KR102225632B1 - Apparatus for estimating distance between wireless communication infrastructures installed at unknown location and method for the same - Google Patents
Apparatus for estimating distance between wireless communication infrastructures installed at unknown location and method for the sameDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102225632B1 KR102225632B1KR1020170031821AKR20170031821AKR102225632B1KR 102225632 B1KR102225632 B1KR 102225632B1KR 1020170031821 AKR1020170031821 AKR 1020170031821AKR 20170031821 AKR20170031821 AKR 20170031821AKR 102225632 B1KR102225632 B1KR 102225632B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- wireless communication
- infrastructure
- distances
- distance
- information
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription242
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription31
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription199
- 238000009434installationMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription46
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription13
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000claimsdescription16
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description18
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description13
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description6
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description5
- 239000000470constituentSubstances0.000description3
- 238000010295mobile communicationMethods0.000description3
- 230000008901benefitEffects0.000description2
- 230000014509gene expressionEffects0.000description2
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000001413cellular effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000004590computer programMethods0.000description1
- 230000006866deteriorationEffects0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 238000013507mappingMethods0.000description1
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description1
- 230000002035prolonged effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000035945sensitivityEffects0.000description1
- 230000003068static effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000description1
- 238000000844transformationMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W64/00—Locating users or terminals or network equipment for network management purposes, e.g. mobility management
- H04W64/003—Locating users or terminals or network equipment for network management purposes, e.g. mobility management locating network equipment
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/02—Services making use of location information
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/02—Services making use of location information
- H04W4/029—Location-based management or tracking services
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Position Fixing By Use Of Radio Waves (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치 및 그 방법에 관한 것이다. 더욱 상세하게, 본 발명은 사용자 단말기들로부터 여러 측정지점에서 수신한 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여 설치 위치를 모르는 복수의 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하며, 추정된 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 이용하여 실내 공간에서 정밀한 위치기반 서비스를 제공하는 장치 및 그 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for estimating a distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location. In more detail, the present invention estimates the distance between a plurality of wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location using wireless communication infrastructure measurement information received at various measurement points from user terminals, and calculates the distance between the estimated wireless communication infrastructures. It relates to an apparatus and a method for providing precise location-based services in an indoor space by using.
무선통신 인프라를 이용한 위치추정 기술은 인프라 종류 및 서비스 범위에 따라 다양한 방식으로 존재한다.Location estimation technology using wireless communication infrastructure exists in various ways depending on the type of infrastructure and the range of services.
지구 궤도 상의 위성신호를 이용하여 사용자의 위치를 결정하는 GNSS(Global Navigation Satellite System)와 같은 GPS 기술들은, 비 가시선(Non-Line Of Sight) 구간인 도심 밀집 지역에서는 다중 경로오차로 인해 위치 오차가 50m에 이르고 특히 실내 지역에서는 수신감도가 저하되어 신호획득을 하지 못해 위치 결정이 어려운 점이 있다. 또한, 가시 위성 저하에 따른 초기위치결정시간(TTFF: Time To First Fix)이 길어지는 문제도 발생한다.GPS technologies such as Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), which determine the user's location using satellite signals in the Earth's orbit, have a location error due to multi-path errors in urban dense areas, which are non-line of sight sections. It reaches 50m, and especially in indoor areas, the reception sensitivity is degraded, so it is difficult to obtain a signal, making it difficult to determine the location. In addition, there is a problem that the time to first fix (TTFF) is prolonged due to the deterioration of the visible satellite.
셀룰러 이동통신 기지국의 위치정보와 측정신호를 이용하여 사용자의 위치를 결정하는 Cell-Id, E-OTD(Enhanced-Opserved Time Difference)와 같은 기술들은 GPS에 비해 초기위치결정시간이 짧으나, 기지국의 배치 밀도에 따라 위치추정 정확도가 달라지고 평균적으로 약 100~800m의 비교적 낮은 위치 정확도를 가져서 수m 정도의 위치 정확도를 요구하는 실내외 항법 서비스 등에 적용하기 어렵다.Technologies such as Cell-Id and E-OTD (Enhanced-Opserved Time Difference), which determine the user's location using the location information and measurement signals of cellular mobile communication base stations, have shorter initial positioning time than GPS, but the deployment of base stations The location estimation accuracy varies depending on the density and has a relatively low location accuracy of about 100 to 800 m on average, making it difficult to apply to indoor or outdoor navigation services that require a location accuracy of several meters.
그에 따라, 실내에서는 주로 Wi-Fi를 이용한 위치추정 기술이 제시되어 왔으며, Wi-Fi 기반 측위 기술은 GPS가 수신되지 않거나 GPS 위치오차가 큰 건물 실내및 도심 밀집지역에서 Wi-Fi AP들로부터의 신호세기 등을 이용하여 수m 수준의 정밀한 위치정보를 제공할 수 있다. 하지만, 차량을 이용한 AP mapping 기술은 Wi-Fi AP의 위치DB 초기 구축에 필요한 비용이 큰 문제가 있다. 또한 수집이 실외 영역에서 이루어지기 때문에 수집 위치는 GPS 위치정보를 사용하는데, 이는 GPS 수신이 어려운 실내 영역에서 수집위치 획득이 불가능한 문제가 있다.Accordingly, indoor location estimation technology using Wi-Fi has been mainly proposed, and Wi-Fi-based positioning technology is not receiving GPS or GPS location error is large indoors of buildings and from Wi-Fi APs in dense urban areas. Using signal strength, etc., precise location information of several meters can be provided. However, the AP mapping technology using a vehicle has a problem in that the cost required for initial establishment of a location DB of a Wi-Fi AP is large. In addition, since the collection is performed in an outdoor area, GPS location information is used for the collection location, which has a problem that it is impossible to obtain a collection location in an indoor area where GPS reception is difficult.
한편, 위치기반 서비스(LBS: Location Based Service)는 최근 단말의 위치정보를 이용한 다양한 정보를 제공하는 서비스(information service)로 정의될 수 있다. 따라서 임의의 단말에 대한 위치기반서비스를 제공하기 위해서는 해당 단말의 위치정보의 계산이 선행되어야 한다. 하지만 실제 환경에서, 특히 실내 환경에서, 단말의 위치를 제공하기 위해서는 설치된 무선통신 인프라의 위치를 정확히 알고 있거나 아니면 사전 수집과정을 통해 정확한 기준위치의 계산 및 해당 기준위치에서의 패턴 수집 등이 반드시 선행되어야 한다.Meanwhile, a location-based service (LBS) may be defined as an information service that provides various information using location information of a recent terminal. Therefore, in order to provide a location-based service for an arbitrary terminal, the calculation of the location information of the corresponding terminal must be preceded. However, in an actual environment, especially in an indoor environment, in order to provide the location of the terminal, it is necessary to know the location of the installed wireless communication infrastructure or to calculate the exact reference location through a pre-collection process and to collect the pattern at the reference location. It should be.
하지만, 초기에 해당 무선통신 인프라(예: Wi-Fi AP)의 설치위치 또는 수집 정보를 획득하기 위해 많은 시간과 인력비용이 소모되며, 만약 초기에 해당 정보를 획득 했더라도 실내 건물 내 인테리어의 변경 및 무선통신 인프라(예: Wi-Fi AP)의 수정/추가/변경 시 해당 정보를 갱신하는데 순차적으로 더 큰 비용이 소모될 수 있는 문제점이 있다.However, it takes a lot of time and manpower cost to acquire the installation location or collection information of the wireless communication infrastructure (e.g., Wi-Fi AP) initially, and changes in the interior of the indoor building even if the information is acquired initially. And when the wireless communication infrastructure (eg, Wi-Fi AP) is modified/added/changed, there is a problem in that a higher cost may be sequentially consumed to update the corresponding information.
본 발명은 복수의 무선통신 인프라들로부터 단말기에 수신된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들간 거리를 추정하는 것을 목적으로 한다.An object of the present invention is to estimate a distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location by using wireless communication infrastructure measurement information received from a terminal from a plurality of wireless communication infrastructures.
또한, 본 발명은 무선통신 인프라들간 거리정보를 이용한 위치기반 서비스를 제공하는 것을 목적으로 한다.In addition, an object of the present invention is to provide a location-based service using distance information between wireless communication infrastructures.
본 발명의 일 실시예는, 복수의 측정지점에서 측정된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 수신하는 수신부; 상기 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여 인접한 무선통신 인프라들을 결정하는 인접 인프라 결정부; 상기 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여, 각각의 상기 측정지점들로부터 인접한 무선통신 인프라들과의 거리들인 측정지점거리들을 계산하는 측정지점거리 계산부; 상기 측정지점거리들을 이용하여, 상기 인접한 무선통신 인프라들 사이의 거리들인 인프라거리들을 추정하는 인프라거리 추정부; 및 상기 인접한 무선통신 인프라들의 정보와 상기 인프라거리들을 저장하는 저장부를 포함하는, 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치를 제공한다.An embodiment of the present invention, a receiving unit for receiving the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information measured at a plurality of measurement points; An adjacent infrastructure determining unit for determining adjacent wireless communication infrastructures using the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information; A measurement point distance calculation unit that calculates measurement point distances, which are distances from each of the measurement points to adjacent wireless communication infrastructures, using the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information; An infrastructure distance estimating unit for estimating infrastructure distances, which are distances between adjacent wireless communication infrastructures, using the measurement point distances; And a storage unit for storing information on the adjacent wireless communication infrastructures and the infrastructure distances, and an apparatus for estimating distances between wireless communication infrastructures of which the installation location is unknown.
상기 인프라거리 추정부는 각각의 상기 측정지점거리들에 상응하는 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되도록 상기 인프라거리들을 추정할 수 있다.The infrastructure distance estimator may estimate the infrastructure distances such that the sum of distance errors corresponding to the respective measurement point distances is minimized.
상기 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치는 상기 인프라거리 정보를 이용하여, 상기 인프라거리들을 이용한 위치기반 서비스를 제공하는 서비스 제공부를 포함할 수 있다.The apparatus for estimating a distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location may include a service provider that provides a location-based service using the infrastructure distances by using the infrastructure distance information.
상기 인프라거리 추정부는 상기 인프라거리들이 상기 측정지점들과의 관계에서 삼각 부등식을 만족하며, 상기 거리오차들 각각이 실 환경에서 측정정보의 변화에 따라 발생할 수 있는 측정지점거리의 변화량 이하라는 조건하에, 상기 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되도록 하는 상기 인프라거리들을 추정할 수 있다.The infrastructure distance estimation unit satisfies the triangular inequality in the relationship between the infrastructure distances and the measurement points, and each of the distance errors is less than or equal to the amount of change in the measurement point distance that may occur according to the change of measurement information in the real environment. , It is possible to estimate the infrastructure distances such that the sum of the distance errors is minimized.
상기 측정지점거리 계산부는 수신전파세기를 이용한 자유공간 경로손실 모델을 통해 측정지점거리들을 계산할 수 있다.The measurement point distance calculation unit may calculate the measurement point distances through a free space path loss model using the received radio wave strength.
본 발명의 다른 일 실시예는, 복수의 측정지점에서 측정된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 수신하는 수신단계; 상기 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여 인접한 무선통신 인프라들을 결정하는 인접 인프라 결정단계; 상기 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여, 각각의 상기 측정지점들로부터 인접한 무선통신 인프라들과의 거리들인 측정지점거리들을 계산하는 측정지점거리 계산단계; 상기 측정지점거리들을 이용하여, 상기 인접한 무선통신 인프라들 사이의 거리들인 인프라거리들을 추정하는 인프라거리 추정단계; 및 상기 인접한 무선통신 인프라들의 정보와 상기 인프라거리들을 저장하는 저장단계를 포함하는, 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 방법을 제공한다.Another embodiment of the present invention is a receiving step of receiving the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information measured at a plurality of measurement points; An adjacent infrastructure determining step of determining adjacent wireless communication infrastructures using the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information; A measurement point distance calculation step of calculating measurement point distances, which are distances from each of the measurement points to adjacent wireless communication infrastructures, using the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information; An infrastructure distance estimation step of estimating infrastructure distances, which are distances between adjacent wireless communication infrastructures, using the measurement point distances; And a storage step of storing the information of the adjacent wireless communication infrastructures and the infrastructure distances. It provides a method of estimating a distance between wireless communication infrastructures of which the installation location is unknown.
상기 인프라거리 추정단계는 각각의 상기 측정지점거리들에 상응하는 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되도록 상기 인프라거리들을 추정할 수 있다.The infrastructure distance estimation step may estimate the infrastructure distances such that the sum of distance errors corresponding to the respective measurement point distances is minimized.
상기 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 방법은 상기 인프라거리 정보를 이용하여, 상기 인프라거리들을 이용한 위치기반 서비스를 제공하는 서비스 제공단계를 포함할 수 있다.The method of estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures of which the installation location is unknown may include a service providing step of providing a location-based service using the infrastructure distances by using the infrastructure distance information.
상기 인프라거리 추정단계는 상기 인프라거리들이 상기 측정지점들과의 관계에서 삼각 부등식을 만족하며, 상기 거리오차들 각각이 실 환경에서 측정정보의 변화에 따라 발생할 수 있는 측정지점거리의 변화량 이하라는 조건하에, 상기 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되도록 하는 상기 인프라거리들을 추정할 수 있다.The infrastructure distance estimation step is a condition that the infrastructure distances satisfy the triangular inequality in relation to the measurement points, and each of the distance errors is less than or equal to the amount of change in the measurement point distance that may occur according to the change of measurement information in the real environment. Below, it is possible to estimate the infrastructure distances such that the sum of the distance errors is minimized.
상기 측정지점거리 계산단계는 수신전파세기를 이용한 자유공간 경로손실 모델을 통해 측정지점거리들을 계산할 수 있다.In the step of calculating the measurement point distance, the measurement point distances may be calculated through a free space path loss model using the received radio wave strength.
본 발명의 또 다른 일 실시예는, 컴퓨터를 이용하여 상기 방법을 실행시키기 위하여 매체에 저장된 컴퓨터 프로그램을 제공한다.Another embodiment of the present invention provides a computer program stored in a medium to execute the method using a computer.
본 발명은 복수의 무선통신 인프라들로부터 단말기에 수신된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들간 거리를 추정할 수 있다.The present invention can estimate the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location by using the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information received by the terminal from a plurality of wireless communication infrastructures.
또한, 본 발명은 무선통신 인프라들간 거리정보를 이용한 위치기반 서비스를 제공할 수 있다.In addition, the present invention can provide a location-based service using distance information between wireless communication infrastructures.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치의 구성을 나타낸 블록도이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 방법을 나타낸 동작 흐름도이다.
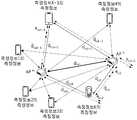
도 3은 임의의 측정지점에서 임의의 사용자 단말기를 통해 측정한 복수 개의 무선통신 인프라들의 측정정보의 예시를 나타낸 도면이다.
도 4는 여러 측정지점에서 수집한 무선통신 인프라들의 측정정보 및 일부 무선통신 인프라들의 위치의 예시를 나타낸 도면이다.
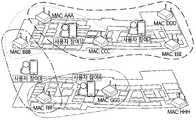
도 5는 여러 측정지점에서 2개의 무선통신 인프라들로부터 수신한 전파의 수신전파세기(RSSI)를 활용하여 계산한 측정지점 거리들의 예시를 나타낸 도면이다.
도 6은 건물 내부의 여러 무선통신 인프라들과 여러 측정지점들, 그리고 각각의 측정지점에 상응하는 인접한 무선통신 인프라들의 예시를 나타낸 도면이다.
도 7은 도 6에 도시된 예시에서, 무선통신 인프라간 상관관계에 따른 상관DB 및 무선통신 인프라간 거리정보에 따른 상관DB의 예시를 나타낸 도면이다.
도 8은 도 7에 도시된 무선통신 인프라간 거리정보에 따른 상관DB의 예시에서, 위치기반 서비스를 이용하는 메시지 송신자와 메시지 수신자들의 위치관계의 일 예를 나타낸 도면이다.
도 9는 도 7에 도시된 무선통신 인프라간 거리정보에 따른 상관DB의 예시에서, 위치기반 서비스를 이용하는 메시지 송신자와 메시지 수신자들의 위치관계의 다른 일 예를 나타낸 도면이다.
도 10은 실제 무선통신 환경의 일 예에서, 각각의 무선통신 인프라들로부터 다른 무선통신 인프라들까지의 홉(Hop) 분포를, 상관관계들을 이용한 홉 분포와 인프라거리들을 이용한 홉 분포를 비교하여 나타낸 도면이다.1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of an apparatus for estimating a distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know an installation location according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a flowchart illustrating a method of estimating a distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know an installation location according to an embodiment of the present invention.
3 is a diagram showing an example of measurement information of a plurality of wireless communication infrastructures measured through a user terminal at an arbitrary measurement point.
4 is a diagram showing an example of measurement information of wireless communication infrastructures collected at various measurement points and locations of some wireless communication infrastructures.
FIG. 5 is a diagram showing examples of distances of measurement points calculated by using the received radio wave strength (RSSI) of radio waves received from two wireless communication infrastructures at various measurement points.
6 is a diagram showing examples of various wireless communication infrastructures and various measurement points inside a building, and adjacent wireless communication infrastructures corresponding to each measurement point.
FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating an example of a correlation DB according to a correlation between wireless communication infrastructures and a correlation DB according to distance information between wireless communication infrastructures in the example shown in FIG. 6.
FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating an example of a location relationship between a message sender and message receivers using a location-based service in an example of a correlation DB according to distance information between wireless communication infrastructures shown in FIG. 7.
9 is a diagram illustrating another example of a location relationship between a message sender and message receivers using a location-based service in an example of a correlation DB according to distance information between wireless communication infrastructures shown in FIG. 7.
FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating a hop distribution from each wireless communication infrastructure to other wireless communication infrastructures in an example of an actual wireless communication environment, by comparing a hop distribution using correlations and a hop distribution using infrastructure distances. It is a drawing.
본 발명은 다양한 변환을 가할 수 있고 여러 가지 실시예를 가질 수 있는 바, 특정 실시예들을 도면에 예시하고 상세하게 설명하고자 한다. 본 발명의 효과 및 특징, 그리고 그것들을 달성하는 방법은 도면과 함께 상세하게 후술되어 있는 실시예들을 참조하면 명확해질 것이다. 여기서, 반복되는 설명, 본 발명의 요지를 불필요하게 흐릴 수 있는 공지 기능, 및 구성에 대한 상세한 설명은 생략한다. 본 발명의 실시형태는 당 업계에서 평균적인 지식을 가진 자에게 본 발명을 보다 완전하게 설명하기 위해서 제공되는 것이다. 따라서, 도면에서의 요소들의 형상 및 크기 등은 보다 명확한 설명을 위해 과장될 수 있다.In the present invention, various transformations may be applied and various embodiments may be provided, and specific embodiments will be illustrated in the drawings and described in detail. Effects and features of the present invention, and a method of achieving them will become apparent with reference to the embodiments described below in detail together with the drawings. Here, repeated descriptions, well-known functions that may unnecessarily obscure the subject matter of the present invention, and detailed descriptions of configurations are omitted. Embodiments of the present invention are provided to more completely explain the present invention to those with average knowledge in the art. Accordingly, the shapes and sizes of elements in the drawings may be exaggerated for clearer explanation.
그러나 본 발명은 이하에서 개시되는 실시예들에 한정되는 것이 아니라 각 실시예들의 전부 또는 일부가 선택적으로 조합되어 구성되어 다양한 형태로 구현될 수 있다. 이하의 실시예에서, 제1, 제2 등의 용어는 한정적인 의미가 아니라 하나의 구성 요소를 다른 구성 요소와 구별하는 목적으로 사용되었다. 또한, 단수의 표현은 문맥상 명백하게 다르게 뜻하지 않는 한 복수의 표현을 포함한다. 또한, 포함하다 또는 가지다 등의 용어는 명세서상에 기재된 특징, 또는 구성요소가 존재함을 의미하는 것이고, 하나 이상의 다른 특징들 또는 구성요소가 부가될 가능성을 미리 배제하는 것은 아니다.However, the present invention is not limited to the embodiments disclosed below, and may be implemented in various forms by selectively combining all or part of each of the embodiments. In the following embodiments, terms such as first and second are used for the purpose of distinguishing one constituent element from other constituent elements rather than a limiting meaning. In addition, expressions in the singular include plural expressions unless the context clearly indicates otherwise. In addition, terms such as include or have means that the features or components described in the specification are present, and do not preclude the possibility of adding one or more other features or components in advance.
이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예들을 상세히 설명하기로 하며, 도면을 참조하여 설명할 때 동일하거나 대응하는 구성 요소는 동일한 도면 부호를 부여하고 이에 대한 중복되는 설명은 생략하기로 한다.Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings, and when describing with reference to the drawings, the same or corresponding constituent elements are denoted by the same reference numerals, and redundant descriptions thereof will be omitted. .
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치(100)의 구성을 나타낸 블록도이다.1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of an
도 1을 참조하면, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치(100)는 수신부(110), 인접 인프라 결정부(120), 측정지점거리 계산부(130), 인프라거리 추정부(140), 저장부(150) 등을 포함한다.Referring to FIG. 1, an
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치(100)는 수신부(110), 인접 인프라 결정부(120), 측정지점거리 계산부(130), 인프라거리 추정부(140), 저장부(150) 및 서비스 제공부(160) 등을 포함한다.In addition, the
상세히, 수신부(110)는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하기 위해, 복수의 측정지점들에서 사용자의 단말기들로부터 측정된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 수신한다.In detail, the receiving
여기서, 데이터 수신부(110)는 다른 네트워크 장치와 유무선 연결을 통해 제어 신호 또는 데이터 신호와 같은 신호를 송수신하기 위해 필요한 하드웨어 및 소프트웨어를 포함하는 장치일 수 있다.Here, the
이때, 무선통신 인프라 측정정보는 정해진 주기에 따라 정기적으로 수신할 수도 있으며, 필요에 따라 수시로 수신할 수도 있다.At this time, the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information may be periodically received according to a predetermined period, or may be received at any time as necessary.
그리고, 무선통신 인프라 측정정보는 이동통신 기지국, Wi-Fi, BT(Bluetooth), BLE(Bluetooth Low Energy), UWB(Ultra-Wide Band) 등 무선통신 및 측위를 위해 전파를 송신하는 장치로부터 전파를 수신했을 때 측정되는 데이터를 의미한다. 해당 데이터에는 식별자, 송신전파세기, 송신주파수, 수신전파세기(RSSI: Received Signal Strength Indicator), 왕복이동시간(RTT: Round Trip Time), 전파도착 수신각(AoA: Angle of Arrival) 등을 포함할 수 있으며 그 외에 각각의 무선통신 인프라별 표준 데이터에 포함되어 수신 가능한 모든 정보를 의미한다.In addition, the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information transmits radio waves from devices that transmit radio waves for wireless communication and positioning, such as mobile communication base stations, Wi-Fi, BT (Bluetooth), BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy), and UWB (Ultra-Wide Band). It refers to the data measured when received. Corresponding data includes identifiers, transmission strength, transmission frequency, Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI), Round Trip Time (RTT), Angle of Arrival (AoA), etc. In addition, it refers to all information that can be received by being included in the standard data for each wireless communication infrastructure.
또한, 복수의 측정지점들은 사용자 단말기가 정적 또는 동적 환경에서 적어도 하나 이상의 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 수신하는 지점을 의미한다. 사용자 단말은 단말 내 OS, 응용 프로그램, 별도 H/W 등을 통해 해당 정보를 일시적 또는 주기적으로 수집할 수 있다. 그리고, 수집된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보는 단말 내 저장장치 등에 임시적 또는 영구적으로 저장될 수도 있고, 혹은 별도의 저장 없이 원격의 서버 등에 전송할 수도 있다.In addition, the plurality of measurement points means a point at which the user terminal receives at least one wireless communication infrastructure measurement information in a static or dynamic environment. The user terminal may temporarily or periodically collect the corresponding information through the OS, an application program, or a separate H/W in the terminal. In addition, the collected wireless communication infrastructure measurement information may be temporarily or permanently stored in a storage device in the terminal, or may be transmitted to a remote server without separate storage.
인접 인프라 결정부(120)는 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여 복수 개의 무선통신 인프라들 중에서 인접한 무선통신 인프라들을 결정한다.The neighboring
여기서, 인접한 무선통신 인프라는 공간적으로 가까이 배치되어 있는 무선통신 인프라를 의미하며, 본 발명에서는 무선통신 인프라의 설치 위치정보를 모르기 때문에 인접 여부는 임의의 측정지점에서 동시에 수집된 무선통신 인프라 집합 간에는 최대 무선통신 신호도달거리 내에서 인접되어 있다고 판단한다.Here, the adjacent wireless communication infrastructure means a wireless communication infrastructure that is spatially adjacent, and in the present invention, since the installation location information of the wireless communication infrastructure is not known, whether or not adjacent is the maximum between the set of wireless communication infrastructures simultaneously collected at an arbitrary measurement point. It is judged that it is adjacent within the reach of the wireless communication signal.
측정지점거리 계산부(130)는 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여, 각각의 측정지점들로부터 인접한 무선통신 인프라들과의 거리들인 측정지점거리들을 계산한다.The measurement point
여기서, 무선통신 인프라 측정정보는 단말기와 무선통신 인프라들과의 인접 강도를 함축하는 수신전파세기(RSSI), 왕복이동시간(RTT) 또는 전파도착 수신각(AoA)와 같은 정보를 포함하고 있으므로, 이를 이용하여 측정지점거리들을 계산할 수 있다.Here, the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information includes information such as received radio wave strength (RSSI), round trip travel time (RTT), or radio wave arrival and reception angle (AoA), which implies the adjacent strength between the terminal and the wireless communication infrastructure, Using this, you can calculate the measurement point distances.
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에서 측정지점거리 계산부(130)는, 수신전파세기를 이용한 자유공간 경로손실 모델을 통하여 측정지점거리들()을 계산할 수 있다.In addition, in an embodiment of the present invention, the measurement point
상세히, 수신기 신호세기()와 송신기 신호세기()의 관계는, 하기 수학식 1(프리스 공식)과 같이 설계된 무선통신 인프라의 파장() 및 송수신 안테나 이득(,)으로 표현 가능하다.In detail, the receiver signal strength ( ) And transmitter signal strength ( The relationship of) is the wavelength ( ) And transmit/receive antenna gain ( , ) Can be expressed.
[수학식 1][Equation 1]
기준거리에서의 자유공간 경로손실()은 하기 수학식 2와 같이 수신기 신호세기()와 송신기 신호세기()로 표현 가능하며, 상기 수학식 1을 이용하면 기준거리(), 설계된 무선통신 인프라의 파장() 및 송수신 안테나 이득(,)으로 표현 가능하다.Free space path loss at the reference distance ( ) Is the receiver signal strength ( ) And transmitter signal strength ( ), and using
[수학식 2][Equation 2]
측정지점거리에서의 자유공간 경로손실()은 하기 수학식 3과 같이 기준거리에서의 자유공간 경로손실(), 경로 손실 지수(), 측정지점거리() 및 기준거리()로 표현 가능하다.Free space path loss at the measurement point distance ( ) Is the free space path loss at the reference distance as shown in
[수학식 3][Equation 3]
측정지점거리()는 상기 수학식 3을 정리하면 하기 수학식 4와 같이 측정지점거리에서의 자유공간 경로손실(), 기준거리에서의 자유공간 경로손실(), 경로 손실 지수() 및 기준거리()로 표현 가능하다. 또한, 측정지점거리에서의 자유공간 경로손실()는 송신기 신호세기()와 수신기 신호세기()의 차이로 표현 가능하다.Measurement point distance ( ) Is the free space path loss at the measurement point distance as shown in
[수학식 4][Equation 4]
상기 수학식들에 따르면, 측정지점거리()는 무선통신 인프라의 송신기 신호세기(), 기준거리에서의 자유공간 경로손실(), 경로 손실 지수(), 수신기 신호세기()의 함수로 계산할 수 있다. 이 때, 송신기 신호세기()는 송신기 사양(specification)에 따라 사전에 주어질 수 있고, 기준거리에서의 자유공간 경로손실()은 설계된 무선통신 인프라의 파장(), 기준거리(), 송수신 안테나 이득(,) 등을 이용하여 사전에 계산될 수 있다. 경로 손실 지수() 역시 전파이동환경에 따라 사전에 주어질 수 있다.According to the above equations, the measurement point distance ( ) Is the transmitter signal strength of the wireless communication infrastructure ( ), free space path loss at the reference distance ( ), path loss index ( ), receiver signal strength ( It can be calculated as a function of ). At this time, the transmitter signal strength ( ) Can be given in advance according to the transmitter specification, and the free space path loss at the reference distance ( ) Is the wavelength of the designed wireless communication infrastructure ( ), reference distance ( ), transmit/receive antenna gain ( , ) Can be calculated in advance. Path loss index( ) Can also be given in advance depending on the environment of radio wave movement.
따라서, 무선통신 인프라로부터 측정지점까지의 거리인 측정지점거리()는 수신기 신호세기()만의 함수로 계산될 수 있으며, 수신전파세기만 측정되면 측정지점거리()를 계산할 수 있다.Therefore, the measurement point distance, which is the distance from the wireless communication infrastructure to the measurement point ( ) Is the receiver signal strength ( ) Can be calculated as a function only, and if only the received wave strength is measured, the measurement point distance ( ) Can be calculated.
인프라거리 추정부(140)는 측정지점거리들을 이용하여, 인접한 무선통신 인프라들 사이의 거리들인 인프라거리들을 추정한다.The infrastructure
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에서 인프라거리 추정부(140)는, 각각의 측정지점거리들에 상응하는 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되도록 인프라거리들을 추정할 수 있다. 측정지점거리 계산부(130)에서는 사용자의 단말기들에서 수집한 무선통신 인프라 측정정보로부터 측정지점거리를 계산하므로, 실제 측정지점과 대상 무선통신 인프라 사이의 거리와 오차가 생길 수 있다. 따라서, 측정지점거리들의 오차인 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되는 인프라거리들을 추정하게되면, 실제 무선통신 인프라들 사이의 거리에 근접할 가능성이 높아진다.In addition, in an embodiment of the present invention, the infrastructure
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에서 인프라거리 추정부(140)는, 거리오차들의 합을 최소화하는 문제를 해결하기 위하여 선형계획법(Linear Programming)을 사용할 수 있다. 특히, 인프라거리들이 측정지점들과의 관계에서 삼각 부등식을 만족하며, 거리오차들 각각이 실 환경에서 측정정보의 변화에 따라 발생할 수 있는 측정지점거리의 변화량보다 작거나 같다는 조건하에, 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되도록 하는 인프라거리들을 추정할 수 있다.In addition, in an embodiment of the present invention, the infrastructure
예를 들어, 무선통신 인프라 m, 무선통신 인프라 n 그리고 N개의 측정지점이 존재하는 환경에서 인프라거리를 추정하는 경우에, 인프라거리()는 각각의 측정지점들에 대해서 하기 수학식 5의 삼각부등식을 충족하여야 한다. 또한, 거리오차들(,) 각각에 대해서, 하기 수학식 6 및 수학식 7과 같이, 실 환경에서 측정정보의 변화에 따라 발생할 수 있는 측정지점거리의 변화량(,)보다 작거나 같도록 제한한다. 하기 수학식 5 내지 7을 만족하면서, 오차거리들의 합()이 최소가 되도록 인프라거리()를 정한다.For example, in the case of estimating the infrastructure distance in an environment in which there are m wireless communication infrastructure, n wireless communication infrastructure, and N measurement points, the infrastructure distance ( ) Must satisfy the trigonometric inequality of
[수학식 5][Equation 5]
[수학식 6][Equation 6]
[수학식 7][Equation 7]
이때,는 무선통신 인프라 m과 측정지점 k와의 계산된 측정지점거리,는 무선통신 인프라 n과 측정지점 k와의 계산된 측정지점거리,는에 상응하는 거리오차,는에 상응하는 거리오차,는에 상응하는 측정지점거리의 변화량,는에 상응하는 측정지점거리의 변화량,은 무선통신 인프라 m과 무선통신 인프라 n 사이의 인프라거리이다.At this time, Is the calculated measurement point distance between the wireless communication infrastructure m and the measurement point k, Is the calculated measurement point distance between the wireless communication infrastructure n and the measurement point k, Is Distance error corresponding to, Is Distance error corresponding to, Is The amount of change in the measurement point distance corresponding to, Is The amount of change in the measurement point distance corresponding to, Is the infrastructure distance between the wireless communication infrastructure m and the wireless communication infrastructure n.
또한, 선형계획법을 사용함에 있어서, 무선통신 인프라 종류 및 측정 공간의 구조 등에 따른 조건들을 추가할 수 있다.In addition, in using the linear programming method, conditions according to the type of wireless communication infrastructure and the structure of the measurement space can be added.
저장부(150)는 인접한 무선통신 인프라들의 정보와 인프라거리들을 저장한다. 여기서, 인접한 무선통신 인프라들의 정보는 인접한 무선통신 인프라 집합 정보나, 무선통신 인프라들과와 측정지점들의 인접 강도를 나타내는 수신전파세기(RSSI), RTT, AoA 등의 정보를 포함할 수 있다. 나아가, 여러 측정지점들에서 수집된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보나 측정지점거리들과 같은 정보도 저장할 수 있다.The
서비스 제공부(160)는 추정된 인프라거리 정보를 이용하여, 무선통신 인프라들 간의 최단거리에 기반한 위치기반 서비스를 제공할 수 있다.The
기존에는 무선통신 인프라 간의 상관관계에 따른 계층에 기반한 위치기반 서비스가 제공되었으나, 본 발명의 일 실시예에서는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리정보에 기반한 위치기반 서비스를 제공하여 보다 정확한 위치기반 서비스를 제공할 수 있다.In the past, a location-based service based on a layer according to a correlation between wireless communication infrastructures was provided, but in an embodiment of the present invention, a location-based service based on distance information between wireless communication infrastructures is provided to provide a more accurate location-based service. I can.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 방법을 나타낸 동작 흐름도이다.2 is a flowchart illustrating a method of estimating a distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know an installation location according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 2를 참조하면, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 방법은 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치(도 1의 100 참조)가, 복수의 측정지점에서 측정된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 수신한다(S201).Referring to FIG. 2, a method for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location according to an embodiment of the present invention is an apparatus for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location (see 100 in FIG. 1). A, wireless communication infrastructure measurement information measured at a plurality of measurement points is received (S201).
이때, 무선통신 인프라 측정정보는 정해진 주기에 따라 정기적으로 수신할 수도 있으며, 필요에 따라 수시로 수신할 수도 있다.At this time, the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information may be periodically received according to a predetermined period, or may be received at any time as necessary.
그리고, 무선통신 인프라 측정정보는 이동통신 기지국, Wi-Fi, BT(Bluetooth), BLE(Bluetooth Low Energy), UWB(Ultra-Wide Band) 등 무선통신 및 측위를 위해 전파를 송신하는 장치로부터 전파를 수신했을 때 측정되는 데이터를 의미한다. 해당 데이터에는 식별자, 송신전파세기, 송신주파수, 수신전파세기(RSSI: Received Signal Strength Indicator), 왕복이동시간(RTT: Round Trip Time), 전파도착 수신각(AoA: Angle of Arrival) 등을 포함할 수 있으며 그 외에 각각의 무선통신 인프라별 표준 데이터에 포함되어 수신 가능한 모든 정보를 의미한다.In addition, the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information transmits radio waves from devices that transmit radio waves for wireless communication and positioning, such as mobile communication base stations, Wi-Fi, BT (Bluetooth), BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy), and UWB (Ultra-Wide Band). It refers to the data measured when received. Corresponding data includes identifiers, transmission strength, transmission frequency, Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI), Round Trip Time (RTT), Angle of Arrival (AoA), etc. In addition, it refers to all information that can be received by being included in the standard data for each wireless communication infrastructure.
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 방법은 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치(도 1의 100 참조)가, 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여 인접한 무선통신 인프라들을 결정한다(S203).In addition, the method of estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location according to an embodiment of the present invention is an apparatus (refer to 100 in FIG. 1) for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location. Adjacent wireless communication infrastructures are determined using the infrastructure measurement information (S203).
여기서, 인접한 무선통신 인프라는 공간적으로 가까이 배치되어 있는 무선통신 인프라를 의미하며, 본 발명에서는 무선통신 인프라의 설치 위치정보를 모르기 때문에 인접 여부는 임의의 측정지점에서 동시에 수집된 무선통신 인프라 집합 간에는 최대 무선통신 신호도달거리 내에서 인접되어 있다고 판단한다.Here, the adjacent wireless communication infrastructure means a wireless communication infrastructure that is spatially adjacent, and in the present invention, since the installation location information of the wireless communication infrastructure is not known, whether or not adjacent is the maximum between the set of wireless communication infrastructures simultaneously collected at an arbitrary measurement point. It is judged that it is adjacent within the reach of the wireless communication signal.
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 방법은 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치(도 1의 100 참조)가, 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여 각각의 측정지점들로부터 인접한 무선통신 인프라들과의 측정지점거리들을 계산한다(S205).In addition, the method of estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location according to an embodiment of the present invention is an apparatus (refer to 100 in FIG. 1) for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location. The measurement point distances from the respective measurement points to adjacent wireless communication infrastructures are calculated using the infrastructure measurement information (S205).
여기서, 무선통신 인프라 측정정보는 단말기와 무선통신 인프라들과의 인접 강도를 함축하는 수신전파세기(RSSI), 왕복이동시간(RTT) 또는 전파도착 수신각(AoA)와 같은 정보를 포함하고 있으므로, 이를 이용하여 측정지점거리들을 계산할 수 있다.Here, the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information includes information such as received radio wave strength (RSSI), round trip travel time (RTT), or radio wave arrival and reception angle (AoA), which implies the adjacent strength between the terminal and the wireless communication infrastructure, Using this, you can calculate the measurement point distances.
나아가, 수신전파세기를 이용한 자유공간 경로손실 모델을 통하여 측정지점거리들을 계산할 수 있다. 측정지점거리()는 무선통신 인프라의 송신기 신호세기(), 기준거리에서 자유공간 경로손실 모델(), 경로 손실 지수(), 수신기 신호세기()의 함수로 계산할 수 있다. 이 때, 송신기 신호세기()는 송신기 사양(specification)에 따라 사전에 주어질 수 있고, 기준거리에서 자유공간 경로손실 모델()은 설계된 무선통신 인프라의 파장(), 기준거리(), 송수신 안테나 이득(,) 등을 이용하여 사전에 계산될 수 있다. 경로 손실 지수() 역시 전파이동환경에 따라 사전에 주어질 수 있다.Furthermore, the measurement point distances can be calculated through a free space path loss model using the received radio wave strength. Measurement point distance ( ) Is the transmitter signal strength of the wireless communication infrastructure ( ), free space path loss model at reference distance ( ), path loss index ( ), receiver signal strength ( It can be calculated as a function of ). At this time, the transmitter signal strength ( ) Can be given in advance according to the transmitter specification, and the free space path loss model ( ) Is the wavelength of the designed wireless communication infrastructure ( ), reference distance ( ), transmit/receive antenna gain ( , ) Can be calculated in advance. Path loss index( ) Can also be given in advance depending on the environment of radio wave movement.
따라서, 무선통신 인프라로부터 측정지점까지의 거리인 측정지점거리()는 수신기 신호세기()만의 함수로 계산될 수 있으며, 수신전파세기만 측정되면 측정지점거리()를 계산할 수 있다.Therefore, the measurement point distance, which is the distance from the wireless communication infrastructure to the measurement point ( ) Is the receiver signal strength ( ) Can be calculated as a function only, and if only the received wave strength is measured, the measurement point distance ( ) Can be calculated.
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 방법은 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치(도 1의 100 참조)가, 측정지점거리들을 이용하여 인접한 무선통신 인프라들 사이의 인프라거리들을 추정한다(S207).In addition, the method for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location according to an embodiment of the present invention is an apparatus for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location (refer to 100 in FIG. 1), the measurement point The infrastructure distances between adjacent wireless communication infrastructures are estimated using the distances (S207).
이 때, 단계(S205)에서 계산한 각각의 측정지점거리들에 상응하는 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되도록, 인프라거리들을 추정할 수 있다. 사용자의 단말기들에서 수집한 무선통신 인프라 측정정보로부터 측정지점거리를 계산하므로, 실제 측정지점과 대상 무선통신 인프라 사이의 거리와 오차가 생길 수 있다. 따라서, 측정지점거리들의 오차인 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되는 인프라거리들을 추정하게되면, 실제 무선통신 인프라들 사이의 거리에 근접할 가능성이 높아진다.In this case, the infrastructure distances may be estimated so that the sum of distance errors corresponding to the respective measurement point distances calculated in step S205 is minimized. Since the measurement point distance is calculated from the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information collected by the user's terminals, a distance and an error may occur between the actual measurement point and the target wireless communication infrastructure. Therefore, when the infrastructure distances in which the sum of distance errors, which is the error of the measurement point distances, is the minimum are estimated, the possibility of approaching the distance between the actual wireless communication infrastructures increases.
그리고, 인프라거리들을 추정함에 있어서, 거리오차들의 합을 최소화하는 문제를 해결하기 위하여 선형계획법을 사용할 수 있다. 특히, 인프라거리들이 측정지점들과의 관계에서 삼각 부등식을 만족하며, 거리오차들 각각이 실 환경에서 측정정보의 변화에 따라 발생할 수 있는 측정지점거리의 변화량보다 작거나 같다는 조건하에, 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되도록 하는 인프라거리들을 추정할 수 있다.And, in estimating infrastructure distances, a linear programming method can be used to solve the problem of minimizing the sum of distance errors. In particular, under the condition that the infrastructure distances satisfy the triangular inequality in relation to the measurement points, and each of the distance errors is less than or equal to the amount of change in the measurement point distance that can occur due to the change of measurement information in the real environment, We can estimate the infrastructure distances that bring the sum to a minimum.
또한, 선형계획법을 사용함에 있어서, 무선통신 인프라 종류 및 측정 공간의 구조 등에 따른 조건들을 추가할 수 있다.In addition, in using the linear programming method, conditions according to the type of wireless communication infrastructure and the structure of the measurement space can be added.
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 방법은 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치(도 1의 100 참조)가, 인접한 무선통신 인프라들의 정보와 인프라거리들을 저장한다(S209). 여기서, 인접한 무선통신 인프라들의 정보는 인접한 무선통신 인프라 집합 정보나, 무선통신 인프라들과와 측정지점들의 인접 강도를 나타내는 수신전파세기(RSSI), RTT, AoA 등의 정보를 포함할 수 있다.In addition, the method for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location according to an embodiment of the present invention is an apparatus for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location (refer to 100 in FIG. 1). Information of communication infrastructures and infrastructure distances are stored (S209). Here, the information on adjacent wireless communication infrastructures may include information on a set of adjacent wireless communication infrastructures or information such as RSSI, RTT, AoA, etc. indicating adjacent strengths of wireless communication infrastructures and measurement points.
나아가, 여러 측정지점들에서 수집된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보나 측정지점거리들과 같은 정보도 저장할 수 있다.Furthermore, information such as wireless communication infrastructure measurement information or measurement point distances collected at various measurement points can be stored.
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 방법은 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치(도 1의 100 참조)가, 무선통신 인프라들 사이의 최단거리에 기반한 위치기반 서비스를 제공한다(S211).In addition, the method for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location according to an embodiment of the present invention is an apparatus for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location (refer to 100 in FIG. 1). A location-based service based on the shortest distance between infrastructures is provided (S211).
기존에는 무선통신 인프라 간의 상관관계에 따른 계층에 기반한 위치기반 서비스가 제공되었으나, 본 발명의 일 실시예에서는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리정보에 기반한 위치기반 서비스를 제공하여 보다 정확한 위치기반 서비스를 제공할 수 있다.In the past, a location-based service based on a layer according to a correlation between wireless communication infrastructures was provided, but in an embodiment of the present invention, a location-based service based on distance information between wireless communication infrastructures is provided to provide a more accurate location-based service. I can.
선택적 실시예에서, 상기 단계들(S201, S203, S205, S207, S209 및 S211)에 있어서, 인접한 무선통신 인프라들을 결정하는 단계(S203)와 측정지점거리들을 계산하는 단계(S205)는 병렬적으로 수행될 수 있다.In an optional embodiment, in the steps (S201, S203, S205, S207, S209, and S211), determining adjacent wireless communication infrastructures (S203) and calculating measurement point distances (S205) are performed in parallel. Can be done.
선택적 실시예에서, 상기 단계들(S201, S203, S205, S207, S209 및 S211)에 있어서, 위치기반 서비스를 제공하는 단계(S211)는 인접한 무선통신 인프라들의 정보와 인프라거리들을 저장하는 단계(S209)보다 먼저 수행될 수 있다.In an optional embodiment, in the steps (S201, S203, S205, S207, S209, and S211), the step of providing a location-based service (S211) is a step of storing information and infrastructure distances of adjacent wireless communication infrastructures (S209). ) Can be performed before.
선택적 실시예에서, 상기 단계들(S201, S203, S205, S207, S209 및 S211)에 있어서, 위치기반 서비스를 제공하는 단계(S211)는 인접한 무선통신 인프라들의 정보와 인프라거리들을 저장하는 단계(S209)와 병렬적으로 수행될 수 있다.In an optional embodiment, in the steps (S201, S203, S205, S207, S209, and S211), the step of providing a location-based service (S211) is a step of storing information and infrastructure distances of adjacent wireless communication infrastructures (S209). ) Can be performed in parallel.
도 3은 임의의 측정지점에서 임의의 사용자 단말기를 통해 측정한 복수 개의 무선통신 인프라들의 측정정보의 예시를 나타낸 도면이다.3 is a diagram showing an example of measurement information of a plurality of wireless communication infrastructures measured through a user terminal at an arbitrary measurement point.
도 3을 참조하면, 예를 들어 임의의 측정지점에서 임의의 사용자 단말기를 통해 4개의 Wi-Fi AP 리스트가 측정되었다고 가정하자. 이 때, 물리적으로 사용자 단말기를 중심으로 Wi-Fi AP 최대 전파도달거리 내에는 4개 Wi-Fi AP(CCC, AAA, BBB, EEE)들이 인접하며, 상기 4개의 Wi-Fi AP들은 인접한 무선통신 인프라로 결정된다.Referring to FIG. 3, it is assumed that, for example, a list of four Wi-Fi APs is measured through a user terminal at an arbitrary measurement point. At this time, physically, four Wi-Fi APs (CCC, AAA, BBB, EEE) are adjacent to each other within the maximum radio coverage distance of the Wi-Fi AP centered on the user terminal, and the four Wi-Fi APs are adjacent wireless communication. It is determined by the infrastructure.
도 3에는 Wi-Fi AP들과 그에 상응하는 수신전파세기(RSSI) 정보가 도시되어 있다. 수신전파세기(RSSI)가 큰 값을 가진다는 것은 사용자 단말기가 상응하는 무선통신 인프라에 가까운 거리에 있음을 의미한다.FIG. 3 shows Wi-Fi APs and RSSI information corresponding thereto. When the received radio wave strength (RSSI) has a large value, it means that the user terminal is close to the corresponding wireless communication infrastructure.
따라서, 도 3에 도시된 예시에서는, 4개의 Wi-Fi AP들이 CCC, AAA, BBB, EEE 순으로 사용자 단말기 또는 측정지점에 가까운 거리에 있다고 판단할 수 있다.Accordingly, in the example shown in FIG. 3, it may be determined that the four Wi-Fi APs are located close to the user terminal or the measurement point in the order of CCC, AAA, BBB, and EEE.
도 4는 여러 측정지점에서 수집한 무선통신 인프라들의 측정정보 및 일부 무선통신 인프라들의 위치의 예시를 나타낸 도면이다.4 is a diagram showing an example of measurement information of wireless communication infrastructures collected at various measurement points and locations of some wireless communication infrastructures.
도 4를 참조하면, 여러 무선통신 인프라 측정정보에는 각각에 상응하는 인접한 무선통신 인프라들에 대한 정보를 포함하고 있다. 예를 들면, 측정지점 1에서 수집된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보에 따르면, 측정지점 1은 Wi-Fi AP가 AAA, BBB, CCC, DDD, EEE 순으로 가깝게 배치되어 있으며, 측정지점 2에서 수집된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보에 따르면, 측정지점 2는 Wi-Fi AP가 BBB, CCC, AAA, DDD 순으로 가깝게 배치되어 있다.Referring to FIG. 4, the measurement information for various wireless communication infrastructures includes information on adjacent wireless communication infrastructures corresponding to each. For example, according to the measurement information of wireless communication infrastructure collected at
또한, 도 4를 참조하면, Wi-Fi AP BBB 및 CCC에서 임의의 측정지점까지 이르는 거리들인 (a)가 측정지점거리이며, Wi-Fi AP BBB와 CCC 사이의 거리인 (b)가 인프라거리이다.In addition, referring to FIG. 4, (a), which is the distances from the Wi-Fi AP BBB and CCC, to an arbitrary measurement point, is the measurement point distance, and (b), which is the distance between the Wi-Fi AP BBB and CCC, is the infrastructure distance. to be.
측정지점거리들은 각 측정지점에서 수집된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보에 포함된 수신전파세기(RSSI), RTT, AoA 등의 정보를 통하여 계산할 수 있으며, 인프라거리는 측정지점거리들에 포함된 거리오차들의 합을 최소화하는 값으로 추정하여 정할 수 있다.Measurement point distances can be calculated through information such as received radio wave strength (RSSI), RTT, and AoA included in the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information collected at each measurement point, and the infrastructure distance is the sum of distance errors included in the measurement point distances. Can be determined by estimating a value that minimizes.
도 5는 여러 측정지점에서 2개의 무선통신 인프라들로부터 수신한 전파의 수신전파세기(RSSI)를 활용하여 계산한 측정지점 거리들의 예시를 나타낸 도면이다.5 is a diagram showing an example of distances of measurement points calculated by using the received radio wave strength (RSSI) of radio waves received from two wireless communication infrastructures at various measurement points.
도 5를 참조하면, 각각의 측정지점들에서 AP m과 AP n에서 측정된 수신전파세기(RSSI)를 이용해 측정지점거리들(예:,)을 계산할 수 있으며, 각각의 측정지점거리들에는 상응하는 측정지점과 AP와의 실제 거리들(예:,) 과의 차이인 오차거리(예:,)들이 포함되어 있다.Referring to FIG. 5, measurement point distances (e.g.: , ) Can be calculated, and the actual distances between the corresponding measuring point and the AP (e.g.: , ) And the error distance (e.g.: , ) Are included.
그리고 AP m과 AP n 사이의 거리인 인프라거리()을 추정함에 있어서, 측정지점거리들을 이용하여 오차거리들의 합이 최소가 되도록 하는 인프라거리를 실제 인프라거리로 추정할 수 있다. 즉, 가 최소가 되는 인프라거리()를 찾을 수 있다.And the infrastructure distance, which is the distance between AP m and AP n ( In estimating ), the infrastructure distance that minimizes the sum of the error distances can be estimated as the actual infrastructure distance by using the measurement point distances. In other words, Infrastructure distance ( ) Can be found.
도 6은 건물 내부의 여러 무선통신 인프라들과 여러 측정지점들, 그리고 각각의 측정지점에 상응하는 인접한 무선통신 인프라들의 예시를 나타낸 도면이다.6 is a diagram showing examples of various wireless communication infrastructures and various measurement points inside a building, and adjacent wireless communication infrastructures corresponding to each measurement point.
도 6을 참조하면, 측정지점 1(사용자 참여 1)에서 수집한 무선통신 인프라 측정정보에 따르면, AP AAA, BBB, CCC가 인접 무선통신 인프라 집합을 구성하고; 측정지점 2(사용자 참여 2) 에서 수집한 무선통신 인프라 측정정보에 따르면, AP AAA, CCC, DDD, EEE가 인접 무선통신 인프라 집합을 구성하고; 측정지점 3(사용자 참여 3)에서 수집한 무선통신 인프라 측정정보에 따르면, AP BBB, FFF가 인접 무선통신 인프라 집합을 구성하고; 측정지점 4(사용자 참여 4)에서 수집한 무선통신 인프라 측정정보에 따르면, AP FFF, GGG가 인접 무선통신 인프라 집합을 구성하며; AP HHH에 대해서는 수집된 무선통신 인프라 측정정보가 없으므로, 인접 무선통신 인프라 집합을 구성하지 않는다.Referring to FIG. 6, according to the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information collected at measurement point 1 (user participation 1), AP AAA, BBB, and CCC constitute a set of adjacent wireless communication infrastructure; According to the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information collected at measurement point 2 (user participation 2), AP AAA, CCC, DDD, EEE constitute a set of adjacent wireless communication infrastructure; According to the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information collected at measurement point 3 (user participation 3), AP BBB and FFF constitute a set of adjacent wireless communication infrastructure; According to the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information collected at measurement point 4 (user participation 4), AP FFF and GGG constitute a set of adjacent wireless communication infrastructure; Since there is no wireless communication infrastructure measurement information collected for AP HHH, it does not constitute a set of adjacent wireless communication infrastructure.
동일한 인접 무선통신 인프라 집합 내에 있는 무선통신 인프라들은 서로 인접하다고 판단할 수 있으며, 기존의 위치기반 서비스들은 특정한 무선통신 인프라들 사이에서 몇 개의 인접 무선통신 인프라 집합을 거치는지와 같은 상관관계를 통한 계층수에 기반하였다.Wireless communication infrastructures within the same set of adjacent wireless communication infrastructures can be determined to be adjacent to each other, and existing location-based services are layered through correlation such as how many adjacent wireless communication infrastructure sets pass between specific wireless communication infrastructures. It was based on number.
도 7은 도 6에 도시된 예시에서, 무선통신 인프라간 상관관계에 따른 상관DB 및 무선통신 인프라간 거리정보에 따른 상관DB의 예시를 나타낸 도면이다.FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating an example of a correlation DB according to a correlation between wireless communication infrastructures and a correlation DB according to distance information between wireless communication infrastructures in the example shown in FIG. 6.
도 7의 좌측부와 도 6을 참조하면, 동일한 인접 무선통신 인프라 집합에 포함된 AP들은 서로 상관관계가 1로 볼 수 있다. 예를 들어, AP DDD와 AP CCC는 도 6에 도시된 측정지점 2(사용자 참여 2)에서 수집한 무선통신 인프라 측정정보에 의해 동일한 인접 무선통신 인프라 집합에 속하여서 상관관계 또는 계층이 1이 된다. 따라서, AP DDD와 AP BBB는 2개의 인접 무선통신 인프라 집합에 걸쳐있어, 상관관계 또는 계층이 2가 된다.Referring to the left part of FIG. 7 and FIG. 6, APs included in the same adjacent wireless communication infrastructure set may have a correlation of 1 to each other. For example, AP DDD and AP CCC belong to the same set of adjacent wireless communication infrastructures according to the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information collected at measurement point 2 (user participation 2) shown in FIG. . Therefore, the AP DDD and the AP BBB span two adjacent wireless communication infrastructure sets, and the correlation or layer becomes 2.
하지만, 도 7의 우측부를 참조하면, 각 무선통신 인프라들 사이를 계층 대신 인프라거리들을 미터(m) 단위로 표시하여, 여러 무선통신 인프라들 사이의 실제 가까운 정도를 더욱 정확히 묘사할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 계층에 따른 상관DB에서는, AP DDD에서 AP EEE에 이르는 경우나 AP DDD에서 AP CCC에 이르는 경우 모두 계층 1에 해당하여 동일한 인접도를 가지지만; 인프라거리에 따른 상관DB에서는, AP DDD에서 AP EEE에 이르는 경우는 거리가 10미터이며, AP DDD에서 AP CCC에 이르는 경우는 거리가 20미터가 되어 인접도가 2배의 차이를 가지게 된다.However, referring to the right part of FIG. 7, infrastructure distances between each of the wireless communication infrastructures are displayed in meters (m) instead of layers, so that the actual degree of closeness between the various wireless communication infrastructures can be more accurately described. For example, in the correlation DB according to the layer, all the cases from AP DDD to AP EEE or from AP DDD to AP CCC correspond to
따라서, 무선통신 인프라간 상관관계에 따른 상관DB를 이용한 경우에는 직접적으로 무선통신 인프라 간의 거리를 추정할 수 없으며, 무선통신 인프라간 거리정보에 따른 상관DB는 더욱 정확한 무선통신 인프라 분포 상황을 반영하며, 더 나은 위치기반 서비스를 제공할 수 있다.Therefore, if the correlation DB according to the correlation between wireless communication infrastructures is used, the distance between wireless communication infrastructures cannot be directly estimated, and the correlation DB according to the distance information between wireless communication infrastructures reflects more accurate wireless communication infrastructure distribution conditions. , It can provide better location-based services.
도 8은 도 7에 도시된 무선통신 인프라간 거리정보에 따른 상관DB의 예시에서, 위치기반 서비스를 이용하는 메시지 송신자와 메시지 수신자들의 위치관계의 일 예를 나타낸 도면이다.FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating an example of a location relationship between a message sender and message receivers using a location-based service in an example of a correlation DB according to distance information between wireless communication infrastructures shown in FIG. 7.
메시지 송신자는 위치기반 서비스를 이용하여 근처에 있는 사람들에게 쿠폰과 같은 콘텐츠를 제공하는 매장주인 등이 될 수 있으며, 메시지 수신자는 위치기반 서비스를 이용하여 근처에 있는 매장들의 할인쿠폰과 같은 콘텐츠를 제공받는 고객 등이 될 수 있다.The message sender can be a store owner who provides contents such as coupons to nearby people using location-based services, and the message receiver provides contents such as discount coupons of nearby stores using location-based services. It can be a receiving customer, etc.
도 8을 참조하면, 위치기반 서비스를 이용하는 메시지 송신자는 무선통신 인프라에 해당하는 AP GGG에 가장 가까이 위치하며, 메시지 수신자 a는 AP FFF에, 메시지 수신자 b는 AP DDD에 가장 가까이 위치한다.Referring to FIG. 8, a message sender using a location-based service is located closest to an AP GGG corresponding to a wireless communication infrastructure, a message receiver a is located closest to an AP FFF, and a message receiver b is located closest to an AP DDD.
따라서, 메시지 수신자 a는 메시지 송신자로부터 상관관계가 1에 해당하며 무선통신 인프라간 최단거리는 15미터에 해당한다. 그리고 메시지 수신자 b는 메시지 송신자로부터 상관관계 4에 해당하며, 무선통신 인프라간 최단거리는 75미터에 해당한다.Therefore, the message receiver a has a correlation of 1 from the message sender, and the shortest distance between wireless communication infrastructures is 15 meters. And the message receiver b corresponds to
만약 위치기반 서비스에서 메시지를 전송하는 범위를 상관관계에 따른 계층을 기준으로 하여 계층 1부터 계층 5로 나누게 되면, 메시지 수신자 a는 계층 1부터 계층 5까지 모두 수신이 가능하게 되며, 메시지 수신자 b는 계층 4부터 계층 5까지 수신 가능하다.If the range of message transmission in the location-based service is divided into
만약 위치기반 서비스에서 메시지를 전송하는 범위를 무선통신 인프라간 거리정보를 기준으로 하여 10미터, 30미터, 50미터, 70미터 및 100미터로 나누게 되면, 메시지 수신자 a는 30미터, 50미터, 70미터 및 100미터의 범위에서 수신 가능하며, 메시지 수신자 b는 100미터의 범위에서만 수신 가능하다.If the range of message transmission in the location-based service is divided into 10 meters, 30 meters, 50 meters, 70 meters and 100 meters based on the distance information between wireless communication infrastructure, the message recipient a is 30 meters, 50 meters, 70 meters. It can receive in the range of meters and 100 meters, and the message recipient b can only receive in the range of 100 meters.
메시지 수신자 b는 메시지 송신자로부터 인프라거리들의 합이 75미터가 되어 상대적으로 멀리 떨어져 있음에도 불구하고 상관관계가 4로 판단되어 상대적으로 가깝다고 판단될 수 있으며, 메시지 수신자 a는 메시지 송신자로부터 인프라거리가 15미터임에도 상관관계가 1로 판단되어 메시지 전송 범위에 따라 상대적으로 가깝다고 판단될 가능성이 있다.Message receiver b can be judged to be relatively close because the correlation is determined to be 4 even though the sum of the infrastructure distances from the message sender is 75 meters away from the message sender, and the message receiver a is 15 meters infrastructure distance from the message sender. Even though the correlation is determined to be 1, there is a possibility that the correlation is determined to be relatively close depending on the message transmission range.
메시지 수신자와 메시지 송신자 사이의 인프라거리들의 합을 기준으로 메시지 전송범위를 정하게 될 경우, 메시지 수신자와 송신자는 보다 정확하고 신뢰할만한 위치기반 서비스를 제공받을 수 있다. 하지만, 메시지 수신자와 메시지 송신자 사이의 상관관계를 기준으로 메시지 전송범위를 정하게 될 경우, 메시지 수신자와 송신자는 거리정보가 부정확하게 반영된 위치기반 서비스를 제공받게 된다.When the message transmission range is determined based on the sum of infrastructure distances between the message receiver and the message sender, the message receiver and the sender can be provided with more accurate and reliable location-based services. However, when the message transmission range is determined based on the correlation between the message receiver and the message sender, the message receiver and the sender are provided with a location-based service in which the distance information is incorrectly reflected.
도 9는 도 7에 도시된 무선통신 인프라간 거리정보에 따른 상관DB의 예시에서, 위치기반 서비스를 이용하는 메시지 송신자와 메시지 수신자들의 위치관계의 다른 일 예를 나타낸 도면이다.9 is a diagram illustrating another example of a location relationship between a message sender and message receivers using a location-based service in the example of a correlation DB according to distance information between wireless communication infrastructures shown in FIG. 7.
도 9를 참조하면, 위치기반 서비스를 이용하는 메시지 송신자는 무선통신 인프라에 해당하는 AP CCC에 가장 가까이 위치하며, 메시지 수신자 a는 AP FFF에, 메시지 수신자 b는 AP DDD에, 메시지 수신자 c는 AP GGG 가장 가까이 위치한다.9, a message sender using a location-based service is located closest to an AP CCC corresponding to a wireless communication infrastructure, a message receiver a to an AP FFF, a message receiver b to an AP DDD, and a message receiver c to an AP GGG. It is located closest to you.
따라서, 메시지 수신자 a는 메시지 송신자로부터 상관관계가 2에 해당하며 무선통신 인프라간 최단거리는 40미터에 해당한다. 그리고 메시지 수신자 b는 메시지 송신자로부터 상관관계 1에 해당하며, 무선통신 인프라간 최단거리는 20미터에 해당한다. 그리고 메시지 수신자 c는 메시지 송신자로부터 상관관계 3에 해당하며, 무선통신 인프라간 최단거리는 55미터에 해당한다.Therefore, the message receiver a has a correlation of 2 from the message sender, and the shortest distance between wireless communication infrastructures is 40 meters. And the message receiver b corresponds to
만약 위치기반 서비스에서 메시지를 전송하는 범위를 상관관계에 따른 계층을 기준으로 하여 계층 1부터 계층 5로 나누게 되면, 메시지 수신자 a는 계층 2부터 계층 5까지 수신이 가능하게 되며, 메시지 수신자 b는 계층 1부터 계층 5까지 모두 수신 가능하다. 또한, 메시지 수신자 c는 계층 3부터 계층 5까지 수신 가능하다.If the range of message transmission in the location-based service is divided into
만약 위치기반 서비스에서 메시지를 전송하는 범위를 무선통신 인프라간 거리정보를 기준으로 하여 10미터, 30미터, 50미터, 70미터 및 100미터로 나누게 되면, 메시지 수신자 a는 50미터, 70미터 및 100미터의 범위에서 수신 가능하며, 메시지 수신자 b는 30미터, 50미터, 70미터 및 100미터의 범위에서 수신 가능하다. 또한, 메시지 수신자 c는 70미터 및 100미터의 범위에서 수신 가능하다.If the range of message transmission in the location-based service is divided into 10 meters, 30 meters, 50 meters, 70 meters and 100 meters based on the distance information between wireless communication infrastructure, the message recipient a is 50 meters, 70 meters and 100 meters. It can receive in the range of meters, and the message recipient b can receive in the ranges of 30 meters, 50 meters, 70 meters and 100 meters. In addition, the message recipient c can receive in the range of 70 meters and 100 meters.
메시지 수신자 a는 메시지 송신자로부터 인프라거리들의 합이 40미터가 되어 상대적으로 멀리 떨어져 있음에도 불구하고 상관관계가 2로 판단되어 상대적으로 가깝다고 판단될 수 있으며, 메시지 수신자 b는 메시지 송신자로부터 인프라거리가 20미터임에도 상관관계가 1로 판단되어 메시지 전송 범위에 따라 상대적으로 가깝다고 판단될 가능성이 있다. 또한, 메시지 수신자 c는 메시지 송신자로부터 인프라거리들의 합이 55미터로 상대적으로 멀리 떨어져 있음에도 불구하고 상관관계가 3으로 판단되어 상대적으로 가깝다고 판단될 가능성이 있다.Message recipient a can be determined to be relatively close because the correlation is determined to be 2 even though the sum of the infrastructure distances from the message sender is 40 meters away, and the message recipient b has an infrastructure distance of 20 meters from the message sender. Even though the correlation is determined to be 1, there is a possibility that the correlation is determined to be relatively close depending on the message transmission range. In addition, although the sum of infrastructure distances from the message sender c is 55 meters away from the message sender, the correlation is determined to be 3, and thus it is likely to be determined to be relatively close.
도 10은 실제 무선통신 환경의 일 예에서, 각각의 무선통신 인프라들로부터 다른 무선통신 인프라들까지의 홉(Hop) 분포를, 상관관계들을 이용한 홉 분포와 인프라거리들을 이용한 홉 분포를 비교하여 나타낸 도면이다.FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating a hop distribution from each wireless communication infrastructure to other wireless communication infrastructures in an example of an actual wireless communication environment, by comparing a hop distribution using correlations and a hop distribution using infrastructure distances. It is a drawing.
상세히, 도 10은 한 건물의 4개 층에서 수신된 식별 가능한 각각의 무선통신 인프라(예: Wi-Fi AP)에서 타겟 무선통신 인프라(예: Wi-Fi AP)간 최단거리 추정시, 계산한 거리정보를 활용하지 않고 상관관계들을 이용한 계층 수(좌측) 및 거리정보를 활용한 계층 수(우측)를 비교한 것이다. x축은 최단거리 추정을 위하여 시작의 기준이 되는 무선통신 AP의 ID를 나타낸 것이며, y축은 각 타겟 무선통신 인프라들의 계층 수의 분포 비율을 나타낸 것이다.In detail, FIG. 10 is a calculated when estimating the shortest distance between target wireless communication infrastructures (eg, Wi-Fi APs) in each identifiable wireless communication infrastructure (eg, Wi-Fi AP) received from four floors of a building. This is a comparison of the number of layers using correlations (left) and the number of layers using distance information (right) without using distance information. The x-axis represents the ID of the wireless communication AP as a starting criterion for the shortest distance estimation, and the y-axis represents the distribution ratio of the number of layers of each target wireless communication infrastructure.
도 10을 참조하면, 한 건물의 4개 층 내에서 타겟 단말에 대한 위치기반 서비스를 제공한다고 가정할 때, 거리정보를 활용하지 않은 경우 대부분 3 계층 이내에서 타겟 단말에 대한 위치기반 서비스(예: 할인쿠폰 제공)를 제공할 수 있다. 즉, 위치기반 서비스를 위해 설정할 수 있는 기준을 상관관계에 기반하게 된다면, 계층을 1에서 3 사이 값으로만 설정해서 서비스를 제공할 수 밖에 없기 때문에, 매우 근사적이고 부정확한 위치기반 서비스를 제공하게 된다.Referring to FIG. 10, assuming that a location-based service for a target terminal is provided within four floors of a building, when distance information is not used, location-based services for a target terminal are mostly within three tiers (e.g.: Discount coupons) can be provided. In other words, if the criterion that can be set for location-based services is based on correlation, since the service must be provided by setting the layer to a value between 1 and 3, it is necessary to provide a very approximate and inaccurate location-based service. do.
반면에 거리정보를 활용하는 경우 계층 간 추정된 거리 정보가 반영되어 6 계층 이내에서 세분화된 위치기반 서비스(예: 할인쿠폰 제공)를 제공할 수 있다. 특히, 기존 위치기반 서비스에서 보편적으로 사용하는 거리 기준 설정(예: 50m)이 가능하기 때문에 보다 정확하게 Trigger하여 맞춤형 위치기반 서비스를 타겟 단말에 제공할 수 있다.On the other hand, when distance information is used, the estimated distance information between layers is reflected to provide detailed location-based services (eg, discount coupons) within 6 levels. In particular, since it is possible to set a distance standard (eg, 50m) that is commonly used in existing location-based services, it is possible to provide a customized location-based service to a target terminal by triggering more accurately.
특히, 거리정보를 활용하여 위치기반 서비스 범위를 결정할 수 있다는 점에서, 기존에 설계된 위치기반 서비스와 호환성이 크고, 설정기준이 직관적이고 명료한 장점이 있다.In particular, since it is possible to determine a range of location-based services using distance information, it is highly compatible with previously designed location-based services, and has an advantage of intuitive and clear setting criteria.
또한, 무선통신 인프라 측정정보가 누적될수록 이를 활용하여 추정된 무선통신 인프라간 거리정보는 보다 정확해 질 수 있다는 장점이 있으며, 만약 무선통신 인프라가 이전 설치되거나 제거되는 경우라도 지속적으로 수집된 최신 측정정보를 활용하여 이를 갱신할 수 있는 장점도 있다.In addition, as the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information is accumulated, the estimated distance information between wireless communication infrastructures can be more accurate. There is also the advantage of being able to update it using information.
무엇보다도 실내 환경에서 초기 수집 없이 사용자 단말이 제공하는 복수의 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 누적하여 이를 기반으로 무선통신 인프라간 상관DB 및 거리정보를 추정하면 해당 실내 환경에서 위치기반 서비스를 제공할 수 있다는 점이 본 발명의 큰 기여라 할 수 있다.Above all, it is possible to provide location-based services in the indoor environment by accumulating the measurement information of a plurality of wireless communication infrastructures provided by the user terminal without initial collection in an indoor environment and estimating the correlation DB and distance information between wireless communication infrastructures based on this. This can be said to be a great contribution of the present invention.
한편, 상술한 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 방법은 다양한 컴퓨터 수단을 통하여 수행될 수 있는 프로그램 명령 형태로 구현되어 컴퓨터로 판독 가능한 기록 매체에 기록될 수 있다. 이 때, 컴퓨터로 판독 가능한 기록매체는 프로그램 명령, 데이터 파일, 데이터 구조 등을 단독으로 또는 조합하여 포함할 수 있다. 한편, 기록매체에 기록되는 프로그램 명령은 본 발명을 위하여 특별히 설계되고 구성된 것들이거나 컴퓨터 소프트웨어 당업자에게 공지되어 사용 가능한 것일 수도 있다.Meanwhile, the above-described method of estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location may be implemented in the form of a program command that can be executed through various computer means and recorded in a computer-readable recording medium. In this case, the computer-readable recording medium may include a program command, a data file, a data structure, or the like alone or in combination. Meanwhile, the program instructions recorded on the recording medium may be specially designed and configured for the present invention, or may be known and usable to those skilled in computer software.
컴퓨터로 판독 가능한 기록매체에는 하드 디스크, 플로피 디스크 및 자기 테이프와 같은 자기 매체(Magnetic Media), CD-ROM, DVD와 같은 광기록 매체(Optical Media), 플롭티컬 디스크(Floptical Disk)와 같은 자기-광매체(Magneto-Optical Media), 및 롬(ROM), 램(RAM), 플래시 메모리 등과 같은 프로그램 명령을 저장하고 수행하도록 특별히 구성된 하드웨어 장치가 포함된다. 한편, 이러한 기록매체는 프로그램 명령, 데이터 구조 등을 지정하는 신호를 전송하는 반송파를 포함하는 광 또는 금속선, 도파관 등의 전송 매체일 수도 있다.Computer-readable recording media include magnetic media such as hard disks, floppy disks, and magnetic tapes, optical media such as CD-ROMs and DVDs, and magnetic media such as floppy disks. Magnetic-Optical Media, and hardware devices specially configured to store and execute program instructions such as ROM, RAM, flash memory, and the like. Meanwhile, such a recording medium may be a transmission medium such as optical or metal wires, waveguides, etc. including carrier waves for transmitting signals specifying program commands, data structures, and the like.
이상에서와 같이 본 발명에 따른 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치 및 그 방법은 상기한 바와 같이 설명된 실시예들의 구성과 방법이 한정되게 적용될 수 있는 것이 아니라, 상기 실시예들은 다양한 변형이 이루어질 수 있도록 각 실시예들의 전부 또는 일부가 선택적으로 조합되어 구성될 수도 있다.As described above, the apparatus and method for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location according to the present invention are not limited to the configuration and method of the embodiments described as described above, but the above embodiments. They may be configured by selectively combining all or part of each of the embodiments so that various modifications may be made.
110: 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치
110: 수신부120: 인접 인프라 결정부
130: 측정지점거리 계산부140: 인프라거리 추정부
150: 저장부160: 서비스 제공부110: Device for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location
110: receiving unit 120: neighboring infrastructure decision unit
130: measurement point distance calculation unit 140: infrastructure distance estimation unit
150: storage unit 160: service provider
Claims (10)
Translated fromKorean상기 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여 인접한 무선통신 인프라들을 결정하는 인접 인프라 결정부;
상기 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여, 각각의 상기 측정지점들로부터 인접한 무선통신 인프라들과의 거리들인 측정지점거리들을 계산하는 측정지점거리 계산부;
상기 측정지점거리들을 이용하여, 상기 인접한 무선통신 인프라들 사이의 거리들인 인프라거리들을 추정하는 인프라거리 추정부; 및
상기 인접한 무선통신 인프라들의 정보와 상기 인프라거리들을 저장하는 저장부를 포함하고,
상기 무선통신 인프라 측정정보는
설치 위치정보를 모르는 복수개의 무선통신 인프라들로부터 수신되고,
상기 인프라거리 추정부는
각각의 상기 측정지점거리들에 상응하는 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되도록 하여, 상기 복수개의 무선통신 인프라들 각각의 설치 위치정보 없이도 상기 인프라거리들을 추정하는 것을 특징으로 하는 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들 간의 거리를 추정하는 장치.A receiving unit for receiving measurement information of a wireless communication infrastructure measured at a plurality of measurement points;
An adjacent infrastructure determining unit for determining adjacent wireless communication infrastructures using the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information;
A measurement point distance calculation unit that calculates measurement point distances, which are distances from each of the measurement points to adjacent wireless communication infrastructures, using the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information;
An infrastructure distance estimating unit for estimating infrastructure distances, which are distances between adjacent wireless communication infrastructures, using the measurement point distances; And
Including a storage unit for storing the information of the adjacent wireless communication infrastructure and the infrastructure distances,
The wireless communication infrastructure measurement information
It is received from a plurality of wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location information,
The infrastructure distance estimation unit
A wireless communication infrastructure that does not know the installation location, characterized in that the sum of distance errors corresponding to the respective measurement point distances is minimized, and the infrastructure distances are estimated without the installation location information of each of the plurality of wireless communication infrastructures. A device that estimates the distance between them.
상기 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들간의 거리를 추정하는 장치는
상기 인프라거리 정보를 이용하여, 상기 인프라거리들을 이용한 위치 기반 서비스를 제공하는 서비스 제공부를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들간의 거리를 추정하는 장치.The method according to claim 1,
The device for estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location
The apparatus for estimating distances between wireless communication infrastructures of which the installation location is unknown, further comprising a service providing unit that provides a location-based service using the infrastructure distances by using the infrastructure distance information.
상기 인프라거리 추정부는
상기 인프라거리들이 상기 측정지점들과의 관계에서 삼각 부등식을 만족하며, 상기 거리오차들 각각이 실 환경에서 측정정보의 변화에 따라 발생할 수 있는 측정지점거리의 변화량 이하라는 조건하에, 상기 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되도록 하는 상기 인프라거리들을 추정하는 것을 특징으로 하는 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들간의 거리를 추정하는 장치.The method according to claim 1,
The infrastructure distance estimation unit
Under the condition that the infrastructure distances satisfy the triangular inequality in relation to the measurement points, and each of the distance errors is less than or equal to the amount of change in the measurement point distance that may occur according to the change of measurement information in the real environment, the distance errors are An apparatus for estimating distances between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location, characterized in that estimating the infrastructure distances such that the sum is minimized.
상기 측정지점거리 계산부는
수신전파세기를 이용한 자유공간 경로손실 모델을 통해 상기 측정지점거리들을 계산하는 것을 특징으로 하는 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들간의 거리를 추정하는 장치.The method according to claim 1,
The measurement point distance calculation unit
An apparatus for estimating distances between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location, characterized in that calculating the measurement point distances through a free space path loss model using received radio wave strength.
상기 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여 인접한 무선통신 인프라들을 결정하는 인접 인프라 결정단계;
상기 무선통신 인프라 측정정보를 이용하여, 각각의 상기 측정지점들로부터 인접한 무선통신 인프라들과의 거리들인 측정지점거리들을 계산하는 측정지점거리 계산단계;
상기 측정지점거리들을 이용하여, 상기 인접한 무선통신 인프라들 사이의 거리들인 인프라거리들을 추정하는 인프라거리 추정단계; 및
상기 인접한 무선통신 인프라들의 정보와 상기 인프라거리들을 저장하는 저장단계
를 포함하고,
상기 무선통신 인프라 측정정보는
설치 위치정보를 모르는 복수개의 무선통신 인프라들로부터 수신되고,
상기 인프라거리 추정단계는
각각의 상기 측정지점거리들에 상응하는 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되도록 하여, 상기 복수개의 무선통신 인프라들 각각의 설치 위치정보 없이도 상기 인프라거리들을 추정하는 것을 특징으로 하는 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들간의 거리를 추정하는 방법.A receiving step of receiving wireless communication infrastructure measurement information measured at a plurality of measurement points;
An adjacent infrastructure determining step of determining adjacent wireless communication infrastructures using the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information;
A measurement point distance calculation step of calculating measurement point distances, which are distances from each of the measurement points to adjacent wireless communication infrastructures, using the wireless communication infrastructure measurement information;
An infrastructure distance estimation step of estimating infrastructure distances, which are distances between adjacent wireless communication infrastructures, using the measurement point distances; And
Storage step of storing the information of the adjacent wireless communication infrastructure and the infrastructure distances
Including,
The wireless communication infrastructure measurement information
It is received from a plurality of wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location information,
The infrastructure distance estimation step
A wireless communication infrastructure that does not know the installation location, characterized in that the sum of distance errors corresponding to the respective measurement point distances is minimized, and the infrastructure distances are estimated without the installation location information of each of the plurality of wireless communication infrastructures. How to estimate the distance between fields.
상기 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들간의 거리를 추정하는 방법은
상기 인프라거리 정보를 이용하여, 상기 인프라거리들을 이용한 위치기반 서비스를 제공하는 서비스 제공단계를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들간의 거리를 추정하는 방법.The method of claim 6,
The method of estimating the distance between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location
And a service providing step of providing a location-based service using the infrastructure distances by using the infrastructure distance information.
상기 인프라거리 추정단계는
상기 인프라거리들이 상기 측정지점들과의 관계에서 삼각 부등식을 만족하며, 상기 거리오차들 각각이 실 환경에서 측정정보의 변화에 따라 발생할 수 있는 측정지점거리의 변화량 이하라는 조건하에, 상기 거리오차들의 합이 최소가 되도록 하는 상기 인프라거리들을 추정하는 것을 특징으로 하는 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들간의 거리를 추정하는 방법.The method of claim 6,
The infrastructure distance estimation step
Under the condition that the infrastructure distances satisfy the triangular inequality in relation to the measurement points, and each of the distance errors is less than or equal to the amount of change in the measurement point distance that may occur according to the change of measurement information in the real environment, the distance errors are A method of estimating distances between wireless communication infrastructures that do not know the installation location, characterized in that estimating the infrastructure distances such that the sum is minimized.
상기 측정지점거리 계산단계는
수신전파세기를 이용한 자유공간 경로손실 모델을 통해 상기 측정지점거리들을 계산하는 것을 특징으로 하는 설치 위치를 모르는 무선통신 인프라들간의 거리를 추정하는 방법.
The method of claim 6,
The measuring point distance calculation step
A method for estimating distances between wireless communication infrastructures of unknown installation locations, characterized in that the measurement point distances are calculated through a free space path loss model using received radio wave strength.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170031821AKR102225632B1 (en) | 2017-03-14 | 2017-03-14 | Apparatus for estimating distance between wireless communication infrastructures installed at unknown location and method for the same |
| KR1020210028326AKR102314946B1 (en) | 2017-03-14 | 2021-03-03 | Apparatus for estimating distance between wireless communication infrastructures installed at unknown location and method for the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170031821AKR102225632B1 (en) | 2017-03-14 | 2017-03-14 | Apparatus for estimating distance between wireless communication infrastructures installed at unknown location and method for the same |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020210028326ADivisionKR102314946B1 (en) | 2017-03-14 | 2021-03-03 | Apparatus for estimating distance between wireless communication infrastructures installed at unknown location and method for the same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20180104921A KR20180104921A (en) | 2018-09-27 |
| KR102225632B1true KR102225632B1 (en) | 2021-03-12 |
Family
ID=63719604
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170031821AActiveKR102225632B1 (en) | 2017-03-14 | 2017-03-14 | Apparatus for estimating distance between wireless communication infrastructures installed at unknown location and method for the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102225632B1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US12041512B2 (en) | 2021-09-27 | 2024-07-16 | Electronics And Telecommunications Research Institute | Method and apparatus for positioning using image and radio signals |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101446032B1 (en)* | 2010-05-06 | 2014-10-02 | 에스케이텔레콤 주식회사 | Method And Apparatus for Measuring Position by Using Wireless LAN Signal |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101352006B1 (en) | 2009-07-27 | 2014-01-15 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Device and method for collecting information related to infrastructure, and positioning method and system using the same |
| KR101174542B1 (en)* | 2009-09-22 | 2012-08-16 | 한양대학교 산학협력단 | Mobile terminal, System and Method for measuring location of mobile terminal |
| KR101608976B1 (en)* | 2013-10-07 | 2016-04-05 | 충남대학교산학협력단 | System and Method of Collaborative Localization Using Short Range Wireless Communication Network Without Location Infrastructure |
| KR20150053311A (en)* | 2013-11-07 | 2015-05-18 | 목포대학교산학협력단 | Effective Indoor Positioning Method in Wireless Sensor Network |
| KR101680151B1 (en)* | 2014-12-11 | 2016-11-28 | 유기석 | Apparatus for providing indoor location information using beacons and method thereof |
- 2017
- 2017-03-14KRKR1020170031821Apatent/KR102225632B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101446032B1 (en)* | 2010-05-06 | 2014-10-02 | 에스케이텔레콤 주식회사 | Method And Apparatus for Measuring Position by Using Wireless LAN Signal |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US12041512B2 (en) | 2021-09-27 | 2024-07-16 | Electronics And Telecommunications Research Institute | Method and apparatus for positioning using image and radio signals |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20180104921A (en) | 2018-09-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8825393B2 (en) | Method for providing location service and mobile terminal | |
| US8406785B2 (en) | Method and system for estimating range of mobile device to wireless installation | |
| EP2805176B1 (en) | Improved positioning system | |
| CA2666802C (en) | Location storage device, wireless terminal, location storage system, location registration method, location update method and program | |
| JP7108626B2 (en) | Method and system for locating a terminal in a wireless communication system | |
| KR20090129835A (en) | Apparatus and system for estimating the location of the terminal | |
| JP2009504529A (en) | Elevator car calling method using wireless node network and system therefor | |
| JP2007322237A (en) | Server device, mobile terminal, and positioning method selection method | |
| WO2016003743A1 (en) | Systems and methods for estimating whether a receiver is inside or outside a building | |
| Elazab et al. | Integrated cooperative localization for connected vehicles in urban canyons | |
| KR101709411B1 (en) | Method for positioning based on weighted triangulation and method for indoor positioning using the same | |
| KR101597437B1 (en) | Indoor localization system and method using ratio of relative received signal strength indicator of radio signal | |
| KR20150079080A (en) | Positioning method based on reliability and apparatus thereof | |
| KR20190107439A (en) | Apparatus for determining position of a terminal | |
| KR20170041055A (en) | Method for tracking user location | |
| US20160066156A1 (en) | Selection of Location-Determination Information | |
| KR20170084637A (en) | Apparatus for updating of positioning infrastructure database automatically and method using the same | |
| CN105657820B (en) | It is a kind of for positioning the method and device of indoor target UE | |
| Khalel | Position location techniques in wireless communication systems | |
| KR102225632B1 (en) | Apparatus for estimating distance between wireless communication infrastructures installed at unknown location and method for the same | |
| KR101901407B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for determining location | |
| KR102314946B1 (en) | Apparatus for estimating distance between wireless communication infrastructures installed at unknown location and method for the same | |
| KR20180031150A (en) | System for location determination using fingerprinting having function of constructing radio map and method for constructing radio map of the same | |
| Buchanan et al. | Analysis and migration of location-finding methods for GSM and 3G networks | |
| KR102766254B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for estimating location |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20170314 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| PA0201 | Request for examination | Patent event code:PA02012R01D Patent event date:20191023 Comment text:Request for Examination of Application Patent event code:PA02011R01I Patent event date:20170314 Comment text:Patent Application | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20200805 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20210224 | |
| A107 | Divisional application of patent | ||
| PA0107 | Divisional application | Comment text:Divisional Application of Patent Patent event date:20210303 Patent event code:PA01071R01D | |
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20210303 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20210304 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20231127 Start annual number:4 End annual number:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20250224 Start annual number:5 End annual number:5 |