KR20170114234A - Method and apparatus for controlling uplink transmission power - Google Patents
Method and apparatus for controlling uplink transmission powerDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20170114234A KR20170114234AKR1020160120963AKR20160120963AKR20170114234AKR 20170114234 AKR20170114234 AKR 20170114234AKR 1020160120963 AKR1020160120963 AKR 1020160120963AKR 20160120963 AKR20160120963 AKR 20160120963AKR 20170114234 AKR20170114234 AKR 20170114234A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- base station
- channel quality
- quality value
- mobile terminal
- target
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription85
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription67
- 238000009499grossingMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000003595spectral effectEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description10
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description4
- 238000011000absolute methodMethods0.000description3
- 238000009825accumulationMethods0.000description3
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description3
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000description3
- 238000013507mappingMethods0.000description2
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description2
- SLVOKEOPLJCHCQ-SEYXRHQNSA-N[(z)-octadec-9-enyl] 2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethyl phosphateChemical compoundCCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCCOP([O-])(=O)OCC[N+](C)(C)CSLVOKEOPLJCHCQ-SEYXRHQNSA-N0.000description1
- 230000015556catabolic processEffects0.000description1
- 239000000470constituentSubstances0.000description1
- 230000010485copingEffects0.000description1
- 238000006731degradation reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000005562fadingMethods0.000description1
- 238000009434installationMethods0.000description1
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. Transmission Power Control [TPC] or power classes
- H04W52/04—Transmission power control [TPC]
- H04W52/18—TPC being performed according to specific parameters
- H04W52/24—TPC being performed according to specific parameters using SIR [Signal to Interference Ratio] or other wireless path parameters
- H04W52/241—TPC being performed according to specific parameters using SIR [Signal to Interference Ratio] or other wireless path parameters taking into account channel quality metrics, e.g. SIR, SNR, CIR or Eb/lo
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. Transmission Power Control [TPC] or power classes
- H04W52/02—Power saving arrangements
- H04W52/0209—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. Transmission Power Control [TPC] or power classes
- H04W52/04—Transmission power control [TPC]
- H04W52/06—TPC algorithms
- H04W52/08—Closed loop power control
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. Transmission Power Control [TPC] or power classes
- H04W52/04—Transmission power control [TPC]
- H04W52/06—TPC algorithms
- H04W52/14—Separate analysis of uplink or downlink
- H04W52/146—Uplink power control
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. Transmission Power Control [TPC] or power classes
- H04W52/04—Transmission power control [TPC]
- H04W52/30—Transmission power control [TPC] using constraints in the total amount of available transmission power
- H04W52/36—Transmission power control [TPC] using constraints in the total amount of available transmission power with a discrete range or set of values, e.g. step size, ramping or offsets
- H04W52/365—Power headroom reporting
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. Transmission Power Control [TPC] or power classes
- H04W52/04—Transmission power control [TPC]
- H04W52/54—Signalisation aspects of the TPC commands, e.g. frame structure
- Y02B60/50—
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/70—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wireless communication networks
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 LTE(long term evolution) 기반의 소형셀(small cell) 기지국 시스템에서 이동 단말의 상향링크(uplink) 송신 전력을 제어하는 방법 및 장치에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for controlling an uplink transmission power of a mobile station in a LTE (Long Term Evolution) based small cell base station system.
무선 통신 시스템에서 상향링크 전력 제어(uplink power control)는 이동 단말의 송신 파워를 최적으로 제어하는 기술이다. 상향링크 전력 제어는 기지국이 필요로 하는 일정 수준의 수신 채널 품질(예, received SINR(signal-to-interference plus noise ratio), received SNR(signal to noise ratio) 등)의 유지, 이웃 기지국과의 간섭(interference)의 최소화, 및 이동 단말의 배터리 수명의 최대화를 위한 것이다. 상향링크 전력 제어는 무선 자원 관리(RRM: radio resource management)의 주요 요소이다.In the wireless communication system, the uplink power control is a technique for optimally controlling the transmission power of the mobile terminal. The uplink power control is performed by maintaining a certain level of reception channel quality required by the base station (e.g., received signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR), received signal to noise ratio (SNR) minimizes interference, and maximizes the battery life of the mobile terminal. Uplink power control is a key element of radio resource management (RRM).
이러한 전력 제어는 이웃셀에 대한 간섭을 최소화하면서 경로 손실(path loss), 및 쉐도잉(shadowing) 등을 포함하는 무선 채널 상태를 고려하여 최적화되어야 한다.This power control should be optimized in consideration of radio channel conditions including path loss, shadowing, and the like while minimizing interference to neighbor cells.
이를 위해, LTE에는 PUSCH(physical uplink shared channel) 및 PUCCH(physical uplink control channel) 채널에 대해 개루프(open-loop) 전력 제어와 폐루프(closed-loop) 전력 제어가 정의되어 있다.To this end, LTE defines open-loop power control and closed-loop power control for physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH) and physical uplink control channel (PUCCH) channels.
한편, 송신 전력이 이동 단말이 송신할 수 있는 최대 전력을 초과하면, 기지국의 PUSCH 수신 성능이 떨어지며 상향링크 성능의 저하와 함께 이동 단말의 배터리 소모가 극심해진다. 따라서, 송신 전력이 이동 단말이 송신할 수 있는 최대 전력을 초과하지 않도록 하여 이동 단말의 배터리 소모를 줄이는 방법이 필요하다.On the other hand, if the transmission power exceeds the maximum power that can be transmitted by the mobile terminal, the PUSCH reception performance of the base station is lowered and the battery consumption of the mobile terminal becomes extreme along with the degradation of the uplink performance. Accordingly, there is a need for a method of reducing battery consumption of the mobile terminal by preventing the transmission power from exceeding the maximum power that can be transmitted by the mobile terminal.
본 발명이 해결하고자 하는 과제는, 기지국에 의해 요구되는 수신 전력이 유지되면서 이동 단말의 배터리 소모가 최소화되도록, 전력을 제어하는 방법 및 장치를 제공하는 것이다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION It is an object of the present invention to provide a method and apparatus for controlling power such that battery consumption of a mobile terminal is minimized while receiving power required by a base station is maintained.
또한 본 발명이 해결하고자 하는 과제는, LTE 기반의 소형셀 기지국 시스템에서 상향링크 송신 전력을 제어하는 방법 및 장치를 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a method and apparatus for controlling uplink transmission power in an LTE-based small cell base station system.
본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 기지국이 이동 단말의 상향링크 송신 전력을 제어하는 방법이 제공된다. 상기 기지국의 제어 방법은, 상기 이동 단말로부터, 상기 이동 단말의 가용 송신 전력량을 수신하는 단계; 상기 가용 송신 전력량에 기초해, 상기 이동 단말의 현재 위치에 대응하는 타겟 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계; 상기 이동 단말로부터 수신되는 상향링크 데이터 채널을 이용해, 수신 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계; 및 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값과 상기 수신 채널 품질 값 간의 차이를 이용해, 송신 전력 제어(TPC: transmit power control)를 결정하는 단계를 포함한다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, a method is provided in which a base station controls uplink transmission power of a mobile station. The control method of the base station includes: receiving, from the mobile terminal, an available transmission power amount of the mobile terminal; Determining a target channel quality value corresponding to a current location of the mobile terminal based on the available transmission power; Determining a received channel quality value using an uplink data channel received from the mobile terminal; And determining transmit power control (TPC) using the difference between the target channel quality value and the received channel quality value.
상기 가용 송신 전력량을 수신하는 단계는, 상기 가용 송신 전력량을 나타내는 전력 헤드룸 보고(PHR: power headroom report)를 수신하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The step of receiving the available transmit power amount may include receiving a power headroom report (PHR) indicating the available transmit power amount.
상기 가용 송신 전력량에 기초해 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계는, 상기 이동 단말의 현재 위치에 대응하는 경로 손실을 얼마만큼 보상하는 지를 나타내는 제1 값이 1 보다 작은 경우에, 상기 PHR을 이용해 상기 경로 손실을 유추하는 단계; 및 상기 유추된 경로 손실에 따라 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.Wherein the step of determining the target channel quality value based on the available transmission power includes the step of, when the first value indicating how much the path loss corresponding to the current position of the mobile terminal is compensated for is less than 1, Inferring the path loss; And determining the target channel quality value according to the inferred path loss.
상기 수신 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계는, 상기 상향링크 데이터 채널에 대해 측정되는 제1 채널 품질 값을 평탄화(smoothing)하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The step of determining the reception channel quality value may include smoothing a first channel quality value measured for the uplink data channel.
상기 평탄화하는 단계는, 이동 평균 필터(moving average filter)인 지수 필터(exponential filter)를 통해, 상기 제1 채널 품질 값을 평탄화하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The flattening may include flattening the first channel quality value through an exponential filter, which is a moving average filter.
상기 지수 필터를 통해 상기 제1 채널 품질 값을 평탄화하는 단계는, 상기 기지국이 랜덤 접속(Random Access)을 위해 최초로 수신하는 M3 메시지에 대한 제2 채널 품질 값을, 상기 지수 필터를 위한 초기값으로써 사용하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The step of flattening the first channel quality value through the exponent filter may further comprise the step of calculating a second channel quality value for the M3 message initially received by the base station for random access as an initial value for the exponential filter And < / RTI >
상기 TPC를 결정하는 단계는, 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값과 상기 TPC의 갱신을 위한 갱신 주기 동안에 결정되는 상기 수신 채널 품질 값 간의 제1 차이를 제1 시점에 계산하는 단계; 및 상기 제1 차이에 기초해 TPC 커맨드를 결정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.Wherein the determining the TPC comprises: calculating a first difference between the target channel quality value and the received channel quality value determined during an update period for updating the TPC at a first time; And determining a TPC command based on the first difference.
상기 갱신 주기는 무선 채널 환경에 따라 변경될 수 있다.The update period may be changed according to the wireless channel environment.
상기 제1 차이에 기초해 상기 TPC 커맨드를 결정하는 단계는, 상기 제1 시점 이후부터 다음의 갱신 주기가 종료되는 시점까지는, 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값과 상기 수신 채널 품질 값 간의 차이를 0으로 설정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.Wherein the step of determining the TPC command based on the first difference comprises setting a difference between the target channel quality value and the received channel quality value to 0 from the first time point to the end of the next update period Step < / RTI >
상기 기지국의 제어 방법은, 상기 가용 송신 전력량과 상기 이동 단말의 현재 위치에 기초해, 상기 이동 단말에게 할당할 수 있는 자원 블록(resource block)의 최대 개수를 결정하는 단계; 및 상기 최대 개수 보다 적은 개수의 자원 블록을 상기 이동 단말에게 할당하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.The control method of the base station includes the steps of: determining a maximum number of resource blocks that can be allocated to the mobile terminal based on the available transmission power and the current location of the mobile terminal; And allocating a number of resource blocks less than the maximum number to the mobile terminal.
상기 기지국은 소형셀 기지국일 수 있다.The base station may be a small cell base station.
상기 타겟 채널 품질 값과 상기 수신 채널 품질 값은 SINR(signal-to-interference plus noise ratio) 및 SNR(signal to noise ratio) 중 하나일 수 있다.The target channel quality value and the received channel quality value may be one of a signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR) and a signal to noise ratio (SNR).
상기 상향링크 데이터 채널은 PUSCH(physical uplink shared channel)일 수 있다.The uplink data channel may be a physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH).
또한 본 발명의 다른 실시예에 따르면, 이동 단말이 상향링크 송신 전력을 제어하는 방법이 제공된다. 상기 이동 단말의 제어 방법은, 기지국에게, 상기 이동 단말의 가용 송신 전력량을 송신하는 단계; 상기 기지국에게, 상향링크 데이터 채널을 송신하는 단계; 및 상기 이동 단말의 경로 손실을 얼마만큼 보상하는 지를 나타내는 제1 값 및 상기 가용 송신 전력량에 기초하는 타겟 채널 품질 값과 상기 상향링크 데이터 채널에 대한 수신 채널 품질 값 간의 차이를 통해 결정되는 송신 전력 제어(TPC: transmit power control)를, 상기 기지국으로부터 수신하는 단계를 포함한다.According to another embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a method for a mobile station to control uplink transmission power. The control method of the mobile terminal may include transmitting to the base station an amount of available transmission power of the mobile terminal; Transmitting an uplink data channel to the base station; And a first value indicating how much the path loss of the mobile terminal is compensated for and a transmission power control value determined through a difference between a target channel quality value based on the available transmission power amount and a reception channel quality value for the uplink data channel (TPC: transmit power control) from the base station.
상기 이동 단말의 제어 방법은, 상기 이동 단말에게 할당될 수 있는 자원 블록(resource block)의 최대 개수 보다 적은 개수의 자원 블록을 상기 기지국으로부터 할당받는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.The control method of the mobile terminal may further include the step of allocating a number of resource blocks less than the maximum number of resource blocks that can be allocated to the mobile station from the base station.
상기 최대 개수는 상기 가용 송신 전력량과 상기 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 기초해 결정될 수 있다.The maximum number may be determined based on the amount of available transmission power and the path loss of the mobile terminal.
또한 본 발명의 또 다른 실시예에 따르면, 기지국이 제공된다. 상기 기지국은, 메모리; 및 상기 메모리와 연결되며, 이동 단말의 전력 헤드룸 보고(PHR: power headroom report)에 기초해 상기 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 대응하는 타겟 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 프로세서를 포함한다.According to yet another embodiment of the present invention, a base station is provided. The base station comprising: a memory; And a processor, coupled to the memory, for determining a target channel quality value corresponding to a path loss of the mobile terminal based on a power headroom report (PHR) of the mobile terminal.
상기 프로세서는, 상기 이동 단말의 PUSCH(physical uplink shared channel)을 통해 결정되는 수신 채널 품질 값과 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값 간의 차이를 이용해, 상기 이동 단말을 위한 송신 전력 제어(TPC: transmit power control) 커맨드를 결정할 수 있다.Wherein the processor is configured to transmit a transmit power control (TPC) command for the mobile station by using a difference between a receive channel quality value determined through a physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH) Can be determined.
상기 프로세서는, 상기 PHR 및 상기 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 기초해 상기 이동 단말에게 할당할 수 있는 자원 블록(resource block)의 최대 개수를 결정하고, 상기 최대 개수 보다 적은 개수의 자원 블록을 상기 이동 단말에게 할당할 수 있다.Wherein the processor determines a maximum number of resource blocks that can be allocated to the mobile terminal based on the PHR and the path loss of the mobile terminal, . ≪ / RTI >
본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, LTE 기반의 소형셀 기지국 시스템에서 상향링크 송신 전력을 제어할 수 있다.According to the embodiment of the present invention, uplink transmission power can be controlled in an LTE-based small cell base station system.
또한 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 이동 단말에 의해 보고되는 PHR(power headroom report)를 기반으로, 기지국에 의해 요구되는 수신 타겟 SNR(또는 수신 타겟 SINR)을 결정할 수 있다.Also, according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a target SNR (or target SINR) required for reception by a base station can be determined based on a power headroom report (PHR) reported by a mobile station.
또한 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 이동 단말로부터 수신되는 PUSCH의 SNR(또는 SINR)을 평탄화하여 수신 SNR(또는 수신 SINR)을 결정할 수 있다.Also, according to an embodiment of the present invention, the SNR (or SINR) of the PUSCH received from the mobile terminal may be flattened to determine the received SNR (or the received SINR).
또한 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 주기적으로 수행되는 TCP 맵퍼(mapper)를 통해, 타겟 SNR(또는 타겟 SINR)과 평탄화된 수신 SNR(또는 평탄화된 수신 SINR) 간의 차이를 기반으로 TPC(transmit power control) 커맨드를 결정할 수 있다.Also, according to an embodiment of the present invention, transmit power control (TPC) is performed based on a difference between a target SNR (or a target SINR) and a flattened received SNR (or a smoothed received SINR) through a TCP mapper periodically performed. ) Command can be determined.
또한 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 이동 단말에 의해 보고되는 PHR을 기반으로 현재 이동 단말의 남은 전력을 추정하여, 최대로 할당할 수 있는 PRB(physical resource block)를 결정할 수 있다.Also, according to the embodiment of the present invention, the remaining power of the mobile station can be estimated based on the PHR reported by the mobile station, and a maximum physical allocation block (PRB) can be determined.
또한 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 상향링크 스케줄러를 통해 최대 PRB 보다 적은 PRB를 할당함으로써, 기지국에 의해 요구되는 수신 전력을 유지하면서 이동 단말의 배터리 소모를 최소화할 수 있다.Also, according to the embodiment of the present invention, by allocating a PRB smaller than the maximum PRB through the UL scheduler, battery consumption of the mobile station can be minimized while maintaining the reception power required by the base station.
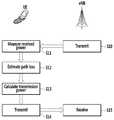
도 1은 개루프(open-loop) 전력 제어의 개념을 나타내는 도면이다.
도 2는 폐루프(closed-loop) 전력 제어의 개념을 나타내는 도면이다.
도 3은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른, 상향링크 폐루프 전력 제어 방법을 나타내는 도면이다.
도 4는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른, 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 기반한 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)을 결정하는 방법을 나타내는 도면이다.
도 5는 컨벤셔널 전력 제어(conventional power control)가 사용되는 경우에 측정된 SNR을 나타내는 도면이다.
도 6은 부분 전력 제어(fractional power control)가 사용되는 경우에 측정된 SNR을 나타내는 도면이다.
도 7은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른, 무선기기(또는 통신노드)를 나타내는 도면이다.1 is a diagram showing the concept of open-loop power control.
2 is a diagram showing the concept of closed-loop power control.
3 is a diagram illustrating an uplink closed loop power control method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
4 is a diagram illustrating a method for determining a target SINR (or target SNR) based on path loss of a mobile terminal, in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
5 is a graph showing the measured SNR when conventional power control is used.
Figure 6 is a plot of measured SNR when fractional power control is used.
7 is a diagram of a wireless device (or communication node) in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
아래에서는 첨부한 도면을 참고로 하여 본 발명의 실시예에 대하여 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 용이하게 실시할 수 있도록 상세히 설명한다. 그러나 본 발명은 여러 가지 상이한 형태로 구현될 수 있으며 여기에서 설명하는 실시예에 한정되지 않는다. 그리고 도면에서 본 발명을 명확하게 설명하기 위해서 설명과 관계없는 부분은 생략하였으며, 명세서 전체를 통하여 유사한 부분에 대해서는 유사한 도면 부호를 붙였다.Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings so that those skilled in the art can easily carry out the present invention. The present invention may, however, be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein. In order to clearly illustrate the present invention, parts not related to the description are omitted, and similar parts are denoted by like reference characters throughout the specification.
본 명세서에서, 동일한 구성요소에 대해서 중복된 설명은 생략한다.In the present specification, duplicate descriptions are omitted for the same constituent elements.
또한 본 명세서에서, 어떤 구성요소가 다른 구성요소에 '연결되어' 있다거나 '접속되어' 있다고 언급된 때에는, 그 다른 구성요소에 직접적으로 연결되어 있거나 또는 접속되어 있을 수도 있지만, 중간에 다른 구성요소가 존재할 수도 있다고 이해되어야 할 것이다. 반면에 본 명세서에서, 어떤 구성요소가 다른 구성요소에 '직접 연결되어' 있다거나 '직접 접속되어' 있다고 언급된 때에는, 중간에 다른 구성요소가 존재하지 않는 것으로 이해되어야 할 것이다.Also, in this specification, when an element is referred to as being "connected" or "connected" to another element, it may be directly connected or connected to the other element, May be present. On the other hand, in the present specification, when an element is referred to as being "directly connected" or "directly connected" to another element, it should be understood that no other element exists in between.
또한, 본 명세서에서 사용되는 용어는 단지 특정한 실시예를 설명하기 위해 사용되는 것으로써, 본 발명을 한정하려는 의도로 사용되는 것이 아니다.Furthermore, terms used herein are used only to describe specific embodiments and are not intended to be limiting of the present invention.
또한 본 명세서에서, 단수의 표현은 문맥상 명백하게 다르게 뜻하지 않는 한, 복수의 표현을 포함할 수 있다.Also, in this specification, the singular forms "a," "an," and "the" include plural referents unless the context clearly dictates otherwise.
또한 본 명세서에서, '포함하다' 또는 '가지다' 등의 용어는 명세서에 기재된 특징, 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부품, 또는 이들을 조합한 것이 존재함을 지정하려는 것일 뿐, 하나 또는 그 이상의 다른 특징, 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부품 또는 이들을 조합한 것의 존재 또는 부가 가능성을 미리 배제하지 않는 것으로 이해되어야 할 것이다.Also, in this specification, the terms " comprise ", or " have ", and the like are used to specify that there is a feature, a number, a step, an operation, an element, a component, But do not preclude the presence or addition of one or more other features, integers, steps, operations, elements, parts, or combinations thereof.
또한 본 명세서에서, '및/또는' 이라는 용어는 복수의 기재된 항목들의 조합 또는 복수의 기재된 항목들 중의 어느 항목을 포함한다. 본 명세서에서, 'A 또는 B'는, 'A', 'B', 또는 'A와 B 모두'를 포함할 수 있다.Also, in this specification, the term 'and / or' includes any combination of the listed items or any of the plurality of listed items. In this specification, 'A or B' may include 'A', 'B', or 'both A and B'.
또한 본 명세서에서, 이동 단말(mobile terminal)은, 단말(terminal), 이동국(mobile station), 진보된 이동국(advanced mobile station), 고신뢰성 이동국(high reliability mobile station), 가입자국(subscriber station), 휴대 가입자국(portable subscriber station), 접근 단말(access terminal), 사용자 장비(user equipment, UE) 등을 지칭할 수도 있고, 이동 단말, 단말, 이동국, 진보된 이동국, 고신뢰성 이동국, 가입자국, 휴대 가입자국, 접근 단말, 사용자 장비 등의 전부 또는 일부의 기능을 포함할 수도 있다.Also, in this specification, a mobile terminal may be referred to as a terminal, a mobile station, an advanced mobile station, a high reliability mobile station, a subscriber station, May refer to a mobile subscriber station, an access terminal, a user equipment (UE), or the like and may refer to a mobile terminal, a terminal, a mobile station, an advanced mobile station, a high- A subscriber station, an access terminal, a user equipment, and the like.
또한 본 명세서에서, 기지국(base station, BS)은, 진보된 기지국(advanced base station), 고신뢰성 기지국(high reliability base station), 노드B(node B, NB), 고도화 노드B(evolved node B, eNodeB, eNB), 접근점(access point), 무선 접근국(radio access station), 송수신 기지국(base transceiver station), MMR(mobile multihop relay)-BS, 기지국 역할을 수행하는 중계기(relay station), 기지국 역할을 수행하는 고신뢰성 중계기(high reliability relay station), 리피터, 매크로 셀 기지국, 소형 셀 기지국 등을 지칭할 수도 있고, 기지국, 진보된 기지국, HR-BS, 노드B, eNodeB, 접근점, 무선 접근국, 송수신 기지국, MMR-BS, 중계기, 고신뢰성 중계기, 리피터, 매크로 셀 기지국, 소형 셀 기지국 등의 전부 또는 일부의 기능을 포함할 수도 있다.Also, in this specification, a base station (BS) includes an advanced base station, a high reliability base station, a node B, an evolved node B, eNodeB, eNB), an access point, a radio access station, a base transceiver station, a mobile multihop relay (MMR) -BS, a relay station serving as a base station, BS, Node B, eNodeB, access point, wireless access, and so on, which may be referred to as a high reliability relay station, a repeater, a macro cell base station, A repeater, a high-reliability repeater, a repeater, a macro cell base station, a small cell base station, or the like.
도 1은 개루프(open-loop) 전력 제어의 개념을 나타내는 도면이다.1 is a diagram showing the concept of open-loop power control.
개루프 전력 제어 방법에서, 기지국은 레퍼런스 신호(reference signal)를 이동 단말에게 송신한다(S10).In the open loop power control method, the base station transmits a reference signal to the mobile terminal (S10).
이동 단말은 기지국에 의해 송신되는 레퍼런스 신호의 수신 전력을 측정한다(S11).The mobile terminal measures the received power of the reference signal transmitted by the base station (S11).
이동 단말은 상기 측정 후에 경로 손실(path loss)을 계산(추정)한다(S12).The mobile terminal calculates (estimates) a path loss after the measurement (S12).
이동 단말은 해당 이동 단말에 설정(configured)된 개루프 전력 제어 값에 기초해 송신 전력을 결정(계산)한다(S13).The mobile terminal determines (calculates) the transmission power based on the open loop power control value configured in the mobile terminal (S13).
이동 단말은 결정된 송신 전력에 기초해 메시지를 기지국에게 송신한다(S14, S15). 이 때, 기지국은 어떠한 피드백도 수행하지 않기 때문에, 이러한 전력 제어를 개루프 전력 제어라 한다.The mobile station transmits a message to the base station based on the determined transmission power (S14, S15). At this time, since the base station does not perform any feedback, this power control is referred to as open loop power control.
도 2는 폐루프(closed-loop) 전력 제어의 개념을 나타내는 도면이다.2 is a diagram showing the concept of closed-loop power control.
폐루프 전력 제어 방법에서, 기지국은 레퍼런스 신호를 이동 단말에게 송신한다(S10).In the closed-loop power control method, the base station transmits a reference signal to the mobile terminal (S10).
이동 단말은 기지국에 의해 송신되는 레퍼런스 신호의 수신 전력을 측정한다(S21).The mobile terminal measures the reception power of the reference signal transmitted by the base station (S21).
이동 단말은 경로 손실을 계산(추정)한다(S22).The mobile terminal calculates (estimates) the path loss (S22).
이동 단말은 해당 이동 단말에 설정된 폐루프 전력 제어 값에 기초해 송신 전력을 결정(계산)한다(S23).The mobile terminal determines (calculates) the transmission power based on the closed loop power control value set in the mobile terminal (S23).
이동 단말은 결정된 송신 전력에 기초해 메시지를 기지국에게 송신한다(S25, S26).The mobile station transmits a message to the base station based on the determined transmission power (S25, S26).
한편, 폐루프 전력 제어 방법에서, 개루프 전력 제어 방법과 다르게, 기지국이 이동 단말로부터 메시지를 수신하는 경우에, 이동 단말에게 송신 전력 조정을 명령한다. 구체적으로, 기지국은 수신 전력과 기지국에 의해 요구되는 타겟 전력 간의 차이를 보정하기 위해서, 송신 전력 제어(TPC: transmit power control) 커맨드를 이동 단말에게 송신할 수 있다(S27).On the other hand, in the closed loop power control method, unlike the open loop power control method, when the base station receives a message from the mobile terminal, it instructs the mobile terminal to adjust the transmission power. Specifically, the base station can transmit a transmit power control (TPC) command to the mobile terminal to correct the difference between the received power and the target power required by the base station (S27).
이동 단말은 TPC 커맨드를 수신하는 경우에, TPC 커맨드가 지시(indicate)하는 전력 오프셋(power offset) 만큼 송신 전력을 보정하여, 송신 전력을 결정한다(S24).When receiving the TPC command, the mobile station corrects the transmission power by the power offset indicated by the TPC command and determines the transmission power (S24).
이동 단말은 S24 과정에 의해 결정된 송신 전력에 기초해 메시지를 기지국에게 송신한다(S25, S26).The mobile station transmits a message to the base station based on the transmission power determined in step S24 (S25, S26).
이를 통해, 기지국은 기지국에 의해 요구되는 수신 타겟 전력을 유지할 수 있다.Thereby, the base station can maintain the target target power required by the base station.
폐루프 전력 제어 방법에서, 기지국은 TPC 커맨드를 결정하기 위해 필요한 이동 단말의 송신 전력과 경로 손실을 알 수 없다. 따라서, TPC 커맨드를 효율적으로 결정하는 방법이 필요하다.In the closed loop power control method, the base station can not know the transmission power and path loss of the mobile terminal necessary to determine the TPC command. Therefore, a method for efficiently determining the TPC command is needed.
한편, 이동 단말의 PUSCH 송신 전력은 아래의 수학식 1과 같이 결정된다.On the other hand, the PUSCH transmission power of the mobile station is determined by Equation (1) below.
수학식 1에서,PCMAX는 이동 단말이 송신할 수 있는 최대 전력을 나타내며, 23±2[dBm]의 값을 가지며, 기지국에 의해 설정된다. 일반적으로 PCMAX는 23[dBm]로 설정된다.In Equation (1), PCMAX indicates a maximum power that can be transmitted by the mobile station, has a value of 23 + - 2 [dBm], and is set by the base station. In general, PCMAX is set to 23 [dBm].
수학식 1에서, MPUSCH는 PUSCH를 통해 송신되는 PRB(physical resource block)의 개수를 나타낸다.In Equation (1), MPUSCH indicates the number of PRBs (physical resource blocks) transmitted through the PUSCH.
수학식 1에서, P0_PUSCH 는 기지국에 의해 요구되는 수신 전력 스펙트럼 밀도(PSD: power spectral density)를 나타내는 파라미터이다. P0_PUSCH 는 P0_nominal와 P0_UE로 구성된다. 즉, P0_PUSCH= P0_nominal+P0_UE이다.In Equation 1, P0_PUSCH is the received power spectral density required by the base station: a parameter that indicates a (power spectral density PSD). P0_PUSCH consists of P0_nominal and P0_UE . Thatis, P 0_ PUSCH = P 0_ nominal + P 0_ UE to be.
P0_nominal은 셀 특정(cell-specific)한 값을 가지며, 셀 내의 모든 이동 단말에게 동일하게 적용된다.P0_nominal Has a cell-specific value, and is equally applied to all mobile terminals in the cell.
P0_UE은 이동 단말 별 송신 전력 설정과 경로 손실 추정 오류(path loss estimation error)에 의해 발생하는 오차를 보상하기 위한 것이다.The P0_UE compensates an error caused by a transmission power setting and a path loss estimation error for each mobile terminal.
P0_nominal은 [-126, 24] dBm 값을 가진다.P0_nominal has a value of [-126, 24] dBm.
P0_UE는 [-8, 7] dB 값을 가진다.P0_UE is [-8, 7] dB has a value.
그리고 P0_PUSCH는 아래의 수학식 2와 같이 계산된다.And P0_PUSCH is calculated as shown in Equation 2 below.
수학식 2에서, α는 경로 손실을 얼마만큼 보상해서 신호를 송신할 것인가의 정도를 나타내는 보상 인자(compensation factor)를 나타내고, SINR0은 α=1인 경우에 기지국에 의해 요구되는 타겟 수신 SINR을 나타내고, Pn은 PRB 당 노이즈 전력(noise power)을 나타내고, PCMAX는 이동 단말의 최대 송신 전력을 나타내고, M0는 기준 송신 PRB 개수를 나타내며 일반적으로 1로 설정될 수 있다.In Equation (2), α represents a compensation factor indicating how much the signal is to be transmitted by compensating for the path loss, and SINR0 represents the target received SINR required by the base station when α = 1 , Pn represents the noise power per PRB, PCMAX represents the maximum transmission power of the mobile terminal, M0 represents the number of reference transmission PRBs, and can be generally set to one.
수학식 1의 α·PL에서, PL은 이동 단말에 의해 추정된 경로 손실을 나타낸다. α는 경로 손실 모두를 보상해서 신호를 송신할 것이지, 경로 손실 일부만을 보상해서 신호를 송신할 것인지를 나타낸다. 구체적으로, α는 {0, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1} 중에 하나의 값을 가질 수 있으며, 기지국에 의해 설정될 수 있다.In? PL of Equation (1), PL represents the path loss estimated by the mobile terminal. α indicates whether to transmit the signal by compensating for all of the path loss, or to compensate only a part of the path loss. Specifically, α can have one of {0, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1} and can be set by the base station.
수학식 1에서, ΔTF는 고속 페이딩(fast fading)에 대응하기 위한 파라미터이다. 구체적으로, 무선기기(예, 이동 단말)가 ΔTF 가 설정된 상태에서 신호를 송신하는 경우에, 할당된 MCS(modulation and coding scheme)에 따라 송신 전력을 추가적으로 보상할 수 있다. 이를 통해, MCS가 바뀔 때 마다 송신 PSD가 변경될 수 있다. ΔTF는 {disable, enable}로 설정되며, 무선기기(예, 이동 단말)는 ΔTF의 설정에 따라서 MCS에 따른 송신 전력 보상을 온/오프(on/off) 할 수 있다.In Equation (1),?TF is a parameter for coping with fast fading. Specifically, when a wireless device (e.g., a mobile terminal) transmits a signal with?TF set, the transmission power can be further compensated according to the allocated modulation and coding scheme (MCS). This allows the transmit PSD to change whenever the MCS changes. ?TF is set to {disable, enable}, and the radio device (e.g., mobile terminal) can turn on / off transmission power compensation according to MCS according to the setting of?TF .
수학식 1에서, f(ΔTPC)은 수신 PSD를 일정하게 유지하기 위하여 사용된다. 구체적으로, 무선기기(예, 기지국)가 이동 단말에게 자원을 할당하여 DCI(downlink control information)를 송신하거나 전력제어의 목적으로 DCI를 송신하는 경우에, 무선기기(예, 기지국)는 이전에 수신된 PUSCH의 수신 전력과 기지국에 의해 요구되는 수신 타겟 전력의 차이를 기준으로 TPC 커맨드를 생성할 수 있다. 그리고 무선기기(예, 기지국)는 생성된 TPC 커맨드를 해당 DCI에 포함시켜 전송함으로써, 무선기기(예, 이동 단말)의 송신 전력을 보정할 수 있다.In Equation (1), f (?TPC ) is used to keep the received PSD constant. Specifically, when a wireless device (e.g., a base station) allocates resources to a mobile terminal to transmit DCI (downlink control information) or DCI for power control purposes, the wireless device The TPC command can be generated on the basis of the difference between the reception power of the PUSCH and the reception target power required by the base station. The wireless device (e.g., base station) can then correct the transmit power of the wireless device (e.g., mobile terminal) by including the generated TPC command in its DCI.
TPC 커맨드는 누적(accumulated) 방법 또는 절대(absolute) 방법을 통해 결정될 수 있다. 구체적으로, TPC 커맨드는 아래의 표 1(Mapping of TPC command field in DCI format 0/3/4)과 표 2(Mapping of TPC command field in DCI format 3A)를 따른다. 누적 방법 또는 절대 방법은 무선기기(예, 기지국)에 의해 설정된다. 누적 방법은 무선기기(예, 이동 단말)가 TPC 커맨드를 수신할 때마다 보상해야 하는 전력 값을 지속적으로 누적하는 방법이다. 절대 방법은 누적 방법과 다르게, 무선기기(예, 이동 단말)가 한번만 보상 값을 송신 전력에 적용하는 방법이다.The TPC command may be determined through an accumulated method or an absolute method. Specifically, the TPC command conforms to Table 1 (Mapping of TPC command field in
DCI format 0/3/4TPC command field in
DCI format 3ATPC command field in
DCI format 3A
표 1 및 표 2에서, δ_PUSCH,c는를 나타낸다. 표 1 및 표 2에서,는 TPC 커맨드 지시 인자에 따라 실제 보상되어야 하는 송신 전력을 나타낸다. 예를 들면, 0의 값을 가지는 TPC 커맨드는 송신 신호의 PSD를 -1dB 만큼 낮추라는 것을 의미한다.In Table 1 and Table 2, 隆 _PUSCH, c is . In Tables 1 and 2, Represents the transmission power that should be actually compensated according to the TPC command indication factor. For example, a TPC command having a value of 0 means that the PSD of the transmission signal is lowered by -1 dB.
수학식 1에서의 이동 단말의 PUSCH 송신 전력을 고려하면, TPC 커맨드를 효율적으로 결정하는 방법이 필요하다. 이를 통해, 이동 단말의 현재 위치에서의 경로 손실을 모르는 상태에서도, 기지국에 의해 요구되는 수신 SNR(또는 수신 SINR)이 맞추어질 수 있다.Considering the PUSCH transmission power of the mobile station in Equation (1), there is a need for a method for efficiently determining the TPC command. Accordingly, the received SNR (or the received SINR) required by the base station can be adjusted even when the path loss at the current position of the mobile terminal is unknown.
또한, 이동 단말의 배터리 소모를 줄이기 위해, 송신 전력은 PCMAX를 넘지 않아야 한다. 만약, 송신 전력이 PCMAX를 넘으면, 기지국의 PUSCH 수신 성능이 떨어지고, 결국에는 상향링크 성능의 저하와 함께 이동 단말의 배터리 소모가 극심해진다.Also, in order to reduce battery consumption of the mobile terminal, the transmission power should not exceed PCMAX . If the transmission power exceeds PCMAX , the PUSCH reception performance of the base station is deteriorated, and eventually the downlink performance deteriorates and the battery consumption of the mobile terminal becomes extreme.
이하에서는 LTE 기반의 소형셀 기지국 시스템에서 상향링크 폐루프 전력 제어를 수행하는 방법, 즉 상향링크 송신 전력을 제어하는 방법에 대하여 설명한다.Hereinafter, a method for performing uplink closed loop power control in an LTE-based small cell base station system, that is, a method for controlling uplink transmission power will be described.
무선기기(예, 소형셀 기지국)는 이동 단말로부터, 이동 단말의 가용 송신 전력량을 나타내는 PHR(power headroom report)을 수신한다. 그리고 무선기기(예, 소형셀 기지국)는 수신된 PHR에 기초해, 이동 단말의 현재 위치에 대하여(이동 단말의 현재 위치 또는 경로 손실에 대응하여) 요구되는 타겟 SNR(또는 타겟 SINR)을 결정한다. 본 명세서에서는, 채널 품질 정보가 SNR 또는 SINR인 경우를 예로 들어, 본 발명의 실시예를 설명한다. 본 명세서에서, 채널 품질 정보가 SNR인 경우를 위해 기술된 내용은 채널 품질 정보가 SINR인 경우에도 동일 또는 유사하게 적용될 수 있으며, 그 반대도 마찬가지이다. 하지만 이는 예시일 뿐이며, 채널 품질 정보가 SNR 또는 SINR이 아닌 경우에도 본 발명의 실시예는 적용될 수 있다.A wireless device (e.g., a small cell base station) receives a power headroom report (PHR) indicating the available transmission power of the mobile terminal from the mobile terminal. Then, the wireless device (e.g., small cell base station) determines the target SNR (or target SINR) required for the current location of the mobile terminal (corresponding to the current position or path loss of the mobile terminal) based on the received PHR . In the present specification, an embodiment of the present invention will be described by taking the case where the channel quality information is SNR or SINR as an example. In this specification, the description for the case where the channel quality information is the SNR can be applied equally or similarly even when the channel quality information is the SINR, and vice versa. However, this is only an example, and the embodiment of the present invention can be applied even when the channel quality information is not SNR or SINR.
무선기기(예, 소형셀 기지국)는 이동 단말로부터 상향링크 데이터 채널(예, PUSCH)를 수신하고, 이를 통해 측정되는 수신 SNR(수신 SINR)에 필터를 적용하여 평탄화(smoothing)된 수신 SNR(또는 수신 SINR)을 결정한다.A wireless device (e.g., a small cell base station) receives a downlink data channel (e.g., PUSCH) from a mobile terminal and applies a filter to the measured received SNR (received SINR) to obtain a smoothed received SNR Reception SINR).
무선기기(예, 소형셀 기지국)는 주기적으로 결정되는 타겟 SNR(또는 타겟 SINR)과 평탄화된 수신 SNR(또는 평탄화된 수신 SNR) 간의 차이를 구하고, 상기 차이에 기초해 TPC 커맨드를 TPC 맵퍼(mapper)를 통해 결정한다.A wireless device (e.g., a small cell base station) may determine the difference between a periodically determined target SNR (or target SINR) and a smoothed received SNR (or smoothed received SNR), and transmit a TPC command based on the difference to a TPC mapper ).
무선기기(예, 소형셀 기지국)는 이동 단말로부터 PHR을 수신하고, PHR과 이동 단말의 현재 위치(또는 경로 손실)에 기초해 이동 단말에게 할당할 수 있는 최대 PRB 개수를 결정한다.A radio device (e.g., a small cell base station) receives the PHR from the mobile terminal and determines the maximum number of PRBs that can be allocated to the mobile terminal based on the PHR and the current location (or path loss) of the mobile terminal.
무선기기(예, 소형셀 기지국)는 상향링크 스케줄러의 스케줄링 시에 최대 PRB 개수보다 적은 개수의 PRB를 이동 단말에게 할당한다.A radio device (e.g., a small cell base station) allocates to the mobile terminal a number of PRBs less than the maximum number of PRBs in the scheduling of the UL scheduler.
무선기기(예, 소형셀 기지국)는 TPC 맵퍼를 통해 결정된 TPC 커맨드를 이동 단말에게 송신한다.The wireless device (e.g., small cell base station) transmits the TPC command determined through the TPC mapper to the mobile terminal.
도 3은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른, 상향링크 폐루프 전력 제어 방법을 나타내는 도면이다.3 is a diagram illustrating an uplink closed loop power control method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 3에 예시된 바와 같이, 상향링크 폐루프 전력 제어를 위하여, 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)을 결정하는 절차(S100), Mmax를 결정하는 절차(S110), SINR 필터(또는 SNR 필터)를 위한 초기값을 결정하는 절차(S120), SINR 필터(또는 SNR 필터)를 사용하는 절차(S130), TPC 커맨드를 결정하는 절차(S140), 그리고 스케줄링 절차(S150)가 수행된다.As illustrated in FIG. 3, for uplink closed loop power control, a procedure S100 for determining a target SINR (or a target SNR), a procedure S110 for determiningMmax , a SINR filter (or SNR filter) A procedure for determining an initial value for the TPC command (S120), a procedure using a SINR filter (or SNR filter) (S130), a procedure for determining a TPC command (S140), and a scheduling procedure (S150) are performed.
먼저, 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)을 결정하는 절차(S100)에 대해서 설명한다.First, a procedure S100 for determining a target SINR (or a target SNR) will be described.
무선기기(예, 소형셀 기지국)는 이동 단말로부터 PHR를 수신할 때마다, 수신된 PHR 값과 α 값을 기준으로, 이동 단말을 위한 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)을 결정한다.Each time a wireless device (e.g., a small cell base station) receives a PHR from a mobile terminal, it determines a target SINR (or target SNR) for the mobile terminal based on the received PHR value and the value a.
타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)은 경로 손실을 얼마만큼 보상할지를 결정하기 위한 α 값과 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 따라 달라진다. 여기서, 이동 단말의 경로 손실은 이동 단말의 현재 위치에 대응할 수 있다.The target SINR (or target SNR) depends on the α value for determining how much the path loss is compensated for and the path loss of the mobile terminal. Here, the path loss of the mobile terminal may correspond to the current position of the mobile terminal.
α=1인 경우에, 무선기기(예, 소형셀 기지국)는 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 관계없이 일정한 수신 전력으로 신호를 수신한다. 즉, 이동 단말이 기지국에 가까이 있던 멀리 있던지 관계없이, 기지국은 동일한 수신 전력으로 신호를 수신한다. 이러한 전력 제어를 컨벤셔널 전력 제어(CPC: conventional power control)라 한다.When? = 1, a radio device (e.g., a small cell base station) receives a signal with a constant received power regardless of the path loss of the mobile terminal. That is, regardless of whether the mobile terminal is near or far from the base station, the base station receives the signal with the same received power. This power control is called conventional power control (CPC).
α < 1 인 경우에, 수신 PSD는 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 따라 달라진다. 즉, 기지국에 가까이 있어 경로 손실이 작은 이동 단말에 대해서는 기지국은 높은 PSD로 신호를 수신하고, 기지국에 멀리 있어 경로 손실이 큰 이동 단말에 대해서는 기지국은 낮은 PSD로 신호를 수신한다. 이러한 전력 제어를 부분 전력 제어(FPC: fractional power control)라 한다.If? <1, the received PSD depends on the path loss of the mobile terminal. That is, the base station receives a signal with a high PSD for a mobile terminal having a small path loss due to its proximity to a base station, and the base station receives a signal with a low PSD for a mobile terminal with a large path loss. This power control is called fractional power control (FPC).
컨벤셔널 전력 제어(CPC)의 P0_PUSCH(기지국에 의해 요구되는 수신 PSD)는 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 관계 없이 모든 이동 단말에 대해서 동일한 값을 가지며, 수학식 2로부터 구해질 수 있다. 수학식 2에 α = 1을 대입하면, 아래의 수학식이 구해진다.Conventional power control (CPC) of a P0_PUSCH (received as required by the base station PSD) has the same value for all mobile terminals regardless of the path loss of the mobile terminal, can be found from equation (2). When? = 1 is substituted into the equation (2), the following equation is obtained.
상기 수학식에서, Pn은 PRB 당 노이즈 전력을 나타내며, 아래의 수학식과 같이 계산된다.In the above equation, Pn represents the noise power per PRB and is calculated according to the following equation.
따라서, α = 1인 경우에, 이동 단말의 송신(Tx) PSD는 아래의 수학식과 같다.Therefore, when? = 1, the transmission (Tx) PSD of the mobile station is expressed by the following equation.
경로 손실은 신호가 기지국에 도달되기 전에 소모되므로, 기지국에서의 수신(Rx) PSD는 아래의 수학식과 같다.Since the path loss is consumed before the signal reaches the base station, the reception (Rx) PSD at the base station is given by the following equation.
따라서, 컨벤셔널 전력 제어(CPC)의 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)은 아래의 수학식 3과 같다.Therefore, the target SINR (or target SNR) of the conventional power control (CPC) is expressed by Equation 3 below.
한편, 부분 전력 제어(FPC)에서는, 이동 단말의 경로 손실 즉, 이동 단말의 현재 위치에 따라 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)이 달라진다. 따라서, 이동 단말의 송신(Tx) PSD는 아래의 수학식과 같다.On the other hand, in the partial power control (FPC), the target SINR (or the target SNR) varies depending on the path loss of the mobile terminal, that is, the current position of the mobile terminal. Therefore, the transmission (Tx) PSD of the mobile station is expressed by the following equation.
경로 손실은 신호가 기지국에 도달되기 전에 소모되므로, 기지국에서의 수신(Rx) PSD는 아래의 수학식 4와 같다.Since the path loss is consumed before the signal reaches the base station, the reception (Rx) PSD at the base station is given by Equation (4) below.
수학식 4에 예시된 바와 같이, 부분 전력 제어(FPC)에서 경로 손실은 중요한 요소이다. 그러나 이동 단말에 대한 경로 손실은 이동 단말에 의해 측정되는 것으로써, 기지국은 이를 직접적으로 알 수 없다. 따라서 기지국은 이동 단말의 PHR을 통해 간접적으로 이동 단말의 경로 손실을 유추하고, 유추된 경로 손실에 따라 이동 단말을 위한 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)을 결정할 수 있다. 이에 대하여, 도 4를 참고하여 자세히 설명한다.As illustrated in equation (4), path loss in partial power control (FPC) is an important factor. However, since the path loss to the mobile terminal is measured by the mobile terminal, the base station can not directly know the path loss. Therefore, the BS indirectly deduces the path loss of the mobile station through the PHR of the mobile station, and can determine the target SINR (or the target SNR) for the mobile station according to the inferred path loss. This will be described in detail with reference to FIG.
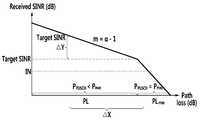
도 4는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른, 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 기반한 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)을 결정하는 방법을 나타내는 도면이다. 도 4에서, 가로 축은 경로 손실을 나타내고 세로 축은 수신 SINR을 나타낸다. 도 4에서, IN은 노이즈 전력을 나타낸다.4 is a diagram illustrating a method for determining a target SINR (or target SNR) based on path loss of a mobile terminal, in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 4, the horizontal axis represents the path loss and the vertical axis represents the reception SINR. In Fig. 4, IN represents the noise power.
도 4에 예시된 바와 같이, 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)은 α에 따른 기울기 m으로 구해진다. m은 아래의 수학식 5와 같다.As illustrated in FIG. 4, the target SINR (or target SNR) is determined by the slope m according to?. m is expressed by Equation (5) below.
수학식 5에서, ΔX와 ΔY는 아래의 수학식과 같다.In Equation (5), DELTA X and DELTA Y are expressed by the following equations.
상기 수학식에서, TargetSINR'은 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 따른 새로운 타겟 SINR을 나타내고, TargetSINR은 α=1인 경우를 위한 수학식 3의 타겟 SINR을 나타낸다.In the above equation, TargetSINR 'denotes a new target SINR according to the path loss of the mobile station, and TargetSINR denotes a target SINR of Equation (3) for a case of? = 1.
그리고, PL과 PLmax는 PHR(Ph)에 기초해, 수학식 1로부터 아래의 수학식 6과 같이 구해질(유추될) 수 있다.Then, PL and PLmax can be obtained (derived) from Equation (1) based on PHR (Ph ) as shown in Equation (6) below.
수학식 6에서, Ph는 이동 단말의 PHR에 의해 지시되는 가용 송신 전력량(즉, power headroom)을 나타내고, PCMAX는 이동 단말의 최대 송신 전력을 나타내고, MPUSCH는 PUSCH를 통해 전송되는 PRB의 개수를 나타내고, PLmax는 최대 경로 손실을 나타낸다. 여기서, Ph는 이동 단말의 최대 송신 전력과 현재 PUSCH 송신 전력 간의 차이에 기초해 구해진다. 구체적으로, Ph는 아래의 표 3과 같은 지시자 형태로 PHR을 통해 보고된다. Ph는 PHR의 지시자에 대응하는 가용 송신 전력량을 나타낸다. 따라서, Ph = 0 인 경우에, 가용 송신 전력량은 0 이며, 경로 손실은 최대가 되어 PLmax가 구해질 수 있다. 이하에서, Ph는 PHR(Ph)로도 표현될 수 있다.In Equation (6), Ph represents the available transmission power amount indicated by the PHR of the mobile station (i.e., power headroom), PCMAX represents the maximum transmission power of the mobile station, and MPUSCH represents the maximum transmission power of the PRB transmitted through the PUSCH And PLmax represents the maximum path loss. Here, Ph is obtained based on the difference between the maximum transmission power of the mobile station and the current PUSCH transmission power. Specifically, Ph is reported through the PHR in the form of indicators as shown in Table 3 below. Ph represents the amount of available transmit power corresponding to the indicator of the PHR. Therefore, when Ph = 0, the available transmit power is 0, and the path loss is maximized, so that PLmax can be obtained. In the following, Ph can also be expressed as PHR (Ph ).
표 3에서, PH는 Ph를 의미한다.In Table 3, PH means Ph .
이를 통해, 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 따른 새로운 타겟 SINR(Target SINR')는 아래의 수학식 7과 같이 구해질 수 있다.Through this, a new target SINR (Target SINR ') according to the path loss of the mobile terminal can be obtained as shown in Equation (7).
수학식 7에서 PH는 Ph를 의미한다.In Equation (7), PH means Ph .
부분 전력 제어(FPC)가 사용되는 경우를 위한 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)은, 수학식 7을 통해 결정될 수 있다.The target SINR (or target SNR) for when partial power control (FPC) is used can be determined via Equation (7).
다음으로, Mmax를 결정하는 절차(S110)에 대해서 설명한다.Next, the procedure for determining Mmax (S110) will be described.
수학식 1에 예시된 바와 같이, PUSCH 송신 전력은 이동 단말의 현재 위치에서의 경로 손실, TPC 커맨드, 및 할당된 PRB의 개수에 따라 결정된다. 특히, 소형셀의 환경과 같이 이동 단말의 경로 손실과 쉐도잉(shadowing)이 급격하게 바뀌지 않는 환경에서, 송신 전력을 변경하는 주요 요인은 할당된 PRB의 개수이다. 이러한 상황에서 이동 단말의 배터리 소모를 줄이기 위해서, 송신 전력이 이동 단말의 최대 송신 전력인 PCMAX를 넘지 않도록 제어되어야 한다.As illustrated in Equation (1), the PUSCH transmission power is determined according to the path loss at the current position of the mobile terminal, the TPC command, and the number of allocated PRBs. Particularly, in an environment where the path loss and shadowing of the mobile terminal do not change suddenly, such as the environment of a small cell, the main factor for changing the transmission power is the number of allocated PRBs. In this situation, in order to reduce battery consumption of the mobile terminal, the transmission power should be controlled not to exceed the maximum transmission power PCMAX of the mobile terminal.
따라서, 무선기기(예, 기지국)는 PHR이 수신될 때마다, PHR 송신을 위해 할당되었던 PRB의 개수를 기반으로, 이동 단말에게 현재 할당할 수 있는 최대 PRB 개수를 결정할 수 있다. 그리고 무선기기(예, 기지국)는 스케줄러의 스케줄링 시에 최대 PRB 개수를 넘지 않는 범위 내에서 이동 단말에게 할당할 PRB 개수를 결정할 수 있다.Thus, each time a PHR is received, the wireless device (e.g., base station) may determine the maximum number of PRBs currently allocated to the mobile terminal, based on the number of PRBs allocated for PHR transmission. The scheduler of the wireless device (e.g., base station) can determine the number of PRBs to be allocated to the mobile terminal within a range not exceeding the maximum number of PRBs.
Mmax는 Pcmax를 넘지 않는 범위 내에서 이동 단말에게 최대로 할당할 수 있는 PRB의 개수를 나타낸다. Mmax을 구하기 위해, 이동 단말의 현재 경로 손실 상태가 고려될 수 있다. 구체적으로, Mmax는 PHR(Ph)에 기초해 아래와 같이 구해질 수 있다.Mmax denotes the maximum number of PRBs that can be allocated to the mobile terminal within a range not exceedingPcmax . To obtain Mmax , the current path loss state of the mobile terminal can be considered. Specifically, Mmax can be obtained as follows based on PHR (Ph ).
수학식 6으로부터 아래의 수학식이 유도될 수 있다.From Equation (6), the following equation can be derived.
그리고 상기 수학식과 수학식 1로부터, 아래의 수학식 8이 유도될 수 있다.From Equation (1) and Equation (1), the following Equation (8) can be derived.
그리고 Mmax에 따른 PCMAX는 아래의 수학식 9와 같이 구해질 수 있다.And PCMAX according to Mmax can be obtained by the following equation (9).
따라서, Mmax는 수학식 8과 수학식 9에 기초해, 아래의 수학식 10과 같이 구해질 수 있다.Therefore, Mmax can be obtained according to Equation (10) based on Equations (8) and (9).
다음으로, SINR 필터(또는 SNR 필터)를 사용하는 절차(S130)에 대해서 설명한다.Next, the procedure (S130) using the SINR filter (or SNR filter) will be described.
기지국이 PUSCH를 수신하는 경우에, 기지국의 PHY(physical) 계층은 PUSCH에 대한 수신 SINR(또는 수신 SNR)을 측정하여 기지국의 스케줄러에 보고한다. 여기서, 측정된 수신 SINR(또는 수신 SNR)은 무선 채널의 상태 및 수신기의 측정 오차 등으로 인해 항상 정확한 값이라고 할 수 없다. 따라서, 기지국은 SINR 필터(또는 SNR 필터)를 통해 수신 SINR(또는 수신 SNR)을 평탄화(smoothing)하여, 평탄화된 수신 SINR(또는 평탄화된 수신 SINR)을 구할 수 있다.When the base station receives the PUSCH, the PHY (physical) layer of the base station measures the received SINR (or received SNR) for the PUSCH and reports it to the scheduler of the base station. Here, the measured received SINR (or received SNR) is not always accurate due to the state of the wireless channel and the measurement error of the receiver. Therefore, the base station can obtain the smoothed received SINR (or the smoothed received SINR) by smoothing the received SINR (or the received SNR) through the SINR filter (or the SNR filter).
기지국은 이동 단말로부터 수신한 PUSCH의 SINR(또는 SNR)에 대한 평탄화를 위하여, 이동 평균 필터(moving average filter) 중 하나인 지수 필터(exponential filter)를 사용할 수 있다. 이 때, 소형셀의 하드웨어 특성상 너무 복잡하지 않은 필터의 사용이 요구되므로, 기지국은 아래의 수학식 11과 같은 단일 스텝 지수 필터(1-step exponential filter)를 사용할 수 있다.The base station may use an exponential filter, which is one of moving average filters, for smoothing the SINR (or SNR) of the PUSCH received from the mobile terminal. At this time, since it is required to use a filter that is not too complicated due to the hardware characteristics of the small cell, the base station can use a 1-step exponential filter as shown in Equation (11) below.
수학식 11에서, Y(t)는 시간 t에서 SINR 필터(또는 SNR 필터)로부터 출력되는 출력 값을 나타내고, Y(t-1)는 시간 t-1에서 SINR 필터(또는 SNR 필터)로부터 출력되는 출력 값을 나타내고, X(t)는 시간 t에서 SINR 필터(또는 SNR 필터)에 입력되는 입력 값(즉, 수신 PUSCH의 SINR(또는 SNR))을 나타낸다. 수학식 11에서, μ는 SINR 필터 파라미터(또는 SNR 필터 파라미터)를 나타내며, 0≤μ≤1 이다. μ는 일반적으로 0.7~0.9의 값을 가질 수 있으며, 실험을 통해 결정될 수 있다.Y (t-1) represents the output value from the SINR filter (or SNR filter) at time t-1, Y And X (t) represents an input value (i.e., SINR (or SNR) of the reception PUSCH) input to the SINR filter (or SNR filter) at time t. In Equation (11), 占 denotes a SINR filter parameter (or SNR filter parameter), and 0? Mu? 1. μ can generally have a value of 0.7 to 0.9 and can be determined experimentally.
다음으로, SINR 필터(또는 SNR 필터)를 위한 초기값을 결정하는 절차(S120)에 대해서 설명한다.Next, a procedure (S120) for determining an initial value for the SINR filter (or SNR filter) will be described.
기지국은 SINR 필터(또는 SNR 필터)를 사용하기 위한 초기값으로써, M3 메시지의 수신 시 획득한 SINR 값(또는 SNR 값)을 사용할 수 있다. 즉, M3 메시지에 대한 수신 SINR 값(또는 수신 SNR 값)은 SINR 필터(또는 SNR 필터)를 위한 초기값으로써 사용될 수 있다. 여기서, M3 메시지는 이동 단말이 기지국에 접속하기 위한 랜덤 접속(random access) 절차에서 기지국이 최초로 수신하는 메시지이다. PRACH(physical random access channel) 프리앰블(preamble)의 수신 SINR 값(또는 SNR 값)을 기준으로, M3 메시지에 대한 전력 제어가 이루어진다.The base station may use the SINR value (or SNR value) acquired at the time of receiving the M3 message as an initial value for using the SINR filter (or the SNR filter). That is, the received SINR value (or received SNR value) for the M3 message may be used as an initial value for the SINR filter (or SNR filter). Here, the M3 message is a message initially received by the base station in a random access procedure for the mobile station to access the base station. Power control is performed on the M3 message based on the received SINR value (or SNR value) of the physical random access channel (PRACH) preamble.
M3 메시지에 대한 전력 제어를 위한는 아래의 수학식 12와 같이 정의될 수 있다.For power control on M3 messages Can be defined as Equation (12) below.
수학식 12에서, Received PRACH SINR는 수신된 PRACH 프리앰블의 SINR(또는 SNR)을 나타낸다. 그리고,는 수신된 PRACH 프리앰블의 SINR(또는 SNR) 대비 M3 수신을 위해 필요한 전력 오프셋을 나타내며, 시스템 정보에 정의된다.In Equation 12, Received PRACH SINR represents the SINR (or SNR) of the received PRACH preamble. And, Represents the power offset required for M3 reception versus the SINR (or SNR) of the received PRACH preamble, and is defined in the system information.
M3(또는 M3 메시지)를 위한 TPC 커맨드는 아래의 표 4와 같다.TPC commands for M3 (or M3 message) are shown in Table 4 below.
다음으로, TPC 커맨드를 결정하는 절차(S140)에 대해서 설명한다.Next, a procedure (S140) for determining the TPC command will be described.
TPC 맵퍼는 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)과 필터링된(평탄화된) 수신 SINR(또는 수신 SNR) 간의 차이에 기초해 TPC 커맨드 값을 결정하는 기능이다.The TPC mapper is a function that determines the TPC command value based on the difference between the target SINR (or target SNR) and the filtered (flattened) received SINR (or received SNR).
만약 TPC 맵퍼가 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)과 필터링된(평탄화된) 수신 SINR(또는 수신 SNR) 간의 차이가 존재할 때마다 TPC 커맨드 값을 결정한다면, 일시적으로 채널이 출렁이는 경우까지도 반영될 수 있고, 이로 인해 전력 제어에 오류가 발생할 수 있다. 이러한 전력 제어 오류를 방지하기 위하여, TPC 맵퍼는 일정한 주기(TPC 커맨드 갱신 주기) 동안에 SINR 필터(또는 SNR 필터)를 통해 결정되는 수신 SINR(또는 수신 SNR)을 기준으로, TPC 커맨드를 결정할 수 있다.If the TPC mapper determines the TPC command value whenever there is a difference between the target SINR (or target SNR) and the filtered (smoothed) received SINR (or received SNR) And this may cause an error in the power control. In order to prevent such a power control error, the TPC mapper can determine the TPC command based on the received SINR (or received SNR) determined through the SINR filter (or SNR filter) for a fixed period (TPC command update period).
기지국의 TPC 맵퍼는 표 1과 표 2에 따라, TPC 커맨드를 아래의 수학식을 이용해 결정할 수 있다.The TPC mapper of the base station can determine the TPC command using the following equation according to Table 1 and Table 2. [
상기 수학식에서,는 타겟 SINR(또는 타겟 SNR)과 수신 SINR(또는 SNR) 간의 차이를 나타내고, ReceivedSINR은 필터링된(평탄화된) 수신 SINR(또는 SNR)을 나타낸다. 구체적으로 상기 수학식에서, ReceivedSINR은 TPC 커맨드 갱신 주기(update period) 동안에 필터링되어(평탄화되어) 결정된 수신 SINR(또는 SNR)을 나타낼 수 있다.In the above equation, Represents the difference between the target SINR (or target SNR) and the received SINR (or SNR), and ReceivedSINR represents the filtered (flattened) received SINR (or SNR). Specifically, in the above equation, ReceivedSINR may be filtered (flattened) during a TPC command update period to indicate a determined received SINR (or SNR).
TPC 커맨드 갱신 주기는 시스템의 설치 환경 또는 무선 채널 환경에 따라 달라질 수 있다.The TPC command update period may vary depending on the installation environment of the system or the wireless channel environment.
기지국은 TPC 커맨드 갱신 주기가 지난 후에를 결정(계산)하여,에 기초한 TPC 커맨드를 이동 단말에게 송신할 수 있다. 그리고 기지국은 그 이후부터 다음의 TPC 커맨드 갱신 주기까지(다음의 TPC 커맨드 갱신 주기가 종료되는 시점까지)는=0 으로 설정하여,에 기초한 TPC 커맨드를 이동 단말에게 송신할 수 있다. 그리고 기지국은 해당 TPC 커맨드 갱신 주기가 지난 후에를 다시 결정하여,에 기초한 TPC 커맨드를 이동 단말에게 송신할 수 있다.After the TPC command update period has elapsed (Calculated) Based on the TPC command, to the mobile terminal. Then, the base station waits until the next TPC command update period (until the next TPC command update period ends) = 0, Based on the TPC command, to the mobile terminal. After the corresponding TPC command update period has elapsed Lt; RTI ID = 0.0 > Based on the TPC command, to the mobile terminal.
다음으로, 스케줄러의 스케줄링 절차(S150)에 대해서 설명한다.Next, the scheduling procedure (S150) of the scheduler will be described.
기지국은 최대 PRB 개수보다 적은 개수의 PRB를 이동 단말에게 할당할 수 있고, TPC 커맨드를 이동 단말에게 송신할 수 있다. 도 3에서, 'M/TPC'의 M은 이동 단말에게 할당되는 PRB의 개수를 나타내며, 'M/TPC'의 TPC는 이동 단말에게 송신되는 TPC 커맨드를 나타낸다.The base station can allocate a smaller number of PRBs to the mobile terminal than the maximum number of PRBs and transmit the TPC command to the mobile terminal. 3, M of 'M / TPC' represents the number of PRBs allocated to the mobile terminal, and TPC of 'M / TPC' represents the TPC command transmitted to the mobile terminal.
도 5는 컨벤셔널 전력 제어(conventional power control)가 사용되는 경우에 측정된 SNR을 나타내는 도면이다. 도 6은 부분 전력 제어(fractional power control)가 사용되는 경우에 측정된 SNR을 나타내는 도면이다. 도 5 및 도 6에서, OLPC는 개루프 전력 제어(open-loop power control)를 나타내고, CLPC는 폐루프 전력 제어(closed-loop power control)를 나타낸다. 도 5 및 도 6에서, P0는 P0_PUSCH를 나타낸다.5 is a graph showing the measured SNR when conventional power control is used. Figure 6 is a plot of measured SNR when fractional power control is used. In FIGS. 5 and 6, OLPC represents open-loop power control and CLPC represents closed-loop power control. In Figures 5 and 6, P0 represents a P0_PUSCH.
구체적으로 도 5 및 도 6에는, 이동 단말이 셀 센터(cell center)에서 셀 엣지(cell edge)로 이동함에 따라, 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 전력 제어 방법을 탑재한 소형셀 기지국이 수신하는 PUSCH의 SNR와 Mmax를 측정한 결과가 예시되어 있다.5 and 6, as the mobile terminal moves from a cell center to a cell edge, a PUSCH (short message service) received by a small cell base station equipped with a power control method according to an embodiment of the present invention, The SNR and the Mmax of the sample are measured.
컨벤셔널 전력 제어(CPC)와 부분 전력 제어(FPC)의 측정 결과에 예시된 바와 같이, 개루프 전력 제어 방법이 사용되는 경우 보다 폐루프 전력 제어 방법이 사용되는 경우에, 수신 SNR이 타켓 SNR을 크게 벗어나지 않으면서 이동 단말의 송신 전력이 제어된다.If the closed-loop power control method is used rather than when the open-loop power control method is used, as illustrated in the measurement results of the conventional power control (CPC) and the partial power control (FPC) The transmission power of the mobile terminal is controlled without largely deviating.
그리고 도 5 및 도 6에 예시된 바와 같이, 이동 단말이 셀 엣지로 갈수록(가로축의 오른쪽으로 갈수록), 이동 단말에 할당될 수 있는 최대 PRB 개수(Mmax)는 제한된다. 이를 통해, 소형셀 기지국은 이동 단말의 배터리가 적게 소모되도록 하면서 이동 단말의 전력 제어를 적응적으로 수행할 수 있다.As illustrated in FIGS. 5 and 6, as the mobile terminal moves toward the cell edge (toward the right of the horizontal axis), the maximum number of PRBs (Mmax ) that can be allocated to the mobile terminal is limited. Accordingly, the small cell base station can adaptively perform power control of the mobile station while reducing battery consumption of the mobile station.
도 7은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른, 무선기기(또는 통신노드)를 나타내는 도면이다. 무선기기(TN100)는 본 명세서에서 기술된 기지국 또는 단말 등일 수 있고, 송신기 또는 수신기일 수 있다.7 is a diagram of a wireless device (or communication node) in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. The wireless device TN100 may be a base station or a terminal, etc., described herein, and may be a transmitter or a receiver.
도 7의 실시예에서, 무선기기(TN100)는 적어도 하나의 프로세서(TN110), 네트워크와 연결되어 통신을 수행하는 송수신 장치(TN120), 및 메모리(TN130)를 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 무선기기(TN100)는 저장 장치(TN140), 입력 인터페이스 장치(TN150), 출력 인터페이스 장치(TN160) 등을 더 포함할 수 있다. 무선기기(TN100)에 포함된 구성 요소들은 버스(bus)(TN170)에 의해 연결되어 서로 통신을 수행할 수 있다.7, the radio device TN100 may include at least one processor (TN110), a transceiver (TN120) connected to a network to perform communication, and a memory (TN130). Further, the radio device TN100 may further include a storage device TN140, an input interface device TN150, an output interface device TN160, and the like. The components included in the wireless device TN100 may be connected by a bus (TN170) and communicate with each other.
프로세서(TN110)는 메모리(TN130) 및 저장 장치(TN140) 중에서 적어도 하나에 저장된 프로그램 명령(program command)을 실행할 수 있다. 프로세서(TN110)는 중앙 처리 장치(CPU: central processing unit), 그래픽 처리 장치(GPU: graphics processing unit), 또는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 방법들이 수행되는 전용의 프로세서를 의미할 수 있다. 프로세서(TN110)는 본 발명의 실시예와 관련하여 기술된 절차, 기능, 및 방법들을 구현하도록 구성될 수 있다. 프로세서(TN110)는 무선기기(TN100)의 각 구성 요소를 제어할 수 있다.The processor TN110 may execute a program command stored in at least one of the memory TN130 and the storage device TN140. The processor TN110 may refer to a central processing unit (CPU), a graphics processing unit (GPU), or a dedicated processor on which methods according to embodiments of the present invention are performed. The processor TN110 may be configured to implement the procedures, functions, and methods described in connection with the embodiments of the present invention. The processor TN110 may control each component of the wireless device TN100.
메모리(TN130) 및 저장 장치(TN140) 각각은 프로세서(TN110)의 동작과 관련된 다양한 정보를 저장할 수 있다. 메모리(TN130) 및 저장 장치(TN140) 각각은 휘발성 저장 매체 및 비휘발성 저장 매체 중에서 적어도 하나로 구성될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 메모리(TN130)는 읽기 전용 메모리(ROM: read only memory) 및 랜덤 액세스 메모리(RAM: random access memory) 중에서 적어도 하나로 구성될 수 있다.Each of the memory TN130 and the storage device TN140 may store various information related to the operation of the processor TN110. Each of the memory TN130 and the storage device TN140 may be constituted of at least one of a volatile storage medium and a nonvolatile storage medium. For example, the memory TN130 may be configured with at least one of a read only memory (ROM) and a random access memory (RAM).
송수신 장치(TN120)는 유선 신호 또는 무선 신호를 송신 또는 수신할 수 있다. 그리고 무선기기(TN100)는 단일 안테나 또는 다중 안테나를 가질 수 있다.The transceiver apparatus TN120 can transmit or receive a wired signal or a wireless signal. And the wireless device (TN100) may have a single antenna or multiple antennas.
한편, 본 발명의 실시예는 지금까지 설명한 장치 및/또는 방법을 통해서만 구현되는 것은 아니며, 본 발명의 실시예의 구성에 대응하는 기능을 실현하는 프로그램 또는 그 프로그램이 기록된 기록 매체를 통해 구현될 수도 있으며, 이러한 구현은 상술한 실시예의 기재로부터 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야의 당업자라면 쉽게 구현할 수 있는 것이다.On the other hand, the embodiments of the present invention are not only implemented by the apparatuses and / or methods described so far, but may also be realized through a program realizing a function corresponding to the configuration of the embodiment of the present invention or a recording medium on which the program is recorded And such an embodiment can be easily implemented by those skilled in the art from the description of the embodiments described above.
이상에서 본 발명의 실시예에 대하여 상세하게 설명하였지만 본 발명의 권리범위는 이에 한정되는 것은 아니고 다음의 청구범위에서 정의하고 있는 본 발명의 기본 개념을 이용한 당업자의 여러 변형 및 개량 형태 또한 본 발명의 권리범위에 속하는 것이다.While the present invention has been particularly shown and described with reference to exemplary embodiments thereof, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited to the disclosed exemplary embodiments, It belongs to the scope of right.
Claims (20)
Translated fromKorean상기 이동 단말로부터, 상기 이동 단말의 가용 송신 전력량을 수신하는 단계;
상기 가용 송신 전력량에 기초해, 상기 이동 단말의 현재 위치에 대응하는 타겟 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계;
상기 이동 단말로부터 수신되는 상향링크 데이터 채널을 이용해, 수신 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계; 및
상기 타겟 채널 품질 값과 상기 수신 채널 품질 값 간의 차이를 이용해, 송신 전력 제어(TPC: transmit power control)를 결정하는 단계
를 포함하는 기지국의 제어 방법.A method for controlling uplink transmission power of a mobile station in a base station,
Receiving an amount of available transmission power of the mobile terminal from the mobile terminal;
Determining a target channel quality value corresponding to a current location of the mobile terminal based on the available transmission power;
Determining a received channel quality value using an uplink data channel received from the mobile terminal; And
Determining transmit power control (TPC) using a difference between the target channel quality value and the received channel quality value
And transmitting the control signal to the base station.
상기 가용 송신 전력량을 수신하는 단계는,
상기 가용 송신 전력량을 나타내는 전력 헤드룸 보고(PHR: power headroom report)를 수신하는 단계를 포함하고,
상기 가용 송신 전력량에 기초해 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계는,
상기 이동 단말의 현재 위치에 대응하는 경로 손실을 얼마만큼 보상하는 지를 나타내는 제1 값이 1 보다 작은 경우에, 상기 PHR을 이용해 상기 경로 손실을 유추하는 단계; 및
상기 유추된 경로 손실에 따라 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계를 포함하는
기지국의 제어 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the step of receiving the available transmit power comprises:
Receiving a power headroom report (PHR) indicating the amount of available transmit power,
Wherein the determining the target channel quality value based on the available transmit power comprises:
Inferring the path loss using the PHR when a first value indicating how much the path loss corresponding to the current position of the mobile terminal is compensated for is less than 1; And
And determining the target channel quality value according to the inferred path loss
A method of controlling a base station.
상기 유추된 경로 손실에 따라 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계는,
아래의 수학식 1을 이용해, 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계를 포함하는
기지국의 제어 방법.
[수학식 1]
(target': 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값, α: 상기 제1 값, Ph: 상기 PHR에 의해 지시되는 가용 송신 전력량, target: α = 1 인 경우를 위한 타겟 채널 품질 값)3. The method of claim 2,
Wherein determining the target channel quality value based on the inferred path loss comprises:
Determining the target channel quality value using Equation (1) < RTI ID = 0.0 >
A method of controlling a base station.
[Equation 1]
(target ': target channel quality value,?: first value, Ph : available transmit power amount indicated by the PHR, target: target channel quality value for case where?
상기 가용 송신 전력량에 기초해 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계는,
상기 이동 단말의 현재 위치에 대응하는 경로 손실을 얼마만큼 보상하는 지를 나타내는 제1 값이 1인 경우에, 아래의 수학식 1을 이용해 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계를 포함하는
기지국의 제어 방법.
[수학식 1]
(target: 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값, P0_CH: 상기 기지국에 의해 요구되는 수신 전력 스펙트럼 밀도(PSD: power spectral density))The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the determining the target channel quality value based on the available transmit power comprises:
And determining the target channel quality value using Equation 1 below if the first value indicating how much the path loss corresponding to the current position of the mobile terminal is compensated for is 1
A method of controlling a base station.
[Equation 1]
(target: the target channel quality value,P0_CH : received power spectral density (PSD) required by the base station)
상기 수신 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 단계는,
상기 상향링크 데이터 채널에 대해 측정되는 제1 채널 품질 값을 평탄화(smoothing)하는 단계를 포함하는
기지국의 제어 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein determining the received channel quality value comprises:
And smoothing a first channel quality value measured for the uplink data channel
A method of controlling a base station.
상기 평탄화하는 단계는,
이동 평균 필터(moving average filter)인 지수 필터(exponential filter)를 통해, 상기 제1 채널 품질 값을 평탄화하는 단계를 포함하는
기지국의 제어 방법.6. The method of claim 5,
Wherein the planarizing step comprises:
And flattening the first channel quality value through an exponential filter that is a moving average filter,
A method of controlling a base station.
상기 평탄화하는 단계는,
아래의 수학식 1과 같이 정의되는 단일 스텝 지수 필터(1-step exponential filter)를 이용해, 상기 제1 채널 품질 값을 평탄화하는 단계를 포함하는
기지국의 제어 방법.
[수학식 1]
(Y(t): 시간 t에서 상기 단일 스텝 지수 필터로부터 출력되는 출력 값, Y(t-1): 시간 t-1에서 상기 단일 스텝 지수 필터로부터 출력되는 출력 값, X(t): 시간 t에서 상기 단일 스텝 지수 필터에 입력되는 상기 제1 채널 품질 값, 0≤μ≤1)6. The method of claim 5,
Wherein the planarizing step comprises:
And flattening the first channel quality value using a 1-step exponential filter defined as: < RTI ID = 0.0 >
A method of controlling a base station.
[Equation 1]
Y (t) is the output value from the single step exponential filter at time t-1, X (t) is the output value from the single step exponential filter at time t The first channel quality value input to the single step exponent filter, 0 < = mu < = 1)
상기 지수 필터를 통해 상기 제1 채널 품질 값을 평탄화하는 단계는,
상기 기지국이 랜덤 접속(Random Access)을 위해 최초로 수신하는 M3 메시지에 대한 제2 채널 품질 값을, 상기 지수 필터를 위한 초기값으로써 사용하는 단계를 포함하는
기지국의 제어 방법.The method according to claim 6,
Wherein the step of flattening the first channel quality value through the exponent filter comprises:
Using the second channel quality value for the M3 message initially received by the base station for random access as an initial value for the exponential filter,
A method of controlling a base station.
상기 TPC를 결정하는 단계는,
상기 타겟 채널 품질 값과 상기 TPC의 갱신을 위한 갱신 주기 동안에 결정되는 상기 수신 채널 품질 값 간의 제1 차이를 제1 시점에 계산하는 단계; 및
상기 제1 차이에 기초해 TPC 커맨드를 결정하는 단계를 포함하는
기지국의 제어 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein determining the TPC comprises:
Calculating at a first time point a first difference between the target channel quality value and the received channel quality value determined during an update period for updating the TPC; And
Determining a TPC command based on the first difference
A method of controlling a base station.
상기 갱신 주기는 무선 채널 환경에 따라 변경되는
기지국의 제어 방법.10. The method of claim 9,
The update period is changed according to the wireless channel environment
A method of controlling a base station.
상기 제1 차이에 기초해 상기 TPC 커맨드를 결정하는 단계는,
상기 제1 시점 이후부터 다음의 갱신 주기가 종료되는 시점까지는, 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값과 상기 수신 채널 품질 값 간의 차이를 0으로 설정하는 단계를 포함하는
기지국의 제어 방법.10. The method of claim 9,
Wherein determining the TPC command based on the first difference comprises:
Setting a difference between the target channel quality value and the received channel quality value to zero from the first time point to the end of the next update period,
A method of controlling a base station.
상기 가용 송신 전력량과 상기 이동 단말의 현재 위치에 기초해, 상기 이동 단말에게 할당할 수 있는 자원 블록(resource block)의 최대 개수를 결정하는 단계; 및
상기 최대 개수 보다 적은 개수의 자원 블록을 상기 이동 단말에게 할당하는 단계
를 더 포함하는 기지국의 제어 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Determining a maximum number of resource blocks that can be allocated to the mobile terminal based on the available transmission power and the current location of the mobile terminal; And
Allocating a number of resource blocks less than the maximum number to the mobile terminal
Further comprising the steps of:
상기 가용 송신 전력량을 수신하는 단계는,
상기 가용 송신 전력량을 나타내는 전력 헤드룸 보고(PHR: power headroom report)를 수신하는 단계를 포함하고,
상기 최대 개수를 결정하는 단계는,
아래의 수학식 1을 이용해 상기 최대 개수를 계산하는 단계를 포함하는
기지국의 제어 방법.
[수학식 1]
(Mmax: 상기 최대 개수, MPUSCH: 상기 상향링크 데이터 채널을 통해 전송되는 자원 블록의 개수, PHR(Ph): 상기 PHR에 의해 지시되는 가용 송신 전력량)13. The method of claim 12,
Wherein the step of receiving the available transmit power comprises:
Receiving a power headroom report (PHR) indicating the amount of available transmit power,
Wherein the determining the maximum number comprises:
Calculating the maximum number using Equation (1) below
A method of controlling a base station.
[Equation 1]
(Mmax : the maximum number, MPUSCH : number of resource blocks transmitted on the uplink data channel, PHR (Ph ): amount of available transmission power indicated by the PHR)
상기 기지국은 소형셀 기지국이고,
상기 타겟 채널 품질 값과 상기 수신 채널 품질 값은 SINR(signal-to-interference plus noise ratio) 및 SNR(signal to noise ratio) 중 하나이고,
상기 상향링크 데이터 채널은 PUSCH(physical uplink shared channel)인
기지국의 제어 방법.The method according to claim 1,
The base station is a small cell base station,
Wherein the target channel quality value and the received channel quality value are one of a signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR) and a signal to noise ratio (SNR)
The uplink data channel is a physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH)
A method of controlling a base station.
기지국에게, 상기 이동 단말의 가용 송신 전력량을 송신하는 단계;
상기 기지국에게, 상향링크 데이터 채널을 송신하는 단계; 및
상기 이동 단말의 경로 손실을 얼마만큼 보상하는 지를 나타내는 제1 값 및 상기 가용 송신 전력량에 기초하는 타겟 채널 품질 값과 상기 상향링크 데이터 채널에 대한 수신 채널 품질 값 간의 차이를 통해 결정되는 송신 전력 제어(TPC: transmit power control)를, 상기 기지국으로부터 수신하는 단계
를 포함하는 이동 단말의 제어 방법.As a method for the mobile station to control the uplink transmission power
Transmitting an amount of available transmission power of the mobile station to the base station;
Transmitting an uplink data channel to the base station; And
A first value indicating how much the path loss of the mobile station is compensated for and a transmission power control value determined through a difference between a target channel quality value based on the available transmission power amount and a reception channel quality value for the uplink data channel Transmitting power control (TPC) from the base station
And transmitting the control information to the mobile terminal.
상기 이동 단말에게 할당될 수 있는 자원 블록(resource block)의 최대 개수 보다 적은 개수의 자원 블록을 상기 기지국으로부터 할당받는 단계를 더 포함하며,
상기 최대 개수는 상기 가용 송신 전력량과 상기 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 기초해 결정되는
이동 단말의 제어 방법.16. The method of claim 15,
Further comprising the step of allocating, from the BS, a number of resource blocks less than the maximum number of resource blocks that can be allocated to the MS,
The maximum number is determined based on the amount of available transmission power and the path loss of the mobile terminal
A method of controlling a mobile terminal.
상기 타겟 채널 품질 값은 아래의 수학식 1에 기초해 결정되는
이동 단말의 제어 방법.
[수학식 1]
(target': 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값, α: 상기 제1 값, Ph: 상기 이동 단말의 가용 송신 전력량, target: α = 1 인 경우를 위한 타겟 채널 품질 값)16. The method of claim 15,
The target channel quality value is determined based on Equation 1 below
A method of controlling a mobile terminal.
[Equation 1]
(target: the target channel quality value,?: the first value, Ph : the amount of available transmit power of the mobile terminal, target: a target channel quality value for case where?
상기 메모리와 연결되며, 이동 단말의 전력 헤드룸 보고(PHR: power headroom report)에 기초해 상기 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 대응하는 타겟 채널 품질 값을 결정하는 프로세서를 포함하며,
상기 프로세서는,
상기 이동 단말의 PUSCH(physical uplink shared channel)을 통해 결정되는 수신 채널 품질 값과 상기 타겟 채널 품질 값 간의 차이를 이용해, 상기 이동 단말을 위한 송신 전력 제어(TPC: transmit power control) 커맨드를 결정하는
기지국.Memory; And
And a processor, coupled to the memory, for determining a target channel quality value corresponding to a path loss of the mobile terminal based on a power headroom report (PHR) of the mobile terminal,
The processor comprising:
A transmit power control (TPC) command for the mobile station is determined using a difference between a receive channel quality value determined through a physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH) of the mobile station and the target channel quality value
Base station.
상기 프로세서는,
상기 PHR 및 상기 이동 단말의 경로 손실에 기초해 상기 이동 단말에게 할당할 수 있는 자원 블록(resource block)의 최대 개수를 결정하고, 상기 최대 개수 보다 적은 개수의 자원 블록을 상기 이동 단말에게 할당하는
기지국.19. The method of claim 18,
The processor comprising:
Determines a maximum number of resource blocks that can be allocated to the mobile terminal based on the PHR and the path loss of the mobile terminal, and allocates a number of resource blocks less than the maximum number to the mobile terminal
Base station.
상기 프로세서는,
아래의 수학식 1을 이용해 상기 최대 개수를 결정하는
기지국.
[수학식 1]
(Mmax: 상기 최대 개수, MPUSCH: PUSCH을 통해 전송되는 자원 블록의 개수, PHR(Ph): 상기 PHR에 의해 지시되는 가용 송신 전력량)
20. The method of claim 19,
The processor comprising:
The maximum number is determined using Equation 1 below
Base station.
[Equation 1]
(Mmax : the maximum number, MPUSCH : number of resource blocks transmitted via PUSCH, PHR (Ph ): available transmission power amount indicated by the PHR)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/451,779US10039062B2 (en) | 2016-04-01 | 2017-03-07 | Uplink transmit power of a mobile controlled by base station based on difference between target and received quality |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR20160040306 | 2016-04-01 | ||
| KR1020160040306 | 2016-04-01 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20170114234Atrue KR20170114234A (en) | 2017-10-13 |
| KR102491936B1 KR102491936B1 (en) | 2023-01-27 |
Family
ID=60139511
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160120963AActiveKR102491936B1 (en) | 2016-04-01 | 2016-09-21 | Method and apparatus for controlling uplink transmission power |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102491936B1 (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20190056965A (en)* | 2017-11-17 | 2019-05-27 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Method and apparatus for controlling uplink power based on downlink path loss estimation |
| CN115361733A (en)* | 2022-08-19 | 2022-11-18 | 大连市共进科技有限公司 | Power adjustment method, device, base station equipment and computer readable storage medium |
| CN116097568A (en)* | 2020-07-30 | 2023-05-09 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | Communication method, terminal device and network device |
| US12302255B2 (en) | 2019-05-08 | 2025-05-13 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Transmit power control for positioning using non-serving cells |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20120058431A (en)* | 2010-11-29 | 2012-06-07 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method for resource allocation to uplink control information in at wireless access system, and user equipment thereof |
| EP2618498A1 (en)* | 2010-09-16 | 2013-07-24 | ZTE Corporation | Method and device for obtaining transmission power control command |
| KR20140086238A (en)* | 2012-12-28 | 2014-07-08 | 에릭슨 엘지 주식회사 | Method and apparatus for controlling of uplink transmission power |
- 2016
- 2016-09-21KRKR1020160120963Apatent/KR102491936B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2618498A1 (en)* | 2010-09-16 | 2013-07-24 | ZTE Corporation | Method and device for obtaining transmission power control command |
| KR20120058431A (en)* | 2010-11-29 | 2012-06-07 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method for resource allocation to uplink control information in at wireless access system, and user equipment thereof |
| KR20140086238A (en)* | 2012-12-28 | 2014-07-08 | 에릭슨 엘지 주식회사 | Method and apparatus for controlling of uplink transmission power |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| ▣ 인용발명1 : Closed loop power control for LTE uplink, Blekinge Institute of Technology School of Engineering (2008.11.) 1부.** |
| 논문:BILAL MUHAMMAD* |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20190056965A (en)* | 2017-11-17 | 2019-05-27 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Method and apparatus for controlling uplink power based on downlink path loss estimation |
| US12302255B2 (en) | 2019-05-08 | 2025-05-13 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Transmit power control for positioning using non-serving cells |
| CN116097568A (en)* | 2020-07-30 | 2023-05-09 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | Communication method, terminal device and network device |
| CN115361733A (en)* | 2022-08-19 | 2022-11-18 | 大连市共进科技有限公司 | Power adjustment method, device, base station equipment and computer readable storage medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR102491936B1 (en) | 2023-01-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10039062B2 (en) | Uplink transmit power of a mobile controlled by base station based on difference between target and received quality | |
| US11115936B2 (en) | Apparatus and methods for communication resource allocation | |
| US8929227B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling uplink transmission power in wireless communication system | |
| EP2260668B1 (en) | Interference reduction in a communication network by scheduling and link adaptation | |
| KR101131669B1 (en) | Combined open loop / closed loop method for controlling uplink power of a mobile station | |
| JP5014820B2 (en) | Mobile communication system, user apparatus and communication method | |
| JP6006224B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for uplink power control in distributed antenna mobile communication system | |
| CN103327594B (en) | Ascending power control method, equipment and system | |
| US20090175187A1 (en) | Method and Arrangement for Triggering Power Headroom Report Transmissions in a Telecommunications System | |
| EP2213131A2 (en) | UPLINK POWER CONTROL WITH INTERFERENCE-OVER-THERMAL (LoT) LOAD CONTROL | |
| KR20110090959A (en) | Improved uplink power control based on interference management and transmission quality control | |
| KR102491936B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling uplink transmission power | |
| CN101627554B (en) | Combined open loop/closed loop method for controlling mobile station uplink power | |
| US9185661B2 (en) | Performing power control based on nominal packet size | |
| CN108401282A (en) | A kind of method and device of adaptive adjustment ascending power parameter | |
| KR102197469B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling uplink power based on downlink path loss estimation |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20160921 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0201 | Request for examination | Patent event code:PA02012R01D Patent event date:20210705 Comment text:Request for Examination of Application Patent event code:PA02011R01I Patent event date:20160921 Comment text:Patent Application | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20220419 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20221026 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20230119 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20230119 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration |