KR20170090657A - blood flow monitoring system during CPR and thereof method - Google Patents
blood flow monitoring system during CPR and thereof methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20170090657A KR20170090657AKR1020160011287AKR20160011287AKR20170090657AKR 20170090657 AKR20170090657 AKR 20170090657AKR 1020160011287 AKR1020160011287 AKR 1020160011287AKR 20160011287 AKR20160011287 AKR 20160011287AKR 20170090657 AKR20170090657 AKR 20170090657A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- signal
- ppg signal
- ppg
- cpr
- cpm
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
- A61B5/026—Measuring blood flow
- A61B5/029—Measuring blood output from the heart, e.g. minute volume
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
- A61B5/021—Measuring pressure in heart or blood vessels
- A61B5/02108—Measuring pressure in heart or blood vessels from analysis of pulse wave characteristics
- A61B5/02125—Measuring pressure in heart or blood vessels from analysis of pulse wave characteristics of pulse wave propagation time
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
- A61B5/024—Measuring pulse rate or heart rate
- A61B5/02416—Measuring pulse rate or heart rate using photoplethysmograph signals, e.g. generated by infrared radiation
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Percussion Or Vibration Massage (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 심폐소생술 수행시, 광용적 맥파(Photo plethysmography, PPG. 맥파)를 이용하여 가슴 압박에 따른 심장의 1회 혈액 박출량을 검출하고, 혈액이 실질적으로 뇌로 흐르는지를 감시하는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치 및 그 제어방법에 관한 것이다. 보다 상세히는, 본 발명은, 심폐소생술 수행시, 흉부 임피던스를 이용하여 분당 심폐소생술(압박) 실시 횟수(compression per minute, CPM)을 구한 후, 심폐소생술 가이드라인의 권장 심폐소생술 CPM과 비교하여 흉부 압박 속도를 조절하게 하는 속도 피드백(feedback) 부와, 심폐소생술 잡음이 제거된 두 PPG 신호로부터 맥파전달시간(pulse wave transit time, PWTT)을 계산 한 후 1회 혈액 박출량(stroke volume)을 유도하여 모니터부로 출력하며 압박정도를 제어하게 하는 CPR 질 정도(CPR quality) 피드백부로 구성되어 있는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치 및 그 제어방법에 관한 것이다. The present invention relates to a blood flow monitor for detecting a single blood ejection amount of a heart due to chest compression by using photoplethysmography (PPG), and monitoring blood flow to the brain, And a control method thereof. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for determining the number of CPRs per minute (CPM) performed using the impedance of the chest during CPR, comparing the CPM with the recommended CPR of the CPR guideline, A pulse rate transit time (PWTT) was calculated from the two PPG signals from which the CPR signal was removed, and then the stroke volume was once induced And a CPR quality feedback unit for outputting the CPR quality to the monitor unit and controlling the degree of compression, and a control method thereof.
심폐소생술(Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, CPR)은 심장마비(심정지)가 발생했을 때 인공적으로 심장과 뇌에 산소가 포함된 혈액을 공급해주는 아주 중요한 응급처치이다. 심장마비가 발생하면 온몸으로의 혈액 순환이 중단되기 때문에, 바로 조치를 취하지 않으면 사망하거나 심각한 뇌손상이 일어날 수 있다. 특히, 뇌는 혈액 공급이 4-5분만 중단되어도, 뇌는 비가역적인 손상을 받기 시작하며, 6분 이상 이루어지지 않으면 환자의 뇌와 모든 장기의 기능이 정지되어 생명을 잃을 수 있다.Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a very important first aid to deliver oxygen-containing blood to the heart and brain artificially when a cardiac arrest (cardiac arrest) occurs. If a heart attack occurs, blood circulation to the whole body is stopped, and if not taken immediately, death or severe brain damage can occur. In particular, the brain begins to irreversibly damage the brain even if the blood supply is interrupted for only 4-5 minutes, and if not done for more than 6 minutes, the brain and all organs of the patient may stop functioning and lose life.
일반적인 심폐소생술은 정상혈류량을 20% 정도 회복하는 반면, 자동 심폐소생술 장치 또는 자동제세동기(Automated Extemal Defibrillator, AED)를 이용하면 100%회복이 가능하여, 심정지 환자의 생존율을 최대 70%까지 높일 수 있다고 한다.Normal cardiopulmonary resuscitation recovers 20% of normal blood flow, while 100% recovery is possible with an automatic cardiopulmonary resuscitation device or an Automated Extemal Defibrillator (AED), increasing the survival rate of cardiac arrest patients by up to 70% .
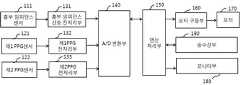
도 1에서와 같이, 응급환자의 가슴부위에 자동 심폐소생술 장치(10)의 흉부압박부(20)이 위치하도록 설치하여, 심폐소생술을 시행하게 한다.As shown in FIG. 1, the
자동 심폐소생술 장치는, 도 2에서와 같이, CPR 센서(110), CPR 센싱 신호 전처리부(130), A/D 변환부(140), 연산처리부(150), 모터구동부(160), 모터(170), 모니터부(180), 송수신부(190)를 포함하여 이루어진다.2, the automatic CPR apparatus includes a
CPR 센서(110)는 심폐소생술(CPR)이 제대로 이루어지고 있는지, 그리고 압박회수 등을 체크하기 위한 센서로, 흉부임피던스 센서로 이루어질 수 있다. CPR 센서(110)에서 검출된 CPR 센싱 신호를, CPR 센싱 신호 전처리부(130)를 통해, 잡음을 제거하고 증폭한 후, A/D 변환부(140)에서 디지탈신호로 변환하여 연산처리부(150)로 전송한다. 연산처리부(150)는 수신된 CPR 센싱 신호를 이용하여 심폐소생술(CPR)의 시행횟수 등을 분석하며, 또한, 흉부압박부(20)의 모터(170)를 구동하기 위한 모터제어신호를 모터구동부(160)로 전송한다.The
미국 심장 협회(American Heart Association, 2010) CPR 가이드라인의 경우 양질의 심폐소생술을 강조하며, 성인의 경우, 분당 압박(심폐소생술 실시) 횟수(compression per minute, CPM)가 100회 이상이며, 심폐소생술 실시(즉, 각 압박시) 5cm 이상의 가슴압박 깊이를 권장하고 있다. 2011 한국형 심폐소생술 가이드라인의 경우 양질의 심폐소생술을 강조하며 성인의 경우 분당 100회 이상 120회 이하의 가슴압박을 권장하고 있다. 최근 들어, 가속도 센서를 이용하여 흉부압박 깊이를 측정하는 연구들이 많이 진행되고 있다.The American Heart Association (CPR) guidelines emphasize good cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), with adults having more than 100 compression per minute (CPM), CPR It is recommended that a chest compression depth of 5 cm or more be performed (ie, at each compression). The Korean version of the 2011 CPR Guidelines emphasizes good quality CPR and recommends chest compressions of 100 times or more per minute to 120 times per minute for adults. Recently, many studies have been carried out to measure the compression depth of chest using an acceleration sensor.
그러나 보다 정확하고 효과적인 심폐소생술이 제대로 시행되고 있는지를 확인하기 위해서는 단순히 압박 깊이를 측정하는 것이 아니라, 실제 심장을 대신해서 심장과 뇌에 산소가 포함된 혈액을 공급해주고 있는지를 확인해야 한다. 이를 위해서는 심폐소생술 실시시, 즉, 각 압박시에, 심장의 1회 혈액 박출량 (stroke volume, S.V.)을 검출하고, 심장의 1회 박출량에 따라 심폐소생술 실시시에 압박정도를 조절하게 하는 것이 요망된다.However, to ensure that a more accurate and effective cardiopulmonary resuscitation is being performed, it is important not to simply measure the pressure depth, but to ensure that the heart and brain are supplying oxygen-enriched blood instead of the actual heart. For this purpose, it is desirable to detect the stroke volume (SV) of the heart at the time of CPR, that is, at the time of each compression, and to control the degree of compression when the CPR is performed according to the stroke volume do.
종래에는 심장의 1회 혈액 박출량 (S.V.)을 심전도를 통해 검출하는 방법들이 제안되었다. 그러나 경우에 따라서 환자가 맥박 또는 혈압을 감지할 수 없는 부정맥인 경우에는 제대로 된 심장의 1회 혈액 박출량을 산출할 수 없다.In the past, methods for detecting the single blood ejection amount (S.V.) of the heart through an electrocardiogram have been proposed. In some cases, however, the patient can not produce a single heart rate of the heart if it is an arrhythmia that can not detect a pulse or blood pressure.
따라서 본 발명은 심폐소생술 수행시, 흉부 임피던스를 이용하여 분당 심폐소생술(압박) 실시 횟수(compression per minute, CPM)을 구한 후, 심폐소생술 가이드라인의 권장 심폐소생술 CPM과 비교하여 흉부 압박 속도를 조절하게 하는 속도 피드백(feedback) 부와, 심폐소생술 잡음이 제거된 두 PPG 신호로부터 PWTT (pulse wave transit time)을 계산 한 후 1회 혈액 박출량(stroke volume)을 유도하여 모니터부로 출력하며 압박정도를 제어하게 하는 CPR 질 정도(CPR quality) 피드백부로 구성되어 있는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치를 제안한다.Therefore, the present invention provides a method for determining the compression per minute (CPM) of CPR using the impedance of the chest during CPR, comparing the CPR with CPM of the CPR guideline (Pulse wave transit time) is calculated from two PPG signals from which CPR noise is removed, and then a stroke volume is derived once to output to the monitor, and the degree of compression is controlled (CPR quality) feedback unit for CPR monitoring.
일반적으로 광용적 맥파(pulse wave)는 심장이 수축과 이완을 반복하면서 발생하는 혈류량의 변화를 감지하여 심장의 박동을 파형으로 나타낸 것으로, 산소포화도, 심박수 등을 계산하는데 사용한다.Generally, the pulse wave of the optic volume is the pulse waveform of the heart by detecting the change of the blood flow caused by repeated contraction and relaxation of the heart, and is used to calculate the oxygen saturation and the heart rate.
선행기술로 국내 등록특허 제10-1456590호는 맥파전달시간을 측정함은 물론이고 동시에 가압맥파의 맥압 변화를 확인함으로써 순환장애에 의한 좌/우 맥압편차, 상/하 맥압편차, 좌/우 맥압 전달시간차, 상/하 맥압 전달시간차의 새로운 분석팩터를 활용해 순환 이상을 검출하는 맥압 및 맥파를 이용한 혈액순환장애 측정 시스템에 관한 것이다.In the prior art, Korean Patent No. 10-1456590 not only measures the pulse wave propagation time, but also confirms the pulse pressure change of the pressure pulse, thereby detecting the left / right pulse pressure deviation, the upper / lower pulse pressure deviation, And a blood circulation disorder measurement system using a pulse wave and a pulse wave for detecting a circulatory abnormality by using a new analysis factor of a time difference of transmission time and an up / down pulse pressure transmission.
국내 등록특허 제10-1456590호는 단순히 맥파전달시간(PWTT), 각 동맥의 맥파신호의 세기를 이용하여 혈액순환 경로특성을 분석하는 것으로, 가슴 압박에 따른 심장의 1회 혈액 박출량을 알 수 없으며, 따라서 이는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치로 사용하기 어렵다.Korean Patent No. 10-1456590 analyzes blood circulation path characteristics by using the pulse wave transfer time (PWTT) and the intensity of the pulse wave signal of each artery, so that it is not possible to know the one-time blood ejection amount due to chest compression , Which is therefore difficult to use as a blood flow monitor for CPR.
본 발명의 해결하고자 하는 과제는, 심폐소생술 수행시, 광용적 맥파를 이용하여 가슴 압박에 따른 심장의 1회 혈액 박출량을 검출하고, 혈액이 실질적으로 뇌로 흐르는지를 감시하는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치 및 그 제어방법을 제공하는 것이다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention provides a blood flow monitor for cardiopulmonary resuscitation, which detects one-time blood ejection amount of the heart due to chest compression by using an optical pulse wave when CPR is performed, and monitors whether blood substantially flows into the brain And a control method thereof.
본 발명의 해결하고자 하는 다른 과제는, 심폐소생술 수행시, 흉부 임피던스를 이용하여 분당 심폐소생술(압박) 실시 횟수(CPM)을 구한 후, 기 설정된 CPM 기준치(즉, 심폐소생술 가이드라인의 권장 심폐소생술 CPM)와 비교하여 흉부 압박 속도를 조절하게 하는 속도 피드백 부와, 심폐소생술 잡음이 제거된 두 PPG 신호로부터 PWTT (pulse wave transit time)을 계산 한 후 1회 혈액 박출량(stroke volume)을 유도하여 모니터부로 출력하며 압박정도를 제어하게 하는 CPR 질 정도(CPR quality) 피드백부로 구성되어 있는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치 및 그 제어방법을 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a method and apparatus for performing a resuscitation (CPM) using the impedance of the chest after CPR, (PWTT) was calculated from the two PPG signals with the CPR signal removed, and the stroke volume was measured once to monitor the pulse volume. And a CPR quality feedback unit for controlling the degree of compression of the CPR, and a control method for the blood flow monitor for CPR.
본 발명의 해결하고자 하는 다른 과제는, 심폐소생술을 수행하는 동안 심정지 환자의 혈액이 뇌로 흐르는지 감시하기 위해, 흉부임피던스를 이용하여 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음을 모델링하여, 잡음을 제거해주는 알고리즘을 포함하여 이루어진 혈액흐름을 감시하는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법을 제공하는 것이다.Another problem to be solved by the present invention is to include an algorithm for removing noise by modeling motion noise by CPR using chest impedance to monitor the blood flow to the brain during cardiopulmonary resuscitation The present invention also provides a method for driving a blood flow monitor for a CPR monitoring the blood flow.
상기 과제를 해결하기 위해, 본 발명의 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치는, 흉부임피던스 센서를 구비하여, 흉부 임피던스 신호를 검출하는 흉부임피던스 검출부; 인체의 한 부분에 장착된 제1 PPG(광용적 맥파) 센서로부터 제1 PPG 신호를 검출하는 제1 PPG 검출부; 인체의 다른 부분에 장착된 제2 PPG 센서로부터 제2 PPG 신호를 검출하는 제2 PPG 검출부; 제1 PPG 검출부 및 제2 PPG 검출부에서 수신된 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서 동잡음을 제거하며, 동잡음이 제거된 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호를 이용하여 맥파전달시간(PWTT)을 계산 한 후 1회 혈액 박출량(S.V.)을 산출하는 연산처리부;연산처리부로부터 수신된 1회 혈액 박출량을 디스플레이하는 모니터부;를 포함하여 이루어진 것을 특징으로 한다.According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided an apparatus for monitoring blood flow for resuscitation of a cardiopulmonary resuscitation, the apparatus comprising: a chest impedance detector having a chest impedance sensor for detecting a chest impedance signal; A first PPG detecting unit for detecting a first PPG signal from a first PPG (optical pulse wave) sensor mounted on a part of a human body; A second PPG detector for detecting a second PPG signal from a second PPG sensor mounted on another part of the human body; The first PPG detecting unit and the second PPG detecting unit remove the motion noise from the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal, respectively, and output the pulse wave propagation time (the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal) An arithmetic processing unit for calculating the blood ejection amount (SV) once after calculating the PWTT, and a monitor unit for displaying the blood ejection amount once received from the operation processing unit.
연산처리부는 흉부 임피던스 신호로부터 CPM(분당 심폐소생술 실시횟수)을 검출한다.The arithmetic processing unit detects CPM (the number of CPRs per minute) from the chest impedance signal.
연산처리부는 검출된 CPM과, 기설정된 CPM 기준치와 비교하여, 흉부 압박 속도를 조절하게 하는 자동 심폐소생술 장치의 모터 속도제어신호를 생성할 수 있다.The operation processing unit may generate a motor speed control signal of an automatic CPR device for controlling the chest compression speed by comparing the detected CPM with a predetermined CPM reference value.
연산처리부는 검출된 CPM과, 기설정된 CPM 기준치와 비교하여, 흉부 압박 속도를 조절하게 하는 알림신호를 모니터부 또는 스피커부로 전송할 수 있다.The operation processing unit may compare the detected CPM with a predetermined CPM reference value and transmit a notification signal to the monitor unit or the speaker unit to adjust the chest compression speed.
연산처리부는, 검출된 1회 혈액 박출량을, 1회 혈액박출량 문턱치와 비교하여, 흉부 압박 강도를 조절하게 하는 자동 심폐소생술 장치의 모터 강도 제어신호를 생성할 수 있다.The arithmetic processing unit can generate the motor intensity control signal of the automatic CPR apparatus which compares the detected one-time blood ejection amount with the one-time blood ejection amount threshold to adjust the chest compressive strength.
연산처리부는, 검출된 1회 혈액 박출량을, 1회 혈액박출량 문턱치와 비교하여, 흉부 압박 강도를 조절하게 하는 알림신호를 모니터부 또는 스피커부로 전송할 수 있다.The operation processing unit may compare the detected blood ejection amount with the once blood ejection amount threshold value and transmit a notification signal to the monitor unit or the speaker unit to adjust the chest pressure intensity.
제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서 동잡음을 제거시, 연산처리부는, 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서 심폐소생술 주파수를 구하고, 심폐소생술 주파수를 이용하여, 흉부압박 시간 사이의 위상을 구하며, 구하여진 위상을 이용하여 심폐소생술에 의한 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서의 동잡음 성분을 구하고, 제1 PPG신호에서 제1 PPG신호에서의 동잡음 성분을 제거하여, 동잡음이 제거된 제1 PPG신호를 검출하며, 제2 PPG신호에서 제2 PPG신호에서의 동잡음 성분을 제거하여, 동잡음이 제거된 제2 PPG신호를 검출한다.When the dynamic noise is removed from each of the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal, the arithmetic processing unit obtains the CPR frequency from the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal, and uses the CPR frequency, Phase of the first PPG signal is obtained and a motion noise component in each of the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal is obtained by CPR and a motion artifact in the first PPG signal is removed from the first PPG signal, Detects the first PPG signal from which the dynamic noise is removed, removes the dynamic noise component from the second PPG signal from the second PPG signal, and detects the second PPG signal from which the dynamic noise is removed.
연산처리부는 흉부임피던스 검출부로부터 수신된 흉부 임피던스 신호에서, 기설정된 흉부임피던스 문턱치를 넘는 흉부 임피던스 신호에서 피크(peak)의 수를 카운팅하여 CPM을 검출하거나, 연산처리부는 흉부임피던스 검출부로부터 수신된 흉부 임피던스 신호에서, 기설정된 흉부임피던스 문턱치를 넘는 흉부 임피던스 신호에서 피크(peak)를 검출하고, CPM을The calculation processing unit may detect the CPM by counting the number of peaks in the chest impedance signal exceeding a predetermined chest impedance threshold in the chest impedance signal received from the chest impedance detecting unit or the calculation processing unit may detect the chest impedance In the signal, a peak is detected in the chest impedance signal above a predetermined threshold impedance, and the CPM
(단, Cr은 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)이며, ti는 i 번째 최대 흉부 압박한 시점의 시간으로, i 번째의 흉부임피던스의 피크를 나타냄)(Where Cr is the number of CPR cycles per minute (CPM), ti is the time of the i-th maximum compression of the chest, which is the peak of the i th thoracic impedance)
에 의해 구할 수 있다.. ≪ / RTI >
또한, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법은, 연산처리부는, 흉부임피던스 검출부, 제1 PPG 검출부, 제2 PPG 검출부로부터, 제1 PPG신호, 제2 PPG신호, 흉부 임피던스 신호를 수신하는, 신호수신 단계; 연산처리부는, 신호수신 단계에서 수신된 제1PPG 신호 및 제2PPG 신호에서, 동잡음을 제거하는, PPG신호의 동잡음 제거단계; 연산처리부는, PPG신호의 동잡음 제거단계에서 동잡음이 제거된 제1PPG 신호 및 제2PPG 신호 각각에서, 맥파전달시간을 계산하기 위한 샘플을 설정하는, PPG 신호에서의 혈류 측정점 설정단계; 연산처리부는 PPG 신호에서의 혈류 측정점 설정단계에서 설정된 제1PPG 신호의 혈류 측정점의 시간과, 제2 PPG신호의 혈류 측정점의 시간의 차를 맥파전달시간으로서 구하는, 맥파전달시간 연산단계; 연산처리부는 맥파전달시간(PWTT)를 이용하여 각 주기의 1회 혈액 박출량을 산출하고, 각 주기별로 연산된 1회 혈액 박출량의 평균값을 구하는, 1회 혈액 박출량 연산단계; 연산처리부는 1회 혈액 박출량 연산단계에서 구하여진 1회 혈액 박출량의 평균값이, 1회 혈액 박출량 문턱치 값과 비교하여, 압박강도 조절을 위한 알림신호를 모니터부 또는 스피커부를 통해 알리는, 압박강도 조절 알림단계;를 포함하여 이루어진 것을 특징으로 한다.The driving method of a blood flow monitoring apparatus for cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to the present invention is characterized in that the operation processing unit is configured to receive a first PPG signal, a second PPG signal, and a chest impedance signal from a chest impedance detecting unit, a first PPG detecting unit, Receiving a signal; The arithmetic processing unit may include a motion noise removing step of removing the motion noise of the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal received in the signal receiving step; The arithmetic processing unit sets a sample for calculating a pulse wave propagation time in each of the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal from which motion noise has been removed in the motion noise removal step of the PPG signal; Calculating a pulse wave propagation time calculating step of calculating a difference between a time of a blood flow measurement point of the first PPG signal set at the blood flow measurement point setting in the PPG signal and a time of the blood flow measurement point of the second PPG signal as a pulse wave propagation time; The arithmetic processing unit calculates the blood ejection amount of each cycle once using the pulse wave transmission time PWTT and obtains an average value of the blood ejection amount calculated once for each cycle; The calculation processing section compares the average value of the blood ejection amount obtained in the one-time blood ejection amount calculation step with the one-time blood ejection amount threshold value and notifies the notification signal for the adjustment of the compression strength through the monitor section or the speaker section. The method comprising the steps of:
PPG 신호에서의 혈류 측정점 설정단계에서, 연산처리부는, 각 주기동안 제1PPG 신호에서 피크를 구하고, 제1PPG 신호의 피크에 연동되는 제2PPG 신호의 피크를 검출하고고, 제1PPG 신호의 피크를 제1PPG 신호의 혈류 측정점으로 하고, 제1PPG 신호의 피크에 연동되는 제2PPG 신호의 피크를 제2 PPG신호의 혈류 측정점으로 한다.In the blood flow measurement point setting step in the PPG signal, the calculation processing unit obtains a peak in the first PPG signal during each period, detects a peak of the second PPG signal linked to the peak of the first PPG signal, and outputs a peak of the first PPG signal 1PPG signal and the peak of the second PPG signal linked to the peak of the first PPG signal is used as the blood flow measurement point of the second PPG signal.
제1PPG 신호의 피크에 연동되는 제2PPG 신호의 피크는, 제1PPG 신호의 피크의 시점의 전후의 제2PPG 신호에서 연산처리부가 피크를 검출하고, 제1PPG 신호의 피크의 시점의 전후의 제2PPG 신호의 피크들에서, 제1PPG 신호의 피크의 시점에 가까운 제2PPG 신호의 피크를, 제1PPG 신호의 피크에 연동되는 제2PPG 신호의 피크로 검출한다.The peak of the second PPG signal interlocked with the peak of the first PPG signal is a peak of the second PPG signal before and after the peak of the first PPG signal and a peak of the second PPG signal before and after the peak of the first PPG signal The peak of the second PPG signal close to the peak of the first PPG signal is detected as the peak of the second PPG signal interlocked with the peak of the first PPG signal.
1회 혈액 박출량 연산단계에서, 연산처리부는 1회 혈액 박출량(S.V.)을 In the one-shot blood volume calculation step, the calculation processing unit calculates the blood volume (S.V.)
(단, PWTT는 맥파전달시간이며, α는 -0.30이며, β는 131.9 ± 16.5 이며, K는 0.96 ± 0.31 임)(However, PWTT is the pulse wave propagation time, and α is -0.30, β is 131.9 ± 16.5, Im K is0. 96 ±0. 31)
에 의해 구하여 진다..
1회 혈액 박출량 연산단계에서 1회 혈액 박출량의 평균값은 5초 동안의 1회 혈액 박출량의 평균값이다.The average value of the blood ejection amount per one time in the one time blood ejection operation step is the average value of the one time blood ejection amount for 5 seconds.
압박강도 조절 알림단계에서, 연산처리부는, 1회 혈액 박출량의 평균값이, 1회 혈액 박출량 문턱치 값보다 크지 않을 경우, 심폐소생술의 압박강도를 높이기 위한, 자동 심폐소생술 장치의 모터강도 제어신호를 생성하여 모터구동부로 전송한다.When the average value of the blood ejection amount once is not larger than the one-time blood ejection amount threshold value, the arithmetic processing unit generates the motor strength control signal of the automatic CPR apparatus for increasing the compression strength of the CPR And transmits it to the motor driver.
신호수신 단계와, PPG신호의 동잡음 제거단계의 사이에, 연산처리부는, 흉부임피던스 검출부, 제1 PPG 검출부, 제2 PPG 검출부로부터, 제1 PPG신호, 제2 PPG신호, 흉부 임피던스 신호를 수신하는, 신호수신 단계; 연산처리부는 신호수신 단계에서 수신된 흉부 임피던스 신호로부터 CPM(분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수)를 계산하는, CPM 연산단계; CPM 연산단계 후, 연산처리부는 CPM이 100보다 큰지 여부를 판단하여, CPM이 100보다 크지 않다면, CPM 증가를 위한 알림신호를 모니터부 또는 스피커부를 통해 알리는, CPM이 100보다 큰지 여부 판단단계; 연산처리부는 CPM이 100보다 큰지 여부 판단단계에서, CPM이 100보다 크다면, CPM이 120보다 작은지 여부를 판단하고, CPM이 120보다 작지 않다면, CPM 감소를 위한 알림신호를 모니터부 또는 스피커부를 통해 알리는, CPM이 120보다 작은지 여부 판단단계;를 더 포함한다.Between the signal reception step and the motion noise removal step of the PPG signal, the calculation processing unit receives the first PPG signal, the second PPG signal, and the chest impedance signal from the chest impedance detection unit, the first PPG detection unit, and the second PPG detection unit Receiving a signal; The calculation processing unit calculates CPM (the number of CPRs per minute) from the received thoracic impedance signal in the signal reception step; Determining whether the CPM is greater than 100, determining whether the CPM is greater than 100, if the CPM is not greater than 100, and informing the CPM by the monitor or the speaker; If the CPM is greater than 100, the calculation processing unit determines whether the CPM is smaller than 120. If the CPM is not smaller than 120, the operation processing unit sends a notification signal for decreasing the CPM to the monitor unit or the speaker unit And determining whether the CPM is less than 120,
CPM이 100보다 큰지 여부 판단단계에서, 연산처리부는 CPM이 100보다 크지 않다면, CPM 증가를 위한 자동 심페소생술 장치의 모터 속도제어신호를 생성하고, CPM이 120보다 작은지 여부 판단단계, 연산처리부는 CPM이 120보다 작지 않다면, CPM 감소를 위한 자동 심페소생술 장치의 모터 속도제어신호를 생성한다.In the step of determining whether the CPM is greater than 100, the operation processing unit generates a motor speed control signal of the automatic CP resuscitation apparatus for CPM increase if the CPM is not greater than 100, a step of determining whether the CPM is smaller than 120, If the CPM is not less than 120, a motor speed control signal of the automatic CPR device for CPM reduction is generated.
PPG신호의 동잡음 제거단계는, 연산처리부는, 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서 피크를 구하고, 구하여진 피크의 주기를 이용하여 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호의 심폐소생술 주파수를 구하고, 구하여진 심폐소생술 주파수를 이용하여 위상을 구하는, 심폐소생술 주파수 계산단계; 연산처리부는, 심폐소생술 주파수 계산단계에서 구하여진 위상을 이용하여 심폐소생술에 의한 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서의 동잡음 성분을 구하는, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분 추정단계; 제1 PPG신호에서, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분 추정단계에서 구한 제1 PPG신호에서의 동잡음 성분을 제거하여, 동잡음이 제거된 제1 PPG신호를 검출하며, 제2 PPG신호에서, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분 추정단계에서 구한 제2 PPG신호에서의 동잡음 성분을 제거하여, 동잡음이 제거된 제2 PPG신호를 검출하는, 혈류 흐름을 측정한 PPG 신호 추정 단계; 를 포함하여 이루어진다.In the dynamic noise removing step of the PPG signal, the arithmetic processing unit obtains a peak in each of the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal, and calculates a CPR signal of the first PPG signal and the CPR signal using the period of the obtained peak A CPR frequency calculation step of calculating a CPR using the obtained CPR frequency; The operation processing unit may include a dynamic noise component estimation step by a CPR method for obtaining a dynamic noise component in each of the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal by CPR using the phase obtained in the CPR frequency calculation step; In the first PPG signal, the dynamic noise component in the first PPG signal obtained in the step of estimating the dynamic noise component by CPR is removed to detect the first PPG signal from which the dynamic noise is removed. In the second PPG signal, A PPG signal estimation step of measuring a flow of blood flow by removing a dynamic noise component in a second PPG signal obtained in the step of estimating a dynamic noise component by a resuscitation to detect a second PPG signal from which motion noise is removed; .
심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분 추정단계에서, 연산처리부는, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분()을In the step of estimating the dynamic noise component by CPR, the arithmetic processing unit calculates the dynamic noise component )of
(단, 제1고조파부터 제N고조파를 구비하여 N개의 고조파를 가질때, ck(n)은 k번째 고조파에서 n번째 샘플의 진폭을 나타내며, θk(n)은 k번째 고조파에서 n번째 샘플의 위상을 나타내며, Φ(n)은 n번째 샘플의 위상을 나타내며, ak(n)는 동상(in-phase) 성분의 진폭의 변이이고, bk(n)는 직각위상(quadrature) 성분의 진폭의 변이이고, SI(n)는 동상 기준신호이고, 직각위상 기준신호이고, a(n)은 LMS 적응 필터의 필터계수로서, n번째 샘플에서의 동상 계수이고, b(n)은 LMS 적응 필터의 필터계수로서, n번째 샘플에서의 직각위상 계수임)(However, the first gajilttae the N harmonics from by having the N-th harmonic harmonic, ck (n) denotes the amplitude of the n-th sample in the k-th harmonic, θk (n) is the n-th sample in the k-th harmonic a represents the phase, Φ (n) is n denotes the phase of the second sample, ak (n) is the variation of the amplitude of in-phase (in-phase) component, bk (n) is the quadrature phase (quadrature) component and the variation of the amplitude, and SI (n) is a statue reference signal, and the quadrature reference signals, a (n) is a filter coefficient of the LMS adaptive filter, n is the statue coefficients in the second sample, b (n) is LMS Filter coefficient of the adaptive filter, which is the quadrature phase coefficient in the nth sample)
에 의해 구한다..
심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법은 혈류 흐름을 측정한 PPG 신호 추정 단계 후, 연산처리부는 다음 샘플에서의 LMS 적응필터의 필터계수를 구하는, LMS 적응 필터계수 갱신 단계;를 더 포함하여 이루어진다.A method of driving a blood flow monitor apparatus for CPR includes an LMS adaptive filter coefficient updating step of calculating a filter coefficient of an LMS adaptive filter in a next sample after a PPG signal estimation step of measuring a blood flow .
LMS 적응 필터계수 갱신 단계에서, 갱신되는 LMS 적응필터의 필터계수인 a(n+1), b(n+1)은In the LMS adaptive filter coefficient updating step, the filter coefficients a (n + 1) and b (n + 1) of the LMS adaptive filter to be updated are
(단, 모든 고조파는 대각(선) 행렬(diagonal matrix) M에서 구룹지어진 서로다른 스텝 사이즈 μk로 배열됨)(Note that all harmonics are arranged in different step sizes muk , grouped in a diagonal matrix M)
에 의해 구하여진다..
본 발명의 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치는, 심폐소생술 수행시, 광용적 맥파를 이용하여 가슴 압박에 따른 심장의 1회 혈액 박출량을 검출하고, 혈액이 실질적으로 뇌로 흐르는지를 감시하여, 보다 정확하고 효과적인 심폐소생술이 제대로 시행되고 있는지를 확인할 수 있다. 다시말해, 기존의 압박 깊이를 추정하는 연구의 경우에는, 심폐소생술 시 심정지 환자에 어떠한 효과과 미치는지 즉시 알 수 없었지만, 본 발명의 경우 혈액의 흐름을 감시하기 때문에 보다 정확하고 효과적으로 심폐소생술이 시행되고 있는지 알 수 있다. 또한 심장의 1회 혈액 박출량을 토대로, 심폐소생술 시행시의 압박정도를 제어할 수 있다.The blood-flow monitoring apparatus for CPR of the present invention detects the one-time blood ejection amount of the heart due to chest compression by using an optical pulse wave when CPR is performed, monitors whether the blood flows substantially into the brain, It is possible to confirm whether effective CPR is properly implemented. In other words, in the case of estimating the existing compression depth, it is not immediately known what effect the cardiopulmonary resuscitation has on the cardiopulmonary patients, but in the present invention, since the blood flow is monitored, more accurate and effective cardiopulmonary resuscitation Able to know. It is also possible to control the degree of compression during CPR, based on the amount of blood that is delivered once.
또한 본 발명의 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치는 심폐소생술 수행시, 흉부 임피던스를 이용하여 분당 심폐소생술(압박) 실시 횟수(CPM)을 구한 후, 기 설정된 CPM 기준치(즉, 심폐소생술 가이드라인의 권장 심폐소생술 CPM)와 비교하여 흉부 압박 속도를 조절하게 하는 속도 피드백 부와, 심폐소생술 잡음이 제거된 두 PPG 신호로부터 PWTT (pulse wave transit time)을 계산 한 후 1회 혈액 박출량(stroke volume)을 유도하여 모니터부로 출력하며 압박정도를 제어하게 하는 CPR 질 정도(CPR quality) 피드백부로 구성되어 있다. 따라서 정확하고 효과적인 심폐소생술이 가능하도록 심폐소생술 장치를 구동시킬 수 있다.In addition, the CPM monitoring apparatus for CPR of the present invention is a CPM monitoring apparatus that, when CPR is performed, obtains CPM (number of CPRs) per minute by using the impedance of the chest and then sets a predetermined CPM reference value (PWTT) was calculated from two PPG signals with CPR removed, and then the stroke volume was calculated once. And CPR quality feedback unit which outputs the output to the monitor unit and controls the degree of compression. Thus, it is possible to drive the CPR device to enable accurate and effective CPR.
또한 본 발명은 심폐소생술을 수행하는 동안 심정지 환자의 혈액이 뇌로 흐르는지 감시하기 위해, 흉부임피던스를 이용하여 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음을 모델링하여, 잡음을 제거해주는 알고리즘을 포함하여 이루어진 혈액흐름을 감시하는 심폐소생술 보조 장치의 구동방법을 제공한다. 따라서 심폐소생술 시행시, 혼입된 동잡음신호를 배제하여 보다 순도 높은 PWTT 신호를 검출하며, 아울러 보다 정확한 1회 혈액 박출량을 검출할 수 있다.In order to monitor the blood flow to the brain during cardiopulmonary resuscitation, the present invention models blood flow by cardiopulmonary resuscitation using chest impedance, and monitors blood flow including an algorithm for removing noise The present invention provides a method for driving a CPR assist device. Therefore, when CPR is performed, it is possible to detect a PWTT signal with higher purity by excluding the mixed motion noise signal, and to detect a more accurate blood flow amount once.
특히 무맥성 전기활동(pulseledss electrical activity; PEA)과 같이 심전도에는 전기적인 활동이 나타나지만, 맥박 또는 혈압을 감지할 수 없는 부정맥의 경우, 1회 혈액 박출량을 산출할 수 없다. 그러나 이러한 경우에도 본 발명을 이용하면 혈액의 흐름을 감지 할 수 있기 때문에 무맥성 전기활동의 판단에도 효과적이다. 추가적으로 본 발명의 경우 심정지 상태에서 심폐소생술 및 전기적 제세동이 시행된 후에 자발 순환 회복(return of spontaneous circulation, ROSC) 유무를 판단하는 지표로도 사용할 수 있다.Electrocardiograms show electrical activity, especially pulseledss electrical activity (PEA), but in the case of arrhythmia that can not detect pulse or blood pressure, one can not produce blood volume. However, even in such a case, since the blood flow can be sensed by using the present invention, it is also effective in determining the pulsating electrical activity. In addition, the present invention can be used as an indicator for determining the presence or absence of a return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) after cardiopulmonary resuscitation and electrical defibrillation in a cardiac arrest state.
도 1은 기존의 자동 심폐소생술 장치의 사용 상태도이다.
도 2는 도 1의 자동 심폐소생술 장치의 구성을 개략적으로 설명하는 설명도이다.
도 3a은 본 발명의 일실시예의 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구성을 개략적으로 설명하기 위한 블럭도이다.
도 3b는 본 발명의 다른 실시예의 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구성을 개략적으로 설명하기 위한 블럭도이다.
도 4는 본 발명에서 제1 PPG센서 및 제2 PPG센서를 장착할 수 있는 위치 후보군을 나타낸다.
도 5는 본 발명의 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 연산처리부의 흐름도이다.
도 6은 흉부임피던스로부터 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)를 검출하는 방법을 설명하는 설명도이다.
도 7은 본 발명의 동잡음 제거과정을 설명하기 위한 모식도이다.1 is a state of use of a conventional automatic cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus.
FIG. 2 is an explanatory view schematically illustrating the configuration of the automatic CPR device of FIG. 1. FIG.
FIG. 3A is a block diagram schematically illustrating a configuration of a blood flow monitor for CPR according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 3B is a block diagram schematically illustrating a configuration of a blood flow monitor for CPR according to another embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG.
4 shows a position candidate group in which the first PPG sensor and the second PPG sensor can be mounted in the present invention.
5 is a flow chart of the arithmetic processing unit of the blood flow monitoring apparatus for cardiopulmonary resuscitation of the present invention.
FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a method for detecting the CPM count from the chest impedance. FIG.
7 is a schematic diagram for explaining a motion noise removing process according to the present invention.
이하, 본 발명의 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치를 첨부한 도면을 참조하여 상세히 설명한다.BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The above and other objects, features and advantages of the present invention will be more apparent from the following detailed description taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, in which: FIG.
도 3a는 본 발명의 일실시예의 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구성을 개략적으로 설명하기 위한 블럭도로, 흉부임피던스 센서(111), 제1 PPG센서(121), 제2 PPG센서(122), 흉부 임피던스 신호 전처리부(131), 제1PPG 전처리부(132), 제2PPG 전처리부(133), A/D 변환부(140), 연산처리부(150), 모터구동부(160), 모터(170), 모니터부(180), 송수신부(190)를 포함하여 이루어진다.FIG. 3A is a block diagram for schematically illustrating the configuration of a blood flow monitor for CPR according to an embodiment of the present invention, a
여기서, A/D 변환부(140), 연산처리부(150), 모터구동부(160), 모터(170), 모니터부(180), 송수신부(190)는 도 1의 자동 심폐소생술 장치(10)의 것과 같은 것을 사용할 수 있다. 경우에 따라서 송수신부(190)는 생략할 수 있다.The A /
흉부임피던스 센서(111)는 CPR 센서(110)로 사용된 센서로, 일반적으로 자동 심폐소생술 장치(10)에 장착되어 있는 센서이다. 흉부임피던스 센서(111)는 자동 심폐소생술 장치(10)에서 흉부 접촉부분에 구비되어, 환자의 흉부로부터 흉부 임피던스 신호를 측정한다.The
흉부 임피던스 신호 전처리부(131)는 흉부임피던스 센서(111)로부터 측정된 흉부 임피던스 신호로부터 잡음을 제거하고 증폭하여 A/D 변환부(140)로 전송한다. The chest impedance
여기서, 흉부임피던스 센서(111), 흉부 임피던스 신호 전처리부(131), A/D 변환부(140)를 흉부 임피던스 검출부라 한다.Here, the
2개의 PPG센서, 즉, 제1 PPG센서(121)와 제2 PPG센서(122) 각각은 얼굴, 머리, 목, 귀 중 어느 한 곳에 장착되며, 광용적 맥파(Photo plethysmography, PPG), 즉 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호를 검출한다.Each of the two PPG sensors, that is, the
PPG센서는 발광 다이오드(발광부)와 포토 다이오드(수광부)로 이루어진다. 즉, 발광 다이오드를 이용하여 적외선 대역의 파장의 광을 인체의 동맥 가까운 부위에 조사하고 이를 포토 다이오드로 측정 부위의 반사광 또는 투과광을 감지하여 광용적 맥파(PPG) 신호를 획득할 수 있다.The PPG sensor is composed of a light emitting diode (light emitting portion) and a photodiode (light receiving portion). That is, light having a wavelength in the infrared band can be irradiated to a portion near the artery of a human body using a light emitting diode, and the PPG signal can be obtained by detecting reflected or transmitted light at a measurement site using the photodiode.
제1PPG 전처리부(132) 및 제2PPG 전처리부(133)는 제1 PPG센서(121) 및 제2 PPG센서(122)에서 검출된 PPG(광용적 맥파) 신호, 즉 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호로부터 잡음을 제거하고 증폭하여 A/D 변환부(140)로 전송한다.The first
여기서, 제1 PPG센서(121), 제1PPG 전처리부(132), A/D 변환부(140)를 제1PPG 검출부라 하며, 제2 PPG센서(122), 제2PPG 전처리부(133), A/D 변환부(140)를 제2PPG 검출부라 한다.Here, the
A/D 변환부(140)는 수신된 제1 PPG신호, 제2 PPG신호 및 흉부임피던스 신호를 디지털 신호로 변환하여 연산처리부(150)로 전송한다.The A /
연산처리부(150)는 흉부 임피던스 신호를 이용하여 환자에게의 분당 심폐소생술(압박) 실시 횟수(compression per minute, CPM)을 구한 후, 구하여진 CPM과, 기설정된 CPM 기준치와 비교하여, 흉부 압박 속도를 조절하게 하는 모터 속도제어신호를 생성하고, 이를 모터 구동부(160)으로 전송한다. 여기서, CPM 기준치는 심폐소생술 가이드라인의 권장 심폐소생술 CPM으로, 공장출하시 메모리부(미도시)에 저장되어 있을 수 있다.The
또한, 연산처리부(150)는 두 PPG 신호, 즉, 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서 동잡음을 제거하며, 동잡음이 제거된 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호를 이용하여 맥파전달시간(pulse wave transit time, PWTT)을 계산 한 후 1회 혈액 박출량(stroke volume)을 산출하여 모니터부로 출력하여, CPR 질 정도(CPR quality)를 모니터링하게 하며, 흉부 압박 강도를 조절하게 하는 모터 강도 제어신호를 생성하고, 이를 모터 구동부(160)으로 전송한다. 여기서, 모터 강도 제어신호와 모터 속도제어신호는 모터 제어신호라 할 수 있다. 또한, 맥파전달시간은 두 동맥 박동처(搏動處) 사이를 맥파가 이동하는데 걸리는 시간을 말한다.In addition, the
연산처리부(150)는 컴퓨터, 마이크로프로세서, 콘트롤러 중 어느 하나로 이루어질 수 있다.The
본 발명에서 2개의 PPG센서, 즉, 제1 PPG센서(121)와 제2 PPG센서(122)를 사용한 이유는 두 PPG 신호 사이의 맥파전달시간을 구하기 위함이다.In the present invention, two PPG sensors, that is, the
일반적으로 심폐소생술을 수행하는 동안 검출된 PPG신호는, 동잡음, 특히, 심폐소생술 시행에 따른 동잡음을 많이 포함하고 있다. 따라서, 연산처리부(150)는 흉부임피던스를 이용하여 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음을 모델링 한 후, 잡음을 제거해주는 알고리즘을 포함한다.Generally, the PPG signal detected during CPR contains a lot of motion noise, especially the CP noise due to CPR. Accordingly, the
모터 구동부(160)은 연산처리부(150)로부터 수신된 모터 속도제어신호 및 모터 강도 제어신호에 따라 모터(170)를 구동시켜 심페소생술을 시행한다.The
본 발명에서 흉부임피던스 센서(111), 흉부 임피던스 신호 전처리부(131), A/D 변환부(140), 연산처리부(150)를 속도 피드백(feedback) 부라 할 수 있으며, 제1 PPG센서(121), 제2 PPG센서(122), 제1PPG 전처리부(132), 제2PPG 전처리부(133), A/D 변환부(140), 연산처리부(150)를 CPR 질 정도(CPR quality) 피드백부라 할 수 있다.In the present invention, the
도 3a에서는 자동 심폐소생술 장치를 사용할 경우를 나타내고 있으나, 이로써 본 발명을 한정하기 위한 것이 아님을 밝혀둔다.FIG. 3A shows the case of using an automatic CPR device, but it is not intended to limit the present invention.
도 3b는 본 발명의 다른 실시예의 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구성을 개략적으로 설명하기 위한 블럭도이다.FIG. 3B is a block diagram schematically illustrating a configuration of a blood flow monitor for CPR according to another embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG.
도 3b는 자동 심폐소생술 장치를 사용하지 않고, 심폐소생술 실시자(구조자)가 심폐소생술을 실시할 경우로, 심폐소생술을 위한 보조장치로서 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치를 사용한다.FIG. 3B shows a case in which a cardiopulmonary resuscitation practitioner (rescuer) performs cardiopulmonary resuscitation without using an automatic cardiopulmonary resuscitation device, and uses a blood flow monitor device for CPR as an assist device for CPR.
도 3b에서는 도 3a에서의 모터구동부(160) 및 모터(170)를 구비하지 않는다.In FIG. 3B, the
도 3b에서, 연산처리부(150)는 흉부 임피던스 신호를 이용하여 환자에게의 분당 심폐소생술(압박) 실시 횟수(compression per minute, CPM)을 구한 후, 구하여진 CPM과, 기설정된 CPM 기준치와 비교하여, 흉부 압박 속도를 조절하게 하는 알림신호를 모니터부(180) 또는 스피커부(185) 또는 알람(미도시)로 출력하게 한다. 또한, 연산처리부(150)는 두 PPG 신호, 즉, 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서 동잡음을 제거하며, 동잡음이 제거된 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호를 이용하여 맥파전달시간(pulse wave transit time, PWTT)을 계산 한 후 1회 혈액 박출량(stroke volume)을 산출하여 모니터부로 출력하여, CPR 질 정도(CPR quality)를 모니터링하게 하며, 흉부 압박 강도를 조절하게 하는 알림신호를 모니터부(180) 또는 스피커부(185) 또는 알람(미도시)로 출력하게 한다.In FIG. 3B, the
도 4는 본 발명에서 제1 PPG센서 및 제2 PPG센서를 장착할 수 있는 위치 후보군을 나타낸다.4 shows a position candidate group in which the first PPG sensor and the second PPG sensor can be mounted in the present invention.
PPG(광용적 맥파) 센서의 부착 위치로는 심장 위쪽에 위치되는 동맥혈 부근에서, 심폐소생술 중 발생하는 환자의 움직임이 적은 곳에 장착한다. 이를 고려한 부착 위치 후보군으로는, 도 4에서와 같이, 눈 밑, 코, 입 안, 목, 귀, 관자, 턱 등이 있다.The PPG (pulse width pulse) sensor is attached to the lower part of the heart located in the upper part of the heart, where the movement of the patient during CPR is less. As a candidate position of the attachment position considering this, there are a beneath the eyes, a nose, a mouth, a neck, an ear, a head, and a jaw as shown in FIG.
도 5는 본 발명의 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 연산처리부의 흐름도이다.5 is a flow chart of the arithmetic processing unit of the blood flow monitoring apparatus for cardiopulmonary resuscitation of the present invention.
심폐소생술 시작단계로, 키입력부(미도시)로부터 시작키(미도시)가 눌러짐에 따라, 연산처리부(150)가 시작키값을 수신하면 연산처리부(150)는 모터제어신호를 모터 구동부(160)으로 출력하여 심폐소생술을 시행한다(S110).When the
신호 수신 및 CPM 연산단계로, 연산처리부(150)는 A/D 변환부(140)를 통해 제1 PPG신호, 제2 PPG신호, 흉부 임피던스 신호를 수신하고(S120), 흉부 임피던스 신호로부터 심폐소생술(압박) 실시 횟수(CPM)를 계산하고, 이를 모니터부(180)로 출력한다(S130).The
연산처리부(150)는, 도 6에서와 같이, 흉부 임피던스 신호에서 기설정된 흉부임피던스 문턱치를 넘는 흉부 임피던스 신호에서 피크(peak)를 검출하고, 피크는 1회 흉부압박을 실시할 때에 최대 흉부 압박한 시점을 나타낸다. 즉, 피크의 수를 카운팅하여 심폐소생술(압박) 실시 횟수(CPM)를 검출할 수 있다.As shown in FIG. 6, the
분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)의 경우 연속적인 흉부압박 시간의 차이를 이용하여 수학식 1과 같이 구할 수 있다.In the case of CPM, the difference between successive chest compressions can be used to calculate Eq. (1).
여기서 Cr은 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수를 말하며, ti는 i 번째 최대 흉부 압박한 시점의 시간을 의미하는 데, 이는 i 번째의 흉부임피던스의 피크를 말한다. 또한, (cpm)은 단위로서 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수를 나타낸다.Here, Cr is the number of CPR cycles per minute, and ti is the time of the i th peak of the chest compressions, which is the peak of the i th thoracic impedance. Also, (cpm) represents the number of CPR per minute as a unit.
분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)가 100보다 큰지 여부 판단단계로, 연산처리부(150)는 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)이 100보다 큰지 여부를 판단하고(S140), 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)가 100보다 크지 않다면, 자동 심폐소생술 장치를 사용할 경우, 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)를 증가시키기 위한 모터 속도제어신호를 생성하게 하며, 또는 자동 심폐소생술 장치 없이(즉, 모터 및 모터구동부가 없이) 사용할 경우는 더 빠른 심폐소생술의 실시를 심폐소생술 시행자(구조자)에게 모니터부 또는 스피커부(또는 알람)(미도시)를 통해 요청한다(S150).In
분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)가 120보다 작은지 여부 판단단계로, 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)가 100보다 큰지 여부 판단단계에서 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)가 100보다 크다면, 연산처리부(150)는 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)이 120보다 작은지 여부를 판단하고(S160), 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)이 120보다 작지 않다면, 자동 심폐소생술 장치를 사용할 경우, 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)를 감소시키기 위한 모터 속도제어신호를 생성하게 하며, 또는 자동 심폐소생술 장치 없이(즉, 모터 및 모터구동부가 없이) 사용할 경우는 더 느린 심폐소생술의 실시를 심폐소생술 시행자(구조자)에게 모니터부 또는 스피커부(또는 알람)(미도시)를 통해 요청한다(S170).If the number of CPRs per minute (CPM) per minute is greater than 100 in the step of determining whether or not the number of CPRs per minute (CPM) is less than 120 and whether or not the number of CPRs per minute CPM is greater than 100, (CPM) is less than 120, and if CPM is not less than 120, then
즉, 2011 한국형 심폐소생술 가이드라인의 경우 양질의 심폐소생술을 위해, 성인의 경우 분당 100회 이상 120회 이하의 가슴압박을 권장하고 있으므로, 본 발명에서는 환자에서의 CPM(분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수)값이 100 cpm 보다 작을 경우 더 빠른 심폐소생술의 실시를 하도록, 모터 속도제어신호를 생성하거나, 심폐소생술 시행자(구조자)에게 요청하고, CPM값이 120 cpm 보다 클 경우, 더 느린 심폐소생술을 실시하도록 모터 속도제어신호를 생성하거나, 심폐소생술 시행자(구조자, 구급자)에게 요청하는 알람 및 디스플레이 기능을 포함하고 있다.That is, in the case of the 2011 Korean type CPR Guideline, since the chest compression of 100 times or more and less than 120 times per minute is recommended for adult CPR, the CPM (number of CPRs per minute) A motor speed control signal is generated or requested from the CPR rescuer (rescuer) so as to perform a faster CPR if the CPM value is less than 100 cpm, and if the CPM value is greater than 120 cpm, Speed control signals, or an alarm and display function that requests CPR rescuers (rescuers, paramedics).
PPG신호에서 동잡음 제거단계로, 연산처리부는, 신호 수신 및 CPM 연산단계에서 수신된 두 PPG신호, 즉, 제1PPG 신호 및 제2PPG 신호에서, 동잡음을 제거한다(S210). 즉, 심폐소생술 시행 과정에서 심폐소생술 시행자가 환자에게 흉부 압박을 진행하는 동안 생체의 움직임이 발생하며, 이러한 생체의 움직임에 따라서 PPG 센서의 움직임도 발생하는데, 이 움직임에 의한 동잡음을 추정하여 제거함으로써 실제 뇌로 향하는 혈류의 움직임만을 관찰할 수 있다. 상세한 동잡음을 제거하는 과정은 후술한다.In operation S210, the operation processor removes motion noise from the two PPG signals received in the signal reception and CPM operation steps, i.e., the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal, from the PPG signal. In other words, during the CPR, the CPR sensor moves according to the movement of the living body during the CPR, while the CPR sensor performs the movement during the compression of the CPR. So that only the movement of the blood flow toward the actual brain can be observed. The process of removing the detailed motion noise will be described later.
두 PPG 신호에서 혈류 측정점을 설정하는 단계로, PPG신호에서 동잡음 제거단계에서 동잡음이 제거된 두 PPG 신호에서, 맥파전달시간을 계산하기 위한, 샘플을 설정한다(S220). 즉, 1주기동안 제1PPG 신호에서 피크를 구하고, 제1PPG 신호의 피크에 연동되는 제2PPG 신호의 피크를 찾고, 제1PPG 신호의 피크를 제1PPG 신호의 혈류 측정점으로 하고, 제1PPG 신호의 피크에 연동되는 제2PPG 신호의 피크를 제2 PPG신호의 혈류 측정점으로 한다.In step S220, a sample is set for calculating a pulse wave transmission time in two PPG signals from which motion noise is removed in the motion noise removal step in the PPG signal. That is, a peak is obtained in the first PPG signal for one period, a peak of the second PPG signal linked to the peak of the first PPG signal is found, a peak of the first PPG signal is set as a blood flow measurement point of the first PPG signal, The peak of the second PPG signal to be interlocked is set as the blood flow measurement point of the second PPG signal.
여기서, 제1PPG 신호의 피크에 연동되는 제2PPG 신호의 피크는, 제1PPG 신호의 피크의 시점의 전후의 제2PPG 신호에서 피크를 검출하고, 제1PPG 신호의 피크의 시점의 전후의 제2PPG 신호의 피크들에서, 제1PPG 신호의 피크의 시점에 가까운 제2PPG 신호의 피크를, 제1PPG 신호의 피크에 연동되는 제2PPG 신호의 피크로 한다.Here, the peak of the second PPG signal interlocked with the peak of the first PPG signal is a peak of the second PPG signal before and after the peak of the first PPG signal, and a peak of the second PPG signal before and after the peak of the first PPG signal. In the peaks, the peak of the second PPG signal close to the peak of the first PPG signal is made the peak of the second PPG signal interlocked with the peak of the first PPG signal.
맥파전달시간 연산단계로, 두 PPG 신호에서 혈류 측정점을 설정하는 단계에서 설정된 제1PPG 신호의 혈류 측정점의 시간과, 제2 PPG신호의 혈류 측정점의 시간의 차를 맥파전달시간(PWTT)으로서 구한다(S230).The difference between the time of the blood flow measuring point of the first PPG signal set at the step of setting the blood flow measuring point in the two PPG signals and the time of the blood flow measuring point of the second PPG signal is obtained as the pulse wave transmitting time PWTT S230).
맥파전달시간(PWTT)은 1회 혈액 박출량(S.V.)를 유도하기 위한 가장 중요한 파라미터로 혈류가 흐르는 시간을 이용한 맥파전달시간으로 혈류의 흐름을 측정하는 두 PPG 센서의 부착 위치를 다르게 함으로써 얻어질 수 있는 것이다.Pulse wave delivery time (PWTT) is the most important parameter for deriving the one time blood flow (SV). It can be obtained by differentiating the attachment position of two PPG sensors which measure the flow of blood flow, It is.
1회 혈액 박출량 연산단계로, 맥파전달시간(PWTT)를 이용하여 수학식 2에 의해 1회 혈액 박출량(S.V.)을 산출한다(S240).The blood ejection amount (S.V.) is calculated by the formula (2) using the pulse wave transfer time (PWTT) in step of calculating the blood volume once (S240).
여기서, α, β, K는 실험 상수로, 공장 출하시 정하여 지거나, 사용 초기에 정하여진 값 일 수 있다. 또는, α는 -0.30일 수 있으며, β는 131.9 ± 16.5 일 수 있으며, K는 0.96 ± 0.31 일 수 있다.Here, α, β, and K are experimental constants, which can be determined at the time of shipment from the factory or set at the beginning of use. Alternatively, alpha may be -0.30, beta may be 131.9 +/- 16.5, and K may be 0. 96 ± 0. 31.
5초 동안의 평균 1회 혈액 박출량 연산단계로, 상가 두 PPG 신호에서 혈류 측정점을 설정하는 단계 내지 상기 1회 혈액 박출량 연산단계를 반복하여 5초 동안 각 주기별로 연산된 1회 혈액 박출량(S.V.)의 평균값(평균 S.V.)을 구한다(S250).(SV) calculated by repeating the step of setting the blood flow measurement point in the two PPG signals and the one step of blood ejection amount calculation step for 5 seconds, (Average SV) (S250).
심폐소생술 퀄리티(질) 평가단계로, 5초 동안 연산된 1회 혈액 박출량(S.V.)의 평균값(평균 S.V.)이, 1회 혈액 박출량(S.V.) 문턱치(TH) 값 보다 큰지를 비교하여(S260), 1회 혈액 박출량(S.V.) 문턱치(TH) 값 보다 크다면, 심폐소생술이 제대로 시행되고 있음의 알림신호를 모니터부(180) 또는 스피커부(185)를 통해 알린다(S280).In step S260, it is determined whether the average value (average SV) of the one-time blood ejection amount (SV) calculated for 5 seconds is greater than the one-time blood ejection amount (SV) threshold value (TH) (SV) threshold value (TH), a notification signal indicating that the CPR is properly performed is notified through the
심폐소생술 압박강도 증가요구 단계로, 심폐소생술 퀄리티(질) 평가단계에서, 5초 동안 연산된 1회 혈액 박출량(S.V.)의 평균값(평균 S.V.)이, 1회 혈액 박출량(S.V.) 문턱치(TH) 값 보다 크지 않다면, 심폐소생술이 제대로 시행되고 있지 않으므로 압박강도를 높여야 한다는 알림신호를 모니터부(180) 또는 스피커부(185)를 통해 알리고(S270), 자동 심폐소생술 장치를 사용할 경우는 압박강도를 높이도록, 연산처리부(150)은 모터강도 제어신호를 생성하여 모터구동부(160)으로 전송한다.(SV) threshold value (TH) of the one-time blood ejection amount (SV) calculated for 5 seconds in the CPR evaluation stage, If the CPR is not properly performed, a notification signal indicating that the CPR should be increased is notified through the
도 7은 본 발명의 동잡음 제거과정을 설명하기 위한 모식도이다.7 is a schematic diagram for explaining a motion noise removing process according to the present invention.
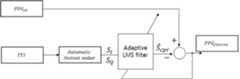
2개의 PPG 신호 각각으로부터 심폐소생술에 의한 잡음을 제거하는 알고리즘은 최소 평균 자승(Least Mean Square, LMS)) 적응 필터 알고리즘(Adaptive LMS filter)을 기반으로 한다.The algorithm for removing CPR noise from each of the two PPG signals is based on a least mean square (LMS) adaptive LMS filter.
심폐소생술이 실시될 때, PPG 센서로부터 측정된 PPG 신호에는 혈류의 흐름을 측정한 용적맥파(PPG) 성분과, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분이 포함되어 있다. 이를 수식으로 나타내면 수학식 3와 같다.When CPR is performed, the PPG signal measured from the PPG sensor contains the PPG component measuring the flow of blood flow and the CPG component by CPR. This can be expressed by the following equation (3).
여기서, PPGIN은 PPG 센서로부터 측정된 PPG 신호를 나타내며, PPGflow는 혈류의 흐름을 측정한 PPG 성분을 나타내며, e는 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분을 나타낸다.Here, PPGIN represents the PPG signal measured from the PPG sensor, PPGflow represents the PPG component measuring theflow of the blood flow, and e represents the dynamic noise component by CPR.
그러나, PPG 센서로부터 측정된 PPG 신호(PPGIN)에 있는, 심폐소생술에 의한 원래의 동잡음 성분(e)을 알 수가 없다. 이를 위해, 최소 평균 자승 알고리즘을 이용하여, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분(e)과 상관관계(correlation)을 갖는 흉부임피던스(TTI)를 이용하여, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분을 추정하여 제거한다. 이때, 추정된 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분을로 나타낸다.However, the original motion artifact (e) due to CPR in the PPG signal (PPGIN ) measured from the PPG sensor can not be known. To do this, we use a minimum mean square algorithm to estimate and remove motion artifacts by CPR using a chest impedance (TTI) with a correlation with the dynamic noise component (e) by CPR . At this time, the motion artifact due to the estimated cardiopulmonary resuscitation Respectively.
최소 평균 자승 알고리즘을 이용하여 심폐소생술 잡음을 추정 및 제거하는 과정은 다음과 같다.The process of estimating and removing CPR noise using the least mean square algorithm is as follows.
첫째, 심폐소생술 주파수 계산단계로, 연산처리부(150)은 심폐소생술 주파수(fi)를 구하고, 심폐소생술 주파수를 이용하여, 흉부압박 시간 사이의 위상(Φ(n))을 구한다.First, in the step of calculating the CPR frequency, the
심폐소생술 주파수는 연속적인 흉부압박 시간의 차이의 역수로 수학식 4에 의해 구할 수 있다.The CPR frequency can be found from equation (4) as the reciprocal of the difference in successive chest compression time.
여기서, fi는 심폐소생술 주파수로, 보다 상세히는 i 번째 흉부압박시의 심폐소생술 주파수이다. ti는 i 번째 최대 흉부 압박한 시점의 시간을 의미하며, ti+1는 i+1 번째 최대 흉부 압박한 시점의 시간을 의미한다.Where fi is the CPR frequency, more specifically the CPR frequency at the i-th chest compression. ti represents the time of the i th maximum compression of the chest, and ti+1 represents the time of the i + 1 th maximum compression of the chest.
여기서, 두 연속적인 흉부압박 시간 사이의 주파수는 일정하다고 가정을 한다. 또한 시간에 따라 심폐소생술 주파수는 변화하지만, 심폐소생술 압박 주기가 거의 일정하기 때문에, 심폐소생술 주파수 역시 거의 일정하다. 연속적인 흉부압박 시간 사이의 위상(phase)(Φ(n))은 심폐소생술 주파수를 이용하여 수학식 5와 같이 구할 수 있다.Here, it is assumed that the frequency between two consecutive chest compressions is constant. Also, the frequency of CPR varies with time, but since CPR compression cycles are almost constant, the CPR frequency is also almost constant. The phase (phi (n)) between consecutive chest compression times can be calculated using
여기서, Φ(n)은 n번째 샘플의 위상을 나타내며, fs는 샘플링 주파수를 나타낸다.Here, Φ (n) denotes the phase of the n-th sample, fs represents the sampling frequency.
둘째, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분 추정단계로, 수학식 6에 의해, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분()을 구한다.Secondly, the step of estimating the dynamic noise component by CPR is to calculate the dynamic noise component by CPR ).
심폐소생술을 실시하는 동안에 심폐소생술 잡음 성분의 경우 심폐소생술 주파수를 기본 주파수로 갖는 준주기적(pseudo periodic)인 신호로 모델링 할 수 있다. 이때 준주기적인 신호는 수학식 6와 같이 심폐소생주파수를 기본 주파수로 갖고, 이 기본 주파수의 고조파를 주파수로 갖으며, 위상과 진폭이 시간에 따라 변화하는 정현파 신호들의 합으로 나타낼 수 있다.During cardiopulmonary resuscitation, the CPR noise model can be modeled as a pseudo periodic signal with the CPR frequency as the fundamental frequency. In this case, the quasi-periodic signal can have a CPR frequency as a fundamental frequency as shown in Equation (6), a harmonic of the fundamental frequency as a frequency, and a sum of sinusoidal signals whose phases and amplitudes vary with time.
여기서, 제1고조파부터 제N고조파를 구비하여 N개의 고조파를 가질때, ck(n)은 k번째 고조파의 시간변이(time-varying) 진폭을 나타내며, θk(n)은 k번째 고조파의 위상을 나타낸다. 즉, ck(n)은 k번째 고조파에서 n번째 샘플의 진폭을 나타내며, θk(n)은 k번째 고조파에서 n번째 샘플의 위상을 나타낸다. ak(n)는 동상(동조) (in-phase) 성분의 진폭의 변이이고, bk(n)는 직각위상(quadrature) 성분의 진폭의 변이이다.Here, the first, gajilttae the N harmonics by having the N-th harmonic from the harmonic ck (n) is the k-th denotes the time variation (time-varying) amplitude of the harmonic, θk (n) is the phase of the k-th harmonic . That is, ck (n) represents the amplitude of the nth sample at the kth harmonic, and θk (n) represents the phase of the nth sample at the kth harmonic. ak (n) is the variation of the amplitude of the in-phase component and bk (n) is the variation of the amplitude of the quadrature component.
SI(n)는 동상(in-phase) 기준신호(reference signals)로, 다음과 같이 나타낸다.SI (n) is an in-phase reference signal, expressed as:
SQ(n)는 직각위상(quadrature) 기준신호로, 다음과 같이 나타낸다.SQ (n) is a quadrature reference signal, expressed as:
시간 n (즉, n번째 샘플)에서의 최소 평균 자승(LMS) 적응 필터의 필터계수로서, a(n)은 시간 n (즉, n번째 샘플)에서의 동상(in-phase) 계수이고, b(n)은 시간 n (또는 n번째 샘플)에서의 직각위상(quadrature) 계수로, 다음과 같이 나타낸다.A (n) is an in-phase coefficient at time n (i.e., the nth sample), and b (n) is a filter coefficient of a least mean square (LMS) adaptive filter at time n (n) is a quadrature coefficient at time n (or nth sample), and is expressed as follows.
셋째, 혈류 흐름을 측정한 PPG 신호 추정 단계로, 수학식 7과 같이, 심폐소생술 과정에서 측정된 PPG 신호(PPGIN)에서, 추정한 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분()을 제거하여, 혈류의 흐름을 측정한 PPG 신호(PPGfiltered)을 구한다.Third, the PPG signal estimation step in which the flow of blood flow is measured. In the PPG signal (PPGIN ) measured in the CPR procedure as shown in Equation (7), the motion noise component ) Is removed, and the PPG signal (PPGfiltered ) obtained by measuring the flow of blood flow is obtained.
넷째, 최소 평균 자승(LMS) 적응 필터계수 갱신(update) 단계로, 시간 n+1 (즉, n+1번째 샘플)에서의 LMS 적응 필터의 필터계수(a(n+1), b(n+1))를 수학식 8에 의해 구한다.Fourth, in the minimum mean square (LMS) adaptive filter coefficient update step, the filter coefficients a (n + 1), b (n) of the LMS adaptive filter at time n + 1 +1)) is obtained by the following equation (8).
즉, 시간에 따라 변화하는 고조파들의 위상과 진폭의 경우, LMS 적응 필터의 필터계수 갱신 방법을 이용하여 수학식 8과 같이 갱신된다.That is, in the case of the phase and amplitude of harmonics that change with time, it is updated as shown in Equation (8) using a method of updating the filter coefficient of the LMS adaptive filter.
모든 고조파는 대각(선) 행렬(diagonal matrix) M에서 구룹지어진 서로다른 스텝 사이즈 μk로 배열된다.All harmonics are arranged in different step sizes μk , grouped in a diagonal matrix M.
첫째의 심폐소생술 주파수 계산단계로부터, 넷째의 최소 평균 자승(LMS) 적응 필터계수 갱신단계까지의 과정을 반복적으로 수행한다면 최소 평균 자승 알고리즘을 이용하여 심폐소생술 잡음을 추정 및 제거하여 뇌로 향하는 혈류의 움직임만을 측정할 수 있다.If the process from the first CPR frequency calculation step to the fourth least mean square (LMS) adaptive filter coefficient update step is repeatedly performed, the minimum mean square algorithm is used to estimate and remove the CPR noise, Can be measured.
이상과 같이 본 발명은 비록 한정된 실시예와 도면에 의해 설명되었으나, 본 발명은 상기의 실시예에 한정되는 것은 아니며, 이는 본 발명이 속하는 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 이러한 기재로부터 다양한 수정 및 변형이 가능하다. 따라서, 본 발명의 사상은 아래에 기재된 특허청구범위에 의해서만 파악되어야 하고, 이의 균등 또는 등가적 변형 모두는 본 발명 사상의 범주에 속한다고 할 것이다.While the present invention has been particularly shown and described with reference to exemplary embodiments thereof, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited to the disclosed exemplary embodiments, but, on the contrary, Modification is possible. Accordingly, it is intended that the scope of the invention be defined by the claims appended hereto, and that all equivalent or equivalent variations thereof fall within the scope of the present invention.
10 : 자동 심폐소생술 장치 110 : CPR 센서
111 : 흉부임피던스 센서 121 : 제1 PPG센서
122 : 제2 PPH센서 131 : 흉부 임피던스 신호 전처리부
132 : 제1PPG 전처리부 133 : 제2PPG 전처리부
140 : A/D 변환부 150 : 연산처리부
160 : 모터구동부 170 : 모터
180 : 모니터부 185 : 스피커부
190 : 송수신부10: Automatic CPR device 110: CPR sensor
111: Chest Impedance Sensor 121: First PPG sensor
122: second PPH sensor 131: chest impedance signal preprocessing section
132: FirstPPG preprocessing unit 133: SecondPPG preprocessing unit
140: A / D converter 150:
160: motor driving unit 170: motor
180: Monitor section 185: Speaker section
190: Transmitting /
Claims (24)
Translated fromKorean인체의 한 부분에 장착된 제1 PPG(광용적 맥파) 센서로부터 제1 PPG 신호를 검출하는 제1 PPG 검출부;
인체의 다른 부분에 장착된 제2 PPG 센서로부터 제2 PPG 신호를 검출하는 제2 PPG 검출부;
제1 PPG 검출부 및 제2 PPG 검출부에서 수신된 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서 동잡음을 제거하며, 동잡음이 제거된 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호를 이용하여 맥파전달시간(PWTT)을 계산 한 후 1회 혈액 박출량(S.V.)을 산출하는 연산처리부;
연산처리부로부터 수신된 1회 혈액 박출량을 디스플레이하는 모니터부;
를 포함하여 이루어진 것을 특징으로 하는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치.A chest impedance detector having a chest impedance sensor for detecting a chest impedance signal;
A first PPG detecting unit for detecting a first PPG signal from a first PPG (optical pulse wave) sensor mounted on a part of a human body;
A second PPG detector for detecting a second PPG signal from a second PPG sensor mounted on another part of the human body;
The first PPG detecting unit and the second PPG detecting unit remove the motion noise from the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal, respectively, and output the pulse wave propagation time (the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal) An arithmetic processing unit for calculating a blood ejection amount (SV) once after calculating PWTT;
A monitor unit for displaying the blood ejection amount once received from the operation processing unit;
And a controller for controlling the flow rate of the blood.
연산처리부는 흉부 임피던스 신호로부터 CPM(분당 심폐소생술 실시횟수)을 검출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the calculation processing unit detects CPM (the number of CPRs per minute) from the chest impedance signal.
연산처리부는 검출된 CPM과, 기설정된 CPM 기준치와 비교하여, 흉부 압박 속도를 조절하게 하는 자동 심폐소생술 장치의 모터 속도제어신호를 생성하는 것을 특징으로 하는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치.3. The method of claim 2,
Wherein the operation processing unit compares the detected CPM with a predetermined CPM reference value to generate a motor speed control signal of an automatic CPR device that adjusts a chest compressing speed.
연산처리부는 검출된 CPM과, 기설정된 CPM 기준치와 비교하여, 흉부 압박 속도를 조절하게 하는 알림신호를 모니터부 또는 스피커부로 전송하는 것을 특징으로 하는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치.3. The method of claim 2,
Wherein the operation processing unit compares the detected CPM with a preset CPM reference value and transmits a notification signal for controlling the chest compression speed to the monitor unit or the speaker unit.
연산처리부는, 검출된 1회 혈액 박출량을, 1회 혈액박출량 문턱치와 비교하여, 흉부 압박 강도를 조절하게 하는 자동 심폐소생술 장치의 모터 강도 제어신호를 생성하는 것을 특징으로 하는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the operation processing unit generates a motor intensity control signal of an automatic CPR device for comparing the detected one-time blood ejection amount with the one-time blood ejection amount threshold value and controlling the chest compressive strength. Device.
연산처리부는, 검출된 1회 혈액 박출량을, 1회 혈액박출량 문턱치와 비교하여, 흉부 압박 강도를 조절하게 하는 알림신호를 모니터부 또는 스피커부로 전송하는 것을 특징으로 하는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the calculation processing unit compares the detected one-time blood ejection amount with the one-time blood ejection amount threshold value, and transmits a notification signal for controlling the chest pressure intensity to the monitor unit or the speaker unit.
제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서 동잡음을 제거시, 연산처리부는,
제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서 심폐소생술 주파수를 구하고, 심폐소생술 주파수를 이용하여, 흉부압박 시간 사이의 위상을 구하며, 구하여진 위상을 이용하여 심폐소생술에 의한 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서의 동잡음 성분을 구하고,
제1 PPG신호에서 제1 PPG신호에서의 동잡음 성분을 제거하여, 동잡음이 제거된 제1 PPG신호를 검출하며, 제2 PPG신호에서 제2 PPG신호에서의 동잡음 성분을 제거하여, 동잡음이 제거된 제2 PPG신호를 검출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치.The method according to claim 1,
When the dynamic noise is removed from each of the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal,
The first PPG signal and the second PPG signal are used to obtain the CPR frequency, the CPR frequency is used to obtain the phase between the compression times, and the first PPG signal by the CPR signal and the second PPG signal using the obtained phase are obtained. The motion noise component in each of the PPG signals is obtained,
Noise component in the first PPG signal is removed from the first PPG signal to detect the first PPG signal from which the motion noise is removed and the dynamic noise component in the second PPG signal is removed from the second PPG signal, And detects the second PPG signal from which noise has been removed.
연산처리부는 흉부임피던스 검출부로부터 수신된 흉부 임피던스 신호에서, 기설정된 흉부임피던스 문턱치를 넘는 흉부 임피던스 신호에서 피크(peak)의 수를 카운팅하여 CPM을 검출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치.3. The method of claim 2,
Wherein the calculation processing unit detects the CPM by counting the number of peaks in the chest impedance signal exceeding the predetermined threshold impedance in the chest impedance signal received from the chest impedance detecting unit.
연산처리부는 흉부임피던스 검출부로부터 수신된 흉부 임피던스 신호에서, 기설정된 흉부임피던스 문턱치를 넘는 흉부 임피던스 신호에서 피크(peak)를 검출하고, CPM을
(단, Cr은 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)이며, ti는 i 번째 최대 흉부 압박한 시점의 시간으로, i 번째의 흉부임피던스의 피크를 나타냄)
에 의해 구하는 것을 특징으로 하는 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치.3. The method of claim 2,
The computation processor detects a peak in a chest impedance signal that exceeds a predetermined threshold impedance in a chest impedance signal received from the chest impedance detector,
(Where Cr is the number of CPR cycles per minute (CPM), ti is the time of the i-th maximum compression of the chest, which is the peak of the i th thoracic impedance)
Wherein the blood flow monitoring device comprises:
연산처리부는, 신호수신 단계에서 수신된 제1PPG 신호 및 제2PPG 신호에서, 동잡음을 제거하는, PPG신호의 동잡음 제거단계;
연산처리부는, PPG신호의 동잡음 제거단계에서 동잡음이 제거된 제1PPG 신호 및 제2PPG 신호 각각에서, 맥파전달시간을 계산하기 위한 샘플을 설정하는, PPG 신호에서의 혈류 측정점 설정단계;
연산처리부는 PPG 신호에서의 혈류 측정점 설정단계에서 설정된 제1PPG 신호의 혈류 측정점의 시간과, 제2 PPG신호의 혈류 측정점의 시간의 차를 맥파전달시간으로서 구하는, 맥파전달시간 연산단계;
연산처리부는 맥파전달시간(PWTT)를 이용하여 각 주기의 1회 혈액 박출량을 산출하고, 각 주기별로 연산된 1회 혈액 박출량의 평균값을 구하는, 1회 혈액 박출량 연산단계;
연산처리부는 1회 혈액 박출량 연산단계에서 구하여진 1회 혈액 박출량의 평균값이, 1회 혈액 박출량 문턱치 값과 비교하여, 압박강도 조절을 위한 알림신호를 모니터부 또는 스피커부를 통해 알리는, 압박강도 조절 알림단계;
를 포함하여 이루어진 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.The operation processing unit includes: a signal receiving step of receiving a first PPG signal, a second PPG signal, and a thoracic impedance signal from the chest impedance detecting unit, the first PPG detecting unit, and the second PPG detecting unit;
The arithmetic processing unit may include a motion noise removing step of removing the motion noise of the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal received in the signal receiving step;
The arithmetic processing unit sets a sample for calculating a pulse wave propagation time in each of the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal from which motion noise has been removed in the motion noise removal step of the PPG signal;
Calculating a pulse wave propagation time calculating step of calculating a difference between a time of a blood flow measurement point of the first PPG signal set at the blood flow measurement point setting in the PPG signal and a time of the blood flow measurement point of the second PPG signal as a pulse wave propagation time;
The arithmetic processing unit calculates the blood ejection amount of each cycle once using the pulse wave transmission time PWTT and obtains an average value of the blood ejection amount calculated once for each cycle;
The calculation processing section compares the average value of the blood ejection amount obtained in the one-time blood ejection amount calculation step with the one-time blood ejection amount threshold value and notifies the notification signal for the adjustment of the compression strength through the monitor section or the speaker section. step;
And a controller for controlling the blood flow monitor device.
PPG 신호에서의 혈류 측정점 설정단계에서, 연산처리부는, 각 주기동안 제1PPG 신호에서 피크를 구하고, 제1PPG 신호의 피크에 연동되는 제2PPG 신호의 피크를 검출하고고, 제1PPG 신호의 피크를 제1PPG 신호의 혈류 측정점으로 하고, 제1PPG 신호의 피크에 연동되는 제2PPG 신호의 피크를 제2 PPG신호의 혈류 측정점으로 하는 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.11. The method of claim 10,
In the blood flow measurement point setting step in the PPG signal, the calculation processing unit obtains a peak in the first PPG signal during each period, detects a peak of the second PPG signal linked to the peak of the first PPG signal, and outputs a peak of the first PPG signal Wherein a peak of a second PPG signal linked to a peak of the first PPG signal is used as a blood flow measurement point of the first PPG signal and a peak of a second PPG signal is used as a blood flow measurement point of the first PPG signal.
제1PPG 신호의 피크에 연동되는 제2PPG 신호의 피크는, 제1PPG 신호의 피크의 시점의 전후의 제2PPG 신호에서 연산처리부가 피크를 검출하고, 제1PPG 신호의 피크의 시점의 전후의 제2PPG 신호의 피크들에서, 제1PPG 신호의 피크의 시점에 가까운 제2PPG 신호의 피크를, 제1PPG 신호의 피크에 연동되는 제2PPG 신호의 피크로 검출하는 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.12. The method of claim 11,
The peak of the second PPG signal interlocked with the peak of the first PPG signal is a peak of the second PPG signal before and after the peak of the first PPG signal and a peak of the second PPG signal before and after the peak of the first PPG signal Characterized in that the peak of the second PPG signal close to the peak of the first PPG signal is detected as the peak of the second PPG signal interlocked with the peak of the first PPG signal at the peaks of the first PPG signal Driving method.
1회 혈액 박출량 연산단계에서, 연산처리부는 1회 혈액 박출량(S.V.)을
(단, PWTT는 맥파전달시간이며, α는 -0.30이며, β는 131.9 ± 16.5 이며, K는 0.96 ± 0.31 임)
에 의해 구하여 지는 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.11. The method of claim 10,
In the one-shot blood volume calculation step, the arithmetic processing unit calculates the blood volume output (SV)
(However, PWTT is the pulse wave propagation time, and α is -0.30, β is 131.9 ± 16.5, Im K is0. 96 ±0. 31)
Wherein the blood flow monitoring device further comprises:
1회 혈액 박출량 연산단계에서 1회 혈액 박출량의 평균값은 5초 동안의 1회 혈액 박출량의 평균값인 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.11. The method of claim 10,
Wherein the average value of the one blood discharge amount in the one blood discharge amount calculation step is an average value of the one blood discharge amount in five seconds.
압박강도 조절 알림단계에서, 연산처리부는, 1회 혈액 박출량의 평균값이, 1회 혈액 박출량 문턱치 값보다 크지 않을 경우, 심폐소생술의 압박강도를 높이기 위한, 자동 심폐소생술 장치의 모터강도 제어신호를 생성하여 모터구동부로 전송하는 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.11. The method of claim 10,
When the average value of the blood ejection amount once is not larger than the one-time blood ejection amount threshold value, the arithmetic processing unit generates the motor strength control signal of the automatic CPR apparatus for increasing the compression strength of the CPR To the motor driving unit. The method for driving the blood flow monitor for CPR according to claim 1,
신호수신 단계와, PPG신호의 동잡음 제거단계의 사이에,
연산처리부는, 흉부임피던스 검출부, 제1 PPG 검출부, 제2 PPG 검출부로부터, 제1 PPG신호, 제2 PPG신호, 흉부 임피던스 신호를 수신하는, 신호수신 단계;
연산처리부는 신호수신 단계에서 수신된 흉부 임피던스 신호로부터 CPM(분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수)를 계산하는, CPM 연산단계;
CPM 연산단계 후, 연산처리부는 CPM이 100보다 큰지 여부를 판단하여, CPM이 100보다 크지 않다면, CPM 증가를 위한 알림신호를 모니터부 또는 스피커부를 통해 알리는, CPM이 100보다 큰지 여부 판단단계;
연산처리부는 CPM이 100보다 큰지 여부 판단단계에서, CPM이 100보다 크다면, CPM이 120보다 작은지 여부를 판단하고, CPM이 120보다 작지 않다면, CPM 감소를 위한 알림신호를 모니터부 또는 스피커부를 통해 알리는, CPM이 120보다 작은지 여부 판단단계;
를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.11. The method of claim 10,
Between the signal reception step and the dynamic noise cancellation step of the PPG signal,
The operation processing unit includes: a signal receiving step of receiving a first PPG signal, a second PPG signal, and a thoracic impedance signal from the chest impedance detecting unit, the first PPG detecting unit, and the second PPG detecting unit;
The calculation processing unit calculates CPM (the number of CPRs per minute) from the received thoracic impedance signal in the signal reception step;
Determining whether the CPM is greater than 100, determining whether the CPM is greater than 100, if the CPM is not greater than 100, and informing the CPM by the monitor or the speaker;
If the CPM is greater than 100, the calculation processing unit determines whether the CPM is smaller than 120. If the CPM is not smaller than 120, the operation processing unit sends a notification signal for decreasing the CPM to the monitor unit or the speaker unit Determining whether the CPM is less than 120;
Further comprising the steps of: monitoring the blood flow rate of the at least one blood flow monitor device;
CPM 연산단계에서, 연산처리부는 흉부임피던스 검출부로부터 수신된 흉부 임피던스 신호에서, 기설정된 흉부임피던스 문턱치를 넘는 흉부 임피던스 신호에서 피크(peak)를 검출하고,
CPM을
단, Cr은 분당 심폐소생술 실시 횟수(CPM)이며, ti는 i 번째 최대 흉부 압박한 시점의 시간으로, i 번째의 흉부임피던스의 피크를 나타냄)
에 의해 구하는 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.17. The method of claim 16,
In the CPM calculation step, the calculation processing unit detects a peak in a thoracic impedance signal exceeding a predetermined threshold impedance value in the thoracic impedance signal received from the thoracic impedance detection unit,
CPM
However, Cr is the number of CPR cycles per minute (CPM), ti is the time of the i th maximum compression of the chest, which is the peak of the i th thoracic impedance.
Wherein the blood flow monitor apparatus further comprises:
CPM이 100보다 큰지 여부 판단단계에서, 연산처리부는 CPM이 100보다 크지 않다면, CPM 증가를 위한 자동 심페소생술 장치의 모터 속도제어신호를 생성하는 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.17. The method of claim 16,
Wherein the step of determining whether the CPM is greater than 100 is characterized in that, if the CPM is not greater than 100, the operation processor generates a motor speed control signal of the automatic CP resuscitation device for CPM increase Way.
CPM이 120보다 작은지 여부 판단단계, 연산처리부는 CPM이 120보다 작지 않다면, CPM 감소를 위한 자동 심페소생술 장치의 모터 속도제어신호를 생성하는 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.17. The method of claim 16,
Determining whether the CPM is less than 120, and if the CPM is not less than 120, generating a motor speed control signal of an automatic CPR resuscitation device for CPM reduction, Way.
연산처리부는, 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서 피크를 구하고, 구하여진 피크의 주기를 이용하여 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호의 심폐소생술 주파수를 구하고, 구하여진 심폐소생술 주파수를 이용하여 위상을 구하는, 심폐소생술 주파수 계산단계;
연산처리부는, 심폐소생술 주파수 계산단계에서 구하여진 위상을 이용하여 심폐소생술에 의한 제1 PPG신호 및 제2 PPG신호 각각에서의 동잡음 성분을 구하는, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분 추정단계;
제1 PPG신호에서, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분 추정단계에서 구한 제1 PPG신호에서의 동잡음 성분을 제거하여, 동잡음이 제거된 제1 PPG신호를 검출하며, 제2 PPG신호에서, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분 추정단계에서 구한 제2 PPG신호에서의 동잡음 성분을 제거하여, 동잡음이 제거된 제2 PPG신호를 검출하는, 혈류 흐름을 측정한 PPG 신호 추정 단계;
를 포함하여 이루어진 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.11. The method of claim 10, wherein removing the dynamic noise of the PPG signal comprises:
The operation processing unit obtains a peak at each of the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal, obtains the CPR signal and the CPG signal CPR frequency using the obtained period of the peak, and uses the obtained CPR frequency A CPR frequency calculation step of calculating a CPR phase;
The operation processing unit may include a dynamic noise component estimation step by a CPR method for obtaining a dynamic noise component in each of the first PPG signal and the second PPG signal by CPR using the phase obtained in the CPR frequency calculation step;
In the first PPG signal, the dynamic noise component in the first PPG signal obtained in the step of estimating the dynamic noise component by CPR is removed to detect the first PPG signal from which the dynamic noise is removed. In the second PPG signal, A PPG signal estimation step of measuring a flow of blood flow by removing a dynamic noise component in a second PPG signal obtained in the step of estimating a dynamic noise component by a resuscitation to detect a second PPG signal from which motion noise is removed;
And a controller for controlling the blood flow monitor device.
심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분 추정단계에서, 연산처리부는, 심폐소생술에 의한 동잡음 성분()을
(단, 제1고조파부터 제N고조파를 구비하여 N개의 고조파를 가질때, ck(n)은 k번째 고조파에서 n번째 샘플의 진폭을 나타내며, θk(n)은 k번째 고조파에서 n번째 샘플의 위상을 나타내며, Φ(n)은 n번째 샘플의 위상을 나타내며, ak(n)는 동상(in-phase) 성분의 진폭의 변이이고, bk(n)는 직각위상(quadrature) 성분의 진폭의 변이이고, SI(n)는 동상 기준신호이고, 직각위상 기준신호이고, a(n)은 LMS 적응 필터의 필터계수로서, n번째 샘플에서의 동상 계수이고, b(n)은 LMS 적응 필터의 필터계수로서, n번째 샘플에서의 직각위상 계수임)
에 의해 구하는 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.21. The method of claim 20,
In the step of estimating the dynamic noise component by CPR, the arithmetic processing unit calculates the dynamic noise component )of
(However, the first gajilttae the N harmonics from by having the N-th harmonic harmonic, ck (n) denotes the amplitude of the n-th sample in the k-th harmonic, θk (n) is the n-th sample in the k-th harmonic a represents the phase, Φ (n) is n denotes the phase of the second sample, ak (n) is the variation of the amplitude of in-phase (in-phase) component, bk (n) is the quadrature phase (quadrature) component and the variation of the amplitude, and SI (n) is a statue reference signal, and the quadrature reference signals, a (n) is a filter coefficient of the LMS adaptive filter, n is the statue coefficients in the second sample, b (n) is LMS Filter coefficient of the adaptive filter, which is the quadrature phase coefficient in the nth sample)
Wherein the blood flow monitor apparatus further comprises:
혈류 흐름을 측정한 PPG 신호 추정 단계 후, 연산처리부는 다음 샘플에서의 LMS 적응필터의 필터계수를 구하는, LMS 적응 필터계수 갱신 단계;
를 더 포함하여 이루어진 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.22. The method of claim 21,
After the PPG signal estimation step in which the blood flow is measured, the arithmetic processing unit includes: an LMS adaptive filter coefficient updating step of obtaining a filter coefficient of the LMS adaptive filter in the next sample;
Further comprising the steps of: (a) monitoring the blood flow rate of the patient;
LMS 적응 필터계수 갱신 단계에서, 갱신되는 LMS 적응필터의 필터계수인 a(n+1), b(n+1)은
(단, 모든 고조파는 대각(선) 행렬(diagonal matrix) M에서 구룹지어진 서로다른 스텝 사이즈 μk로 배열됨)
에 의해 구하여지는 것을 특징으로 하는, 심폐소생술용 혈액흐름 감시장치의 구동방법.23. The method of claim 22,
In the LMS adaptive filter coefficient updating step, the filter coefficients a (n + 1) and b (n + 1) of the LMS adaptive filter to be updated are
(Note that all harmonics are arranged in different step sizes muk , grouped in a diagonal matrix M)
Wherein the blood flow monitoring device further comprises:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160011287AKR101884377B1 (en) | 2016-01-29 | 2016-01-29 | blood flow monitoring system during CPR and thereof method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160011287AKR101884377B1 (en) | 2016-01-29 | 2016-01-29 | blood flow monitoring system during CPR and thereof method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20170090657Atrue KR20170090657A (en) | 2017-08-08 |
| KR101884377B1 KR101884377B1 (en) | 2018-08-07 |
Family
ID=59653191
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160011287AExpired - Fee RelatedKR101884377B1 (en) | 2016-01-29 | 2016-01-29 | blood flow monitoring system during CPR and thereof method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101884377B1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20200104675A (en)* | 2019-02-27 | 2020-09-04 | 연세대학교 원주산학협력단 | Apparatus and Method for CPR Bio-feedback based on Photoplethysmography |
| EP4011287A1 (en)* | 2020-12-11 | 2022-06-15 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation decision support |
| CN120037097A (en)* | 2025-04-21 | 2025-05-27 | 苏州尚领医疗科技有限公司 | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation compression control device, computing apparatus, and computer-readable storage medium |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5228449A (en)* | 1991-01-22 | 1993-07-20 | Athanasios G. Christ | System and method for detecting out-of-hospital cardiac emergencies and summoning emergency assistance |
| US20100022886A1 (en)* | 2005-11-17 | 2010-01-28 | Koninklijke Philips Electronic N.V. | CPR Guided by Vascular Flow Measurement |
| US20120203077A1 (en)* | 2011-02-09 | 2012-08-09 | David Da He | Wearable Vital Signs Monitor |
| JP2015516185A (en)* | 2012-03-13 | 2015-06-11 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エヌ ヴェ | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation device with physiological sensor |
| WO2015121114A1 (en)* | 2014-02-11 | 2015-08-20 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Determining return of spontaneous circulation during cpr |
- 2016
- 2016-01-29KRKR1020160011287Apatent/KR101884377B1/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5228449A (en)* | 1991-01-22 | 1993-07-20 | Athanasios G. Christ | System and method for detecting out-of-hospital cardiac emergencies and summoning emergency assistance |
| US20100022886A1 (en)* | 2005-11-17 | 2010-01-28 | Koninklijke Philips Electronic N.V. | CPR Guided by Vascular Flow Measurement |
| US20120203077A1 (en)* | 2011-02-09 | 2012-08-09 | David Da He | Wearable Vital Signs Monitor |
| JP2015516185A (en)* | 2012-03-13 | 2015-06-11 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エヌ ヴェ | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation device with physiological sensor |
| WO2015121114A1 (en)* | 2014-02-11 | 2015-08-20 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Determining return of spontaneous circulation during cpr |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20200104675A (en)* | 2019-02-27 | 2020-09-04 | 연세대학교 원주산학협력단 | Apparatus and Method for CPR Bio-feedback based on Photoplethysmography |
| EP4011287A1 (en)* | 2020-12-11 | 2022-06-15 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation decision support |
| WO2022122539A1 (en)* | 2020-12-11 | 2022-06-16 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation decision support |
| CN120037097A (en)* | 2025-04-21 | 2025-05-27 | 苏州尚领医疗科技有限公司 | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation compression control device, computing apparatus, and computer-readable storage medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR101884377B1 (en) | 2018-08-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107920951B (en) | Automatic cardio-pulmonary resuscitation device | |
| US10463566B2 (en) | Pulse oximetry-based cardio-pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) quality feedback systems and methods | |
| EP2502560B1 (en) | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation monitoring apparatus | |
| US12121493B2 (en) | System and method for optimization of CPR chest compressions | |
| US20130060148A1 (en) | Pulse detection using patient physiological signals | |
| CN113545978B (en) | CPR parameter feedback method and device for cardiopulmonary resuscitation | |
| CN101999889B (en) | Biological information monitor | |
| CN111989034A (en) | Devices, systems and methods for supporting the detection of recovery of spontaneous circulation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation | |
| CA2776907A1 (en) | Method of determining depth of compressions during cardio-pulmonary resuscitation | |
| EP3065820B1 (en) | Apparatus for tracking a specific blood pressure | |
| JP2016529031A (en) | System and method for distinguishing manual CPR from automated CPR | |
| KR101884377B1 (en) | blood flow monitoring system during CPR and thereof method | |
| WO2018234569A1 (en) | DEVICE, SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DETECTING PULSE AND / OR PULSE INFORMATION OF PATIENT | |
| WO2017072626A1 (en) | System and method to automatically adjust, notify or stop chest compressions when a spontaneous pulse is detected during automated cardiopulmonary resuscitation | |
| JPWO2019201689A5 (en) | ||
| WO2017056042A1 (en) | Cpr assistance system | |
| JP7312547B2 (en) | Determining Compression Rates for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation | |
| KR102318511B1 (en) | Apparatus and Method for CPR Bio-feedback based on Photoplethysmography | |
| AU2013201712B2 (en) | Method of determining depth of compressions during cardio-pulmonary resuscitation | |
| KR102535887B1 (en) | Apparatus for estimating intracranial pressure of non invasive using eeg signals based on learning and method thereof | |
| AU2020201210B2 (en) | Defibrillator providing cardio pulmonary resuscitation feedback | |
| JP2003260032A (en) | Pulse wave measuring apparatus and bathtub hemomanometer having the same | |
| AU2016201047A1 (en) | Method of determining depth of compressions during cardio-pulmonary resuscitation | |
| HK1250908B (en) | Automatic cardiopulmonary resuscitation device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| D13-X000 | Search requested | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D13-srh-X000 | |
| D14-X000 | Search report completed | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D14-srh-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | St.27 status event code:A-1-1-Q10-Q12-nap-PG1501 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| T11-X000 | Administrative time limit extension requested | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T11-oth-X000 | |
| T11-X000 | Administrative time limit extension requested | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T11-oth-X000 | |
| E13-X000 | Pre-grant limitation requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-3-E10-E13-lim-X000 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| T12-X000 | Administrative time limit extension not granted | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T12-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 Fee payment year number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:6 | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U13-oth-PC1903 Not in force date:20240801 Payment event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | St.27 status event code:N-4-6-H10-H13-oth-PC1903 Ip right cessation event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE Not in force date:20240801 |