KR20080035926A - Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Core-External Structured Gold Nanoparticles Containing Magnetic Nanoparticles as T2 Contrast Agent, Cancer Diagnosis and Cancer Treatment - Google Patents
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Core-External Structured Gold Nanoparticles Containing Magnetic Nanoparticles as T2 Contrast Agent, Cancer Diagnosis and Cancer TreatmentDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20080035926A KR20080035926AKR1020060102604AKR20060102604AKR20080035926AKR 20080035926 AKR20080035926 AKR 20080035926AKR 1020060102604 AKR1020060102604 AKR 1020060102604AKR 20060102604 AKR20060102604 AKR 20060102604AKR 20080035926 AKR20080035926 AKR 20080035926A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- nanoparticles
- cancer
- magnetic
- gold
- diameter
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
- 206010028980NeoplasmDiseases0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription89
- 201000011510cancerDiseases0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription88
- 239000010931goldSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription82
- 229910052737goldInorganic materials0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription82
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-NgoldChemical compound[Au]PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription71
- 239000002105nanoparticleSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription66
- 238000002595magnetic resonance imagingMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription30
- 239000002122magnetic nanoparticleSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription27
- 239000002872contrast mediaSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription26
- 238000011282treatmentMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription16
- 238000003745diagnosisMethods0.000titledescription7
- 230000005291magnetic effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription56
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription33
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-NSilicium dioxideChemical groupO=[Si]=OVYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription24
- 239000003446ligandSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription20
- 239000002078nanoshellSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription18
- 239000000032diagnostic agentSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription14
- 229940039227diagnostic agentDrugs0.000claimsabstractdescription14
- 229940124597therapeutic agentDrugs0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 239000012830cancer therapeuticSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 229910001260Pt alloyInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription18
- 229920001515polyalkylene glycolPolymers0.000claimsdescription16
- 229910017052cobaltInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription12
- 239000010941cobaltSubstances0.000claimsdescription12
- GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncobalt atomChemical compound[Co]GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription12
- 229910000859α-FeInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription12
- SZVJSHCCFOBDDC-UHFFFAOYSA-Niron(II,III) oxideInorganic materialsO=[Fe]O[Fe]O[Fe]=OSZVJSHCCFOBDDC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription10
- PWHULOQIROXLJO-UHFFFAOYSA-NManganeseChemical compound[Mn]PWHULOQIROXLJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- 229910052748manganeseInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription8
- 239000011572manganeseSubstances0.000claimsdescription8
- 150000002343goldChemical class0.000claimsdescription7
- 108091023037AptamerProteins0.000claimsdescription6
- 229910003321CoFeInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription6
- 229910020707Co—PtInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription6
- 229910045601alloyInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000000956alloySubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 229910001566austeniteInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription6
- GUBSQCSIIDQXLB-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncobalt platinumChemical compound[Co].[Pt].[Pt].[Pt]GUBSQCSIIDQXLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- 229940014144folateDrugs0.000claimsdescription6
- OVBPIULPVIDEAO-LBPRGKRZSA-Nfolic acidChemical compoundC=1N=C2NC(N)=NC(=O)C2=NC=1CNC1=CC=C(C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(O)=O)C=C1OVBPIULPVIDEAO-LBPRGKRZSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- 235000019152folic acidNutrition0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000011724folic acidSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- OBACEDMBGYVZMP-UHFFFAOYSA-Niron platinumChemical compound[Fe].[Fe].[Pt]OBACEDMBGYVZMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- 108090000765processed proteins & peptidesProteins0.000claimsdescription6
- 230000017074necrotic cell deathEffects0.000claimsdescription5
- 230000001678irradiating effectEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000005670electromagnetic radiationEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000002372labellingMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000003795chemical substances by applicationSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-Niron(III) oxideInorganic materialsO=[Fe]O[Fe]=OJEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- AMWRITDGCCNYAT-UHFFFAOYSA-Lhydroxy(oxo)manganese;manganeseChemical compound[Mn].O[Mn]=O.O[Mn]=OAMWRITDGCCNYAT-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000claims20
- 206010037660PyrexiaDiseases0.000claims1
- 238000003384imaging methodMethods0.000abstractdescription2
- 239000006249magnetic particleSubstances0.000abstractdescription2
- 239000002202Polyethylene glycolSubstances0.000description7
- 239000002086nanomaterialSubstances0.000description7
- 229920001223polyethylene glycolPolymers0.000description7
- 238000013399early diagnosisMethods0.000description6
- 238000010438heat treatmentMethods0.000description6
- 239000002245particleSubstances0.000description6
- 101001012157Homo sapiens Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2Proteins0.000description5
- 102100030086Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2Human genes0.000description5
- 238000010521absorption reactionMethods0.000description5
- 239000000377silicon dioxideSubstances0.000description5
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description4
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description4
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description4
- 238000003786synthesis reactionMethods0.000description4
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description3
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-NironSubstances[Fe]XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 230000005415magnetizationEffects0.000description3
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description3
- 229940031182nanoparticles iron oxideDrugs0.000description3
- 229920000642polymerPolymers0.000description3
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthylene glycolChemical compoundOCCOLYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- UQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NIron oxideChemical compound[Fe]=OUQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 240000002390Pandanus odoratissimusSpecies0.000description2
- 235000005311Pandanus odoratissimusNutrition0.000description2
- 238000000418atomic force spectrumMethods0.000description2
- 230000001419dependent effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 239000012091fetal bovine serumSubstances0.000description2
- 238000000338in vitroMethods0.000description2
- 238000011534incubationMethods0.000description2
- 230000031700light absorptionEffects0.000description2
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000description2
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description2
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description2
- 230000008685targetingEffects0.000description2
- 241000894006BacteriaSpecies0.000description1
- 108091003079Bovine Serum AlbuminProteins0.000description1
- 206010006187Breast cancerDiseases0.000description1
- 229910052688GadoliniumInorganic materials0.000description1
- QPCDCPDFJACHGM-UHFFFAOYSA-NN,N-bis{2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl}glycineChemical compoundOC(=O)CN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(=O)O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=OQPCDCPDFJACHGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000012980RPMI-1640 mediumSubstances0.000description1
- 229910004298SiO 2Inorganic materials0.000description1
- GLNADSQYFUSGOU-GPTZEZBUSA-JTrypan blueChemical compound[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].C1=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=C2C=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C(/N=N/C3=CC=C(C=C3C)C=3C=C(C(=CC=3)\N=N\C=3C(=CC4=CC(=CC(N)=C4C=3O)S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)C)=C(O)C2=C1NGLNADSQYFUSGOU-GPTZEZBUSA-J0.000description1
- 102000004142TrypsinHuman genes0.000description1
- 108090000631TrypsinProteins0.000description1
- 125000004429atomChemical group0.000description1
- 230000002238attenuated effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description1
- 201000008274breast adenocarcinomaDiseases0.000description1
- 229910002091carbon monoxideInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000004113cell cultureMethods0.000description1
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description1
- 239000008367deionised waterSubstances0.000description1
- 229910021641deionized waterInorganic materials0.000description1
- 230000001066destructive effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description1
- 238000002405diagnostic procedureMethods0.000description1
- 238000000502dialysisMethods0.000description1
- 230000004069differentiationEffects0.000description1
- 239000006185dispersionSubstances0.000description1
- 239000012153distilled waterSubstances0.000description1
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000description1
- 238000012377drug deliveryMethods0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- UIWYJDYFSGRHKR-UHFFFAOYSA-Ngadolinium atomChemical compound[Gd]UIWYJDYFSGRHKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000011521glassSubstances0.000description1
- 125000004435hydrogen atomChemical group[H]*0.000description1
- WGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-NhydroxyacetaldehydeNatural productsOCC=OWGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000006698inductionEffects0.000description1
- WTFXARWRTYJXII-UHFFFAOYSA-Niron(2+);iron(3+);oxygen(2-)Chemical compound[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Fe+2].[Fe+3].[Fe+3]WTFXARWRTYJXII-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 201000005243lung squamous cell carcinomaDiseases0.000description1
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000description1
- 229910021645metal ionInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 238000012638near-infrared photothermal therapyMethods0.000description1
- 230000001338necrotic effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000005298paramagnetic effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000004065semiconductorSubstances0.000description1
- 239000002109single walled nanotubeSubstances0.000description1
- 238000001179sorption measurementMethods0.000description1
- 238000000264spin echo pulse sequenceMethods0.000description1
- 230000004083survival effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000009885systemic effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007704transitionEffects0.000description1
- 239000012588trypsinSubstances0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K49/00—Preparations for testing in vivo
- A61K49/06—Nuclear magnetic resonance [NMR] contrast preparations; Magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] contrast preparations
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K49/00—Preparations for testing in vivo
- A61K49/06—Nuclear magnetic resonance [NMR] contrast preparations; Magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] contrast preparations
- A61K49/18—Nuclear magnetic resonance [NMR] contrast preparations; Magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] contrast preparations characterised by a special physical form, e.g. emulsions, microcapsules, liposomes
- A61K49/1818—Nuclear magnetic resonance [NMR] contrast preparations; Magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] contrast preparations characterised by a special physical form, e.g. emulsions, microcapsules, liposomes particles, e.g. uncoated or non-functionalised microparticles or nanoparticles
- A61K49/1887—Agglomerates, clusters, i.e. more than one (super)(para)magnetic microparticle or nanoparticle are aggregated or entrapped in the same maxtrix
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B82—NANOTECHNOLOGY
- B82Y—SPECIFIC USES OR APPLICATIONS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MEASUREMENT OR ANALYSIS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF NANOSTRUCTURES
- B82Y5/00—Nanobiotechnology or nanomedicine, e.g. protein engineering or drug delivery
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Nanotechnology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
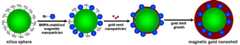
Translated fromKorean도 1은 본 발명의 합성 과정을 단계적으로 묘사한 그림이다.1 is a step-by-step depiction of the synthesis process of the present invention.
도 2는 본 발명의 각 합성 과정에 해당하는 중간 물질과 결과물의 투과 전자 현미경(TEM) 사진이다.2 is a transmission electron microscope (TEM) photograph of the intermediate and the resultant corresponding to each synthesis process of the present invention.
도 3는 본 발명에 따른 자성 금 나노 입자의 수분산 상태의 사진이다.3 is a photograph of the water dispersion state of the magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
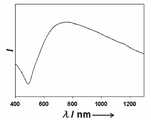
도 4는 본 발명에 따른 자성 금 나노 입자의 가시 광선-근적외선 (Vis-NIR) 흡수 곡선이다.4 is a visible-near-infrared (Vis-NIR) absorption curve of magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
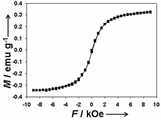
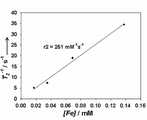
도 5는 본 발명에 따른 자성 금 나노 입자의 장-의존 자력 곡선이다.5 is a field-dependent magnetic force curve of magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
도 6은 본 발명에 따른 자성 금 나노 입자의 농도에 따른 T2 영상이다.6 is a T2 image according to the concentration of magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
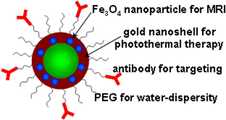
도 7은 본 발명에 따른 자성 금 나노 입자의 표면 개질에 의한 표적 지향성 자성 금 나노 입자를 묘사한 그림이다.7 is a diagram depicting a target-directed magnetic gold nanoparticles by surface modification of the magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
도 8은 본 발명에 따른 자성 금 나노 입자의 농도에 따른 r2 이완성이다.8 is r2 relaxation according to the concentration of the magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
도 9는 본 발명에 따른 표적 지향성 자성 금 나노 입자를 이용한 암세포의 선택적 자기공명영상이다.9 is a selective magnetic resonance imaging of cancer cells using the target-directed magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
도 10은 본 발명에 따른 표적 지향성 자성 금 나노 입자를 이용한, 근적외선 레이저의 세기에 따른, 암세포의 선택적이고 비파괴적이며 매우 빠른 괴사를 나타내는 그림이다.10 is a diagram showing the selective, non-destructive and very rapid necrosis of cancer cells according to the intensity of the near infrared laser using the target-directed magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
도 11은 본 발명에 따른 표적 지향성 자성 금 나노 입자를 통해 괴사된 암세포의 확대 그림이다.11 is an enlarged view of cancer cells necroticized through the target-directed magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
a) S. J. Oldenburg, R. D. Averitt, S. L. Westcott, N. J. Halas,Chem. Phys. Lett.1998,288, 243; b) L. R. Hirsch, R. J. Stafford, J. A. Bankson, S. R. Sershen, B. Rivera, R. E. Price, J. D. Hazla, N. J. Halas, J. L. West,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA2003,100, 13549, c) D. P. O'Neal, L. R. Hirsch, N. J. Halas, J. D. Payne, J. L. West,Cancer Lett.2004,209, 171, d) C. Loo, A. Lowery, N. J. Halas, J. L. West, R. Drezek,Nano Lett.2005,5, 709, e) S. I. Stoeva, F. Huo, J.-S. Lee, C. A. Mirkin,J. Am. Chem. Soc.2005,127, 15362.a) SJ Oldenburg, RD Averitt, SL Westcott, NJ Halas,Chem. Phys. Lett.1998 ,288 , 243; b) LR Hirsch, RJ Stafford, JA Bankson, SR Sershen, B. Rivera, RE Price, JD Hazla, NJ Halas, JL West,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA2003 ,100 , 13549, c) DP O'Neal, LR Hirsch, NJ Halas, JD Payne, JL West,Cancer Lett.2004 ,209 , 171, d) C. Loo, A. Lowery, NJ Halas, JL West, R. Drezek,Nano Lett .2005 ,5 , 709, e) SI Stoeva, F. Huo, J.-S. Lee, CA Mirkin,J. Am. Chem. Soc.2005 ,127 , 15362.
본 발명은 자성체 나노입자가 함유된 금으로 이루어진 외각(쉘, shell)과 실리카 코어로 이루어진 자성 금 나노입자의 자기공명영상(MRI) T2 조영제, 암 진단제 및 암 치료제로서의 용도에 관한 것이다. 보다 상세하게는, 금 나노 외각에 내 포되는 자성체 입자 자성을 이용하여 자기공명영상의 T2 조영제로서의 용도, 자성 금 나노입자의 표면에 결합된 표적 지향성 리간드가 암세포에 결합하는 성질를 이용한 암 진단제로서의 용도, 근적외선 영역의 전자기파 펄스의 에너지를 흡수한 금 나노 외각이 방출하는 열를 이용하여 암세포만을 선택적으로 괴사시키는 암 치료제로서의 용도 및 상기 자성 금 나노입자를 이용한 암 진단 방법과 치료 방법에 대한 것이다.FIELD OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T2 contrast agents, shell diagnostics and cancer treatments of magnetic gold nanoparticles consisting of a shell and a shell made of gold containing magnetic nanoparticles. More specifically, the magnetic particle magnetization contained in the gold nano-shells is used as a T2 contrast agent of magnetic resonance imaging, and as a cancer diagnostic agent using the property that the target directional ligand bound to the surface of the magnetic gold nanoparticles binds to cancer cells. The present invention relates to a cancer therapeutic agent that selectively kills only cancer cells by using heat emitted by the gold nanoshells absorbing the energy of electromagnetic wave pulses in the near infrared region, and a cancer diagnosis method and treatment method using the magnetic gold nanoparticles.
본 명세서에서 자기공명영상(MRI, Magnetic Resonance Image)은 자기장 안에서 수소 원자의 스핀이 이완되는 현상을 이용해 신체의 생화학적 정보를 영상으로 얻는 방법이다. 그리고 나노입자란 크기가 수 내지 수백 나노미터(nm, 10억분의 1 미터인 물질, 크기로 인해 원자와 벌크물질의 중간적인 성질을 갖는다)인 입자를 말한다.Magnetic resonance image (MRI) in the present specification is a method of obtaining the biochemical information of the body by using the phenomenon that the spin of the hydrogen atoms in the magnetic field is relaxed. And nanoparticles are particles ranging in size from several hundreds to hundreds of nanometers (nm, a billionth of a meter, because of their intermediate properties between atoms and bulk materials).
또한 이완현상이란 MRI에서 90도 펄스에 의하여 에너지를 흡수하고 높은 에너지 준위로 천이한 핵 스핀은 다음 순간부터 에너지를 방출하면서 원래의 정상 상태로 되돌아 가는 현상으로서, 이러한 이완 과정은 T1 이완과 T2 이완으로 나눌 수 있다. T1 이완이란, 종이완은 Z축 방향의 자화성분 Mz가 원래의 값으로 돌아오는 과정으로서 이상태를 T1으로 표현하는데, T1은 신호가 처음값의 63%로 돌아올때 까지의 시간이다.In addition, the relaxation phenomenon is a nuclear spin that absorbs energy by a 90-degree pulse in MRI and transitions to a high energy level, and then releases energy from the next moment and returns to its original steady state. This relaxation process is T1 relaxation and T2 relaxation. Can be divided into T1 relaxation refers to the process of returning the magnetization component Mz in the Z-axis to its original value and expressing this state as T1, where T1 is the time until the signal returns to 63% of the initial value.
T2 이완이란, 횡이완의 경우 각 스핀은 X-Y 평면상에서 균등하게 넓어지며 거시적 자화 M의 성분 My는 지수 함수적으로 감쇠하는데 이러한 감쇠 상태는 수신 코일에 유도되는 고주파 전류에 의해 검출되고 이는 자유 유도 감쇠 신호(free induction decay, FID) 신호이며, T2란 FID 신호가 처음값의 37%로 감쇠할 때까지의 시간이 T2 이다.In the case of T2 relaxation, in the case of lateral relaxation, each spin is equally widened on the XY plane and the component My of macroscopic magnetization M is exponentially attenuated. This attenuation state is detected by the high frequency current induced in the receiving coil, which is a free induced attenuation. Signal (free induction decay, FID) signal, T2 is the time until the FID signal attenuates to 37% of the initial value is T2.
그리고, 본 명세서에서의 조영제란 MRI 검사시에 조직간의 음영 대비를 증가시키는 물질로 T1 조영제와 T2 조영제가 있다. T1 조영제는 T1 이완시에 조직간의 음영대비를 증가시키는 물질로 가돌리늄 제제인 Gd-DTPA 나 망간 제제인 Mn-DTPA등 금속 이온 착화물이 사용되고 있다. T2 조영제는 T2 이완시에 조직간의 음영대비를 증가시키는 물질로 현재 자성을 띄는 산화철 제제인 Feridex 등이 사용되고 있다.In addition, the contrast agent in the present specification includes a T1 contrast agent and a T2 contrast agent as a material for increasing the contrast between shadows at the time of MRI examination. T1 contrast agent is a substance that increases the contrast between tissues in T1 relaxation, and metal ion complexes such as Gd-DTPA, a gadolinium preparation, and Mn-DTPA, a manganese preparation, are used. T2 contrast agent is a substance that increases the contrast between shadows when T2 relaxes. Feridex, which is a magnetic iron oxide agent, is currently used.
본 명세서에서의 r2이완도(r2 relaxivity)란 T2 이완시간을 줄여 주는 정도를 나타내는 값을 의미한다.In the present specification, r2 relaxivity means a value indicating a degree of reducing the T2 relaxation time.
본 발명에 따른 자성 금 나노입자에 포함된 자성체 나노입자, 금 나노 외각, 또는 반도체 나노 입자와 같은 무기계 나노입자는 그 크기에 따라 다양한 광학적 특성과 자성 특성을 나타내기 때문에 이들의 합성 방법에 대한 많은 연구가 이루어지고 있다.Inorganic nanoparticles such as magnetic nanoparticles, gold nanoshells, or semiconductor nanoparticles included in the magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention exhibit various optical and magnetic properties depending on their size, and thus, many of the methods for the synthesis of the magnetic gold nanoparticles have been described. Research is being done.
그리고 최근에는 이러한 무기계 나노 입자의 독특한 성질을 이용하여 진단, 영상, 치료, 약물 전달 등의 생의학적인 분야에 응용하려는 시도가 활발히 진행되고 있다. 그 중 나노 입자를 암세포의 조기 진단과 그에 이은 적절한 치료에 응용하고자 하는 연구는 매우 중요하다.In recent years, attempts have been actively made to apply such unique properties of inorganic nanoparticles to biomedical fields such as diagnosis, imaging, treatment, and drug delivery. Among them, research to apply nanoparticles to early diagnosis and subsequent treatment of cancer cells is very important.
암의 치료 가능성을 높이는데 있어서 가장 중요한 것은 암세포의 조기 진단과 그에 따른 적합한 치료이다. 암세포의 조기 진단에 있어서는 암세포가 분화 초 기 단계에서 진단하는 것이 매우 중요하다. 이러한 암의 조기 진단에 있어서 나노 입자는 중요한 역할을 담당할 수 있다.The most important factor in improving the treatment potential of cancer is the early diagnosis and appropriate treatment of cancer cells. In the early diagnosis of cancer cells, it is very important that the cancer cells are diagnosed at an early stage of differentiation. Nanoparticles may play an important role in the early diagnosis of these cancers.
나노 입자를 이용하면 그 크기에 의한 암세포에서의 축적이 가능하고 암 특이적인 리간드를 결합시켜서 암을 조기에 진단할 수 있는 가능성이 있다. 상자성 특성을 지닌 산화철 나노 입자의 경우 이미 MRI T2 조영제로서 상용화되어 쓰여지고 있는 실정이다.If nanoparticles are used, their size can accumulate in cancer cells, and there is a possibility of early diagnosis of cancer by binding cancer-specific ligands. In the case of iron oxide nanoparticles with paramagnetic properties, it is already being used as a commercial MRI T2 contrast agent.
진단뿐만 아니라 암의 치료에 있어서도 나노 물질은 앞으로 중요한 역할을 할 것으로 보인다. 최근 들어 비파괴적인 열치료 방법에 대한 연구가 많이 보고되었다. Rice 대학의 Halas 교수와 West 교수 연구팀에서는 금 나노 쉘을 합성하여 이를 열치료에 의한 암세포의 괴사에 응용하였다.Nanomaterials will play an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Recently, many studies on nondestructive heat treatment methods have been reported. Professors Halas and West at Rice University synthesized gold nanoshells and applied them to cancer cell necrosis by heat treatment.
상기 금 나노입자는 실리카 핵 부분과 그 위의 금 나노 외각부로 이루어진 나노 구조물인데 핵과 외각의 두께 비율에 따라 빛의 흡수 파장이 가시 광선 영역에서 근적외선 (NIR) 영역까지 조절된다. 공동 연구팀은 NIR 흡수 단면적이 매우 큰 금 나노 쉘을 합성하여, 금 나노 쉘 표면에 암세포 특위적인 항체를 결합시킨 후 이를 암세포에 반응시키고, 여기에 NIR 연속파 레이저 (CW laser)를 조사하였다.The gold nanoparticles are nanostructures consisting of a silica nucleus portion and a gold nanosurface portion thereon, and the absorption wavelength of light is controlled from the visible region to the near infrared (NIR) region according to the thickness ratio of the nucleus and the outer shell. The team synthesized a gold nanoshell with a very large NIR absorption cross-section, combined the cancer cell-specific antibody on the surface of the gold nanoshell, and reacted it to the cancer cells, and examined the NIR continuous laser.
금 나노 쉘에 의해 흡수된 NIR 빛은 열로 바뀌어 암세포를 효과적으로 괴사시킬 수 있었다. 800 nm 내지 1200 nm의 NIR 영역의 빛은 생체 조직에 의한 흡수가 최소에 달하기 때문에 가시 광선에 비해 조직 깊숙한 곳 도달할 수 있다. 따라서 절개 부위를 최소화하고 NIR 영역의 빛을 조사함으로써 원하는 열치료 효과를 가져 올 수 있다. 금 나노 쉘 이외에도 높은 광흡수 단면적을 가진 금 나노 막대나 단일벽 탄소 나노 튜브를 이용한 암세포의 열치료에 대한 연구도 보고되었다.The NIR light absorbed by the gold nanoshells turned into heat, effectively killing cancer cells. Light in the NIR region of 800 nm to 1200 nm can reach deeper tissue than visible light because absorption by biological tissue is minimal. Therefore, minimizing the incision site and irradiating light of the NIR region can bring the desired heat treatment effect. In addition to the gold nanoshells, studies of heat treatment of cancer cells using gold nanorods or single-walled carbon nanotubes with high light absorption cross sections have been reported.
이러한 연구 결과들을 기반으로 진단과 치료에 이용되는 각각의 나노 물질을 하나로 결합시킨 다기능성 나노 물질을 이용하여 암세포의 진단과 치료를 효과적으로 동시에 수행할 수 있을 것이다. 특히 이미 널리 이용되는 MRI를 이용한 진단과 비파괴적인 NIR을 이용한 열치료를 동시에 가능케 하는 나노 물질은 그 좋은 예가 될 수 있다. 따라서 최근에 이와 같은 의학적으로 유용한 다기능성 나노 물질의 응용에 대한 새로운 기술의 개발이 요구되고 있다.Based on the results of these studies, multifunctional nanomaterials in which each nanomaterial used for diagnosis and treatment are combined into one can be used to effectively diagnose and treat cancer cells simultaneously. In particular, nanomaterials, which make it possible to simultaneously diagnose MRI and heat treatment using NIR, are good examples. Therefore, there is a recent need for the development of new technologies for the application of such medically useful multifunctional nanomaterials.
그러므로 본 발명의 목적은, 자성 금 나노입자의 자기공명영상의 T2 조영제로서의 용도를 제공하는 것이다. 이를 통하여 선행기술에 의한 자기공명영상 보다 선명한 자기공명영상을 얻는 방법을 제공하는 것이다.It is therefore an object of the present invention to provide a use of magnetic gold nanoparticles as a T2 contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging. This provides a method of obtaining a clear magnetic resonance image than the magnetic resonance image according to the prior art.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은, 상기 자성 금 나노입자의 조영제로서의 효과를 이용하여 암을 진단하는 암 진단제로서의 용도를 제공하는 것이다. 상기 입자의 조영 효과로 인하여 효과적인 암 진단 방법을 제공하는 것이다.Still another object of the present invention is to provide a use as a cancer diagnostic agent for diagnosing cancer by utilizing the effect of the magnetic gold nanoparticles as a contrast agent. It is to provide an effective cancer diagnostic method due to the contrast effect of the particles.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은, 상기 입자의 자성 금 나노 외각(Mag-GNS)의 높은 광흡수를 통한 암세포의 치료제로서의 용도 및 치료 방법을 제공하는 것이다. 즉, Mag-GNS 표면의 목표 지향성 리간드를 통해 암세포에 선택적으로 Mag-GNS를 집적할 수 있고 이를 통해 암세포를 MRI를 통해 조기 진단하고, 진단한 암세포를 NIR 파장의 laser를 암세포에 조사함으로써 선택적으로 암세포만 괴사시킬 수 있다.It is still another object of the present invention to provide a use and a method of treating the cancer cells as therapeutic agents for cancer cells through high light absorption of the magnetic gold nano-shells (Mag-GNS). That is, Mag-GNS can be selectively integrated into cancer cells through a target-directed ligand on the surface of Mag-GNS. This enables early diagnosis of cancer cells through MRI and selective diagnosis of cancer cells by irradiating NIR wavelength laser to cancer cells. Only cancer cells can be necrotic.
전술한 본 발명의 일차적인 목적은, 실리카 코어(silica core), 자성체 나노 입자가 내포된 금 외각층의 구조를 갖는 자성 금 나노입자와 상기 나노입자의 표면에 결합된 폴리알킬렌글리콜, 그리고 상기 폴리알킬렌글리콜에 결합된 표적 지향성 리간드를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 자기공명영상용 T2 조영제를 제공함으로써 달성될 수 있다.The primary object of the present invention described above is a silica core, a magnetic gold nanoparticle having a structure of a gold outer layer containing magnetic nanoparticles, a polyalkylene glycol bonded to the surface of the nanoparticles, and It can be achieved by providing a T2 contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging, characterized in that it comprises a target directional ligand bound to polyalkylene glycol.
상기 자성 금 나노입자의 실리카 나노입자 코어의 지름은 바람직하게는 50 nm 내지 500 nm이고, 가장 바람직하게는 100 nm 내지 200 nm이다. 그리고 상기 자성 금 나노입자의 금 나노 외각층의 두께는 바람직하게는 5 nm 내지 50 nm이고, 가장 바람직하게는 10 nm 내지 20 nm이다. 도 5는 본 발명에 따른 자성 금 나노 쉘의 장-의존 자력 곡선이다.The diameter of the silica nanoparticle core of the magnetic gold nanoparticles is preferably 50 nm to 500 nm, most preferably 100 nm to 200 nm. And the thickness of the gold nano outer layer of the magnetic gold nanoparticles is preferably 5 nm to 50 nm, most preferably 10 nm to 20 nm. 5 is a field-dependent magnetic force curve of a magnetic gold nanoshell according to the present invention.
상기 자성 금 나노 입자의 금 외각층 부분에 내포될 수 있는 자성 나노 입자는, 마그네타이트(Fe3O4), 마그헤마이트(gamma-Fe3O4), 코발트 페라이트(CoFe2O4), 망간 옥사이드(MnO), 망간 페라이트(MnFe2O4), 아이언-플래티늄 합금(Fe-Pt alloy), 코발트-플래티늄 합금(Co-Pt alloy) 및 코발트(Co)로 이루어진 군 중에서 선택된 어느 하나 또는 2 이상의 나노입자 혼합물로 이루어진다.Magnetic nanoparticles that can be embedded in the outer layer of the gold nanoparticles of the magnetic nanoparticles, magnetite (Fe3 O4 ), maghemite (gamma-Fe3 O4 ), cobalt ferrite (CoFe2 O4 ), manganese At least one selected from the group consisting of oxide (MnO), manganese ferrite (MnFe2 O4 ), iron-platinum alloy (Fe-Pt alloy), cobalt-platinum alloy (Co-Pt alloy), and cobalt (Co) It consists of a nanoparticle mixture.
상기 자성 금 나노입자의 금 외각층 부분에 내포될 수 있는 자성체 나노입자의 지름은 바람직하게는 2 nm 내지 30 nm이고, 가장 바람직하게는 2 nm 내지 20 nm이다.The diameter of the magnetic nanoparticles that may be included in the gold outer layer portion of the magnetic gold nanoparticles is preferably 2 nm to 30 nm, most preferably 2 nm to 20 nm.
본 발명의 표적 지향성 리간드는 암에 특이적으로 결합하는 데 이용된다.Target directional ligands of the invention are used to specifically bind cancer.
본 발명의 폴리알킬렌글리콜은 상기 자성 금 나노입자에 생체 적합성을 부여하고, 본 발명의 금 나노쉘에 내포된 자성체 나노입자는 자기공명영상의 T2 조영제로서 이용된다. 도 6은 본 발명에 따른 자성 금 나노 입자의 농도에 따른 T2 영상이다. 그리고 도 9는 본 발명에 따른 표적 지향성 자성 금 나노 입자를 이용한 암세포의 선택적 자기공명영상이다.The polyalkylene glycol of the present invention imparts biocompatibility to the magnetic gold nanoparticles, and the magnetic nanoparticles contained in the gold nanoshells of the present invention are used as a T2 contrast agent of magnetic resonance images. 6 is a T2 image according to the concentration of magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention. 9 is a selective magnetic resonance imaging of cancer cells using the target-directed magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은, 자성체 나노 입자가 내포된 금 외각층의 구조를 갖는 자성 금 나노 입자와 상기 나노 입자의 표면에 결합된 폴리알킬렌글리콜, 그리고 상기 폴리알킬렌글리콜에 결합된 표적 지향성 리간드를 포함함으로써, 상기 표적 지향성 리간드가 암세포에 선택적으로 결합되고 외부 전자기파 조사에 반응하여 암세포 위치를 표지하기 위한 암 진단제를 제공함으로써 달성될 수 있다.Still another object of the present invention is to provide a magnetic gold nanoparticle having a structure of a gold outer layer containing magnetic nanoparticles, a polyalkylene glycol bonded to a surface of the nanoparticle, and a target directivity bonded to the polyalkylene glycol. By including a ligand, the target directional ligand can be achieved by selectively binding cancer cells and providing a cancer diagnostic agent for labeling cancer cell locations in response to external electromagnetic radiation.
상기 입자가 암세포와 특이적으로 결합하여 암의 발병 여부를 진단할 수 있게 된다. 본 발명에서 사용되는 표적 지향적 리간드는 anti-HER2/neu와 같은 암 표적 지향적 항체 (cancer targeting antibody), 폴레이트 (folate), 앱타머(aptamer), 태트 펩타이드 (TAT peptide)로 이루어진 군 중에서 선택된다.The particles specifically bind to cancer cells, and thus diagnose the onset of cancer. Target-oriented ligands used in the present invention is selected from the group consisting of cancer targeting antibodies such as anti-HER2 /neu , folate, aptamer, TAT peptide .
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은, 실리카 코어(silica core), 자성체 나노 입자가 내포된 금 외각층의 구조를 갖는 자성 금 나노입자와 상기 나노입자의 표면에 결합된 폴리알킬렌글리콜, 그리고 상기 폴리알킬렌글리콜에 결합된 표적 지향성 리간드를 포함함으로써, 암세포와 결합된 채 근적외선 영역의 전자기파 펄스(pulse)의 조사에 의하여 발생하는 열로 암세포를 괴사시키기 위한 암 치료제를 제공함으로써 달성될 수 있다.Still another object of the present invention is to provide a silica core, a magnetic gold nanoparticle having a structure of a gold outer layer containing magnetic nanoparticles, a polyalkylene glycol bonded to the surface of the nanoparticle, and the polyalkyl By including a target directional ligand bound to len glycol, it can be achieved by providing a cancer therapeutic agent for necrosis of cancer cells with heat generated by irradiation of electromagnetic pulses in the near infrared region while being bound to cancer cells.
상기 금 외각층이 근적외선 영역의 레이저 펄스를 흡수하여 열로 바꾸어 암세포를 효과적으로 괴사시키게 된다. 도 4는 본 발명에 따른 자성 금 나노 입자의 가시 광선-근적외선 (Vis-NIR) 흡수 곡선이다.The outer layer of gold absorbs laser pulses in the near-infrared region and converts them into heat to effectively kill cancer cells. 4 is a visible-near-infrared (Vis-NIR) absorption curve of magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
상기 자성-금나노쉘에 조사되는 레이저 펄스의 파장은 바람직하게는 600 nm 내지 1500 nm이고, 가장 바람직하게는 700 nm 내지 900 nm이다.The wavelength of the laser pulse irradiated to the magnetic-gold nanoshell is preferably 600 nm to 1500 nm, most preferably 700 nm to 900 nm.
상기 자성-금나노쉘에 조사되는 레이저의 펄스 폭 (pulse width)는 바람직하게는 10 fs 내지 200 ps이고, 가장 바람직하게는 10 fs 내지 50 ps이다.The pulse width of the laser irradiated to the magnetic-gold nanoshell is preferably 10 fs to 200 ps, most preferably 10 fs to 50 ps.
상기 자성-금나노쉘에 조사되는 레이저 펄스의 세기는 바람직하게는 1 mW/cm2 내지 1000 mW/cm2 가장 바람직하게는 10 mW/cm2 내지 200 mW/cm2 이다.The intensity of the laser pulses irradiated on the magnetic-gold nanoshell is preferably 1 mW / cm2 to 1000 mW / cm2 Most preferably 10 mW / cm2 to 200 mW / cm2 .
상기 자성-금나노쉘에 조사되는 레이저 펄스의 진동수(frequency)는 바람직하게는 0.1 kHz 내지 1 MHz (1000 kHz)이고 가장 바람직하게는 0.1 kHz 내지 10 kHz이다.The frequency of the laser pulses irradiated on the magnetic-gold nanoshell is preferably 0.1 kHz to 1 MHz (1000 kHz) and most preferably 0.1 kHz to 10 kHz.
상기 자성-금나노쉘에 레이저 펄스를 조사하는 시간은 바람직하게는 1초 내지 10시간이고, 좀 더 바람직하게는 1초 내지 10분이고, 가장 바람직하게는 1초 내지 60초이다.The time for irradiating the laser pulse to the magnetic-gold nanoshell is preferably 1 second to 10 hours, more preferably 1 second to 10 minutes, and most preferably 1 second to 60 seconds.
이하, 본 발명의 구성 요소와 기술적 특징을 다음의 실시 예들을 통하여 보다 상세하게 설명하고자 한다. 그러나 하기의 실시 예들은 본 발명을 상세하게 설명하기 위한 것일 뿐, 본 발명의 구성요소의 기술적 범위를 실시 예들에 예시한 것 들로 한정하고자 하는 것은 아니다.Hereinafter, the components and technical features of the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to the following embodiments. However, the following embodiments are only intended to describe the present invention in detail, and are not intended to limit the technical scope of the components of the present invention to those illustrated in the embodiments.
자성 금 나노 입자의 합성은 크게 두 부분으로 나누어 진다. 첫째, 산화철 나노 입자를 실리카 구의 표면에 조립하는 과정과, 둘째, 산화철 나노 입자가 조립된 실리카 구의 표면 위에 금 나노 외각층을 성장시키는 과정이다. Fe3O4 나노입자와 실리카 구의 조립은 우리가 이전에 보고한 논문에 기술된 바와 같은 방법이다 (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2006,45, 4789). 금 나노 외각층을 SiO2/Fe3O4 입자 위에 성장시키는 것은 기존에 보고된 실리카 입자 표면에 금 외각층을 성장시키는 방법과 동일하다 (Langmuir,2002,18, 524).The synthesis of magnetic gold nanoparticles is divided into two parts. First, assembling the iron oxide nanoparticles on the surface of the silica sphere, and second, growing the gold nano outer layer on the surface of the silica sphere to which the iron oxide nanoparticles are assembled. The assembly of Fe3 O4 nanoparticles and silica spheres is the method as described in the paper we reported earlier (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. ,2006 ,45 , 4789). The growth of gold nanolayers on SiO2 / Fe3 O4 particles is the same as the growth of gold envelopes on previously reported silica particle surfaces (Langmuir ,2002 ,18 , 524).
실시예 1 : 자성 금 나노 외각층(Mag-GNS)표면에 폴리에틸렌글리콜(PEG) 도입Example 1 Introduction of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) on the Surface of Magnetic Gold Nano-External Layer (Mag-GNS)
Mag-GNS의 표면에 폴리에틸렌글리콜 고분자를 결합시켜 주기 위해서는 입자를 PEG-SH (분자량= 5000, 20 μM)와 함께 물에 넣고 2시간 동안 저어준 후, 원심분리로 남아있는 PEG-SH 반응 용액으로부터 제거하였다. PEG가 결합된 Mag-GNS를 이온이 제거된 증류수에 재분산시켰다.To bind the polyethylene glycol polymer to the surface of Mag-GNS, the particles were added to PEG-SH (molecular weight = 5000, 20 μM) in water, stirred for 2 hours, and then centrifuged from the remaining PEG-SH reaction solution. Removed. PEG-bound Mag-GNS was redispersed in deionized water.
실시예 2 : Mag-GNS와 항체의 결합 (Mag-GNS-AbExample 2 Binding of Antibodies to Mag-GNS (Mag-GNS-AbHER2/HER2 /neuneu))
항체를 Mag-GNS의 표면에 도입하기 위하여 피리딜디설파이드-N-하이드록시석신이미드 폴리에틸렌 글리콜(OPSS-PEG-NHS, 분자량= 2000)을 사용하였다. NaHCO3 (100 mM, pH 8.5, 24 mL) 에 용해되어 있는 OPSS-PEG-NHS (16 mg)를 anti-HER2/neu (160 μg)에 재분산시켰다. 이 조건하에서 고분자의 농도는 사용된 anti-HER2/neu 에 비해서 과량이다. 반응은 4oC에서 밤새 진행시켰다. 항체에 붙지 않은 고분자는 투석으로 제거하였다. 물질의 표적화를 용이하게 하기위해 PEG가 붙은 항체를 한시간의 반응을 통하여 Mag-GNS의 표면에 도입하였다. 항체 결합 이 후에 비선택적 흡착을 방지하고 생체 적합성을 높이기 위해 PEG-thiol (분자량 = 5000, 2 μM, 8 mL)으로 한 시간 동안 반응시켜 표면을 더 바꾸었다.Pyridyldisulfide-N-hydroxysuccinimide polyethylene glycol (OPSS-PEG-NHS, molecular weight = 2000) was used to introduce the antibody to the surface of Mag-GNS. OPSS-PEG-NHS (16 mg) dissolved in NaHCO3 (100 mM, pH 8.5, 24 mL) was redispersed in anti-HER2 /neu (160 μg). Under these conditions, the polymer concentration is excessive compared to the anti-HER2 /neu used. The reaction proceeded overnight at 4o C. Polymers that did not adhere to the antibody were removed by dialysis. Antibodies with PEG were introduced to the surface of Mag-GNS via an hour's reaction to facilitate targeting of the material. After antibody binding, the surface was further changed by reaction with PEG-thiol (molecular weight = 5000, 2 μM, 8 mL) for 1 hour to prevent non-selective adsorption and increase biocompatibility.
실시예 3 : Mag-GNS-AbExample 3 Mag-GNS-AbHER2/HER2 /nene 존재하에서의 세포 배양 Cell culture in the presence
두 종류의 세포계, SKBR3 (인간 유방 선암)과 H520 (인간 폐 편평상피세포 암)이 10 %의 우태혈청(FBS, Terra Cell)을 포함한 RPMI-1640 배지 (Hyclone)에서 37oC, 5 % CO2조건하에 배양되었다.Two cell lines, SKBR3 (Human Breast Adenocarcinoma) and H520 (Human Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma), contained 37° C, 5% CO in RPMI-1640 medium (Hyclone) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Terra Cell). Incubated under2 conditions.
표적지향적 자기 공명 영상을 위하여 세포들은 T-75 플라스크 (Nalge Nunc International)에서 배양되었다. 세균들을 Mag-GNS-AbHER2/neu 용액과 함께 37oC에서 4시간 배양하였다. 배양 후, 세포들을 PBS 완충용액으로 씻어내고 긁어 모은 후, 1500rpm으로 원심 분리하였다.Cells were cultured in T-75 flasks (Nalge Nunc International) for targeted magnetic resonance imaging. The bacteria were incubated at 37° C. for 4 hours with Mag-GNS-AbHER2 /neu solution. After incubation, the cells were washed with PBS buffer, scraped, and centrifuged at 1500 rpm.
표적지향적 근적외선 광열 치료를 위해 세포들을 트립신으로 떼어내어 2-well Lab-Tek 유리 슬라이드(Nalge Nunc International)에 다시 붙이고 성장시켰다. 세포들을 Mag-GNS-AbHER2/neu 용액과 함께 37oC에서 한 시간 배양하였다. 배양 후, 세포들을 PBS 완충용액으로 씻어내고 다양한 세기의 근적외선 레이저 빛에 노 출시켰다.Cells were detached with trypsin for targeted near-infrared photothermal treatment and re-attached to 2-well Lab-Tek glass slides (Nalge Nunc International). The cells were incubated with Mag-GNS-AbHER2 /neu solution for one hour at 37° C. After incubation, the cells were washed with PBS buffer and exposed to near-infrared laser light of various intensities.
실시예 4 : 생체 밖에서 (in vitro) 암세포의 자기 공명 영상Example 4 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Cancer Cells in Vitro
특성이완도(r2)의 측정을 위하여 PEG가 붙은 Mag-GNS를 증류수에 분산시키거나 세포들을 Mag-GNS-AbHER2/neu 와 함께 배양시킨 후 진폭 변화도가 80 mT/m 이고 시간당 출력전압 최대 변화량이 200 ms/m인 3.0T의 전신 자기 공명 영상 장치(Philips, Achieva ver. 1.2, Philips Medical Systems, Best, The Netherlands)에서 테스트하여 보았다. r2 측정을 위해 멀티 슬라이스 터보 스핀 에코 시퀀스(TR/TE = 5000/20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120, 140, 160, 180, 200 ms, in-plane 해상도 = 200 ◎200 mm2, slice thickness = 500 mm)내에서 10개의 다른 반향 시간을 이용하여 스핀-스핀 이완시간을 측정하였다. 이미지는 Levenberg-Margardt방법으로 Matlap 프로그램을 이용하여 T2 값을 계산하였다. T2 에서의 각각의 ROIs (200 - 300 픽셀) 신호의 세기가 각각의 농도에 대해 측정되었고 특성이완도 계산에 사용되었다. 도 8은 본 발명에 따른 자성 금 나노 입자의 농도에 따른 r2 이완성이고, 도 9는 본 발명에 따른 표적 지향성 자성 금 나노 입자를 이용한 암세포의 선택적 자기공명영상이다.To measure the characteristic relaxation (r2), Mag-GNS with PEG was dispersed in distilled water or the cells were incubated with Mag-GNS-AbHER2 /neu and the amplitude variation was 80 mT / m and the maximum output voltage per hour The change was tested on a 3.0T systemic magnetic resonance imaging device (Philips, Achieva ver. 1.2, Philips Medical Systems, Best, The Netherlands) with 200 ms / m. Multi-slice turbo spin echo sequences for r2 measurements (TR / TE = 5000/20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120, 140, 160, 180, 200 ms, in-plane resolution = 200 ◎ 200 mm2 , slice spin-spin relaxation time was measured using 10 different echo times within thickness = 500 mm). The images were calculated for T2 values using the Matlap program by Levenberg-Margardt method. The intensity of each ROIs (200-300 pixels) signal at T2 was measured for each concentration and used to calculate characteristic relaxation. 8 is r2 relaxation according to the concentration of the magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention, Figure 9 is a selective magnetic resonance image of cancer cells using the target-directed magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
실시예 5 : 생체 밖에서 (in vitro) 암세포의 근적외선 광열 치료Example 5 Near Infrared Photothermal Therapy of Cancer Cells in Vitro
광열 치료를 위해 우리는 전형적인 재생-확대되는 티타늄-사파이어 레이저를 사용하였다. 이 레이저는 800nm 에 중심 피크가 나오는 기본적인 펄스를 만들어냈다. 상기 펄스의 폭은 130 fs이었다. 이러한 펨토초의 레이저는 1 kHz의 펄스 주 파수를 가지고 작동하며 에너지 안정성은 보통 1% 이내이므로 표적과 균등한 상호작용을 할 수 있는 높은 빛의 세기 프로파일을 제공하였다. 세포들은 다양한 세기의, 800nm 파장과 1mm 크기의 지름을 가지는 레이저에 10초 동안 노출되었다. 근적외선 처리 이후에 세포들의 생존을 보기 위하여 0.4 % 의 트립판 블루로 세포들을 10분 동안 염색한다. 이 때 죽은 세포들은 푸른색으로 염색되었다. 도 11은 본 발명에 따른 표적 지향성 자성 금 나노 입자를 통해 괴사된 암세포의 확대 그림이다.For the photothermal treatment we used a typical regenerative-enlarging titanium-sapphire laser. The laser produced a basic pulse with a center peak at 800 nm. The width of the pulse was 130 fs. These femtosecond lasers operate with a pulse frequency of 1 kHz and their energy stability is typically within 1%, providing a high light intensity profile for evenly interacting with the target. The cells were exposed for 10 seconds to lasers of various intensity, 800 nm wavelength and 1 mm diameter. Cells are stained for 10 minutes with 0.4% trypan blue to see the survival of cells after near infrared treatment. The dead cells were stained blue. 11 is an enlarged view of cancer cells necroticized through the target-directed magnetic gold nanoparticles according to the present invention.
본 발명에 따르면, 자성 금 나노입자는 MRI T2 조영제 및 암세포의 MRI 진단과 NIR 레이저를 이용한 열치료에 이용할 수 있는 다기능성 나노 물질로서, 암의 진단과 치료를 동시에 구현할 수 있는 우수한 성능을 기대할 수 있다. 동시에 레이저 펄스를 이용할 경우 매우 빠른 시간 내에 암세포를 괴사시킬 수 있다.According to the present invention, the magnetic gold nanoparticles are multifunctional nanomaterials that can be used for MRI T2 contrast agent and MRI diagnosis of cancer cells and heat treatment using NIR laser, and can be expected to have excellent performance for simultaneously diagnosing and treating cancer. have. At the same time, using laser pulses can kill cancer cells in a very short time.
Claims (34)
Translated fromKoreanPriority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020060102604AKR20080035926A (en) | 2006-10-20 | 2006-10-20 | Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Core-External Structured Gold Nanoparticles Containing Magnetic Nanoparticles as T2 Contrast Agent, Cancer Diagnosis and Cancer Treatment |
| PCT/KR2007/005154WO2008048074A1 (en) | 2006-10-20 | 2007-10-19 | Use of core-shell gold nanoparticle which contains magnetic nanoparticles for mri t2 contrast agent, cancer diagnostic and therapy |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020060102604AKR20080035926A (en) | 2006-10-20 | 2006-10-20 | Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Core-External Structured Gold Nanoparticles Containing Magnetic Nanoparticles as T2 Contrast Agent, Cancer Diagnosis and Cancer Treatment |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20080035926Atrue KR20080035926A (en) | 2008-04-24 |
Family
ID=39314243
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020060102604ACeasedKR20080035926A (en) | 2006-10-20 | 2006-10-20 | Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Core-External Structured Gold Nanoparticles Containing Magnetic Nanoparticles as T2 Contrast Agent, Cancer Diagnosis and Cancer Treatment |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR20080035926A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2008048074A1 (en) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011149233A3 (en)* | 2010-05-24 | 2012-05-03 | 한국과학기술원 | Magnetic-nanoparticle/platinum-nanoparticle/porous-carbon composite and method for preparing same |
| WO2012173288A1 (en)* | 2011-06-14 | 2012-12-20 | 서울대학교산학협력단 | Magnetic resonance imaging t2 contrast medium for cell contrasting, and method for manufacturing same |
| KR101355985B1 (en)* | 2011-11-29 | 2014-01-29 | (주)유 바이오메드 | Composition for diagnosis of multi-cancer |
| WO2014021630A1 (en)* | 2012-07-31 | 2014-02-06 | 포항공과대학교 산학협력단 | Aptamer specific to integrin αvβ3 and use thereof |
| WO2014182136A1 (en)* | 2013-05-10 | 2014-11-13 | 고려대학교 산학협력단 | Recombinant self-assembling protein comprising target-oriented peptide and use thereof |
| WO2019083323A3 (en)* | 2017-10-27 | 2019-06-13 | 전남대학교 산학협력단 | Magnetic nanostructure and method for producing same |
| CN111939275A (en)* | 2020-07-28 | 2020-11-17 | 同济大学 | Bimodal contrast agent, preparation method and application thereof |
Families Citing this family (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8323618B2 (en) | 2007-11-07 | 2012-12-04 | University Of Houston System | Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and uses thereof |
| EP2448557A1 (en)* | 2009-07-01 | 2012-05-09 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Stimuli-responsive carriers for mpi-guided drug delivery |
| EP2305310A1 (en) | 2009-09-25 | 2011-04-06 | Asociación Centro de Investigación Cooperativa en Biomateriales - CIC biomaGUNE | Gold -coated magnetic glyconanoparticles functionalised with proteins for use as diagnostic and therapeutic agents |
| RU2471502C1 (en)* | 2011-08-04 | 2013-01-10 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение науки Томский научный центр Сибирского отделения Российской академии наук (ТНЦ СО РАН) | Contrast agent for t1 and/or t2 magnetic resonant scanning and method for preparing it |
| US20140065076A1 (en)* | 2012-08-30 | 2014-03-06 | Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. | Container with concentrated substance and method of using the same |
| CN103055312A (en)* | 2012-12-29 | 2013-04-24 | 浙江大学 | Application of ferroferric oxide as photo-thermal sensitive material |
| CN103713028A (en)* | 2013-04-26 | 2014-04-09 | 南京大学 | Nanometer structure electrochemical cell sensor preparation method, produced nanometer structure electrochemical cell sensor and use thereof |
| WO2016015173A1 (en)* | 2014-07-29 | 2016-02-04 | 北京福纳康生物技术有限公司 | Tumor treatment method for blocking tumor vasculature by means of nanomaterial and external radiation source |
| CN104436193B (en)* | 2014-11-07 | 2017-02-08 | 东华大学 | Preparation method of folic acid coupled gold nano-rod/polypyrrole/ferroferric oxide multifunctional composite nano diagnosis and treatment agent |
| CN110496970B (en)* | 2018-05-16 | 2022-04-01 | 中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所 | Composite nano material, preparation method and application thereof |
| US11471542B2 (en) | 2018-08-06 | 2022-10-18 | Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University | Curcumin-based magnetic nanostructured system for dual response of imaging and therapeutics |
| CN110559453B (en)* | 2019-10-15 | 2021-11-05 | 南京晓庄学院 | A kind of magnetic nanoparticle for imaging guidance and preparation method thereof |
| US20210145867A1 (en)* | 2019-11-15 | 2021-05-20 | Board Of Regents, The University Of Texas System | Plasmonic enhanced magnetic nanoparticles hyperthermia |
| CN112300788B (en)* | 2020-11-02 | 2023-05-26 | 中山大学 | Core-point shell structured magneto-optical nano probe and preparation method and application thereof |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6203778B1 (en)* | 1998-12-08 | 2001-03-20 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Particulate radiopaque contrast agent for diagnostic imaging and microvascular characterization |
| WO2002030473A1 (en)* | 2000-10-11 | 2002-04-18 | Targesome, Inc. | Targeted therapeutic agents |
- 2006
- 2006-10-20KRKR1020060102604Apatent/KR20080035926A/ennot_activeCeased
- 2007
- 2007-10-19WOPCT/KR2007/005154patent/WO2008048074A1/enactiveApplication Filing
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011149233A3 (en)* | 2010-05-24 | 2012-05-03 | 한국과학기술원 | Magnetic-nanoparticle/platinum-nanoparticle/porous-carbon composite and method for preparing same |
| WO2012173288A1 (en)* | 2011-06-14 | 2012-12-20 | 서울대학교산학협력단 | Magnetic resonance imaging t2 contrast medium for cell contrasting, and method for manufacturing same |
| KR101355985B1 (en)* | 2011-11-29 | 2014-01-29 | (주)유 바이오메드 | Composition for diagnosis of multi-cancer |
| WO2014021630A1 (en)* | 2012-07-31 | 2014-02-06 | 포항공과대학교 산학협력단 | Aptamer specific to integrin αvβ3 and use thereof |
| KR101405440B1 (en)* | 2012-07-31 | 2014-06-20 | 연세대학교 산학협력단 | Aptamer specifically binding to integrinαvβ3 and use thereof |
| WO2014182136A1 (en)* | 2013-05-10 | 2014-11-13 | 고려대학교 산학협력단 | Recombinant self-assembling protein comprising target-oriented peptide and use thereof |
| US9814907B2 (en) | 2013-05-10 | 2017-11-14 | Korea University Research And Business Foundation | Recombinant self-assembling protein comprising target-oriented peptide and use thereof |
| WO2019083323A3 (en)* | 2017-10-27 | 2019-06-13 | 전남대학교 산학협력단 | Magnetic nanostructure and method for producing same |
| CN111939275A (en)* | 2020-07-28 | 2020-11-17 | 同济大学 | Bimodal contrast agent, preparation method and application thereof |
| CN111939275B (en)* | 2020-07-28 | 2022-10-25 | 同济大学 | Bimodal contrast agent, preparation method and application thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2008048074A1 (en) | 2008-04-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR20080035926A (en) | Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Core-External Structured Gold Nanoparticles Containing Magnetic Nanoparticles as T2 Contrast Agent, Cancer Diagnosis and Cancer Treatment | |
| Das et al. | Tailor made magnetic nanolights: Fabrication to cancer theranostics applications | |
| Efremova et al. | Magnetite-Gold nanohybrids as ideal all-in-one platforms for theranostics | |
| Shevtsov et al. | Targeting experimental orthotopic glioblastoma with chitosan-based superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (CS-DX-SPIONs) | |
| Lee et al. | Iron oxide based nanoparticles for multimodal imaging and magnetoresponsive therapy | |
| Lee et al. | Magnetic nanoparticles for multi-imaging and drug delivery | |
| Shi et al. | Photo-fluorescent and magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications | |
| Wang et al. | Fe3O4@ PVP@ DOX magnetic vortex hybrid nanostructures with magnetic-responsive heating and controlled drug delivery functions for precise medicine of cancers | |
| Na et al. | Inorganic nanoparticles for MRI contrast agents | |
| Zhang et al. | Near-infrared light-mediated photodynamic/photothermal therapy nanoplatform by the assembly of Fe3O4 carbon dots with graphitic black phosphorus quantum dots | |
| Groman et al. | Ultrasmall mixed ferrite colloids as multidimensional magnetic resonance imaging, cell labeling, and cell sorting agents | |
| US20060140867A1 (en) | Coated stent assembly and coating materials | |
| Lu et al. | Hydroxyl–PEG–phosphonic acid-stabilized superparamagnetic manganese oxide-doped iron oxide nanoparticles with synergistic effects for dual-mode MR imaging | |
| Xu et al. | Fluorescein-polyethyleneimine coated gadolinium oxide nanoparticles as T 1 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)–cell labeling (CL) dual agents | |
| Park et al. | Photodynamic anticancer activities of multifunctional cobalt ferrite nanoparticles in various cancer cells | |
| Liu et al. | Magnetic nanomaterials-mediated cancer diagnosis and therapy | |
| Aseri et al. | Magnetic nanoparticles: Magnetic nano-technology using biomedical applications and future prospects | |
| K Sharma et al. | Advances in multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles | |
| Neamtu et al. | Magnetic nanoparticles for magneto-resonance imaging and targeted drug delivery | |
| Mehrmohammadi et al. | Enhanced pulsed magneto-motive ultrasound imaging using superparamagneticnanoclusters | |
| Ahmad et al. | Bovine serum albumin (BSA) and cleaved-BSA conjugated ultrasmall Gd2O3 nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and application to MRI contrast agents | |
| Wu et al. | Irregularly shaped iron nitride nanoparticles as a potential candidate for biomedical applications: from synthesis to characterization | |
| Joshi | Multifunctional metal ferrite nanoparticles for MR imaging applications | |
| Polo et al. | Magnetic nanoparticles for cancer therapy and bioimaging | |
| Song et al. | A multifunctional nanoprobe based on europium (iii) complex–Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles for bimodal time-gated luminescence/magnetic resonance imaging of cancer cells in vitro and in vivo |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20061020 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0201 | Request for examination | Patent event code:PA02012R01D Patent event date:20100621 Comment text:Request for Examination of Application Patent event code:PA02011R01I Patent event date:20061020 Comment text:Patent Application | |
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20111215 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E601 | Decision to refuse application | ||
| PE0601 | Decision on rejection of patent | Patent event date:20120706 Comment text:Decision to Refuse Application Patent event code:PE06012S01D Patent event date:20111215 Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event code:PE06011S01I |