a full-fledged ventral bone block.
При решении задачи достигается следующий технический результат:
1. Высокая механическая прочность и большая площадь опоры при минимальном объеме самой конструкции.When solving the problem, the following technical result is achieved:
1. High mechanical strength and large bearing area with a minimum volume of the structure itself.
2. Высота и форма конструкции обеспечивает ее контакт с наиболее прочными участками тел позвонков. 2. The height and shape of the structure ensures its contact with the most durable sections of the vertebral bodies.
3. Подбор размера конструкции позволяет нормализовать как высоту межпозвонкового промежутка, устранить инклинацию суставных отростков, так и сегментарный угол (как уменьшить, так и увеличить). 3. The selection of the size of the structure allows you to normalize both the height of the intervertebral gap, eliminate the inclination of the articular processes, and the segmental angle (both reduce and increase).
4. Наличие зубцов увеличивает площадь контакта конструкции с костной поверхностью, обеспечивает надежную стабилизацию оперированного сегмента позвоночника во всех направлениях (наклонах и осевой ротации) вплоть до периода формирования вентрального костного блока, тем самым является профилактикой развития ложных суставов, проваливания трансплантатов в тела позвонков, их дислокации или переломов до завершения периода перестройки. 4. The presence of teeth increases the area of contact between the structure and the bone surface, provides reliable stabilization of the operated segment of the spine in all directions (inclinations and axial rotation) up to the period of formation of the ventral bone block, thereby preventing the development of false joints, failure of transplants into the vertebral bodies, their dislocations or fractures before the completion of the adjustment period.
5. Конструкция обеспечивает установку по ее центру костного пластического материала в максимально допустимом объеме и до установки самой конструкции в межтеловой промежуток, что обеспечивает большую площадь и плотность контакта костных трансплантатов с замыкательными пластинками тел позвонков. 5. The design ensures that bone plastic material is installed at its center in the maximum allowable volume and before the structure is installed in the interbody gap, which ensures a large area and density of contact between bone grafts and the contact plates of the vertebral bodies.
Технический результат позволяет получить при использовании конструкции в клинике положительный лечебный, экономический эффект. Жесткая фиксация вентральных отделов создает оптимальные условия на период формирования вентрального костного блока, позволяет проводить костную пластику, не усложняя хирургической техники; в ряде случаев исключается необходимость к дополнительной жесткой внешней иммобилизации. В подавляющем большинстве случаев снимается необходимость в дополнительной задней стабилизации позвоночника (задние спондилодезы, транспедикулярная фиксация). Конструкция позволяет восстановить биомеханические взаимоотношения в оперированном позвоночном двигательном сегменте (сегментарный угол, высоту межпозвонкового промежутка). Межтеловой фиксатор может быть использован с учетом модификации размеров для аналогичных целей в любом отделе позвоночника. Использование фиксатора позволяет сократить период стационарного лечения. The technical result allows to obtain a positive therapeutic, economic effect when using the design in the clinic. Rigid fixation of the ventral sections creates optimal conditions for the period of formation of the ventral bone block, allows bone grafting without complicating the surgical technique; in some cases, the need for additional rigid external immobilization is excluded. In the vast majority of cases, the need for additional posterior stabilization of the spine (posterior spinal fusion, transpedicular fixation) is removed. The design allows you to restore biomechanical relationships in the operated vertebral motor segment (segmental angle, the height of the intervertebral gap). The interbody fixer can be used taking into account size modifications for similar purposes in any part of the spine. The use of a fixative can reduce the period of inpatient treatment.
Поставленная задача решается тем, что фиксатор состоит из 2-х колец овоидной формы, соединенных между собой вертикальными стойками с овальными промежутками; высота задних стоек меньше высоты передних на 2-4 мм, наружные поверхности колец имеют зубцы с наклоном внутрь высотой 1 мм. The problem is solved in that the latch consists of 2 rings of ovoid shape, interconnected by vertical uprights with oval gaps; the height of the rear legs is less than the height of the front by 2-4 mm, the outer surfaces of the rings have teeth with an inward inclination of 1 mm height.
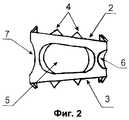
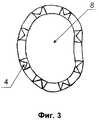
На фиг. 1 представлен межтеловой фиксатор, общий вид; на фиг. 2 - вид сбоку; на фиг. 3 - вид сверху. Межтеловой фиксатор состоит из:
1 - корпус фиксатора;
2 - верхнее кольцо;
3 - нижнее кольцо;
4 - зубцы;
5 - овальные отверстия;
6 - центральное отверстие.In FIG. 1 shows the interbody retainer, general view; in FIG. 2 is a side view; in FIG. 3 is a plan view. The interbody latch consists of:
1 - housing lock;
2 - the upper ring;
3 - lower ring;
4 - teeth;
5 - oval holes;
6 - the Central hole.
Межтеловой фиксатор используется следующим образом: доступ к поясничным дискам левосторонний парамедианный. Брюшинный мешок мобилизуется вправо, кпереди и кверху. Обнажается передняя поверхность нижне-поясничного отдела позвоночника. Диск удаляется полностью вместе с замыкательными пластинками смежных тел позвонков до кровоточащей спонгиозы. В положении гиперэкстензии вбиваются межтеловые фиксаторы с аутотрансплантатом внутри. Размеры эндофиксаторов соответствуют предварительному предоперационному планированию и детально уточняются непосредственно в ране. Аутотрансплантат берется типично из гребня крыла левой подвздошной кости. The interbody lock is used as follows: access to the lumbar discs is left-sided paramedian. The peritoneal sac is mobilized to the right, anterior and upward. The front surface of the lower lumbar spine is exposed. The disk is removed completely together with the locking plates of the adjacent vertebral bodies until a bleeding spongiosis. In the hyperextension position, interbody fixators with an autograft inside are driven in. The sizes of endofixers correspond to preliminary preoperative planning and are specified in detail directly in the wound. An autograft is typically taken from the wing crest of the left iliac bone.
Б-ой - Е. Возраст - 41 год. История болезни - 834/97. Диагноз - Поясничный межпозвонковый остеохондроз с преимущественным поражением L5-S1 диска в стадии сегментарной нестабильности, дегенеративный стеноз позвоночного канала на этом уровне, дегенеративный спондилолистез L5 позвонка. Синдром каудогенной перемежающейся хромоты. Название операции. 1. Тотальная дискэктомия L5-S1 и расклинивающий корпородез межтеловым фиксатором и аутотрансплантатами. 2. Взятие аутотрансплантатов из гребня крыла левой подвздошной кости. Дата. 28 мая 1997 года. Час. 10.00-11.40. Обезболивание - эндотрахеальный наркоз. Описание операции. 1. Левосторонний внебрюшинный парамедианный доступ. Линейный разрез от точки на 2 см выше лона, послойно рассечены кожа, подкожная клетчатка, фасции, передний листок влагалища прямой мышцы живота, отступя 1,5 см от белой линии. Прямая мышца мобилизована и смещена кнаружи. В проекции ее наружнего края рассечены задний листок влагалища с поперечной фасцией живота в нижней трети. Брюшинный мешок мобилизован и вместе с левым мочеточником смещен вправо, кпереди и кверху. Обнажено левое забрюшинное пространство. Расслоена превертебральная фасция в области бифуркации аорты и обнажена передняя поверхность L5-S1 диска. Подвздошные сосуды под защитой элеваторов смещены вправо и влево. Межпозвонковый диск L5-S1 резко снижен по высоте, полностью лишен тургора. Диск удален вместе с замыкательными пластинками тел смежных позвонков до кровоточащей спонгиозы. В образованный дефект в положении гиперэкстензии нижне-поясничного отдела позвоночника, достигнутой с помощью валика операционного стола, вбит межтеловой фиксатор высотой 10 мм с фиксированными в нем двумя компактно-спонгиозных аутотрансплантата. По устранении гиперэкстензии фиксатор хорошо заклинился в своем ложе. Гемостаз по ходу операции. Рана ушита послойно. Внутривенно введен гентамицин 240 мг. В подкожную клетчатку вставлено 3 резиновых выпускника. Асептическая повязка. 2. Линейным разрезом в проекции гребня крыла левой подвздошной кости послойно рассечены кожа, клетчатка, фасции. Поднадкостнично выделен и резецирован участок гребня размерами 4 на 1,5 на 1,5 см. Гемостаз. Послойные швы раны. Резиновый выпускник к костной ране. Асептическая повязка. B-th - E. Age - 41 years. Medical history - 834/97. Diagnosis - Lumbar intervertebral osteochondrosis with a primary lesion of L5-S1 disk in the stage of segmental instability, degenerative spinal stenosis at this level, degenerative spinal lysthesis of the L5 vertebra. Caudogenic intermittent claudication syndrome. The name of the operation. 1. Total discectomy L5-S1 and proppant corporodesis with interbody fixer and autografts. 2. Taking autografts from the crest of the wing of the left iliac bone. Date. May 28, 1997. Hour. 10.00-11.40. Anesthesia - endotracheal anesthesia. Operation description. 1. Left-sided extraperitoneal paramedian access. Linear incision from a
Claims (1)
Translated fromRussianPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU98106515/14ARU2177278C2 (en) | 1998-03-31 | 1998-03-31 | Interbody fixative for surgical treatment of lumbar intervertebral osteochondrosis |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU98106515/14ARU2177278C2 (en) | 1998-03-31 | 1998-03-31 | Interbody fixative for surgical treatment of lumbar intervertebral osteochondrosis |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU98106515A RU98106515A (en) | 2000-01-27 |
| RU2177278C2true RU2177278C2 (en) | 2001-12-27 |
Family
ID=20204461
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU98106515/14ARU2177278C2 (en) | 1998-03-31 | 1998-03-31 | Interbody fixative for surgical treatment of lumbar intervertebral osteochondrosis |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2177278C2 (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2319473C2 (en)* | 2006-04-24 | 2008-03-20 | ФГУ Новосибирский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии (ФГУ ННИИТО Росздрава) | An inter-body endofixator |
| RU2339343C1 (en)* | 2007-08-13 | 2008-11-27 | Федеральное государственное унитарное предприятие "Красноярский машиностроительный завод" ФГУП "Красмаш" | Implant for intrabody fixation of vertebrae |
| RU2428146C2 (en)* | 2008-10-24 | 2011-09-10 | Ульрих Гмбх Унд Ко. Кг | Implant for installation between bodies of spine vertebrae |
| US9597198B2 (en) | 2006-02-15 | 2017-03-21 | Ldr Medical | Transforaminal intersomatic cage for an intervertebral fusion graft and an instrument for implanting the cage |
| RU2792942C1 (en)* | 2022-02-10 | 2023-03-28 | федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Северо-Западный государственный медицинский университет имени И.И. Мечникова" Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации | Truss reinforcing cage for forming a combined implant to replace a removed disc during operations on the thoracic and lumbar spine and a jig-injector for installing and filling a truss reinforcing cage |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU1326261A1 (en)* | 1985-07-04 | 1987-07-30 | Центральный научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии им.Н.Н.Приорова | Fixative for spinal column |
| EP0355411A1 (en)* | 1988-08-10 | 1990-02-28 | Ace Medical Company | Intramedullary rod for femur stabilization |
| SU1572428A1 (en)* | 1987-07-13 | 1990-06-23 | Kh Nii Ortoped Travmatolog | Spinal column correction device |
| US5041114A (en)* | 1986-06-23 | 1991-08-20 | Pfizer Hospital Products Group, Inc. | Modular femoral fixation system |
- 1998
- 1998-03-31RURU98106515/14Apatent/RU2177278C2/ennot_activeIP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU1326261A1 (en)* | 1985-07-04 | 1987-07-30 | Центральный научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии им.Н.Н.Приорова | Fixative for spinal column |
| US5041114A (en)* | 1986-06-23 | 1991-08-20 | Pfizer Hospital Products Group, Inc. | Modular femoral fixation system |
| SU1572428A1 (en)* | 1987-07-13 | 1990-06-23 | Kh Nii Ortoped Travmatolog | Spinal column correction device |
| EP0355411A1 (en)* | 1988-08-10 | 1990-02-28 | Ace Medical Company | Intramedullary rod for femur stabilization |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9597198B2 (en) | 2006-02-15 | 2017-03-21 | Ldr Medical | Transforaminal intersomatic cage for an intervertebral fusion graft and an instrument for implanting the cage |
| US10758363B2 (en) | 2006-02-15 | 2020-09-01 | Ldr Medical | Transforaminal intersomatic cage for an intervertebral fusion graft and an instrument for implanting the cage |
| RU2319473C2 (en)* | 2006-04-24 | 2008-03-20 | ФГУ Новосибирский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии (ФГУ ННИИТО Росздрава) | An inter-body endofixator |
| RU2339343C1 (en)* | 2007-08-13 | 2008-11-27 | Федеральное государственное унитарное предприятие "Красноярский машиностроительный завод" ФГУП "Красмаш" | Implant for intrabody fixation of vertebrae |
| RU2428146C2 (en)* | 2008-10-24 | 2011-09-10 | Ульрих Гмбх Унд Ко. Кг | Implant for installation between bodies of spine vertebrae |
| RU2792942C1 (en)* | 2022-02-10 | 2023-03-28 | федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Северо-Западный государственный медицинский университет имени И.И. Мечникова" Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации | Truss reinforcing cage for forming a combined implant to replace a removed disc during operations on the thoracic and lumbar spine and a jig-injector for installing and filling a truss reinforcing cage |
| RU2793066C1 (en)* | 2022-02-10 | 2023-03-28 | федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Северо-Западный государственный медицинский университет им. И.И. Мечникова" Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации | Truss reinforcing cage for replacing the removed disc during surgery on the cervical spine performed by an anterior approach, and a jig-injector for its installation |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20230277327A1 (en) | Methods and apparatus for minimally invasive modular interbody fusion devices | |
| AU770261B2 (en) | Artificial disc implant | |
| US8911498B2 (en) | Intervertebral prosthetic disc | |
| US20030060825A1 (en) | Anterior lumbar spacer | |
| US20020099444A1 (en) | Modular interbody fusion implant | |
| David | Lumbar disc prosthesis: surgical technique, indications and clinical results in 22 patients with a minimum of 12 months follow-up | |
| JP2002501782A (en) | Allogeneic intervertebral implant | |
| WO1995020370A1 (en) | Vertebral body prosthetic implant | |
| AU2002251773A1 (en) | Modular interbody fusion implant | |
| Chang | Oligosegmental correction of post-traumatic thoracolumbar angular kyphosis | |
| Ray | Spinal interbody fusions: a review, featuring new generation techniques | |
| RU2177278C2 (en) | Interbody fixative for surgical treatment of lumbar intervertebral osteochondrosis | |
| RU2129411C1 (en) | Correcting spondilodesis method | |
| Yoshimoto et al. | Deep vein thrombosis due to migrated graft bone after posterior lumbosacral interbody fusion: Case report | |
| AU735572B2 (en) | Threaded fusion cage anchoring device and method | |
| RU2073494C1 (en) | Method to treat compression spine syndrome | |
| RU2152759C2 (en) | Method for treating the cases of sacroiliac articulation rupture | |
| SU1650114A1 (en) | Method for frontal spodylosyndesis | |
| RU2279860C2 (en) | Method for surgical treatment of vertebral tumors | |
| RU2279859C2 (en) | Method for surgical treating aftereffects of vertebral fractures | |
| RU2065731C1 (en) | Method for frontal spondylosyndesis of children | |
| RU2726399C1 (en) | Method of posterior-transforaminal interbody spinal fusion accompanied by decompressor-stabilizing operations on lumbar spine | |
| RU2319473C2 (en) | An inter-body endofixator | |
| RU2221511C1 (en) | Method for fixing arch in performing laminoplastic lumbar vertebral column segment repair | |
| RU2195220C2 (en) | Method of vertebral column stabilization in cerebrospinal trauma |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees | Effective date:20060401 |