KR102508519B1 - A method and apparatus for performing privacy-preserving reinforcement learning using homomorphic encryption - Google Patents
A method and apparatus for performing privacy-preserving reinforcement learning using homomorphic encryptionDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102508519B1 KR102508519B1KR1020200160144AKR20200160144AKR102508519B1KR 102508519 B1KR102508519 B1KR 102508519B1KR 1020200160144 AKR1020200160144 AKR 1020200160144AKR 20200160144 AKR20200160144 AKR 20200160144AKR 102508519 B1KR102508519 B1KR 102508519B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- cloud server
- user terminal
- reinforcement learning
- vector
- encrypted
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/008—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols involving homomorphic encryption
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/60—Protecting data
- G06F21/602—Providing cryptographic facilities or services
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/60—Protecting data
- G06F21/62—Protecting access to data via a platform, e.g. using keys or access control rules
- G06F21/6218—Protecting access to data via a platform, e.g. using keys or access control rules to a system of files or objects, e.g. local or distributed file system or database
- G06F21/6245—Protecting personal data, e.g. for financial or medical purposes
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N20/00—Machine learning
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0816—Key establishment, i.e. cryptographic processes or cryptographic protocols whereby a shared secret becomes available to two or more parties, for subsequent use
- H04L9/0819—Key transport or distribution, i.e. key establishment techniques where one party creates or otherwise obtains a secret value, and securely transfers it to the other(s)
- H04L9/0825—Key transport or distribution, i.e. key establishment techniques where one party creates or otherwise obtains a secret value, and securely transfers it to the other(s) using asymmetric-key encryption or public key infrastructure [PKI], e.g. key signature or public key certificates
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/30—Public key, i.e. encryption algorithm being computationally infeasible to invert or user's encryption keys not requiring secrecy
- H04L9/3006—Public key, i.e. encryption algorithm being computationally infeasible to invert or user's encryption keys not requiring secrecy underlying computational problems or public-key parameters
- H04L9/302—Public key, i.e. encryption algorithm being computationally infeasible to invert or user's encryption keys not requiring secrecy underlying computational problems or public-key parameters involving the integer factorization problem, e.g. RSA or quadratic sieve [QS] schemes
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Bioethics (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 개인정보 보호 강화 학습에 관한 것으로, 더욱 상세하게는 동형 암호화를 이용한 개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 수행하기 위한 방법 및 장치에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to personal information protection reinforcement learning, and more particularly, to a method and apparatus for performing personal information protection reinforcement learning using homomorphic encryption.
최근 몇 년 동안 인공 지능(AI) 기술이 비약적으로 발전하고 AI 서비스가 일상생활에서 활발히 활용되고 있다. AI 서비스를 제공하기 위해서는 엄청난 양의 컴퓨팅 및 스토리지 리소스가 지속적이고 안정적으로 필요하다.In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) technology has developed by leaps and bounds, and AI services are being actively used in daily life. To provide AI services, huge amounts of computing and storage resources are constantly and reliably required.
컴퓨팅 및 스토리지 자원이 고객 측에 제한되어 있기 때문에 클라우드 컴퓨팅은 컴퓨팅 및 스토리지 자원 부족 문제를 해결하기 위해 AI 서비스 플랫폼에서 중요한 역할을 할 것으로 예상된다.Because computing and storage resources are limited on the customer side, cloud computing is expected to play an important role in AI service platforms to solve the problem of lack of computing and storage resources.
클라우드 컴퓨팅은 인터넷에 연결된 데이터 센터에서 실행되는 가상 머신(VM) 및 컨테이너와 같은 가상화 기술을 사용하여 고객의 개인 데이터 및 프로세스를 원격으로 저장하고 실행할 수 있는 기술이다.Cloud computing is a technology that allows customers' personal data and processes to be stored and executed remotely using virtualization technologies such as virtual machines (VMs) and containers running in data centers connected to the Internet.
배포 및 사용 비용, 시스템 안정성, 사용 및 관리 용이성 측면에서 장점으로 인해 AI 서비스 및 응용 프로그램의 개발 및 생산에 크게 기여한다.Due to its advantages in terms of deployment and use cost, system stability, and ease of use and management, it makes a great contribution to the development and production of AI services and applications.
강화 학습(RL)은 에너지, 헬스 케어, 금융 등 다양한 응용 분야에서 인공 지능 제공을 목표로 활발히 연구되고 있는 가장 중요한 학습 전략 중 하나이다.Reinforcement learning (RL) is one of the most important learning strategies being actively researched with the goal of providing artificial intelligence in various application fields such as energy, health care, and finance.
RL 알고리즘은 주어진 환경에서 상태 및 성능 관찰을 사용하여 리워드를 극대화하는 행동을 찾는 정책을 개발한다. 복잡하고 역동적인 환경에서 유능한 성능에 도달하려면 RL 알고리즘에 대한 여러 훈련 반복이 필요하다.RL algorithms use state and performance observations in a given environment to develop policies that seek reward-maximizing actions. Several training iterations for the RL algorithm are required to reach competent performance in a complex and dynamic environment.
따라서 클라우드 컴퓨팅 인프라는 특히 많은 사용자가 방대한 양의 공유 데이터를 공유하고 처리해야 하는 경우 고품질 RL 기반 서비스를 구현하는데 매우 유용하다.Therefore, cloud computing infrastructure is very useful for implementing high-quality RL-based services, especially when large amounts of shared data need to be shared and processed by many users.
그러나 RL 서비스를 이용하고자 하는 사용자는 의료, 금융 데이터 등 민감한 개인 정보를 클라우드 컴퓨팅 인프라의 클라우드 서버로 전송해야 하므로 심각한 데이터 프라이버시 문제가 발생할 수 있으나, 이에 대한 연구는 미흡한 실정이다.However, since users who want to use RL services must transmit sensitive personal information such as medical and financial data to a cloud server of cloud computing infrastructure, serious data privacy problems may occur, but research on this is insufficient.
본 발명은 전술한 문제점을 해결하기 위하여 창출된 것으로, 동형 암호화를 이용한 개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 수행하기 위한 방법 및 장치를 제공하는 것을 그 목적으로 한다.The present invention was created to solve the above problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide a method and apparatus for performing personal information protection reinforcement learning using homomorphic encryption.
본 발명의 목적들은 이상에서 언급한 목적들로 제한되지 않으며, 언급되지 않은 또 다른 목적들은 아래의 기재로부터 명확하게 이해될 수 있을 것이다.The objects of the present invention are not limited to the objects mentioned above, and other objects not mentioned will be clearly understood from the description below.
상기한 목적들을 달성하기 위하여, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버의 동작 방법은 (a) 사용자 단말로부터 HE(Homomorphic Encryption) 비밀키를 이용하여 1차 암호화된 후 공개키를 이용하여 2차 암호화된 암호문을 수신하는 단계; (b) 클라우드 서버의 개인키를 이용하여 상기 2차 암호화된 암호문을 복호화하여 상기 1차 암호화된 암호문을 생성하는 단계; (c) 강화학습 모델을 이용하여 상기 1차 암호화된 암호문에 대한 Q-벡터를 생성하는 단계; (d) 상기 생성된 Q-벡터를 상기 공개키를 이용하여 암호화하는 단계; 및 (e) 상기 암호화된 Q-벡터를 상기 사용자 단말에게 송신하는 단계;를 포함할 수 있다.In order to achieve the above objects, a method of operating a cloud server for personal information protection reinforcement learning according to an embodiment of the present invention is (a) after primary encryption using a Homomorphic Encryption (HE) secret key from a user terminal Receiving a second encrypted ciphertext using a public key; (b) generating the first encrypted ciphertext by decrypting the secondly encrypted ciphertext using a private key of a cloud server; (c) generating a Q-vector for the primary encrypted ciphertext using a reinforcement learning model; (d) encrypting the generated Q-vector using the public key; and (e) transmitting the encrypted Q-vector to the user terminal.
실시예에서, 상기 암호화된 Q-벡터는, 상기 사용자 단말에 의해, 상기 사용자 단말의 개인키를 이용하여 1차 복호화된 후, 상기 HE 비밀키를 이용하여 2차 복호화될 수 있다.In an embodiment, the encrypted Q-vector may be first decrypted by the user terminal using a private key of the user terminal and then secondarily decrypted using the HE private key.
실시예에서, 상기 2차 복호화된 Q-벡터에 포함된 최대 Q 값은, 상기 사용자 단말에 의해, 상기 강화학습 모델에 대한 리워드(reward)를 최대화하기 위한 행동(action) 정보를 결정하기 위해 이용될 수 있다.In an embodiment, the maximum Q value included in the secondary decoded Q-vector is used by the user terminal to determine action information for maximizing a reward for the reinforcement learning model. It can be.
실시예에서, 상기 결정된 행동 정보는, 상기 사용자 단말에 의해, 외부 전자장치에게 송신될 수 있다.In an embodiment, the determined action information may be transmitted to an external electronic device by the user terminal.
실시예에서, 상기 송신된 행동 정보는, 상기 외부 전자장치에 의해, 상기 강화학습 모델에 대한 상태(state) 정보 및 리워드를 결정하기 위해 이용될 수 있다.In an embodiment, the transmitted behavioral information may be used by the external electronic device to determine state information and a reward for the reinforcement learning model.
실시예에서, 상기 공개키와 개인키는, RSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) 암호화 방식에 기반하여 결정될 수 있다.In an embodiment, the public key and the private key may be determined based on a Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) encryption method.
실시예에서, 상기 개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버의 동작 방법은, 상기 (b) 단계 이후에, 상기 1차 암호화된 암호문을 이용하여 상기 강화학습 모델에 대한 Q-테이블 업데이트를 수행하는 단계;를 더 포함할 수 있다.In an embodiment, the operating method of the cloud server for the personal information protection reinforcement learning includes, after the step (b), performing a Q-table update for the reinforcement learning model using the primary encrypted ciphertext. ; may be further included.
실시예에서, 개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버 장치는 사용자 단말로부터 HE(Homomorphic Encryption) 비밀키를 이용하여 1차 암호화된 후 공개키를 이용하여 2차 암호화된 암호문을 수신하는 통신부; 및 클라우드 서버의 개인키를 이용하여 상기 2차 암호화된 암호문을 복호화하여 상기 1차 암호화된 암호문을 생성하고, 강화학습 모델을 이용하여 상기 1차 암호화된 암호문에 대한 Q-벡터를 생성하며, 상기 생성된 Q-벡터를 상기 공개키를 이용하여 암호화하는 제어부;를 포함하고, 상기 통신부는, 암호화된 Q-벡터를 상기 사용자 단말에게 송신할 수 있다.In an embodiment, the cloud server device for personal information protection reinforcement learning includes a communication unit for receiving a second encrypted ciphertext using a public key after primary encryption using a Homomorphic Encryption (HE) secret key from a user terminal; and decrypting the secondary encrypted ciphertext using a private key of a cloud server to generate the primary encrypted ciphertext, generating a Q-vector for the primary encrypted ciphertext using a reinforcement learning model, and a control unit that encrypts the generated Q-vector using the public key, and the communication unit may transmit the encrypted Q-vector to the user terminal.
실시예에서, 상기 암호화된 Q-벡터는, 상기 사용자 단말에 의해, 상기 사용자 단말의 개인키를 이용하여 1차 복호화된 후, 상기 HE 비밀키를 이용하여 2차 복호화될 수 있다.In an embodiment, the encrypted Q-vector may be first decrypted by the user terminal using a private key of the user terminal and then secondarily decrypted using the HE private key.
실시예에서, 상기 2차 복호화된 Q-벡터에 포함된 최대 Q 값은, 상기 사용자 단말에 의해, 상기 강화학습 모델에 대한 리워드(reward)를 최대화하기 위한 행동(action) 정보를 결정하기 위해 이용될 수 있다.In an embodiment, the maximum Q value included in the secondary decoded Q-vector is used by the user terminal to determine action information for maximizing a reward for the reinforcement learning model. It can be.
실시예에서, 상기 결정된 행동 정보는, 상기 사용자 단말에 의해, 외부 전자장치에게 송신될 수 있다.In an embodiment, the determined action information may be transmitted to an external electronic device by the user terminal.
실시예에서, 상기 송신된 행동 정보는, 상기 외부 전자장치에 의해, 상기 강화학습 모델에 대한 상태(state) 정보 및 리워드를 결정하기 위해 이용될 수 있다.In an embodiment, the transmitted behavioral information may be used by the external electronic device to determine state information and a reward for the reinforcement learning model.
실시예에서, 상기 공개키와 개인키는, RSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) 암호화 방식에 기반하여 결정될 수 있다.In an embodiment, the public key and the private key may be determined based on a Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) encryption method.
실시예에서, 상기 제어부는, 상기 1차 암호화된 암호문을 이용하여 상기 강화학습 모델에 대한 Q-테이블 업데이트를 수행할 수 있다.In an embodiment, the control unit may perform a Q-table update for the reinforcement learning model using the first encrypted ciphertext.
상기한 목적들을 달성하기 위한 구체적인 사항들은 첨부된 도면과 함께 상세하게 후술될 실시예들을 참조하면 명확해질 것이다.Specific details for achieving the above objects will become clear with reference to embodiments to be described later in detail in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
그러나, 본 발명은 이하에서 개시되는 실시예들에 한정되는 것이 아니라, 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 구성될 수 있으며, 본 발명의 개시가 완전하도록 하고 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자(이하, "통상의 기술자")에게 발명의 범주를 완전하게 알려주기 위해서 제공되는 것이다.However, the present invention is not limited to the embodiments disclosed below, and may be configured in a variety of different forms, so that the disclosure of the present invention is complete and those of ordinary skill in the art to which the present invention belongs ( It is provided hereafter to fully inform the "ordinary skilled person") of the scope of the invention.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 의하면, 클라우드 컴퓨팅 환경에서 FHE (Fully Homomorphic Encryption) 방식을 이용한 SCC-PPRL (Secure Centralized Computation Privacy Preserving Reinforcement Learning) 알고리즘을 통해 단일 클라우드 서버에 데이터를 저장하고 처리하기 때문에, 통신 오버 헤드 측면에서 더 효율적일 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, since data is stored and processed in a single cloud server through a Secure Centralized Computation Privacy Preserving Reinforcement Learning (SCC-PPRL) algorithm using a Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) method in a cloud computing environment, communication It can be more efficient in terms of overhead.
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 의하면, 동형 연산을 이용한 반복적인 Q-값 계산시 오류 증가를 상쇄할 수 있도록 하여 부트스트랩핑 알고리즘 없이 FHE 방식의 오류 증가를 제한할 수 있다.In addition, according to an embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to limit the increase in error of the FHE scheme without a bootstrapping algorithm by making it possible to offset the increase in error during iterative Q-value calculation using isomorphic operation.
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 의하면, 여러 사용자 단말의 클라우드 환경에서 공유 FHE 키로 암호화된 데이터 교환에 RSA 암호화를 적용하여 동일한 FHE 키를 공유하는 사용자 간의 기밀성을 보장할 수 있다.In addition, according to an embodiment of the present invention, confidentiality between users sharing the same FHE key can be guaranteed by applying RSA encryption to data exchange encrypted with a shared FHE key in a cloud environment of multiple user terminals.
본 발명의 효과들은 상술된 효과들로 제한되지 않으며, 본 발명의 기술적 특징들에 의하여 기대되는 잠정적인 효과들은 아래의 기재로부터 명확하게 이해될 수 있을 것이다.The effects of the present invention are not limited to the above-mentioned effects, and the potential effects expected by the technical features of the present invention will be clearly understood from the description below.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 클라우드 통신 시스템을 도시한 도면이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 최적의 행동 선택의 예를 도시한 도면이다.
도 3a 및 3b는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 복호화 오류 성능 그래프를 도시한 도면이다.
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 Q-함수 업데이트의 예를 도시한 도면이다.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 동형 산술 연산에 의한 복호화 오류 성능 그래프를 도시한 도면이다.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 이진 벡터의 차연 감소를 도시한 도면이다.
도 7은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 프로즌 레이크 환경의 예를 도시한 도면이다.
도 8은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 개인정보 Q-학습의 성공률 그래프를 도시한 도면이다.
도 9a 및 9b는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 계산 복잡도 성능 그래프를 도시한 도면이다.
도 10a 내지 10d는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 통신 오버헤드 성능 그래프를 도시한 도면이다.
도 11은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버의 동작 방법을 도시한 도면이다.
도 12는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 클라우드 서버의 기능적 구성을 도시한 도면이다.1 is a diagram illustrating a cloud communication system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a diagram illustrating an example of optimal action selection according to an embodiment of the present invention.
3A and 3B are diagrams illustrating decoding error performance graphs according to an embodiment of the present invention.
4 is a diagram illustrating an example of Q-function update according to an embodiment of the present invention.
5 is a diagram illustrating a decoding error performance graph by an isomorphic arithmetic operation according to an embodiment of the present invention.
6 is a diagram illustrating difference reduction of binary vectors according to an embodiment of the present invention.
7 is a diagram illustrating an example of a frozen lake environment according to an embodiment of the present invention.
8 is a graph showing a success rate of personal information Q-learning according to an embodiment of the present invention.
9A and 9B are diagrams illustrating computational complexity performance graphs according to an embodiment of the present invention.
10A to 10D are diagrams illustrating communication overhead performance graphs according to an embodiment of the present invention.
11 is a diagram illustrating an operating method of a cloud server for personal information protection reinforcement learning according to an embodiment of the present invention.
12 is a diagram illustrating a functional configuration of a cloud server according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명은 다양한 변경을 가할 수 있고, 여러 가지 실시예들을 가질 수 있는 바, 특정 실시예들을 도면에 예시하고 이를 상세히 설명하고자 한다.Since the present invention can make various changes and have various embodiments, specific embodiments will be illustrated in the drawings and described in detail.
청구범위에 개시된 발명의 다양한 특징들은 도면 및 상세한 설명을 고려하여 더 잘 이해될 수 있을 것이다. 명세서에 개시된 장치, 방법, 제법 및 다양한 실시예들은 예시를 위해서 제공되는 것이다. 개시된 구조 및 기능상의 특징들은 통상의 기술자로 하여금 다양한 실시예들을 구체적으로 실시할 수 있도록 하기 위한 것이고, 발명의 범위를 제한하기 위한 것이 아니다. 개시된 용어 및 문장들은 개시된 발명의 다양한 특징들을 이해하기 쉽게 설명하기 위한 것이고, 발명의 범위를 제한하기 위한 것이 아니다.Various features of the invention disclosed in the claims may be better understood in consideration of the drawings and detailed description. Devices, methods, manufacturing methods, and various embodiments disclosed in the specification are provided for illustrative purposes. The disclosed structural and functional features are intended to enable a person skilled in the art to specifically implement various embodiments, and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention. The disclosed terms and phrases are intended to provide an easy-to-understand description of the various features of the disclosed invention, and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention.
본 발명을 설명함에 있어서, 관련된 공지기술에 대한 구체적인 설명이 본 발명의 요지를 불필요하게 흐릴 수 있다고 판단되는 경우, 그 상세한 설명을 생략한다.In describing the present invention, if it is determined that a detailed description of related known technologies may unnecessarily obscure the subject matter of the present invention, the detailed description will be omitted.
이하, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 동형 암호화를 이용한 개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 수행하기 위한 방법 및 장치를 설명한다.Hereinafter, a method and apparatus for performing personal information protection reinforcement learning using homomorphic encryption according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described.
일 실시예에서, 동형 암호화(Homomorphic Encryption, HE)와 관련하여, 데이터 프라이버시 문제는 지속적이고 광범위하게 제기되었다. 예를 들어, 신뢰할 수 없는 서비스 공급자는 서비스를 제공하기 위한 작업을 위해 복호화된 콘텐츠에 액세스할 수 있으며 공격자가 암호화 시스템의 복호화 키를 훔칠 수 있다. HE 기술은 제 3자가 암호 복호화 없이 직접 암호문에 대한 산술 연산을 수행할 수 있도록 하여 데이터 프라이버시를 보호하기 위해 이용될 수 있다.In one embodiment, with respect to Homomorphic Encryption (HE), data privacy concerns have been persistent and widespread. For example, an untrusted service provider can access decrypted content for operations to provide services, and an attacker can steal the decryption key of an encryption system. HE technology can be used to protect data privacy by allowing third parties to directly perform arithmetic operations on ciphertext without encryption/decryption.
일 실시예에서, 강화 학습(reinforcement learning, RL)과 관련하여, RL은 환경(environment)에 정의된 에이전트(agent)가 현재 상태를 인식하고 누적 리워드를 최대화하기 위해 행동 또는 행동 시퀀스를 선택하는 방법과 관련된 학습 알고리즘을 의미할 수 있다.In one embodiment, with respect to reinforcement learning (RL), RL is a method by which an agent defined in an environment recognizes a current state and selects an action or sequence of actions to maximize a cumulative reward. It may mean a learning algorithm related to .
기본 RL 모델은 Markov 의사 결정 프로세스(Markov decision process)를 기반으로 하며, 에이전트 상태 공간(state space) S, 행동 공간(action space) A 및 리워드 공간(reward space) R로 구성될 수 있다. 모든 이산 시간 스텝(discrete time step) t에서 에이전트는 현재 상태 st ∈ S 및 가능한 행동 공간 A(st)를 가질 수 있다.The basic RL model is based on the Markov decision process, and can be composed of an agent state space S, an action space A, and a reward space R. At every discrete time step t, an agent can have a current state st ∈ S and a possible action space A(st ).
에이전트는 행동 at ∈ A(st)를 취하고, 환경에서 새로운 상태 st+1과 리워드 rt+1을 받을 수 있다.An agent can take an action at ∈ A(st ) and receive a new state st+1 and a reward rt+1 from the environment.
RL의 에이전트는 누적 리워드(cumulative reward)를 극대화하기 위해 환경과의 이러한 상호 작용을 기반으로 정책를 결정할 수 있다. 본 발명에서 RL은 Q-학습(learning) 알고리즘을 사용하여 구현될 수 있다.Agents in RL base their policies on these interactions with the environment to maximize the cumulative reward. can decide In the present invention, RL can be implemented using a Q-learning algorithm.
Q-학습 알고리즘에서는 Q-함수를 업데이트하여 최적의 정책을 학습하고, 현재 상태에 대한 행동을 수행하여 얻을 수 있는 리워드를 추정할 수 있다. Q-함수는 처음에 상수 값을 가질 수 있다.In the Q-learning algorithm, the optimal policy can be learned by updating the Q-function, and the reward that can be obtained by performing an action on the current state can be estimated. A Q-function can initially have a constant value.
에이전트는 시간 t에 상태 st에서 행동 at를 수행한 다음 상태가 새로운 상태 st+1로 전환될 수 있다. 이때 리워드 rt+1은 환경에서 획득하고 Q-함수는 하기 <수학식 1>과 같이 업데이트될 수 있다.An agent can perform an action at in state st at time t and then transition to a new state st+1 . At this time, the reward rt+1 may be obtained from the environment and the Q-function may be updated as shown in
여기서,는 학습률(learning rate)이고는 할인 요인(discount factor)을 나타낸다. 에이전트는 Q-함수 업데이트 절차를 통해 최대 Q-값을 선택하여 주어진 상태에 대한 최적의 행동를 얻을 수 있다.here, is the learning rate and represents a discount factor. The agent can obtain the optimal action for a given state by selecting the maximum Q-value through the Q-function update procedure.
그러나, 에이전트가 항상 최대 Q-값을 사용하는 경우 에이전트는 로컬 최대 값을 검색할 수 있다. Q-학습 알고리즘의 성능을 향상시키기 위해,-그리디(greedy) 정책이 채택되어 행동이 확률로 무작위로 선택될 수 있다. 여기서는 0과 1 사이의 양의 작은 숫자일 수 있다.However, if the agent always uses the maximum Q-value, the agent can retrieve the local maximum. To improve the performance of the Q-learning algorithm, A greedy policy can be adopted so that actions can be chosen randomly with probabilities. here may be a small positive number between 0 and 1.
따라서, 현재 상태에서 행동 at를 선택할 확률은 하기 <수학식 2>와 같이 나타낼 수 있다.Therefore, the current state The probability of selecting the action at in can be expressed as in
여기서,는 행동 세트(action set) A의 카디널리티(cardinality)이며, at*=를 나타낸다. 따라서, 탐색의 빈도(frequency)는 값을 조정하여 결정될 수 있다.here, is the cardinality of action set A, at* = indicates Accordingly, the frequency of search may be determined by adjusting the value.
발굴(exploitation)와 탐색 사이에는 트레이드오프 문제가 있기 때문에, RL 알고리즘에서를 결정하는 문제가 중요할 수 있다.Since there is a trade-off problem between exploitation and exploration, in RL algorithms The issue of determining can be important.
일 실시예에서, LWE(learning with error) 기반 HE와 관련하여, HE를 사용하면 암호문을 복호화하지 않고 직접 산술 연산을 수행할 수 있다. 본 발명에서는 PPRL 알고리즘의 구현을 위해 LWE-기반 암호화 시스템에 기반한 FHE 기법이 사용될 수 있다.In one embodiment, in relation to learning with error (LWE)-based HE, if HE is used, arithmetic operations can be performed directly without decrypting ciphertext. In the present invention, an FHE technique based on an LWE-based encryption system may be used to implement the PPRL algorithm.
LWE-기반 암호화 시스템에서는, 암호화 체계의 모든 모듈로(modulo)를 10의 거듭 제곱으로 선택하여 10진수 시스템을 나타낼 수 있다. M은 일반 텍스트 공간(plaintext space),은 M의 i번째 요소,은 M의 카디널리티를 나타낼 수 있다.In LWE-based cryptosystems, it is possible to represent a decimal number system by selecting all modulos of the cryptographic scheme as powers of 10. M is plaintext space, is the ith element of M, may represent the cardinality of M.
일반 텍스트의 집합은로 제한될 수 있다. 또한는 모듈로의 정수 집합을 나타낼 수 있다. 여기서 L은 LWE 암호화를 위한 매개 변수이며 보안을 강화하기 위해 암호문에 삽입되는 오류의 경계로 사용될 수 있다.The set of plain text is may be limited to also as a modulo can represent a set of integers. Here, L is a parameter for LWE encryption and can be used as a boundary for errors inserted into ciphertext to enhance security.
비밀키 sk는와 같은 크기 N의 정수 벡터로 선택될 수 있다. 그런 다음 일반 텍스트 mi mi의 암호문는 하기 <수학식 3>과 같이 나타낼 수 있다.The secret key sk is It can be selected as an integer vector of size N, such as Then the ciphertext in plaintext mimi Can be expressed as in
여기서는 균일한 분포에서 샘플링된 랜덤 행렬이고, ei는 균일 확률로 {1, 2, ..., r}에서 무작위로 샘플링된 주입된 오류이고, r은 L/2보다 작은 양의 정수를 나타낸다. L/2 및 C는 암호문 공간을 나타낸다.here is a random matrix sampled from a uniform distribution, ei is the injected error randomly sampled at {1, 2, ..., r} with uniform probability, and r denotes a positive integer less than L/2 . L/2 and C represent the ciphertext space.
이후, <수학식 3>으로 암호화된 암호문은 가독성을 위해 대신로 표시될 수 있다. 임의 오류 ei는 암호화 프로세스에서 암호문에 삽입될 수 있다.After that, the ciphertext encrypted by <
sk를 풀기 위해 {mi,} 쌍이 많이 주어지더라도 암호 시스템의 보안은 격자 문제(lattice problem)의 최악의 난이도를 기반으로 하기 때문에, 문제는 매우 어려울 수 있다. 본 발명에서는 격자 문제들 중 LWE 문제를 기반으로 하는 암호 시스템을 사용할 수 있다.To solve for sk {mi , } Given many pairs, the problem can be very difficult, since the security of cryptosystems is based on the worst-case difficulty of the lattice problem. In the present invention, an encryption system based on the LWE problem among lattice problems can be used.
복호화 과정에서는 비밀키 벡터를 나타내고,는 반올림 작업(rounding operation)을 나타낼 수 있다. 그런 다음 암호문는 하기 <수학식 4>와 같이 복호화될 수 있다.in the decryption process denotes the secret key vector, may represent a rounding operation. Then passphrase may be decoded as shown in
ei가 L/2보다 작기 때문에, 복호화 결과를 성공적으로 얻을 수 있다. 일반 텍스트는로 제한될 수 있다. 이 시스템에서 음의 정수를 나타내기 위해, <수학식 4>의 복호화된 결과가 p/2보다 크면, 상기 복호화된 결과에서 p를 빼서 음(negative)으로 만들 수 있다.Since ei is less than L/2, the decryption result can be successfully obtained. Plain text is may be limited to In order to represent a negative integer in this system, if the decoded result of <
EncA 및 Dec는 각각 <수학식 3>을 사용하는 암호화 및 복호화 함수를 나타내고, +C는 암호문 공간에 대한 덧셈 연산(addition operation)을 나타낸다. 동형 덧셈 연산은 하기 <수학식 5>와 같이 나타낼 수 있다.EncA and Dec denote encryption and decryption functions using <
여기서, Xadd는 (X1+X2), madd는 (m1+m2), eadd는 (e1+e2)를 나타낸다. 그런 다음 <수학식 5>의 동형 덧셈 결과는 복호화 함수 <수학식 4>를 사용하여 하기 <수학식 6>과 같이 복호화될 수 있다.Here, Xadd represents (X1 +X2 ), madd represents (m1 +m2 ), and eadd represents (e1 +e2 ). Then, the isomorphic addition result of <
m1+m2 M 및 (e1+e2)가 L/2보다 작은 경우에 해당할 수 있다. <수학식 6>과 같이 ei는 양의 값이므로, 복호화없이 연속적으로 수행되는 동형 덧셈 연산의 수가 증가함에 따라 암호문의 오류 크기가 누적될 수 있다.m1 +m2 This may correspond to a case where M and (e1 +e2 ) are smaller than L/2. Since ei is a positive value as shown in
많은 동형 덧셈 연산의 결과, 오류의 합이 L/2보다 큰 경우, 복호화 오류가 발생할 수 있다. 주입된 임의 오류의 최대 값은 r를 나타낸다.result of many isomorphic addition operations, sum of errors If is greater than L/2, a decoding error may occur. The maximum value of the injected random error represents r.
각 동형 덧셈에 대한 누적 오차의 상한은로 계산할 수 있다. 동형 뺄셈 연산(homomorphic subtraction operation)의 경우 암호화 및 복호화 절차는 동형 덧셈 연산과 동일하며 동형 뺄셈 연산은 -C로 표시될 수 있다.The upper bound of the cumulative error for each isomorphic addition is can be calculated with For a homomorphic subtraction operation, the encryption and decryption procedures are the same as for a homomorphic addition operation, and a homomorphic subtraction operation can be denoted by -C.
FHE 방식에서 동형 곱셈(homomorphic multiplication)은 동형 덧셈보다 더 복잡한 연산일 수 있다. 또한, 동형 곱셈에서 오류 증가의 크기가 더 크기 때문에 LWE-기반 암호 시스템에서 오류 경계 내에서 오류 증가의 크기를 줄이기 위해서는 효과적인 동형 곱셈 연산이 필요할 수 있다.In the FHE scheme, homomorphic multiplication may be a more complex operation than homomorphic addition. In addition, since the magnitude of the error increment is larger in homomorphic multiplication, an effective homomorphic multiplication operation may be required to reduce the magnitude of the error increment within the error boundary in the LWE-based cryptosystem.
동형 곱셈의 구현을 위해 곱셈은 <수학식 3>을 사용하여 암호화되지만 곱셈기에 대한 암호화 함수가 변경될 수 있다. R은일 수 있고, 여기서, Kronecker 곱은로 표시되고 IN+1은 크기 N+1의 단위 행렬로 표시될 수 있다. 그런 다음 암호화 승수에 대한 함수는 하기 <수학식 7>과 같이 나타낼 수 있다.For the implementation of homomorphic multiplication, multiplication is encrypted using <
여기서은 크기의 제로 벡터일 수 있다. 이하, <수학식 7>에 의해 암호화된 암호문은 가독성을 위해 대신로 표시할 수 있다. ci는 암호문의 요소(element)를 나타낼 수 있다. ci=이고, 여기서는 ci의 (k+1)번째 싱글 디짓(single digit)일 수 있다. 그런 다음 인수를 분해하는 함수가 하기 <수학식 8>과 같이 나타낼 수 있다.here silver can be a zero vector of magnitude. Hereinafter, the ciphertext encrypted by Equation 7 is for readability instead can be displayed as ci is the ciphertext can represent an element of ci = and here may be a (k+1)th single digit of ci . Then, a function for decomposing factors can be expressed as in
이 함수를 사용하면,은에 대해 공식의 산술 연산으로 획득될 수 있다.는 암호문 공간의 곱셈을 나타낸다. 동형 곱셈은 하기 <수학식 9>와 같이 비밀 벡터(secret vector) sv로 표현될 수 있다.Using this function, silver About official It can be obtained by the arithmetic operation of represents the multiplication of the ciphertext space. Homomorphic multiplication can be expressed as a secret vector sv as shown in Equation 9 below.
여기서 O는이고 em2는 암호문 O 내부의 오류 벡터(error vector)일 수 있다. 그러면 동형 곱셈의 결과는 하기 <수학식 10>과 같이 복호화될 수 있다.where O is and em2 may be an error vector inside the ciphertext O. Then, the result of homomorphic multiplication can be decoded as shown in Equation 10 below.
m1m2 M 및보다 작을 수 있다. 각 동형 곱셈에 대한 누적 오차의 상한은 Bmul=로 계산할 수 있다.의 요소 범위는 0에서 9까지일 수 있다.m1 m2 M and may be smaller than The upper bound of the cumulative error for each homomorphic multiplication is Bmul= can be calculated with The element range of may be from 0 to 9.
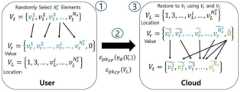
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 클라우드 통신 시스템(100)을 도시한 도면이다.1 is a diagram illustrating a
도 1을 참고하면, 클라우드 통신 시스템(100)은 키 관리 센터(key generation center, KGC)(110), 클라우드 서버(120), 사용자 단말(130) 및 외부 전자장치(140)를 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 1 , the
사용자 단말(130)은 주어진 외부 전자장치(140)와의 상호 작용을 통해 데이터를 수집하고 수집된 데이터는 클라우드 서버(120)로 전달되며 데이터는 클라우드 서버(120)에서 강화 학습(Reinforcement Learning, RL) 서비스를 제공하기 위해 이용될 수 있다.The
일 실시예에서, 외부 전자장치(140)는 환경, 에이전트 또는 이와 동등한 기술적 의미를 갖는 용어로 지칭될 수 있다.In one embodiment, the external
일 실시예에서, RL 서비스에 Q-학습 알고리즘을 채택하고, 클라우드 서버(120)는 여러 사용자 단말(130)의 공유 데이터를 이용하여 업데이트되는 Q-학습을 위한 Q-테이블을 관리할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the Q-learning algorithm is adopted for the RL service, and the
클라우드 서버(120)는 클라우드 플랫폼(cloud platform, CP) 또는 이와 동등한 기술적 의미를 갖는 용어로 지칭될 수 있다.The
본 발명에 따르면. 여러 사용자 단말(130)의 개인 정보에 민감한 데이터를 수집, 공유, 처리하는 클라우드 통신 시스템(100)에서 사용자 단말(130)의 개인 정보를 보호할 수 있는 암호화 시스템이 제안될 수 있다.according to the present invention. In the
본 발명에 따른 암호화 시스템은 LWE-기반 FHE 방식을 사용하여 클라우드 서버(120)와 사용자 단말(130) 간의 데이터 프라이버시를 보호하고 RSA 기반 공개키 방식을 사용하여 클라우드에서 여러 사용자 단말(130) 간의 개인 정보를 보호할 수 있다.The encryption system according to the present invention uses the LWE-based FHE method to protect data privacy between the
일 실시예에서, 사용자 단말(130)은 공유 Q-테이블을 사용하여 동형 산술 연산(homomorphic arithmetic operation)을 수행하기 위해 동일한 FHE 키를 공유할 수 있다.In one embodiment,
FHE 체계에서, 클라우드 서버(120)는 각 사용자 단말(130)이 다른 키, 즉,를 사용하는 경우, 암호화된 암호문을 사용하여 동형 산술 연산을 수행할 수 없을 수 있다.In the FHE system, the
여기서는에 대한 사용자 단말(130) ui의 비밀키로 HE 함수를 사용하는 mi의 암호문을 나타낸다. Nu는 Q-테이블을 공유하는 사용자 단말(130) 수를 나타낸다.here Is It represents the cipher text of mi using the HE function as the secret key of the user terminal 130 ui for . Nu represents the number of
그러나, 여러 사용자 단말(130)이 동일한 키를 사용하는 경우, 데이터 프라이버시를 보존하기가 어려울 수 있다.However, when
본 발명에 따른 암호 시스템은 HE 방식에 대해 대칭적 비밀(symmetrical secret)을 사용할 수 있다.The encryption system according to the present invention may use a symmetrical secret for the HE method.
동일한 FHE 키를 공유하는 사용자 단말(130)에게 기밀성을 제공하기 위해 RSA 알고리즘 기반 암호화가 클라우드 서버(120)와 사용자 단말(130) 간의 데이터 교환에 적용될 수 있다. 공유된 FHE 키로 암호화된 개인 정보에 민감한 데이터는 암호화 시스템의 RSA 암호화에 의해 다시 암호화될 수 있다.In order to provide confidentiality to the
즉, 본 발명에 따른 암호화 시스템은 사용자 단말(130) 간의 프라이버시를 보호하기 위해 RSA 암호화를 사용하여 FHE로 암호화된 값을 암호화하는 이중 암호화(double encryption, DE) 기술을 사용할 수 있다.That is, the encryption system according to the present invention may use double encryption (DE) technology to encrypt a value encrypted with FHE using RSA encryption to protect privacy between
서비스를 요청한 사용자 단말(130)이 사용자 정보를 클라우드 서버(120)로 전송하면, HE로 암호화된 값은 클라우드 서버(120)의 RSA 알고리즘 용 공개키(public key)로 암호화되어 클라우드 서버(120)만이 동형 암호화 값에 접근할 수 있다.When the
또한, 클라우드 서버(120)가 동형 연산 결과를 전달하면, 사용자 단말(130)의 공개키로 결과를 다시 암호화하여, 서비스를 요청한 사용자 단말(130)만 사용자 단말(130)의 개인키(private key)를 사용하여 데이터에 액세스할 수 있도록 할 수 있다.In addition, when the
클라우드 서버(120)의 공개키로 암호화된 암호문과 i번째 사용자 단말(130)의 공개키로 암호화된 암호문은 각각 및로 표시할 수 있다.The ciphertext encrypted with the public key of the
본 발명에 따른 DE 체계를 사용하는 PPRL 알고리즘의 절차에서, KGC(110)는 신뢰할 수 있는 기관을 의미하며, 동일한 RL 서비스를 요청하는 사용자 단말(130)은 KGC(110)에 의한 인증 과정을 통해 그룹화될 수 있다.In the procedure of the PPRL algorithm using the DE system according to the present invention,
이후, KGC(110)는 LWE-기반 FHE 방식을 이용하여 대칭 비밀키(symmetrical secret key)를 생성한 후, 신뢰 채널을 통해 그룹에 속한 인증된 사용자 단말(130)에게 대칭 비밀키를 전달할 수 있다.Thereafter, the
또한, KGC(110)는 RSA 알고리즘을 기반으로 공개키 및 개인키의 쌍을 생성하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 채널을 통해 각 사용자 단말(130) 및 클라우드 서버(120)에 대한 개인키를 제공할 수 있다.In addition, the
그러면, 도 1의 ① 과정에서, 클라우드 서버(120)의 공개키가 사용자 단말(130)에게 전달되고, 사용자 단말(130)의 공개키가 클라우드 서버(120)로 전달될 수 있다.Then, in
사용자 단말(130)은 리워드를 극대화하기 위해 행동을 전달하고, 외부 전자장치(140)는 도 1의 ② 과정과 같이 행동을 수행 한 후, 사용자 단말(130)에게 리워드 rt 및 상태 st를 보고할 수 있다.The
도 1의 ③ 과정에서, PPRL 알고리즘에 대한 사용자 단말(130) 측 절차를 통해, FHE 방식의 비밀키는 사용자 단말(130) 측에만 보관되며 네트워크를 통해 공유되지 않으며, 대칭 비밀키를 이용한 동형 암호화 및 복호화 작업은 사용자 단말(130) 측에서만 수행할 수 있다.In
Q-학습 알고리즘을 수행하기 위해 사용자 단말(130)은 상태 및 행동 정보를 이진 벡터로 인코딩할 수 있다.To perform the Q-learning algorithm, the
또한, 사용자 단말(130)은 Q-테이블 업데이트를 위해 리워드 관련 데이터를 암호화할 수 있다.In addition, the
사용자 단말(130) 간의 데이터 프라이버시를 보호하기 위해 HE 방식을 사용하여 비밀키로 암호화된 값은 클라우드 서버(120)의 RSA 공개키로 다시 암호화된 후 이중 암호화된 값이 클라우드 서버(120)로 전송될 수 있다.In order to protect data privacy between
사용자 단말(130)이 전달한 이중 암호화 값을 받은 후 클라우드 서버(120)는 클라우드 서버(120)의 RSA 개인키를 사용하여 RSA 복호화를 수행하여 HE 방식으로 암호화된 값을 얻을 수 있다.After receiving the double encryption value transmitted by the
동형 암호화 값을 사용하여 클라우드 서버(120)는 Q-테이블 업데이트를 수행하고, 도 1의 ④ 과정에서, 사용자 단말(130) 측에서 행동 선택을 위한 Q 벡터를 생성할 수 있다.Using the homomorphic encryption value, the
인증된 사용자 단말(130) 간의 개인 정보 보호를 위해 클라우드 서버(120)는 RL 기반 서비스를 요청한 사용자 단말(130)의 RSA 공개키를 이용하여 Q-벡터를 암호화한 후 이중 암호화된 값을 사용자 단말(130)에게 전송할 수 있다.To protect personal information between the authenticated
이중 암호화된 Q-벡터를 수신한 사용자 단말(130)은 사용자 단말(130)의 RSA 개인키와 HE 방식 기반 비밀키를 사용하여 벡터를 복호화하고, 도 1의 ⑤ 과정에서와 같이 주어진 외부 전자장치(140)에서 벡터의 최대값을 찾아 누적 리워드를 극대화할 수 있는 행동(action)을 선택할 수 있다. 일 실시예에서, 도 1의 ②-⑤ 과정의 절차가 반복될 수 있다.Upon receiving the double-encrypted Q-vector, the
본 발명에 따르면, 클라우드 컴퓨팅 플랫폼을 위한 개인 정보 보호 강화 학습(privacy-preserving reinforcement learning, PPRL) 프레임 워크가 제안될 수 있다.According to the present invention, a privacy-preserving reinforcement learning (PPRL) framework for a cloud computing platform may be proposed.
본 발명에 따라 제안된 프레임 워크는 FHE(Fully Homomorphic Encryption)를 위해 LWE(Learning with Error)를 기반으로 하는 암호화 시스템을 활용할 수 있다.The framework proposed according to the present invention can utilize an encryption system based on LWE (Learning with Error) for Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE).
또한, 본 발명에 따르면, 클라우드 컴퓨팅 환경에서 FHE(fully homomorphic encryption) 기법을 이용한 안전한 Q-학습을 위한 SCC-PPRL(Secure Centralized Computation PPRL) 기법이 제안될 수 있다.In addition, according to the present invention, a Secure Centralized Computation PPRL (SCC-PPRL) technique for secure Q-learning using a fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) technique in a cloud computing environment may be proposed.
본 발명에 따라 제안된 SCC-PPRL 방식은 통신 오버 헤드를 줄이고 동기화 문제를 방지하기 위해 타사의 지원 없이 단일 클라우드 서버에 데이터를 저장하고 처리할 수 있다.The SCC-PPRL method proposed according to the present invention can store and process data in a single cloud server without support from third parties in order to reduce communication overhead and prevent synchronization problems.
본 발명에 따라 제안된 알고리즘은 반복적인 Q-값 계산 중에 오류의 증가를 상쇄할 수 있도록 함으로써 부트 스트랩핑 알고리즘 없이 FHE 방식의 오류 증가를 제한할 수 있다.The algorithm proposed according to the present invention can limit the increase in error of the FHE scheme without a bootstrapping algorithm by allowing it to offset the increase in error during iterative Q-value calculation.
또한, 본 발명에 따라 제안된 알고리즘은 암호화된 Q-테이블 업데이트 작업을 단순화하기 위해 바이너리 인코딩 형식으로 상태 및 행동 정보를 교환할 수 있다.In addition, the proposed algorithm according to the present invention can exchange state and behavior information in binary encoding format to simplify the encrypted Q-table update task.
또한, 본 발명에 따라 제안된 알고리즘은 상기 공유된 FHE 키에 의해 암호화된 클라우드 서버(120)와 사용자 단말(130) 간의 FHE 데이터의 교환을 위해, RSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) 알고리즘을 기반으로 한 공개키 암호화를 적용하여, 클라우드 시스템에서 동일한 FHE 키를 공유하는 사용자 단말(130)에게 기밀성을 제공할 수 있다.In addition, the algorithm proposed according to the present invention is based on the Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) algorithm for the exchange of FHE data between the
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 최적의 행동 선택의 예를 도시한 도면이다.2 is a diagram illustrating an example of optimal action selection according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 2를 참고하면, 누적 리워드를 극대화하는 보안 행동 선택 알고리즘을 확인할 수 있다. 즉, 암호화된 데이터만을 사용하여 주어진 환경에서 누적 리워드를 극대화하는 행동을 찾기 위해 안전한 행동 선택 알고리즘이 제안될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 2 , a security action selection algorithm maximizing an accumulated reward can be confirmed. That is, a secure action selection algorithm can be proposed to find an action that maximizes the cumulative reward in a given environment using only encrypted data.
본 발명에 따라 제안된 보안 행동 선택 알고리즘은 현재 상태에 해당하는 Q 값을 포함하는 Q-벡터를 선택하고, Q-벡터의 Q 값 중 최대 Q 값을 가지는 요소를 찾을 수 있다.The security action selection algorithm proposed according to the present invention may select a Q-vector including a Q value corresponding to the current state and find an element having a maximum Q value among the Q values of the Q-vector.
먼저, 상수 값으로 초기화된 Q-테이블이 클라우드 서버(120) 측에 저장되고, Q-테이블의 모든 값은 PPRL 알고리즘의 시스템 구성 단계에서 <수학식 3>을 사용하여 HE 함수로 암호화될 수 있다.First, a Q-table initialized with a constant value is stored on the
Q-학습 알고리즘에 대한 상태 및 행동의 수를 각각 Ns 및 Na로 설정한 후, 사용자 단말(130)이 시간 t에서 가질 수 있는 상태 및 행동 집합은 및 At=로 설정될 수 있다.After setting the number of states and actions for the Q-learning algorithm to Ns and Na , respectively, the set of states and actions that the
상태 정보는 이진 벡터 형식으로 전송될 수 있다.는 현재 상태에 해당하는 이진 벡터를 나타낸다. 현재 상태 st가 시간 t에서 sit와 같으면 i번째 요소 vit는 1로 설정되는 반면, 이진 벡터의 다른 요소는 0으로 설정되고 벡터는 FHE 비밀키로 암호화될 수 있다.Status information can be transmitted in binary vector format. represents a binary vector corresponding to the current state. If the current state st equals sit at time t, the ith element vit is set to 1, while the other elements of the binary vector are set to 0 and the vector can be encrypted with the FHE secret key.
Vt의 (Ns-1) 요소는 0의 값을 가지지만, HE 기법을 적용한 후 암호화된 값이 다를 수 있다. 값이 1인 다른 요소도 암호화될 때마다 임의의 값을 가질 수 있다.The (Ns -1) element of Vt has a value of 0, but the encrypted value after applying the HE technique may be different. Other elements with a value of 1 can also have random values each time they are encrypted.
따라서, 클라우드 서버(120)는 사용자 단말(130)로부터 암호화된 Vt를 수신할 때 사용자 단말(130)의 상태 정보를 알 수 없을 수 있다.Accordingly, the
도 2를 참고하면, 본 발명에 따른 보안 행동 선택 알고리즘이 Ns=4, Na=4 및 st=s3t인 예제에 대해 어떻게 작동하는지 확인할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 2 , it can be seen how the security action selection algorithm according to the present invention operates in the case of Ns =4, Na =4 and st =s3t .
<수학식 3>과 <수학식 7>로 암호화된 암호문은 도 2에서 각각 및로 표시될 수 있다. 누적 리워드를 최대화하는 행동을 선택하기 위해, 사용자 단말(130)은 클라우드 서버(120)에게 s3t를 나타내는 암호화된 이진 벡터를 송신할 수 있다.Ciphertexts encrypted by <
클라우드 서버(120) 측에서, 이진 벡터의 i번째 요소와 Q-테이블의 i번째 행에 있는 각 요소 간의 동형 곱셈 연산은 이진 벡터, 즉, j={1, ..., 4}에 대해를 사용하여 수행될 수 있다.On the
동형 덧셈 연산은 각 열의 합, 즉, j={1, ..., 4}에 대해을 얻기 위해 수행될 수 있다.The isomorphic addition operation is for the sum of each column i.e. j={1, ..., 4} can be performed to obtain
도 2에서와 같이 클라우드 서버(120)는 동형 산술 연산을 사용하여 s3t에 해당하는 선택된 Q-벡터를 구하여 사용자 단말(130)에게 반환할 수 있다.As shown in FIG. 2 , the
복호화를 수행한 후, 사용자 단말(130)은 현재 상태가 s3t일 때 현재 상태에 해당하는 Q-벡터를 얻을 수 있다. 마지막으로, 최대 Q-값을 가진 것을 선택하여 상태에 대한 행동을 결정할 수 있다.After performing decoding, the
일 실시예에서, 하기 <표 1>과 같이, 본 발명에 따라 제안된 보안 행동 선택 알고리즘의 절차를 확인할 수 있다.In one embodiment, as shown in Table 1 below, the procedure of the security action selection algorithm proposed according to the present invention can be confirmed.
2: (@User) Double-encrypt binary vector for current state
3: and send to the CP.
4: (@CP) Decrypts the vector using the private key.
5: for do
6: for do
7: (@CP).
8: end for
9: (@CP).
10: end for
11: (@CP) Encrypt Q-vector using
12: public key of user ui and send the vector to the user.
13: (@User) Double-decrypt the Q-vector.
14: (@User) Generate a random number nr in [0, 1]
15: if then
16: (@User) Select randomly a Q-value in Qst.
17: else
18: (@User) Select a Q-value using max function
19:.
20: end if
21: (@User) Find by using index x that
22: satisfies =.
23: Output: Q-value and action.1: Input: .
2: (@User) Double-encrypt binary vector for current state
3: and send to the CP.
4: (@CP) Decrypts the vector using the private key.
5: for do
6: for do
7: (@CP) .
8: end for
9: (@CP) .
10: end for
11: (@CP) Encrypt Q-vector using
12: public key of user ui and send the vector to the user.
13: (@User) Double-decrypt the Q-vector.
14: (@User) Generate a random number nr in [0, 1]
15: if then
16: (@User) Select randomly a Q-value in Qst .
17: else
18: (@User) Select a Q-value using max function
19: .
20: end if
21: (@User) Find by using index x that
22: satisfies = .
23: Output: Q-value and action .
<표 1>의 시작 부분에서 이진 벡터 Vt는 사용자 단말(130)의 현재 상태에 의해 결정될 수 있다.At the beginning of <Table 1>, the binary vector Vt may be determined by the current state of the
2-3 행에서 사용자 단말(130)은 클라우드 서버(120)와 사용자 단말(130) 간의 데이터 프라이버시를 위해 <수학식 7>을 사용하여 FHE 비밀키로 이진 벡터 Vt를 암호화한 다음, 클라우드 서버(120)의 RSA 공개키를 사용하여 다중 사용자 단말(130) 사이의 데이터 프라이버시를 위해를 다시 암호화할 수 있다.In lines 2-3, the
사용자 단말(130)은 현재 상태에 해당하는 Q-벡터를 얻기 위해 클라우드 서버(120)로 이중 암호화된 값을 전송할 수 있다. 클라우드 서버(120)는 암호화된 이진 벡터를 수신하고 자체 RSA 개인키로 복호화하여를 얻을 수 있다. 벡터의 모든 요소는 이진 값이므로 6-8 행의 for 루프가 수행된 후 현재 상태에 해당하는 Q 값을 제외하고의 복호화된 값은 0이 될 수 있다.The
9 행에서 클라우드 서버(120)는 7 행의 계산 결과를 사용하여 동형 덧셈 연산을 수행하고, 9 행의 연산에서 얻은 결과도 현재 상태에 해당하는 Q-값과 동일할 수 있다.In line 9, the
11-12 행에서 클라우드 서버(120)는 5-10 행의 for-루프가 수행된 후 현재 상태에 해당하는 Q 값을 저장하는 선택된 Q-벡터 Qst를 얻을 수 있다.In lines 11 to 12, the
그런 다음 클라우드 서버(120)는 RL 서비스를 요청하는 사용자 단말(130) ui의 공개키를 사용하여 벡터를 암호화하고 암호화된 벡터를 사용자 단말(130)에게 보낼 수 있다.Then, the
사용자 단말(130)은 13 행의 FHE 비밀키와 자체 RSA 개인키를 사용하여 수신된 Q-벡터를 이중 복호화할 수 있다.The
본 발명에 따라 제안된 알고리즘에서는 프라이버시 보호 Q-학습 알고리즘의 성능을 향상시키기 위해-그리디 정책을 채택할 수 있다.-그리디 정책을 사용하여 사용자 단말(130)은 Q-값를 선택하여 14-20 행의 복호화된 Q-벡터의 모든 요소 중에서 행동을 찾을 수 있다.In the algorithm proposed according to the present invention, to improve the performance of the privacy protection Q-learning algorithm - Greedy policy can be adopted. -Using the greedy policy, the
사용자 단말(130)은 16 행에서 탐색할 확률로 복호화된 Q-벡터의 모든 요소 중 하나의 요소를 무작위로 선택할 수 있다.The
반면, 사용자 단말(130)은 복호화된 Q-벡터의 모든 요소 중에서 최대 값을 찾아서 18-19 행에서 확률(1-)로에 최대 값을 할당할 수 있다.On the other hand, the
마지막으로 사용자 단말(130)은 21-22 행에서를 충족하는 인덱스 x를 사용하여 환경에서 사용 가능한 동작 At의 집합에서 동작을 선택할 수 있다.Finally, the
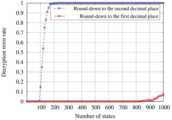
도 3a 및 3b는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 복호화 오류 성능 그래프를 도시한 도면이다.3A and 3B are diagrams illustrating decoding error performance graphs according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 3a 및 3b를 참고하면, 연속적인 동형 동작으로 인한 누적 오류 억제를 확인할 수 있다.Referring to FIGS. 3A and 3B , suppression of accumulated errors due to continuous isomorphic operations can be confirmed.
LWE-기반 암호화 시스템에서는 보안을 강화하기 위해 무작위로 샘플링된 오류가 주입될 수 있다. 복호화없이 연속적으로 수행되는 동형 산술 연산의 수가 증가함에 따라 누적 오류의 크기가 증가할 수 있다.In LWE-based cryptosystems, randomly sampled errors can be injected to enhance security. As the number of consecutively performed isomorphic arithmetic operations increases, the size of the accumulated error may increase.
누적된 오류의 크기가 특정 임계 값을 초과하면 완전히 제거되지 않고 나머지 오류가 일반 텍스트 값에 추가될 수 있다. 일 실시예에서, 상태 수가 증가함에 따라 동형 덧셈 연산의 수가 증가할 수 있다.If the size of the accumulated errors exceeds a certain threshold, they are not completely removed and the remaining errors may be added to the plaintext value. In one embodiment, the number of isomorphic addition operations may increase as the number of states increases.
따라서 상태 수가 매우 많을 경우 누적 오류가 크게 증가하여 LWE-기반 암호화 시스템에서 복호화 오류 가능성이 높아질 수 있다. 이는 상태의 수를 제한해야 함을 의미할 수 있다. 복호화 후 남은 오류는 성공적으로 제거되어야 할 수 있다. 그렇지 않으면 복호화 오류없이 연속적으로 수행할 수 있는 동형 연산의 수를 늘릴 수 없을 수 있다.Therefore, when the number of states is very large, the accumulation error increases significantly, which can increase the possibility of decryption errors in LWE-based cryptosystems. This may mean that the number of states must be limited. Errors remaining after decryption may need to be successfully removed. Otherwise, it may not be possible to increase the number of isomorphic operations that can be successively performed without decoding errors.
나머지 오류가 데이터에 미치는 영향을 줄이기 위해 확장 및 삭제 방법이 제안될 수 있다. 일반적으로 암호화 시스템 작업은 정수만 처리할 수 있다.Expansion and deletion methods can be proposed to reduce the impact of remaining errors on data. In general, cryptographic system operations can only handle integers.
Q-학습 알고리즘에서 사용되는 부동 소수점 수는 큰 수를 곱하여 정수로 표시할 수 있다. 사용자 단말(130)이 숫자 데이터를 클라우드 서버(120)에 보낼 때마다 사용자 단말(130)은 데이터에 10d를 곱하고 반올림할 수 있다. 여기서 d는 소수점 자리수를 나타내는 정수이다.Floating point numbers used in Q-learning algorithms can be expressed as integers by multiplying large numbers. Whenever the
사용자 단말(130)이 클라우드 서버(120)로부터 데이터를 받으면 사용자 단말(130)은 데이터를 10d로 나누어 해당 부동 소수점 값을 얻을 수 있다. d는 고정되어 있으며 클라우드 서버(120)와 사용자 단말(130)에게 미리 알려져 있다. 가드 디지트(guard digit) g를 사용하여 나머지 오류가 데이터에 미치는 영향을 줄이기 위해 d를 일시적으로 증가시켜 암호문의 데이터를 보호할 것을 제안할 수 있다.When the
본 발명에 따른 방식에서는 사용자 단말(130)이 데이터를 클라우드 서버(120)로 전송할 때마다 숫자 데이터에 10g를 추가로 곱한 후 암호화할 수 있다. 즉, v 값은 round(v10d)10g로 변환되어 암호화될 수 있다.In the method according to the present invention, whenever the
클라우드 서버(120)는 여러 동형 연산을 수행하고 결과를 사용자 단말(130)에게 보낼 수 있다. 사용자 단말(130)이 이를 수신하고 복호화한 후 사용자 단말(130)은 결과를 10g로 나눈 다음 반올림할 수 있다.The
즉, 복호화된 값 u는 반올림(u10-g)10-d로 변환될 수 있다. 이때 동형 연산으로 인한 오차가 10g 미만이면 성공적으로 제거할 수 있다.That is, the decrypted value u is rounded up (u 10-g ) Can be converted to 10-d . At this time, if the error due to the isomorphic operation is less than 10g , it can be successfully removed.
예를 들어 가드 숫자 g가 1이고 d가 2라고 가정할 수 있다. 클라우드 서버(120)가 사용자 단말(130)에게 결과 값 5220을 반환하면 사용자 단말(130)은 10을 나누고 소수점 이하로 잘라서 522 값을 얻을 수 있다.For example, we can assume that the guard number g is 1 and d is 2. When the
사용자 단말(130)은 522를로 나누고 마지막으로 원하는 값인 5.22를 얻을 수 있다. 사용자 단말(130)이 나머지 오류로 인해 5220 대신 5222 값을 받는 경우를 고려할 수 있다. 이 경우에도 사용자 단말(130)은 5.22를 얻을 수 있다. 이는 반올림 연산을 통해 가드 디지트를 사용하여 나머지 오류 2를 버려주기 때문일 수 있다.The
따라서 복호화 과정 이후에 나머지 오류가 존재하더라도 제안된 방식에서는 일정 수준 이하의 나머지 오류를 성공적으로 제거할 수 있다.Therefore, even if residual errors exist after the decoding process, the proposed method can successfully remove remaining errors below a certain level.
도 3을 참고하면, 동형 산술 연산으로 인한 복호화 오류의 결과를 확인할 수 있다. 도 3(a)를 참고하면, d=3인 경우 상태 수에 따른 평균 복호화 오류를 확인할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 3 , a result of a decoding error due to an isomorphic arithmetic operation can be confirmed. Referring to FIG. 3(a), when d=3, the average decoding error according to the number of states can be confirmed.
평균 복호화 오류는 동형 연산이 있는 값과 없는 값 사이의 불일치를 평균하여 계산될 수 있다. 각 경우에 대해 시뮬레이션은 평균화를 위해 1000회 수행될 수 있다.The average decoding error can be calculated by averaging the discrepancies between values with and without isomorphic operations. For each case the simulation can be performed 1000 times for averaging.
도 3(a)에서 볼 수 있듯이 LWE-기반 암호 시스템의 오류 증가 문제로 인해 상태 수가 증가함에 따라 평균 복호화 오류는 단조롭게 증가할 수 있다.As shown in FIG. 3(a), the average decryption error monotonically increases as the number of states increases due to the error increase problem of the LWE-based cryptosystem.
도 3(b)을 참고하면, 스케일링 및 폐기 방법에 대한 복호화 오류율을 확인할 수 있다. 파란색 선과 빨간색 선은 각각 d=2 및 g=1 및 d=1 및 g=2에 대한 암호 복호화 오류율을 나타낸다. 파란색 선과 빨간색 선의 오류율은 각각 80개 미만 및 800개 미만의 상태 수에 대해 0일 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 3(b), decoding error rates for scaling and discarding methods can be confirmed. The blue and red lines represent the encryption/decryption error rates for d=2 and g=1 and d=1 and g=2, respectively. The error rates for the blue and red lines can be zero for the number of states less than 80 and less than 800, respectively.
따라서 본 발명에 따른 방식은 상태 수가 일정 수준 이하로 유지되면 나머지 오류를 성공적으로 제거할 수 있다.Therefore, the method according to the present invention can successfully remove remaining errors when the number of states is kept below a certain level.
그러나 상태 수가 너무 많아지면 제안된 스케일링 및 폐기 방법을 적용한 후에도 오류가 남아 있을 수 있다.However, if the number of states becomes too large, errors may remain even after applying the proposed scaling and discarding methods.
복호화 오류를 더욱 줄이기 위해 동형 연산의 수가 시스템이 수용할 수 있는 동형 연산의 수보다 큰 경우 긴 일련의 동형 연산을 여러 조각으로 나눌 수 있다.To further reduce decoding errors, a long series of isomorphic operations can be broken into pieces if the number of isomorphic operations is greater than the number of isomorphic operations the system can accommodate.
즉, 다수의 동형 연산을 실행해야 하는 경우 동형 연산의 최종 결과를 보내는 대신 작은 조각의 중간 결과 nf를 계산하여 하나씩 보낼 수 있다.That is, if you need to execute multiple isomorphic operations, instead of sending the final result of the isomorphic operation, you can compute small pieces of intermediate result nf and send them one by one.
Nw는 복호화 오류 없이 수행할 수 있는 동형 연산의 수를 나타낸다. 그런 다음 nf는 반올림(Ns/Nw)으로 제공될 수 있다. <표 1>에서 동형 덧셈은 9 행에서 Ns번 수행될 수 있다. 모든 Nw 동형 연산에 대해 중간 결과가 얻어질 수 있다.Nw represents the number of isomorphic operations that can be performed without decoding errors. Then nf can be given as rounded (Ns /Nw ). In <Table 1>, homomorphic addition can be performed Ns times in row 9. Intermediate results can be obtained for all Nw isomorphic operations.
동형 덧셈 및 곱셈 Bmul 및 Bmul에 대한 누적 오차의 상한을 사용하여 Nw 동형 덧셈에 대한 누적 오차의 상한은 NwBmul로 제공될 수 있다. 이는, 동형 덧셈이 알고리즘 1의 7 행에 있는 동형 곱셈의 결과를 사용하여 Nw번 수행되기 때문일 수 있다.The upper bound of the cumulative error for isomorphic addition and multiplication Bmul and Bmul is Nw with the upper bound of the cumulative error for isomorphic addition is Nw It can be provided as Bmul . This may be because the isomorphic addition is performed Nw times using the result of the isomorphic multiplication in line 7 of
복호화 오류 없이 동형 연산을 수행하려면 누적 오류의 상한이 시스템이 수용할 수 있는 오류 범위보다 작아야 할 수 있다.In order to perform isomorphic operations without decoding errors, the upper bound of the cumulative error may need to be less than the error range that the system can accept.
시스템이 수용할 수 있는 오차 범위는 10g일 수 있다. 그런 다음 Nw의 값은 하기 <수학식 11>과 같이 부등식을 충족하는 최대 값으로 결정될 수 있다.The error range that the system can accept may be 10g . Then, the value of Nw may be determined as the maximum value that satisfies the inequality as shown in Equation 11 below.
<수학식 11>에서 가장 큰 Nw 값을 사용하여 긴 일련의 동형 연산이 nf 조각으로 나뉠 수 있다. 클라우드 서버(120)는 분할된 동형 연산 조각을 사용하여 중간 결과 nf를 계산하여 사용자 단말(130)에게 보낼 수 있다.A long series of isomorphic operations using the largest Nw value in Equation 11 can be divided into nf fragments. The
중간 결과를 받은 후 사용자 단말(130)은 암호 복호화 오류 없이 결과를 복호화할 수 있다. 그런 다음 사용자 단말(130)은 복호화된 중간 결과를 추가하여 원래 전체 동형 연산의 결과를 얻을 수 있다.After receiving the intermediate result, the
사용자 단말(130)은 조작 횟수에 관계없이 복호화 오류 없이 원하는 결과를 얻을 수 있다.The
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 Q-함수 업데이트의 예를 도시한 도면이다.4 is a diagram illustrating an example of Q-function update according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 4를 참고하면, 암호화된 상태 및 행동 값으로 클라우드 서버(120)의 Q-테이블 업데이트의 예를 확인할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 4 , an example of updating the Q-table of the
프라이버시 보호를 위해 상태 및 행동 값이 암호화되고 클라우드 서버(120)가 복호화하지 않는 경우 클라우드 서버(120)에 대한 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘을 확인할 수 있다.When state and action values are encrypted for privacy protection and the
<표 1>에서 사용자 단말(130)은 <수학식 1>의 표준 Q 함수에 따라 최대 Q-값과 리워드 값을 사용하여 업데이트된 Q-값 Qu를 계산할 수 있다. 사용자 단말(130)이 계산한 Q-값은 클라우드 서버(120)가 관리하는 Q-테이블에서 업데이트할 수 있다.In <Table 1>, the
그러나 클라우드 서버(120)가 Q-테이블의 어떤 요소를 업데이트해야 하는지 알 수 있다면 사용자 단말(130)의 상태와 행동에 대한 정보가 클라우드 서버(120)에 노출될 수 있다.However, if the
문제는 Q-테이블의 NsNa 요소 중 어느 것이 업데이트되는지 클라우드 서버(120)에게 알리지 않고 암호문만 사용하여 이전 Q-값을 새로운 Q-값으로 대체하는 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘이 요구될 수 있다. 본 발명에 따라 제안된 PPRL에서 사용자 단말(130)은 다음과 같은 암호화된 값을 클라우드 서버(120)로 보낼 수 있다.The problem is that the Ns of the Q-table A Q-table update algorithm may be required that replaces old Q-values with new Q-values using only ciphertext without telling the
1)-업데이트할 암호화된 Q-값.One) -Encrypted Q-value to update.
2)-행동을 나타내는 암호화된 이진 벡터.2) - An encrypted binary vector representing an action.
3)-상태를 나타내는 암호화된 이진 벡터.3) - An encrypted binary vector representing the state.
여기서, 행동 a*t는 (V-A)의 상태 Vt에 대해 수행된 것처럼로 인코딩될 수 있다. 시간 t에서 i번째 행동이 선택되면 Wt의 i번째 요소는 1로 설정되고 다른 모든 요소는 0으로 설정될 수 있다.where action a*t is performed for state Vt of (VA) as can be encoded as At time t, when the i-th action is selected, the i-th element of Wt may be set to 1 and all other elements set to 0.
Wt의 (Na-1) 요소가 0이더라도 0에 대한 암호문은 동일하지 않으므로 클라우드 서버(120)는 Na 행동 중 어떤 행동이 선택되었는지 인식할 수 없다.Even if the (Na -1) element of Wt is 0, since the ciphertext for 0 is not the same, the
이진 벡터의 모든 요소는 <수학식 7>을 사용하여 암호화될 수 있다. (V-C1)을 사용하여 하기 <수학식 12>와 같이 클라우드 서버(120)에 대한 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘이 제안될 수 있다.All elements of the binary vector can be encoded using Equation 7. A Q-table update algorithm for the
곱셈 vitwjt는 Qi,j의 위치가 업데이트할 위치와 같을 경우에만 1이 될 수 있다. 각 이진 벡터의 한 요소만 1로 표시되기 때문일 수 있다. 다른 경우에는 곱셈 결과가 0이 될 수 있다.multiplication vit wjt can be 1 only when the position of Qi,j is the same as the position to be updated. This could be because only one element of each binary vector is marked as 1. In other cases, the multiplication result may be zero.
따라서 이진 벡터의 요소를 사용하면 클라우드 서버(120)는 <수학식 12>의 동형 산술 연산을 사용하여 Q-테이블의 특정 위치를 알지 않고도 Q-테이블을 업데이트할 수 있다.Accordingly, when elements of the binary vector are used, the
예를 들어, 도 4를 참고하면, st=s2t, at=a2t, Ns=2 및 Na=2에 대한 업데이트 절차의 예를 확인할 수 있다.For example, referring to FIG. 4 , examples of update procedures for st =s2t , at =a2t , Ns =2 and Na =2 can be seen.
<수학식 12>의 동형 연산 후 Q-값 Q2,2가 Qu로 업데이트되고, Q-테이블의 나머지 값은 변경되지 않은 상태로 유지될 수 있다. v2t 및 w2t의 동형 곱셈만 도 4와 같이 1이기 때문일 수 있다.After the isomorphic operation of <Equation 12>, the Q-value Q2,2 is updated to Qu, and the remaining values of the Q-table may remain unchanged. This may be because only the isomorphic multiplication of v2t and w2t is 1 as shown in FIG. 4 .
하기 <표 2>를 참고하면, 본 발명에 따라 제안된 보안 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 절차를 확인할 수 있다.Referring to Table 2 below, the procedure of the secure Q-table update algorithm proposed according to the present invention can be confirmed.
2: (@User) Calculate,
3:.
4: if and are not empty then
5: (@User)
6: (@User)
7: (@User) Double-encrypt Qu and Wt.
8: (@User) Send to the CP.
9: (@CP) Decrypts the values using the private key.
10: for do
11: for do
12: (@CP)
13:
14: end for
15: end for
16: (@CP)
17: else
18: (@User)
19: (@User) Double-encrypt Wt and send
20: (@CP) Decrypts the value using the private key.
21: (@CP)
22: end if
23: Output: Updated Q-table.1: Input: .
2: (@User) Calculate ,
3: .
4: if and are not empty then
5: (@User)
6: (@User)
7: (@User) Double-encrypt Qu and Wt .
8: (@User) Send to the CP.
9: (@CP) Decrypts the values using the private key.
10: for do
11: for do
12: (@CP)
13:
14: end for
15: end for
16: (@CP)
17: else
18: (@User)
19: (@User) Double-encrypt Wt and send
20: (@CP) Decrypts the value using the private key.
21: (@CP)
22: end if
23: Output: Updated Q-table.
<표 2>에 대한 입력은 학습률, 할인 계수, 환경 rt의 리워드, 알고리즘 1 Q*s로 얻은 최대 Q 값, 이진 벡터일 수 있다.The input for <Table 2> is the learning rate , the discount coefficient , the reward of the environment rt, the maximum Q value obtained by Algorithm 1 Q*s , the binary vector can be
사용자 단말(130)은 새로 업데이트된 Q-값을 얻기 위해 부동 소수점 숫자와를 사용하여 2-3 행의 곱셈을 계산할 수 있다. 첫 번째 반복에서 및는 다음 업데이트 반복을 위해 18 행에 저장될 수 있다.The
반면, 사용자 단말(130)은 Q-테이블을 업데이트하기 위해 이전 반복에서 저장한와를 사용하여 업데이트된 Q-값 Qu를 계산하고 현재 정보 및는 5-6 행에 표시된 대로 다음 업데이트 반복을 위해 저장될 수 있다.On the other hand, the
사용자 단말(130)은 HE 함수 <수학식 3>으로 업데이트된 Q-값 Qu를 암호화하고 HE 함수 <수학식 7>로 이진 벡터 Wt를 암호화할 수 있다.The
그런 다음 사용자 단말(130)은 클라우드 서버(120)의 RSA 공개키를 사용하여 암호문 및를 암호화하여 클라우드 서버(120)로 보낼 수 있다. 첫 번째 반복에서 사용자 단말(130)은 이진 벡터 Wt만 암호화하여 19 행의 클라우드 서버(120)로 보낼 수 있다.Then, the
사용자 단말(130)이 보낸 암호화된 값을 수신 한 후 클라우드 서버(120)는 9 행과 20 행에서 자체 RSA 개인키를 사용하여 복호화할 수 있다. 첫 번째 반복의 경우 이진 벡터만 21 행에 저장될 수 있다.After receiving the encrypted value sent by the
그렇지 않으면, 클라우드 서버(120)는 Q-테이블을 업데이트하기 위해 동형 산술 연산을 수행한 다음는 10-16 행에 표시된 대로 저장될 수 있다.Otherwise, the
<표 1>을 참고하면,에 대해 이전에 보낸 상태를 나타내는 이진 벡터는 사용자 단말(130)에 의해 이전에 송신된 행동을 나타내는 이진 벡터로 업데이트할 위치를 찾는데 사용될 수 있다.Referring to <Table 1>, The binary vector representing the previously sent state for is the
따라서 12-13 행에서 <수학식 12>를 사용하여 암호문만 사용하여 암호화된 Q-테이블을 성공적으로 업데이트할 수 있다.Therefore, the encrypted Q-table can be successfully updated using only the ciphertext using <Equation 12> in lines 12-13.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 동형 산술 연산에 의한 복호화 오류 성능 그래프를 도시한 도면이다.5 is a diagram illustrating a decoding error performance graph by an isomorphic arithmetic operation according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 5를 참고하면, 본 발명에 따른 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 오류 분석을 확인할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 5 , error analysis of the Q-table update algorithm according to the present invention can be confirmed.
본 발명에 따라 제안된 방식에서는 FHE에 LWE-기반 암호화 시스템을 사용할 수 있다. 암호화 시스템의 보안 수준을 높이기 위해 주입된 랜덤 오류가 복호화 없이 연속적인 동형 연산을 수행한 후 누적되기 때문에 연속적인 동형 연산이 증가함에 따라 LWE-기반 암호화 시스템에서 복호화 오류 확률이 증가할 수 있다.In the scheme proposed according to the present invention, an LWE-based encryption system can be used for FHE. Since the random error injected to increase the security level of the encryption system is accumulated after performing consecutive homomorphic operations without decryption, the probability of decryption error in the LWE-based encryption system may increase as the number of consecutive homomorphic operations increases.
기존 체계에서는 부트 스트래핑 알고리즘을 사용하여 오류 증가를 억제할 수 있다. 그러나 알고리즘은 계산 복잡도가 높고 오류가 일정 수준 이상 누적될 때마다 주기적으로 실행되어야 할 수 있다.In existing schemes, bootstrapping algorithms can be used to suppress error growth. However, the algorithm has high computational complexity and may need to be executed periodically whenever errors accumulate above a certain level.
본 발명에 따라 제안된 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘은 부트 스트래핑 알고리즘 없이 오류 증가를 제어할 수 있다. 이는 암호화된 Q 값을 업데이트하는 반복 횟수가 계속 증가하더라도 오류의 크기가 수렴하기 때문일 수 있다.The Q-table update algorithm proposed according to the present invention can control error increase without a bootstrapping algorithm. This may be because the size of the error converges even if the number of iterations for updating the encrypted Q value continues to increase.
일 실시예에서, 누적 오류는 <수학식 12>를 사용하여 암호화된 Q-값을 업데이트하는 반복 횟수가 증가함에 따라 수렴할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the cumulative error may converge as the number of repetitions of updating the encrypted Q-value using Equation 12 increases.
일 실시예에서, 누적된 오차의 수렴을 증명하기 위해 클라우드 서버(120) 측에서 Q-테이블을 업데이트하는 반복 횟수가 증가함에 따라 오차가 어떻게 변하는지 분석할 수 있다. 여기서,는 <수학식 12>의 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘에 대한 오류 변경을 나타낼 수 있다. 이 경우,는 하기 <수학식 13>과 같이 나타낼 수 있다.In one embodiment, in order to prove the convergence of the accumulated errors, it is possible to analyze how the errors change as the number of iterations for updating the Q-table increases on the
여기서, ef와 eu는 각각 이전 Q-값과 업데이트된 Q-값에 대해 <수학식 3>을 사용하여 HE 함수에 주입된 오류이고, ekv 및 ekw는 상태와 행동을 각각 나타내는 이진 벡터에 대한 <수학식 7>을 사용하여 HE 함수에 주입된 오류 벡터의 k번째 요소이고, cku, ckwu, ckf 및 ckwf는 및의 k번째 요소이고, Q는를 나타낸다.Here, ef and eu are errors injected into the HE
일 실시예에서, 하기 <표 3>에는 및의 네 가지 경우가 있을 수 있다.In one embodiment, in Table 3 below and There can be four cases of
<표 3>에 나와 있는 것처럼 및의 합은 반복 횟수가 충분히 증가함에 따라 0으로 수렴할 수 있다.As shown in <Table 3> and The sum of can converge to 0 as the number of iterations increases sufficiently.
분해된 벡터의 요소는 0에서 9까지의 정수 값 범위에 있고 <수학식 8>과 같이 균일 한 분포를 따르며 오류 ekv 및 ekw는 동일한 균일 분포에서 샘플링될 수 있다.Elements of the decomposed vector are in the range of integer values from 0 to 9 and follow a uniform distribution as shown in
그러면 오류 변화는 간단히로 나타낼 수 있다.then change the error is simply can be expressed as
elu와 elf는 각각 l번째 반복에서 업데이트된 Q-값과 이전 Q-값의 오류를 나타낼 수 있다.=1 및=1인 경우,는와 동일하기 때문에, l번째 반복에서의 오류 변화는로 표현될 수 있다.elu and elf may indicate the error of the updated Q-value and the previous Q-value in the lth iteration, respectively. =1 and =1, Is Since is equal to , the error change at the lth iteration is can be expressed as
즉, 오차 변화의 합은로 나타낼 수 있다. 따라서는 및의 모든 경우에 대해 수렴하므로 <수학식 12>를 사용하여 암호 복호화없이 암호화된 Q-값을 업데이트하는 반복 횟수가 증가하더라도 오류가 누적되지 않을 수 있다.That is, the error change is the sum of can be expressed as thus Is and Since it converges in all cases of Equation 12, errors may not accumulate even if the number of iterations for updating the encrypted Q-value without encryption/decryption increases.
일 실시예에서, 도 5를 참고하면, 암호화된 Q 값을 업데이트하기 위한 반복 횟수와 관련하여 <수학식 12>의 동형 산술 연산으로 인해 발생하는 암호 복호화 오류를 확인할 수 있다.In one embodiment, referring to FIG. 5 , an encryption/decryption error occurring due to the isomorphic arithmetic operation of <Equation 12> in relation to the number of iterations for updating the encrypted Q value can be confirmed.
이 경우, 상태와 행동의 수는 각각 12와 4이고 d는 3으로 설정될 수 있다. 다른 매개 변수는 도 3의 환경에서와 동일할 수 있다.In this case, the number of states and actions are 12 and 4, respectively, and d can be set to 3. Other parameters may be the same as in the environment of FIG. 3 .
도 5의 복호화 오류는 Q-테이블 업데이트를 위한 반복 횟수가 증가하더라도 0.001 이상으로 증가하지 않고 0에서 0.001 사이에서 변동할 수 있다.The decoding error of FIG. 5 may fluctuate between 0 and 0.001 without increasing to 0.001 or more even if the number of iterations for updating the Q-table increases.
그 결과, <수학식 12>에서 복호화없이 연속적인 동형 산술 연산 횟수가 증가하더라도 본 발명에 따라 제안된 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘에서 누적 오차는 계속 증가하지 않을 수 있다.As a result, even if the number of consecutive isomorphic arithmetic operations increases without decoding in Equation 12, the cumulative error may not continue to increase in the Q-table update algorithm proposed according to the present invention.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 이진 벡터의 차연 감소를 도시한 도면이다.6 is a diagram illustrating difference reduction of binary vectors according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 6을 참고하면, 임의 선택 방법을 사용하여 상태 및 행동 표현에 대한 이진 벡터의 차원 감소를 확인할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 6 , it is possible to confirm the dimensionality reduction of binary vectors for state and action expressions using a random selection method.
본 발명에 따라 제안된 PPRL 알고리즘에서는 주어진 환경에 따라 상태와 행동의 수를 결정할 수 있다. 상태 및 행동의 수가 매우 많으면 상태 및 행동의 교환으로 인해 클라우드 서버(120)와 사용자 단말(130)간에 상당한 통신 오버 헤드가 발생할 수 있다.In the PPRL algorithm proposed according to the present invention, the number of states and actions can be determined according to a given environment. If the number of states and actions is very large, significant communication overhead may occur between the
사용자 단말(130)이 상태 및 행동에 대해 전송하는 이진 벡터에는 상태 및 행동을 나타내는 이진 벡터의 모든 요소가 하나의 요소를 제외하고 0의 값을 갖기 때문에 많은 중복 정보가 포함될 수 있다.The binary vector transmitted by the
상태 및 행동의 수가 많을 때 이진 벡터는 통신 오버 헤드를 줄이기 위해 중복 정보가 적은 축소 형식으로 표시될 수 있다. 사용자 단말(130)은 전체 이진 벡터를 보내는 대신 이진 벡터의 Ns 요소 중 '1' 요소를 포함하는 Nrs 요소를 무작위로 선택하고 인덱스와 함께 Nrs 요소를 보낼 수 있다.When the number of states and actions is large, binary vectors can be represented in a reduced form with less redundant information to reduce communication overhead. Insteadof sending the entire binary vector, the
그러면 클라우드 서버(120)는 선택한 상태 또는 행동이 Nrs 요소 중 하나임을 알고 있지만 정확히 선택된 상태 또는 행동을 지정할 수는 없을 수 있다.Then, the
사용자 단말(130)이 Nrs 요소를 보낼 때 하나의 0 요소를 보내야 하며 클라우드 서버(120)는 수신되지 않은 다른 요소 (Ns-Nrs)에 대해을 사용할 수 있다.When the
도 6을 참고하면, 사용자 단말(130)이 상태 표현을 위한 이진 벡터를 클라우드 서버(120)에 전송할 때 통신 오버 헤드를 줄이는 절차를 확인할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 6 , a procedure for reducing communication overhead when the
① 과정에서, 이진 벡터 대신 사용자 단말(130)이 해당 인덱스를 나타내는 벡터와 이진 벡터의 Ns 요소 중 Nrs 요소를 선택하여 벡터를 생성할 수 있다. 여기서 ‘1’의 요소는 Vr에 포함될 수 있다.① In the process, the binary vector Instead, the
② 과정에서, 사용자 단말(130)은 <수학식 7>에서 HE 함수를 사용하여 Vr을 암호화하고, 클라우드 서버(120)에 대한 RSA 공개키로 및 VL을 다시 암호화한 다음, 클라우드 서버(120)에게 RSA 암호화 벡터 및를 송신할 수 있다.② In the process, the
③ 과정에서, 암호화된 벡터를 수신한 후, 클라우드 서버(120)는 자신의 RSA 개인키를 사용하여 이를 복호화할 수 있다. 사용자 단말(130)이 보낸 요소의 수가 줄어들더라도 클라우드 서버(120)는 각 요소의 암호문이 동일하지 않기 때문에 Nrs 요소 중 어떤 상태가 선택되었는지 인식할 수 없을 수 있다.In
또한, 클라우드 서버(120)는 VL에 저장된 인덱스 번호를 사용하여 Vt의 적절한 위치에 Vr의 요소를 배치하고 Vt의 나머지 위치를으로 채울 수 있다.In addition, the
사용자 단말(130)이 상태 표현을 위해 암호화된 이진 벡터를 보낼 때 전송할 요소의 수가 Ns에서 (2Nrs+1)로 줄어들 수 있다.When the
따라서 상태 수가 매우 많더라도 이진 벡터의 차원을 조정하여 통신 오버 헤드를 일정 수준 이하로 억제할 수 있다.Therefore, even if the number of states is very large, the communication overhead can be suppressed below a certain level by adjusting the dimension of the binary vector.
일 실시예에서, 오버 헤드 분석 관련하여, 컴퓨팅 및 통신 오버 헤드 측면에서 제안된 개인 정보 보호 Q-학습 알고리즘의 이론적 분석을 확인할 수 있다.In one embodiment, with respect to overhead analysis, we can confirm the theoretical analysis of the proposed privacy Q-learning algorithm in terms of computing and communication overhead.
컴퓨팅 오버 헤드 측면에서, 본 발명에 따른 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘은 이론적으로 계산 복잡성 측면에서 분석될 수 있다. 본 발명에 따라 제안된 알고리즘의 계산 복잡성은 LWE-기반 암호화 시스템의 매개 변수뿐만 아니라 상태 및 행동의 수에 의해 영향을 받을 수 있다.In terms of computing overhead, the SCC-PPRL algorithm according to the present invention can be theoretically analyzed in terms of computational complexity. The computational complexity of the proposed algorithm according to the present invention can be influenced by the number of states and actions as well as the parameters of the LWE-based cryptographic system.
p는 일반 텍스트 집합의 카디널리티, L은 보안 수준을 향상시키기 위해 암호문에 주입되는 임의 오류의 제한을 나타내는 매개 변수이며, N은 암호문의 벡터 크기일 수 있다.p is the cardinality of the plaintext set, L is a parameter indicating the limit of random errors injected into the ciphertext to improve the security level, and N can be the vector size of the ciphertext.
또한, 본 발명에 따라 제안된 알고리즘에는 DE 방식에 대한 RSA 알고리즘이 포함될 수 있다. RSA 암호화 및 암호 복호화의 계산 복잡성은 RSA 공개키 및 개인키의 크기에 영향을 받을 수 있다.Also, the proposed algorithm according to the present invention may include the RSA algorithm for the DE scheme. The computational complexity of RSA encryption and decryption may be affected by the size of the RSA public and private keys.
일 실시예에서, Rn은 두 개의 큰 소수의 곱을 나타낼 수 있다. RSA 알고리즘의 키 생성 절차에 따라 RSA 공개키와 개인키에 대해 각각 및을 사용하여 정수 Re 및 Rd를 결정할 수 있으며, RSA 공개키와 RSA 개인키는 (Rn, Re) 및 (Rn, Rd)에 의해 나타낼 수 있다.In one embodiment, Rn is two large prime numbers can represent the product of According to the key generation procedure of the RSA algorithm, each of the RSA public key and private key and The integers Re and Rd can be determined using , and the RSA public key and RSA private key can be represented by (Rn , Re ) and (Rn , Rd ).
RSA 암호화 및 복호화의 계산 복잡성은 각각 및로 나타낼 수 있다. RSA 암호화 및 복호화의 지수화 연산에는 각각 Re 및 Rd 곱셈이 필요하기 때문일 수 있다.The computational complexity of RSA encryption and decryption is respectively and can be expressed as This may be because the exponentiation operation of RSA encryption and decryption requires multiplication of Re and Rd , respectively.
사용자 단말(130)과 클라우드 서버(120)에서 각각 보안 행동 선택 알고리즘과 보안 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 계산 복잡성을 분석할 수 있다.Computational complexity of the secure action selection algorithm and the secure Q-table update algorithm may be analyzed in the
일 실시예에서, 하기 <표 4>를 참고하면, 각각 사용자 단말(130) 및 클라우드 서버(120)에 대한 보안 행동 선택 알고리즘 및 보안 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 계산 복잡성을 확인할 수 있다.In one embodiment, referring to Table 4 below, calculation complexity of a security action selection algorithm and a security Q-table update algorithm for the
1) 사용자 단말(130) 측 행동 선택 알고리즘의 오버 헤드 측면에서, 보안 행동 선택 알고리즘을 위해서는 HE와 RSA 알고리즘을 이용한 DE 방식과 사용자 단말(130) 측에서 최대 값을 찾는 함수가 필요할 수 있다.1) In terms of the overhead of the action selection algorithm on the
<수학식 7>을 사용하는 HE 함수의 계산 복잡도는 mi와 R 간의 곱셈의 계산 복잡도와 HE 함수 <수학식 3>을 사용하여 제로 벡터를 암호화하는 계산 복잡도 때문에 <수학식 7>과 같이 둘 다로 주어질 수 있다.The computational complexity of the HE function using <Equation 7> is divided into two as in <Equation 7> due to the computational complexity of multiplying mi and R and the computational complexity of encrypting the zero vector using the HE function <
또한 동형 복호화 함수와 행동 선택을 위한 최대 값을 찾는 함수의 계산 복잡도는 각각와일 수 있다.In addition, the computational complexity of the homomorphic decoding function and the function for finding the maximum value for action selection are respectively and can be
<수학식 7>을 사용하는 HE 함수는 Ns번 실행되고, 동형 복호화 함수는 Na번 실행되고, 최대 값을 찾는 함수는 한 번 실행되며, DE 체계에 대한 RSA 암호화 및 복호화 함수가 사용자 단말(130) 측에서 각각번과번 실행될 수 있다.The HE function using <Equation 7> is executed Ns times, the homomorphic decryption function is executed Na times, the function to find the maximum value is executed once, and the RSA encryption and decryption function for the DE scheme is executed at the user terminal ( 130) from each side Bun and can be executed once.
따라서 사용자 단말(130)에 대한 보안 행동 선택 알고리즘의 계산 복잡도는로 제공될 수 있다.Therefore, the computational complexity of the security action selection algorithm for the
2) 클라우드 서버(120) 측 행동 선택 알고리즘의 오버 헤드 측면에서, 클라우드 서버(120) 측에서 보안 행동 선택 알고리즘을 수행하려면 동형 곱셈, 동형 덧셈, RSA 암호화 및 복호화 작업이 필요할 수 있다.2) In terms of the overhead of the action selection algorithm on the
동형 곱셈의 계산 복잡도는로 나타낼 수 있다. 이는 <수학식 9>와 같이 분해 함수 <수학식 8>의 계산 복잡도와 분해된 벡터와 <수학식 7>로 암호화된 암호문 간의 행렬 곱셈이 각각 및이기 때문일 수 있다.The computational complexity of homomorphic multiplication is can be expressed as As shown in <Equation 9>, the calculation complexity of the decomposition function <
동형 덧셈의 계산 복잡도는 <수학식 5>에서에 의해 제공될 수 있다. 따라서 동형 곱셈과 동형 덧셈이회 수행되고, RSA 암호화 및 복호화가 각각 및 회 수행되기 때문에 클라우드 서버(120) 측 보안 행동 선택 알고리즘의 계산 복잡도는로 주어질 수 있다.The computational complexity of homomorphic addition is can be provided by So, isomorphic multiplication and isomorphic addition It is performed twice, and RSA encryption and decryption are performed respectively. and Since it is performed twice, the computational complexity of the security action selection algorithm on the
3) 사용자 단말(130) 측 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘 오버 헤드 측면에서, 보안 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 구현을 위해 사용자 단말(130) 측의 계산 복잡성은로 제공될 수 있다. 이는 <수학식 7>과 <수학식 3>을 사용한 HE 함수가 각각 Na번과 1번 수행되고 RSA 암호화 함수가번 수행되기 때문일 수 있다.3) In terms of the overhead of the Q-table update algorithm on the
4) 클라우드 서버(120) 측 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘 오버 헤드 측면에서, 클라우드 서버(120) 측 보안 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 계산 복잡도는일 수 있다. 동형 곱셈과 동형 덧셈이 각각 4NsNa 및 2NsNa번 수행되기 때문일 수 있다. RSA 알고리즘의 복호화 함수는회 수행될 수 있다.4) In terms of the cloud server 120-side Q-table update algorithm overhead, the computational complexity of the cloud server 120-side security Q-table update algorithm is can be This may be because isomorphic multiplication and isomorphic addition are performed 4Ns Na and 2Ns Na times, respectively. The decryption function of the RSA algorithm is can be performed twice.
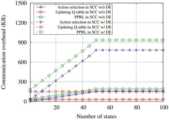
일 실시예에서, 통신 오버 헤드 관련하여, 사용자 단말(130)의 개인 정보 보호를 위해 본 발명에 따라 제안된 알고리즘에서는 LWE-기반의 FHE 알고리즘과 RSA 알고리즘을 활용할 수 있다.In one embodiment, in relation to communication overhead, the LWE-based FHE algorithm and the RSA algorithm may be utilized in the algorithm proposed according to the present invention to protect personal information of the
LWE-기반 FHE 체계에서 암호화된 값은 행렬 형식을 가지며 해당 행렬의 각 요소는 반올림 (logq/log2) 비트일 수 있다. 보안 행동 선택 알고리즘의 경우 사용자 단말(130)은 크기의 Ns 행렬을 전송하여 상태 정보를 나타내고 크기의 Na 행렬을 수신하여 행동을 선택할 수 있다.In the LWE-based FHE scheme, an encrypted value has a matrix format, and each element of the matrix may be a rounded (logq/log2) bit. In the case of the security action selection algorithm, the
파티션 수 nf는 반올림 (Ns/Nw)으로 구할 수 있다. 보안 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘을 위해 사용자 단말(130)은 크기의 Na 행렬과 크기의 행렬을 클라우드 서버(120)로 보낼 수 있다.The number of partitions nf can be obtained by rounding up (Ns/Nw). For the secure Q-table update algorithm, the
따라서 통신 오버 헤드는 LWE-기반 암호화 시스템의 매개 변수, 상태 수 및 행동 수의 영향을 받을 수 있다.Therefore, the communication overhead can be affected by the number of parameters, number of states and number of actions in the LWE-based cryptosystem.
또한, HE 함수로 암호화된 값을 DE 방식의 RSA 암호화 알고리즘으로 다시 암호화하면 각 행렬의 요소는 Rn 비트가 될 수 있다.In addition, if the value encrypted by the HE function is re-encrypted by the DE-type RSA encryption algorithm, each element of the matrix may be Rn bits.
따라서, 행렬의 모든 요소를 이중 암호화하는 FDE(Full Double Encryption) 방식은 Rn이 반올림 (logq/log2)보다 훨씬 클 경우 통신 오버 헤드를 크게 증가시킬 수 있다.Therefore, the Full Double Encryption (FDE) method of double-encrypting all elements of a matrix can significantly increase communication overhead when Rn is much larger than rounding (logq/log2).
그러나 RSA 알고리즘으로 매트릭스의 일부 요소만 암호화하더라도 HE 알고리즘으로 암호화된 값을 복호화하기 위해서는 매트릭스의 모든 값이 필요하기 때문에 본 발명에 따른 방법의 보안 수준은 여전히 충분히 높을 수 있다.However, even if only some elements of the matrix are encrypted by the RSA algorithm, the security level of the method according to the present invention can still be sufficiently high because all the values of the matrix are required to decrypt the values encrypted by the HE algorithm.
따라서 DE 방식의 통신 오버 헤드를 줄이기 위해 FDE 방식을 적용하는 대신 매트릭스의 일부 요소만 암호화하여 구현할 수 있다. 상태 및 행동의 수는 주어진 환경에 의해 결정되며 암호화 시스템의 매개 변수는 시스템 구성 프로세스에서 선택될 수 있다.Therefore, instead of applying the FDE method to reduce the communication overhead of the DE method, only some elements of the matrix can be encrypted and implemented. The number of states and actions is determined by the given environment, and the parameters of the cryptographic system can be selected in the system configuration process.
따라서 주어진 환경의 복잡성으로 인해 상태 및 행동의 수가 매우 많은 경우 통신 오버 헤드가 크게 증가할 수 있다.Therefore, communication overhead can increase significantly if the number of states and actions is very large due to the complexity of a given environment.
임의 선택 방법으로 이진 벡터의 차원을 줄이면 사용자 단말(130)과 클라우드 서버(120)간에 교환되는 중복 데이터가 줄어들 기 때문에 통신 오버 헤드를 줄일 수 있다.When the dimension of the binary vector is reduced by the random selection method, redundant data exchanged between the
사용자 단말(130)이 암호화된 상태 정보를 보낼 때, 제안된 방식을 채택하면 통신 오버 헤드가에서로 감소될 수 있다.When the
따라서 Ns보다 훨씬 적은 수로 Nrs를 선택할 수 있으므로 통신 오버 헤드를 크게 줄일 수 있다.Therefore, since Nrs can be selected with a much smaller number than Ns , the communication overhead can be greatly reduced.
도 7은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 프로즌 레이크(frozen lake) 환경의 예를 도시한 도면이다.7 is a diagram illustrating an example of a frozen lake environment according to an embodiment of the present invention.
클라우드 컴퓨팅 환경에서 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘의 타당성을 확인하기 위해 본 발명에 따라 제안된 프라이버시 보호 Q-학습을 간단한 프로즌 레이크 문제에 적용할 수 있다.In order to verify the validity of the SCC-PPRL algorithm in a cloud computing environment, the privacy-preserving Q-learning proposed according to the present invention can be applied to a simple frozen lake problem.
도 7을 참고하면, 프로즌 레이크 환경의 예를 확인할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 7 , an example of a frozen lake environment can be confirmed.
여기서, S는 에이전트의 시작점을 나타내고, G는 목표를 나타낼 수 있다. 흰색과 회색 상자는 각각 안전한 표면과 구멍을 나타낼 수 있다.Here, S represents the starting point of the agent, and G may represent the goal. White and gray boxes can represent safe surfaces and holes, respectively.
에이전트가 홀에 도달하면 에이전트는 미션을 실패하고 시작 지점으로 돌아 가야할 수 있다. 에이전트는 Q-학습 알고리즘을 통해 허점을 피하여 목표에 도달하기 위한 최적의 경로를 찾을 수 있다.If the agent reaches the hall, the agent may fail the mission and have to return to the starting point. The agent can find the optimal path to reach the goal by avoiding loopholes through the Q-learning algorithm.
도 8의 결과를 얻기 위한 프로즌 레이크 시뮬레이션 환경 구성은 LWE 암호 시스템 p, L, r 및 N의 매개 변수는 각각,, 10 및 4일 수 있다.In the configuration of the Frozen Lake simulation environment for obtaining the result of FIG. 8, the parameters of the LWE cryptosystem p, L, r and N are respectively , , 10 and 4.
이 시뮬레이션 환경에서 할인 계수와 학습률는 각각 0.9와 0.1이고-그리디(greedy) 정책에 대한는 0.1일 수 있다. 행동의 수는 4로 설정될 수 있다.Discount factor in this simulation environment and learning rate are 0.9 and 0.1, respectively. - Regarding the greedy policy may be 0.1. The number of actions can be set to 4.
도 8은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 개인정보 Q-학습의 성공률 그래프를 도시한 도면이다.8 is a graph showing a success rate of personal information Q-learning according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 8을 참고하면, 에피소드 수와 관련하여 프로즌 레이크 환경에서 서로 다른 수의 상태에 대해 제안된 SCC-PPRL 방식의 성공률을 확인할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 8 , it is possible to confirm the success rate of the proposed SCC-PPRL method for different numbers of states in a Frozen Lake environment in relation to the number of episodes.
상태의 수가 증가함에 따라 문제의 복잡성이 증가하기 때문에 도 8과 같이 수렴 속도가 감소할 수 있다. 시뮬레이션의 세 가지 경우 모두 40개 에피소드 이전에 0.9 이상의 성공률을 보였으며 속도는 다음과 같이 거의 1로 수렴될 수 있다. 에피소드 수가 증가할 수 있다.Since the complexity of the problem increases as the number of states increases, the convergence speed may decrease as shown in FIG. 8 . All three cases of the simulation showed a success rate of 0.9 or higher before 40 episodes, and the rate can converge to almost 1 as follows. The number of episodes may increase.
이것은 사용자 단말(130)이 클라우드 서버(120)에 암호문만 제공하더라도 제안된 개인 정보 보호 Q-학습 알고리즘이 성공적으로 작동함을 확인할 수 있다. 따라서 사용자 단말(130)은 개인 정보 유출 없이 클라우드 서버(120)로부터 RL 기반 서비스를 받을 수 있다.This confirms that the proposed personal information protection Q-learning algorithm works successfully even if the
일 실시예에서, 개인 정보 보호 Q-학습의 오버 헤드 관련하여, 본 발명에 따라 제안된 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘의 효과는 계산 및 통신 오버 헤드 측면에서 SMC (Secure Multiparty Computation) 기반 알고리즘과 비교하여 검증될 수 있다.In one embodiment, with respect to the overhead of privacy Q-learning, the effectiveness of the SCC-PPRL algorithm proposed according to the present invention can be verified compared to Secure Multiparty Computation (SMC) based algorithms in terms of computational and communication overhead. can
SMC 기반 PPRL 알고리즘의 AHE (Additive Homomorphic Encryption) 방식을 사용하는 분산 공개키 암호 시스템에서는 키 크기를 1024 비트로 선택하고 클라우드 컴퓨팅 기반 서비스 공급자는 시뮬레이션 환경에서 분산 암호화 시스템을 위한 하나의 클라우드 서버(120)와 하나의 HSP(health service provider)로 구성될 수 있다.In the distributed public key cryptosystem using the AHE (Additive Homomorphic Encryption) method of the SMC-based PPRL algorithm, the key size is selected as 1024 bits, and the cloud computing-based service provider provides one cloud server (120) and one cloud server (120) for the distributed encryption system in a simulation environment. It may consist of one health service provider (HSP).
개인키는 두 개의 부분 개인키로 분할될 수 있다. 그런 다음 클라우드 서버(120)에는 부분 개인키가 있고, HSP에는 나머지 부분 개인키가 있다.A private key can be split into two partial private keys. Then, the
반면, 본 발명에 따라 제안된 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘에 DE 기법을 사용하는 암호 시스템에서는 RSA 알고리즘에 사용되는 키 크기를 1024 비트로 선택하고 LWE-기반 FHE 기법 p, L, r, N은,, 10 및 10으로 선택될 수 있다.On the other hand, in the encryption system using the DE technique for the SCC-PPRL algorithm proposed according to the present invention, the key size used in the RSA algorithm is selected as 1024 bits, and the LWE-based FHE technique p, L, r, and N are , , 10 and 10 can be selected.
또한 본 발명에 따라 제안된 DE 기법을 이용한 SCC 기반 PPRL 알고리즘에서는 DE 기법이 행렬의 일부 요소에만 적용 되더라도 사용자 단말(130) 간의 데이터 프라이버시를 유지할 수 있으므로 시뮬레이션 연구를 위해 DE 기법이 행렬의 10%에 적용될 수 있다.In addition, in the SCC-based PPRL algorithm using the DE technique proposed according to the present invention, even if the DE technique is applied to only some elements of the matrix, data privacy between
도 9a 및 9b는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 계산 복잡도 성능 그래프를 도시한 도면이다.9A and 9B are diagrams illustrating computational complexity performance graphs according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 9a 및 9b를 참고하면, 계산 오버 헤드 측면에서, 본 발명에 따라 제안된 SCC-PPRL 방식의 계산 오버 헤드와 개발된 SMC 기반 PPRL 방식의 계산 오버 헤드를 비교하기 위해 RCC(Relative Computational Complexity)를 계산할 수 있다.9a and 9b, in terms of computational overhead, RCC (Relative Computational Complexity) is used to compare the computational overhead of the SCC-PPRL scheme proposed according to the present invention with the computational overhead of the developed SMC-based PPRL scheme. can be calculated
일 실시예에서, RCC는 하기 <수학식 14>와 같이 나타낼 수 있다.In one embodiment, RCC can be expressed as in Equation 14 below.
도 9는 제안된 SCC-PPRL의 RCC와 SMC 기반 PPRL 알고리즘을 상태 수와 행동 수에 따라 나타낸 것이다. 행동 수는 도 9(a)에서 10으로 설정되고, 상태 수는 도 9(b)에서 10으로 설정될 수 있다.9 shows the RCC and SMC based PPRL algorithms of the proposed SCC-PPRL according to the number of states and the number of actions. The number of actions may be set to 10 in FIG. 9(a), and the number of states may be set to 10 in FIG. 9(b).
RCC가 1보다 작으면 본 발명에 따라 제안된 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘의 계산 오버 헤드가 SMC 기반 알고리즘보다 적을 수 있다.If RCC is less than 1, the calculation overhead of the SCC-PPRL algorithm proposed according to the present invention may be less than that of the SMC-based algorithm.
도 9(a)와 도 9(b)를 참고하면, 각각 상태와 행동의 수가 증가함에 따라 보안 행동 선택 및 보안 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘에서 RCC를 확인할 수 있다.Referring to FIGS. 9(a) and 9(b) , as the number of states and actions increases, RCC can be confirmed in the security action selection and security Q-table update algorithms.
도 9(a) 및 도 9(b)에서 볼 수 있듯이 SMC 및 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘의 계산 복잡도가 Ns 및 Na에 대해 모두 선형적으로 증가하기 때문에, RCC는 상태 및 행동 수가 증가함에 따라 특정 값으로 수렴될 수 있다.As shown in Fig. 9(a) and Fig. 9(b), since the computational complexity of the SMC and SCC-PPRL algorithms increases linearly for both Ns and Na, RCC increases to a specific value as the number of states and actions increases. can converge.
또한, RCC의 값은 항상 1보다 작기 때문에 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘의 계산 오버 헤드가 SMC 기반 알고리즘보다 적음을 알 수 있다.In addition, since the value of RCC is always less than 1, it can be seen that the computational overhead of the SCC-PPRL algorithm is less than that of the SMC-based algorithm.
SMC 기반 알고리즘에서 분산 컴퓨팅 서버의 협력을 통한 암호화 및 복호화 작업은 암호화 및 복호화 절차의 지수화 작업이 덧셈과 곱셈과 같은 다른 작업보다 훨씬 많은 계산을 필요로 하기 때문에 계산 복잡성에 지배적인 영향을 미칠 수 있다.In SMC-based algorithms, the encryption and decryption operations through the cooperation of distributed computing servers can have a dominant effect on the computational complexity because the exponentiation operations of encryption and decryption procedures require much more computation than other operations such as addition and multiplication. .
PPRL 기반 서비스의 경우 AHE 기반 분산 암호화 시스템을 사용하는 SMC 기반 알고리즘은 곱셈, 비교, 동등성 테스트와 같은 기본 동형 연산마다 여러 번의 암호화 및 복호화 작업이 필요하기 때문에 많은 암호화 및 복호화 작업이 필요할 수 있다.In the case of PPRL-based services, SMC-based algorithms using AHE-based distributed cryptosystems may require many encryption and decryption operations because each basic isomorphic operation such as multiplication, comparison, and equality test requires multiple encryption and decryption operations.
반면 본 발명에 따라 제안된 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘에서는 데이터 교환 절차에서만 암호화 및 복호화 행동을 수행할 수 있다.On the other hand, in the SCC-PPRL algorithm proposed according to the present invention, encryption and decryption actions can be performed only in the data exchange procedure.
본 발명에 따라 제안된 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘에 DE 기법을 적용한 경우 도 9(a)와 도9(a)와 같이 DE 기법이 없는 것보다 행동 선택 및 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 RCC가 더 클 수 있다.When the DE technique is applied to the SCC-PPRL algorithm proposed according to the present invention, the RCC of the action selection and Q-table update algorithm can be larger than that without the DE technique, as shown in FIGS. 9(a) and 9(a). .
DE 체계를 사용하는 알고리즘이 DE 체계가 없는 알고리즘보다 계산 복잡도가 높은 이유는 추가 RSA 암호화 및 암호 복호화 작업이 필요하기 때문일 수 있다.The reason why algorithms using DE schemes have higher computational complexity than algorithms without DE schemes may be because additional RSA encryption and decryption operations are required.
도 9(a)에서 상태 수가 증가함에 따라 행동 선택 알고리즘의 RCC가 증가할 수 있다.In FIG. 9(a), as the number of states increases, the RCC of the action selection algorithm may increase.
이는 행동 선택 알고리즘에서 상태 수가 증가할수록 상태를 나타내는 이진 벡터의 요소 수가 증가하기 때문일 수 있다.This may be because the number of elements of the binary vector representing the state increases as the number of states increases in the action selection algorithm.
DE 방식을 사용한 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 RCC는 상태 수에 관계없이 사용자 단말(130)과 클라우드 서버(120) 간의 정보 교환 량이 거의 동일하기 때문에 DE 방식이 없는 경우에 가까울 수 있다.Since the amount of information exchange between the
도 9(b)에서, Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 RCC는 행동 수가 증가할수록 행동을 나타내는 이진 벡터의 요소 수가 증가하기 때문일 수 있다.In FIG. 9(b), the RCC of the Q-table update algorithm may be because the number of elements of a binary vector representing an action increases as the number of actions increases.
행동 선택 알고리즘에서는 행동 수가 증가함에 따라 선택된 Q-벡터의 요소 수가 증가할 수 있다.In the action selection algorithm, as the number of actions increases, the number of elements of the selected Q-vector may increase.
그러나 <수학식 3>으로 암호화된 선택된 Q-벡터의 크기가 <수학식 7>에 의해 암호화된 행동을 나타내는 이진 벡터의 크기보다 작기 때문에, DE 방식에 의한 계산 복잡성 증가의 영향은 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 효과보다 작을 수 있다.However, since the size of the selected Q-vector encrypted by <
따라서 행동 수가 증가하더라도 DE 방식이 적용된 행동 선택 알고리즘의 RCC는 증가하지 않는다.Therefore, even if the number of actions increases, the RCC of the action selection algorithm to which the DE method is applied does not increase.
도 10a 내지 10d는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 통신 오버헤드 성능 그래프를 도시한 도면이다.10A to 10D are diagrams illustrating communication overhead performance graphs according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 10a 내지 10d를 참고하면, 통신 오버 헤드 측면에서, 본 발명에 따라 제안된 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘과 SMC 기반 PPRL 알고리즘의 통신 오버 헤드의 효율성을 비교하기 위해 각 PPRL 알고리즘이 실행되는 동안 생성되는 통신 데이터의 양을 측정할 수 있다.10a to 10d, in terms of communication overhead, communication data generated while each PPRL algorithm is executed in order to compare the communication overhead efficiency of the SCC-PPRL algorithm proposed according to the present invention and the SMC-based PPRL algorithm. amount can be measured.
시뮬레이션 환경에서 상태 및 행동의 수가 50개 이상인 경우 이진 벡터의 차원을 줄이는 기술은 Nrs=50으로 활성화될 수 있다.In the simulation environment, when the number of states and actions is more than 50, the technique of reducing the dimensionality of binary vectors can be activated with Nrs =50.
도 10(a)와 도 10(b)를 참고하면, 본 발명에 따라 제안된 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘에서 행동 선택과 Q-테이블 업데이트를 위한 통신 오버 헤드를 상태 수와 행동 수에 따라 확인할 수 있다.Referring to FIGS. 10(a) and 10(b), in the SCC-PPRL algorithm proposed according to the present invention, communication overhead for action selection and Q-table update can be confirmed according to the number of states and actions.
이 경우, PPRL 알고리즘의 오버 헤드를 플로팅할 수 있다. 이는 행동 선택 및 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘에 대한 통신 오버 헤드의 합계일 수 있다.In this case, the overhead of the PPRL algorithm can be plotted. This can be the sum of the communication overhead for the action selection and Q-table update algorithms.
행동 수는 도 10(a)에서 10으로 설정되고 상태 수는 도 10(b)에서 10으로 설정될 수 있다. 도 10(a)에서 행동 선택 알고리즘의 통신 오버 헤드는 상태 수가 50개까지 증가할수록 증가하고, 상태 수가 50개를 초과하면 레벨이 낮아질 수 있다.The number of actions may be set to 10 in FIG. 10(a) and the number of states may be set to 10 in FIG. 10(b). In FIG. 10(a), the communication overhead of the action selection algorithm increases as the number of states increases up to 50, and the level may decrease when the number of states exceeds 50.
이는 행동 선택 알고리즘의 상태를 나타내는 이진 벡터의 요소 수가 상태 수가 50개까지 증가할수록 증가하기 때문일 수 있다. 상태 수가 50개를 초과하면 이진 벡터의 차원을 줄이는 기술은 다음과 설명될 수 있다. 행동 선택 알고리즘에 적용되며 통신 오버 헤드 증가를 성공적으로 억제할 수 있다.This may be because the number of elements of the binary vector representing the states of the action selection algorithm increases as the number of states increases up to 50. When the number of states exceeds 50, the technique of reducing the dimensionality of the binary vector can be described as follows. It is applied to the action selection algorithm and can successfully suppress the increase in communication overhead.
반면, Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘에서 사용자 단말(130)과 클라우드 서버(120) 간의 통신 데이터는 개수에 따라 변하지 않기 때문에 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 통신 오버 헤드는 상태 수에 관계없이 거의 일정한 것으로 관찰될 수 있다. 상태가 증가할 수 있다.On the other hand, since the communication data between the
또한, DE 방식의 요소에 RSA 암호화를 적용하면 전송할 행렬의 각 요소의 길이가 길어지기 때문에 DE 방식을 사용하는 알고리즘의 통신 오버 헤드가 DE 방식이 없는 알고리즘보다 높을 수 있다.In addition, if RSA encryption is applied to elements of the DE method, the length of each element of the matrix to be transmitted becomes longer, so the communication overhead of an algorithm using the DE method may be higher than that of an algorithm without the DE method.
도 10(b)에서 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 통신 오버 헤드는 행동 수가 50개까지 증가할수록 증가하고, 행동 수가 50개를 초과하면 변동이 없게 된다.In FIG. 10(b), the communication overhead of the Q-table update algorithm increases as the number of actions increases up to 50, and there is no change when the number of actions exceeds 50.
이는 행동 수가 50개까지 증가할수록 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 행동을 나타내는 이진 벡터의 수가 증가하기 때문일 수 있다.This may be because the number of binary vectors representing the actions of the Q-table update algorithm increases as the number of actions increases up to 50.
행동 수가 50개를 초과하면 이진 벡터의 차원을 줄이는 기술이 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘에 적용되어 통신 오버 헤드 증가를 성공적으로 억제할 수 있다.When the number of actions exceeds 50, the technique of reducing the dimensionality of the binary vector is applied to the Q-table update algorithm, which can successfully suppress the increase in communication overhead.
행동 선택 알고리즘의 통신 오버 헤드는 행동 수가 증가함에 따라 클라우드 서버(120)에 의해 반환된 선택된 Q-벡터의 요소 수가 증가하기 때문에 행동 수가 증가함에 따라 증가할 수 있다.The communication overhead of the action selection algorithm may increase as the number of actions increases because the number of elements of the selected Q-vector returned by the
이진 벡터에 대해 <수학식 7>에 의해 암호화된 행렬의 크기가 선택된 Q-벡터에 대해 <수학식 3>에 의해 암호화된 행렬의 크기보다 크기 때문에, Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 통신 오버 헤드가 행동 선택 알고리즘보다 훨씬 빠르게 증가할 수 있다.Since the size of the matrix encrypted by Equation 7 for a binary vector is larger than the size of the matrix encrypted by
또한 도 10(a)와 같은 이유로 도 10(b)에서도 DE 방식을 적용하면 통신 오버 헤드가 증가하는 것을 알 수 있다.In addition, for the same reason as in FIG. 10 (a), it can be seen that communication overhead increases when the DE method is applied in FIG. 10 (b).
비교를 위해 도 10(c)와 도 10(d)의 상태 및 행동 수와 관련하여 SMC 기반 PPRL 알고리즘에서 행동 선택 및 Q-테이블 업데이트에 대한 통신 오버 헤드를 플로팅할 수 있다.For comparison, the communication overhead for action selection and Q-table update in the SMC-based PPRL algorithm can be plotted with respect to the state and number of actions in Fig. 10(c) and Fig. 10(d).
PPRL 알고리즘의 오버 헤드는 행동 선택 및 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘에 대한 통신 오버 헤드의 합계일 수 있다.The overhead of the PPRL algorithm can be the sum of the communication overhead for the action selection and Q-table update algorithms.
상태 및 행동 수가 증가함에 따라 행동 선택 및 Q-테이블 업데이트 알고리즘의 통신 오버 헤드가 지속적으로 증가할 수 있다.As the number of states and actions increases, the communication overhead of the action selection and Q-table update algorithms may continue to increase.
또한, SMC 기반 알고리즘의 통신 오버 헤드는 본 발명에 따라 제안된 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘의 통신 오버 헤드에 비해 선형 적으로 증가하고 매우 커지는 것을 알 수 있다.In addition, it can be seen that the communication overhead of the SMC-based algorithm increases linearly and is very large compared to the communication overhead of the SCC-PPRL algorithm proposed according to the present invention.
분산 암호화를 사용하는 SMC 기반 PPRL 알고리즘은 PPRL 알고리즘 구현을 위한 곱셈, 비교, 동등성 테스트와 같은 HE 기본 함수를 수행하기 위해 클라우드 서버(120)와 HSP간에 많은 데이터 교환이 필요하기 때문일 수 있다.This may be because the SMC-based PPRL algorithm using distributed encryption requires a lot of data exchange between the
반대로, 본 발명에 따라 제안된 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘은 제3자 지원 없이 단일 클라우드 서버에 데이터를 저장하고 처리하기 때문에 PPRL 알고리즘에 대한 통신 오버 헤드가 크게 줄어들 수 있다. 따라서 본 발명에 따라 제안한 SCC-PPRL 알고리즘의 통신 오버 헤드는 SMC 기반 PPRL 알고리즘보다 훨씬 적을 수 있다.Conversely, since the SCC-PPRL algorithm proposed according to the present invention stores and processes data in a single cloud server without third party support, communication overhead for the PPRL algorithm can be greatly reduced. Therefore, the communication overhead of the SCC-PPRL algorithm proposed according to the present invention can be much lower than that of the SMC-based PPRL algorithm.
도 11은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버(120)의 동작 방법을 도시한 도면이다.11 is a diagram illustrating an operating method of the
도 11을 참고하면, S1101 단계는, 사용자 단말(130)로부터 HE 비밀키를 이용하여 1차 암호화된 후 공개키를 이용하여 2차 암호화된 암호문을 수신하는 단계이다.Referring to FIG. 11 , step S1101 is a step of receiving, from the
즉, 사용자 단말(130)은 HE 비밀키를 이용하여 데이터를 1차 암호화하여 1차 암호화된 암호문을 생성하고, 공개키를 이용하여 1차 암호화된 암호문을 2차 암호화하여 2차 암호화된 암호문을 생성한 후, 2차 암호화된 암호문을 클라우드 서버(120)에게 송신할 수 있다.That is, the
일 실시예에서, HE 비밀키는 HE 방식에 기반한 대칭 비밀키(symmetrical secret ket) 또는 이와 동등한 기술적 의미를 갖는 용어로 지칭될 수 있다.In one embodiment, the HE secret key may be referred to as a symmetrical secret ket based on the HE scheme or a term having an equivalent technical meaning.
S1103 단계는, 클라우드 서버(120)의 개인키를 이용하여 2차 암호화된 암호문을 복호화하여 1차 암호화된 암호문을 생성하는 단계이다.Step S1103 is a step of generating a first encrypted ciphertext by decrypting the secondly encrypted ciphertext using the private key of the
S1105 단계는, 강화학습 모델을 이용하여 1차 암호화된 암호문에 대한 Q-벡터를 생성하는 단계이다. 예를 들어, 강화학습 모델은 Q-학습을 위한 SCC(Secure Centralized Computation)-PPRL(Privacy Preserving Reinforcement Learning) 모델을 포함할 수 있다.Step S1105 is a step of generating a Q-vector for the primary encrypted ciphertext using a reinforcement learning model. For example, the reinforcement learning model may include a Secure Centralized Computation (SCC)-Privacy Preserving Reinforcement Learning (PPRL) model for Q-learning.
S1107 단계는, Q-벡터를 공개키를 이용하여 암호화하는 단계이다.Step S1107 is a step of encrypting the Q-vector using the public key.
일 실시예에서, S1105 단계 이후에, 1차 암호화된 암호문을 이용하여 강화학습 모델에 대한 Q-테이블 업데이트를 수행할 수 있다.In one embodiment, after step S1105, Q-table update for the reinforcement learning model may be performed using the first encrypted ciphertext.
S1109 단계는, 암호화된 Q-벡터를 사용자 단말(130)에게 송신하는 단계이다.Step S1109 is a step of transmitting the encrypted Q-vector to the
일 실시예에서, 암호화된 Q-벡터는, 사용자 단말(130)에 의해, 사용자 단말의 개인키를 이용하여 1차 복호화된 후, HE 비밀키를 이용하여 2차 복호화될 수 있다.In one embodiment, the encrypted Q-vector may be decrypted first by the
일 실시예에서, 2차 복호화된 Q-벡터에 포함된 적어도 하나의 Q 값 중 최대 Q 값은, 사용자 단말(130)에 의해, 강화학습 모델에 대한 리워드(reward)를 최대화하기 위한 행동(action) 정보를 결정하기 위해 이용될 수 있다.In one embodiment, the maximum Q value among at least one Q value included in the secondary decoded Q-vector is an action by the
일 실시예에서, 상기 결정된 행동 정보는, 사용자 단말(130)에 의해, 외부 전자장치(140)에게 송신될 수 있다.In one embodiment, the determined behavior information may be transmitted to the external
일 실시예에서, 상기 송신된 행동 정보는, 외부 전자장치(140)에 의해, 강화학습 모델에 대한 상태(state) 정보 및 리워드를 결정하기 위해 이용될 수 있다.In one embodiment, the transmitted behavioral information may be used by the external
일 실시예에서, 공개키와 개인키는, RSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) 암호화 방식에 기반하여 결정될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 공개키는 RSA 공개키 또는 이와 동등한 기술적 의미를 갖는 용어로 지칭되고, 개인키는 RSA 개인키 또는 이와 동등한 기술적 의미를 갖는 용어로 지칭될 수 있다.In one embodiment, the public key and the private key may be determined based on a Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) encryption method. For example, the public key may be referred to as an RSA public key or a term having an equivalent technical meaning, and the private key may be referred to as an RSA private key or a term having a technical meaning equivalent thereto.
도 12는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 클라우드 서버(120)의 기능적 구성을 도시한 도면이다.12 is a diagram showing a functional configuration of the
도 12를 참고하면, 클라우드 서버(120)는 통신부(1210), 제어부(1220) 및 저장부(1230)를 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 12 , the
통신부(1210)는 사용자 단말(130)로부터 HE(Homomorphic Encryption) 비밀키를 이용하여 1차 암호화된 후 공개키를 이용하여 2차 암호화된 암호문을 수신할 수 있다.The
일 실시예에서, 통신부(1210)는 유선 통신 모듈 및 무선 통신 모듈 중 적어도 하나를 포함할 수 있다. 통신부(1210)의 전부 또는 일부는 '송신부', '수신부' 또는 '송수신부(transceiver)'로 지칭될 수 있다.In one embodiment, the
제어부(1220)는 클라우드 서버(120)의 개인키를 이용하여 2차 암호화된 암호문을 복호화하여 1차 암호화된 암호문을 생성하고, 강화학습 모델을 이용하여 1차 암호화된 암호문에 대한 Q-벡터를 생성하고, 상기 생성된 Q-벡터를 공개키를 이용하여 암호화할 수 있다.The
이후, 통신부(1210)는 암호화된 Q-벡터를 사용자 단말(130)에게 송신할 수 있다.Then, the
일 실시예에서, 제어부(1220)는 적어도 하나의 프로세서 또는 마이크로(micro) 프로세서를 포함하거나, 또는, 프로세서의 일부일 수 있다. 또한, 제어부(1220)는 CP(communication processor)라 지칭될 수 있다. 제어부(1220)는 본 발명의 다양한 실시예에 따른 클라우드 서버(120)의 동작을 제어할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the
저장부(1230)는 개인키 및 공개키를 저장할 수 있다. 또한, 저장부(1230)는 강화학습 모델을 저장할 수 있다.The
일 실시예에서, 저장부(1230)는 휘발성 메모리, 비휘발성 메모리 또는 휘발성 메모리와 비휘발성 메모리의 조합으로 구성될 수 있다. 그리고, 저장부(1230)는 제어부(1220)의 요청에 따라 저장된 데이터를 제공할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the
도 12를 참고하면, 클라우드 서버(120)는 통신부(1210), 제어부(1220) 및 저장부(1230)를 포함할 수 있다. 본 발명의 다양한 실시 예들에서 클라우드 서버(120)는 도 12에 설명된 구성들이 필수적인 것은 아니어서, 도 12에 설명된 구성들보다 많은 구성들을 가지거나, 또는 그보다 적은 구성들을 가지는 것으로 구현될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 12 , the
이상의 설명은 본 발명의 기술적 사상을 예시적으로 설명한 것에 불과한 것으로, 통상의 기술자라면 본 발명의 본질적인 특성이 벗어나지 않는 범위에서 다양한 변경 및 수정이 가능할 것이다.The above description is only illustrative of the technical idea of the present invention, and various changes and modifications may be made by those skilled in the art without departing from the essential characteristics of the present invention.
본 명세서에 개시된 다양한 실시예들은 순서에 관계없이 수행될 수 있으며, 동시에 또는 별도로 수행될 수 있다.The various embodiments disclosed herein may be performed out of order, concurrently or separately.
일 실시예에서, 본 명세서에서 설명되는 각 도면에서 적어도 하나의 단계가 생략되거나 추가될 수 있고, 역순으로 수행될 수도 있으며, 동시에 수행될 수도 있다.In one embodiment, at least one step may be omitted or added in each figure described herein, may be performed in reverse order, or may be performed concurrently.
본 명세서에 개시된 실시예들은 본 발명의 기술적 사상을 한정하기 위한 것이 아니라, 설명하기 위한 것이고, 이러한 실시예들에 의하여 본 발명의 범위가 한정되는 것은 아니다.The embodiments disclosed herein are not intended to limit the technical spirit of the present invention, but are intended to explain, and the scope of the present invention is not limited by these embodiments.
본 발명의 보호범위는 청구범위에 의하여 해석되어야 하며, 그와 동등한 범위 내에 있는 모든 기술 사상은 본 발명의 권리범위에 포함되는 것으로 이해되어야 한다.The protection scope of the present invention should be interpreted according to the claims, and all technical ideas within the equivalent range should be understood to be included in the scope of the present invention.
100: 클라우드 통신 시스템
110: 키 관리 센터
120: 클라우드 서버
130: 사용자 단말
140: 외부 전자장치
1210: 통신부
1220: 제어부
1230: 저장부100: cloud communication system
110: key management center
120: cloud server
130: user terminal
140: external electronic device
1210: communication department
1220: control unit
1230: storage unit
Claims (14)
Translated fromKorean(b) 상기 클라우드 서버의 개인키를 이용하여 상기 2차 암호화된 암호문을 복호화하여 상기 1차 암호화된 암호문을 생성하는 단계;
(c) 강화학습 모델을 이용하여 상기 1차 암호화된 암호문에 대한 Q-벡터를 생성하는 단계;
(d) 상기 생성된 Q-벡터를 상기 사용자 단말의 공개키를 이용하여 암호화하는 단계; 및
(e) 상기 암호화된 Q-벡터를 상기 사용자 단말에게 송신하는 단계;
를 포함하는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버의 동작 방법.
(a) receiving a second encrypted ciphertext using a public key of a cloud server after primary encryption using a Homomorphic Encryption (HE) secret key from a user terminal;
(b) generating the first encrypted ciphertext by decrypting the secondly encrypted ciphertext using the private key of the cloud server;
(c) generating a Q-vector for the primary encrypted ciphertext using a reinforcement learning model;
(d) encrypting the generated Q-vector using the public key of the user terminal; and
(e) transmitting the encrypted Q-vector to the user terminal;
including,
Operation method of cloud server for personal information protection reinforcement learning.
상기 암호화된 Q-벡터는, 상기 사용자 단말에 의해, 상기 사용자 단말의 개인키를 이용하여 1차 복호화된 후, 상기 HE 비밀키를 이용하여 2차 복호화되는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버의 동작 방법.
According to claim 1,
The encrypted Q-vector is first decrypted by the user terminal using the private key of the user terminal and then secondarily decrypted using the HE private key.
Operation method of cloud server for personal information protection reinforcement learning.
상기 2차 복호화된 Q-벡터에 포함된 최대 Q 값은, 상기 사용자 단말에 의해, 상기 강화학습 모델에 대한 리워드(reward)를 최대화하기 위한 행동(action) 정보를 결정하기 위해 이 용되는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버의 동작 방법.
According to claim 2,
The maximum Q value included in the secondary decoded Q-vector is used by the user terminal to determine action information for maximizing a reward for the reinforcement learning model,
Operation method of cloud server for personal information protection reinforcement learning.
상기 결정된 행동 정보는, 상기 사용자 단말에 의해, 외부 전자장치에게 송신되는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버의 동작 방법.
According to claim 3,
The determined behavior information is transmitted by the user terminal to an external electronic device,
Operation method of cloud server for personal information protection reinforcement learning.
상기 송신된 행동 정보는, 상기 외부 전자장치에 의해, 상기 강화학습 모델 에 대한 상태(state) 정보 및 리워드를 결정하기 위해 이용되는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버의 동작 방법.
According to claim 4,
The transmitted behavioral information is used by the external electronic device to determine state information and a reward for the reinforcement learning model.
Operation method of cloud server for personal information protection reinforcement learning.
상기 공개키와 개인키는, RSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) 암호화 방식에 기반하여 결정되는,
개인정보 보호 강 화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버의 동작 방법.
According to claim 1,
The public key and the private key are determined based on Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) encryption method,
Operation method of cloud server for personal information protection reinforcement learning.
상기 (b) 단계 이후에,
상기 1차 암호화된 암호문을 이용하여 상기 강화학습 모델에 대한 Q-테이블 업데이트를 수행하는 단계;
를 더 포함하는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버의 동작 방법.
According to claim 1,
After step (b),
performing a Q-table update for the reinforcement learning model using the primary encrypted ciphertext;
Including more,
Operation method of cloud server for personal information protection reinforcement learning.
상기 클라우드 서버의 개인키를 이용하여 상기 2차 암호화된 암호문을 복호화하여 상기 1차 암호화된 암호문을 생성하고,
강화학습 모델을 이용하여 상기 1차 암호화된 암호문에 대한 Q-벡터를 생성 하며,
상기 생성된 Q-벡터를 상기 사용자 단말의 공개키를 이용하여 암호화하는 제어부;
를 포함하고,
상기 통신부는, 암호화된 Q-벡터를 상기 사용자 단말에게 송신하는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버 장치.
A communication unit for receiving a second encrypted ciphertext using a public key of a cloud server after primary encryption using a Homomorphic Encryption (HE) secret key from a user terminal; and
Decrypting the secondary encrypted ciphertext using the private key of the cloud server to generate the primary encrypted ciphertext;
Generating a Q-vector for the primary encrypted ciphertext using a reinforcement learning model;
a controller for encrypting the generated Q-vector using a public key of the user terminal;
including,
The communication unit transmits an encrypted Q-vector to the user terminal,
Cloud server device for privacy-preserving reinforcement learning.
상기 암호화된 Q-벡터는, 상기 사용자 단말에 의해, 상기 사용자 단말의 개인키를 이용하여 1차 복호화된 후, 상기 HE 비밀키를 이용하여 2차 복호화되는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버 장치.
According to claim 8,
The encrypted Q-vector is first decrypted by the user terminal using the private key of the user terminal and then secondarily decrypted using the HE private key.
Cloud server device for privacy-preserving reinforcement learning.
상기 2차 복호화된 Q-벡터에 포함된 최대 Q 값은, 상기 사용자 단말에 의해, 상기 강화학습 모델에 대한 리워드(reward)를 최대화하기 위한 행동(action) 정보를 결정하기 위해 이용되는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버 장치.
According to claim 9,
The maximum Q value included in the secondary decoded Q-vector is used by the user terminal to determine action information for maximizing a reward for the reinforcement learning model,
Cloud server device for privacy-preserving reinforcement learning.
상기 결정된 행동 정보는, 상기 사용자 단말에 의해, 외부 전자장치에게 송신되는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버 장치.
According to claim 10,
The determined behavior information is transmitted by the user terminal to an external electronic device,
Cloud server device for privacy-preserving reinforcement learning.
상기 송신된 행동 정보는, 상기 외부 전자장치에 의해, 상기 강화학습 모델에 대한 상태(state) 정보 및 리워드를 결정하기 위해 이용되는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버 장치.
According to claim 11,
The transmitted behavior information is used by the external electronic device to determine state information and a reward for the reinforcement learning model.
Cloud server device for privacy-preserving reinforcement learning.
상기 공개키와 개인키는, RSA(Rivest-Shamir -Adleman) 암호화 방식에 기반하여 결정되는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버 장치.
According to claim 8,
The public key and the private key are determined based on the Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) encryption method,
Cloud server device for privacy-preserving reinforcement learning.
상기 제어부는,
상기 1차 암호화된 암호문을 이용하여 상기 강화학습 모델에 대한 Q-테이블 업데이트를 수행하는,
개인정보 보호 강화 학습을 위한 클라우드 서버 장치.According to claim 8,
The control unit,
Performing a Q-table update for the reinforcement learning model using the primary encrypted ciphertext,
Cloud server device for privacy-preserving reinforcement learning.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR20200145536 | 2020-11-03 | ||
| KR1020200145536 | 2020-11-03 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20220059869A KR20220059869A (en) | 2022-05-10 |
| KR102508519B1true KR102508519B1 (en) | 2023-03-09 |
Family
ID=81591842
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020200160144AActiveKR102508519B1 (en) | 2020-11-03 | 2020-11-25 | A method and apparatus for performing privacy-preserving reinforcement learning using homomorphic encryption |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102508519B1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116132046B (en)* | 2022-12-07 | 2025-08-01 | 中国电子科技集团公司第三十研究所 | Estimation method, medium, equipment and system for decryption error rate of lattice-based encryption algorithm |
| CN118312486B (en)* | 2024-06-11 | 2024-09-06 | 浙江天正信息科技有限公司 | Data security circulation method based on cross-domain data communication sharing platform |
| CN119483888A (en)* | 2024-11-04 | 2025-02-18 | 西安电子科技大学 | Privacy protection method for end-cloud collaboration based on homomorphic encryption and additive secret sharing |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20100067816A (en)* | 2008-12-12 | 2010-06-22 | 주식회사 케이티 | Personalization recommendation service for preserving privacy providing method and server thereof |
| KR102068622B1 (en) | 2019-03-14 | 2020-01-21 | 차수정 | Failure prediction system for heterogeneous network security system |
- 2020
- 2020-11-25KRKR1020200160144Apatent/KR102508519B1/enactiveActive
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| Ahmed Moustafa, 외 1명. "Multi-Objective Service Composition Using Reinforcement Learning." International Conference on Service-Oriented Computing. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2013. |
| Zhuzhu Wang 외 3명. "LiPSG: Lightweight Privacy-Preserving Q-Learning-Based Energy Management for the IoT-Enabled Smart Grid." IEEE Internet of Things Journal 7.5 (2020) |
| ZuobinYing 외 4명. "OIDPR: Optimized Insulin Dosage based on Privacy-Preserving Reinforcement Learning." 2020 IFIP Networking Conference (Networking). IEEE, 2020. |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20220059869A (en) | 2022-05-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Liang et al. | Searchable attribute-based mechanism with efficient data sharing for secure cloud storage | |
| Park et al. | Privacy-preserving reinforcement learning using homomorphic encryption in cloud computing infrastructures | |
| US8559631B1 (en) | Systems and methods for efficient decryption of attribute-based encryption | |
| US7346162B2 (en) | Public key cryptography using matrices | |
| Sen | Homomorphic encryption-theory and application | |
| KR102508519B1 (en) | A method and apparatus for performing privacy-preserving reinforcement learning using homomorphic encryption | |
| Applebaum et al. | Semantic security under related-key attacks and applications | |
| Singh et al. | Generalisations of NTRU cryptosystem | |
| CN111404952B (en) | Transformer substation data encryption transmission method and device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| AU3180699A (en) | A method and apparatus for cryptographically secure algebraic key establishment protocols | |
| Hoang et al. | Forward-secure data outsourcing based on revocable attribute-based encryption | |
| CN116055152A (en) | Grid-based access control encryption and decryption method and system | |
| Karati et al. | Provably secure and authenticated data sharing protocol for IoT‐based crowdsensing network | |
| Saeed et al. | Improved cloud storage security of using three layers cryptography algorithms | |
| Venema et al. | TinyABE: Unrestricted ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption for embedded devices and low-quality networks | |
| KR101575681B1 (en) | Method of attribute-based encryption | |
| CN108599941A (en) | Random asymmetries expand byte encryption of communicated data method | |
| JP2004246350A (en) | Encryption device and decryption device, and encryption system, encryption method and decryption method provided with them | |
| CN120188438A (en) | System and method for distributing key generation data in a secure network | |
| Hassan et al. | An authorized equality test on identity‐based cryptosystem for mobile social networking applications | |
| Vajda | Construction for searchable encryption with strong security guarantees | |
| Hillmann | Lightweight Public Key Encryption in Post-Quantum Computing Era | |
| Khan et al. | Classical to Post-Quantum Secure ABE-IBE Proxy Re-Encryption Scheme. | |
| US20250088347A1 (en) | Homomorphic cryptographic system including noise estimator and operation method thereof | |
| Fu et al. | Outsource the Ciphertext Decryption of Inner Product Predicate Encryption Scheme Based on Prime Order Bilinear Map. |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20201125 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20220804 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20230126 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20230306 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20230306 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration |