KR20060070665A - Dynamic IP Address Assignment for IP-based Keyphone System - Google Patents
Dynamic IP Address Assignment for IP-based Keyphone SystemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20060070665A KR20060070665AKR1020040109210AKR20040109210AKR20060070665AKR 20060070665 AKR20060070665 AKR 20060070665AKR 1020040109210 AKR1020040109210 AKR 1020040109210AKR 20040109210 AKR20040109210 AKR 20040109210AKR 20060070665 AKR20060070665 AKR 20060070665A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- address
- received message
- terminal
- message type
- allocation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L61/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services for addressing or naming
- H04L61/50—Address allocation
- H04L61/5007—Internet protocol [IP] addresses
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L2101/00—Indexing scheme associated with group H04L61/00
- H04L2101/60—Types of network addresses
- H04L2101/618—Details of network addresses
- H04L2101/622—Layer-2 addresses, e.g. medium access control [MAC] addresses
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
- Small-Scale Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean도 1은 일반적인 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 블록구성도이고,1 is a block diagram of a general IP-based key phone system,
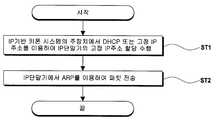
도 2는 종래 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 IP 주소 고정 할당 방법을 보인 흐름도이며,2 is a flowchart illustrating an IP address fixed allocation method of a conventional IP-based key phone system;
도 3은 본 발명에 의한 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 IP 주소 동적 할당 방법을 보인 흐름도이고,3 is a flowchart illustrating an IP address dynamic allocation method of an IP-based key phone system according to the present invention;
도 4는 도 3에서 제 10 단계인 ST10의 상세흐름도이며,FIG. 4 is a detailed flowchart of ST10 as a tenth step in FIG.
도 5는 도 3에서 제 30 단계인 ST30의 상세흐름도이고,FIG. 5 is a detailed flowchart of the step 30 of ST30 of FIG. 3;
도 6은 본 발명이 적용되는 IP 기반 키폰 시스템에서 IP 주소 동적 할당 예를 보인 블록구성도이며,Figure 6 is a block diagram showing an example of IP address dynamic allocation in the IP-based key phone system to which the present invention is applied,
도 7은 본 발명에서 사용하는 IP 할당 메시지 포맷의 예를 보인 개념도이다.7 is a conceptual diagram illustrating an example of an IP allocation message format used in the present invention.
* 도면의 주요 부분에 대한 부호의 설명 *Explanation of symbols on the main parts of the drawings
10 : 주장치10: main device
20 : IP 단말기20: IP terminal
본 발명은 IP(Internet Protocol, 인터넷 프로토콜) 기반 키폰 시스템의 IP 주소 동적 할당 방법에 관한 것으로, 특히 IP 기반 키폰 시스템에서 IP 멀티캐스트를 사용한 시그널링을 통하여 동일한 LAN(Local Area Network) 상에 있는 IP 단말기들에 IP 주소를 동적으로 할당하고 관리하며 이러한 과정 중 교환된 정보를 기반으로 ARP(Address Resolution Protocol, 주소 도출 프로토콜)를 통하지 않는 패킷 전송이 가능하게 하여 LAN 상의 트래픽을 감소시키고 패킷 전송 속도를 향상시키기에 적당하도록 한 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 IP 주소 동적 할당 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method for dynamically allocating an IP address of an IP (Internet Protocol) based key phone system, and in particular, an IP terminal on the same local area network (LAN) through signaling using IP multicast in an IP based key phone system. IP addresses are dynamically assigned and managed, and based on the information exchanged during this process, packets can be sent without using the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), reducing traffic on the LAN and improving packet transmission speed. The present invention relates to a method for dynamically assigning an IP address of an IP-based keyphone system, which is suitable for the purpose of making it suitable.
일반적으로 IP 기반 키폰 시스템은 한정된 국선을 키폰 주장치에 설치하고 IP 단말기 및 일반 전화기를 연결하여 여러 사람이 동시에 사용할 수 있도록 설계된 효율적인 간이 교환 시스템이다. 이러한 IP 기반 키폰 시스템은 국선 및 내선과 연결되어 음성안내 기능, 끼여들기 기능, 방송 기능, 수신거부 기능, 원격유지보수 기능 등을 수행할 수 있다.In general, an IP-based keyphone system is an efficient simple switching system designed to be used by several people at the same time by installing a limited trunk line in the keyphone main unit and connecting an IP terminal and a general telephone. The IP-based key phone system may be connected to a trunk line and an extension to perform a voice guidance function, interrupting function, broadcasting function, reception rejection function, remote maintenance function, and the like.
도 1은 일반적인 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 블록구성도이다.1 is a block diagram of a general IP-based key phone system.
여기서 참조번호 10은 IP 기반 키폰 시스템에서 주기능을 수행하는 주장치이고, 참조번호 20은 상기 주장치(10)와 LAN을 통해 연결되어 사용자가 사용할 수 있게 하는 IP 단말기이다.Here,
도 2는 종래 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 IP 주소 고정 할당 방법을 보인 흐름도이다.2 is a flowchart illustrating an IP address fixed allocation method of a conventional IP-based key phone system.
이에 도시된 바와 같이, IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 주장치(10)에서 DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, 동적 상위 구성 프로토콜) 또는 고정 IP 주소를 이용하여 IP 단말기(20)의 고정 IP 주소 할당을 수행하는 제 1 단계(ST1)와; 상기 제 1 단계 후 상기 IP 단말기(20)에서 ARP를 이용하여 패킷 전송을 수행하는 제 2 단계(ST2)를 수행한다.As shown in the drawing, a first device for performing a static IP address allocation of the
이러한 종래 기술의 동작을 첨부한 도면에 의거하여 상세히 설명하면 다음과 같다.The operation of the prior art will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
먼저 기존의 IP 기반 키폰 시스템과 같은 VoIP(Voice over Internet Protocol) 시스템의 경우, 동일한 LAN 상의 IP 단말기(20)에 IP 주소를 할당하기 위하여 외부의 DHCP 서버를 이용하거나 고정 IP 주소를 수동으로 입력하는 경우가 많고, 시스템에 내장되어 있는 내부 DHCP 서버를 이용하여 IP 주소를 할당하는 경우도 있다.First, in the case of a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) system such as an existing IP-based key phone system, an external DHCP server or a fixed IP address is manually input to assign an IP address to the
여기서 DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)는 IP 주소를 비롯한 각종 TCP/IP(Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, 전송 제어 프로토콜-인터넷 프로토콜) 프로토콜 기본 설정을 개별 클라이언트들에 자동적으로 할당하는 방식의 프로토콜로서, 네트워크 관리자들이 조직 내의 네트워크 상에서 IP 주소를 중앙에서 관리하고 할당해줄 수 있도록 해주는 프로토콜이다. 인터넷의 TCP/IP 프로토콜에서는 각 단말기들이 고유한 IP 주소를 가져야만 인터넷에 접속할 수 있다. 그래서 단말기 사용자들이 인터넷에 접속할 때, IP 주소는 각 단말기에 반드시 할당되어야만 한다. DHCP를 사용하지 않는 경우에는 각 컴퓨터마다 IP 주소가 수작업으로 입력되어야만 하며, 만약 단말기들이 네트워크의 다른 부분에 속한 장소로 이동되면 새로운 IP 주소를 입력해야 한다. DHCP는 네트워크 관리자가 중앙에서 IP 주소를 관리하고 할당하며, 단말기가 네트워크의 다른 장소에 접속되었을 때 자동으로 새로운 IP 주소를 보내줄 수 있게 해준다.Here, DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a protocol that automatically assigns various TCP / IP (Transmission Control Protocol-Internet Protocol) protocol preferences to individual clients, including IP addresses. It is a protocol that allows administrators to centrally manage and assign IP addresses on networks within an organization. In the TCP / IP protocol of the Internet, each terminal must have a unique IP address to access the Internet. So when terminal users connect to the Internet, an IP address must be assigned to each terminal. If you are not using DHCP, you will need to manually enter an IP address for each computer, and if the terminals are moved to a different part of the network, you will need to enter a new IP address. DHCP allows network administrators to centrally manage and assign IP addresses, and to automatically send new IP addresses when the device is connected to another location on the network.
DHCP에 관련된 사양 및 기준은 RFC(Request For Comments) 1533, 1534, 1541, 1542, 2131 등에 정의되어 있다. 그래서 DHCP는 기본적으로 TCP/IP 설정을 자동 관리하며, 개별 시스템에 IP 주소와 관련된 설정 정보를 부여한다. 구성은 DHCP 클라이언트와 서버로 구성되어 있다.Specifications and criteria related to DHCP are defined in Request For Comments (RFC) 1533, 1534, 1541, 1542, 2131, and the like. Thus, DHCP automatically manages TCP / IP configuration by default, giving configuration information related to IP addresses to individual systems. The configuration consists of a DHCP client and a server.
이때 DHCP 클라이언트는 IP 단말기(20) 등으로 구성되는데, 시스템이 시작하면 DHCP 서버에 자신의 시스템을 위한 IP 주소를 요청한다. 그리고 IP 단말기(20)와 같은 DHCP 클라이언트는 DHCP 서버로부터 IP 주소를 대여받게 되면 TCP/IP 설정은 초기화되고, 다른 호스트와 TCP/IP 프로토콜을 사용해서 통신할 수 있게 된다.At this time, the DHCP client is configured with an
또한 DHCP 서버는 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 주장치(10)가 이에 해당하게 되는데, DHCP 서버는 DHCP 클라이언트로부터의 IP 주소 대여 요청에 응답하며, 이를 위해서 할당 가능한 IP 주소들의 영역인 스코프(Scope, 범위)를 유지 관리한다.In addition, the DHCP server corresponds to the
이러한 DHCP를 이용하여 IP 주소를 할당할 경우에는 DHCP 서버에 설정되어 있는 IP 주소의 범위 내에서 IP 주소의 할당이 이루어지게 된다(ST1).When the IP address is allocated using the DHCP, the IP address is allocated within the range of the IP address set in the DHCP server (ST1).
또한 LAN 상에서 패킷을 전송하기 위해서는 ARP를 이용하여 목적지 IP 주소에 대한 MAC(Media Access Control, 매체 액세스 제어) 주소를 얻은 후, 이 MAC 주소를 패킷 전송에 사용하게 된다.In addition, in order to transmit a packet on a LAN, a MAC (Media Access Control) address for a destination IP address is obtained using ARP, and the MAC address is used for packet transmission.
여기서 ARP(Address Resolution Protocol)는 IP 네트워크 상에서 IP 주소를 물리적 네트워크 주소로 대응시키기 위해 사용되는 프로토콜이다.Here, ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a protocol used to map an IP address to a physical network address on an IP network.
예를 들어, IP 호스트 A가 IP 호스트 B에게 IP 패킷을 전송고자 할 때 IP 호스트 B의 물리적 네트워크 주소를 모르는 경우, ARP 프로토콜을 사용하여 목적지 IP 주소 B와 브로드캐스팅 물리적 네트워크 주소 FFFFFFFFFFFF를 가지는 ARP 패킷을 네트워크 상에 전송한다. IP호스트 B는 자신의 IP 주소가 목적지에 있는 ARP 패킷을 수신하면 자신의 물리적 네트워크 주소를 A에게 응답한다.For example, if IP host A wants to send an IP packet to IP host B, and it does not know the physical network address of IP host B, an ARP packet with destination IP address B and broadcasting physical network address FFFFFFFFFFFF using the ARP protocol Send it over the network. IP host B responds to A with its physical network address when it receives an ARP packet whose IP address is at its destination.
이와 같은 방식으로 수집된 IP 주소와 이에 해당하는 물리적 네트워크 주소 정보는 각 IP 호스트의 ARP 캐시라 불리는 메모리에 테이블 형태로 저장된 후 다음 패킷 전송시에 다시 사용된다. ARP와는 역으로, IP 호스트가 자신의 물리 네트워크 주소는 알지만 IP 주소를 모르는 경우, 서버로부터 IP주소를 요청하기 위해서는 RARP(Reverse Address Resolution Protocol, 역주소 도출 프로토콜)를 사용한다.The IP address and the corresponding physical network address information collected in this way are stored in a table in memory called ARP cache of each IP host and used again in the next packet transmission. In contrast to ARP, when an IP host knows its physical network address but does not know its IP address, it uses the Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) to request an IP address from a server.
그래서 이러한 MAC 주소가 유효한 동안에는 ARP 캐쉬에 저장된 MAC 주소를 사용한다. ARP 엔트리의 유지 시간 이후에는 해당 정보는 ARP 캐쉬에 저장되어 일정 시간 동안 유지되며, 해당 IP 주소에 대한 ARP 캐쉬 엔트리가 IP 주소에 대한 엔트리가 폐기되기 때문에, 이후에 같은 IP 주소로 패킷을 보낼 때에는 다시 ARP 요구(Request) 패킷을 보내 MAC 주소를 다시 얻어와야 한다(ST2).So while these MAC addresses are valid, they use the MAC address stored in the ARP cache. After the retention time of an ARP entry, the information is stored in the ARP cache and maintained for a period of time, and when an ARP cache entry for that IP address is discarded, the entry for the IP address is discarded. ARP request packet should be sent again to get MAC address again (ST2).
그러나 이러한 종래 기술은 다음과 같은 문제점이 있었다.However, this conventional technology has the following problems.
즉, IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 경우, 주장치의 직접적인 제어를 받는 수십 내지는 수백 개의 IP 단말기(20)가 존재하게 된다. 이러한 경우, 모든 IP 단말기에 공인 IP 주소를 사용하게 되면 비용상, 관리상 부담이 커지기 때문에 사설 IP 주소를 사용하는 것이 대부분의 경우 유리하다. 따라서 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 주장치(10)에서는 이러한 사설 IP 주소를 각 IP 단말기에 할당을 하고 관리하게 된다.That is, in the case of the IP-based key phone system, there are tens or hundreds of
IP 단말기에 IP 주소를 할당하기 위한 대표적인 방법이 DHCP를 이용하는 방법이다. 주장치에 DHCP 서버를 내장시키고 각 IP 단말기에 DHCP 클라이언트를 내장시켜 IP 주소를 할당하게 되는데, 여기에는 몇 가지 문제점이 있게 된다.DHCP is a representative method for allocating IP addresses to IP terminals. A DHCP server is built into the host device and a DHCP client is built into each IP terminal to assign IP addresses. There are some problems.
우선, IP 기반 키폰 시스템이 위치하는 LAN 세그먼트 내에 PC(Personal Computer) 등을 위한 DHCP 서버가 이미 존재하고 있을 경우, 복수 개의 DHCP 서버의 존재로 인한 충돌로 결국 하나의 DHCP 서버만을 사용하게 된다. PC를 위한 DHCP 서버와 주장치(10)에 내장되어 있는 DHCP 서버는 프로토콜 자체는 동일할지라도 DHCP를 관리 및 운용하는 어플리케이션 자체가 상당히 다르기 때문에 어느 한쪽은 불편함이나 기능적인 제약을 감수해야만 하는 문제점이 있었다.First, when a DHCP server for a personal computer (PC) or the like already exists in a LAN segment in which an IP-based key phone system is located, only one DHCP server is used due to a collision due to the existence of a plurality of DHCP servers. The DHCP server for the PC and the DHCP server built into the
또 다른 문제점은 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 주장치 입장에서 볼 때, IP 주소의 할당 및 관리를 PC의 경우 보다 훨씬 융통성 있고 자유롭게 관리할 수 있어야 하는데, DHCP라는 프로토콜 자체와 사용중인 DHCP 프로토콜에서 제공하는 기능에 의한 제약으로 인하여 시스템 자체에 기능적인 제약이 가해질 수 있다는 점이다.Another problem is that from the point of view of the main device of the IP-based keyphone system, the allocation and management of IP addresses should be much more flexible and freely manageable than that of the PC. Due to this limitation, functional restrictions may be imposed on the system itself.
그래서 PC의 경우 위치 이동이 적고 네트워크 관련된 속도 등에 제약이 적지만, 실시간성이 중요한 통신 시스템에서는 속도와 함께 기능상 유연성이 매우 중요하다. 이는 IP 기반 시스템이라 할 지라도 TDM(Time Division Multiplexing, 시분할 다중송신) 방식을 사용하는 기존의 키폰 교환기가 내부적으로 자유롭게 구현하여 제공하던 모든 기능이 LAN 상에서 최소한 동일한 수준 이상으로 구현되어야 하 기 때문이며, 이를 위해서는 기존의 일반적 용도의 프로토콜에서 벗어나 필요한 기능만을 좀더 융통성 있게 운용할 수 있는 프로토콜이 요구된다.Therefore, in the case of PC, the location movement is less and the network-related speed is limited, but in the communication system where real-time is important, the flexibility along with the speed is very important. This is because, even in an IP-based system, all the functions that the existing keyphone exchanger using TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) scheme freely implemented internally should be implemented at least the same level on the LAN. To this end, there is a need for a protocol that can more flexibly operate only necessary functions beyond the existing general purpose protocol.
또한 ARP의 경우, 일정 시간 이후에는 ARP 요구/응답(Request/Reply) 패킷들을 통해 MAC 주소를 얻어와야 하기 때문에 LAN 상의 트래픽 증가와 패킷 전송의 지연요소로서 작용하게 되는 문제점이 있게 된다.In addition, in the case of ARP, since a MAC address must be obtained through ARP Request / Reply packets after a certain time, there is a problem in that it acts as an increase in traffic on the LAN and a delay factor of packet transmission.
여기서 ARP 캐쉬 엔트리에 시간 제약을 두는 것은 해당 MAC 주소를 갖는 장치의 IP 주소 등이 변경되었을 경우, 즉각적인 변경은 힘들더라도 결국에는 변경된 사항이 적용되도록 하기 위해서 인데, IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 경우 IP 주소와 MAC 주소의 관리를 명확히 함으로써 ARP를 사용하지 않고 패킷을 전송함으로써 불필요한 부담과 낭비요소를 제거할 필요성이 있게 것이다.The time limit on the ARP cache entry is that if the IP address of the device having the MAC address is changed, it is difficult to make an immediate change, but in the end, the change is applied. By clarifying the management of MAC addresses, there will be a need to remove unnecessary burden and waste by sending packets without using ARP.
이에 본 발명은 상기와 같은 종래의 제반 문제점을 해결하기 위해 제안된 것으로, 본 발명의 목적은 IP 기반 키폰 시스템에서 IP 멀티캐스트를 사용한 시그널링을 통하여 동일한 LAN 상에 있는 IP 단말기들에 IP 주소를 동적으로 할당하고 관리하며 이러한 과정 중 교환된 정보를 기반으로 ARP를 통하지 않는 패킷 전송이 가능하게 하여 LAN 상의 트래픽을 감소시키고 패킷 전송 속도를 향상시킬 수 있는 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 IP 주소 동적 할당 방법을 제공하는데 있다.Accordingly, the present invention has been proposed to solve the above conventional problems, and an object of the present invention is to dynamically assign an IP address to IP terminals on the same LAN through signaling using IP multicast in an IP-based keyphone system. And IP address dynamic allocation method of IP-based keyphone system that can reduce the traffic on the LAN and improve the packet transmission speed by enabling the packet transmission through ARP based on the information exchanged during this process. It is.
상기와 같은 목적을 달성하기 위하여 본 발명의 일실시예에 의한 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 IP 주소 동적 할당 방법은,In order to achieve the above object, the IP address dynamic allocation method of the IP-based key phone system according to an embodiment of the present invention,
IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 주장치에서 IP 단말기의 동적 IP 주소 할당을 수행하 는 제 10 단계와; 상기 제 10 단계 후 IP 단말기에서 IP 주소와 MAC 주소 정보를 사용하여 패킷 전송을 수행하는 제 30 단계를 포함하여 수행함을 그 기술적 구성상의 특징으로 한다.A tenth step of performing dynamic IP address allocation of the IP terminal in the main device of the IP-based key phone system; After the tenth step, the IP terminal includes a thirty step of performing packet transmission using the IP address and the MAC address information.
이하, 상기와 같은 본 발명, IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 IP 주소 동적 할당 방법의 기술적 사상에 따른 일실시예를 도면을 참조하여 설명하면 다음과 같다.Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention as described above according to the technical idea of the IP address dynamic allocation method of the IP-based key phone system will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 3은 본 발명에 의한 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 IP 주소 동적 할당 방법을 보인 흐름도이다.3 is a flowchart illustrating an IP address dynamic allocation method of an IP-based key phone system according to the present invention.
이에 도시된 바와 같이, IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 주장치(10)에서 IP 단말기(20)의 동적 IP 주소 할당을 수행하는 제 10 단계(ST10)와; 상기 제 10 단계 후 IP 단말기(20)에서 IP 주소와 MAC 주소 정보를 사용하여 패킷 전송을 수행하는 제 30 단계(ST30)를 포함하여 수행한다.As shown therein, a tenth step ST10 of performing dynamic IP address allocation of the
도 4는 도 3에서 제 10 단계인 ST10의 상세흐름도이다.FIG. 4 is a detailed flowchart of ST10 as a tenth step in FIG. 3.
이에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 제 10 단계(ST10)는, 상기 주장치(10)가 시작되면 IP 주소 할당 영역을 설정하고 초기화를 수행한 다음 수신 메시지 타입이 무엇인지 판별하는 제 11 단계(ST11)(ST12)와; 상기 제 11 단계에서 수신 메시지 타입이 IP 주소 할당 요청이면, IP 주소 할당 데이터베이스를 검색하고 예약한 다음 IP 주소 할당 명령을 전송하는 제 12 단계(ST13 ~ ST15)를 포함하여 수행한다.As shown in FIG. 10, the tenth step ST10 may include setting an IP address allocation area and performing initialization after the
이에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 제 10 단계(ST10)는, 상기 주장치(10)가 시작되면 IP 주소 할당 영역을 설정하고 초기화를 수행한 다음 수신 메시지 타입이 무 엇인지 판별하는 제 11 단계(ST11)(ST12)와; 상기 제 11 단계에서 수신 메시지 타입이 IP 주소 정보 요청이면, IP 주소 정보 보고를 상기 IP 단말기(20)로 전송하는 제 13 단계(ST16)(ST17)를 포함하여 수행한다.As shown in FIG. 10, in the tenth step ST10, when the
이에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 제 10 단계(ST10)는, 상기 주장치(10)가 시작되면 IP 주소 할당 영역을 설정하고 초기화를 수행한 다음 수신 메시지 타입이 무엇인지 판별하는 제 11 단계(ST11)(ST12)와; 상기 제 11 단계에서 수신 메시지 타입이 IP 주소 충돌 보고이면, IP 주소 할당 데이터베이스를 검색하고 예약한 다음 IP 주소 할당 명령을 전송하는 제 14 단계(ST18 ~ ST20)를 포함하여 수행한다.As shown in FIG. 10, the tenth step ST10 may include setting an IP address allocation area and performing initialization after the
이에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 제 10 단계(ST10)는, 상기 주장치(10)가 시작되면 IP 주소 할당 영역을 설정하고 초기화를 수행한 다음 수신 메시지 타입이 무엇인지 판별하는 제 11 단계(ST11)(ST12)와; 상기 제 11 단계에서 수신 메시지 타입이 IP 주소 메시지 확인이면, IP 주소 할당 예약이 되었는지 판별하는 제 15 단계(ST21)(ST22)와; 상기 제 15 단계에서 IP 주소 할당 예약이 되어 있으면 IP 주소 할당 데이터베이스를 확인하는 제 16 단계(ST23)와; 상기 제 15 단계에서 IP 주소 할당 예약이 되어 있지 않으면, 상위 프로세서에 통보하는 제 17 단계(ST25)를 포함하여 수행한다.As shown in FIG. 10, the tenth step ST10 may include setting an IP address allocation area and performing initialization after the
이에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 제 10 단계(ST10)는, 상기 주장치(10)가 시작되면 IP 주소 할당 영역을 설정하고 초기화를 수행한 다음 수신 메시지 타입이 무엇인지 판별하는 제 11 단계(ST11)(ST12)와; 상기 제 11 단계에서 수신 메시지 타입이 IP 주소 정보 보고이면, 상위 프로세서에 통보하는 제 18 단계(ST24)(ST25)를 포함하여 수행한다.As shown in FIG. 10, the tenth step ST10 may include setting an IP address allocation area and performing initialization after the
도 5는 도 3에서 제 30 단계인 ST30의 상세흐름도이다.FIG. 5 is a detailed flowchart of the step 30 of ST30 in FIG. 3.
이에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 제 30 단계(ST30)는, 상기 IP 단말기(20)가 시작되면 초기화를 수행한 다음 주소 할당 요청을 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 상기 주장치(10)로 전송한 다음 수신 메시지 타입이 무엇인지 판별하는 제 31 단계(ST31 ~ ST33)와; 상기 제 31 단계에서 수신 메시지 타입이 IP 주소 할당 명령이면, IP 주소를 재초기화시키는 제 32 단계(ST34)(ST35)를 포함하여 수행한다.As shown in FIG. 30, in the thirtieth step ST30, when the
이에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 제 30 단계(ST30)는, 상기 IP 단말기(20)가 시작되면 초기화를 수행한 다음 주소 할당 요청을 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 상기 주장치(10)로 전송한 다음 수신 메시지 타입이 무엇인지 판별하는 제 31 단계(ST31 ~ ST33)와; 상기 제 31 단계에서 수신 메시지 타입이 IP 주소 정보 요청이면, IP 주소 정보 보고를 상기 주장치(10)로 전송하는 제 33 단계(ST36)(ST37)를 포함하여 수행한다.As shown in FIG. 30, in the thirtieth step ST30, when the
이에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 제 30 단계(ST30)는, 상기 IP 단말기(20)가 시작되면 초기화를 수행한 다음 주소 할당 요청을 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 상기 주장치(10)로 전송한 다음 수신 메시지 타입이 무엇인지 판별하는 제 31 단계(ST31 ~ ST33)와; 상기 제 31 단계에서 수신 메시지 타입이 IP 주소 정보 보고이면, 상위 프로세서에 통보하는 제 33 단계(ST38)(ST40)를 포함하여 수행한다.As shown in FIG. 30, in the thirtieth step ST30, when the
이에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 제 30 단계(ST30)는, 상기 IP 단말기(20)가 시작되면 초기화를 수행한 다음 주소 할당 요청을 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 상기 주장 치(10)로 전송한 다음 수신 메시지 타입이 무엇인지 판별하는 제 31 단계(ST31 ~ ST33)와; 상기 제 31 단계에서 수신 메시지 타입이 메시지 수신 확인이면, 상위 프로세서에 통보하는 제 34 단계(ST39)(ST40)를 포함하여 수행한다.As shown therein, the thirtieth step ST30 may be performed when the
이와 같이 구성된 본 발명에 의한 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 IP 주소 동적 할당 방법의 동작을 첨부한 도면에 의거 상세히 설명하면 다음과 같다.An operation of the IP address dynamic allocation method of the IP-based key phone system according to the present invention configured as described above will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
먼저 본 발명은 IP 기반 키폰 시스템에서 IP 멀티캐스트를 사용한 시그널링을 통하여 동일한 LAN 상에 있는 IP 단말기들에 IP 주소를 동적으로 할당하고 관리하고자 한 것이다.First, the present invention is to dynamically allocate and manage IP addresses to IP terminals on the same LAN through signaling using IP multicast in an IP-based keyphone system.
본 발명은 크게 두 가지 영역으로 나누어진다. 하나는 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 주장치에 의한 IP 단말기의 동적 IP 주소 할당이고, 다른 하나는 ARP 없이 각 단말기의 IP 주소와 MAC 주소 정보를 사용하여 패킷을 전송하는 것이다.The present invention is largely divided into two areas. One is dynamic IP address allocation of an IP terminal by a main device of an IP-based key phone system, and the other is to transmit a packet using IP address and MAC address information of each terminal without ARP.
여기서 IP 기반 키폰 시스템은 도 1과 같이 크게 주장치(10)와 IP 단말기(20)로 나뉘어 진다. 세부적으로 나누면 IP 단말기는 IP 전화기와 IP 게이트웨이(Gateway)로 분류될 수 있으나 여기서는 IP 단말기로 통칭하도록 한다.Here, the IP-based key phone system is largely divided into the
그래서 주장치(10)는 호 처리(Call Processing)를 담당하는 장치로 모든 IP 단말기(20)는 주장치(10)의 제어를 받아 동작하게 되고, 주장치(10)와 IP 단말기(20) 간의 통신은 TCP/IP 프로토콜을 통해 이루어지게 된다.Thus, the
IP 기반 키폰 시스템을 설치할 때 중요한 사항은 주장치(10)와 각각의 IP 단말기(20)에 IP 주소를 설정하는 작업이다.When installing an IP-based key phone system, an important matter is to set an IP address for the
그래서 주장치(10)의 경우는 하나의 장치이고, 일반적으로 HTTP(HyperText Transfer Protocol, 하이퍼텍스트 전송프로토콜), 텔넷(Telecommunication Network, Telnet) 등의 프로토콜을 사용하야 하는 경우가 많기 때문에 수동으로 IP 주소를 설정하거나 설치되는 LAN에 존재하는 DHCP 서버를 이용하게 된다.Therefore, in case of the
하지만 IP 단말기(20)의 경우, 설치되는 LAN에 존재하는 PC 등 다른 네트워크 장치들과는 다른 방법으로 다른 영역의 IP 주소를 할당함으로써 서로간의 충돌을 막고 주장치를 통한 시스템 전체의 관리를 용이하게 할 수 있다.However, in the case of the
따라서 일반적으로 사용되는 DHCP 등 표준화된 프로토콜이 아닌 IP 기반 키폰 시스템만을 위한 독립적인 프로토콜을 사용함으로써 이러한 독립성과 안정성을 확보할 수 있도록 한다.Therefore, it is possible to secure such independence and stability by using independent protocol only for IP-based keyphone system, not standardized protocol such as DHCP.
본 발명의 또 하나의 장점으로는 IP 주소 할당에 있어서의 유연성을 들 수 있다.Another advantage of the present invention is its flexibility in IP address assignment.
DHCP 프로토콜이 잘 구성된 프로토콜이기는 하지만, 주장치(10)의 입장에서 볼 때 DHCP를 사용하여 IP 단말기(20)들에 대한 IP 주소 할당 및 관리를 하기 위해서는 일반화되고 규격화된 프로토콜이 오히려 기능상의 제약을 가져오게 된다.Although the DHCP protocol is a well-formed protocol, from the standpoint of the
ARP의 경우도 IP 기반 키폰 시스템에서는 일반적인 네트워크 장치들과는 다르게 운용될 수 있는데, 이는 IP 기반 키폰 시스템이 중앙 집중적인 구조 하에서 주장치(10)가 IP 단말기(20)들을 완전히 통제할 수 있다는 사실에 기인한다.In case of ARP, the IP-based keyphone system can be operated differently from the general network devices. This is due to the fact that the
그래서 본 발명에서는 IP 주소 할당과 관리가 완전히 제어되는 환경에서 ARP를 사용하지 않고도 초기의 시스템 구동시에 교환되는 정보를 기반으로 패킷을 상호 전송할 수 있도록 한다.Therefore, in the present invention, in the environment where IP address allocation and management are completely controlled, packets can be mutually transmitted based on information exchanged at the time of initial system operation without using ARP.
도 6은 본 발명이 적용되는 IP 기반 키폰 시스템에서 IP 주소 동적 할당 예를 보인 블록구성도이다.6 is a block diagram showing an example of IP address dynamic allocation in an IP-based key phone system to which the present invention is applied.
그래서 IP 주소 할당을 위한 패킷은 IP 멀티캐스트 패킷에 실려 전송된다.Thus, the packet for IP address assignment is carried in the IP multicast packet.
IP 멀티캐스트는 도 6의 멀티캐스트 멤버 간의 패킷 전송에서 나타나 있는 것 처럼, 특정 멀티캐스트 IP 주소와 포트를 설정하여 그에 대한 멤버쉽 등록을 하게 되면 해당 멀티캐스트 멤버들에 한해서만 패킷을 수신할 수 있게 된다.As shown in the packet transmission between multicast members of FIG. 6, IP multicast sets a specific multicast IP address and port and registers membership for it, so that only the multicast members can receive packets. .
이러한 IP 멀티캐스트를 통해서 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 초기 패킷 전송은 다른 네트워크 장치들로부터 분리되어 행해지게 되므로 브로드캐스트 등을 사용하는 것보다 네트워크의 효율이나 안정성이 높아지게 된다.Since the initial packet transmission of the IP-based keyphone system is performed separately from other network devices through the IP multicast, the efficiency and stability of the network is higher than that of the broadcast.
이러한 본 발명의 동작을 좀더 상세히 설명하면 다음과 같다.Referring to the operation of the present invention in more detail as follows.
도 7은 본 발명에서 사용하는 IP 할당 메시지 포맷의 예를 보인 개념도이다.7 is a conceptual diagram illustrating an example of an IP allocation message format used in the present invention.
먼저 주장치(10)는 초기화 과정에서 IP 단말들에 어느 영역의 IP 주소를 할당할 지에 관한 정보를 가지고 있어야 한다(ST11).First, the
이러한 정보가 설정된 이후에 주장치는 IP 단말기로부터의 메시지를 기다리게 된다(ST12).After this information is set, the assertion waits for a message from the IP terminal (ST12).
IP 단말기(20)는 초기화 과정을 끝낸 후(ST31), 도 5의 IP 할당 메시지 포맷의 형태를 가지는 IP 주소 할당 요청 패킷을 멀티캐스트로 보내게 된다(ST32). 이때 오퍼레이션 필드는 "IP 주소 할당 요청", 수신자 ID 타입은 아직 주장치(10)의 MAC 주소를 모르기 때문에 "주장치 또는 모든 IP 단말기", 수신자 ID는 "주장치"로 설정한다.After completing the initialization process (ST31), the
또한 메시지 시퀀스 번호는 0이 아닌 숫자에서 시작하여 패킷이 보내질 때마다 1씩 증가하게 되고, 응답(ACK) 시퀀스 번호는 특정 메시지 시퀀스 번호를 지닌 패킷을 수신했음을 상대방에게 알리는 용도로 사용하는데 현 단계에서는 해당사항이 없으므로 0으로 설정한다.In addition, the message sequence number starts from a non-zero number and increases by 1 each time a packet is sent. The ACK sequence number is used to inform the other party that a packet with a specific message sequence number has been received. Set to 0 because there is no applicable.
또한 발신자 타입을 "IP 단말기"로 설정하고 현재 설정되어 있는 IP 주소와 MAC 주소 등을 해당 필드에 넣는다. 이 메시지에서는 고정 필드만 사용하고 옵션 필드는 사용하지 않는다.It also sets the sender type to "IP terminal" and puts the currently set IP address and MAC address into the corresponding fields. This message uses only fixed fields, not optional fields.
그래서 주장치(10)가 IP 주소 할당 요청 패킷을 받으면(ST13), 자신이 관리하는 IP 주소 할당 데이터베이스를 검색하여 아직 예약 및 사용되고 있지 않은 IP 주소를 찾아(ST14) 해당 IP 단말기(20)로 IP 주소 할당 명령 패킷을 보내게 된다(ST15).Thus, when the
이 패킷의 오퍼레이션 필드는 "IP 주소 할당 명령", 수신자 ID 타입은 "MAC 주소", 수신자 ID는 앞서 받은 IP 주소 할당 요청 패킷의 발신자 MAC 주소 필드의 값을 복사해 넣는다. 메시지 시퀀스 번호 필드에는 0이 아닌 숫자에서 시작하여 패킷이 보내질 때 마다 하나씩 증가하는 값을 설정하고, 응답 시퀀스 번호 필드에는 앞서 받은 IP 주소 할당 요청 메시지의 메시지 시퀀스 번호에 있는 값을 복사해 넣는다. 이는 해당 메시지 시퀀스 번호에 해당하는 패킷을 수신했음을 상대방에게 알려주는 역할을 한다.The operation field of this packet is "IP address assignment command", the receiver ID type is "MAC address", and the receiver ID copies the value of the sender MAC address field of the previously received IP address allocation request packet. In the message sequence number field, start with a non-zero number and increment one by one each time a packet is sent. In the response sequence number field, copy the value in the message sequence number of the previously received IP address assignment request message. This informs the other party that a packet corresponding to the corresponding message sequence number has been received.
또한 발신자 타입은 "주장치"로 설정하고 발신자 IP 주소와 발신자 MAC 주소 필드를 자신의 주소로 설정한다. IP 주소 할당 명령 메시지에는 자신의 IP 주소 할 당 데이터베이스를 검색하여 예약해 둔 IP 주소 등과 게이트웨이 주소, DNS(Domain Name Server, 도메인 네임 서버) 주소 등 가외의 주소 정보를 옵션 필드에 넣는다.The sender type is also set to "main unit" and the sender IP address and sender MAC address fields are set to their own addresses. In the IP address assignment command message, additional IP address information such as gateway address and DNS (Domain Name Server) address is searched for in the optional field.
그러면 IP 단말기(20)는 주장치(10)로부터 받은 IP 주소 할당 명령 메시지에 대하여 메시지를 수신했음을 메시지 수신 확인 메시지를 통해 알려주게 되는데(ST39), 오퍼레이션 필드에 "메시지 수신 확인", 수신자 ID 타입에 "MAC 주소", 수신자 ID에 주장치의 MAC 주소를 앞서 받은 메시지에서 복사하여 넣는다.Then, the
그리고 자신의 메시지 시퀀스 번호를 설정하고 앞서 받은 메시지의 메시지 시퀀스 번호를 응답 시퀀스 번호 필드에 복사하여 넣어 주장치(10)에 해당 메시지를 수신했음을 알린다(ST40).Then, it sets its own message sequence number and copies the message sequence number of the previously received message into the response sequence number field to inform the
이때 발신자 타입을 "IP 단말기"로 설정하고, 자신의 주소 정보를 "발신자 IP 주소" 및 "발신자 MAC 주소" 필드에 넣는다. 여기서는 고정 필드만 사용한다.At this time, the sender type is set to "IP terminal", and its address information is put into the "sender IP address" and "sender MAC address" fields. Only fixed fields are used here.
그런 다음 주장치(10)는 IP 단말기(20)로부터 메시지 수신 확인 메시지를 받으면(ST21), IP 주소 할당이 이루어 진 것으로 판단하고(ST22) 자신의 IP 주소 할당 데이터베이스에 설정된 예약상태를 확인상태로 변경하게 된다(ST23).Then, when the
이러한 일련의 과정을 거치는 중에 주장치(10)와 IP 단말기(20)는 서로에 대한 IP 주소와 MAC 주소를 알 수 있게 되며 이에 대한 사항을 저장해 둔다.During this series of processes, the
이 외에도 부가 기능으로 IP 주소 정보 요청(ST16)(ST17)(ST36)(ST37)과 IP 주소 정보 보고(ST24)(ST25)(ST38)(ST40) 메시지가 있는데, 메시지의 형태는 각각 IP 주소 할당 요청과 IP 주소 할당 명령 메시지와 같다.In addition, there are IP address information request (ST16) (ST17) (ST36) (ST37) and IP address information report (ST24) (ST25) (ST38) (ST40) messages. Same as request and IP address allocation command message.
이 메시지들은 IP 주소 할당 과정에 직접 사용되지는 않으나, 상위 프로세스 의 필요에 따라 상대방의 IP 주소 설정 상태를 검사하는 용도로 사용될 수 있다.These messages are not used directly in the IP address assignment process, but can be used to check the other party's IP address configuration as required by the higher level process.
IP 주소 충돌 보고 메시지는 IP 단말기가 동작 중 같은 IP 주소가 다른 장치에도 사용되고 있음을 확인하였을 때 주장치(10)에 이 사실을 보고하기 위한 메시지이다(S6T18 ~ ST20). 메시지는 고정 필드만을 사용하며 옵션 필드를 통한 가외의 정보는 넣지 않는다.The IP address conflict report message is a message for reporting this fact to the
그래서 주장치(10)가 이 메시지를 받으면 자신의 IP 주소 할당 데이터베이스 및 핑 테스트(Ping Test)를 통해 IP 주소 중복이 확인되면 관련 IP 단말기에 IP 주소 할당 명령을 다시 내리게 된다(ST20)(ST34)(ST35).Therefore, when the
이러한 과정을 거치게 되면 주장치(10)와 IP 단말기(20)가 서로에 대한 IP 주소와 MAC 주소 정보를 갖게 되기 때문에 ARP를 사용하여 서로의 MAC 주소를 얻어 올 필요가 없게 된다.When this process is performed, since the
따라서 주장치(10)와 IP 단말기(20)는 상대방에 대한 IP 주소와 MAC 주소 정보를 자신의 ARP 캐쉬 또는 ARP 엔트리에 저장하여 해당 주소로 패킷 전송시에 ARP 없이 패킷을 전송하도록 한다.Therefore, the
만일 ARP 캐쉬 또는 ARP 테이블 외에 MAC 주소 활용을 위한 더 효율적인 방법이 있다면 그 방법을 사용하도록 한다.If there is a more efficient way to use MAC address besides ARP cache or ARP table, use it.
이처럼 본 발명은 IP 기반 키폰 시스템에서 IP 멀티캐스트를 사용한 시그널링을 통하여 동일한 LAN 상에 있는 IP 단말기들에 IP 주소를 동적으로 할당하고 관리하며 이러한 과정 중 교환된 정보를 기반으로 ARP를 통하지 않는 패킷 전송이 가능하게 하여 LAN 상의 트래픽을 감소시키고 패킷 전송 속도를 향상시키게 되는 것 이다.As such, the present invention dynamically allocates and manages IP addresses to IP terminals on the same LAN through signaling using IP multicast in an IP-based keyphone system, and transmits packets through ARP based on information exchanged during this process. This will reduce the traffic on the LAN and improve the packet transfer rate.
이상에서 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예를 설명하였으나, 본 발명은 다양한 변화와 변경 및 균등물을 사용할 수 있다. 본 발명은 상기 실시예를 적절히 변형하여 동일하게 응용할 수 있음이 명확하다. 따라서 상기 기재 내용은 하기 특허청구범위의 한계에 의해 정해지는 본 발명의 범위를 한정하는 것이 아니다.Although the preferred embodiment of the present invention has been described above, the present invention may use various changes, modifications, and equivalents. It is clear that the present invention can be applied in the same manner by appropriately modifying the above embodiments. Accordingly, the above description does not limit the scope of the invention as defined by the limitations of the following claims.
이상에서 살펴본 바와 같이, 본 발명에 의한 IP 기반 키폰 시스템의 IP 주소 동적 할당 방법은 IP 기반 키폰 시스템이 설치되어 있는 LAN 상에 존재하는 DHCP 서버 등과의 충돌을 방지하고, 주장치에 의해서 완전히 통제 가능한 IP 주소 할당으로 네트워크의 효율과 안정성이 증대되는 효과가 있게 된다.As described above, the IP address dynamic allocation method of the IP-based keyphone system according to the present invention prevents a collision with a DHCP server or the like existing on the LAN where the IP-based keyphone system is installed, and can be fully controlled by the host device. Address assignment increases the efficiency and stability of the network.
또한 본 발명은 기존의 DHCP 등 표준 프로토콜 사용으로 인한 기능적 제약을 극복할 수 있게 함으로써 시스템에 기능상의 유연성을 제공할 수 있는 효과도 있게 된다.In addition, the present invention is able to overcome the functional limitations caused by the use of standard protocols, such as DHCP, there is also an effect that can provide a functional flexibility to the system.
더불어 IP 주소 동적 할당을 통해 얻은 정보는 주장치의 중앙 집중적인 통제에 의해서 얻은 정보이기 때문에 ARP를 사용하여 MAC 주소를 가져올 필요성이 발생하지 않는다. 따라서 ARP를 사용하지 않고 패킷을 전송하기 때문에 네트워크상의 트래픽 감소와 패킷 전송속도 향상 등의 장점이 있게 된다.In addition, since the information obtained through the dynamic allocation of IP addresses is obtained by the centralized control of the master device, there is no need to obtain MAC addresses using ARP. Therefore, since the packet is transmitted without using ARP, there are advantages such as traffic reduction and packet transmission speed on the network.
Claims (10)
Translated fromKoreanPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020040109210AKR100687614B1 (en) | 2004-12-21 | 2004-12-21 | Dynamic IP Address Assignment for IP-based Keyphone System |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020040109210AKR100687614B1 (en) | 2004-12-21 | 2004-12-21 | Dynamic IP Address Assignment for IP-based Keyphone System |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20060070665Atrue KR20060070665A (en) | 2006-06-26 |
| KR100687614B1 KR100687614B1 (en) | 2007-02-27 |
Family
ID=37164262
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020040109210AExpired - Fee RelatedKR100687614B1 (en) | 2004-12-21 | 2004-12-21 | Dynamic IP Address Assignment for IP-based Keyphone System |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100687614B1 (en) |
Cited By (38)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2009028856A1 (en)* | 2007-08-24 | 2009-03-05 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US7733819B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2010-06-08 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US7782808B2 (en) | 2007-07-02 | 2010-08-24 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US7881259B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2011-02-01 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US7912006B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2011-03-22 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US7934244B2 (en) | 2007-04-13 | 2011-04-26 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US7975281B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2011-07-05 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8014333B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2011-09-06 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8051451B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2011-11-01 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8069463B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2011-11-29 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8069462B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2011-11-29 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US8078945B2 (en) | 2007-04-10 | 2011-12-13 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US8077744B2 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2011-12-13 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcast system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcast data, and data processing method for use in the same |
| US8087052B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2011-12-27 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8149744B2 (en) | 2007-07-25 | 2012-04-03 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US8161511B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-04-17 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8175065B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-05-08 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in the digital broadcasting system |
| US8185925B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-05-22 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in the digital broadcasting system |
| US8276178B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-09-25 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8375413B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2013-02-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in a digital broadcasting system |
| US8396043B2 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2013-03-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcast system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcast data, and data processing method for use in the same |
| US8407743B2 (en) | 2008-08-22 | 2013-03-26 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method for processing additional information related to an announced service or content in an NRT service and a broadcast receiver |
| US8413194B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2013-04-02 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8683529B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2014-03-25 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8954829B2 (en) | 2007-07-04 | 2015-02-10 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data |
| US8964856B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2015-02-24 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8984381B2 (en) | 2006-04-29 | 2015-03-17 | LG Electronics Inc. LLP | DTV transmitting system and method of processing broadcast data |
| US9185413B2 (en) | 2006-02-10 | 2015-11-10 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Channel equalizer and method of processing broadcast signal in DTV receiving system |
| US9198005B2 (en) | 2007-03-26 | 2015-11-24 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data |
| US9392281B2 (en) | 2006-10-12 | 2016-07-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital television transmitting system and receiving system and method of processing broadcasting data |
| US9490936B2 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2016-11-08 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcast system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcast data, and data processing method for use in the same |
| US9521441B2 (en) | 2007-03-30 | 2016-12-13 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data |
| US9564989B2 (en) | 2006-05-23 | 2017-02-07 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital television transmitting system and receiving system and method of processing broadcast data |
| US9736508B2 (en) | 2007-03-26 | 2017-08-15 | Lg Electronics Inc. | DTV receiving system and method of processing DTV signal |
| USRE46728E1 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2018-02-20 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| USRE46891E1 (en) | 2005-10-05 | 2018-06-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method of processing traffic information and digital broadcast system |
| USRE47183E1 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2018-12-25 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| CN111756865A (en)* | 2019-03-28 | 2020-10-09 | 苏州铭威天欣信息科技有限公司 | A communication management method between a base station and a user terminal |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003134253A (en) | 2001-10-22 | 2003-05-09 | Hitachi Communication Technologies Ltd | IP telephone system and IP telephone management method |
| JP2003134117A (en) | 2001-10-22 | 2003-05-09 | Hitachi Communication Technologies Ltd | IP telephone, call manager, and method of obtaining IP address of IP telephone |
| JP2003273899A (en) | 2002-03-15 | 2003-09-26 | Nef:Kk | PRIVATE BRANCH EXCHANGE COMPATIBLE WITH VoIP AND TELEPHONE EXCHANGE SYSTEM COMPATIBLE WITH VoIP USING THE SAME AND METHOD FOR DYNAMICALLY ALLOCATION OF IP ADDRESS |
| JP3916542B2 (en) | 2002-10-07 | 2007-05-16 | 沖電気工業株式会社 | Address assignment system |
- 2004
- 2004-12-21KRKR1020040109210Apatent/KR100687614B1/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Cited By (101)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USRE47294E1 (en) | 2005-10-05 | 2019-03-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method of processing traffic information and digital broadcast system |
| USRE49757E1 (en) | 2005-10-05 | 2023-12-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method of processing traffic information and digital broadcast system |
| USRE48627E1 (en) | 2005-10-05 | 2021-07-06 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method of processing traffic information and digital broadcast system |
| USRE46891E1 (en) | 2005-10-05 | 2018-06-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method of processing traffic information and digital broadcast system |
| US9185413B2 (en) | 2006-02-10 | 2015-11-10 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Channel equalizer and method of processing broadcast signal in DTV receiving system |
| US10277255B2 (en) | 2006-02-10 | 2019-04-30 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Channel equalizer and method of processing broadcast signal in DTV receiving system |
| US8984381B2 (en) | 2006-04-29 | 2015-03-17 | LG Electronics Inc. LLP | DTV transmitting system and method of processing broadcast data |
| US9680506B2 (en) | 2006-04-29 | 2017-06-13 | Lg Electronics Inc. | DTV transmitting system and method of processing broadcast data |
| US9178536B2 (en) | 2006-04-29 | 2015-11-03 | Lg Electronics Inc. | DTV transmitting system and method of processing broadcast data |
| US9425827B2 (en) | 2006-04-29 | 2016-08-23 | Lg Electronics Inc. | DTV transmitting system and method of processing broadcast data |
| US9564989B2 (en) | 2006-05-23 | 2017-02-07 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital television transmitting system and receiving system and method of processing broadcast data |
| US10057009B2 (en) | 2006-05-23 | 2018-08-21 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital television transmitting system and receiving system and method of processing broadcast data |
| US9392281B2 (en) | 2006-10-12 | 2016-07-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital television transmitting system and receiving system and method of processing broadcasting data |
| US10454616B2 (en) | 2006-10-12 | 2019-10-22 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital television transmitting system and receiving system and method of processing broadcasting data |
| US9831986B2 (en) | 2006-10-12 | 2017-11-28 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital television transmitting system and receiving system and method of processing broadcasting data |
| US9198005B2 (en) | 2007-03-26 | 2015-11-24 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data |
| US10070160B2 (en) | 2007-03-26 | 2018-09-04 | Lg Electronics Inc. | DTV receiving system and method of processing DTV signal |
| US9924206B2 (en) | 2007-03-26 | 2018-03-20 | Lg Electronics Inc. | DTV receiving system and method of processing DTV signal |
| US10244274B2 (en) | 2007-03-26 | 2019-03-26 | Lg Electronics Inc. | DTV receiving system and method of processing DTV signal |
| US9912354B2 (en) | 2007-03-26 | 2018-03-06 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data |
| US9736508B2 (en) | 2007-03-26 | 2017-08-15 | Lg Electronics Inc. | DTV receiving system and method of processing DTV signal |
| US9521441B2 (en) | 2007-03-30 | 2016-12-13 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data |
| US8078945B2 (en) | 2007-04-10 | 2011-12-13 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US8335975B2 (en) | 2007-04-10 | 2012-12-18 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US7934244B2 (en) | 2007-04-13 | 2011-04-26 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US8495695B2 (en) | 2007-04-13 | 2013-07-23 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| USRE46398E1 (en) | 2007-04-13 | 2017-05-09 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| USRE47857E1 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2020-02-11 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcast system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcast data, and data processing method for use in the same |
| US10097312B2 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2018-10-09 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcast system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcast data, and data processing method for use in the same |
| US9860016B2 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2018-01-02 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcast system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcast data, and data processing method for use in the same |
| USRE46244E1 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2016-12-20 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcast system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcast data, and data processing method for use in the same |
| US8325766B2 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2012-12-04 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcast system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcast data, and data processing method for use in the same |
| USRE46728E1 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2018-02-20 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US8077744B2 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2011-12-13 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcast system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcast data, and data processing method for use in the same |
| US8396043B2 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2013-03-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcast system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcast data, and data processing method for use in the same |
| US9490936B2 (en) | 2007-06-26 | 2016-11-08 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcast system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcast data, and data processing method for use in the same |
| US10045078B2 (en) | 2007-07-02 | 2018-08-07 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US7782808B2 (en) | 2007-07-02 | 2010-08-24 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US9438931B2 (en) | 2007-07-02 | 2016-09-06 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US8107790B2 (en) | 2007-07-02 | 2012-01-31 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US9078046B2 (en) | 2007-07-02 | 2015-07-07 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US9660764B2 (en) | 2007-07-04 | 2017-05-23 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Broadcast transmitter and method of processing broadcast service data for transmission |
| US9094159B2 (en) | 2007-07-04 | 2015-07-28 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Broadcasting transmitting system and method of processing broadcast data in the broadcast transmitting system |
| US9444579B2 (en) | 2007-07-04 | 2016-09-13 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Broadcast transmitter and method of processing broadcast service data for transmission |
| US8954829B2 (en) | 2007-07-04 | 2015-02-10 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data |
| US9184770B2 (en) | 2007-07-04 | 2015-11-10 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Broadcast transmitter and method of processing broadcast service data for transmission |
| US8149744B2 (en) | 2007-07-25 | 2012-04-03 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US9912589B2 (en) | 2007-07-25 | 2018-03-06 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US9294884B2 (en) | 2007-07-25 | 2016-03-22 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US8654693B2 (en) | 2007-07-25 | 2014-02-18 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US8214872B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-07-03 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US9755849B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2017-09-05 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US7733819B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2010-06-08 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8964856B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2015-02-24 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8752098B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2014-06-10 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US7881259B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2011-02-01 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8683529B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2014-03-25 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US9307273B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2016-04-05 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US9338484B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2016-05-10 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US9369154B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2016-06-14 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US7912006B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2011-03-22 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US7933232B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2011-04-26 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8014333B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2011-09-06 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8510781B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2013-08-13 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8413194B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2013-04-02 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8051451B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2011-11-01 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8375413B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2013-02-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in a digital broadcasting system |
| US8276040B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-09-25 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8276178B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-09-25 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US9608766B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2017-03-28 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| USRE47183E1 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2018-12-25 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8223787B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-07-17 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US9668005B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2017-05-30 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8116276B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-02-14 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US10044453B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2018-08-07 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| WO2009028856A1 (en)* | 2007-08-24 | 2009-03-05 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US9100199B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2015-08-04 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8199714B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-06-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8185925B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-05-22 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in the digital broadcasting system |
| US8175065B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-05-08 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in the digital broadcasting system |
| US8161511B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-04-17 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8149755B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-04-03 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8121064B2 (en) | 2007-08-24 | 2012-02-21 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8230463B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2012-07-24 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8533762B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2013-09-10 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US9380432B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2016-06-28 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8220026B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2012-07-10 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US8087052B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2011-12-27 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8069462B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2011-11-29 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and data processing method |
| US8069463B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2011-11-29 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US7975281B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2011-07-05 | Lg Electronics, Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8141119B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2012-03-20 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US9924220B2 (en) | 2007-09-21 | 2018-03-20 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data in digital broadcasting system |
| US8407743B2 (en) | 2008-08-22 | 2013-03-26 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method for processing additional information related to an announced service or content in an NRT service and a broadcast receiver |
| US10165336B2 (en) | 2008-08-22 | 2018-12-25 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method for processing additional information related to an advances service or content in an NRT service and a broadcast receiver |
| US8646008B2 (en) | 2008-08-22 | 2014-02-04 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method for processing additional information related to an announced service or content in an NRT service and a broadcast receiver |
| US9681177B2 (en) | 2008-08-22 | 2017-06-13 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method for processing additional information related to an announced service or content in an NRT service and a broadcast receiver |
| US9210452B2 (en) | 2008-08-22 | 2015-12-08 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method for processing additional information related to an announced service or content in an NRT service and a broadcast receiver |
| US9015769B2 (en) | 2008-08-22 | 2015-04-21 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method for processing additional information related to an announced service or content in an NRT service and a broadcast receiver |
| CN111756865A (en)* | 2019-03-28 | 2020-10-09 | 苏州铭威天欣信息科技有限公司 | A communication management method between a base station and a user terminal |
| CN111756865B (en)* | 2019-03-28 | 2024-02-09 | 苏州铭威天欣信息科技有限公司 | A communication management method between base station and user terminal |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR100687614B1 (en) | 2007-02-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100687614B1 (en) | Dynamic IP Address Assignment for IP-based Keyphone System | |
| US5617540A (en) | System for binding host name of servers and address of available server in cache within client and for clearing cache prior to client establishes connection | |
| US5878212A (en) | System for updating mapping or virtual host names to layer-3 address when multimedia server changes its usage state to busy or not busy | |
| JP3903014B2 (en) | Internet protocol address conversion apparatus, home network system using the same, and communication method therefor | |
| US6944167B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for dynamic allocation of private address space based upon domain name service queries | |
| US6243749B1 (en) | Dynamic network address updating | |
| US20010023459A1 (en) | DNS server, DHCP server, terminal and communication system | |
| JPH10247946A (en) | Network connection method and method and name server | |
| WO2007016850A1 (en) | A method, system and apparatus for accessing the web server | |
| JP3420512B2 (en) | Dynamic domain name system | |
| KR20020016734A (en) | Network address translation system and method being capable of accessing to node having private IP address from external network and computer-readable medium recording the method | |
| EP1187426B1 (en) | Method for using a unique IP address in a private IP address domain | |
| CN1528080A (en) | Method and equipment for determining virtual address of terminal equipment | |
| US7570647B2 (en) | LAN type internet access network and subscriber line accommodation method for use in the same network | |
| CN100391213C (en) | Method for transferring data between internal data network and public data network and device for implementing the method | |
| US7085836B1 (en) | System and method for automatic private IP address selection | |
| KR100355288B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for providing service server functionality to the hosts of a private network | |
| KR20030058267A (en) | An IP Automatic Assignment's Method in the way of Central IP Management thorugh Intermediate DHCP Server | |
| KR19990050416A (en) | IP address translation method providing full access between non-Internet service network and Internet service network | |
| KR20010073827A (en) | Method for expanding address for internet protocol version 4 in internet edge router | |
| KR100487296B1 (en) | a system for supporting movement of host computer and method therefor | |
| JP2003179603A (en) | Communication control method in communication system, program, transmitter and receiver | |
| KR19990048446A (en) | IP address translation method providing full access between non-Internet service network and Internet service network | |
| WO2000024166A9 (en) | Dynamic ip address assignment | |
| TW508935B (en) | Communication system automatically setting up basic data of voice over IP telephone equipment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| N231 | Notification of change of applicant | ||
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| R17-X000 | Change to representative recorded | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R17-oth-X000 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | St.27 status event code:A-1-1-Q10-Q12-nap-PG1501 | |
| D13-X000 | Search requested | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D13-srh-X000 | |
| D14-X000 | Search report completed | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D14-srh-X000 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Fee payment year number:1 St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Fee payment year number:4 St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Fee payment year number:5 St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20120119 Year of fee payment:6 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Fee payment year number:6 St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee | ||
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | Not in force date:20130222 Payment event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U13-oth-PC1903 | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | Ip right cessation event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE Not in force date:20130222 St.27 status event code:N-4-6-H10-H13-oth-PC1903 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 |