KR102799600B1 - Electronic device for efficiently training neural network model based on frequency analysis of traing image data and controlling method thereof - Google Patents
Electronic device for efficiently training neural network model based on frequency analysis of traing image data and controlling method thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102799600B1 KR102799600B1KR1020210174786AKR20210174786AKR102799600B1KR 102799600 B1KR102799600 B1KR 102799600B1KR 1020210174786 AKR1020210174786 AKR 1020210174786AKR 20210174786 AKR20210174786 AKR 20210174786AKR 102799600 B1KR102799600 B1KR 102799600B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- learning
- frequency components
- neural network
- learning images
- network model
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/045—Combinations of networks
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20048—Transform domain processing
- G06T2207/20056—Discrete and fast Fourier transform, [DFT, FFT]
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 개시는 전자 장치 및 전자 장치의 제어 방법에 관한 것으로서, 구체적으로는 학습 영상 데이터에 대한 주파수 분석에 기초하여 신경망 모델을 학습시키는 전자 장치 및 이의 제어 방법에 관한 것이다.The present disclosure relates to an electronic device and a method for controlling the electronic device, and more particularly, to an electronic device for training a neural network model based on frequency analysis of learning image data and a method for controlling the same.
근래 인공 지능 기술의 눈부신 발전은 기존 산업의 가치를 제고하고 새로운 산업을 창출하고 있다. 인공 지능은 기본적으로 많은 학습 데이터를 기반으로 하고 있으며, 이를 효율적으로 신경망 모델(예: 분류기)의 학습에 활용하는 것은 매우 중요한 일이다. 그런데, 학습 데이터(예: 학습 영상) 양이 많아지면 학습 시간이 많이 걸리거나, 학습의 결과가 최적의 결과로 수렴되지 않고 발산하는 경우가 발생할 수 있다.The recent remarkable development of artificial intelligence technology is increasing the value of existing industries and creating new industries. Artificial intelligence is fundamentally based on a large amount of learning data, and it is very important to efficiently utilize this for learning neural network models (e.g. classifiers). However, if the amount of learning data (e.g. learning images) increases, the learning time may take a long time, or the learning results may not converge to the optimal result and may diverge.
종래 기술에 따르면, 학습 영상에 대한 특정한 기준 없이 신경망 모델을 학습시키기 때문에 학습의 수렴 속도가 느리거나, 수렴이 잘 이루어지지 않는 문제가 발생할 수 있다. 구체적으로, 종래 기술에 따라 신경망 모델을 학습하는 경우, 학습이 진행됨에 따라 학습의 에러율이 감소하지 않는 구간이 발생할 수 있으며, 이 경우 학습 영상을 무작위로 다시 섞어서 학습하거나, 신경망 모델의 구조를 변경하여 다시 학습하는 과정을 반복하여야 한다.According to the conventional technology, since the neural network model is trained without specific criteria for the training images, the convergence speed of the training may be slow or the convergence may not occur well. Specifically, when the neural network model is trained according to the conventional technology, a section in which the error rate of the training does not decrease as the training progresses may occur, and in this case, the training images must be randomly shuffled and trained, or the process of changing the structure of the neural network model and training again must be repeated.
따라서, 종래 기술에 대해서는 신경망 모델의 학습 과정에서 발생된 문제점을 분석하기 어렵고, 신경망 모델의 학습에 소요되는 시간이 많이 든다는 한계가 지적되고 있다.Therefore, it has been pointed out that the conventional technology has limitations in that it is difficult to analyze problems that occur during the learning process of a neural network model and that it takes a lot of time to learn a neural network model.
본 개시는 상술한 바와 같은 필요성에 따른 것으로서, 본 개시의 목적은 학습 영상의 주파수 분석에 기초하여 신경망 모델을 효율적이고 안정적으로 학습시킬 수 있는 전자 장치 및 전자 장치의 제어 방법을 제공함에 있다.The present disclosure is made in response to the above-described necessity, and the purpose of the present disclosure is to provide an electronic device and a method for controlling the electronic device capable of efficiently and stably training a neural network model based on frequency analysis of a learning image.
상술한 바와 같은 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 개시의 일 실시 예에 따르면, 전자 장치는 메모리 및 신경망 모델의 학습을 위한 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분을 분석하여, 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득하고, 상기 평균 주파수 성분의 집합에 기초하여, 저주파수 영역이 제외된 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정하며, 상기 타겟 주파수 영역에 포함된 복수의 영역 별 주파수 성분의 합에 기초하여, 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 그룹핑하기 위한 그룹핑 기준을 결정하고, 상기 그룹핑 기준에 기초하여 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑하며, 상기 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 낮은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상부터 상기 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 높은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상 순으로 상기 신경망 모델에 입력하여 상기 신경망 모델을 학습시키는 프로세서를 포함한다.According to one embodiment of the present disclosure to achieve the above-described purpose, the electronic device includes a processor configured to analyze frequency components for each of a plurality of learning images for learning a memory and a neural network model, to obtain a set of average frequency components for the plurality of learning images, to determine a target frequency range from which a low frequency range is excluded based on the set of average frequency components, to determine a grouping criterion for grouping the plurality of learning images based on a sum of frequency components for each of a plurality of regions included in the target frequency range, to group the plurality of learning images into a plurality of groups based on the grouping criterion, and to input learning images included in a group having a low frequency component among the plurality of groups in order from learning images included in a group having a high frequency component among the plurality of groups to the neural network model to train the neural network model.
여기서, 상기 프로세서는 고속 푸리에 변환(fast fourier transform, FFT)을 이용하여 상기 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분을 분석할 수 있다.Here, the processor can analyze frequency components for each of the plurality of learning images using a fast Fourier transform (FFT).
한편, 상기 프로세서는 상기 평균 주파수 성분의 집합 중 최대 값을 식별하고, 상기 평균 주파수 성분의 집합 중 상기 최대 값의 1/2인 주파수 성분에 대응되는 지점부터 상기 평균 주파수 성분의 집합 중 상기 최대 값의 1/10인 주파수 성분에 대응되는 지점까지의 영역을 식별하는 것에 기초하여, 상기 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정할 수 있다.Meanwhile, the processor can determine the target frequency range based on identifying a maximum value among the set of average frequency components, and identifying a range from a point corresponding to a frequency component that is half the maximum value among the set of average frequency components to a point corresponding to a frequency component that is 1/10 the maximum value among the set of average frequency components.
한편, 상기 프로세서는 상기 복수의 학습 영상의 중심점과의 거리에 기초하여, 상기 타겟 주파수 영역을 동일한 면적을 갖는 제1 개수의 영역들로 구분함으로써 상기 복수의 영역을 결정하고, 상기 복수의 영역 각각에 대한 주파수 성분의 합을 산출하여 상기 중심점과의 거리가 가까운 영역부터 상기 중심점과의 거리가 먼 영역까지 순차적으로 배열하며, 상기 배열된 주파수 성분의 합에서 상기 주파수 성분의 합이 급격하게 증가하는 경계를 기준으로 상기 복수의 영역을 구분함으로써, 상기 그룹핑 기준을 결정할 수 있다.Meanwhile, the processor determines the plurality of regions by dividing the target frequency region into a first number of regions having the same area based on the distances from the center points of the plurality of learning images, calculates the sum of frequency components for each of the plurality of regions and sequentially arranges them from a region having a close distance from the center point to a region having a far distance from the center point, and determines the grouping criterion by dividing the plurality of regions based on a boundary where the sum of the frequency components rapidly increases in the sum of the arranged frequency components.
한편, 상기 프로세서는 상기 복수의 학습 영상 별로 상기 그룹핑 기준에 따른 주파수 성분의 합을 산출하는 것에 기초하여, 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 상기 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑할 수 있다.Meanwhile, the processor can group the plurality of learning images into the plurality of groups based on calculating the sum of frequency components according to the grouping criteria for each of the plurality of learning images.
한편, 상기 프로세서는 상기 신경망 모델의 학습이 진행되는 동안 상기 신경망 모델의 학습에 따른 에러율에 대한 정보를 획득하고, 상기 에러율에 대한 정보에 기초하여 상기 학습이 비정상적으로 수행되었는지 여부를 식별하며, 상기 학습이 비정상적으로 수행된 것으로 식별되면, 상기 타겟 주파수 영역을 상기 제1 개수와 상이한 제2 개수의 영역들로 구분함으로써 상기 복수의 영역을 재 결정하고, 상기 재 결정된 복수의 영역에 기초하여 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 재그룹핑한 후, 상기 신경망 모델을 재학습시킬 수 있다.Meanwhile, the processor obtains information on an error rate according to the learning of the neural network model while the learning of the neural network model is in progress, identifies whether the learning has been performed abnormally based on the information on the error rate, and if the learning has been identified as being performed abnormally, re-determines the plurality of regions by dividing the target frequency region into a second number of regions different from the first number, and re-groups the plurality of learning images into a plurality of groups based on the re-determined plurality of regions, and then re-trains the neural network model.
여기서, 상기 프로세서는 상기 학습이 진행되는 동안 상기 에러율이 기 설정된 임계 값 이상으로 증가하면, 상기 학습이 비정상적으로 수행된 것으로 식별할 수 있다.Here, the processor can identify that the learning is performed abnormally if the error rate increases above a preset threshold value while the learning is in progress.
한편, 상기 프로세서는 상기 복수의 그룹 별 학습 영상을 각각 상이한 신경망 모델의 학습에 이용할 수 있다.Meanwhile, the processor can use the plurality of group-specific learning images to learn different neural network models.
상술한 바와 같은 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 개시의 일 실시 예에 따르면, 전자 장치의 제어 방법은 신경망 모델의 학습을 위한 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분을 분석하여, 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득하는 단계, 상기 평균 주파수 성분의 집합에 기초하여, 저주파수 영역이 제외된 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정하는 단계, 상기 타겟 주파수 영역에 포함된 복수의 영역 별 주파수 성분의 합에 기초하여, 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 그룹핑하기 위한 그룹핑 기준을 결정하는 단계, 상기 그룹핑 기준에 기초하여 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑하는 단계 및 상기 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 낮은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상부터 상기 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 높은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상 순으로 상기 신경망 모델에 입력하여 상기 신경망 모델을 학습시키는 단계를 포함한다.According to an embodiment of the present disclosure for achieving the above-described purpose, a control method of an electronic device includes the steps of analyzing frequency components for each of a plurality of learning images for learning a neural network model, thereby obtaining a set of average frequency components for the plurality of learning images, determining a target frequency range from which a low frequency range is excluded based on the set of average frequency components, determining a grouping criterion for grouping the plurality of learning images based on a sum of frequency components for each of a plurality of regions included in the target frequency range, grouping the plurality of learning images into a plurality of groups based on the grouping criterion, and inputting learning images included in a group having a low frequency component among the plurality of groups in order from learning images included in a group having a high frequency component among the plurality of groups into the neural network model to learn the neural network model.
상술한 바와 같은 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 개시의 일 실시 예에 따르면, 전자 장치의 제어 방법을 실행하는 프로그램을 포함하는 비일시적 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록매체에 있어서, 상기 전자 장치의 제어 방법은 신경망 모델의 학습을 위한 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분을 분석하여, 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득하는 단계, 상기 평균 주파수 성분의 집합에 기초하여, 저주파수 영역이 제외된 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정하는 단계, 상기 타겟 주파수 영역에 포함된 복수의 영역 별 주파수 성분의 합에 기초하여, 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 그룹핑하기 위한 그룹핑 기준을 결정하는 단계, 상기 그룹핑 기준에 기초하여 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑하는 단계 및 상기 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 낮은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상부터 상기 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 높은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상 순으로 상기 신경망 모델에 입력하여 상기 신경망 모델을 학습시키는 단계를 포함한다.According to one embodiment of the present disclosure for achieving the above-described object, a non-transitory computer-readable recording medium including a program for executing a method for controlling an electronic device, the method for controlling an electronic device includes the steps of: analyzing frequency components for each of a plurality of learning images for learning a neural network model, thereby obtaining a set of average frequency components for the plurality of learning images; determining a target frequency range from which a low frequency range is excluded based on the set of average frequency components; determining a grouping criterion for grouping the plurality of learning images based on a sum of frequency components for each of a plurality of regions included in the target frequency range; grouping the plurality of learning images into a plurality of groups based on the grouping criterion; and inputting learning images included in a group having a low frequency component among the plurality of groups into the neural network model in that order from learning images included in a group having a high frequency component among the plurality of groups, thereby training the neural network model.
도 1은 본 개시의 일 실시 예에 따른 전자 장치의 제어 방법을 나타내는 흐름도,
도 2는 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득하는 과정을 예시적으로 나타내는 도면,
도 3은 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 나타내는 영상을 복수의 주파수 영역으로 구분하는 과정을 나타내는 도면,
도 4는 복수의 주파수 영역 중 하나의 주파수 영역의 반직선 상의 주파수 크기를 나타내는 그래프,
도 5는 타겟 주파수 영역을 구분하는 복수의 영역을 나타내는 도면,
도 6은 복수의 영역 별 주파수 성분의 합에 기초하여 그룹핑 기준을 결정하는 과정을 나타내는 도면,
도 7은 그룹핑 기준에 따라 하나의 학습 영상에 대한 그룹을 할당하는 과정을 예시적으로 설명하기 위한 도면,
도 8은 신경망 모델의 학습이 정상적으로 수행되는 경우의 학습 에러율을 나타내는 도면,
도 9는 신경망 모델의 학습이 비정상적으로 수행되는 경우의 학습 에러율을 나타내는 도면,
도 10은 본 개시에 따른 복수의 그룹 별 학습 영상을 각각 상이한 신경망 모델의 학습에 이용하는 실시 예에 대해 설명하기 위한 도면, 그리고,
도 11은 본 개시의 일 실시 예에 따른 전자 장치의 구성을 간략하게 나타내는 블록도이다.FIG. 1 is a flowchart showing a method for controlling an electronic device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
Figure 2 is a diagram exemplarily showing the process of obtaining a set of average frequency components for multiple learning images.
Figure 3 is a diagram showing a process of dividing an image representing a set of average frequency components into multiple frequency domains.
Figure 4 is a graph showing the frequency size on a straight line in one of multiple frequency domains.
Figure 5 is a diagram showing multiple areas that distinguish a target frequency range;
Figure 6 is a diagram showing a process of determining a grouping criterion based on the sum of frequency components for each of multiple areas.
Figure 7 is a drawing for exemplarily explaining the process of assigning a group to a single learning image according to the grouping criteria.
Figure 8 is a diagram showing the learning error rate when learning of a neural network model is performed normally.
Figure 9 is a diagram showing the learning error rate when learning of a neural network model is performed abnormally.
FIG. 10 is a diagram for explaining an embodiment of using multiple group-specific learning images according to the present disclosure for learning different neural network models, and
FIG. 11 is a block diagram briefly illustrating the configuration of an electronic device according to one embodiment of the present disclosure.
본 실시 예들은 다양한 변환을 가할 수 있고 여러 가지 실시 예를 가질 수 있는바, 특정 실시 예들을 도면에 예시하고 상세한 설명에 상세하게 설명하고자 한다. 그러나 이는 특정한 실시 형태에 대해 범위를 한정하려는 것이 아니며, 본 개시의 실시 예의 다양한 변경(modifications), 균등물(equivalents), 및/또는 대체물(alternatives)을 포함하는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. 도면의 설명과 관련하여, 유사한 구성요소에 대해서는 유사한 참조 부호가 사용될 수 있다.The present embodiments may have various modifications and may have various embodiments, and specific embodiments are illustrated in the drawings and described in detail in the detailed description. However, this is not intended to limit the scope to specific embodiments, but should be understood to include various modifications, equivalents, and/or alternatives of the embodiments of the present disclosure. In connection with the description of the drawings, similar reference numerals may be used for similar components.
본 개시를 설명함에 있어서, 관련된 공지 기능 혹은 구성에 대한 구체적인 설명이 본 개시의 요지를 불필요하게 흐릴 수 있다고 판단되는 경우 그에 대한 상세한 설명은 생략한다.In describing the present disclosure, if it is determined that a specific description of a related known function or configuration may unnecessarily obscure the gist of the present disclosure, a detailed description thereof will be omitted.
덧붙여, 하기 실시 예는 여러 가지 다른 형태로 변형될 수 있으며, 본 개시의 기술적 사상의 범위가 하기 실시 예에 한정되는 것은 아니다. 오히려, 이들 실시 예는 본 개시를 더욱 충실하고 완전하게 하고, 당업자에게 본 개시의 기술적 사상을 완전하게 전달하기 위하여 제공되는 것이다.In addition, the following embodiments may be modified in various other forms, and the scope of the technical idea of the present disclosure is not limited to the following embodiments. Rather, these embodiments are provided to make the present disclosure more faithful and complete, and to fully convey the technical idea of the present disclosure to those skilled in the art.
본 개시에서 사용한 용어는 단지 특정한 실시 예를 설명하기 위해 사용된 것으로, 권리범위를 한정하려는 의도가 아니다. 단수의 표현은 문맥상 명백하게 다르게 뜻하지 않는 한, 복수의 표현을 포함한다.The terminology used in this disclosure is only used to describe specific embodiments and is not intended to limit the scope of the rights. The singular expression includes the plural expression unless the context clearly indicates otherwise.
본 개시에서, "가진다," "가질 수 있다," "포함한다," 또는 "포함할 수 있다" 등의 표현은 해당 특징(예: 수치, 기능, 동작, 또는 부품 등의 구성요소)의 존재를 가리키며, 추가적인 특징의 존재를 배제하지 않는다.In this disclosure, expressions such as “has,” “can have,” “includes,” or “may include” indicate the presence of a corresponding feature (e.g., a component such as a number, function, operation, or part), and do not exclude the presence of additional features.
본 개시에서, "A 또는 B," "A 또는/및 B 중 적어도 하나," 또는 "A 또는/및 B 중 하나 또는 그 이상"등의 표현은 함께 나열된 항목들의 모든 가능한 조합을 포함할 수 있다. 예를 들면, "A 또는 B," "A 및 B 중 적어도 하나," 또는 "A 또는 B 중 적어도 하나"는, (1) 적어도 하나의 A를 포함, (2) 적어도 하나의 B를 포함, 또는 (3) 적어도 하나의 A 및 적어도 하나의 B 모두를 포함하는 경우를 모두 지칭할 수 있다.In this disclosure, the expressions “A or B,” “at least one of A and/or B,” or “one or more of A or/and B” can include all possible combinations of the listed items. For example, “A or B,” “at least one of A and B,” or “at least one of A or B” can all refer to (1) including at least one A, (2) including at least one B, or (3) including both at least one A and at least one B.
본 개시에서 사용된 "제1," "제2," "첫째," 또는 "둘째,"등의 표현들은 다양한 구성요소들을, 순서 및/또는 중요도에 상관없이 수식할 수 있고, 한 구성요소를 다른 구성요소와 구분하기 위해 사용될 뿐 해당 구성요소들을 한정하지 않는다.The expressions “first,” “second,” “first,” or “second,” etc., used in this disclosure can describe various components, regardless of order and/or importance, and are only used to distinguish one component from other components and do not limit the components.
어떤 구성요소(예: 제1 구성요소)가 다른 구성요소(예: 제2 구성요소)에 "(기능적으로 또는 통신적으로) 연결되어((operatively or communicatively) coupled with/to)" 있다거나 "접속되어(connected to)" 있다고 언급된 때에는, 상기 어떤 구성요소가 상기 다른 구성요소에 직접적으로 연결되거나, 다른 구성요소(예: 제3 구성요소)를 통하여 연결될 수 있다고 이해되어야 할 것이다.When it is stated that a component (e.g., a first component) is "(operatively or communicatively) coupled with/to" or "connected to" another component (e.g., a second component), it should be understood that said component can be directly coupled to said other component, or can be coupled through another component (e.g., a third component).
반면에, 어떤 구성요소(예: 제1 구성요소)가 다른 구성요소(예: 제2 구성요소)에 "직접 연결되어" 있다거나 "직접 접속되어" 있다고 언급된 때에는, 상기 어떤 구성요소와 상기 다른 구성요소 사이에 다른 구성요소(예: 제3 구성요소)가 존재하지 않는 것으로 이해될 수 있다.On the other hand, when it is said that a component (e.g., a first component) is "directly connected" or "directly connected" to another component (e.g., a second component), it can be understood that no other component (e.g., a third component) exists between said component and said other component.
본 개시에서 사용된 표현 "~하도록 구성된(또는 설정된)(configured to)"은 상황에 따라, 예를 들면, "~에 적합한(suitable for)," "~하는 능력을 가지는(having the capacity to)," "~하도록 설계된(designed to)," "~하도록 변경된(adapted to)," "~하도록 만들어진(made to)," 또는 "~를 할 수 있는(capable of)"과 바꾸어 사용될 수 있다. 용어 "~하도록 구성된(또는 설정된)"은 하드웨어적으로 "특별히 설계된(specifically designed to)" 것만을 반드시 의미하지 않을 수 있다.The expression "configured to" as used in this disclosure can be used interchangeably with, for example, "suitable for," "having the capacity to," "designed to," "adapted to," "made to," or "capable of." The term "configured to" does not necessarily mean only "specifically designed to" in terms of hardware.
대신, 어떤 상황에서는, "~하도록 구성된 장치"라는 표현은, 그 장치가 다른 장치 또는 부품들과 함께 "~할 수 있는" 것을 의미할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 문구 "A, B, 및 C를 수행하도록 구성된(또는 설정된) 프로세서"는 해당 동작을 수행하기 위한 전용 프로세서(예: 임베디드 프로세서), 또는 메모리 장치에 저장된 하나 이상의 소프트웨어 프로그램들을 실행함으로써, 해당 동작들을 수행할 수 있는 범용 프로세서(generic-purpose processor)(예: CPU 또는 application processor)를 의미할 수 있다.Instead, in some contexts, the phrase "a device configured to" can mean that the device, in conjunction with other devices or components, is "capable of" doing. For example, the phrase "a processor configured (or set) to perform A, B, and C" can mean a dedicated processor (e.g., an embedded processor) to perform the operations, or a generic-purpose processor (e.g., a CPU or application processor) that can perform the operations by executing one or more software programs stored in a memory device.
실시 예에 있어서 '모듈' 혹은 '부'는 적어도 하나의 기능이나 동작을 수행하며, 하드웨어 또는 소프트웨어로 구현되거나 하드웨어와 소프트웨어의 결합으로 구현될 수 있다. 또한, 복수의 '모듈' 혹은 복수의 '부'는 특정한 하드웨어로 구현될 필요가 있는 '모듈' 혹은 '부'를 제외하고는 적어도 하나의 모듈로 일체화되어 적어도 하나의 프로세서로 구현될 수 있다.In the embodiments, a 'module' or 'part' performs at least one function or operation and may be implemented by hardware or software or a combination of hardware and software. In addition, a plurality of 'modules' or a plurality of 'parts' may be integrated into at least one module and implemented by at least one processor, except for a 'module' or 'part' that needs to be implemented by a specific hardware.
한편, 도면에서의 다양한 요소와 영역은 개략적으로 그려진 것이다. 따라서, 본 발명의 기술적 사상은 첨부한 도면에 그려진 상대적인 크기나 간격에 의해 제한되지 않는다.Meanwhile, various elements and areas in the drawings are schematically drawn. Therefore, the technical idea of the present invention is not limited by the relative sizes or intervals drawn in the attached drawings.
이하에서는 첨부한 도면을 참고하여 본 개시에 따른 실시 예에 대하여 본 개시가 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 용이하게 실시할 수 있도록 상세히 설명한다.Hereinafter, with reference to the attached drawings, embodiments according to the present disclosure will be described in detail so that a person having ordinary knowledge in the technical field to which the present disclosure pertains can easily implement the present disclosure.
도 1은 본 개시의 일 실시 예에 따른 전자 장치(100)의 제어 방법을 나타내는 흐름도이다. 그리고, 도 2 내지 도 9는 본 개시의 일 실시 예에 제어 방법의 단계들을 보다 상세하게 설명하기 위한 도면이다. 이하에서는 도 1 내지 도 9를 함께 참조하여 본 개시의 다양한 실시 예에 대해 설명한다.FIG. 1 is a flowchart illustrating a control method of an electronic device (100) according to an embodiment of the present disclosure. In addition, FIGS. 2 to 9 are drawings for explaining in more detail the steps of the control method according to an embodiment of the present disclosure. Hereinafter, various embodiments of the present disclosure will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 9 together.
본 개시에 따른 전자 장치(100)는 학습 영상의 주파수 성분 분석에 기초하여 신경망 모델을 학습시킬 수 있는 장치를 말한다. 특히, 본 개시에 따른 신경망 모델은 입력된 영상이 기 정의된 복수의 도메인 중 어떠한 도메인에 해당되는지 여부를 식별할 수 있는 분류기(classifier)일 수 있으며, 신경망 모델은 CNN(Convolutional Neural Network)과 같은 신경망을 포함할 수 있다. 다만 본 개시에 따른 신경망 모델의 유형과 신경망 모델에 포함된 신경망의 종류에 특별한 제한이 따르는 것은 아니다.The electronic device (100) according to the present disclosure refers to a device capable of learning a neural network model based on frequency component analysis of a learning image. In particular, the neural network model according to the present disclosure may be a classifier capable of identifying which domain among a plurality of predefined domains an input image corresponds to, and the neural network model may include a neural network such as a CNN (Convolutional Neural Network). However, there is no particular limitation on the type of the neural network model according to the present disclosure and the type of the neural network included in the neural network model.
도 1을 참조하면, 전자 장치(100)는 신경망 모델의 학습을 위한 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분을 분석하여, 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득할 수 있다(S110).Referring to FIG. 1, the electronic device (100) can analyze frequency components for each of a plurality of learning images for learning a neural network model, and obtain a set of average frequency components for the plurality of learning images (S110).
구체적으로, 전자 장치(100)는 복수의 학습 영상 별로 고속 푸리에 변환(fast fourier transform, FFT)을 수행하여 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득할 수 있다. 그리고, 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분의 집합이 획득되면, 전자 장치(100)는 복수의 학습 영상에서 서로 대응되는 위치의 화소끼리 주파수 성분의 크기(magnitude) 값을 모두 더한 후 복수의 학습 영상의 개수로 나누는 정규화 과정을 수행하여, 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득할 수 있다. 본 개시를 설명함에 있어서는 고속 푸리에 변환을 주파수 성분의 방법의 예시로 들어 설명할 것이지만, 그 밖에도 다양한 주파수 성분 분석 방법이 이용될 수 있음은 물론이다.Specifically, the electronic device (100) can perform a fast Fourier transform (FFT) on each of the plurality of learning images to obtain a set of frequency components for each of the plurality of learning images. Then, when the set of frequency components for each of the plurality of learning images is obtained, the electronic device (100) can perform a normalization process of adding all the magnitude values of the frequency components between pixels at corresponding positions in the plurality of learning images and then dividing the sum by the number of the plurality of learning images, thereby obtaining a set of average frequency components for the plurality of learning images. In describing the present disclosure, the fast Fourier transform will be described as an example of a method for analyzing frequency components, but it should be understood that various other frequency component analysis methods may be used.
도 2는 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득하는 과정을 예시적으로 나타내는 도면이다. 도 2의 예시를 참조하면, N 개의 학습 영상 각각에 대해 고속 푸리에 변환(FFT)을 수행하여 N 개의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득할 수 있다. N 개의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분의 집합은 도 2에 도시된 영상들과 같이 표현될 수 있다.Fig. 2 is a diagram exemplarily showing a process of obtaining a set of average frequency components for multiple learning images. Referring to the example of Fig. 2, a fast Fourier transform (FFT) is performed on each of N learning images to obtain a set of frequency components for each of N learning images. The set of frequency components for each of N learning images can be expressed as the images illustrated in Fig. 2.
N 개의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분의 집합이 획득되면, 전자 장치(100)는 서로 대응되는 위치의 화소(pixel)끼리 주파수 성분의 크기(magnitude) 값을 모두 더한 후 N으로 나누는 정규화 과정을 수행하여, N 개의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득할 수 있다. 도 2의 '화소값'은 주파수 성분의 크기를 말한다. 한편, N 개의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합은 도 2에 도시된 가장 우측의 영상과 같이 표현될 수 있다.When a set of frequency components for each of the N learning images is obtained, the electronic device (100) performs a normalization process of adding up all the magnitude values of the frequency components of the pixels at corresponding positions and dividing them by N, thereby obtaining a set of average frequency components for the N learning images. The 'pixel value' of Fig. 2 refers to the magnitude of the frequency component. Meanwhile, the set of average frequency components for each of the N learning images can be expressed as the rightmost image illustrated in Fig. 2.
여기서, 서로 대응되는 위치의 화소라 함은 예를 들어, 도 2의 첫번째 학습 영상에 대한 주파수 성분의 집합을 나타내는 영상의 '화소'와 도 2의 두번째 학습 영상에 대한 주파수 성분의 집합을 나타내는 영상의 '화소'와 같은 화소들을 말한다.Here, the pixels at corresponding positions refer to pixels such as, for example, a 'pixel' of an image representing a set of frequency components for the first learning image in Fig. 2 and a 'pixel' of an image representing a set of frequency components for the second learning image in Fig. 2.
평균 주파수 성분의 집합이 획득되면, 전자 장치(100)는 평균 주파수 성분의 집합에 기초하여, 저주파수 영역이 제외된 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정할 수 있다(S120).Once a set of average frequency components is obtained, the electronic device (100) can determine a target frequency range excluding a low frequency range based on the set of average frequency components (S120).
대부분의 영상은 중심에 많은 저주파 성분을 가지고 있기 때문에 중심부의 주파수 성분이 타겟 주파수 영역에 포함되면 학습 영상 별 고유한 주파수 성분의 분석이 어렵게 되며, 또한 후술하는 바와 같은 그룹핑 기준 설정 단계에서 저주파 성분이 너무 많이 포함되면 대부분의 학습 영상이 낮은 주파수 성분을 갖는 그룹으로 구분될 수 있다는 문제가 있다.Since most images have many low-frequency components in the center, if the frequency components in the center are included in the target frequency range, it becomes difficult to analyze the unique frequency components for each learning image. In addition, if too many low-frequency components are included in the grouping criterion setting step described later, there is a problem that most learning images may be classified into groups with low frequency components.
따라서, 전자 장치(100)는 저주파수 영역이 제외된 영역을 타겟 주파수 영역으로 결정할 수 있다. 일 실시 예에 있어서, 전자 장치(100)는 평균 주파수 성분의 집합 중 최대 값을 식별할 수 있다. 그리고, 전자 장치(100)는 평균 주파수 성분의 집합 중 최대 값의 1/2인 주파수 성분에 대응되는 지점부터 평균 주파수 성분의 집합 중 최대 값의 1/10인 주파수 성분에 대응되는 지점까지의 영역을 식별하는 것에 기초하여, 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정할 수 있다. 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정하는 과정에 대해서는 도 3 및 도 4를 참조하여 보다 구체적으로 설명한다.Accordingly, the electronic device (100) can determine a region excluding the low-frequency region as the target frequency region. In one embodiment, the electronic device (100) can identify a maximum value among a set of average frequency components. Then, the electronic device (100) can determine the target frequency region based on identifying a region from a point corresponding to a frequency component that is 1/2 of the maximum value among the set of average frequency components to a point corresponding to a frequency component that is 1/10 of the maximum value among the set of average frequency components. The process of determining the target frequency region will be described in more detail with reference to FIGS. 3 and 4.
도 3은 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 나타내는 영상을 복수의 주파수 영역으로 구분하는 과정을 나타내는 도면이고, 도 4는 복수의 주파수 영역 중 하나의 주파수 영역의 반직선 상의 주파수 크기를 나타내는 그래프이다.Figure 3 is a diagram showing a process of dividing an image representing a set of average frequency components into multiple frequency domains, and Figure 4 is a graph showing the frequency size on a straight line of one frequency domain among the multiple frequency domains.
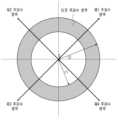
도 3을 참조하면, 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 나타내는 영상은 평균 주파수 성분의 중심을 원점으로 하는 좌표를 기준으로 도 3에 도시된 바와 같은 제1 주파수 영역, 제2 주파수 영역, 제3 주파수 영역 및 제4 주파수 영역으로 구분될 수 있다. 그리고, 제1 주파수 영역, 제2 주파수 영역, 제3 주파수 영역 및 제4 주파수 영역에는 원점에서 시작하여 서로 45도의 각도를 갖는 방향으로 뻗어 나가는 4개의 반직선이 포함될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 3, an image representing a set of average frequency components can be divided into a first frequency domain, a second frequency domain, a third frequency domain, and a fourth frequency domain as illustrated in FIG. 3 based on coordinates that take the center of the average frequency components as the origin. In addition, the first frequency domain, the second frequency domain, the third frequency domain, and the fourth frequency domain can include four ray lines that start from the origin and extend in directions having an angle of 45 degrees to each other.
4개의 반직선 중 제1 주파수 영역의 반직선 상의 주파수 값(크기)을 그래프로 나타내면, 도 4에 도시된 바와 같이, 중심(직류)의 주파수 크기가 가장 크고, 외곽으로 갈수록 주파수 크기가 다소 줄어드는 형태가 나타날 수 있다. 이 경우, 주파수 최대값(max, 일반적으로 중심 값)의 1/2크기가 되는 지점을 r1, 최대값의 1/10크기가 되는 지점을 r2로 결정할 수 있다. 상술한 과정을 제1 주파수 영역, 제2 주파수 영역, 제3 주파수 영역 및 제4 주파수 영역 각각의 반직선 상의 주파수 값들에 대해 반복적으로 수행하면, 4개의 r1과 r2 값이 산출되며, 이 값들의 평균을 최종적인 r1과 r2로 사용할 수 있다. 도 3의 색칠된 영역은 최종적인 r1부터 r2까지의 영역이 타겟 주파수 영역으로 결정되었음을 나타낸다. 타겟 주파수 영역은 r1 및 r2와 같은 반지름을 기준으로 하여 원의 형태로 결정될 수 있으며, 다만 이는 일 실시 예에 불과할 분 원의 형태가 아닌 다른 형태로 결정될 수도 있다.If the frequency values (magnitude) on the straight line of the first frequency domain among the four straight lines are represented as a graph, as illustrated in FIG. 4, the frequency magnitude at the center (DC) may be the largest and the frequency magnitude may decrease somewhat as it goes toward the periphery. In this case, the point that is half the magnitude of the maximum frequency value (max, generally the center value) may be determined as r1, and the point that is 1/10 the magnitude of the maximum value may be determined as r2. If the above process is repeatedly performed for the frequency values on the straight lines of each of the first frequency domain, the second frequency domain, the third frequency domain, and the fourth frequency domain, four r1 and r2 values are calculated, and the average of these values can be used as the final r1 and r2. The colored area in FIG. 3 indicates that the area from r1 to r2 is determined as the target frequency area. The target frequency range can be determined in the shape of a circle based on radii such as r1 and r2, but this is only an example and may be determined in a shape other than a circle.
한편, 이상에서는 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 나타내는 영상을 4 개의 주파수 영역으로 구분하였으나, 본 개시가 이에 국한되는 것은 아니며 주파수 영역의 개수는 실시 예에 따라 달라질 수 있다. 또한, 이상에는 주파수 최대값(일반적으로 중심값)의 1/2크기가 되는 지점을 r1, 최대값의 1/10크기가 되는 지점을 r2로 결정하는 것을 전제로 하였으나, r1 및 r2에 대응되는 크기 또한 실시 예에 따라 달리 결정될 수 있음은 물론이다.Meanwhile, in the above, the image representing the set of average frequency components is divided into four frequency domains, but the present disclosure is not limited thereto, and the number of frequency domains may vary depending on the embodiment. In addition, in the above, it is assumed that the point that is half the size of the maximum frequency value (generally the center value) is determined as r1, and the point that is 1/10 the size of the maximum value is determined as r2, but it goes without saying that the sizes corresponding to r1 and r2 may also be determined differently depending on the embodiment.
타겟 주파수 영역이 결정되면, 전자 장치(100)는 타겟 주파수 영역에 포함된 복수의 영역 별 주파수 성분의 합에 기초하여, 복수의 학습 영상을 그룹핑하기 위한 그룹핑 기준을 결정할 수 있다(S130).Once the target frequency range is determined, the electronic device (100) can determine a grouping criterion for grouping multiple learning images based on the sum of frequency components for each of multiple areas included in the target frequency range (S130).
구체적으로, 전자 장치(100)는 복수의 학습 영상의 중심점과의 거리에 기초하여, 타겟 주파수 영역을 동일한 면적을 갖는 제1 개수의 영역들로 구분함으로써 복수의 영역을 결정할 수 있다. 본 개시에 있어서 복수의 영역이라는 용어는 타겟 주파수 영역을 구분한 결과를 나타낸다. 타겟 주파수 영역이 결정된 경우이므로, 서로 동일한 면적을 갖도록 하는 복수의 영역은 복수의 영역의 개수에 따라 자연히 결정될 수 있다. 한편, 복수의 영역의 넓이가 동일해야 한다는 조건은 일 실시 예에 불과하다.Specifically, the electronic device (100) can determine a plurality of regions by dividing the target frequency region into a first number of regions having the same area based on the distances from the center points of the plurality of learning images. In the present disclosure, the term plurality of regions indicates the result of dividing the target frequency region. Since the target frequency region is determined, a plurality of regions having the same area can be naturally determined according to the number of the plurality of regions. Meanwhile, the condition that the areas of the plurality of regions must be the same is only one embodiment.
전자 장치(100)는 복수의 영역 각각에 대한 주파수 성분의 합을 산출하여 중심점과의 거리가 가까운 영역부터 중심점과의 거리가 먼 영역까지 순차적으로 배열할 수 있다. 그리고, 전자 장치(100)는 배열된 주파수 성분의 합에서 주파수 성분의 합이 급격하게 증가하는 경계를 기준으로 복수의 영역을 구분함으로써, 복수의 학습 영상을 그룹핑하기 위한 그룹핑 기준을 결정할 수 있다. 그룹핑 기준을 결정하는 방법에 대해서는 도 5 및 도 6을 참조하여 보다 구체적으로 설명한다.The electronic device (100) can calculate the sum of frequency components for each of a plurality of regions and sequentially arrange them from regions with a close distance to the center point to regions with a far distance from the center point. Then, the electronic device (100) can determine a grouping criterion for grouping a plurality of learning images by dividing the plurality of regions based on a boundary where the sum of frequency components in the arranged sum of frequency components rapidly increases. A method for determining the grouping criterion will be described in more detail with reference to FIGS. 5 and 6.
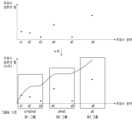
도 5는 타겟 주파수 영역을 구분하는 복수의 영역을 나타내는 도면이고, 도 6은 복수의 영역 별 주파수 성분의 합에 기초하여 그룹핑 기준을 결정하는 과정을 나타내는 도면이다.Figure 5 is a diagram showing multiple areas that distinguish a target frequency range, and Figure 6 is a diagram showing a process of determining a grouping criterion based on the sum of frequency components for each of multiple areas.
도 5를 참조하면, 타겟 주파수 영역은 영역을 동일한 면적을 갖는 복수의 영역으로 구분될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 일반적인 영상의 주파수 특성을 고려할 때 복수의 영역의 개수인 제1 개수는 5개 또는 6개일 수 있으나 이에 국한되는 것은 아니며, 후술하는 바와 같이 학습을 수행한 결과에 따라 재학습을 위해 변경될 수도 있다. 한편, 도 5에서는 복수의 영역 중 영역 a1 및 a2만을 명시적으로 나타내었으나, 이는 도시의 편의를 위한 것일 뿐이다.Referring to Fig. 5, the target frequency domain can be divided into multiple domains having the same area. For example, considering the frequency characteristics of a general image, the first number of multiple domains can be 5 or 6, but is not limited thereto, and can be changed for re-learning according to the results of learning as described below. Meanwhile, in Fig. 5, only domains a1 and a2 among the multiple domains are explicitly shown, but this is only for convenience of illustration.
도 6을 참조하면, 타겟 주파수 영역을 구분하는 복수의 영역은 영역 a1, a2, a3, a4, a5 및 a6를 포함할 수 있다. 그리고, 영역 a1, a2, a3, a4, a5 및 a6의 주파수 성분의 합은 도 6의 상단 그래프와 같이 나타날 수 있다. 도 6의 상단 그래프를 참조하면, 영역 a3 및 a4의 경계와 영역 a5 및 a6의 경계를 기준으로 주파수 성분의 합의 크기가 급격하게 증가함을 알 수 있다. 따라서, 영역 a3 및 a4의 경계와 영역 a5 및 a6의 경계라는 두 개의 경계를 기준으로 그룹핑 기준을 결정할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 6, a plurality of regions that distinguish the target frequency range may include regions a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, and a6. And, the sum of the frequency components of regions a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, and a6 may be represented as in the upper graph of FIG. 6. Referring to the upper graph of FIG. 6, it can be seen that the size of the sum of the frequency components increases rapidly based on the boundaries of regions a3 and a4 and the boundaries of regions a5 and a6. Therefore, the grouping criteria may be determined based on two boundaries, that is, the boundaries of regions a3 and a4 and the boundaries of regions a5 and a6.
보다 명확한 설명을 위해 도 6의 하단 그래프를 참조하면, 영역 a1, a2, a3, a4, a5 및 a6의 주파수 성분의 합을 누적적으로 나타낼 때, 영역 a3 및 a4의 경계와 영역 a5 및 a6의 경계라는 두 개의 경계를 기준으로 그래프의 기울기가 급격하게 증가함을 확인할 수 있다. 따라서, 영역 a3 및 a4의 경계와 영역 a5 및 a6의 경계라는 두 개의 경계를 기준으로 하여, 영역 a1+a2+a3를 제1 그룹, 영역 a4+a5를 제 2그룹, 그리고 영역 a6을 그룹 3으로 하는 그룹핑 기준을 결정할 수 있다.Referring to the lower graph of Fig. 6 for a clearer explanation, when the sum of the frequency components of areas a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, and a6 is cumulatively represented, it can be confirmed that the slope of the graph increases rapidly based on two boundaries, that is, the boundary of areas a3 and a4 and the boundary of areas a5 and a6. Therefore, based on two boundaries, that is, the boundary of areas a3 and a4 and the boundary of areas a5 and a6, it is possible to determine a grouping criterion that makes area a1+a2+a3 the first group, area a4+a5 the second group, and area a6 the third group.
그룹핑 기준이 결정되면, 전자 장치(100)는 그룹핑 기준에 기초하여 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑할 수 있다(S140).Once the grouping criteria are determined, the electronic device (100) can group multiple learning images into multiple groups based on the grouping criteria (S140).
구체적으로, 전자 장치(100)는 복수의 학습 영상 별로 그룹핑 기준에 따른 주파수 성분의 합을 산출하는 것에 기초하여, 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑(또는 구분, 구별, 분할)할 수 있다.Specifically, the electronic device (100) can group (or distinguish, differentiate, divide) multiple learning images into multiple groups based on calculating the sum of frequency components according to grouping criteria for each of multiple learning images.
도 7은 그룹핑 기준에 따라 하나의 학습 영상에 대한 그룹을 할당하는 과정을 예시적으로 설명하기 위한 도면이다. 도 7을 참조하면, 학습 영상에 대해 고속 푸리에 변환을 수행하여, 그 학습 영상에 대한 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득할 수 있다. 개별 학습 영상에 대한 고속 푸리에 변환의 결과는 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득하는 과정에서 산출된 바 있으므로, 앞서 산출되어 메모리에 저장된 결과를 이용할 수도 있다.Fig. 7 is a diagram for exemplarily explaining a process of assigning a group to a learning image according to a grouping criterion. Referring to Fig. 7, a fast Fourier transform is performed on a learning image to obtain a set of frequency components for the learning image. Since the result of the fast Fourier transform for an individual learning image has been calculated in the process of obtaining a set of average frequency components, the result that has been calculated in advance and stored in memory can also be used.
학습 영상에 대한 주파수 성분의 집합이 획득되면, 그룹핑 기준에 따른 복수의 그룹 각각에 대응되는 주파수 성분의 합을 산출할 수 있다. 그 결과를 도 7에 도시된 바와 같이 그래프로 나타내면, 제1 그룹(영역 a1+a2+a3)에 대응되는 주파수 성분의 합이 v1이고, 제2 그룹(영역 a4+a5)에 대응되는 주파수 성분의 합이 v2이며, 제3 그룹(영역 a6)에 대응되는 주파수 성분의 합이 v3라는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 이 경우, 복수의 그룹 중 제1 그룹에 대응되는 주파수 성분의 합이 가장 크기 때문에, 해당 학습 영상은 제1 그룹으로 분류될 수 있다. 이러한 과정을 복수의 학습 영상 모두에 대해서 수행하여, 복수의 학습 영상 각각을 복수의 그룹 중 하나의 그룹으로 할당할 수 있다.When a set of frequency components for a learning image is obtained, the sum of frequency components corresponding to each of a plurality of groups according to the grouping criteria can be calculated. When the result is represented in a graph as illustrated in Fig. 7, it can be confirmed that the sum of frequency components corresponding to the first group (area a1+a2+a3) is v1, the sum of frequency components corresponding to the second group (area a4+a5) is v2, and the sum of frequency components corresponding to the third group (area a6) is v3. In this case, since the sum of frequency components corresponding to the first group among the plurality of groups is the largest, the learning image can be classified into the first group. This process can be performed for all of the plurality of learning images, so that each of the plurality of learning images can be assigned to one of the plurality of groups.
한편, 특정 학습 영상에서 복수의 그룹 별 주파수 성분의 합이 동일한 경우에는 복수의 그룹 중 해당 그룹에 포함된 영역의 개수가 큰 그룹을 그 학습 영상의 그룹으로 할당할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 도 7의 예에서 v1과 v2가 동일한 경우, 해당 그룹에 포함된 영역(a4, a5)의 개수가 2개인 제2 그룹 대신 해당 그룹에 포함된 영역(a1, a2, a3)의 개수가 3개인 제1 그룹을 그 학습 영상의 그룹으로 할당할 수 있다. 그 밖에도 복수의 그룹을 결정하기 위한 기준은 개발자 또는 사용자의 설정에 따라 달리 결정될 수 있다.Meanwhile, if the sum of frequency components of multiple groups is the same in a specific learning image, a group with a larger number of regions included in the group among the multiple groups can be assigned as the group of the learning image. For example, in the example of Fig. 7, if v1 and v2 are the same, the first group with three regions (a1, a2, a3) included in the group can be assigned as the group of the learning image instead of the second group with two regions (a4, a5) included in the group. In addition, the criteria for determining multiple groups can be determined differently depending on the settings of the developer or user.
복수의 학습 영상이 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑되면, 전자 장치(100)는 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 낮은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상부터 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 높은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상 순으로 신경망 모델에 입력하여 신경망 모델을 학습시킬 수 있다(S150).When multiple learning images are grouped into multiple groups, the electronic device (100) can train the neural network model by inputting learning images included in a group with a low frequency component among the multiple groups to the neural network model in that order, starting from learning images included in a group with a high frequency component among the multiple groups (S150).
구체적으로, 상술한 예와 같이 영역 a1+a2+a3를 제1 그룹, 영역 a4+a5를 제 2그룹, 그리고 영역 a6을 그룹 3으로 하는 그룹핑 기준에 따라 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 그룹핑이 수행된 경우, 전자 장치(100)는 주파수 성분이 가장 낮은 제1 그룹의 학습 영상들을 이용하여 신경망 모델을 학습시키고, 다음으로 제2 그룹의 학습 영상들을 이용하여 신경망 모델을 학습시키며, 마지막으로 주파수 성분이 가장 높은 제3 그룹의 학습 영상들을 이용하여 신경망 모델을 학습시킬 수 있다.Specifically, when grouping of multiple learning images is performed according to a grouping criterion in which areas a1+a2+a3 are group 1, areas a4+a5 are
한편, 전자 장치(100)는 신경망 모델의 학습이 진행되는 동안 신경망 모델의 학습에 따른 에러율에 대한 정보를 획득할 수 있다. 학습에 따른 에러율은 신경망 모델의 학습 에러의 정도 및 테스트 에러의 정도 등을 총칭하기 위한 용어로 사용되며, 특히 신경망 모델의 과적합(overfitting)을 나타내는 지표를 의미할 수 있다.Meanwhile, the electronic device (100) can obtain information on the error rate according to the learning of the neural network model while the learning of the neural network model is in progress. The error rate according to the learning is used as a term to collectively refer to the degree of learning error and the degree of test error of the neural network model, and in particular, can mean an indicator indicating overfitting of the neural network model.
전자 장치(100)는 에러율에 대한 정보에 기초하여 학습이 비정상적으로 수행되었는지 여부를 식별할 수 있다. 그리고, 학습이 진행되는 동안 에러율이 기 설정된 임계 값 이상으로 증가하면, 전자 장치(100)는 학습이 비정상적으로 수행된 것으로 식별할 수 있다.The electronic device (100) can identify whether learning has been performed abnormally based on information about the error rate. And, if the error rate increases above a preset threshold value while learning is in progress, the electronic device (100) can identify that learning has been performed abnormally.
학습이 비정상적으로 수행된 것으로 식별되면, 전자 장치(100)는 타겟 주파수 영역을 제1 개수와 상이한 제2 개수의 영역들로 구분함으로써 복수의 영역을 재 결정할 수 있다. 그 후, 전자 장치(100)는 재 결정된 복수의 영역에 기초하여 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 재그룹핑한 후, 신경망 모델을 재학습시킬 수 있다.If learning is identified as being performed abnormally, the electronic device (100) can re-determine the plurality of regions by dividing the target frequency region into a second number of regions different from the first number. Thereafter, the electronic device (100) can re-group the plurality of learning images into a plurality of groups based on the re-determined plurality of regions, and then re-train the neural network model.
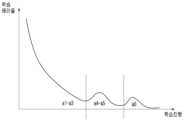
도 8은 신경망 모델의 학습이 정상적으로 수행되는 경우의 학습 에러율을 나타내는 도면이고, 도 9는 신경망 모델의 학습이 비정상적으로 수행되는 경우의 학습 에러율을 나타내는 도면이다.Figure 8 is a diagram showing the learning error rate when learning of a neural network model is performed normally, and Figure 9 is a diagram showing the learning error rate when learning of a neural network model is performed abnormally.
도 8에 도시된 바와 같이, 신경망 모델의 학습이 정상적으로 수행되는 경우에는 복수의 그룹의 경계 상에서 학습 에러율이 어느 정도 증가하다가도 학습이 진행됨에 따라 다시 낮아지는 패턴을 나타낸다. 반면, 도 9에 도시된 바와 같이, 신경망 모델의 학습이 비정상적으로 수행되는 경우에는 특정 구간에서 학습 에러율이 크게 증가하는 패턴을 나타낸다.As shown in Fig. 8, when learning of a neural network model is performed normally, a pattern is shown in which the learning error rate increases to a certain extent on the boundaries of multiple groups and then decreases again as learning progresses. On the other hand, as shown in Fig. 9, when learning of a neural network model is performed abnormally, a pattern is shown in which the learning error rate significantly increases in a specific section.
따라서, 전자 장치(100)는 신경망 모델의 학습이 진행되는 동안 에러율이 기 설정된 임계 값 이상으로 증가하였는지 여부 및/또는 에러율의 증가가 기 설정된 임계 구간 이상 동안 지속되었는지 여부를 식별함으로써, 신경망 모델의 학습이 비정상적으로 수행되었는지 여부를 식별할 수 있다.Accordingly, the electronic device (100) can identify whether the learning of the neural network model is performed abnormally by identifying whether the error rate increases beyond a preset threshold value while the learning of the neural network model is in progress and/or whether the increase in the error rate continues for a preset threshold period or longer.
특히, 신경망 모델의 비정상적인 학습은 복수의 그룹 별 학습 영상의 난이도의 차이가 크거나, 복수의 그룹 내 학습 영상의 개수가 적절하지 않기 때문에 발생할 수 있다. 따라서, 학습이 비정상적으로 수행된 것으로 식별되면, 전자 장치(100)는 타겟 주파수 영역을 제1 개수와 상이한 제2 개수의 영역들로 구분함으로써 복수의 영역을 재 결정할 수 있으며, 이에 따라 복수의 그룹의 개수가 변경될 수 있고, 그 결과 복수의 그룹에 포함되는 학습 영상의 종류와 개수 또한 변경될 수 있다.In particular, abnormal learning of the neural network model may occur because the difficulty difference of learning images for each of the multiple groups is large, or the number of learning images within the multiple groups is not appropriate. Therefore, if learning is identified as being performed abnormally, the electronic device (100) may re-determine the multiple regions by dividing the target frequency region into a second number of regions different from the first number, and accordingly, the number of the multiple groups may be changed, and as a result, the types and numbers of learning images included in the multiple groups may also be changed.
전자 장치(100)는 상술한 바와 같은 재그룹핑 과정을 수행한 후, 다시 주파수 성분이 낮은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상부터 주파수 성분이 높은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상 순으로 신경망 모델에 입력하여 신경망 모델을 재학습시킬 수 있으며, 재그룹핑과 재학습 과정은 신경망 모델이 정상적으로 학습될 때까지 계속될 수 있다.After performing the regrouping process as described above, the electronic device (100) can retrain the neural network model by inputting the training images included in the group with low frequency components in order from the training images included in the group with high frequency components, and the regrouping and retraining process can continue until the neural network model is trained normally.
이상에서 상술한 실시 예에 따르면, 본 개시에 따른 전자 장치(100)는 복수의 학습 영상을 주파수 성분 분석에 따라 그룹핑함으로써 신경망 모델을 효율적이고 안정적으로 학습시킬 수 있다. 특히, 전자 장치(100)는 신경망 모델의 학습이 진행되는 동안 비정상적인 학습이 이루어지고 있는지 여부를 모니터링하여 학습 영상을 재그룹핑하고 다시 신경망 모델을 학습시킴으로써, 학습 결과의 수렴이 잘 이루어지도록 하며, 수렴 속도 또한 더욱 빠르게 할 수 있다According to the above-described embodiment, the electronic device (100) according to the present disclosure can efficiently and stably train a neural network model by grouping a plurality of learning images according to frequency component analysis. In particular, the electronic device (100) monitors whether abnormal learning is occurring while learning a neural network model is in progress, regroups the learning images, and trains the neural network model again, thereby ensuring that the learning results converge well and also making the convergence speed faster.
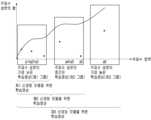
도 10은 본 개시에 따른 복수의 그룹 별 학습 영상을 각각 상이한 신경망 모델의 학습에 이용하는 실시 예에 대해 설명하기 위한 도면이다.FIG. 10 is a diagram for explaining an embodiment in which multiple group-specific learning images according to the present disclosure are used for learning different neural network models.
이상에서는 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑한 후 주파수 성분이 낮은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상부터 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 높은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상 순으로 신경망 모델의 학습에 이용하는 실시 예를 설명하였다.In the above, an embodiment is described in which multiple learning images are grouped into multiple groups and then used for learning a neural network model in order from learning images included in a group with low frequency components to learning images included in a group with high frequency components among the multiple groups.
그런데, 본 개시의 다른 실시 예에 따르면, 전자 장치(100)는 복수의 그룹 별 학습 영상을 각각 상이한 신경망 모델의 학습에 이용할 수 있다. 여기서, 상이한 신경망 모델은 입력된 영상이 기 정의된 복수의 도메인 중 어떠한 도메인에 해당되는지 여부를 식별할 수 있는 복수의 분류기일 수 있다.However, according to another embodiment of the present disclosure, the electronic device (100) can use multiple group-specific learning images to learn different neural network models, respectively. Here, the different neural network models can be multiple classifiers that can identify which domain among multiple predefined domains an input image corresponds to.
구체적으로, 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑하기까지의 과정은 도 1 내지 도 9를 참조하여 상술한 실시 예와 마찬가지의 과정을 통해 수행될 수 있다. 즉, 도 10에 도시된 바와 같이, 본 개시에 따른 복수의 학습 영상은 상술한 예와 같이 영역 a1+a2+a3를 제1 그룹, 영역 a4+a5를 제 2그룹, 그리고 영역 a6을 그룹 3으로 하는 그룹핑 기준에 따라 그룹핑될 수 있다.Specifically, the process of grouping multiple learning images into multiple groups can be performed through the same process as the embodiment described above with reference to FIGS. 1 to 9. That is, as illustrated in FIG. 10, multiple learning images according to the present disclosure can be grouped according to a grouping criterion of making area a1+a2+a3 a first group, area a4+a5 a second group, and area a6 a
이 경우, 도 10의 실시 예에 따르면, 전자 장치(100)는 주파수 성분이 가장 낮은 제1 그룹의 학습 영상들을 이용하여 제1 신경망 모델을 학습시키고, 다음으로 제2 그룹의 학습 영상들을 이용하여 제2 신경망 모델을 학습시키며, 마지막으로 주파수 성분이 가장 높은 제3 그룹의 학습 영상들을 이용하여 제3 신경망 모델을 학습시킬 수 있다.In this case, according to the embodiment of FIG. 10, the electronic device (100) can train a first neural network model using the training images of the first group having the lowest frequency components, then train a second neural network model using the training images of the second group, and finally train a third neural network model using the training images of the third group having the highest frequency components.
제1 그룹의 학습 영상들은 주파수 성분이 가장 낮은 학습 영상들로서, 이를 이용한 제1 신경망 모델은 다소 저조한 성능을 갖지만 복잡도가 낮고 속도가 빠를 수 있다. 제2 그룹의 학습 영상들은 제1 그룹의 학습 영상들에 비해 주파수 성분이 다소 높은 학습 영상들로서, 이를 이용한 제2 신경망 모델의 경우 제1 신경망 모델에 비해 복잡도가 다소 증가하고 속도는 느려지지만, 성능은 더 우수할 수 있다. 이처럼 전자 장치(100)의 사용자는 다양한 신경망 모델을 생성하여 적절한 응용 분야에 활용할 수 있다.The learning images of the first group are learning images with the lowest frequency components, and the first neural network model using these images may have somewhat poor performance, but may have low complexity and be fast. The learning images of the second group are learning images with somewhat higher frequency components than the learning images of the first group, and the second neural network model using these images may have somewhat increased complexity and be slow compared to the first neural network model, but may have better performance. In this way, the user of the electronic device (100) can create various neural network models and utilize them in appropriate application fields.
결론적으로, 도 10을 참조하여 상술한 실시 예에 따르면, 전자 장치(100)는 학습 영상을 몇 개의 그룹으로 그룹핑함으로써, 각 그룹 별 학습 영상을 다양한 신경망 모델의 학습에 적절하게 이용할 수 있게 된다.In conclusion, according to the embodiment described above with reference to FIG. 10, the electronic device (100) groups learning images into several groups, thereby enabling the learning images of each group to be appropriately utilized for learning various neural network models.
한편, 도 1 내지 도 10을 참조하여 상술한 전자 장치(100)의 제어 방법은 프로그램으로 구현되어 전자 장치(100)에 제공될 수 있다. 특히, 전자 장치(100)의 제어 방법을 포함하는 프로그램은 비일시적 판독 가능 매체(non-transitory computer readable medium)에 저장되어 제공될 수 있다.Meanwhile, the control method of the electronic device (100) described above with reference to FIGS. 1 to 10 may be implemented as a program and provided to the electronic device (100). In particular, the program including the control method of the electronic device (100) may be stored and provided in a non-transitory computer readable medium.
구체적으로, 전자 장치(100)의 제어 방법을 실행하는 프로그램을 포함하는 비일시적 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록매체에 있어서, 전자 장치(100)의 제어 방법은 신경망 모델의 학습을 위한 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분을 분석하여, 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득하는 단계, 평균 주파수 성분의 집합에 기초하여, 저주파수 영역이 제외된 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정하는 단계, 타겟 주파수 영역에 포함된 복수의 영역 별 주파수 성분의 합에 기초하여, 복수의 학습 영상을 그룹핑하기 위한 그룹핑 기준을 결정하는 단계, 그룹핑 기준에 기초하여 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑하는 단계 및 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 낮은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상부터 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 높은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상 순으로 신경망 모델에 입력하여 신경망 모델을 학습시키는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.Specifically, in a non-transitory computer-readable recording medium including a program for executing a method for controlling an electronic device (100), the method for controlling an electronic device (100) may include a step of analyzing frequency components for each of a plurality of learning images for learning a neural network model, thereby obtaining a set of average frequency components for the plurality of learning images; a step of determining a target frequency range from which a low frequency range is excluded based on the set of average frequency components; a step of determining a grouping criterion for grouping the plurality of learning images based on a sum of frequency components for each of a plurality of regions included in the target frequency range; a step of grouping the plurality of learning images into a plurality of groups based on the grouping criterion; and a step of inputting learning images included in a group having a low frequency component among the plurality of groups into a neural network model in that order from learning images included in a group having a high frequency component among the plurality of groups, thereby training the neural network model.
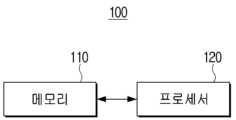
도 11은 본 개시의 일 실시 예에 따른 전자 장치(100)의 구성을 간략하게 나타내는 블록도이다.FIG. 11 is a block diagram briefly illustrating the configuration of an electronic device (100) according to one embodiment of the present disclosure.
도 11에 도시된 바와 같이, 본 개시의 일 실시 예에 따른 전자 장치(100)는 메모리(110) 및 프로세서(120)를 포함한다. 그러나, 도 11에 도시된 바와 같은 구성들은 예시적인 것에 불과할 뿐이며, 본 개시를 실시함에 있어 도 11에 도시된 바와 같은 구성에 더하여 새로운 구성이 추가되거나 일부 구성이 생략될 수 있음은 물론이다.As illustrated in FIG. 11, an electronic device (100) according to an embodiment of the present disclosure includes a memory (110) and a processor (120). However, the configurations illustrated in FIG. 11 are merely exemplary, and it is to be understood that new configurations may be added or some configurations may be omitted in addition to the configuration illustrated in FIG. 11 when implementing the present disclosure.
메모리(110)에는 전자 장치(100)에 관한 적어도 하나의 인스트럭션(instruction)이 저장될 수 있다. 그리고, 메모리(110)에는 전자 장치(100)를 구동시키기 위한 O/S(Operating System)가 저장될 수 있다. 또한, 메모리(110)에는 본 개시의 다양한 실시 예들에 따라 전자 장치(100)가 동작하기 위한 각종 소프트웨어 프로그램이나 애플리케이션이 저장될 수도 있다. 그리고, 메모리(110)는 플래시 메모리(Flash Memory) 등과 같은 반도체 메모리나 하드디스크(Hard Disk) 등과 같은 자기 저장 매체 등을 포함할 수 있다.At least one instruction regarding the electronic device (100) may be stored in the memory (110). In addition, an O/S (Operating System) for driving the electronic device (100) may be stored in the memory (110). In addition, various software programs or applications for operating the electronic device (100) according to various embodiments of the present disclosure may be stored in the memory (110). In addition, the memory (110) may include a semiconductor memory such as a flash memory or a magnetic storage medium such as a hard disk.
구체적으로, 메모리(110)에는 본 개시의 다양한 실시 예에 따라 전자 장치(100)가 동작하기 위한 각종 소프트웨어 모듈이 저장될 수 있으며, 프로세서(120)는 메모리(110)에 저장된 각종 소프트웨어 모듈을 실행하여 전자 장치(100)의 동작을 제어할 수 있다. 즉, 메모리(110)는 프로세서(120)에 의해 액세스되며, 프로세서(120)에 의한 데이터의 독취/기록/수정/삭제/갱신 등이 수행될 수 있다.Specifically, various software modules for operating the electronic device (100) according to various embodiments of the present disclosure may be stored in the memory (110), and the processor (120) may control the operation of the electronic device (100) by executing various software modules stored in the memory (110). That is, the memory (110) is accessed by the processor (120), and data reading/recording/modifying/deleting/updating, etc. may be performed by the processor (120).
한편, 본 개시에서 메모리(110)라는 용어는 메모리(110), 프로세서(120) 내 롬(미도시), 램(미도시) 또는 전자 장치(100)에 장착되는 메모리 카드(미도시)(예를 들어, micro SD 카드, 메모리 스틱)를 포함하는 의미로 사용될 수 있다.Meanwhile, in the present disclosure, the term memory (110) may be used to mean a memory (110), a ROM (not shown) in a processor (120), a RAM (not shown), or a memory card (not shown) (e.g., a micro SD card, a memory stick) mounted in an electronic device (100).
특히, 본 개시에 따른 다양한 실시 예에 있어서, 메모리(110)에는 신경망 모델의 학습을 위한 복수의 학습 영상, 신경망 모델의 가중치, 레이어 및 파라미터에 대한 데이터, 주파수 성분 분석을 위한 알고리즘에 대한 정보, 본 개시에 따른 타겟 주파수 영역의 결정을 위한 알고리즘에 대한 정보, 그룹핑 기준의 결정 기준에 대한 정보 등과 같은 다양한 데이터/정보가 저장될 수 있다.In particular, in various embodiments according to the present disclosure, various data/information such as a plurality of learning images for learning a neural network model, data on weights, layers and parameters of the neural network model, information on an algorithm for frequency component analysis, information on an algorithm for determining a target frequency area according to the present disclosure, information on a determination criterion of a grouping criterion, etc. may be stored in the memory (110).
그 밖에도 본 개시의 목적을 달성하기 위한 범위 내에서 필요한 다양한 정보가 메모리(110)에 저장될 수 있으며, 메모리(110)에 저장된 정보는 외부 장치로부터 수신되거나 사용자에 의해 입력됨에 따라 갱신될 수도 있다.In addition, various information necessary within the scope of achieving the purpose of the present disclosure may be stored in the memory (110), and the information stored in the memory (110) may be updated as received from an external device or input by a user.
프로세서(120)는 전자 장치(100)의 전반적인 동작을 제어한다. 구체적으로, 프로세서(120)는 메모리(110)를 포함하는 전자 장치(100)의 구성과 연결되며, 상술한 바와 같은 메모리(110)에 저장된 적어도 하나의 인스트럭션을 실행함으로써, 전자 장치(100)의 동작을 전반적으로 제어할 수 있다.The processor (120) controls the overall operation of the electronic device (100). Specifically, the processor (120) is connected to the configuration of the electronic device (100) including the memory (110), and can control the overall operation of the electronic device (100) by executing at least one instruction stored in the memory (110) as described above.
프로세서(120)는 다양한 방식으로 구현될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 프로세서(120)는 주문형 집적 회로(Application Specific Integrated Circuit, ASIC), 임베디드 프로세서, 마이크로 프로세서, 하드웨어 컨트롤 로직, 하드웨어 유한 상태 기계(hardware Finite State Machine, FSM), 디지털 신호 프로세서(Digital Signal Processor, DSP) 중 적어도 하나로 구현될 수 있다. 한편, 본 개시에서 프로세서(120)라는 용어는 CPU(Central Processing Unit), GPU(Graphic Processing Unit) 및 MPU(Main Processing Unit)등을 포함하는 의미로 사용될 수 있다.The processor (120) may be implemented in various ways. For example, the processor (120) may be implemented as at least one of an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC), an embedded processor, a microprocessor, hardware control logic, a hardware finite state machine (FSM), and a digital signal processor (DSP). Meanwhile, the term processor (120) in the present disclosure may be used to mean a central processing unit (CPU), a graphic processing unit (GPU), and a main processing unit (MPU).
특히, 본 개시에 따른 다양한 실시 예에 있어서, 프로세서(120)는 학습 영상의 주파수 성분 분석에 기초하여 신경망 모델을 학습시킬 수 있다.In particular, in various embodiments according to the present disclosure, the processor (120) can train a neural network model based on frequency component analysis of a learning image.
일 실시 예에 따르면, 프로세서(120)는 신경망 모델의 학습을 위한 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분을 분석하여, 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득할 수 있다. 구체적으로, 프로세서(120)는 고속 푸리에 변환(fast fourier transform, FFT)을 이용하여 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분을 분석하고, 그 결과에 기초하여 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득할 수 있다.According to one embodiment, the processor (120) may analyze frequency components for each of a plurality of learning images for learning a neural network model, and obtain a set of average frequency components for the plurality of learning images. Specifically, the processor (120) may analyze frequency components for each of a plurality of learning images using a fast Fourier transform (FFT), and obtain a set of average frequency components for the plurality of learning images based on the results.
평균 주파수 성분의 집합이 획득되면, 프로세서(120)는 평균 주파수 성분의 집합에 기초하여, 저주파수 영역이 제외된 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정할 수 있다. 구체적으로, 프로세서(120)는 평균 주파수 성분의 집합 중 최대 값을 식별하고, 평균 주파수 성분의 집합 중 최대 값의 1/2인 주파수 성분에 대응되는 지점부터 평균 주파수 성분의 집합 중 최대 값의 1/10인 주파수 성분에 대응되는 지점까지의 영역을 식별하는 것에 기초하여, 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정할 수 있다.Once the set of average frequency components is obtained, the processor (120) can determine a target frequency range excluding a low-frequency range based on the set of average frequency components. Specifically, the processor (120) can determine the target frequency range based on identifying a maximum value among the set of average frequency components and identifying a range from a point corresponding to a frequency component that is half the maximum value among the set of average frequency components to a point corresponding to a frequency component that is 1/10 the maximum value among the set of average frequency components.
타겟 주파수 영역이 결정되면, 프로세서(120)는 타겟 주파수 영역에 포함된 복수의 영역 별 주파수 성분의 합에 기초하여, 복수의 학습 영상을 그룹핑하기 위한 그룹핑 기준을 결정할 수 있다.Once the target frequency range is determined, the processor (120) can determine a grouping criterion for grouping multiple learning images based on the sum of frequency components for each of multiple areas included in the target frequency range.
구체적으로, 프로세서(120)는 복수의 학습 영상의 중심점과의 거리에 기초하여, 타겟 주파수 영역을 동일한 면적을 갖는 제1 개수의 영역들로 구분함으로써 복수의 영역을 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(120)는 복수의 영역 각각에 대한 주파수 성분의 합을 산출하여 중심점과의 거리가 가까운 영역부터 중심점과의 거리가 먼 영역까지 순차적으로 배열할 수 있다. 그리고, 프로세서(120)는 배열된 주파수 성분의 합에서 주파수 성분의 합이 급격하게 증가하는 경계를 기준으로 복수의 영역을 구분함으로써, 복수의 학습 영상을 그룹핑하기 위한 그룹핑 기준을 결정할 수 있다.Specifically, the processor (120) can determine the plurality of regions by dividing the target frequency region into a first number of regions having the same area based on the distances from the center points of the plurality of learning images. The processor (120) can calculate the sum of the frequency components for each of the plurality of regions and sequentially arrange them from a region having a close distance from the center point to a region having a far distance from the center point. In addition, the processor (120) can determine a grouping criterion for grouping the plurality of learning images by dividing the plurality of regions based on a boundary where the sum of the frequency components in the arranged sum of the frequency components rapidly increases.
그룹핑 기준이 결정되면, 프로세서(120)는 그룹핑 기준에 기초하여 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑할 수 있다. 구체적으로, 복수의 학습 영상 별로 그룹핑 기준에 따른 주파수 성분의 합을 산출하는 것에 기초하여, 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑할 수 있다.Once the grouping criteria are determined, the processor (120) can group multiple learning images into multiple groups based on the grouping criteria. Specifically, multiple learning images can be grouped into multiple groups based on calculating the sum of frequency components according to the grouping criteria for each of the multiple learning images.
복수의 학습 영상이 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑되면, 프로세서(120)는 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 낮은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상부터 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 높은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상 순으로 신경망 모델에 입력하여 신경망 모델을 학습시킬 수 있다.When multiple learning images are grouped into multiple groups, the processor (120) can input learning images included in a group with low frequency components among the multiple groups to the neural network model in that order, starting from learning images included in a group with high frequency components among the multiple groups, to train the neural network model.
한편, 프로세서(120)는 신경망 모델의 학습이 진행되는 동안 신경망 모델의 학습에 따른 에러율에 대한 정보를 획득하고, 에러율에 대한 정보에 기초하여 학습이 비정상적으로 수행되었는지 여부를 식별할 수 있다. 학습이 비정상적으로 수행된 것으로 식별되면, 프로세서(120)는 타겟 주파수 영역을 제1 개수와 상이한 제2 개수의 영역들로 구분함으로써 복수의 영역을 재 결정하고, 재 결정된 복수의 영역에 기초하여 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 재그룹핑한 후, 신경망 모델을 재학습시킬 수 있다. 특히, 프로세서(120)는 학습이 진행되는 동안 에러율이 기 설정된 임계 값 이상으로 증가하면, 학습이 비정상적으로 수행된 것으로 식별할 수 있다.Meanwhile, the processor (120) can obtain information on an error rate according to learning of the neural network model while learning of the neural network model is in progress, and can identify whether learning is performed abnormally based on the information on the error rate. If learning is identified as being performed abnormally, the processor (120) can re-determine a plurality of regions by dividing the target frequency region into a second number of regions different from the first number, and can re-group a plurality of learning images into a plurality of groups based on the re-determined plurality of regions, and then re-learn the neural network model. In particular, if the error rate increases above a preset threshold value while learning is in progress, the processor (120) can identify that learning is performed abnormally.
한편, 프로세서(120)는 복수의 그룹 별 학습 영상을 각각 상이한 신경망 모델의 학습에 이용할 수도 있다.Meanwhile, the processor (120) may also use multiple group-specific learning images to learn different neural network models.
프로세서(120)의 제어를 바탕으로 한 본 개시에 따른 다양한 실시 예에 대해서는 도 1 내지 도 10을 참조하여 상술하였으므로 상세한 내용에 대한 중복 설명은 생략한다.Various embodiments according to the present disclosure based on the control of the processor (120) have been described above with reference to FIGS. 1 to 10, so a redundant description of the details will be omitted.
한편, 이상에서 상술한 바와 같은 신경망 모델 및 분류기 등에 관련된 기능은 메모리(110) 및 프로세서(120)를 통해 수행될 수 있다. 프로세서(120)는 하나 또는 복수의 프로세서(120)로 구성될 수 있다. 이때, 하나 또는 복수의 프로세서(120)는 CPU, AP 등과 같은 범용 프로세서(120), GPU. VPU 등과 같은 그래픽 전용 프로세서(120) 또는 NPU와 같은 인공 지능 전용 프로세서(120)일 수 있다.Meanwhile, functions related to the neural network model and classifier, etc., as described above, may be performed through the memory (110) and the processor (120). The processor (120) may be composed of one or more processors (120). In this case, the one or more processors (120) may be a general-purpose processor (120) such as a CPU, an AP, etc., a graphics-only processor (120) such as a GPU, a VPU, etc., or an artificial intelligence-only processor (120) such as an NPU.
하나 또는 복수의 프로세서(120)는, 비휘발성 메모리(110) 및 휘발성 메모리(110)에 저장된 기 정의된 동작 규칙 또는 인공 지능 모델에 따라, 입력 데이터를 처리하도록 제어한다. 기 정의된 동작 규칙 또는 인공 지능 모델은 학습을 통해 만들어진 것을 특징으로 한다.One or more processors (120) are controlled to process input data according to predefined operation rules or artificial intelligence models stored in nonvolatile memory (110) and volatile memory (110). The predefined operation rules or artificial intelligence models are characterized by being created through learning.
여기서, 학습을 통해 만들어진다는 것은, 다수의 학습 데이터들에 학습 알고리즘을 적용함으로써, 원하는 특성의 기 정의된 동작 규칙 또는 인공 지능 모델이 만들어짐을 의미한다. 이러한 학습은 본 개시에 따른 인공 지능이 수행되는 기기 자체에서 이루어질 수도 있고, 별도의 서버/시스템을 통해 이루어 질 수도 있다.Here, being created through learning means that a predefined operation rule or artificial intelligence model with desired characteristics is created by applying a learning algorithm to a large number of learning data. Such learning may be performed in the device itself on which the artificial intelligence according to the present disclosure is performed, or may be performed through a separate server/system.
인공 지능 모델은, 복수의 신경망 레이어들로 구성될 수 있다. 각 레이어는 복수의 가중치(weight values)을 갖고 있으며, 이전(previous) 레이어의 연산 결과와 복수의 가중치의 연산을 통해 레이어의 연산을 수행한다. 신경망의 예로는, CNN (Convolutional Neural Network), DNN (Deep Neural Network), RNN (Recurrent Neural Network), RBM (Restricted Boltzmann Machine), DBN (Deep Belief Network), BRDNN(Bidirectional Recurrent Deep Neural Network), GAN(Generative Adversarial Networks) 및 심층 Q-네트워크 (Deep Q-Networks)이 있으며, 본 개시에서의 신경망은 명시한 경우를 제외하고 전술한 예에 한정되지 않는다.An artificial intelligence model may be composed of multiple neural network layers. Each layer has multiple weight values, and performs layer operations through the operation results of the previous layer and the operations of the multiple weights. Examples of neural networks include CNN (Convolutional Neural Network), DNN (Deep Neural Network), RNN (Recurrent Neural Network), RBM (Restricted Boltzmann Machine), DBN (Deep Belief Network), BRDNN (Bidirectional Recurrent Deep Neural Network), GAN (Generative Adversarial Network), and Deep Q-Networks, and the neural networks in the present disclosure are not limited to the above-described examples unless otherwise specified.
학습 알고리즘은, 다수의 학습 데이터들을 이용하여 소정의 대상 기기(예컨대, 로봇)을 훈련시켜 소정의 대상 기기 스스로 결정을 내리거나 예측을 할 수 있도록 하는 방법이다. 학습 알고리즘의 예로는, 지도형 학습(supervised learning), 비지도형 학습(unsupervised learning), 준지도형 학습(semi-supervised learning) 또는 강화 학습(reinforcement learning)이 있으며, 본 개시에서의 학습 알고리즘은 명시한 경우를 제외하고 전술한 예에 한정되지 않는다.A learning algorithm is a method of training a given target device (e.g., a robot) using a plurality of learning data so that the given target device can make decisions or predictions on its own. Examples of learning algorithms include supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning, or reinforcement learning, and the learning algorithm in the present disclosure is not limited to the above-described examples unless otherwise specified.
기기로 읽을 수 있는 저장매체는, 비일시적(non-transitory) 저장매체의 형태로 제공될 수 있다. 여기서, '비일시적 저장매체'는 실재(tangible)하는 장치이고, 신호(signal)(예: 전자기파)를 포함하지 않는다는 것을 의미할 뿐이며, 이 용어는 데이터가 저장매체에 반영구적으로 저장되는 경우와 임시적으로 저장되는 경우를 구분하지 않는다. 예로, '비일시적 저장매체'는 데이터가 임시적으로 저장되는 버퍼를 포함할 수 있다.The storage medium that can be read by the device may be provided in the form of a non-transitory storage medium. Here, the term 'non-transitory storage medium' means only that it is a tangible device and does not contain signals (e.g., electromagnetic waves), and this term does not distinguish between cases where data is stored semi-permanently in the storage medium and cases where data is stored temporarily. For example, a 'non-transitory storage medium' may include a buffer in which data is temporarily stored.
일 실시 예에 따르면, 본 문서에 개시된 다양한 실시 예들에 따른 방법은 컴퓨터 프로그램 제품(computer program product)에 포함되어 제공될 수 있다. 컴퓨터 프로그램 제품은 상품으로서 판매자 및 구매자 간에 거래될 수 있다. 컴퓨터 프로그램 제품은 기기로 읽을 수 있는 저장 매체(예: compact disc read only memory (CD-ROM))의 형태로 배포되거나, 또는 어플리케이션 스토어(예: 플레이 스토어TM)를 통해 또는 두개의 사용자 장치들(예: 스마트폰들) 간에 직접, 온라인으로 배포(예: 다운로드 또는 업로드)될 수 있다. 온라인 배포의 경우에, 컴퓨터 프로그램 제품(예: 다운로더블 앱(downloadable app))의 적어도 일부는 제조사의 서버, 어플리케이션 스토어의 서버, 또는 중계 서버의 메모리(110)와 같은 기기로 읽을 수 있는 저장 매체에 적어도 일시 저장되거나, 임시적으로 생성될 수 있다.According to one embodiment, the method according to the various embodiments disclosed in the present document may be provided as included in a computer program product. The computer program product may be traded between a seller and a buyer as a commodity. The computer program product may be distributed in the form of a machine-readable storage medium (e.g., a compact disc read only memory (CD-ROM)), or may be distributed online (e.g., downloaded or uploaded) via an application store (e.g., Play StoreTM ) or directly between two user devices (e.g., smartphones). In the case of online distribution, at least a part of the computer program product (e.g., a downloadable app) may be at least temporarily stored or temporarily generated in a machine-readable storage medium, such as a server of a manufacturer, a server of an application store, or a memory (110) of an intermediary server.
이상에서 상술한 바와 같은 본 개시의 다양한 실시 예들에 따른 구성 요소(예: 모듈 또는 프로그램) 각각은 단수 또는 복수의 개체로 구성될 수 있으며, 전술한 해당 서브 구성 요소들 중 일부 서브 구성 요소가 생략되거나, 또는 다른 서브 구성 요소가 다양한 실시 예에 더 포함될 수 있다. 대체적으로 또는 추가적으로, 일부 구성 요소들(예: 모듈 또는 프로그램)은 하나의 개체로 통합되어, 통합되기 이전의 각각의 해당 구성 요소에 의해 수행되는 기능을 동일 또는 유사하게 수행할 수 있다.Each of the components (e.g., modules or programs) according to the various embodiments of the present disclosure as described above may be composed of a single or multiple entities, and some of the corresponding sub-components described above may be omitted, or other sub-components may be further included in the various embodiments. Alternatively or additionally, some of the components (e.g., modules or programs) may be integrated into one entity to perform the same or similar functions performed by each corresponding component prior to integration.
다양한 실시 예들에 따른, 모듈, 프로그램 또는 다른 구성 요소에 의해 수행되는 동작들은 순차적, 병렬적, 반복적 또는 휴리스틱하게 실행되거나, 적어도 일부 동작이 다른 순서로 실행되거나, 생략되거나, 또는 다른 동작이 추가될 수 있다.According to various embodiments, operations performed by a module, program or other component may be executed sequentially, in parallel, iteratively or heuristically, or at least some operations may be executed in a different order, omitted, or other operations may be added.
한편, 본 개시에서 사용된 용어 "부" 또는 "모듈"은 하드웨어, 소프트웨어 또는 펌웨어로 구성된 유닛을 포함하며, 예를 들면, 로직, 논리 블록, 부품, 또는 회로 등의 용어와 상호 호환적으로 사용될 수 있다. "부" 또는 "모듈"은, 일체로 구성된 부품 또는 하나 또는 그 이상의 기능을 수행하는 최소 단위 또는 그 일부가 될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 모듈은 ASIC(application-specific integrated circuit)으로 구성될 수 있다.Meanwhile, the term "part" or "module" used in the present disclosure includes a unit composed of hardware, software or firmware, and may be used interchangeably with terms such as logic, logic block, component, or circuit. The "part" or "module" may be an integrally composed component or a minimum unit performing one or more functions or a part thereof. For example, the module may be composed of an ASIC (application-specific integrated circuit).
본 개시의 다양한 실시 예들은 기기(machine)(예: 컴퓨터)로 읽을 수 있는 저장 매체(machine-readable storage media에 저장된 명령어를 포함하는 소프트웨어로 구현될 수 있다. 기기는 저장 매체로부터 저장된 명령어를 호출하고, 호출된 명령어에 따라 동작이 가능한 장치로서, 개시된 실시 예들에 따른 전자 장치(예: 전자 장치(100))를 포함할 수 있다.Various embodiments of the present disclosure may be implemented as software including instructions stored in a machine-readable storage media that can be read by a machine (e.g., a computer). The device is a device that can call instructions stored from the storage media and operate according to the called instructions, and may include an electronic device (e.g., an electronic device (100)) according to the disclosed embodiments.
상기 명령이 프로세서에 의해 실행될 경우, 프로세서가 직접 또는 상기 프로세서의 제어 하에 다른 구성요소들을 이용하여 상기 명령에 해당하는 기능을 수행할 수 있다. 명령은 컴파일러 또는 인터프리터에 의해 생성 또는 실행되는 코드를 포함할 수 있다.When the above instruction is executed by the processor, the processor may perform a function corresponding to the instruction directly or by using other components under the control of the processor. The instruction may include code generated or executed by a compiler or an interpreter.
이상에서는 본 개시의 바람직한 실시 예에 대하여 도시하고 설명하였지만, 본 개시는 상술한 특정의 실시 예에 한정되지 아니하며, 청구범위에서 청구하는 본 개시의 요지를 벗어남이 없이 당해 개시가 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 다양한 변형실시가 가능한 것은 물론이고, 이러한 변형실시들은 본 개시의 기술적 사상이나 전망으로부터 개별적으로 이해되어서는 안 될 것이다.Although the preferred embodiments of the present disclosure have been illustrated and described above, the present disclosure is not limited to the specific embodiments described above, and various modifications may be made by a person skilled in the art to which the present disclosure pertains without departing from the gist of the present disclosure as claimed in the claims, and such modifications should not be individually understood from the technical idea or prospect of the present disclosure.
100:전자 장치110: 메모리
120: 프로세서100:Electronic devices 110:Memory
120: Processor
Claims (10)
Translated fromKorean메모리; 및
신경망 모델의 학습을 위한 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분을 분석하여, 상기 복수의 학습 영상에서 서로 대응되는 위치의 화소별로 주파수 성분에 대한 크기 값의 합을 상기 복수의 학습 영상의 개수로 나눔으로써 상기 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득하고,
상기 평균 주파수 성분의 집합에 기초하여, 저주파수 영역이 제외된 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정하며,
상기 타겟 주파수 영역에 포함된 복수의 영역 별 평균 주파수 성분의 합에 기초하여, 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 그룹핑하기 위한 그룹핑 기준을 결정하고,
상기 그룹핑 기준에 기초하여 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑하며,
상기 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 낮은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상부터 상기 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 높은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상 순으로 상기 신경망 모델에 입력하여 상기 신경망 모델을 학습시키는 프로세서; 를 포함하는 전자 장치.
In electronic devices,
memory; and
By analyzing the frequency components for each of multiple learning images for learning a neural network model, the sum of the magnitude values for the frequency components for each pixel at a corresponding position in the multiple learning images is divided by the number of the multiple learning images, thereby obtaining a set of average frequency components for the multiple learning images.
Based on the set of above average frequency components, a target frequency range excluding the low frequency range is determined,
Based on the sum of the average frequency components of the plurality of regions included in the target frequency region, a grouping criterion for grouping the plurality of learning images is determined,
Based on the above grouping criteria, the plurality of learning images are grouped into multiple groups,
An electronic device comprising: a processor for training the neural network model by inputting learning images included in a group having a low frequency component among the plurality of groups in order from learning images included in a group having a high frequency component among the plurality of groups into the neural network model;
상기 프로세서는,
고속 푸리에 변환(fast fourier transform, FFT)을 이용하여 상기 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분을 분석하는 전자 장치.
In the first paragraph,
The above processor,
An electronic device that analyzes frequency components for each of the plurality of training images using a fast Fourier transform (FFT).
상기 프로세서는,
상기 평균 주파수 성분의 집합 중 최대 값을 식별하고,
상기 최대 값의 1/2에 대응되는 지점부터 상기 최대 값의 1/10에 대응되는 지점까지의 영역을 식별하는 것에 기초하여, 상기 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정하는 전자 장치.
In the first paragraph,
The above processor,
Identify the maximum value among the set of above average frequency components,
An electronic device that determines the target frequency range based on identifying an area from a point corresponding to 1/2 of the maximum value to a point corresponding to 1/10 of the maximum value.
상기 프로세서는,
상기 복수의 학습 영상의 중심점과의 거리에 기초하여, 상기 타겟 주파수 영역을 동일한 면적을 갖는 제1 개수의 영역들로 구분함으로써 상기 복수의 영역을 결정하고,
상기 복수의 영역 각각에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 합을 산출하여 상기 중심점과의 거리가 가까운 영역부터 상기 중심점과의 거리가 먼 영역까지 순차적으로 배열하며,
상기 배열된 평균 주파수 성분의 합에서 상기 평균 주파수 성분의 합이 급격하게 증가하는 경계를 기준으로 상기 복수의 영역을 구분함으로써, 상기 그룹핑 기준을 결정하는 전자 장치.
In the first paragraph,
The above processor,
Based on the distance from the center point of the plurality of learning images, the plurality of regions are determined by dividing the target frequency region into a first number of regions having the same area,
The average frequency component sum for each of the above multiple areas is calculated and arranged sequentially from areas that are close to the center point to areas that are far from the center point.
An electronic device that determines the grouping criteria by dividing the plurality of areas based on a boundary where the sum of the average frequency components increases rapidly from the sum of the average frequency components arranged above.
상기 프로세서는,
상기 복수의 학습 영상 별로 상기 그룹핑 기준에 따른 주파수 성분의 합을 산출하는 것에 기초하여, 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 상기 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑하는 전자 장치.
In the first paragraph,
The above processor,
An electronic device that groups the plurality of learning images into the plurality of groups based on calculating the sum of frequency components according to the grouping criteria for each of the plurality of learning images.
상기 프로세서는,
상기 신경망 모델의 학습이 진행되는 동안 상기 신경망 모델의 학습에 따른 에러율에 대한 정보를 획득하고,
상기 에러율에 대한 정보에 기초하여 상기 학습이 비정상적으로 수행되었는지 여부를 식별하며,
상기 학습이 비정상적으로 수행된 것으로 식별되면, 상기 타겟 주파수 영역을 상기 제1 개수와 상이한 제2 개수의 영역들로 구분함으로써 상기 복수의 영역을 재 결정하고,
상기 재 결정된 복수의 영역에 기초하여 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 재그룹핑한 후, 상기 신경망 모델을 재학습시키는 전자 장치.
In the fourth paragraph,
The above processor,
While the learning of the above neural network model is in progress, information on the error rate according to the learning of the above neural network model is obtained,
Based on the information about the above error rate, identify whether the above learning was performed abnormally,
If the above learning is identified as being performed abnormally, the plurality of regions are re-determined by dividing the target frequency region into a second number of regions different from the first number,
An electronic device that regroups the plurality of learning images into a plurality of groups based on the plurality of re-determined regions, and then retrains the neural network model.
상기 프로세서는,
상기 학습이 진행되는 동안 상기 에러율이 기 설정된 임계 값 이상으로 증가하면, 상기 학습이 비정상적으로 수행된 것으로 식별하는 전자 장치.
In Article 6,
The above processor,
An electronic device that identifies that the learning is performed abnormally when the error rate increases above a preset threshold value while the learning is in progress.
상기 프로세서는,
상기 복수의 그룹 별 학습 영상을 각각 상이한 신경망 모델의 학습에 이용하는 전자 장치.
In the first paragraph,
The above processor,
An electronic device that uses the above multiple group-specific learning images to train different neural network models.
신경망 모델의 학습을 위한 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분을 분석하여, 상기 복수의 학습 영상에서 서로 대응되는 위치의 화소별로 주파수 성분에 대한 크기 값의 합을 상기 복수의 학습 영상의 개수로 나눔으로써 상기 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득하는 단계;
상기 평균 주파수 성분의 집합에 기초하여, 저주파수 영역이 제외된 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정하는 단계;
상기 타겟 주파수 영역에 포함된 복수의 영역 별 평균 주파수 성분의 합에 기초하여, 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 그룹핑하기 위한 그룹핑 기준을 결정하는 단계;
상기 그룹핑 기준에 기초하여 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑하는 단계; 및
상기 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 낮은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상부터 상기 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 높은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상 순으로 상기 신경망 모델에 입력하여 상기 신경망 모델을 학습시키는 단계; 를 포함하는 전자 장치의 제어 방법.
In a method for controlling an electronic device,
A step of analyzing frequency components for each of a plurality of learning images for learning a neural network model, and obtaining a set of average frequency components for the plurality of learning images by dividing the sum of the magnitude values for the frequency components for each pixel at a corresponding position in the plurality of learning images by the number of the plurality of learning images;
A step of determining a target frequency range excluding a low frequency range based on the set of above average frequency components;
A step of determining a grouping criterion for grouping the plurality of learning images based on the sum of average frequency components of the plurality of regions included in the target frequency region;
A step of grouping the plurality of learning images into a plurality of groups based on the grouping criteria; and
A method for controlling an electronic device, comprising: a step of inputting learning images included in a group having a low frequency component among the plurality of groups to the neural network model in that order, starting from learning images included in a group having a high frequency component among the plurality of groups, to train the neural network model;
상기 전자 장치의 제어 방법은,
신경망 모델의 학습을 위한 복수의 학습 영상 각각에 대한 주파수 성분을 분석하여, 상기 복수의 학습 영상에서 서로 대응되는 위치의 화소별로 주파수 성분에 대한 크기 값의 합을 상기 복수의 학습 영상의 개수로 나눔으로써 상기 복수의 학습 영상에 대한 평균 주파수 성분의 집합을 획득하는 단계;
상기 평균 주파수 성분의 집합에 기초하여, 저주파수 영역이 제외된 타겟 주파수 영역을 결정하는 단계;
상기 타겟 주파수 영역에 포함된 복수의 영역 별 평균 주파수 성분의 합에 기초하여, 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 그룹핑하기 위한 그룹핑 기준을 결정하는 단계;
상기 그룹핑 기준에 기초하여 상기 복수의 학습 영상을 복수의 그룹으로 그룹핑하는 단계; 및
상기 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 낮은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상부터 상기 복수의 그룹 중 주파수 성분이 높은 그룹에 포함된 학습 영상 순으로 상기 신경망 모델에 입력하여 상기 신경망 모델을 학습시키는 단계; 를 포함하는 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록매체.
A non-transitory computer-readable recording medium comprising a program for executing a method of controlling an electronic device,
The method of controlling the above electronic device is:
A step of analyzing frequency components for each of a plurality of learning images for learning a neural network model, and obtaining a set of average frequency components for the plurality of learning images by dividing the sum of the magnitude values for the frequency components for each pixel at a corresponding position in the plurality of learning images by the number of the plurality of learning images;
A step of determining a target frequency range excluding a low frequency range based on the set of above average frequency components;
A step of determining a grouping criterion for grouping the plurality of learning images based on the sum of average frequency components of the plurality of regions included in the target frequency region;
A step of grouping the plurality of learning images into a plurality of groups based on the grouping criteria; and
A computer-readable recording medium comprising: a step of training the neural network model by inputting training images included in a group having a low frequency component among the plurality of groups in order from training images included in a group having a high frequency component among the plurality of groups into the neural network model;
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020210174786AKR102799600B1 (en) | 2021-12-08 | 2021-12-08 | Electronic device for efficiently training neural network model based on frequency analysis of traing image data and controlling method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020210174786AKR102799600B1 (en) | 2021-12-08 | 2021-12-08 | Electronic device for efficiently training neural network model based on frequency analysis of traing image data and controlling method thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20230086302A KR20230086302A (en) | 2023-06-15 |
| KR102799600B1true KR102799600B1 (en) | 2025-04-23 |
Family
ID=86763944
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020210174786AActiveKR102799600B1 (en) | 2021-12-08 | 2021-12-08 | Electronic device for efficiently training neural network model based on frequency analysis of traing image data and controlling method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102799600B1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102829252B1 (en)* | 2024-10-31 | 2025-07-03 | 한국과학기술원 | Method and apparatus of variate tokenization for time series forecasting |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20170076438A1 (en) | 2015-08-31 | 2017-03-16 | Cape Analytics, Inc. | Systems and methods for analyzing remote sensing imagery |
| US20180204111A1 (en) | 2013-02-28 | 2018-07-19 | Z Advanced Computing, Inc. | System and Method for Extremely Efficient Image and Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence Platform |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11026642B2 (en)* | 2019-03-29 | 2021-06-08 | Canon Medical Systems Corporation | Apparatuses and a method for artifact reduction in medical images using a neural network |
- 2021
- 2021-12-08KRKR1020210174786Apatent/KR102799600B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20180204111A1 (en) | 2013-02-28 | 2018-07-19 | Z Advanced Computing, Inc. | System and Method for Extremely Efficient Image and Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence Platform |
| US20170076438A1 (en) | 2015-08-31 | 2017-03-16 | Cape Analytics, Inc. | Systems and methods for analyzing remote sensing imagery |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20230086302A (en) | 2023-06-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11023806B2 (en) | Learning apparatus, identifying apparatus, learning and identifying system, and recording medium | |
| KR20170140214A (en) | Filter specificity as training criterion for neural networks | |
| JP2017201526A (en) | Recognition device, training device and method based on deep neural network | |
| CN107209873A (en) | Hyper parameter for depth convolutional network is selected | |
| US20190138899A1 (en) | Processing apparatus, processing method, and nonvolatile recording medium | |
| CN108140142A (en) | selective backpropagation | |
| KR102532748B1 (en) | Method and device for learning neural network | |
| JP7732299B2 (en) | Learning device, learning method, and program | |
| AU2015207945A1 (en) | Method for training an artificial neural network | |
| JP7073171B2 (en) | Learning equipment, learning methods and programs | |
| US20180137413A1 (en) | Diverse activation functions for deep neural networks | |
| US20190079469A1 (en) | Adaptive control of negative learning for limited reconstruction capability auto encoder | |
| CN116964619A (en) | Electronic device for enhancing image quality and method of enhancing image quality by using the same | |
| US10984637B2 (en) | Haptic control interface for detecting content features using machine learning to induce haptic effects | |
| TW202303456A (en) | Method of optimizing neural network model | |
| CN115147670B (en) | Object processing method and device | |
| KR102799600B1 (en) | Electronic device for efficiently training neural network model based on frequency analysis of traing image data and controlling method thereof | |
| JP2020177582A (en) | Learning device, learning method, program and recognition device | |
| KR20240121054A (en) | Method and apparatus for training a defect detection model | |
| CN114091597A (en) | Countermeasure training method, device and equipment based on adaptive group sample disturbance constraint | |
| CN116710974A (en) | Domain adaptation using domain countermeasure learning in composite data systems and applications | |
| JP7211430B2 (en) | Machine learning device, machine learning method, and program | |
| KR20210089038A (en) | Electronic apparatus and method for controlling thereof | |
| WO2024060839A1 (en) | Object operation method and apparatus, computer device, and computer storage medium | |
| JP7367859B2 (en) | Learning device, trained model generation method, classification device, classification method, and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20211208 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20241209 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20250416 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration |