KR102282454B1 - Surveillance system - Google Patents
Surveillance systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102282454B1 KR102282454B1KR1020150099227AKR20150099227AKR102282454B1KR 102282454 B1KR102282454 B1KR 102282454B1KR 1020150099227 AKR1020150099227 AKR 1020150099227AKR 20150099227 AKR20150099227 AKR 20150099227AKR 102282454 B1KR102282454 B1KR 102282454B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- period
- network camera
- gateway
- beacon
- beacon signal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N7/00—Television systems
- H04N7/18—Closed-circuit television [CCTV] systems, i.e. systems in which the video signal is not broadcast
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W52/00—Power management, e.g. Transmission Power Control [TPC] or power classes
- H04W52/02—Power saving arrangements
- H04W52/0209—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices
- H04W52/0225—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices using monitoring of external events, e.g. the presence of a signal
- H04W52/0248—Power saving arrangements in terminal devices using monitoring of external events, e.g. the presence of a signal dependent on the time of the day, e.g. according to expected transmission activity
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/70—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wireless communication networks
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Closed-Circuit Television Systems (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은, 감시 시스템에 관한 것으로서, 보다 상세하게는, 네트워크 카메라가 게이트웨이를 통하여 클라이언트 장치와 통신하는 감시 시스템에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a monitoring system, and more particularly, to a monitoring system in which a network camera communicates with a client device through a gateway.
일반적인 감시 시스템에 있어서, 네트워크 카메라는 게이트웨이를 통하여 클라이언트 장치와 통신한다. 이벤트가 발생하면, 네트워크 카메라는 영상을 포착 및 압축하고, 압축 결과의 정지 영상 또는 동영상을 클라이언트 장치에게 전송한다. 대부분의 무선 네트워크 카메라들은 배터리의 전원을 사용하므로, 배터리의 수명 연장을 위하여 소비 전력을 줄이는 것이 중요하다.In a general surveillance system, a network camera communicates with a client device through a gateway. When an event occurs, the network camera captures and compresses an image, and transmits a still image or moving image of the compression result to the client device. Since most wireless network cameras use battery power, it is important to reduce power consumption to prolong battery life.
네트워크 카메라에 있어서, 전송될 영상의 압축율이 높을수록, 영상 데이터의 총 전송 시간이 짧아지면서 배터리의 수명이 길어지지만 화질이 나빠진다. 전송될 영상의 압축율이 낮을수록, 영상 데이터의 총 전송 시간이 길어지면서 배터리의 수명이 짧아지지만 화질이 좋아진다.In a network camera, the higher the compression rate of the image to be transmitted, the shorter the total transmission time of the image data, the longer the battery life, but the worse the image quality. The lower the compression rate of the image to be transmitted, the longer the total transmission time of the image data, the shorter the battery life, but the better the image quality.
상기 배경 기술의 문제점은, 발명자가 본 발명의 도출을 위해 보유하고 있었거나, 본 발명의 도출 과정에서 습득한 내용으로서, 반드시 본 발명의 출원 전에 일반 공중에게 공지된 내용이라 할 수는 없다.The problem of the background art is the content that the inventor possessed for the derivation of the present invention or acquired during the derivation of the present invention, and it cannot be said that the content is known to the general public before the filing of the present invention.
본 발명의 실시예는, 네트워크 카메라가 영상 압축율을 상대적으로 높이지 않고서도 영상 데이터의 총 전송 시간을 줄일 수 있고, 이에 따라 네트워크 카메라의 배터리 수명이 상대적으로 연장될 수 있게 해주는 감시 시스템을 제공하고자 한다.An embodiment of the present invention is to provide a monitoring system that allows the network camera to reduce the total transmission time of image data without relatively increasing the image compression rate, and thus the battery life of the network camera can be relatively extended. do.
본 발명의 일 측면의 감시 시스템에서는, 네트워크 카메라가 게이트웨이를 통하여 클라이언트 장치와 통신한다.In the monitoring system of one aspect of the present invention, a network camera communicates with a client device through a gateway.
상기 게이트웨이가 비콘(beacon) 신호를 제1 주기에 의하여 상기 네트워크 카메라에게 주기적으로 전송함에 따라, 상기 네트워크 카메라는 상기 비콘(beacon) 신호를 수신할 때마다 이벤트 발생 여부를 판단한다.As the gateway periodically transmits a beacon signal to the network camera according to a first cycle, the network camera determines whether an event has occurred whenever it receives the beacon signal.
상기 게이트웨이는, 상기 네트워크 카메라로부터의 영상 데이터가 수신되는 동안에, 상기 비콘(beacon) 신호를 상기 제1 주기보다 긴 제2 주기에 의하여 상기 네트워크 카메라에게 주기적으로 전송한다.The gateway periodically transmits the beacon signal to the network camera by a second period longer than the first period while the image data from the network camera is being received.
바람직하게는, 상기 네트워크 카메라에서의 상기 제1 주기는 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기와 휴면(inactivity) 주기를 포함한다. 또한, 상기 네트워크 카메라에서의 상기 제1 주기의 위상은 상기 게이트웨이에서의 상기 제1 주기의 위상에 비하여 상기 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기만큼 앞서 있다.Preferably, the first period in the network camera includes a beacon standby period and an inactivity period. In addition, the phase of the first period in the network camera is ahead of the phase of the first period in the gateway by the beacon waiting period.
바람직하게는, 상기 네트워크 카메라에서의 상기 제2 주기는 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기와 영상 전송 주기를 포함한다. 또한, 상기 네트워크 카메라에서의 상기 제2 주기의 위상은 상기 게이트웨이에서의 상기 제2 주기의 위상에 비하여 상기 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기만큼 앞서 있다.Preferably, the second period in the network camera includes a beacon waiting period and an image transmission period. In addition, the phase of the second period in the network camera is ahead of the phase of the second period in the gateway by the beacon waiting period.
바람직하게는, 상기 제1 주기에서의 상기 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기는 상기 제2 주기에서의 상기 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기와 동일한 길이의 시간을 가진다.Preferably, the beacon waiting period in the first period has a length of time equal to the beacon waiting period in the second period.
바람직하게는, 상기 네트워크 카메라는, 이벤트가 발생되었다고 판단되면, 이벤트 발생 신호를 상기 게이트웨이에게 전송한 후에 영상 데이터를 상기 게이트웨이에게 전송한다.Preferably, when it is determined that an event has occurred, the network camera transmits an event generation signal to the gateway and then transmits image data to the gateway.
바람직하게는, 상기 게이트웨이는, 상기 이벤트 발생 신호의 수신 시점으로부터 상기 영상 데이터의 수신 종료 시점까지, 상기 비콘(beacon) 신호를 상기 제2 주기에 의하여 상기 네트워크 카메라에게 주기적으로 전송한다.Preferably, the gateway periodically transmits the beacon signal to the network camera according to the second period from the time of reception of the event occurrence signal to the end of reception of the image data.
본 발명의 실시예의 감시 시스템에 의하면, 상기 게이트웨이는, 상기 네트워크 카메라로부터의 영상 데이터가 수신되는 동안에, 상기 비콘(beacon) 신호를 상기 제1 주기보다 긴 제2 주기에 의하여 상기 네트워크 카메라에게 주기적으로 전송한다.According to the monitoring system of the embodiment of the present invention, the gateway periodically sends the beacon signal to the network camera by a second period longer than the first period while the video data from the network camera is being received. send.
즉, 상기 네트워크 카메라는 영상 데이터를 상기 게이트웨이에게 송신하는 동안에 상대적으로 긴 상기 제2 주기에 의하여 상기 비콘(beacon) 신호를 주기적으로 수신한다. 여기에서, 상기 네트워크 카메라에서의 상기 제2 주기는 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기와 영상 전송 주기를 포함한다.That is, the network camera periodically receives the beacon signal according to the relatively long second period while transmitting the image data to the gateway. Here, the second period in the network camera includes a beacon waiting period and an image transmission period.
이에 따라, 상기 네트워크 카메라는 상대적으로 긴 영상 전송 주기를 적용하여 영상 데이터를 상기 게이트웨이에게 주기적으로 전송할 수 있다. 즉, 일정한 시간 동안에 상대적으로 많은 양의 영상 데이터가 전송될 수 있으므로, 영상 데이터의 총 전송 시간이 상대적으로 짧아질 수 있다.Accordingly, the network camera may periodically transmit image data to the gateway by applying a relatively long image transmission period. That is, since a relatively large amount of image data may be transmitted for a predetermined time, the total transmission time of the image data may be relatively short.
따라서, 본 실시예의 감시 시스템에 의하면, 상기 네트워크 카메라가 영상 압축율을 상대적으로 높이지 않고서도 영상 데이터의 총 전송 시간을 줄일 수 있고, 이에 따라 상기 네트워크 카메라의 배터리 수명이 상대적으로 연장될 수 있다.Accordingly, according to the monitoring system of the present embodiment, the network camera can reduce the total transmission time of image data without relatively increasing the image compression rate, and thus the battery life of the network camera can be relatively extended.
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예의 감시 시스템을 보여주는 도면이다.
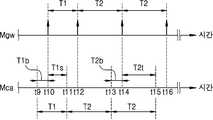
도 2는 도 1의 네트워크 카메라와 게이트웨이의 통신 과정을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 3은 이벤트가 발생되지 않은 기간에서의 네트워크 카메라와 게이트웨이의 통신 과정을 보여주는 타이밍도이다.
도 4는 이벤트가 발생된 경우의 네트워크 카메라와 게이트웨이의 통신 과정을 보여주는 타이밍도이다.
도 5는 도 2의 단계 S206에서의 영상 데이터의 구조를 상세히 보여주는 도면이다.1 is a diagram showing a monitoring system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining a communication process between the network camera of FIG. 1 and a gateway.
3 is a timing diagram illustrating a communication process between a network camera and a gateway in a period in which no event occurs.
4 is a timing diagram illustrating a communication process between a network camera and a gateway when an event occurs.
FIG. 5 is a diagram showing in detail the structure of image data in step S206 of FIG. 2 .
하기의 설명 및 첨부된 도면은 본 발명에 따른 동작을 이해하기 위한 것이며, 본 기술 분야의 통상의 기술자가 용이하게 구현할 수 있는 부분은 생략될 수 있다.The following description and accompanying drawings are for understanding the operation according to the present invention, and parts that can be easily implemented by those skilled in the art may be omitted.
또한 본 명세서 및 도면은 본 발명을 제한하기 위한 목적으로 제공된 것은 아니고, 본 발명의 범위는 청구의 범위에 의하여 정해져야 한다. 본 명세서에서 사용된 용어들은 본 발명을 가장 적절하게 표현할 수 있도록 본 발명의 기술적 사상에 부합하는 의미와 개념으로 해석되어야 한다.In addition, the specification and drawings are not provided for the purpose of limiting the present invention, and the scope of the present invention should be defined by the claims. The terms used in this specification should be interpreted with meanings and concepts consistent with the technical idea of the present invention so that the present invention can be most appropriately expressed.
이하 첨부된 도면들을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예가 상세히 설명된다.DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예의 감시 시스템을 보여준다.1 shows a monitoring system of an embodiment of the present invention.
도 1을 참조하면, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 게이트웨이(102)를 통하여 클라이언트 장치(103)와 통신한다. 이벤트가 발생하면, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 영상을 포착 및 압축하고, 압축 결과의 정지 영상 또는 동영상을 클라이언트 장치(103)에게 전송한다. 대부분의 무선 네트워크 카메라들은 배터리의 전원을 사용하므로, 배터리의 수명 연장을 위하여 소비 전력을 줄이는 것이 중요하다.Referring to FIG. 1 , a
게이트웨이(102)가 비콘(beacon) 신호를 제1 주기에 의하여 네트워크 카메라(101)에게 주기적으로 전송함에 따라, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 비콘(beacon) 신호를 수신할 때마다 이벤트 발생 여부를 판단한다.As the
게이트웨이(102)는, 네트워크 카메라(101)로부터의 영상 데이터가 수신되는 동안에, 비콘(beacon) 신호를 제1 주기보다 긴 제2 주기에 의하여 네트워크 카메라(101)에게 주기적으로 전송한다.The
도 2는 도 1의 네트워크 카메라(101)와 게이트웨이(102)의 통신 과정을 설명하기 위한 도면이다. 도 2를 참조하여 이를 설명하면 다음과 같다.FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining a communication process between the
네트워크 카메라(101)는 일정 시간의 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기 동안에 비콘 신호를 기다린다(단계 S201).The
비콘 대기 주기의 종료 시점에서, 게이트웨이(102)는 제1 주기의 비콘 신호를 네트워크 카메라(101)에게 전송한다(단계 S202).At the end of the beacon waiting period, the
비콘(beacon) 신호를 수신한 네트워크 카메라(101)는 이벤트 발생 여부를 판단한다(단계 S203). The
이벤트가 발생되지 않았다고 판단되면, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 일정 시간의 휴면(inactivity) 주기 동안에 소비 전력을 줄이기 위한 휴면 모드를 수행한다(단계 S204). 이와 같은 휴면 모드에 의하여 네트워크 카메라(101)의 소비 전력이 줄어들 수 있다. 휴면 주기가 종료되면 상기 단계 S201 및 그 다음 단계(S203)가 다시 수행된다.If it is determined that no event has occurred, the
이벤트가 발생되었다고 판단되면, 단계들 S205 내지 S209가 수행된다.If it is determined that the event has occurred, steps S205 to S209 are performed.
단계 S205에 있어서, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 이벤트 발생 신호를 게이트웨이(102)에게 전송한다(단계 S205). 다음에, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 일정한 영상 전송 주기 동안에 영상 데이터를 게이트웨이(102)에게 전송한다(단계 S206).In step S205, the
다음에, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 일정 시간의 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기 동안에 비콘 신호를 기다린다(단계 S207).Next, the
비콘 대기 주기의 종료 시점에서, 게이트웨이(102)는 제1 주기보다 긴 제2 주기의 비콘 신호를 네트워크 카메라(101)에게 전송한다(단계 S208).At the end of the beacon standby period, the
다음에, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 영상 데이터가 모두 전송되었는지의 여부를 판단한다(단계 S209). 여기에서, 단계들 S206 및 S207은 영상 데이터가 모두 전송될 때까지 반복적으로 수행된다. 영상 데이터가 모두 전송되었으면, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 상기 단계 S204 및 그 다음 단계들을 다시 수행한다.Next, the
도 2의 통신 과정에 대하여 도 3 및 4를 참조하여 보다 상세하게 설명될 것이다.The communication process of FIG. 2 will be described in more detail with reference to FIGS. 3 and 4 .
도 3은 이벤트가 발생되지 않은 기간에서의 네트워크 카메라(도 2의 101)와 게이트웨이(도 2의 102)의 통신 과정을 보여준다. 여기에서, 이벤트가 발생되지 않은 기간이란 도 2의 단계들 S201 내지 S204의 수행 기간이다.FIG. 3 shows a communication process between the network camera ( 101 in FIG. 2 ) and the gateway ( 102 in FIG. 2 ) in a period in which no event occurs. Here, the period in which the event does not occur is the period in which steps S201 to S204 of FIG. 2 are performed.
도 3에서 참조 부호 Mgw는 게이트웨이(102)의 동작 타이밍도를, Mca는 네트워크 카메라(101)의 동작 타이밍도를, T1은 상기 제1 주기를, T1b는 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기를, 그리고 T1s는 휴면(inactivity) 주기를 각각 가리킨다.In FIG. 3, reference numeral Mgw denotes an operation timing diagram of the
본 실시예의 경우, 제1 주기(T1)는 250 밀리-초(ms), 비콘 대기 주기(T1b)는 5 밀리-초(ms), 그리고 휴면 주기(T1s)는 245 밀리-초(ms)이다.In this embodiment, the first period T1 is 250 milliseconds (ms), the beacon waiting period T1b is 5 milliseconds (ms), and the sleep period T1s is 245 milliseconds (ms). .
도 2 및 3을 참조하여 도 3의 타이밍도를 설명하면 다음과 같다.The timing diagram of FIG. 3 will be described with reference to FIGS. 2 and 3 as follows.
네트워크 카메라(101)에서의 제1 주기(T1)는 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기(T1b)와 휴면(inactivity) 주기(T1s)를 포함한다. 네트워크 카메라(101)에서의 제1 주기(T1)의 위상은 게이트웨이(102)에서의 제1 주기(T1)의 위상에 비하여 비콘 대기 주기(T1b)만큼 앞서 있다. 예를 들어, 네트워크 카메라(101)에서의 제1 주기(T1)의 시작 시점 t1은 게이트웨이(102)에서의 제1 주기(T1)의 시작 시점 t2에 비하여 비콘 대기 주기(T1b)만큼 앞서 있다.The first period T1 in the
t1 ~ t2 시간의 비콘 대기 주기(T1b)에서, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 비콘 신호를 기다린다(단계 S201).In the beacon waiting period T1b of time t1 to t2, the
t2 시점에서 게이트웨이(102)로부터의 비콘 신호가 수신되면(단계 S202), 네트워크 카메라(101)는 이벤트 발생 여부를 판단한다(단계 S203).When the beacon signal from the
t2 시점에서 이벤트가 발생되지 않았다고 판단되면, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 t2 ~ t3 시간의 휴면(inactivity) 주기 동안에 소비 전력을 줄이기 위한 휴면 모드를 수행한다(단계 S204). 이와 같은 휴면 모드에 의하여 네트워크 카메라(101)의 소비 전력이 줄어들 수 있다.If it is determined that the event has not occurred at time t2, the
상기와 같은 t1 ~ t3의 제1 주기(T1)는 그 이후의 시간에서도 이벤트가 발생될 때까지 반복적으로 적용된다.The first period T1 of t1 to t3 as described above is repeatedly applied until an event occurs even at a time thereafter.
도 4는 이벤트가 발생된 경우의 네트워크 카메라(101)와 게이트웨이(102)의 통신 과정을 보여준다. 여기에서, 이벤트가 발생된 경우의 통신 과정은 도 2의 단계들 S205 내지 S209에 해당된다. 도 4에서 참조 부호 T2는 상기 제2 주기를, T2b는 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기를, 그리고 T2t는 영상 전송 주기를 각각 가리킨다. 도 4에서 도 3과 동일한 참조 부호는 동일한 기능의 대상을 가리킨다.4 shows a communication process between the
본 실시예의 경우, 제2 주기(T2)는 400 밀리-초(ms), 비콘 대기 주기(T1b)는 5 밀리-초(ms), 그리고 휴면 주기(T1s)는 395 밀리-초(ms)이다.In the present embodiment, the second period T2 is 400 milliseconds (ms), the beacon waiting period T1b is 5 milliseconds (ms), and the sleep period T1s is 395 milliseconds (ms). .
도 2 및 4를 참조하여 도 4의 타이밍도를 설명하면 다음과 같다.The timing diagram of FIG. 4 will be described with reference to FIGS. 2 and 4 as follows.
네트워크 카메라(101)에서의 제2 주기(T2)는 비콘 대기 주기(T2b)와 영상 전송 주기(T2t)를 포함한다. 네트워크 카메라(101)에서의 제2 주기(T2)의 위상은 게이트웨이(102)에서의 제2 주기(T2)의 위상에 비하여 비콘 대기 주기(T1b)만큼 앞서 있다. 예를 들어, 네트워크 카메라(101)에서의 제2 주기(T2)의 시작 시점 t11은 게이트웨이(102)에서의 제2 주기(T2)의 시작 시점 t12에 비하여 비콘 대기 주기(T1b, T2b)만큼 앞서 있다. 여기에서, 제1 주기(T1)에서의 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기(T1b)는 제2 주기(T2)에서의 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기(T2b)와 동일한 길이의 시간을 가진다.The second period T2 in the
t9 ~ t10 시간의 비콘 대기 주기(T1b)에서, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 비콘 신호를 기다린다(단계 S201).In the beacon waiting period T1b of time t9 to t10, the
t10 시점에서 게이트웨이(102)로부터의 비콘 신호가 수신되면(단계 S202), 네트워크 카메라(101)는 이벤트 발생 여부를 판단한다(단계 S203).When the beacon signal from the
t10 시점에서 이벤트가 발생되지 않았다고 판단되면, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 t10 ~ t11 시간의 휴면(inactivity) 주기 동안에 소비 전력을 줄이기 위한 휴면 모드를 수행한다(단계 S204). 이와 같은 휴면 모드에 의하여 네트워크 카메라(101)의 소비 전력이 줄어들 수 있다.If it is determined that no event has occurred at time t10, the
반복적으로, t11 ~ t12 시간의 비콘 대기 주기(T1b)에서, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 비콘 신호를 기다린다(단계 S201).Repeatedly, in the beacon waiting period T1b of time t11 to t12, the
t12 시점에서 게이트웨이(102)로부터의 비콘 신호가 수신되면(단계 S202), 네트워크 카메라(101)는 이벤트 발생 여부를 판단한다(단계 S203).When the beacon signal from the
t12 시점에서 이벤트가 발생되었다고 판단되면, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 이벤트 발생 신호를 게이트웨이(102)에게 전송한다(단계 S205). 다음에, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 t12 ~ t13의 영상 전송 주기(T2t) 동안에 영상 데이터를 게이트웨이(102)에게 전송한다(단계 S206).If it is determined that an event has occurred at time t12, the
상기와 같은 t11 ~ t13의 제2 주기(T2)는 그 이후의 시간에서도 영상 데이터가 모두 전송될 때까지 반복적으로 적용된다.The second period T2 of t11 to t13 as described above is repeatedly applied until all the image data is transmitted even after that time.
요약하면, 게이트웨이(102)는, 네트워크 카메라(101)로부터의 영상 데이터가 수신되는 동안에, 비콘(beacon) 신호를 제1 주기(T1)보다 긴 제2 주기(T2)에 의하여 네트워크 카메라(101)에게 주기적으로 전송한다.In summary, while the video data from the
즉, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 영상 데이터를 게이트웨이(102)에게 송신하는 동안에 상대적으로 긴 제2 주기(T2)에 의하여 비콘(beacon) 신호를 주기적으로 수신한다. 여기에서, 네트워크 카메라(101)에서의 제2 주기(T2)는 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기(T2b)와 영상 전송 주기(T2t)를 포함한다.That is, the
이에 따라, 네트워크 카메라(101)는 상대적으로 긴 영상 전송 주기(T2t)를 적용하여 영상 데이터를 게이트웨이(102)에게 주기적으로 전송할 수 있다. 즉, 일정한 시간 동안에 상대적으로 많은 양의 영상 데이터가 전송될 수 있으므로, 영상 데이터의 총 전송 시간이 상대적으로 짧아질 수 있다.Accordingly, the
예를 들어, 제1 주기(T1)가 250 밀리-초(ms)인 경우, 100 초 동안에서의 제1 주기의 횟수는 100/0.25 이다. 비콘 대기 주기(T1b,T2b)가 5 밀리-초(ms)인 경우, 100 초 동안에서의 총 비콘-대기 시간(초) Tb100은 아래의 수학식 1에 의하여 계산된다.For example, if the first period T1 is 250 milli-seconds (ms), the number of the first period in 100 seconds is 100/0.25. When the beacon waiting period (T1b, T2b) is 5 milliseconds (ms), the total beacon-waiting time (second) Tb100 for 100 seconds is calculated by
따라서, 종래의 기술처럼 제1 주기(T1)만이 적용된 경우, 100 초 동안에서의 총 영상-전송 시간 Tt100은 아래의 수학식 2에 의하여 계산된다.Accordingly, when only the first period T1 is applied as in the prior art, the total image-transmission time Tt100 for 100 seconds is calculated by Equation 2 below.
즉, 종래의 기술처럼 제1 주기(T1)만이 적용된 경우, 100 초 동안에서의 총 영상-전송 시간 Tt100은 98 초이다.That is, when only the first period T1 is applied as in the prior art, the total image-transmission time Tt100 for 100 seconds is 98 seconds.
이에 대하여, 영상이 전송되는 동안에 400 밀리-초(ms)의 제2 주기(T2)가 적용된 경우, 100 초 동안에서의 제2 주기의 횟수는 100/0.4 이다. 비콘 대기 주기(T1b,T2b)가 5 밀리-초(ms)이므로, 100 초 동안에서의 총 비콘-대기 시간(초) Tb100은 아래의 수학식 3에 의하여 계산된다.In contrast, when the second period T2 of 400 milliseconds (ms) is applied while the image is transmitted, the number of the second period in 100 seconds is 100/0.4. Since the beacon waiting period (T1b, T2b) is 5 milliseconds (ms), the total beacon-waiting time (second) Tb100 for 100 seconds is calculated by Equation 3 below.
따라서, 영상이 전송되는 동안에 본 발명의 실시예에 따라 400 밀리-초(ms)의 제2 주기(T2)가 적용된 경우, 100 초 동안에서의 유효 영상-전송 시간 Tt100은 아래의 수학식 4에 의하여 계산된다.Therefore, when the second period T2 of 400 milliseconds (ms) is applied according to the embodiment of the present invention while the image is being transmitted, the effective image-transmission time Tt100 for 100 seconds is the
즉, 영상이 전송되는 동안에 본 발명의 실시예에 따라 400 밀리-초(ms)의 제2 주기(T2)가 적용된 경우, 100 초 동안에서의 유효 영상-전송 시간 Tt100은 98.75 초이다.That is, when the second period T2 of 400 milliseconds (ms) is applied while the image is being transmitted, the effective image-transmission time Tt100 for 100 seconds is 98.75 seconds.
따라서, 본 발명의 실시예에 의하면, 100 초 동안에서의 유효 영상-전송 시간 Tt100은 종래 기술에 비하여 0.75 초가 증가되었다. 즉, 네트워크 카메라(101)의 전송률이 1024 Kbps(Killo bits per second)인 경우, 100 초 동안에서의 총 영상-전송 양은 종래 기술에 비하여 0.75 X 1024 (= 768) Kbps가 증가되었다.Accordingly, according to the embodiment of the present invention, the effective video-transmission time Tt100 for 100 seconds is increased by 0.75 seconds compared to the prior art. That is, when the transmission rate of the
따라서, 본 실시예의 감시 시스템에 의하면, 네트워크 카메라(101)가 영상 압축율을 상대적으로 높이지 않고서도 영상 데이터의 총 전송 시간을 줄일 수 있고, 이에 따라 네트워크 카메라(101)의 배터리 수명이 상대적으로 연장될 수 있다.Therefore, according to the monitoring system of the present embodiment, the
도 5는 도 2의 단계 S206에서의 영상 데이터의 구조를 상세히 보여준다. 도 5를 참조하여 이를 설명하면 다음과 같다.FIG. 5 shows the structure of the image data in step S206 of FIG. 2 in detail. This will be described with reference to FIG. 5 as follows.
본 실시예의 경우, 단계 S206에서의 영상 데이터는 적어도 한 멀티-데이터 패킷(MDP)을 포함한다. 멀티-데이터 패킷(MDP)은 23 개의 일련의 데이터 패킷들(DP1 내지 DP23)을 포함한다. 이와 같은 멀티-데이터 패킷(MDP)이 게이트웨이(102)에게 전송됨에 따라, 게이트웨이(102)로부터의 확인 응답 절차가 대폭 줄어들 수 있다. 그러므로 영상 데이터의 총 전송 시간이 보다 줄어들 수 있다.In the case of this embodiment, the image data in step S206 includes at least one multi-data packet (MDP). The multi-data packet MDP includes a series of 23 data packets DP1 to DP23. As such a multi-data packet (MDP) is transmitted to the
42 바이트(bytes)의 각각의 데이터 패킷(DP1 내지 DP23)은 10 바이트의 통신용 포킷(pocket, 501) 및 32 바이트의 페이로드(payload, 502)를 포함한다.Each data packet DP1 to DP23 of 42 bytes includes a
페이로드(502)는, 네트워크 카메라(101)에서 압축된 결과의 정지 영상 데이터의 일부이다.The
통신용 포킷(501)은 1 바이트의 프리앰블(preamble), 5 바이트의 어드레스, 1 바이트의 길이 정보(403), 1 바이트의 헤드, 및 CRC(Cyclic Redundancy Checking) 코드를 포함한다.The
게이트웨이(102)는 통신용 포킷(pocket) 내의 길이 정보(503)에 의하여 데이터 패킷(DP1 내지 DP23)의 길이를 알 수 있다.The
1 바이트의 헤드는 5 비트(bits)의 데이터-패킷 식별 번호(IDpack), 1 비트의 짝수번째-홀수번째 정보 ID(IDevod), 1 비트의 데이터 존재-정보 ID(IDtran), 및 1 비트의 응답 요청 ID(IDreac)를 포함한다. 데이터-패킷 식별 번호(IDpack)는 각각의 데이터-패킷(DP1 내지 DP23)의 일련 번호를 의미한다. 짝수번째-홀수번째 정보 ID(IDevod)는 이전(transaction) 처리를 위한 정보이다. 데이터 존재-정보 ID(IDtran)는 32 바이트의 페이로드(payload)에 실제 데이터가 존재하는지의 여부를 가리킨다. 응답 요청 ID(IDreac)는 게이트웨이(도 2의 102)가 응답을 해야하는지의 여부를 가리킨다.A head of 1 byte has a data-packet identification number (IDpack) of 5 bits, an even-odd information ID (IDevod) of 1 bit, a data presence-information ID (IDtran) of 1 bit, and 1 bit of Contains the response request ID (IDreac). The data-packet identification number IDpack means a serial number of each data-packet DP1 to DP23. The even-odd information ID (IDevod) is information for transaction processing. The data presence-information ID (IDtran) indicates whether actual data exists in a payload of 32 bytes. The response request ID IDreac indicates whether the gateway (102 in FIG. 2) should respond.
이상 설명된 바와 같이, 본 실시예의 감시 시스템에 의하면, 게이트웨이는, 네트워크 카메라로부터의 영상 데이터가 수신되는 동안에, 비콘(beacon) 신호를 제1 주기보다 긴 제2 주기에 의하여 네트워크 카메라에게 주기적으로 전송한다.As described above, according to the monitoring system of the present embodiment, the gateway periodically transmits a beacon signal to the network camera by a second period longer than the first period while the video data from the network camera is received. do.
즉, 네트워크 카메라는 영상 데이터를 게이트웨이에게 송신하는 동안에 상대적으로 긴 제2 주기에 의하여 비콘(beacon) 신호를 주기적으로 수신한다. 여기에서, 네트워크 카메라에서의 제2 주기는 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기와 영상 전송 주기를 포함한다.That is, the network camera periodically receives a beacon signal with a relatively long second period while transmitting image data to the gateway. Here, the second period in the network camera includes a beacon standby period and an image transmission period.
이에 따라, 네트워크 카메라는 상대적으로 긴 영상 전송 주기를 적용하여 영상 데이터를 게이트웨이에게 주기적으로 전송할 수 있다. 즉, 일정한 시간 동안에 상대적으로 많은 양의 영상 데이터가 전송될 수 있으므로, 영상 데이터의 총 전송 시간이 상대적으로 짧아질 수 있다.Accordingly, the network camera may periodically transmit image data to the gateway by applying a relatively long image transmission period. That is, since a relatively large amount of image data may be transmitted for a predetermined time, the total transmission time of the image data may be relatively short.
따라서, 본 실시예의 감시 시스템에 의하면, 네트워크 카메라가 영상 압축율을 상대적으로 높이지 않고서도 영상 데이터의 총 전송 시간을 줄일 수 있고, 이에 따라 네트워크 카메라의 배터리 수명이 상대적으로 연장될 수 있다.Therefore, according to the monitoring system of the present embodiment, the network camera can reduce the total transmission time of image data without relatively increasing the image compression rate, and thus the battery life of the network camera can be relatively extended.
이제까지 본 발명에 대하여 바람직한 실시예를 중심으로 살펴보았다. 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자는 본 발명의 본질적인 특성에서 벗어나지 않는 범위에서 변형된 형태로 본 발명을 구현할 수 있음을 이해할 것이다.So far, the present invention has been focused on preferred embodiments. Those of ordinary skill in the art to which the present invention pertains will understand that the present invention can be implemented in modified forms without departing from the essential characteristics of the present invention.
그러므로 상기 개시된 실시예는 한정적인 관점이 아니라 설명적인 관점에서 고려되어야 한다. 본 발명의 범위는 전술한 설명이 아니라 특허청구범위에 나타나 있으며, 특허청구범위에 의해 청구된 발명 및 청구된 발명과 균등한 발명들은 본 발명에 포함된 것으로 해석되어야 한다.Therefore, the disclosed embodiments are to be considered in an illustrative rather than a restrictive sense. The scope of the present invention is indicated in the claims rather than the above description, and it should be construed that the invention claimed by the claims and inventions equivalent to the claimed invention are included in the present invention.
감시 시스템 뿐만 아니라 일반적인 영상 전송 분야에도 이용될 가능성이 크다.It is highly likely to be used not only in surveillance systems but also in general video transmission fields.
101 : 네트워크 카메라,102 : 게이트웨이,
103 : 클라이언트 장치,
Mgw : 게이트웨이의 동작 타이밍도,
Mca : 네트워크 카메라의 동작 타이밍도,
T1 : 제1 주기,T2 : 제2 주기,
T1b, T2b : 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기,T1s : 휴면(inactivity) 주기,
T2t : 영상 전송 주기.101: network camera, 102: gateway,
103: client device;
Mgw: operation timing diagram of the gateway,
Mca: operation timing diagram of network camera,
T1: first cycle, T2: second cycle,
T1b, T2b: beacon standby cycle, T1s: inactivity cycle,
T2t: Video transmission period.
Claims (6)
Translated fromKorean상기 게이트웨이가 비콘(beacon) 신호를 제1 주기에 의하여 상기 네트워크 카메라에게 주기적으로 전송함에 따라, 상기 네트워크 카메라는 상기 비콘(beacon) 신호를 수신할 때마다 이벤트 발생 여부를 판단하고,
상기 게이트웨이는, 상기 네트워크 카메라로부터의 영상 데이터가 수신되는 동안에, 상기 비콘(beacon) 신호를 상기 제1 주기보다 긴 제2 주기에 의하여 상기 네트워크 카메라에게 주기적으로 전송하며,
상기 네트워크 카메라에서의 상기 제1 주기는 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기와 휴면(inactivity) 주기를 포함하고,
상기 네트워크 카메라에서의 상기 제1 주기의 위상은 상기 게이트웨이에서의 상기 제1 주기의 위상에 비하여 상기 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기만큼 앞서 있는, 감시 시스템.A monitoring system in which a network camera communicates with a client device through a gateway,
As the gateway periodically transmits a beacon signal to the network camera according to a first cycle, the network camera determines whether an event occurs every time it receives the beacon signal,
The gateway periodically transmits the beacon signal to the network camera by a second period longer than the first period while the image data from the network camera is received,
The first period in the network camera includes a beacon standby period and an inactivity period,
and the phase of the first period in the network camera is ahead of the phase of the first period in the gateway by the beacon waiting period.
상기 네트워크 카메라에서의 상기 제2 주기는 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기와 영상 전송 주기를 포함하고,
상기 네트워크 카메라에서의 상기 제2 주기의 위상은 상기 게이트웨이에서의 상기 제2 주기의 위상에 비하여 상기 비콘(beacon) 대기 주기만큼 앞서 있는, 감시 시스템.3. The method of claim 2,
The second period in the network camera includes a beacon waiting period and an image transmission period,
and the phase of the second period in the network camera is ahead of the phase of the second period in the gateway by the beacon waiting period.
상기 게이트웨이가 비콘(beacon) 신호를 제1 주기에 의하여 상기 네트워크 카메라에게 주기적으로 전송함에 따라, 상기 네트워크 카메라는 상기 비콘(beacon) 신호를 수신할 때마다 이벤트 발생 여부를 판단하고,
상기 게이트웨이는, 상기 네트워크 카메라로부터의 영상 데이터가 수신되는 동안에, 상기 비콘(beacon) 신호를 상기 제1 주기보다 긴 제2 주기에 의하여 상기 네트워크 카메라에게 주기적으로 전송하며,
상기 네트워크 카메라는,
이벤트가 발생되었다고 판단되면, 이벤트 발생 신호를 상기 게이트웨이에게 전송한 후에 영상 데이터를 상기 게이트웨이에게 전송하는, 감시 시스템.A monitoring system in which a network camera communicates with a client device through a gateway,
As the gateway periodically transmits a beacon signal to the network camera according to a first cycle, the network camera determines whether an event occurs every time it receives the beacon signal,
The gateway periodically transmits the beacon signal to the network camera by a second period longer than the first period while the image data from the network camera is received,
The network camera is
When it is determined that an event has occurred, the video data is transmitted to the gateway after transmitting an event occurrence signal to the gateway.
상기 게이트웨이가 비콘(beacon) 신호를 제1 주기에 의하여 상기 네트워크 카메라에게 주기적으로 전송함에 따라, 상기 네트워크 카메라는 상기 비콘(beacon) 신호를 수신할 때마다 이벤트 발생 여부를 판단하고,
상기 게이트웨이는, 상기 네트워크 카메라로부터의 영상 데이터가 수신되는 동안에, 상기 비콘(beacon) 신호를 상기 제1 주기보다 긴 제2 주기에 의하여 상기 네트워크 카메라에게 주기적으로 전송하며,
상기 게이트웨이는,
상기 이벤트 발생 신호의 수신 시점으로부터 상기 영상 데이터의 수신 종료 시점까지, 상기 비콘(beacon) 신호를 상기 제2 주기에 의하여 상기 네트워크 카메라에게 주기적으로 전송하는, 감시 시스템.A monitoring system in which a network camera communicates with a client device through a gateway,
As the gateway periodically transmits a beacon signal to the network camera according to a first cycle, the network camera determines whether an event occurs every time it receives the beacon signal,
The gateway periodically transmits the beacon signal to the network camera by a second period longer than the first period while the image data from the network camera is received,
The gateway is
A monitoring system for periodically transmitting the beacon signal to the network camera according to the second period from the time of reception of the event occurrence signal to the end of reception of the image data.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150099227AKR102282454B1 (en) | 2015-07-13 | 2015-07-13 | Surveillance system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150099227AKR102282454B1 (en) | 2015-07-13 | 2015-07-13 | Surveillance system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20170008026A KR20170008026A (en) | 2017-01-23 |
| KR102282454B1true KR102282454B1 (en) | 2021-07-27 |
Family
ID=57989921
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150099227AActiveKR102282454B1 (en) | 2015-07-13 | 2015-07-13 | Surveillance system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102282454B1 (en) |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATE526801T1 (en)* | 2006-01-11 | 2011-10-15 | Qualcomm Inc | COMMUNICATION METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR SENDING PRIORITY INFORMATION VIA BEACON SIGNALS |
| BR112013012814B1 (en) | 2010-10-26 | 2019-10-08 | Nec Corporation | VIDEO DECODING DEVICE AND VIDEO DECODING METHOD |
| KR101215549B1 (en)* | 2011-02-01 | 2012-12-26 | 성현규 | User centered remote monitoring safety system using radio camera module and mobile phone |
- 2015
- 2015-07-13KRKR1020150099227Apatent/KR102282454B1/enactiveActive
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20170008026A (en) | 2017-01-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4321284B2 (en) | Streaming data transmission apparatus and information distribution system | |
| CN102045772B (en) | Data transmission method and device | |
| CN112436994B (en) | Data transmission method and electronic equipment | |
| EP2587860A1 (en) | Feedback method and device for header compression feedback information | |
| KR102300300B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for communicating packets using header compression | |
| CN102118792B (en) | Method and device for transmitting data packets | |
| CN111315004B (en) | A communication method and system, data transmission device, and data reception device | |
| US8467302B2 (en) | Wireless data transmission method, transmitting system, and receiving system | |
| CN107911842B (en) | Data transmission method, system, medium and device of Lora network server | |
| CN106537959B (en) | Method for encoding and decoding frames in a telecommunication network | |
| CN102938683B (en) | A kind of method and apparatus of data processing | |
| WO2022083371A1 (en) | Data transmission method and device | |
| US8804766B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for compressing communication packets | |
| WO2016112837A1 (en) | Data information transmission method, device, and system | |
| KR102402881B1 (en) | Surveillance system | |
| KR102282454B1 (en) | Surveillance system | |
| CN114500672A (en) | Data transmission method and system | |
| US20160119888A1 (en) | Wireless communication device, non-transitory computer readable medium, and wireless communication system | |
| CN110636035B (en) | Communication method, device and readable storage medium | |
| US9008077B2 (en) | Method for quick map recovery in case of error in MoCA | |
| CN108924060B (en) | Method, device and system for VOLTE data transmission | |
| JP4692412B2 (en) | Voice packet signal receiver | |
| WO2019011086A1 (en) | Pre-defined dictionary synchronization method and terminal | |
| CN109379170B (en) | Remapping confirmation method based on End/Start Mark in PDCP UM mode | |
| KR20140036874A (en) | Method for compressing tcp header and recording-medium recorded program thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20150713 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | Patent event date:20180919 Comment text:Notification of Change of Applicant Patent event code:PN23011R01D | |
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0201 | Request for examination | Patent event code:PA02012R01D Patent event date:20200603 Comment text:Request for Examination of Application Patent event code:PA02011R01I Patent event date:20150713 Comment text:Patent Application | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20210106 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20210618 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20210721 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20210722 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20240625 Start annual number:4 End annual number:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20250624 Start annual number:5 End annual number:5 |