KR102547997B1 - Neural network operation accelerating method and appratus using effective memory access scheme - Google Patents
Neural network operation accelerating method and appratus using effective memory access schemeDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102547997B1 KR102547997B1KR1020210054199AKR20210054199AKR102547997B1KR 102547997 B1KR102547997 B1KR 102547997B1KR 1020210054199 AKR1020210054199 AKR 1020210054199AKR 20210054199 AKR20210054199 AKR 20210054199AKR 102547997 B1KR102547997 B1KR 102547997B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- memory
- neural network
- data
- determining
- interleaving unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/06—Physical realisation, i.e. hardware implementation of neural networks, neurons or parts of neurons
- G06N3/063—Physical realisation, i.e. hardware implementation of neural networks, neurons or parts of neurons using electronic means
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F13/00—Interconnection of, or transfer of information or other signals between, memories, input/output devices or central processing units
- G06F13/14—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer
- G06F13/16—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer for access to memory bus
- G06F13/1605—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer for access to memory bus based on arbitration
- G06F13/1647—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer for access to memory bus based on arbitration with interleaved bank access
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F13/00—Interconnection of, or transfer of information or other signals between, memories, input/output devices or central processing units
- G06F13/14—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer
- G06F13/20—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer for access to input/output bus
- G06F13/28—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer for access to input/output bus using burst mode transfer, e.g. direct memory access DMA, cycle steal
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D10/00—Energy efficient computing, e.g. low power processors, power management or thermal management
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Bus Control (AREA)
- Advance Control (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean실시예들은 효율적인 메모리 접근 방식을 이용한 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 방법 및 장치에 관한 것이다.Embodiments relate to a method and apparatus for accelerating neural network computation using an efficient memory access method.
하드웨어 가속(hardware acceleration)은 컴퓨팅에서 일부 기능을 CPU에서 구동하는 소프트웨어 방식보다 더 빠르게 수행할 수 있는 하드웨어의 사용을 말한다.Hardware acceleration is the use of hardware in computing to perform some functions faster than software methods running them on the CPU.
하드웨어 가속은 GPU(Graphics Processing Unit)의 블리팅 가속 기능과 CPU(Central Processing Unit)의 복잡한 기능에 대한 함수가 있다.Hardware acceleration has functions for the blitting acceleration function of the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) and complex functions of the CPU (Central Processing Unit).
최근 하드웨어 가속기는 CNN(Convolutional Neural Networks)와 같은 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 분야에서 가장 효과적인 해결방법 중에 하나가 되었다. 특히, 하드웨어 가속기는 대용량의 연산을 수행하는 애플리케이션(application)에서 많이 사용되는데, 이는 애플리케이션의 연산 속도 및 에너지 효율을 크게 향상시킬 수 있다.Recently, hardware accelerators have become one of the most effective solutions in the field of neural network computation, such as CNN (Convolutional Neural Networks). In particular, hardware accelerators are widely used in applications that perform large-capacity calculations, which can greatly improve calculation speed and energy efficiency of applications.
따라서, 하드웨어 가속기의 성능을 향상시킬 수 있는 기술의 개발이 요구되고 있다.Therefore, there is a demand for development of a technology capable of improving the performance of the hardware accelerator.
실시예들은 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 기술을 제공할 수 있다. 다만, 기술적 과제는 상술한 기술적 과제들로 한정되는 것은 아니며, 또 다른 기술적 과제들이 존재할 수 있다.Embodiments may provide a neural network computation acceleration technique. However, the technical challenges are not limited to the above-described technical challenges, and other technical challenges may exist.
일 실시예에 따른 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치는, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 위한 데이터 및 상기 데이터가 저장되는 메모리에 대한 정보를 수신하는 수신기와, 상기 정보에 기초하여 상기 데이터를 저장하기 위한 상기 메모리의 인터리빙(interleaving) 단위를 결정하고, 상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 메모리에 대한 접근 간격(access interval)을 결정하고, 상기 인터리빙 단위 및 상기 접근 간격에 기초하여 메모리에 저장된 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행하기 위한 상기 데이터의 상기 메모리 상의 주소를 결정하고, 상기 주소에 기초하여 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행하는 프로세서를 포함한다.A neural network calculation accelerator according to an embodiment includes a receiver for receiving data for neural network calculation and information about a memory in which the data is stored, and interleaving the memory for storing the data based on the information ( The data for determining an interleaving unit, determining an access interval for the memory based on the interleaving unit, and performing the neural network operation stored in the memory based on the interleaving unit and the access interval and a processor determining an address on the memory of and performing the neural network operation based on the address.
상기 프로세서는, 상기 메모리에 접근하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 미해결 트랜잭션(outstanding transaction)에 기초하여 상기 인터리빙 단위를 결정할 수 있다.The processor may determine the interleaving unit based on an outstanding transaction of a DMA controller accessing the memory.
상기 프로세서는, 상기 메모리의 채널(channel), 랭크(rank) 또는 뱅크(bank) 단위로 상기 인터리빙 단위를 결정할 수 있다.The processor may determine the interleaving unit in units of channels, ranks, or banks of the memory.
상기 프로세서는, 상기 메모리에 접근하는 DMA(Direct Memory Access) 컨트롤러의 개수 및 상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 접근 간격을 결정할 수 있다.The processor may determine the access interval based on the number of direct memory access (DMA) controllers accessing the memory and the interleaving unit.
상기 프로세서는, 상기 DMA 컨트롤러 중에서 활성화된 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수에 기초하여 상기 접근 간격을 결정할 수 있다.The processor may determine the access interval based on the number of activated DMA controllers among the DMA controllers.
상기 프로세서는, 상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 데이터를 상기 메모리에 할당하고, 할당된 메모리에 대한 상기 DMA 컨트롤러의 접근 여부에 기초하여 상기 접근 간격을 결정할 수 있다.The processor may allocate the data to the memory based on the interleaving unit, and determine the access interval based on whether the DMA controller accesses the allocated memory.
상기 프로세서는, 상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 분할된 메모리 공간의 인터리빙 오프셋을 결정하고, 상기 메모리 공간 내에서의 상기 데이터의 데이터 오프셋을 결정할 수 있다.The processor may determine an interleaving offset of a divided memory space based on the interleaving unit, and determine a data offset of the data within the memory space.
상기 데이터는, 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산의 입력 데이터, 상기 뉴럴 네트워크의 가중치 및 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산의 출력 데이터를 포함할 수 있다.The data may include input data of the neural network calculation, weights of the neural network, and output data of the neural network calculation.
상기 접근 간격 내에서 적어도 두 종류의 메모리 접근이 발생될 수 있다.At least two types of memory access may occur within the access interval.
일 실시예에 따른 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 방법은, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 위한 데이터 및 상기 데이터가 저장되는 메모리에 대한 정보를 수신하는 단계와, 상기 정보에 기초하여 상기 데이터를 저장하기 위한 상기 메모리의 인터리빙(interleaving) 단위를 결정하는 단계와, 상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 메모리에 대한 접근 간격(access interval)을 결정하는 단계와, 상기 인터리빙 단위 및 상기 접근 간격에 기초하여 메모리에 저장된 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행하기 위한 상기 데이터의 상기 메모리 상의 주소를 결정하는 단계와, 상기 주소에 기초하여 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행하는 단계를 포함한다.A method for accelerating a neural network operation according to an embodiment includes receiving data for a neural network operation and information about a memory in which the data is stored, and interleaving the memory for storing the data based on the information ( Determining an interleaving unit, determining an access interval to the memory based on the interleaving unit, and performing the neural network operation stored in the memory based on the interleaving unit and the access interval. Determining an address on the memory of the data for processing, and performing the neural network operation based on the address.
상기 인터리빙 단위를 결정하는 단계는, 상기 메모리에 접근하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 미해결 트랜잭션(outstanding transaction)에 기초하여 상기 인터리빙 단위를 결정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The determining of the interleaving unit may include determining the interleaving unit based on an outstanding transaction of a DMA controller accessing the memory.
상기 인터리빙 단위를 결정하는 단계는, 상기 메모리의 채널(channel), 랭크(rank) 또는 뱅크(bank) 단위로 상기 인터리빙 단위를 결정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The determining of the interleaving unit may include determining the interleaving unit in units of channels, ranks, or banks of the memory.
상기 접근 간격을 결정하는 단계는, 상기 메모리에 접근하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수 및 상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 접근 간격을 결정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The determining of the access interval may include determining the access interval based on the number of DMA controllers accessing the memory and the interleaving unit.
상기 메모리에 접근하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수 및 상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 접근 간격을 결정하는 단계는, 상기 DMA 컨트롤러 중에서 활성화된 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수에 기초하여 상기 접근 간격을 결정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The determining of the access interval based on the number of DMA controllers accessing the memory and the interleaving unit may include determining the access interval based on the number of activated DMA controllers among the DMA controllers. .
상기 메모리에 접근하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수 및 상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 접근 간격을 결정하는 단계는, 상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 데이터를 상기 메모리에 할당하는 단계와, 할당된 메모리에 대한 상기 DMA 컨트롤러의 접근 여부에 기초하여 상기 접근 간격을 결정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.Determining the access interval based on the number of DMA controllers accessing the memory and the interleaving unit may include allocating the data to the memory based on the interleaving unit, and the DMA controller for the allocated memory It may include determining the access interval based on whether the access or not.
상기 주소를 결정하는 단계는, 상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 분할된 메모리 공간의 인터리빙 오프셋을 결정하는 단계와, 상기 메모리 공간 내에서의 상기 데이터의 데이터 오프셋을 결정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.The determining of the address may include determining an interleaving offset of a divided memory space based on the interleaving unit, and determining a data offset of the data within the memory space.
상기 데이터는, 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산의 입력 데이터, 상기 뉴럴 네트워크의 가중치 및 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산의 출력 데이터를 포함할 수 있다.The data may include input data of the neural network calculation, weights of the neural network, and output data of the neural network calculation.
상기 접근 간격 내에서 적어도 두 종류의 메모리 접근이 발생될 수 있다.At least two types of memory access may occur within the access interval.
도 1은 일 실시예에 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치의 개략적인 블록도를 나타낸다.
도 2는 도 1에 도시된 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치의 구현의 일 예를 나타낸다.
도 3은 도 1에 도시된 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치의 구현의 다른 예를 나타낸다.
도 4는 도 1에 도시된 메모리의 구현의 예를 나타낸다.
도 5는 데이터를 메모리에 할당하는 과정을 나타낸다.
도 6은 인터리빙 단위에 따른 메모리의 데이터 처리 과정을 나타낸다.
도 7은 인터리빙 단위에 따른 통신 대역폭을 나타낸다.
도 8a는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 위해 할당된 DMA 컨트롤러 및 메모리의 예를 나타낸다.
도 8b는 메모리 접근 간격에 따른 DMA 컨트롤러의 동작을 나타낸다.
도 9는 DMA 컨트롤러의 동작을 나타낸다.
도 10은 레이어 DMA 컨트롤러의 구현의 예를 나타낸다.
도 11은 도 10의 레지스터에 대한 설명을 나타낸다.
도 12는 메모리 상의 주소를 결정하는 과정을 나타내는 의사 코드(pseudo code)를 나타낸다.
도 13a는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 위한 통신 체계(communication scheme)의 일 예를 나타낸다.
도 13b는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 위한 통신 체계(communication scheme)의 다른 예를 나타낸다.
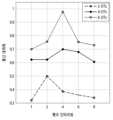
도 14는 통신 체계에 따른 성능을 나타낸다.
도 15는 통신 체계에 따른 대역폭을 나타낸다.
도 16은 도 1에 도시된 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치의 동작의 흐름도를 나타낸다.1 shows a schematic block diagram of a neural network accelerator according to an embodiment.
FIG. 2 shows an example of implementation of the neural network operation accelerator shown in FIG. 1 .
FIG. 3 shows another example of implementation of the neural network operation accelerator shown in FIG. 1 .
4 shows an example of an implementation of the memory shown in FIG. 1 .
5 shows a process of allocating data to a memory.
6 shows a data processing process of a memory according to an interleaving unit.
7 shows communication bandwidth according to interleaving units.
8A shows an example of a DMA controller and memory allocated for neural network operation.
8B shows the operation of the DMA controller according to the memory access interval.
9 shows the operation of the DMA controller.
10 shows an example implementation of a layer DMA controller.
FIG. 11 shows a description of the registers of FIG. 10 .
12 shows pseudo code illustrating a process of determining an address on a memory.
13A shows an example of a communication scheme for neural network computation.
13B shows another example of a communication scheme for neural network computation.
14 shows performance according to a communication system.
15 shows a bandwidth according to a communication system.
FIG. 16 is a flowchart of an operation of the neural network calculation accelerator shown in FIG. 1 .
실시예들에 대한 특정한 구조적 또는 기능적 설명들은 단지 예시를 위한 목적으로 개시된 것으로서, 다양한 형태로 변경되어 구현될 수 있다. 따라서, 실제 구현되는 형태는 개시된 특정 실시예로만 한정되는 것이 아니며, 본 명세서의 범위는 실시예들로 설명한 기술적 사상에 포함되는 변경, 균등물, 또는 대체물을 포함한다.Specific structural or functional descriptions of the embodiments are disclosed for illustrative purposes only, and may be changed and implemented in various forms. Therefore, the form actually implemented is not limited only to the specific embodiments disclosed, and the scope of the present specification includes changes, equivalents, or substitutes included in the technical idea described in the embodiments.
제1 또는 제2 등의 용어를 다양한 구성요소들을 설명하는데 사용될 수 있지만, 이런 용어들은 하나의 구성요소를 다른 구성요소로부터 구별하는 목적으로만 해석되어야 한다. 예를 들어, 제1 구성요소는 제2 구성요소로 명명될 수 있고, 유사하게 제2 구성요소는 제1 구성요소로도 명명될 수 있다.Although terms such as first or second may be used to describe various components, such terms should only be construed for the purpose of distinguishing one component from another. For example, a first element may be termed a second element, and similarly, a second element may be termed a first element.
어떤 구성요소가 다른 구성요소에 "연결되어" 있다고 언급된 때에는, 그 다른 구성요소에 직접적으로 연결되어 있거나 또는 접속되어 있을 수도 있지만, 중간에 다른 구성요소가 존재할 수도 있다고 이해되어야 할 것이다.It should be understood that when an element is referred to as being “connected” to another element, it may be directly connected or connected to the other element, but other elements may exist in the middle.
단수의 표현은 문맥상 명백하게 다르게 뜻하지 않는 한, 복수의 표현을 포함한다. 본 명세서에서, "포함하다" 또는 "가지다" 등의 용어는 설명된 특징, 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부분품 또는 이들을 조합한 것이 존재함으로 지정하려는 것이지, 하나 또는 그 이상의 다른 특징들이나 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부분품 또는 이들을 조합한 것들의 존재 또는 부가 가능성을 미리 배제하지 않는 것으로 이해되어야 한다.Singular expressions include plural expressions unless the context clearly dictates otherwise. In this specification, terms such as "comprise" or "have" are intended to designate that the described feature, number, step, operation, component, part, or combination thereof exists, but one or more other features or numbers, It should be understood that the presence or addition of steps, operations, components, parts, or combinations thereof is not precluded.
다르게 정의되지 않는 한, 기술적이거나 과학적인 용어를 포함해서 여기서 사용되는 모든 용어들은 해당 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 일반적으로 이해되는 것과 동일한 의미를 가진다. 일반적으로 사용되는 사전에 정의되어 있는 것과 같은 용어들은 관련 기술의 문맥상 가지는 의미와 일치하는 의미를 갖는 것으로 해석되어야 하며, 본 명세서에서 명백하게 정의하지 않는 한, 이상적이거나 과도하게 형식적인 의미로 해석되지 않는다.Unless defined otherwise, all terms used herein, including technical or scientific terms, have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art. Terms such as those defined in commonly used dictionaries should be interpreted as having a meaning consistent with the meaning in the context of the related art, and unless explicitly defined in this specification, it should not be interpreted in an ideal or excessively formal meaning. don't
이하, 실시예들을 첨부된 도면들을 참조하여 상세하게 설명한다. 첨부 도면을 참조하여 설명함에 있어, 도면 부호에 관계없이 동일한 구성 요소는 동일한 참조 부호를 부여하고, 이에 대한 중복되는 설명은 생략하기로 한다.Hereinafter, embodiments will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. In the description with reference to the accompanying drawings, the same reference numerals are given to the same components regardless of reference numerals, and overlapping descriptions thereof will be omitted.
도 1은 일 실시예에 따른 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치의 개략적인 블록도를 나타낸다.1 shows a schematic block diagram of a neural network operation accelerator according to an embodiment.
도 1을 참조하면, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 데이터를 처리함으로써 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 결과를 생성할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 1 , the neural
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 가속기(400)를 이용하여 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행할 수 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 가속기(400)를 이용하여 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행할 수 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 가속기(400) 내부 또는 외부에 구현될 수 있다.The neural
가속기(400)는 GPU(Graphics Processing Unit), FPGA(Field Programmable Gate Array), ASIC(Application Specific Integrated Circuit) 또는 AP(Application Processor)를 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 가속기(400)는 가상 머신(Virtual Machine)와 같이 소프트웨어 컴퓨팅 환경으로 구현될 수도 있다.The
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 뉴럴 네트워크를 학습시킬 수 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 학습된 뉴럴 네트워크에 기초하여 추론을 수행할 수 있다.The neural
뉴럴 네트워크(또는 인공 신경망)는 기계학습과 인지과학에서 생물학의 신경을 모방한 통계학적 학습 알고리즘을 포함할 수 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크는 시냅스의 결합으로 네트워크를 형성한 인공 뉴런(노드)이 학습을 통해 시냅스의 결합 세기를 변화시켜, 문제 해결 능력을 가지는 모델 전반을 의미할 수 있다.Neural networks (or artificial neural networks) can include statistical learning algorithms that mimic biological neurons in machine learning and cognitive science. A neural network may refer to an overall model having a problem-solving ability by changing synaptic coupling strength through learning of artificial neurons (nodes) formed in a network by synaptic coupling.
뉴럴 네트워크의 뉴런은 가중치 또는 바이어스의 조합을 포함할 수 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크는 하나 이상의 뉴런 또는 노드로 구성된 하나 이상의 레이어(layer)를 포함할 수 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크는 뉴런의 가중치를 학습을 통해 변화시킴으로써 임의의 입력으로부터 예측하고자 하는 결과를 추론할 수 있다.Neurons in a neural network may contain a combination of weights or biases. A neural network may include one or more layers composed of one or more neurons or nodes. A neural network can infer a result to be predicted from an arbitrary input by changing the weight of a neuron through learning.
뉴럴 네트워크는 심층 뉴럴 네트워크 (Deep Neural Network)를 포함할 수 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크는 CNN(Convolutional Neural Network), RNN(Recurrent Neural Network), 퍼셉트론(perceptron), 다층 퍼셉트론(multilayer perceptron), FF(Feed Forward), RBF(Radial Basis Network), DFF(Deep Feed Forward), LSTM(Long Short Term Memory), GRU(Gated Recurrent Unit), AE(Auto Encoder), VAE(Variational Auto Encoder), DAE(Denoising Auto Encoder), SAE(Sparse Auto Encoder), MC(Markov Chain), HN(Hopfield Network), BM(Boltzmann Machine), RBM(Restricted Boltzmann Machine), DBN(Depp Belief Network), DCN(Deep Convolutional Network), DN(Deconvolutional Network), DCIGN(Deep Convolutional Inverse Graphics Network), GAN(Generative Adversarial Network), LSM(Liquid State Machine), ELM(Extreme Learning Machine), ESN(Echo State Network), DRN(Deep Residual Network), DNC(Differentiable Neural Computer), NTM(Neural Turning Machine), CN(Capsule Network), KN(Kohonen Network) 및 AN(Attention Network)를 포함할 수 있다.The neural network may include a deep neural network. Neural networks include CNN (Convolutional Neural Network), RNN (Recurrent Neural Network), perceptron, multilayer perceptron, FF (Feed Forward), RBF (Radial Basis Network), DFF (Deep Feed Forward), LSTM (Long Short Term Memory), GRU (Gated Recurrent Unit), AE (Auto Encoder), VAE (Variational Auto Encoder), DAE (Denoising Auto Encoder), SAE (Sparse Auto Encoder), MC (Markov Chain), HN (Hopfield Network), BM(Boltzmann Machine), RBM(Restricted Boltzmann Machine), DBN(Depp Belief Network), DCN(Deep Convolutional Network), DN(Deconvolutional Network), DCIGN(Deep Convolutional Inverse Graphics Network), GAN(Generative Adversarial Network) ), LSM (Liquid State Machine), ELM (Extreme Learning Machine), ESN (Echo State Network), DRN (Deep Residual Network), DNC (Differentiable Neural Computer), NTM (Neural Turning Machine), CN (Capsule Network), It may include a Kohonen Network (KN) and an Attention Network (AN).
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 마더보드(motherboard)와 같은 인쇄 회로 기판(printed circuit board(PCB)), 집적 회로(integrated circuit(IC)), 또는 SoC(system on chip)로 구현될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 애플리케이션 프로세서(application processor)로 구현될 수 있다.The neural
또한, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 PC(personal computer), 데이터 서버, 또는 휴대용 장치 내에 구현될 수 있다.In addition, the neural
휴대용 장치는 랩탑(laptop) 컴퓨터, 이동 전화기, 스마트 폰(smart phone), 태블릿(tablet) PC, 모바일 인터넷 디바이스(mobile internet device(MID)), PDA(personal digital assistant), EDA(enterprise digital assistant), 디지털 스틸 카메라(digital still camera), 디지털 비디오 카메라(digital video camera), PMP(portable multimedia player), PND(personal navigation device 또는 portable navigation device), 휴대용 게임 콘솔(handheld game console), e-북(e-book), 또는 스마트 디바이스(smart device)로 구현될 수 있다. 스마트 디바이스는 스마트 와치(smart watch), 스마트 밴드(smart band), 또는 스마트 링(smart ring)으로 구현될 수 있다.Portable devices include laptop computers, mobile phones, smart phones, tablet PCs, mobile internet devices (MIDs), personal digital assistants (PDAs), and enterprise digital assistants (EDAs). , digital still camera, digital video camera, portable multimedia player (PMP), personal navigation device or portable navigation device (PND), handheld game console, e-book ( e-book) or a smart device. A smart device may be implemented as a smart watch, a smart band, or a smart ring.
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 수신기(100) 및 프로세서(200)를 포함한다. 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 메모리(300)를 더 포함할 수 있다.The neural
수신기(100)는 수신 인터페이스를 포함할 수 있다. 수신기(100)는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 위한 데이터 및 데이터가 저장되는 메모리(300)에 대한 정보(이하, 정보라 함)를 수신할 수 있다. 데이터는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산의 입력 데이터, 뉴럴 네트워크의 가중치 및 뉴럴 네트워크 연산의 출력 데이터를 포함할 수 있다.The
수신기(100)는 수신한 데이터 및 메모리(300)에 대한 정보를 프로세서(200)로 출력할 수 있다.The
프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)에 저장된 데이터를 처리할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)에 저장된 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 코드(예를 들어, 소프트웨어) 및 프로세서(200)에 의해 유발된 인스트럭션(instruction)들을 실행할 수 있다.The
"프로세서(200)"는 목적하는 동작들(desired operations)을 실행시키기 위한 물리적인 구조를 갖는 회로를 가지는 하드웨어로 구현된 데이터 처리 장치일 수 있다. 예를 들어, 목적하는 동작들은 프로그램에 포함된 코드(code) 또는 인스트럭션들(instructions)을 포함할 수 있다."
예를 들어, 하드웨어로 구현된 데이터 처리 장치는 마이크로프로세서(microprocessor), 중앙 처리 장치(central processing unit), 프로세서 코어(processor core), 멀티-코어 프로세서(multi-core processor), 멀티프로세서(multiprocessor), ASIC(Application-Specific Integrated Circuit), FPGA(Field Programmable Gate Array)를 포함할 수 있다.For example, a data processing unit implemented in hardware includes a microprocessor, a central processing unit, a processor core, a multi-core processor, and a multiprocessor. , Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC), and Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA).
프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)에 대한 정보에 기초하여 데이터를 저장하기 위한 메모리(300)의 인터리빙(interleaving) 단위를 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)를 제어하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 미해결 트랜잭션(outstanding transaction(OT))에 기초하여 인터리빙 단위를 결정할 수 있다.The
프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)의 채널(channel), 랭크(rank) 또는 뱅크(bank) 단위로 인터리빙 단위를 결정할 수 있다.The
프로세서(200)는 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 메모리(300)에 대한 접근 간격(access interval)을 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)를 제어하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수 및 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 접근 간격을 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)를 제어하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수 및 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 접근 간격을 결정할 수 있다.The
프로세서(200)는 DMA 컨트롤러 중에서 활성화된 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수에 기초하여 접근 간격을 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 데이터를 메모리(300)에 할당할 수 있다.The
프로세서(200)는 할당된 메모리에 대한 DMA 컨트롤러의 접근 여부에 기초하여 접근 간격을 결정할 수 있다.The
프로세서(200)는 인터리빙 단위 및 접근 간격에 기초하여 메모리(300)에 저장된 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행하기 위한 데이터의 메모리(300) 상의 주소를 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 분할된 메모리 공간의 인터리빙 오프셋을 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 메모리 공간 내에서의 데이터의 데이터 오프셋을 결정할 수 있다.The
프로세서(200)는 메모리(300) 상의 주소에 기초하여 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행할 수 있다. 접근 간격 내에서 적어도 두 종류의 메모리 접근이 발생될 수 있다. 메모리 접근의 종류는 입력 읽기(read input), 가중치 읽기(read weight) 또는 출력 쓰기(write output)를 포함할 수 있다.The
메모리(300)는 프로세서(200)에 의해 실행가능한 인스트럭션들(또는 프로그램)을 저장할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 인스트럭션들은 프로세서의 동작 및/또는 프로세서의 각 구성의 동작을 실행하기 위한 인스트럭션들을 포함할 수 있다.The
메모리(300)는 휘발성 메모리 장치 또는 불휘발성 메모리 장치로 구현될 수 있다.The
휘발성 메모리 장치는 DRAM(dynamic random access memory), SRAM(static random access memory), T-RAM(thyristor RAM), Z-RAM(zero capacitor RAM), 또는 TTRAM(Twin Transistor RAM)으로 구현될 수 있다.The volatile memory device may be implemented as dynamic random access memory (DRAM), static random access memory (SRAM), thyristor RAM (T-RAM), zero capacitor RAM (Z-RAM), or twin transistor RAM (TTRAM).
불휘발성 메모리 장치는 EEPROM(Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory), 플래시(flash) 메모리, MRAM(Magnetic RAM), 스핀전달토크 MRAM(Spin-Transfer Torque(STT)-MRAM), Conductive Bridging RAM(CBRAM), FeRAM(Ferroelectric RAM), PRAM(Phase change RAM), 저항 메모리(Resistive RAM(RRAM)), 나노 튜브 RRAM(Nanotube RRAM), 폴리머 RAM(Polymer RAM(PoRAM)), 나노 부유 게이트 메모리(Nano Floating Gate Memory(NFGM)), 홀로그래픽 메모리(holographic memory), 분자 전자 메모리 소자(Molecular Electronic Memory Device), 또는 절연 저항 변화 메모리(Insulator Resistance Change Memory)로 구현될 수 있다.Non-volatile memory devices include electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM), flash memory, magnetic RAM (MRAM), spin-transfer torque (STT)-MRAM (conductive bridging RAM), and conductive bridging RAM (CBRAM). , FeRAM (Ferroelectric RAM), PRAM (Phase change RAM), Resistive RAM (RRAM), Nanotube RRAM (Polymer RAM (PoRAM)), Nano Floating Gate Memory Memory (NFGM)), holographic memory, molecular electronic memory device (Molecular Electronic Memory Device), or Insulator Resistance Change Memory.
도 2 및 도 3은 도 1에 도시된 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치의 구현의 예들을 나타낸다.2 and 3 show examples of implementation of the neural network computation accelerator shown in FIG. 1 .
도 2 및 도 3을 참조하면, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 메모리 컨트롤러(250)(예: DRAM 컨트롤러)의 특징을 파악해서 하드웨어 가속기의 성능 최적화하는 효율적인 뱅크 인터리빙 (bank interleaving) 단위를 탐색할 수 있다.2 and 3, the neural
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 DMA (Direct Memory Access)에 적은 양의 컨트롤 레지스터(control register)를 추가함으로써, 가속기(230)(예: 도 1의 가속기(400))의 성능을 향상시킬 수 있다.The neural
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 간격 당 뱅크 할당 (per-interval bank allocation)을 통해서, 가속기(230)의 통신 대역폭을 최대화할 수 있다. 이를 통해, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 성능을 최대로 가속화할 수 있다.The neural
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 프로세서(210), 가속기(230), 메모리 컨트롤러(250) 및 메모리(270)를 포함할 수 있다.The neural
가속기(230)는 DMA 컨트롤러(311), DMA 컨트롤러(313) 및 DMA 컨트롤러(315)를 포함할 수 있다. 가속기(230)는 온 칩 버퍼(331), 온 칩 버퍼(333), 온 칩 버퍼(335), 온 칩 버퍼(337), 온 칩 버퍼(371) 및 온 칩 버퍼(373)를 포함할 수 있다. 가속기(230)는 MAC 어레이(350)를 포함할 수 있다.The
DMA 컨트롤러(311)는 입력 읽기 동작을 관할하고, DMA 컨트롤러(313)는 가중치 읽기 동작을 관할하고, DMA 컨트롤러(315)는 출력 쓰기 동작을 관할할 수 있다.The
온 칩 버퍼(331) 및 온 칩 버퍼(335)는 입력 버퍼일 수 있고, 온 칩 버퍼(333) 및 온 칩 버퍼(337)는 가중치 버퍼일 수 있다.The on-chip buffer 331 and the on-
MAC 어레이(350)는 곱셈기, 덧셈기 및 누산기를 포함할 수 있다. 온 칩 버퍼(371) 및 온 칩 버퍼(373)는 출력 버퍼일 수 있다.
가속기(230)는 온 칩 버스(on-chip bus)를 통해서 DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)와 연결될 수 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 뱅크 인터리빙 및 간격 당 뱅크 할당을 통해 DRAM과 온 칩 버스 사이의 통신 대역폭(communication bandwidth) 병목현상 (bottleneck)을 해결함으로써 뉴럴 네트워크 연산의 성능을 효과적으로 가속시킬 수 있다.The
가속기(230)는 CNNs(Convolutional Neural Networks) 연산을 수행할 수 있다. 가속기(230)는 DMA 컨트롤러(311, 313 및 315)를 통해서 온 칩 버스 (on-chip bus)에 연결되며, DRAM(Dynamic Random Access Memory)에 접근하여 가속기(230)가 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 하기 위해 필요한 데이터(예: 픽셀(pixel) 및 가중치(weight)들을 주고받을 수 있다.The
DMA 컨트롤러(311, 313 및 315)는 프로세서(예: 도 1의 프로세서(200))의 제어를 통해서 메모리(예: DRAM)으로부터 픽셀 (pixel)과 가중치 (weight)를 내부의 온 칩 버퍼(331, 333, 335 및 337)로 전송할 수 있다. MAC 어레이(350)는 여러 개의 MAC 연산기를 포함하도록 구성되어 뉴럴 네트워크 연산(예: CNNs 연산)을 병렬적으로 처리할 수 있다. 연산이 완료된 데이터(예: 픽셀)들은 DMA 컨트롤러(315)를 통해서 메모리에 저장될 수 있다.The
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행하기 위해서 연산하는 과정과 통신하는 과정을 이중 버퍼(double buffering)를 통해서 동시에 수행할 수 있다.The neural
DMA 컨트롤러(311, 313 및 315)는 미해결 트랜잭션(outstanding transaction)이라는 방식으로 통신할 수 있다. 미해결 트랜잭션은 앞서 요청한 통신이 완료되지 않아도 다음 요청을 할 수 있는 최대 개수를 의미할 수 있다. DMA 컨트롤러(311, 313 및 315)는 온 칩 버스의 마스터로 동작할 수 있다.
도 4는 도 1에 도시된 메모리의 구현의 예를 나타내고, 도 5는 데이터를 메모리에 할당하는 과정을 나타낸다.4 shows an example of implementation of the memory shown in FIG. 1, and FIG. 5 shows a process of allocating data to the memory.
도 4 및 도 5를 참조하면, 메모리(예: 도 1의 메모리(300))는 하나 이상의 메모리 장치(410)를 포함할 수 있다. 메모리 장치(410)는 메모리 컨트롤러(430)에 의해 제어될 수 있다. 메모리 컨트롤러(430)는 프로세서(예: 도 1의 프로세서(200)) 또는 메모리(300)에 포함될 수 있다.Referring to FIGS. 4 and 5 , a memory (eg, the
메모리 장치(410)는 하나 이상의 채널(channel)을 포함하고, 채널은 하나 이상의 랭크(rank)를 포함하고, 랭크는 하나 이상의 뱅크(bank)(450)를 포함할 수 있다.The memory device 410 may include one or more channels, each channel may include one or more ranks, and each rank may include one or more banks 450 .
채널은 메모리 장치(410)에서 입력 또는 출력이 발생할 경우, 메모리 컨트롤러에 연결되어 하나의 데이터 경로를 공유하는 묶음을 의미할 수 있다.A channel may refer to a bundle that is connected to a memory controller and shares one data path when input or output occurs in the memory device 410 .
랭크는 하나의 채널 내에서 하나 이상의 메모리의 논리적 묶음을 의미할 수 있고, 뱅크는 메모리 장치(410)의 입출력 단위를 의미할 수 있다.A rank may mean a logical bundle of one or more memories within one channel, and a bank may mean an input/output unit of the memory device 410 .
메모리 장치(410)는 칩 0(411), 칩1(412), ..., 칩n을 포함할 수 있다. 각각의 칩은 내부의 뱅크(540)들로 구성될 수 있다. 뱅크(540)의 로우 버퍼(row buffer)는 일정 시간 동안 한 행에 대해서만 입출력을 처리할 수 있다. 통신 대역폭을 높이기 위해서, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 위한 데이터(예: 픽셀 또는 가중치)들은 여러 개의 뱅크(450)에 할당될 수 있다.The memory device 410 may include
메모리 컨트롤러(430) 데이터를 뱅크(450)에 할당할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 입력이 이미지인 경우, 입력 픽셀은 여러 개의 채널(C)로 구성되어 있고, 연산에 필요한 만큼의 입력 픽셀의 양(예: TC x TH x TW)이 DMAC을 통해서 가속기로 전달될 수 있다.Data of the memory controller 430 may be allocated to the bank 450 . For example, if the input is an image, the input pixels consist of several channels (C), and the amount of input pixels (eg TC x TH x TW) required for calculation is transmitted to the accelerator through DMAC. can
모든 픽셀을 한 개의 뱅크(450)에 할당할 수 있지만, 도 5의 예시와 같이 복수의 뱅크(예: 뱅크 0 및 뱅크 1)에 할당할 경우, DMA 버스트(burst)에서 볼 수 있듯이 빈틈없이 병렬적으로 뱅크에 접근이 가능하여 대역폭을 최대화할 수 있다.All pixels can be allocated to one bank 450, but when allocated to multiple banks (e.g.,
이때, 뱅크들에 접근하는 순서(또는, 뱅크 인터리빙)에 따라 통신 대역폭은 달라질 수 있다.At this time, the communication bandwidth may vary according to the order of accessing the banks (or bank interleaving).
도 6은 인터리빙 단위에 따른 메모리의 데이터 처리 과정을 나타내고, 도 7은 인터리빙 단위에 따른 통신 대역폭을 나타낸다.6 shows a process of processing data in a memory according to interleaving units, and FIG. 7 shows communication bandwidth according to interleaving units.
도 6 및 도 7을 참조하면, 프로세서(200)는 뱅크 인터리빙을 조절함으로써 통신 대역폭을 향상시킬 수 있다. 2개의 마스터(예: 마스터0 및 마스터 1)는 2개의 DMAC을 포함할 수 있다. 각각의 마스터는 2개의 미해결 트랜잭션으로 동작할 수 있다.Referring to FIGS. 6 and 7 , the
도 6의 로우 메이저 오더(row-major order)는 한 뱅크에서 행에 있는 데이터들에 대해서 우선 접근하고 다음 행에 접근하는 것을 의미할 수 있다.The row-major order of FIG. 6 may mean first accessing data in a row in one bank and then accessing a next row.
도 6의 예시는 미해결 트랜잭션이 2 개일 경우를 나타내지만, 실시예에 따라 미해결 트랜잭션은 2 개 이상일 수 있다. 도 6의 예시의 (a)는 1개의 데이터 요청마다 뱅크 인터리빙을 하는 경우를 나타내고, (b)는 2개의 데이터 요청마다 뱅크 인터리빙을 하는 경우를 나타내고, (c)는 4개의 요청마다 뱅크 인터리빙을 하는 경우를 나타낼 수 있다.The example of FIG. 6 shows a case where there are two unresolved transactions, but depending on embodiments, there may be two or more unresolved transactions. In the example of FIG. 6, (a) shows a case where bank interleaving is performed for every one data request, (b) shows a case where bank interleaving is performed every two data requests, and (c) shows a case where bank interleaving is performed every four requests. case can be indicated.
세 가지 경우 중에서 (b)의 뱅크 인터리빙 방식이 동일한 시간 동안 가장 많은 양의 데이터를 전송할 수 있다. 다시 말해, (b)의 뱅크 인터리빙 방식이 동일한 시간당 가장 많은 데이터를 전송한 경우를 나타내므로, 가장 큰 통신 대역폭을 가질 수 있다.Among the three cases, the bank interleaving method of (b) can transmit the largest amount of data during the same time period. In other words, since the bank interleaving method of (b) represents the case of transmitting the most data per same time period, it can have the largest communication bandwidth.
다양한 경우의 뱅크 인터리빙 중에서 DMA 컨트롤러에 할당된 미해결 트랜잭션과 동일한 수의 뱅크 인터리빙을 수행할 경우에 최대의 통신 대역폭을 가질 수 있다.Among various cases of bank interleaving, when the same number of bank interleaving as outstanding transactions allocated to the DMA controller is performed, the maximum communication bandwidth can be obtained.
도 7의 예시는, 도 6에서 나타난 뱅크 인터리빙에 따른 통신 대역폭에 대한 실험 결과를 나타낼 수 있다. 위에서 설명한 것과 같이, DMAC에 할당된 미해결 트랜잭션과 동일한 뱅크 인터리빙의 경우에서 최대의 통신 대역폭을 가질 수 있다.The example of FIG. 7 may represent an experiment result for communication bandwidth according to bank interleaving shown in FIG. 6 . As described above, it is possible to have the maximum communication bandwidth in the case of bank interleaving equal to the outstanding transaction allocated to the DMAC.
다만, 미해결 트랜잭션이 6인 경우(6 OTs)에서 최대의 통신 대역폭을 나타내는 뱅크 인터리빙이 6이 아닌 것은 메모리(예: DRAM)의 뱅크 내부의 행 버퍼가 최대 4번 재사용이 가능하다는 규칙을 가지기 때문일 수 있다. 이러한 재사용 규칙이 존재 경우, DMA 컨트롤러의 미해결 트랜잭션과는 상이한 수의 뱅크 인터리빙에서 최대의 통신폭을 가질 수 있다.However, if the number of outstanding transactions is 6 (6 OTs), bank interleaving, which represents the maximum communication bandwidth, is not 6 because the row buffer inside the bank of memory (eg DRAM) has a rule that can be reused up to 4 times. can When such a reuse rule exists, it is possible to have a maximum communication width in bank interleaving with a different number of outstanding transactions of the DMA controller.
도 8a는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 위해 할당된 DMA 컨트롤러 및 메모리의 예를 나타내고, 도 8b는 메모리 접근 간격에 따른 DMA 컨트롤러의 동작을 나타내고, 도 9는 DMA 컨트롤러의 동작을 나타낸다.8A shows an example of a DMA controller and memory allocated for neural network operation, FIG. 8B shows the operation of the DMA controller according to memory access intervals, and FIG. 9 shows the operation of the DMA controller.
도 8a 내지 도 9를 참조하면, 프로세서(예: 도 1의 프로세서(200))는 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 메모리(예: 도 1의 메모리(300))에 대한 접근 간격(access interval)을 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)를 제어하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수 및 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 접근 간격을 결정할 수 있다.Referring to FIGS. 8A to 9 , a processor (eg, the
도 8a의 예시는, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산(예: CNN 연산)을 수행하기 위해서 할당된 DMA 컨트롤러와 메모리(300)(예: DRAM)의 뱅크 상태를 나타낼 수 있다.The example of FIG. 8A may represent a bank state of a DMA controller and a memory 300 (eg, DRAM) allocated to perform a neural network operation (eg, CNN operation).
프로세서(200)는 뱅크에 할당된 데이터를 각각의 접근 간격에 표기할 수 있다. 도 8a의 예시에서, 3M은 3개의 DMAC가 할당된 것을 의미하고, 6O3I5W는 뱅크에 할당된 픽셀의 종류를 2진수로 나타낸 것을 의미할 수 있다.The
예를 들어, 뱅크 2, 뱅크 1 및 뱅크 0을 각각 B2, B1, B0라고 표기할 때, O(output)는 (1, 1, 0)이고, 십진수로 6을 의미할 수 있다. I(input)는 (0, 1, 1)이고, 십진수로 3을 의미할 수 있다. W(weight)는 (1, 0, 1)이고, 십진수로 5를 의미할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 이러한 뱅크 할당을 6O3I5W로 표현할 수 있다.For example, when
프로세서(200) 하드웨어 가속기의 연산 시간을 접근 간격(예: DMA 간격(interval))들의 집합으로 표현할 수 있다. 각각의 접근 간격은 DMA가 활성화되었는지 여부를 나타낼 수 있고, DMA가 접근하는 뱅크의 정보를 포함할 수 있다.The computation time of the hardware accelerator of the
도 8b의 예시에서, DMA 간격 0에서는, WODMAC만 활성화되었기 때문에, 프로세서(200)는 DRAM의 뱅크 1 및 뱅크 2에 접근할 수 있다. 이는, 통신 프리미티브(communication primitive)의 6W에 대응될 수 있다.In the example of FIG. 8B , in
DMA 간격 1에서는, RI-DMAC도 활성화되었기 때문에, 프로세서(200)는 활성화되었기 때문에, 뱅크 2, 뱅크 1 및 뱅크0에 접근할 수 있다. 이는, 통신 프리미티브의 6W3R에 대응할 수 있다.In
프로세서(200)는 새로운 DMA 컨트롤러가 활성화되거나 통신이 완료된 시점을 기준으로 접근 간격을 종료할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 접근 간격 0은 RI-DMAC가 활성화된 시점이 종료 시점이고, DMA 간격 1은 WO-DMAC의 통신이 모두 완료된 시점일 수 있다.The
도 9의 예시에서 DMA 설정(set DMA)은 DMAC가 접근하는 뱅크의 주소들을 프로세서(200)(예: 마이크로 프로세서)를 이용하여 설정하는 시간을 의미할 수 있다. 종래의 메모리 컨트롤 방식은 연속한 주소가 아닐 경우, DMA설정 시간이 통신하는 도중에도 필요하기 때문에 통신 대역폭에 제한될 수 있지만, 프로세서(200)는 이미 결정된 메모리의 데이터 레이아웃(layout)을 이용하여 통신하기 전에 일부의 시간만 사용하여 DMA 설정을 수행함으로써 통신 대역폭을 향상시킬 수 있다.In the example of FIG. 9 , DMA set (set DMA) may refer to a time for setting bank addresses accessed by the DMAC using the processor 200 (eg, a microprocessor). Conventional memory control methods may be limited in communication bandwidth because DMA setting time is required even during communication when addresses are not contiguous, but the
도 10은 레이어 DMA 컨트롤러의 구현의 예를 나타내고, 도 11은 도 10의 레지스터에 대한 설명을 나타낸다.10 shows an example of implementation of a layer DMA controller, and FIG. 11 shows a description of the registers of FIG. 10 .
도 10 및 도 11을 참조하면, 레이어 DMA 컨트롤러는 레지스터(1010), 메인 컨트롤러(1030) 및 복수의 데이터 이동기를 포함할 수 있다. 복수의 데이터 이동기(data mover)는 제1 데이터 이동기(1050), 제2 데이터 이동기(1070) 및 제3 데이터 이동기(1090)를 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIGS. 10 and 11 , the layer DMA controller may include a register 1010, a main controller 1030, and a plurality of data movers. The plurality of data movers may include a first data mover 1050 , a second data mover 1070 and a third data mover 1090 .
메인 컨트롤러(1030)는 프로세서(예: 도 1의 프로세서(200))로부터 뉴럴 네트워크 연산에 사용될 데이터의 시작 주소, 할당된 뱅크의 개수, 뱅크 인터리빙 단위를 수신한 후에, 통신에 사용될 모든 주소들을 연산할 수 있다.The main controller 1030 calculates all addresses to be used for communication after receiving the start address of data to be used for neural network operation, the number of allocated banks, and a bank interleaving unit from a processor (eg,
레지스터(1010)는 4 종류의 레지스터를 포함할 수 있다. 레지스터(1010)는 컨트롤 레지스터, 채널 레지스터, 통신 레지스터 및 주소 레지스터를 포함할 수 있다.The register 1010 may include four types of registers. Registers 1010 may include control registers, channel registers, communication registers, and address registers.
컨트롤 레지스터(예: DMACR 및 DMASR)는 DMA의 상태를 저장할 수 있다. 채널 레지스터(예: IN_CHANNEL, OUT_CHANNEL, O 및 I_W)는 픽셀의 정보를 저장할 수 있다. 통신 레지스터(예: BURST_LENGTH 및 NMOT)는 DMA 통신을 위한 정보를 저장할 수 있다. 주소 레지스터(예: BASE_I, I_BANK_OFFSET, BASE_W, W_BANK_OFFSET, BASE_O 및 O_BASE_OFFSET)는 연산을 위한 주소 정보를 저장할 수 있다.Control registers (such as DMACR and DMASR) can store the state of the DMA. Channel registers (eg IN_CHANNEL, OUT_CHANNEL, O and I_W) can store pixel information. Communication registers (eg, BURST_LENGTH and NMOT) may store information for DMA communication. Address registers (eg, BASE_I, I_BANK_OFFSET, BASE_W, W_BANK_OFFSET, BASE_O, and O_BASE_OFFSET) can store address information for operations.
도 12는 메모리 상의 주소를 결정하는 과정을 나타내는 의사 코드(pseudo code)를 나타낸다.12 shows pseudo code illustrating a process of determining an address on a memory.
도 12를 참조하면, 프로세서(예: 도 1의 프로세서(200)) 또는 레이어 DMAC 컨트롤러는 인터리빙 단위 및 접근 간격에 기초하여 메모리(예: 도 1의 메모리(300))에 저장된 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행하기 위한 데이터의 메모리(300) 상의 주소를 결정할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 12, a processor (eg, the
프로세서(200)는 또는 레이어 DMAC 컨트롤러는 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 분할된 메모리 공간의 인터리빙 오프셋을 결정하고, 메모리 공간 내에서의 데이터의 데이터 오프셋을 결정할 수 있다.The
도 12의 예시는, 프로세서(200) 또는 레이어 DMAC 컨트롤러가 메인 컨트롤러(예: 도 10의 메인 컨트롤러(1030))를 통해 계산하는 입력 픽셀, 가중치, 출력 픽셀의 주소 중에서 출력 픽셀의 오프셋을 계산하는 의사 코드를 나타낼 수 있다.The example of FIG. 12 is an example of calculating an offset of an output pixel among addresses of input pixels, weights, and output pixels calculated by the
메인 컨트롤러(1030)는 채널 레지스터와 주소 레지스터를 통해서 현재 통신해야 할 픽셀이 DRAM의 몇 번째 뱅크에 저장되어 있는지 계산함으로써 인터리빙 오프셋(예: bank_offset)을 획득하고, 해당 DRAM 뱅크에서 몇 번째로 저장된 픽셀인지를 계산함으로써 데이터 오프셋(예: pixel_offset)을 획득할 수 있다.The main controller 1030 obtains an interleaving offset (eg, bank_offset) by calculating in which bank of the DRAM the pixel to be communicated currently is stored through the channel register and the address register, and obtains the pixel which is stored in the DRAM bank. By calculating the perception, the data offset (eg pixel_offset) can be obtained.
프로세서(200) 또는 레이어 DMAC 컨트롤러는 오프셋을 획득하는 과정을 반복하여 뉴럴 네트워크의 전체 레이어의 통신에 사용될 모든 주소를 연산할 수 있다.The
도 13a 및 도 13b는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 위한 통신 체계(communication scheme)의 예들을 나타낸다.13A and 13B show examples of communication schemes for neural network computation.
도 13a 및 도 13b를 참조하면, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(예: 도 1의 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10))는 CNN 연산을 수행할 수 있다. 도 13a 및 도 13b의 예시는CNN을 수행하기 위한 통신 체계 (communication scheme)이다. 통신 체계(communication scheme)는 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수와 메모리(예: DRAM)의 뱅크 할당으로 정의될 수 있다.Referring to FIGS. 13A and 13B , a neural network calculation accelerator (eg, the neural
프로세서(예: 도 1의 프로세서(200)) 또는 레이어 DMAC 컨트롤러는 통신 체계를 이용하여 연산 시간에 따라서 활성화된 DMA 컨트롤러를 기준으로 접근 간격(예: DMA 간격)을 나눌 수 있다.A processor (eg, the
각각의 접근 간격들에서 활성화된 DMA 컨트롤러에 따라서 메모리의 뱅크 할당은 달라질 수 있다. 도 13a의 예시에서, DMA 간격 0은 WO-DMAC만 활성화되어 있기 때문에 프로세서(200)는 뱅크 2(또는, 4W)에 접근하고, DMA 간격 1은 RI-DMAC가 추가로 활성화되기 때문에, 프로세서(200)는 뱅크 2와 0에 (또는, 4W1R) 접근할 수 있다. DMA 간격 2는 3개의 DMAC가 모두 활성화되었기 때문에, 프로세서(200)는 또는 레이어 DMAC 컨트롤러는 뱅크 2, 1 및 0 모두 접근할 수 있다.Depending on the DMA controller activated in each access interval, the bank assignment of memory may vary. In the example of FIG. 13A, since only WO-DMAC is activated in
도 13b의 예시는 DMA 컨트롤러가 2개만 있는 경우를 나타낼 수 있다. 도 13b의 예시에서, R-DMAC는 입력 픽셀(I)과 가중치(W)의 통신을 모두 처리할 수 있다.The example of FIG. 13B may represent a case in which there are only two DMA controllers. In the example of FIG. 13B, R-DMAC can handle communication of both input pixels (I) and weights (W).
도 14는 통신 체계에 따른 성능을 나타내고, 도 15는 통신 체계에 따른 대역폭을 나타낸다.14 shows performance according to a communication system, and FIG. 15 shows bandwidth according to a communication system.
도 14의 예시는, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치(10)가 뉴럴 네트워크(예: AlexNet)을 수행할 경우의 통신 체계의 성능을 나타낼 수 있다. 도 14의 예시에서, 처리 패스의 듀레이션(duration of processing pass)은 DMA 컨트롤러가 할당된 개수에 따라서 달라지고, 메모리(예: DRAM)의 뱅크 할당에 따라서 달라질 수 있다.The example of FIG. 14 may represent performance of a communication system when the neural
도 14에서 점선으로 표시된 성능은 통신 체계가 얻을 수 있는 최대성능을 의미할 수 있다. 이 최대 성능은 통신 체계에서 설정한 뱅크 할당과 관계없이, 접근 간격(예: DMA 간격)에서 얻을 수 있는 최대 통신 대역폭을 얻기 위해 할당된 메모리의 뱅크 할당을 의미할 수 있다.Performance indicated by a dotted line in FIG. 14 may mean maximum performance that a communication system can obtain. This maximum performance may refer to bank allocation of memory allocated to obtain the maximum communication bandwidth obtainable in an access interval (eg, DMA interval), regardless of bank allocation set in the communication system.
도 15의 예시에서, 프로세서(예: 도 1의 프로세서(200) 또는 레이어 DMAC 컨트롤러는 뱅크 할당에 따른 통신 대역폭을 파악하고, 각 접근 간격마다 활성화된 DMA 컨트롤러에 따라 통신 대역폭을 최대로 얻을 수 있는 뱅크를 할당을 파악함으로써 뉴럴 네트워크 연산의 최대 성능을 달성될 수 있다.In the example of FIG. 15, a processor (e.g., the
예를 들어, 상술한 도13a의 DMA 간격 0에서 WO-DMAC는 1개의 DRAM 뱅크에 접근할 수 있지만, 도 15의 예시에서 3개 뱅크(즉, 1W 대신 7W)에 접근하는 것이 통신 대역폭을 더 많이 사용할 수 있다. 또한, DMA 간격 1은 WO-DMAC 뿐만 아니라 RI-DMAC도 활성화되게 되는데, 이 경우, 그림 14에 따르면 최대 대역폭은 1W6R에서 달성될 수 있다.For example, in
프로세서(200)는 또는 레이어 DMAC 컨트롤러는 각각의 접근 간격에서 활성화된 DMA 컨트롤러에 따라 메모리의 뱅크에 데이터를 할당함으로써 최대 성능을 확보할 수 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크의 종류에 따라, 이전 레이어의 출력 픽셀이 다음 레이어의 입력 픽셀이 되는 경우에, 프로세서(200)는 정확한 연산을 하기 위해 접근 간격 당 뱅크 할당(per-interval bank allocation) 정보를 저장할 수 있다.The
도 16은 도 1에 도시된 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치의 동작의 흐름도를 나타낸다.FIG. 16 is a flowchart of an operation of the neural network calculation accelerator shown in FIG. 1 .
수신기(100)는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 위한 데이터 및 데이터가 저장되는 메모리(300)에 대한 정보를 수신할 수 있다(1610).The
프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)에 대한 정보에 기초하여 데이터를 저장하기 위한 메모리(300)의 인터리빙(interleaving) 단위를 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)를 제어하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 미해결 트랜잭션(outstanding transaction)에 기초하여 인터리빙 단위를 결정할 수 있다(1630). 프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)의 채널(channel), 랭크(rank) 또는 뱅크(bank) 단위로 인터리빙 단위를 결정할 수 있다.The
프로세서(200)는 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 메모리(300)에 대한 접근 간격(access interval)을 결정할 수 있다(1650). 프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)를 제어하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수 및 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 접근 간격을 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 메모리(300)를 제어하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수 및 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 접근 간격을 결정할 수 있다.The
프로세서(200)는 DMA 컨트롤러 중에서 활성화된 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수에 기초하여 접근 간격을 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 데이터를 메모리(300)에 할당할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 할당된 메모리에 대한 DMA 컨트롤러의 접근 여부에 기초하여 접근 간격을 결정할 수 있다.The
프로세서(200)는 인터리빙 단위 및 접근 간격에 기초하여 메모리(300)에 저장된 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행하기 위한 데이터의 메모리(300) 상의 주소를 결정할 수 있다(1670). 프로세서(200)는 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 분할된 메모리 공간의 인터리빙 오프셋을 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(200)는 메모리 공간 내에서의 데이터의 데이터 오프셋을 결정할 수 있다.The
프로세서(200)는 메모리(300) 상의 주소에 기초하여 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행할 수 있다(1690). 접근 간격 내에서 적어도 두 종류의 메모리 접근이 발생될 수 있다. 메모리 접근의 종류는 입력 읽기(read input), 가중치 읽기(read weight) 또는 출력 쓰기(write output)를 포함할 수 있다.The
이상에서 설명된 실시예들은 하드웨어 구성요소, 소프트웨어 구성요소, 및/또는 하드웨어 구성요소 및 소프트웨어 구성요소의 조합으로 구현될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 실시예들에서 설명된 장치, 방법 및 구성요소는, 예를 들어, 프로세서, 콘트롤러, ALU(arithmetic logic unit), 디지털 신호 프로세서(digital signal processor), 마이크로컴퓨터, FPGA(field programmable gate array), PLU(programmable logic unit), 마이크로프로세서, 또는 명령(instruction)을 실행하고 응답할 수 있는 다른 어떠한 장치와 같이, 범용 컴퓨터 또는 특수 목적 컴퓨터를 이용하여 구현될 수 있다. 처리 장치는 운영 체제(OS) 및 상기 운영 체제 상에서 수행되는 소프트웨어 애플리케이션을 수행할 수 있다. 또한, 처리 장치는 소프트웨어의 실행에 응답하여, 데이터를 접근, 저장, 조작, 처리 및 생성할 수도 있다. 이해의 편의를 위하여, 처리 장치는 하나가 사용되는 것으로 설명된 경우도 있지만, 해당 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자는, 처리 장치가 복수 개의 처리 요소(processing element) 및/또는 복수 유형의 처리 요소를 포함할 수 있음을 알 수 있다. 예를 들어, 처리 장치는 복수 개의 프로세서 또는 하나의 프로세서 및 하나의 컨트롤러를 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 병렬 프로세서(parallel processor)와 같은, 다른 처리 구성(processing configuration)도 가능하다.The embodiments described above may be implemented as hardware components, software components, and/or a combination of hardware components and software components. For example, the devices, methods and components described in the embodiments may include, for example, a processor, a controller, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU), a digital signal processor, a microcomputer, a field programmable gate (FPGA). array), programmable logic units (PLUs), microprocessors, or any other device capable of executing and responding to instructions. The processing device may execute an operating system (OS) and software applications running on the operating system. A processing device may also access, store, manipulate, process, and generate data in response to execution of software. For convenience of understanding, there are cases in which one processing device is used, but those skilled in the art will understand that the processing device includes a plurality of processing elements and/or a plurality of types of processing elements. It can be seen that it can include. For example, a processing device may include a plurality of processors or a processor and a controller. Other processing configurations are also possible, such as parallel processors.
소프트웨어는 컴퓨터 프로그램(computer program), 코드(code), 명령(instruction), 또는 이들 중 하나 이상의 조합을 포함할 수 있으며, 원하는 대로 동작하도록 처리 장치를 구성하거나 독립적으로 또는 결합적으로(collectively) 처리 장치를 명령할 수 있다. 소프트웨어 및/또는 데이터는, 처리 장치에 의하여 해석되거나 처리 장치에 명령 또는 데이터를 제공하기 위하여, 어떤 유형의 기계, 구성요소(component), 물리적 장치, 가상 장치(virtual equipment), 컴퓨터 저장 매체 또는 장치, 또는 전송되는 신호 파(signal wave)에 영구적으로, 또는 일시적으로 구체화(embody)될 수 있다. 소프트웨어는 네트워크로 연결된 컴퓨터 시스템 상에 분산되어서, 분산된 방법으로 저장되거나 실행될 수도 있다. 소프트웨어 및 데이터는 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록 매체에 저장될 수 있다.Software may include a computer program, code, instructions, or a combination of one or more of the foregoing, which configures a processing device to operate as desired or processes independently or collectively. The device can be commanded. Software and/or data may be any tangible machine, component, physical device, virtual equipment, computer storage medium or device, intended to be interpreted by or provide instructions or data to a processing device. , or may be permanently or temporarily embodied in a transmitted signal wave. Software may be distributed on networked computer systems and stored or executed in a distributed manner. Software and data may be stored on computer readable media.
실시예에 따른 방법은 다양한 컴퓨터 수단을 통하여 수행될 수 있는 프로그램 명령 형태로 구현되어 컴퓨터 판독 가능 매체에 기록될 수 있다. 컴퓨터 판독 가능 매체는 프로그램 명령, 데이터 파일, 데이터 구조 등을 단독으로 또는 조합하여 포함할 수 있으며 매체에 기록되는 프로그램 명령은 실시예를 위하여 특별히 설계되고 구성된 것들이거나 컴퓨터 소프트웨어 당업자에게 공지되어 사용 가능한 것일 수도 있다. 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록 매체의 예에는 하드 디스크, 플로피 디스크 및 자기 테이프와 같은 자기 매체(magnetic media), CD-ROM, DVD와 같은 광기록 매체(optical media), 플롭티컬 디스크(floptical disk)와 같은 자기-광 매체(magneto-optical media), 및 롬(ROM), 램(RAM), 플래시 메모리 등과 같은 프로그램 명령을 저장하고 수행하도록 특별히 구성된 하드웨어 장치가 포함된다. 프로그램 명령의 예에는 컴파일러에 의해 만들어지는 것과 같은 기계어 코드뿐만 아니라 인터프리터 등을 사용해서 컴퓨터에 의해서 실행될 수 있는 고급 언어 코드를 포함한다.The method according to the embodiment may be implemented in the form of program instructions that can be executed through various computer means and recorded on a computer readable medium. The computer readable medium may include program instructions, data files, data structures, etc. alone or in combination, and the program instructions recorded on the medium may be specially designed and configured for the embodiment or may be known and usable to those skilled in the art of computer software. may be Examples of computer-readable recording media include magnetic media such as hard disks, floppy disks and magnetic tapes, optical media such as CD-ROMs and DVDs, and magnetic media such as floptical disks. - includes hardware devices specially configured to store and execute program instructions, such as magneto-optical media, and ROM, RAM, flash memory, and the like. Examples of program instructions include high-level language codes that can be executed by a computer using an interpreter, as well as machine language codes such as those produced by a compiler.
위에서 설명한 하드웨어 장치는 실시예의 동작을 수행하기 위해 하나 또는 복수의 소프트웨어 모듈로서 작동하도록 구성될 수 있으며, 그 역도 마찬가지이다.The hardware device described above may be configured to operate as one or a plurality of software modules to perform the operations of the embodiments, and vice versa.
이상과 같이 실시예들이 비록 한정된 도면에 의해 설명되었으나, 해당 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 이를 기초로 다양한 기술적 수정 및 변형을 적용할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 설명된 기술들이 설명된 방법과 다른 순서로 수행되거나, 및/또는 설명된 시스템, 구조, 장치, 회로 등의 구성요소들이 설명된 방법과 다른 형태로 결합 또는 조합되거나, 다른 구성요소 또는 균등물에 의하여 대치되거나 치환되더라도 적절한 결과가 달성될 수 있다.As described above, although the embodiments have been described with limited drawings, those skilled in the art can apply various technical modifications and variations based on this. For example, the described techniques may be performed in an order different from the method described, and/or components of the described system, structure, device, circuit, etc. may be combined or combined in a different form than the method described, or other components may be used. Or even if it is replaced or substituted by equivalents, appropriate results can be achieved.
그러므로, 다른 구현들, 다른 실시예들 및 특허청구범위와 균등한 것들도 후술하는 특허청구범위의 범위에 속한다.Therefore, other implementations, other embodiments, and equivalents of the claims are within the scope of the following claims.
Claims (15)
Translated fromKorean상기 정보에 기초하여 상기 데이터를 저장하기 위한 상기 메모리의 인터리빙(interleaving) 단위를 결정하고,
상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 메모리에 대한 접근 간격(access interval)을 결정하고,
상기 인터리빙 단위 및 상기 접근 간격에 기초하여 메모리에 저장된 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행하기 위한 상기 데이터의 상기 메모리 상의 주소를 결정하고,
상기 주소에 기초하여 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행하는 프로세서
를 포함하고,
상기 프로세서는,
상기 메모리에 접근하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 미해결 트랜잭션(outstanding transaction)에 기초하여 상기 인터리빙 단위를 결정하는, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치.
a receiver receiving data for neural network calculation and information about a memory in which the data is stored; and
determining an interleaving unit of the memory for storing the data based on the information;
Determine an access interval for the memory based on the interleaving unit;
determining an address on the memory of the data for performing the neural network operation stored in the memory based on the interleaving unit and the access interval;
A processor performing the neural network operation based on the address
including,
the processor,
and determining the interleaving unit based on an outstanding transaction of a DMA controller accessing the memory.
상기 프로세서는,
상기 메모리의 채널(channel), 랭크(rank) 또는 뱅크(bank) 단위로 상기 인터리빙 단위를 결정하는
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치.
According to claim 1,
the processor,
Determining the interleaving unit in units of channels, ranks, or banks of the memory
Neural network accelerator.
상기 프로세서는,
상기 메모리에 접근하는 DMA(Direct Memory Access) 컨트롤러의 개수 및 상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 접근 간격을 결정하는
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치.
According to claim 1,
the processor,
Determining the access interval based on the number of direct memory access (DMA) controllers accessing the memory and the interleaving unit
Neural network accelerator.
상기 프로세서는,
상기 DMA 컨트롤러 중에서 활성화된 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수에 기초하여 상기 접근 간격을 결정하는
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치.
According to claim 4,
the processor,
Determining the access interval based on the number of activated DMA controllers among the DMA controllers
Neural network accelerator.
상기 프로세서는,
상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 데이터를 상기 메모리에 할당하고,
할당된 메모리에 대한 상기 DMA 컨트롤러의 접근 여부에 기초하여 상기 접근 간격을 결정하는
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치.
According to claim 4,
the processor,
Allocating the data to the memory based on the interleaving unit;
Determining the access interval based on whether the DMA controller accesses the allocated memory
Neural network accelerator.
상기 프로세서는,
상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 분할된 메모리 공간의 인터리빙 오프셋을 결정하고,
상기 메모리 공간 내에서의 상기 데이터의 데이터 오프셋을 결정하는
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치.
According to claim 1,
the processor,
determining an interleaving offset of a divided memory space based on the interleaving unit;
Determining a data offset of the data within the memory space
Neural network accelerator.
상기 데이터는,
상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산의 입력 데이터, 상기 뉴럴 네트워크의 가중치 및 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산의 출력 데이터를 포함하는
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치.
According to claim 1,
The data is
Including input data of the neural network operation, weights of the neural network, and output data of the neural network operation
Neural network accelerator.
상기 접근 간격 내에서 적어도 두 종류의 메모리 접근이 발생되는
뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 장치.
According to claim 1,
At least two types of memory accesses occur within the access interval
Neural network accelerator.
상기 정보에 기초하여 상기 데이터를 저장하기 위한 상기 메모리의 인터리빙(interleaving) 단위를 결정하는 단계;
상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 메모리에 대한 접근 간격(access interval)을 결정하는 단계;
상기 인터리빙 단위 및 상기 접근 간격에 기초하여 메모리에 저장된 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행하기 위한 상기 데이터의 상기 메모리 상의 주소를 결정하는 단계; 및
상기 주소에 기초하여 상기 뉴럴 네트워크 연산을 수행하는 단계
를 포함하고,
상기 인터리빙 단위를 결정하는 단계는,
상기 메모리에 접근하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 미해결 트랜잭션(outstanding transaction)에 기초하여 상기 인터리빙 단위를 결정하는 단계
를 포함하는, 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 방법.
Receiving data for neural network calculation and information about a memory in which the data is stored;
determining an interleaving unit of the memory for storing the data based on the information;
determining an access interval for the memory based on the interleaving unit;
determining an address on the memory of the data for performing the neural network operation stored in the memory based on the interleaving unit and the access interval; and
performing the neural network operation based on the address;
including,
The step of determining the interleaving unit,
determining the interleaving unit based on an outstanding transaction of a DMA controller accessing the memory;
A method for accelerating a neural network operation, comprising:
상기 인터리빙 단위를 결정하는 단계는,
상기 메모리의 채널(channel), 랭크(rank) 또는 뱅크(bank) 단위로 상기 인터리빙 단위를 결정하는 단계
를 포함하는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 방법.
According to claim 10,
The step of determining the interleaving unit,
Determining the interleaving unit in units of channels, ranks, or banks of the memory
A neural network operation acceleration method comprising a.
상기 접근 간격을 결정하는 단계는,
상기 메모리에 접근하는 DMA 컨트롤러의 개수 및 상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 상기 접근 간격을 결정하는 단계
를 포함하는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 방법.
According to claim 10,
Determining the access interval,
determining the access interval based on the number of DMA controllers accessing the memory and the interleaving unit;
A neural network operation acceleration method comprising a.
상기 주소를 결정하는 단계는,
상기 인터리빙 단위에 기초하여 분할된 메모리 공간의 인터리빙 오프셋을 결정하는 단계; 및
상기 메모리 공간 내에서의 상기 데이터의 데이터 오프셋을 결정하는 단계
를 포함하는 뉴럴 네트워크 연산 가속 방법.
According to claim 10,
The step of determining the address is,
determining an interleaving offset of a divided memory space based on the interleaving unit; and
determining a data offset of the data within the memory space;
A neural network operation acceleration method comprising a.
A computer program stored in a computer readable recording medium to be combined with hardware to execute the method of any one of claims 10 and 12 to 14.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020210054199AKR102547997B1 (en) | 2021-04-27 | 2021-04-27 | Neural network operation accelerating method and appratus using effective memory access scheme |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020210054199AKR102547997B1 (en) | 2021-04-27 | 2021-04-27 | Neural network operation accelerating method and appratus using effective memory access scheme |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20220147280A KR20220147280A (en) | 2022-11-03 |
| KR102547997B1true KR102547997B1 (en) | 2023-06-27 |
Family
ID=84040713
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020210054199AActiveKR102547997B1 (en) | 2021-04-27 | 2021-04-27 | Neural network operation accelerating method and appratus using effective memory access scheme |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102547997B1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102789885B1 (en)* | 2022-12-12 | 2025-04-01 | 주식회사 모빌린트 | Device for connecting between dma and dram using reorder buffer and memory interleaving, method using the same |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20130090147A (en)* | 2012-02-03 | 2013-08-13 | 안병익 | Neural network computing apparatus and system, and method thereof |
- 2021
- 2021-04-27KRKR1020210054199Apatent/KR102547997B1/enactiveActive
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20220147280A (en) | 2022-11-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102607993B1 (en) | Neural network operation appratus and method using quantization | |
| US11803733B2 (en) | Method for implementing neural network model in heterogeneous computing platform and apparatus for performing the same | |
| US12430181B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for partitioning neural network data | |
| KR102547997B1 (en) | Neural network operation accelerating method and appratus using effective memory access scheme | |
| KR20210113004A (en) | Code generation method and appratus ofr neural network operation | |
| US12223444B2 (en) | Accelerator for processing inference tasks in parallel and operating method thereof | |
| US12400120B2 (en) | Method and apparatus with neural network operation using sparsification | |
| JP7431263B2 (en) | Neural network calculation method and device | |
| US20220269597A1 (en) | Memory mapping method and apparatus | |
| KR20210091947A (en) | Distributed processing method and apparatus of neural network model | |
| KR102626850B1 (en) | Neural network-based energy harvesting method and system | |
| KR102700292B1 (en) | Processor device dynamically reconfiguring communication characteristics of neural network accelerator, method for operating the same | |
| KR102675414B1 (en) | Neural network operation method and apparatus | |
| KR102479793B1 (en) | Neural network training method and appratus using fedetrated learning | |
| KR102682630B1 (en) | Neural network operation appratus and method | |
| KR102614909B1 (en) | Neural network operation method and appratus using sparsification | |
| KR102666670B1 (en) | Label prediction method, appratus based neural network and training method for group-labeling-learning using effective embedding vector generation | |
| KR102871424B1 (en) | Neural network operation method and appratus | |
| KR20230041450A (en) | Neural network operation method and appratus | |
| KR20240100056A (en) | Nueralnetwork operation apparatus and method using multiple neural processing unit | |
| KR20230068864A (en) | Apparatus and method for neural network operation | |
| KR20230063519A (en) | Apparatus and method for neural network operation | |
| KR20240106510A (en) | Nueral network operation apparatus and method | |
| KR20220097168A (en) | Deep learning-based joint source and channel coding method and apparatus for performing the same | |
| KR20240101230A (en) | Neural network computing device and method for homomorphically encrypted data |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | St.27 status event code:A-1-1-Q10-Q12-nap-PG1501 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| E13-X000 | Pre-grant limitation requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-3-E10-E13-lim-X000 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Fee payment year number:1 St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 |