KR20190122935A - Radio resource managing method and network control apparatus using the method - Google Patents
Radio resource managing method and network control apparatus using the methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20190122935A KR20190122935AKR1020180046471AKR20180046471AKR20190122935AKR 20190122935 AKR20190122935 AKR 20190122935AKR 1020180046471 AKR1020180046471 AKR 1020180046471AKR 20180046471 AKR20180046471 AKR 20180046471AKR 20190122935 AKR20190122935 AKR 20190122935A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- link
- xhole
- radio resource
- access link
- node
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/16—Central resource management; Negotiation of resources or communication parameters, e.g. negotiating bandwidth or QoS [Quality of Service]
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W24/00—Supervisory, monitoring or testing arrangements
- H04W24/10—Scheduling measurement reports ; Arrangements for measurement reports
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W88/00—Devices specially adapted for wireless communication networks, e.g. terminals, base stations or access point devices
- H04W88/18—Service support devices; Network management devices
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 무선 자원 관리 방법 및 이를 이용하는 네트워크 제어 장치에 관한 것으로, 더욱 상세하게는 무선 자원을 공유하는 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크를 제공하는 무선 노드를 포함하는 네트워크에서의 무선 자원 관리 방법, 상기 방법을 이용하는 네트워크 제어 장치 및 무선통신 디바이스에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a radio resource management method and a network control apparatus using the same, and more particularly, to a radio resource management method in a network including an xhole link and an access link sharing radio resources, the method It relates to a network control apparatus and a wireless communication device using.
기존의 이동통신 네트워크에서 프론트홀, 미드홀, 백홀 상에서 트래픽을 전송하기 위해서는 각각 전용의 전송 네트워크를 필요로 하였다. 이렇듯 별도의 전용 네트워크를 사용함으로 인해 투자 부담이 매우 높고, 운용 및 관리에 어려움이 많았다. 그에 따라, 최근 하나의 네트워크를 프론트홀(fronthaul) 네트워크, 미드홀(midhaul) 네트워크, 그리고 백홀(backhaul) 네트워크로 이용할 수 있는 엑스홀(Xhaul) 네트워크가 그 대안으로 제시되고 있다. 더욱이 최근 유선 대비 유연하고 손쉬운 무선의 특성을 이용한 무선 엑스홀 네트워크 기술도 제안되고 있다.In the existing mobile communication network, a dedicated transmission network was required to transmit traffic on the front hole, the mid hole, and the back hole. As a result of using a separate dedicated network, the investment burden was very high and operation and management were difficult. Accordingly, the Xhaul network, which can use one network as a fronthaul network, a midhaul network, and a backhaul network, has recently been proposed as an alternative. In addition, wireless XHole network technology using a flexible and easy wireless feature compared to a wired line has recently been proposed.
한편, 이러한 엑스홀을 이용해 프론트홀, 미드홀, 백홀 트래픽 전송을 하는 이동통신 기지국의 발전 방향과 관련하여, 많은 개수의 기지국이 높은 밀도(ultra dense)로 설치되는 시나리오가 향후 이동통신 네트워크 설치 시나리오로 유력하게 대두되고 있다. 이 경우, 종래의 매크로 셀 기지국보다 커버리지가 작은 다수의 소형 셀 기지국이 사용된다. 높은 밀도의 소형 셀 기지국의 설치와 관련하여 유선보다 설치가 편리한 무선 소형 셀 기지국이 적합한 것으로 여겨지고 있다.On the other hand, the scenario in which a large number of base stations are installed in a high density (ultra dense) with respect to the development direction of the mobile communication base station that transmits the front hole, mid hole, and backhaul traffic using these X-holes It is emerging as a strong force. In this case, a number of small cell base stations with smaller coverage than conventional macro cell base stations are used. With regard to the installation of high density small cell base stations, wireless small cell base stations which are easier to install than wired are considered suitable.
이러한 네트워크 구조에서 종래의 무선 자원 할당 방법을 따르면, 사용자 단말에게 액세스 링크를 제공하는 기지국이 필요한 프론트홀, 미드홀, 백홀을 위해 무선 엑스홀을 이용할 경우 각각 고정된 크기의 전용 무선 자원을 사용하게 된다. 하지만, 높은 밀도의 소형 셀 기지국 설치 시나리오에서 각 소형 셀 기지국이 필요로 하는 액세스용 무선 자원 및 엑스홀 무선 자원은 매크로 셀 기지국 대비 매우 적을 뿐만 아니라 시간에 따라 크게 변화하는 특성을 가진다. 이러한 특성을 고려할 때, 액세스 링크 및 엑스홀 링크 각각에 대해 크기가 고정된 전용 자원을 사용하는 것은 무선 자원 사용 효율 면에서 효율이 낮아지는 단점을 가지게 된다. 이는, 액세스 링크 및 액스홀 링크 각각을 위한 전용 무선 자원의 크기는 각 링크의 최대 요구량에 맞추어 할당되나, 시간에 따라 필요한 무선 자원의 양이 크게 변화함에 따라 사용되지 않는 무선 자원이 발생하기 마련이기 때문이다.According to the conventional radio resource allocation method in such a network structure, when a base station providing an access link to a user terminal uses wireless X-holes for the required fronthaul, midhole, and backhaul, each of the fixed radio resources has a fixed size. do. However, in the high density small cell base station installation scenario, the access radio resource and the X-hole radio resource required by each small cell base station are very small compared to the macro cell base station, and have characteristics that vary greatly with time. In consideration of these characteristics, the use of a dedicated size fixed resource for each of the access link and the XHole link has a disadvantage in that the efficiency of the radio resource usage becomes low. The size of the dedicated radio resource for each of the access link and the access hole link is allocated according to the maximum demand of each link, but the unused radio resource is generated as the amount of radio resources required changes significantly with time. Because.
정리하면, 엑스홀 링크와 액세스 링크를 사용하는 기지국에서 종래의 방식에 따라 무선 자원을 사용하는 경우 무선자원의 사용 효율이 낮다는 문제점이 있다.In summary, there is a problem in that the use efficiency of radio resources is low when the radio resources are used in the conventional method in the base station using the XHole link and the access link.
상기와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위한 본 발명의 목적은, 무선 자원을 공유하는 엑스홀 링크와 액세스 링크를 제공하는 적어도 하나의 무선 노드를 포함하는 무선 네트워크에서의 무선자원 관리 방법을 제공하는 데 있다.An object of the present invention for solving the above problems is to provide a radio resource management method in a wireless network including at least one radio node providing an access hole and an X-hole link sharing a radio resource.
상기와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위한 본 발명의 다른 목적은, 상기 무선 자원 관리하는 방법을 이용하는 네트워크 제어 장치를 제공하는 데 있다.Another object of the present invention for solving the above problems is to provide a network control apparatus using the radio resource management method.
상기와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위한 본 발명의 또 다른 목적은 무선통신 디바이스를 제공하는 데 있다.Another object of the present invention for solving the above problems is to provide a wireless communication device.
상기 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 무선통신 디바이스는 무선통신 네트워크에서 다른 무선통신 디바이스와 연동하는 엑스홀 링크와 적어도 하나의 단말과 연동하는 액세스 링크를 제공하는 디바이스로서, 프로세서; 및 상기 프로세서를 통해 실행되는 적어도 하나의 명령을 저장하는 메모리를 포함하고, 상기 적어도 하나의 명령은 상기 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크가 무선 자원을 공유하도록 상기 무선 자원을 관리하는 명령을 포함할 수 있다.A wireless communication device according to an embodiment of the present invention for achieving the above object is a device for providing an X-hole link for interworking with another wireless communication device in the wireless communication network and an access link for interworking with at least one terminal; And a memory configured to store at least one instruction executed by the processor, wherein the at least one instruction may include instructions for managing the radio resource such that the exhaul link and the access link share a radio resource. have.
상기 적어도 하나의 명령은, 상기 무선통신 네트워크 내에 위치하는 네트워크 제어 장치로부터 수신한 무선자원 분할 비율에 따라 상기 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원량을 조정하도록 하는 명령을 더 포함할 수 있다.The at least one command may further include a command to adjust the amount of resources allocated to the exhaul link and the access link according to a radio resource division ratio received from a network control apparatus located in the wireless communication network.
상기 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원량을 조정하도록 하는 명령은, 상기 무선통신 디바이스가 포함하는 섹터의 연결 정보 및 사용자 단말 연동 정보를 상기 무선통신 네트워크 내 네트워크 제어 장치로 전송하도록 하는 명령; 상기 엑스홀 링크의 주파수 효율 및 상기 액세스 링크의 주파수 효율을 측정하여 상기 네트워크 제어 장치로 보고하도록 하는 명령; 상기 네트워크 제어 장치로부터 무선자원 분할 비율을 수신하도록 하는 명령; 및 상기 무선자원 분할 비율에 따라 상기 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원량을 조정하도록 하는 명령을 포함할 수 있다.The command to adjust the amount of resources allocated to the X-hole link and the access link, the command to transmit the connection information and the user terminal interworking information of the sector included in the wireless communication device to the network control device in the wireless communication network; Measuring the frequency efficiency of the X-hole link and the frequency efficiency of the access link to report to the network control device; Receiving a radio resource division ratio from the network control device; And adjusting an amount of resources allocated to the XHole link and the access link according to the radio resource division ratio.
상기 엑스홀 링크의 통달 거리(transmission range)는 상기 액세스 링크의 통달 거리보다 길 수 있다. 예를 들어, 상기 엑스홀 링크의 통달 거리는 상기 액세스 링크의 통달 거리의 2배일 수 있다.The transmission range of the XHole link may be longer than that of the access link. For example, the communication distance of the X-hole link may be twice the communication distance of the access link.
상기 적어도 하나의 명령은, 상기 무선자원 분할 비율이 변경되는 경우, 상기 네트워크 제어 장치로부터 자원할당 비율 관련 업데이트 메시지를 수신하도록 하는 명령을 더 포함할 수 있다.The at least one command may further include a command to receive a resource allocation rate related update message from the network control apparatus when the radio resource division ratio is changed.
상기 업데이트 메시지는, 변경되는 무선자원 분할 비율, 상기 변경되는 무선자원 분할 비율이 적용되는 TTI(Transmit Time Interval), 상기 업데이트 메시지의 송신자 정보, 및 상기 업데이트 메시지가 전달되어야 할 무선 노드 내 섹터들에 대한 정보 중 적어도 하나를 포함할 수 있다.The update message is transmitted to a radio resource division ratio to be changed, a transmit time interval (TTI) to which the changed radio resource division ratio is applied, sender information of the update message, and sectors in a radio node to which the update message should be delivered. It may include at least one of the information about.
상기 무선자원 분할 비율은, 최소 경로 처리량을 갖는 단말의 경로 처리량을 극대화시키는, 전체 무선 자원 대비 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원의 비율일 수 있다.The radio resource splitting ratio may be a ratio of resources allocated to an access link to total radio resources, maximizing path throughput of a terminal having a minimum path throughput.
상기 엑스홀 링크에 할당되는 자원과 상기 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원은 시간축 상에서 또는 주파수축 상에서 직교적으로 분할될 수 있다.Resources allocated to the XHole link and resources allocated to the access link may be divided orthogonally on the time axis or on the frequency axis.
상기 다른 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 무선자원 관리 방법은 엑스홀 링크와 액세스 링크를 제공하는 적어도 하나의 무선 노드를 포함하는 네트워크의 무선 자원을 관리하는 방법으로서, 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로부터 상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치를 수신하는 단계; 및 상기 무선 노드가 제공하는 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크가 무선 자원을 공유하되, 상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 관련 측정치에 기반하여 무선 자원을 분배하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In accordance with another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method for managing radio resources of a network including at least one radio node providing an X-hole link and an access link. Receiving the xhaul link and access link measurements from a wireless node of a; And sharing the radio resources between the XHole link and the access link provided by the wireless node, and distributing the radio resources based on the XHole link and access link related measurements.
상기 무선 자원을 분배하는 단계는, 상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치를 이용해 엑스홀 링크의 처리량 및 액세스 링크의 처리량을 산출하는 단계;The step of distributing the radio resource may include calculating throughput of an XHole link and throughput of an access link using the XHole Link and Access Link measurements;
상기 엑스홀 링크의 처리량 및 액세스 링크의 처리량으로부터 무선자원 분할 비율을 결정하는 단계; 및 상기 무선자원 분할 비율을 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로 제공하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.Determining a radio resource partition ratio from the throughput of the XHole link and the throughput of an access link; And providing the radio resource division ratio to the at least one radio node.
상기 무선자원 분할 비율은, 최소 경로 처리량을 갖는 단말의 경로 처리량을 극대화시키는, 전체 무선 자원 대비 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원의 비율일 수 있다.The radio resource splitting ratio may be a ratio of resources allocated to an access link to total radio resources, maximizing path throughput of a terminal having a minimum path throughput.
상기 엑스홀 링크의 통달 거리(transmission range)는 상기 액세스 링크의 통달 거리보다 길 수 있다. 예를 들어, 상기 엑스홀 링크의 통달 거리는 상기 액세스 링크의 통달 거리의 2배일 수 있다.The transmission range of the XHole link may be longer than that of the access link. For example, the communication distance of the X-hole link may be twice the communication distance of the access link.
상기 방법은 상기 무선자원 분할 비율이 변경되는 경우, 자원할당 비율 관련 업데이트 메시지를 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로 제공하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.The method may further include providing a resource allocation rate related update message to the at least one wireless node when the radio resource splitting ratio is changed.
상기 업데이트 메시지는, 변경되는 무선자원 분할 비율, 상기 변경되는 무선자원 분할 비율이 적용되는 TTI(Transmit Time Interval), 상기 업데이트 메시지의 송신자 정보, 및 상기 업데이트 메시지가 전달되어야 할 무선 노드 내 섹터들에 대한 정보 중 적어도 하나를 포함할 수 있다.The update message is transmitted to a radio resource division ratio to be changed, a transmit time interval (TTI) to which the changed radio resource division ratio is applied, sender information of the update message, and sectors in a radio node to which the update message should be delivered. It may include at least one of the information about.
상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치는, 상기 엑스홀 링크의 주파수 효율 및 상기 액세스 링크의 주파수 효율을 포함할 수 있다.The XHole link and access link measurements may include the frequency efficiency of the XHole link and the frequency efficiency of the access link.
상기 엑스홀 링크에 할당되는 자원과 상기 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원은 시간축 상에서 또는 주파수축 상에서 직교적으로 분할될 수 있다.Resources allocated to the XHole link and resources allocated to the access link may be divided orthogonally on the time axis or on the frequency axis.
상기 또 다른 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 네트워크 제어 장치는 무선 자원을 공유하는 엑스홀 링크와 액세스 링크를 제공하는 적어도 하나의 무선 노드를 포함하는 무선 네트워크의 자원을 관리하는 네트워크 제어 장치로서, 프로세서; 및 상기 프로세서를 통해 실행되는 적어도 하나의 명령을 저장하는 메모리를 포함하고, 상기 적어도 하나의 명령은, 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로부터 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치를 수신하도록 하는 명령; 및 상기 무선 노드가 제공하는 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크가 무선 자원을 공유하되, 상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 관련 측정치에 기반하여 무선 자원을 분배하도록 하는 명령을 포함할 수 있다.Network control apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention for achieving the above another object is a network for managing resources of a wireless network including at least one radio node for providing an access link and an X-hole link sharing a radio resource A control device, comprising: a processor; And a memory for storing at least one instruction executed by the processor, wherein the at least one instruction comprises: instructions to receive an Xhole link and access link measurements from the at least one wireless node; And sharing the radio resource between the XHole link and the access link provided by the wireless node, and distributing the radio resource based on the XHOLE link and access link related measurements.
상기 무선 자원을 분배하도록 하는 명령은, 상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치를 이용해 엑스홀 링크의 처리량 및 액세스 링크의 처리량을 산출하도록 하는 명령; 상기 엑스홀 링크의 처리량 및 액세스 링크의 처리량으로부터 무선자원 분할 비율을 결정하도록 하는 명령; 및 상기 무선자원 분할 비율을 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로 제공하도록 하는 명령을 포함할 수 있다.The instructions for distributing the radio resource may include instructions for calculating throughput of an XHole link and throughput of an access link using the XHole Link and Access Link measurements; Determine a radio resource splitting ratio from the throughput of the XHole link and the throughput of an access link; And providing the radio resource division ratio to the at least one radio node.
상기와 같은 본 발명의 실시예들에 따르면 본 발명에 따르면, 주어진 무선 자원을 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크가 공유하여 사용하되 각각의 링크에 사용되는 무선 자원의 량을 네트워크 상황에 맞게 변경이 가능하여 무선 자원을 효율적으로 사용하는 이점이 있다.According to the embodiments of the present invention as described above, according to the present invention, the X-hole link and the access link share a given radio resource, but the amount of radio resources used for each link can be changed according to the network situation. There is an advantage of using radio resources efficiently.
또한, 본 발명에 따르면, 측정치를 바탕으로 최소 경로 처리량을 가지는 사용자 단말의 경로 처리량을 최대화하도록 각 링크가 사용하는 자원의 비율을 결정할 수 있다.In addition, according to the present invention, the ratio of resources used by each link may be determined to maximize the path throughput of the user terminal having the minimum path throughput based on the measurement.
그에 따라, 각 링크가 사용하는 자원의 량을 변화시키면서 가장 적절한 자원 비율을 찾는 기존의 소모적인 방법 대비 시행 착오에 수반하는 자원 비율 결정 비용과 시간을 절약할 수 있는 이점이 있다.Accordingly, there is an advantage in that the cost and time of resource ratio determination associated with trial and error can be saved compared to the existing wasteful method of finding the most appropriate resource ratio while varying the amount of resources used by each link.
도 1은 FDM 방식을 이용한 엑스홀 링크 자원 및 액세스 링크 자원 분할 방법의 개념도이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 모바일 엑스홀 네트워크 구조를 도시한다.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 IXA 네트워크가 셀룰러화되는 예를 나타낸 개념도이다.
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 IXA 네트워크에서의 단방향 다운링크 데이터 흐름의 예를 도시한다.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 IXA 노드와 연관된 세 가지 유형의 링크를 나타낸다.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 자원 분할에 따른 링크 별 자원 분할 구조도이다.
도 7은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 자원할당 비율 결정 방법의 동작 흐름도이다.
도 8은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 자원할당 비율 변경 방법의 동작 흐름도이다.
도 9는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 무선 네트워크 제어 장치의 블록 구성도이다.1 is a conceptual diagram of an XHole link resource and access link resource partitioning method using an FDM scheme.
2 illustrates a mobile XHole network structure according to an embodiment of the present invention.
3 is a conceptual diagram illustrating an example in which an IXA network is cellularized according to an embodiment of the present invention.
4 shows an example of a unidirectional downlink data flow in an IXA network according to an embodiment of the present invention.
5 illustrates three types of links associated with IXA nodes in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
6 is a diagram illustrating a structure of resource division for each link according to resource partitioning according to an embodiment of the present invention.
7 is a flowchart illustrating a method of determining a resource allocation ratio according to an embodiment of the present invention.
8 is a flowchart illustrating a method of changing a resource allocation ratio according to an embodiment of the present invention.
9 is a block diagram of an apparatus for controlling a wireless network according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명은 다양한 변경을 가할 수 있고 여러 가지 실시예를 가질 수 있는 바, 특정 실시예들을 도면에 예시하고 상세한 설명에 상세하게 설명하고자 한다. 그러나, 이는 본 발명을 특정한 실시 형태에 대해 한정하려는 것이 아니며, 본 발명의 사상 및 기술 범위에 포함되는 모든 변경, 균등물 내지 대체물을 포함하는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. 각 도면을 설명하면서 유사한 참조부호를 유사한 구성요소에 대해 사용하였다.As the invention allows for various changes and numerous embodiments, particular embodiments will be illustrated in the drawings and described in detail in the written description. However, this is not intended to limit the present invention to specific embodiments, it should be understood to include all modifications, equivalents, and substitutes included in the spirit and scope of the present invention. In describing the drawings, similar reference numerals are used for similar elements.
제1, 제2, A, B 등의 용어는 다양한 구성요소들을 설명하는 데 사용될 수 있지만, 상기 구성요소들은 상기 용어들에 의해 한정되어서는 안 된다. 상기 용어들은 하나의 구성요소를 다른 구성요소로부터 구별하는 목적으로만 사용된다. 예를 들어, 본 발명의 권리 범위를 벗어나지 않으면서 제1 구성요소는 제2 구성요소로 명명될 수 있고, 유사하게 제2 구성요소도 제1 구성요소로 명명될 수 있다. "및/또는"이라는 용어는 복수의 관련된 기재된 항목들의 조합 또는 복수의 관련된 기재된 항목들 중의 어느 항목을 포함한다.Terms such as first, second, A, and B may be used to describe various components, but the components should not be limited by the terms. The terms are used only for the purpose of distinguishing one component from another. For example, without departing from the scope of the present invention, the first component may be referred to as the second component, and similarly, the second component may also be referred to as the first component. The term “and / or” includes any combination of a plurality of related items or any of a plurality of related items.
어떤 구성요소가 다른 구성요소에 "연결되어" 있다거나 "접속되어" 있다고 언급된 때에는, 그 다른 구성요소에 직접적으로 연결되어 있거나 또는 접속되어 있을 수도 있지만, 중간에 다른 구성요소가 존재할 수도 있다고 이해되어야 할 것이다. 반면에, 어떤 구성요소가 다른 구성요소에 "직접 연결되어" 있다거나 "직접 접속되어" 있다고 언급된 때에는, 중간에 다른 구성요소가 존재하지 않는 것으로 이해되어야 할 것이다.When a component is referred to as being "connected" or "connected" to another component, it may be directly connected to or connected to that other component, but it may be understood that other components may be present in between. Should be. On the other hand, when a component is said to be "directly connected" or "directly connected" to another component, it should be understood that there is no other component in between.
본 출원에서 사용한 용어는 단지 특정한 실시예를 설명하기 위해 사용된 것으로, 본 발명을 한정하려는 의도가 아니다. 단수의 표현은 문맥상 명백하게 다르게 뜻하지 않는 한, 복수의 표현을 포함한다. 본 출원에서, "포함하다" 또는 "가지다" 등의 용어는 명세서상에 기재된 특징, 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부품 또는 이들을 조합한 것이 존재함을 지정하려는 것이지, 하나 또는 그 이상의 다른 특징들이나 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부품 또는 이들을 조합한 것들의 존재 또는 부가 가능성을 미리 배제하지 않는 것으로 이해되어야 한다.The terminology used herein is for the purpose of describing particular example embodiments only and is not intended to be limiting of the present invention. Singular expressions include plural expressions unless the context clearly indicates otherwise. In this application, the terms "comprise" or "have" are intended to indicate that there is a feature, number, step, operation, component, part, or combination thereof described in the specification, and one or more other features. It is to be understood that the present invention does not exclude the possibility of the presence or the addition of numbers, steps, operations, components, components, or a combination thereof.
다르게 정의되지 않는 한, 기술적이거나 과학적인 용어를 포함해서 여기서 사용되는 모든 용어들은 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 일반적으로 이해되는 것과 동일한 의미를 가지고 있다. 일반적으로 사용되는 사전에 정의되어 있는 것과 같은 용어들은 관련 기술의 문맥 상 가지는 의미와 일치하는 의미를 가지는 것으로 해석되어야 하며, 본 출원에서 명백하게 정의하지 않는 한, 이상적이거나 과도하게 형식적인 의미로 해석되지 않는다.Unless defined otherwise, all terms used herein, including technical or scientific terms, have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art. Terms such as those defined in the commonly used dictionaries should be construed as having meanings consistent with the meanings in the context of the related art and shall not be construed in ideal or excessively formal meanings unless expressly defined in this application. Do not.
본 명세서에서 엑스홀(Xhaul)은 프론트홀, 미드홀, 그리고 백홀을 통칭하는 데 사용될 수 있다. 엑스홀 네트워크(Xhaul network)는 프론트홀(fronthaul) 네트워크, 미드홀(midhaul) 네트워크 그리고 백홀(backhaul) 네트워크를 모두 지원하는 하나의 통합된 네트워크를 의미할 수 있다.In the present specification, Xhaul may be used to collectively refer to a front hole, a mid hole, and a back hole. The Xhaul network may refer to a single integrated network supporting all of the fronthaul network, the midhaul network, and the backhaul network.
본 명세서에서 프론트홀은, C-RAN(Centralized RAN) 구조에서 집중화된 BBU(Baseband Unit)와 분산화된 RRH(Remote Radio Head) 사이의 인터페이스인 CPRI(Common Public Radio Interface)와 같은 Baseband Digital IQ Stream 형태의 데이터 전송을 제공하는 네트워크 구간을 말한다. 미드홀은, 하나의 기지국 기능을 두 개의 기능 개체로 기능 분할(function split) 함에 있어 통신 프로토콜 스택 상에서 CPRI 대비 상위이면서 PDCP(Packet Data Convergence Protocol) 이하에서 기능 분할을 할 때 분할된 두 기능 개체 사이의 데이터 전송을 제공하는 네트워크 구간을 말한다. 마지막으로 백홀은, 기지국과 핵심네트워크(core network) 사이의 데이터 전송을 제공하는 네트워크 또는 기지국과 기지국 사이의 데이터 전송을 제공하는 네트워크 구간을 지칭한다.In the present specification, the front hole is a baseband digital IQ stream type such as a common public radio interface (CPRI), which is an interface between a centralized baseband unit (BBU) and a distributed remote radio head (RRH) in a centralized RAN (C-RAN) structure. Network section that provides data transmission. The mid-hole is a function split between two functional entities that is higher than CPRI on the communication protocol stack and divides the functions below PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol) in function splitting a single base station function into two functional entities. Network section that provides data transmission. Finally, the backhaul refers to a network providing data transmission between a base station and a core network or a network section providing data transmission between a base station and a base station.
또한, 본 명세서에서 언급하는 엑스홀은 별다른 언급이 없어도 무선 자원을 이용하여 데이터를 전송하는 무선 엑스홀을 의미할 수 있다.In addition, the X-hole referred to herein may refer to a wireless X-hole to transmit data using radio resources even if not mentioned otherwise.
본 명세서 내에 언급되는 액스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크의 통합(integration)은 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크가 동일한 무선 자원을 공유하여 두 개의 링크를 하나의 네트워크 노드에서 같이 제공하는 것을 의미할 수 있다. 통합이라는 의미를 가지되, 이러한 통합의 대상이 되는 두 링크의 의미를 더 명확히 나타낼 필요가 있는 곳에서는 IXA(Integration of Xhaul & Access)라는 표현이 사용되었다.Integration of an access hole and an access link as referred to herein may mean that the xhole link and the access link share the same radio resource to provide two links together in one network node. Where the meaning of integration is needed, but the need to clarify the meaning of the two links that are the subject of this integration, the expression IXA (Integration of Xhaul & Access) is used.
또한, 엑스홀 링크(Xhaul link)는 XL로, 액세스 링크(access link)는 AL로 축약하여 표기될 수 있다.In addition, the Xhaul link may be abbreviated as XL and the access link may be abbreviated as AL.
본 명세서에서 모바일 엑스홀 네트워크(Mobile Xhaul Network, MXN)는 무선 엑스홀 네트워크의 한 예로 언급된다. IXA를 지원하는 MXN, 또는 축약되어 표현된 "IXA 네트워크"는 본 발명에 따른 네트워크의 하나의 예를 의미한다. 또한, IXA 노드는 이러한 IXA 네트워크를 구성하는 노드 또는 IXA 네트워크에 포함되는 노드를 의미할 수 있다.In the present specification, a mobile xhaul network (MXN) is referred to as an example of a wireless xhaul network. MXN supporting IXA, or abbreviated "IXA network" means one example of a network according to the present invention. In addition, the IXA node may mean a node constituting such an IXA network or a node included in the IXA network.
본 발명의 실시예에 따른 모바일 엑스홀 네트워크는 다수의 노드를 포함하여 구성될 수 있다. 각 노드는 무선 XL 및 AL을 동시에 제공할 수도 있고, XL만 제공할 수도 있다. XL 및 AL을 동시에 제공하는 것을 IXA(Integration of Xhaul and Access)라고 정의하고 IXA 기능을 가진 노드를 IXA 노드라고 한다. XL만을 제공하는 노드를 XDU(Xhaul Distributed Unit) 노드라고 정의할 수 있다. 따라서, IXA 노드 중에서 XL만을 제공하는 노드가 XDU가 될 수도 있다. 본 명세서는 IXA 노드는 XDU를 포함하되, XL 노드만을 제공한다는 의미로 사용될 때만 XDU라고 특정할 수 있다.The mobile xhole network according to the embodiment of the present invention may be configured to include a plurality of nodes. Each node may provide wireless XL and AL at the same time, or only XL. Providing both XL and AL at the same time is defined as IXA (Integration of Xhaul and Access), and nodes with IXA capabilities are called IXA nodes. A node providing only XL may be defined as an XDU (Xhaul Distributed Unit) node. Therefore, XDU may be a node providing only XL among IXA nodes. In this specification, an IXA node may include an XDU, but may be designated as an XDU only when used to mean that only an XL node is provided.
또한, 기지국(base station, BS)은 진보된 기지국(advanced base station, ABS), 고신뢰성 기지국(high reliability base station, HR-BS), 노드B(node B), 고도화 노드B(evolved node B, eNodeB), gNB(next generation node B) 접근점(access point, AP), 무선 접근국(radio access station, RAS), 송수신 기지국(base transceiver station, BTS), MMR(mobile multihop relay)-BS, 기지국 역할을 수행하는 중계기(relay station, RS), 기지국 역할을 수행하는 중계 노드(relay node, RN), 기지국 역할을 수행하는 진보된 중계기(advanced relay station, ARS), 기지국 역할을 수행하는 고신뢰성 중계기(high reliability relay station, HR-RS), 소형 기지국[펨토 기지국(femotoBS), 홈 노드B(home node B, HNB), 홈 eNodeB(HeNB), 피코 기지국(pico BS), 메트로 기지국(metro BS), 마이크로 기지국(micro BS) 등] 등을 지칭할 수도 있고, ABS, 노드B, eNodeB, AP, RAS, BTS, MMR-BS, RS, RN, ARS, HR-RS, 소형 기지국 등의 전부 또는 일부의 기능을 포함할 수도 있다.In addition, a base station (BS) may be an advanced base station (ABS), a high reliability base station (HR-BS), a node B (node B), an advanced node B (evolved node B, eNodeB), next generation node B (gNB) access point (AP), radio access station (RAS), base transceiver station (BTS), mobile multihop relay (BSR) -BS, base station Relay station (RS) serving as a role, relay node (RN) serving as a base station, advanced relay station (ARS) serving as a base station, high reliability relay serving as a base station (high reliability relay station (HR-RS)), small base station (femto base station (femotoBS), home node B (home node B (HNB), home eNodeB (HeNB), pico base station (pico BS), metro base station (metro BS) , Micro BS, etc.], and may include ABS, Node B, eNodeB, AP, RAS, BTS, MMR-BS, RS, RN, ARS, HR-RS, small base. It may also include all or part of the functions of the station.
또한 기지국은 셀의 형태에 따라 매크로(Macro) 셀, 원격무선(remote radio head, RRH) 셀, 피코(Pico) 셀, 마이크로(Micro) 셀, 펨토(Femto) 셀 등의 기지국을 지칭할 수 있다.In addition, the base station may refer to a base station such as a macro cell, a remote radio head (RRH) cell, a pico cell, a micro cell, a femto cell, or the like according to a cell type. .
기지국과 단말 간의 통신은 다양한 RAT(radio access technology)(예를 들어, 4G 통신 기술, 5G 통신 기술, WiBro(wireless broadband) 기술, WLAN(wireless local area network) 기술, WPAN(wireless personal area network) 기술 등)에 기초하여 수행될 수 있다.The communication between the base station and the terminal is a variety of radio access technology (RAT) (for example, 4G communication technology, 5G communication technology, wireless broadband (WiBro) technology, wireless local area network (WLAN) technology, wireless personal area network (WPAN) technology) And the like).
이하, 본 발명에 따른 바람직한 실시예를 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 상세하게 설명한다.Hereinafter, exemplary embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 1은 FDM 방식을 이용한 엑스홀 링크 자원 및 액세스 링크 자원 분할 방법의 개념도이다.1 is a conceptual diagram of an XHole link resource and access link resource partitioning method using an FDM scheme.
도 1은 IXA에서 XL 및 AL 두 개의 링크가 FDM(Frequency Division Multiplexing) 방식으로 무선 자원을 공유하여 사용하는 예를 나타낸다. 공유된 무선 자원을 제 1 링크 및 제 2 링크의 두 가지 링크용 자원으로 나누어 사용하는 무선 노드들로 구성된 무선 네트워크의 대표적인 예가 인밴드 셀프-엑스홀(inband self-Xhaul)이다. 여기서, 인밴드 셀프-엑스홀이란, 하나의 노드가 동일한 무선 자원을 공유하여 엑스홀 링크(XL)과 액세스 링크(AL)을 동시에 제공하되, 공유된 무선 자원을 XL과 AL이 배타적으로 나누어 가지는 것을 의미한다.1 illustrates an example in which two links of an XL and an AL share a radio resource in a frequency division multiplexing (FDM) scheme in IXA. An in-band self-Xhaul is a representative example of a wireless network composed of wireless nodes that use a shared radio resource by dividing it into two link resources, a first link and a second link. Here, in-band self-exal means that one node shares the same radio resource and simultaneously provides the XHole link XL and the access link AL, but the shared radio resource is exclusively divided between the XL and the AL. Means that.
도 1을 참조하면, XL과 AL이 무선 자원을 공유한다는 것은 두 종류의 링크가 주어진 주파수-시간 자원을 직교적인(orthogonal) 두 부분의 자원으로 나누어 사용함을 의미한다. 구체적인 자원 분할은 본 발명에 따른 무선 자원 관리(Radio Resource Management) 방법에 따라 결정된다.Referring to FIG. 1, the fact that XL and AL share radio resources means that two types of links divide a given frequency-time resource into two orthogonal resources. Specific resource partitioning is determined according to a radio resource management method according to the present invention.
본 발명에서 제안하는 무선 자원 관리 방법에 따른 자원 분할은 도 1에 도시된 FDM 방식뿐 아니라 TDM(Time Division Multiplexing) 방식에도 적용이 가능하다. 즉, 본 발명에 따른 무선 자원 관리 방법에 따른 자원 분할 방식은 주파수 또는 시간 자원의 분할량을 결정하는 방식이므로, 주파수 분할 방식은 물론 시간 분할 방식에도 적용될 수 있다.Resource division according to the radio resource management method proposed by the present invention can be applied not only to the FDM scheme shown in FIG. 1 but also to a time division multiplexing (TDM) scheme. That is, the resource partitioning method according to the radio resource management method according to the present invention is a method of determining the amount of division of frequency or time resources, and thus may be applied to the time division method as well as the frequency division method.
한편, 각 IXA 노드마다 서로 다른 자원 분할을 사용하는 경우에도, 하나의 IXA 노드 영역 내에서는 XL 및 AL 이 서로 배타적(orthogonal) 자원을 사용하지만, 인접한 IXA 노드의 XL 또는 AL과는 중첩된 자원 영역을 사용할 수 있다. 따라서, XL로부터 AL로의 간섭 또는 AL로부터 XL로의 간섭이 발생할 수 있다. 이러한 XL과 AL의 간섭을 크로스-홀 간섭(cross-haul interference)으로 정의한다.On the other hand, even if each IXA node uses a different resource partition, the resource areas overlapped with XL or AL of adjacent IXA nodes, although XL and AL use orthogonal resources within one IXA node area. Can be used. Thus, interference from XL to AL or interference from AL to XL may occur. This interference between XL and AL is defined as cross-haul interference.
따라서, 크로스-홀 간섭을 회피하기 위해서는 적용 범위 측면에서 전역적(global)이고 적용 대상 측면에서 공통(common)인 자원분할이 필요하다. 본 발명에서는 IXA 네트워크 내의 모든 IXA 노드에 적용되는, 전역적(global)으로 공통인 자원분할 및 무선 자원 관리 방법을 제안한다.Therefore, in order to avoid cross-hole interference, resource division that is global in terms of coverage and common in terms of application is required. The present invention proposes a globally common resource division and radio resource management method applied to all IXA nodes in an IXA network.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 모바일 엑스홀 네트워크 구조를 도시한다.2 illustrates a mobile XHole network structure according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 2에서 도시하는 네트워크는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 IXA를 지원하는 MXN(Mobile Xhaul Network) 구조의 일 실시예이다. 도 2를 참조하면, 본 발명에 따른 모바일 엑스홀 네트워크는 코어 네트워크와 연결되며, 적어도 하나의 IXA 노드(100), XCU(200), 적어도 하나의 IXA 노드(100)와 연결되는 적어도 하나의 사용자 단말(300)을 포함하여 구성될 수 있다.The network shown in FIG. 2 is an embodiment of a Mobile Xhaul Network (MXN) structure supporting IXA according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 2, the mobile XHall network according to the present invention is connected to the core network and at least one user connected to the at least one
모바일 엑스홀 네트워크를 구성하는 각 IXA 노드(100)는 주어진 무선 자원을 공유하여 XL과 AL을 지원한다. 즉, 본 발명에 따른 IXA 노드는 인밴드 셀프-엑스홀 노드일 수 있다. 여기서, IXA 노드는 무선통신 디바이스, 예를 들어, 기지국일 수 있다.Each
또한, 사용자 단말(terminal)은 이동 단말(mobile terminal, MT), 이동국(mobile station, MS), 진보된 이동국(advanced mobile station, AMS), 고신뢰성 이동국(high reliability mobile station, HR-MS), 가입자국(subscriber station, SS), 휴대 가입자국(portable subscriber station, PSS), 접근 단말(access terminal, AT), 사용자 장비(user equipment, UE) 등을 지칭할 수도 있고, MT, MS, AMS, HR-MS, SS, PSS, AT, UE 등의 전부 또는 일부의 기능을 포함할 수도 있다.In addition, the user terminal may be a mobile terminal (MT), a mobile station (MS), an advanced mobile station (AMS), a high reliability mobile station (HR-MS), It may also refer to a subscriber station (SS), a portable subscriber station (PSS), an access terminal (AT), a user equipment (UE), or the like, and may include MT, MS, AMS, It may also include all or part of the functionality of the HR-MS, SS, PSS, AT, UE and the like.
도 2를 참조하면, IXA 노드와 IXA 노드 사이는 XL(Xhaul link)를 통해 연결되고, IXA 노드와 사용자 단말 사이는 AL(Access link)을 통해 연결된다. 여기서, 엑스홀 경로(Xhaul path)는 IXA 네트워크 내 하나의 IXA 노드에서 다른 IXA 노드로 데이터가 흘러가는 하나 또는 그 이상의 엑스홀 링크의 집합으로 정의될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 2, an IXA node and an IXA node are connected through an XL (Xhaul link), and an IXA node and a user terminal are connected through an access link (AL). Here, the Xhaul path may be defined as a set of one or more XHole links through which data flows from one IXA node to another IXA node in the IXA network.
예를 들어, 도 2에 도시된 바와 같이 IXA 네트워크가 백홀 네트워크로 사용될 경우, 다운링크 데이터는 코어(Core)로부터 출발하여, 코어가 연결된 노드부터 사용자 단말이 연결된 노드까지 엑스홀 경로를 통해 전송되고, 이후 사용자 단말이 연결된 노드부터 사용자 단말까지는 AL을 통해 전송된다.For example, as shown in FIG. 2, when the IXA network is used as a backhaul network, downlink data is transmitted from the core to the node to which the user terminal is connected through the X-hole path. After that, the node from the node to which the user terminal is connected is transmitted through the AL.
한편, 도 2에 도시된 XCU(Xhaul Centralized Unit)(200)는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 IXA 네트워크 내 모든 IXA 노드에 적용되는 자원분할을 담당한다. 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, XCU(200)는 IXA 네트워크 전체에 걸친 전역적인 무선 자원 관리를 담당하고, 링크 단위의 무선 자원 관리는 각 링크의 무선 자원 관리를 담당하는 주체에 의해서 수행될 수 있다.On the other hand, the Xhaul Centralized Unit (XCU) 200 shown in FIG. 2 is responsible for resource division applied to all IXA nodes in the IXA network according to an embodiment of the present invention. According to an embodiment of the present invention, the
본 발명이 고려하는 네트워크 구조에서 XL 및 AL의 통달 거리(transmission range)의 관계는 XL 통달 거리 ≥ AL 통달 거리로 설정된다. 이러한 설정은 아래의 이유에 의해 설명될 수 있다.In the network structure considered by the present invention, the relationship between the transmission range of the XL and the AL is set to the XL communication distance? This setting can be explained for the following reasons.
첫 번째로, 극심한 단가 경쟁을 해야 하는 사용자 단말을 고려해야 하는 AL과 달리 XL에는 좀 더 높은 시스템 사양을 요구하는 무선 전송 기술 사용이 가능하다는 점이다.First, unlike AL, which requires user terminals to compete for extreme price, XL can use radio transmission technology that requires higher system specifications.
두 번째로, 배터리를 이용하는 사용자 단말의 제약이 적용되는 AL 대비 XL는 사용 전력 제한에서 비교적 자유롭다.Secondly, XL compared to AL, to which the limitation of the user terminal using the battery is applied, is relatively free from power usage limitation.
세 번째로, 사용자 단말의 폼 팩터(form factor) 제한으로 인해 물리적인 안테나 개수 및 크기에 제한을 받는 AL 대비 XL는 이러한 제한에서 비교적 자유롭다. 예를 들어, XL은 매시브 어레이(massive array)를 이용한 고 이득 안테나(high gain antenna) 등의 사용이 가능하다.Third, XL compared to AL, which is limited in the number and size of physical antennas due to form factor limitation of the user terminal, is relatively free from this limitation. For example, the XL can be used such as a high gain antenna using a massive array.
마지막으로, XL는 일반적으로 큰 전송 용량을 고려하기 때문에 향후 주파수 대역이 풍부한 밀리미터파(mmWave; millimeter wave) 대역을 사용할 것으로 여겨진다. 따라서, LoS(Line of Sight)를 요구하는 밀리미터파의 전송 특징을 고려할 경우 XL 링크는 LoS 확보가 용이한 루프탑(Rooftop) 환경을 가지므로, AL보다 양호한 채널 환경을 가지게 된다. 더욱이, 밀리미터파 사용시 AL 대비 XL에서 장애물(obstacle)의 방해(blocking) 등으로 인한 무선 전송 채널의 급격한 변화가 일어날 확률이 낮다.Finally, because XL generally takes into account large transmission capacities, it is believed that the millimeter wave (mmWave) band, which is rich in future frequency bands, will be used. Therefore, when considering the transmission characteristics of the millimeter wave that requires a line of sight (LoS), the XL link has a better roof environment than the AL since the XL link has a rooftop environment that is easy to secure the LoS. Moreover, the use of millimeter waves is less likely to result in drastic changes in the wireless transmission channel due to obstructions such as obstacle blocking in the XL compared to AL.
본 발명에서는 XL 및 AL의 통달 거리(transmission range) 관계는 XL 통달 거리 ≥ AL 통달 거리로 설정되는 네트워크 구조를 기반으로 한 무선 자원 관리 방법을 제안한다.The present invention proposes a radio resource management method based on a network structure in which a communication range relationship between XL and AL is set to XL communication distance ≥ AL communication distance.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 IXA 네트워크가 셀룰러화되는 예를 나타낸 개념도이다.3 is a conceptual diagram illustrating an example in which an IXA network is cellularized according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 3은 본 발명에 따른 XL 통달 거리 ≥ AL 통달 거리인 관계에 주목하여, 일정 영역에서 AL 링크를 제공하기 위해 셀룰러화된 IXA 네트워크의 예를 나타낸다.3 illustrates an example of a IXA network cellularized to provide an AL link in a given area, noting the relationship of XL distance ≥ AL distance according to the present invention.
본 발명이 적용되는 무선 네트워크에서IXA 노드(100)는 섹터화(sectorized)되어 있음을 가정한다. 본 발명에서 XL 무선 자원 관리를 담당하는 주체는 해당 XL 양단의 섹터 중에서 마스터의 역할을 수행하는 섹터일 수 있으며, 해당 섹터를 마스터 섹터(M)라고 정의할 수 있다. XL 양단의 섹터 중에서 마스터 섹터가 아닌 섹터를 슬레이브 섹터(S)라고 정의할 수 있다. 또한, AL 무선 자원 관리를 담당하는 주체는 해당 AL을 가지는 IXA 노드의 섹터가 된다.It is assumed that the
IXA 노드가 사용자 단말에게 액세스 서비스를 제공할 때, 일정 영역을 AL 통달 거리로 나누어 셀룰러화한다. 도 3에서는 엑스홀 링크의 통달 거리가 액세스 링크의 통달 거리의 2 배일 때의 예를 도시한다. 도 3에서 도시한 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면 액세스 서비스가 제공되는 일정 영역은 IXA 노드를 중심으로 한 육각형 영역만큼의 크기 및 면적으로 설정될 수 있다. 여기서, 육각형 영역은 하나의 노드가 액세스 서비스를 담당하는 영역으로, 비 지향성 안테나를 이용한 옴니 셀(omni cell) 이거나, 육각형 전체 영역을 다시 동일한 크기로 분할하여 3 섹터, 또는 6 섹터 등으로도 구분할 수 있다.When an IXA node provides an access service to a user terminal, the IXA node is cellularized by dividing a certain area by an AL communication distance. 3 shows an example when the communication distance of the exhole link is twice the communication distance of the access link. According to the exemplary embodiment of the present invention illustrated in FIG. 3, a predetermined area where an access service is provided may be set to the size and area of a hexagonal area around the IXA node. Here, the hexagonal area is an area in which one node is in charge of an access service, and may be an omni cell using a non-directional antenna, or may be divided into three sectors or six sectors by dividing the entire hexagonal area into the same size again. Can be.
본 발명은 이러한 통합 네트워크 구조에서 각각의 링크가 사용하는 자원의 비율을 결정함에 있어, 자원의 량을 일일이 변화시켜 가면서 가장 적절한 자원 비율을 찾는 소모적인 방법이 아닌, 측정치를 바탕으로 연산에 의해 자원 비율 및 자원량을 결정할 수 있는 무선 자원 관리 방법을 제안한다.In determining the ratio of resources used by each link in such an integrated network structure, the present invention is not a wasteful method of finding the most appropriate resource ratio by varying the amount of resources. We propose a radio resource management method that can determine the rate and resource amount.
구체적으로, 본 발명이 제공하는 무선 자원 관리 방법은 IXA 네트워크를 이용한 단말 중 가장 낮은 경로 처리량(path throughput)을 갖는 단말의 경로 처리량을 최대화하는 자원 분할비를 제공한다. 여기서, 단말의 경로 처리량은 코어로부터 단말까지의 데이터 흐름을 기준으로 할 때, 단말이 실제적으로 경험하는 다운링크 처리량(throughput)으로 정의될 수 있다. 단말의 경로 처리량에 대해서는 이하에서 좀더 상세히 설명하도록 한다.Specifically, the radio resource management method provided by the present invention provides a resource partition ratio for maximizing the path throughput of a terminal having the lowest path throughput among terminals using the IXA network. Here, the path throughput of the terminal may be defined as the downlink throughput that the terminal actually experiences based on the data flow from the core to the terminal. The path throughput of the terminal will be described in more detail below.
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 IXA 네트워크에서의 단방향 다운링크 데이터 흐름의 예를 도시한다.4 shows an example of a unidirectional downlink data flow in an IXA network according to an embodiment of the present invention.
IXA 네트워크에 포함된 전체 IXA 노드의 개수가일 때, 각각의 IXA 노드를로 표기할 수 있다. IXA 노드가 모두개의 섹터로 구성될 때, 임의의 한 섹터는로 표기할 수 있다. 또한, IXA 노드의 엑스홀 경로는 IXA 노드와 코어를 연결하는 XL 링크들의 집합으로 정의되고,으로 표기될 수 있다. 여기서,는 IXA 노드의 엑스홀 경로상에 있는 아웃-플로우(out-flow) XL(= IXA 노드의 엑스홀 경로상에 있는 인-플로우(in-flow) XL)로 정의될 수 있다.The total number of IXA nodes in the IXA network , Each IXA node It can be written as IXA node Everyone When composed of four sectors, any one sector It can be written as Also, IXA node Xhole Paths to IXA Nodes Defined as a set of XL links connecting the core to It may be indicated by. here, IXA node Out-flow XL (= IXA node on xhole path of It can be defined as in-flow XL on the XHole path of.
예를 들어, 도 4를 참조하면, IXA 노드의 엑스홀 경로상에 있어서 코어에 가장 가까운 IXA 노드는이고,와을 연결하는 XL이 이다. 또한, IXA 노드의 엑스홀 경로상에 있어서와 가장 가까운 IXA 노드는이고,와을 연결하는 XL이이다. 섹터화된 IXA 노드의 경우, 섹터마다 다른 엑스홀 경로를 가질 수도 있다. 섹터가 가지는 엑스홀 경로에 대한 엑스홀 경로 처리량을 로 표기한다. 경로 처리량은 bps(bits per second)로 표시된다.For example, referring to FIG. 4, an IXA node The IXA node closest to the core in the xhole path of ego, Wow XL to connect to be. Also, IXA node On the xhole path of The closest IXA node to ego, Wow XL to connect to be. In the case of sectorized IXA nodes, each sector may have a different xhole path. Sector The XHole path throughput for the XHole path It is written as. Path throughput is expressed in bits per second (bps).
섹터와 AL로 연결된 단말이 총개일 때, 섹터와 AL로 연결된 임의의 한 단말은로 표기할 수 있다.Sector Terminal connected to and AL When sector Any terminal connected with and AL It can be written as
도 4의 실시예에서는 코어로부터 단말로의 다운링크만을 고려한 단방향(uni-directional) 직렬(tandem) IXA 네트워크를 도시하고 있다. 도 4에서 섹터의 개수=6 인 경우를 나타낸다. 도 4의 네트워크는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 통합 네트워크 구조에서 각각의 링크가 사용하는 자원의 비율을 결정하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 IXA 네트워크의 일 예이다.The embodiment of FIG. 4 illustrates a uni-directional tandem IXA network considering only the downlink from the core to the terminal. Number of sectors in FIG. The case of = 6 is shown. 4 is an example of an IXA network for explaining a method of determining a ratio of resources used by each link in an integrated network structure according to an embodiment of the present invention.
XCU는 제어에만 관련하므로 단방향 트래픽의 표현에 집중하기 위해 도 4에 도시되어 있지 않으나, 임의의 IXA 노드 또는 코어와 유선 링크를 통해 연결되어 있고, 모든 IXA 노드와 제어 정보를 교환할 수 있다.XCU is not shown in FIG. 4 in order to concentrate on the representation of unidirectional traffic since it relates only to control, but is connected via a wired link with any IXA node or core, and can exchange control information with all IXA nodes.
설명의 편의를 위해 코어로부터 사용자 단말로의 단방향(uni-directional) 트래픽을 고려한다. 즉, 트래픽은 코어로부터 발생하는 것으로 가정한다. 코어로부터 발생된 트래픽은 코어와 탠덤 IXA 네트워크를 연결하는 유선 링크를 통해에 전달된다. 이 유선 링크는 탠덤 IXA 네트워크가 요구하는 대역폭을 충분히 만족시키는 광대역 링크일 수 있다.Consider uni-directional traffic from the core to the user terminal for convenience of description. In other words, it is assumed that traffic originates from the core. Traffic from the core is routed over the wired link between the core and the Tandem IXA network. Is passed on. This wired link may be a broadband link that satisfies the bandwidth required by a Tandem IXA network.
IXA 노드의 인-플로우 XL은 섹터와 연결되고, 아웃-플로우 XL은 섹터와 연결된다. 인-플로우 XL를 통해 IXA 노드로 전달된 트래픽은, 목적지가내의 섹터와 연결된 단말일 경우 AL 통해 단말로 전송된다. 그렇지 않다면, 즉, 목적지가내의 섹터와 연결된 단말이 아닌 경우, 전달되어 온 트래픽은 아웃-플로우 XL를 통해 IXA 노드로 전달된다. 다시 말해, IXA 노드 차제는 트래픽을 새롭게 생성하는 원천(source) 또는 수신된 트래픽을 소비/감소시키는 목적지(destination)가 될 수 없다. 따라서, IXA 노드에서는 아래 수학식 1에 의해 정의되는 단방향 트래픽 보존식이 항상 성립한다.IXA node In-flow XL Silver sector Connected to the out-flow XL Silver sector Connected with In-flow XL Through IXA nodes Traffic sent to Sectors within Terminal connected to AL if Through terminal Is sent to. If not, that is, the destination Sectors within If it is not connected with the terminal, the forwarded traffic is out-flow XL Through IXA nodes Is passed to. In other words, an IXA node delegation cannot be a source of new traffic or a destination of consuming / reducing received traffic. Thus, IXA node In
수학식 1에서는 엑스홀 링크에 할당된 주파수-시간 자원,는 액세스 링크에 할당된 주파수-시간 자원을 나타낸다. 또한,는 엑스홀 링크의 주파수 효율(spectral efficiency), 즉, 단위 주파수-시간 자원에서 보낼 수 있는 정보량(bits/sec/Hz 단위를 가짐)을 나타낸다. 또한,는 액세스 링크의 주파수 효율을 나타낸다.In
여기서, 주파수 효율과 주파수-시간 자원의 곱은 정보량, 즉 트래픽을 의미한다. 따라서, 수학식 1의 좌변은 인-플로우 정보량/트래픽을, 수학식 1의 우변은 아웃-플로우 정보량/트래픽과 IXA 내의 각각의 섹터에 연결된 단말로 전달되는 모든 정보량/트래픽을 나타낸다.Here, the product of the frequency efficiency and the frequency-time resource means the amount of information, that is, the traffic. Accordingly, the left side of
본 발명에서는, IXA 네트워크에서 공유된 무선 자원을 XL을 위한 자원과 AL을 위한 자원 두 부분으로 직교적(orthogonal)으로 분할한다. 이러한 자원 분할을 위해, 먼저 자원 분할 구조를 결정해야 한다. 여기서, 도 4에서와 같이 다운링크만 고려한다 할지라도, 자원 분할 구조를 결정함에 있어 자기-간섭(self-interference)을 고려해야 한다. 자기-간섭은 한 노드의 서로 다른 섹터가 수신과 송신을 동시에 수행할 때, 송신하는 섹터에서의 송신 신호가 수신하는 섹터의 수신 신호에 대한 간섭으로 작용하는 현상이다. 따라서, XL용 자원은 이러한 자기-간섭을 피할 수 있는 구조인 것이 바람직하다.In the present invention, the radio resources shared in the IXA network are orthogonally divided into two parts, a resource for the XL and a resource for the AL. For such resource partitioning, the resource partitioning structure must first be determined. Here, although only the downlink is considered as in FIG. 4, self-interference should be considered in determining the resource partition structure. Self-interference is a phenomenon in which when a different sector of a node simultaneously performs reception and transmission, a transmission signal in a transmitting sector acts as an interference to a received signal of a receiving sector. Therefore, the resource for XL is preferably a structure that can avoid such self-interference.
이하에서 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 자원 분할 구조를 설명함에 있어, XL용 자원과 AL용 자원의 TDM(Time Division Multiplexing) 방식의 자원 분할 구조가 사용된다. 하지만 TDM 방식은 하나의 예시일 뿐, TDM 방식의 자원 분할 구조 및 그에 대한 설명에서 시간과 주파수 위치를 바꾸면 손쉽게 FDM 방식의 자원 분할 구조 및 그에 대한 설명으로 변환 가능함이 이해될 수 있다.In the following description of the resource partitioning structure according to an embodiment of the present invention, a resource division structure of a time division multiplexing (TDM) method of an XL resource and an AL resource is used. However, the TDM scheme is just one example, and it can be understood that the resource division structure of the TDM scheme and the description thereof can be easily converted to the resource division structure and the description of the FDM scheme by changing the time and frequency position.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 IXA 노드와 연관된 세 가지 유형의 링크를 나타낸다.5 illustrates three types of links associated with IXA nodes in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
IXA 노드(100-1)는 해당 노드로 유입되는 인-플로우 XL인, 해당 노드로부터 유출되는 아웃-플로우 XL인, 및 해당 노드와 연동하는 단말 로 향하는 AL인 의 3 개의 링크와 연관된다.IXA node 100-1 is an in-flow XL that , Out-flow XL leaked from that node , And terminal interworking with the node AL to go to Is associated with three links.
도 5를 참조하여, 자기 간섭을 회피하고 각 링크들의 전송이 동시에 이루어질 수 있는지 여부를 설명한다.Referring to FIG. 5, it will be described whether the transmission of each link can be performed at the same time to avoid magnetic interference.
우선, 링크 와 링크의 경우, 두 링크가 같은 섹터에 포함될 수 없다. 이는 해당 섹터가 수신과 송신을 동시에 하는 전이중(full duplex) 기능을 요구하기 때문이다. 본 발명의 실시예에서 무선 송수신 장치는 반이중(half duplex) 장치만을 고려한다.First of all, the link And link In this case, two links cannot be included in the same sector. This is because the sector requires a full duplex function to simultaneously receive and transmit. In an embodiment of the present invention, the radio transceiver only considers a half duplex device.
다시 말해, 본 발명의 실시예에서 동일한 섹터 내에서 양 링크의 동시 전송은 고려하지 않는다. 동시 전송을 위해서는 두 개의 디지털 체인을 필요로 하기 때문에 하드웨어 복잡도가 높아지고, 두 링크가 전송 전력을 나누어 가지므로 양 링크의 통달 거리를 축소시키는 단점이 발생하기 때문이다. 하지만, 무엇보다도 XL의 수신 XDU(Xhaul Distributed Unit)가 AL의 수신 단말과 동일한 방위각(azimuth angle)에 있을 경우, 간섭으로 인해 XL 수신 시 간섭, 특히, AL의 수신 시 간섭이 심각하기 때문이다.In other words, in the embodiment of the present invention, simultaneous transmission of both links within the same sector is not considered. Because two digital chains are required for simultaneous transmission, hardware complexity increases and two links share transmission power, which reduces the communication distance of both links. But above all, XL Receive XDU (Xhaul Distributed Unit) This is because when the interference is at the same azimuth angle as the receiving terminal of, the interference when receiving the XL, particularly, when receiving the AL is severe.
또한, 링크 와 링크 가 포함된 섹터가 서로 다른 섹터이더라도 에서의 수신과에서의 송신이 동시에 일어날 경우 자기 간섭이 발생할 수 있다. 따라서, 본 발명의 일 실시예에서는, 과는 XL용으로 할당된 자원을 시간축상 직교적으로 분할하여 사용한다.Also, link And link Even if the sectors containing Reception at Magnetic transmission can occur if the transmissions at the same time occur. Thus, in one embodiment of the present invention, and Uses partitions allocated for XL orthogonally on the time base.
단말로 향하는 링크와 엑스홀 링크 간, 즉 와 및 와의 경우, 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크는 직교적으로 분할된 자원을 사용하므로 자기 간섭이 발생하지 않는다.Between the link to the terminal and the XHole link, Wow And Wow In the case of, the XHole link and the access link use orthogonally divided resources, so that no magnetic interference occurs.
이상 살펴본 바와 같은 IXA 노드에서의 세가지 링크의 동시 전송 가능성 으로부터 아래 수학식 2에 의해 나타낼 수 있는 자원 분할이 가능하다.From the possibility of simultaneous transmission of three links in the IXA node as described above, resource division represented by
수학식 2에서 R은 사용 가능한 전체 무선 자원을 나타낸다.를 섹터에서의 AL용 자원의 크기, 즉, 로 정의하면, 수학식 2에 따른 자원 분할식은 아래 수학식 3으로 표현될 수 있다.In
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 자원 분할에 따른 링크 별 자원 분할 구조도이다.6 is a diagram illustrating a structure of resource division for each link according to resource partitioning according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 6의 좌측에는 본 실실예에서 고려하는 2개의 IXA 노드 (100-1) 및 (100-2)와 연관되는 3가지 유형의 5개의 링크가 도시된다. IXA 노드 및 가 모두개의 섹터로 구성된다고 했을 때, 본 실시예에서는 각 노드가 링크의 종류 및 링크의 송수신 여부에 따라 서로 다른 3가지 종류의 섹터를 가진다고 가정한다. 따라서, 도 6의 우측에는 2개의 노드별 각 3종류의 섹터, 즉, 총 6개의 섹터에 대한 자원 분할 구조( 에 대한 자원분할 구조(6a) 및 에 대한 자원분할 구조(6b))가 도시된다.On the left side of Fig. 6 are two IXA nodes considered in this practical example. (100-1) and Three types of five links are shown that are associated with 100-2. IXA node And Everyone In this embodiment, it is assumed that each node has three different types of sectors depending on the type of link and whether the link is transmitted or received. Therefore, on the right side of Fig. 6, the resource partitioning structure for each of three types of sectors of two nodes, that is, six sectors in total ( Partitioning structure (6a) for
도 6의 자원 분할 구조도에서 네트워크 전체의 XL 자원과 AL 자원의 경계는 시간 축 상에서 분리 정렬(align)되는데, 이는 XL와 AL 사이의 간섭(cross-haul interference)을 없애기 위한 것이다.In the resource partition structure diagram of FIG. 6, the boundary between the XL resource and the AL resource of the entire network is aligned on the time axis, so as to eliminate cross-haul interference between the XL and the AL.
네트워크 전체의 모든 IXA 노드의 모든 섹터에 공통적으로 적용하는 자원 분할 구조에 대한 식은, 앞서 살펴본 자원 분할 관련 수학식을 IXA 노드의 인덱스 x 및 섹터 인덱스 s에 독립적으로 구성하면 도출될 수 잇다. 이를 위해, 네트워크 전체의 모든 IXA 노드의 모든 섹터에 공통적으로 적용되는 XL 용 무선 자원을라 하고, AL 용 자원을라고 정의한다. 즉,,The equation for the resource partitioning structure commonly applied to all sectors of all IXA nodes throughout the network can be derived by independently configuring the above-described resource partitioning equations independently on the index x and the sector index s of the IXA node. For this purpose, radio resources for the XL, which are common to all sectors of all IXA nodes throughout the network, Resource for AL It is defined as. In other words, ,
으로 정의하면, 자원 분할 식은 아래 수학식 4와 같이 간단히 통합 표현될 수 있다. In this case, the resource partition equation can be simply expressed as in Equation 4 below.
도 6의 자원 분할 구조도에서 네트워크 전체의 XL 자원과 AL 자원의 경계는 시간 축 상에서 분리 정렬(align)되는데, 이는 XL와 AL 사이의 간섭(cross-haul interference)을 제거하기 위한 것이다.In the resource partition structure diagram of FIG. 6, the boundary between the XL resource and the AL resource of the entire network is aligned on the time axis to remove cross-haul interference between the XL and the AL.
한편, 사용자 단말 관점에서 가장 중요한 메트릭(metric) 중의 하나가 높은 처리량(throughput)이다. 사용자가 최종적으로 수신하는 트래픽은 코어로부터 XL들을 거쳐 최종적으로 AL를 거쳐 사용자 단말로 전달되는 트래픽이다. 그러므로, 사용자 단말이 최종적으로 수신하는 트래픽은 각 링크에서 해당 단말의 트래픽에 할당된 처리량에 의해 제한(bound)된다. 따라서, 사용자가 직접적으로 경험하는 트래픽 처리량은 트래픽 전송 경로 상의 최저 처리량을 가지는 링크에 의해 제약될 수밖에 없다. 그러므로, 단말에 대한 경로 처리량(path throughput)은 아래 수학식 5와 같이 정의될 수 있다.On the other hand, one of the most important metrics from the user terminal point of view is high throughput. The traffic that the user finally receives is traffic that passes from the core through the XLs and finally through the AL to the user terminal. Therefore, the traffic finally received by the user terminal is bounded by the throughput allocated to the traffic of that terminal on each link. Therefore, the traffic throughput experienced directly by the user is inevitably limited by the link having the lowest throughput on the traffic transmission path. Therefore, the terminal Path throughput for May be defined as in Equation 5 below.
수학식 5에서,는 XL에서 단말에 할당된 링크 처리량이다. 또한, min(ㆍ) 함수 내 제일 마지막 요소인는 경로 상의 최종 링크인 AL에서의 링크 처리량을 나타낸다.In Equation 5, XL Terminal Link throughput allocated to. Also, the last element in the min (·) function Denotes the link throughput in AL which is the last link on the path.
전체 무선 자원에 대한 AL용 자원의 비를 라고 할 때, 본 발명의 실시예에서는, 네트워크 전체에서 최소 경로 처리량을 가지는 단말의 경로 처리량을 극대화시키는 α, 즉 자원분할 비율를 결정하는 방법을 제안한다.The ratio of resources for AL to total radio resources In this case, the embodiment of the present invention proposes a method of determining α, that is, resource partition ratio, which maximizes the path throughput of a terminal having the minimum path throughput in the entire network.
이를 위해, 네트워크 전체에서 최소 경로 처리량 은 수학식 6과 같이 정의될 수 있다.To do this, the minimum path throughput across the network May be defined as in Equation 6.
forfor
또한, 본 발명에 따른 목적 함수(objective function)은 아래 수학식 7과 같이 나타낼 수 있다.In addition, an objective function according to the present invention may be represented by Equation 7 below.
다만, 수학식 7은 앞서 살펴본 수학식 4()에 의해 제한된다. 이와 같은 제한을 가지고 상기 목적 함수를 만족시키는 자원분할 비율 α를 찾기 위해서는, 경로를 구성하는 XL 및 AL 각각의 스케줄링 정책에 대한 정의가 필요하다.However, Equation 7 is expressed in the above Equation 4 ( Limited by). In order to find the resource partition ratio α that satisfies the objective function with this limitation, a definition of the scheduling policy of each of XL and AL constituting the path is required.
먼저 AL의 스케줄링 정책과 관련, 네트워크 내의 모든 섹터의 AL를 담당하는 섹터 별 AL 스케줄러는 라운드-로빈(Round-robin) 스케줄링을 한다고 가정한다. 라운드-로빈(Round-robin) 스케줄링 시 AL 전체 자원을 연결된 각 단말이 균등히 나누어 가지게 된다. 따라서, 단말가 가지는 AL 자원은이다.First, in relation to the scheduling policy of an AL, a sector-by-sector AL scheduler in charge of AL of all sectors in a network assumes round-robin scheduling. When round-robin scheduling is performed, each connected terminal is divided evenly among the entire AL resources. Thus, the terminal Has an AL resource to be.
다음으로, XL의 스케줄링 정책과 관련, 네트워크 내의 모든 XL를 담당하는 마스터 섹터의 XL 스케줄러는 사용자 비례(user-proportional) 스케줄링을 한다고 가정한다. 즉, 하나의 XL 처리량을 해당 XL를 공유하는 모든 단말이 균등히 나누어 가진다고 가정한다. 따라서, XL에서 단말에 할당된 XL 링크 처리량는 수학식 8과 같이 나타낼 수 있다.Next, with respect to the XL's scheduling policy, it is assumed that the XL scheduler of the master sector that is responsible for all XLs in the network has user-proportional scheduling. That is, it is assumed that all of the terminals sharing one XL evenly share the XL throughput. Thus, XL Terminal Link throughput allocated to Can be expressed as in Equation 8.
본 발명에 따른 목적함수를 간단한 선형식(linear equation)으로 나타내기 위해 앞서의 스케줄링 정책에 기반하여 아래와 같은 두 계수(coefficient)를 정의한다.In order to represent the objective function according to the present invention as a simple linear equation, the following two coefficients are defined based on the above scheduling policy.
이렇게 되면, 경로 처리량은 아래 수학식 9와 같이 간단히 나타낼 수 있다.In this case, the path throughput can be simply expressed as in Equation 9 below.
그러면, 의 정의로부터 이고 이다.then, From the definition of ego to be.
이로써, 주어진 문제는 선형식,, 그리고 을 만족하는 최대의를 구하는 선형 프로그래밍(linear programming)에 의한 최적화(optimization) 문제로 정의될 수 있다.Thus, the given problem is linear , , And To satisfy It can be defined as an optimization problem by linear programming.
최대의은일 때 얻어질 수 있다. 그러므로, 이 때의 최적화된 자원 분할 비율는 이다.Maximum silver Can be obtained when Therefore, the optimized resource partition ratio at this time Is to be.
또한, 이 때의 최적화된은 아래 수학식 10과 같이 정의될 수 있다.Also, the optimization at this time May be defined as in Equation 10 below.
앞서 설명한 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 자원 분할 비율의 결정은, IXA 노드를 통한 측정, XCU를 통한 측정된 정보의 취합 또는 수집을 거쳐 XCU에 의해 수행될 수 있다.Determination of the resource partition ratio according to the embodiment of the present invention described above may be performed by the XCU through measurement through the IXA node, collection or collection of measured information through the XCU.
본 발명의 실시예에 따른 자원 분할 비율을 결정하기 위해서는 우선 엑스홀 링크들의 주파수 효율 및 액세스 링크들의 주파수 효율에 대한 측정이 필요하다.In order to determine a resource partition ratio according to an embodiment of the present invention, first, measurement of the frequency efficiency of the XHole links and the frequency efficiency of the access links is required.
본 발명에 따른 자원 분할 비율을 결정하기 위해서는, 먼저 네트워크 내의 모든 엑스홀 링크들의 주파수 효율이 측정되어야 한다.In order to determine the resource partition ratio according to the present invention, first, the frequency efficiency of all Xhole links in the network must be measured.
다시 말해, XL의 주파수 효율의 측정이 필요하다. 여기서, 엑스홀 링크의 주파수 효율의 측정은 XL의 마스터 섹터에 의해 수행될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 엑스홀 링크의 주파수 효율의 측정은, 일정 시간 길이를 가지는 이동하는 시간 구간에 대해 수행되거나, 시간 간격마다 수행될 수 있다. 측정을 수행한 마스터 섹터는 측정된 값을 XCU에게 보고하며, XCU는 네트워크 내 모든 XL의 주파수 효율 정보를 수집/취합할 수 있다.In other words, XL Frequency efficiency Measurement is required. Here, the measurement of the frequency efficiency of the X-hole link is XL It can be performed by the master sector of. For example, the measurement of the frequency efficiency of the X-hole link, a moving time interval having a certain time length Or for It may be performed every time interval. The master sector performing the measurement reports the measured value to the XCU, which can collect / gather frequency efficiency information of all XLs in the network.
본 발명에 따른 자원 분할 비율을 결정하기 위해서는 또한, 네트워크 내의 모든 액세스 링크들의 주파수 효율이 측정되어야 한다.In order to determine the resource partition ratio according to the present invention, the frequency efficiency of all access links in the network must also be measured.
즉, IXA 노드의 섹터와 단말의 연결에 쓰이는 AL의 주파수 효율인이 측정되어야 한다. 따라서, 측정의 주체는 단말가 연결된 섹터가 될 수 있다. 액세스 링크의 주파수 효율의 측정은, 예를 들어, 이동하는 시간 구간에 대해 수행되거나 시간 간격마다 수행될 수도 있다. 섹터는 측정 값을 XCU에게 보고하며, XCU는 네트워크 내 모든 AL의 주파수 효율 정보를 수집/취합할 수 있다.That is, IXA node Sector Terminal AL used to connect Frequency efficiency of This should be measured. Therefore, the subject of measurement is the terminal Connected sector Can be The measurement of the frequency efficiency of the access link is, for example, a moving time interval. Performed on or It may be performed every time interval. Sector Reports the measurement to the XCU, which can collect / gather frequency efficiency information for all ALs in the network.
다음으로, XCU는 엑스홀 링크들의 주파수 효율 및 액세스 링크들의 주파수 효율을 이용해 자원 분할비의 결정하기 위해 앞서 언급한 계수를 계산한다. 앞서 살펴본 바와 같이는으로 정의될 수 있다.Next, the XCU uses the aforementioned coefficients to determine the resource partition ratio using the frequency efficiency of the XHole links and the frequency efficiency of the access links. Calculate As we saw earlier Is It can be defined as.
의 계산을 위해서는 하나의 IXA 노드뿐만이 아니라,등과 같이 다수의 IXA 노드들로부터 필요한 정보가 수집되어야 한다. 또한,의 분모에 있는 와 같은 팩터들 역시 다수의 IXA 노드의 모든 섹터로부터 수집되는 정보를 통해 산출될 수 있다. For the calculation of not only one IXA node, Necessary information must be collected from multiple IXA nodes. Also, In the denominator of Factors such as may also be calculated through information collected from all sectors of multiple IXA nodes.
따라서, 계산의 주체는 XCU이 된다. XCU의 xRM(Xhaul Resource Management)이 네트워크 내의 모든 IXA 노드들의 섹터들로부터 엑스홀의 주파수 효율인를 보고받고, 해당 정보를 취합하여 사용한다. 또한, XCU는 각 섹터 별로 연결되어 있는 사용자 수()에 대한 정보를 획득하여를 계산한다. 값은 시간 구간 또는의 정수 배의 시간마다 계산 및 업데이트된다.therefore, The subject of the calculation is the XCU. Xhaul Resource Management (xRM) of the XCU is the frequency efficiency of the XHole from the sectors of all IXA nodes in the network. Report and receive and use the information collected. In addition, XCU is the number of users connected by sector ( ) Get information about Calculate The value is a time interval or The integer times of are calculated and updated every time.
여기서, xRM(Xhaul Resource Management)은 XCU 내의 블록으로, IXA를 지원하는 MXN 네트워크 전반의 자원 관리 기능을 수행한다. 한편, XCU는 단말,의 AL의 링크 처리량 계산에 필요한 계수,도 계산한다.는 으로 정의될 수 있다.의 계산에는 섹터 내에서 얻을 수 있는 정보들만 필요하다. 섹터가 측정한를 이용하여 직접을 계산하여 XCU로 보고하는 것도 가능하다. 하지만, XCU는 이미를 알고 있다. 또한,는 오직 자원 분할에만 쓰이는 정보임에 반해는 네트워크 모니터링과 같은 다른 기능에도 사용될 수 있다. 따라서, 섹터는 직접을 계산하여 XCU로 보고하지 않고 자신이 측정한를 XCU에게 보고하고, 이를 바탕으로 XCU가을 계산한다. 값은 시간 구간 또는의 정수 배의 시간마다 계산 및 업데이트된다.Here, xhaul resource management (xRM) is a block in the XCU, and performs resource management functions for the entire MXN network supporting IXA. On the other hand, the XCU is a terminal, Coefficients needed to calculate the link throughput of AL, Calculate also. Is It can be defined as. The computation of requires only the information that can be obtained in the sector. Sector Measured by Directly using It is also possible to calculate and report to XCU. However, XCU already Know. Also, Is used only for resource partitioning, Can also be used for other functions such as network monitoring. Thus, sector Direct Is calculated by the user and not reported to the XCU. Is reported to the XCU, and the XCU Calculate The value is a time interval or The integer times of are calculated and updated every time.
XCU는 상기한 측정 항목들을 토대로 계산한및를 아래 수학식 11식에 대입하여 전체 주파수-시간자원 대비 액세스 링크에 대한 자원의 비율,를 산출한다.XCU calculates based on the above And By substituting
XCU는 시간 구간 동안 측정한 측정치에 기초하여 산출한 α의 값을 시간 구간 또는의 정수 배의 시간마다 계산 및 업데이트한다.XCU time interval Is a time interval based on the measured value or Calculate and update every hour of integer times.
상기 수학식 11에 의해 도출된 자원분할 비율이 그대로 IXA 네트워크에 적용될 수도 있지만, 네트워크에 실제 적용되는 분할 비율 α의 값은 양자화(Quantized)된 값일 수 있다. 즉, 전체 네트워크에 실제에 적용될 수 있는 α의 값은, 테이블 형태로 정리 가능한 유한한 개수의 값들 중 하나로 변환, 적용될 다. 예를 들어, XCU는 수학식 11에 따라 산출한 α값을 테이블 내 값들과 비교하고 테이블 내 값들 중 α 와 가장 근사한 값을 선택하여 실제 네트워크 전체에 적용할 수 있다.Although the resource division ratio derived by
산출된 자원분할 비율을 양자화하여 실제 네트워크에 적용하는 방법은 아래의 경우들에서 바람직할 수 있다.A method of quantizing the calculated resource division ratio and applying it to an actual network may be preferable in the following cases.
첫 번째로, 크로스-홀 간섭(cross-haul interference)을 회피하기 위해, 네트워크 내의 모든 IXA 노드의 α 값을 새롭게 업데이트된 값으로 동시에 적용하는 것은 많은 시그널링 오버헤드를 수반하는 아주 높은 비용이 소모될 수 있다. 설령 네트워크에 임의의 α 값 적용이 가능하다고 하더라도, α 값이 조금 바뀌었다고(예를 들어, α의 변경 정도가 양자화 스텝보다 작은 경우) 높은 비용이 수반되는 전체적인 업데이트 동작을 수행하는 것은 비효율적일 수 있다. 따라서, 이러한 경우는 양자화된 자원분할 비율을 네트워크에 적용함으로써 빈번한 업데이트 동작을 방지할 수 있다.First, in order to avoid cross-haul interference, simultaneously applying the α value of all IXA nodes in the network to the newly updated values would be very expensive, involving a lot of signaling overhead. Can be. Even if an arbitrary value of α can be applied to the network, it may be inefficient to perform a global update operation that involves a high cost if the value of α has changed slightly (e.g. if the degree of change of α is less than the quantization step). have. Therefore, in such a case, frequent update operation can be prevented by applying the quantized resource division ratio to the network.
두 번째로, XL 또는 AL의 전송 기술이 사용 가능한 대역폭이 양자화되어 있는 경우, 양자화된 자원분할 비율을 사용하는 것이 바람직하다. 대부분의 무선 접속 기술에서 사용 가능한 대역폭이 양자화되어 있는 것을 고려하면 대부분의 IXA 네트워크가 이에 해당할 수 있다.Secondly, if the available bandwidth of the XL or AL transmission technique is quantized, it is preferable to use the quantized resource division ratio. Considering that the bandwidth available in most radio access technologies is quantized, most IXA networks can do this.
이상 살펴본 바와 같은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 자원할당 비율 결정 방법을 정리하여 도 7에서 도시한다.A method of determining resource allocation ratios according to an embodiment of the present invention as described above is shown in FIG. 7.
도 7은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 자원할당 비율 결정 방법의 동작 흐름도이다.7 is a flowchart illustrating a method of determining a resource allocation ratio according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 7에 도시된 자원할당 비율 결정 방법의 동작 주체는 XCU(200)일 수 있다. XCU(200)는 IXA 노드(100)로부터 액세스 링크와 관련한 측정치들을 보고받고 본 발명에 따른 자원할당 비율을 결정한다.The operation subject of the resource allocation ratio determination method illustrated in FIG. 7 may be the
IXA 노드(100)는 액세스 링크를 담당하는 eNB/gNB(110) 및 엑스홀 링크를 담당하는 XDU(120)를 포함할 수 있다.The
XCU(200)는 xRM(210), xTD(220), 및 xPM(230)을 포함할 수 있다. xRM(Xhaul Resource Management)은 IXA를 지원하는 MXN 네트워크 전반의 자원 관리 기능을 수행하는 블록이다. 또한, xTD(Xhaul Topology Database)는 전체 네트워크의 토폴로지를 저장하고, xPM(Xhaul Path Management)은 네트워크 내의 경로 관리를 담당한다.The
우선 XCU 내 xRM(210)은 네트워크 내의 모든 섹터의 연결(attach) 정보를 획득한다(S710). 섹터의 연결 정보는 eNB/gNB(110)의 각 섹터 및 XDU(120)의 각 섹터로부터 XCU(200) 내 xRM(210)로 전달된다. 여기서, 연결 정보는 해당 노드가 XCU에 등록되어 MXN을 구성하는 노드로 인식되어 동작할 수 있게 하는 정보이다. 획득된 연결(attach) 정보는 경로 갱신(path update)를 위해 xPM(230)으로 전달되고 xTD에 저장된다(S720, S730). 한편, 도시하지는 않았으나, xRM은 IXA 노드의 eNB/gNB의 섹터 로부터 IXA 노드 구성(configuration) 정보를 수신한다. IXA 노드 구성 정보는 IXA 노드가 XCU에 의해 인식되는 데 필요한 정보로서, IXA 노드를 구성하는 XDU 및 eNB/gNB의 식별 정보를 포함한다. 이러한 식별 정보는 xTD(220)에 전달되며, xTD(220)는 IXA 노드를 포함하는 전체 네트워크 토폴로지 정보를 저장한다(S730).First, the
XCU는 XDU(120)로부터 사용자 연동(user association) 정보를 수집하여(S740), 액세스 링크로 연결된 단말의 개수를 업데이트한다(S750). xRM(210)은 또한 XDU(120)로부터 엑스홀 링크의 주파수 효율 를 수집하고(S760), xTD(220)에 저장된 네트워크 토폴로지 및 경로 정보를 획득한다(S761).XCU collects user association information from the XDU 120 (S740), the number of terminals connected by an access link Update (S750). The
xRM(210)은 엑스홀 링크의 주파수 효율, 그리고 네트워크 토폴로지 및 경로 정보를 이용해 해당 단말과 연관된 경로에서 최소 엑스홀 링크 처리량 계산에 필요한 계수를 계산한다(S770).는The
로 표현될 수 있다.It can be expressed as.
xRM(210)은 또한, eNB/gNB(110)로부터 액세스 링크의 주파수 효율를 수신하고(S780), 액세스 링크의 주파수 효율을 이용해 액세스 링크의 처리량 계산에 필요한 계수 를 계산한다(S790). xRM(210)은 엑스홀 링크 처리량 계산에 필요한 계수 및 액세스 링크의 처리량 계산에 필요한 계수 를 이용해 전체 자원 대비 액세스 링크 자원의 비율로 정의되는 본 발명에 따른 자원분할 비율를 계산한다(S795).The
상술한 절차에 따라 XCU에 의해 결정되는 자원 분할 비율는 네트워크 내의 모든 노드의 모든 섹터에게 전달되며, 각 섹터는 XCU로부터 제공받은 자원분할 비율에 따라 엑스홀 링크와 액세스 링크의 자원량을 조정할 수 있다.Resource division ratio determined by the XCU according to the above procedure Is transmitted to all sectors of all nodes in the network, and each sector may adjust the amount of resources of the XHole link and the access link according to the resource partition ratio provided from the XCU.
도 8은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 자원할당 비율 변경 방법의 동작 흐름도이다.8 is a flowchart illustrating a method of changing a resource allocation ratio according to an embodiment of the present invention.
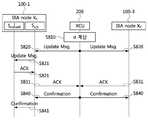
도 8의 자원할당 비율 변경 방법은 적어도 하나의 IXA 노드(100-1, 100-3) 및 XCU(200) 간에 이루어지는 동작을 중심으로 설명된다. 도 8의 실시예는 하나의 셀프-백홀(Self-Xhaul) XDU 내 모든 섹터가 다른 섹터와 1:1 제어 링크로 연동되며, 해당 네트워크가 탠뎀 네트워크(tandem network)인 것을 전제로 한다. 즉, 하나의 XDU에는 하나의 마스터 섹터 및 하나의 마스터 섹터가 반드시 존재하는 경우를 전제로 한다. 이러한 전제가 없을 경우, 슬레이브 섹터도 본인이 있는 XDU 내의 모든 섹터에 대해 업데이트 메시지를 포워딩해야 한다.The method of changing the resource allocation ratio of FIG. 8 will be described based on the operation performed between the at least one IXA node 100-1 and 100-3 and the
앞서 설명한 바와 같이 XCU에 의해 결정되는 자원분할 비율 α는 네트워크 내의 모든 노드의 모든 섹터에게 전달되며, 각 섹터는 자원분할 비율에 따라 엑스홀 링크와 액세스 링크의 자원량을 조절할 수 있다. XCU는 자원분할 비율 α를 계산하고(S810), 업데이트가 필요한 경우 연관된 IXA 노드로 업데이트 메시지를 전송한다(S820).As described above, the resource splitting ratio α determined by the XCU is transmitted to all sectors of all nodes in the network, and each sector can adjust the resource amount of the XHole link and the access link according to the resource splitting ratio. The XCU calculates a resource allocation ratio α (S810) and transmits an update message to the associated IXA node when an update is necessary (S820).
여기서, 네트워크에 실제 적용되는 분할 비율 α의 값이 양자화되어 있을 있다. 이러한 양자화 값들은 표로 정리되거나 또는 간단한 식으로부터 도출 가능한 유한한 개수의 값들이다. 따라서, XCU가 각각의 섹터에게 전달하는 값은 계산에 의해 도출한 값이 아닌, α가 가질 수 있는 가능한 값을 정리한 표에서의 인덱스 또는, 실제 적용할 α의 값을 도출하는 간단한 식에 쓰이는 파라미터일 수도 있다.Here, the value of the division ratio α actually applied to the network may be quantized. These quantization values are a finite number of values that can be tabulated or derived from simple equations. Therefore, the value that XCU delivers to each sector is not a value derived by calculation, but an index in a table of possible values that α can have, or a simple expression of deriving the value of α to be actually applied. It may be a parameter.
또한, XCU(200)가 결정된 전역적 자원 할당 비에 따른 자원 분할비 변경을 위해 네트워크네 모든 섹터와 변경 절차에 따른 시그널링을 교환할 경우 모든 시그널링이 XCU에 집중되는 이슈가 있을 뿐만 아니라 시그널링 오버헤드가 매우 높아질 수 있다. 따라서, 본 발명에서는 네트워크 내의 모든 섹터로 업데이트 메시지를 송신하지는 않는다. 이 경우 전체 네트워크의 입장에서, 특히, XCU의 입장에서 시그널링 오버헤드가 대폭적으로 감소한다는 장점을 가지게 된다.In addition, when the
도 8에서의 업데이트 메시지는의 정보 튜플(information tuple)을 포함할 수 있다. 본 실시예에서 업데이트 메시지는 임의의 IXA 노드의 특정 섹터 하나에만 전송되는데, 이러한 특정 섹터를 대표 섹터라고 칭하기로 한다. 도 8은 섹터가 대표 섹터일 경우의 자원 분할비 변경 절차의 예를 나타낸다.The update message in Figure 8 It may include an information tuple of (information tuple). In this embodiment, the update message is sent only to one specific sector of any IXA node, which will be referred to as a representative sector. 8 is a sector Shows an example of a procedure for changing a resource partition ratio when is a representative sector.
업데이트 메시지에 포함된 정보 튜플에서,은 함께 전달되는 자원 분할 비율가 적용되는 TTI(Transmit Time Interval)을 지정한다.는 신규 업데이트 메시지에 포함된 정보를 이전 업데이트 메시지에 포함된 정보와 구별하여 식별하기 위하여 XCU가 해당 메시지에 부여하는 시퀀스 번호이다.는 업데이트 메시지의 송신자를 표시하는 1 비트 값으로, 예를 들어 값이 "0"이면 송신자가 XCU(의 xRM)임을 나타내고, "1"이면 XCU(의 xRM)가 아님을 나타낼 수 있다.In the information tuple included in the update message: Is the percentage of resource splits passed together Specifies the TTI (Transmit Time Interval) to which is applied. Is a sequence number assigned to the message by the XCU in order to distinguish the information included in the new update message from the information included in the previous update message. Is a 1-bit value that indicates the sender of the update message, for example A value of "0" may indicate that the sender is XCU (xRM), and a value of "1" may indicate that it is not XCU (xRM).
XCU(200)는 네트워크 내의 모든 IXA 노드(도 8에서는 100-1, 100-3)에게인 업데이트 메시지를 전송한다(S820). XCU(200)는 각 IXA 노드의 모든 섹터로 업데이트 메시지를 보내지는 않으며 각 노드의 대표 섹터에게만 업데이트 메시지를 전송한다. 업데이트 메시지를 수신한 대표 섹터는 자신이 받은 업데이트 메시지에서의 값을 1로 변경하고 나머지 값은 유지하여 리스트에 있는 동일 IXA 노드 내의 다른 섹터들에게 전달한다(S821).The
여기서, 대표 섹터는 XCU(200)로부터 업데이트 메시지를 수신한 직후에 곧바로 ACK 로 회신하지 않는다. XCU(200)는 대표 섹터만이 아니라, 대표 섹터가 포함된 IXA 노드 내의 모든 섹터들에 대한 성공적인 업데이트 메시지 전달이 수행되었는지 확인할 필요가 있기 때문이다.Here, the representative sector does not immediately reply with an ACK immediately after receiving the update message from the
대표 섹터로부터의 값이 1인 업데이트 메시지를 수신한 각 섹터들은 메시지 수신 직후 대표 섹터에게 ACK를 회신한다(S830). 자신이 속한 IXA 노드내의 모든 섹터들로부터 ACK을 받은 대표 섹터은 XCU에게 ACK을 송신한다(S830). 즉, 대표 섹터들은 자신을 포함하여 자신이 관리하는 섹터들이 업데이트 메시지를 성공적으로 수신하였다는 의미의 ACK를 XCU(200)로 전송한다.From representative sector Each sector receiving the update message having a value of 1 returns an ACK to the representative sector immediately after the message is received (S830). Representative sector that has received an ACK from all sectors in its IXA node Transmits an ACK to the XCU (S830). That is, the representative sectors transmit an ACK to the
여기서, 대표 섹터가 자신이 속한 IXA 노드내의 모든 섹터들로부터 ACK을 다 수신하였는지 판단하는 기준은 아래와 같다.Here, the criterion for determining whether the representative sector has received all the ACKs from all sectors in the IXA node to which the representative sector belongs is as follows.
우선, XCU는 IXA 노드 내에 포함된 모든 섹터들 각각을 알고 있다. 따라서, 대표 섹터에게 업데이트 메시지를 보낼 때 업데이트 메시지를 전달해야 하는 다른 섹터들의 리스트인를 업데이트 메시지에 포함시켜 보낸다. 따라서, 대표 섹터는 리스트 상에 포함된 모든 섹터들이 자신에게 ACK을 보내온 것을 확인함으로써 모든 섹터들로부터 ACK을 수신하였는지 판단할 수 있다.First, the XCU knows each of all sectors contained within the IXA node. Thus, when sending an update message to a representative sector, a list of other sectors to which Is sent in the update message. Therefore, the representative sector can determine whether all sectors included in the list have received ACKs from all sectors by confirming that they have sent ACKs to them.
XCU가 업데이트 메시지를 전달한 모든 IXA 노드들(도 8에서는 100-1, 100-3)의 대표 섹터들로부터 ACK을 수신하면 네트워크 내의 네트워크 내의 모든 대표 섹터들에게 다시 컨펌 메시지를 송신한다(S840). 컨펌 메시지를 수신한 대표 섹터는 업데이트 메시지를 전달한 방법과 동일한 방법으로 자신이 속한 IXA 노드 내 모든 섹터들에게 컨펌(Confirm) 메시지를 전달함으로써(S841), 각각의 섹터들이 업데이트 메시지에 포함된 파라미터를 적용하도록 한다.When the XCU receives the ACK from the representative sectors of all the IXA nodes (100-1 and 100-3 in FIG. 8) that delivered the update message, the XCU transmits a confirmation message to all the representative sectors in the network in step S840. The representative sector receiving the confirmation message transmits a confirmation message to all sectors in the IXA node to which it belongs in the same manner as the method of delivering the update message (S841), whereby each sector receives the parameter included in the update message. To apply.
도 8에 도시된 무선자원 관리 방법을 수행하는 XCU는 네트워크 제어 장치일 수 있으며, 본 발명의 일 일시예에 따른 네트워크 제어 장치는 무선 자원을 공유하는 엑스홀 링크와 액세스 링크를 제공하는 적어도 하나의 무선 노드를 포함하는 무선 네트워크에서 무선자원 관리 방법을 수행한다.The XCU performing the radio resource management method illustrated in FIG. 8 may be a network control device. The network control device according to an embodiment of the present invention may include at least one Xhole link and an access link that share radio resources. A radio resource management method is performed in a wireless network including a wireless node.
네트워크 제어 장치에 의해 수행되는 무선자원 관리 방법은, 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로부터 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치를 수신하는 단계; 상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치를 이용해 엑스홀 링크의 처리량 및 액세스 링크의 처리량을 산출하는 단계; 상기 엑스홀 링크의 처리량 및 액세스 링크의 처리량으로부터 무선자원 분할 비율을 결정하는 단계; 및 상기 무선자원 분할 비율을 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로 제공하는 단계를 포함할 수 있으며, 상기 무선자원 분할 비율이 변경되는 경우, 자원할당 비율 관련 업데이트 메시지를 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로 제공하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.A radio resource management method performed by a network control apparatus includes: receiving xhaul link and access link measurements from at least one radio node; Calculating throughput of an XHole link and throughput of an access link using the XHole Link and Access Link measurements; Determining a radio resource partition ratio from the throughput of the XHole link and the throughput of an access link; And providing the radio resource division ratio to the at least one radio node. When the radio resource division ratio is changed, providing an update message related to a resource allocation ratio to the at least one radio node. It may further include.
도 9는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 무선 네트워크 제어 장치의 블록 구성도이다.9 is a block diagram of an apparatus for controlling a wireless network according to an embodiment of the present invention.
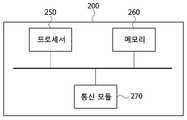
도 9를 참조하면, 무선 네트워크 제어 장치(200)는 프로세서(250) 및 프로세서를 통해 실행되는 적어도 하나의 명령 및 명령 수행의 결과를 저장하는 메모리(260)를 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 9, the
여기서, 적어도 하나의 명령은, 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로부터 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치를 수신하도록 하는 명령; 상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치를 이용해 엑스홀 링크의 처리량 및 액세스 링크의 처리량을 산출하도록 하는 명령; 상기 엑스홀 링크의 처리량 및 액세스 링크의 처리량으로부터 무선자원 분할 비율을 결정하도록 하는 명령; 및 상기 무선자원 분할 비율을 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로 제공하도록 하는 명령을 포함할 수 있으며, 무선자원 분할 비율이 변경되는 경우, 자원할당 비율 관련 업데이트 메시지를 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로 제공하도록 하는 명령을 더 포함할 수 있다.Here, the at least one instruction includes instructions for receiving an xhaul link and access link measurements from the at least one wireless node; Instructions for calculating the throughput of the XHole link and the throughput of the access link using the XHole Link and Access Link measurements; Determine a radio resource splitting ratio from the throughput of the XHole link and the throughput of an access link; And providing the radio resource division ratio to the at least one radio node, and when the radio resource division ratio is changed, providing an update message related to resource allocation ratio to the at least one radio node. The command may further include.
여기서, 무선자원 분할 비율은 최소 경로 처리량을 갖는 단말의 경로 처리량을 극대화시키는, 전체 무선 자원 대비 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원의 비율일 수 있다.Here, the radio resource splitting ratio may be a ratio of resources allocated to the access link to the total radio resources, which maximizes the path throughput of the terminal having the minimum path throughput.
상기 엑스홀 링크의 통달 거리(transmission range)는 상기 액세스 링크의 통달 거리보다 길 수 있는데, 예를 들어, 엑스홀 링크의 통달 거리(transmission range)는 상기 액세스 링크의 통달 거리의 2배일 수 있다.The transmission range of the exhole link may be longer than the access range of the access link. For example, the transmission range of the exhole link may be twice the communication distance of the access link.
무선 네트워크 제어 장치는 또한 네트워크 내 무선통신 디바이스와의 통신을 수행하기 위한 통신 모듈(270)을 더 포함할 수 있다. 본 발명에 따른 무선 네트워크 제어 장치는 XCU(Xhaul Centralized Unit)일 수 있다. 또한, 여기서, 무선통신 디바이스는 적어도 하나의 IXA 노드일 수 있다.The apparatus for controlling a wireless network may further include a
한편, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 무선통신 디바이스는 무선통신 네트워크에서 다른 통신 디바이스와 연동하는 엑스홀 링크와 적어도 하나의 단말과 연동하는 액세스 링크를 제공할 수 있다.On the other hand, the wireless communication device according to an embodiment of the present invention may provide an X-hole link for interworking with other communication devices and an access link for interworking with at least one terminal in a wireless communication network.
여기서, 무선통신 디바이스는 프로세서; 및 상기 프로세서를 통해 실행되는 적어도 하나의 명령을 저장하는 메모리를 포함할 수 있으며, 상기 적어도 하나의 명령은, 상기 무선통신 디바이스가 포함하는 섹터의 연결 정보 및 사용자 단말 연동 정보를 상기 무선통신 네트워크 내 네트워크 제어 장치로 전송하도록 하는 명령; 상기 엑스홀 링크의 주파수 효율 및 상기 액세스 링크의 주파수 효율을 측정하여 상기 네트워크 제어 장치로 보고하도록 하는 명령; 상기 네트워크 제어 장치로부터 무선자원 분할 비율을 수신하도록 하는 명령; 및 상기 무선자원 분할 비율에 따라 상기 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원량을 조정하도록 하는 명령을 포함할 수 있으며, 무선자원 분할 비율이 변경되는 경우, 상기 네트워크 제어 장치로부터 자원할당 비율 관련 업데이트 메시지를 수신하도록 하는 명령을 더 포함할 수 있다.Here, the wireless communication device comprises a processor; And a memory configured to store at least one command executed by the processor, wherein the at least one command includes connection information of a sector included in the wireless communication device and user terminal interworking information in the wireless communication network. Command to transmit to a network control device; Measuring the frequency efficiency of the X-hole link and the frequency efficiency of the access link to report to the network control device; Receiving a radio resource division ratio from the network control device; And adjusting the amount of resources allocated to the XHole link and the access link according to the radio resource splitting ratio. When the radio splitting ratio is changed, the resource allocation ratio related update is updated from the network control apparatus. It may further comprise a command to receive a message.
상기 업데이트 메시지는, 변경되는 무선자원 분할 비율, 상기 변경되는 무선자원 분할 비율이 적용되는 TTI(Transmit Time Interval), 상기 업데이트 메시지의 송신자 정보, 및 상기 업데이트 메시지가 전달되어야 할 무선 노드 내 섹터들에 대한 정보 중 적어도 하나를 포함할 수 있다.The update message is transmitted to a radio resource division ratio to be changed, a transmit time interval (TTI) to which the changed radio resource division ratio is applied, sender information of the update message, and sectors in a radio node to which the update message should be delivered. It may include at least one of the information about.
본 발명의 실시예에 따른 방법의 동작은 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 기록매체에 컴퓨터가 읽을 수 있는 프로그램 또는 코드로서 구현하는 것이 가능하다. 컴퓨터가 읽을 수 있는 기록매체는 컴퓨터 시스템에 의해 읽혀질 수 있는 데이터가 저장되는 모든 종류의 기록장치를 포함한다. 또한 컴퓨터가 읽을 수 있는 기록매체는 네트워크로 연결된 컴퓨터 시스템에 분산되어 분산 방식으로 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 프로그램 또는 코드가 저장되고 실행될 수 있다.The operation of the method according to an embodiment of the present invention can be embodied as a computer readable program or code on a computer readable recording medium. Computer-readable recording media include all kinds of recording devices that store data that can be read by a computer system. The computer readable recording medium can also be distributed over network coupled computer systems so that the computer readable program or code is stored and executed in a distributed fashion.
또한, 컴퓨터가 읽을 수 있는 기록매체는 롬(rom), 램(ram), 플래시 메모리(flash memory) 등과 같이 프로그램 명령을 저장하고 수행하도록 특별히 구성된 하드웨어 장치를 포함할 수 있다. 프로그램 명령은 컴파일러(compiler)에 의해 만들어지는 것과 같은 기계어 코드뿐만 아니라 인터프리터(interpreter) 등을 사용해서 컴퓨터에 의해 실행될 수 있는 고급 언어 코드를 포함할 수 있다.In addition, the computer-readable recording medium may include a hardware device specifically configured to store and execute program instructions, such as a ROM, a RAM, a flash memory, and the like. Program instructions may include high-level language code that can be executed by a computer using an interpreter, as well as machine code such as produced by a compiler.
본 발명의 일부 측면들은 장치의 문맥에서 설명되었으나, 그것은 상응하는 방법에 따른 설명 또한 나타낼 수 있고, 여기서 블록 또는 장치는 방법 단계 또는 방법 단계의 특징에 상응한다. 유사하게, 방법의 문맥에서 설명된 측면들은 또한 상응하는 블록 또는 아이템 또는 상응하는 장치의 특징으로 나타낼 수 있다. 방법 단계들의 몇몇 또는 전부는 예를 들어, 마이크로프로세서, 프로그램 가능한 컴퓨터 또는 전자 회로와 같은 하드웨어 장치에 의해(또는 이용하여) 수행될 수 있다. 몇몇의 실시예에서, 가장 중요한 방법 단계들의 하나 이상은 이와 같은 장치에 의해 수행될 수 있다.While some aspects of the invention have been described in the context of an apparatus, it may also represent a description according to a corresponding method, where a block or apparatus corresponds to a method step or a feature of a method step. Similarly, aspects described in the context of a method may also be indicated by the features of the corresponding block or item or corresponding device. Some or all of the method steps may be performed by (or using) a hardware device such as, for example, a microprocessor, a programmable computer, or an electronic circuit. In some embodiments, one or more of the most important method steps may be performed by such an apparatus.
실시예들에서, 프로그램 가능한 로직 장치(예를 들어, 필드 프로그머블 게이트 어레이)가 여기서 설명된 방법들의 기능의 일부 또는 전부를 수행하기 위해 사용될 수 있다. 실시예들에서, 필드 프로그머블 게이트 어레이는 여기서 설명된 방법들 중 하나를 수행하기 위한 마이크로프로세서와 함께 작동할 수 있다. 일반적으로, 방법들은 어떤 하드웨어 장치에 의해 수행되는 것이 바람직하다.In embodiments, a programmable logic device (eg, a field programmable gate array) may be used to perform some or all of the functionality of the methods described herein. In embodiments, the field programmable gate array may operate in conjunction with a microprocessor to perform one of the methods described herein. In general, the methods are preferably performed by any hardware apparatus.
이상 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예를 참조하여 설명하였지만, 해당 기술 분야의 숙련된 당업자는 하기의 특허 청구의 범위에 기재된 본 발명의 사상 및 영역으로부터 벗어나지 않는 범위 내에서 본 발명을 다양하게 수정 및 변경시킬 수 있음을 이해할 수 있을 것이다.Although it has been described above with reference to preferred embodiments of the present invention, those skilled in the art will be able to variously modify and change the present invention without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention described in the claims below. It will be appreciated.
100, 100-1, 100-2, 100-3: IXA 노드
110: eNB/gNB120: XDU
200: XCU210: xRM
220: xTD230: xPM
250: 프로세서 260: 메모리
270: 통신 모듈100, 100-1, 100-2, 100-3: IXA nodes
110: eNB / gNB 120: XDU
200: XCU 210: xRM
220: xTD 230: xPM
250: processor 260: memory
270: communication module
Claims (20)
Translated fromKorean프로세서; 및
상기 프로세서를 통해 실행되는 적어도 하나의 명령을 저장하는 메모리를 포함하고,
상기 적어도 하나의 명령은,
상기 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크가 무선 자원을 공유하도록 상기 무선 자원을 관리하는 명령을 포함하는, 무선통신 디바이스.A wireless communication device providing an X-hole link for interworking with another wireless communication device and an access link for interworking with at least one terminal in a wireless communication network,
A processor; And
A memory storing at least one instruction executed by the processor,
The at least one command is
And managing the radio resource such that the xhole link and the access link share a radio resource.
상기 적어도 하나의 명령은,
상기 무선통신 네트워크 내에 위치하는 네트워크 제어 장치로부터 수신한 무선자원 분할 비율에 따라 상기 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원량을 조정하도록 하는 명령을 더 포함하는, 무선통신 디바이스.The method according to claim 1,
The at least one command is
And adjusting an amount of resources allocated to the X-hole link and the access link according to a radio resource division ratio received from a network control apparatus located in the wireless communication network.
상기 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원량을 조정하도록 하는 명령은,
상기 무선통신 디바이스가 포함하는 섹터의 연결 정보 및 사용자 단말 연동 정보를 상기 무선통신 네트워크 내 네트워크 제어 장치로 전송하도록 하는 명령;
상기 엑스홀 링크의 주파수 효율 및 상기 액세스 링크의 주파수 효율을 측정하여 상기 네트워크 제어 장치로 보고하도록 하는 명령;
상기 네트워크 제어 장치로부터 무선자원 분할 비율을 수신하도록 하는 명령; 및
상기 무선자원 분할 비율에 따라 상기 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원량을 조정하도록 하는 명령을 포함하는, 무선통신 디바이스.The method according to claim 2,
The command to adjust the amount of resources allocated to the XHole link and the access link,
Transmitting the connection information and the user terminal interworking information of the sector included in the wireless communication device to a network control apparatus in the wireless communication network;
Measuring the frequency efficiency of the X-hole link and the frequency efficiency of the access link to report to the network control device;
Receiving a radio resource division ratio from the network control device; And
And adjusting an amount of resources allocated to the XHole link and the access link according to the radio resource splitting ratio.
상기 엑스홀 링크의 통달 거리(transmission range)는 상기 액세스 링크의 통달 거리보다 긴, 무선통신 디바이스.The method according to claim 1,
And wherein a transmission range of the XHole link is longer than a communication distance of the access link.
상기 엑스홀 링크의 통달 거리는 상기 액세스 링크의 통달 거리의 2배인, 무선통신 디바이스.The method according to claim 4,
And wherein the communication distance of the exhole link is twice the communication distance of the access link.
상기 적어도 하나의 명령은,
상기 무선자원 분할 비율이 변경되는 경우, 상기 네트워크 제어 장치로부터 자원할당 비율 관련 업데이트 메시지를 수신하도록 하는 명령을 더 포함하는, 무선통신 디바이스.The method according to claim 2,
The at least one command is
And receiving a resource allocation ratio related update message from the network control apparatus when the radio resource division ratio is changed.
상기 업데이트 메시지는,
변경되는 무선자원 분할 비율, 상기 변경되는 무선자원 분할 비율이 적용되는 TTI(Transmit Time Interval), 상기 업데이트 메시지의 송신자 정보, 및 상기 업데이트 메시지가 전달되어야 할 무선 노드 내 섹터들에 대한 정보 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는, 무선통신 디바이스.The method according to claim 6,
The update message,
At least one of a radio resource segmentation rate to be changed, a transmit time interval (TTI) to which the radio resource segmentation rate is applied, sender information of the update message, and information on sectors in a radio node to which the update message should be delivered. Comprising a, wireless communication device.
상기 무선자원 분할 비율은,
최소 경로 처리량을 갖는 단말의 경로 처리량을 극대화시키는, 전체 무선 자원 대비 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원의 비율인, 무선통신 디바이스.The method according to claim 1,
The radio resource division ratio is,
A ratio of resources allocated to an access link to total radio resources, maximizing path throughput of a terminal with a minimum path throughput.
상기 엑스홀 링크에 할당되는 자원과 상기 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원은 시간축 상에서 또는 주파수축 상에서 직교적으로 분할되는, 무선통신 디바이스.The method according to claim 2,
And the resources allocated to the XHole link and the resources allocated to the access link are divided orthogonally on the time axis or on the frequency axis.
상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로부터 상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치를 수신하는 단계; 및
상기 무선 노드가 제공하는 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크가 무선 자원을 공유하되, 상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 관련 측정치에 기반하여 무선 자원을 분배하는 단계를 포함하는, 무선자원 관리 방법.A method of managing radio resources in a network comprising at least one radio node providing an xhole link and an access link, the method comprising:
Receiving the xhaul link and access link measurements from the at least one wireless node; And
And sharing the radio resources between the XHole link and the access link provided by the wireless node, and distributing the radio resources based on the XHole link and access link related measurements.
상기 무선 자원을 분배하는 단계는,
상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치를 이용해 엑스홀 링크의 처리량 및 액세스 링크의 처리량을 산출하는 단계;
상기 엑스홀 링크의 처리량 및 액세스 링크의 처리량으로부터 무선자원 분할 비율을 결정하는 단계; 및
상기 무선자원 분할 비율을 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로 제공하는 단계를 포함하는, 무선자원 관리 방법.The method according to claim 10,
Distributing the radio resource,
Calculating throughput of an XHole link and throughput of an access link using the XHole Link and Access Link measurements;
Determining a radio resource partition ratio from the throughput of the XHole link and the throughput of an access link; And
Providing the radio resource splitting ratio to the at least one radio node.
상기 무선자원 분할 비율은,
최소 경로 처리량을 갖는 단말의 경로 처리량을 극대화시키는, 전체 무선 자원 대비 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원의 비율인, 무선자원 관리 방법.The method according to claim 11,
The radio resource division ratio is,
A radio resource management method, which is a ratio of resources allocated to an access link to total radio resources, which maximizes path throughput of a terminal having a minimum path throughput.
상기 엑스홀 링크의 통달 거리(transmission range)는 상기 액세스 링크의 통달 거리보다 긴, 무선자원 관리 방법.The method according to claim 10,
And a transmission range of the X-hole link is longer than that of the access link.
상기 엑스홀 링크의 통달 거리(transmission range)는 상기 액세스 링크의 통달 거리의 2배인, 무선자원 관리 방법.The method according to claim 13,
And a transmission range of the X-hole link is twice the communication range of the access link.
상기 무선자원 분할 비율이 변경되는 경우, 자원할당 비율 관련 업데이트 메시지를 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로 제공하는 단계를 더 포함하는, 무선자원 관리 방법.The method according to claim 11,
And providing a resource allocation ratio related update message to the at least one wireless node when the radio resource splitting ratio is changed.
상기 업데이트 메시지는,
변경되는 무선자원 분할 비율, 상기 변경되는 무선자원 분할 비율이 적용되는 TTI(Transmit Time Interval), 상기 업데이트 메시지의 송신자 정보, 및 상기 업데이트 메시지가 전달되어야 할 무선 노드 내 섹터들에 대한 정보 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는, 무선자원 관리 방법.The method according to claim 15,
The update message,
At least one of a radio resource segmentation rate to be changed, a transmit time interval (TTI) to which the radio resource segmentation rate is applied, sender information of the update message, and information on sectors in a radio node to which the update message should be delivered. Including, radio resource management method.
상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치는,
상기 엑스홀 링크의 주파수 효율 및 상기 액세스 링크의 주파수 효율을 포함하는, 무선자원 관리 방법.The method according to claim 10,
The XHole link and access link measurements are
And a frequency efficiency of the X-hole link and a frequency efficiency of the access link.
상기 엑스홀 링크에 할당되는 자원과 상기 액세스 링크에 할당되는 자원은 시간축 상에서 또는 주파수축 상에서 직교적으로 분할되는, 무선자원 관리 방법.The method according to claim 10,
The resource allocated to the XHole link and the resource allocated to the access link are divided orthogonally on the time axis or on the frequency axis.
프로세서; 및
상기 프로세서를 통해 실행되는 적어도 하나의 명령을 저장하는 메모리를 포함하고,
상기 적어도 하나의 명령은,
상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로부터 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치를 수신하도록 하는 명령; 및
상기 무선 노드가 제공하는 엑스홀 링크와 상기 액세스 링크가 무선 자원을 공유하되, 상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 관련 측정치에 기반하여 무선 자원을 분배하도록 하는 명령을 포함하는, 네트워크 제어 장치.A network control apparatus for managing a resource of a wireless network including an Xhole link sharing a radio resource and at least one radio node providing an access link, comprising:
A processor; And
A memory storing at least one instruction executed by the processor,
The at least one command is
Instructions for receiving Xhole link and access link measurements from the at least one wireless node; And
And sharing the radio resource between the xhole link provided by the wireless node and the access link, but distributing the radio resource based on the xhole link and access link related measurements.
상기 무선 자원을 분배하도록 하는 명령은,
상기 엑스홀 링크 및 액세스 링크 측정치를 이용해 엑스홀 링크의 처리량 및 액세스 링크의 처리량을 산출하도록 하는 명령;
상기 엑스홀 링크의 처리량 및 액세스 링크의 처리량으로부터 무선자원 분할 비율을 결정하도록 하는 명령; 및
상기 무선자원 분할 비율을 상기 적어도 하나의 무선 노드로 제공하도록 하는 명령을 포함하는, 네트워크 제어 장치.
The method according to claim 19,
The command to distribute the radio resource,
Instructions for calculating the throughput of the XHole link and the throughput of the access link using the XHole Link and Access Link measurements;
Determine a radio resource splitting ratio from the throughput of the XHole link and the throughput of an access link; And
And providing the radio resource splitting ratio to the at least one wireless node.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180046471AKR20190122935A (en) | 2018-04-23 | 2018-04-23 | Radio resource managing method and network control apparatus using the method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180046471AKR20190122935A (en) | 2018-04-23 | 2018-04-23 | Radio resource managing method and network control apparatus using the method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20190122935Atrue KR20190122935A (en) | 2019-10-31 |
Family
ID=68420862
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180046471AWithdrawnKR20190122935A (en) | 2018-04-23 | 2018-04-23 | Radio resource managing method and network control apparatus using the method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR20190122935A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20250058388A (en)* | 2023-10-23 | 2025-04-30 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Method and apparatus for managing and allocating radio resource in wireless communication system |
- 2018
- 2018-04-23KRKR1020180046471Apatent/KR20190122935A/ennot_activeWithdrawn
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20250058388A (en)* | 2023-10-23 | 2025-04-30 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Method and apparatus for managing and allocating radio resource in wireless communication system |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100950357B1 (en) | System and method for allocating channels in a wireless network | |
| Wang et al. | Backhauling 5G small cells: A radio resource management perspective | |
| EP2625916B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for controlling a wireless feeder network | |
| US11509391B2 (en) | Adaptive multiple access scheme in integrated access and backhaul networks | |
| RU2420038C2 (en) | Method to control access to wireless channel tdma from units of linear or tree-type topology networks | |
| CN109314547B (en) | Hybrid wireless communication system | |
| US20120243513A1 (en) | Radio communication system, base station apparatus, and radio communication method | |
| US20110312267A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for relaying multiple links in a communication system | |
| WO2015127618A1 (en) | Cell, small cell, and method for scheduling communication link resources | |
| KR101902343B1 (en) | Network device and user device and methods thereof | |
| US9143292B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling a signal path of a radio communication | |
| Ni et al. | Graph theory and its applications to future network planning: Software-defined online small cell management | |
| EP3501223B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for allocating radio resources | |
| KR20190122935A (en) | Radio resource managing method and network control apparatus using the method | |
| US20240243797A1 (en) | Spatial domain simultaneous operation in soft resources in iab | |
| US20240008017A1 (en) | Technique for Allocating Spatial Radio Resources for an Integrated Access and Backhaul Node | |
| US20230388995A1 (en) | Iab hierarchical du resource configuration | |
| US20220345911A1 (en) | Improved spectrum utilization in a wireless communication network | |
| KR101781195B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling interference in wifi integrated small cell environment | |
| EP2789206B1 (en) | Integrated microwave backhaul support in cellular products | |
| JP6663391B2 (en) | Network system | |
| US20140219125A1 (en) | Base-station device and communication method | |
| US20240089940A1 (en) | Configure iab frequency-domain resource utilization | |
| Li et al. | Mobile association for wireless heterogeneous networks with cooperative relays: optimal framework and implementation schemes | |
| KR20190122496A (en) | Radio resource controlling method, wireless communicaiton device and network control apparatus using the method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20180423 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| PC1203 | Withdrawal of no request for examination |