KR20160121348A - Method and apparatus for estimating effective channel of functional near-infrared spectroscopy - Google Patents
Method and apparatus for estimating effective channel of functional near-infrared spectroscopyDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20160121348A KR20160121348AKR1020150079615AKR20150079615AKR20160121348AKR 20160121348 AKR20160121348 AKR 20160121348AKR 1020150079615 AKR1020150079615 AKR 1020150079615AKR 20150079615 AKR20150079615 AKR 20150079615AKR 20160121348 AKR20160121348 AKR 20160121348A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- channel
- channels
- blood flow
- effective
- classification
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription50
- 238000004497NIR spectroscopyMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription18
- 230000003727cerebral blood flowEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription51
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription39
- 230000007177brain activityEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription32
- 238000004611spectroscopical analysisMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription21
- 230000033001locomotionEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription12
- 238000007781pre-processingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 230000029058respiratory gaseous exchangeEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 230000017531blood circulationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription8
- 210000004761scalpAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription7
- 230000006266hibernationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 210000004556brainAnatomy0.000claimsdescription20
- 230000005059dormancyEffects0.000claimsdescription18
- 238000012706support-vector machineMethods0.000claimsdescription9
- 230000003247decreasing effectEffects0.000claimsdescription7
- 238000013507mappingMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000000059patterningMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 230000005021gaitEffects0.000description28
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description15
- 238000012549trainingMethods0.000description15
- 238000011282treatmentMethods0.000description13
- 102000001554HemoglobinsHuman genes0.000description10
- 108010054147HemoglobinsProteins0.000description10
- 210000003710cerebral cortexAnatomy0.000description10
- 208000006011StrokeDiseases0.000description9
- 230000004913activationEffects0.000description8
- 238000002560therapeutic procedureMethods0.000description7
- 238000002599functional magnetic resonance imagingMethods0.000description6
- 230000009467reductionEffects0.000description6
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description5
- 238000011156evaluationMethods0.000description5
- 210000000974brodmann areaAnatomy0.000description4
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description4
- 230000001054cortical effectEffects0.000description3
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description3
- 239000006185dispersionSubstances0.000description3
- 210000003128headAnatomy0.000description3
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000description3
- 230000001537neural effectEffects0.000description3
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description2
- 230000002490cerebral effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000007012clinical effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000000004hemodynamic effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000000691measurement methodMethods0.000description2
- 230000007659motor functionEffects0.000description2
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description2
- 238000004445quantitative analysisMethods0.000description2
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description2
- 238000005316response functionMethods0.000description2
- 206010017577Gait disturbanceDiseases0.000description1
- 230000001133accelerationEffects0.000description1
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000013459approachMethods0.000description1
- 238000013528artificial neural networkMethods0.000description1
- 230000036992cognitive tasksEffects0.000description1
- 239000003086colorantSubstances0.000description1
- 230000007585cortical functionEffects0.000description1
- 238000002567electromyographyMethods0.000description1
- 230000010482emotional regulationEffects0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000000284extractSubstances0.000description1
- 230000006872improvementEffects0.000description1
- 230000003902lesionEffects0.000description1
- 210000003141lower extremityAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000000337motor cortexAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000004118muscle contractionEffects0.000description1
- 238000001584occupational therapyMethods0.000description1
- 230000003647oxidationEffects0.000description1
- 238000007254oxidation reactionMethods0.000description1
- 230000002093peripheral effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000002600positron emission tomographyMethods0.000description1
- 210000000976primary motor cortexAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000011084recoveryMethods0.000description1
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description1
- 238000012552reviewMethods0.000description1
- 230000003238somatosensory effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000003068static effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000000638stimulationEffects0.000description1
- 230000002123temporal effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000001225therapeutic effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000004382visual functionEffects0.000description1
- 230000004584weight gainEffects0.000description1
- 235000019786weight gainNutrition0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/0059—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence
- A61B5/0082—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence adapted for particular medical purposes
- A61B5/0084—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence adapted for particular medical purposes for introduction into the body, e.g. by catheters
- A61B5/0086—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence adapted for particular medical purposes for introduction into the body, e.g. by catheters using infrared radiation
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/0059—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence
- A61B5/0075—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence by spectroscopy, i.e. measuring spectra, e.g. Raman spectroscopy, infrared absorption spectroscopy
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
- A61B5/026—Measuring blood flow
- A61B5/0261—Measuring blood flow using optical means, e.g. infrared light
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/103—Measuring devices for testing the shape, pattern, colour, size or movement of the body or parts thereof, for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/11—Measuring movement of the entire body or parts thereof, e.g. head or hand tremor or mobility of a limb
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/103—Measuring devices for testing the shape, pattern, colour, size or movement of the body or parts thereof, for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/11—Measuring movement of the entire body or parts thereof, e.g. head or hand tremor or mobility of a limb
- A61B5/1123—Discriminating type of movement, e.g. walking or running
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/7235—Details of waveform analysis
- A61B5/7264—Classification of physiological signals or data, e.g. using neural networks, statistical classifiers, expert systems or fuzzy systems
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Dentistry (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Fuzzy Systems (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Investigating Or Analysing Materials By Optical Means (AREA)
- Measuring Pulse, Heart Rate, Blood Pressure Or Blood Flow (AREA)
- Measurement Of The Respiration, Hearing Ability, Form, And Blood Characteristics Of Living Organisms (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 기능적 근적외선 분광법(fNIRS; Functional near-infrared spectroscopy)의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법 및 장치에 관한 것으로, 특히, 사람이 운동이나 인지와 관련된 작업을 수행할 때, 사람의 머리에 쓰는 형태로 착용된 기능적 근적외선 분광법 장치를 사용하여 측정된 사람의 대뇌피질의 혈류 정보로부터 뇌활성도를 획득함에 있어, 수행하고 있는 작업과 밀접히 관련성이 높은 유효한 측정 위치를 결정하기 위한 방법 및 장치에 관한 것이다.Field of the Invention [0002] The present invention relates to an effective positioning method and apparatus for measuring brain activity of functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), and more particularly, The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for determining an effective measurement position closely related to a task being performed in acquiring brain activity from blood flow information of a human cerebral cortex measured using a functional NIR spectroscopy apparatus will be.
뇌졸중 환자의 보행 재활 치료를 위해 주로 사용해왔던 고전적 재활 치료법은 정적인 상태에서 체중 부하나 체중 이동, 균형 훈련 등이 있다. 그러나, 이러한 치료법은 근육의 수축 양상 및 일반적 상태를 호전시키지만 치료 후에도 이상 보행이 계속 나타난다.Classical rehabilitation treatments that have been used mainly for the gait rehabilitation of stroke patients include weight gain, weight shift, and balance training in a static state. However, this therapy improves muscle contraction and general condition, but abnormal gait continues to appear after treatment.
최근에는 뇌졸중 환자의 보행 양상을 증진시키기 위한 재활 훈련으로 기능적 전기 자극, 트레드밀 보행 훈련, 로봇 보조 보행 치료 등이 새로운 치료적 접근법으로 이용되고 있다. 이러한 치료법을 일반적인 치료와 병행하여 실시할 경우, 보행 특성의 결과에 유의할 만한 향상이 나타나는 것으로 알려졌다.Recently, functional electrical stimulation, treadmill walking training, and robot - assisted walking therapy have been used as a new therapeutic approach for rehabilitation training to improve the walking pattern of stroke patients. It is known that when these treatments are performed concurrently with general treatment, significant improvement is shown in the results of gait characteristics.
현재 뇌졸중 환자의 하지 근력, 운동 기능 및 보행 능력에 대한 임상적 평가를 위해 Motoricity Index, Fugl-Meyer Index, Rivermead Motor Assessment 및 Functional Ambulatory Category(Holden et al.,1984, Collen et al., 1990, Demeurisse et al., 1980) 등을 사용하고 있다.In the present study, we used the Motoricity Index, the Fugl-Meyer Index, the Rivermead Motor Assessment, and the Functional Ambulatory Category (Holden et al., 1984, Collen et al., 1990, Demeurisse et al., 1980).
이러한 평가 항목들은 균형 감각, 관절 범위, 독립 보행 여부 등 하지 운동 기능에 대한 임상 치료 효과를 평가할 수 있지만, 뇌가소성적 관점에서 운동 기능이 회복됨에 따라 대뇌피질의 활성 변화 및 운동신경망의 재구성 등을 평가할 수는 없었다.These evaluation items can evaluate clinical treatment effects on lower limb movements such as balance sense, joint range, and independent walking. However, as the motor function is restored from the viewpoint of brain plasticity, changes in cerebral cortical activity and reconstruction of motor neural network I could not evaluate it.
한편, 부분 체중 부하 트레드밀 재활 훈련은 뇌졸중 이후 보행 기능 향상을 위한 방법으로 널리 쓰이고 있지만, 그에 대한 효과 및 재활 치료를 위한 적절한 시기에 관해서는 알려진 바가 없다.On the other hand, partial weighted treadmill rehabilitation training has been widely used as a method to improve gait after stroke, but the effect on it and the appropriate timing for rehabilitation therapy are not known.
특히, 기존 연구(Cochrane review 2012 stroke, Duncan et al.,2011, Morone et al., 2012)에 따르면, 일반 지면 보행 재활, 트레드밀 재활 및 로봇 보조 보행 재활 치료의 임상적 치료 효과나 최적의 활용 방법은 확립되어 있지 않은 상태이다.In particular, according to previous studies (Cochrane Review 2012, Duncan et al., 2011, Morone et al., 2012), clinical treatment effects and optimal use of generalized floor walking rehabilitation, treadmill rehabilitation, Is not yet established.
따라서, 일반적인 보행 치료 방법인 트레드밀 보행 재활 치료에 대한 뇌가소성적 측면에서의 임상적 치료 효과의 고찰을 통해 보행 재활 치료의 기능적 회복에 대한 뇌가소성적 임상평가 방법에 대한 기반 기술 확보가 요구되고 있다.Therefore, it is required to acquire the basic technology for the clinical evaluation of brain plasticity for the functional recovery of gait rehabilitation by examining the effect of clinical treatment on brain plasticity in treadmill gait rehabilitation .
또한, 보행 재활 치료의 뇌가소성적 평가를 위한 기존의 뇌활성화 측정 방법인 fMRI(Functional MRI), PET(positron emission tomography) 등은 앙와위(supine position) 상태인 누운 상태로 하는 보행과 관련된 운동에 대해서도 측정이 매우 제한적으로 가능하나 특히 보행의 본질적 요소인 중력 가속도 하의 보행 상태를 실시간으로 측정할 수 없다.In addition, fMRI (Functional MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), which are used to measure brain activation for gait evaluation of gait rehabilitation, have been used for supine position (gait) Measurements are very limited, but gait under gravitational acceleration, an essential element of walking, can not be measured in real time.
이에 비해 최근 각광받고 있는 비침습적인 뇌활성화 측정 방법 중 fNIRS, EEG(electroencephalogram) 등은 보행 훈련 상태를 실시간 측정이 가능하나, 머리, 체간 등의 움직임이나, 호흡, 심박 등 생리적 잡음 등 원하지 않는 잡음 등으로 인해 보행과 관련된 신경생리학적 정보가 포함된 충실한 뇌활성도 신호의 획득이 곤란한 문제점이 있다.In contrast, fNIRS and EEG (electroencephalogram) among non-invasive brain activation measurement methods, which are currently in the spotlight, can measure the gait training in real time. However, it is possible to measure the movement of the head, trunk, It is difficult to acquire a faithful brain activity signal including neurophysiological information related to gait.
따라서, 뇌혈류 신호(fNIRS, EEG)의 측정뿐 아니라 근신호(EMG; electromyography), 운동 생리 신호(Goniometer, IMU 등) 등을 함께 측정 및 분석함으로써 잡음에 강인한 정확한 뇌혈류 신호의 물리적 특성을 분석하고 이를 활용해 더 효율적인 보행 재활 치료 방법이 요구되고 있다.Therefore, by measuring and analyzing not only the cerebral blood flow signals (fNIRS, EEG) but also the electromyography (EMG) and goniometer (IMU) signals, the physical characteristics of the cerebral blood flow signal And it is necessary to utilize it for more effective gait rehabilitation treatment method.
한편, 다른 비침습적인 뇌활성화 측정 방법으로, 사람의 대뇌피질에 분포하는 뇌혈류의 산화 또는 불산화 헤모글로빈의 농도를 측정할 수 있는 기능적 근적외선 분광법이 있다.Another non-invasive method of measuring brain activation is the functional near-infrared spectroscopy, which measures the concentration of hemoglobin or oxidation of cerebral blood flow in the human cerebral cortex.
일반적으로 기능적 근적외선 분광법은 기능적 자기공명영상법(fMRI)에 비해 저가의 장비로 측정이 간편하고 사람이 움직이는 동안에도 측정이 가능하여 환자의 운동 재활 훈련 목적의 임상 재활 치료나 동작과 관련한 다양한 작업 수행 시 뇌의 기능적 연구 등에 적극적으로 활용되고 있으며, 그 수요가 증가 추세에 있다.In general, functional near-infrared spectroscopy (FIR) is more cost-effective than functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and can be measured while the human being is moving. Therefore, various tasks related to clinical rehabilitation treatment or motion for patient's exercise rehabilitation training The brain is actively used for functional research, and the demand is increasing.
그러나 기능적 근적외선 분광법은 기능적 자기공명영상법(fMRI)에 비해 물리적으로 공간해상도가 낮아서 정확한 뇌활성 위치 식별이 어려운 한계가 있어, 이를 해결하기 위한 다양한 방법들이 시도되고 있으나 주로 하드웨어적인 측정 방식이나 측정 장치 관점에만 의존하고 있는 실정이다.However, functional near-infrared (FIR) spectroscopy has a limitation in that it is difficult to accurately identify the active site due to its low spatial resolution compared with the functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Various methods have been tried to solve this problem, It depends on the viewpoint.
따라서 측정 방식과 측정 장치에 상관없이 정확한 뇌활성 위치 식별을 할 수 있는 소프트웨어적인 기법의 개발이 요망된다.Therefore, it is desirable to develop a software technique that can accurately identify the active brain location regardless of the measurement method and the measurement device.
상기와 같은 종래 기술의 문제점을 해결하기 위해, 본 발명의 일 실시예는 기능적 근적외선 분광법에 의해 측정된 뇌혈류 정보에 대해 통계적 기법과 학습 기법을 이용하여 수행 작업과 밀접히 관련성이 높은 뇌활성 위치를 효과적으로 결정할 수 있는 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법 및 장치를 제공하고자 한다.In order to solve the problems of the prior art as described above, one embodiment of the present invention uses a statistical technique and a learning technique for cerebral blood flow information measured by functional near-infrared spectroscopy, And a method and apparatus for effective positioning according to brain activity measurement of a functional near-infrared spectroscopy method which can be effectively determined.
위와 같은 과제를 해결하기 위한 본 발명의 일 측면에 따르면, 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법이 제공된다. 상기 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법은 기능적 근적외선 분광법(fNIRS; Functional near-infrared spectroscopy)에 의해 두피의 복수의 위치에 대응하는 N개의 측정 채널로부터 뇌혈류 신호를 획득하는 단계; 상기 획득된 뇌혈류 신호에서 피험자의 호흡, 혈액 순환, 움직임을 포함하는 잡음 성분을 제거하는 단계; 상기 잡음 제거된 신호를 수행 및 휴지에 대한 시계열 자료들로 구분하여 수행-휴지 분류 적합도를 산출하고, 상기 산출된 분류 적합도에 따라 우선 순위를 부여하는 사전 처리 단계; 및 상기 우선 순위별 감소율에 따라 M개의 우등 채널과 N-M개의 열등 채널을 분류하고, 상기 M개의 우등 채널 각각에 대한 상기 N-M개의 열등 채널의 상관도가 모두 제 1 기준값 이상이면, 해당 L개의 열등 채널을 상기 우등 채널로 재분류하여 최종적으로 M+L개의 유효 채널을 결정하는 단계를 포함한다.According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided an effective positioning method according to the measurement of brain activity of a functional near infrared ray spectroscopy. The method of determining the effective position according to the brain activity measurement of the functional near-infrared spectroscopy may include obtaining a cerebral blood flow signal from N measurement channels corresponding to a plurality of positions of the scalp by functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS); Removing noise components including respiration, blood circulation, and movement of the subject from the acquired cerebral blood flow signal; A pre-processing step of dividing the noise-removed signal into time-series data for performance and dormancy to calculate a performance-dormant classification fitness and giving priority to the calculated classification fitness; And classifying the M number of good channels and the number of NM poor channels according to the priority decreasing rate, and if the correlations of the NM number of poor channels with respect to each of the M number of good channels are equal to or greater than a first reference value, Lt; RTI ID = 0.0 > M + L < / RTI > effective channels.
일 실시예에서, 상기 사전 처리 단계는 상기 잡음 제거된 신호를 수행 및 휴지에 대한 시계열 자료로 정렬하는 단계; 공통 공간 패턴화(Common Spatial Pattern; CSP)를 이용하여 상기 정렬된 자료를 수행 및 휴지를 독립 변인으로 하는 새로운 분류 공간으로 사상하는 단계; 상기 분류 공간 상에서 상기 채널에 대하여 수행 및 휴지를 구별하는 구별 함수를 생성하는 단계; 및 SVM(support vector machine) 알고리즘을 이용하여 상기 생성된 구별 함수로부터 상기 각 채널에 대한 수행-휴지 분류 적합도를 연산하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the pre-processing step comprises: sorting the noise canceled signal into time series data for performance and dormancy; Mapping the sorted data to a new classification space having independent parameters such as pause and hibernation using common space pattern (CSP); Generating a discrimination function for discriminating performance and dormancy for the channel on the classification space; And a step of computing an execution-pause classification fitness for each channel from the generated distinct function using an SVM (support vector machine) algorithm.
일 실시예에서, 상기 유효 채널을 결정하는 단계는 상기 우선 순위별 감소율이 제 2 기준값보다 크면, 상기 우등 채널로 분류하고, 상기 제 2 기준값 이하이면, 상기 열등 채널로 분류하는 단계; 상기 우등 채널 각각에 대한 상기 열등 채널의 일대일 상관도를 연산하는 단계; 및 상기 열등 채널 중에서 상기 우등 채널 모두에 대하여 상기 연산된 상관도가 상기 제 1 기준값 이상인 열등 채널을 상기 우등 채널로 재분류하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the determining of the effective channel may include classifying the channel into the superior channel if the rate of decrease by priority is greater than the second reference value, and classifying the channel into the inferior channel if the rate is less than the second reference value. Calculating a one-to-one correlation of the inferior channel with respect to each of the superior channels; And reclassifying the poor channel having the calculated degree of correlation for all of the good channels to the good channel equal to or greater than the first reference value.
일 실시예에서, 상기 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법은 상기 결정된 최종 유효 채널에 따라 상기 뇌혈류 신호를 획득하기 위한 관련 광극 위치를 결정하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the method of determining an effective position according to brain activity measurement of the functional near infrared ray spectroscopy may further include determining an associated light position for acquiring the cerebral blood flow signal according to the determined final effective channel.
본 발명의 일 측면에 따르면, 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 장치가 제공된다. 상기 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 장치는 기능적 근적외선 분광법(fNIRS)에 의해 뇌혈류 신호를 획득하는 데이터 획득부; 기능적 근적외선 분광법(fNIRS)에 의해 두피의 복수의 위치에 대응하는 N개의 측정 채널로부터 뇌혈류 신호를 획득하는 데이터 획득부; 상기 획득된 뇌혈류 신호에서 피험자의 호흡, 혈액 순환, 움직임을 포함하는 잡음 성분을 제거하는 잡음 제거부; 상기 잡음 제거된 신호를 수행 및 휴지에 대한 시계열 자료들로 구분하여 수행-휴지 분류 적합도를 산출하고, 상기 산출된 분류 적합도에 따라 우선 순위를 부여하는 사전 처리부; 및 상기 우선 순위별 감소율에 따라 M개의 우등 채널과 N-M개의 열등 채널을 분류하고, 상기 M개의 우등 채널 각각에 대한 상기 N-M개의 열등 채널의 상관도가 모두 제 1 기준값 이상이면, 해당 L개의 열등 채널을 상기 우등 채널로 재분류하여 최종적으로 M+L개의 유효 채널을 결정하는 유효 채널 결정부를 포함한다.According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided an effective position determining apparatus for measuring brain activity of a functional near infrared ray spectroscopy. An effective position determining device according to the brain activity measurement of the functional near infrared ray spectroscopy includes a data acquiring part for acquiring a cerebral blood flow signal by functional near infrared ray spectroscopy (fNIRS); A data obtaining unit for obtaining a cerebral blood flow signal from N measurement channels corresponding to a plurality of positions of the scalp by functional near infrared ray spectroscopy (fNIRS); A noise eliminator for removing a noise component including respiration, blood circulation, and movement of the subject in the acquired cerebral blood flow signal; A pre-processing unit for dividing the noise-removed signal into time series data for performance and dormancy to calculate a performance-dormant classification fitness and giving priority to the calculated classification fitness according to the calculated classification fitness; And classifying the M number of good channels and the number of NM poor channels according to the priority decreasing rate, and if the correlations of the NM number of poor channels with respect to each of the M number of good channels are equal to or greater than a first reference value, And determines an M + L effective channel finally.
일 실시예에서, 상기 사전 처리부는 상기 잡음 제거된 신호를 수행 및 휴지에 대한 시계열 자료로 정렬하고, 공통 공간 패턴화(CSP)를 이용하여 상기 정렬된 자료를 수행 및 휴지를 독립 변인으로 하는 새로운 분류 공간으로 사상하며, 상기 분류 공간 상에서 상기 채널에 대하여 수행 및 휴지를 구별하는 구별 함수를 생성하고, SVM 알고리즘을 이용하여 상기 생성된 구별 함수로부터 상기 각 채널에 대한 수행-휴지 분류 적합도를 연산할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the preprocessor may be configured to sort the noise canceled signal with time series data for performance and dormancy, and to perform the sorted data using common space patterning (CSP) And generates a discrimination function for distinguishing performance and pauses for the channel on the classification space, and calculates an execution-pause classification suitability for each channel from the generated discrimination function using the SVM algorithm .
일 실시예에서, 상기 유효 채널 결정부는 상기 우선 순위별 감소율이 제 2 기준값보다 크면, 상기 우등 채널로 분류하고, 상기 제 2 기준값 이하이면, 상기 열등 채널로 분류하고, 상기 우등 채널 각각에 대한 상기 열등 채널의 일대일 상관도를 연산하여 상기 열등 채널 중에서 상기 우등 채널 모두에 대하여 상기 연산된 상관도가 상기 제 1 기준값 이상인 열등 채널을 상기 우등 채널로 재분류할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the valid channel determination unit classifies the effective channel into the good channel if the rate of decrease by priority is greater than the second reference value, classifies the channel into the poor channel if the rate is below the second reference value, To-one correlation of the inferior channel to reclassify the inferior channel having the calculated degree of correlation to the first reference value or higher with respect to all of the inferior channels.
일 실시예에서, 상기 유효 채널 결정부는 상기 결정된 최종 유효 채널에 따라 상기 뇌혈류 신호를 획득하기 위한 관련 광극 위치를 결정할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the effective channel determination unit may determine an associated light pole position for acquiring the cerebral blood flow signal according to the determined final effective channel.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법 및 장치는 보행 재활, 작업 치료 등에서 임상적으로 중요한 신뢰성이 높은 대뇌피질의 활성 위치에 대한 정보를 제공할 수 있어, 환자의 재활 상태에 따른 측정 위치의 선택이 가능하다.The effective positioning method and apparatus according to the measurement of brain activity of the functional near infrared ray spectroscopy according to the embodiment of the present invention can provide information about the active position of the cerebral cortex which is clinically important in gait rehabilitation, , It is possible to select the measurement position according to the rehabilitation state of the patient.
또한, 본 발명의 실시예는 생리 신호를 활용한 보행 재활 치료의 뇌가소성적 임상 평가의 준정량적(quasi-quantitative) 방법으로 활용 가능하며, 따라서 뇌 질환의 병변 크기 및 위치, 발병 시기 등에 따른 재활 치료의 적용 시기, 치료 과정 등에 활용할 수 있다.In addition, the embodiment of the present invention can be utilized as a quasi-quantitative method for clinical evaluation of brain plasticity in gait rehabilitation therapy using physiological signals, and accordingly, Time of application, treatment period, etc.
또한, 본 발명의 실시예는 측정 기기 및 하드웨어에 상관없이 뇌활성 위치를 정확히 식별할 수 있는 소프트웨어의 제공이 가능하다.In addition, the embodiment of the present invention can provide software that can accurately identify the brain activation position irrespective of the measuring instrument and the hardware.
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법의 순서도이다.
도 2는 도 1의 방법을 적용하기 위한 (a)측정 장치를 착용한 상태 및 (b) 전극의 설치한 상태의 사진이다.
도 3은 뇌졸중 환자의 트레밀 보행 재활 훈련시 기능적 근적외선 분광 장치를 활용한 뇌혈류 신호 측정 위치를 나타낸 도면이다.
도 4는 뇌졸중 환자의 트레밀 보행 재활 훈련시 뇌혈류 신호 측정 순서를 나타낸 그래프이다.
도 5는 뇌졸중 환자의 트레드밀 보행 재활 훈련 시 뇌혈류 신호 측정으로부터 획득된 (a) 대뇌피질의 뇌활성 영상, (b) 각 채널에서의 산화헤모글로빈 농도의 변화를 나타낸 그래프, 및 (c) 산화헤모글로빈 농도의 피크 값을 나타낸 표이다.
도 6은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 방법을 적용한 유효 채널 추출 결과를 나타낸 (a) 뇌활성 영상, (b), 채널 분류 결과의 그래프, (c) 각 채널에서의 산화헤모글로빈 농도의 변화를 나타낸 그래프, 및 (d) 산화헤모글로빈 농도의 피크 값을 나타낸 표이다.
도 7은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 장치의 개략적 블록도이다.1 is a flowchart of an effective positioning method according to a brain activity measurement of a functional near infrared ray spectroscopy according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a photograph of a state in which (a) a measurement apparatus is worn and (b) an electrode is installed, in order to apply the method of FIG.
FIG. 3 is a view showing a location of a cerebral blood flow signal measurement using a functional NIR spectroscope during a tremillal gait rehabilitation training of a stroke patient.
FIG. 4 is a graph showing a procedure for measuring cerebral blood flow signals during a tremile walking rehabilitation training in a stroke patient.
FIG. 5 is a graph showing the cerebral cortex brain activity image obtained from cerebral blood flow signal measurement during treadmill gait rehabilitation training in a stroke patient, (b) a graph showing changes in the concentration of oxidized hemoglobin in each channel, and (c) And the peak value of the concentration.
FIG. 6 is a graph showing a result of extracting effective channels using the method according to an embodiment of the present invention, (a) a brain activity image, (b) a graph of channel classification results, and (c) a change in the concentration of oxidized hemoglobin in each channel Graph, and (d) the peak value of the concentration of oxidized hemoglobin.
FIG. 7 is a schematic block diagram of an effective positioning apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention for measuring brain activity of functional near-infrared spectroscopy.
이하, 첨부한 도면을 참고로 하여 본 발명의 실시예에 대하여 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 용이하게 실시할 수 있도록 상세히 설명한다. 본 발명은 여러 가지 상이한 형태로 구현될 수 있으며 여기에서 설명하는 실시예에 한정되지 않는다. 도면에서 본 발명을 명확하게 설명하기 위해서 설명과 관계없는 부분은 생략하였으며, 명세서 전체를 통하여 동일 또는 유사한 구성요소에 대해서는 동일한 참조부호를 붙였다.Hereinafter, exemplary embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings, which will be readily apparent to those skilled in the art to which the present invention pertains. The present invention may be embodied in many different forms and is not limited to the embodiments described herein. In order to clearly illustrate the present invention, parts not related to the description are omitted, and the same or similar components are denoted by the same reference numerals throughout the specification.
본 발명은 기존 활발히 연구되고 있는 트레드밀을 활용한 보행 재활 치료에서 보행 시 대뇌피질의 변화 양상만을 관찰하는 것과 달리, 뇌활성 부위를 정확하게 찾아내기 위한 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method for precisely locating a brain active site, as opposed to observing only changes in the cerebral cortex during gait in gait rehabilitation therapy using a treadmill that has been actively studied.
또한, 본 발명은 임상적 효과에 대한 연구가 진행되고 있는 트레드밀을 사용한 로봇보조 보행치료(Lokomat, Walkbot 등)의 임상적 효과 검증 등 적절한 치료 방법 도출에 활용하기 위한 것으로서, 두피의 복수의 위치에 독립적으로 위치한 다수의 측정 채널로부터 측정된 각각의 뇌혈류 신호를 각 채널별로 과제 수행기(task-on period, 이하 '수행')와 휴지기(task-off period, 이하 '휴지')의 시계열(time series) 자료들로 구분하여 정렬하고, 이들 정렬된 자료들에 대해 통계적 기법을 활용하여 개별 채널에 있어 수행과 휴지를 함수적으로 구별할 수 있으며, 이 구별 함수에 대해 학습 기법을 이용하여 개별 채널에 있어 수행과 휴지의 구별의 차이를 수치적으로 산출하여 이들 구별 수치의 크기에 따라 채널들의 순위가 정해지며, 우등 채널을 적절한 개수로 선택(cutoff)하여 이 우등 채널들과 열등 채널들 간의 상관도를 통계적 기법에 의해 수치적으로 계산하여 상관도가 일정 수준으로 높은 열등 채널들을 포함하여 최종적으로 유효 채널로 선정함으로써 이 유효 채널에 해당하는 측정 위치를 수행 작업과 직접적으로 연관된 뇌활성 위치로 결정할 수 있는 방법 및 장치에 관한 것이다.In addition, the present invention is to be used for deriving an appropriate treatment method such as a clinical effect test of a robot-assisted walking therapy (Lokomat, Walkbot, etc.) using a treadmill in which clinical effects are being studied, Each cerebral blood flow signal measured from a plurality of independent measurement channels is divided into a time series of task-on period and a task-off period, ), And sorting and sorting these data, we can use statistical techniques to distinguish between performance and dormancy in individual channels. We can use this learning method to distinguish between individual channels The difference between performance and idle is numerically calculated, and the order of channels is determined according to the size of the discriminant value, and the number of good channels is cut off The correlation between the right channel and the inferior channel is calculated numerically by a statistical technique, and finally, the effective channel is selected including the inferior channels having a certain degree of correlation, so that the measurement position corresponding to the effective channel is performed To a brain active location that is directly associated with the task.
한편, 뇌 신호 측정 및 대뇌피질의 활성 상태 분석을 위한 기존의 연구는 대부분 브로드만 영역(Brodmann Area; BA)을 기준으로 비교 분석이 이루어지고 있다.On the other hand, conventional studies for brain signal measurement and cerebral cortical activity analysis are mostly based on the Brodmann area (BA).
이러한 브로드만 영역(BA)은 대뇌피질을 세포구축학적(cytoarchitectonic) 방법으로 52개의 영역(브로드만 영역)으로 나누어 정의한다. 여기서, 브로드만 영역은 실행기능(Executive function), 운동 기능(Motor function), 체지각(Somatosensory), 흥미(Attention), 시각 기능(Visual function) 기억(Memory), 감정 조절(Emotional regulation), 청각(Sound) 등의 대뇌피질 기능(Cortical Functions)으로 구분될 수 있다.This Brodmann area (BA) is defined by dividing the cerebral cortex into 52 regions (Broadman region) by the cytoarchitectonic method. Here, the Broadman region includes an executive function, a motor function, a somatosensory, an attention, a visual function, a memory, an emotional regulation, And cortical functions such as sound.
한편, 보행 기능과 관련된 대뇌피질 영역은 브로드만 영역에 대하여 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9 번 영역이다. 본 발명은 이와 같은 영역에 대한 뇌혈류 신호를 활용하여 적절한 치료 방법을 도출할 수 있는 방안을 제시한다.
On the other hand, the cerebral cortex area related to the gait function is 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 9 regions for the Broadman region. The present invention suggests a method for deriving an appropriate treatment method by utilizing the cerebral blood flow signal for such a region.
이하에서는 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법을 보다 상세히 설명하도록 한다. 도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법의 순서도이고, 도 2는 도 1의 방법을 적용하기 위한 (a)측정 장치를 착용한 상태 및 (b) 전극의 설치한 상태의 사진이며, 도 3은 뇌졸중 환자의 트레밀 보행 재활 훈련시 기능적 근적외선 분광 장치를 활용한 뇌혈류 신호 측정 위치를 나타낸 도면이고, 도 4는 뇌졸중 환자의 트레밀 보행 재활 훈련시 뇌혈류 신호 측정 순서를 나타낸 그래프이다.Hereinafter, an effective positioning method according to the measurement of brain activity of functional NIR spectroscopy according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a flowchart of an effective positioning method according to the measurement of brain activity of functional NIR spectroscopy according to an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a state (a) FIG. 3 is a view showing a position of a cerebral blood flow signal measurement using a functional near-infrared ray spectroscopic apparatus during a tremillal gait rehabilitation training of a stroke patient, and FIG. 4 is a view showing a position A cerebral blood flow signal measurement procedure.
본 발명의 실시예에 따른 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법(100)은 뇌혈류 신호를 획득하는 단계(S101), 획득된 뇌혈류 신호에서 잡음 성분을 제거하는 단계(S102), 잡음 제거된 신호에 대하여 수행-휴지의 분류 적합도 나열하도록 사전 처리하는 단계(S103 내지 S106), 및 분류 적합도에 의해 분류된 우등 채널 및 열등 채널을 분류 및 재분류하여 유효 채널에 따른 유효 위치를 결정하는 단계(S107 내지 S110)로 구성된다.The
보다 상세히 설명하면, 도 1에 도시된 바와 같이, 먼저, 기능적 근적외선 분광법(fNIRS)에 의해 두피의 복수의 위치에 대응하는 N개의 측정 채널로부터 뇌혈류 신호를 획득할 수 있다(단계 S101).More specifically, as shown in FIG. 1, a cerebral blood flow signal can be obtained from N measurement channels corresponding to a plurality of positions of the scalp by functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) (step S101).
여기서, 비침습적인 뇌활성화 측정 방법으로서, 기능적 근적외선 분광법(fNIRS)을 이용하거나 EEG를 이용하여 보행 훈련 상태를 실시간으로 측정하면서 뇌혈류 신호를 획득할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 도 2에 도시된 바와 같이, 뇌졸중 환자가 트레드밀 보행 재활 훈련을 실시하는 도중에 기능적 근적외선 분광 장치를 장착하여 뇌혈류 신호를 획득할 수 있다. 이때, 도 3에 도시된 바와 같이, 뇌혈류 신호 측정을 위해, 예를 들면, 수광극 10개와 발광극 10개의 광극을 사용할 수 있으며, 이 경우, 총 31개의 광흡수 채널을 형성할 수 있다. 이와 같이 두피의 복수의 위치에서 N개의 측정 채널로부터 뇌혈류 신호를 획득할 수 있다.Here, as a non-invasive brain activation measuring method, the cerebral blood flow signal can be obtained by using functional near infrared ray spectroscopy (fNIRS) or measuring the gait training state in real time using EEG. For example, as shown in FIG. 2, a cerebral blood flow signal can be acquired by mounting a functional NIR spectroscope during a stroke patient's treadmill walking rehabilitation training. As shown in FIG. 3, for example, 10 light receiving poles and 10 light emitting poles can be used for measuring cerebral blood flow signals. In this case, a total of 31 light absorbing channels can be formed. Thus, cerebral blood flow signals can be obtained from N measurement channels at a plurality of locations on the scalp.
한편, 뇌혈류 신호의 획득은 휴지 및 수행에 대하여 일정한 시간적 측정 순서로 이루어지는데, 예를 들면, 도 4에 도시된 바와 같이, 보행 동작을 수행으로, 정지 및 유지 동작을 휴지로 정의하고, 휴지 20초 및 수행 20초를 하나의 구획으로 하여 총 3개의 시간 구획과 마지막 휴지 20초 구획을 포함하여 총 140초 동안 실시할 수 있다.On the other hand, the acquisition of the cerebral blood flow signal is performed in a predetermined temporal measurement order with respect to the stopping and performing. For example, as shown in Fig. 4, the walking operation is performed, 20 seconds, and 20 seconds as a single compartment, for a total of 140 seconds including a total of three time zones and a final dormant 20 second zone.
다음으로, 획득된 뇌혈류 신호에서 피험자의 호흡, 혈액 순환, 움직임 등과 같은 생체 잡음 성분을 제거할 수 있다(단계 S102). 즉, 측정된 뇌혈류 신호에 대한 신호 품질 개선을 위해 잡음을 제거할 수 있다.Next, a bio-noise component such as respiration, blood circulation, movement, etc. of the subject can be removed from the acquired cerebral blood flow signal (step S102). That is, noise can be removed to improve the signal quality of the measured cerebral blood flow signal.
이때, 측정된 기능적 근적외선 분광법(fNIRS)의 뇌혈류 신호를 혈류 역학적 반응 함수(hemodynamic response function; hrf), 웨이블릿 변환(Wavelet Transform), 또는 유한 임펄스 응답 필터(finite impulse response filter; FIR)를 이용하여 잡음 성분을 제거할 수 있다.At this time, the cerebral blood flow signal of the measured functional near infrared ray spectroscopy (fNIRS) is measured using a hemodynamic response function (hrf), a wavelet transform, or a finite impulse response filter (FIR) Noise components can be removed.
이와 같이, 머리, 체간 등의 움직임이나 호흡, 심박 등 생리적 잡음 등 원하지 않는 잡음을 제거하여 보행과 관련된 신경생리학적 정보를 포함하는 뇌혈류 신호만을 획득할 수 있다.Thus, only the cerebral blood flow signal including neurophysiological information related to gait can be obtained by removing unwanted noise such as movement of the head, trunk, etc. and physiological noise such as breathing and heartbeat.
다음으로, 잡음 제거된 뇌혈류 신호를 수행 및 휴지에 대한 시계열 자료로 정렬할 수 있다(단계 S103). 이때, 뇌혈류 신호는 각 채널별로 수행 및 휴지의 시계열 자료들로 구분하여 예를 들면, 행렬 형태로 정렬할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 31개의 채널에 대한 수행 60초 및 휴지 80초로 획득된 데이터를 31 X 600(수행), 31 X 800(휴지)로 각각 구조화하여 행렬로 나타낼 수 있다.Next, the noise-canceled cerebral blood flow signal can be sorted into time series data for execution and rest (step S103). At this time, the cerebral blood flow signals can be sorted into time series data of execution and pause for each channel, for example, in a matrix form. For example, data obtained for 60 seconds and 80 seconds of dormancy for 31 channels can be expressed as a matrix of 31 X 600 (performance) and 31 X 800 (dormancy), respectively.
다음으로, 정렬된 자료를 수행 및 휴지를 독립 변인으로 하는 새로운 분류 공간으로 사상할 수 있다(단계 S104). 이때, 분류 공간으로의 사상은 다양한 수학적, 통계적인 기법을 이용할 수 있으며, 예를 들면, 공통 공간 패턴화(CSP)를 이용할 수 있다.Next, the sorted data can be mapped to a new classification space having independent variables such as performance and dormancy (step S104). At this time, mapping to the classification space can use various mathematical and statistical techniques, for example, common space patterning (CSP) can be used.
여기서, 공통 공간 패턴화(CSP)는 수행 및 휴지의 두 클래스에 대한 분산 차이를 크게 하는 공간 필터(spatial filter)일 수 있다. 이와 같은 공통 공간 패턴(CSP)에 의해, 뇌혈류 신호가 더 뚜렷하게 드러나도록 하거나 특징의 차원을 줄일 수 있다.Here, the common space patterning (CSP) may be a spatial filter that increases the dispersion difference for two classes of performance and dormancy. Such a common spatial pattern (CSP) can make the cerebral blood flow signal more distinct or reduce the dimension of the feature.
다음으로, 분류 공간 상에서 채널에 대하여 수행 및 휴지를 구별하는 구별 함수를 생성할 수 있다(단계 S105). 여기서, 수행-휴지 분류 공간 상에서 채널들의 자료는 수행 및 휴지가 구별되는 형태로 집중 또는 분산되어 있기 때문에, 이를 구별할 수 있는 수행-휴지 구별 함수를 수학적으로 정의할 수 있다. 이러한 구별 함수는 예를 들면, 수행 및 휴지 계열에 대한 분산 차이를 최대로 하는 벡터(support vector)로서, SVM 알고리즘을 이용하여 생성될 수 있다.Next, it is possible to generate a discrimination function for discriminating performance and pause for the channel in the classification space (step S105). Here, since the data of the channels in the performance-idle classification space are concentrated or distributed in a form in which execution and discontinuity are discriminated, it is possible to mathematically define a performance-discontinuity discrimination function that can discriminate the performance-discontinuity function. This distinction function can be generated, for example, using a SVM algorithm as a support vector that maximizes the dispersion difference for execution and dormancy sequences.
다음으로, 생성된 구별 함수로부터 각 채널에 대한 수행-휴지 분류 적합도를 연산할 수 있다(단계 S106). 여기서, 수행-휴지 분류 적합도는 각 채널들이 수행과 휴지가 얼마나 뚜렷하게 구별될 수 있는지를 나타내는 값으로서, 정의된 구별 함수로부터 각 채널들에 대해 수행-휴지 구별에 대한 점수를 연산한 결과일 수 있다. 이러한 수행-휴지 분류 적합도는 최적의 통계적, 수학적 기법에 의해 연산될 수 있으며, 수행 및 휴지의 최대 분산에 대한 수학식일 수 있다.Next, the performance-dormancy classification fitness for each channel can be calculated from the generated discrimination function (step S106). Here, the performance-idle classification fitness is a value indicating how clearly the performance and the idle state of each channel can be distinguished from each other, and may be a result of calculating scores for the performance-idle discrimination for each channel from the defined discrimination function . This performance-dormant classification fitness can be computed by an optimal statistical and mathematical technique and can be a mathematical expression for the maximum variance of performance and downtime.
이와 같이 연산된 수행-휴지 분류 적합도에 따라 채널들을 분류 적합도 순위로 정렬할 수 있다. 여기서, 순위에 따라 분류 적합도 최상위 채널로부터 최하위 채널까지 우선 순위를 부여하여 저장할 수 있다.The channels can be sorted according to classification fitness ranking according to the computed performance-hung classification fitness. Here, priority can be given to the lowest-order channel from the highest-order channel of the classification suitability in accordance with the order and stored.
다음으로, 우선 순위별 감소율에 따라 우등 채널과 열등 채널을 분류할 수 있다(단계 S107). 여기서, 우선 순위별 감소율은 채널간 미분치로서, 이전 상위 채널의 분류 적합도에 대한 해당 채널의 분류 적합도의 상대적인 감소값을 의미한다. 즉, 순위별 채널들 사이의 감소값이 급격히 저하되는 채널을 기준으로 이전 상위 채널까지를 우등 채널로 분류하고, 나머지 채널들을 열등 채널로 분류하여 각각 저장할 수 있다.Next, the superior channel and the poor channel can be classified according to the priority decreasing rate (step S107). Here, the reduction rate by priority means an inter-channel differential value, which means a relative decrease value of the classification fitness of the corresponding channel with respect to the classification fitness of the previous upper channel. That is, it is possible to classify up to the previous upper channel as a superior channel and classify the remaining channels into the poor channel based on the channel in which the decrease value between the channels according to the ranking drops sharply.
이때, 감소값의 변화가 크지 않거나 일정한 경우에는 합리적인 수준에서 임의의 감소값을 제 2 기준값(Δ)으로 지정할 수 있다. 즉, 우선 순위별 감소율이 제 2 기준값(Δ)보다 크면, 우등 채널로 분류하고, 제 2 기준값(Δ) 이하이면, 열등 채널로 분류할 수 있다. 여기서, 우등 채널이 M개라고 가정하면, 열등 채널은 N-M개일 수 있다.At this time, if the change of the decrease value is not large or constant, an arbitrary decrease value at a reasonable level can be designated as the second reference value (?). That is, if the rate of decrease by priority is larger than the second reference value?, It is classified as a superior channel, and if it is less than the second reference value?, It can be classified as a poor channel. Here, assuming that there are M number of good channel, the poor channel may be N-M number.
대안적으로, 이러한 감소율은 분류 적합도의 학습 오차의 연산에 의해 수행될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 분류 적합도가 최하위인 채널부터 채널을 줄여가면서 분류 적합도 학습 오차를 반복적으로 갱신함에 따라 오차의 감소율이 현저히 떨어지는 채널이 식별되었을 때를 기준으로 학습 오차에 영향이 미미한 채널들은 우등 채널로 현저한 오차율이 식별된 채널까지는 열등 채널로 분류할 수 있다.Alternatively, this rate of reduction may be performed by computing the learning error of the classification fitness. For example, if a channel with a significantly lower error rate is identified by repeatedly updating the classification fitness learning error while decreasing the channel from the channel with the lowest classification fitness, the channels with little influence on the learning error are classified into the superior channel A channel with a marked error rate can be classified as an inferior channel.
다음으로, 우등 채널 각각에 대한 열등 채널의 일대일 상관도를 연산할 수 있다(단계 S108). 즉, M개의 우등 채널 각각에 대하여 N-M개의 열등 채널들을 일대일 상관도를 계산할 수 있다. 여기서, 채널 상관도는 알려진 통계적, 수학적 기법을 사용하여 연산되며, 예를 들면, 신호 정합성(coherence)을 이용하여 연산될 수 있다.Next, one-to-one correlation of the inferior channel with respect to each of the superior channels can be calculated (step S108). That is, one-to-one correlation can be calculated for N-M inferior channels for each of the M honorable channels. Here, the channel correlation is calculated using known statistical and mathematical techniques, and can be calculated using, for example, signal coherence.
다음으로, 연산된 상관도에 따라 열등 채널의 일부를 우등 채널로 재분류하여 최종 유효 채널을 추출할 수 있다(단계 S109). 이때, 연산된 채널 상관도를 최대 1로 기준으로 할 때, 제 1 기준값(Λ) 이상인 채널들을 열등 채널에서 탈출 가능한 후보 채널로 정하고, 이들 후보 채널들 중에서 우등 채널 모두와 상관도가 제 1 기준값(Λ) 이상인 채널을 우등 채널로 재분류할 수 있다. 즉, 열등 채널 중에서 우등 채널 모두에 대하여 상관도가 상기 제 1 기준값 이상인 열등 채널을 우등 채널로 재분류할 수 있다.Next, according to the computed correlation, a part of the inferior channel may be reclassified as the superior channel to extract the final effective channel (step S109). At this time, when the calculated channel correlation degree is set to a maximum of 1, the channels having a first reference value Λ or more are defined as candidate channels that can be escaped from the poor channel, and the correlation with all the good channels among the candidate channels is set as a first reference value (Λ) or higher can be reclassified as a superior channel. That is, it is possible to reclassify a poor channel whose correlation degree is equal to or higher than the first reference value with respect to all good channels among the poor channels as a good channel.
여기서, 제 1 기준값(Λ)은 예를 들면, 0.7로 가정할 수 있지만, 상황에 따라 더 높은 값으로 설정할 수 있다. 또한, 열등 채널에서 탈출된 후보 채널의 수가 L개라고 가정하면, M개의 우등 채널 각각에 대한 N-M개의 열등 채널의 상관도가 모두 제 1 기준값 이상이면, 해당 L개의 열등 채널을 열등 채널에서 탈출시켜 우등 채널로 재분류하여 최종적으로 M+L개의 유효 채널을 결정할 수 있다. 이때, 나머지 N-(M+L)개의 채널들은 열등 채널에 잔류시킨다.Here, the first reference value? Can be assumed to be, for example, 0.7, but it can be set to a higher value depending on the situation. Assuming that the number of candidate channels escaped from the inferior channel is L, if all the correlation values of the NM inferior channels for each of the M honorable channels are equal to or greater than the first reference value, the corresponding L inferior channel is escaped from the inferior channel Lt; RTI ID = 0.0 > M + L < / RTI > effective channels. At this time, the remaining N- (M + L) channels remain in the inferior channel.
다음으로, 결정된 최종 유효 채널에 따라 뇌혈류 신호를 획득하기 위한 관련 광극 위치를 결정할 수 있다(단계 S110). 상기와 같이 최종적인 M+L개의 유효 채널이 추출되면, 이 채널들이 측정하는 위치가 수행하고 있는 작업(운동 과제, 인지 과제 등)과 직접적으로 연관성이 높은 곳으로 결정할 수 있다. 이때, 통계적 뇌활성 영상과 비교 분석하고, 유효 채널들에 대한 산화헤모글로빈 농도 변화를 기초로 유효 채널로서 적합함을 검증하고, 유효 채널의 형성에 관여한 발광극과 수광극을 결정할 수 있다.Next, an associated light position for acquiring the cerebral blood flow signal may be determined according to the determined final effective channel (step S110). When the final M + L effective channels are extracted as described above, it can be determined that the positions measured by the channels are directly related to the work (exercise task, cognitive task, etc.) being performed. At this time, it can be compared with the statistical brain activation image, and it can be verified that it is suitable as an effective channel based on the change of the oxidized hemoglobin concentration to the effective channels, and the light emitting pole and the light receiving pole involved in forming the effective channel can be determined.
이와 같은 방법에 의해 본 발명은 보행 재활, 작업 치료 등에서 임상적으로 중요한 신뢰성이 높은 대뇌피질의 활성 위치에 대한 정보를 제공할 수 있어, 환자의 재활 상태에 따른 측정 위치의 선택이 가능하며, 생리 신호를 활용한 보행 재활 치료의 뇌가소성적 임상 평가의 준정량적 방법으로 활용 가능하며, 뇌 질환의 병변 크기 및 위치, 발병 시기 등에 따른 재활 치료의 적용 시기, 치료 과정 등에 활용할 수 있고, 측정 기기 및 하드웨어에 상관없이 뇌활성 위치를 정확히 식별할 수 있는 소프트웨어의 제공이 가능하다.
According to this method, the present invention can provide information on the active position of the cerebral cortex having high reliability, which is clinically important in gait rehabilitation, occupational therapy, etc., so that it is possible to select the measurement position according to the rehabilitation state of the patient, It can be used as a semi-quantitative method of brain plasticity evaluation of gait rehabilitation therapy using signal. It can be applied to the timing and the treatment process of rehabilitation according to lesion size, position, It is possible to provide software that can accurately identify the brain active location regardless of hardware.
이하, 도 5 및 도 6을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법에 대한 실험예를 설명한다.Hereinafter, an example of an effective positioning method according to the measurement of brain activity of the functional near infrared ray spectroscopy according to the embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 5 and 6. FIG.
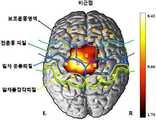
도 5는 뇌졸중 환자의 트레드밀 보행 재활 훈련 시 뇌혈류 신호 측정으로부터 획득된 (a) 대뇌피질의 뇌활성 영상, (b) 각 채널에서의 산화헤모글로빈 농도의 변화를 나타낸 그래프, 및 (c) 산화헤모글로빈 농도의 피크 값을 나타낸 표이고, 도 6은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 방법을 적용한 유효 채널 추출 결과를 나타낸 (a) 뇌활성 영상, (b), 채널 분류 결과의 그래프, (c) 각 채널에서의 산화헤모글로빈 농도의 변화를 나타낸 그래프, 및 (d) 산화헤모글로빈 농도의 피크 값을 나타낸 표이다.FIG. 5 is a graph showing the cerebral cortex brain activity image obtained from cerebral blood flow signal measurement during treadmill gait rehabilitation training in a stroke patient, (b) a graph showing changes in the concentration of oxidized hemoglobin in each channel, and (c) (B), a graph of channel classification results, (c) a graph showing the results of each channel, and FIG. 6 And (d) a table showing the peak value of the concentration of oxidized hemoglobin.
도 5a를 참조하면, 뇌활성 영상의 예로서, 이는 대뇌 피질 영역에서 뇌활성이 발생하는 확률적 가능성을 수치와 색채의 명암으로 상대적으로 표시된 것이다. 이러한 영상은 SPM(Statistical Parametric Mapping)이라는 통계적 기법에 의해 구현한 것으로 밝은 색일수록 수치가 클수록 해당하는 대뇌피질 영역에서 다른 영역에 비해 뇌활성이 일어날 확률이 상대적으로 높다는 것을 의미한다.Referring to FIG. 5A, as an example of a brain activity image, it is a probability that the brain activity occurs in the cerebral cortex area is relatively displayed with the contrast of the numerical value and the color. This image is implemented by Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM), which means that the larger the number of bright colors, the higher the probability of brain activation than the other regions in the corresponding cortical area.
이러한 이유로, 도 5b 및 도 5c에 도시된 바와 같이, 해당 피험자는 12번 채널을 중심으로 주변 채널들에서 높은 뇌활성이 관찰되고 있고, 따라서, 일차운동 대뇌피질의 활성이 가장 활발하고 더불어 보조운동 영역과 전운동 대뇌피질에서 뇌활성이 일어나고 있음을 나타내고 있다.For this reason, as shown in FIG. 5B and FIG. 5C, the subject has a high brain activity in the peripheral channels around the 12th channel, and thus the activity of the primary motor cortex is most active, Region and the entire motor cortex, indicating that brain activity is occurring.
도 6a를 참조하면, 유효 채널 추출의 결과서, 동일한 실험에 대한 결과인 도 5a의 뇌활성 영상에서 추출된 유효 채널을 원모양 숫자로 나타낸 것이다. 이때, 도 6b에 도시된 바와 같이, 채널 사이의 분류 적합도의 감소율에 따라 우등 채널과 열등 채널을 구분하여 우등 채널을 유효 채널로 추출할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 6A, the effective channel extracted from the brain activity image of FIG. 5A, which is a result of the same experiment, is shown by circled numbers. At this time, as shown in FIG. 6B, the superior channel and the poor channel can be distinguished according to the reduction rate of the classification fitness between the channels, and the superior channel can be extracted as the effective channel.
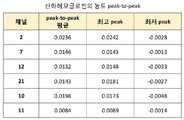
여기서, 결정된 유효 채널의 번호는 우선 순위에 따라 2, 7, 12, 21, 10, 그리고 11채널이다. 이로부터 해당 피험자가 보행 훈련을 수행할 때, 피험자의 뇌활성의 정보가 상기 유효 채널들에서 타 채널에 비해 더 많이 검출되고 있으며, 도 6c에 도시된 바와 같이, 수행 및 휴지에서 산화헤모글로빈 농도의 변화가 높고 낮음으로 뚜렷하게 구별될 수 있다.Here, the determined effective channel numbers are 2, 7, 12, 21, 10, and 11 channels according to priority. When the subject performs gait training, the brain activity information of the subject is detected more in the effective channels than in the other channels. As shown in FIG. 6C, the concentration of oxidized hemoglobin Changes can be clearly distinguished by high and low.
또한, 도 6d에 도시된 바와 같이, 뇌활성의 정도를 나타내는 산화헤모글로빈 농도의 수행-휴지 간 최대 파고치(peak-to-peak)의 평균값이 유효 채널들에서 큰 값으로 획득된 것으로 나타난다. 이로부터 추출된 유효 채널들이 피험자의 보행 훈련과 밀접히 관련된 뇌활성 정보를 제공하는 채널이라 판단할 수 있으며, 이 채널의 형성에 관여한 발광극 T2, T4, T5, T7 과 수광극 R1, R3, R4, R7(도 3 참조)이 유효한 측정 위치로 결정될 수 있다.
Also, as shown in FIG. 6D, it is shown that the average value of the peak-to-peak between performance and hibernation of the concentration of oxidized hemoglobin indicating the degree of brain activity is obtained as a large value in the effective channels. T4, T5, and T7, which are involved in the formation of the channel, and the light-receiving poles R1, R3, and R4, which are involved in the formation of the channel, R4, and R7 (see FIG. 3) can be determined as valid measurement positions.
이하, 도 7을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 채널 추출 장치를 설명한다. 도 7은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 채널 추출 장치의 개략적 블록도이다.Hereinafter, an effective channel extracting apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 7 is a schematic block diagram of an effective channel extracting apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention for measuring brain activity of functional NIR spectroscopy.
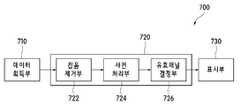
도 7을 참조하면, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 장치(700)는 데이터 획득부(710), 유효 위치 추출부(720), 및 표시부(730)를 포함한다.7, the
데이터 획득부(710)는 기능적 근적외선 분광법(fNIRS)에 의해 뇌혈류 신호를 획득할 수 있다. 이러한 데이터 획득부(710)는 기능적 근적외선 분광법(fNIRS) 또는 EEG를 이용하여 보행 훈련 상태를 실시간으로 측정하면서 뇌혈류 신호를 획득할 수 있다. 여기서, 데이터 획득부(710)는 예를 들면, 수광극 10개와 발광극 10개의 광극으로 구성될 수 있으며, 이 경우, 총 31개의 광흡수 채널을 형성할 수 있다.The
유효 위치 추출부(720)는 데이터 획득부(710)에서 획득된 뇌혈류 신호에 대하여 유효 위치를 추출하며, 잡음 제거부(722), 사전 처리부(724), 및 유효 채널 결정부(726)를 포함한다.The valid
잡음 제거부(722)는 획득된 뇌혈류 신호에서 피험자의 호흡, 혈액 순환, 움직임을 포함하는 생체 잡음 성분을 제거할 수 있다. 이러한 잡음 제거부(722)는 혈류 역학적 반응 함수 처리부, 웨이블릿 변환부, 또는 유한 임펄스 응답 필터일 수 있으며, 측정된 기능적 근적외선 분광법(fNIRS)의 뇌혈류 신호에 대한 잡음 성분을 제거할 수 있다. 이와 같이, 잡음 제거부(722)는 머리, 체간 등의 움직임이나 호흡, 심박 등 생리적 잡음 등 원하지 않는 잡음을 제거하여 보행과 관련된 신경생리학적 정보를 포함하는 뇌혈류 신호만을 획득할 수 있다.The
사전 처리부(724)는 잡음 제거된 신호를 수행 및 휴지에 대한 시계열 자료들로 구분하여 수행-휴지 분류 적합도를 산출하고, 산출된 분류 적합도에 따라 우선 순위를 부여할 수 있다.The
보다 구체적으로, 사전 처리부(724)는 잡음 제거된 신호를 수행 및 휴지에 대한 시계열 자료로 정렬할 수 있다. 여기서, 시계열 자료는 31 X 600(수행), 31 X 800(휴지)로 각각 구조화하여 행렬로 나타낼 수 있다.More specifically, the
사전 처리부(724)는 정렬된 자료를 수행 및 휴지를 독립 변인으로 하는 새로운 분류 공간으로 사상할 수 있다. 여기서, 분류 공간으로의 사상은 다양한 수학적, 통계적인 기법을 이용할 수 있으며, 예를 들면, 공통 공간 패턴화(CSP)를 이용할 수 있다.The
사전 처리부(724)는 분류 공간 상에서 채널에 대하여 수행 및 휴지를 구별하는 구별 함수를 생성할 수 있다. 이러한 구별 함수는 예를 들면, 수행 및 휴지 계열에 대한 분산 차이를 최대로 하는 벡터(support vector)로서, SVM 알고리즘을 이용하여 생성될 수 있다.The
사전 처리부(724)는 SVM 알고리즘을 이용하여 생성된 구별 함수로부터 각 채널에 대한 수행-휴지 분류 적합도를 연산할 수 있다. 이러한 수행-휴지 분류 적합도는 최적의 통계적, 수학적 기법에 의해 연산될 수 있으며, 수행 및 휴지의 최대 분산에 대한 수학식일 수 있다.The
유효 채널 결정부(726)는 우선 순위별 감소율에 따라 M개의 우등 채널과 N-M개의 열등 채널을 분류하고, M개의 우등 채널 각각에 대한 N-M개의 열등 채널의 상관도가 모두 제 1 기준값(Λ) 이상이면, 해당 L개의 열등 채널을 우등 채널로 재분류하여 최종적으로 M+L개의 유효 채널을 결정할 수 있다.The effective
보다 구체적으로, 유효 채널 결정부(726)는 분류 적합도에 대한 우선 순위별 감소율이 제 2 기준값(Δ)보다 크면, 우등 채널로 분류하고, 제 2 기준값(Δ) 이하이면, 열등 채널로 분류할 수 있다. 여기서, 우선 순위별 감소율은 채널간 미분치로서, 이전 상위 채널의 분류 적합도에 대한 해당 채널의 분류 적합도의 상대적인 감소값을 의미한다.More specifically, the effective
유효 채널 결정부(726)는 우등 채널 각각에 대한 열등 채널의 일대일 상관도를 연산하여 열등 채널 중에서 우등 채널 모두에 대하여 연산된 상관도가 제 1 기준값(Λ) 이상인 열등 채널을 상기 우등 채널로 재분류할 수 있다. 여기서, 채널 상관도는 알려진 통계적, 수학적 기법을 사용하여 연산되며, 예를 들면, 신호 정합성(coherence)을 이용하여 연산될 수 있다. 즉, 유효 채널 결정부(726)는 열등 채널 중에서 우등 채널 모두에 대하여 상관도가 상기 제 1 기준값 이상인 열등 채널을 우등 채널로 재분류할 수 있다. 여기서, 재분류된 채널이 L개라고 가정하면, 유효 채널 결정부(726)는 최종적으로 M+L개의 유효 채널을 결정하고, 나머지 N-(M+L)개의 채널들은 열등 채널에 잔류시킬 수 있다.The effective
또한, 유효 채널 결정부(726)는 결정된 최종 유효 채널에 따라 뇌혈류 신호를 획득하기 위한 관련 광극 위치를 결정할 수 있다. 이때, 통계적 뇌활성 영상과 비교 분석하고, 유효 채널들에 대한 산화헤모글로빈 농도 변화를 기초로 유효 채널로서 적합함을 검증하고, 유효 채널의 형성에 관여한 발광극과 수광극을 결정할 수 있다.Also, the effective
표시부(730)는 유효 위치 추출부(720)에서 처리되는 과정을 디스플레이할 수 있다. 이러한 표시부(730)는 유효 위치 추출부(720)에 연결된 디스플레이일 수 있다.The
이상에서 본 발명의 일 실시예에 대하여 설명하였으나, 본 발명의 사상은 본 명세서에 제시되는 실시 예에 제한되지 아니하며, 본 발명의 사상을 이해하는 당업자는 동일한 사상의 범위 내에서, 구성요소의 부가, 변경, 삭제, 추가 등에 의해서 다른 실시 예를 용이하게 제안할 수 있을 것이나, 이 또한 본 발명의 사상범위 내에 든다고 할 것이다.While the present invention has been particularly shown and described with reference to exemplary embodiments thereof, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited to the disclosed exemplary embodiments, It will be understood by those skilled in the art that various changes in form and details may be made therein without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims.
700 : 유효 위치 결정 장치710 : 데이터 획득부
720 : 유효 위치 추출부722 : 잡음 제거부
724 : 사전 처리부726 : 유효 채널 결정부
730 : 표시부700: effective position determining device 710: data obtaining unit
720: Valid position extracting unit 722: Noise removing unit
724: Preprocessing section 726: Effective channel determining section
730:
Claims (8)
Translated fromKorean상기 획득된 뇌혈류 신호에서 피험자의 호흡, 혈액 순환, 움직임을 포함하는 잡음 성분을 제거하는 단계;
상기 잡음 제거된 신호를 수행 및 휴지에 대한 시계열 자료들로 구분하여 수행-휴지 분류 적합도를 산출하고, 상기 산출된 분류 적합도에 따라 우선 순위를 부여하는 사전 처리 단계; 및
상기 우선 순위별 감소율에 따라 M개의 우등 채널과 N-M개의 열등 채널을 분류하고, 상기 M개의 우등 채널 각각에 대한 상기 N-M개의 열등 채널의 상관도가 모두 제 1 기준값 이상이면, 해당 L개의 열등 채널을 상기 우등 채널로 재분류하여 최종적으로 M+L개의 유효 채널을 결정하는 단계를 포함하는 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법.Obtaining a cerebral blood flow signal from N measurement channels corresponding to a plurality of positions of the scalp by functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS);
Removing noise components including respiration, blood circulation, and movement of the subject from the acquired cerebral blood flow signal;
A pre-processing step of dividing the noise-removed signal into time-series data for performance and dormancy to calculate a performance-dormant classification fitness and giving priority to the calculated classification fitness; And
Classifying the M number of good channels and the number of NM poor channels according to the priority decreasing rate and if the correlations of the NM number of poor channels with respect to each of the M number of good channels are equal to or greater than a first reference value, And finally determining M + L effective channels by reclassifying the right channel into the right channel.
상기 사전 처리 단계는,
상기 잡음 제거된 신호를 수행 및 휴지에 대한 시계열 자료로 정렬하는 단계;
공통 공간 패턴화(Common Spatial Pattern; CSP)를 이용하여 상기 정렬된 자료를 수행 및 휴지를 독립 변인으로 하는 새로운 분류 공간으로 사상하는 단계;
상기 분류 공간 상에서 상기 채널에 대하여 수행 및 휴지를 구별하는 구별 함수를 생성하는 단계; 및
SVM(support vector machine) 알고리즘을 이용하여 상기 생성된 구별 함수로부터 상기 각 채널에 대한 수행-휴지 분류 적합도를 연산하는 단계를 포함하는 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법.The method according to claim 1,
The pre-
Sorting the noise canceled signal into time series data for execution and pause;
Mapping the sorted data to a new classification space having independent parameters such as pause and hibernation using common space pattern (CSP);
Generating a discrimination function for discriminating performance and dormancy for the channel on the classification space; And
And computing a performance-pause classification fitness for each channel from the generated distinct function using a SVM (support vector machine) algorithm.
상기 유효 채널을 결정하는 단계는,
상기 우선 순위별 감소율이 제 2 기준값보다 크면, 상기 우등 채널로 분류하고, 상기 제 2 기준값 이하이면, 상기 열등 채널로 분류하는 단계;
상기 우등 채널 각각에 대한 상기 열등 채널의 일대일 상관도를 연산하는 단계; 및
상기 열등 채널 중에서 상기 우등 채널 모두에 대하여 상기 연산된 상관도가 상기 제 1 기준값 이상인 열등 채널을 상기 우등 채널로 재분류하는 단계를 포함하는 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein determining the valid channel comprises:
Classifying the channel into the good channel if the rate of decrease according to the priority is greater than the second reference value and classifying it into the poor channel if the rate is lower than the second reference value;
Calculating a one-to-one correlation of the inferior channel with respect to each of the superior channels; And
And recategorizing, for all of the poor channels, the poor channel whose calculated degree of correlation is equal to or greater than the first reference value, to the superior channel, based on brain activity measurement of the functional near-infrared spectroscopy.
상기 결정된 최종 유효 채널에 따라 상기 뇌혈류 신호를 획득하기 위한 관련 광극 위치를 결정하는 단계를 더 포함하는 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 방법.The method according to claim 1,
And determining an associated light pole position for acquiring the cerebral blood flow signal according to the determined final effective channel. ≪ RTI ID = 0.0 > 18. < / RTI >
기능적 근적외선 분광법(fNIRS)에 의해 두피의 복수의 위치에 대응하는 N개의 측정 채널로부터 뇌혈류 신호를 획득하는 데이터 획득부;
상기 획득된 뇌혈류 신호에서 피험자의 호흡, 혈액 순환, 움직임을 포함하는 잡음 성분을 제거하는 잡음 제거부;
상기 잡음 제거된 신호를 수행 및 휴지에 대한 시계열 자료들로 구분하여 수행-휴지 분류 적합도를 산출하고, 상기 산출된 분류 적합도에 따라 우선 순위를 부여하는 사전 처리부; 및
상기 우선 순위별 감소율에 따라 M개의 우등 채널과 N-M개의 열등 채널을 분류하고, 상기 M개의 우등 채널 각각에 대한 상기 N-M개의 열등 채널의 상관도가 모두 제 1 기준값 이상이면, 해당 L개의 열등 채널을 상기 우등 채널로 재분류하여 최종적으로 M+L개의 유효 채널을 결정하는 유효 채널 결정부를 포함하는 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 장치.A data obtaining unit for obtaining a cerebral blood flow signal by functional near infrared ray spectroscopy (fNIRS);
A data obtaining unit for obtaining a cerebral blood flow signal from N measurement channels corresponding to a plurality of positions of the scalp by functional near infrared ray spectroscopy (fNIRS);
A noise eliminator for removing a noise component including respiration, blood circulation, and movement of the subject in the acquired cerebral blood flow signal;
A pre-processing unit for dividing the noise-removed signal into time series data for performance and dormancy to calculate a performance-dormant classification fitness and giving priority to the calculated classification fitness according to the calculated classification fitness; And
Classifying the M number of good channels and the number of NM poor channels according to the priority decreasing rate and if the correlations of the NM number of poor channels with respect to each of the M number of good channels are equal to or greater than a first reference value, And an effective channel determining unit for determining the M + L effective channels by reclassifying the right channel into the good channel.
상기 사전 처리부는,
상기 잡음 제거된 신호를 수행 및 휴지에 대한 시계열 자료로 정렬하고,
공통 공간 패턴화(CSP)를 이용하여 상기 정렬된 자료를 수행 및 휴지를 독립 변인으로 하는 새로운 분류 공간으로 사상하며,
상기 분류 공간 상에서 상기 채널에 대하여 수행 및 휴지를 구별하는 구별 함수를 생성하고,
SVM 알고리즘을 이용하여 상기 생성된 구별 함수로부터 상기 각 채널에 대한 수행-휴지 분류 적합도를 연산하는 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 장치.6. The method of claim 5,
The pre-
Sorting the noise canceled signal into time series data for execution and rest,
Mapping the sorted data to a new classification space having independent parameters such as the execution and the rest using the common space patterning (CSP)
Generating a distinction function for distinguishing execution and pause for the channel on the classification space,
An effective position determining device according to a brain activity measurement of a functional near infrared ray spectroscopy method for calculating an execution-pause classification fitness for each channel from the generated discrimination function using an SVM algorithm.
상기 유효 채널 결정부는,
상기 우선 순위별 감소율이 제 2 기준값보다 크면, 상기 우등 채널로 분류하고, 상기 제 2 기준값 이하이면, 상기 열등 채널로 분류하고,
상기 우등 채널 각각에 대한 상기 열등 채널의 일대일 상관도를 연산하여 상기 열등 채널 중에서 상기 우등 채널 모두에 대하여 상기 연산된 상관도가 상기 제 1 기준값 이상인 열등 채널을 상기 우등 채널로 재분류하는 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 장치.6. The method of claim 5,
The valid channel determination unit may determine,
Classifying the channel into the superior channel if the rate of decrease according to the priority is greater than the second reference value, classifying the channel into the poor channel if the rate is less than the second reference value,
One-to-one correlation of the inferior channel with respect to each of the superior channels, and reclassifying the inferior channel having the calculated degree of correlation to the superior channel to the superior channel for all of the inferior channels, Of the brain.
상기 유효 채널 결정부는 상기 결정된 최종 유효 채널에 따라 상기 뇌혈류 신호를 획득하기 위한 관련 광극 위치를 결정하는 기능적 근적외선 분광법의 뇌활성도 측정에 따른 유효 위치 결정 장치.6. The method of claim 5,
Wherein the effective channel determination unit determines an associated light pole position for acquiring the cerebral blood flow signal according to the determined final effective channel.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR20150050186 | 2015-04-09 | ||
| KR1020150050186 | 2015-04-09 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20160121348Atrue KR20160121348A (en) | 2016-10-19 |
| KR101703547B1 KR101703547B1 (en) | 2017-02-07 |
Family
ID=57250932
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150079615AActiveKR101703547B1 (en) | 2015-04-09 | 2015-06-05 | Method and apparatus for estimating effective channel of functional near-infrared spectroscopy |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101703547B1 (en) |
Cited By (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20190140705A (en) | 2018-06-12 | 2019-12-20 | 재단법인대구경북과학기술원 | Method and Device for removing noise from Functional near-infrared spectroscopy signal |
| CN110680282A (en)* | 2019-10-09 | 2020-01-14 | 黑龙江洛唯智能科技有限公司 | A method, device and system for detecting temporary abnormal state of the brain |
| WO2020209688A1 (en) | 2019-04-12 | 2020-10-15 | 한국과학기술원 | Method, system, and non-transitory computer-readable recording medium for estimating biometric information about head using machine learning |
| KR102211049B1 (en)* | 2020-12-01 | 2021-02-04 | (주)엔브레인 | (AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED BRAIN INFORMATION PROVIDING DEVICE USING BIOMETRIC INFORMATION |
| KR102211030B1 (en)* | 2020-12-01 | 2021-02-04 | (주)엔브레인 | AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED BRAIN INFORMATION PROVIDING DEVICES USING BRAIN STIMULATION |
| KR102211048B1 (en)* | 2020-12-01 | 2021-02-04 | (주)엔브레인 | AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED BRAIN INFORMATION PROVIDING DEVICES USING AUDITORY INFORMATION |
| KR102211050B1 (en)* | 2020-12-01 | 2021-02-04 | (주)엔브레인 | AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED BRAIN INFORMATION PROVIDING DEVICES USING MEDICAL IMAGING INFORMATION |
| KR102222335B1 (en)* | 2020-12-01 | 2021-03-04 | (주)엔브레인 | AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED DEVICE THAT PROVIDES BRAIN INFORMATION BASED ON INFORMATION COLLECTED WHILE THE USER IS IN MOTION |
| KR102241759B1 (en)* | 2020-07-22 | 2021-04-20 | (주)엔브레인 | AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED BRAIN INFORMATION PROVIDING DEVICES |
| KR102288267B1 (en)* | 2020-07-22 | 2021-08-11 | 액티브레인바이오(주) | AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED METHOD OF PROVIDING BRAIN INFORMATION |
| CN113633262A (en)* | 2021-08-13 | 2021-11-12 | 嘉兴知芯电子科技有限公司 | Near-infrared spectrum brain function imaging system and imaging signal sampling method |
| KR102571116B1 (en)* | 2023-02-21 | 2023-08-24 | 고려대학교 세종산학협력단 | Method and device of brain-computer interface based on optimal channel selection algorithm using nirs |
| KR20240002544A (en) | 2022-06-29 | 2024-01-05 | 원광대학교산학협력단 | Method for determining suicide risk group using fNIRS signal |
| KR102693054B1 (en)* | 2023-11-06 | 2024-08-06 | 김우섭 | Dementia diagnosis system based on olfaction test and dementia diagnosis method based on olfaction test using the same |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102090671B1 (en) | 2017-09-15 | 2020-03-18 | 재단법인 대구경북과학기술원 | Method and Device for removing noise from multi-channel fNIRS |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20140107494A1 (en)* | 2011-05-31 | 2014-04-17 | Nagoya Institute Of Technology | Cognitive Impairment Determination Apparatus, Cognitive Impairment Determination System and Program |
| KR20140051591A (en) | 2012-10-23 | 2014-05-02 | 주식회사 싸이버메딕 | Walking analysis treadmill of unweight control |
- 2015
- 2015-06-05KRKR1020150079615Apatent/KR101703547B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20140107494A1 (en)* | 2011-05-31 | 2014-04-17 | Nagoya Institute Of Technology | Cognitive Impairment Determination Apparatus, Cognitive Impairment Determination System and Program |
| KR20140051591A (en) | 2012-10-23 | 2014-05-02 | 주식회사 싸이버메딕 | Walking analysis treadmill of unweight control |
Cited By (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20190140705A (en) | 2018-06-12 | 2019-12-20 | 재단법인대구경북과학기술원 | Method and Device for removing noise from Functional near-infrared spectroscopy signal |
| WO2020209688A1 (en) | 2019-04-12 | 2020-10-15 | 한국과학기술원 | Method, system, and non-transitory computer-readable recording medium for estimating biometric information about head using machine learning |
| KR20200120551A (en) | 2019-04-12 | 2020-10-21 | 한국과학기술원 | Method, system and non-transitory computer-readable recording medium for estimating bio information about head by using machine learning |
| CN110680282A (en)* | 2019-10-09 | 2020-01-14 | 黑龙江洛唯智能科技有限公司 | A method, device and system for detecting temporary abnormal state of the brain |
| KR102241759B1 (en)* | 2020-07-22 | 2021-04-20 | (주)엔브레인 | AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED BRAIN INFORMATION PROVIDING DEVICES |
| KR102298943B1 (en)* | 2020-07-22 | 2021-09-09 | 액티브레인바이오(주) | AI(Artificial Intelligence) based informative method provides brain information determined when the user is in motion, and information for brain activation |
| KR102298940B1 (en)* | 2020-07-22 | 2021-09-09 | 액티브레인바이오(주) | AI(Artificial Intelligence) based device provides brain information determined when the user is in motion, and information for brain activation |
| KR102288267B1 (en)* | 2020-07-22 | 2021-08-11 | 액티브레인바이오(주) | AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED METHOD OF PROVIDING BRAIN INFORMATION |
| KR102211049B1 (en)* | 2020-12-01 | 2021-02-04 | (주)엔브레인 | (AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED BRAIN INFORMATION PROVIDING DEVICE USING BIOMETRIC INFORMATION |
| KR102222335B1 (en)* | 2020-12-01 | 2021-03-04 | (주)엔브레인 | AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED DEVICE THAT PROVIDES BRAIN INFORMATION BASED ON INFORMATION COLLECTED WHILE THE USER IS IN MOTION |
| KR102211050B1 (en)* | 2020-12-01 | 2021-02-04 | (주)엔브레인 | AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED BRAIN INFORMATION PROVIDING DEVICES USING MEDICAL IMAGING INFORMATION |
| KR102211048B1 (en)* | 2020-12-01 | 2021-02-04 | (주)엔브레인 | AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED BRAIN INFORMATION PROVIDING DEVICES USING AUDITORY INFORMATION |
| KR102211030B1 (en)* | 2020-12-01 | 2021-02-04 | (주)엔브레인 | AI(Artificial Intelligence) BASED BRAIN INFORMATION PROVIDING DEVICES USING BRAIN STIMULATION |
| CN113633262A (en)* | 2021-08-13 | 2021-11-12 | 嘉兴知芯电子科技有限公司 | Near-infrared spectrum brain function imaging system and imaging signal sampling method |
| CN113633262B (en)* | 2021-08-13 | 2023-08-18 | 嘉兴知芯电子科技有限公司 | Near infrared spectrum brain function imaging system and imaging signal sampling method |
| KR20240002544A (en) | 2022-06-29 | 2024-01-05 | 원광대학교산학협력단 | Method for determining suicide risk group using fNIRS signal |
| KR102571116B1 (en)* | 2023-02-21 | 2023-08-24 | 고려대학교 세종산학협력단 | Method and device of brain-computer interface based on optimal channel selection algorithm using nirs |
| KR102693054B1 (en)* | 2023-11-06 | 2024-08-06 | 김우섭 | Dementia diagnosis system based on olfaction test and dementia diagnosis method based on olfaction test using the same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR101703547B1 (en) | 2017-02-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101703547B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for estimating effective channel of functional near-infrared spectroscopy | |
| Oliveira et al. | Induction and separation of motion artifacts in EEG data using a mobile phantom head device | |
| US4736751A (en) | Brain wave source network location scanning method and system | |
| JP7221693B2 (en) | Method and magnetic imaging device for cataloging cortical function in the human brain | |
| Gow Jr et al. | Lexical influences on speech perception: a Granger causality analysis of MEG and EEG source estimates | |
| Chen et al. | Scalp EEG-based pain detection using convolutional neural network | |
| KR102143900B1 (en) | System for providing subject-independent brain-computer interface and method thereof | |
| US20160029965A1 (en) | Artifact as a feature in neuro diagnostics | |
| Brosnan et al. | Evidence accumulation during perceptual decisions in humans varies as a function of dorsal frontoparietal organization | |
| US20070179396A1 (en) | Method and System for Detecting and Classifying Facial Muscle Movements | |
| KR101535352B1 (en) | Measurement of depression depth with frontal lobe brain waves | |
| CA2657407A1 (en) | Analysis of brain patterns using temporal measures | |
| Kohan et al. | Interview based connectivity analysis of EEG in order to detect deception | |
| Jiang et al. | Characterization of bimanual cyclical tasks from single-trial EEG-fNIRS measurements | |
| Khalid et al. | Epileptic MEG spikes detection using amplitude thresholding and dynamic time warping | |
| CN113614751A (en) | Electroencephalogram signal identification and extraction | |
| Wang et al. | On the channel density of EEG signals for reliable biometric recognition | |
| Kaur et al. | Using virtual reality to examine the neural and physiological anxiety-related responses to balance-demanding target-reaching leaning tasks | |
| Euler et al. | Reliable activation to novel stimuli predicts higher fluid intelligence | |
| Ramanand et al. | Complexity quantification of dense array EEG using sample entropy analysis | |
| Zhou et al. | Upper-limb functional assessment after stroke using mirror contraction: A pilot study | |
| JP6834318B2 (en) | Stress evaluation device and method | |
| Bodda et al. | Computational analysis of EEG activity during stance and swing gait phases | |
| JP7206287B2 (en) | Systems for real-time measurement of cognitive activity and methods of calibrating such systems | |
| Hu et al. | Spectral homogeneity cross frequencies can be a quality metric for the large-scale resting EEG preprocessing |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20150605 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20170104 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0702 | Registration of establishment of national patent | Patent event code:PR07021E01D Comment text:Registration of Establishment of National Patent Patent event date:20170201 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20170201 End annual number:20 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration |