KR102382194B1 - Electronic device providing double layer haptic model for high band width and high resolution texture expression and operating method thereof - Google Patents
Electronic device providing double layer haptic model for high band width and high resolution texture expression and operating method thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102382194B1 KR102382194B1KR1020200081825AKR20200081825AKR102382194B1KR 102382194 B1KR102382194 B1KR 102382194B1KR 1020200081825 AKR1020200081825 AKR 1020200081825AKR 20200081825 AKR20200081825 AKR 20200081825AKR 102382194 B1KR102382194 B1KR 102382194B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- models
- electronic device
- macro pattern
- micro
- texture
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/01—Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer
- G06F3/016—Input arrangements with force or tactile feedback as computer generated output to the user
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- User Interface Of Digital Computer (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean다양한 실시예들은 고대역폭 고해상도 질감 표현을 위한 이중 계층 햅틱 모델을 제공하는 전자 장치 및 그의 동작 방법에 관한 것이다.Various embodiments relate to an electronic device that provides a double-layered haptic model for high-bandwidth, high-resolution texture representation, and an operating method thereof.
일반적으로, 전자 장치는 사용자의 움직임에 대응하여 햅틱 신호를 발생시킴으로써, 사용자로 하여금, 가상의 촉감을 느끼게 한다. 그런데, 전자 장치가 다양한 표면들을 표현하는 데에는 한계가 있다. 예를 들어, 평평하게 절단된 벽돌의 표면과 외력에 의해 깨져서 불규칙하게 부서진 벽돌의 표면은 같은 벽돌 입자의 소재를 가지고 있지만, 표면의 불규칙한 정도가 다르기 때문에, 실질적인 촉감은 매우 다르다. 반면, 불규칙하게 부서진 벽돌과 같은 형태를 가지고 있다 하더라도, 실리콘으로 형성된 물체는 부서진 벽돌과 표면의 불규칙힌 정도는 같지만, 소재가 다르기 때문에, 실질적인 촉감은 다르다.In general, an electronic device generates a haptic signal in response to a user's movement, thereby allowing the user to feel a virtual touch. However, there is a limit to the ability of the electronic device to express various surfaces. For example, the surface of a brick cut flat and the surface of a brick broken and broken by an external force have the same brick material, but because the degree of surface irregularity is different, the actual touch is very different. On the other hand, even if it has the same shape as an irregularly broken brick, an object formed of silicon has the same degree of surface irregularity as the broken brick, but because the material is different, the actual feel is different.
다양한 실시예들은, 다양한 표면들을 표현할 수 있는 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 전자 장치 및 그의 동작 방법을 제공한다.Various embodiments provide an electronic device that generates a haptic signal capable of representing various surfaces and an operating method thereof.
다양한 실시예들은, 햅틱 신호를 기반으로, 표면의 규칙성 및 질감을 모두 표현할 수 있는 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 전자 장치 및 그의 동작 방법을 제공한다.Various embodiments provide an electronic device that generates a haptic signal capable of expressing both regularity and texture of a surface based on the haptic signal, and an operating method thereof.
다양한 실시예들은, 고대역폭 고해상도 질감 표현을 위한 이중 계층 햅틱 모델을 제공하는 전자 장치 및 그의 동작 방법을 제공한다.Various embodiments provide an electronic device that provides a double-layered haptic model for high-bandwidth, high-resolution texture representation, and an operating method thereof.
다양한 실시예들에 따른 전자 장치의 동작 방법은, 가상 객체의 표면에 대한 규칙성을 표현하기 위한 매크로 패턴 모델을 결정하는 동작, 상기 가상 객체의 상기 표면의 질감을 표현하기 위한 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 결정하는 동작, 및 상기 결정된 매크로 패턴 모델과 상기 결정된 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 기반으로, 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 동작을 포함할 수 있다.An operating method of an electronic device according to various embodiments may include determining a macro pattern model for expressing regularity with respect to a surface of a virtual object, and at least two micro textures for expressing a texture of the surface of the virtual object It may include an operation of determining models, and an operation of generating a haptic signal based on the determined macro pattern model and the determined micro texture models.
다양한 실시예들에 따른 전자 장치는, 메모리, 및 상기 메모리와 연결되고, 상기 메모리에 저장된 적어도 하나의 명령을 실행하도록 구성된 프로세서를 포함하고, 상기 프로세서는, 가상 객체의 표면에 대한 규칙성을 표현하기 위한 매크로 패턴 모델을 결정하고, 상기 가상 객체의 상기 표면의 질감을 표현하기 위한 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 결정하고, 상기 결정된 매크로 패턴 모델과 상기 결정된 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 기반으로, 햅틱 신호를 발생시키도록 구성될 수 있다.An electronic device according to various embodiments includes a memory and a processor connected to the memory and configured to execute at least one instruction stored in the memory, wherein the processor expresses regularity of a surface of a virtual object determining a macro pattern model for performing a function, determining at least two micro texture models for expressing the texture of the surface of the virtual object, and generating a haptic signal based on the determined macro pattern model and the determined micro texture models It can be configured to
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 전자 장치가 매크로 패턴 모델과 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 기반으로 햅틱 신호를 발생시킴으로써, 다양한 표면들을 표현할 수 있다. 이 때 전자 장치는 매크로 패턴 모델에 따라, 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 혼합하여, 가상 객체의 표면에 대한 규칙성과 질감을 모두 표현할 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the electronic device may represent various surfaces by generating a haptic signal based on a macro pattern model and at least two micro texture models. In this case, the electronic device may express both the regularity and the texture of the surface of the virtual object by mixing micro-texture models according to the macro pattern model.
도 1은 다양한 실시예들에 따른 전자 장치를 도시하는 도면이다.
도 2 및 도 3은 다양한 실시예들에 따른 전자 장치의 동작 특징을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 4는 다양한 실시예들에 따른 전자 장치의 동작 방법을 도시하는 도면이다.1 is a diagram illustrating an electronic device according to various embodiments of the present disclosure;
2 and 3 are diagrams for explaining operational characteristics of an electronic device according to various embodiments of the present disclosure;
4 is a diagram illustrating a method of operating an electronic device according to various embodiments of the present disclosure;
이하, 본 발명의 실시예를 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 상세하게 설명한다.Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 1은 다양한 실시예들에 따른 전자 장치(100)를 도시하는 도면이다. 도 2 및 도 3은 다양한 실시예들에 따른 전자 장치(100)의 동작 특징을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.1 is a diagram illustrating an electronic device 100 according to various embodiments. 2 and 3 are diagrams for explaining operation characteristics of the electronic device 100 according to various embodiments of the present disclosure.
도 1을 참조하면, 다양한 실시예들에 따른 전자 장치(100)는 카메라 모듈(110), 센서 모듈(120), 통신 모듈(130), 입력 모듈(140), 출력 모듈(150), 햅틱 모듈(160), 메모리(170) 또는 프로세서(180) 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다. 어떤 실시예에서, 전자 장치(100)의 구성 요소들 중 적어도 어느 하나가 생략될 수 있으며, 적어도 하나의 다른 구성 요소가 추가될 수 있다. 어떤 실시예에서, 전자 장치(100)의 구성 요소들 중 적어도 어느 두 개가 하나의 통합된 회로로 구현될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 전자 장치(100)는 스마트폰(smart phone), 휴대폰, 내비게이션, 컴퓨터, 노트북, 디지털방송용 단말, PDA(personal digital assistants), PMP(portable multimedia player), 태블릿 PC, 게임 콘솔(game console), 웨어러블 디바이스(wearable device), AR(augmented reality) 디바이스, VR(virtual reality) 디바이스, IoT(internet of things) 디바이스, 또는 로봇(robot) 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 1 , an electronic device 100 according to various embodiments includes a camera module 110 , a sensor module 120 , a
카메라 모듈(110)은 전자 장치(100)에서 영상을 촬영할 수 있다. 이 때 카메라 모듈(110)은 전자 장치(100)의 미리 정해진 위치에 설치되어, 영상을 촬영할 수 있다. 그리고, 카메라 모듈(110)은 영상 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 카메라 모듈(110)은 렌즈, 적어도 하나의 이미지 센서, 이미지 시그널 프로세서 또는 플래시 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다.The camera module 110 may capture an image in the electronic device 100 . In this case, the camera module 110 may be installed at a predetermined position of the electronic device 100 to capture an image. In addition, the camera module 110 may generate image data. For example, the camera module 110 may include at least one of a lens, at least one image sensor, an image signal processor, and a flash.
센서 모듈(120)은 전자 장치(100)의 상태 또는 전자 장치(100)의 외부 환경을 감지할 수 있다. 그리고 센서 모듈(120)은 전자 장치(100)의 상태 또는 전자 장치(100)의 외부 환경에 대한 센싱 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 센서 모듈(120)은 가속도(acceleration) 센서, 힘(force) 센서, 위치(position) 센서, 자이로스코프(gyroscope) 센서, 레이더(RADAR) 센서, 라이다(LiDAR) 센서 또는 초음파 센서 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다.The sensor module 120 may detect a state of the electronic device 100 or an external environment of the electronic device 100 . In addition, the sensor module 120 may generate sensing data for the state of the electronic device 100 or the external environment of the electronic device 100 . For example, the sensor module 120 may include an acceleration sensor, a force sensor, a position sensor, a gyroscope sensor, a radar (RADAR) sensor, a lidar (LiDAR) sensor, or an ultrasonic sensor. may include at least one of
통신 모듈(130)은 전자 장치(100)에서 외부 장치(102, 104)와 통신을 수행할 수 있다. 통신 모듈(130)은 전자 장치(100)와 외부 장치(102, 104) 간 통신 채널을 수립하고, 통신 채널을 통해, 외부 장치(102, 104)와 통신을 수행할 수 있다. 여기서, 외부 장치(102, 104)는 위성, 기지국, 서버 또는 다른 전자 장치 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다. 통신 모듈(130)은 유선 통신 모듈 또는 무선 통신 모듈 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다. 유선 통신 모듈은 외부 장치(102)와 유선으로 연결되어, 유선으로 통신할 수 있다. 무선 통신 모듈은 근거리 통신 모듈 또는 원거리 통신 모듈 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다. 근거리 통신 모듈은 외부 장치(102)와 근거리 통신 방식으로 통신할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 근거리 통신 방식은, 블루투스(Bluetooth), 와이파이 다이렉트(WiFi direct), 또는 적외선 통신(IrDA; infrared data association) 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다. 원거리 통신 모듈은 외부 장치(104)와 원거리 통신 방식으로 통신할 수 있다. 여기서, 원거리 통신 모듈은 네트워크(190)를 통해 외부 장치(104)와 통신할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 네트워크(190)는 셀룰러 네트워크, 인터넷, 또는 LAN(local area network)이나 WAN(wide area network)과 같은 컴퓨터 네트워크 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다.The
입력 모듈(140)은 전자 장치(100)의 적어도 하나의 구성 요소에 사용될 신호를 입력할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 입력 모듈(140)은 마이크로폰(microphone), 마우스(mouse) 또는 키보드(keyboard) 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다. 어떤 실시예에서, 입력 모듈(140)은 터치를 감지하도록 설정된 터치 회로(touch circuitry) 또는 터치에 의해 발생되는 힘의 세기를 측정하도록 설정된 센서 회로 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다.The input module 140 may input a signal to be used in at least one component of the electronic device 100 . For example, the input module 140 may include at least one of a microphone, a mouse, and a keyboard. In some embodiments, the input module 140 may include at least one of a touch circuitry configured to sense a touch or a sensor circuit configured to measure the intensity of a force generated by the touch.
출력 모듈(150)은 전자 장치(100)의 외부로 정보를 제공할 수 있다. 이 때 출력 모듈(150)은 표시 모듈 또는 오디오 모듈 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다. 표시 모듈은 정보를 시각적으로 출력할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 표시 모듈은 디스플레이, 홀로그램 장치, 또는 프로젝터 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다. 어떤 실시예에서, 표시 모듈은 입력 모듈(140)의 터치 회로 또는 센서 회로 중 적어도 어느 하나와 조립되어, 터치 스크린으로 구현될 수 있다. 오디오 모듈은 정보를 소리로 출력할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 오디오 모듈은 스피커 또는 리시버 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다.The output module 150 may provide information to the outside of the electronic device 100 . In this case, the output module 150 may include at least one of a display module and an audio module. The display module may visually output information. For example, the display module may include at least one of a display, a hologram device, and a projector. In some embodiments, the display module may be implemented as a touch screen by being assembled with at least one of a touch circuit and a sensor circuit of the input module 140 . The audio module may output information as sound. For example, the audio module may include at least one of a speaker and a receiver.
햅틱 모듈(160)은 햅틱 신호를 발생시킬 수 있다. 햅틱 신호는, 전자 장치(100)의 사용자가 촉감을 통해서 인지할 수 있는 자극을 나타내며, 기계적인 자극, 예컨대 진동 신호나 움직임, 또는 전기적인 자극 중 적어도 어느 하나로 이루어질 수 있다. 햅틱 모듈(160)은 전기적 신호를 기계적인 자극 또는 전기적인 자극 중 적어도 어느 하나로 변환함으로써, 햅틱 신호를 발생시킬 수 있다.The haptic module 160 may generate a haptic signal. The haptic signal represents a stimulus that can be recognized by the user of the electronic device 100 through tactile sense, and may be made of at least one of a mechanical stimulus, for example, a vibration signal, a movement, or an electrical stimulus. The haptic module 160 may generate a haptic signal by converting the electrical signal into at least one of a mechanical stimulus and an electrical stimulus.
메모리(170)는 전자 장치(100)의 적어도 하나의 구성 요소에 의해 사용되는 다양한 데이터를 저장할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 메모리(170)는 휘발성 메모리 또는 비휘발성 메모리 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다. 데이터는 적어도 하나의 프로그램 및 이와 관련된 입력 데이터 또는 출력 데이터를 포함할 수 있다. 프로그램은 메모리(170)에 적어도 하나의 명령을 포함하는 소프트웨어로서 저장될 수 있으며, 예컨대 운영 체제, 미들 웨어 또는 어플리케이션 중 적어도 어느 하나를 포함할 수 있다.The
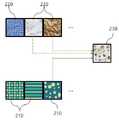
프로세서(180)는 메모리(170)의 프로그램을 실행하여, 전자 장치(100)의 적어도 하나의 구성 요소를 제어할 수 있다. 이를 통해, 프로세서(180)는 데이터 처리 또는 연산을 수행할 수 있다. 이 때 프로세서(180)는 메모리(170)에 저장된 명령을 실행할 수 있다. 다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는, 햅틱 모듈(160)을 통해, 가상 객체의 표면에 대한 햅틱 신호를 발생시킬 수 있다. 이를 통해, 전자 장치(100)의 사용자는 촉감을 통해, 햅틱 신호로부터 가상 객체의 표면을 인지할 수 있다. 이 때 프로세서(180)는, 도 2에 도시된 바와 같이 하나의 매크로 패턴 모델(macro pattern model)(210)과 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(micro texture model)(220)들을 기반으로, 햅틱 모델(haptik model)(230)을 생성하고, 햅틱 모델(230)을 이용하여, 햅틱 신호를 발생시킬 수 있다. 여기서, 매크로 패턴 모델은 가상 객체의 표면에 대한 규칙성을 표현하고, 마이크로 패턴 모델들은 가상 객체의 표면의 질감을 표현할 수 있다.The
이를 위해, 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들이 구현될 수 있다. 이 때 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들은 다양한 방법으로 구현될 수 있다.To this end, a plurality of
일 예로, 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들은, 도 3에 도시된 바와 같이 실제 객체에 대한 이미지로부터 생성될 수 있다. 이를 위해, 이미지의 필터링(filtering)을 통해, 이미지의 각 픽셀에 대한 정보, 예컨대 밝기 또는 색상 중 적어도 어느 하나 및 이미지 내 경계 등이 추출될 수 있다. 각 픽셀에 대한 정보는 각 픽셀의 컬러 값에 대한 선형 조합으로 계산될 수 있다. 이미지 내 경계는 경계 추출 필터에 의한 각 픽셀의 색상에 대한 콘볼루션 연산을 통해 추출될 수 있다. 이를 통해, 이미지는 복수 개의 영역들로 분할될 수 있다. 여기서, 각 픽셀은 밝기에 따라, 영역들 중 어느 하나로 분류될 수 있다. 밝기가 80 이하이면, 제 1 영역으로 결정되고, 밝기가 80을 초과하고 160 이하이면, 제 2 영역으로 결정되고, 밝기가 160을 초과하면, 제 3 영역으로 결정될 수 있다. 또는, 각 픽셀은 색상에 따라, 영역들 중 어느 하나로 분류될 수 있다. 레드(red; R) 색상이 그린(green; G) 색상 또는 블루(blue; B) 색상 보다 크면, 제 1 영역으로 결정되고, 그렇지 않으면, 제 2 영역으로 결정될 수 있다. 또는, 각 픽셀은 경계 추출 필터에 의해 연산된 값에 따라, 영역들 중 어느 하나로 분류될 수 있다. 경계 추출 필터에 의해 연산된 값이 이미지의 전체 평균값 보다 크면, 제 1 영역으로 결정되고, 그렇지 않으면, 제 2 영역으로 결정될 수 있다.As an example, the plurality of
다른 예로, 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들은, 일정한 패턴들이 반복되는 구조로 구현될 수 있다. 여기서, 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들은, 체스판과 같이, 사각형 형태의 영역들이 배열된 구조로 구현될 수 있다. 영역들은 동일한 사이즈로 이루어질 수 있으며, 영역들 중 적어도 어느 두 개는 서로 다른 사이즈들로 이루어질 수도 있다. 또는, 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들은, 바둑판과 같이, 줄 형태의 영역들과 복수 개의 줄들에 의해 구분되는 영역들이 배열된 구조로 구현될 수 있다. 줄들은 일정한 굵기로 이루어질 수 있으며, 줄들 중 적어도 어느 두 개는 서로 다른 굵기들로 이루어질 수도 있다. 한편, 줄들은 일정한 간격들로 이격될 수 있으며, 다양한 간격들로 이격될 수도 있다.As another example, the plurality of
또 다른 예로, 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들은 통계적으로 구현될 수 있다. 여기서, 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들은, 예컨대 가우시안 분포를 기반으로 구현될 수 있다. 평균 0, 표준 편차 1인 가우시안 분포에서, a 개의 값들이 2차원 공간의 x 좌표들로 정해지고, a 개의 값들이 2차원 공간의 y 좌표들로 정해지고, a 개의 값들이 각 위치에서의 원형 영역의 반지름으로 정해질 수 있다. 이를 통해, 특정 통계 분포를 바탕으로, 각 그룹의 빈도나 크기의 배치가 결정됨으로써, 복수 개의 영역들로 이루어지는 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들이 구현될 수 있다.As another example, the plurality of
또 다른 예로, 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들은, 예컨대 셀룰러 오토마타(cellular automata) 또는 신경망(neural network)를 이용한 인공 지능 등을 통해 구현될 수 있다. 여기서, 미리 설정되는 기준값을 기반으로, 그레이 스케일(gray scale) 값을 구분함으로써, 복수 개의 영역들로 이루어지는 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들이 구현될 수 있다.As another example, the plurality of
아울러, 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들이 구현될 수 있다. 이 때 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들은 다양한 방법으로 구현될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들은 데이터 중심(data-driven) 방법으로 구현될 수 있다. 이를 위해, 사람이 실제 객체의 표면과 접촉할 때 인가되는 힘과 속도 등의 제 1 측정 데이터, 및 동시에 사람이 느끼는 진동이나 힘 등의 제 2 측정 데이터가 검출될 수 있다. 일 예로, 실제 객체와 사람의 신체에 각종 센서들이 부착되고, 사람이 실제 객체의 표면과 접촉할 때, 센서들을 통해, 제 1 측정 데이터와 제 2 측정 데이터가 검출될 수 있다. 그리고, 제 1 측정 데이터와 제 2 측정 데이터에 대한 분석을 통해, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들이 구현될 수 있다. 여기서, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들은, 다양한 전기적 신호들이 속도 정보와 힘 정보에 각각 매핑된 테이블 구조로 구현될 수 있다.In addition, a plurality of
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는 전자 장치(100)의 위치와 속도 및 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 사용자로부터의 힘을 측정할 수 있다. 프로세서(180)는 센서 모듈(120) 또는 통신 모듈(130) 중 적어도 어느 하나를 통해, 전자 장치(100)의 위치를 측정할 수 있다. 일 예로, 프로세서(180)는 통신 모듈(130)을 통해, 외부 장치(104), 예컨대 위성 또는 기지국과 통신하여, 전자 장치(100)의 위치를 측정할 수 있다. 프로세서(180)는 센서 모듈(120)을 통해, 전자 장치(100)의 속도와 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘을 측정할 수 있다. 또는, 프로세서(180)는 센서 모듈(120)을 통해, 전자 장치(100)의 가속도를 측정할 수 있다. 일 예로, 프로세서(180)는 전자 장치(100)의 가속도로부터 전자 장치(100)의 속도와 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘을 추정할 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는 하나의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)과 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(180)는 전자 장치(100)의 위치를 기반으로, 매크로 패턴 모델(210)를 결정할 수 있다. 그리고, 프로세서(180)는 매크로 패턴 모델(210)을 기반으로, 전자 장치(100)의 위치에 대응하여 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 결정할 수 있다. 또한, 프로세서(180)는 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로, 전자 장치(100)의 속도와 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘에 대응하여 햅틱 신호를 발생시킬 수 있다. 이 때 프로세서(180)는 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로, 전자 장치(100)의 속도 및 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘과 함께, 이전에 발생된 햅틱 신호들에 대한 히스토리(history)에 대응하여 햅틱 신호를 발생시킬 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the
일 실시예에 따르면, 메모리(170)는 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들과 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 저장하고 있을 수 있다. 예를 들면, 프로세서(180)는 통신 모듈(130)을 통해, 외부 장치(102, 104)로부터 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들과 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 수신하고, 이들을 메모리(170)에 저장할 수 있다. 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들은 위치 정보와 각각 매핑되어 있을 수 있다. 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들은 속도 정보 및 힘 정보와 각각 매핑되어 있거나, 가속도 정보와 각각 매핑되어 있을 수 있다. 이를 통해, 프로세서(180)는 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들 중 어느 하나 및 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들 중 적어도 어느 두 개를 선택할 수 있다.According to an embodiment, the
다른 실시예에 따르면, 외부 장치(102, 104)가 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들과 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 저장하고 있을 수 있다. 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들은 위치 정보와 각각 매핑되어 있을 수 있다. 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들은 속도 정보 및 힘 정보와 각각 매핑되어 있거나, 가속도 정보와 각각 매핑되어 있을 수 있다. 이러한 경우, 프로세서(180)는 통신 모듈(130)을 통해, 외부 장치(102, 104)에 전자 장치(100)의 위치와 속도 및 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘을 전송할 수 있다. 이를 통해, 외부 장치(102, 104)는 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들 중 어느 하나 및 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들 중 적어도 어느 두 개를 선택할 수 있다. 따라서, 프로세서(180)는 통신 모듈(130)을 통해, 외부 장치(102, 104)에서 선택된 매크로 패턴 모델(210)과 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 수신할 수 있다.According to another embodiment, the external devices 102 and 104 may store a plurality of
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는 하나의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)과 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로, 햅틱 신호를 발생시킬 수 있다. 프로세서(180)는 매크로 패턴 모델(210)에 따라, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 혼합하여, 햅틱 모델(230)을 생성할 수 있다. 일 실시예에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는 매크로 패턴 모델(210)의 전체 영역에 대해, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 균일하게 혼합할 수 있다. 이 때 프로세서(180)는 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 미리 정해진 비율로 혼합할 수 있다. 다른 실시예에 따르면, 매크로 패턴 모델(210)은 복수 개의 영역들을 포함할 수 있다. 여기서, 영역들은 규칙적으로 배열될 수 있으며, 불규칙적으로 배열될 수도 있다. 한편, 영역들은 모두 동일한 사이즈로 이루어질 수 있으며, 영역들 중 적어도 어느 두 개는 서로 다른 사이즈들로 이루어질 수도 있다. 이 때 프로세서(180)는 영역들에 따라 서로 다른 비율들로, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 혼합할 수 있다. 그리고, 프로세서(180)는 햅틱 모듈(160)을 통해, 햅틱 모델(230)을 이용하여, 햅틱 신호를 발생시킬 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the
다양한 실시예들에 따른 전자 장치(100)는, 메모리(170), 및 메모리(170)와 연결되고, 메모리(170)에 저장된 적어도 하나의 명령을 실행하도록 구성된 프로세서(180)를 포함할 수 있다.The electronic device 100 according to various embodiments may include a
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는, 가상 객체의 표면에 대한 규칙성을 표현하기 위한 매크로 패턴 모델(210)을 결정하고, 가상 객체의 표면의 질감을 표현하기 위한 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 결정하고, 결정된 매크로 패턴 모델(210)과 결정된 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로, 햅틱 신호를 발생시키도록 구성될 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는, 결정된 매크로 패턴 모델(210)에 따라, 결정된 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 혼합하여, 햅틱 모델(230)을 생성하고, 햅틱 모델(230)을 이용하여, 햅틱 신호를 발생시키도록 구성될 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는, 매크로 패턴 모델(210)을 기반으로, 전자 장치(100)의 위치에 대응하여 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 결정하도록 구성될 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로, 전자 장치(100)의 속도 및 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘에 대응하여 햅틱 신호를 발생시키도록 구성될 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로, 속도 및 힘과 함께, 이전에 발생된 햅틱 신호들에 대한 히스토리에 대응하여 햅틱 신호를 발생시키하도록 구성되는 장치.According to various embodiments, the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 전자 장치(100)는, 외부 장치(102, 104)와 통신하기 위한 통신 모듈(130)을 더 포함할 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the electronic device 100 may further include a
일 실시예에 따르면, 메모리(170)는, 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들과 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 저장하고 있을 수 있다.According to an embodiment, the
일 실시예에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는, 저장된 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들 중 어느 하나를 선택하고, 저장된 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들 중 적어도 어느 두 개를 선택하도록 구성될 수 있다.According to an embodiment, the
일 실시예에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는, 통신 모듈(130)을 통해, 외부 장치(102, 104)로부터 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들과 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 수신하도록 구성될 수 있다.According to an embodiment, the
다른 실시예에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는, 통신 모듈(130)을 통해, 위치를 기반으로, 외부 장치(102, 104)로부터 매크로 패턴 모델(210)을 수신하도록 구성될 수 있다.According to another embodiment, the
다른 실시예에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는, 통신 모듈(130)을 통해, 속도 및 힘을 기반으로, 외부 장치(102, 104)로부터 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 수신하도록 구성될 수 있다.According to another embodiment, the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 매크로 패턴 모델(210)은, 실제 객체에 대한 이미지로부터 생성되며, 이미지의 각 픽셀에 대한 정보를 기반으로 구분되는 복수 개의 영역들로 이루어질 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들은, 매크로 패턴 모델(210)의 영역들에 따라 다르게 혼합될 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the
도 4는 다양한 실시예들에 따른 전자 장치(100)의 동작 방법을 도시하는 도면이다.4 is a diagram illustrating a method of operating the electronic device 100 according to various embodiments of the present disclosure.
도 4를 참조하면, 전자 장치(100)는 410 동작에서 전자 장치(100)의 위치와 속도 및 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘을 측정할 수 있다. 프로세서(180)는 전자 장치(100)의 위치와 속도 및 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 사용자로부터의 힘을 측정할 수 있다. 프로세서(180)는 센서 모듈(120) 또는 통신 모듈(130) 중 적어도 어느 하나를 통해, 전자 장치(100)의 위치를 측정할 수 있다. 일 예로, 프로세서(180)는 통신 모듈(130)을 통해, 외부 장치(104), 예컨대 위성 또는 기지국과 통신하여, 전자 장치(100)의 위치를 측정할 수 있다. 프로세서(180)는 센서 모듈(120)을 통해, 전자 장치(100)의 속도와 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘을 측정할 수 있다. 또는, 프로세서(180)는 센서 모듈(120)을 통해, 전자 장치(100)의 가속도를 측정할 수 있다. 일 예로, 프로세서(180)는 전자 장치(100)의 가속도로부터 전자 장치(100)의 속도와 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘을 추정할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 4 , in
전자 장치(100)는 420 동작에서 하나의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)을 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(180)는 전자 장치(100)의 위치를 기반으로, 매크로 패턴 모델(210)를 결정할 수 있다.The electronic device 100 may determine one
전자 장치(100)는 430 동작에서 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 결정할 수 있다. 프로세서(180)는 매크로 패턴 모델(210)을 기반으로, 전자 장치(100)의 위치에 대응하여 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 결정할 수 있다.The electronic device 100 may determine at least two
전자 장치(100)는 440 동작에서 매크로 패턴 모델(210)과 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로, 햅틱 모델(230)을 생성할 수 있다. 프로세서(180)는 매크로 패턴 모델(210)에 따라, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 혼합하여, 햅틱 모델(230)을 생성할 수 있다. 프로세서(180)는 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로, 전자 장치(100)의 속도와 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘에 대응하여 햅틱 모델(230)을 생성할 수 있다. 이 때 프로세서(180)는 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로, 전자 장치(100)의 속도 및 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘과 함께, 이전에 발생된 햅틱 신호들에 대한 히스토리에 대응하여 햅틱 모델(230)을 생성할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 메모리(170)는 자동회귀 형태의 테이블 구조로, 전자 장치(100)의 속도 및 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘의 쌍에 대해, n 개의 계수들(α1, α2, α3, ..., αn)을 저장하고 있을 수 있다. 이를 통해, 프로세서(180)는 전자 장치(100)의 속도 및 전자 장치(100)에 인가되는 힘의 쌍을 기반으로, n 개의 계수들(α1, α2, α3, ..., αn)을 결정할 수 있다. 그리고, 프로세서(180)는 이전에 발생된 햅틱 신호들에 대한 히스토리로부터, n 개의 햅틱 신호들(Yt-1, Yt-2, Yt-3, ..., Yt-n)을 결정할 수 있다. 이를 통해, 프로세서(180)는, 하기 [수학식 1]과 같이 n 개의 계수들과 n 개의 햅틱 신호들을 기반으로, 새로운 햅틱 모델(230)을 결정할 수 있다.In
일 실시예에 따르면, 프로세서(180)는 매크로 패턴 모델(210)의 전체 영역에 대해, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 균일하게 혼합할 수 있다. 이 때 프로세서(180)는 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 미리 정해진 비율로 혼합할 수 있다. 다른 실시예에 따르면, 매크로 패턴 모델(210)은 복수 개의 영역들을 포함할 수 있다. 여기서, 영역들은 규칙적으로 배열될 수 있으며, 불규칙적으로 배열될 수도 있다. 한편, 영역들은 모두 동일한 사이즈로 이루어질 수 있으며, 영역들 중 적어도 어느 두 개는 서로 다른 사이즈들로 이루어질 수도 있다. 이 때 프로세서(180)는 영역들에 따라 서로 다른 비율들로, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 혼합할 수 있다.According to an embodiment, the
전자 장치(100)는 450 동작에서 햅틱 모델(230)을 이용하여, 햅틱 신호를 발생시킬 수 있다. 프로세서(180)는 햅틱 모듈(160)을 통해, 햅틱 모델(230)을 이용하여, 햅틱 신호를 발생시킬 수 있다.The electronic device 100 may generate a haptic signal by using the
다양한 실시예들에 따른 전자 장치(100)의 동작 방법은, 가상 객체의 표면에 대한 규칙성을 표현하기 위한 매크로 패턴 모델(210)을 결정하는 동작, 가상 객체의 표면의 질감을 표현하기 위한 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 결정하는 동작, 및 결정된 매크로 패턴 모델(210)과 결정된 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로, 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 동작을 포함할 수 있다.The operating method of the electronic device 100 according to various embodiments includes an operation of determining a
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 동작은, 결정된 매크로 패턴 모델(210)에 따라, 결정된 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 혼합하여, 햅틱 모델(230)을 생성하는 동작, 및 햅틱 모델(230)을 이용하여, 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 동작을 포함할 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the operation of generating a haptic signal includes an operation of generating the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 결정하는 동작은, 매크로 패턴 모델(210)을 기반으로, 전자 장치의 위치에 대응하여 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 결정하는 동작을 포함할 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the operation of determining the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 동작은, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로, 전자 장치(100)의 속도 및 전자 장치에 인가되는 힘에 대응하여 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 동작을 포함하는 방법.According to various embodiments, the operation of generating a haptic signal includes an operation of generating a haptic signal in response to a speed of the electronic device 100 and a force applied to the electronic device based on the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 동작은, 속도 및 힘과 함께, 이전에 발생된 햅틱 신호들에 대한 히스토리에 대응하여 햅틱 신호를 발생시킬 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the operation of generating a haptic signal may generate a haptic signal in response to a history of previously generated haptic signals together with speed and force.
일 실시예에 따르면, 전자 장치(100)는, 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들과 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 저장하고 있을 수 있다.According to an embodiment, the electronic device 100 may store a plurality of
일 실시예에 따르면, 매크로 패턴 모델(210)을 결정하는 동작은, 저장된 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들 중 어느 하나를 선택하는 동작을 포함할 수 있다.According to an embodiment, the operation of determining the
일 실시예에 따르면, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 결정하는 동작은, 저장된 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들 중 적어도 어느 두 개를 선택하는 동작을 포함할 수 있다.According to an embodiment, the operation of determining the
일 실시예에 따르면, 전자 장치(100)는, 외부 장치(102, 104)로부터 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델(210)들과 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 수신할 수 있다.According to an embodiment, the electronic device 100 may receive a plurality of
다른 실시예에 따르면, 매크로 패턴 모델(210)을 결정하는 동작은, 위치를 기반으로, 외부 장치(102, 104)로부터 매크로 패턴 모델(210)을 수신하는 방법.According to another embodiment, the determining of the
다른 실시예에 따르면, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 결정하는 동작은, 속도 및 힘을 기반으로, 외부 장치(102, 104)로부터 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 수신할 수 있다.According to another embodiment, the operation of determining the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 매크로 패턴 모델(210)은, 실제 객체에 대한 이미지로부터 생성되며, 이미지의 각 픽셀에 대한 정보를 기반으로 구분되는 복수 개의 영역들로 이루어질 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들은, 영역들에 따라 다르게 혼합될 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the
본 문서의 다양한 실시예들은 컴퓨터 장치(예: 전자 장치(100))에 의해 읽을 수 있는 기록 매체(storage medium)(예: 메모리(130))에 저장된 하나 이상의 명령들을 포함하는 컴퓨터 프로그램으로서 구현될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 컴퓨터 장치의 프로세서(예: 프로세서(140))는, 기록 매체로부터 저장된 하나 이상의 명령들 중 적어도 하나를 호출하고, 그것을 실행할 수 있다. 이것은 컴퓨터 장치가 호출된 적어도 하나의 명령에 따라 적어도 하나의 기능을 수행하도록 운영되는 것을 가능하게 한다. 하나 이상의 명령들은 컴파일러에 의해 생성된 코드 또는 인터프리터에 의해 실행될 수 있는 코드를 포함할 수 있다. 컴퓨터 장치로 읽을 수 있는 기록 매체는, 비일시적(non-transitory) 기록 매체의 형태로 제공될 수 있다. 여기서, ‘비일시적’은 기록 매체가 실재(tangible)하는 장치이고, 신호(signal)(예: 전자기파)를 포함하지 않는다는 것을 의미할 뿐이며, 이 용어는 데이터가 기록 매체에 반영구적으로 저장되는 경우와 임시적으로 저장되는 경우를 구분하지 않는다.Various embodiments of the present document may be implemented as a computer program including one or more instructions stored in a storage medium (eg, memory 130) readable by a computer device (eg, electronic device 100). can For example, the processor (eg, the processor 140 ) of the computer device may call at least one of one or more instructions stored from a recording medium and execute it. This enables the computer device to be operated to perform at least one function in accordance with at least one command invoked. The one or more instructions may include code generated by a compiler or code executable by an interpreter. The computer-readable recording medium may be provided in the form of a non-transitory recording medium. Here, 'non-transitory' only means that the recording medium is a tangible device and does not contain a signal (eg, electromagnetic wave), and this term is used in cases where data is semi-permanently stored in the recording medium and It does not distinguish between temporary storage cases.
다양한 실시예들에 따른 컴퓨터 프로그램은, 가상 객체의 표면에 대한 규칙성을 표현하기 위한 매크로 패턴 모델(210)을 결정하는 동작, 가상 객체의 표면의 질감을 표현하기 위한 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 결정하는 동작, 및 결정된 매크로 패턴 모델(210)과 결정된 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로, 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 동작을 실행할 수 있다.The computer program according to various embodiments performs an operation of determining the
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 전자 장치(100)가 매크로 패턴 모델(210)과 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 기반으로 햅틱 신호를 발생시킴으로써, 다양한 표면들을 표현할 수 있다. 이 때 전자 장치(100)는 매크로 패턴 모델(210)에 따라, 마이크로 텍스처 모델(220)들을 혼합하여, 가상 객체의 표면에 대한 규칙성과 질감을 모두 표현할 수 있다.According to various embodiments, the electronic device 100 may represent various surfaces by generating a haptic signal based on the
본 문서의 다양한 실시예들 및 이에 사용된 용어들은 본 문서에 기재된 기술을 특정한 실시 형태에 대해 한정하려는 것이 아니며, 해당 실시 예의 다양한 변경, 균등물, 및/또는 대체물을 포함하는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. 도면의 설명과 관련하여, 유사한 구성 요소에 대해서는 유사한 참조 부호가 사용될 수 있다. 단수의 표현은 문맥상 명백하게 다르게 뜻하지 않는 한, 복수의 표현을 포함할 수 있다. 본 문서에서, "A 또는 B", "A 및/또는 B 중 적어도 하나", "A, B 또는 C" 또는 "A, B 및/또는 C 중 적어도 하나" 등의 표현은 함께 나열된 항목들의 모든 가능한 조합을 포함할 수 있다. "제 1", "제 2", "첫째" 또는 "둘째" 등의 표현들은 해당 구성 요소들을, 순서 또는 중요도에 상관없이 수식할 수 있고, 한 구성 요소를 다른 구성 요소와 구분하기 위해 사용될 뿐 해당 구성 요소들을 한정하지 않는다. 어떤(예: 제 1) 구성 요소가 다른(예: 제 2) 구성 요소에 "(기능적으로 또는 통신적으로) 연결되어" 있다거나 "접속되어" 있다고 언급된 때에는, 상기 어떤 구성 요소가 상기 다른 구성 요소에 직접적으로 연결되거나, 다른 구성 요소(예: 제 3 구성 요소)를 통하여 연결될 수 있다.The various embodiments of this document and the terms used therein are not intended to limit the technology described in this document to a specific embodiment, but it should be understood to include various modifications, equivalents, and/or substitutions of the embodiments. In connection with the description of the drawings, like reference numerals may be used for like components. The singular expression may include the plural expression unless the context clearly dictates otherwise. In this document, expressions such as “A or B”, “at least one of A and/or B”, “A, B or C” or “at least one of A, B and/or C” refer to all of the items listed together. Possible combinations may be included. Expressions such as “first”, “second”, “first” or “second” can modify the corresponding components regardless of order or importance, and are only used to distinguish one component from another. It does not limit the corresponding components. When an (eg, first) component is referred to as being “connected (functionally or communicatively)” or “connected” to another (eg, second) component, that component is It may be directly connected to the component or may be connected through another component (eg, a third component).
본 문서에서 사용된 용어 "모듈"은 하드웨어, 소프트웨어 또는 펌웨어로 구성된 유닛을 포함하며, 예를 들면, 로직, 논리 블록, 부품, 또는 회로 등의 용어와 상호 호환적으로 사용될 수 있다. 모듈은, 일체로 구성된 부품 또는 하나 또는 그 이상의 기능을 수행하는 최소 단위 또는 그 일부가 될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 모듈은 ASIC(application-specific integrated circuit)으로 구성될 수 있다.As used herein, the term “module” includes a unit composed of hardware, software, or firmware, and may be used interchangeably with terms such as, for example, logic, logic block, component, or circuit. A module may be an integrally formed part or a minimum unit or a part of performing one or more functions. For example, the module may be configured as an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC).
다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 기술한 구성 요소들의 각각의 구성 요소(예: 모듈 또는 프로그램)는 단수 또는 복수의 개체를 포함할 수 있다. 다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 전술한 해당 구성 요소들 중 하나 이상의 구성 요소들 또는 동작들이 생략되거나, 또는 하나 이상의 다른 구성 요소들 또는 동작들이 추가될 수 있다. 대체적으로 또는 추가적으로, 복수의 구성 요소들(예: 모듈 또는 프로그램)은 하나의 구성 요소로 통합될 수 있다. 이런 경우, 통합된 구성 요소는 복수의 구성 요소들 각각의 구성 요소의 하나 이상의 기능들을 통합 이전에 복수의 구성 요소들 중 해당 구성 요소에 의해 수행되는 것과 동일 또는 유사하게 수행할 수 있다. 다양한 실시예들에 따르면, 모듈, 프로그램 또는 다른 구성 요소에 의해 수행되는 동작들은 순차적으로, 병렬적으로, 반복적으로, 또는 휴리스틱하게 실행되거나, 동작들 중 하나 이상이 다른 순서로 실행되거나, 생략되거나, 또는 하나 이상의 다른 동작들이 추가될 수 있다.According to various embodiments, each component (eg, a module or a program) of the described components may include a singular or a plurality of entities. According to various embodiments, one or more components or operations among the above-described corresponding components may be omitted, or one or more other components or operations may be added. Alternatively or additionally, a plurality of components (eg, a module or a program) may be integrated into one component. In this case, the integrated component may perform one or more functions of each component of the plurality of components identically or similarly to those performed by the corresponding component among the plurality of components prior to integration. According to various embodiments, operations performed by a module, program, or other component are executed sequentially, in parallel, repeatedly, or heuristically, or one or more of the operations are executed in a different order, omitted, or , or one or more other operations may be added.
Claims (20)
Translated fromKorean가상 객체의 표면에 대한 규칙성을 표현하기 위한 매크로 패턴 모델을 결정하는 동작;
상기 가상 객체의 상기 표면의 질감을 표현하기 위한 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 결정하는 동작; 및
상기 결정된 매크로 패턴 모델과 상기 결정된 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 기반으로, 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 동작을 포함하고,
상기 매크로 패턴 모델을 결정하는 동작은,
상기 전자 장치의 위치를 측정하는 동작; 및
상기 위치를 기반으로, 상기 매크로 패턴 모델을 결정하는 동작을 포함하고,
상기 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 결정하는 동작은,
상기 매크로 패턴 모델을 기반으로, 상기 위치에 대응하여 상기 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 결정하는 동작을 포함하는 방법.
A method of operating an electronic device, comprising:
determining a macro pattern model for expressing regularity with respect to the surface of the virtual object;
determining at least two micro-texture models for representing the texture of the surface of the virtual object; and
and generating a haptic signal based on the determined macro pattern model and the determined micro texture models,
The operation of determining the macro pattern model is,
measuring a position of the electronic device; and
Based on the location, comprising the operation of determining the macro pattern model,
The operation of determining the micro-texture models comprises:
and determining the micro texture models corresponding to the position based on the macro pattern model.
상기 결정된 매크로 패턴 모델에 따라, 상기 결정된 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 혼합하여, 햅틱 모델을 생성하는 동작; 및
상기 햅틱 모델을 이용하여, 상기 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 동작을 포함하는 방법.
The method of claim 1, wherein the generating of the haptic signal comprises:
generating a haptic model by mixing the determined micro-texture models according to the determined macro pattern model; and
and generating the haptic signal by using the haptic model.
상기 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 기반으로, 상기 전자 장치의 속도 및 상기 전자 장치에 인가되는 힘에 대응하여 상기 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 동작을 포함하는 방법.
The method of claim 1, wherein the generating of the haptic signal comprises:
and generating the haptic signal in response to a speed of the electronic device and a force applied to the electronic device, based on the microtexture models.
상기 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 기반으로, 상기 속도 및 상기 힘과 함께, 이전에 발생된 햅틱 신호들에 대한 히스토리에 대응하여 상기 햅틱 신호를 발생시키는 방법.
The method of claim 4, wherein the generating of the haptic signal comprises:
A method for generating the haptic signal in response to a history of previously generated haptic signals, along with the velocity and the force, based on the microtexture models.
복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델들과 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 저장하고 있고,
상기 매크로 패턴 모델을 결정하는 동작은,
상기 저장된 매크로 패턴 모델들 중 어느 하나를 선택하는 동작을 포함하고,
상기 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 결정하는 동작은,
상기 저장된 마이크로 텍스처 모델들 중 적어도 어느 두 개를 선택하는 동작을 포함하는 방법.
According to claim 1, wherein the electronic device,
It stores a plurality of macro pattern models and a plurality of micro texture models,
The operation of determining the macro pattern model is,
Including the operation of selecting any one of the stored macro pattern models,
The operation of determining the micro-texture models comprises:
and selecting at least any two of the stored micro-texture models.
외부 장치로부터 상기 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델들과 상기 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 수신하는 방법.
The method of claim 6, wherein the electronic device comprises:
A method of receiving the plurality of macro pattern models and the plurality of micro texture models from an external device.
메모리; 및
상기 메모리와 연결되고, 상기 메모리에 저장된 적어도 하나의 명령을 실행하도록 구성된 프로세서를 포함하고,
상기 프로세서는,
가상 객체의 표면에 대한 규칙성을 표현하기 위한 매크로 패턴 모델을 결정하고,
상기 가상 객체의 상기 표면의 질감을 표현하기 위한 적어도 두 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 결정하고,
상기 결정된 매크로 패턴 모델과 상기 결정된 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 기반으로, 햅틱 신호를 발생시키도록 구성되고,
상기 프로세서는,
상기 전자 장치의 위치를 측정하고,
상기 위치를 기반으로, 상기 매크로 패턴 모델을 결정하고,
상기 매크로 패턴 모델을 기반으로, 상기 위치에 대응하여 상기 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 결정하도록 구성되는 장치.
In an electronic device,
Memory; and
a processor coupled to the memory and configured to execute at least one instruction stored in the memory;
The processor is
Determining a macro pattern model for expressing regularity on the surface of a virtual object,
determining at least two micro-texture models for representing the texture of the surface of the virtual object;
configured to generate a haptic signal based on the determined macro pattern model and the determined micro texture models;
The processor is
measuring the position of the electronic device;
Based on the location, determine the macro pattern model,
and determine, based on the macro pattern model, the micro texture models corresponding to the location.
상기 결정된 매크로 패턴 모델에 따라, 상기 결정된 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 혼합하여, 햅틱 모델을 생성하고,
상기 햅틱 모델을 이용하여, 상기 햅틱 신호를 발생시키도록 구성되는 장치.
The method of claim 11 , wherein the processor comprises:
generating a haptic model by mixing the determined micro-texture models according to the determined macro pattern model;
an apparatus configured to generate the haptic signal using the haptic model.
상기 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 기반으로, 상기 전자 장치의 속도 및 상기 전자 장치에 인가되는 힘에 대응하여 상기 햅틱 신호를 발생시키도록 구성되는 장치.
The method of claim 11 , wherein the processor comprises:
and generate the haptic signal in response to a speed of the electronic device and a force applied to the electronic device, based on the microtexture models.
상기 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 기반으로, 상기 속도 및 상기 힘과 함께, 이전에 발생된 햅틱 신호들에 대한 히스토리에 대응하여 상기 햅틱 신호를 발생시키도록 구성되는 장치.
15. The method of claim 14, wherein the processor,
and generate the haptic signal in response to a history of previously generated haptic signals, along with the velocity and the force, based on the microtexture models.
복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델들과 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 저장하고 있고,
상기 프로세서는,
상기 저장된 매크로 패턴 모델들 중 어느 하나를 선택하고,
상기 저장된 마이크로 텍스처 모델들 중 적어도 어느 두 개를 선택하도록 구성되는 장치.
The method of claim 11 , wherein the memory comprises:
It stores a plurality of macro pattern models and a plurality of micro texture models,
The processor is
Select any one of the stored macro pattern models,
and select at least any two of the stored micro-texture models.
외부 장치와 통신하기 위한 통신 모듈을 더 포함하고,
상기 프로세서는,
상기 통신 모듈을 통해, 상기 외부 장치로부터 상기 복수 개의 매크로 패턴 모델들과 상기 복수 개의 마이크로 텍스처 모델들을 수신하도록 구성되는 장치.
17. The method of claim 16,
Further comprising a communication module for communicating with an external device,
The processor is
and receive the plurality of macro pattern models and the plurality of micro texture models from the external device through the communication module.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190158086 | 2019-12-02 | ||
| KR20190158086 | 2019-12-02 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20210068974A KR20210068974A (en) | 2021-06-10 |
| KR102382194B1true KR102382194B1 (en) | 2022-04-04 |
Family
ID=76378292
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020200081825AActiveKR102382194B1 (en) | 2019-12-02 | 2020-07-03 | Electronic device providing double layer haptic model for high band width and high resolution texture expression and operating method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102382194B1 (en) |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20090024375A (en)* | 2007-09-04 | 2009-03-09 | 삼성전자주식회사 | System and method for improving visual tactile feel of textures according to texture properties |
| KR101992070B1 (en)* | 2009-03-12 | 2019-06-21 | 임머숀 코퍼레이션 | Systems and methods for a texture engine |
| US20130085893A1 (en)* | 2011-09-30 | 2013-04-04 | Ebay Inc. | Acquisition and use of query images with image feature data |
| US9196134B2 (en)* | 2012-10-31 | 2015-11-24 | Immersion Corporation | Method and apparatus for simulating surface features on a user interface with haptic effects |
| US9330544B2 (en)* | 2012-11-20 | 2016-05-03 | Immersion Corporation | System and method for simulated physical interactions with haptic effects |
| KR102275712B1 (en)* | 2014-10-31 | 2021-07-09 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Rendering method and apparatus, and electronic apparatus |
| US9600076B2 (en)* | 2014-12-19 | 2017-03-21 | Immersion Corporation | Systems and methods for object manipulation with haptic feedback |
| US9466188B2 (en)* | 2014-12-24 | 2016-10-11 | Immersion Corporation | Systems and methods for haptically-enabled alarms |
- 2020
- 2020-07-03KRKR1020200081825Apatent/KR102382194B1/enactiveActive
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 유용희 외 5인. 촉각기반 비디오 및 오디오 스트리밍 기술 개발. HCI 2009 학술대회, 538-541페이지. 한국 HCI학회. 2009년. 1부.* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20210068974A (en) | 2021-06-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102595150B1 (en) | Method for controlling multiple virtual characters, device, apparatus, and storage medium | |
| CN113486765B (en) | Gesture interaction method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| KR101975906B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for scaling layout of application program in visual display unit | |
| US12192394B2 (en) | Electronic device including rollable display | |
| CN108989678B (en) | Image processing method and mobile terminal | |
| US9311565B2 (en) | 3D scanning with depth cameras using mesh sculpting | |
| CN113052919B (en) | A visual sensor calibration method and device, electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN110084204B (en) | Image processing method and device based on target object posture and electronic equipment | |
| KR102648993B1 (en) | Electronic device for providing avatar based on emotion state of user and method thereof | |
| KR102347232B1 (en) | Electronic device for providing visual localization based on outdoor three-dimension map information and operating method thereof | |
| CN109495616B (en) | Photographing method and terminal equipment | |
| CN112970054A (en) | Electronic device for controlling display position or area of image according to change of content of image | |
| US20240212546A1 (en) | Electronic device comprising variable display and method for operating same | |
| KR102643447B1 (en) | Electronic device for location-based ar linking of object-based augmentation contents and operating method thereof | |
| KR20210115165A (en) | Electronic device for recognizing visual stimulus based on spontaneous selective neural response of deep artificial neural network and operating method thereof | |
| CN114247145B (en) | Method and device for displaying collision special effect of virtual object and electronic equipment | |
| KR102382194B1 (en) | Electronic device providing double layer haptic model for high band width and high resolution texture expression and operating method thereof | |
| WO2021004413A1 (en) | Handheld input device and blanking control method and apparatus for indication icon of handheld input device | |
| KR102063408B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for interaction with virtual objects | |
| US11449219B2 (en) | Electronic device including display device including touch sensor for controlling a cursor | |
| CN107977591B (en) | Two-dimensional code image identification method and mobile terminal | |
| CN109194943B (en) | An image processing method and terminal device | |
| CN112308766A (en) | Image data display method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| KR20150024009A (en) | Method for providing user input feedback and apparatus for the same | |
| CN117828962B (en) | Oil friction determination method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20200703 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20210830 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20220328 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20220330 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20220330 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration |