KR102376397B1 - A Data Augmentation Method for End-to-End Autonomous Driving Using Fast and Accurate Viewpoint Transformation - Google Patents
A Data Augmentation Method for End-to-End Autonomous Driving Using Fast and Accurate Viewpoint TransformationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102376397B1 KR102376397B1KR1020210127176AKR20210127176AKR102376397B1KR 102376397 B1KR102376397 B1KR 102376397B1KR 1020210127176 AKR1020210127176 AKR 1020210127176AKR 20210127176 AKR20210127176 AKR 20210127176AKR 102376397 B1KR102376397 B1KR 102376397B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- image
- camera
- enhancement
- pixel
- autonomous driving
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N5/00—Computing arrangements using knowledge-based models
- G06N5/02—Knowledge representation; Symbolic representation
- G06N5/022—Knowledge engineering; Knowledge acquisition
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T3/00—Geometric image transformations in the plane of the image
- G06T3/40—Scaling of whole images or parts thereof, e.g. expanding or contracting
- G06T3/4007—Scaling of whole images or parts thereof, e.g. expanding or contracting based on interpolation, e.g. bilinear interpolation
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T3/00—Geometric image transformations in the plane of the image
- G06T3/60—Rotation of whole images or parts thereof
- H04N5/23212—
- H04N5/23299—
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30248—Vehicle exterior or interior
- G06T2207/30252—Vehicle exterior; Vicinity of vehicle
- G06T2207/30256—Lane; Road marking
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Image Processing (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 시점 변환을 이용한 End-to-End AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법에 관한 것으로서, 더욱 상세하게는 입력되는 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하여 이루어지는 회전 증강(Rotational Augmentation)과 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행 이동하여 이루어지는 이동 증강(Translational Augmentation)의 실행으로 이미지를 정확하고 빠르게 변형시켜 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉽도록 하는 AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to an end-to-end AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method using viewpoint transformation, and more particularly, rotational augmentation made by changing the angle of a camera with respect to an input image and a camera report It relates to an AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method that makes it easy to learn in an artificial neural network by accurately and quickly transforming an image by executing translational augmentation, which is performed by moving in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which it is located.
자율주행 기술은 미래에 촉망되는 기술 중 하나로서, 최근 딥러닝의 발전에 힘입어 인공신경망을 활용한 자율주행 기술이 각광받고 있다.Autonomous driving technology is one of the promising technologies in the future, and thanks to the recent development of deep learning, autonomous driving technology using artificial neural networks is in the spotlight.
이에, 인공신경망을 활용한 기존의 자율주행 방법은 물체인식/거리추정→판단→제어 등 여러 단계를 거쳐 제어 명령을 내리도록 이루어져 있었고, 또한 최근에는 이미지를 인공신경망에 입력하여 바로 제어 명령(Steering, throttle)을 출력할 수 있도록 하는 End-to-End learning(E2E) 연구되고 있다.Therefore, the existing autonomous driving method using an artificial neural network consisted of issuing a control command through several steps such as object recognition/distance estimation → judgment → control. , throttle) are being studied for End-to-End learning (E2E).
상기 E2E는 기존의 단계적 학습 방법에 비해 성능이 각 단계에 해당하는 유닛에 대한 성능에 제한 받지 않고 인식에서 주행판단으로 직접 연결이 가능하여 더 나은 자율주행 성능을 가질 수 있는 것으로, 이는 기존의 단계적 학습방법에서 인식 유닛의 출력이 정확하지 않을 경우, 해당 출력을 입력받는 판단 유닛, 제어 유닛 또한 출력이 부정확해지고, 데이터 레이블링이 쉽다는 장점은 있다.Compared to the existing step-by-step learning method, the E2E performance is not limited by the performance of the unit corresponding to each step, and it can be directly connected from recognition to driving judgment, so that it can have better autonomous driving performance. In the learning method, when the output of the recognition unit is not correct, the output of the determination unit and the control unit receiving the corresponding output is also inaccurate, and there are advantages in that data labeling is easy.
이에, 기존의 방법에서는 각 단계별 유닛을 학습시키기 위해서 서로 다른 레이블링 방법이 필요하다.Accordingly, in the existing method, different labeling methods are required to learn the units for each step.
예를 들어, 인식 유닛에서는 이미지로부터 어떤 부분이 도로이고 비도로인지 픽셀별로 레이블링을 해야하고, 판단 유닛에서는 인식 유닛으로부터 출력된 결과로부터 정확한 판단방법(steering, throttle)을 레이블해야 하는 반면에, E2E의 경우 단순히 일반적인 주행을 하면서 각 프레임 별로 steering, throttle 값을 기록하는 것만으로도 충분히 각 이미지에 대한 레이블링이 완성되므로 레이블링에 필요한 노력이 훨씬 적다.For example, in the recognition unit, it is necessary to label each pixel which part is a road and a non-road from the image, and in the judgment unit, an accurate judgment method (steering, throttle) must be labeled from the result output from the recognition unit, whereas E2E In this case, labeling for each image is completed enough by simply recording steering and throttle values for each frame while driving normally, so the effort required for labeling is much less.
상기와 같이, E2E를 위한 레이블링은 기존의 방법에 비해서 쉽고 빠르게 얻을 수 있지만, 여전히 자율주행에 필요한 데이터를 얻기에는 충분하지 못하는 문제가 있다.As described above, the labeling for E2E can be obtained easily and quickly compared to the existing method, but there is still a problem in that it is not sufficient to obtain the data required for autonomous driving.
즉, 첨부도면 도 1에 도시된 바와 같이, 학습된 자율주행 차량이 한번 학습된 경로를 벗어나게 되면, 보지 못한 장면을 입력받게 되고 부정확한 제어 명령을 야기하여 도로를 완전히 이탈하게 문제가 있고, 이는 학습된 데이터에 차량이 트랙을 벗어났을 때 회복하도록 제어하는 데이터가 없기 때문이다.That is, as shown in the accompanying drawings, when the learned autonomous driving vehicle deviates from the learned route once, it receives an unseen scene and causes an inaccurate control command to completely deviate from the road. This is because there is no data to control the vehicle to recover when it goes off track.
최근 문헌들에서는 자율 주행을 위한 여러 연구가 진행되고 있는데, 주로 자율 주행을 위한 모델 학습 방법이나 자율 주행 데이터의 데이터 레이블링 방법을 연구하고 있다.In recent literature, several studies for autonomous driving are being conducted, mainly researching a model learning method for autonomous driving or a data labeling method of autonomous driving data.
즉, 선행기술로 특허공개공보 제10-2021-0084287호는 자율 주행 차량 운행을 지원하는 대상체 추적이 개시되어 있고, 특허공개공보 제10-2021-0057943호는 자율 주행 데이터의 데이터 레이블링 방법, 장치 및 컴퓨터프로그램이 개시되어 있으며, 특허등록공보 제10-2177880호는 자율주행용 클래스 레이블링 장치가 개시되어 있고, 특허등록공보 제10-2137213호는 자율 주행을 위한 모델 학습 장치 및 방법과 자율 주행 장치가 개시되어 있다.That is, as prior art, Patent Laid-Open No. 10-2021-0084287 discloses object tracking supporting autonomous driving vehicle operation, and Patent Laid-Open Publication No. 10-2021-0057943 discloses a data labeling method and apparatus for autonomous driving data and a computer program are disclosed, Patent Registration No. 10-2177880 discloses a class labeling device for autonomous driving, and Patent Registration No. 10-2137213 discloses a model learning apparatus and method for autonomous driving and autonomous driving device is disclosed.
본 발명은 입력되는 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하여 이루어지는 회전 증강과 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행 이동하여 이루어지는 이동 증강의 실행으로 이미지를 정확하고 빠르게 변형시켜 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉽게 하기 위한 AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법을 제공하는데 목적이 있다.The present invention provides an easy to learn artificial neural network by accurately and rapidly transforming an image by performing rotation enhancement made by changing the angle of the camera with respect to an input image and movement enhancement made by moving in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the camera is viewed. The purpose of this is to provide a method for augmenting AI autonomous driving imitation learning data.
본 발명의 해결하고자 하는 과제는 이상에서 언급한 것으로 제한되지 않으며, 언급되지 않은 또 다른 해결하고자 하는 과제는 아래의 기재로부터 본 발명이 속하는 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 명확하게 이해될 수 있을 것이다.The problems to be solved of the present invention are not limited to those mentioned above, and other problems to be solved that are not mentioned will be clearly understood by those of ordinary skill in the art to which the present invention belongs from the following description.
본 발명은 상술한 기술적 과제를 달성하기 위해 시점 변환을 이용한 End-to-End AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 장치가 수행하는 AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법으로서, 원본 이미지를 입력받는 단계; 입력된 이미지에 대해 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키는 단계; 상기 평행이동하여 증강시킨 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키는 단계; 상기 평행이동 증강과 회전 증강에 의해 미처 옮겨지지 못한 빈 픽셀들을 채우기 위한 보간 단계; 상기 보간이 수행되면 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉬운 이미지 증강이 완료되는 단계를 포함하고,The present invention provides an AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method performed by an end-to-end AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation device using viewpoint transformation to achieve the above-described technical task, the method comprising: receiving an original image; Augmenting the input image by moving in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the camera is viewed; rotating the augmented image to change the angle of the camera with respect to the image augmented by the parallel movement; an interpolation step for filling empty pixels that have not been moved by the translation enhancement and rotation enhancement; Comprising the step of completing the image augmentation easy to learn in the artificial neural network when the interpolation is performed,
상기 원본 이미지를 입력하는 단계에서, 상기 이미지 내 각 픽셀별의 깊이(depth) 값들을 하기 식으로 구하되, 카메라 높이(camera height)와 초점 거리(focal length)를 고려하여 구하게 되고, 이때 상기 깊이 값들 중 제1 깊이 값은, 평지임을 가정하여 픽셀별 깊이를 추정할 수 있도록의 식으로 구하고, 같은 높이의 픽셀들은 같은 깊이를 갖으며, 상기 깊이 값들 중 제2 깊이 값은, 이미지 높이(H)의 반보다 낮은 위치의 픽셀별 깊이를 추정할 있도록의 식으로 구하고, 이미지 높이(H)의 반보다 높은 위치의 픽셀들은 무한의 값을 갖으며, i가 낮을수록 이미지의 위쪽에 위치하고, 상기 깊이 값들 중 제3 깊이 값은, 이미지 높이의 반보다 높은 위치의 픽셀별 깊이를 추정할 있도록의 식으로 구하고,는 카메라의 높이이며, 상기 초점 거리(,)는, 이며, 여기서, 화각을, 이미지의 한 변의 길이를 L, 이미지의 가로 길이를 W, 세로 길이를 H, 가로/세로 화각을,, 이미지의 세로방향 i, 이미지 가로방향 j 이다.In the step of inputting the original image, the depth values for each pixel in the image are obtained by the following formula, and are obtained in consideration of a camera height and a focal length, and in this case, the depth The first depth value among the values is assumed to be flat so that the depth for each pixel can be estimated. , and pixels of the same height have the same depth, and the second depth value among the depth values is used to estimate the depth of each pixel at a position lower than half of the image height (H). obtained by the equation of , pixels at positions higher than half the image height H have infinite values, and as i is lower, they are located at the upper part of the image, and the third depth value among the depth values is less than half the image height. To estimate the depth of each pixel at a high location to obtain in the manner of is the height of the camera, and the focal length ( , )Is , and where, the angle of view is , the length of one side of the image is L, the horizontal length of the image is W, the vertical length is H, and the horizontal/vertical angle of view is , , is the vertical direction of the image i, and the horizontal direction of the image is j.
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 상기 각 픽셀에 해당하는 좌표값을 추정하고 변환한 후에 다시 평면 이미지(image plane)에 투영하는 방식으로 하기 수학식으로 계산하되, 상기 계산으로 구한의 변환을 통해 이미지의 모든 픽셀 위치를 새로운 위치)로 옮겨서 회전 증강(회전 증강) 이미지를 완성하고, 제1 깊이, 제2 깊이 및 제3 깊이 값이고, 회전 증강에 에 의해 카메라의 각도가 오른쪽으로 θ만큼 옮겨지면 회전 변환을 통해 각 픽셀의 x, z 값들이 변환되며, 카메라는 y방향을 축으로 움직이기 때문에 y는 변화되지 않으며,According to an embodiment of the present invention, the coordinate value corresponding to each pixel is estimated and transformed, and then calculated by the following equation in a way of projecting it back to an image plane, but obtained by the calculation Every pixel position in the image through the transformation of to new location ) to complete the rotational augmented (rotational augmented) image, which are the first depth, second depth, and third depth values, and when the angle of the camera is shifted to the right by θ by rotational augmentation, The x and z values are converted, and the y does not change because the camera moves in the y direction.
상기 변환된 좌표를 통해 평면 이미지에 투영되는 좌표를 구하게 된다.the transformed Coordinates projected onto a flat image through coordinates will save
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 상기 각 픽셀에 해당하는 좌표값을 추정하고 변환한 후에 다시 평면 이미지에 투영하는 방식으로 하기 수학식으로 계산하되, 상기 계산으로 구한의 변환을 통해 모든 픽셀 좌표(i,j)를 로 이동시켜 이동 증강(이동 증강)을 완성하고, 상기에서 구한 제1 깊이, 제2 깊이 및 제3 깊이의 값을 통해서 각 픽셀들의 (x, y, z) 좌표는According to an embodiment of the present invention, the coordinate value corresponding to each pixel is estimated and transformed, and then it is calculated by the following equation in a way that it is projected on a flat image again, but obtained by the calculation All pixel coordinates (i,j) through the transformation of to complete movement augmentation (movement augmentation), and the (x, y, z) coordinates of each pixel through the values of the first depth, the second depth and the third depth obtained above are
여기서, d는 해당 픽셀(i,j)의 깊이이고, 회전 증강에 의해 카메라의 각도가 오른쪽으로만큼 옮겨지면 회전 변환을 통해 각 픽셀의 x, z 값들이 변환되며, 카메라는 y방향을 축으로 움직이기 때문에 y는 변화되지 않으며,Here, d is the depth of the pixel (i,j), and the angle of the camera is shifted to the right by rotation enhancement. If it is moved as much as that, the x and z values of each pixel are transformed through rotation transformation, and y does not change because the camera moves along the y direction.
상기 좌표가 이동 증강에 의해으로 변환되고, 이동 증강에서는 x좌표만 변화되며, 카메라를 오른쪽으로 t만큼 이동시켰을 때 각 좌표는 변환되고,는이 투영되는 것이다.remind Coordinates are moved by augmentation , and only the x-coordinate is changed in the movement enhancement, and when the camera is moved to the right by t, each coordinate is transformed, Is This will be projected.
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 회전 증강과 이동 증강의 안티스티어링(anti-steering,)를 계산하고,According to an embodiment of the present invention, anti-steering of rotation enhancement and movement enhancement (anti-steering, ) is calculated,
상기 안티스티어링은이고,The anti-steering ego,
여기서, △θ는 회전 증강에 의한 차량의 회전 각도이고,where Δθ is the rotation angle of the vehicle byrotation enhancement ,
△t는 이동 증강에 의한 차량이 오른쪽으로 이동한 거리이며,과는 하이퍼 파라미터(hyper-parameter) 이다.Δt is the distance the vehicle has moved to the right due to movement enhancement, class is a hyper-parameter.
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 넘파이 벡터화(Numpy vectorization)를 활용하여 회전 증강과 이동 증강 과정의 속도를 향상시키고, 회전 증강과 이동 증강에 의해 손실되는 일부 픽셀(pixel)들을 가장 인접 삽입(Nearest neighbor interpolation)으로 채우며, 회전 증강과 이동 증강에 의해 손실되는 일부 픽셀(pixel)들을 선형 삽입(Linear interpolation)으로 채우는 것이다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the speed of the rotation enhancement and movement enhancement process is improved by utilizing NumPy vectorization, and some pixels lost by the rotation enhancement and movement enhancement are inserted to the nearest It is filled with neighbor interpolation, and some pixels lost by rotation enhancement and movement enhancement are filled with linear interpolation.
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 시점 변환을 이용한 End-to-End AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 장치로서, 원본 이미지를 입력하는 입력부; 상기 입력부를 통해 입력되는 원본 이미지를 저장하고, 증강되어 변형된 이미지를 저장하는 저장부; 상기 저장부에 저장된 원본 이미지를 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉽도록 증강시키는 프로세서부를 포함하되, 상기 프로세서부는 입력된 이미지에 대해 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키고, 상기 평행이동하여 증강시킨 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키며, 상기 평행이동 증강과 회전 증강에 의해 미처 옮겨지지 못한 빈 픽셀들을 채우는 보간이 수행되고, 상기 보간이 수행되면 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉬운 이미지 증강이 완료된다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, there is provided an end-to-end AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation device using viewpoint transformation, comprising: an input unit for inputting an original image; a storage unit for storing the original image input through the input unit and storing the augmented and transformed image; A processor unit for augmenting the original image stored in the storage unit to be easily learned by the artificial neural network, wherein the processor unit augments the input image by moving in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the camera is viewed, and by moving the parallel The augmented image is rotationally augmented to transform the angle of the camera, and interpolation is performed to fill empty pixels that have not been moved by the translation enhancement and rotation enhancement. This is done.
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 상기 프로세서부는 상기 이미지 내 각 픽셀의 제1 깊이, 제2 깊이 및 제3 깊이를 하기 식으로 구하되, 카메라 높이와 초점 거리를 고려하여 구하고, 상기 제1 깊이 값은로 이루어지고, 이는 평지임을 가정하여 픽셀별 깊이를 추정하고, 같은 높이의 픽셀들은 같은 깊이를 갖으며, 상기 제2 깊이 값은로 이루어지고, 이는 이미지 높이(H)의 반보다 높은 위치의 픽셀들은 무한의 값을 갖으며, i가 낮을수록 이미지의 위쪽에 위치하고, 상기 제3 깊이 값은로 이루어지고, 이는 이미지 높이의 반보다 낮은 위치의 픽셀들에 대한 것이며,는 카메라의 높이이고,According to an embodiment of the present invention, the processor unit obtains the first depth, the second depth, and the third depth of each pixel in the image in the following manner, taking the camera height and focal length into consideration, and the first depth value silver , and the depth of each pixel is estimated assuming that it is flat, pixels of the same height have the same depth, and the second depth value is In this case, pixels at positions higher than half of the image height H have infinite values, and as i is lower, they are located at the top of the image, and the third depth value is , which is for pixels at a position lower than half the image height, is the height of the camera,
상기 초점 거리(,)는, 이며,the focal length ( , )Is , is,
여기서, 화각을, 이미지의 한 변의 길이를 L, 이미지의 가로 길이를 W, 세로 길이를 H, 가로/세로 화각을,, 이미지의 세로방향 i, 이미지 가로방향 j 이다.Here, the angle of view , the length of one side of the image is L, the horizontal length of the image is W, the vertical length is H, and the horizontal/vertical angle of view is , , is the vertical direction of the image i, and the horizontal direction of the image is j.
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 상기 프로세서부는 상기 각 픽셀에 해당하는 좌표값을 추정하고 변환한 후에 다시 평면 이미지에 투영하는 방식으로 하기 수학식으로 계산하되, 상기 계산으로 구한의 변환을 통해 이미지의 모든 픽셀 위치를 새로운 위치)로 옮겨서 회전 증강 이미지를 완성하고, 상기에서 구한 제1 깊이 값, 제2 깊이 값 및 제3 깊이 값들을 통해서 각 픽셀들의 (x, y, z) 좌표는이고, 여기서, d는 해당 픽셀(i,j)의 깊이이고, 회전 증강에 의해 카메라의 각도가 오른쪽으로만큼 옮겨지면 회전 변환을 통해 각 픽셀의 x, z 값들이 변환되며, 카메라는 y방향을 축으로 움직이기 때문에 y는 변화되지 않으며,According to an embodiment of the present invention, the processor unit estimates and transforms the coordinate value corresponding to each pixel, and then calculates it by the following equation in a manner that is projected onto a flat image again, but obtained by the calculation Every pixel position in the image through the transformation of to new location ) to complete the rotation augmented image, and the (x, y, z) coordinates of each pixel through the first, second, and third depth values obtained above are , where d is the depth of the corresponding pixel (i, j), and the angle of the camera is shifted to the right by rotation enhancement. If it is moved as much as that, the x and z values of each pixel are transformed through rotation transformation, and y does not change because the camera moves along the y direction.
상기 변환된 좌표를 통해 평면 이미지에 투영되는 좌표를 구한다.the transformed Coordinates projected onto a flat image through coordinates save
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 상기 프로세서부는 상기 각 픽셀에 해당하는 좌표값을 추정하고 변환한 후에 다시 평면 이미지에 투영하는 방식으로 하기 수학식으로 계산하되, 상기 계산으로 구한의 변환을 통해 모든 픽셀 좌표(i,j)를 로 이동시켜 이동 증강을 완성하고, 상기에서 구한 깊이 값을 통해서 각 픽셀들의 (x, y, z) 좌표는이며, 여기서, d는 해당 픽셀(i,j)의 깊이이고, 회전 증강에 의해 카메라의 각도가 오른쪽으로만큼 옮겨지면 회전 변환을 통해 각 픽셀의 x, z 값들이 변환되며, 카메라는 y방향을 축으로 움직이기 때문에 y는 변화되지 않으며,According to an embodiment of the present invention, the processor unit estimates and transforms the coordinate value corresponding to each pixel, and then calculates it by the following equation in a manner that is projected onto a flat image again, but obtained by the calculation All pixel coordinates (i,j) through the transformation of to complete the movement enhancement, and the (x, y, z) coordinates of each pixel through the depth value obtained above are , where d is the depth of the corresponding pixel (i,j), and the angle of the camera is shifted to the right by rotation enhancement. If it is moved as much as that, the x and z values of each pixel are transformed through rotation transformation, and y does not change because the camera moves along the y direction.
상기 좌표가 이동 증강에 의해으로 변환되고, 이동 증강에서는 x좌표만 변화되며, 카메라를 오른쪽으로 t만큼 이동시켰을 때 각 좌표는 변환되고,는이 투영되는 것이다.remind Coordinates are moved by augmentation , and only the x-coordinate is changed in the movement enhancement, and when the camera is moved to the right by t, each coordinate is transformed, Is This will be projected.
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 상기 프로세서부는 회전 증강과 이동 증강의 안티스티어링()를 계산하고,According to an embodiment of the present invention, the processor unit anti-steering of rotation enhancement and movement enhancement ( ) is calculated,
상기 안티스티어링은이고,The anti-steering ego,
여기서, △θ는 회전 증강에 의한 차량의 회전 각도이고,where Δθ is the rotation angle of the vehicle byrotation enhancement ,
△t는 이동 증강에 의한 차량이 오른쪽으로 이동한 거리이며,과는 하이퍼 파라미터 이다.Δt is the distance the vehicle has moved to the right due to movement enhancement, class is a hyperparameter.
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 상기 프로세서부는 넘파이 벡터화을 활용하여 회전 증강과 이동 증강 과정의 속도를 향상시키고, 회전 증강과 이동 증강에 의해 손실되는 일부 픽셀(pixel)들을 가장 인접 삽입으로 채우며, 회전 증강과 이동 증강에 의해 손실되는 일부 픽셀(pixel)들을 선형 삽입으로 채우는 것이다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the processor unit uses NumPy vectorization to improve the speed of the rotation enhancement and movement enhancement process, fills some pixels lost by the rotation enhancement and movement enhancement with the closest insertion, and rotates It is to fill some pixels lost by augmentation and movement augmentation with linear interpolation.
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 컴퓨터 프로그램을 저장하고 있는 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록매체로서, 상기 컴퓨터 프로그램은, 프로세서에 의해 실행되면, 원본 이미지를 입력하는 단계; 입력된 이미지에 대해 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키는 단계; 상기 평행이동하여 증강시킨 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키는 단계; 상기 평행이동 증강과 회전 증강에 의해 미처 옮겨지지 못한 빈 픽셀들을 채우기 위한 보간 단계; 상기 보간이 수행되면 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉬운 이미지 증강이 완료되는 단계를 포함하여 AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법을 상기 프로세서가 수행하도록 하기 위한 명령어를 포함한다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a computer-readable recording medium storing a computer program, the computer program comprising: inputting an original image when executed by a processor; Augmenting the input image by moving in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the camera is viewed; rotating the augmented image to change the angle of the camera with respect to the image augmented by the parallel movement; an interpolation step for filling empty pixels that have not been moved by the translation enhancement and rotation enhancement; When the interpolation is performed, it includes instructions for causing the processor to perform the AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method, including the step of completing the image augmentation that is easy to learn in the artificial neural network.
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록매체에 저장되어 있는 컴퓨터 프로그램으로서, 상기 컴퓨터 프로그램은, 프로세서에 의해 실행되면, 원본 이미지를 입력하는 단계; 입력된 이미지에 대해 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키는 단계; 상기 평행이동하여 증강시킨 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키는 단계; 상기 평행이동 증강과 회전 증강에 의해 미처 옮겨지지 못한 빈 픽셀들을 채우기 위한 보간 단계; 상기 보간이 수행되면 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉬운 이미지 증강이 완료되는 단계를 포함하여 AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법을 상기 프로세서가 수행하도록 하기 위한 명령어를 포함한다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a computer program stored in a computer-readable recording medium, the computer program comprising: inputting an original image when executed by a processor; Augmenting the input image by moving in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the camera is viewed; rotating the augmented image to change the angle of the camera with respect to the image augmented by the parallel movement; an interpolation step for filling empty pixels that have not been moved by the translation enhancement and rotation enhancement; When the interpolation is performed, it includes instructions for causing the processor to perform the AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method, including the step of completing the image augmentation that is easy to learn in the artificial neural network.
본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 입력되는 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하여 이루어지는 회전 증강과 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행 이동하여 이루어지는 이동 증강의 실행으로 인해 이미지를 정확하고 빠르게 변형시켜 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉽게 하는 효과가 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the image is accurately and quickly transformed due to the execution of rotation enhancement made by changing the angle of the camera with respect to the input image and movement enhancement made by parallel movement in the direction perpendicular to the direction in which the camera is viewed. It has the effect of making the artificial neural network easier to learn.
또한, 본 발명의 실시 예에 따르면, 자율주행에 필요한 데이터를 충분히 얻도록 하여 학습된 데이터에 차량이 트랙을 벗어났을 때 회복 제어가 가능하게 되는 효과가 있다.In addition, according to an embodiment of the present invention, data necessary for autonomous driving is sufficiently obtained to enable recovery control when the vehicle deviates from the track based on the learned data.
도 1은 일반적으로 학습된 자율주행 차량이 한번 학습된 경로를 벗어난 경우에 대해 설명하기 위한 예시 도면이다.
도 2는 인위적으로 카메라를 이동시키거나 화전시켰을 때의 이미지에 대한 증강을 개략적으로 설명하기 위한 예시 도면이다.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시에 따른 이미지의 증강시키는 과정을 설명하기 위해 보여주는 흐름 구성 도면이다.
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 회전 증강과 이동 증강의 개념을 설명하기 위해 보여주는 예시 도면이다.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 카메라 높이(camera height)와 초점 거리(focal length)를 이용해서 픽셀별 깊이를 추정하는 과정을 설명하기 위한 예시 도면이다.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 회전 변환인 카메라를 위에서 바라볼 때의 좌표을 보여주기 위한 예시 도면이다.
도 7은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 벡터화(Vectorization) 전후 코드 및 속도 차이를 보여주기 위한 예시 도면이다.
도 8 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 회전 증강과 보간(Interpolation)이 수행되는 상태를 보여주는 예 도면이다.
도 9 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 모노큘러 뎁스 에스터메이션(monocular depth estimation)인 이미지로부터 픽셀별 깊이 정보를 예측하는 인공 신경망 예시를 보여주는 도면이다.
도 10은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강과정을 수행할 수 있는 장치에 대한 블럭 구성 도면이다.1 is an exemplary view for explaining a case in which a generally learned autonomous driving vehicle deviates from a once learned path.
FIG. 2 is an exemplary diagram schematically illustrating augmentation of an image when a camera is artificially moved or fired.
3 is a flow configuration diagram illustrating a process of augmenting an image according to an embodiment of the present invention.
4 is an exemplary view to explain the concepts of rotation enhancement and movement enhancement according to an embodiment of the present invention.
5 is an exemplary view for explaining a process of estimating a depth for each pixel using a camera height and a focal length according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 6 is an exemplary view for showing coordinates when the camera that is rotational transformation is viewed from above according to an embodiment of the present invention.
7 is an exemplary diagram illustrating a code and speed difference before and after vectorization according to an embodiment of the present invention.
8 is an exemplary view showing a state in which rotation enhancement and interpolation are performed according to an embodiment of the present invention.
9 is a diagram illustrating an example of an artificial neural network for predicting depth information for each pixel from an image that is monocular depth estimation according to an embodiment of the present invention.
10 is a block diagram of an apparatus capable of performing an autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation process according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명의 이점 및 특징, 그리고 그것들을 달성하는 방법은 첨부되는 도면과 함께 후술되어 있는 실시예들을 참조하면 명확해질 것이다. 그러나 본 발명은 이하에서 개시되는 실시예들에 한정되는 것이 아니라 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 구현될 수 있으며, 단지 본 실시예들은 본 발명의 개시가 완전하도록 하고, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 발명의 범주를 완전하게 알려주기 위해 제공되는 것이며, 본 발명은 청구항의 범주에 의해 정의될 뿐이다.Advantages and features of the present invention and methods of achieving them will become apparent with reference to the embodiments described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. However, the present invention is not limited to the embodiments disclosed below, but may be implemented in various different forms, and only these embodiments allow the disclosure of the present invention to be complete, and common knowledge in the art to which the present invention pertains It is provided to fully inform those who have the scope of the invention, and the present invention is only defined by the scope of the claims.
본 명세서에서 사용되는 용어에 대해 간략히 설명하고, 본 발명에 대해 구체적으로 설명하기로 한다.Terms used in this specification will be briefly described, and the present invention will be described in detail.
본 발명에서 사용되는 용어는 본 발명에서의 기능을 고려하면서 가능한 현재 널리 사용되는 일반적인 용어들을 선택하였으나, 이는 당 분야에 종사하는 기술자의 의도 또는 판례, 새로운 기술의 출현 등에 따라 달라질 수 있다. 또한, 특정한 경우는 출원인이 임의로 선정한 용어도 있으며, 이 경우 해당되는 발명의 설명 부분에서 상세히 그 의미를 기재할 것이다. 따라서 본 발명에서 사용되는 용어는 단순한 용어의 명칭이 아닌, 그 용어가 가지는 의미와 본 발명의 전반에 걸친 내용을 토대로 정의되어야 한다.The terms used in the present invention have been selected as currently widely used general terms as possible while considering the functions in the present invention, but these may vary depending on the intention or precedent of a person skilled in the art, the emergence of new technology, and the like. In addition, in a specific case, there is a term arbitrarily selected by the applicant, and in this case, the meaning will be described in detail in the description of the corresponding invention. Therefore, the term used in the present invention should be defined based on the meaning of the term and the overall content of the present invention, rather than the name of a simple term.
명세서 전체에서 어떤 부분이 어떤 구성요소를 '포함'한다고 할 때, 이는 특별히 반대되는 기재가 없는 한 다른 구성요소를 제외하는 것이 아니라 다른 구성요소를 더 포함할 수 있음을 의미하고, 단수의 표현은 문맥상 명백하게 다르게 뜻하지 않는 한, 복수의 표현을 포함한다.In the entire specification, when a part 'includes' a certain element, this means that other elements may be further included, rather than excluding other elements, unless otherwise stated, and the expression in the singular is A plural expression is included unless the context clearly dictates otherwise.
아래에서는 첨부한 도면을 참고하여 본 발명의 실시예에 대하여 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 용이하게 실시할 수 있도록 상세히 설명한다. 그리고 도면에서 본 발명을 명확하게 설명하기 위해서 설명과 관계없는 부분은 생략하고, 또한 첨부한 도면을 참조하여 설명함에 있어, 도면 부호에 관계없이 동일한 구성 요소는 동일한 참조부호를 부여하고 이에 대한 중복되는 설명은 생략하기로 하며, 본 발명을 설명함에 있어서 관련된 공지 기술에 대한 구체적인 설명이 본 발명의 요지를 불필요하게 흐릴 수 있다고 판단되는 경우 그 상세한 설명을 생략한다.Hereinafter, with reference to the accompanying drawings, the embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail so that those of ordinary skill in the art can easily implement them. And in order to clearly explain the present invention in the drawings, parts irrelevant to the description are omitted, and in the description with reference to the accompanying drawings, the same components regardless of the reference signs are given the same reference signs and overlapped The description will be omitted, and when it is determined that a detailed description of a related known technology may unnecessarily obscure the subject matter of the present invention, the detailed description thereof will be omitted.
먼저, 도 2를 참조하면, 인위적으로 카메라를 이동(Translational) 및 회전(Rotational) 했을 때의 이미지를 증강시키는 것으로, 즉 30도 좌측에서 본 이미지인 좌측 이미지와, 원본 이미지와, 30도 우측을 본 이미지인 우측 이미지인 것이고, 각각 이미지의 하단에 기재된 값(0.3, 0, -0.3)들은 해당 각도로부터 원본의 각도로 회복하기 위해 주어야 하는 Steering 값을 의미하며, 이와 같이 증강된 데이터를 얻기 위해서는 3개의 카메라를 이용하여 얻는 방법과 원본 이미지로부터 이미지를 변형시켜 합성하는 방법으로 수행하게 된다.First, referring to FIG. 2, the image is augmented when the camera is artificially moved (Translational) and rotated (Rotational), that is, the image viewed from the left at 30 degrees, the left image, the original image, and the right 30 degrees This image is the right image, and the values (0.3, 0, -0.3) at the bottom of each image mean the Steering value that must be given to recover the original angle from the corresponding angle. It is carried out by the method of obtaining it using three cameras and the method of synthesizing the image by transforming it from the original image.
도 3을 참조하면, 시점 변환을 이용한 End-to-End AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강하는 과정을 보여주는 것으로, 먼저 원본 이미지를 입력하고(Input image, 10), 입력된 이미지에 대해 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키며(Shift Augmentation, 20), 상기 평행이동하여 증강시킨 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키고(Rotate Augmentation, 30), 상기 평행이동 증강과 회전 증강에 의해 미처 옮겨지지 못한 빈 픽셀들을 채우기 위해 보간(Interpolation, 40)를 수행하며, 상기 보간(40)이 수행되면 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉬운 이미지 증강(Augmented image, 50)이 완료되는 것이다.Referring to FIG. 3, it shows the process of augmenting the end-to-end AI autonomous driving imitation learning data using viewpoint transformation, first inputting the original image (Input image, 10), and looking at the camera for the input image It is augmented by moving in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction (Shift Augmentation, 20), and rotationally augmented to transform the angle of the camera with respect to the image augmented by the translation (Rotate Augmentation, 30), and the translation augmentation and rotation augmentation Interpolation (40) is performed to fill empty pixels that have not been moved by the .
여기서, 본 발명인 자율주행 모방학습 데이터를 증강하기 위해서는 데이터 증강에 필요한 값을 준비하게 되는데, 이때 회전 증강과 이동 증강으로 나누어, 상기 회전 증강는 카메라의 각도를 변형한 것이고, 상기 이동 증강는 카메라를 보고있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행 이동한 것이다(첨부도면 도 4 참조).Here, in order to augment the self-driving imitation learning data of the present invention, a value required for data augmentation is prepared. At this time, divided into rotational augmentation and movement augmentation, the rotational augmentation is a modification of the angle of the camera, and the movement augmentation is looking at the camera. It moves in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction (refer to FIG. 4 of the attached drawing).
즉, 본 발명의 증강 과정을 수행하기 위해서는 하기와 같은 최소한의 파라메터(parameter)가 필요하고, 고유 파라미터(Intrinsic parameter)는 초점 거리(focal length) 또는 화각(FOV)에 대한 것이고, 비고유 파라미터(Extrinsic parameter)는 카메라의 높이에 대한 것이다.That is, in order to perform the augmentation process of the present invention, the following minimum parameters are required, and the intrinsic parameter is for a focal length or an angle of view (FOV), and a non-intrinsic parameter ( Extrinsic parameter) is for the height of the camera.
상기 초점 거리는 물체의 상이 맺히는 평면 이미지와 초점과의 거리를 픽셀 단위로 나타낸 것이고, 초점 거리가 제공되지 않았을 때는 카메라의 화각으로부터 추정할 수 있다.The focal length represents the distance between the focal point and the plane image on which the object is formed in units of pixels, and when the focal length is not provided, it may be estimated from the angle of view of the camera.
이때, 초점 거리(focal length)를 f, 화각을, 이미지의 한 변의 길이를 L이라고 할 때, 초점 거리는 식으로 이루어진다.In this case, the focal length is f and the angle of view is , when the length of one side of the image is L, the focal length is done in this way
보통은 이미지의 가로 및 세로 길이가 다르고, 화각도 가로 및 세로 방향으로 다를 수 있기 때문에 초점 거리도 x, y 방향으로 각각 구한다.In general, since the horizontal and vertical lengths of the image are different and the angle of view can be different in the horizontal and vertical directions, the focal length is also obtained in the x and y directions, respectively.
즉, 이미지의 가로 길이를 W, 세로 길이를 H, 가로/세로 화각을,라 할 때, 각각의 초점 거리,는 다음과 같이 구할 수 있는 것이다.That is, the horizontal length of the image is W, the vertical length is H, and the horizontal/vertical angle of view is , When , each focal length , can be obtained as follows.
,,
그리고, 모든 픽셀별로 깊이 값들을 추정해야 한다.In addition, depth values must be estimated for every pixel.
여기서, i는 이미지의 세로방향, j는 가로방향 인덱스(index)이다.Here, i is the vertical direction of the image, and j is the horizontal direction index.
이에, 평지임을 가정하여 픽셀별 깊이를 추정할 수 있도록 같은 높이의 픽셀들은 같은 깊이를 가지는 하기의 식을 통해 제1 깊이 값을 구하게 된다.Accordingly, pixels of the same height have the same depth so that the depth for each pixel can be estimated on the assumption that it is flat, and the first depth value is obtained through the following equation.
상기 제1 깊이 값은으로 구하게 된다.The first depth value is will be saved with
또한, 이미지 높이(H)의 반보다 높은 위치의 픽셀별 깊이를 추정할 수 있도록 하기의 식을 통해 제2 깊이 값을 구하게 되는데, 이는 이미지 높이(H)의 반보다 높은 위치의 픽셀들은 무한의 값을 갖게 되고, i가 낮을수록 이미지의 위쪽에 위치하게 되는 제2 깊이 값을 구하게 된다.In addition, the second depth value is obtained through the following equation so that the depth of each pixel at a position higher than half of the image height H can be estimated. has a value, and as i is lower, a second depth value positioned above the image is obtained.
상기 제2 깊이 값은의 식으로 구하게 된다.The second depth value is is obtained in the manner of
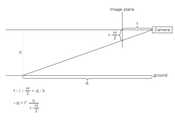
또한, 도 5를 참조하면 이미지 높이의 반보다 낮은 위치의 픽셀별 깊이를 추정할 수 있도록 하기의 식을 통해 제3 깊이 값을 구할 수 있다.In addition, referring to FIG. 5 , a third depth value may be obtained through the following equation so that the depth of each pixel at a position lower than half of the image height may be estimated.
상기 제3 깊이 값은의 식으로 구하게 된다.The third depth value is is obtained in the manner of
여기서,는 카메라의 높이를 나타낸다.here, is the height of the camera.
그리고, 회전 증강에 의해 픽셀들이 옮겨질 위치를 추정하는 과정으로, 즉이다.And, as a process of estimating the positions to which pixels are to be moved by rotation enhancement, that is, am.
상기에서 구한 깊이를 통해서 각 픽셀들의 (x, y, z) 좌표를 다음과 같이 추정할 수 있다.Through the depth obtained above, the (x, y, z) coordinates of each pixel can be estimated as follows.
여기서, d는 해당 픽셀(i,j)의 깊이를 나타낸다.Here, d represents the depth of the corresponding pixel (i, j).
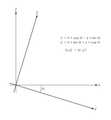
도 6을 참조하면, 회전 증강에 의해 카메라의 각도가 오른쪽으로만큼 옮겨지면 회전 변환을 통해 각 픽셀의 x, z 값들이 변환되고, 카메라는 y방향을 축으로 움직이기 때문에 y는 변화되지 않는다.Referring to FIG. 6 , the angle of the camera is shifted to the right by rotation enhancement. When moved by as much as , the x and z values of each pixel are transformed through rotation transformation, and the y does not change because the camera moves in the y direction.
이를 하기 식으로 나타낼 수 있는 것이다.This can be expressed by the following formula.
이에, 변환된 좌표를 통해 평면 이미지에 투영되는 좌표를 하기와 같이 구한다.Accordingly, converted Coordinates projected onto a flat image through coordinates is obtained as follows.
상기에서 구한 변환을 통해 이미지의 모든 픽셀 위치 (i,j)를 새로운 위치로 옮겨서 회전 증강 이미지를 완성하게 된다.rescued above Convert every pixel position (i,j) in the image to a new position to complete the rotation augmented image.
또한, 이동 증강에 의해 픽셀들이 옮겨질 위치를 추정하는 과정이다.Also, it is a process of estimating a position to which pixels are to be moved by movement augmentation.
각 픽셀(i,j)의 (x, y, z)좌표는 상기의 회전 증강에서 구한 방법과 같은 방식으로 구할 수 있다.The (x, y, z) coordinates of each pixel (i, j) can be obtained in the same way as the method obtained in the above rotation enhancement.
다음으로,좌표가 이동 증강에 의해으로 변환되는 식을 구한다.to the next, Coordinates are moved by augmentation Find the expression that converts to .
여기서, 이동 증강에서는 x좌표만 변화되고, 카메라를 오른쪽으로 t만큼 이동시켰을 때 각 좌표는 다음과 같이 변환된다.Here, in the movement enhancement, only the x-coordinate is changed, and when the camera is moved to the right by t, each coordinate is converted as follows.
마지막으로,이 투영되는 은 다음과 같다.Finally, which is projected Is as follows.
마찬가지로, 모든 픽셀 좌표 (i,j)를로 이동시켜 이동 증강을 완성하게 된다.Similarly, all pixel coordinates (i,j) Move to to complete the movement augmentation.
또한, 회전 증강에 의해 차량이만큼 회전했을 때 입력으로 들어오는 이미지를 합성하였고, 차량은 다시 제 각도로 돌아오기 위해서만큼의 안티스티어링을 주도록 해야한다.In addition, due to rotation enhancement, the vehicle When it has rotated as much as it is, the input image is synthesized, and the vehicle returns to its original angle. It should give you enough anti-steering.
예를 들어, 차량이 30도 만큼 오른쪽으로 틀어졌을 때, 기존의 스티어링(steering) 값에 -0.3만큼 더하여 본래의 각도로 돌아올 수 있도록 유도할 수 있다.For example, when the vehicle is turned to the right by 30 degrees, it can be induced to return to the original angle by adding -0.3 to the existing steering value.
이동 증강도 마찬가지로 오른쪽으로 만큼 이동했으면 그 만큼 안티스티어링을 주어야 제 경로로 돌아올 수 있는 것이다.Movement augmentation is also to the right If you have moved as much as possible, you need to apply that much anti-steering to get back on your path.
상기 이동 증강과 회전 증강을 순서대로 거쳐 본래 원본 위치에서만큼 각이 틀어지고,만큼 오른쪽으로 차량이 이동되었다고 하면, 본 발명을 통해 구하고자 하는 안티스티어링 값은식으로 구하게 된다.After the movement enhancement and rotation enhancement in order, the original position The angle is so twisted, If the vehicle is moved to the right by as much as to be saved in this way.
여기서,과는 하이퍼 파라미터이기 때문에 실험적으로 구하도록 한다.here, class Since is a hyperparameter, it should be obtained experimentally.
그리고, 초기 하이퍼 파라미터,에 대한 설정은 회전 증강에서 틀어질 수 있는 최대 각도를 정하고, 해당 각도에서 반대방향으로 꺾어야할 안티파라미터 값을라고 정하면으로 설정할 수 있다.And, the initial hyperparameter , The setting for is the maximum angle that can be shifted in rotational augmentation. and set the anti-parameter value to be bent in the opposite direction from the angle. If you decide can be set to
마찬가지로, 이동 증강에서 이동될 수 있는 최대 거리를로 정하고 해당 위치에서의 안티 파라미터 값을라고 정하면,로 설정할 수 있다.Similarly, the maximum distance that can be moved in movement augmentation is and set the anti-parameter value at that location. If you set can be set to
예를 들어, 30도 꺾은 각도에서는 -0.3 만큼 안티 파라미터를 주어야 한다고 하면, 로 계산되고, 또한 오른쪽으로 3.0m 떨어진 곳에서는 -0.2만큼 안티파라미터 주어야 한다고 하면, 로 계산할 수 있다.For example, if you have to give an anti-parameter by -0.3 at a 30 degree angle, , and if you need to give an anti-parameter by -0.2 at a distance of 3.0 m to the right, can be calculated as
이에 따라, 증강(augmentation)으로 생성된 데이터에 대한 새로운 스티어링(steering) 값은로 이루어진다.Accordingly, a new steering value for data generated by augmentation is is made of
상기 회전 증강과 이동 증강은 이미지 내의 모든 픽셀 위치(i,j)를로 하나씩 이동시키는 것으로, 이는 계산량(computational complexity)을 구하면)이 되므로 계산 속도 측면에서 비효율적인 것이다.The rotation enhancement and movement enhancement are all pixel positions (i, j) in the image. is moved one by one, which is calculated by calculating the computational complexity. ), so it is inefficient in terms of calculation speed.
상기의 계산 속도를 높이기 위해 파이썬(Python) 라이브러리인 넘파이를 활용하여 벡터화(vectorization)하게 된다.In order to speed up the above calculation, vectorization is performed using NumPy, a Python library.
상기 벡터화는 반복되는 스칼라 값의 연산을 벡터/행렬 연산으로 변환하여 병렬적인 연산을 하게 만드는 것으로, 벡터화를 을 통해 계산 속도를 수십배 빠르게 할 수 있다.The vectorization converts repeated operations of scalar values into vector/matrix operations so that parallel operations are performed, and the calculation speed can be increased several tens of times through vectorization.
즉, 도 7을 참조하면, 회전 증강의 실제 코드 중 일부로서, 좌측 부분은 벡터화를 적용하기 전의 코드를 보여주는 것이고, 우측 부분은 벡터화를 적용한 후의 코드를 보여주는 것이며, 이를 토대로 확인한 바로는 벡터화를 적용한 후에는 반복문(이중 for 문)이 사라진 것을 확인할 수가 있고, 속도도 약 30배 높아졌음을 확인할 수가 있다.That is, referring to Figure 7, as a part of the actual code of rotation enhancement, the left part shows the code before vectorization is applied, and the right part shows the code after vectorization is applied. Afterwards, it can be confirmed that the loop (double for statement) has disappeared, and the speed has also increased by about 30 times.
또한, 상기 회전 증강과 이동 증강에 의해 미처 옮겨지지 못한 빈 픽셀들이 존재하게 되고, 이들을 채우기 위해서는 적절한 보간(interpolation) 방법을 사용할 수 있는데, 본 발명에서는 속도를 높이기 위해 가장 간단한 가장 인접 방법을 사용한다.In addition, there are empty pixels that have not been moved due to the rotation enhancement and movement enhancement, and an appropriate interpolation method can be used to fill them. In the present invention, the simplest and closest method is used to increase speed .
상기 가장 인접은 비어있는 픽셀(pixel)을 가장 가까운 픽셀(pixel)로 채우는 방법으로서, 보간(Interpolation) 과정 또한 벡터화하여 빠르게 계산될 수 있도록 한다.The closest is a method of filling an empty pixel with the nearest pixel, and the interpolation process is also vectorized so that it can be calculated quickly.
즉, 도 8을 참조하면, 좌측 이미지는 원본 이미지이고, 가운데 이미지는 10도 가량 오른쪽으로 회전 증강한 이미지이며, 우측 이미지는 보간(Interpolation)으로 비어있는 픽셀(pixel)들을 채운 이미지인 것이다.That is, referring to FIG. 8 , the left image is an original image, the middle image is an image rotated to the right by about 10 degrees, and the right image is an image in which empty pixels are filled by interpolation.
참조도면 도 9는 본 발명에 의해 수행된 모노큘러 뎁스 에스터메이션(monocular depth estimation)으로서, 이는 이미지로부터 픽셀별 깊이 정보를 예측하는 인공 신경망 예시를 보여주는 것이고, 이미지 내 각 픽셀의 깊이를 가정할 때, 모노큘러 뎁스 에스터메이션 뉴럴 네트워크(monocular depth estimation neural network)를 활용하여 구한 다음 회전 증강과 이동 증강을 수행할 수가 있는 것이다.9 is a monocular depth estimation performed by the present invention, which shows an example of an artificial neural network for predicting depth information for each pixel from an image, assuming the depth of each pixel in the image , is obtained using a monocular depth estimation neural network, and then rotation and movement augmentation can be performed.
도 10을 참조하면, 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강장치(100)는 크게 입력부(110), 저장부(120) 및 프로세서부(130)로 구성된다.Referring to FIG. 10 , the autonomous driving imitation learning
상기 입력부(110)는 증강시키기 위한 원본 이미지를 입력하게 되고, 상기 저장부(120)는 입력부(110)를 통해 입력되는 원본 이미지를 저장하고, 증강되어 변형된 이미지를 저장하게 되며, 상기 프로세서부(130)는 저장부(120)에 저장된 원본 이미지를 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉽도록 증강시키는 역활을 수행하게 된다.The
즉, 상기 프로세서부(130)는 입력된 이미지에 대해 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키고, 또한 상기 평행이동하여 증강시킨 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키며, 상기 평행이동 증강과 회전 증강에 의해 미처 옮겨지지 못한 빈 픽셀들을 채우는 보간이 수행되고, 상기 보간이 수행되면 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉬운 이미지 증강이 완료되는 것이다.That is, the
이에, 상기 프로세서부(130)는 넘파이 벡터화를 활용하여 회전 증강과 이동 증강 과정의 속도를 향상시킬 수가 있고, 회전 증강과 이동 증강에 의해 손실되는 일부 픽셀(pixel)들을 가장 인접 삽입으로 채우는 기능을 수행하게 되며, 회전 증강과 이동 증강에 의해 손실되는 일부 픽셀(pixel)들을 선형 삽입으로 채우는 기능을 수행하게 된다.Accordingly, the
다양한 실시 예에 따르면, 컴퓨터 프로그램을 저장하고 있는 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록매체로서, 상기 컴퓨터 프로그램은, 프로세서에 의해 실행되면, 원본 이미지를 입력하는 단계와, 입력된 이미지에 대해 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키는 단계와, 상기 평행이동하여 증강시킨 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키는 단계와, 상기 평행이동 증강과 회전 증강에 의해 미처 옮겨지지 못한 빈 픽셀들을 채우기 위한 보간 단계와, 상기 보간이 수행되면 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉬운 이미지 증강이 완료되는 단계를 포함하는 방법을 상기 프로세서가 수행하도록 하기 위한 명령어를 포함할 수 있다.According to various embodiments, there is provided a computer-readable recording medium storing a computer program, wherein the computer program, when executed by a processor, includes the steps of: inputting an original image; The step of augmenting by translation in the specified direction, the step of rotationally enhancing the camera angle to change the angle of the camera with respect to the image augmented by the translational movement; It may include instructions for causing the processor to perform a method including an interpolation step, and the step of completing image enhancement that is easy to learn in an artificial neural network when the interpolation is performed.
다양한 실시 예에 따르면, 컴퓨터 프로그램을 저장하고 있는 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록 매체로서, 상기 컴퓨터 프로그램은 프로세서에 의해 실행되면, 원본 이미지를 입력하는 단계와, 입력된 이미지에 대해 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키는 단계와, 상기 평행이동하여 증강시킨 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키는 단계와, 상기 평행이동 증강과 회전 증강에 의해 미처 옮겨지지 못한 빈 픽셀들을 채우기 위한 보간 단계와, 상기 보간이 수행되면 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉬운 이미지 증강이 완료되는 단계를 포함하는 방법을 상기 프로세서가 수행하도록 하기 위한 명령어를 포함할 수 있다.According to various embodiments, there is provided a computer-readable recording medium storing a computer program, wherein when the computer program is executed by a processor, inputting an original image; The step of augmenting by translation in a direction, the step of rotationally augmenting the image to transform the angle of the camera with respect to the image augmented by the translational movement, and interpolation to fill empty pixels that have not yet been moved by the augmented translation and rotational augmentation and instructions for causing the processor to perform a method including the step of completing the image augmentation, which is easy to learn in the artificial neural network, when the interpolation is performed.
본 발명에 첨부된 각 흐름도의 각 단계의 조합들은 컴퓨터 프로그램 인스트럭션들에 의해 수행될 수도 있다. 이들 컴퓨터 프로그램 인스트럭션들은 범용 컴퓨터, 특수용 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비의 프로세서에 탑재될 수 있으므로, 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비의 프로세서를 통해 수행되는 그 인스트럭션들이 흐름도의 각 단계에서 설명된 기능들을 수행하는 수단을 생성하게 된다. 이들 컴퓨터 프로그램 인스트럭션들은 특정 방식으로 기능을 구현하기 위해 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비를 지향할 수 있는 컴퓨터 이용 가능 또는 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록매체에 저장되는 것도 가능하므로, 그 컴퓨터 이용가능 또는 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록매체에 저장된 인스트럭션들은 흐름도의 각 단계에서 설명된 기능을 수행하는 인스트럭션 수단을 내포하는 제조 품목을 생산하는 것도 가능하다. 컴퓨터 프로그램 인스트럭션들은 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비 상에 탑재되는 것도 가능하므로, 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비 상에서 일련의 동작 단계들이 수행되어 컴퓨터로 실행되는 프로세스를 생성해서 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비를 수행하는 인스트럭션들은 흐름도의 각 단계에서 설명된 기능들을 실행하기 위한 단계들을 제공하는 것도 가능하다.Combinations of each step in each flowchart attached to the present invention may be performed by computer program instructions. These computer program instructions may be embodied in a processor of a general purpose computer, special purpose computer, or other programmable data processing equipment, such that the instructions performed by the processor of the computer or other programmable data processing equipment provide the functions described in each step of the flowchart. It creates a means to do these things. These computer program instructions may also be stored in a computer-usable or computer-readable medium that may direct a computer or other programmable data processing equipment to implement a function in a particular manner, and thus the computer-usable or computer-readable medium. The instructions stored in the recording medium are also possible to produce an article of manufacture including instruction means for performing the functions described in each step of the flowchart. The computer program instructions may also be mounted on a computer or other programmable data processing equipment, such that a series of operational steps are performed on the computer or other programmable data processing equipment to create a computer-executed process to create a computer or other programmable data processing equipment. It is also possible that instructions for performing the processing equipment provide steps for performing the functions described in each step of the flowchart.
또한, 각 단계는 특정된 논리적 기능(들)을 실행하기 위한 하나 이상의 실행 가능한 인스트럭션들을 포함하는 모듈, 세그먼트 또는 코드의 일부를 나타낼 수 있다. 또, 몇 가지 대체 실시예들에서는 단계들에서 언급된 기능들이 순서를 벗어나서 발생하는 것도 가능함을 주목해야 한다. 예컨대, 잇달아 도시되어 있는 두 개의 단계들은 사실 실질적으로 동시에 수행되는 것도 가능하고 또는 그 단계들이 때때로 해당하는 기능에 따라 역순으로 수행되는 것도 가능하다.Further, each step may represent a module, segment, or portion of code comprising one or more executable instructions for executing the specified logical function(s). It should also be noted that in some alternative embodiments it is also possible for the functions recited in the steps to occur out of order. For example, it is possible that two steps shown one after another may in fact be performed substantially simultaneously, or that the steps may sometimes be performed in the reverse order according to the corresponding function.
이상의 설명은 본 발명의 기술 사상을 예시적으로 설명한 것에 불과한 것으로서, 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 본 발명의 본질적인 품질에서 벗어나지 않는 범위에서 다양한 수정 및 변형이 가능할 것이다. 따라서, 본 발명에 개시된 실시예들은 본 발명의 기술 사상을 한정하기 위한 것이 아니라 설명하기 위한 것이고, 이러한 실시예에 의하여 본 발명의 기술 사상의 범위가 한정되는 것은 아니다. 본 발명의 보호 범위는 아래의 청구범위에 의하여 해석되어야 하며, 그와 균등한 범위 내에 있는 모든 기술사상은 본 발명의 권리범위에 포함되는 것으로 해석되어야 할 것이다.The above description is merely illustrative of the technical spirit of the present invention, and various modifications and variations will be possible without departing from the essential quality of the present invention by those skilled in the art to which the present invention pertains. Accordingly, the embodiments disclosed in the present invention are not intended to limit the technical spirit of the present invention, but to explain, and the scope of the technical spirit of the present invention is not limited by these embodiments. The protection scope of the present invention should be interpreted by the following claims, and all technical ideas within the scope equivalent thereto should be interpreted as being included in the scope of the present invention.
100 : 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 장치
110 : 입력부
120 : 저장부
130 : 프로세서부100: autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation device
110: input unit
120: storage
130: processor unit
Claims (14)
Translated fromKorean원본 이미지를 입력받는 단계;
입력된 이미지에 대해 카메라가 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키는 단계;
상기 평행이동하여 증강시킨 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키는 단계;
상기 평행이동 증강과 회전 증강에 의해 미처 옮겨지지 못한 빈 픽셀들을 채우기 위한 보간 단계;
상기 보간이 수행되면 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉬운 이미지 증강이 완료되는 단계;를 포함하고,
상기 원본 이미지를 입력하는 단계에서,
상기 이미지 내 각 픽셀의 깊이 값들을 하기 식으로 구하되, 카메라 높이와 초점 거리를 고려하여 구하는,
AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법.
상기 깊이 값들 중 제1 깊이 값은, 평지임을 가정하여 픽셀별 깊이를 추정할 수 있도록의 식으로 구하고, 같은 높이의 픽셀들은 같은 깊이를 갖으며,
상기 깊이 값들 중 제2 깊이 값은, 이미지 높이(H)의 반보다 낮은 위치의 픽셀별 깊이를 추정할 있도록의 식으로 구하고, 이미지 높이(H)의 반보다 높은 위치의 픽셀들은 무한의 값을 갖으며, i가 낮을수록 이미지의 위쪽에 위치하고,
상기 깊이 값들 중 제3 깊이 값은, 이미지 높이의 반보다 높은 위치의 픽셀별 깊이를 추정할 있도록의 식으로 구하고,는 카메라의 높이이며,
상기 초점 거리(,)는
, 이며,
여기서, 화각을, 이미지의 한 변의 길이를 L, 이미지의 가로 길이를 W, 세로 길이를 H, 가로/세로 화각을,, 이미지의 세로방향 i, 이미지 가로방향 j 임As an AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method performed by an end-to-end AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation device using viewpoint transformation,
receiving an original image;
Augmenting the input image by moving in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the camera is looking;
rotating the augmented image to change the angle of the camera with respect to the image augmented by the parallel movement;
an interpolation step for filling empty pixels that have not been moved by the translation enhancement and rotation enhancement;
Including; when the interpolation is performed, the image augmentation that is easy to learn in the artificial neural network is completed;
In the step of inputting the original image,
The depth values of each pixel in the image are obtained by the following formula, but obtained in consideration of the camera height and focal length,
AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method.
A first depth value among the depth values is assumed to be flat so that the depth for each pixel can be estimated. , and pixels of the same height have the same depth,
A second depth value among the depth values is used to estimate the depth of each pixel at a position lower than half of the image height (H). Obtained by the equation of , pixels at positions higher than half of the image height (H) have infinite values, and as i is lower, they are located at the top of the image,
A third depth value among the depth values is used to estimate the depth of each pixel at a position higher than half the image height. to obtain in the manner of is the height of the camera,
the focal length ( , )Is
, is,
Here, the angle of view , the length of one side of the image is L, the horizontal length of the image is W, the vertical length is H, and the horizontal/vertical angle of view is , , the vertical direction of the image is i, the image horizontal direction is j
원본 이미지를 입력받는 단계;
입력된 이미지에 대해 카메라가 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키는 단계;
상기 평행이동하여 증강시킨 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키는 단계;
상기 평행이동 증강과 회전 증강에 의해 미처 옮겨지지 못한 빈 픽셀들을 채우기 위한 보간 단계;
상기 보간이 수행되면 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉬운 이미지 증강이 완료되는 단계;를 포함하고,
상기 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키는 단계에서,
상기 각 픽셀에 해당하는 좌표값을 추정하고 변환한 후에 다시 평면 이미지에 투영하는 방식으로 하기 수학식으로 계산하되, 상기 계산으로 구한의 변환을 통해 이미지의 모든 픽셀 위치를 새로운 위치)로 옮겨서 회전 증강 이미지를 완성하는,
AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법.
각 픽셀들의 (x, y, z) 좌표는
여기서, d는 해당 픽셀(i,j)의 depth이고, 회전 증강에 의해 카메라의 각도가 오른쪽으로만큼 옮겨지면 회전 변환을 통해 각 픽셀의 x, z 값들이 변환되며, 카메라는 y방향을 축으로 움직이기 때문에 y는 변화되지 않으며,
상기 변환된 좌표를 통해 평면 이미지에 투영되는 좌표를 구함As an AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method performed by an end-to-end AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation device using viewpoint transformation,
receiving an original image;
Augmenting the input image by moving in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the camera is looking;
rotating the augmented image to change the angle of the camera with respect to the image augmented by the parallel movement;
an interpolation step for filling empty pixels that have not been moved by the translation enhancement and rotation enhancement;
Including; when the interpolation is performed, the image augmentation that is easy to learn in the artificial neural network is completed;
In the step of augmenting rotation to change the angle of the camera,
Estimate and transform the coordinate values corresponding to each pixel, and then calculate by the following equation in a manner that is projected onto a flat image again. Every pixel position in the image through the transformation of to new location ) to complete the rotation augmented image,
AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method.
The (x, y, z) coordinates of each pixel are
Here, d is the depth of the corresponding pixel (i, j), and the angle of the camera is shifted to the right by rotation enhancement. If it is moved as much as that, the x and z values of each pixel are transformed through rotation transformation, and y does not change because the camera moves along the y direction.
the transformed Coordinates projected onto a flat image through coordinates looking for
원본 이미지를 입력받는 단계;
입력된 이미지에 대해 카메라가 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키는 단계;
상기 평행이동하여 증강시킨 이미지에 대해 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키는 단계;
상기 평행이동 증강과 회전 증강에 의해 미처 옮겨지지 못한 빈 픽셀들을 채우기 위한 보간 단계;
상기 보간이 수행되면 인공신경망에 학습하기 쉬운 이미지 증강이 완료되는 단계;를 포함하고,
상기 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키는 단계에서,
상기 각 픽셀에 해당하는 좌표값을 추정하고 변환한 후에 다시 평면 이미지에 투영하는 방식으로 하기 수학식으로 계산하되, 상기 계산으로 구한의 변환을 통해 모든 픽셀 좌표(i,j)를 로 이동시켜 이동 증강을 완성하는,
AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법.
제1 깊이 값, 제2 깊이 값 및 제3 깊이 값을 통해서 각 픽셀들의 (x, y, z) 좌표는
여기서, d는 해당 픽셀(i,j)의 depth이고, 회전 증강에 의해 카메라의 각도가 오른쪽으로만큼 옮겨지면 회전 변환을 통해 각 픽셀의 x, z 값들이 변환되며, 카메라는 y방향을 축으로 움직이기 때문에 y는 변화되지 않으며,
상기 좌표가 이동 증강에 의해으로 변환되고, 이동 증강에서는 x좌표만 변화되며, 카메라를 오른쪽으로 t만큼 이동시켰을 때 각 좌표는 변환되고,는이 투영되는 것임As an AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method performed by an end-to-end AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation device using viewpoint transformation,
receiving an original image;
Augmenting the input image by moving in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the camera is looking;
rotating the augmented image to change the angle of the camera with respect to the image augmented by the parallel movement;
an interpolation step for filling empty pixels that have not been moved by the translation enhancement and rotation enhancement;
Including; when the interpolation is performed, the image augmentation that is easy to learn in the artificial neural network is completed;
In the step of augmenting by moving in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the camera is viewed,
Estimate and transform the coordinate values corresponding to each pixel, and then calculate by the following equation in a manner that is projected onto a flat image again. All pixel coordinates (i,j) through the transformation of to complete the movement augmentation by moving to
AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method.
(x, y, z) coordinates of each pixel through the first depth value, the second depth value, and the third depth value are
Here, d is the depth of the corresponding pixel (i, j), and the angle of the camera is shifted to the right by rotation enhancement. If it is moved as much as that, the x and z values of each pixel are transformed through rotation transformation, and y does not change because the camera moves along the y direction.
remind Coordinates are moved by augmentation , and only the x-coordinate is changed in the movement enhancement, and when the camera is moved to the right by t, each coordinate is transformed, Is This is projected
상기 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키는 단계와, 상기 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키는 단계에서,
회전 증강과 이동 증강의 안티스티어링()를 계산하는,
AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법.
상기 안티스티어링은이고,
여기서, △θ는회전 증강에 의한 차량의 회전 각도이고,
△t는 이동 증강에 의한 차량이 오른쪽으로 이동한 거리이며,과는 하이퍼 파라미터 임5. The method according to any one of claims 2 to 4,
In the step of augmenting by moving in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the camera is viewed, and in the step of augmenting rotation to change the angle of the camera,
Anti-steering with rotational enhancement and movement enhancement ( ) to calculate,
AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method.
The anti-steering ego,
Here, Δθ isis the rotation angle of the vehicle by rotation enhancement,
Δt is the distance the vehicle has moved to the right due to movement enhancement, class is a hyperparameter
상기 카메라를 보고 있는 방향에 수직된 방향으로 평행이동하여 증강시키는 단계와, 상기 카메라의 각도를 변형하도록 회전 증강시키는 단계에서,
넘파이 벡터화를 활용하여 회전 증강과 이동 증강 과정의 속도를 향상시키는,
AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법.5. The method according to any one of claims 2 to 4,
In the step of augmenting by moving in parallel in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the camera is viewed, and in the step of augmenting rotation to change the angle of the camera,
Utilizing NumPy vectorization to speed up the rotation augmentation and movement augmentation processes,
AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method.
상기 보간 단계에서,
회전 증강과 이동 증강에 의해 손실되는 일부 픽셀(pixel)들을 가장 인접 삽입으로 채우는,
AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법.5. The method according to any one of claims 2 to 4,
In the interpolation step,
Filling in some pixels lost by rotation enhancement and translation enhancement with the nearest insertion,
AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method.
상기 보간 단계에서,
회전 증강과 이동 증강에 의해 손실되는 일부 픽셀(pixel)들을 선형 삽입으로 채우는,
AI 자율주행 모방학습 데이터 증강 방법.5. The method according to any one of claims 2 to 4,
In the interpolation step,
Filling some pixels lost by rotational and translational enhancements with linear interpolation,
AI autonomous driving imitation learning data augmentation method.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020210127176AKR102376397B1 (en) | 2021-09-27 | 2021-09-27 | A Data Augmentation Method for End-to-End Autonomous Driving Using Fast and Accurate Viewpoint Transformation |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020210127176AKR102376397B1 (en) | 2021-09-27 | 2021-09-27 | A Data Augmentation Method for End-to-End Autonomous Driving Using Fast and Accurate Viewpoint Transformation |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR102376397B1true KR102376397B1 (en) | 2022-03-21 |
Family
ID=80937510
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020210127176AActiveKR102376397B1 (en) | 2021-09-27 | 2021-09-27 | A Data Augmentation Method for End-to-End Autonomous Driving Using Fast and Accurate Viewpoint Transformation |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102376397B1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20240146789A (en) | 2023-03-30 | 2024-10-08 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Method for generatinng artificial intelligence economic forecast model based on economic principle imitation and apparatus using the same |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102137213B1 (en) | 2015-11-16 | 2020-08-13 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | Apparatus and method for traning model for autonomous driving, autonomous driving apparatus |
| KR102177880B1 (en) | 2019-03-08 | 2020-11-12 | 현대모비스 주식회사 | Class labeling apparatus for autonomous driving |
| KR20210057943A (en) | 2019-11-13 | 2021-05-24 | 주식회사 라이드플럭스 | Method, apparatus and computer program for conducting automatic driving data labeling |
| KR20210084287A (en) | 2019-12-27 | 2021-07-07 | 모셔널 에이디 엘엘씨 | Object tracking supporting autonomous vehicle navigation |
- 2021
- 2021-09-27KRKR1020210127176Apatent/KR102376397B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102137213B1 (en) | 2015-11-16 | 2020-08-13 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | Apparatus and method for traning model for autonomous driving, autonomous driving apparatus |
| KR102177880B1 (en) | 2019-03-08 | 2020-11-12 | 현대모비스 주식회사 | Class labeling apparatus for autonomous driving |
| KR20210057943A (en) | 2019-11-13 | 2021-05-24 | 주식회사 라이드플럭스 | Method, apparatus and computer program for conducting automatic driving data labeling |
| KR20210084287A (en) | 2019-12-27 | 2021-07-07 | 모셔널 에이디 엘엘씨 | Object tracking supporting autonomous vehicle navigation |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| W. Li et al., "AADS: Augmented autonomous driving simulation using data-driven algorithms," SCIENCE ROBOTICS (2019.03.13.)** |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20240146789A (en) | 2023-03-30 | 2024-10-08 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Method for generatinng artificial intelligence economic forecast model based on economic principle imitation and apparatus using the same |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Pillai et al. | Superdepth: Self-supervised, super-resolved monocular depth estimation | |
| US11636686B2 (en) | Structure annotation | |
| US11442464B2 (en) | Bird's eye view map based recognition and motion prediction for autonomous systems | |
| US12260576B2 (en) | Unsupervised depth prediction neural networks | |
| US11064178B2 (en) | Deep virtual stereo odometry | |
| US10574967B2 (en) | Autonomous performance of an operation on an object using a generated dense 3D model of the object | |
| EP3942794B1 (en) | Depth-guided video inpainting for autonomous driving | |
| CN102722697B (en) | Unmanned aerial vehicle autonomous navigation landing visual target tracking method | |
| Erçelik et al. | 3d object detection with a self-supervised lidar scene flow backbone | |
| KR20130030208A (en) | Egomotion estimation system and method | |
| US11847802B2 (en) | System and method for computing the 3D position of a semantic landmark in images from the real world | |
| US11210802B2 (en) | Systems and methods for conditioning training data to avoid learned aberrations | |
| JP2015501471A (en) | Calibration method for on-board computer-based vision system | |
| US10939042B1 (en) | Simulated rolling shutter image data | |
| US12347125B2 (en) | Using histograms for self-supervised depth estimation | |
| CN117256008A (en) | Real-time localization using image data | |
| US20230080638A1 (en) | Systems and methods for self-supervised learning of camera intrinsic parameters from a sequence of images | |
| KR102376397B1 (en) | A Data Augmentation Method for End-to-End Autonomous Driving Using Fast and Accurate Viewpoint Transformation | |
| Ge et al. | Vipose: Real-time visual-inertial 6d object pose tracking | |
| US11657506B2 (en) | Systems and methods for autonomous robot navigation | |
| CN119427349A (en) | A target-driven mobile grasping control method for multi-scenario environments | |
| Morales et al. | Real-time adaptive obstacle detection based on an image database | |
| Thakur et al. | Sceneednet: A deep learning approach for scene flow estimation | |
| US12380582B2 (en) | Warping depth features for depth estimation | |
| CN117095130A (en) | Three-dimensional modeling method and system thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20210927 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0302 | Request for accelerated examination | Patent event date:20211015 Patent event code:PA03022R01D Comment text:Request for Accelerated Examination Patent event date:20210927 Patent event code:PA03021R01I Comment text:Patent Application | |
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20211223 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20220312 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20220315 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20220316 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20250304 Start annual number:4 End annual number:4 |