KR102099699B1 - Device and method avoiding collision of autonomous surface vehicle considering uncertainty of trajectory prediction - Google Patents
Device and method avoiding collision of autonomous surface vehicle considering uncertainty of trajectory predictionDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102099699B1 KR102099699B1KR1020180125963AKR20180125963AKR102099699B1KR 102099699 B1KR102099699 B1KR 102099699B1KR 1020180125963 AKR1020180125963 AKR 1020180125963AKR 20180125963 AKR20180125963 AKR 20180125963AKR 102099699 B1KR102099699 B1KR 102099699B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- collision
- unmanned watercraft
- unmanned
- probability
- path
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription26
- 230000033001locomotionEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription55
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 230000002265preventionEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000claimsdescription29
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000claimsdescription15
- 238000009795derivationMethods0.000claimsdescription12
- 238000011156evaluationMethods0.000claimsdescription11
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription9
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000claimsdescription8
- 230000006698inductionEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000013459approachMethods0.000description7
- 230000008439repair processEffects0.000description7
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description5
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description3
- 238000009792diffusion processMethods0.000description2
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000description2
- 208000027418Wounds and injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 230000001133accelerationEffects0.000description1
- 230000033228biological regulationEffects0.000description1
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description1
- 238000007796conventional methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000006378damageEffects0.000description1
- 230000007123defenseEffects0.000description1
- 238000013461designMethods0.000description1
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000001939inductive effectEffects0.000description1
- 208000014674injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 238000009434installationMethods0.000description1
- 238000012423maintenanceMethods0.000description1
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000description1
- 230000008520organizationEffects0.000description1
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description1
- 230000035755proliferationEffects0.000description1
- 238000012827research and developmentMethods0.000description1
- 238000000926separation methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000004088simulationMethods0.000description1
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B63—SHIPS OR OTHER WATERBORNE VESSELS; RELATED EQUIPMENT
- B63B—SHIPS OR OTHER WATERBORNE VESSELS; EQUIPMENT FOR SHIPPING
- B63B43/00—Improving safety of vessels, e.g. damage control, not otherwise provided for
- B63B43/18—Improving safety of vessels, e.g. damage control, not otherwise provided for preventing collision or grounding; reducing collision damage
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B63—SHIPS OR OTHER WATERBORNE VESSELS; RELATED EQUIPMENT
- B63B—SHIPS OR OTHER WATERBORNE VESSELS; EQUIPMENT FOR SHIPPING
- B63B43/00—Improving safety of vessels, e.g. damage control, not otherwise provided for
- B63B43/18—Improving safety of vessels, e.g. damage control, not otherwise provided for preventing collision or grounding; reducing collision damage
- B63B43/20—Feelers
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B63—SHIPS OR OTHER WATERBORNE VESSELS; RELATED EQUIPMENT
- B63B—SHIPS OR OTHER WATERBORNE VESSELS; EQUIPMENT FOR SHIPPING
- B63B79/00—Monitoring properties or operating parameters of vessels in operation
- B63B79/10—Monitoring properties or operating parameters of vessels in operation using sensors, e.g. pressure sensors, strain gauges or accelerometers
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B63—SHIPS OR OTHER WATERBORNE VESSELS; RELATED EQUIPMENT
- B63B—SHIPS OR OTHER WATERBORNE VESSELS; EQUIPMENT FOR SHIPPING
- B63B79/00—Monitoring properties or operating parameters of vessels in operation
- B63B79/40—Monitoring properties or operating parameters of vessels in operation for controlling the operation of vessels, e.g. monitoring their speed, routing or maintenance schedules
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S5/00—Position-fixing by co-ordinating two or more direction or position line determinations; Position-fixing by co-ordinating two or more distance determinations
- G01S5/0009—Transmission of position information to remote stations
- G01S5/0072—Transmission between mobile stations, e.g. anti-collision systems
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G3/00—Traffic control systems for marine craft
- G08G3/02—Anti-collision systems
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B63—SHIPS OR OTHER WATERBORNE VESSELS; RELATED EQUIPMENT
- B63B—SHIPS OR OTHER WATERBORNE VESSELS; EQUIPMENT FOR SHIPPING
- B63B35/00—Vessels or similar floating structures specially adapted for specific purposes and not otherwise provided for
- B63B2035/006—Unmanned surface vessels, e.g. remotely controlled
- B63B2732/00—
- Y02T70/747—
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Ocean & Marine Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Control Of Position, Course, Altitude, Or Attitude Of Moving Bodies (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치 및 방법에 관한 것으로, 특히 확장칼만필터(EKF) 기반의 추적필터를 통해 무인수상선과 장애물의 운동 정보를 추정하고, 추정된 운동 정보의 불확실성 및 무인수상선의 안전 경계 영역을 고려하여 확률 흐름(probability flow) 개념을 이용한 근사-해석적 방법으로 충돌 확률을 평가하고, 무인수상선의 운항 경로 상에 예상되는 충돌 위험 영역을 정의하고, 국제해상충돌예방규칙 및 무인수상선의 운동역학적 특성을 고려한 회피 경로를 생성하며, 무인수상선이 생성된 회피 경로를 추종하게 하는, 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치 및 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for avoiding collision of an unmanned watercraft, in particular, estimating motion information of an unmanned watercraft and an obstacle through an tracking filter based on an extended Kalman filter (EKF), and the uncertainty of the estimated motion information and the safety of the unmanned watercraft The probability of collision is evaluated by an approximate-analytic method using the concept of probability flow in consideration of the boundary region, and the expected collision risk region is defined in the course of operation of the unmanned watercraft, and international maritime collision prevention rules and unmanned It relates to an apparatus and method for collision avoidance of an unmanned watercraft, which generates an avoidance route considering the kinematic properties of the line, and allows the unmanned watercraft to follow the generated avoidance route.
최근 국내·외에서 해양 관리를 위한 환경 감시 및 조사, 해양 자원 개발을 위한 탐사, 해양 구조물 설치 및 상태 관측, 해양 영토 방위 등의 목적으로 원격무인잠수정(ROVs:Remotely Operated Vehicles) 및 자율무인잠수정(AUVs:Autonomous Underwater Vehicles)을 비롯하여 무인수상선(ASVs:Autonomous Surface Vehicles)과 같은 다양한 형태의 해양 무인시스템이 개발되고 있다. 그 중에서 무인수상선은 무인잠수정에 비해서 통신, 항법, 탐색 범위, 속도와 운용 시간, 탑재 중량 측면에서 보다 더 효율적으로 장시간 연속적인 작업을 요하는 임무를 수행하기에 활용도가 매우 높다. 이와 같은 이유로 기존 유인 선박을 이용한 해양 임무를 대체하기 위해서도 무인수상선의 활용 범위가 점차 확대되고 있으며, 현재까지는 대부분 원격조종에 의해 제한된 영역에서 활용되고 있다. 무인수상선의 활용 범위를 보다 더 확장하기 위해서는 해상에서 자율적으로 임무를 수행할 수 있는 자율 운항 기술이 함께 개발되어야 하며, 기본적으로 운용 환경을 고려한 시스템 설계 및 제작 기술, 급변하는 주변 환경에 대응하기 위한 상황 인식 기술, 항법 및 제어 기술에 대한 연구개발이 필요하다. 특히, 유인 선박이 운항하는 해상 혹은 내수면에서 무인수상선을 동시에 운용하다 보면 충돌과 같은 예기치 못한 사고가 발생하여 인명 피해를 초래할 수도 있다. 따라서 무인수상선의 운항 경로 상에 잠재된 충돌 위험을 사전에 인지하고 자율적으로 회피 경로를 생성하여 충돌 위험을 낮추며 안전하게 충돌을 피하기 위한 기술 개발이 요구된다.Recently, remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and autonomous submersible vehicles (AUVs) are used for the purpose of monitoring and surveying the environment for marine management at home and abroad, exploration for marine resource development, installation and status observation of marine structures, and defense of marine territory. Various types of marine unmanned systems such as: Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (ASVs) and Autonomous Surface Vehicles (ASVs) have been developed. Among them, the unmanned watercraft is very useful for performing missions that require continuous operation for a long time more efficiently than the unmanned submersible in terms of communication, navigation, search range, speed and operating time, and payload weight. For this reason, the scope of use of the unmanned watercraft is gradually expanding to replace the marine mission using existing manned vessels, and until now, it is mostly used in a limited area by remote control. In order to further expand the scope of use of the unmanned watercraft, autonomous navigation technology that can autonomously perform missions in the sea must be developed, and system design and manufacturing technology that considers the operating environment is basically designed to respond to the rapidly changing environment. Research and development on situational awareness technology, navigation and control technology is needed. In particular, if an unmanned watercraft is operated at sea or inland water operated by a manned vessel at the same time, an unexpected accident such as a collision may occur and cause personal injury. Therefore, there is a need to develop a technology to recognize potential dangers of collision on an unmanned watercraft's navigation path in advance and autonomously create an evasion path to reduce collision risks and safely avoid collisions.
한국 특허 공개 2017-0058719호에는 무인 선박의 경로 추종 및 장애물과의 충돌 회피 제어방법이 개시되어 있다. 이 충돌 회피 제어방법은 선박의 움직일 수 있는 공간정보를 탐색하고, 탐색한 공간에 대한 정보를 고려하여 충돌을 회피할 수 있는 최적의 충돌회피 경로를 제공해줄 수 있도록 한 무인 선박의 경로 추종 및 장애물과의 충돌 회피 제어방법을 제공하는 것을 특징으로 한다.Korean Patent Publication No. 2017-0058719 discloses a method for controlling an unmanned ship following a path and avoiding collision with an obstacle. This collision avoidance control method seeks the ship's movable space information and considers the information about the searched space, so that it can provide the optimal collision avoidance route to avoid the collision and obstruct the route of the unmanned ship. It is characterized by providing a collision avoidance control method with.
그러나 이와 같은 종래의 기술은 항법 및 탐지 센서들을 이용하여 접근하는 해상 장애물의 운동 정보를 추정함에 있어서 센서 및 추적필터의 오차와 같은 요소들로 인한 운동 정보의 불확실성을 고려하지 않았다. 따라서 무인수상선 및 장애물에 대해 추정한 운동 정보에 포함된 항법 및 탐지 센서와 추적필터의 불확실성을 고려하여 무인수상선의 운항 경로를 예측하고, 잠재된 충돌 위험을 정량적으로 평가하는 새로운 방법이 필요하게 되었다.However, such a conventional technique does not take into account the uncertainty of motion information due to factors such as errors of the sensor and the tracking filter in estimating motion information of a sea obstacle approaching using navigation and detection sensors. Therefore, a new method for predicting the route of operation of an unmanned watercraft and quantitatively evaluating a potential collision risk is needed considering the uncertainty of navigation and detection sensors and tracking filters included in the motion information estimated for unmanned watercraft and obstacles. .
따라서 본 발명은 상기와 같은 점에 착안하여 이루어진 것으로서, 본 발명의 목적은 운항 경로 상에 잠재된 충돌 위험을 사전에 인지하고 이를 효과적으로 회피할 수 있게 하여 무인수상선의 충돌 위험을 현저히 낮출 수 있는, 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치 및 방법을 제공하는 데에 있다.Therefore, the present invention has been made in view of the above points, and the object of the present invention is to reduce the risk of collision of an unmanned watercraft by significantly recognizing potential dangers of collision on an operational route in advance and effectively avoiding them. It is to provide an apparatus and method for avoiding collision of an unmanned watercraft.
상기의 목적을 달성하기 위해 본 발명의 실시형태에 의한 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치 및 방법은 무인수상선에 탑재되어 무인수상선의 운동 정보를 계측하는 항법 센서; 상기 무인수상선에 탑재되어 접근하는 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 계측하는 탐지 센서; 상기 항법 센서 및 탐지 센서로부터 무인수상선의 운동 정보와 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 입력받아 이들 정보를 바탕으로 이동 장애물의 운동 정보를 추정하도록 구성된 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터; 상기 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터로부터 추정된 운동 정보를 기초로 설정된 시간 동안 상기 무인수상선과 장애물의 운항 경로를 예측하고, 상기 항법 센서 및 탐지 센서의 계측 오차로부터 야기된 운동 정보의 불확실성과 무인수상선의 안전 경계 영역을 고려하여 확률 흐름 개념을 이용한 근사-해석적 방법으로 충돌 확률을 평가하도록 구성된 충돌 확률 평가부; 예측된 상기 운항 경로 상에서 충돌 확률이 설정된 값을 초과하면 충돌 위험 영역을 운항 경로 상에 설정하고, 국제해상충돌예방규칙과 상기 무인수상선의 운동역학적 특성을 고려하여 충돌 회피 경로를 생성하고, 해당 충돌 회피 경로에서 회피 경유점을 추출하도록 구성된 충돌 회피 경로 생성부; 및 상기 충돌 회피 경로 생성부에 의해 추출된 회피 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 상기 무인수상선이 추종하도록 구성된 경로 추종 및 제어부를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In order to achieve the above object, a collision avoidance apparatus and method for an unmanned watercraft according to an embodiment of the present invention include a navigation sensor mounted on an unmanned watercraft to measure motion information of the unmanned watercraft; A detection sensor mounted on the unmanned watercraft and measuring relative information with a moving obstacle approaching; An extended Kalman filter-based tracking filter configured to receive motion information of an unmanned watercraft and relative information of a moving obstacle from the navigation sensor and detection sensor and estimate motion information of the moving obstacle based on the information; Prediction of flight routes of the unmanned watercraft and obstacles for a set time based on the motion information estimated from the tracking filter based on the extended Kalman filter, and uncertainty and uncertainty of motion information caused by measurement errors of the navigation sensor and the detection sensor A collision probability evaluation unit configured to evaluate collision probability by an approximate-analytic method using a probability flow concept in consideration of a line's safety boundary region; When the probability of collision on the predicted navigation route exceeds a set value, a collision risk zone is set on the navigation route, and a collision avoidance route is generated in consideration of the International Maritime Collision Prevention Rules and the kinematic characteristics of the unmanned watercraft. A collision avoidance path generation unit configured to extract an evasion waypoint from the avoidance path; And a path tracking and control unit configured to allow the unmanned watercraft to follow a straight path between avoidance points extracted by the collision avoiding path generating unit.
상기 실시형태에 의한 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치에 있어서, 상기 운동 정보의 불확실성은 상기 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터에 의해 계산되는 오차 공분산에 의해 표현되며, 상기 오차 공분산은 [수학식 6]에 의해 규정될 수 있다.In the collision avoidance apparatus of the unmanned watercraft according to the above embodiment, the uncertainty of the motion information is expressed by an error covariance calculated by the tracking filter based on the extended Kalman filter, and the error covariance is expressed by [Equation 6]. Can be specified.
[수학식 6][Equation 6]
[여기서,는 오차 공분산 행렬이고,는의 예측값이며,는의 편미분을 사용하여 구해진 행렬이며,는 시스템 노이즈임] [here, Is the error covariance matrix, The Is the predicted value of The Is a matrix obtained using partial derivative of, Is system noise]
상기 실시형태에 의한 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치에 있어서, 상기 충돌 확률은 [수학식 7]에 의해 규정될 수 있다.In the collision avoidance apparatus of the unmanned watercraft according to the above embodiment, the collision probability can be defined by [Equation 7].
[수학식 7][Equation 7]
[여기서,는 충돌 확률을 나타내며,는 결합된 안전 경계 영역 내에 유입되거나 유출되는 불확실성의 시간에 따른 변화량을 의미하며, c는 결합된 안전 경계 영역의 경계선이며, t0 ~ tf는 무인수상선과 장애물의 운항 경로를 예측하는 시간임] [here, Denotes the probability of collision, Is the change over time of uncertainty that flows into or out of the combined safety boundary area, c is the boundary line of the combined safety boundary area, and t0 to tf is the time to predict the flight path of the unmanned watercraft and obstacles. ]
상기 실시형태에 의한 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치에 있어서, 상기 무인수상선이 회피 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 추종하기 위해서 시선각 유도법칙 및 수선경로 유도법칙을 적용할 수 있다.In the collision avoidance apparatus of the unmanned watercraft according to the above-described embodiment, the line of sight derivation law and the waterway path derivation law can be applied to the unmanned watercraft to follow a straight line path between the evasion points.
상기 목적을 달성하기 위해 본 발명의 다른 실시형태에 의한 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 방법은 항법 센서에 의해 무인수상선의 운동 정보를 계측하는 단계; 탐지 센서에 의해 접근하는 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 계측하는 단계; 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터가 상기 항법 센서 및 탐지 센서로부터 무인수상선의 운동 정보와 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 입력받아 이들 정보를 바탕으로 이동 장애물의 운동 정보를 추정하는 단계; 충돌 확률 평가부가 상기 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터로부터 추정된 운동 정보를 기초로 설정된 시간 동안 상기 무인수상선과 이동 장애물의 운항 경로를 예측하고, 상기 항법 센서 및 탐지 센서의 계측 오차로부터 야기된 운동 정보의 불확실성과 무인수상선의 안전 경계 영역을 고려하여 확률 흐름 개념을 이용한 근사-해석적 방법으로 충돌 확률을 평가하는 단계; 충돌 회피 경로 생성부가 예측된 상기 운항 경로 상에서 충돌 확률이 설정된 값을 초과하면 충돌 위험 영역을 운항 경로 상에 설정하고, 국제해상충돌예방규칙과 상기 무인수상선의 운동역학적 특성을 고려하여 충돌 회피 경로를 생성하고, 해당 충돌 회피 경로에서 회피 경유점을 추출하는 단계; 및 경로 추종 및 제어부가 상기 충돌 회피 경로 생성부에 의해 추출된 회피 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 상기 무인수상선이 추종하도록 하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In order to achieve the above object, a collision avoidance method of an unmanned watercraft according to another embodiment of the present invention includes measuring motion information of an unmanned watercraft by a navigation sensor; Measuring relative information with a moving obstacle approached by a detection sensor; A tracking filter based on an extended Kalman filter receiving motion information of an unmanned watercraft and relative information of a moving obstacle from the navigation sensor and the detection sensor and estimating motion information of the moving obstacle based on the information; The collision probability evaluation unit predicts a flight path of the unmanned watercraft and a moving obstacle for a set time based on the motion information estimated from the tracking filter based on the extended Kalman filter, and motion information caused by measurement errors of the navigation sensor and the detection sensor Evaluating the probability of collision by an approximate-analytic method using the probability flow concept considering the uncertainty of and the safety boundary region of the unmanned watercraft; When the collision avoidance path generation unit exceeds the set collision probability on the predicted flight path, a collision risk region is set on the flight path, and the collision avoidance path is considered in consideration of international maritime collision prevention rules and the kinematic characteristics of the unmanned watercraft. Generating and extracting an evasion point from the collision avoidance path; And a step of allowing the unmanned watercraft to follow a straight path between the avoidance points extracted by the collision avoidance path generation unit and the path tracking and control unit.
본 발명의 실시형태에 의한 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치 및 방법에 의하면, 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터가 항법 센서 및 탐지 센서로부터 무인수상선의 운동 정보와 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 입력받아 이들 정보를 바탕으로 이동 장애물의 운동 정보를 추정하며; 충돌 확률 평가부가 상기 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터로부터 추정된 운동 정보를 기초로 설정된 시간 동안 상기 무인수상선과 이동 장애물의 운항 경로를 예측하고, 상기 항법 센서 및 탐지 센서의 계측 오차로부터 야기된 운동 정보의 불확실성과 무인수상선의 안전 경계 영역을 고려하여 확률 흐름 개념을 이용한 근사-해석적 방법으로 충돌 확률을 평가하며; 충돌 회피 경로 생성부가 예측된 상기 운항 경로 상에서 충돌 확률이 설정된 값을 초과하면 충돌 위험 영역을 운항 경로 상에 설정하고, 국제해상충돌예방규칙과 상기 무인수상선의 운동역학적 특성을 고려하여 충돌 회피 경로를 생성하고, 해당 충돌 회피 경로에서 회피 경유점을 추출하며; 경로 추종 및 제어부가 상기 충돌 회피 경로 생성부에 의해 추출된 회피 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 상기 무인수상선이 추종하도록 구성됨으로써; 운항 경로 상에 잠재된 충돌 위험을 사전에 인지하고 이를 효과적으로 회피할 수 있게 하여 무인수상선의 충돌 위험을 현저히 낮출 수 있다는 뛰어난 효과가 있다.According to an apparatus and method for collision avoidance of an unmanned watercraft according to an embodiment of the present invention, an extended Kalman filter-based tracking filter receives motion information of an unmanned watercraft and relative information between moving obstacles from a navigation sensor and a detection sensor, and receives the information. Estimate movement information of the moving obstacle based on the background; The collision probability evaluation unit predicts a flight path of the unmanned watercraft and a moving obstacle for a set time based on the motion information estimated from the tracking filter based on the extended Kalman filter, and motion information caused by measurement errors of the navigation sensor and the detection sensor The probability of collision is evaluated by an approximate-analytic method using the probability flow concept, taking into account the uncertainty of and the safety boundary region of the unmanned watercraft; When the collision avoidance path generation unit exceeds the set collision probability on the predicted flight path, a collision risk region is set on the flight path, and the collision avoidance path is considered in consideration of international maritime collision prevention rules and the kinematic characteristics of the unmanned watercraft. Generating, and extracting an evasion point from the collision avoidance path; A path follow-up and a control unit is configured such that the unmanned waterline tracks a straight path between avoidance points extracted by the collision avoidance path generation unit; It has the outstanding effect that it can significantly reduce the risk of collision of an unmanned watercraft by making it possible to recognize in advance the potential collision risk on the flight route and effectively avoid it.
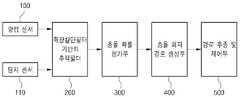
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 의한, 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치에 대한 블록 구성도이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 실시예에 의한, 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치를 이용한 충돌 회피 방법을 설명하기 위한 플로우챠트이다.
도 3은 예측 시간에 따라 변하는 무인수상선과 이동 장애물의 경로 불확실성을 나타내는 도면이다.
도 4는 무인수상선의 예측 운항 경로 상의 충돌 위험 영역을 나타낸 도면으로서, (a)는 운항 경로 예측 시간에서의 순간 충돌 위험 영역을 나타내며, (b)는 운항 경로 예측 시간마다의 연속적으로 누적된 충돌 위험 영역을 나타낸다.
도 5는 안전 경계 영역을 고려한 충돌 위험 영역을 근사화한 도면으로서, (a)는 C-스페이스(space)를 나타내며, (b)는 근사화된 충돌 위험 영역을 나타낸다.
도 6은 Dubins 곡선을 이용한 회피 경로를 나타낸 도면이다.
도 7은 시선 각 및 수선 경로 유도 법칙을 적용한 경로 추종을 나타낸 도면이다.1 is a block diagram of an apparatus for avoiding collision of an unmanned watercraft according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a flowchart for explaining a collision avoidance method using a collision avoidance apparatus of an unmanned watercraft according to an embodiment of the present invention.
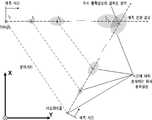
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing path uncertainty of an unmanned watercraft and a moving obstacle that changes according to a prediction time.
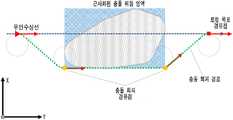
4 is a view showing a collision risk region on the predicted navigation path of an unmanned watercraft, (a) represents an instantaneous collision danger region in the flight path prediction time, and (b) continuously accumulated collisions for each flight path prediction time. It represents the danger zone.
FIG. 5 is an approximation of a collision danger area considering a safety boundary area, (a) represents a C-space, and (b) represents an approximate collision danger area.
6 is a view showing the avoidance path using the Dubins curve.
7 is a view showing a path follower to which the gaze angle and the repair path induction law are applied.
이하, 본 발명의 실시예를 도면을 참조하여 상세히 설명하기로 한다.Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 의한, 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치에 대한 블록 구성도이다.1 is a block diagram of an apparatus for avoiding collision of an unmanned watercraft according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명을 설명하기에 앞서 무인수상선과 이동 장애물은 2차원 평면상에서 초기에 주어진 경로를 따라 일정한 속도와 방향으로 운항한다고 가정한다.Before explaining the present invention, it is assumed that the unmanned watercraft and moving obstacles operate at a constant speed and direction along a initially given path on a two-dimensional plane.
본 발명의 실시예에 의한 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치는, 도 1에 도시된 바와 같이, 항법 센서(100), 탐지 센서(110), 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터(200), 충돌 확률 평가부(300), 충돌 회피 경로 생성부(400), 및 경로 추종 및 제어부(500)를 포함한다.An apparatus for avoiding collision of an unmanned watercraft according to an embodiment of the present invention, as shown in FIG. 1, a
항법 센서(100)는 무인수상선에 탑재되어 무인수상선의 운동 정보를 계측하는 역할을 하는 GPS 및 IMU와 같은 관성 항법 센서이다.The
탐지 센서(110)는 무인수상선에 탑재되어 접근하는 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 계측하는 역할을 하는 레이더, 라이다, 카메라, 선박식별장치(AIS) 등과 같은 탐지 센서이다.The
확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터(200)는 항법 센서(100) 및 탐지 센서(110)로부터 무인수상선의 운동 정보와 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 입력받아 이들 정보를 바탕으로 이동 장애물의 운동 정보(위치, 속도, 방위 등을 포함함)를 추정하는 역할을 한다.The
확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터(200)에 있어서, 상태 변수(x)는 다음의 [수학식 1]과 같다.In the
[수학식 1][Equation 1]
[여기서,는 무인수상선의 위치, 방위 및 속도에 대한 상태벡터이고,는 이동 장애물의 위치, 방위 및 속도에 대한 상태벡터이며,는 백터의 전치 행렬를 나타내며,는 무인수상선의 X축 좌표값이며,는 무인수상선의 Y축 좌표값이며,는 무인수상선의 선수각을 의미하며,는 무인수상선의 속도임. 그리고는 이동 장애물의 X축 좌표값이며,는 이동 장애물의 Y축 좌표값이며,는 이동 장애물의 선수각이며,는 이동 장애물의 속도임][here, Is the state vector for the position, azimuth and speed of the unmanned watercraft, Is a state vector for the position, orientation and speed of a moving obstacle, Denotes the vector's transpose matrix, Is the X axis coordinate value of the unmanned watercraft, Is the Y axis coordinate value of the unmanned watercraft, Means the bow angle of the unmanned watercraft, Is the speed of the unmanned watercraft. And Is the X-axis coordinate value of the moving obstacle, Is the coordinate value of the Y axis of the moving obstacle, Is the forward angle of the moving obstacle, Is the speed of the moving obstacle]
확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터(200)에 있어서, 시스템 모델은 다음의 [수학식 2]와 같이 표현될 수 있다.In the
[수학식 2][Equation 2]
또한, 위의 [수학식 2]는 다음의 [수학식 3]과 같이 무인수상선과 이동 장애물의 3자유도 기구학 모델로 표현될 수 있다.In addition, the above [Equation 2] can be expressed as a three-degree-of-freedom kinematic model of the unmanned watercraft and moving obstacles as in [Equation 3] below.
[수학식 3][Equation 3]
[여기서,는 시스템에 작용하는 환경 외란에 의한 프로세스 잡음(process noise) 벡터로서, 평균값이 0이고, 분산이 Q인 정규 분포를 따른다고 가정하였음][here, Is a process noise vector due to environmental disturbances acting on the system, which is assumed to follow a normal distribution with an average value of 0 and a variance of Q.]
확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터(200)에 있어서, 계측 모델은 상대 거리 정보와 방위 정보를 동시에 계측한다고 가정하였기에 다음 [수학식 5]와 같이 표현된다.In the
[수학식 5][Equation 5]
[여기서,는 계측치의 행렬이고,는 무인수상선의 항법 센서로부터 계측된 정보이며,는 무인수상선에 탑재된 센서들을 이용하여 계측한 이동 장애물과의 상대적인 정보를 나타내며,는 무인수상선과 이동 장애물간의 상대 방위각을 의미하고,는 고정 좌표계에서 무인수상선과 장애물의 위치 간의 각도를 나타내며,는 상대 거리를 의미하며,는 평균값 0이고, 분산이 R인 정규 분포를 따르는 계측 센서의 측정 잡음(measurement noise) 벡터임][here, Is the matrix of measurements, Is the information measured from the navigation sensor of the UAV, Indicates relative information with moving obstacles measured using sensors mounted on an unmanned watercraft, Is the relative azimuth between the unmanned watercraft and the moving obstacle, Denotes the angle between the unmanned watercraft and the position of the obstacle in the fixed coordinate system, Means relative distance, Is a measurement noise vector of a measurement sensor with a normal distribution with mean value 0 and variance R]
확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터(200)는 항법 센서(100) 및 탐지 센서(110)로부터 입력된 무인수상선의 운동 정보와 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보, 시스템 모델, 및 계측 모델을 통해 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터(200)의 예측(predict) 및 보정(update) 단계를 거쳐 이동 장애물의 운동 정보를 추정한다. 추정된 운동 정보에는 외란에 의한 항법 센서 및 계측 센서의 오차뿐만 아니라 시스템 모델과 계측 모델에서의 오차가 반영되어 있으며, 추정된 이동 장애물의 운동 정보의 불확실성은 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적필터(200)에 의해 계산되는 오차 공분산(error covariance)에 의해 표현되며, 오차 공분산은 다음의 [수학식 6]에 의해 규정된다.The
[수학식 6][Equation 6]
[여기서,는 오차 공분산 행렬이고,는의 예측값이며,는의 편미분을 사용하여 구해진 행렬이며,는 시스템 노이즈임][here, Is the error covariance matrix, The Is the predicted value of The Is a matrix obtained using partial derivative of, Is system noise]
충돌 확률 평가부(300)는 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터(200)로부터 추정된 운동 정보를 기초로 설정된 시간 동안 무인수상선과 이동 장애물의 운항 경로를 예측하고, 항법 센서(100) 및 탐지 센서(110)의 계측 오차로부터 야기된 운동 정보의 불확실성과 무인수상선의 안전 경계 영역을 고려하여 확률 흐름 개념을 이용한 근사-해석적 방법으로 충돌 확률을 평가하는 역할을 한다.The collision
운동 정보의 불확실성은 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터(200)로부터의 오차 공분산으로부터 계산되어 확률밀도함수(probability density function)로 표현되며, 그 분포는 다변수 정규분포(multivariate Gaussian distribution)의 가정 하에 2차원 평면상에서 신뢰구간을 의미하는 확률 타원(probability ellipse)으로 정의하였다. 결과적으로 운항 경로를 예측하는 동안 확률 타원은, 도 3에 도시된 바와 같이, 초기 예측 시점보다 선수방향과 선수의 수선방향으로 확산(diffusion)하며, 이동(drift)하는 특성을 보인다. 그리고 무인수상선과 이동 장애물이 서로 근접함에 따라 서로의 확률 타원이 겹쳐진 영역이 발생하게 되는데, 이 영역을 근사-해석적 방법으로 계산하여 정량적인 충돌 위험을 제시하였다.The uncertainty in the motion information is calculated from the error covariance from the tracking
무인수상선과 이동 장애물의 크기 정보를 고려하기 위해 각 위치를 중심으로 안전 경계 영역(safe separation zone)을 각각 설정하였다. 이동 장애물의 경우에는 레이더, 라이다, 카메라, 선박식별장치(AIS)와 같은 탐지 센서를 통해 계측된 정보를 기반으로 크기를 추정하여 설정 가능하다고 가정하였다. 충돌 위험을 효율적으로 계산하기 위해 무인수상선의 확률 타원은 좌표 변환(coordinate transformation)을 통해 이동 장애물의 확률 타원과 결합하여 장애물의 중심으로 그 위치를 옮겼다. 그와 동시에, 무인수상선의 안전 경계 영역 또한 좌표 변환에 의해 이동 장애물의 안전 경계 영역과 결합되어 무인수상선의 위치를 중심으로 변환하였다. 그리고 이 안전 경계 영역으로 결합된 확률 타원의 양이 유입되거나 유출되는 정도를 누적함으로써 [수학식 7]과 같이 충돌 확률(collision probability)을 규정하였다.In order to take into account the size information of the unmanned watercraft and moving obstacles, a safe separation zone was set for each location. In the case of moving obstacles, it was assumed that it can be set by estimating the size based on information measured through detection sensors such as radar, lidar, camera, and ship identification device (AIS). To calculate the collision risk efficiently, the probability ellipse of the unmanned watercraft is moved to the center of the obstacle by combining it with the probability ellipse of the moving obstacle through coordinate transformation. At the same time, the safety boundary area of the unmanned watercraft was also combined with the safety boundary area of the moving obstacle by coordinate transformation to convert it to the center of the unmanned watercraft. Also, by accumulating the degree of the inflow or outflow of the amount of the probability ellipse bound to the safety boundary region, collision probability was defined as in [Equation 7].
[수학식 7][Equation 7]
[여기서,는 충돌 확률을 나타내며,는 결합된 안전 경계 영역 내에 유입되거나 유출되는 불확실성의 시간에 따른 변화량을 의미하며, c는 결합된 안전 경계 영역의 경계선이며, t0 ~ tf는 무인 수상선과 장애물의 운항 경로를 예측하는 시간임][here, Denotes the probability of collision, Is the change over time of uncertainty that flows into or out of the combined safety boundary area, c is the boundary line of the combined safety boundary area, and t0 to tf is the time to predict the flight path of the unmanned watercraft and obstacles. ]
안전 경계 영역 내에서는 불확실성의 양이 자체적으로 새로 생성되거나 소멸되지 않으므로, 항상 무인수상선의 위치를 중심으로 결합된 안전 경계 영역의 경계선(boundary)을 통해 유입되거나 유출된다고 가정하였다. 따라서 안전 경계 영역의 경계선에서 확률 타원의 확산 및 이동에 의해 확률 흐름이 변하므로 경계선의 단위 호 길이에서 확률 타원의 확산과 이동에 의한 양을 계측하였다. 그리고 다음 [수학식 8]과 같이 경계선의 전 영역으로 확장하여 tk 시점에서의 총합을 계산하였다.Since the amount of uncertainty within the safety boundary area does not newly generate or disappear on its own, it is assumed that it always flows in or out through the boundary of the safety boundary area centered on the position of the unmanned watercraft. Therefore, since the probability flow changes due to the diffusion and movement of the probability ellipse at the boundary of the safety boundary area, the amount of the proliferation and movement of the probability ellipse at the unit arc length of the boundary was measured. Then, as shown in [Equation 8], it was extended to the entire area of the boundary line, and the total at tk was calculated.
[수학식 8][Equation 8]
[여기서, C는 결합된 안전 경계 영역의 경계선이고, ds는 그 경계선의 미소 단위인 호 요소를 나타내며, n은 안전 경계 영역의 경계선 바깥 방향으로 향하는 법선벡터로서 이 벡터 연산에 의해 계산된 음수는 유입되는 확률 흐름을 의미하며, 양수는 유출되는 확률 흐름을 나타내며, D는 확산 상수(diffusion coefficient) 행렬로서 경로를 예측하는 동안 결합된 확률 타원의 크기 변화율에 의해 결정되고,는 예측 시간에 따른 이동 장애물의 위치를 중심으로 결합된 확률 타원을 의미하며 2차원 상에서의 다변수 정규분포로 표현됨][Wherein, C is the boundary line of the combined safety boundary area, ds denotes the arc element that is a small unit of the boundary line, and n is a normal vector directed outward of the boundary line of the safety boundary area, and the negative number calculated by this vector operation is Means the inflow probability flow, positive number represents the outflow probability flow, D is the diffusion coefficient matrix, which is determined by the rate of change of the magnitude of the combined probability ellipse while predicting the path, Is a probability ellipse combined around the position of a moving obstacle according to the prediction time, expressed as a multivariate normal distribution in 2D]
충돌 회피 경로 생성부(400)는 충돌 확률 평가부(300)에 의해 예측된 운항 경로 상에서 충돌 확률이 설정된 값을 초과하면 충돌 위험 영역으로 정의하고, 국제해상충돌예방규칙과 무인수상선의 운동역학적 특성을 고려하여 충돌 회피 경로를 생성하고, 해당 충돌 회피 경로에서 회피 경유점을 추출하는 역할을 한다.The collision avoidance
충돌 확률이 설정된 값을 초과한다는 것은 결합된 안전 경계 영역과 확률 타원이 특정 시점에서부터 겹쳐지는 영역이 상당 부분 존재한다는 의미와 동일하다. 따라서 운항 경로를 예측하는 동안 연속적으로 겹쳐진 영역이 발생할 수 있으며, 겹쳐진 영역들을 앞으로의 충돌 위험 가능성이 내재된 영역으로 간주하고, 이 영역들을 순간 충돌 위험 영역으로 정의하였다. 도 4의 (a)와 같이 2차원 평면상에서 무인수상선과 이동 장애물의 운항 경로 예측 시점마다의 순간 충돌 위험 영역을 각각 표현하였으며, 이를 연속적으로 누적하여 도 4의 (b)와 같이 충돌 위험 영역을 표현하였다.If the collision probability exceeds the set value, it is the same as the meaning that the combined safety boundary area and the area where the probability ellipse overlaps from a specific point in time exist. Therefore, while predicting the flight route, overlapping areas may occur continuously, and the overlapping areas are regarded as areas with potential danger of future collisions, and these areas are defined as momentary collision risk areas. As shown in Fig. 4 (a), the danger zones of instantaneous collisions are predicted for each time of the flight route prediction time of the unmanned watercraft and moving obstacles on the two-dimensional plane. Expressed.
무인수상선의 안전한 자율 운항을 위해서는 국제해상충돌예방규칙에 의거한 침로 변경을 통해 예측 운항 경로 상에 설정된 충돌 위험 영역을 회피해야 한다. 이 규정에 의하면, 두 선박 간의 충돌 상황이 발생할 수 있는 상황을 자선의 선수방향을 기준으로 전방(head-on)에서 접근 상황, 좌/우현(crossing)에서의 접근 상황, 추월(overtaking) 상황과 같이 크게 세 가지로 분류하였다. 전방 접근의 경우에는 조우하는 선박 모두 피항 의무선으로 각 선박의 우현방향으로 침로를 변경해야 하며, 추월의 경우에는 추월을 시도하는 선박이 피항 의무선으로 앞의 선박 좌현 혹은 우현으로 회피하며 운항해야 한다. 그리고 좌/우현 접근 상황에서는 두 선박 중 좌측에 위치한 선박이 피항 의무선으로 이 선박을 기준으로 우측에 있는 선박(침로 유지선)의 선미 쪽으로 선회하여 충돌을 피해야만 한다. 본 발명에서는 전방 접근 및 추월 상황을 비롯하여 좌/우현에서의 접근 상황 중 무인수상선이 피항 의무를 지닌 이동 장애물의 우현 접근 상황을 각조우 상황으로 설정하였으며, 이러한 상황들에서 회피 시에 안전 경계 영역 및 선회반경을 고려한 경로를 계획하였다.For the safe and autonomous operation of an unmanned watercraft, the collision danger zone set on the predicted flight route should be avoided by changing the course according to the International Maritime Collision Prevention Rules. According to this regulation, the situation in which a collision situation between two ships may occur is approached from the head-on, the approaching situation from the left / right side, and the overtaking situation based on the bow direction of the ship. They were divided into three categories. In the case of forward approach, all encountering vessels must change the course in the starboard direction of each ship as the obligatory obligatory ship, and in the case of overtaking, the ship attempting to overtake must be evacuated to the port side or starboard side of the preceding vessel as the evacuated obligatory ship. do. And in the left / right approach situation, the ship located on the left side of the two ships must be avoided by turning to the stern of the ship on the right side (route maintenance line) based on this ship as the evacuation duty ship. In the present invention, the approach situation of the starboard approach of a moving obstacle in which the unmanned watercraft is obliged to evacuate from the approach situation in the left / right side, as well as the forward approach and overtaking situation, is set to each encounter situation. A route considering the turning radius was planned.
무인수상선과 이동 장애물의 안전 경계 영역을 고려하여 회피경로를 계획하기 위해 앞서 설정된 충돌 위험 영역 내의 각 위치를 중심으로 결합된 안전 경계 영역의 외곽선을 포함한 영역을 C-스페이스(Configuration space) 영역으로 변환하여 도 5의 (a)와 같이 표현하였다. 그리고 Graham Scan 알고리듬을 적용하여 최외각 경계점들을 추출하고, 계산상의 효율을 높이고자 이 점들을 모두 포괄하는 최소사각영역으로 확장하여 도 5의 (b)와 같이 충돌 위험 영역을 근사화하였다.In order to plan the evasion route by considering the safety boundary area of the unmanned watercraft and moving obstacles, the area including the outline of the safety boundary area combined around each position in the previously set collision danger area is converted into a C-space (Configuration space) area. It was expressed as shown in Figure 5 (a). Then, the outermost boundary points were extracted by applying the Graham Scan algorithm, and the collision risk area was approximated as shown in FIG.
무인수상선이 충돌 위험을 회피하기 위해서 근사화된 충돌 위험 영역의 각 꼭지점들을 회피 경유점의 후보군으로 정하였다. 그리고 무인수상선의 선수방향을 기준하여 우현으로 침로를 변경하기 위해 무인수상선의 현 위치에서 선수방향 벡터를 기준으로 각 후보군과의 외적(cross product)을 취한 결과의 부호가 양수인 회피 경유점들을 선정하였다. 등속으로 운항하는 무인수상선의 선회반경과 선정된 경유점에서의 선수방향을 고려한 회피 경로를 생성하기 위해 Dubins 곡선 기법을 적용하였다. 일반적으로 등속 운항하는 무인수상선의 최소 선회반경은 실해역 시험을 통해 선회반경을 정확하게 계측해야하지만, 국제해사기구(IMO : International Maritime Organization) 산하의 Maritime Security Committee에서는 보편적으로 선박 길이의 5배를 최소 선회반경으로 규정하고 있으므로, 본 발명에서는 무인수상선의 선회반경을 선체 길이의 5배로 설정하였다. 도 6과 같이, 무인수상선의 기존 경유점, 회피 경유점, 선회반경 그리고 경유점에서의 선수방향을 고려한 Dubins 곡선 기반의 회피 경로를 생성하였으며, 그 경로를 추종하기 위해 일정한 간격만큼 떨어진 경유점들을 새로 추출하였다.In order to avoid the danger of the collision with the unmanned watercraft, each vertex of the approximate collision danger region was selected as a candidate group for the avoidance transit point. Then, in order to change the course to the starboard based on the direction of the bow of the unmanned watercraft, evasion breakpoints with the sign of the result of taking cross products with each candidate group based on the bow vector at the current position of the unmanned watercraft were selected. . The Dubins curve technique is applied to create an evasive route considering the turning radius of an unmanned watercraft operating at constant speed and the direction of the athlete at the selected waypoint. In general, the minimum turning radius of an unmanned watercraft operated at constant speed must be accurately measured through the actual sea area test, but the Maritime Security Committee under the International Maritime Organization (IMO) generally has a minimum of 5 times the ship's length. Since it is defined as the turning radius, in the present invention, the turning radius of the unmanned watercraft is set to 5 times the length of the hull. As shown in FIG. 6, a Dubins curve-based evasion route was created in consideration of the existing transit point, evasion transit point, turning radius, and direction of transit at the unmanned watercraft, and transit points spaced apart at regular intervals to follow the route. Extracted fresh.
경로 추종 및 제어부(500)는 충돌 회피 경로 생성부(400)에 의해 추출된 회피 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 무인수상선이 추종하게 하는 역할을 한다.The path tracking and
무인수상선이 회피 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 추종하기 위해서 시선각 유도법칙 및 수선경로 유도법칙을 적용하였으며, 각각의 유도법칙에 대한 개념이 도 7에 도시되어 있다.In order for the unmanned watercraft to follow a straight-line path between avoidance points, a gaze angle derivation law and a repair path derivation law are applied, and the concept of each derivation law is illustrated in FIG. 7.
시선각 유도법칙은 현재 무인수상선의 위치와 선수각 정보를 기준으로 목표 경유점간의 방위각을 이용하여 방위각 오차 정보를 최소화하기 위한 방법이며, 다음 [수학식 9]를 통해 방위각 오차 정보를 계산하였다.The gaze angle derivation law is a method for minimizing azimuth error information using the azimuth angle between a target transit point based on the current unmanned watercraft position and bow angle information, and azimuth error information was calculated by the following [Equation 9].
[수학식 9][Equation 9]
[여기서,와는 목표 경유점 및 현재 무인수상선의 위치를 2차원 좌표로 표현한 것이며,는 무인수상선의 선수각을 의미하며,는 방위각 오차 정보를 의미함][here, Wow Is the two-dimensional coordinates of the target waypoint and the position of the current unmanned watercraft, Means the bow angle of the unmanned watercraft, Means azimuth error information]
한편, 수선경로 유도법칙은 이전 경유점과 목표 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 따라 운용해야 하는 환경에서 경로로부터 수선방향으로 떨어진 거리 오차를 최소화하는데 주로 적용되고 있으며, 이 오차는 다음 [수학식 10]과 같이 계산된다.On the other hand, the law of inducing the repair path is mainly applied to minimize the distance error in the direction of the repair from the path in the environment in which a straight line path between the previous stop point and the target stop point should be operated, and this error is expressed by the following [Equation 10]. It is calculated together.
[수학식 10][Equation 10]
[여기서,는 이전 경유점의 좌표를 의미하며,는 수선거리 오차를 나타냄][here, Means the coordinates of the previous waypoint, Indicates repair distance error]
무인수상선은 일정한 속도로 운항하며, 선미의 방향타 제어를 통해 침로를 변경하면서 경유점을 추종한다고 가정할 때, 무인수상선의 운동방정식은 수평면에서 3자유도로 근사화되어 Nomoto 1차 모델인 다음 [수학식 11]과 같이 나타낼 수 있다.Assuming that the unmanned watercraft operate at a constant speed and follow the waypoint while changing the course through the stern rudder control, the motion equation of the unmanned watercraft is approximated by 3 degrees of freedom in the horizontal plane, which is the first model of Nomoto and then [Math 11].
[수학식 11][Equation 11]
[여기서, T 및 K는 무인수상선의 선수각속도에 대한 시정수와 선회 모멘트 관련 계수를 각각 나타내고, 및은 무인수상선의 선수각속도 및 선수각가속도를 나타내며,는 침로 변경을 위한 방향타 각도의 제어입력을 나타냄][Here, T and K represent the time constant and the turning moment-related coefficient for the angular velocity of the unmanned watercraft, respectively, And Denotes the angular velocity and the angular acceleration of the unmanned watercraft, Indicates control input of rudder angle to change course]
위에서 정의한 시선각 오차 및 수선경로 오차를 최소화하기 위한 제어입력을 도출하기 위해 다음 [수학식 12]와 같이 PD 제어기를 설계하여 적용할 수 있다.To derive a control input for minimizing the viewing angle error and repair path error defined above, a PD controller can be designed and applied as shown in [Equation 12].
[수학식 12][Equation 12]
[여기서, 및은 시선각 유도법칙에 대한 비례 이득값 및 미분 이득값을 나타내고, 및는 수선경로 유도법칙에 대한 비례 이득값 및 미분 이득값을 나타내며 극점배치기법을 통해 일차적으로 설정하고 시뮬레이션을 통해 조정하며 최종적으로 설정한 값이며,는 이전 경유점에서 목표 경유점까지의 도달 거리 대비 현재 무인수상선의 위치에서 목표 경유점까지의 도달 거리의 비를 나타내며 1보다 클 경우에는 1로 설정하였음][here, And Denotes a proportional gain value and a differential gain value for the viewing angle derivation law, And Denotes the proportional gain value and the differential gain value for the repair path derivation law, and is the value that is first set through the pole placement method, adjusted through simulation, and finally set, Denotes the ratio of the distance from the previous point to the target waypoint to the target waypoint from the location of the current unmanned watercraft and set to 1 if greater than 1]
이와 같은 파라미터를 통해 현재 무인수상선의 위치에서 목표 경유점까지의 거리가 멀수록 시선각 유도법칙에 보다 많은 가중치를 부여하고, 가까워질수록 수선경로 유도법칙에 가중치를 부여하도록 제어기를 설계하였다.Through these parameters, the controller is designed to give more weight to the gaze-angle derivation law as the distance from the current unmanned watercraft's position to the target transit point increases, and closer to the water-route derivation law.
이하, 상기한 바와 같이 구성된 본 발명의 실시예에 의한 무인 수상선의 충돌 회피 장치를 이용한 충돌 회피 방법을 설명하기로 한다.Hereinafter, a collision avoidance method using a collision avoidance apparatus of an unmanned watercraft according to an embodiment of the present invention configured as described above will be described.
도 2는 본 발명의 실시예에 의한, 무인 수상선의 충돌 회피 장치를 이용한 충돌 회피 방법을 설명하기 위한 플로우챠트로서, 여기서 S는 스텝(step)을 나타낸다.2 is a flowchart for explaining a collision avoidance method using a collision avoidance apparatus of an unmanned watercraft according to an embodiment of the present invention, where S represents a step.
먼저, 항법 센서(100)에 의해 무인 수상선의 운동 정보를 계측하고(S10), 탐지 센서(110)에 의해 접근하는 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보(상대 거리 또는 방위 정보)를 계측한다(S20).First, motion information of an unmanned watercraft is measured by the navigation sensor 100 (S10), and relative information (relative distance or azimuth information) with a moving obstacle approached by the
이어서, 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터(200)가 항법 센서(100) 및 탐지 센서(110)로부터 무인 수상선의 운동 정보와 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 입력받아 이들 정보를 바탕으로 이동 장애물의 운동 정보를 추정한다(S30).Subsequently, the extended Kalman filter-based
이후, 충돌 확률 평가부(300)가 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터(200)로부터 추정된 운동 정보를 기초로 설정된 시간 동안 무인수상선과 장애물의 운항 경로를 예측하고, 항법 센서(100) 및 탐지 센서(110)의 계측 오차로부터 야기된 운동 정보의 불확실성과 무인수상선의 안전 경계 영역을 고려하여 확률 흐름 개념을 이용한 근사-해석적 방법으로 충돌 확률을 평가한다(S40).Subsequently, the collision
이어서, 충돌 회피 경로 생성부(400)가 스텝(S40)에서 예측된 운항 경로 상에서 충돌 확률이 설정된 값을 초과하면 충돌 위험 영역으로 정의하고, 국제해상 충돌예방규칙과 무인 수상선의 운동역학적 특성을 고려하여 충돌 회피 경로를 생성하고, 해당 충돌 회피 경로에서 회피 경유점을 추출한다(S50).Subsequently, if the collision avoidance
이어서, 경로 추종 및 제어부(500)가 스텝(S50)에서 충돌 회피 경로 생성부(400)에 의해 추출된 회피 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 무인 수상선이 추종하도록 한다(S60).Subsequently, the path tracking and
본 발명의 실시예에 의한 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치 및 방법에 의하면, 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터가 항법 센서 및 탐지 센서로부터 무인수상선의 운동 정보와 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 입력받아 이들 정보를 바탕으로 이동 장애물의 운동 정보를 추정하며; 충돌 확률 평가부가 상기 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터로부터 추정된 운동 정보를 기초로 설정된 시간 동안 상기 무인수상선과 장애물의 운항 경로를 예측하고, 상기 항법 센서 및 탐지 센서의 계측 오차로부터 야기된 운동 정보의 불확실성과 무인수상선의 안전 경계 영역을 고려하여 확률 흐름 개념을 이용한 근사-해석적 방법으로 충돌 확률을 평가하며; 충돌 회피 경로 생성부가 예측된 상기 운항 경로 상에서 충돌 확률이 설정된 값을 초과하면 충돌 위험 영역을 운항 경로 상에 설정하고, 국제해상충돌예방규칙과 상기 무인수상선의 운동역학적 특성을 고려하여 충돌 회피 경로를 생성하고, 해당 충돌 회피 경로에서 회피 경유점을 추출하며; 경로 추종 및 제어부가 상기 충돌 회피 경로 생성부에 의해 추출된 회피 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 상기 무인수상선이 추종하도록 구성됨으로써, 운항 경로 상에 잠재된 충돌 위험을 사전에 인지하고 이를 효과적으로 회피할 수 있게 하여 무인수상선의 충돌 위험을 현저히 낮출 수 있다.According to an apparatus and method for collision avoidance of an unmanned watercraft according to an embodiment of the present invention, an extended Kalman filter-based tracking filter receives motion information of an unmanned watercraft and relative information between moving obstacles from navigation sensors and detection sensors Estimate movement information of the moving obstacle based on the background; The collision probability evaluation unit predicts the flight paths of the unmanned watercraft and obstacles for a predetermined time based on the motion information estimated from the tracking filter based on the extended Kalman filter, and of the motion information caused by measurement errors of the navigation sensor and the detection sensor. The probability of collision is evaluated by an approximate-analytic method using the probability flow concept, taking into account the uncertainty and the safety boundary region of the unmanned watercraft; When the collision avoidance path generation unit exceeds the set collision probability on the predicted flight path, a collision risk region is set on the flight path, and the collision avoidance path is considered in consideration of international maritime collision prevention rules and the kinematic characteristics of the unmanned watercraft. Generating, and extracting an evasion point from the collision avoidance path; The route following and the control unit is configured such that the unmanned watercraft follow the straight line route between the avoidance points extracted by the collision avoidance route generation unit, so that potential collision risks on the navigation route can be recognized in advance and effectively avoided. By doing so, the risk of collision of an unmanned watercraft can be significantly reduced.
도면과 명세서에는 최적의 실시예가 개시되었으며, 특정한 용어들이 사용되었으나 이는 단지 본 발명의 실시형태를 설명하기 위한 목적으로 사용된 것이지 의미를 한정하거나 특허청구범위에 기재된 본 발명의 범위를 제한하기 위하여 사용된 것은 아니다. 그러므로 본 기술 분야의 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 이로부터 다양한 변형 및 균등한 타 실시예가 가능하다는 점을 이해할 수 있을 것이다. 따라서 본 발명의 진정한 기술적 보호범위는 첨부된 특허청구범위의 기술적 사상에 의해 정해져야 할 것이다.In the drawings and the specification, an optimal embodiment has been disclosed, and specific terms have been used, but this is only for the purpose of explaining an embodiment of the present invention, and is used to limit the meaning or to limit the scope of the present invention described in the claims. It is not done. Therefore, those skilled in the art will appreciate that various modifications and other equivalent embodiments are possible. Therefore, the true technical protection scope of the present invention should be determined by the technical spirit of the appended claims.
100: 항법 센서
110: 탐지 센서
200: 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터
300: 충돌 확률 평가부
400: 충돌 회피 경로 생성부
500: 경로 추종 및 제어부100: navigation sensor
110: detection sensor
200: Extended Kalman Filter based tracking filter
300: collision probability evaluation unit
400: collision avoidance path generation unit
500: path tracking and control
Claims (8)
Translated fromKorean상기 무인수상선에 탑재되어 접근하는 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 계측하는 탐지 센서;
상기 항법 센서 및 탐지 센서로부터 무인수상선의 운동 정보와 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 입력받아 이들 정보를 바탕으로 이동 장애물의 운동 정보를 추정하도록 구성된 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터;
상기 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터로부터 추정된 운동 정보를 기초로 설정된 시간 동안 상기 무인수상선과 장애물의 운항 경로를 예측하고, 상기 항법 센서 및 탐지 센서의 계측 오차로부터 야기된 운동 정보의 불확실성과 무인수상선의 안전 경계 영역을 고려하여 확률 흐름 개념을 이용한 근사-해석적 방법으로 충돌 확률을 평가하도록 구성된 충돌 확률 평가부;
예측된 상기 운항 경로 상에서 충돌 확률이 설정된 값을 초과하면 충돌 위험 영역을 운항 경로 상에 설정하고, 국제해상충돌예방규칙과 상기 무인수상선의 운동역학적 특성을 고려하여 충돌 회피 경로를 생성하고, 해당 충돌 회피 경로에서 회피 경유점을 추출하도록 구성된 충돌 회피 경로 생성부; 및
상기 충돌 회피 경로 생성부에 의해 추출된 회피 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 상기 무인수상선이 추종하도록 구성된 경로 추종 및 제어부;를 포함하며,
상기 운동 정보의 불확실성은 상기 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터에 의해 계산되는 오차 공분산에 의해 표현되며,
상기 오차 공분산은 [수학식 6]에 의해 규정되는, 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치.
[수학식 6]
[여기서,는 오차 공분산 행렬이고,는의 예측값이며,는의 편미분을 사용하여 구해진 행렬이며,는 시스템 노이즈임]A navigation sensor mounted on the unmanned watercraft to measure motion information of the unmanned watercraft;
A detection sensor mounted on the unmanned watercraft and measuring relative information with a moving obstacle approaching;
An extended Kalman filter-based tracking filter configured to receive motion information of an unmanned watercraft and relative information of a moving obstacle from the navigation sensor and detection sensor and estimate motion information of the moving obstacle based on the information;
Prediction of flight routes of the unmanned watercraft and obstacles for a set time based on the motion information estimated from the tracking filter based on the extended Kalman filter, and uncertainty and uncertainty of motion information caused by measurement errors of the navigation sensor and the detection sensor A collision probability evaluation unit configured to evaluate collision probability by an approximate-analytic method using a probability flow concept in consideration of a line's safety boundary region;
When the probability of collision on the predicted navigation route exceeds a set value, a collision risk zone is set on the navigation route, and a collision avoidance route is generated in consideration of the International Maritime Collision Prevention Rules and the kinematic characteristics of the unmanned watercraft. A collision avoidance path generation unit configured to extract an evasion waypoint from the avoidance path; And
It includes; a path tracking and a control unit configured to follow the unmanned water line along a straight path between the avoidance points extracted by the collision avoidance path generating unit;
The uncertainty of the motion information is expressed by the error covariance calculated by the tracking filter based on the extended Kalman filter,
The error covariance is defined by [Equation 6], collision avoidance device of the unmanned watercraft.
[Equation 6]
[here, Is the error covariance matrix, The Is the predicted value of The Is a matrix obtained using partial derivative of, Is system noise]
상기 충돌 확률은 [수학식 7]에 의해 규정되는, 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치.
[수학식 7]
[여기서,는 충돌 확률을 나타내며,는 결합된 안전 경계 영역내에 유입되거나 유출되는 불확실성의 시간에 따른 변화량을 의미하며, c는 결합된 안전 경계 영역의 경계선이며, t0 ~ tf는 무인수상선과 장애물의 운항 경로를 예측하는 시간임]According to claim 1,
The collision probability is defined by [Equation 7], collision avoidance device of the unmanned watercraft.
[Equation 7]
[here, Denotes the probability of collision, Is the change over time of uncertainty that flows into or out of the combined safety boundary area, c is the boundary line of the combined safety boundary area, and t0 ~ tf is the time to predict the route of operation of the unmanned watercraft and obstacles. ]
상기 무인수상선이 회피 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 추종하기 위해서 시선각 유도법칙 및 수선경로 유도법칙을 적용하는, 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 장치.According to claim 1,
Collision avoidance apparatus of an unmanned watercraft, wherein the unmanned watercraft applies the line of sight derivation law and the waterway path derivation law in order to follow a straight path between avoidance points.
항법 센서에 의해 무인수상선의 운동 정보를 계측하는 단계;
탐지 센서에 의해 접근하는 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 계측하는 단계;
확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터가 상기 항법 센서 및 탐지 센서로부터 무인수상선의 운동 정보와 이동 장애물과의 상대 정보를 입력받아 이들 정보를 바탕으로 이동 장애물의 운동 정보를 추정하는 단계;
충돌 확률 평가부가 상기 확장칼만필터 기반의 추적 필터로부터 추정된 운동 정보를 기초로 설정된 시간 동안 상기 무인수상선과 장애물의 운항 경로를 예측하고, 상기 항법 센서 및 탐지 센서의 계측 오차로부터 야기된 운동 정보의 불확실성과 무인수상선의 안전 경계 영역을 고려하여 확률 흐름 개념을 이용한 근사-해석적 방법으로 충돌 확률을 평가하는 단계;
충돌 회피 경로 생성부가 예측된 상기 운항 경로 상에서 충돌 확률이 설정된 값을 초과하면 충돌 위험 영역을 운항 경로 상에 설정하고, 국제해상충돌예방규칙과 상기 무인수상선의 운동역학적 특성을 고려하여 충돌 회피 경로를 생성하고, 해당 충돌 회피 경로에서 회피 경유점을 추출하는 단계; 및
경로 추종 및 제어부가 상기 충돌 회피 경로 생성부에 의해 추출된 회피 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 상기 무인수상선이 추종하도록 하는 단계를 포함하는, 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 방법.As a collision avoidance method using the collision avoidance device of the unmanned watercraft described in claim 1:
Measuring motion information of the unmanned watercraft by a navigation sensor;
Measuring relative information with a moving obstacle approached by a detection sensor;
A tracking filter based on an extended Kalman filter receiving motion information of an unmanned watercraft and relative information of a moving obstacle from the navigation sensor and the detection sensor and estimating motion information of the moving obstacle based on the information;
The collision probability evaluation unit predicts the flight paths of the unmanned watercraft and obstacles for a predetermined time based on the motion information estimated from the tracking filter based on the extended Kalman filter, and of the motion information caused by measurement errors of the navigation sensor and the detection sensor. Evaluating the probability of collision by an approximate-analytic method using the probability flow concept in consideration of uncertainty and a safety boundary region of an unmanned watercraft;
If the collision avoidance path generation unit exceeds the set collision probability on the predicted flight path, a collision risk region is set on the flight path, and the collision avoidance path is determined by considering international maritime collision prevention rules and the kinematic characteristics of the unmanned watercraft. Generating and extracting an evasion point from the collision avoidance path; And
And a step of causing the unmanned watercraft to follow a straight path between avoidance points extracted by the route tracking and control unit extracted by the collision avoidance route generation unit.
상기 충돌 확률은 [수학식 7]에 의해 규정되는, 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 방법.
[수학식 7]
[여기서,는 충돌 확률을 나타내며,는 결합된 안전 경계 영역내에 유입되거나 유출되는 불확실성의 시간에 따른 변화량을 의미하며, c는 결합된 안전 경계 영역의 경계선이며, t0 ~ tf는 무인수상선과 장애물의 운항 경로를 예측하는 시간임]The method of claim 5,
The collision probability is defined by [Equation 7], collision avoidance method of the unmanned watercraft.
[Equation 7]
[here, Denotes the probability of collision, Is the change over time of uncertainty that flows into or out of the combined safety boundary area, c is the boundary line of the combined safety boundary area, and t0 ~ tf is the time to predict the route of operation of the unmanned watercraft and obstacles. ]
상기 무인수상선이 회피 경유점간의 일직선 경로를 추종하기 위해서 시선각 유도법칙 및 수선경로 유도법칙을 적용하는, 무인수상선의 충돌 회피 방법.The method of claim 5,
A method of avoiding collision of an unmanned watercraft, wherein the unmanned watercraft applies the law of induction of a line of sight and a law of waterline induction in order to follow a straight path between avoidance points.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180125963AKR102099699B1 (en) | 2018-10-22 | 2018-10-22 | Device and method avoiding collision of autonomous surface vehicle considering uncertainty of trajectory prediction |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180125963AKR102099699B1 (en) | 2018-10-22 | 2018-10-22 | Device and method avoiding collision of autonomous surface vehicle considering uncertainty of trajectory prediction |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR102099699B1true KR102099699B1 (en) | 2020-04-13 |
Family
ID=70224540
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180125963AActiveKR102099699B1 (en) | 2018-10-22 | 2018-10-22 | Device and method avoiding collision of autonomous surface vehicle considering uncertainty of trajectory prediction |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102099699B1 (en) |
Cited By (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102314809B1 (en)* | 2020-12-24 | 2021-10-21 | 한화시스템 주식회사 | Anti-collision system of unmanned underwater vehicle by image target analysis |
| KR102339185B1 (en)* | 2021-01-07 | 2021-12-14 | 한화시스템 주식회사 | Collision avoidance/overtaking apparatus of unmanned surface vehicle |
| CN114115240A (en)* | 2021-11-04 | 2022-03-01 | 北京三快在线科技有限公司 | Control method and device for unmanned equipment |
| CN114706402A (en)* | 2022-04-16 | 2022-07-05 | 西北工业大学 | Adaptive motion planning method for unmanned ship based on model predictive control |
| CN114995425A (en)* | 2022-06-02 | 2022-09-02 | 航天时代(青岛)海洋装备科技发展有限公司 | A time-optimized and energy-optimized autonomous tracking method for unmanned boats |
| CN114995409A (en)* | 2022-05-25 | 2022-09-02 | 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院 | Unmanned ship autonomous cruise control system and cruise method |
| CN115129045A (en)* | 2022-05-19 | 2022-09-30 | 北京工商大学 | A Path Planning Method for Unmanned Ship Based on Hull Dynamic Constraint Model |
| CN115220456A (en)* | 2022-07-29 | 2022-10-21 | 大连海事大学 | Unmanned ship path tracking finite time input saturation control method under random interference |
| CN116300982A (en)* | 2023-03-03 | 2023-06-23 | 新兴际华(北京)智能装备技术研究院有限公司 | Underwater vehicle and path tracking control method and device thereof |
| KR20230137719A (en)* | 2022-03-22 | 2023-10-05 | 한국해양과학기술원 | Device and method for verifying autonomous navigation system of autonomous ship |
| KR102594522B1 (en)* | 2022-10-13 | 2023-10-25 | 한국해양대학교 산학협력단 | Evaluation and visualization method of navigation risk using positional domain to prevent marine accidents due to delay in the auto-remote of maritime autonomous surface ships |
| CN117870688A (en)* | 2024-01-12 | 2024-04-12 | 哈尔滨工业大学(威海) | Unmanned vehicle navigation obstacle modeling method and system based on Gaussian probability model |
| WO2024144365A1 (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2024-07-04 | 주식회사 아비커스 | Device and method for calculating ship collision risk |
| CN118314771A (en)* | 2024-06-11 | 2024-07-09 | 中国水产科学研究院渔业工程研究所 | Ship collision risk assessment method and system |
| CN119058750A (en)* | 2024-11-01 | 2024-12-03 | 新石器慧通(北京)科技有限公司 | A method, device, equipment and storage medium for autonomous driving decision making |
| KR102752303B1 (en) | 2024-04-04 | 2025-01-10 | 한화시스템 주식회사 | Machine learning based propulsion control apparatus and method for naval ship |
| CN119323903A (en)* | 2024-12-12 | 2025-01-17 | 哈尔滨工业大学(威海) | Ship anti-collision integrated method and system based on radar fusion |
| CN119806164A (en)* | 2025-03-13 | 2025-04-11 | 武汉理工大学 | Method and device for deciding collision avoidance of ship in limited water area based on uncertainty modeling |
| US20250178701A1 (en)* | 2023-11-30 | 2025-06-05 | Furuno Electric Co., Ltd. | Navigation planning system and navigation planning method |
| EP4597036A1 (en)* | 2024-02-02 | 2025-08-06 | Furuno Electric Company Limited | Navigation planning system and navigation planning method |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10175597A (en)* | 1996-12-20 | 1998-06-30 | Tokimec Inc | Maneuver support device and its method |
| KR20100137858A (en)* | 2009-06-23 | 2010-12-31 | 삼성중공업 주식회사 | Apparatus for setting collision avoidance path, system for controlling path and method for controlling collision avoidance path |
| KR101370649B1 (en)* | 2012-09-04 | 2014-03-10 | 주식회사 한화 | Route control method for the autonomous underwater vehicle |
| KR20140067417A (en)* | 2012-11-26 | 2014-06-05 | 서울과학기술대학교 산학협력단 | Localization system of under water robots |
| JP2016162270A (en)* | 2015-03-03 | 2016-09-05 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Proximity detection device and proximity detection method |
- 2018
- 2018-10-22KRKR1020180125963Apatent/KR102099699B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10175597A (en)* | 1996-12-20 | 1998-06-30 | Tokimec Inc | Maneuver support device and its method |
| KR20100137858A (en)* | 2009-06-23 | 2010-12-31 | 삼성중공업 주식회사 | Apparatus for setting collision avoidance path, system for controlling path and method for controlling collision avoidance path |
| KR101370649B1 (en)* | 2012-09-04 | 2014-03-10 | 주식회사 한화 | Route control method for the autonomous underwater vehicle |
| KR20140067417A (en)* | 2012-11-26 | 2014-06-05 | 서울과학기술대학교 산학협력단 | Localization system of under water robots |
| JP2016162270A (en)* | 2015-03-03 | 2016-09-05 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Proximity detection device and proximity detection method |
Cited By (27)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102314809B1 (en)* | 2020-12-24 | 2021-10-21 | 한화시스템 주식회사 | Anti-collision system of unmanned underwater vehicle by image target analysis |
| KR102339185B1 (en)* | 2021-01-07 | 2021-12-14 | 한화시스템 주식회사 | Collision avoidance/overtaking apparatus of unmanned surface vehicle |
| CN114115240A (en)* | 2021-11-04 | 2022-03-01 | 北京三快在线科技有限公司 | Control method and device for unmanned equipment |
| CN114115240B (en)* | 2021-11-04 | 2024-02-27 | 北京三快在线科技有限公司 | Unmanned equipment control method and device |
| KR20230137719A (en)* | 2022-03-22 | 2023-10-05 | 한국해양과학기술원 | Device and method for verifying autonomous navigation system of autonomous ship |
| KR102682320B1 (en)* | 2022-03-22 | 2024-07-05 | 한국해양과학기술원 | Device and method for verifying autonomous navigation system of autonomous ship |
| CN114706402A (en)* | 2022-04-16 | 2022-07-05 | 西北工业大学 | Adaptive motion planning method for unmanned ship based on model predictive control |
| CN115129045A (en)* | 2022-05-19 | 2022-09-30 | 北京工商大学 | A Path Planning Method for Unmanned Ship Based on Hull Dynamic Constraint Model |
| CN114995409A (en)* | 2022-05-25 | 2022-09-02 | 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院 | Unmanned ship autonomous cruise control system and cruise method |
| CN114995425A (en)* | 2022-06-02 | 2022-09-02 | 航天时代(青岛)海洋装备科技发展有限公司 | A time-optimized and energy-optimized autonomous tracking method for unmanned boats |
| CN114995425B (en)* | 2022-06-02 | 2024-05-07 | 航天时代(青岛)海洋装备科技发展有限公司 | An autonomous tracking method for unmanned boats based on time optimization and energy optimization |
| CN115220456A (en)* | 2022-07-29 | 2022-10-21 | 大连海事大学 | Unmanned ship path tracking finite time input saturation control method under random interference |
| KR102594522B1 (en)* | 2022-10-13 | 2023-10-25 | 한국해양대학교 산학협력단 | Evaluation and visualization method of navigation risk using positional domain to prevent marine accidents due to delay in the auto-remote of maritime autonomous surface ships |
| WO2024144365A1 (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2024-07-04 | 주식회사 아비커스 | Device and method for calculating ship collision risk |
| US12397886B2 (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2025-08-26 | Avikus Co., Ltd. | Apparatus and method for calculating the collison risk of a ship |
| CN116300982A (en)* | 2023-03-03 | 2023-06-23 | 新兴际华(北京)智能装备技术研究院有限公司 | Underwater vehicle and path tracking control method and device thereof |
| CN116300982B (en)* | 2023-03-03 | 2024-06-07 | 新兴际华(北京)智能装备技术研究院有限公司 | Underwater vehicle and path tracking control method and device thereof |
| US20250178701A1 (en)* | 2023-11-30 | 2025-06-05 | Furuno Electric Co., Ltd. | Navigation planning system and navigation planning method |
| CN117870688A (en)* | 2024-01-12 | 2024-04-12 | 哈尔滨工业大学(威海) | Unmanned vehicle navigation obstacle modeling method and system based on Gaussian probability model |
| EP4597036A1 (en)* | 2024-02-02 | 2025-08-06 | Furuno Electric Company Limited | Navigation planning system and navigation planning method |
| KR102752303B1 (en) | 2024-04-04 | 2025-01-10 | 한화시스템 주식회사 | Machine learning based propulsion control apparatus and method for naval ship |
| CN118314771A (en)* | 2024-06-11 | 2024-07-09 | 中国水产科学研究院渔业工程研究所 | Ship collision risk assessment method and system |
| CN119058750B (en)* | 2024-11-01 | 2025-04-01 | 新石器慧通(北京)科技有限公司 | Automatic driving decision method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN119058750A (en)* | 2024-11-01 | 2024-12-03 | 新石器慧通(北京)科技有限公司 | A method, device, equipment and storage medium for autonomous driving decision making |
| CN119323903A (en)* | 2024-12-12 | 2025-01-17 | 哈尔滨工业大学(威海) | Ship anti-collision integrated method and system based on radar fusion |
| CN119806164A (en)* | 2025-03-13 | 2025-04-11 | 武汉理工大学 | Method and device for deciding collision avoidance of ship in limited water area based on uncertainty modeling |
| CN119806164B (en)* | 2025-03-13 | 2025-06-13 | 武汉理工大学 | Method and device for deciding collision avoidance of ship in limited water area based on uncertainty modeling |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102099699B1 (en) | Device and method avoiding collision of autonomous surface vehicle considering uncertainty of trajectory prediction | |
| CN107329477B (en) | Unmanned ship navigation and automatic driving equipment and method thereof | |
| Polvara et al. | Obstacle avoidance approaches for autonomous navigation of unmanned surface vehicles | |
| Hagen et al. | MPC-based collision avoidance strategy for existing marine vessel guidance systems | |
| Campbell et al. | A review on improving the autonomy of unmanned surface vehicles through intelligent collision avoidance manoeuvres | |
| Wilthil et al. | Radar-based maritime collision avoidance using dynamic window | |
| KR101831264B1 (en) | Autonomous navigation system and method for a maneuverable platform | |
| KR20230011310A (en) | Ship's automatic guidance method, ship's automatic guidance program, ship's automatic guidance system and ship | |
| Almeida et al. | Radar based collision detection developments on USV ROAZ II | |
| Campbell et al. | A rule-based heuristic method for COLREGS-compliant collision avoidance for an unmanned surface vehicle | |
| CN113671968B (en) | Real-time collision prevention method for unmanned surface vessel | |
| Johansen et al. | Ship collision avoidance using scenario-based model predictive control | |
| Kufoalor et al. | Autonomous COLREGs-compliant decision making using maritime radar tracking and model predictive control | |
| JP2021018484A (en) | Peripheral situation rendering method, navigation avoidance operation learning program, navigation avoidance operation learning system, and marine vessel | |
| Johansen et al. | Unmanned aerial surveillance system for hazard collision avoidance in autonomous shipping | |
| KR102617981B1 (en) | Collision avoidance system for autonomous ships | |
| Kim et al. | Field experiment of autonomous ship navigation in canal and surrounding nearshore environments | |
| KR20180094286A (en) | Path Planning System of Unmanned Surface Vehicle for Autonomous Tracking of Underwater Acoustic Target | |
| Park et al. | Autonomous collision avoidance for unmanned surface ships using onboard monocular vision | |
| KR20220132909A (en) | System for autonomous ship berthing reflecting weather conditions | |
| Son et al. | On the sea trial test for the validation of an autonomous collision avoidance system of unmanned surface vehicle, ARAGON | |
| Bitar | Towards the development of autonomous ferries | |
| Sans-Muntadas et al. | Spiral path planning for docking of underactuated vehicles with limited FOV | |
| De Schaetzen et al. | Real-time navigation for autonomous surface vehicles in ice-covered waters | |
| Helgesen et al. | Experimental validation of camera-based maritime collision avoidance for autonomous urban passenger ferries |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20181022 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20190802 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20200201 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20200406 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20200407 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20230321 Start annual number:4 End annual number:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20240327 Start annual number:5 End annual number:5 |