KR20210046487A - Apparatus and method for analyzing data contained in the database - Google Patents
Apparatus and method for analyzing data contained in the databaseDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20210046487A KR20210046487AKR1020190130253AKR20190130253AKR20210046487AKR 20210046487 AKR20210046487 AKR 20210046487AKR 1020190130253 AKR1020190130253 AKR 1020190130253AKR 20190130253 AKR20190130253 AKR 20190130253AKR 20210046487 AKR20210046487 AKR 20210046487A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- data
- attribute
- vector
- embedding
- vectors
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/22—Indexing; Data structures therefor; Storage structures
- G06F16/2228—Indexing structures
- G06F16/2237—Vectors, bitmaps or matrices
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/21—Design, administration or maintenance of databases
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/28—Databases characterised by their database models, e.g. relational or object models
- G06F16/284—Relational databases
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromKorean본 개시는 크로스 레이어 맵핑(cross layer mapping)과 관련되고, 더 특히 표현 학습(representation technique)에 기초한 크로스 레이어 맵핑(cross layer mapping) 방법과 관련된다.The present disclosure relates to cross layer mapping, and more particularly to a cross layer mapping method based on a representation technique.
최근, 정보 통신 기술(information technology)의 발전으로, 웹 데이터(Web data) 및 사물 인터넷 데이터(IoT, Internet of Things data)와 같은, 다양한 유형의 데이터가 급 성장하는 추세를 보여주고 있다. 이러한 대량의 데이터를 활용하는 방법은 학술 및 산업계에서 중요한 문제가 되었다.Recently, with the development of information technology, various types of data such as Web data and Internet of Things data (IoT) are showing a rapid growth trend. How to use this large amount of data has become an important issue in academic and industrial circles.
데이터의 이질성으로 인해, 데이터 간의 관계는 몹시 혼란스럽고 구별하기 어렵다. 따라서, 데이터 분석(data analysis) 전에, 서로 다른 수준의 데이터 관계들이 분석될 필요가 있다. 서로 다른 수준의 데이터 관계들이 분석된다면, 데이터 분석 알고리즘은 더 정확하게 데이터를 조사할 수 있다. 이러한 맥락에서, 크로스 레이어 맵핑은 중요한 연구 방향이 될 수 있다. 데이터 분석(data analysis) 전, 크로스 레이어 데이터를 맵핑하여 구조화 된 데이터를 얻는 방법이 요구되는 실정이다.Due to the heterogeneity of the data, the relationships between the data are extremely confusing and difficult to distinguish. Therefore, before data analysis, different levels of data relationships need to be analyzed. If different levels of data relationships are analyzed, the data analysis algorithm can examine the data more accurately. In this context, cross-layer mapping can be an important research direction. Before data analysis, a method of obtaining structured data by mapping cross-layer data is required.
본 개시의 일 실시예는, 표현 학습(representation technique)에 기초한 크로스 레이어 맵핑(cross layer mapping) 방법을 제공할 수 있다.An embodiment of the present disclosure may provide a cross layer mapping method based on a representation technique.
본 개시의 일 실시예는, 데이터 베이스의 각 레이어 별 임베딩 벡터를 생성하는 방법을 제공할 수 있다.An embodiment of the present disclosure may provide a method of generating an embedding vector for each layer of a database.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 데이터 분석 장치가 데이터 베이스에 포함된 데이터를 분석하는 방법이 개시된다. 보다 상세하게, 데이터를 분석하는 방법은 복수 개의 속성(Attribute)들이 포함된 제 1 데이터 테이블(Data Table)에서 하나의 속성을 선택하고, 상기 선택된 속성인 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터(Data)를 입력 받는 단계; 상기 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들을 생성하는 단계; 상기 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들에 기초하여 상기 제 1 속성에 대응하는 속성 벡터를 생성하는 단계; 상기 복수 개의 속성들 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들을 생성하고, 상기 복수 개의 속성 벡터들에 기초하여 상기 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대응하는 제 1 테이블 벡터를 생성하는 단계; 및 상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 하나의 데이터인 제 1 데이터에 대한 제 1 임베딩 벡터, 상기 제 1 속성에 대한 제 1 속성 벡터 및 상기 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대한 제 1 테이블 벡터 중 하나를 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)의 대상으로 선택하고, 제 2 데이터 테이블과 맵핑을 수행하는 단계;를 포함할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, a method for analyzing data included in a database by a data analysis device is disclosed. In more detail, the method of analyzing data includes selecting one attribute from a first data table including a plurality of attributes, and selecting a plurality of data included in the first attribute that is the selected attribute. ) To input; Generating a plurality of embedding vectors corresponding to each of the plurality of data; Generating an attribute vector corresponding to the first attribute based on the plurality of embedding vectors; Generating a plurality of attribute vectors corresponding to each of the plurality of attributes, and generating a first table vector corresponding to the first data table based on the plurality of attribute vectors; And cross-layer mapping one of a first embedding vector for first data, which is one data included in the first attribute, a first attribute vector for the first attribute, and a first table vector for the first data table. Selecting a target for (Cross Layer Mapping) and performing mapping with a second data table; may be included.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 데이터 베이스에 포함된 데이터를 분석하는 데이터 분석 장치가 개시될 수 있다. 데이터 분석 장치는 복수 개의 속성(Attribute)들이 포함된 제 1 데이터 테이블(Data Table)에서 하나의 속성을 선택하고, 상기 선택된 속성인 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터(Data)를 입력 받는 입력부; 상기 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들을 생성하는 임베딩 벡터 생성부; 상기 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들에 기초하여 상기 제 1 속성에 대응하는 속성 벡터를 생성하는 속성 벡터 생성부; 상기 복수 개의 속성들 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들을 생성하고, 상기 복수 개의 속성 벡터들에 기초하여 상기 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대응하는 제 1 테이블 벡터를 생성하는 테이블 벡터 생성부; 및 상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 하나의 데이터인 제 1 데이터에 대한 제 1 임베딩 벡터, 상기 제 1 속성에 대한 제 1 속성 벡터 및 상기 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대한 제 1 테이블 벡터 중 하나를 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)의 대상으로 선택하고, 제 2 데이터 테이블과 맵핑을 수행하는 크로스 레이어 맵핑부;를 포함할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, a data analysis apparatus for analyzing data included in a database may be disclosed. The data analysis apparatus includes: an input unit that selects one attribute from a first data table including a plurality of attributes and receives a plurality of data included in the first attribute that is the selected attribute; An embedding vector generator generating a plurality of embedding vectors corresponding to each of the plurality of data; An attribute vector generator configured to generate an attribute vector corresponding to the first attribute based on the plurality of embedding vectors; A table vector generator configured to generate a plurality of attribute vectors corresponding to each of the plurality of attribute vectors, and to generate a first table vector corresponding to the first data table based on the plurality of attribute vectors; And cross-layer mapping one of a first embedding vector for first data, which is one data included in the first attribute, a first attribute vector for the first attribute, and a first table vector for the first data table. It may include a cross-layer mapping unit that selects as a target for (Cross Layer Mapping) and performs mapping with the second data table.
본 발명의 일 실시예들은 데이터 베이스에 포함된 데이터를 분석하는 데이터 분석 장치 및 방법에 모두 적용될 수 있다.Embodiments of the present invention can be applied to both a data analysis apparatus and a method for analyzing data included in a database.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 제 2 데이터 테이블은 제 2 속성 및 제 2 속성에 포함된 제 2 데이터를 포함하되, 크로스 레이어 맵핑부는 상기 제 2 데이터 테이블에 대해 생성된 제 2 테이블 벡터, 상기 제 2 속성에 대해 생성된 제 2 속성 벡터 및 상기 제 2 데이터에 대해 생성된 제 2 임베딩 벡터 중 적어도 하나와 상기 선택된 크로스 레이어 맵핑 대상과의 유사 값을 판단하고, 상기 유사 값이 임계 값 이상이면 서로 맵핑할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the second data table includes a second attribute and second data included in the second attribute, and the cross-layer mapping unit includes a second table vector generated for the second data table, the A similarity value between at least one of a second attribute vector generated for a second attribute and a second embedding vector generated for the second data and the selected cross-layer mapping target is determined, and if the similarity value is greater than or equal to a threshold value They can be mapped to each other.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 상기 임베딩 벡터 생성부가 상기 제 1 임베딩 벡터를 생성하는 경우, 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 생성하고, 상기 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 사용하여 상기 제 1 임베딩 벡터의 값을 예측할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, when the embedding vector generator generates the first embedding vector, a plurality of initialization vectors corresponding to each of a plurality of data included in a first attribute are generated, and the plurality of initialization vectors The value of the first embedding vector can be predicted using s.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 임베딩 벡터 생성부는 복수 개의 데이터 각각의 유형을 판단하여 상기 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 생성할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the embedding vector generator may generate the plurality of initialization vectors by determining a type of each of a plurality of data.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 하나의 데이터에 대해 판단된 데이터 유형이 텍스트인 경우, 임베딩 벡터 생성부는 상기 하나의 데이터에 포함된 단어 각각에 대해 기 학습된 워드 임베딩 벡터를 할당하고, 상기 워드 임베딩 벡터에 기초하여 상기 하나의 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터를 생성할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, when the data type determined for one data is text, the embedding vector generator allocates a pre-learned word embedding vector for each word included in the one data, and the word An initialization vector corresponding to the one piece of data may be generated based on the embedding vector.
본 발명이 일 실시예에 따라, 하나의 데이터에 대해 판단된 데이터 유형이 텍스트가 아닌 경우, 상기 임베딩 벡터 생성부는 랜덤한 벡터 값을 상기 하나의 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터로 결정할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, when a data type determined for one piece of data is not text, the embedding vector generator may determine a random vector value as an initialization vector corresponding to the piece of data.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 임베딩 벡터 생성부는 상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터를 기 설정된 정렬 기준에 따라 정렬하고, 정렬된 순서를 고려하여 기 설정된 개수의 데이터를 선택하고, 임베딩 벡터 생성부는 상기 선택된 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터를 이용하여 상기 제 1 임베딩 벡터의 값을 예측하고, 상기 제 1 임베딩 벡터를 생성할 수 있다. 이때, 상기 기 설정된 기준에 따를 때, 상기 선택된 데이터는 상기 제 1 데이터에 앞서 연속적으로 선 정렬된 한 개 이상의 데이터일 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the embedding vector generation unit sorts a plurality of data included in the first attribute according to a preset sorting criterion, selects a preset number of data in consideration of the sorted order, and embedding vector The generator may predict a value of the first embedding vector using an initialization vector corresponding to the selected data and generate the first embedding vector. In this case, in accordance with the preset criterion, the selected data may be one or more pieces of data that are continuously line-aligned prior to the first data.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 제 1 속성 벡터는 상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들의 합산 값 또는 평균 값에 기초하여 생성될 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the first attribute vector may be generated based on a sum value or an average value of a plurality of embedding vectors corresponding to each of a plurality of data included in the first attribute.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 제 1 테이블 벡터는 상기 제 1 테이블 벡터에 포함된 복수 개의 속성 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들의 합산 값 또는 평균 값에 기초하여 생성될 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the first table vector may be generated based on a sum value or an average value of a plurality of attribute vectors corresponding to each of a plurality of attributes included in the first table vector.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 데이터 베이스에 포함된 데이터를 분석하는 데이터 분석 장치를 포함한 시스템의 개요도이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른, 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)에 대한 개념도이다.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 데이터 분석 장치가 데이터 베이스에 포함된 데이터를 분석하는 흐름도이다.
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른, 본 발명의 데이터 베이스의 구조 및 크로스 레이어 맵핑을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 임베딩 벡터를 생성하는 흐름도이다.
도 6는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 기 설정된 기준에 따라 정렬된 복수 개의 데이터를 나타낸 도면이다.
도 7은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 데이터 분석 장치가 임베딩 벡터를 생성하는 방법을 나타낸 도면이다.
도 8은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른, 데이터 베이스에 포함된 데이터를 분석하는 데이터 분석 장치의 구성도이다.
도 9는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른, 데이터 베이스에 포함된 데이터를 분석하는 데이터 분석 장치의 블록도이다.1 is a schematic diagram of a system including a data analysis device for analyzing data included in a database according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a conceptual diagram for cross layer mapping according to an embodiment of the present invention.
3 is a flowchart of a data analysis apparatus analyzing data included in a database according to an embodiment of the present invention.
4 is a diagram illustrating a structure of a database and cross-layer mapping according to an embodiment of the present invention.
5 is a flowchart of generating an embedding vector according to an embodiment of the present invention.
6 is a diagram illustrating a plurality of pieces of data arranged according to a preset criterion according to an embodiment of the present invention.
7 is a diagram illustrating a method of generating an embedding vector by a data analysis device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
8 is a block diagram of a data analysis apparatus for analyzing data included in a database according to an embodiment of the present invention.
9 is a block diagram of a data analysis apparatus for analyzing data included in a database according to an embodiment of the present invention.
아래에서는 첨부한 도면을 참조하여 본 개시가 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 용이하게 실시할 수 있도록 본 개시의 실시예를 상세히 설명한다. 그러나 본 개시는 여러 가지 상이한 형태로 구현될 수 있으며 여기에서 설명하는 실시예에 한정되지 않는다. 그리고 도면에서 본 개시를 명확하게 설명하기 위해서 설명과 관계없는 부분은 생략하였으며, 명세서 전체를 통하여 유사한 부분에 대해서는 유사한 도면 부호를 붙였다.Hereinafter, embodiments of the present disclosure will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings so that those of ordinary skill in the art may easily implement the present disclosure. However, the present disclosure may be implemented in various different forms and is not limited to the embodiments described herein. In addition, in the drawings, parts irrelevant to the description are omitted in order to clearly describe the present disclosure, and similar reference numerals are attached to similar parts throughout the specification.
명세서 전체에서, 어떤 부분이 다른 부분과 "연결"되어 있다고 할 때, 이는 "직접적으로 연결"되어 있는 경우뿐 아니라, 그 중간에 다른 소자를 사이에 두고 "전기적으로 연결"되어 있는 경우도 포함한다. 또한 어떤 부분이 어떤 구성요소를 "포함"한다고 할 때, 이는 특별히 반대되는 기재가 없는 한 다른 구성요소를 제외하는 것이 아니라 다른 구성요소를 더 포함할 수 있는 것을 의미한다.Throughout the specification, when a part is said to be "connected" with another part, this includes not only "directly connected" but also "electrically connected" with another element interposed therebetween. . In addition, when a part "includes" a certain component, it means that other components may be further included rather than excluding other components unless specifically stated to the contrary.
이하 첨부된 도면을 참고하여 본 개시를 상세히 설명하기로 한다.Hereinafter, the present disclosure will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 데이터 베이스에 포함된 데이터를 분석하는 데이터 분석 장치를 포함한 시스템의 개요도이다.1 is a schematic diagram of a system including a data analysis device for analyzing data included in a database according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명은, 이종 장치에 저장되어 있는 데이터 베이스의 데이터를 자동으로 맵핑하기 위한 발명으로, 테이블-열-값(Table to column to Value)의 관계를 파악하여 연결시키는 방법에 대한 것이다.The present invention is an invention for automatically mapping data in a database stored in heterogeneous devices, and relates to a method of identifying and connecting a table-to-column-value relationship.
도 1을 참조하면, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 이종 장치에 저장되어 있는 제 1 데이터 베이스(110)와 다른 제 N 데이터 베이스(120)를 분석하여, 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)을 수행할 수 있다. 이때, 본 발명에서, 각 데이터 베이스는 하나 이상의 테이블을 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 1, the
이때, 본 발명에 따르면, 사일로(Silo)화된 데이터 베이스의 스키마(Schema)들을 크로스 레이어(cross layer)로 자동으로 연결해서 더 고도화된 통합 분석을 수행할 수 있다. 또한, 본 발명에 따르면, 열(Column), 값(value)들 간의 시멘틱(Semantic)한 통합을 통해서 보다 고도화된 통합 분석을 제공할 수 있다.In this case, according to the present invention, a more advanced integrated analysis can be performed by automatically connecting schemas of a siloed database in a cross layer. In addition, according to the present invention, a more advanced integrated analysis can be provided through semantic integration between columns and values.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른, 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)에 대한 개념도이다.2 is a conceptual diagram for cross layer mapping according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명에 따르면, 데이터 베이스 내에 존재하는 관계 혼동(relationship confusion)의 문제를 해결하기 위한 표현 기법(representation technique)에 기초한 크로스 레이어 맵핑 방법(cross layer mapping method)이 제공될 수 있다. 데이터 베이스 내에서 주어진 표들, 값들, 열(세로줄)은 본 발명의 크로스 레이어 맵핑 방법(cross layer mapping method)으로 서로 연결(mapping)될 수 있다.According to the present invention, a cross layer mapping method based on a representation technique for solving a problem of relationship confusion existing in a database may be provided. Tables, values, and columns (vertical lines) given in the database may be mapped to each other by the cross layer mapping method of the present invention.
도 2를 참고하여, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)이 설명될 수 있다. 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)이란, 서로 다른 데이터 베이스에 포함된 테이블, 속성, 데이터를 맵핑하는 것을 의미할 수 있다. 특히, 데이터를 제1 레이어, 속성을 제2 레이어, 테이블을 제3 레이어로 정의하였을 때, 본 발명에 따르면, 레이어 간 교차되는 맵핑이 수행될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 2, cross layer mapping according to an embodiment of the present invention may be described. Cross layer mapping may mean mapping tables, attributes, and data included in different databases. In particular, when data is defined as a first layer, an attribute is defined as a second layer, and a table is defined as a third layer, according to the present invention, intersecting mapping between layers may be performed.
도 2에 따를 때, 연결 (a)는 데이터의 값-속성(value-Attribute) 맵핑을 의미할 수 있다. 즉, 연결 (a)는 제 1 데이터 베이스의 데이터 A-2-2와 제 2 데이터 베이스의 속성 B-1간의 맵핑을 의미할 수 있다.According to FIG. 2, connection (a) may mean data value-attribute mapping. That is, connection (a) may mean mapping between data A-2-2 of the first database and attribute B-1 of the second database.
연결 (b)는 속성-테이블 (Attribute-Table) 맵핑을 의미할 수 있다. 즉, 연결 (b)는 제 1 데이터 베이스의 속성 A-2와 제 2 데이터 베이스의 테이블 B간의 맵핑을 의미할 수 있다.Connection (b) may mean attribute-table mapping. That is, connection (b) may mean mapping between attribute A-2 of the first database and table B of the second database.
연결 (c)는 데이터의 값- 테이블 (value-Table)간 맵핑을 의미할 수 있다. 즉, 연결 (c)는 제 1 데이터 베이스의 데이터 A-2-2와 제 2 데이터 베이스의 테이블 B간의 맵핑을 의미할 수 있다.Connection (c) may mean mapping between a value-table of data. That is, connection (c) may mean mapping between data A-2-2 of the first database and table B of the second database.
다만, 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)은 도 2의 구성에 한정되지 않는다. 예를 들어, 도 2에는 도시되지 않았으나, 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)은 제 1 데이터 베이스의 속성과 제 2 데이터 베이스의 값이 연결된 값-속성(value-Attribute) 맵핑, 제 1 데이터 베이스의 테이블 A와 제 2 데이터 베이스의 값이 연결된 값-테이블 (value-Table) 맵핑, 제 1 데이터 베이스의 테이블 A와 제 2 데이터 베이스의 속성이 연결된 속성-테이블 (Attribute-Table) 맵핑 등이 더 존재할 수 있을 것이다.However, cross layer mapping is not limited to the configuration of FIG. 2. For example, although not shown in FIG. 2, cross layer mapping is a value-attribute mapping in which an attribute of a first database and a value of a second database are connected, and There are more value-table mappings in which the values of table A and the second database are connected, and attribute-table mappings in which the attributes of table A in the first database and the second database are connected. I will be able to.
도 2에서 상술한 바와 같이 데이터, 속성, 테이블은 서로 다른 레이어에 대응되는 구성이므로, 이들 간의 유사 값을 직접 판단할 수는 없다는 한계가 존재한다. 최근 몇 년 동안 표현 학습(representation Learning)은 뜨거운 연구 방향이었다. 표현 학습은 벡터를 사용하여 데이터를 표현함으로써, 데이터를 임베디드 공간에 맵핑하는 방법에 해당될 수 있다. 이때, 표현 학습에 의해 얻어진 고차원의 벡터들(The high-dimensional vectors)은 데이터의 패턴을 숨길 수 있다. 값(value), 속성(attribute) 및 표(table)을 벡터로 표현함으로서, 이들 간의 유사 값은 쉽고 정확하게 계산될 수 있다. 데이터 인스턴스들이 테이블의 기본 단위이기 때문에, 임베딩(embedding)은 데이터 인스턴스들부터 시작될 수 있다.As described above in FIG. 2, since data, attributes, and tables are configured to correspond to different layers, there is a limitation that it is not possible to directly determine similar values between them. In recent years, representation learning has been a hot research direction. Expression learning may correspond to a method of mapping data to an embedded space by representing data using vectors. At this time, the high-dimensional vectors obtained by expression learning may hide the pattern of data. By expressing values, attributes and tables as vectors, similar values between them can be calculated easily and accurately. Since data instances are the basic unit of a table, embedding can start with data instances.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 데이터 분석 장치가 데이터 베이스에 포함된 데이터를 분석하는 흐름도이다.3 is a flowchart of a data analysis apparatus analyzing data included in a database according to an embodiment of the present invention.
동작 S310에서 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 복수 개의 속성(Attribute)들이 포함된 제 1 데이터 테이블(Data Table)에서 하나의 속성을 선택할 수 있다. 또한, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 선택된 속성인 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터(Data)를 입력 받을 수 있다.In operation S310, the
이때, 본 발명에서 데이터 테이블이란 , 정보들이 수집 또는 관리되어 있는 테이블을 의미할 수 있다. 이때, 일 예로, 데이터 테이블에는 공통적인 특징을 가진 데이터들이 구성될 수 있다. 또한, 데이터 테이블은 특정 업무, 목적 등을 위해 관리되어야 하는 데이터들로 구성될 수도 있다. 또한, 데이터 베이스에는 한 개 이상의 데이터 테이블들이 포함될 수 있다. 또한, 데이터 테이블은 데이터들이 행과 열을 기준으로 정렬된 표의 형식으로 정리된 것을 의미할 수 있다.In this case, in the present invention, the data table may mean a table in which information is collected or managed. In this case, as an example, data having common characteristics may be configured in the data table. In addition, the data table may be composed of data that must be managed for a specific task or purpose. Also, one or more data tables may be included in the database. In addition, the data table may mean that data is arranged in a table format arranged on the basis of rows and columns.
또한, 본 발명에서, 제 1 데이터 테이블(Data Table) 은 데이터 분석 처리 대상으로 선택 또는 결정된 데이터 테이블에 해당될 수 있다. 보다 상세하게는, 제 1 데이터 테이블은 제 1 데이터 베이스에 포함된 한 개 이상의 데이터 테이블들 중에서, 데이터 처리 및 크로스 레이어 맵핑을 수행하기 위해 선택된 하나의 데이터 테이블을 의미할 수 있다. 또한, 제 1 데이터 테이블은 크로스 맵핑의 대상이 될 수 있다.In addition, in the present invention, the first data table may correspond to a data table selected or determined as an object for data analysis processing. In more detail, the first data table may mean one data table selected to perform data processing and cross-layer mapping from among one or more data tables included in the first database. Also, the first data table may be a target of cross-mapping.
이때, 본 발명에서 속성이란, 다수의 데이터 인스턴스들(data instances)을 포함하는 테이블의 열(column)을 의미할 수 있다. 이때, 속성은 데이터, 데이터 인스턴스들, 값 등을 분류하는 하나의 기준을 의미할 수 있다. 또한 속성은 데이터 테이블의 세로줄에 해당될 수 있다. 또한, 속성은 필드(field)에 대응될 수 있고, 데이터 테이블의 열(column)에 대응될 수 있다.In this case, in the present invention, the attribute may mean a column of a table including a plurality of data instances. In this case, the attribute may mean one criterion for classifying data, data instances, values, and the like. Also, the attribute may correspond to the vertical line of the data table. Also, the attribute may correspond to a field and may correspond to a column of a data table.
본 발명에서, 제 1 속성(Attribute) 는 데이터 분석 처리 대상으로 선택 또는 결정된 속성에 해당될 수 있다. 또한, 데이터 분석 장치(100)가 맵핑되는 속성(attribute)으로 선택한 속성을 의미할 수 있다. 보다 상세하게는, 제 1 속성은 제 1 데이터 테이블에 포함된 한 개 이상의 속성들 중에서, 데이터 처리 및 크로스 레이어 맵핑을 수행하기 위해 선택된 하나의 속성을 의미할 수 있다. 또한, 제 1 속성은 크로스 맵핑의 대상이 될 수 있다.In the present invention, the first attribute may correspond to an attribute selected or determined as an object for data analysis processing. In addition, it may mean an attribute selected as an attribute to which the
본 발명에서 데이터란, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 데이터 인스턴스(data instance)에 대응될 수 있다. 또한, 데이터는 값(value)에 대응될 수도 있다. 또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 데이터는 텍스트(문자형) 유형의 데이터와 비텍스트형 유형의 데이터로 나뉠 수 있다.In the present invention, data may correspond to a data instance according to an embodiment of the present invention. Also, data may correspond to a value. Further, according to an embodiment of the present invention, data may be divided into text (character) type data and non-text type data.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 데이터는 데이터 베이스에서 테이블의 형식으로 저장될 수 있다. 또한, 데이터는 한 개 이상의 속성에 따라 테이블 내에서 분류되어 저장 및 관리될 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, data may be stored in the form of a table in a database. In addition, data may be classified, stored, and managed in a table according to one or more attributes.
본 발명의 다른 일 실시예에 따라, 데이터 베이스에서 데이터는 지식 그래프의 형식으로 구현될 수 있다. 본 발명에서 제 1 데이터는, 데이터 분석 처리 대상으로 선택 또는 결정된 데이터에 해당될 수 있다. 또한, 데이터 분석 장치(100)가 맵핑되는 데이터(data)로 선택한 데이터를 의미할 수 있다. 보다 상세하게는, 제 1 데이터는 제 1 속성에 포함된 한 개 이상의 데이터들 중에서, 데이터 처리 및 크로스 레이어 맵핑을 수행하기 위해 선택된 하나의 데이터를 의미할 수 있다. 또한, 제 1 데이터는 크로스 맵핑의 대상이 될 수 있다.According to another embodiment of the present invention, data in a database may be implemented in the form of a knowledge graph. In the present invention, the first data may correspond to data selected or determined as an object for data analysis processing. In addition, it may mean data selected as data to which the
또한, 본 발명에서, 제 2 데이터 테이블(Data Table)은 제 1 데이터 테이블과 크로스 맵핑을 하기 위한 타겟에 해당될 수 있다. 보다 상세하게는, 제 2 데이터 테이블은 제 2 데이터 베이스에 포함된 한 개 이상의 데이터 테이블들 중에서, 제 1 데이터 테이블과 크로스 레이어 맵핑을 수행하기 위해 선택된 하나의 데이터 테이블을 의미할 수 있다.In addition, in the present invention, the second data table may correspond to a target for cross-mapping with the first data table. In more detail, the second data table may mean one data table selected to perform cross-layer mapping with the first data table from among one or more data tables included in the second database.
하기의 도면들에서, 상술한 데이터 베이스 내부의 구조를 더 자세하게 설명된다.In the following drawings, the structure inside the database described above is described in more detail.
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른, 본 발명의 데이터 베이스의 구조 및 크로스 레이어 맵핑을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.4 is a diagram illustrating a structure of a database and cross-layer mapping according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 4를 참고하여, 동작 S310을 설명하도록 한다. 또한 도 4를 참고하여, 상술한 제 1 테이블, 제 1 속성, 제 1 데이터 및 제 2 테이블 등의 정의 및 관계가 더 상세하게 확인될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 4, operation S310 will be described. In addition, with reference to FIG. 4, definitions and relationships of the above-described first table, first attribute, first data, and second table may be confirmed in more detail.
데이터 분석 장치(100)는 하나의 데이터 테이블에 포함된 복수의 데이터들 분석 및 처리할 수 있다. 이때, 도 4를 참고할 때, 데이터 분석 장치(100)가 분석 및 처리하는 데이터 테이블로 Account(계정) 데이터 테이블이 선택될 수 있다. 따라서, 일 예로, Account 데이터 테이블이 제 1 데이터 테이블(Data Table)로 선택될 수 있다.The
이때, 일 예로, 도 4의 Account 데이터 테이블은 고객(Customer) 정보를 포함할 수 있으며, 고객 정보와 관련된 정보가 수집되어 있거나, 관리되고 있는 테이블일 수 있다.In this case, as an example, the Account data table of FIG. 4 may include customer information, and may be a table in which information related to customer information is collected or managed.
이때, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 복수 개의 속성들이 포함된 Account 데이터 테이블에서 하나의 속성(Attribute)을 선택할 수 있다. 도 4에 따를 때, 데이터 분석 장치(100)가 처리하는 속성으로 CA_B_NAME 속성이 선택될 수 있다. 따라서, 일 예로, CA_B_NAME 속성이 제 1 속성으로 선택될 수 있다.In this case, the
도 4를 참고할 때, Account 데이터 테이블은 CDC_DSN 속성, CA_ID 속성, CA_B_NAME 속성, CA_C_NAME 속성을 포함할 수 있다. CDC_DSN 속성은 시스템에서 부여된 incremental id 를 의미할 수 있다. CA_ID 속성은 고객 아이디(customer id)를 의미할 수 있다. CA_B_NAME 속성은 회사 담당자 이름을 의미할 수 있다. CA_C_NAME 속성은 고객(customer)의 이름을 의미할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 4, the Account data table may include a CDC_DSN property, a CA_ID property, a CA_B_NAME property, and a CA_C_NAME property. The CDC_DSN attribute may mean an incremental id assigned by the system. The CA_ID attribute may mean a customer ID. The CA_B_NAME attribute may mean the name of a company person in charge. The CA_C_NAME attribute may mean the name of a customer.
데이터 분석 장치(100)는 선택된 속성인 제 1 속성에 대응되는 CA_B_NAME 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터를 입력 받을 수 있다. 도 4에 따를 때, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 HR_O.R.Elyssa, HR_H.Mirjam, HR_B..J.Marc, HR_T.K.Guillema, HR_M.Brena를 입력 받을 수 있다. 도 4의 CA_B_NAME 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터에서, HR_는 Human Resource의 약자이며, 그 뒤의 문자는 사람의 이름을 의미할 수 있다. 따라서, HR_B..J.Marc의 경우, Human Resource 부서의 J.Marc를 의미할 수 있다. 또한, 도 4의 CA_C_NAME 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터에서, C_는 customer 약자이며, 그 뒤의 문자는 이름을 의미할 수 있다.The
도 4에 따를 때, 제 1 데이터 테이블과 크로스 맵핑이 수행되는 제 2 테이블로 Human Resource(인적 자원) 데이터 테이블이 선택될 수 있다. 이때, Human Resource 데이터 테이블은, Human Resource 정보를 포함할 수 있다. 이때, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 제 1 데이터 테이블인 Account 데이터 테이블과 Human Resource 데이터 테이블 간의 관계를 확인할 수 있다. 보다 상세하게는, 확인된 결과에 따라서, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 Account 데이터 테이블의 각 레이어에 대응되는 구성들과 Human Resource 데이터 테이블의 각 레이어에 대응되는 구성들과 맵핑을 수행할 수 있다.According to FIG. 4, a Human Resource data table may be selected as a first data table and a second table on which cross-mapping is performed. In this case, the Human Resource data table may include Human Resource information. In this case, the
이때, Human Resource 데이터 테이블은 First Name 속성, Last Name 속성, Manager_ID 속성 등을 포함할 수 있다.In this case, the Human Resource data table may include a First Name property, a Last Name property, and a Manager_ID property.
도 4에서, (a) 연결은 Account 데이터 테이블의 데이터인 ‘HR_B..J.Marc’ 가 Human Resource 데이터 테이블의 ‘First Name’ 속성 및 ‘Last Name’ 속성과 맵핑(map)되는 값-속성(Value-Attribute) 맵핑 시나리오를 의미할 수 있다. 값-속성(Value-Attribute) 맵핑은 제 1 데이터인 ‘HR_B..J.Marc’가 두 개 속성들(attributes)인 ‘First Name’ 속성 및 ‘Last Name’ 속성과 연관되어 있음을 의미할 수 있다.In FIG. 4, (a) the connection is the value-attribute that'HR_B..J.Marc', which is the data of the Account data table, is mapped with the'First Name' attribute and the'Last Name' attribute of the Human Resource data table ( Value-Attribute) may mean a mapping scenario. Value-Attribute mapping may mean that the first data'HR_B..J.Marc' is associated with the two attributes, the'First Name' attribute and the'Last Name' attribute. have.
도 4에서, (b) 연결은 Account 데이터 테이블의 ‘CA_B_NAME’ 속성(attribute)이 Human Resource 데이터 테이블로 맵핑(map)되는 속성-테이블(Attribute-Table) 맵핑 시나리오를 의미할 수 있다.In FIG. 4, (b) connection may refer to an attribute-table mapping scenario in which the “CA_B_NAME” attribute of the Account data table is mapped to the Human Resource data table.
또한, 도 4에서 (c) 연결은 Account 데이터 테이블의 데이터인 ‘HR_B..J.Marc’을 제 2 데이터 테이블인 Human Resource 데이터 테이블로 맵핑(map)하는 값-테이블(Value-Table) 맵핑 시나리오를 의미할 수 있다.In addition, in Figure 4 (c) the connection is a value-table mapping scenario in which'HR_B..J.Marc', which is the data of the Account data table, is mapped to the Human Resource data table, which is the second data table. Can mean
이와 같이, 데이터 분석 장치(100)가 크로스 레이어 맵핑(cross layer mapping)을 수행한 후에는 데이터 검색을 위한 더 유용한 정보를 획득할 수 있다. 데이터 분석 장치(100)가 담당자인 ‘HR_B..J.Marc’에 대한 더 상세한 분석을 얻고자 하는 경우, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 도 4의 (c) 연결(값-테이블(Value-Table) 연결)에 기초하여 인적 자원(Human Resource) 테이블에 대해 문의할 수 있다.As described above, after the
동작 S320에서 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들을 생성할 수 있다. 즉, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 복수 개의 데이터 각각을 고차원 공간(high dimensional space)으로 임베드(embed)할 수 있다.In operation S320, the
본 발명에서 임베딩 벡터란, 데이터를 고차원 공간으로 임베딩하여 생성된 벡터를 의미할 수 있다. 보다 상세하게, 데이터, 데이터 인스턴스, 값(value) 등 각각에 대응하여 생성되는 사용자가 설정한 차원의 벡터에 해당될 수 있다. 이때, 사용자가 설정한 차원은 고차원일 수 있다. 또한, 데이터 각각을 대표 또는 표현할 할 수 있는 벡터일 수 있다.In the present invention, the embedding vector may mean a vector generated by embedding data into a high-dimensional space. In more detail, it may correspond to a vector of a dimension set by a user that is created corresponding to each of data, data instances, and values. In this case, the dimension set by the user may be a high dimension. In addition, it may be a vector capable of representing or expressing each of the data.
보다 상세하게, 데이터 분석 장치(100)가 제 1 임베딩 벡터를 생성하는 경우, 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 생성할 수 있다. 또한, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 사용하여 제 1 임베딩 벡터의 값을 예측할 수 있다.In more detail, when the
해당 동작에 대한 보다 상세한 설명은 도 5 내지 7에서 수행된다.A more detailed description of the operation is performed in FIGS. 5 to 7.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 임베딩 벡터를 생성하는 흐름도이다.5 is a flowchart of generating an embedding vector according to an embodiment of the present invention.
먼저,는개의 데이터(data)를 포함하는 i 번째 데이터 테이블을 나타낼 수 있다. 이때, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, i 번째 데이터 테이블은 데이터 분석 대상으로 선택된 제 1 데이터 테이블을 의미할 수 있다. 설명의 편의를 위하여, i 번째 데이터 테이블이 분석 대상으로 선택되었으며, i 번째 데이터 테이블을 제 1 데이터 테이블이라 표현하여 설명하도록 한다.first, Is It may represent an i-th data table including data (data). In this case, according to an embodiment of the present invention, the i-th data table may mean a first data table selected as a data analysis target. For convenience of explanation, the i-th data table has been selected as an analysis target, and the i-th data table is expressed as a first data table to be described.
또한,는 i번째 테이블 내의 j번째 속성을 의미할 수 있다. 이때, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, i번째 테이블 내의 j번째 속성은 제 1 데이터 테이블에서 데이터 분석 대상으로 선택된 제 1 속성을 의미할 수 있다. 설명의 편의를 위하여, j번째 속성이 분석 대상으로 선택되었으며, j 번째 속성을 제 1 속성이라 표현하여 설명하도록 한다.Also, May mean the j-th attribute in the i-th table. In this case, according to an embodiment of the present invention, the j-th attribute in the i-th table may mean a first attribute selected as a data analysis target in the first data table. For convenience of explanation, the j-th attribute has been selected as an analysis target, and the j-th attribute is expressed as a first attribute to be described.
또한,는 i번째 테이블의 j 번째 속성 내의 k번째 데이터를 의미할 수 있다. 본 발명에서 i번째 테이블의 j 번째 속성 내의 k번째 데이터는 데이터 맵핑 대상으로 선택된 제 1 데이터를 의미할 수 있다. 설명의 편의를 위하여, i번째 테이블의 j 번째 속성 내의 k번째 데이터가 분석 대상으로 선택되었으며, k번째 데이터를 제 1 데이터라 표현하여 설명하도록 한다.Also, May mean k-th data in the j-th attribute of the i-th table. In the present invention, the k-th data in the j-th attribute of the i-th table may mean first data selected as a data mapping target. For convenience of explanation, the k-th data in the j-th attribute of the i-th table has been selected as an analysis target, and the k-th data is expressed as first data to be described.
먼저, 동작 S510에서 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 복수 개의 데이터 각각의 유형을 판단할 수 있다. 그리고, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 판단된 데이터 각각의 유형에 기초하여 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 생성할 수 있다.First, in operation S510, the
이때, 초기화 벡터란, 결정된 차원에서 생성된 벡터를 의미할 수 있다. 이때, 초기화 벡터는 임베딩 벡터를 예측하는데 사용될 수 있다. 또한, 초기화 벡터의 벡터 차원은 하나의 속성에 포함된 데이터들 각각이 모두 동일할 수 있다. 또한, 본 발명에서 초기화 벡터란, 임베딩 벡터가 초기화된 형태에 해당될 수 있다.In this case, the initialization vector may mean a vector generated in a determined dimension. In this case, the initialization vector may be used to predict the embedding vector. In addition, the vector dimension of the initialization vector may be the same for each of the data included in one property. In addition, in the present invention, the initialization vector may correspond to a form in which the embedding vector is initialized.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 하나의 데이터에 대해 판단된 데이터 유형이 텍스트인 경우, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 하나의 데이터에 포함된 단어 각각에 대해 기 학습된 워드 임베딩 벡터를 할당할 수 있다. 그리고, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 워드 임베딩 벡터에 기초하여 하나의 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터를 생성할 수 있다. 보다 상세하게, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 데이터에 포함된 각 단어에 대해, 단어 임베딩 사전에 기초하여 각 단어에 대한 단어 임베딩 벡터를 결정할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, when the data type determined for one data is text, the
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 텍스트로 유형이 판단된 제 1 데이터는 한 개 이상의 단어를 포함할 수 있다. 이때, 하나의 데이터에 포함된 각 단어는로 정의될 수 있다. 제 1 데이터에 포함된 각 단어 에 대해 기 학습된 워드 임베딩 사전에 기초하여, 워드 임베딩 벡터가 할당될 수 있다. 이때, 기 학습된 워드 임베딩 사전은 Word2Vec, Glove 등이 사용될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되지 않는다.First data whose type is determined as text according to an embodiment of the present invention May contain more than one word. At this time, each word included in one data is Can be defined as First data Each word contained in Based on the word embedding dictionary previously learned for the word embedding vector Can be assigned. In this case, as the pre-learned word embedding dictionary, Word2Vec, Glove, or the like may be used, but is not limited thereto.
예를 들어, 제 1 데이터가 'SAMSUNG Galaxy'에 해당되는 경우, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 제 1 데이터의 유형을 텍스트로 판단할 수 있다. 그리고, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 기 학습된 워드 임베딩 사전을 이용하여, SAMSUNG, Galaxy 각각에 대해 워드 임베딩 벡터를 할당할 수 있다.For example, when the first data corresponds to'SAMSUNG Galaxy', the
그리고, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 하나 이상의 워드 임베딩 벡터에 기초하여, 제 1 데이터에 대한 초기화 벡터 ()를 생성할 수 있다. 이때, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 하나 이상의 워드 임베딩 벡터들을 하나의 벡터로 합산 또는 평균하여, 제 1 데이터에 대한 초기화 벡터 ()를 생성할 수 있다.And, the
본 발명의 다른 일 실시예에 따라, 하나의 데이터에 대해 판단된 데이터 유형이 텍스트가 아닌 경우, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 랜덤한 벡터 값을 하나의 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터로 결정할 수 있다.According to another embodiment of the present invention, when the data type determined for one piece of data is not text, the
보다 상세하게, 하나의 데이터에 대해 판단된 데이터 유형이 비텍스트 데이터(Non-text data)인 경우, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 랜덤한 벡터 값으로 제 1 데이터에 대한 초기화 벡터 ()를 결정할 수 있다 이때, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 원-핫 벡터(One-hot vector)로 표현될 수 있는 랜덤한 벡터 값을 초기화 벡터로 결정할 수 있다.In more detail, when the data type determined for one piece of data is non-text data, the
도 6는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 기 설정된 기준에 따라 정렬된 복수 개의 데이터를 나타낸 도면이다.6 is a diagram illustrating a plurality of pieces of data arranged according to a preset criterion according to an embodiment of the present invention.
데이터 처리 장치가 데이터를 분석하기 위해 선택한 데이터 테이블이 CS_Service 데이터 테이블이라고 가정하여 설명을 하도록 한다. 즉, CS_Service 데이터 테이블은, 본 발명의 제 1 데이터 테이블로 선택될 수 있다. 이때, CS_Service 데이터 테이블, Phone_Sales 데이터 테이블, Gear_Sales 데이터 테이블, SSD_Salessms 데이터 테이블은 각각 다른 데이터 베이스에 속한 데이터 테이블에 해당될 수 있다.It is assumed that the data table selected by the data processing device to analyze data is the CS_Service data table. That is, the CS_Service data table may be selected as the first data table of the present invention. In this case, the CS_Service data table, the Phone_Sales data table, the Gear_Sales data table, and the SSD_Salessms data table may respectively correspond to data tables belonging to different databases.
이때, CS_Service 데이터 테이블은 model_id 속성을 포함하고 있다. 이때, model_id 속성은 데이터 처리 또는 맵핑을 수행하기 위해 선택된 속성으로, 본 발명의 제 1 속성으로 선택될 수 있다. CS_Service 데이터 테이블의 model_id 속성에는 GS_8105, GG_2100, GN_8297, GS_8100, GG_2003이라는 복수 개의 데이터가 포함될 수 있다.At this time, the CS_Service data table includes the model_id attribute. In this case, the model_id attribute is an attribute selected to perform data processing or mapping, and may be selected as the first attribute of the present invention. The model_id attribute of the CS_Service data table may include a plurality of data such as GS_8105, GG_2100, GN_8297, GS_8100, and GG_2003.
예를 들어, 제 1 데이터로 선택된 데이터가 'GS_8105'인 경우, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 제 1 데이터의 유형을 텍스트가 아닌 것으로 판단할 수 있다. 그리고, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 랜덤하게 생성된 원 핫 벡터(one-hot vector) 를 이용하여, 제 1 데이터에 대응되는 초기화 벡터 ()를 생성할 수 있다.For example, when the data selected as the first data is'GS_8105', the
또한, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 CS_Service 데이터 테이블의 model_id 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대해 초기화 벡터를 생성할 수 있다. 즉, 도 6을 참고하면, GS_8105, GG_2100, GN_8297, GS_8100, GG_2003 각각에 대한 초기화 벡터()들이 생성될 수 있다.In addition, the
동작 S520에서 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터를 기 설정된 정렬 기준에 따라 정렬할 수 있다. 제 1 속성 내의 모든 데이터는 기 설정된 정렬 기준에 따라 특유의 순서로 정렬될 수 있다. 이때, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터는 알파벳 순서에 따라 정렬될 수 있으나, 상술한 정렬 기준으로 한정되지 않는다.In operation S520, the
도 6의 (b)를 참고할 때, CS_Service 데이터 테이블의 model_id 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터가 알파벳 순으로 정렬된 것을 확인할 수 있다. 즉, 도 6의 (a)에서 규칙 없이 존재하였던 복수 개의 데이터들은 알파벳 순으로 도 6(b)과 같이 정렬될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 6B, it can be seen that a plurality of data included in the model_id attribute of the CS_Service data table are arranged in alphabetical order. That is, a plurality of data that existed without rules in FIG. 6A may be arranged alphabetically as shown in FIG. 6B.
동작 S530에서 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 정렬된 순서를 고려하여 기 설정된 개수의 데이터를 선택할 수 있다. 그리고, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 선택된 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터를 이용하여 제 1 임베딩 벡터의 값을 예측할 수 있다. 또한, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 예측된 제 1 임베딩 벡터의 값을 이용하여, 제 1 임베딩 벡터를 생성할 수 있다. 보다 상세하게, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 선택된 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터를 이용하여 뉴럴 네트워크에서 제 1 데이터에 대한 제 1 임베딩 값을 예측할 수 있다.In operation S530, the
본 발명에서, 기 설정된 개수의 데이터를 선택하는 경우, 기 설정된 개수는 사용자가 설정할 수 있는 값에 해당될 수 있다. 일 예로, k 개가 선택될 수 있으며, 해당 값은 데이터의 양, 데이터의 처리 속도, 예측 결과 등을 고려하여 설정될 수 있다.In the present invention, when selecting a preset number of data, the preset number may correspond to a value that can be set by a user. For example, k numbers may be selected, and the corresponding values may be set in consideration of the amount of data, data processing speed, prediction result, and the like.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 기 설정된 기준에 따를 때, 선택된 데이터는 제 1 데이터에 앞서 연속적으로 선 정렬된 한 개 이상의 데이터일 수 있다. 예로, 도 6(b)를 참고하면, 제 1 데이터로 선택된 데이터가 GS_8105이고, 선택하기로 기 설정된 개수의 데이터가 2개인 경우, 데이터 GN_8297, 데이터 GS_8100의 초기화 벡터를 이용하여, 제 1 데이터인 GS_8105의 제 1 임베딩 벡터를 생성할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, when following a preset criterion, the selected data may be one or more pieces of data that are continuously line-aligned prior to the first data. For example, referring to FIG. 6(b), when the data selected as the first data is GS_8105, and there are two preset numbers of data to be selected, the first data, which is, by using an initialization vector of data GN_8297 and data GS_8100 A first embedding vector of GS_8105 may be generated.
보다 상세하게, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 제 1 데이터인 GS_8105에 대해, 앞선 2 개의 데이터인 GN_8297, GS_8100의 초기 벡터들을 이용하여, 뉴럴 네트워크에서 제 1 데이터인 GS_8105에 대해 예측을 수행할 수 있다. 그리고, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 예측된 값을 제 1 데이터인 GS_8105의 임베딩 벡터로 생성할 수 있다.In more detail, the
도 7은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 데이터 분석 장치가 임베딩 벡터를 생성하는 방법을 나타낸 도면이다.7 is a diagram illustrating a method of generating an embedding vector by a data analysis device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 7의 인풋 레이어(Input layer)에는 선택된 기 설정된 개수의 데이터가 인풋 데이터로 입력될 수 있다. 즉, 본 발명의 일 예시에 따라, 인풋 레이어(Input layer)에 ti-k 부터 ti-1까지의 k개의 데이터가 입력될 수 있다. 또한, 아웃풋 레이어(Output layer)에서는 제 1 데이터인 ti에 대한 임베딩 벡터가 출력될 수 있다.In the input layer of FIG. 7, a selected preset number of data may be input as input data. That is, according to an example of the present invention, k pieces of data from ti-k to ti-1 may be input to an input layer. In addition, an embedding vector for ti, which is the first data, may be output in an output layer.
일 예로, 도 6을 참고할 때, 제 1 데이터가 GS_8105에 해당되고, k가 2 개라면, GN_8297, GS_8100가 선택될 수 있다. 이때, 인풋 레이어(Input layer)에는 GN_8297, GS_8100의 초기화 벡터가 입력될 수 있다. 만약 ti-k 데이터가 GN_8297에 대응되고, GN_8297의 초기화 벡터가 도 7과 같은 {0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,...,0}인 경우, GN_8297의 초기화 벡터가 인풋 레이어에 입력될 수 있다. 또한, ti-1 데이터가 GS_8100에 대응되고, GS_8100의 초기화 벡터가 도 7과 같은 {0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,...,0}인 경우, GS_8100의 초기화 벡터가 인풋 레이어에 입력될 수 있다. 이때, GN_8297, GS_8100들의 원-핫 벡터(one-hot vector) 부터 GS_8105의 원-핫 벡터(one-hot vector)가 생성 되도록 hidden layer가 학습될 수 있다. 학습 된 hidden layer의 값이 바로 아웃풋 레이어(output layer)의 임베딩 벡터로 생성될 수 있다. 상술한 예에서는, 학습된 hidden layer의 값이 제 1 데이터인 GS_8105의 임베딩 벡터(embedding vector)로 생성될 수 있다.For example, referring to FIG. 6, if the first data corresponds to GS_8105 and k is two, GN_8297 and GS_8100 may be selected. In this case, initialization vectors of GN_8297 and GS_8100 may be input to an input layer. If ti-k data corresponds to GN_8297 and the initialization vector of GN_8297 is {0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,...,0} as shown in FIG. 7, the initialization vector of GN_8297 May be input to the input layer. In addition, when the ti-1 data corresponds to GS_8100 and the initialization vector of GS_8100 is {0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,...,0} as shown in FIG. 7, the initialization of GS_8100 Vectors can be input to the input layer. In this case, a hidden layer may be learned so that a one-hot vector of GS_8105 is generated from a one-hot vector of GN_8297 and GS_8100. The learned hidden layer value can be directly generated as an embedding vector of an output layer. In the above-described example, the learned hidden layer value may be generated as an embedding vector of GS_8105, which is the first data.
즉, 상술한 바와 같이, 뉴럴 네트워크 및 표현 기법을 사용하여, 각 데이터들의 임베딩 벡터가 훈련될 수 있다. 훈련 후, 각 임베딩 벡터들은 업데이트가 될 수 있다. 또는, 각 초기화 벡터들은 각 임베딩 벡터들로 업데이트 될 수 있다. 또는, 각 데이터에 할당되었던 초기화 벡터 값들이 업데이트될 수 있다. 최종적으로, 제 1 데이터에 대응하는 제 1 임베딩 벡터가 생성될 수 있다.That is, as described above, an embedding vector of each data may be trained using a neural network and a representation technique. After training, each embedding vector can be updated. Alternatively, each initialization vector may be updated with each embedding vector. Alternatively, initialization vector values allocated to each data may be updated. Finally, the first data The first embedding vector corresponding to Can be created.
동작 S330에서 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들에 기초하여 상기 제 1 속성에 대응하는 속성 벡터를 생성할 수 있다.In operation S330, the
데이터 분석 장치(100)는 하나의 속성에 포함된 복수의 데이터에 대한 복수의 임베딩 벡터들을 하나로 집계할 수 있다. 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 속성 벡터는 해당 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들의 합산 값 또는 평균 값에 기초하여 생성될 수 있다.The
본 발명에서 속성 벡터란, 속성 각각에 대응하여 생성되는 사용자가 설정한 차원의 벡터에 해당될 수 있다. 이때, 사용자가 설정한 차원은 고차원일 수 있다. 또한, 속성 각각을 대표 또는 표현할 할 수 있는 벡터일 수 있다.In the present invention, the attribute vector may correspond to a vector of a dimension set by a user that is generated corresponding to each attribute. In this case, the dimension set by the user may be a high dimension. In addition, it may be a vector capable of representing or expressing each attribute.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 제 1 속성 벡터는 제 1 속성에 대한 속성 벡터에 해당될 수 있다. 즉, 제 1 속성 벡터는 데이터 분석 처리 대상으로 선택 또는 결정된 제 1 속성에 대한 속성 벡터를 의미할 수 있다. 따라서, 제 1 속성 벡터는 크로스 맵핑을 판단하기 위한 유사 값을 결정할 때, 이용되는 값에 해당될 수 있다. 이때, 제 1 속성 벡터는 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들의 합산 값 또는 평균 값에 기초하여 생성될 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the first attribute vector may correspond to an attribute vector for the first attribute. That is, the first attribute vector may mean an attribute vector for the first attribute selected or determined as a data analysis processing target. Accordingly, the first attribute vector may correspond to a value used when determining a similarity value for determining cross-mapping. In this case, the first attribute vector may be generated based on a sum value or an average value of a plurality of embedding vectors corresponding to each of the plurality of data included in the first attribute.
동작 S330에서 집계 연산은 제 1 속성를 대표하는 제 1속성 벡터 를 얻기 위하여, 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수개의 데이터들의 임베딩 벡터들을 합 또는 평균할 수 있다.In operation S330, the aggregation operation is the first property The first attribute vector representing In order to get, the first property Embedding vectors of a plurality of data included in may be summed or averaged.
수학식 1 및 수학식 2는 각각 제 1 속성에 대한 합산 작업(the addition operation) 및 평균 종합 작업(average aggregation operation)을 나타낼 수 있다. 이때,는 제 1 데이터 테이블 Ti에 얼마나 많은 튜플(tuple)들이 있는지를 나타내는 값이다.
동작 S340에서 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 복수 개의 속성들 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들을 생성할 수 있다. 그리고, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들에 기초하여 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대응하는 제 1 테이블 벡터를 생성할 수 있다.In operation S340, the
데이터 분석 장치(100)는 하나의 테이블에 포함된 복수의 속성에 대한 복수의 속성 벡터들을 하나로 집계할 수 있다. 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 테이블 벡터는 해당 테이블에 포함된 복수 개의 속성 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들의 합산 값 또는 평균 값에 기초하여 생성될 수 있다.The
본 발명에서 테이블 벡터란, 테이블 각각에 대응하여 생성되는 사용자가 설정한 차원의 벡터에 해당될 수 있다. 이때, 사용자가 설정한 차원은 고차원일 수 있다. 또한, 테이블 각각을 대표 또는 표현할 할 수 있는 벡터일 수 있다.In the present invention, the table vector may correspond to a vector of a dimension set by a user that is generated corresponding to each table. In this case, the dimension set by the user may be a high dimension. In addition, it may be a vector capable of representing or expressing each of the tables.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 제 1 테이블 벡터는 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대한 테이블 벡터에 해당될 수 있다. 즉, 제 1 테이블 벡터는 데이터 분석 처리 대상으로 선택 또는 결정된 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대한 테이블 벡터를 의미할 수 있다. 따라서, 제 1 테이블 벡터는 크로스 맵핑을 판단하기 위한 유사 값을 결정할 때, 이용되는 값에 해당될 수 있다. 이때, 제 1 테이블 벡터는 제 1 데이터 테이블에 포함된 복수 개의 속성 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들의 합산 값 또는 평균 값에 기초하여 생성될 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the first table vector may correspond to a table vector for the first data table. That is, the first table vector may mean a table vector for the first data table selected or determined as a data analysis processing target. Accordingly, the first table vector may correspond to a value used when determining a similarity value for determining cross-mapping. In this case, the first table vector may be generated based on a sum value or an average value of a plurality of attribute vectors corresponding to each of the plurality of attributes included in the first data table.
동작 S330에서, 제 1 데이터 테이블 Ti내의 각 속성은 임베딩 벡터(embedding vector)로 표현될 수 있다. 간단하게, V(Ti)는 모든 속성 벡터들을 집계하여 생성될 수 있다.In operation S330, each attribute in the first data table Ti Is an embedding vector It can be expressed as Simply put, V(Ti ) can be created by aggregating all attribute vectors.
수학식 3 및 수학식 4는 각각 속성에 대한 합산 작업(the addition operation) 및 평균 종합 작업(average aggregation operation)을 나타낼 수 있다. 이때,는 얼마나 많은 속성들이table Ti 에 있는지를 나타내는 값에 해당될 수 있다.Equation 3 and Equation 4 are each attribute It can represent the addition operation and the average aggregation operation. At this time, May correspond to a value indicating how many properties are in table Ti.
동작 S350에서 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 하나의 데이터인 제 1 데이터에 대한 제 1 임베딩 벡터, 상기 제 1 속성에 대한 제 1 속성 벡터 및 상기 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대한 제 1 테이블 벡터 중 하나를 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)의 대상으로 선택할 수 있다. 또한, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 제 2 데이터 테이블과 맵핑을 수행할 수 있다.In operation S350, the
이때, 제 2 데이터 테이블은 제 2 속성 및 제 2 속성에 포함된 제 2 데이터를 포함할 수 있다.In this case, the second data table may include a second attribute and second data included in the second attribute.
본 발명에서 제 2 테이블 벡터는 제 2 데이터 테이블에 대해 생성된 테이블 벡터를 의미할 수 있다. 보다 상세하게, 제 1 테이블과 맵핑을 수행하는 대상인 제 2 데이터 테이블에 대해 생성된 테이블 벡터로, 제 1 테이블에 대해 선택된 크로스 레이어 맵핑의 대상과 비교되는 테이블 벡터를 의미할 수 있다.In the present invention, the second table vector may mean a table vector generated for the second data table. In more detail, as a table vector generated for a first table and a second data table that is a target for mapping, it may mean a table vector that is compared with a target for cross-layer mapping selected for the first table.
본 발명에서 제 2 속성 벡터는 제 2 속성에 대해 생성된 속성 벡터를 의미할 수 있다. 보다 상세하게, 제 1 테이블과 맵핑을 수행하는 대상인 제 2 데이터 테이블의 제 2 속성에 대해 생성된 속성 벡터로, 제 1 테이블에 대해 선택된 크로스 레이어 맵핑의 대상과 비교되는 속성 벡터를 의미할 수 있다.In the present invention, the second attribute vector may mean an attribute vector generated for the second attribute. In more detail, it is an attribute vector generated for the second attribute of the second data table, which is a target for mapping with the first table, and may mean an attribute vector that is compared with the target of the cross-layer mapping selected for the first table. .
본 발명에서 제 2 임베딩 벡터는 제 2 데이터에 대해 생성된 임베딩 벡터를 의미할 수 있다. 보다 상세하게, 제 1 테이블과 맵핑을 수행하는 대상인 제 2 테이블의 제 2 데이터에 대해 생성된 임베딩 벡터로, 제 1 테이블에 대해 선택된 크로스 레이어 맵핑의 대상과 비교되는 임베딩 벡터를 의미할 수 있다.In the present invention, the second embedding vector may mean an embedding vector generated for second data. In more detail, the embedding vector is an embedding vector generated for the second data of the second table, which is a target for mapping with the first table, and may mean an embedding vector that is compared with the target of the cross-layer mapping selected for the first table.
데이터 분석 장치(100)는 제 2 데이터 테이블에 대해 생성된 제 2 테이블 벡터, 제 2 속성에 대해 생성된 제 2 속성 벡터 및 제 2 데이터에 대해 생성된 제 2 임베딩 벡터 중 적어도 하나와 선택된 크로스 레이어 맵핑 대상과의 유사 값을 판단할 수 있다. 이때, 선택된 크로스 레이어 맵핑 대상은 제 1 테이블 벡터, 제 1 속성 벡터 및 제 1 임베딩 벡터 중 적어도 하나 이상의 벡터를 의미할 수 있다.The
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 유사 값을 구하기 위해 코사인 유사성이 이용될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되지 않으며, 벡터 간의 유사성을 계산할 수 있는 방법은 모두 포함할 수 있다. 따라서, 본 발명에서 유사성 식(the similarity function()은 벡터들간의 유사성을 계산할 수 있는 모든 식들이 해당될 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, cosine similarity may be used to obtain a similarity value, but the present invention is not limited thereto, and methods for calculating the similarity between vectors may be included. Therefore, in the present invention, the similarity function ( ) Can be any equation that can calculate the similarity between vectors.
또한, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 유사 값이 임계 값 이상이면 서로 맵핑할 수 있다.In addition, the
보다 상세하게, 데이터 분석 장치(100)가 수행하는 크로스 레이어 맵핑은, 값-속성(Value-Attribute) 맵핑, 속성-테이블(Attribute-Table) 맵핑 및 값-테이블(Value-Table) 맵핑으로 구분될 수 있다. 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 각 맵핑들은 1대 n 맵핑에 해당될 수 있다.In more detail, the cross-layer mapping performed by the
먼저, 값-속성 맵핑(Value-Attribute Mapping)은 제 1 테이블의 값과 제 2 테이블간의 속성 맵핑을 의미할 수 있다. 또한 값-속성 맵핑(Value-Attribute Mapping)은 제 1 테이블의 속성과 제 2 테이블의 값 맵핑을 의미할 수 있다. 이때, 값(vlaue)은 본 발명의 데이터와 대응되는 개념에 해당될 수 있다.First, value-attribute mapping may mean attribute mapping between a value of a first table and a second table. In addition, value-attribute mapping may mean mapping an attribute of a first table and a value of a second table. In this case, the value vlaue may correspond to a concept corresponding to the data of the present invention.
본 발명의 일 실시예를 설명하기 위해, i번째 데이터 테이블의 j 번째 속성에 포함된 k 번째 데이터가 제 1 데이터로 선택될 수 있다. 또한 제 1 데이터와 다른, i'번째 데이터 테이블의 j'번째 속성이 비교 대상인 제 2 속성으로 선택될 수 있다.To illustrate an embodiment of the present invention, the k-th data included in the j-th attribute of the i-th data table May be selected as the first data. Also the first data Different from, the j'th attribute of the i'th data table It may be selected as the second attribute to be compared.
제 1 데이터와 제 2 속성간의 유사 값은 제 1 데이터에 대한 제 1 임베딩 벡터 및 제 2 속성에 대한 제 2 속성 벡터에 기초하여, 수학식 5를 이용하여 결정될 수 있다.The similarity value between the first data and the second attribute may be determined using Equation 5 based on the first embedding vector for the first data and the second attribute vector for the second attribute.
이때, 값-속성 맵핑(Value-Attribute Mapping)의 임계값은 사용자에 의해 설정될 수 있다. 만약 수학식 5를 이용한 유사 값이보다 크다면, 제 1 데이터는 대응되는 속성인 제 2 속성과 맵핑될 수 있다.At this time, the threshold value of Value-Attribute Mapping Can be set by the user. If the similarity value using Equation 5 is If it is greater than, the first data may be mapped to a second attribute, which is a corresponding attribute.
또한, 속성-테이블 맵핑(Attribute-Table Mapping)은 제 1 테이블의 제 1 속성과 제 2 테이블간의 맵핑을 의미할 수 있다. 또한 속성-테이블 맵핑(Attribute-Table Mapping)은 제 1 테이블과 제 2 테이블의 속성간의 맵핑을 의미할 수 있다.In addition, attribute-table mapping may mean mapping between a first attribute of a first table and a second table. In addition, attribute-table mapping may mean mapping between attributes of a first table and a second table.
본 발명의 일 실시예를 설명하기 위해,내의 각 속성은 제 1 속성으로 선택될 수 있다. 또한,는 제 2 데이터 테이블로 선택될 수 있다.To describe an embodiment of the present invention, Each attribute within May be selected as the first attribute. Also, May be selected as the second data table.
내의 각 속성에 대하여, 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 하기의 수학식 6에 따라 유사 값을 계산할 수 있다. 만약 유사 값이 사용자가 설정한 보다 크다면, 제 1 속성 은 대응되는 테이블인 제 2 테이블로 맵핑 될 수 있다.Each attribute within With respect to, the
또한, 값-테이블 맵핑(Value-Table Mapping)은 제 1 테이블의 데이터와 제 2 테이블간의 맵핑을 의미할 수 있다. 또한 값-테이블 맵핑(Value-Table Mapping)은 제 1 테이블과 제 2 테이블의 데이터 간의 맵핑을 의미할 수 있다. 이때, 값(vlaue)은 본 발명의 데이터와 대응되는 개념에 해당될 수 있다.Also, value-table mapping may mean mapping between data of a first table and a second table. In addition, value-table mapping may mean mapping between data of a first table and a second table. In this case, the value vlaue may correspond to a concept corresponding to the data of the present invention.
각 데이터 인스턴스 또는 데이터를 제 1 데이터로 선택할 수 있다. 또한,는 제 2 데이터 테이블로 선택될 수 있다. 이에 대하여 제 1 데이터 와 다른 테이블들 간의 유사 값은 수학식 7과 같이 그들의 임베딩 벡터 및 테이블 벡터로 얻어질 수 있다. 만약 유사 값이 기 설정된 임계값인보다 크다면, 제 1 데이터는 대응되는 테이블인 제 2 테이블로 맵핑 될 수 있다.Each data instance or data Can be selected as the first data. Also, May be selected as the second data table. About this first data Similar values between and other tables can be obtained as their embedding vector and table vector as shown in Equation 7. If the similar value is the preset threshold If it is greater than, the first data may be mapped to a second table, which is a corresponding table.
도 6을 참고할 때, 유사한 속성 및 데이터 테이블들은 유사하거나 동일한 데이터 시퀀스(sequence)를 포함할 수 있다. 이것은 유사한 복수의 데이터는 유사한 콘텍스트(context)를 공유하는 것을 의미한다. 이 특징의 장점을 이용하여, 고효율 데이터 인스턴트 임베딩을 얻을 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 6, similar attributes and data tables may include similar or identical data sequences. This means that a plurality of similar data share a similar context. By taking advantage of this feature, high-efficiency data instant embedding can be obtained.
도 8은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른, 데이터 베이스에 포함된 데이터를 분석하는 데이터 분석 장치의 구성도이다.8 is a block diagram of a data analysis apparatus for analyzing data included in a database according to an embodiment of the present invention.
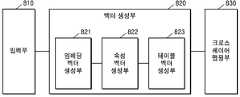
데이터 베이스에 포함된 데이터를 분석하는 데이터 분석 장치(100)는 입력부(810), 벡터 생성부(820) 및 크로스 레이어 맵핑부(830) 등을 포함할 수 있다. 이때, 벡터 생성부(820)는 임베딩 벡터 생성부(821), 속성 벡터 생성부(822) 및 테이블 벡터 생성부(823)를 포함할 수 있다.The
입력부(810)는 통신 모듈을 더 포함할 수 있다. 일 예로, 통신을 통해 데이터를 입력받을 수 있다. 본 발명에서, 입력부(810)는 복수 개의 속성(Attribute)들이 포함된 제 1 데이터 테이블(Data Table)에서 하나의 속성을 선택하고, 상기 선택된 속성인 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터(Data)를 입력 받을 수 있다.The
본 발명에서, 벡터 생성부(820) 및 크로스 레이어 맵핑부(830)는 프로세서에서 구동되는 프로그램에 해당될 수 있다. 또한, 벡터 생성부(820) 및 크로스 레이어 맵핑부(830)가 프로세서에서 구동되는 프로그램에 해당되는 경우, 프로그램은 메모리에 저장되어 있을 수 있다. 보다 상세하게, 메모리에는 벡터 생성부(820)의 동작을 수행하기 위한 프로그램이 저장될 수 있다. 즉, 메모리에는 임베딩 모듈 벡터를 생성하고, 속성 벡터를 생성하고, 테이블 벡터를 생성하기 위한 프로그램이 저장될 수 있다. 또한, 메모리에는 크로스 레이어 맵핑을 수행하기 위한 프로그램이 저장될 수 있다. 프로세서는 메모리에 저장된 프로그램들을 실행할 수 있다. 따라서, 프로세서는 임베딩 모듈 벡터를 생성하고, 속성 벡터를 생성하고, 테이블 벡터를 생성하고, 크로스 레이어 맵핑을 수행하는 동작을 수행할 수 할 수 있다.In the present invention, the
임베딩 벡터 생성부(821)는 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들을 생성할 수 있다. 임베딩 벡터 생성부(821)가 제 1 임베딩 벡터를 생성하는 경우, 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 생성하고, 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 사용하여 제 1 임베딩 벡터의 값을 예측할 수 있다. 또한, 임베딩 벡터 생성부(821)는 복수 개의 데이터 각각의 유형을 판단하여 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 생성할 수 있다.The embedding
이때, 하나의 데이터에 대해 판단된 데이터 유형이 텍스트인 경우, 임베딩 벡터 생성부(821)는 하나의 데이터에 포함된 단어 각각에 대해 기 학습된 워드 임베딩 벡터를 할당하고, 워드 임베딩 벡터에 기초하여 하나의 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터를 생성할 수 있다. 다른 일예로, 하나의 데이터에 대해 판단된 데이터 유형이 텍스트가 아닌 경우, 임베딩 벡터 생성부(821)는 랜덤한 벡터 값을 하나의 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터로 결정할 수 있다. 임베딩 벡터 생성부(821)는 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터를 기 설정된 기준에 따라 정렬하고, 정렬된 순서를 고려하여 기 설정된 개수의 데이터를 선택하고, 임베딩 벡터 생성부(821)는 선택된 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터를 이용하여 제 1 임베딩 벡터의 값을 예측하고, 제 1 임베딩 벡터를 생성할 수 있다. 이때, 기 설정된 기준에 따를 때, 선택된 데이터는 제 1 데이터에 앞서 연속적으로 선 정렬된 한 개 이상의 데이터에 해당될 수 있다.At this time, if the data type determined for one data is text, the embedding
속성 벡터 생성부(822)는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들에 기초하여 제 1 속성에 대응하는 속성 벡터를 생성할 수 있다. 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 제 1 속성 벡터는 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들의 합산 값 또는 평균 값에 기초하여 생성될 수 있다.The
테이블 벡터 생성부(823)는 복수 개의 속성들 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들을 생성하고, 복수 개의 속성 벡터들에 기초하여 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대응하는 제 1 테이블 벡터를 생성할 수 있다. 제 1 테이블 벡터는 제 1 테이블 벡터에 포함된 복수 개의 속성 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들의 합산 값 또는 평균 값에 기초하여 생성될 수 있다.The
크로스 레이어 맵핑부(830)는 제 1 속성에 포함된 하나의 데이터인 제 1 데이터에 대한 제 1 임베딩 벡터, 제 1 속성에 대한 제 1 속성 벡터 및 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대한 제 1 테이블 벡터 중 하나를 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)의 대상으로 선택하고, 제 2 데이터 테이블과 맵핑을 수행할 수 있다. 이때, 제 2 데이터 테이블은 제 2 속성 및 제 2 속성에 포함된 제 2 데이터를 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 상기 크로스 레이어 맵핑부(830)는 제 2 데이터 테이블에 대해 생성된 제 2 테이블 벡터, 제 2 속성에 대해 생성된 제 2 속성 벡터 및 제 2 데이터에 대해 생성된 제 2 임베딩 벡터 중 적어도 하나와 선택된 크로스 레이어 맵핑 대상과의 유사 값을 판단할 수 있다. 또한, 크로스 레이어 맵핑부(830)는 유사 값이 임계 값 이상이면 서로 맵핑할 수 있다.The
도 9는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른, 데이터 베이스에 포함된 데이터를 분석하는 데이터 분석 장치의 블록도이다.9 is a block diagram of a data analysis apparatus for analyzing data included in a database according to an embodiment of the present invention.
데이터 분석 장치(100)는 프로세서(미도시) 및 메모리(미도시)를 포함할 수 있으며, 입력부 및 출력부를 더 포함할 수 있다.The
메모리에 저장된 프로그램들은 그 기능에 따라 복수 개의 모듈들로 분류할 수 있는데, 데이터 인스턴스 임베딩 모듈, 속성 임베딩 모듈, 테이블 임베딩 모듈 및 크로스 레이어 맵핑 모듈은 데이터를 분석하기 위한 프로그램들에 저장된 모듈 등으로 분류될 수 있다. 이때, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 데이터 인스턴스 임베딩 모듈, 속성 임베딩 모듈, 테이블 임베딩 모듈 및 크로스 레이어 맵핑 모듈은 데이터를 분석하기 위한 프로그램들에 저장된 모듈들에 해당될 수 있다.Programs stored in memory can be classified into a plurality of modules according to their function. Data instance embedding module, attribute embedding module, table embedding module, and cross-layer mapping module are classified into modules stored in programs for analyzing data, etc. Can be. In this case, according to an embodiment of the present invention, the data instance embedding module, the attribute embedding module, the table embedding module, and the cross layer mapping module may correspond to modules stored in programs for analyzing data.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라, 데이터 인스턴스 임베딩 모듈은 임베딩 벡터 생성부(821)와 대응되는 모듈에 해당될 수 있으며, 임베딩 벡터 생성부(821)의 동작을 수행할 수 있다. 보다 상세하게, 데이터 인스턴스 임베딩 모듈은, 본 발명에서 임베딩 벡터를 생성하기 위한 모듈에 해당될 수 있다. 본 발명에서 데이터 인스턴스는 데이터를 의미할 수 있다. 데이터 인스턴스 임베딩 모듈은, 데이터 인스턴스들 또는 값(value) 등을 벡터들(vectors)로 임베딩 시키는 기능을 수행할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the data instance embedding module may correspond to a module corresponding to the embedding
또한 속성 임베딩 모듈은 속성 벡터 생성부(822)와 대응되는 모듈에 해당될 수 있으며, 속성 벡터 생성부(822)의 동작을 수행할 수 있다. 속성 임베딩 모듈은 속성 또는 열 내부의 데이터 인스턴스들의 모든 임베딩 벡터들을 집계하여, 속성을 대표하는 벡터를 생성할 수 있다.In addition, the attribute embedding module may correspond to a module corresponding to the attribute
또한, 테이블 임베딩 모듈은 테이블 벡터 생성부(823)와 대응되는 모듈에 해당될 수 있으며, 테이블 벡터 생성부(823)의 동작을 수행할 수 있다. 테이블 임베딩 모듈은, 테이블(table)을 대표하는 벡터를 생성하기 위해 모든 속성 벡터들을 테이블(table) 벡터로 합산할 수 있다.In addition, the table embedding module may correspond to a module corresponding to the table
크로스 레이어 맵핑 모듈(cross layer mapping module)은 크로스 레이어 맵핑부(830)와 대응되는 모듈에 해당될 수 있으며, 크로스 레이어 맵핑부(830)의 동작을 수행할 수 있다. 크로스 레이어 맵핑 모듈은 데이터 인스턴스 또는 값에 대한 임베딩 벡터들, 속성 벡터들 및 테이블 벡터들을 입력 값으로 취하고, 유사 값을 계산하여, 레이어간 맵핑을 수행할 수 있다.The cross layer mapping module may correspond to a module corresponding to the cross
메모리에 저장된 프로그램들은 프로세서에 의해 실행됨으로써 그 기능을 수행할 수 있다. 이러한 방식으로, 크로스 레이어 맵핑 문제(cross layer mapping problem)는 임베딩 스페이스(embedding space)에서 해결될 수 있다.Programs stored in the memory can perform their functions by being executed by the processor. In this way, a cross layer mapping problem can be solved in an embedding space.
본 개시의 일 실시예는 컴퓨터에 의해 실행되는 프로그램 모듈과 같은 컴퓨터에 의해 실행 가능한 명령어를 포함하는 기록 매체의 형태로도 구현될 수 있다. 컴퓨터 판독 가능 매체는 컴퓨터에 의해 액세스될 수 있는 임의의 가용 매체일 수 있고, 휘발성 및 비휘발성 매체, 분리형 및 비분리형 매체를 모두 포함한다. 또한, 컴퓨터 판독가능 매체는 컴퓨터 저장 매체 및 통신 매체를 포함할 수 있다. 컴퓨터 저장 매체는 컴퓨터 판독가능 명령어, 데이터 구조, 프로그램 모듈 또는 기타 데이터와 같은 정보의 저장을 위한 임의의 방법 또는 기술로 구현된 휘발성 및 비휘발성, 분리형 및 비분리형 매체를 모두 포함한다. 통신 매체는 전형적으로 컴퓨터 판독가능 명령어, 데이터 구조, 또는 프로그램 모듈과 같은 변조된 데이터 신호의 기타 데이터를 포함할 수 있다.An embodiment of the present disclosure may also be implemented in the form of a recording medium including instructions executable by a computer, such as a program module executed by a computer. Computer-readable media can be any available media that can be accessed by a computer, and includes both volatile and nonvolatile media, removable and non-removable media. Further, the computer-readable medium may include a computer storage medium and a communication medium. Computer storage media includes both volatile and nonvolatile, removable and non-removable media implemented in any method or technology for storage of information such as computer readable instructions, data structures, program modules or other data. Communication media may typically contain computer readable instructions, data structures, or other data in a modulated data signal such as a program module.
또한, 본 명세서에서, "부"는 프로세서 또는 회로와 같은 하드웨어 구성(hardware component), 및/또는 프로세서와 같은 하드웨어 구성에 의해 실행되는 소프트웨어 구성(software component)일 수 있다.In addition, in this specification, the "unit" may be a hardware component such as a processor or a circuit, and/or a software component executed by a hardware configuration such as a processor.
또한, 본 명세서에서, "a, b 또는 c 중 적어도 하나를 포함한다"는 "a만 포함하거나, b만 포함하거나, c만 포함하거나, a 및 b를 포함하거나, b 및 c를 포함하거나, a 및 c를 포함하거나, a, b 및 c를 모두 포함하는 것을 의미할 수 있다.In addition, in the present specification, “including at least one of a, b or c” means “including only a, only b, only c, including a and b, or including b and c, It may mean including a and c, or including all of a, b, and c.
전술한 본 개시의 설명은 예시를 위한 것이며, 본 개시가 속하는 기술분야의 통상의 지식을 가진 자는 본 개시의 기술적 사상이나 필수적인 특징을 변경하지 않고서 다른 구체적인 형태로 쉽게 변형이 가능하다는 것을 이해할 수 있을 것이다. 그러므로 이상에서 기술한 실시예들은 모든 면에서 예시적인 것이며 한정적이 아닌 것으로 이해해야만 한다. 예를 들어, 단일형으로 설명되어 있는 각 구성 요소는 분산되어 실시될 수도 있으며, 마찬가지로 분산된 것으로 설명되어 있는 구성 요소들도 결합된 형태로 실시될 수 있다.The above description of the present disclosure is for illustrative purposes only, and those of ordinary skill in the art to which the present disclosure pertains will be able to understand that it is possible to easily transform it into other specific forms without changing the technical spirit or essential features of the present disclosure. will be. Therefore, it should be understood that the embodiments described above are illustrative and non-limiting in all respects. For example, each component described as a single type may be implemented in a distributed manner, and similarly, components described as being distributed may also be implemented in a combined form.
본 개시의 범위는 상기 상세한 설명보다는 후술하는 특허청구범위에 의하여 나타내어지며, 특허청구범위의 의미 및 범위 그리고 그 균등 개념으로부터 도출되는 모든 변경 또는 변형된 형태가 본 개시의 범위에 포함되는 것으로 해석되어야 한다.The scope of the present disclosure is indicated by the claims to be described later rather than the detailed description, and all changes or modified forms derived from the meaning and scope of the claims and their equivalent concepts should be interpreted as being included in the scope of the present disclosure. do.
Claims (20)
Translated fromKorean복수 개의 속성(Attribute)들이 포함된 제 1 데이터 테이블(Data Table)에서 하나의 속성을 선택하고, 상기 선택된 속성인 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터(Data)를 입력 받는 단계;
상기 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들을 생성하는 단계;
상기 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들에 기초하여 상기 제 1 속성에 대응하는 속성 벡터를 생성하는 단계;
상기 복수 개의 속성들 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들을 생성하고, 상기 복수 개의 속성 벡터들에 기초하여 상기 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대응하는 제 1 테이블 벡터를 생성하는 단계; 및
상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 하나의 데이터인 제 1 데이터에 대한 제 1 임베딩 벡터, 상기 제 1 속성에 대한 제 1 속성 벡터 및 상기 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대한 제 1 테이블 벡터 중 하나를 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)의 대상으로 선택하고, 제 2 데이터 테이블과 맵핑을 수행하는 단계;를 포함하는, 데이터 분석 방법.
In the method for the data analysis device to analyze the data included in the database,
Selecting one attribute from a first data table including a plurality of attributes and receiving a plurality of data included in the first attribute, which is the selected attribute;
Generating a plurality of embedding vectors corresponding to each of the plurality of data;
Generating an attribute vector corresponding to the first attribute based on the plurality of embedding vectors;
Generating a plurality of attribute vectors corresponding to each of the plurality of attributes, and generating a first table vector corresponding to the first data table based on the plurality of attribute vectors; And
Cross-layer mapping of one of a first embedding vector for first data, which is one data included in the first attribute, a first attribute vector for the first attribute, and a first table vector for the first data table ( Cross Layer Mapping) and performing mapping with the second data table; including, data analysis method.
상기 제 2 데이터 테이블은 제 2 속성 및 제 2 속성에 포함된 제 2 데이터를 포함하되,
상기 제 2 데이터 테이블에 대해 생성된 제 2 테이블 벡터, 상기 제 2 속성에 대해 생성된 제 2 속성 벡터 및 상기 제 2 데이터에 대해 생성된 제 2 임베딩 벡터 중 적어도 하나와 상기 선택된 크로스 레이어 맵핑 대상과의 유사 값을 판단하고, 상기 유사 값이 임계 값 이상이면 서로 맵핑하는, 데이터 분석 방법.
The method of claim 1,
The second data table includes a second attribute and second data included in the second attribute,
At least one of a second table vector generated for the second data table, a second attribute vector generated for the second attribute, and a second embedding vector generated for the second data, and the selected cross-layer mapping target; And determining a similarity value of and mapping each other if the similarity value is greater than or equal to a threshold value.
상기 제 1 임베딩 벡터를 생성하는 경우,
상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 생성하고, 상기 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 사용하여 상기 제 1 임베딩 벡터의 값을 예측하는, 데이터 분석 방법.
The method of claim 1,
When generating the first embedding vector,
A data analysis method of generating a plurality of initialization vectors corresponding to each of a plurality of data included in the first attribute, and predicting a value of the first embedding vector using the plurality of initialization vectors.
상기 복수 개의 데이터 각각의 유형을 판단하여 상기 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 생성하는, 데이터 분석 방법.
The method of claim 3,
The data analysis method of determining the type of each of the plurality of data to generate the plurality of initialization vectors.
하나의 데이터에 대해 판단된 데이터 유형이 텍스트인 경우,
상기 하나의 데이터에 포함된 단어 각각에 대해 기 학습된 워드 임베딩 벡터를 할당하고, 상기 워드 임베딩 벡터에 기초하여 상기 하나의 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터를 생성하는, 데이터 분석 방법.
The method of claim 4,
If the data type determined for one piece of data is text,
Allocating a pre-learned word embedding vector for each word included in the one data, and generating an initialization vector corresponding to the one data based on the word embedding vector.
하나의 데이터에 대해 판단된 데이터 유형이 텍스트가 아닌 경우, 랜덤한 벡터 값을 상기 하나의 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터로 결정하는, 데이터 분석 방법.
The method of claim 4,
When a data type determined for one piece of data is not text, a random vector value is determined as an initialization vector corresponding to the piece of data.
상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터를 기 설정된 정렬 기준에 따라 정렬하고, 정렬된 순서를 고려하여 기 설정된 개수의 데이터를 선택하고,
상기 선택된 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터를 이용하여 상기 제 1 임베딩 벡터의 값을 예측하고, 상기 제 1 임베딩 벡터를 생성하는, 데이터 분석 방법.
The method of claim 3,
Sorting a plurality of data included in the first attribute according to a preset sorting criterion, selecting a preset number of data in consideration of the sorted order,
Predicting a value of the first embedding vector using an initialization vector corresponding to the selected data, and generating the first embedding vector.
상기 기 설정된 기준에 따를 때, 상기 선택된 데이터는 상기 제 1 데이터에 앞서 연속적으로 선 정렬된 한 개 이상의 데이터인, 데이터 분석 방법.
The method of claim 7,
When conforming to the preset criterion, the selected data is one or more pieces of data that are continuously line-aligned prior to the first data.
상기 제 1 속성 벡터는 상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들의 합산 값 또는 평균 값에 기초하여 생성되는, 데이터 분석 방법.
The method of claim 1,
The first attribute vector is generated based on a sum value or an average value of a plurality of embedding vectors corresponding to each of a plurality of data included in the first attribute.
상기 제 1 테이블 벡터는 상기 제 1 테이블 벡터에 포함된 복수 개의 속성 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들의 합산 값 또는 평균 값에 기초하여 생성되는, 데이터 분석 방법.
The method of claim 1,
The first table vector is generated based on a sum value or an average value of a plurality of attribute vectors corresponding to each of a plurality of attributes included in the first table vector.
복수 개의 속성(Attribute)들이 포함된 제 1 데이터 테이블(Data Table)에서 하나의 속성을 선택하고, 상기 선택된 속성인 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터(Data)를 입력 받는 입력부;
상기 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들을 생성하는 임베딩 벡터 생성부;
상기 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들에 기초하여 상기 제 1 속성에 대응하는 속성 벡터를 생성하는 속성 벡터 생성부;
상기 복수 개의 속성들 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들을 생성하고, 상기 복수 개의 속성 벡터들에 기초하여 상기 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대응하는 제 1 테이블 벡터를 생성하는 테이블 벡터 생성부; 및
상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 하나의 데이터인 제 1 데이터에 대한 제 1 임베딩 벡터, 상기 제 1 속성에 대한 제 1 속성 벡터 및 상기 제 1 데이터 테이블에 대한 제 1 테이블 벡터 중 하나를 크로스 레이어 맵핑(Cross Layer Mapping)의 대상으로 선택하고, 제 2 데이터 테이블과 맵핑을 수행하는 크로스 레이어 맵핑부;를 포함하는, 데이터 분석 장치.
In a data analysis device for analyzing data included in a database,
An input unit that selects one attribute from a first data table including a plurality of attributes and receives a plurality of data included in the first attribute, which is the selected attribute;
An embedding vector generator generating a plurality of embedding vectors corresponding to each of the plurality of data;
An attribute vector generator configured to generate an attribute vector corresponding to the first attribute based on the plurality of embedding vectors;
A table vector generator configured to generate a plurality of attribute vectors corresponding to each of the plurality of attribute vectors, and to generate a first table vector corresponding to the first data table based on the plurality of attribute vectors; And
Cross-layer mapping of one of a first embedding vector for first data, which is one data included in the first attribute, a first attribute vector for the first attribute, and a first table vector for the first data table ( A cross-layer mapping unit that selects as a target of (Cross Layer Mapping) and performs mapping with the second data table.
상기 제 2 데이터 테이블은 제 2 속성 및 제 2 속성에 포함된 제 2 데이터를 포함하되,
상기 크로스 레이어 맵핑부는 상기 제 2 데이터 테이블에 대해 생성된 제 2 테이블 벡터, 상기 제 2 속성에 대해 생성된 제 2 속성 벡터 및 상기 제 2 데이터에 대해 생성된 제 2 임베딩 벡터 중 적어도 하나와 상기 선택된 크로스 레이어 맵핑 대상과의 유사 값을 판단하고, 상기 유사 값이 임계 값 이상이면 서로 맵핑하는, 데이터 분석 장치.
The method of claim 11,
The second data table includes a second attribute and second data included in the second attribute,
The cross-layer mapping unit includes at least one of a second table vector generated for the second data table, a second attribute vector generated for the second attribute, and a second embedding vector generated for the second data, and the selected A data analysis device that determines a similarity value with a cross-layer mapping target and maps each other when the similarity value is greater than or equal to a threshold value.
상기 임베딩 벡터 생성부가 상기 제 1 임베딩 벡터를 생성하는 경우,
상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 생성하고, 상기 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 사용하여 상기 제 1 임베딩 벡터의 값을 예측하는, 데이터 분석 장치.
The method of claim 11,
When the embedding vector generator generates the first embedding vector,
A data analysis apparatus for generating a plurality of initialization vectors corresponding to each of a plurality of data included in the first attribute, and predicting a value of the first embedding vector using the plurality of initialization vectors.
상기 임베딩 벡터 생성부는 상기 복수 개의 데이터 각각의 유형을 판단하여 상기 복수 개의 초기화 벡터들을 생성하는, 데이터 분석 장치.
The method of claim 13,
The embedding vector generator determines the type of each of the plurality of data to generate the plurality of initialization vectors.
하나의 데이터에 대해 판단된 데이터 유형이 텍스트인 경우,
상기 임베딩 벡터 생성부는 상기 하나의 데이터에 포함된 단어 각각에 대해 기 학습된 워드 임베딩 벡터를 할당하고, 상기 워드 임베딩 벡터에 기초하여 상기 하나의 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터를 생성하는, 데이터 분석 장치.
The method of claim 14,
If the data type determined for one piece of data is text,
The embedding vector generation unit allocates a pre-learned word embedding vector for each word included in the one data, and generates an initialization vector corresponding to the one data based on the word embedding vector.
하나의 데이터에 대해 판단된 데이터 유형이 텍스트가 아닌 경우, 상기 임베딩 벡터 생성부는 랜덤한 벡터 값을 상기 하나의 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터로 결정하는, 데이터 분석 장치.
The method of claim 14,
When the data type determined for one piece of data is not text, the embedding vector generator determines a random vector value as an initialization vector corresponding to the piece of data.
상기 임베딩 벡터 생성부는 상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터를 기 설정된 정렬 기준에 따라 정렬하고, 정렬된 순서를 고려하여 기 설정된 개수의 데이터를 선택하고,
상기 임베딩 벡터 생성부는 상기 선택된 데이터에 대응하는 초기화 벡터를 이용하여 상기 제 1 임베딩 벡터의 값을 예측하고, 상기 제 1 임베딩 벡터를 생성하는, 데이터 분석 장치.
The method of claim 13,
The embedding vector generator sorts a plurality of data included in the first attribute according to a preset sorting criterion, and selects a preset number of data in consideration of the sorted order,
The embedding vector generation unit predicts a value of the first embedding vector using an initialization vector corresponding to the selected data and generates the first embedding vector.
상기 기 설정된 기준에 따를 때, 상기 선택된 데이터는 상기 제 1 데이터에 앞서 연속적으로 선 정렬된 한 개 이상의 데이터인, 데이터 분석 장치.
The method of claim 17,
When conforming to the preset criterion, the selected data is one or more pieces of data that are continuously line-aligned prior to the first data.
상기 제 1 속성 벡터는 상기 제 1 속성에 포함된 복수 개의 데이터 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 임베딩 벡터들의 합산 값 또는 평균 값에 기초하여 생성되는, 데이터 분석 장치.
The method of claim 11,
The first attribute vector is generated based on a sum value or an average value of a plurality of embedding vectors corresponding to each of a plurality of data included in the first attribute.
상기 제 1 테이블 벡터는 상기 제 1 테이블 벡터에 포함된 복수 개의 속성 각각에 대응하는 복수 개의 속성 벡터들의 합산 값 또는 평균 값에 기초하여 생성되는, 데이터 분석 장치.The method of claim 11,
The first table vector is generated based on a sum value or an average value of a plurality of attribute vectors corresponding to each of a plurality of attributes included in the first table vector.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190130253AKR102755297B1 (en) | 2019-10-18 | 2019-10-18 | Apparatus and method for analyzing data contained in the database |
| PCT/KR2020/013752WO2021075793A1 (en) | 2019-10-18 | 2020-10-08 | Data analysis device and method for analyzing data included in database |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190130253AKR102755297B1 (en) | 2019-10-18 | 2019-10-18 | Apparatus and method for analyzing data contained in the database |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20210046487Atrue KR20210046487A (en) | 2021-04-28 |
| KR102755297B1 KR102755297B1 (en) | 2025-01-17 |
Family
ID=75537898
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190130253AActiveKR102755297B1 (en) | 2019-10-18 | 2019-10-18 | Apparatus and method for analyzing data contained in the database |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102755297B1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2021075793A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114185879B (en)* | 2021-11-16 | 2025-03-25 | 中国银行保险信息技术管理有限公司 | Heterogeneous data mapping method, device and equipment based on machine learning algorithm |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20160123801A (en)* | 2015-04-17 | 2016-10-26 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Reference satellite database generating system by using mapping tables |
| KR20190038240A (en)* | 2017-09-28 | 2019-04-08 | 한국과학기술원 | System and method for embedding named-entity |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20150042866A (en)* | 2008-12-02 | 2015-04-21 | 아브 이니티오 테크놀로지 엘엘시 | Mapping instances of a dataset within a data management system |
| KR101170969B1 (en)* | 2011-09-20 | 2012-08-06 | 주식회사 월드비즈넷 | Data mapping method on sharing data base and data mapping system thereof |
| US11361242B2 (en)* | 2016-10-28 | 2022-06-14 | Meta Platforms, Inc. | Generating recommendations using a deep-learning model |
- 2019
- 2019-10-18KRKR1020190130253Apatent/KR102755297B1/enactiveActive
- 2020
- 2020-10-08WOPCT/KR2020/013752patent/WO2021075793A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20160123801A (en)* | 2015-04-17 | 2016-10-26 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Reference satellite database generating system by using mapping tables |
| KR20190038240A (en)* | 2017-09-28 | 2019-04-08 | 한국과학기술원 | System and method for embedding named-entity |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR102755297B1 (en) | 2025-01-17 |
| WO2021075793A1 (en) | 2021-04-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US12265538B2 (en) | Schema-adaptable data enrichment and retrieval | |
| US10467234B2 (en) | Differentially private database queries involving rank statistics | |
| CN109240901B (en) | Performance analysis method, performance analysis device, storage medium, and electronic apparatus | |
| US10235425B2 (en) | Entity fingerprints | |
| CA2998839C (en) | Differentially private processing and database storage | |
| Maleki et al. | A comprehensive literature review of the rank reversal phenomenon in the analytic hierarchy process | |
| US10289615B2 (en) | Natural language query resolution for high dimensionality data | |
| US11599826B2 (en) | Knowledge aided feature engineering | |
| JP2021510858A (en) | Relevance calculation method, relevance calculation device, data query device and non-temporary computer-readable recording medium | |
| CN108021984A (en) | Method and system for determining feature importance of machine learning samples | |
| US20180196871A1 (en) | System and method for metadata correlation using natural language processing | |
| US12353477B2 (en) | Providing an object-based response to a natural language query | |
| US11023481B2 (en) | Navigation platform for performing search queries | |
| WO2019129520A1 (en) | Systems and methods for combining data analyses | |
| US11593700B1 (en) | Network-accessible service for exploration of machine learning models and results | |
| CN114253990A (en) | Database query method, apparatus, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| CA3020921A1 (en) | Query optimizer for combined structured and unstructured data records | |
| CN107729915A (en) | Method and system for determining important features of machine learning samples | |
| US20220238193A1 (en) | Methods and systems for managing patient-centric information | |
| CN109800147A (en) | A kind of test cases generation method and terminal device | |
| CN114780648A (en) | Task scheduling method, device, computer equipment, storage medium and program product | |
| US10867249B1 (en) | Method for deriving variable importance on case level for predictive modeling techniques | |
| CN115883172A (en) | Anomaly monitoring method and device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| KR102755297B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for analyzing data contained in the database | |
| Schepers et al. | TwoMP: A MATLAB graphical user interface for two-mode partitioning |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20191018 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0201 | Request for examination | Patent event code:PA02012R01D Patent event date:20221018 Comment text:Request for Examination of Application Patent event code:PA02011R01I Patent event date:20191018 Comment text:Patent Application | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20241216 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration |