RU2063771C1 - Method of sterilization of medical instruments - Google Patents
Method of sterilization of medical instrumentsDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2063771C1 RU2063771C1RU93032702ARU93032702ARU2063771C1RU 2063771 C1RU2063771 C1RU 2063771C1RU 93032702 ARU93032702 ARU 93032702ARU 93032702 ARU93032702 ARU 93032702ARU 2063771 C1RU2063771 C1RU 2063771C1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- sterilization
- water
- medical instruments
- instruments
- mixture
- Prior art date
Links
- 230000001954sterilising effectEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription12
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription6
- 238000004659sterilization and disinfectionMethods0.000titleabstractdescription10
- 230000000844anti-bacterial effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription6
- 229920003169water-soluble polymerPolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 239000003899bactericide agentSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription3
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-MChloride anionChemical compound[Cl-]VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000claimsdescription4
- VKYKSIONXSXAKP-UHFFFAOYSA-NhexamethylenetetramineChemical compoundC1N(C2)CN3CN1CN2C3VKYKSIONXSXAKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- 125000000472sulfonyl groupChemical group*S(*)(=O)=O0.000claimsdescription3
- 235000010299hexamethylene tetramineNutrition0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004312hexamethylene tetramineSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229960004011methenamineDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 229920000642polymerPolymers0.000description6
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterChemical compoundOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 241000699670Mus sp.Species0.000description2
- 241000700159RattusSpecies0.000description2
- 239000007864aqueous solutionSubstances0.000description2
- 239000003960organic solventSubstances0.000description2
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000description2
- 241000700198CaviaSpecies0.000description1
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-NHydrogenChemical compound[H][H]UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000001580bacterial effectEffects0.000description1
- 210000000748cardiovascular systemAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000003169central nervous systemAnatomy0.000description1
- 150000001875compoundsChemical class0.000description1
- 238000011109contaminationMethods0.000description1
- 230000001186cumulative effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000000881depressing effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000002489hematologic effectEffects0.000description1
- 229910052739hydrogenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000001257hydrogenSubstances0.000description1
- 238000007654immersionMethods0.000description1
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000description1
- 231100000053low toxicityToxicity0.000description1
- 238000002844meltingMethods0.000description1
- 230000008018meltingEffects0.000description1
- 244000005700microbiomeSpecies0.000description1
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000description1
- 210000004400mucous membraneAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000004806packaging method and processMethods0.000description1
- 210000005259peripheral bloodAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000011886peripheral bloodSubstances0.000description1
- 239000003208petroleumSubstances0.000description1
- 239000000843powderSubstances0.000description1
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description1
- 239000008174sterile solutionSubstances0.000description1
- 239000008223sterile waterSubstances0.000description1
- 210000002784stomachAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000004094surface-active agentSubstances0.000description1
- 239000012224working solutionSubstances0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Apparatus For Disinfection Or Sterilisation (AREA)
- Agricultural Chemicals And Associated Chemicals (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromRussianПредполагаемое изобретение относится к области медицины, а именно к химической стерилизации, и может быть использовано для обработки хирургического инструментария в полевых условиях, при стихийных бедствиях, в экспедициях. The alleged invention relates to medicine, namely to chemical sterilization, and can be used to process surgical instruments in the field, during natural disasters, in expeditions.
Известен способ стерилизации медицинского инструментария с помощью водного раствора водорода /Приказ МЗ СССР N 408 от 12 июня 1989 г./. Применение 6% водного раствора H2O2 для стерилизации предусматривает 6 часовую экспозицию инструментария в стерилизующем растворе и последующее погружение в стерильную воду на 5 минут.A known method of sterilization of medical instruments using an aqueous solution of hydrogen / Order of the Ministry of Health of the USSR N 408 dated June 12, 1989 /. The use of a 6% aqueous solution of H2 O2 for sterilization involves a 6-hour exposure of the instruments in the sterilizing solution and subsequent immersion in sterile water for 5 minutes.
Приготовление рабочего раствора должно осуществляться в условиях аптеки, срок хранения составляет 7 дней, при этом необходимо: постоянный контроль за содержанием активно действующего начала. Посуда для хранения должна иметь притертую пробку, хранение осуществляется в прохладном месте. Preparation of the working solution should be carried out in a pharmacy, the shelf life is 7 days, and it is necessary: constant monitoring of the content of the active principle. Storage utensils must have a ground stopper; storage is carried out in a cool place.
Целью изобретения является сокращение времени стерилизации, увеличение длительности хранения стерильного медицинского инструментария. The aim of the invention is to reduce sterilization time, increase the duration of storage of sterile medical instruments.
Способ стерилизации осуществляется следующим образом:
К водорастворимому полимеру добавляют бактерицид растворимый в воде /бактерицидные препараты должны быть взяты в действующих концентрациях на микроорганизмы/ в полученную смесь погружают обрабатываемый инструментарий, достают, высушивают на открытом воздухе и помещают в герметичную упаковку.The sterilization method is as follows:
A water-soluble bactericide is added to the water-soluble polymer / bactericidal preparations must be taken in effective concentrations on microorganisms / the processed tools are immersed in the resulting mixture, removed, dried in the open air and placed in an airtight container.
Для приготовления полимер бактерицидной смеси использовали водорастворимый полимер олигомерный сульфонил пирролидийный хлорид /ОСПХ/ 98 частей и водорастворимый бактерицид-хлористый три хлораллил гексаметилен тетрамин /ХТХ ГМТА/ 2 части
ХТХ ГМТА синтезирован филиалом Уфимского нефтяного института и предложен для защиты ПАВ от биоповреждения.To prepare the polymer bactericidal mixture, we used a water-soluble polymer oligomeric sulfonyl pyrrolidium chloride / OSPH / 98 parts and a water-soluble bactericide-chloride three chlorall hexamethylene tetramine / ХТХ ГМТА / 2 parts
ХТХ ГМТА synthesized by a branch of the Ufa Petroleum Institute and proposed to protect surfactants from biodeterioration.
Вещество представляет собой порошок желтого цвета, хорошо растворим в воде и нерастворим в органических растворителях. Мол. масса 241, тем-ра плавления 173oC.
The substance is a yellow powder, soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents. Like weight 241, melting point 173o C.
DL 50 дм белых мышей 1850 ± 382 мг/кг
DL 50 дм белых крыс 5200±848,5 мг/кг
DL 50 дм морских свинок 1500 мг/кг.DL 50 dm white mice 1850 ± 382 mg / kg
DL 50 dm of white rats 5200 ± 848.5 mg / kg
DL 50 dm guinea pigs 1500 mg / kg.
Кумулятивные св-ва соединения не выражены, по классификации Г.Н.Красновского оно отнесено к 3 4 классу опасности. Cumulative properties of the compounds are not expressed; according to G.N.Krasnovsky's classification, it is assigned to the 3–4 hazard class.
Олигомерный сульфонил пирролидийный хлорид /ОСПХ/. Авторское свидетельство N 1530631, 1989 г. Oligomeric sulfonyl pyrrolidium chloride / OSPH /. Copyright certificate N 1530631, 1989
Логарифмическое число вязкости 0,2 0,24 ОСПХ растворим в воде, не растворим в органических растворителях. В-во малотоксичное (LD при введении в желудок крысам 17000 мг/кг, для мышей 6200 мг/кг) не раздражает слизистые оболочки и кожу, не изменяет деятельности сердечно-сосудистой системы, не оказывает депрессирующего действия на ц.н.с. не изменяет гематологические показатели периферической крови, не всасывается через неповрежденную кожу. На основании постановления Гос. комитета стандартов ОСПХ относится к 4-му классу малоопасных веществ.
Logarithmic viscosity number 0.2 0.24 OSPH soluble in water, insoluble in organic solvents. Low toxicity (LD when injected into the stomach of rats 17,000 mg / kg, for mice 6,200 mg / kg) does not irritate the mucous membranes and skin, does not alter the activity of the cardiovascular system, does not have a depressing effect on the central nervous system does not change the hematological parameters of peripheral blood, is not absorbed through intact skin. Based on the decision of the State. The OSHP Standards Committee belongs to the 4th class of low-hazard substances.
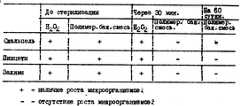
Берем контрольные смывы с нестерильного медицинского инструментария и засеваем на среду АГВ, для определения бактериальной обсемененности. Обрабатываемые предметы, погружает в полимер бактерицидную смесь, через 20 - 30 секунд, достаем и высушиваем на открытом воздухе. We take control washes from non-sterile medical instruments and inoculate on AGV medium to determine bacterial contamination. Processed items, immerses the bactericidal mixture in the polymer, after 20 - 30 seconds, remove and dry in the open air.
Через 10 15 минут после обработки инструменты можно использовать по назначению, для этого необходимо чистым перевязочным материалом смоченным в любом стерильном растворе протереть обработанные предметы для удаления полимербактерицидной пленки. 10-15 minutes after processing, the tools can be used for their intended purpose, for this it is necessary to wipe the treated items with a clean dressing moistened in any sterile solution to remove the polymer bactericidal film.
Результаты исследования приведены в таблице. The results of the study are shown in the table.
Для длительного хранения обработанный инструментарий помещают в герметическую упаковку. For long-term storage, the processed tools are placed in hermetic packaging.
Пример 1. Example 1
Для приготовления полимер бактерицидной смеси 2 г ХТХ ГМТА растворили в водорастворимом полимере ОСПХ, доведя объем до 100 мл. To prepare the polymer of the bactericidal mixture, 2 g of ХТХ ГМТА was dissolved in the water-soluble OSPH polymer, bringing the volume to 100 ml.
В полученную смесь погрузили хирургический инструментарий, через 15 секунд достали, высушили на воздухе, через 30 минут обработанные предметы - стерильные. Surgical instruments were immersed in the resulting mixture, after 15 seconds they were removed, dried in air, and after 30 minutes, the treated objects were sterile.
Проведенные исследования свидетельствуют, что предложенный способ стерилизации медицинского инструментария с помощью полимер бактерицидной смеси, является эффективным, так как сокращает время стерилизации, увеличивает длительность хранения стерильного инструментария, не требует дополнительных затрат. ТТТ1 Studies show that the proposed method of sterilization of medical instruments using a polymer bactericidal mixture is effective, as it reduces the sterilization time, increases the storage time of sterile instruments, does not require additional costs. TTT1
Claims (1)
Translated fromRussianPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU93032702ARU2063771C1 (en) | 1993-06-23 | 1993-06-23 | Method of sterilization of medical instruments |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU93032702ARU2063771C1 (en) | 1993-06-23 | 1993-06-23 | Method of sterilization of medical instruments |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2063771C1true RU2063771C1 (en) | 1996-07-20 |
| RU93032702A RU93032702A (en) | 1996-11-10 |
Family
ID=20143796
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU93032702ARU2063771C1 (en) | 1993-06-23 | 1993-06-23 | Method of sterilization of medical instruments |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2063771C1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2206339C2 (en)* | 2001-06-29 | 2003-06-20 | Всероссийский научно-исследовательский институт ветеринарной санитарии, гигиены и экологии | Method for sterilizing instruments |
| RU2247372C2 (en)* | 2003-04-28 | 2005-02-27 | ГУП "Московский городской центр дезинфекции" (МГЦД) | Method for assay of blood trace by oxidation reaction of 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7431189B2 (en)* | 2006-08-02 | 2008-10-07 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Pneumatically powered surgical cutting and fastening instrument with mechanical linkage coupling end effector and trigger motion |
| US20080029574A1 (en)* | 2006-08-02 | 2008-02-07 | Shelton Frederick E | Pneumatically powered surgical cutting and fastening instrument with actuator at distal end |
| US7740159B2 (en) | 2006-08-02 | 2010-06-22 | Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc. | Pneumatically powered surgical cutting and fastening instrument with a variable control of the actuating rate of firing with mechanical power assist |
- 1993
- 1993-06-23RURU93032702Apatent/RU2063771C1/enactive
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| Вашков В.И. Средства и методы стерилизации, применяемые в медицине. М., Медицина, 1973, с. 199-200.* |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2206339C2 (en)* | 2001-06-29 | 2003-06-20 | Всероссийский научно-исследовательский институт ветеринарной санитарии, гигиены и экологии | Method for sterilizing instruments |
| RU2247372C2 (en)* | 2003-04-28 | 2005-02-27 | ГУП "Московский городской центр дезинфекции" (МГЦД) | Method for assay of blood trace by oxidation reaction of 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| ES2216008T3 (en) | PREPARATION OF A BONE FOR YOUR TRANSPLANTATION. | |
| CA2126866C (en) | Preparation of bone for transplantation | |
| FI77575C (en) | STERILIZERINGBEHANDLING MED VAETESUPEROXID AV ARTIKLAR OCH NEUTRALISERING AV DENNAS RESTMAENGDER. | |
| KR100416153B1 (en) | Germicide composition | |
| IE56088B1 (en) | The use of chlorine dioxide gas as a chemosterilizing agent | |
| WO2005000364B1 (en) | Sterilization methods and apparatus which employ additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant | |
| PT772669E (en) | SALINA SOLUTION FOR THE TREATMENT OF CONTACT LENSES | |
| JPH0635368B2 (en) | Composition comprising biguanide and pyrimidine having high bactericidal activity | |
| HU228749B1 (en) | Positions and methods for cleaning contact lenses | |
| RU2063771C1 (en) | Method of sterilization of medical instruments | |
| WO1997027879A1 (en) | Solution for preserving and sterilizing contact lenses | |
| WO2008125884A2 (en) | Preservation composition | |
| US5211912A (en) | Method for disinfecting red blood cells, blood products, and corneas | |
| JPS62129202A (en) | Sterilization and disinfection agent and method for using thereof | |
| WO1993014793A1 (en) | Use of fluorine interhalogen compounds as a sterilizing agent | |
| CA1210019A (en) | Insoluble polymeric contact preservatives | |
| CN107898776A (en) | It is a kind of to be used to kill skin mucosa disinfectant of virus and preparation method thereof | |
| RU2629664C1 (en) | Method for bone samples machining in vitro | |
| RU2071788C1 (en) | Agent for wound treatment | |
| RU2210388C2 (en) | Method for sterilizing surgical suture material | |
| Dakin et al. | A handbook of antiseptics | |
| RU2062752C1 (en) | Agent for disinfection of sewage and tap water from helminth eggs | |
| NL1002484C2 (en) | Ophthalmologically useful composition, eye liquids and contact lens care preparations prepared therewith, and method for cleaning / disinfecting contact lenses. | |
| SU770496A1 (en) | Method of sterilizing biological tissues | |
| JPS5929207B2 (en) | How to sterilize food |