KR20200070776A - Method and apparatus for generating block in blockchain system - Google Patents
Method and apparatus for generating block in blockchain systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20200070776A KR20200070776AKR1020180158287AKR20180158287AKR20200070776AKR 20200070776 AKR20200070776 AKR 20200070776AKR 1020180158287 AKR1020180158287 AKR 1020180158287AKR 20180158287 AKR20180158287 AKR 20180158287AKR 20200070776 AKR20200070776 AKR 20200070776A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- block
- consensus
- chain
- general
- nodes
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/01—Protocols
- H04L67/10—Protocols in which an application is distributed across nodes in the network
- H04L67/104—Peer-to-peer [P2P] networks
- H04L67/1044—Group management mechanisms
- H04L67/1046—Joining mechanisms
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/12—Applying verification of the received information
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/01—Protocols
- H04L67/10—Protocols in which an application is distributed across nodes in the network
- H04L67/104—Peer-to-peer [P2P] networks
- H04L67/1044—Group management mechanisms
- H04L67/1053—Group management mechanisms with pre-configuration of logical or physical connections with a determined number of other peers
- H04L67/1057—Group management mechanisms with pre-configuration of logical or physical connections with a determined number of other peers involving pre-assessment of levels of reputation of peers
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Financial Or Insurance-Related Operations Such As Payment And Settlement (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법 및 장치에 관한 것으로, 특히 블록체인 시스템에서 대표자들의 비정상 행위를 방지하고 블록에 저장된 데이터의 완결성을 강화할 수 있는 블록 생성 방법 및 장치에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a block generation method and apparatus of a blockchain system, and more particularly, to a block generation method and apparatus that can prevent abnormal behavior of representatives in the blockchain system and enhance the integrity of data stored in the block.
블록체인은 참여노드의 구성에 따라 퍼블릭(public) 블록체인과 프라이빗(private) 블록체인, 컨소시움(consortium) 블록체인으로 나뉜다. 퍼블릭 블록체인은 익명의 노드(anonymous node)가 자유롭게 참여할 수 있으며 관리자 개념이 없이 참여자 모두가 동등한 권한을 갖는 P2P(Peer-to-Peer) 네트워크로 구성된다. 프라이빗 블록체인은 사전에 인증된 노드(authenticated node)만 참여가 가능하며 노드 별로 관리자(supervisor), 참여자(participant)와 같은 서로 다른 권한(authority)을 가질 수 있다. 컨소시움 블록체인은 프라이빗 블록체인과 마찬가지로 사전에 승인된 노드만 참여가 가능하지만 퍼블릭 블록체인과 같이 참여노드 간 동등한 권한을 갖는 특징이 있다.Blockchains are divided into public blockchains, private blockchains, and consortium blockchains according to the composition of the participating nodes. The public blockchain is composed of a peer-to-peer (P2P) network where anonymous nodes can participate freely and all participants have equal authority without the concept of an administrator. Private blockchains can only participate in authenticated nodes in advance, and can have different authorities, such as supervisors and participants, for each node. Like the private blockchain, the consortium blockchain can only participate in pre-approved nodes, but like the public blockchain, it has the feature of having equal authority between participating nodes.
퍼블릭 블록체인은 참여노드가 유동적으로 변화하기 때문에 전체 합의가 불가능하여 작업증명(PoW: Proof-of-Work) 및 지분증명(PoS: Proof-of-Stake)의 방식으로 블록생성을 위한 대표자(representative)를 선출하고 선출된 대표자는 블록을 생성하여 다른 참여노드에게 전파한다. 하지만 이러한 작업은 참여노드 간 비동기로 진행되어 다수의 대표자가 동시에 선출되거나 생성된 블록의 전파 시 네트워크 지연 등으로 인해 블록체인의 분기(fork)가 발생한다. 발생한 분기를 하나의 체인으로 유지하기 위해 비트코인(Bitcoin)을 비롯한 대다수의 퍼블릭 블록체인 응용에서 최장 체인 법칙(longest chain rule)를 적용하여 분기 중 가장 긴 블록체인을 참여노드가 채택하고 채택된 체인에 저장된 트랜잭션(Tx, transaction)만이 데이터의 비가역성을 확률적으로 보장 받게 된다. Nakamoto에 따르면 하나의 거래가 블록에 포함되어 그 뒤로 5개의 블록이 이어진 6-컨펌(six-confirm)을 받을 경우에 해커의 컴퓨팅 파워가 전체 네트워크의 10%를 차지하는 경우로 가정하더라도 해킹으로 인해 거래가 변경될 확률이 0.1% 미만이 되어 비가역성을 보장함을 밝히고 있다. 하지만 이는 블록 데이터의 완전한 비가역성을 보장하지 않는다. 만약 이를 해결하기 위해 N번의 컨펌 이후 블록의 데이터를 바꿀 수 없는 규칙을 넣는다면, N-컨펌을 가진 분기된 체인(branch)이 2개 발생하여 longest chain rule에 의해 선택되는 상황에서 이를 처리할 수 없는 예외가 발생하게 된다. N의 크기를 조절하여 이러한 문제를 해결하고자 하여 N의 크기를 크게 하면 완결성 보장의 의미가 작아지고 N이 작으면 예외상황은 더 많이 발생할 수 있다. N의 수의 관계없이 블록길이가 N 보다 큰 분기된 체인이 생성될 확률은 '0'에 가까울 순 있어도 '0'이 아니기 때문에 N 컨펌 이후 블록의 수정을 제한하는 완결성 제공방식은 블록체인 시스템을 교착상태(deadlock)가 존재하는 시스템으로 만든다. 따라서 참여노드를 제어할 수 없는 퍼블릭 블록체인에서는 대부분 데이터의 완결성을 제공하지 않는다. 하지만 그럼에도 퍼블릭 블록체인에서 데이터 완결성에 대한 문제는 거의 일어나지 않는다. 그 이유는 작업증명을 통한 합의방법으로 악의적인 사용자가 블록체인 네트워크 내에 큰 지분의 컴퓨팅 파워를 확보하여도 지난 블록을 변경하여 재생성하는 것이 현실적으로 어렵게 설계되었다. 또한 퍼블릭 블록체인의 특성으로 인해 악의적인 사용자 또는 그룹이 블록체인 내 높은 컴퓨팅 파워를 확보하려면 많은 비용이 들기 때문에 공격비용 대비 얻을 수 있는 이득이 많지 않은 경제적 이유로 이와 같은 공격 시도를 하지 않는다.Public blockchains cannot be fully agreed because the participating nodes change dynamically, so they are representatives for block creation in the manner of Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS). ) Is elected and the elected representative creates a block and spreads it to other participating nodes. However, these tasks are performed asynchronously between the participating nodes, and a fork of the blockchain occurs due to network delays when multiple representatives are simultaneously elected or propagated the generated blocks. The longest chain rule of the branch is adopted and adopted by the participating node by applying the longest chain rule in most public blockchain applications including Bitcoin to keep the branch that occurred as one chain. Only the transactions stored in (Tx, transaction) are guaranteed to be irreversible. According to Nakamoto, even if a hacker's computing power occupies 10% of the entire network when one transaction is included in a block and receives a six-confirm followed by five blocks, the transaction changes due to hacking It is revealed that the probability of becoming less than 0.1% guarantees irreversibility. However, this does not guarantee complete irreversibility of the block data. To solve this, if you put a rule that cannot change the data of a block after N confirmations, two branched chains with N-confirmation occur and can be handled in the situation selected by the longest chain rule. There will be no exception. In order to solve this problem by adjusting the size of N, if the size of N is increased, the meaning of guarantee of completeness decreases, and when N is small, an exception may occur more. The probability of creating a branched chain with a block length greater than N, regardless of the number of N, is not '0' even though it may be close to '0'. Make a deadlock system. Therefore, most public blockchains that cannot control the participating nodes do not provide completeness of data. However, the problem of data integrity in public blockchains rarely occurs. The reason is that it is realistically difficult to regenerate and change the last block even if a malicious user secures a large stake of computing power in the blockchain network through a consensus method through proof of work. In addition, due to the nature of the public blockchain, malicious users or groups do not attempt such an attack for economic reasons because there is not much gain to gain from the attack cost because it costs a lot to secure high computing power in the blockchain.
프라이빗 블록체인과 컨소시움 블록체인에서는 전체 참여노드를 사전에 설정하여 네트워크 관리자 또는 참여자들이 서로 정보를 공유 할 수 있으므로 참여노드의 전체 합의가 가능하여 블록의 완결성을 보장할 수 있다. 프라이빗/컨소시움 블록체인에서 일반적으로 쓰이는 PBFT(Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance)의 경우, 전체 노드 합의를 위해서 모든 노드가 블록정보를 브로드캐스트를 하므로 네트워크 트래픽과 지연이 증가하고 서명에 따른 프로세스 오버헤드가 증가한다. 이는 데이터 처리속도 감소로 이어지기 때문에 데이터 처리속도를 보완하기 위해 제안된 DBFT(Delegated Byzantine Fault Tolerance) 합의방법은 대표자를 선정하여 블록을 생성하지만 이는 전체 합의된 블록이 아니므로 완결성을 보장한다고 보기 어렵다. 사전에 대표자 선정 시 일반 참여노드가 대표자에게 자신의 합의 권한을 위임하는 절차를 통하여 전체 합의의 법적의미는 보장할 수 있지만 기술적으로 전체노드가 블록을 확인하여 서명한 것이 아니기 때문에 기술적인 데이터 완결성을 갖지 못한다. 또한 프라이빗/컨소시움 블록체인에서는 승인된 노드 간에 BFT(Byzantine Fault Tolerance) 계열의 합의 방법을 사용하여 참여노드의 2/3 이상이 합의하면 블록이 생성되고 퍼블릭 블록체인 대비 참여 노드 수가 적어 비교적 시빌 공격(sybil attack)과 같은 사이버공격에 취약할 수 있다. 특히 대표자에 의한 BFT 합의 방법은 합의에 참여하는 노드수가 제한적이기 때문에 대표자들 간의 악의적 합의 또는 해커의 공격에 의해 비정상적 블록을 생성하거나 일반 참여노드에게 잘못된 블록 정보를 전달 수 있다. 또한 PBFT 방식의 합의를 통해 생성된 블록은 대표자 중 리더의 서명만으로 블록이 보호되고 있기 때문에 리더의 서명이 탈취 당할 경우, 기존 블록의 변조도 가능할 수 있다. 따라서, 블록의 완결성을 보장하며, 데이터 처리 속도를 유지하기 위한 대표자 합의 방식에서 대표자의 합의 결과를 감사(audit)할 수 있는 방법이 필요하다. 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 COINSTACK과 같은 일부 프라이빗 블록체인 플랫폼의 경우 앵커링(anchoring) 이라는 기법을 제안하였다. 앵커링은 프라이빗 블록체인에서 소수의 노드가 블록을 생성하면서 주기적으로 중간 해쉬값을 퍼블릭 블록체인에 트랜잭션으로 정보를 등록하여 기존 프라이빗 블록의 변조를 감지할 수 있도록 하는 것이다. 하지만 이러한 방법은 항상 퍼블릭 블록체인과 연결이 가능한 경우에 동작이 가능하다. 만약 폐쇄망에서 프라이빗/컨소시움 블록체인을 사용한다면 퍼블릭 블록체인과 연결이 가능한 제3의 관리자 또는 노드가 필요하게 된다. 또한 퍼블릭 블록체인에 정보를 등록하는 수수료가 주기적으로 발생하게 되는 단점이 있다.In the private blockchain and the consortium blockchain, all the participating nodes can be set in advance so that network managers or participants can share information with each other, so the entire agreement of the participating nodes is possible to ensure the completeness of the block. In the case of PBFT (Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance), which is commonly used in private/consortium blockchains, all nodes broadcast block information for consensus of all nodes, so network traffic and latency increase and process overhead due to signature increases . Since this leads to a decrease in data processing speed, the proposed method of DBFT (Delegated Byzantine Fault Tolerance) proposed to complement the data processing speed selects representatives to generate blocks, but it is difficult to guarantee completeness because it is not an entire agreed block. . When the representative is selected in advance, the legal meaning of the entire agreement can be guaranteed through the process by which the general participating node delegates his or her consensus authority to the representative, but technically the integrity of the technical data is not guaranteed because the entire node has not signed and signed the block. Do not have In addition, in the private/consortium blockchain, if more than two-thirds of the participating nodes agree by using the Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus method among the approved nodes, blocks are created and the number of participating nodes is relatively small compared to the public blockchain. sybil attack). In particular, since the number of nodes participating in the consensus is limited in the BFT consensus method by representatives, it is possible to create abnormal blocks or to transmit incorrect block information to general participating nodes due to malicious consensus among representatives or hacker attacks. In addition, since the block created through the agreement of the PBFT method is protected only by the leader's signature among the representatives, if the leader's signature is stolen, modification of the existing block may be possible. Therefore, there is a need for a method capable of auditing the result of a representative's agreement in a representative agreement method to ensure the integrity of the block and maintain the data processing speed. To solve this problem, some private blockchain platforms such as COINSTACK proposed an anchoring technique. Anchoring is to enable the detection of tampering with existing private blocks by periodically registering intermediate hash values as transactions in the public blockchain while a few nodes create blocks in the private blockchain. However, this method can always work when it is possible to connect to the public blockchain. If a private/consortium blockchain is used in a closed network, a third manager or node that can connect to the public blockchain is required. In addition, there is a disadvantage in that fees for registering information in the public blockchain occur periodically.
관련하여 한국공개특허 제2018-0014534호는 "블록체인 기반 트랜잭션 검증 시스템 및 그 방법"을 개시한다.In relation to this, Korean Patent Publication No. 2018-0014534 discloses a "blockchain based transaction verification system and method".
본 발명의 목적은 블록체인의 대표자 합의 방식에서 대표자의 행위를 감시하고, 데이터 완결성을 제공하여 블록에 저장된 데이터의 보안성을 높이는 것이다.The object of the present invention is to increase the security of data stored in a block by monitoring the behavior of the representative in the consensus agreement method of the blockchain and providing data integrity.
그리고, 본 발명의 목적은 대표자 노드로 블록을 생성하여 일반 PBFT(Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance) 대비 네트워크 트래픽을 줄이고 통신 지연을 줄임으로써 전체적인 처리 속도를 높이는 것이다.And, an object of the present invention is to increase the overall processing speed by reducing the network traffic and reducing communication delay compared to a general PBFT (Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance) by creating a block with a representative node.
또한, 본 발명의 목적은 대표자 노드 합의를 통해 합의 속도 및 트랜잭션 처리 속도를 유지하며 유연한 노드 확장이 가능한 기술을 제공하는 것이다.In addition, it is an object of the present invention to provide a technique capable of flexible node expansion while maintaining a consensus rate and transaction processing speed through consensus node consensus.
상기한 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법은 리더 노드에서 클라이언트 노드에서의 트랜잭션에 대응하여 제1 합의 블록을 생성하는 단계; 복수의 리플리카 노드에서 상기 제1 합의 블록을 검증하여, 상기 제1 합의 블록을 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계; 상기 체인에 일반체인 블록이 기 설정된 K 개가 추가될 때마다 상기 제1 합의 블록의 생성과 병렬적으로 상기 리더 노드에서 제2 합의 블록을 생성하는 단계; 및 복수의 일반 노드에서 상기 제2 합의 블록을 검증하여, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계를 포함한다.A block generation method of a blockchain system according to the present invention for achieving the above object includes generating a first consensus block in response to a transaction in a client node in a leader node; Verifying the first consensus block in a plurality of replica nodes, defining the first consensus block as a regular chain block and adding it to the chain; Generating a second consensus block in the leader node in parallel with the generation of the first consensus block whenever K pieces with a predetermined number of general chain blocks are added to the chain; And verifying the second consensus block in a plurality of general nodes, and defining the second consensus block as a definite chain block and adding it to the chain.
이 때, 상기 제1 합의 블록을 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계는, 상기 제1 합의 블록을 상기 리더 노드에서 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드로 전달하는 단계; 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드 각각이 상호간에 상기 리더 노드로부터 전달받은 상기 제1 합의 블록이 동일한지 검증하는 단계; 상기 검증하는 단계에서 기 설정된 특정 수치 이상의 동일성이 있는 것으로 판단되는 경우 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드 각각이 상기 제1 합의 블록을 체인에 추가하는 것에 대한 동의 여부를 확인하는 단계; 및 상기 동의 여부를 확인하는 단계에서 기 설정된 소정 수치 이상의 동의가 있는 경우 상기 제1 합의 블록을 상기 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.At this time, the step of defining the first consensus block as a general chain block and adding it to the chain includes: transferring the first consensus block from the leader node to the plurality of replica nodes; Verifying that each of the plurality of replica nodes is identical to the first consensus block received from the leader node to each other; Determining whether each of the plurality of replica nodes agrees to add the first consensus block to the chain when it is determined in the verifying step that there is more than a predetermined predetermined value; And when there is more than a predetermined predetermined value in the step of confirming whether to agree, defining the first consensus block as the general chain block and adding it to the chain.
이 때, 상기 리더 노드 및 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드는 블록체인 시스템에서 기 정의된 복수의 대표자 노드에 포함될 수 있다.At this time, the leader node and the plurality of replica nodes may be included in a plurality of representative nodes defined in the blockchain system.
이 때, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계는, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 상기 리더 노드에서 상기 복수의 일반 노드로 전달하는 단계; 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록을 서명으로 봉인하여 제2 합의검증 패킷으로 다른 일반 노드들에 전달하는 단계; 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각에서 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하는 단계; 및 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 상기 제2 합의 블록과 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는 경우, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 상기 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.At this time, the step of defining the second consensus block as a definite chain block and adding it to the chain includes: transferring the second consensus block from the leader node to the plurality of general nodes; Each of the plurality of general nodes sealing the second consensus block with a signature and transmitting the second consensus verification packet to other general nodes; Determining whether the identity of the second consensus block and the second consensus verification packet received from each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value; And when the identity of the second consensus block and the second consensus verification packet received by each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value, the second consensus block is defined as the confirmation chain block and added to the chain. It may include steps.
이 때, 상기 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하는 단계에서, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치 이하인 것으로 판단된 경우 상기 제2 합의 블록을 폐기하고, 상기 체인에 일반체인 블록이 K의 2배수가 추가되었을 때 상기 리더 노드에서 제2 합의 블록을 생성하는 단계와 상기 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계를 반복할 수 있다.At this time, in the step of determining whether the predetermined value exceeds the predetermined value, if it is determined that the plurality of general nodes each has the same identity between the second agreement block and the received second agreement verification packet, the predetermined value is lower than the predetermined value. Discarding the second consensus block, and when the normal chain block is added to the chain by a multiple of K, generating a second consensus block at the leader node and defining the second consensus block as a definite chain block to the chain. The steps to add can be repeated.
이 때, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 수가 기 설정된 특정 수치를 넘는지 판단하는 단계를 더 포함하며, 상기 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하는 단계는 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 수가 기 설정된 특정 수치를 넘는 경우 진행될 수 있다.At this time, the method further includes determining whether the number of the second consensus verification packets received by each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value, and determining whether the number of the second consensus verification packets exceeds a predetermined value. It may proceed when the number of the second consensus verification packets received by each of the general nodes exceeds a predetermined value.
이 때, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록을 서명으로 봉인하여 제2 합의검증 패킷으로 다른 일반 노드들에 전달하는 단계는, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록, 상기 체인에 추가된 일반체인 블록 및 상기 제2 합의 블록의 번호 중 적어도 하나를 검증한 검증 결과를 상기 제2 합의 블록과 함께 서명으로 봉인할 수 있다.At this time, each of the plurality of normal nodes sealing the second agreement block with a signature and transmitting the second agreement block to other general nodes as a second agreement verification packet includes: each of the plurality of normal nodes is the second agreement block, the The verification result verifying at least one of the general chain block added to the chain and the number of the second consensus block may be sealed with a signature together with the second consensus block.
또한, 상기한 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 장치는 리더 노드에서 클라이언트 노드에서의 트랜잭션에 대응하여 제1 합의 블록을 생성하도록 제어하는 제1 합의 블록 생성부; 복수의 리플리카 노드에서 상기 제1 합의 블록을 검증하여, 상기 제1 합의 블록을 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어하는 일반체인 블록 추가부; 상기 체인에 일반체인 블록이 기 설정된 K 개가 추가될 때마다 상기 제1 합의 블록의 생성과 병렬적으로 상기 리더 노드에서 제2 합의 블록을 생성하도록 제어하는 제2 합의 블록 생성부; 및 복수의 일반 노드에서 상기 제2 합의 블록을 검증하여, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어하는 확정체인 블록 추가부를 포함한다.In addition, the block generating apparatus of the blockchain system according to the present invention for achieving the above object is a first consensus block generator for controlling a leader node to generate a first consensus block in response to a transaction in a client node; A general chain block adding unit that verifies the first consensus block from a plurality of replica nodes and controls the first consensus block to be added to the chain by defining it as a general chain block; A second consensus block generator configured to control the leader node to generate a second consensus block in parallel with the generation of the first consensus block whenever K pieces with a predetermined number of general chain blocks are added to the chain; And a confirmation chain block adding unit for verifying the second agreement block in a plurality of general nodes and controlling the second agreement block to be added to the chain by defining it as a confirmation chain block.
이 때, 상기 일반체인 블록 추가부는, 상기 제1 합의 블록을 상기 리더 노드에서 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드로 전달하도록 제어하고, 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드 각각이 상호간에 상기 리더 노드로부터 전달받은 상기 제1 합의 블록이 동일한지 검증하도록 제어하며, 기 설정된 특정 수치 이상의 동일성이 있는 것으로 판단되는 경우 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드 각각이 상기 제1 합의 블록을 체인에 추가하는 것에 대한 동의 여부를 확인하도록 제어하고, 기 설정된 소정 수치 이상의 동의가 있는 경우 상기 제1 합의 블록을 상기 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어할 수 있다.At this time, the general chain block adding unit controls the first consensus block to be transferred from the leader node to the plurality of replica nodes, and each of the plurality of replica nodes receives each other from the leader node. 1 Controls to verify whether the consensus block is the same, and if it is determined that there is an identity equal to or greater than a predetermined number, each of the plurality of replica nodes is controlled to confirm whether or not to agree to add the first consensus block to the chain. , If there is an agreement of a predetermined number or more, the first consensus block may be defined as the general chain block and controlled to be added to the chain.
이 때, 상기 리더 노드 및 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드는 블록체인 시스템에서 기 정의된 복수의 대표자 노드에 포함될 수 있다.At this time, the leader node and the plurality of replica nodes may be included in a plurality of representative nodes defined in the blockchain system.
이 때, 상기 확정체인 블록 추가부는, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 상기 리더 노드에서 상기 복수의 일반 노드로 전달하도록 제어하고, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록을 서명으로 봉인하여 제2 합의검증 패킷으로 다른 일반 노드들에 전달하도록 제어하며, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각에서 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하도록 제어하고, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 상기 제2 합의 블록과 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는 경우, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 상기 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어할 수 있다.At this time, the definite chain block adding unit controls the second consensus block to be delivered from the leader node to the plurality of general nodes, and each of the plurality of general nodes seals the second consensus block with a signature, thereby providing a second It is controlled to transmit to other general nodes as a consensus verification packet, and controls to determine whether the identity of the second consensus block and the second consensus verification packet received from each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value, When the identity of the second consensus block and the second consensus verification packet received by each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value, the second consensus block is defined as the confirmation chain block and controlled to be added to the chain can do.
이 때, 상기 확정체인 블록 추가부는, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치 이하인 것으로 판단된 경우 상기 제2 합의 블록을 폐기하고, 상기 체인에 일반체인 블록이 K의 2배수가 추가되었을 때 상기 리더 노드에서 제2 합의 블록을 생성하도록 제어하고, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어할 수 있다.At this time, the block of the confirmation chain, the second consensus block is discarded when it is determined that each of the plurality of general nodes has the same identity between the second consensus block and the received second consensus verification packet as below a predetermined value. And, when the general chain block is added to the chain by a multiple of K, the leader node controls to generate a second consensus block, and the second consensus block is defined as a definite chain block to be added to the chain. have.
이 때, 상기 확정체인 블록 추가부는, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 수가 기 설정된 특정 수치를 넘는 경우, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하도록 제어할 수 있다.In this case, when the number of the second consensus verification packets received by each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value, the block addition unit of the confirmation chain receives each of the plurality of general nodes with the second consensus block. It can be controlled to determine whether the identity of the second consensus verification packet exceeds a predetermined value.
이 때, 상기 확정체인 블록 추가부는, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록, 상기 체인에 추가된 일반체인 블록 및 상기 제2 합의 블록의 번호 중 적어도 하나를 검증한 검증 결과를 상기 제2 합의 블록과 함께 서명으로 봉인하여 제2 합의검증 패킷으로 다른 일반 노드들에 전달하도록 제어할 수 있다.At this time, the definite chain block adding unit may include a verification result in which each of the plurality of general nodes verifies at least one of the second consensus block, the general chain block added to the chain, and the number of the second consensus block. It can be sealed to be signed with the 2 consensus block and transmitted to other general nodes as a second consensus verification packet.
본 발명에 따르면, 블록체인의 대표자 합의 방식에서 대표자의 행위를 감시하고, 데이터 완결성을 제공하여 블록에 저장된 데이터의 보안성을 높일 수 있다.According to the present invention, it is possible to increase the security of data stored in a block by monitoring the behavior of the representative and providing data integrity in a representative agreement method of the blockchain.
그리고, 본 발명은 대표자 노드로 블록을 생성하여 일반 PBFT(Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance) 대비 네트워크 트래픽을 줄이고 통신 지연을 줄임으로써 전체적인 처리 속도를 높일 수 있다.In addition, the present invention can increase the overall processing speed by reducing the network traffic and reducing the communication delay compared to a general PBFT (Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance) by creating a block as a representative node.
또한, 본 발명은 대표자 노드 합의를 통해 합의 속도 및 트랜잭션 처리 속도를 유지하며 유연한 노드 확장이 가능하다.In addition, the present invention maintains the consensus rate and transaction processing speed through consensus node agreement, and enables flexible node expansion.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법을 나타낸 동작흐름도이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 장치를 나타낸 블록도이다.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 기술에 있어서 체인 즉, 일반 체인 및 확정 체인의 특징을 설명하기 표이다.
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법에 있어서 일반체인 블록을 체인에 추가하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법에 있어서 일반체인 블록과 확정체인 블록의 생성 관계를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법에 있어서 확정체인 블록을 체인에 추가하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.1 is an operation flow diagram showing a block generation method of a blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a block diagram showing a block generation device of a blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
3 is a table for explaining the characteristics of a chain, that is, a general chain and a definite chain in the block generation technology of the blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
4 is a view for explaining a method of adding a general chain block to the chain in the block generation method of the blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
5 is a view for explaining the relationship between the normal chain block and the definite chain block in the block generation method of the blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
6 is a view for explaining a method of adding a definite chain block to a chain in a block generation method of a blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명을 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 상세히 설명하면 다음과 같다. 여기서, 반복되는 설명, 본 발명의 요지를 불필요하게 흐릴 수 있는 공지 기능, 및 구성에 대한 상세한 설명은 생략한다. 본 발명의 실시형태는 당 업계에서 평균적인 지식을 가진 자에게 본 발명을 보다 완전하게 설명하기 위해서 제공되는 것이다. 따라서, 도면에서의 요소들의 형상 및 크기 등은 보다 명확한 설명을 위해 과장될 수 있다.If described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings the present invention. Here, repeated descriptions, well-known functions that may unnecessarily obscure the subject matter of the present invention, and detailed description of the configuration will be omitted. Embodiments of the present invention are provided to more fully describe the present invention to those skilled in the art. Therefore, the shape and size of elements in the drawings may be exaggerated for a more clear description.
이하, 본 발명에 따른 바람직한 실시예를 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 상세하게 설명한다.Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법을 나타낸 동작흐름도이다.1 is an operation flow diagram showing a block generation method of a blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 1을 참조하면, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법은 먼저, 리더 노드에서 클라이언트 노드에서의 트랜잭션에 대응하여 제1 합의 블록을 생성한다(S110).Referring to FIG. 1, in a block generation method of a blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention, first, a first consensus block is generated in a leader node in response to a transaction in a client node (S110 ).
이 후 복수의 리플리카 노드에서 상기 제1 합의 블록을 검증하여, 제1 합의 블록을 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가한다(S120). 이 때, S120 단계는 보다 구체적으로 제1 합의 블록을 상기 리더 노드에서 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드로 전달하는 단계, 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드 각각이 상호간에 상기 리더 노드로부터 전달받은 상기 제1 합의 블록이 동일한지 검증하는 단계, 상기 검증하는 단계에서 기 설정된 특정 수치 이상의 동일성이 있는 것으로 판단되는 경우 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드 각각이 상기 제1 합의 블록을 체인에 추가하는 것에 대한 동의 여부를 확인하는 단계 및 상기 동의 여부를 확인하는 단계에서 기 설정된 소정 수치 이상의 동의가 있는 경우 상기 제1 합의 블록을 상기 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다. 이 때, 리더 노드 및 복수의 리플리카 노드는 블록체인 시스템에서 기 정의된 복수의 대표자 노드에 포함된 노드일 수 있다.Thereafter, the first consensus block is verified by a plurality of replica nodes, and the first consensus block is defined as a general chain block and added to the chain (S120). At this time, step S120 is more specifically, the step of delivering a first consensus block from the leader node to the plurality of replica nodes, each of the plurality of replica nodes is the first consensus block received from the leader node to each other Verifying whether this is the same, if it is determined that there is an identity equal to or greater than a predetermined value set in the verifying step, confirming whether or not each of the plurality of replica nodes agrees to add the first consensus block to the chain. And when there is more than a predetermined predetermined value in the step of confirming whether to agree, defining the first consensus block as the general chain block and adding it to the chain. At this time, the leader node and the plurality of replica nodes may be nodes included in a plurality of representative nodes defined in the blockchain system.
상기 체인에 일반체인 블록이 기 설정된 K 개가 추가될 때마다 상기 제1 합의 블록의 생성과 병렬적으로 상기 리더 노드에서 제2 합의 블록을 생성한다(S130).Whenever K pieces with a predetermined number of general chain blocks are added to the chain, a second consensus block is generated at the leader node in parallel with the generation of the first consensus block (S130).
이 후 복수의 일반 노드에서 상기 제2 합의 블록을 검증하여, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가한다(S140). 이러한 S140 단계는 보다 구체적으로 제2 합의 블록을 리더 노드에서 복수의 일반 노드로 전달하는 단계, 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 제2 합의 블록을 서명으로 봉인하여 제2 합의검증 패킷으로 다른 일반 노드들에 전달하는 단계, 복수의 일반 노드 각각에서 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하는 단계 및 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 제2 합의 블록과 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는 경우, 제2 합의 블록을 상기 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.Thereafter, the second consensus block is verified by a plurality of general nodes, and the second consensus block is defined as a definite chain block and added to the chain (S140). In step S140, more specifically, the second consensus block is transferred from the leader node to a plurality of general nodes, and each of the plurality of general nodes seals the second consensus block with a signature to other general nodes with a second consensus verification packet. Transmitting, determining whether the identity of the second consensus block and the received second consensus verification packet at each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value, and the second consensus block received by each of the plurality of general nodes. 2 If the identity of the consensus verification packet exceeds a predetermined value, a second consensus block may be defined as the confirmation chain block and added to the chain.
그리고 S140 단계의 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하는 단계에서, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치 이하인 것으로 판단된 경우 상기 제2 합의 블록을 폐기한다. 이 후 체인에 일반체인 블록이 K의 2배수가 추가되었을 때 S130 단계 및 S140 단계를 다시 시작할 수 있다.And in the step of determining whether the predetermined value exceeds the predetermined value in step S140, if it is determined that the identity of the second agreement block and the second agreement verification packet received by each of the plurality of general nodes is equal to or less than a predetermined value Discard the second consensus block. After this, when the normal chain block is added twice as many as K to the chain, steps S130 and S140 may be restarted.
또한, S140 단계는 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 수가 기 설정된 특정 수치를 넘는지 판단하는 단계를 더 포함하여 진행될 수 있다. 그리고 S140 단계의 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하는 단계는 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 수가 기 설정된 특정 수치를 넘는 경우 진행될 수 있다.Further, step S140 may further include determining whether the number of the second consensus verification packets received by each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value. In addition, the step of determining whether a predetermined value exceeds a predetermined value in step S140 may be performed when the number of the second consensus verification packets received by each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value.
또한, S140 단계의 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록을 서명으로 봉인하여 제2 합의검증 패킷으로 다른 일반 노드들에 전달하는 단계는, 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록, 체인에 추가된 일반체인 블록 및 제2 합의 블록의 번호 중 적어도 하나를 검증한 검증 결과를 제2 합의 블록과 함께 서명으로 봉인하여 진행될 수 있다.In addition, in the step S140, each of the plurality of normal nodes seals the second agreement block with a signature and transmits the second agreement block to other general nodes as a second agreement verification packet. The verification result verifying at least one of the numbers of the general chain block and the second consensus block added to may be performed by sealing the signature together with the second consensus block.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 장치를 나타낸 블록도이다.2 is a block diagram showing a block generation device of a blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 2를 참조하면, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 장치(200)는 제1 합의 블록 생성부(210), 일반체인 블록 추가부(220), 제2 합의 블록 생성부(230) 및 확정체인 블록 추가부(240)를 포함한다.Referring to FIG. 2, the
제1 합의 블록 생성부(210)는 리더 노드에서 클라이언트 노드에서의 트랜잭션에 대응하여 제1 합의 블록을 생성하도록 제어한다.The first consensus
일반체인 블록 추가부(220)는 복수의 리플리카 노드에서 상기 제1 합의 블록을 검증하여, 제1 합의 블록을 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어한다. 보다 구체적으로, 일반체인 블록 추가부(220)는 제1 합의 블록을 리더 노드에서 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드로 전달하도록 제어하고, 복수의 리플리카 노드 각각이 상호간에 리더 노드로부터 전달받은 제1 합의 블록이 동일한지 검증하도록 제어하며, 기 설정된 특정 수치 이상의 동일성이 있는 것으로 판단되는 경우 복수의 리플리카 노드 각각이 제1 합의 블록을 체인에 추가하는 것에 대한 동의 여부를 확인하도록 제어하고, 기 설정된 소정 수치 이상의 동의가 있는 경우 제1 합의 블록을 상기 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어할 수 있다. 이 때, 리더 노드 및 복수의 리플리카 노드는 블록체인 시스템에서 기 정의된 복수의 대표자 노드에 포함될 수 있다.The general chain
제2 합의 블록 생성부(230)는 체인에 일반체인 블록이 기 설정된 K 개가 추가될 때마다 제1 합의 블록의 생성과 병렬적으로 리더 노드에서 제2 합의 블록을 생성하도록 제어한다.The second consensus
확정체인 블록 추가부(240)는 복수의 일반 노드에서 제2 합의 블록을 검증하여, 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어한다. 보다 구체적으로, 확정체인 블록 추가부(240)는 제2 합의 블록을 리더 노드에서 상기 복수의 일반 노드로 전달하도록 제어하고, 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 제2 합의 블록을 서명으로 봉인하여 제2 합의검증 패킷으로 다른 일반 노드들에 전달하도록 제어하며, 복수의 일반 노드 각각에서 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하도록 제어하고, 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 제2 합의 블록과 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는 경우, 제2 합의 블록을 상기 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어할 수 있다. 또한, 확정체인 블록 추가부(240)는 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치 이하인 것으로 판단된 경우 제2 합의 블록을 폐기한다. 그리고, 확정체인 블록 추가부(240)는 체인에 일반체인 블록이 K의 2배수가 추가되었을 때 리더 노드에서 제2 합의 블록을 생성하도록 제어하고, 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어할 수 있다.The confirmation chain
그리고, 확정체인 블록 추가부(240)는 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 제2 합의검증 패킷의 수가 기 설정된 특정 수치를 넘는 경우, 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하도록 제어할 수 있다. 또한, 확정체인 블록 추가부(240)는 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 제2 합의 블록, 체인에 추가된 일반체인 블록 및 제2 합의 블록의 번호 중 적어도 하나를 검증한 검증 결과를 제2 합의 블록과 함께 서명으로 봉인하여 제2 합의검증 패킷으로 다른 일반 노드들에 전달하도록 제어할 수 있다.In addition, when the number of second consensus verification packets received by each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value, the definite chain
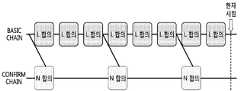
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 기술에 있어서 체인 즉, 일반 체인 및 확정 체인의 특징을 설명하기 표이다. 먼저, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 기술에 있어서, 일반 체인(basic chain)은 참여 노드 중 대표자 노드를 선정하여 블록을 생성하고 합의한다. 그리고, 확정 체인(confirm chain)은 주기적으로 전체 참여노드 중 대표자를 제외한 모든 노드가 기존의 생성된 블록의 묶음에 대한 정보에 대해 블록을 생성하고 합의한다. 그리고 도 3을 참조하면, 체인에 포함되는 일반 체인과 확정 체인의 목적, 합의 주체, 포함 서명, 블록생성주기 및 블록 내용에 대한 요지를 확인할 수 있다.3 is a table for explaining the characteristics of a chain, that is, a general chain and a definite chain in the block generation technology of the blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention. First, in the block generation technology of a blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention, a basic chain selects a representative node from among participating nodes to generate a block and agrees. Then, in the confirmation chain, periodically, all nodes except representatives among all the participating nodes generate and agree on the block information of the existing generated block. And, referring to FIG. 3, it is possible to check the general chain included in the chain and the purpose of the definite chain, the subject of consensus, the inclusive signature, the block generation cycle, and the contents of the block.
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법에 있어서 일반체인 블록을 체인에 추가하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.4 is a view for explaining a method of adding a general chain block to the chain in the block generation method of the blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 4를 참조하면, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법은 기본적으로 PBFT 방식을 참고할 수 있다. 그리고 다음과 같은 예시로 일반체인 블록이 체인에 추가될 수 있다. 이 때, 합의 관련 노드는 리더(Leader), 리플리카(Replica), 클라이언트(Client)로 구성된다.Referring to FIG. 4, a block generation method of a blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention may basically refer to the PBFT method. And, with the following example, a normal chain block can be added to the chain. At this time, the consensus-related node is composed of a leader, a replica, and a client.
1. 클라이언트(C)로부터 트랜잭션(transaction)이 발행되고, 본 단계에서 리더(0)에서 전송된다.1. A transaction is issued from the client C, and transmitted at the reader 0 in this step.
2. pre-prepare: 리더 노드(Leader)는 블록을 생성하여 리플리카 노드 (Replica 1,2,3)에게 전파한다.2. Pre-prepare: The leader node creates a block and spreads it to the replica nodes (
3. prepare: 각 구성원들은 리더 노드로부터 받은 블록이 서로 동일한지 확인한다.3. prepare: Each member checks whether the blocks received from the leader node are the same.
4. commit: 블록이 대다수가 동일하다면(2/3 이상), 이 블록을 검증하고 체인 추가를 찬성할 것인지 확인한다.4. commit: If the majority of the blocks are the same (more than two-thirds), verify this block and see if you will agree to add the chain.
5. reply: 대다수가(2/3 이상) 찬성했다면, 각각 블록을 체인에 추가하고 클라이언트에게 결과를 알린다. 만약, 대다수가 찬성한 것이 아니라면, 블록을 체인에 추가하지 않고 클라이언트에게 결과를 알린다.5. reply: If the majority (over 2/3) agreed, each block is added to the chain and the client is notified of the result. If the majority are not in favor, the result is notified to the client without adding the block to the chain.
위와 같은 절차를 통해 L개의 대표자 노드는 일반체인의 블록을 합의하고 일반체인에 K 개의 블록이 생성될 때 마다 N개의 전체 노드는 전체합의를 통해 확정체인의 블록을 생성한다. 일반체인에서 클라이언트는 참여 노드 누구나 될 수 있고 리더와 리플리카 노드는 대표자노드만 될 수 있다. 대표자 노드는 참여 노드 중에서 선출되며 정기적으로 교체할 수 있다.Through the above procedure, the L representative nodes agree on the block of the general chain, and whenever K blocks are created on the general chain, N total nodes create blocks of the confirmed chain through the entire agreement. In the general chain, the client can be any participating node, and the leader and replica nodes can be only representative nodes. The representative node is selected from the participating nodes and can be replaced regularly.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법에 있어서 일반체인 블록과 확정체인 블록의 생성 관계를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.5 is a view for explaining the relationship between the normal chain block and the definite chain block in the block generation method of the blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
제안하는 합의 방법의 실시 예를 나타낸다(K=3). 일반체인은 블록체인 내에서 발생하는 트랜잭션을 기반으로 L개의 대표자 노드가 합의하여 생성한다. 'L 합의'로 표시된 블록에는 대표자 노드 중 리더 노드의 서명이 첨부된다. 도 5의 확정체인은 일반체인에서 K개 블록이 생성될 때마다 N개의 전체 노드가 합의하여 블록을 생성한다.An example of the proposed consensus method is shown (K=3). The general chain is created by agreement between L representative nodes based on transactions occurring within the blockchain. The block marked'L consensus' is the signature of the leader node among the representative nodes. In the confirmation chain of FIG. 5, whenever all K blocks are generated in the general chain, N all nodes agree to generate a block.
확정체인은 일반체인과 함께 병렬적으로 생성된다. 대표자노드에 의해 생성된 'L 합의' 블록은 일반노드에게 전달되고 일반 노드는 본 합의에 문제가 없는지 각자 검증하는 작업을 실시한다. 대표자 노드의 리더 노드는 일반체인에 K개의 블록이 생성되면 K+1 번째 'L 합의' 블록 생성시 'N 합의' 블록을 생성하여 모든 일반 노드에게 전달하여 일반 노드간 전체합의 과정을 실행한다. 전체합의가 완료되면 확정체인에 블록이 생성되고 이는 완결성을 갖는 블록이 된다.The definite chain is created in parallel with the normal chain. The'L consensus' block created by the representative node is delivered to the general node, and the general node performs each task to verify that there is no problem with this agreement. When K blocks are created in the general chain, the leader node of the representative node creates an'N consensus' block when it creates a K+1th'L consensus' block, and delivers it to all general nodes to execute the overall consensus process among general nodes. When the entire agreement is completed, a block is created in the confirmation chain, which becomes a block with completeness.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법에 있어서 확정체인 블록을 체인에 추가하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.6 is a view for explaining a method of adding a definite chain block to a chain in a block generation method of a blockchain system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 6을 참조하면, 확정체인에 대한 자세한 합의 절차는 주 합의 단계(main stage)와 확장 합의 단계(extended stage)로 구성될 수 있다. 하나의 'N 합의' 블록을 만드는 과정을 한 라운드로 정의할 수 있다. 주 합의 단계는 다음과 같다.Referring to FIG. 6, the detailed consensus process for the confirmation chain may be composed of a main consensus stage and an extended consensus stage. The process of creating one'N consensus' block can be defined as one round. The main consensus steps are:
1. Prepare 단계에서 리더노드는 'N 합의' 블록을 생성하여 일반노드에게 전달한다. 2. 일반노드는 리더노드로부터 'N 합의' 블록을 받으면 각 노드가 소유한 정보를 이용하여 내용 검증한다. 이 때, 최근 'L 합의' 블록, 'N 합의' 블록, 'N 합의' 블록번호를 검증할 수 있다. 3. Commit 단계에서 일반노드는 검증결과와 함께 'N 합의' 블록을 자신의 서명으로 봉인한 'N 합의 검증' 패킷을 모든 일반노드에게 브로드캐스팅 한다.1. In the prepare phase, the leader node creates an'N consensus' block and delivers it to the general node. 2. When a normal node receives an'N consensus' block from a leader node, it verifies the contents using information owned by each node. At this time, the recent'L consensus' block,'N consensus' block, and'N consensus' block number can be verified. 3. In the Commit phase, the general node broadcasts the'N consensus verification' packet, which sealed the'N consensus' block with its signature, to all the general nodes.
4. 각 일반노드는 'N 합의 검증' 패킷을 수신 후, 자신의 검증결과와 비교하여 다음의 행동을 한다. 이 때, 각 노드는 비동기로 운영되어, 최초 'N 합의 검증' 패킷 수신 후 일정 타임아웃 시간(T0)내 수신한 패킷을 대상으로 결과를 산출한다.4. Each normal node receives the'N consensus verification' packet and compares it with its verification result to perform the following actions. At this time, each node is operated asynchronously, and after receiving the initial'N consensus verification' packet, the result is calculated for the received packet within a predetermined timeout time (T0).
수신한 패킷의 송신자 수가 전체 노드 수의 2/3가 넘고,The number of senders of the received packet exceeds 2/3 of the total number of nodes,
(1.1) 자신과 같은 결과가 2/3 가 넘으면,(1.1) If your result is more than 2/3,
(Action a) 합의된 것으로 간주하고 자신의 체인에 'N 합의' 블록 등록 후 라운드 종료한다.(Action a) It is regarded as agreed and the round ends after registering'N consensus' block in its chain.
(1.2) 자신과 다른 결과가 2/3 이상이고,(1.2) The result is 2/3 or more different from yourself.
(1.2.1) 다른 결과의 동일성이 2/3 이상이면,(1.2.1) If the sameness of different results is more than 2/3,
(Action b) 자신의 최신 K개의 'L 합의' 블록을 수신한 블록 정보로 교체 후 라운드 종료한다. 이 때, 다수 정보를 보유한 노드에게 최신 K개의 'L 합의' 블록을 요청하여 수신한다.(Action b) The latest K'L consensus' blocks are replaced with the received block information and the round ends. At this time, the latest K'L consensus' blocks are requested and received from the node having a large number of information.
(1.2.2) 다른 결과의 동일성이 2/3 이하이면,(1.2.2) If the identity of other results is 2/3 or less,
(Action c) 오류를 브로드캐스팅 하여 블록체인 네트워크에 알리고, 현재 N 블록 파기 후 라운드 종료한다.(Action c) Broadcast the error to the blockchain network, destroy the current N block and end the round.
5. 다음 N 블록 생성시, 이전 N 블록이 파기 됐을 경우, 파기에 포함된 L 합의 블록 정보를 포함하여 신규 N블록 생성한다. 이 때, 2K 개의 'L 합의' 블록 정보로 신규 N 블록을 생성한다. (리더 변경 가능)5. When generating the next N block, if the previous N block is destroyed, a new N block is generated including the L consensus block information included in the destruction. At this time, a new N block is generated with 2K'L consensus' block information. (Leader can be changed)
확장 합의 단계는 데이터의 완결성을 보완하기 위한 것으로 전체 노드의 서명을 포함한 블록을 생성하기 위한 단계이다. 이 때, 목적에 따라 선택적으로 실행이 가능하다.The extended consensus step is to complement the integrity of the data and is a step for generating a block including the signature of the entire node. At this time, it can be selectively executed according to the purpose.
1. 주 합의 단계 이후, 리더노드는 일반노드로부터 수집된 'N 합의 검증' 패킷의 정보를 정합하여 새로운 '서명' 블록을 생성하여 일반노드에게 전송한다.1. After the main consensus step, the leader node matches the information of the'N consensus verification' packet collected from the general node to generate a new'signature' block and transmits it to the general node.
2. 일반노드는 리더노드로부터 수신한 '서명' 블록을 브로드캐스팅하여 서로 같은 정보를 수신하였는지 확인한다.2. The normal node broadcasts the'signature' block received from the leader node to check whether the same information has been received.
3. 수신한 블록이 2/3 이상 같으면, 블록을 체인에 추가하고, 같지 않으면 블록을 폐기한다.3. If the received block is equal to 2/3 or more, the block is added to the chain. Otherwise, the block is discarded.
본 발명에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 기술에 의하면, 해커는 현재 시점에서 N 합의 이전의 블록에 대해 정보를 변경하기 위해서는 2/3*N 이상의 노드의 서명을 탈취해야 하기 때문에 기존 대표자 합의 방식에 비해 더 높은 완결성을 제공할 수 있다. 그리고 앵커링 기법과 달리 퍼블릭 블록체인 네트워크에 의존하지 않고 데이터 완결성을 강화할 수 있다.According to the block generation technology of the blockchain system according to the present invention, a hacker needs to steal a signature of 2/3*N or more nodes in order to change information about a block prior to the N agreement at the present time, so the existing representative agreement method Compared to this, it can provide higher completeness. And unlike anchoring techniques, data integrity can be enhanced without relying on the public blockchain network.
이상에서와 같이 본 발명에 따른 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법 및 장치는 상기한 바와 같이 설명된 실시예들의 구성과 방법이 한정되게 적용될 수 있는 것이 아니라, 상기 실시예들은 다양한 변형이 이루어질 수 있도록 각 실시예들의 전부 또는 일부가 선택적으로 조합되어 구성될 수도 있다.As described above, the block generation method and apparatus of the blockchain system according to the present invention are not limited to the configuration and method of the described embodiments as described above, and the above embodiments are provided so that various modifications can be made. All or some of the embodiments may be configured by selectively combining.
200; 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성
210; 제1 합의 블록 생성부
220; 일반체인 블록 추가부
230; 제2 합의 블록 생성부
240; 확정체인 블록 추가부200; Block creation of blockchain system
210; First consensus block generator
220; General Chain Block Addition
230; Second consensus block generation unit
240; Confirmation Chain Block Addition
Claims (14)
Translated fromKorean복수의 리플리카 노드에서 상기 제1 합의 블록을 검증하여, 상기 제1 합의 블록을 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계;
상기 체인에 일반체인 블록이 기 설정된 K 개가 추가될 때마다 상기 제1 합의 블록의 생성과 병렬적으로 상기 리더 노드에서 제2 합의 블록을 생성하는 단계; 및
복수의 일반 노드에서 상기 제2 합의 블록을 검증하여, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법.Generating a first consensus block in response to the transaction at the client node at the leader node;
Verifying the first consensus block in a plurality of replica nodes, defining the first consensus block as a regular chain block and adding it to the chain;
Generating a second consensus block in the leader node in parallel with the generation of the first consensus block whenever K pieces with a predetermined number of general chain blocks are added to the chain; And
And verifying the second consensus block in a plurality of general nodes, defining the second consensus block as a definite chain block, and adding the block to the chain.
상기 제1 합의 블록을 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계는,
상기 제1 합의 블록을 상기 리더 노드에서 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드로 전달하는 단계;
상기 복수의 리플리카 노드 각각이 상호간에 상기 리더 노드로부터 전달받은 상기 제1 합의 블록이 동일한지 검증하는 단계;
상기 검증하는 단계에서 기 설정된 특정 수치 이상의 동일성이 있는 것으로 판단되는 경우 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드 각각이 상기 제1 합의 블록을 체인에 추가하는 것에 대한 동의 여부를 확인하는 단계; 및
상기 동의 여부를 확인하는 단계에서 기 설정된 소정 수치 이상의 동의가 있는 경우 상기 제1 합의 블록을 상기 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Defining the first consensus block as a general chain block and adding it to the chain,
Transferring the first consensus block from the leader node to the plurality of replica nodes;
Verifying that each of the plurality of replica nodes is identical to the first consensus block received from the leader node to each other;
Determining whether each of the plurality of replica nodes agrees to add the first consensus block to the chain when it is determined in the verifying step that there is more than a predetermined predetermined value; And
And in the step of confirming whether to agree, if there is more than a predetermined number of agreement, defining the first consensus block as the general chain block and adding it to the chain.
상기 리더 노드 및 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드는 블록체인 시스템에서 기 정의된 복수의 대표자 노드에 포함되는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법.The method according to claim 1,
The leader node and the plurality of replica nodes are included in a plurality of representative nodes previously defined in a blockchain system.
상기 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계는,
상기 제2 합의 블록을 상기 리더 노드에서 상기 복수의 일반 노드로 전달하는 단계;
상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록을 서명으로 봉인하여 제2 합의검증 패킷으로 다른 일반 노드들에 전달하는 단계;
상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각에서 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하는 단계; 및
상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 상기 제2 합의 블록과 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는 경우, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 상기 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Defining the second consensus block as a definite chain block and adding it to the chain,
Transferring the second consensus block from the leader node to the plurality of general nodes;
Each of the plurality of general nodes sealing the second consensus block with a signature and transmitting the second consensus verification packet to other general nodes;
Determining whether the identity of the second consensus block and the second consensus verification packet received from each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value; And
When the identity of the second consensus block and the second consensus verification packet received by each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value, adding the second consensus block to the chain by defining the second consensus block as the confirmation chain block Block generation method of a blockchain system comprising a.
상기 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하는 단계에서, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치 이하인 것으로 판단된 경우 상기 제2 합의 블록을 폐기하고,
상기 체인에 일반체인 블록이 K의 2배수가 추가되었을 때 상기 리더 노드에서 제2 합의 블록을 생성하는 단계와 상기 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하는 단계를 반복하는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법.The method according to claim 4,
In the step of determining whether the predetermined predetermined value is exceeded, the second agreement is determined when each of the plurality of general nodes determines that the identity of the second agreement block and the second agreement verification packet received is equal to or less than a predetermined value. Discard the block,
When the general chain block is added twice the number of K to the chain, the step of generating a second consensus block in the leader node and repeating the step of defining the second consensus block as a definite chain block and adding it to the chain. Block generation method of the blockchain system.
상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 수가 기 설정된 특정 수치를 넘는지 판단하는 단계를 더 포함하며,
상기 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하는 단계는 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 수가 기 설정된 특정 수치를 넘는 경우 진행되는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법.The method according to claim 4,
Further comprising the step of determining whether the number of the second consensus verification packet received by each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value,
The step of determining whether the predetermined value exceeds a predetermined value is performed when the number of the second consensus verification packets received by each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value.
상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록을 서명으로 봉인하여 제2 합의검증 패킷으로 다른 일반 노드들에 전달하는 단계는,
상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록, 상기 체인에 추가된 일반체인 블록 및 상기 제2 합의 블록의 번호 중 적어도 하나를 검증한 검증 결과를 상기 제2 합의 블록과 함께 서명으로 봉인하는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 방법.The method according to claim 4,
The step of each of the plurality of general nodes sealing the second consensus block with a signature and transmitting the second consensus verification packet to other general nodes,
Each of the plurality of general nodes seals the verification result verifying at least one of the second consensus block, the general chain block added to the chain, and the number of the second consensus block with the second consensus block with a signature. Characteristic of the block generation method of the blockchain system.
복수의 리플리카 노드에서 상기 제1 합의 블록을 검증하여, 상기 제1 합의 블록을 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어하는 일반체인 블록 추가부;
상기 체인에 일반체인 블록이 기 설정된 K 개가 추가될 때마다 상기 제1 합의 블록의 생성과 병렬적으로 상기 리더 노드에서 제2 합의 블록을 생성하도록 제어하는 제2 합의 블록 생성부; 및
복수의 일반 노드에서 상기 제2 합의 블록을 검증하여, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어하는 확정체인 블록 추가부를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 장치.A first consensus block generator configured to control the leader node to generate the first consensus block in response to the transaction at the client node;
A general chain block adding unit that verifies the first consensus block from a plurality of replica nodes and controls the first consensus block to be added to the chain by defining it as a general chain block;
A second consensus block generator configured to control the leader node to generate a second consensus block in parallel with the generation of the first consensus block whenever K pieces with a predetermined number of general chain blocks are added to the chain; And
Block generation apparatus of a blockchain system, characterized in that it comprises a confirmation chain block addition unit that verifies the second agreement block by a plurality of general nodes and controls the second agreement block to be added to the chain by defining it as a confirmation chain block. .
상기 일반체인 블록 추가부는,
상기 제1 합의 블록을 상기 리더 노드에서 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드로 전달하도록 제어하고,
상기 복수의 리플리카 노드 각각이 상호간에 상기 리더 노드로부터 전달받은 상기 제1 합의 블록이 동일한지 검증하도록 제어하며,
기 설정된 특정 수치 이상의 동일성이 있는 것으로 판단되는 경우 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드 각각이 상기 제1 합의 블록을 체인에 추가하는 것에 대한 동의 여부를 확인하도록 제어하고,
기 설정된 소정 수치 이상의 동의가 있는 경우 상기 제1 합의 블록을 상기 일반체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어하는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 장치.The method according to claim 8,
The general chain block addition unit,
Control to transfer the first consensus block from the leader node to the plurality of replica nodes,
Each of the plurality of replica nodes controls each other to verify whether the first consensus block received from the leader node is the same,
When it is determined that there is an identity equal to or greater than a predetermined value, each of the plurality of replica nodes is controlled to confirm whether or not to agree to add the first consensus block to the chain,
The block generating apparatus of the blockchain system, characterized in that if there is a consent of a predetermined number or more, the first consensus block is defined as the general chain block and controlled to be added to the chain.
상기 리더 노드 및 상기 복수의 리플리카 노드는 블록체인 시스템에서 기 정의된 복수의 대표자 노드에 포함되는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 장치.The method according to claim 8,
The leader node and the plurality of replica nodes are included in a plurality of representative nodes previously defined in a blockchain system.
상기 확정체인 블록 추가부는,
상기 제2 합의 블록을 상기 리더 노드에서 상기 복수의 일반 노드로 전달하도록 제어하고,
상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록을 서명으로 봉인하여 제2 합의검증 패킷으로 다른 일반 노드들에 전달하도록 제어하며,
상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각에서 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하도록 제어하고,
상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 상기 제2 합의 블록과 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는 경우, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 상기 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어하는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 장치.The method according to claim 8,
The confirmation chain block addition unit,
Control to transfer the second consensus block from the leader node to the plurality of general nodes,
Each of the plurality of general nodes is controlled to seal the second consensus block with a signature and transmit the second consensus verification packet to other general nodes,
Each of the plurality of general nodes is controlled to determine whether the identity of the second consensus block and the received second consensus verification packet exceeds a predetermined value,
When the identity of the second consensus block and the second consensus verification packet received by each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined value, the second consensus block is defined as the confirmation chain block and controlled to be added to the chain Block generation device of the blockchain system, characterized in that.
상기 확정체인 블록 추가부는,
상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치 이하인 것으로 판단된 경우 상기 제2 합의 블록을 폐기하고,
상기 체인에 일반체인 블록이 K의 2배수가 추가되었을 때 상기 리더 노드에서 제2 합의 블록을 생성하도록 제어하고, 상기 제2 합의 블록을 확정체인 블록으로 정의하여 체인에 추가하도록 제어하는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 장치.The method according to claim 11,
The confirmation chain block addition unit,
If it is determined that each of the plurality of general nodes has the same identity between the second consensus block and the second consensus verification packet as received, the second consensus block is discarded,
When the general chain block is added to the chain by a multiple of K, the leader node controls to generate a second consensus block, and defines the second consensus block as a definite chain block to control it to be added to the chain. Block generation device of the blockchain system.
상기 확정체인 블록 추가부는,
상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 수가 기 설정된 특정 수치를 넘는 경우, 상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록과 수신한 상기 제2 합의검증 패킷의 동일성이 기 설정된 소정 수치를 넘는지 판단하도록 제어하는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 장치.The method according to claim 11,
The confirmation chain block addition unit,
When the number of the second consensus verification packets received by each of the plurality of general nodes exceeds a predetermined predetermined value, the identity of each of the plurality of general nodes and the second consensus verification packet received by each of the plurality of general nodes is determined. Block generation device of the blockchain system, characterized in that the control to determine whether to exceed the predetermined value set.
상기 확정체인 블록 추가부는,
상기 복수의 일반 노드 각각이 상기 제2 합의 블록, 상기 체인에 추가된 일반체인 블록 및 상기 제2 합의 블록의 번호 중 적어도 하나를 검증한 검증 결과를 상기 제2 합의 블록과 함께 서명으로 봉인하여 제2 합의검증 패킷으로 다른 일반 노드들에 전달하도록 제어하는 것을 특징으로 하는 블록체인 시스템의 블록 생성 장치.The method according to claim 11,
The confirmation chain block addition unit,
Each of the plurality of general nodes seals the verification result verifying at least one of the second consensus block, the general chain block added to the chain, and the number of the second consensus block with the second consensus block by signing the signature. 2 Block generation device of a blockchain system, characterized in that it is controlled to deliver to other general nodes as a consensus verification packet.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180158287AKR102175949B1 (en) | 2018-12-10 | 2018-12-10 | Method and apparatus for generating block in blockchain system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180158287AKR102175949B1 (en) | 2018-12-10 | 2018-12-10 | Method and apparatus for generating block in blockchain system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20200070776Atrue KR20200070776A (en) | 2020-06-18 |
| KR102175949B1 KR102175949B1 (en) | 2020-11-09 |
Family
ID=71142913
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180158287AActiveKR102175949B1 (en) | 2018-12-10 | 2018-12-10 | Method and apparatus for generating block in blockchain system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102175949B1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113255003A (en)* | 2021-06-15 | 2021-08-13 | 中国电子科技网络信息安全有限公司 | Block chain system safety management and control method |
| WO2022035178A1 (en)* | 2020-08-14 | 2022-02-17 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method and apparatus for reducing orphan blocks for a blockchain |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101727525B1 (en)* | 2016-09-05 | 2017-04-17 | 주식회사 스케일체인 | Block chain based distributed storage method and device thereof |
| KR20180079847A (en)* | 2017-01-03 | 2018-07-11 | 아주대학교산학협력단 | Person to person trading method and apparatus by using blockchain and distributed hash table |
| KR20180113140A (en)* | 2017-04-05 | 2018-10-15 | 삼성에스디에스 주식회사 | System for processing data based on blockchain and Operating method thereof |
- 2018
- 2018-12-10KRKR1020180158287Apatent/KR102175949B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101727525B1 (en)* | 2016-09-05 | 2017-04-17 | 주식회사 스케일체인 | Block chain based distributed storage method and device thereof |
| KR20180079847A (en)* | 2017-01-03 | 2018-07-11 | 아주대학교산학협력단 | Person to person trading method and apparatus by using blockchain and distributed hash table |
| KR20180113140A (en)* | 2017-04-05 | 2018-10-15 | 삼성에스디에스 주식회사 | System for processing data based on blockchain and Operating method thereof |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022035178A1 (en)* | 2020-08-14 | 2022-02-17 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method and apparatus for reducing orphan blocks for a blockchain |
| US12381749B2 (en) | 2020-08-14 | 2025-08-05 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method and apparatus for reducing orphan blocks for a blockchain |
| CN113255003A (en)* | 2021-06-15 | 2021-08-13 | 中国电子科技网络信息安全有限公司 | Block chain system safety management and control method |
| CN113255003B (en)* | 2021-06-15 | 2022-03-18 | 中国电子科技网络信息安全有限公司 | Block chain system safety management and control method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR102175949B1 (en) | 2020-11-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US12341908B2 (en) | Computer-implemented method and system for transferring access to a digital asset | |
| Zhou et al. | COCA: A secure distributed online certification authority | |
| EP3486817A1 (en) | Blockchain-based identity authentication method, device, node and system | |
| KR20210134655A (en) | Security systems and related methods | |
| Jan et al. | A verifiably secure ECC based authentication scheme for securing IoD using FANET | |
| US5790669A (en) | Lightweight non-repudiation system and method | |
| Sani et al. | Xyreum: A high-performance and scalable blockchain for iiot security and privacy | |
| Annessi et al. | It's about time: Securing broadcast time synchronization with data origin authentication | |
| JP7472158B2 (en) | Method for providing a digital signature to a message | |
| KR20200070776A (en) | Method and apparatus for generating block in blockchain system | |
| WO2006046006A1 (en) | A method of determining reliability of information | |
| Hiltunen et al. | Enhancing survivability of security services using redundancy | |
| Costea et al. | Secure opportunistic multipath key exchange | |
| CN117353941A (en) | A group key negotiation and verification method based on elliptic curve | |
| Oberoi et al. | ADRCN: A framework to detect and mitigate malicious Insider Attacks in Cloud-Based environment on IaaS | |
| Mukathe et al. | Blockchain-Powered Authenticated Key Agreement Scheme With Reputation-Incentive Mechanism for Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication in IoV | |
| Lee et al. | A public‐key based authentication and key establishment protocol coupled with a client puzzle | |
| Yuzik et al. | Blockchain-based security for heterogeneous IoT systems. | |
| Groza et al. | On the use of one-way chain based authentication protocols in secure control systems | |
| McDaniel et al. | Antigone: Implementing policy in secure group communication | |
| Mödinger et al. | Pixy: A Privacy-Increasing Group Creation Scheme | |
| Solat | KeyChallenge: a novel sybil attack mitigation technique based on cryptographic key generation | |
| CN117879874B (en) | A triple security protection method and system for SDWAN system | |
| Songsiri | A new approach for computation result protection in the mobile agent paradigm | |
| Malik et al. | A Secure Authentication and Key Establishment Protocol for IoT Devices Using ECCMD |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| R15-X000 | Change to inventor requested | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R15-oth-X000 | |
| R16-X000 | Change to inventor recorded | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R16-oth-X000 | |
| D13-X000 | Search requested | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D13-srh-X000 | |
| D14-X000 | Search report completed | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D14-srh-X000 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | St.27 status event code:A-1-1-Q10-Q12-nap-PG1501 | |
| E13-X000 | Pre-grant limitation requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-3-E10-E13-lim-X000 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 Fee payment year number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:6 |