RU2141249C1 - Method for diagnosing and predicting hypertension disease in patients before thirty - Google Patents
Method for diagnosing and predicting hypertension disease in patients before thirtyDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2141249C1 RU2141249C1RU96101317/14ARU96101317ARU2141249C1RU 2141249 C1RU2141249 C1RU 2141249C1RU 96101317/14 ARU96101317/14 ARU 96101317/14ARU 96101317 ARU96101317 ARU 96101317ARU 2141249 C1RU2141249 C1RU 2141249C1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- vessels
- brain
- reg
- amplitude
- blood vessels
- Prior art date
Links
- 206010020772HypertensionDiseases0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription10
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription9
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000titleabstractdescription4
- 210000004556brainAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription22
- 230000010349pulsationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 230000000007visual effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 208000028867ischemiaDiseases0.000claimsabstractdescription3
- 210000000275circle of willisAnatomy0.000claimsabstract2
- 230000006442vascular toneEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 210000004204blood vesselAnatomy0.000abstractdescription5
- 230000002490cerebral effectEffects0.000abstractdescription5
- 238000003745diagnosisMethods0.000abstractdescription5
- 230000001360synchronised effectEffects0.000abstractdescription5
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000abstract1
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000abstract1
- 230000036770blood supplyEffects0.000description7
- 210000004720cerebrumAnatomy0.000description2
- 230000001256tonic effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000002792vascularEffects0.000description2
- 206010008190Cerebrovascular accidentDiseases0.000description1
- 208000006011StrokeDiseases0.000description1
- 239000008280bloodSubstances0.000description1
- 210000004369bloodAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000017531blood circulationEffects0.000description1
- 230000003727cerebral blood flowEffects0.000description1
- 208000026106cerebrovascular diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 235000012907honeyNutrition0.000description1
- 210000001595mastoidAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000000653nervous systemAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000004393prognosisMethods0.000description1
- 208000019553vascular diseaseDiseases0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement And Recording Of Electrical Phenomena And Electrical Characteristics Of The Living Body (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromRussianИзобретение относится к области медицины и касается запросов диагностики и прогнозирования гипертонической болезни (ГБ) у людей. The invention relates to medicine and relates to the diagnosis and prognosis of hypertension (GB) in humans.
Известен способ, основанный на синхронной регистрации пульсового кровенаполнения одноименных сосудов левого и правого полушарий головного мозга, используемый в качестве дополнительной информации для подтверждения сосудистых заболеваний мозга (Зенков Л.Р., Ронкин М.Д. Функциональная диагностика нервных болезней, М., Мед., 1991, с. 392 - 423) - метод, основанный на колебаниях импеданса, вызываемых пульсовыми колебаниями кровенаполнения мозга (А. А. Кедров, 1954., Bertha соавт., 1955 г., Хаджиев Д., Цепов А., 1964 г.). В настоящее время окончательно сформировалось мнение, что изменения импеданса мозга обусловлены колебаниями мозгового кровотока. Реоэнцефалограмма (РЭГ), являясь кривой пульсовых колебаний электрического сопротивления мозга, отражает объемные изменения мозговых сосудов при прохождении каждой пульсовой волны. Следовательно, амплитуда РЭГ является прежде всего показателем интенсивности наполнения исследуемой области мозга. Поскольку объемная скорость кровотока зависит от величины просвета сосудов, т.е. от степени тонического напряжения сосудистой стенки, РЭГ отражает не только пульсовые колебания кровенаполнения, но и изменения эластичности и тонуса мозговых сосудов (Зенков Л.А., Ронкин М.А. Функциональная диагностика нервной системы, М. , 1991, с. 423-518, Яруллина Х.Х. Клиническая реоэнцефалография, М., Мед., 1983). A known method based on the synchronous registration of pulse blood supply of the same vessels in the left and right hemispheres of the brain, used as additional information to confirm vascular diseases of the brain (Zenkov L.R., Ronkin M.D. Functional diagnosis of nervous diseases, M., Honey. , 1991, pp. 392 - 423) - a method based on impedance fluctuations caused by pulse fluctuations in the blood supply to the brain (A. A. Kedrov, 1954., Bertha et al., 1955, Khadzhiev D., Tsepov A., 1964 .). Currently, the opinion has finally formed that changes in brain impedance are caused by fluctuations in cerebral blood flow. Rheoencephalogram (REG), being a curve of pulse fluctuations in the electrical resistance of the brain, reflects the volumetric changes in the cerebral vessels during the passage of each pulse wave. Therefore, the amplitude of the REG is primarily an indicator of the intensity of filling of the studied area of the brain. Since the volumetric blood flow velocity depends on the size of the vascular lumen, i.e. from the degree of tonic tension of the vascular wall, REG reflects not only pulse fluctuations in blood supply, but also changes in the elasticity and tone of the cerebral vessels (Zenkov L.A., Ronkin M.A. Functional diagnosis of the nervous system, M., 1991, pp. 423-518 , Yarullina Kh.Kh. Clinical rheoencephalography, M., Med., 1983).
Сконструированы и используются отечественные реографы: одноканальный реограф типа РГ-1-01, РГ-4-02, двухканальный реограф "Реовар" французской фирмы, двухканальный реограф "Дуореограф" итальянской фирмы. С помощью реографа производится синхронная запись парных фронтомастоидальных (РМ) и окципитомастоидальных (ОМ) отведений. Получаемая кривая, обозначенная термином "реоэнцефалограмма", подвергается визуальной и математической обработке. Domestic rheographs were designed and used: a single-channel rheograph of the type RG-1-01, RG-4-02, a two-channel rheograph "Reovar" of a French company, a two-channel rheograph "Duoreograph" of an Italian company. Using a rheograph, synchronous recording of paired frontomastoidal (RM) and occipitomastoidal (OM) leads is performed. The resulting curve, designated by the term "rheoencephalogram", is subjected to visual and mathematical processing.
Показателем интенсивности пульсовых колебаний кровенаполнения исследуемой области мозга является величина амплитуды РЭГ. Амплитуда РЭГ измеряется от основания реографической волны до точки максимального подъема ее вершины, полученная величина измеряется в миллиметрах, затем путем сравнения со стандартным эталоном преобразуется в единицы омического сопротивления - таким образом получают реографический индекс в омах. У здоровых людей для фронтомастоидальных отведений он равен 0,15 Ом, для окципито-мастоидальных отведений - 0,09 Ом. Показателем разницы амплитуды РЭГ парных сосудов полушарий головного мозга служит коэффициент асимметрии (КА), разница полученных величин амплитуд парных сосудов левого и правого полушарий головного мозга, выраженная в процентах, рассматривается как КА - показатель, отражающий различия в наполнении полушарий головного мозга, в норме составляющий 5-20%. Длительность реографической кривой от начала до точки максимального подъема (анакротическая фаза) измеряется отрезком времени в секундах (м/сек). Среднее значение длительности анакротической фазы в норме равно 0,12 сек, отношение этой величины к длительности всей волны отражает состояние тонуса сосудов головного мозга, выраженное в процентах, и составляет не более 17,6%. Длительность фазы от вершины до конца реоэнцефалограммы (катакротическая фаза) у здоровых людей равняется 0,46-0,48 сек. При анализе РЭГ определяют соотношение между высотой дикротического зубца и высотой реографической волны и таким образом оценивают тоническое напряжение сосудов головного мозга. Однако из-за непостоянства дикротической волны этот показатель не всегда надежен. An indicator of the intensity of pulse fluctuations in the blood supply to the studied area of the brain is the magnitude of the amplitude of the REG. The amplitude of the REG is measured from the base of the rheographic wave to the point of maximum rise of its peak, the obtained value is measured in millimeters, then, by comparison with the standard standard, it is converted to ohmic resistance units - this way the rheographic index in ohms is obtained. In healthy people, it is 0.15 Ohm for front mastoid leads, and 0.09 Ohm for occipitoid-mastoid leads. The difference in the amplitude of the REG of paired vessels of the cerebral hemispheres is the asymmetry coefficient (KA), the difference in the values of the amplitudes of the paired vessels of the left and right hemispheres of the brain, expressed as a percentage, is considered as a KA - an indicator reflecting the differences in the filling of the cerebral hemispheres, normally making 5-20%. The duration of the rheographic curve from the beginning to the point of maximum rise (anacrotic phase) is measured by the length of time in seconds (m / s). The average value of the duration of the anacrotic phase is normally 0.12 seconds, the ratio of this value to the duration of the entire wave reflects the state of the tone of the vessels of the brain, expressed as a percentage, and does not exceed 17.6%. The duration of the phase from the top to the end of the rheoencephalogram (catacrotic phase) in healthy people is 0.46-0.48 seconds. In the analysis of REG, the ratio between the height of the dicrotic tooth and the height of the rheographic wave is determined and thus the tonic tension of the vessels of the brain is evaluated. However, due to the inconstancy of the dicrotic wave, this indicator is not always reliable.
Особенности РЭГ при гипертонической болезни, как правило, заключаются уже в изменении формы кривых, а также в снижении амплитуды реографических волн, появлении дополнительных волн, которые нередко превышают вершину основной волны, смещение дикротической волны к вершине. Эти изменения РЭГ при ГБ отражают уменьшение кровенаполнения мозга на фоне значительного повышения тонуса сосудов головного мозга (Адибаев О.А., 1978, цит. по: Зенков Л.Р., Ронкин М.А., с.475). The features of REG in hypertension, as a rule, consist in changing the shape of the curves, as well as in reducing the amplitude of the rheographic waves, the appearance of additional waves, which often exceed the top of the main wave, and the shift of the dicrotic wave to the top. These changes in REG in hypertension reflect a decrease in blood supply to the brain against a background of a significant increase in the tone of cerebral vessels (Adibaev O.A., 1978, cited from: Zenkov L.R., Ronkin M.A., p.475).
Однако о помощью указанного способа без дополнительного анализа РЭГ не представляется возможным прогнозировать ГБ. However, using this method without additional REG analysis, it is not possible to predict GB.
Задачей заявленного изобретения является получение возможности уточнения диагноза ГБ, а также прогнозирования ГБ у пациентов до 30 лет путем соответствующей обработки и анализа реоэнцефалограмм. The objective of the claimed invention is to obtain the possibility of clarifying the diagnosis of GB, as well as predicting GB in patients under 30 years of age by appropriate processing and analysis of rheoencephalograms.
Для достижения указанного результата в способе диагностики и прогнозирования ГБ, заключающемся в синхронной регистрации пульсового кровенаполнения парных сосудов левого и правого полушарий головного мозга с последующей визуальной и математической обработкой данных регистрации, включающей определение амплитуды пульсации, тонуса сосудов и КА парных сосудов левого и правого полушарий сосудов Вилизневого круга и в сравнении полученных данных с аналогичными показателями у здоровых лиц, при значении КА более 20% диагностируют окклюзию одного из парных сосудов головного мозга, вызывающую ишемию зоны головного мозга, которая питается окклюзированным сосудом, таким образом, основываясь на этом факте, диагностируют и прогнозируют ГБ. To achieve the specified result in the method for diagnosing and predicting hypertension, which consists in synchronous recording of pulse blood supply to the paired vessels of the left and right hemispheres of the brain, followed by visual and mathematical processing of the registration data, including determining the amplitude of the pulsation, vascular tone and spacecraft of the paired vessels of the left and right hemispheres of blood vessels Vilicarum circle and in comparison of the obtained data with similar indicators in healthy individuals, with a CA value of more than 20%, occlusion is diagnosed of the paired vessels of the brain, causing ischemia of the area of the brain that feeds on an occluded vessel, thus, based on this fact, GB is diagnosed and predicted.
Например, больной Мордвинкин В.А., 29 лет, болен гипертонической болезнью. For example, a patient Mordvinkin V.A., 29 years old, is sick with hypertension.
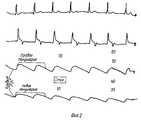
РЭГ от 07.12.92 г. (фиг. 1 и 2). REG from 07.12.92, (Fig. 1 and 2).
Тип кривой - гипертонический (см. фиг. 1 и 2). The type of curve is hypertonic (see Figs. 1 and 2).
FMD = 100 Ом,,
FMS = 550 Ом, KA = 100%,
OMD = 70 Ом,
OMS = 40 Ом, KA = 75%.FMD = 100 ohms, ,
FMS = 550 Ohm, KA = 100%,
OMD = 70 ohms,
OMS = 40 Ohms, KA = 75%.
Согласно способу анализируют и обрабатывают данные кривых регистрации парных сосудов левого и правого полушарий головного мозга. Как следует из рассмотрения данных (см. фиг.1 и 2), кровенаполнение парных сосудов правого и левого полушарий существенно различается. Так, видно, что амплитуды кривых левого полушария головного мозга (фиг. 1 и 2) существенно снижены по сравнению с амплитудами кривых правого полушария, что связано с окклюзией сосудов левого полушария. Синхронная запись одноименных (парных) сосудов с учетом КА позволит выявить зону нарушения мозгового кровообращения и особенности перераспределения крови, представит возможность установить степень окклюзии сосудов головного мозга. According to the method, the data of the registration curves of paired vessels of the left and right hemispheres of the brain are analyzed and processed. As follows from a review of the data (see figures 1 and 2), the blood supply to the paired vessels of the right and left hemispheres is significantly different. So, it is seen that the amplitudes of the curves of the left hemisphere of the brain (Fig. 1 and 2) are significantly reduced compared with the amplitudes of the curves of the right hemisphere, which is associated with occlusion of the vessels of the left hemisphere. Synchronous recording of the vessels of the same name (paired), taking into account the spacecraft, will reveal the zone of cerebrovascular accident and blood redistribution, will provide an opportunity to establish the degree of occlusion of cerebral vessels.
Таким образом, дополнительный анализ данных РЭГ, обработка их с учетом КА дает возможность прогнозирования ГБ у людей до 30 лет. Порядок обработки кривых РЭГ, определения КА и сопоставления с данными здорового человека может быть алгоритмизирован и введен в программу для автоматического формирования заключения. Thus, an additional analysis of the REG data, their processing taking into account the CA makes it possible to predict GB in people under 30 years of age. The procedure for processing the REG curves, determining the spacecraft, and comparing it with the data of a healthy person can be algorithmized and entered into the program to automatically generate a conclusion.
Claims (1)
Translated fromRussianPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU96101317/14ARU2141249C1 (en) | 1996-01-19 | 1996-01-19 | Method for diagnosing and predicting hypertension disease in patients before thirty |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU96101317/14ARU2141249C1 (en) | 1996-01-19 | 1996-01-19 | Method for diagnosing and predicting hypertension disease in patients before thirty |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU96101317A RU96101317A (en) | 1998-03-27 |
| RU2141249C1true RU2141249C1 (en) | 1999-11-20 |
Family
ID=20176044
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU96101317/14ARU2141249C1 (en) | 1996-01-19 | 1996-01-19 | Method for diagnosing and predicting hypertension disease in patients before thirty |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2141249C1 (en) |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2181260C2 (en)* | 2000-07-26 | 2002-04-20 | Новокузнецкий государственный институт усовершенствования врачей | Method for predicting chances of arising hypertension |
| RU2261039C2 (en)* | 2002-09-20 | 2005-09-27 | ООО "Инновационно-коммерческая компания Медмарк" | Method for estimating arterial bloodstream tone |
| RU2263465C2 (en)* | 2003-10-22 | 2005-11-10 | Томский научно-исследовательский институт курортологии и физиотерапии МЗ РФ | Method for detecting the mechanism in alteration of vertebro- basillar circulation in children |
| RU2296505C2 (en)* | 2004-11-01 | 2007-04-10 | Военно-медицинский институт Федеральной службы безопасности Российской Федерации (ВМИ ФСБ России) | Method for predicting structural-functional alterations in erythrocytic and vascular cell membranes in patients with arterial hypertension |
| WO2010041205A2 (en) | 2008-10-07 | 2010-04-15 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Monitoring of acute stroke patients |
| US7998080B2 (en) | 2002-01-15 | 2011-08-16 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Method for monitoring blood flow to brain |
| US8187197B2 (en) | 2002-01-15 | 2012-05-29 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Cerebral perfusion monitor |
| US8211031B2 (en) | 2002-01-15 | 2012-07-03 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Non-invasive intracranial monitor |
| US9307918B2 (en) | 2011-02-09 | 2016-04-12 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Devices and methods for monitoring cerebral hemodynamic conditions |
- 1996
- 1996-01-19RURU96101317/14Apatent/RU2141249C1/ennot_activeIP Right Cessation
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| Адибаев О.А. 1978, цит. по: Зенков Л.Р., Ронкин М.А. Функциональная диагностика нервной системы. - М.: Медицина, 1991, с.475.* |
Cited By (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2181260C2 (en)* | 2000-07-26 | 2002-04-20 | Новокузнецкий государственный институт усовершенствования врачей | Method for predicting chances of arising hypertension |
| US8187197B2 (en) | 2002-01-15 | 2012-05-29 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Cerebral perfusion monitor |
| US8702615B2 (en) | 2002-01-15 | 2014-04-22 | Osran Medical Technologies, Ltd. | Device for monitoring blood flow to brain |
| US8512253B2 (en) | 2002-01-15 | 2013-08-20 | Orsan Medical Technologies, Ltd | Cerebral perfusion monitor |
| US7998080B2 (en) | 2002-01-15 | 2011-08-16 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Method for monitoring blood flow to brain |
| US8211031B2 (en) | 2002-01-15 | 2012-07-03 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Non-invasive intracranial monitor |
| RU2261039C2 (en)* | 2002-09-20 | 2005-09-27 | ООО "Инновационно-коммерческая компания Медмарк" | Method for estimating arterial bloodstream tone |
| RU2263465C2 (en)* | 2003-10-22 | 2005-11-10 | Томский научно-исследовательский институт курортологии и физиотерапии МЗ РФ | Method for detecting the mechanism in alteration of vertebro- basillar circulation in children |
| RU2296505C2 (en)* | 2004-11-01 | 2007-04-10 | Военно-медицинский институт Федеральной службы безопасности Российской Федерации (ВМИ ФСБ России) | Method for predicting structural-functional alterations in erythrocytic and vascular cell membranes in patients with arterial hypertension |
| WO2010041205A2 (en) | 2008-10-07 | 2010-04-15 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Monitoring of acute stroke patients |
| CN102238905A (en)* | 2008-10-07 | 2011-11-09 | 奥森医疗科技有限公司 | Measurement of cerebral hemodynamic parameters |
| WO2010041204A3 (en)* | 2008-10-07 | 2010-06-03 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Measurement of cerebral hemodynamic parameters |
| WO2010041205A3 (en)* | 2008-10-07 | 2010-06-03 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Monitoring of acute stroke patients |
| CN102238905B (en)* | 2008-10-07 | 2015-05-27 | 奥森医疗科技有限公司 | Measurement of cerebral hemodynamic parameters |
| EP3031395A1 (en)* | 2008-10-07 | 2016-06-15 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Monitoring of acute stroke patients |
| US9307918B2 (en) | 2011-02-09 | 2016-04-12 | Orsan Medical Technologies Ltd. | Devices and methods for monitoring cerebral hemodynamic conditions |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Benjamin et al. | Why is left ventricular hypertrophy so predictive of morbidity and mortality? | |
| Poredos | Intima-media thickness: indicator of cardiovascular risk and measure of the extent of atherosclerosis | |
| Salim et al. | Effect of beta-adrenergic blockade on aortic root rate of dilation in the Marfan syndrome | |
| Cuspidi et al. | Evaluation of target organ damage in arterial hypertension: which role for qualitative funduscopic examination? | |
| Verhorst et al. | Left atrial appendage flow velocity assessment using transesophageal echocardiography in nonrheumatic atrial fibrillation and systemic embolism | |
| Press et al. | Hippocampal abnormalities in amnesic patients revealed by high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging | |
| Hermida et al. | 2013 Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring recommendations for the diagnosis of adult hypertension, assessment of cardiovascular and other hypertension-associated risk, and attainment of therapeutic Goals: joint recommendations from the International Society for Chronobiology (ISC), American Association of Medical Chronobiology and Chronotherapeutics (AAMCC), Spanish Society of Applied Chronobiology, Chronotherapy, and Vascular Risk (SECAC), Spanish Society of Atherosclerosis (SEA), and Romanian Society of Internal Medicine (RSIM) | |
| Uematsu et al. | Measurement of carotid blood flow in man and its clinical application. | |
| Kennedy et al. | Ambulatory blood pressure in healthy normotensive males | |
| Shahi et al. | Regression of hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy and left ventricular diastolic function | |
| RU2141249C1 (en) | Method for diagnosing and predicting hypertension disease in patients before thirty | |
| EP2224846B1 (en) | Method and apparatus to determine the end of the systolic part of a pressure curve | |
| US7092751B2 (en) | Detection of atrial arrhythmia | |
| Sandoo et al. | A methodological approach to non-invasive assessments of vascular function and morphology | |
| Eagle et al. | Left ventricular ejection fraction physician estimates compared with gated blood pool scan measurements | |
| Pouta et al. | Changes in maternal heart dimensions and plasma atrial natriuretic peptide levels in the early puerperium of normal and pre‐eclamptic pregnancies | |
| RU96101317A (en) | METHOD FOR DIAGNOSTIC AND FORECAST OF HYPERTENSIVE DISEASE IN PEOPLE UNDER 30 YEARS OF AGE | |
| KR102035731B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for measuring pain depth using photoplethysmograph | |
| KR101002079B1 (en) | Blood Vessel Measurement Method | |
| Mowafy et al. | Optic nerve sheath diameter versus extra-vascular lung water detected by ultrasound in volume status prediction in severe preeclampsia | |
| Ostrowska et al. | A short P-wave duration is associated with incident heart failure in the elderly: a 15 years follow-up cohort study | |
| Aronow et al. | Usefulness of echocardiographie and electrocardiographic left ventricular hypertrophy in predicting new cardiac events and atherothrombotic brain infarction in elderly patients with systemic hypertension or coronary artery disease | |
| Silagy et al. | Isolated systolic hypertension: does it really exist on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring? | |
| Gordon et al. | Unstimulated renal venous renin ratio predicts improvement in hypertension following nephrectomy for unilateral renal disease | |
| Lauersen et al. | Evaluation of the accuracy of a new ultrasonic fetal heart rate monitor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees | Effective date:20050120 |