KR20170087837A - NeuroVascular Unit(NVU)-On-a-Chip And Method Of Fabricating The Same - Google Patents
NeuroVascular Unit(NVU)-On-a-Chip And Method Of Fabricating The SameDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20170087837A KR20170087837AKR1020170012464AKR20170012464AKR20170087837AKR 20170087837 AKR20170087837 AKR 20170087837AKR 1020170012464 AKR1020170012464 AKR 1020170012464AKR 20170012464 AKR20170012464 AKR 20170012464AKR 20170087837 AKR20170087837 AKR 20170087837A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- channel
- extracellular matrix
- brain
- human
- cells
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N35/00—Automatic analysis not limited to methods or materials provided for in any single one of groups G01N1/00 - G01N33/00; Handling materials therefor
- G01N35/08—Automatic analysis not limited to methods or materials provided for in any single one of groups G01N1/00 - G01N33/00; Handling materials therefor using a stream of discrete samples flowing along a tube system, e.g. flow injection analysis
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01L—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL LABORATORY APPARATUS FOR GENERAL USE
- B01L3/00—Containers or dishes for laboratory use, e.g. laboratory glassware; Droppers
- B01L3/50—Containers for the purpose of retaining a material to be analysed, e.g. test tubes
- B01L3/502—Containers for the purpose of retaining a material to be analysed, e.g. test tubes with fluid transport, e.g. in multi-compartment structures
- B01L3/5027—Containers for the purpose of retaining a material to be analysed, e.g. test tubes with fluid transport, e.g. in multi-compartment structures by integrated microfluidic structures, i.e. dimensions of channels and chambers are such that surface tension forces are important, e.g. lab-on-a-chip
- B01L3/502707—Containers for the purpose of retaining a material to be analysed, e.g. test tubes with fluid transport, e.g. in multi-compartment structures by integrated microfluidic structures, i.e. dimensions of channels and chambers are such that surface tension forces are important, e.g. lab-on-a-chip characterised by the manufacture of the container or its components
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N5/00—Undifferentiated human, animal or plant cells, e.g. cell lines; Tissues; Cultivation or maintenance thereof; Culture media therefor
- C12N5/06—Animal cells or tissues; Human cells or tissues
- C12N5/0602—Vertebrate cells
- C12N5/0618—Cells of the nervous system
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N5/00—Undifferentiated human, animal or plant cells, e.g. cell lines; Tissues; Cultivation or maintenance thereof; Culture media therefor
- C12N5/06—Animal cells or tissues; Human cells or tissues
- C12N5/0602—Vertebrate cells
- C12N5/0618—Cells of the nervous system
- C12N5/0622—Glial cells, e.g. astrocytes, oligodendrocytes; Schwann cells
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N5/00—Undifferentiated human, animal or plant cells, e.g. cell lines; Tissues; Cultivation or maintenance thereof; Culture media therefor
- C12N5/06—Animal cells or tissues; Human cells or tissues
- C12N5/0602—Vertebrate cells
- C12N5/0618—Cells of the nervous system
- C12N5/0623—Stem cells
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/48—Biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Haemocytometers
- G01N33/50—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing
- G01N33/5005—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing involving human or animal cells
- G01N33/5008—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing involving human or animal cells for testing or evaluating the effect of chemical or biological compounds, e.g. drugs, cosmetics
- G01N33/5044—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing involving human or animal cells for testing or evaluating the effect of chemical or biological compounds, e.g. drugs, cosmetics involving specific cell types
- G01N33/5058—Neurological cells
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01L—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL LABORATORY APPARATUS FOR GENERAL USE
- B01L2300/00—Additional constructional details
- B01L2300/08—Geometry, shape and general structure
- B01L2300/0861—Configuration of multiple channels and/or chambers in a single devices
- B01L2300/0877—Flow chambers
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2513/00—3D culture
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N35/00—Automatic analysis not limited to methods or materials provided for in any single one of groups G01N1/00 - G01N33/00; Handling materials therefor
- G01N2035/00178—Special arrangements of analysers
- G01N2035/00237—Handling microquantities of analyte, e.g. microvalves, capillary networks
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Tropical Medicine & Parasitology (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- Clinical Laboratory Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Developmental Biology & Embryology (AREA)
- Apparatus Associated With Microorganisms And Enzymes (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 체외에서 인간의 뇌를 모사할 수 있는 미세유체 칩에 관한 것으로서, 보다 상세하게는, 뇌질환과 관련한 신약 개발과 맞춤치료를 위하여 혈뇌 장벽 구조를 포함하는 인간 뇌조직과 유사한 환경을 체외에서 모사하고자 뇌조직세포 공배양 기술을 이용하여 미세 유체 플랫폼에 다양한 인간 유래 뇌조직 세포(human brain cell)를 3차원 집적시킨 신경혈관단위-온-칩 및 그 칩의 제조방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a microfluidic chip capable of simulating a human brain in vitro. More specifically, the present invention relates to a microfluidic chip capable of simulating human brain tissue including a blood brain barrier structure To a neurovascular unit-on-chip in which various human-derived human brain cells are three-dimensionally integrated into a microfluidic platform by using a technique of co-culturing brain tissue, and a method for manufacturing the same.
2차원 세포 배양(two-dimensional(2D)) 모델이 의생명과학 연구에서 가치를 인정받음에도 불구하고, 상기 2차원 세포 배양 모델은 세균 배양 접시(petri dish)를 이용하여 접시 바닥에 세포를 2차원으로 배양시키므로 많은 세포 타입의 조직 특이적 분화 기능들(tissue-specific, differentiated functions)을 설명하지 못하거나 생체내(in vivo)의 조직 기능과 약물 활성도를 정확하게 예측하지 못한다.Two-Dimensional Cell Culture (Two-Dimensional (2D) Model) Despite its value in bioscience research, the two-dimensional cell culture model uses a petri dish to place cells on the bottom of the dish Dimensionally, it fails to account for tissue-specific, differentiated functions of many cell types or to accurately predict tissue function and drug activity in vivo.
특히, 생체 내에서 3차원 접촉을 하고 있는 뉴런(neuron) 및 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell)를 가지는 뇌조직세포의 경우 상기 2차원 세포 배양 모델의 한계로 인해서, 살아있는 조직의 공간적 구조과 생화학적 복잡성을 잘 모사하는 3차원 세포 배양 모델에 대한 관심이 높아지고 있다.Particularly, in the case of brain tissue cells having neurons and neural stem cells which are in contact with each other in a three-dimensional manner in vivo, due to the limitations of the two-dimensional cell culture model, the spatial structure and biochemical complexity of living tissues Interest in the well-simulated three-dimensional cell culture model is increasing.
3차원 세포 배양 모델은 생체내 상태(situation)를 잘 모방하므로 생체외 실험에서 방향적 성장과 세포-세포 연결의 복잡성을 구현할 수 있고, 더불어 3차원 세포 배양 모델은 2차원 세포 배양 모델에 비하여 개선된 세포 생존(improved cell survival)과 향상된 신경줄기세포 분화(enhanced neuronal differentiation)를 보여준다.The three-dimensional cell culture model mimics the situation in vivo, so it can realize the directional growth and the complexity of cell-cell connection in an in vitro experiment. In addition, the three-dimensional cell culture model can be improved Improved cell survival and enhanced neuronal differentiation.
따라서, 3차원 세포 배양 모델은 분자 기반(molecular basis)의 조직 기능을 연구하는데 있어서 2차원 세포 배양 모델 대비 다양한 질병 상태의 신호기전(signaling pathway)과 약물 반응(drug responsiveness)을 잘 포착하는데 유용하다.Thus, the three-dimensional cell culture model is useful for capturing the signaling pathway and drug responsiveness of various disease states versus the two-dimensional cell culture model in studying the molecular basis of tissue function .
한편, 일 예로써, 3차원 세포 배양 모델이 'Recreating blood-brain barrier physiology and structure on chip: A novel neurovascular microfluidic bioreactor' 의 제목을 갖는 논문(아래의 '선행기술문헌' 란에서 상세한 사항을 참조요)에 개시되었다.As an example, a three-dimensional cell culture model is described in a paper entitled " Recreating Blood-brain barrier physiology and structure on chip ", which is titled " A novel neurovascular microfluidic bioreactor " ).
상기 논문은 생체 외에서 신경혈관 미세유체 바이오반응기(neurovascular microfluidic bioreactor)를 이용하여 혈뇌 장벽(Blood-Brain Barrier; BBB)을 모사하는 3차원 세포 배양 모델을 제시하였다. 여기서, 상기 혈뇌 장벽은 혈관내피세포(endothelial cells) 혈관주위세포(pericyte)와 별아교세포(astrocyte)로 구성되며 혈액과 뇌조직 사이에 물질의 이동을 제한하는 관문(gatekeeper)이다.The above paper presents a three-dimensional cell culture model that simulates the blood-brain barrier (BBB) using a neurovascular microfluidic bioreactor in vitro. Herein, the blood-brain barrier is composed of endothelial cells pericyte and astrocyte and is a gatekeeper that restricts the movement of substances between blood and brain tissue.
즉, 상기 혈뇌 장벽은 뇌조직에서 요구되는 혈액 내의 영양분을 혈액으로부터 뇌를 향해 들여보내고 잠재적으로 해로운 물질을 혈액으로부터 외부로 배출시키는 역할을 한다. 여기서, 상기 신경혈관 미세유체 바이오반응기는 유리(glass) 상에 순차적으로 적층되는 제1 내지 제3 폴리디메틸실록세인(PolyDiMethylSiloxane; PDMS) 층과, 제1 및 제2 폴리디메틸실록세인 층 사이에 폴리카보네이트 맴브레인(polycarbonate membrane)을 이용하여 동작된다.That is, the blood-brain barrier plays a role of letting the nutrients in the blood, which are required in the brain tissue, from the blood toward the brain and discharging potentially harmful substances from the blood to the outside. Here, the neurovascular microfluidic bioreactor comprises first to third polyDiMethylSiloxane (PDMS) layers sequentially stacked on a glass, and a poly (dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) layer between the first and second polydimethylsiloxane layers. And is operated using a polycarbonate membrane.
상기 맴브레인은 반투과성이며, 미세유체 맥관구조(microfluidic vasculature) 및 뇌 격실들(brain compartments)을 만든다. 상기 제1 폴리디메틸실록세인 층은 내피 세포에 도관 중막 공급(vascular media supply)을 위한 두 개의 관류 포트를 가지며, 상기 제2 및 제3 폴리디메틸실록세인 층은 브레인 중막 공급(brain media supply)을 위한 네 개의 관류 포트를 갖는다.The membrane is semipermeable and produces microfluidic vasculature and brain compartments. Wherein the first polydimethylsiloxane layer has two perfusion ports for vascular media supply to endothelial cells and the second and third polydimethylsiloxane layers comprise a brain media supply And has four perfusion ports.
상기 맴브레인의 양 측에 세포들을 성장시키기 위해, 우선적으로 상기 제1 폴리디메틸실록세인 층이 제2 및 제3 폴리디메틸실록세인 층보다 더 상위 레벨로 위치되어 맴브레인의 도관 측에 혈관내피 세포를 심기 위해 두 개의 관류 포트를 통해 관류된다.To grow cells on both sides of the membrane, preferentially the first polydimethylsiloxane layer is positioned at a higher level than the second and third polydimethylsiloxane layers to plant vascular endothelial cells on the catheter side of the membrane And is perfused through two perfusion ports.
다음으로, 상기 제1 폴리디메틸실록세인 층이 제2 및 제3 폴리디메틸실록세인 층보다 더 하위 레벨로 위치된 후에, 상기 제2 및 제3 폴리디메틸실록세인 층은 맴브레인의 브레인 측에 콜라겐(collagen)에 포함되는 뉴런(neuron), 별아교세포(astrocyte) 및 혈관주위세포(pericyte)를 심기 위해 네 개의 관류 포트를 통해 관류된다.Next, after the first polydimethylsiloxane layer is positioned at a lower level than the second and third polydimethylsiloxane layers, the second and third polydimethylsiloxane layers are coated with collagen at the brain side of the membrane neurons, astrocyte, and pericyte, which are contained in the collagen of the brain.
다음으로, 상기 혈관내피 세포, 뉴런, 별아교세포 및 혈관주위세포가 제1 내지 제2 폴리디메틸실록세인 층에서 세포 배양액을 통해 배양되어 멤브레인 주변에 혈뇌장벽을 형성한다. 그러나, 상기 신경혈관 미세유체 바이오반응기는 혈뇌장벽을 형성하는 동안 제1 폴리디메틸실록세인 층을 기준으로 뒤집어져야 하고, 혈관내피 세포, 별아교세포 및 혈관주위세포로 이루어지는 혈뇌장벽을 포함하는 생체내 신경혈관단위(NeuroVascular Unit; NVU)를 충분히 구현하지 못한다.Next, the vascular endothelial cells, neurons, astrocytes, and perivascular cells are cultured in the first to second polydimethylsiloxane layers through a cell culture solution to form a blood-brain barrier around the membrane. However, the neurovascular microfluidic bioreactor must be inverted on the basis of the first polydimethylsiloxane layer during the formation of the blood-brain barrier, and the in vivo nerve including the blood-brain barrier composed of vascular endothelial cells, astrocytic cells, It does not fully implement the neurovascular unit (NVU).
왜냐하면, 상기 신경혈관단위는 생체내 혈뇌 장벽의 구조 관점에서 볼 때에 맴브레인의 도관 측과 브레인 측에 각각 위치되어 맴브레인으로 분리된 혈관내피 세포와 혈관주위세포를 가지므로 불완전하게 모사되었고 생체내 혈뇌 장벽과 그 주변의 구조적인 관점에서 볼 때에 혈관내피 세포, 혈관주위세포, 뉴런 및 별아교세포 이외에 다른 뇌조직 세포를 더 요구하기 때문이다.The neurovascular unit is imperfectly replicated because it has vascular endothelial cells and pericytes separated by membranes located on the conduit side and the brain side of the membrane in terms of the structure of the in vivo blood-brain barrier, And from the structural point of view around it, it requires more brain tissue cells besides vascular endothelial cells, pericytes, neurons and astrocytes.
또한, 상기 신경혈관 미세유체 바이오반응기는 혈관내피세포를 제1 폴리디메틸실록세인 층에서 맴브레인을 따라 2차원적으로 배양시켜 생체내 혈뇌 장벽을 충분히 구현하지 못하고, 공기 또는 약물을 흡수하는 특성을 갖는 폴리디메틸실록세인 층에 혈관내피세포와 배양액을 접촉시키므로 혈뇌장벽과 관련하여 생체내 기작과 다른 양상을 보여준다.In addition, the neurovascular microfluidic bioreactor is a device for culturing vascular endothelial cells two-dimensionally along the membrane in the first polydimethylsiloxane layer, which can not sufficiently implement the in vivo blood-brain barrier, Because the polydimethylsiloxane layer is contacted with the vascular endothelial cells and the culture solution, the vascular mechanism is different from that in vivo.
따라서 종래 개발된 생체 외 신경혈관단위의 모사 기술은 체내 기작과 다른 양상을 보이고 있어 후보 약물에 대한 효능과 독성 여부에 대한 예측도가 낮다는 문제점이 있는 바, 뇌질환 연구 및 뇌질환에 대한 우수한 신약 개발, 환자맞춤형 치료를 위해 모사도가 높은 신경혈관단위 모사칩의 개발이 필요한 실정이다.Therefore, there is a problem that the conventionally developed in vitro neurovascular unit simulating technique is different from that in the body and there is a low predictability about the efficacy and toxicity of the candidate drug. Therefore, It is necessary to develop a neurovascular unit simulated chip with high degree of simulation for new drug development and patient-customized treatment.
본 발명은 종래 문제점을 해결하기 위해 안출된 것으로, 본 발명의 목적은 배양액을 관류시키는 미세유체 플랫폼기술을 이용하여 세포외기질(extra-cellular matrix, ECM)을 모사하는 단일 공간에서 인간 유래 뇌조직세포 5종 이상을 3차원으로 공배양함으로써 생체 외에서 인간 뇌의 신경혈관단위(NeuroVascular Unit; NVU)를 최대한 재현하는데 적합한 신경혈관단위-온-칩 및 그 칩의 제조 방법을 제공하는데 있다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention has been made to solve the conventional problems, and it is an object of the present invention to provide a method and an apparatus for analyzing an extra-cellular matrix (ECM) using microfluidic platform technology, The present invention provides a neurovascular unit-on-chip suitable for reproducing the neurovascular unit (NVU) of a human brain in vivo as much as possible by co-culturing more than five kinds of cells in three dimensions and a method for producing the same.
본 발명에 따르는 신경혈관단위-온-칩(neurovascular unit-on-a-chip; NVU-on-a-chip)은 반고체(gel) 상태의 세포외기질(extracellular matrix; ECM) 모사 물질(70)과 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)을 관통하고 있으며 배양액이 관류되는 적어도 하나의 채널(channel, 75); 및 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)과 상기 적어도 하나의 채널(75)을 둘러싸며, 상기 적어도 하나의 채널(75)과 유체적으로 연통하도록 상기 적어도 하나의 채널(75)과 동일 개수로 이루어진 통로(50)를 가지는 기판(10)을 포함하고, 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)은 상기 채널(75)의 외벽에 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 함유하고, 상기 채널(75)의 내벽에는 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(brain microvessel endothelial cell lining, 91)이 형성되고, 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들과 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)은 상기 채널(75)을 통해 접촉되어 인간 뇌의 혈뇌 장벽(Blood Brain Barrier; BBB)과, 상기 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)을 포함하는 상기 인간 뇌의 신경혈관단위(NeuroVascular Unit; NVU)를 모사하고, 상기 기판(10)은 중앙 영역에서 상부 면(US)을 관통하여 상기 상부 면(US)으로부터 하부 면(LS)을 향해 소정 깊이로 연장되도록 상기 하부 면(LS) 및 상기 상부 면(US) 사이에 위치되는 셀 고정 웰(cell fixing well, 20)에 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)을 안착시키는 것을 특징으로 한다.A neurovascular unit-on-a-chip (NVU-on-a-chip) according to the present invention is an extracellular matrix (ECM) mimetic 70 in a semi- At least one channel (75) penetrating the extracellular matrix mimic material (70) and through which the culture fluid is perfused; And at least one channel (75) surrounding said extracellular matrix mimic material (70) and said at least one channel (75) and in fluid communication with said at least one channel (75) Wherein the extracellular matrix
상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)은, 콜라겐, 피브로넥틴, 피브린, 피브리노겐, 엘라스틴, 히알루론산, 프로테오글리칸, 라미닌, 헤파린 설페이트, 콘드로틴 설페이트, 케라탄 설페이트 및 마트리젤 (Matrigel) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 세포외기질, 알지네이트, 폴리에틸렌글라이콜, 실리콘 하이드로젤, 폴리아크릴아마이드, 폴리데틸렌옥사이드, 폴리피롤리딘, 글리코사미노글리칸 및 폴리헤마 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 하이드로젤, 상기 세포외기질과 상기 하이드로젤의 혼합물, 상기 세포외기질의 화학적 변형체, 상기 하이드로젤의 화학적 변형체, 또는 상기 세포외기질의 상기 화학적 변형체와 상기 하이드로젤의 상기 화학적 변형체의 혼합물을 포함할 수 있다.Wherein the extracellular matrix mimetic 70 comprises at least one of collagen, fibronectin, fibrin, fibrinogen, elastin, hyaluronic acid, proteoglycans, laminin, heparin sulphate, conroutein sulphate, keratan sulphate and Matrigel A hydrogel comprising at least one of an extracellular matrix, alginate, polyethylene glycol, silicone hydrogel, polyacrylamide, polyphenylene oxide, polypyrrolidine, glycosaminoglycan and polyhema, A mixture of hydrogels, a chemical modification of said extracellular matrix, a chemical modification of said hydrogel, or a mixture of said chemical modification of said extracellular matrix and said chemical modification of said hydrogel.
상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 뉴런(neuron, 92), 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell, 93), 미세아교세포(microglia, 94), 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95) 및 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 하나 이상을 포함할 수 있다.The plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells include
상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 뉴런(neuron, 92), 미세아교세포(microglia, 94), 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95) 및 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)를 포함할 수 있다.The plural kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells may include
상기 혈뇌장벽(BBB)은 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91), 상기 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95)와 상기 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)를 포함할 수 있다.The BBB may include the brain microvascular
상기 신경혈관단위는 상기 혈뇌장벽(BBB), 상기 뉴런(neuron, 92), 상기 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell, 93)와 상기 미세아교세포(microglia, 94)를 포함할 수 있다.The neurovascular unit may include the BBB, the
상기 기판(10)은, 유리(glass)를 포함하는 투명 세라믹류, 폴리디메틸실록세인(PolyDiMethylSiloxane; PDMS)과 에코플렉스(ecoflex) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 실리콘고무류, 폴리스티렌(polystyrene), 폴리메틸메타크릴레이트(polymethylmethacrylate), 폴리프로필렌(polypropylene), 폴리카보네이트(polycarbonate)와 폴리우레탄(polyurethane) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 엔지니어링 플라스틱류, 상기 투명 세라믹류, 상기 실리콘고무류와 상기 엔지니어링 플라스틱류 중 적어도 두 개를 포함하는 혼합물, 상기 투명 세라믹류의 화학적 변형체, 상기 실리콘고무류의 화학적 변형체, 상기 엔지니어링 플라스틱류의 화학적 변형체, 또는 상기 투명 세라믹류의 상기 화학적 변형체, 상기 실리콘고무류의 상기 화학적 변형체와 상기 엔지니어링 플라스틱류의 상기 화학적 변형체 중 적어도 두 개를 포함하는 혼합물을 포함할 수 있다.The
상기 통로(50)는 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)의 양 측부에서 제1 통로(35) 및 제2 통로(45)로 분리되어 상기 기판(10)을 관통할 수 있다.The
상기 기판(10)과 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)은 사각 형상으로 이루어져 제1 측벽(WS1)과 제2 측벽(WS2)을 각각 가지고, 상기 제1 측벽(WS1)은 상기 기판(10)의 두께 방향으로 상기 제2 측벽(WS2)보다 큰 높이를 가지고, 상기 제1 측벽(WS1)과 상기 제2 측벽(WS2)은 상기 상부 면(US)과 각을 이루면서 상기 상부 면(US)과 접촉되어 서로 마주보고, 상기 제1 통로(35) 및 상기 제2 통로(45)의 각각은 상기 기판(10)의 제1 측벽(WS1), 그리고 상기 제1 측벽(WS1)과 마주보는 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)의 제2 측벽(WS2)에서 개구되어 상기 제1 측벽(WS1)과 상기 제2 측벽(WS2)에 유입구(IP) 및 유출구(OP)를 가질 수 있다.The
상기 채널(75)의 상기 외벽이 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에 접촉함으로써 상기 인간 뇌에서 상기 혈뇌장벽을 포함하는 상기 신경혈관단위를 모사하는 3차원 공배양이 가능하고, 상기 기판(10)과 상기 채널(75)의 접촉을 최소화하여 시험 대상 약물이 상기 기판(10)에 흡착되어 생체내 기작과 다른 양상을 보이는 것을 피할 수 있다.The outer wall of the
본 발명에 따르는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법은 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 함유하는 반고체(gel) 상태의 세포외기질(extracellular matrix; ECM) 모사 물질(70)을 관통하는 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계; 상기 채널(75)의 내벽에 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)을 형성하는 단계; 및 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)과 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 이용하여 상기 채널(75)을 통해 인간 뇌의 혈뇌 장벽(Blood Brain Barrier; BBB)과, 상기 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)을 포함하는 상기 인간 뇌의 신경혈관단위를 모사하는 단계를 포함하고,The method of manufacturing a neurovascular unit-on-chip according to the present invention is a method of manufacturing a neurovascular unit-on-a-chip, comprising the steps of: (a) passing a channel of an extracellular matrix (ECM)
상기 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계는 평탄한 형상으로 이루어져 상하로 마주보는 하부 면(LS) 및 상부 면(US)과 함께 상기 하부 면(LS) 및 상기 상부 면(US)을 이어주는 제1 측벽(WS1), 상기 상부 면(US)의 중앙 영역에서 상기 상부 면(US)을 관통하여 상기 상부 면(US)으로부터 상기 하부 면(LS)을 향해 소정 깊이로 연장하도록 상기 하부 면(LS) 및 상기 상부 면(US) 사이에 제2 측벽(WS2)으로 한정되는 셀 고정 웰(20), 그리고 상기 셀 고정 웰(20) 주변에서 상기 채널(75)과 유체적으로 연통하도록 상기 채널(75)과 동일 개수로 이루어진 적어도 하나의 통로(50)를 포함하는 기판(10)을 준비하는 단계를 포함한다.The step of forming the
상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)은, 콜라겐, 피브로넥틴, 피브린, 피브리노겐, 엘라스틴, 히알루론산, 프로테오글리칸, 라미닌, 헤파린 설페이트, 콘드로틴 설페이트, 케라탄 설페이트 및 마트리젤 (Matrigel) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 세포외기질, 알지네이트, 폴리에틸렌글라이콜, 실리콘 하이드로젤, 폴리아크릴아마이드, 폴리데틸렌옥사이드, 폴리피롤리딘, 글리코사미노글리칸 및 폴리헤마 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 하이드로젤, 상기 세포외기질과 상기 하이드로젤의 혼합물, 상기 세포외기질의 화학적 변형체, 상기 하이드로젤의 화학적 변형체, 또는 상기 세포외기질의 상기 화학적 변형체와 상기 하이드로젤의 상기 화학적 변형체의 혼합물을 포함할 수 있다.Wherein the extracellular matrix mimetic 70 comprises at least one of collagen, fibronectin, fibrin, fibrinogen, elastin, hyaluronic acid, proteoglycans, laminin, heparin sulphate, conroutein sulphate, keratan sulphate and Matrigel A hydrogel comprising at least one of an extracellular matrix, alginate, polyethylene glycol, silicone hydrogel, polyacrylamide, polyphenylene oxide, polypyrrolidine, glycosaminoglycan and polyhema, A mixture of hydrogels, a chemical modification of said extracellular matrix, a chemical modification of said hydrogel, or a mixture of said chemical modification of said extracellular matrix and said chemical modification of said hydrogel.
상기 통로(50)는 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)의 양 측부에 제1 통로(35)와 제2 통로(45)로 분리되어 형성될 수 있다.The
상기 기판(10)은, 유리(glass)를 포함하는 투명 세라믹류, 폴리디메틸실록세인(PolyDiMethylSiloxane; PDMS)과 에코플렉스(ecoflex) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 실리콘고무류, 폴리스티렌(polystyrene), 폴리메틸메타크릴레이트(polymethylmethacrylate), 폴리프로필렌(polypropylene), 폴리카보네이트(polycarbonate)와 폴리우레탄(polyurethane) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 엔지니어링 플라스틱류, 상기 투명 세라믹류, 상기 실리콘고무류와 상기 엔지니어링 플라스틱류 중 적어도 두 개를 포함하는 혼합물, 상기 투명 세라믹류의 화학적 변형체, 상기 실리콘고무류의 화학적 변형체, 상기 엔지니어링 플라스틱류의 화학적 변형체, 또는 상기 투명 세라믹류의 상기 화학적 변형체, 상기 실리콘고무류의 상기 화학적 변형체와 상기 엔지니어링 플라스틱류의 상기 화학적 변형체 중 적어도 두 개를 포함하는 혼합물을 포함할 수 있다.The
상기 제1 통로(35)와 상기 제2 통로(45)는 상기 기판(10)을 관통하여 상기 기판(10)의 제1 측벽(WS1), 그리고 상기 제1 측벽(WS1)과 마주보는 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)의 제2 측벽(WS2)에서 개구될 수 있다.The
상기 제1 통로(35)와 상기 제2 통로(45)의 각각은 상기 제1 측벽(WS1)과 상기 제2 측벽(WS2)에 유입구(IP) 및 유출구(OP)를 가질 수 있다.Each of the
상기 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계는 상기 제1 통로(35), 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)과 상기 제2 통로(45)에 마이크로니들(60)을 삽입하는 단계; 및 반액체(sol) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질을 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)에 채우는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.The step of forming the channel (75) includes the steps of inserting the micro needle (60) into the first passageway (35), the cell fixation well (20) and the second passageway (45); And filling the cell fixation well 20 with an extracellular matrix mimic material in a semi-liquid (sol) state.
상기 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계는 상기 반액체(sol) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질을 경화하여 상기 반고체(gel) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)로 변환하는 단계; 및 상기 반고체 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)로부터 상기 마이크로니들(60)을 제거하여 상기 반고체 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)을 관통하는 상기 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.The step of forming the channel (75) comprises curing the semi-liquid (sol) extracellular matrix mimetic to convert it into the semi-solid state extracellular matrix mimetic (70); And removing the
상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)을 형성하는 단계는, 상기 채널(75)에 뇌혈관내피 세포(brain endothelial cell, 84)를 주입하여 채널(75)의 상기 내벽에 상기 뇌혈관내피 세포(84)를 고정하는 단계; 및 뇌혈관내피 세포가 포함된 배양액(88)을 상기 채널(75)에 유입시키면서 상기 배양액(88)을 상기 채널(75)의 상기 내벽에 고정된 상기 뇌혈관내피 세포(84)에 접촉시켜 상기 채널(75)의 상기 내벽을 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)으로 피복시키는 단계를 포함하고, 상기 배양액(88)은 상기 채널(75)의 상기 내벽에서 상기 뇌혈관내피 세포(84)와 상기 채널(75)의 외벽에서 상기 반 고체 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)을 통해 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 공배양시킬 수 있다.In the step of forming the brain microvascular
상기 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)과 신경혈관단위(NVU)의 모사 단계는, 상기 채널(75) 내에 상기 배양액(88)의 흐름 동안 상기 배양액(88)을 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에 접촉시켜 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에서 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 공배양시키는 단계; 및 상기 채널(75)을 통해 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)에 접촉시키는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The step of simulating the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the neurovascular unit (NVU) is performed by bringing the
상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 뉴런(92), 신경줄기세포(93), 미세아교세포(94), 별아교세포(95) 및 혈관주위세포(96)로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 하나 이상을 포함할 수 있다.The plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells include at least one selected from the group consisting of
상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 뉴런(92), 미세아교세포(94), 별아교세포(95) 및 혈관주위세포(96)를 포함할 수 있다.The plural kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells may include
상기 혈뇌장벽(BBB)은 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91), 상기 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95)와 상기 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)를 포함할 수 있다.The BBB may include the brain microvascular
상기 신경혈관단위는 상기 혈뇌장벽(BBB), 상기 뉴런(neuron, 92), 상기 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell, 93)와 상기 미세아교세포(microglia, 94)를 포함할 수 있다.The neurovascular unit may include the BBB, the
상기 채널(75)의 외벽이 상기 반 고체 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에 접촉함으로써 상기 인간 뇌에서 상기 신경혈관단위를 모사하는 3차원 공배양이 가능하고, 기판(10)과 상기 채널(75)의 접촉을 최소화하여 시험 대상 약물이 상기 기판(10)에 흡착되어 생체내 기작과 다른 양상을 보이는 것을 피할 수 있다.The outer wall of the
본 발명은 기판에 위치되는 셀 고정 웰과 셀 고정 웰의 양 측부에 서로 마주보는 통로들을 이용하여 통로들과 각각 연통하는 채널들을 갖는 세포외기질(extracellular matrix; ECM) 모사 물질을 셀 고정 웰에 안착시키고 통로들과 채널들에 배양액의 반복적인 흐름 동안 각각의 채널에서 채널의 내벽을 충분히 덮는 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막과 채널의 외벽에서 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막을 따라 세포외기질(ECM) 모사 물질 내에 복수 종류의 인간 유래 뇌조직 세포들을 3차원 공배양시킬 수 있다.The present invention is based on the discovery that an extracellular matrix (ECM) mimetic having a cell-fixing well located on a substrate and channels communicating with the channels using opposed paths on opposite sides of the cell-fixing well, (ECM) mimics along the brain microvessel endothelial cell membrane on the outer surface of the brain microvessel endothelial membrane and channel that adequately cover the inner wall of the channel in each channel during the repeated flow of culture to the channels and channels. A plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells can be co-cultured three-dimensionally.
본 발명은 채널의 내벽을 둘러싸는 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막과 채널을 한정하는 세포외기질(ECM) 모사 물질 내의 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 3차원으로 공배양시켜 채널을 통해 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(brain microvascular endothelial cell lining)과 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 직접 접촉시키므로 인간 뇌의 혈뇌 장벽(Brain Blood Barrier; BBB)과 인간 뇌에서 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)을 포함하는 신경혈관단위(NeuroVascular Unit; NVU)를 모사하고 기판과 채널의 접촉을 최소화하여 시험 대상 약물이 기판에 흡착되어 생체내 기작과 다른 양상을 보이는 것을 피할 수 있게 한다.The present invention relates to a method for the simultaneous cultivation of a plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells in an extracellular matrix (ECM) mimic substance defining a channel of a microvascular endothelial cell membrane and a channel surrounding an inner wall of a channel, Since the brain microvascular endothelial cell lining and multiple kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells are in direct contact with each other, the brain blood vessel barrier (BBB) in the human brain and the neurovascular unit (NVU) and minimizes the contact between the substrate and the channel so that the drug to be tested is adsorbed on the substrate and avoids a different aspect from the in vivo mechanism.
본 발명은 기판 상에서 인간 뇌의 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)과 인간 뇌에서 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)을 포함하는 신경혈관단위를 모사하는 난치성 뇌질환 유효성 평가 플랫폼을 통해 맞춤형 뇌질환 치료기술을 빠른 시간 내에 개발 가능하게 하고 난치성 뇌질환 유효성 평가 플랫폼의 개발 기술을 인간의 여타 질환에 확대 적용 가능하므로 뇌질환과 바이오 산업에서 새로운 시장을 형성할 수 있게 한다.The present invention enables rapid development of a customized brain disease treatment technology through a refractory brain disease efficacy evaluation platform that simulates neurovascular units including the blood brain barrier (BBB) in the human brain and the blood vessel barrier (BBB) in the human brain on a substrate And can develop new technologies for brain disease and bio industry by expanding the development technology of refractory brain disease efficacy evaluation platform to other human diseases.
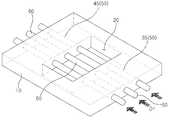
도 1은 본 발명에 따른 신경혈관단위-온-칩을 개략적으로 보여주는 사시도이다.
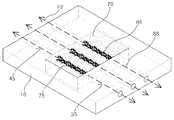
도 2는 도 1의 A 영역에서 취해진 세포외기질 모사 물질을 개략적으로 보여주는 단면도이다.
도 3 내지 도 9는 도 1의 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법을 설명하는 개략도이다.1 is a perspective view schematically showing a neurovascular unit-on-chip according to the present invention.
Figure 2 is a cross-sectional view schematically illustrating an extracellular matrix mimetic taken at region A of Figure 1;
FIGS. 3 to 9 are schematic views illustrating a method of manufacturing the neurovascular unit-on-chip of FIG.
후술하는 본 발명에 대한 상세한 설명은, 본 발명이 실시될 수 있는 특정 실시 예를 예시로서 도시하는 첨부 도면을 참조한다. 이들 실시 예는 당업자가 본 발명을 실시할 수 있기에 충분하도록 상세히 설명된다. 본 발명의 다양한 실시 예는 서로 다르지만 상호 배타적일 필요는 없음이 이해되어야 한다. 예를 들어, 여기에 기재되어 있는 특정 형상, 구조 및 특성은 일 실시 예에 관련하여 본 발명의 정신 및 범위를 벗어나지 않으면서 다른 실시 예로 구현될 수 있다. 또한, 각각의 개시된 실시예 내의 개별 구성요소의 위치 또는 배치는 본 발명의 정신 및 범위를 벗어나지 않으면서 변경될 수 있음이 이해되어야 한다. 따라서, 후술하는 상세한 설명은 한정적인 의미로서 취하려는 것이 아니며, 본 발명의 범위는, 적절하게 설명된다면, 그 청구항들이 주장하는 것과 균등한 모든 범위와 더불어 첨부된 청구항에 의해서만 한정된다. 도면에서 유사한 참조부호는 여러 측면에 걸쳐서 동일하거나 유사한 기능을 지칭하며, 길이 및 면적, 두께 등과 그 형태는 편의를 위하여 과장되어 표현될 수도 있다.The following detailed description of the invention refers to the accompanying drawings, which illustrate, by way of illustration, specific embodiments in which the invention may be practiced. These embodiments are described in sufficient detail to enable those skilled in the art to practice the invention. It should be understood that the various embodiments of the present invention are different, but need not be mutually exclusive. For example, certain features, structures, and characteristics described herein may be implemented in other embodiments without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention in connection with one embodiment. It is also to be understood that the position or arrangement of the individual components within each disclosed embodiment may be varied without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention. The following detailed description is, therefore, not to be taken in a limiting sense, and the scope of the present invention is to be limited only by the appended claims, along with the full scope of equivalents to which such claims are entitled, if properly explained. In the drawings, like reference numerals refer to the same or similar functions throughout the several views, and length and area, thickness, and the like may be exaggerated for convenience.
이하에서는, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 본 발명을 용이하게 실시할 수 있도록 하기 위하여, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예들에 관하여 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 상세히 설명하기로 한다.Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings, so that those skilled in the art can easily carry out the present invention.
도 1은 본 발명에 따른 신경혈관단위-온-칩을 개략적으로 보여주는 사시도이고, 도 2는 도 1의 A 영역에서 취해진 세포외기질 모사 물질을 개략적으로 보여주는 단면도이다.FIG. 1 is a perspective view schematically showing a neurovascular unit-on-chip according to the present invention, and FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view schematically showing an extracellular matrix mimetic material taken in region A of FIG.
도 1 및 도 2를 참조하면, 본 발명에 따르는 신경혈관 단위-온-칩(100)은 기판(10), 세포외기질(extracellular matrix; ECM) 모사 물질(70) 및 복수의 채널(75)을 포함한다. 상기 기판(10)은 중앙 영역에서 상부 면(US)을 관통하여 상부 면(US)으로부터 하부 면(LS)을 향해 연장되도록 하부 면(LS) 및 상부 면(US) 사이에 위치되는 셀 고정 웰(cell fixing well, 20)에 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)을 안착시킨다.1 and 2, a neurovascular unit-on-
상기 기판(10)은, 유리(glass)를 포함하는 투명 세라믹류, 폴리디메틸실록세인(PolyDiMethylSiloxane; PDMS)과 에코플렉스(ecoflex) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 실리콘고무류, 폴리스티렌(polystyrene), 폴리메틸메타크릴레이트(polymethylmethacrylate), 폴리프로필렌(polypropylene), 폴리카보네이트(polycarbonate)와 폴리우레탄(polyurethane) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 엔지니어링 플라스틱류, 투명 세라믹류, 실리콘고무류와 엔지니어링 플라스틱류 중 적어도 두 개를 포함하는 혼합물, 투명 세라믹류의 화학적 변형체, 실리콘고무류의 화학적 변형체, 엔지니어링 플라스틱류의 화학적 변형체, 또는 투명 세라믹류의 화학적 변형체, 실리콘고무류의 화학적 변형체와 엔지니어링 플라스틱류의 화학적 변형체 중 적어도 두 개를 포함하는 혼합물을 포함할 수 있다.The
상기 기판(10)과 셀 고정 웰(20)은 사각 형상으로 이루어져 제1 측벽(WS1)과 제2 측벽(WS2)을 각각 갖는다. 상기 제1 측벽(WS1)은 기판(10)의 두께 방향으로 제2 측벽(WS2)보다 큰 높이를 갖는다. 상기 제1 측벽(WS1)과 제2 측벽(WS2)은 상부 면(US)과 각을 이루면서 상부 면(US)과 접촉되어 서로 마주본다. 상기 세포외기질(ECM) 모사 물질(70)은 반 고체 상태(gel)이고 도 2에 도시된 바와 같이 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 함유한다. 바람직하게는, 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 뉴런(neuron, 92), 미세아교세포(microglia, 94), 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95) 및 주피세포(pericyte, 96)를 포함한다.The
일 예로써, 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 뉴런(neuron, 92), 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell, 93), 미세아교세포(microglia, 94), 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95) 및 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 하나 이상을 포함할 수 있으며, 본 발명에 따른 신경혈관단위-온-칩(100)을 이용할 경우, 상기 신경혈관단위-온-칩(100)은 위에서 기술한 5가지 종류의 뇌조직 세포들을 동시에 공배양 할 수 있다.As an example, the plural kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells are divided into
뇌질환 치료제의 개발을 위한 효능분석 및 안정성 분석을 위해 사용되는 세포는 체외에서 배양된 단일 종류의 뇌세포를 사용하는 것이 대부분이었으며, 2~3 종류의 세포를 함께 사용하는 경우에도 2차원적으로 배양된 뇌세포를 대상으로 하는 경우가 다반사였다. 최근에는 단일 종류, 또는 2-3 종류의 세포를 작은 덩어리(spheroid) 모양으로 3차원 배양하는 기술이 개발되어 사용된다.Most of the cells used for efficacy analysis and stability analysis for the development of therapeutic agents for brain diseases use a single type of brain cell cultured in vitro, and even when two or three kinds of cells are used together, The cultured brain cells were subject to a variety of cases. Recently, a technique of three-dimensionally culturing a single type, or 2-3 kinds of cells in the form of a small globe (spheroid) has been developed and used.
한편, 상기 신경혈관단위-온-칩(100)은 뇌미세혈관내피세포(brain microvessel endothelial cell lining, 91), 뉴런(neuron, 92), 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell, 93), 미세아교세포(microglia, 94), 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95) 및 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)로 이루어진 군 중에서 선택되는 하나 이상의 세포를 3차원 형태로 배양할 수 있는 효과가 있으며, 상기 세포들(91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96)은 인간유래의 뇌조직으로부터 수득하여 사용할 수 있다.On the other hand, the neurovascular unit-on-
뇌를 구성하고 있는 뇌조직 내 존재하는 세포의 한 종류로써, 상기 뉴런(neuron, 92)은 신경계를 이루는 단위로 신경세포를 일컫는다. 상기 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell, 93)는 자기 재생산이 가능하고 신경계통 세포로의 분화능을 가진 세포이다. 또한 상기 미세아교세포(microglia, 94)는 중배엽에서 유래한 중추 신경계의 신경아교세포, 소교세포라고도 하며 조직 안에서 물질의 운반, 파괴, 제거를 담당하는 식세포 작용을 하고, 중추 신경계의 조직을 지지하는 역할을 할 뿐만 아니라 신경세포에 필요한 물질을 공급하고 신경 세포의 활동에 적합한 화학적 환경을 조성하는 기능을 한다.As a kind of cells existing in the brain tissue constituting the brain, the neuron (92) refers to a nerve cell as a unit constituting the nervous system. The neural stem cell (93) is a cell capable of self-renewal and capable of differentiating into a neural lineage cell. Also, the microglia (94) are called neuroglial cells and microglia of the central nervous system derived from mesodermal lobe. They act as phagocytic cells responsible for transporting, destroying and removing substances in the tissues, and support the tissues of the central nervous system But also supplies the necessary substances to the nerve cells and functions to create a chemical environment suitable for the activity of the nerve cells.
또한, 상기 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95)는 신경조직을 지지하는 신경아교를 이루는 세포중 하나로서 아스트로사이트 또는 성상교세포라고도 하며, 세포체가 작고 여러 방향으로 갈라져 나가는 돌기를 가지고 있으며 뉴런의 구조와 대사를 돕는 역할을 한다. 상기 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)는 모세혈관벽은 편평한 내피세포만으로 이루어지고 그 주위를 감싸는 명료한 평활근층이나 결합조직층이 없으며 내피세포의 기저막층에는 산재성으로 결합조직성 세포가 나타나는데 이 세포가 혈관주위세포로서, 식작용을 하는 것으로 알려져 있다.In addition, astrocyte (95) is one of the cells forming the glial glue which supports the nerve tissue. It is also called astrocytes or astrocytes. It has a small cell body and protrudes in various directions, and its structure and metabolism It helps. The peripheral blood cells (pericyte) 96 are composed of only flat endothelial cells, and there is no clear smooth muscle layer or connective tissue layer surrounding the capillary wall, and connective tissue cells are scattered in the basement membrane layer of endothelial cells. As perivascular cells, it is known to cause phagocytosis.
이상에서 기술한 세포들(92, 93, 94, 95, 96)은 뇌조직 내에 존재하는 세포들로서 뇌 안에서 3차원적으로 존재하고 있으며, 상기 신경혈관단위-온-칩(100)은 혈뇌장벽을 포함하는 생체내 뇌조직을 모방할 수 있도록 이들 뇌조직세포들(92, 93, 94, 95, 96)을 체외에서 성공적으로 공배양할 수 있음을 확인하였다.
여기서, 세포배양이 세포 생물학, 조직엔지니어링, 바이오 메디컬 엔지니어링, 의약품 개발을 위한 약물 동태학 등에서 매우 중요한 단계로서, 시험관 내 세포 배양은 다양한 세포를 다량으로 배양하는 것을 가능하게 한다. 그러나 이 같이 시험관 내 배양된 세포가 생체 내에서 성장된 세포와는 동일하지 않는데, 이는 생물학적 시스템 환경이 체내와 체외가 상이하기 때문이다.Here, cell culture is a very important step in cell biology, tissue engineering, biomedical engineering, pharmacokinetics for drug development, etc. In vitro cell culture enables a large amount of various cells to be cultured. However, such in vitro cultured cells are not identical to cells grown in vivo, because the biological system environment is different between the body and the in vitro.
또한, 같은 조직 또는 같은 장기에서 유래된 서로 다른 세포들을 함께 배양하는 공배양은 배양하고자 하는 세포들이 잘 생존하면서 세포들이 가지고 있는 고유의 활성을 그대로 유지할 수 있어야 하는데, 서로 다른 세포들을 함께 배양할 경우 그 조건을 만족시키기 위한 조건을 확립하는 것이 쉽지 않다.In addition, co-culture in which different cells derived from the same tissue or the same organs are co-cultured should be able to maintain the intrinsic activity of the cells while the cells to be cultured are alive well, It is not easy to establish a condition for satisfying the condition.
그러나 본 발명은 다양한 종류의 뇌조직세포를 혈뇌장벽을 포함하는 3차원의 뇌조직과 유사하도록 함께 공배양할 수 있는 조건을 조성해 준다. 또한, 본 발명에 따른 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)은 세포외기질을 동일하게 또는 유사하게 구현할 수 있는 물질로서 이에 제한되지는 않으나, 콜라겐, 피브로넥틴, 피브린, 피브리노겐, 엘라스틴, 히알루론산, 프로테오글리칸, 라미닌, 헤파린 설페이트, 콘드로틴 설페이트, 케라탄 설페이트 및 마트리젤 (Matrigel) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 세포외기질, 알지네이트, 폴리에틸렌글라이콜, 실리콘 하이드로젤, 폴리아크릴아마이드, 폴리데틸렌옥사이드, 폴리피롤리딘, 글리코사미노글리칸 및 폴리헤마 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 하이드로젤, 세포외기질과 상기 하이드로젤의 혼합물, 세포외기질의 화학적 변형체, 하이드로젤의 화학적 변형체, 또는 세포외기질의 화학적 변형체와 하이드로젤의 상기 화학적 변형체의 혼합물을 포함할 수 있다.However, the present invention provides a condition in which various types of brain tissue cells can be co-cultured so as to resemble three-dimensional brain tissue including a blood-brain barrier. In addition, the extracellular matrix
상기 복수의 채널(75)은 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)을 관통하여 형성된다. 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)은 하나의 채널(75)을 한정할 수 있다. 상기 복수의 채널(75)은 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에서 평행하게 위치되지만, 이에 한정되지 않는다. 상기 복수의 채널(75)은 도 9의 배양액(88)을 관류시킬 수 있다. 각 채널(75)의 내벽에는 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)이 형성되어 있다. 여기서, 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)은 채널(75)의 외벽에 또는 채널(75)의 주변에 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 함유한다. 이 때에, 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)은 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에 공배양되는 별아교세포(95) 및 혈관주위세포(96)와 함께 혈뇌 장벽(Blood Brain Barrier; BBB)을 형성하고 있다.The plurality of
상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)은 채널(75)의 내벽을 따라 긴밀하게 위치되어 채널(75)의 내벽을 피복하거나 충분히 덮는다. 한편, 상기 기판(10)은 채널(75)과 동일 개수로 이루어지는 통로(50)를 포함한다. 상기 통로(50)는 셀 고정 웰(20)의 양 측부에서 제1 통로(35)와 제2 통로(45)로 분리되어 기판(10)을 관통하며 채널(75)과 유체적으로 연통되어 있다.The brain microvascular
상기 제1 통로(35)와 제2 통로(45)는 제1 측벽(WS1)에서 개구된다. 상술한 바를 고려하면, 상기 신경혈관 단위-온-칩(100)은 기판(10), 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)과 복수의 채널(75)을 구비하여 복수의 채널(75)을 통해 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들과 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)을 접촉시켜 인간 뇌의 혈뇌 장벽(Blood Brain Barrier; BBB)과, 인간 뇌에서 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)을 포함하는 신경혈관단위(NeuroVascular Unit; NVU)의 구조를 모사한다.The
상기 신경혈관단위(NeuroVascular Unit; NVU)는 혈뇌장벽(BBB), 뉴런(neuron, 92), 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell, 93) 및 미세아교세포(microglia, 94)를 바탕으로 구현된다. 또한, 상기 채널(75)의 외벽이 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에 접촉함으로써, 상기 신경혈관 단위-온-칩(100)은 인간 뇌에서 혈뇌장벽(BBB)을 포함한 신경혈관단위(NVU)를 모사하는 3차원 공배양을 가능하게 한다.The neurovascular unit (NVU) is implemented based on the BBB,
또한, 상기 기판(10)과 채널(75)의 접촉을 최소화해서, 시험 대상 약물(도면에 미 도시)이 기판(10)에 흡착되어 생체내 기작과 다른 양상을 보이는 것을 피할 수 있다.In addition, it is possible to minimize the contact between the
도 3 내지 도 9는 도 1의 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법을 설명하는 개략도이다.FIGS. 3 to 9 are schematic views illustrating a method of manufacturing the neurovascular unit-on-chip of FIG.
도 3 내지 도 9를 참조하면, 본 발명에 따른 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법은 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 함유하는 반고체(gel) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(도 7의 70)을 관통하는 채널(도 7의 75)을 형성하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다. 이 경우에, 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)은, 콜라겐, 피브로넥틴, 피브린, 피브리노겐, 엘라스틴, 히알루론산, 프로테오글리칸, 라미닌, 헤파린 설페이트, 콘드로틴 설페이트, 케라탄 설페이트 및 마트리젤 (Matrigel) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 세포외기질, 알지네이트, 폴리에틸렌글라이콜, 실리콘 하이드로젤, 폴리아크릴아마이드, 폴리데틸렌옥사이드, 폴리피롤리딘, 글리코사미노글리칸 및 폴리헤마 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 하이드로젤, 세포외기질과 하이드로젤의 혼합물, 세포외기질의 화학적 변형체, 하이드로젤의 화학적 변형체, 또는 세포외기질의 화학적 변형체와 하이드로젤의 화학적 변형체의 혼합물을 포함할 수 있다.3 to 9, a method of manufacturing a neurovascular unit-on-chip according to the present invention includes the steps of: preparing a plurality of kinds of extracellular matrix mimetics in a gel state containing human- 70 of FIG. 7) that pass through the channels 70 (see FIG. 7). In this case, the extracellular matrix mimetic 70 may be at least one of collagen, fibronectin, fibrin, fibrinogen, elastin, hyaluronic acid, proteoglycans, laminin, heparin sulfate, conoptotin sulfate, keratan sulfate and Matrigel. A hydrogel comprising at least one of alginate, polyethylene glycol, silicone hydrogel, polyacrylamide, polydehyylene oxide, polypyrrolidine, glycosaminoglycan and polyhema, an extracellular matrix comprising one, A mixture of a substrate and a hydrogel, a chemical modification of an extracellular matrix, a chemical modification of a hydrogel, or a chemical modification of an extracellular matrix and a chemical modification of a hydrogel.
상기 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계는, 우선적으로, 평탄한 형상으로 이루어져 상하로 마주보는 하부 면(LS) 및 상부 면(US)과 함께 하부 면(LS) 및 상부 면(US)을 이어주는 제1 측벽(WS1), 상부 면(US)의 중앙 영역에서 상부 면(US)을 관통하여 상부 면(US)으로부터 하부 면(LS)을 향해 연장하도록 하부 면(LS) 및 상부 면(US) 사이에 제2 측벽(WS2)으로 한정되는 셀 고정 웰(20), 그리고 셀 고정 웰(20) 주변에서 적어도 하나의 통로(50)를 포함하는 기판을 준비하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The step of forming the
상기 기판(10)은, 유리(glass)를 포함하는 투명 세라믹류, 폴리디메틸실록세인(PolyDiMethylSiloxane; PDMS)과 에코플렉스(ecoflex) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 실리콘고무류, 폴리스티렌(polystyrene), 폴리메틸메타크릴레이트(polymethylmethacrylate), 폴리프로필렌(polypropylene), 폴리카보네이트(polycarbonate)와 폴리우레탄(polyurethane) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 엔지니어링 플라스틱류, 투명 세라믹류, 실리콘고무류와 엔지니어링 플라스틱류 중 적어도 두 개를 포함하는 혼합물, 투명 세라믹류의 화학적 변형체, 실리콘고무류의 화학적 변형체, 엔지니어링 플라스틱류의 화학적 변형체, 또는 투명 세라믹류의 화학적 변형체, 실리콘고무류의 화학적 변형체와 엔지니어링 플라스틱류의 화학적 변형체 중 적어도 두 개를 포함하는 혼합물을 포함할 수 있다.The
상기 통로(50)는 셀 고정 웰(20)의 양 측부에 제1 통로(35)와 제2 통로(45)로 분리되어 형성될 수 있다. 상기 제1 통로(35)와 제2 통로(45)는 기판(10)을 관통하여 기판(10)의 제1 측벽(WS1), 그리고 제1 측벽(WS1)과 마주보는 셀 고정 웰(20)의 제2 측벽(WS2)에서 개구된다. 상기 제1 통로(35)와 제2 통로(45)는 셀 고정 웰(20)을 통해 일직선으로 마주하도록 기판(10)에 위치된다.The
상기 제1 통로(35)와 제2 통로(45)의 각각은 제1 측벽(WS1)과 제2 측벽(WS2)에 유입구(IP) 및 유출구(OP)를 가질 수 있다. 상기 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계는, 제1 통로(35), 셀 고정 웰(20)과 제2 통로(45)에 마이크로니들(60)을 삽입하는 단계 및 반액체(sol) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(도면에 미 도시)을 셀 고정 웰(20)에 채우는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다. 이 경우에, 상기 마이크로니들(60)은 제1 방향(D1)을 따라 제1 통로(35)를 지나 셀 고정 웰(20)을 경유하여 제2 통로(45)에 삽입될 수 있다.Each of the
상기 반액체(sol) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질은 셀 고정 웰(20)에서 마이크로니들(60)을 따라 위치하여 마이크로니들(60)과 접촉하고 마이크로니들(60)을 둘러싸서 마이크로니들(60)을 덮을 수 있다. 이 경우에, 상기 반액체 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질 내에 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들이 함유되어 있는데, 바람직하게는, 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 뉴런(neuron), 미세아교세포(microglia), 별아교세포(astrocyte) 및 혈관주위세포(pericyte)를 포함할 수 있다.The extracellular matrix mimic material in the semi-liquid state is located along the microneedle 60 in the cell fixation well 20 and contacts the
일 예로써, 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 뉴런(neuron), 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell), 미세아교세포(microglia), 별아교세포(astrocyte) 및 혈관주위세포(pericyte)로 이루어진 군에서 하나 이상을 포함할 수도 있다. 또한, 상기 채널(70)을 형성하는 단계는, 반액체(sol) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질을 경화하여 반고체(gel) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)로 변환하는 단계, 및 반고체 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)로부터 마이크로니들(60)을 제거하여 반고체 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)을 관통하는 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.For example, the plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells are divided into a group consisting of neurons, neural stem cells, microglia, astrocyte, and pericyte And may include one or more. In addition, the step of forming the
상기 반고체(gel) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)은 반액체(sol) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질에 소정 온도의 열을 가해서 형성될 수 있다. 상기 마이크로니들(60)은 제2 방향(D2)을 따라 기판(10)의 제2 통로(45)를 지나 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)의 채널(75)을 경유하여 기판(10)의 제1 통로(35)로부터 분리될 수 있다. 상기 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계가 완료된 후에, 상기 채널(75)의 내벽에 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)을 형성하는 단계가 수행될 수 있다.The extracellular matrix
상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)을 형성하는 단계는, 채널(75)에 뇌혈관내피 세포(brain endothelial cell, 84)를 주입하여 채널(75)의 내벽에 뇌혈관내피 세포(84)를 고정하는 단계; 및 뇌혈관내피 세포가 포함된 배양액(88)을 채널(75)에 유입시키면서 배양액(88)을 채널(75)의 내벽에 고정된 뇌혈관내피 세포(84)에 접촉시켜 채널(75)의 내벽을 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)으로 피복시키는 단계를 포함할 수 있다. 상기 배양액(88)은 채널(75)의 내벽에서 뇌혈관내피 세포와 채널(75)의 외벽에서 반 고체 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)을 통해 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 공배양시킬 수 있다.In the step of forming the brain microvascular
상기 뇌혈관내피 세포(83)의 고정은 제1 흐름선(F1)을 따라 기판(10)의 제1 통로(35), 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)의 채널(75)과 기판(10)의 제2 통로(45)에 뇌혈관내피 세포 주입액을 흘려 보내고, 뇌혈관내피 세포 주입액의 흐름 동안 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)의 채널(75)의 내벽에 뇌혈관내피 세포(84)를 드문드문 도 8과 같이 부착시켜 수행될 수 있다.The fixation of the cerebral blood vessel endothelial cells 83 is performed along the first flow line F1 with the
이 경우에, 상기 배양액(88)은 제2 흐름선(F2)을 따라 기판(10)의 제1 통로(35), 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)의 채널(75)과 기판(10)의 제2 통로(45), 그리고 기판(10)의 제2 통로(45), 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)의 채널(75)과 기판(10)의 제1 통로(35)에 반복적으로 흘려 보내질 수 있다. 상기 배양액(88)은 제2 흐름선(F2)을 따라 기판(10)과 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에 흐르는 동안 채널(75)의 내벽에 드문 드문 부착된 도 8의 뇌혈관내피 세포(84)를 도 9와 같이 증식, 배양 또는 성장시켜 뇌혈관내피 세포(84)를 이용하여 채널(75)의 내벽에 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)을 도 1과 같이 형성할 수 있다.In this case, the
상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)은 채널(75)의 내벽을 따라 위치되어 채널(75)의 내벽을 덮는다. 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)이 형성된 후에, 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)과 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 이용하여 채널(75)을 통해 인간 뇌의 혈뇌 장벽(Blood Brain Barrier; BBB)과, 인간 뇌에서 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)을 포함하는 신경혈관단위(NeuroVascular Unit; NVU)를 모사하는 단계가 수행된다. 여기서, 상기 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)과 신경혈관단위(NVU)의 모사 단계는 채널(75) 내에 배양액(88)의 흐름 동안 배양액(88)을 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에 접촉시켜 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에서 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 배양시키는 단계; 및 상기 채널(75)을 통해 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)에 접촉시키는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The brain microvascular
이 때에, 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 도 2에 도시된 바와 같이 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)에 접촉되는 뉴런(neuron, 92), 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell, 93), 미세아교세포(microglia, 94), 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95) 및 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)를 포함할 수 있다. 상기 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)은 뇌미세혈관내피 세포막(91), 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95)와 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)를 포함할 수 있다. 상기 신경혈관단위(NVU)는 혈뇌 장벽(BBB), 뉴런(neuron, 92), 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell, 93) 및 미세아교세포(microglia, 94)를 포함할 수 있다.At this time, the plural kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells are divided into a
이를 통해서, 상기 기판(10)과 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)은 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에서 구현되는 신경혈관단위(NVU)의 구조를 이용하여 신경혈관단위-온-칩(도 1의 100)을 구성하도록 수행될 수 있다. 여기서, 상기 채널(75)의 외벽이 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에 접촉함으로써 인간 뇌에서 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)을 포함하는 신경혈관단위(NVU)를 모사하는 3차원 공배양이 가능하고, 상기 기판(10)과 채널(75)의 접촉을 최소화하여 시험 대상 약물이 기판(10)에 흡착되어 생체내 기작과 다른 양상을 보이는 것을 피할 수 있다.The
10; 기판, 20; 셀 고정 웰
35; 제1 통로, 45; 제2 통로
50; 통로, 70; 세포외기질 모사 물질
75; 채널, 91; 뇌혈관내피 세포막
100; 신경혈관단위-온-칩, BBB; 혈뇌 장벽
LS; 하부 면, US; 상부 면
WS1; 제1 측벽, WS2; 제2 측벽10; A substrate, 20; Cell fixing well
35; A first passage, 45; The second passage
50;
75; Channel, 91; Cerebrovascular endothelial membrane
100; Neurovascular unit-on-chip, BBB; Blood-brain barrier
LS; Lower surface, US; Upper surface
WS1; A first side wall, WS2; The second side wall
Claims (25)
Translated fromKorean상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)과 상기 적어도 하나의 채널(75)을 둘러싸며, 상기 적어도 하나의 채널(75)과 유체적으로 연통하도록 상기 적어도 하나의 채널(75)과 동일 개수로 이루어진 통로(50)를 가지는 기판(10)을 포함하고,
상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)은 상기 채널(75)의 외벽에 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 함유하고,
상기 채널(75)의 내벽에는 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(brain microvessel endothelial cell lining, 91)이 형성되고,
상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들과 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)은 상기 채널(75)을 통해 접촉되어 인간 뇌의 혈뇌 장벽(Blood Brain Barrier; BBB)과, 상기 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)을 포함하는 상기 인간 뇌의 신경혈관단위(NeuroVascular Unit; NVU)를 모사하고,
상기 기판(10)은 중앙 영역에서 상부 면(US)을 관통하여 상기 상부 면(US)으로부터 하부 면(LS)을 향해 소정 깊이로 연장되도록 상기 하부 면(LS) 및 상기 상부 면(US) 사이에 위치되는 셀 고정 웰(cell fixing well, 20)에 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)을 안착시키는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩(neurovascular unit-on-a-chip; NVU-on-a-chip).At least one channel 75 through which an extracellular matrix (ECM) mimetic material 70 in a semi-solid state and the extracellular matrix mimetic material 70 pass and a culture liquid is perfused; And
A channel (75) surrounding said extracellular matrix mimic material (70) and said at least one channel (75) and in fluid communication with said at least one channel (75) (10) having a substrate (50)
The extracellular matrix mimetic material 70 contains a plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells on the outer wall of the channel 75,
A brain microvessel endothelial cell lining 91 is formed on the inner wall of the channel 75,
The plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells and the brain microvascular endothelial cell membrane 91 are in contact with each other through the channel 75 to form a blood brain barrier (BBB) (NVU) of the human brain, which contains the neurovascular unit (NVU)
The substrate 10 has a central region between the lower surface LS and the upper surface US so as to extend through the upper surface US to a predetermined depth from the upper surface US toward the lower surface LS. Wherein the neurovascular unit-on-chip (NVU-on-chip) is placed on a cell fixing well (20) -a-chip).
상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)은,
콜라겐, 피브로넥틴, 피브린, 피브리노겐, 엘라스틴, 히알루론산, 프로테오글리칸, 라미닌, 헤파린 설페이트, 콘드로틴 설페이트, 케라탄 설페이트 및 마트리젤 (Matrigel) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 세포외기질,
알지네이트, 폴리에틸렌글라이콜, 실리콘 하이드로젤, 폴리아크릴아마이드, 폴리데틸렌옥사이드, 폴리피롤리딘, 글리코사미노글리칸 및 폴리헤마 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 하이드로젤,
상기 세포외기질과 상기 하이드로젤의 혼합물,
상기 세포외기질의 화학적 변형체,
상기 하이드로젤의 화학적 변형체, 또는
상기 세포외기질의 상기 화학적 변형체와 상기 하이드로젤의 상기 화학적 변형체의 혼합물을 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩.The method according to claim 1,
The extracellular matrix mimetic 70 may be, for example,
An extracellular matrix comprising at least one of collagen, fibronectin, fibrin, fibrinogen, elastin, hyaluronic acid, proteoglycan, laminin, heparin sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfate and Matrigel,
Hydrogels comprising at least one of alginate, polyethylene glycol, silicone hydrogel, polyacrylamide, polyphenylene oxide, polypyrrolidine, glycosaminoglycan and polyhema,
A mixture of the extracellular matrix and the hydrogel,
Chemical modifications of the extracellular matrix,
A chemical modification of the hydrogel, or
A neurovascular unit-on-chip comprising a mixture of said chemical modification of said extra-cellular quality and said chemical modification of said hydrogel.
상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 뉴런(neuron, 92), 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell, 93), 미세아교세포(microglia, 94), 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95) 및 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 하나 이상을 포함하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩.The method according to claim 1,
The plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells include neurons 92, neural stem cells 93, microglia 94, astrocytes 95 and pericytes, 96). ≪ / RTI >
상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 뉴런(neuron, 92), 미세아교세포(microglia, 94), 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95) 및 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)를 포함하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩.The method according to claim 1,
The plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells are divided into a neurovascular unit-on which includes neurons 92, microglia 94, astrocyte 95 and pericyte 96 -chip.
상기 혈뇌장벽(BBB)은 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91), 상기 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95)와 상기 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)를 포함하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩.The method of claim 3,
The cerebellum barrier (BBB) comprises the brain microvascular endothelial cell membrane (91), astrocyte (95) and pericyte (96) pericyte.
상기 신경혈관단위는 상기 혈뇌장벽(BBB), 상기 뉴런(neuron, 92), 상기 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell, 93)와 상기 미세아교세포(microglia, 94)를 포함하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩.6. The method of claim 5,
The neurovascular unit is a neurovascular unit-on-chip (BBB) comprising the BBB, the neuron 92, the neural stem cell 93 and the microglia 94 .
상기 기판(10)은,
유리(glass)를 포함하는 투명 세라믹류,
폴리디메틸실록세인(PolyDiMethylSiloxane; PDMS)과 에코플렉스(ecoflex) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 실리콘고무류,
폴리스티렌(polystyrene),폴리메틸메타크릴레이트(polymethylmethacrylate), 폴리프로필렌(polypropylene),폴리카보네이트(polycarbonate)와 폴리우레탄(polyurethane) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 엔지니어링 플라스틱류,
상기 투명 세라믹류, 상기 실리콘고무류와 상기 엔지니어링 플라스틱류 중 적어도 두 개를 포함하는 혼합물,
상기 투명 세라믹류의 화학적 변형체,
상기 실리콘고무류의 화학적 변형체,
상기 엔지니어링 플라스틱류의 화학적 변형체, 또는
상기 투명 세라믹류의 상기 화학적 변형체, 상기 실리콘고무류의 상기 화학적 변형체와 상기 엔지니어링 플라스틱류의 상기 화학적 변형체 중 적어도 두 개를 포함하는 혼합물을 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩.The method according to claim 1,
The substrate (10)
Transparent ceramics including glass,
Silicone rubbers containing at least one of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and ecoflex,
Engineering plastics including at least one of polystyrene, polymethylmethacrylate, polypropylene, polycarbonate, and polyurethane,
A mixture comprising the transparent ceramics, the silicone rubber and at least two of the engineering plastics,
Chemical transformations of said transparent ceramics,
Chemical modifications of said silicone rubbers,
A chemical modification of said engineering plastics, or
A mixture comprising at least two of said chemical transformations of said transparent ceramics, said chemical transformations of said silicone rubbers and said chemical transformations of said engineering plastics.
상기 통로(50)는 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)의 양 측부에서 제1 통로(35) 및 제2 통로(45)로 분리되어 상기 기판(10)을 관통하는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩.The method according to claim 1,
Characterized in that the passage (50) is divided into a first passage (35) and a second passage (45) on both sides of the cell fixing well (20) and penetrates the substrate (10) -chip.
상기 기판(10)과 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)은 사각 형상으로 이루어져 제1 측벽(WS1)과 제2 측벽(WS2)을 각각 가지고,
상기 제1 측벽(WS1)은 상기 기판(10)의 두께 방향으로 상기 제2 측벽(WS2)보다 큰 높이를 가지고,
상기 제1 측벽(WS1)과 상기 제2 측벽(WS2)은 상기 상부 면(US)과 각을 이루면서 상기 상부 면(US)과 접촉되어 서로 마주보고,
상기 제1 통로(35) 및 상기 제2 통로(45)의 각각은 상기 기판(10)의 제1 측벽(WS1), 그리고 상기 제1 측벽(WS1)과 마주보는 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)의 제2 측벽(WS2)에서 개구되어 상기 제1 측벽(WS1)과 상기 제2 측벽(WS2)에 유입구(IP) 및 유출구(OP)를 가지는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩.9. The method of claim 8,
The substrate 10 and the cell fixing well 20 have a rectangular shape and have a first side wall WS1 and a second side wall WS2,
The first sidewall WS1 has a height greater than the second sidewall WS2 in the thickness direction of the substrate 10,
The first sidewall WS1 and the second sidewall WS2 form an angle with the upper surface US and come into contact with the upper surface US to face each other,
Each of the first passage 35 and the second passage 45 has a first side wall WS1 of the substrate 10 and a second side wall WS1 of the cell fixing well 20 facing the first side wall WS1. Wherein the first sidewall WS1 and the second sidewall WS2 are open at the second sidewall WS2 and have an inlet IP and an outlet OP at the first sidewall WS1 and the second sidewall WS2.
상기 채널(75)의 상기 외벽이 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에 접촉함으로써 상기 인간 뇌에서 상기 혈뇌장벽을 포함하는 상기 신경혈관단위를 모사하는 3차원 공배양이 가능하고, 상기 기판(10)과 상기 채널(75)의 접촉을 최소화하여 시험 대상 약물이 상기 기판(10)에 흡착되어 생체내 기작과 다른 양상을 보이는 것을 피할 수 있는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩.The method according to claim 1,
The outer wall of the channel 75 is in contact with the extracellular matrix mimetic material 70 so that three-dimensional co-cultivation is possible in which the neural blood vessel unit including the blood-brain barrier is simulated in the human brain. ) And the channel (75) is minimized so that the drug to be tested can be adsorbed on the substrate (10) to avoid the appearance of a different mechanism from the in vivo mechanism.
상기 채널(75)의 내벽에 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)을 형성하는 단계; 및
상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)과 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 이용하여 상기 채널(75)을 통해 인간 뇌의 혈뇌 장벽(Blood Brain Barrier; BBB)과, 상기 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)을 포함하는 상기 인간 뇌의 신경혈관단위(NeuroVascular Unit; NVU)를 모사하는 단계를 포함하고,
상기 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계는 평탄한 형상으로 이루어져 상하로 마주보는 하부 면(LS) 및 상부 면(US)과 함께 상기 하부 면(LS) 및 상기 상부 면(US)을 이어주는 제1 측벽(WS1), 상기 상부 면(US)의 중앙 영역에서 상기 상부 면(US)을 관통하여 상기 상부 면(US)으로부터 상기 하부 면(LS)을 향해 소정 깊이로 연장하도록 상기 하부 면(LS) 및 상기 상부 면(US) 사이에 제2 측벽(WS2)으로 한정되는 셀 고정 웰(20), 그리고 상기 셀 고정 웰(20) 주변에서 상기 채널(75)과 유체적으로 연통하도록 상기 채널(75)과 동일 개수로 이루어진 적어도 하나의 통로(50)를 포함하는 기판(10)을 준비하는 단계를 포함하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.Forming a channel (75) through the extracellular matrix (ECM) mimetic material (70) in a gel state containing a plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells;
Forming a microvascular endothelial cell membrane (91) on the inner wall of the channel (75); And
The blood brain barrier (BBB) and the blood-brain barrier (BBB) of the human brain are transmitted through the channel 75 using the brain microvascular endothelial cell membrane 91 and the plural kinds of human- (NVU) of the human brain, wherein the neurovascular unit (NVU)
The step of forming the channel 75 may be performed in a flat shape and may include a lower side LS and a upper side US and a first side wall connecting the lower surface LS and the upper surface US WS and a lower surface LS extending from the upper surface US toward the lower surface LS through the upper surface US in a central region of the upper surface US, A cell fixation well 20 defined by a second sidewall WS2 between the top surface US and a channel fixation well 20 in fluid communication with the channel 75 around the cell fixation well 20. [ Comprising the step of preparing a substrate (10) comprising at least one passage (50) of the same number.
상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)은,
콜라겐, 피브로넥틴, 피브린, 피브리노겐, 엘라스틴, 히알루론산, 프로테오글리칸, 라미닌, 헤파린 설페이트, 콘드로틴 설페이트, 케라탄 설페이트 및 마트리젤 (Matrigel) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 세포외기질,
알지네이트, 폴리에틸렌글라이콜, 실리콘 하이드로젤, 폴리아크릴아마이드, 폴리데틸렌옥사이드, 폴리피롤리딘, 글리코사미노글리칸 및 폴리헤마 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 하이드로젤,
상기 세포외기질과 상기 하이드로젤의 혼합물,
상기 세포외기질의 화학적 변형체,
상기 하이드로젤의 화학적 변형체, 또는
상기 세포외기질의 상기 화학적 변형체와 상기 하이드로젤의 상기 화학적 변형체의 혼합물을 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.12. The method of claim 11,
The extracellular matrix mimetic 70 may be, for example,
An extracellular matrix comprising at least one of collagen, fibronectin, fibrin, fibrinogen, elastin, hyaluronic acid, proteoglycan, laminin, heparin sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfate and Matrigel,
Hydrogels comprising at least one of alginate, polyethylene glycol, silicone hydrogel, polyacrylamide, polyphenylene oxide, polypyrrolidine, glycosaminoglycan and polyhema,
A mixture of the extracellular matrix and the hydrogel,
Chemical modifications of the extracellular matrix,
A chemical modification of the hydrogel, or
Wherein the composition comprises a mixture of the chemical modification of the extracellular matrix and the chemical modification of the hydrogel.
상기 통로(50)는 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)의 양 측부에 제1 통로(35)와 제2 통로(45)로 분리되어 형성되는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.12. The method of claim 11,
Wherein the passage (50) is divided into a first passage (35) and a second passage (45) on both sides of the cell fixing well (20).
상기 기판(10)은,
유리(glass)를 포함하는 투명 세라믹류,
폴리디메틸실록세인(PolyDiMethylSiloxane; PDMS)과 에코플렉스(ecoflex) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 실리콘고무류,
폴리스티렌(polystyrene),폴리메틸메타크릴레이트(polymethylmethacrylate), 폴리프로필렌(polypropylene), 폴리카보네이트(polycarbonate)와 폴리우레탄(polyurethane) 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 엔지니어링 플라스틱류,
상기 투명 세라믹류, 상기 실리콘고무류와 상기 엔지니어링 플라스틱류 중 적어도 두 개를 포함하는 혼합물,
상기 투명 세라믹류의 화학적 변형체,
상기 실리콘고무류의 화학적 변형체,
상기 엔지니어링 플라스틱류의 화학적 변형체, 또는
상기 투명 세라믹류의 상기 화학적 변형체, 상기 실리콘고무류의 상기 화학적 변형체와 상기 엔지니어링 플라스틱류의 상기 화학적 변형체 중 적어도 두 개를 포함하는 혼합물을 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.14. The method of claim 13,
The substrate (10)
Transparent ceramics including glass,
Silicone rubbers containing at least one of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and ecoflex,
Engineering plastics including at least one of polystyrene, polymethylmethacrylate, polypropylene, polycarbonate, and polyurethane,
A mixture comprising the transparent ceramics, the silicone rubber and at least two of the engineering plastics,
Chemical transformations of said transparent ceramics,
Chemical modifications of said silicone rubbers,
A chemical modification of said engineering plastics, or
A mixture comprising at least two of said chemical transformations of said transparent ceramics, said chemical transformations of said silicone rubbers and said chemical transformations of said engineering plastics. .
상기 제1 통로(35)와 상기 제2 통로(45)는 상기 기판(10)을 관통하여 상기 기판(10)의 제1 측벽(WS1), 그리고 상기 제1 측벽(WS1)과 마주보는 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)의 제2 측벽(WS2)에서 개구되는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.14. The method of claim 13,
The first passage 35 and the second passage 45 pass through the substrate 10 and are connected to the first side wall WS1 of the substrate 10 and the first side wall WS1, Is opened in the second sidewall (WS2) of the fixed well (20).
상기 제1 통로(35)와 상기 제2 통로(45)의 각각은 상기 제1 측벽(WS1)과 상기 제2 측벽(WS2)에 유입구(IP) 및 유출구(OP)를 가지는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.14. The method of claim 13,
Wherein each of the first passage 35 and the second passage 45 has an inlet IP and an outlet OP at the first sidewall WS1 and the second sidewall WS2. A method for manufacturing a blood vessel unit-on-chip.
상기 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계는
상기 제1 통로(35), 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)과 상기 제2 통로(45)에 마이크로니들(60)을 삽입하는 단계; 및
반액체(sol) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질을 상기 셀 고정 웰(20)에 채우는 단계를 더 포함하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.14. The method of claim 13,
The step of forming the channel (75)
Inserting the microneedles (60) into the first passageway (35), the cell fixation well (20) and the second passageway (45); And
Further comprising filling the cell fixation well (20) with an extracellular matrix mimic material in a semi-liquid (sol) state.
상기 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계는
상기 반액체(sol) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질을 경화하여 상기 반고체(gel) 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)로 변환하는 단계; 및
상기 반고체 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)로부터 상기 마이크로니들(60)을 제거하여 상기 반고체 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)을 관통하는 상기 채널(75)을 형성하는 단계를 더 포함하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.18. The method of claim 17,
The step of forming the channel (75)
Curing the semi-liquid (sol) extracellular matrix mimetic to convert it into the semi-solid state extracellular matrix mimetic 70; And
Further comprising removing the micro needle 60 from the semi-solid extracellular matrix mimetic material 70 to form the channel 75 through the semi-solid extracellular matrix mimetic material 70 A method of manufacturing a neurovascular unit-on-chip.
상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)을 형성하는 단계는,
상기 채널(75)에 뇌혈관내피 세포(brain endothelial cell, 84)를 주입하여 채널(75)의 상기 내벽에 상기 뇌혈관내피 세포(84)를 고정하는 단계; 및
뇌혈관내피 세포가 포함된 배양액(88)을 상기 채널(75)에 유입시키면서 상기 배양액(88)을 상기 채널(75)의 상기 내벽에 고정된 상기 뇌혈관내피 세포(84)에 접촉시켜 상기 채널(75)의 상기 내벽을 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)으로 피복시키는 단계를 포함하고,
상기 배양액(88)은 상기 채널(75)의 상기 내벽에서 상기 뇌혈관내피 세포(84)와 상기 채널(75)의 외벽에서 상기 반 고체 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)을 통해 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 공배양시키는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.12. The method of claim 11,
The step of forming the microvascular endothelial cell membrane (91)
Injecting a brain endothelial cell (84) into the channel (75) to fix the cerebral vascular endothelial cells (84) on the inner wall of the channel (75); And
A culture solution 88 containing cerebral vascular endothelial cells is introduced into the channel 75 while the culture solution 88 is contacted with the cerebral vascular endothelial cells 84 fixed to the inner wall of the channel 75, And coating the inner wall of the brain microvascular endothelial cell membrane (75) with the brain microvascular endothelial cell membrane (91)
The culture solution 88 is supplied to the cerebral blood vessel endothelial cells 84 and the outer wall of the channel 75 at the inner wall of the channel 75 through the semi-solid state extracellular matrix mimetic material 70, Wherein the human-derived brain tissue cells are co-cultured.
상기 혈뇌 장벽(BBB)과 신경혈관단위(NVU)의 모사 단계는,
상기 채널(75) 내에 상기 배양액(88)의 흐름 동안 상기 배양액(88)을 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에 접촉시켜 상기 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에서 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 공배양시키는 단계; 및
상기 채널(75)을 통해 상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들을 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91)에 접촉시키는 단계를 포함하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.20. The method of claim 19,
The step of simulating the BBB and neural vessel units (NVU)
Wherein the culture solution 88 is contacted with the extracellular matrix mimetic material 70 during the flow of the culture solution 88 in the channel 75 to form the extracellular matrix mimetic material 70, Co-culturing the cells; And
And contacting the plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells with the brain microvascular endothelial cell membrane (91) through the channel (75).
상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 뉴런(92), 신경줄기세포(93), 미세아교세포(94), 별아교세포(95) 및 혈관주위세포(96)로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 하나 이상을 포함하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.21. The method of claim 20,
The plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells include at least one selected from the group consisting of neurons 92, neural stem cells 93, microglia cells 94, astrocytic cells 95 and perivascular cells 96 A method of manufacturing a neurovascular unit-on-chip.
상기 복수 종류의 인간유래 뇌조직 세포들은 뉴런(92), 미세아교세포(94), 별아교세포(95) 및 혈관주위세포(96)를 포함하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.21. The method of claim 20,
Wherein the plurality of kinds of human-derived brain tissue cells include neurons (92), microglia cells (94), astrocytes (95), and perivascular cells (96).
상기 혈뇌장벽(BBB)은 상기 뇌미세혈관내피세포 막(91), 상기 별아교세포(astrocyte, 95)와 상기 혈관주위세포(pericyte, 96)를 포함하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.22. The method of claim 21,
Wherein the BBB comprises the brain microvascular endothelial cell membrane (91), astrocyte (95), and pericyte (96) pericyte.
상기 신경혈관단위는 상기 혈뇌장벽(BBB), 상기 뉴런(neuron, 92), 상기 신경줄기세포(neural stem cell, 93)와 상기 미세아교세포(microglia, 94)를 포함하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.24. The method of claim 23,
The neurovascular unit is a neurovascular unit-on-chip (BBB) comprising the BBB, the neuron 92, the neural stem cell 93 and the microglia 94 ≪ / RTI >
상기 채널(75)의 외벽이 상기 반 고체 상태의 세포외기질 모사 물질(70)에 접촉함으로써 상기 인간 뇌에서 상기 신경혈관단위를 모사하는 3차원 공배양이 가능하고, 기판(10)과 상기 채널(75)의 접촉을 최소화하여 시험 대상 약물이 상기 기판(10)에 흡착되어 생체내 기작과 다른 양상을 보이는 것을 피할 수 있는 것을 특징으로 하는 신경혈관단위-온-칩의 제조 방법.12. The method of claim 11,
The outer wall of the channel 75 contacts the semi-solid state extracellular matrix mimetic material 70 to enable the three-dimensional co-culture to simulate the neurovascular unit in the human brain, (75) is minimized so that the drug to be tested is adsorbed on the substrate (10) to avoid the appearance of a different mechanism from the in vivo mechanism.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170012464AKR101822784B1 (en) | 2016-01-21 | 2017-01-26 | NeuroVascular Unit(NVU)-On-a-Chip And Method Of Fabricating The Same |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160007354 | 2016-01-21 | ||
| KR1020170012464AKR101822784B1 (en) | 2016-01-21 | 2017-01-26 | NeuroVascular Unit(NVU)-On-a-Chip And Method Of Fabricating The Same |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160007354Division | 2016-01-21 | 2016-01-21 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20170087837Atrue KR20170087837A (en) | 2017-07-31 |
| KR101822784B1 KR101822784B1 (en) | 2018-01-30 |
| KR101822784B9 KR101822784B9 (en) | 2021-10-27 |
Family
ID=59419012
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170012464AActiveKR101822784B1 (en) | 2016-01-21 | 2017-01-26 | NeuroVascular Unit(NVU)-On-a-Chip And Method Of Fabricating The Same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101822784B1 (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114480122A (en)* | 2022-01-24 | 2022-05-13 | 中国人民解放军海军军医大学 | Establishment and application of a co-culture model of blood-brain barrier and glioma based on microfluidic chip |
| WO2022109319A1 (en)* | 2020-11-20 | 2022-05-27 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Novel tissue culture systems and reduced gravity culture method for the production of vascularized tissue |
| KR20220095066A (en)* | 2020-12-29 | 2022-07-06 | (주) 마이크로핏 | manufacturing method of 3D brain blood barrier structure of 3D brain blood barrier organ-on-a-chip using reverse rapid liquid printing and 3D brain blood barrier organ-on-a-chip comprising the same |
| WO2022145743A1 (en)* | 2020-12-29 | 2022-07-07 | (주) 마이크로핏 | Method for producing three-dimensional blood-brain barrier structure of blood-brain barrier organ-on-a-chip using reverse rapid liquid printing, and blood-brain barrier organ-on-a-chip comprising same |
| CN116478819A (en)* | 2023-06-20 | 2023-07-25 | 清华大学 | A microfluidic system for constructing a three-dimensional organ microenvironment model and its preparation method and application |
| KR20240102330A (en)* | 2022-12-26 | 2024-07-03 | 충북대학교 산학협력단 | NeuroVascular Unit(NVU)-On-a-Chip for analyzing brain cancer |
| CN118956598A (en)* | 2024-07-31 | 2024-11-15 | 国科宁波生命与健康产业研究院 | A blood-brain barrier-glioma organ chip and its preparation method and use |
| CN119859580A (en)* | 2025-01-14 | 2025-04-22 | 中国人民解放军总医院第四医学中心 | Multi-system microvascular co-culture microfluidic chip and preparation method thereof |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015116149A (en)* | 2013-12-18 | 2015-06-25 | 国立大学法人 東京大学 | Three-dimentional gel chip for observing interaction between microvasculature and tissue |
- 2017
- 2017-01-26KRKR1020170012464Apatent/KR101822784B1/enactiveActive
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022109319A1 (en)* | 2020-11-20 | 2022-05-27 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Novel tissue culture systems and reduced gravity culture method for the production of vascularized tissue |
| KR20220095066A (en)* | 2020-12-29 | 2022-07-06 | (주) 마이크로핏 | manufacturing method of 3D brain blood barrier structure of 3D brain blood barrier organ-on-a-chip using reverse rapid liquid printing and 3D brain blood barrier organ-on-a-chip comprising the same |
| WO2022145743A1 (en)* | 2020-12-29 | 2022-07-07 | (주) 마이크로핏 | Method for producing three-dimensional blood-brain barrier structure of blood-brain barrier organ-on-a-chip using reverse rapid liquid printing, and blood-brain barrier organ-on-a-chip comprising same |
| CN114480122A (en)* | 2022-01-24 | 2022-05-13 | 中国人民解放军海军军医大学 | Establishment and application of a co-culture model of blood-brain barrier and glioma based on microfluidic chip |
| KR20240102330A (en)* | 2022-12-26 | 2024-07-03 | 충북대학교 산학협력단 | NeuroVascular Unit(NVU)-On-a-Chip for analyzing brain cancer |
| WO2024144173A1 (en)* | 2022-12-26 | 2024-07-04 | 충북대학교 산학협력단 | Neurovascular unit-on-a-chip for brain tumor analysis |
| CN116478819A (en)* | 2023-06-20 | 2023-07-25 | 清华大学 | A microfluidic system for constructing a three-dimensional organ microenvironment model and its preparation method and application |
| CN116478819B (en)* | 2023-06-20 | 2023-09-26 | 清华大学 | A microfluidic system for constructing a three-dimensional organ microenvironment model and its preparation method and application |
| CN118956598A (en)* | 2024-07-31 | 2024-11-15 | 国科宁波生命与健康产业研究院 | A blood-brain barrier-glioma organ chip and its preparation method and use |
| CN119859580A (en)* | 2025-01-14 | 2025-04-22 | 中国人民解放军总医院第四医学中心 | Multi-system microvascular co-culture microfluidic chip and preparation method thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR101822784B1 (en) | 2018-01-30 |
| KR101822784B9 (en) | 2021-10-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101822784B1 (en) | NeuroVascular Unit(NVU)-On-a-Chip And Method Of Fabricating The Same | |
| Geraili et al. | Controlling differentiation of stem cells for developing personalized organ‐on‐chip platforms | |
| US20230015127A1 (en) | Device for in-vitro modelling in-vivo tissues of organs | |
| Zhang et al. | Organ-on-a-chip devices advance to market | |
| US10030219B2 (en) | Neurovascular unit(NVU)-on-a-chip and method of fabricating the same | |
| Harink et al. | Regeneration-on-a-chip? The perspectives on use of microfluidics in regenerative medicine | |
| Gupta et al. | Lab-on-a-chip devices as an emerging platform for stem cell biology | |
| US9618500B2 (en) | Vascular model, method for producing said model and use thereof | |
| US10744505B2 (en) | Microfluidic device for in vitro 3D cell culture experimentation | |
| US20090191631A1 (en) | 3-D petri-dish for the culture and studies of cells | |
| CN109804057A (en) | Cell culture apparatus and cell culture processes | |
| Webster et al. | Development of microfluidic devices for biomedical and clinical application | |
| NL2011895C2 (en) | Fluidic device and perfusion system for in vitro tissue reconstruction. | |
| FI131135B1 (en) | Microfluidic cell culture device and method for cell cultivation | |
| Zhang et al. | Cells in microfluidics | |
| KR20220165668A (en) | Microfluidic chip compiring tumor spheroid | |
| WO2018079866A1 (en) | Microfluidic chip for co-culturing cells | |
| EP4148117A1 (en) | Cell culture apparatus, methods for cell cultivation by using the same, cell culture incubator comprising the same, and uses of the cell culture apparatus | |
| KR102678639B1 (en) | Microfluid chip for spheroid or organoid and method for producing spheroid or organoid model using the same | |
| KR102744474B1 (en) | Microfluidic device for forming 3-dimensional tissue barrier | |
| Hsieh et al. | Applications of fabricated micro-and nanostructures in biomedicine | |
| PL240748B1 (en) | Magnetic-hydrodynamic microfluidic platform, method of its production and method of artificial tissue culture in a magnetic micropole | |
| KR20240052866A (en) | Cell culture device, cell culture method using the same, cell culture incubator including the same, and use of the cell culture device | |
| CN117957303A (en) | Cell culture device, cell culture method using the cell culture device, cell culture incubator including the cell culture device, and use of the cell culture device | |
| WO2020262656A1 (en) | Microfluidic device, method for producing same, and method for culturing three-dimensional tissue |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0107 | Divisional application | Comment text:Divisional Application of Patent Patent event date:20170126 Patent event code:PA01071R01D Filing date:20160121 Application number text:1020160007354 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20170216 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| AMND | Amendment | ||
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application | ||
| PE0601 | Decision on rejection of patent | Patent event date:20170925 Comment text:Decision to Refuse Application Patent event code:PE06012S01D Patent event date:20170216 Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event code:PE06011S01I | |
| AMND | Amendment | ||
| PX0901 | Re-examination | Patent event code:PX09011S01I Patent event date:20170925 Comment text:Decision to Refuse Application Patent event code:PX09012R01I Patent event date:20170516 Comment text:Amendment to Specification, etc. | |
| PX0701 | Decision of registration after re-examination | Patent event date:20171228 Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event code:PX07013S01D Patent event date:20171127 Comment text:Amendment to Specification, etc. Patent event code:PX07012R01I Patent event date:20170925 Comment text:Decision to Refuse Application Patent event code:PX07011S01I Patent event date:20170516 Comment text:Amendment to Specification, etc. Patent event code:PX07012R01I | |
| X701 | Decision to grant (after re-examination) | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20180122 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20180122 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20210222 Start annual number:4 End annual number:4 | |
| G170 | Re-publication after modification of scope of protection [patent] | ||
| PG1701 | Publication of correction | Patent event code:PG17011E01I Patent event date:20211021 Comment text:Request for Publication of Correction Publication date:20211027 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20220103 Start annual number:5 End annual number:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20230102 Start annual number:6 End annual number:6 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20240130 Start annual number:7 End annual number:7 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20241226 Start annual number:8 End annual number:8 |