KR102095335B1 - Apparatus and method for generating and using neural network model applying accelerated computation - Google Patents
Apparatus and method for generating and using neural network model applying accelerated computationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102095335B1 KR102095335B1KR1020170152180AKR20170152180AKR102095335B1KR 102095335 B1KR102095335 B1KR 102095335B1KR 1020170152180 AKR1020170152180 AKR 1020170152180AKR 20170152180 AKR20170152180 AKR 20170152180AKR 102095335 B1KR102095335 B1KR 102095335B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- data
- matrix
- unit
- neural network
- network model
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/0464—Convolutional networks [CNN, ConvNet]
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G06N3/084—Backpropagation, e.g. using gradient descent
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 합성곱 신경망(convolution neural network, CNN) 모델을 이용하여 영상(image) 데이터와 같은 인식 대상 데이터를 인식하는 데 있어서, 연산량을 줄임으로써 인식의 속도를 향상시키기 위한 장치 및 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for improving the speed of recognition by reducing a computation amount in recognizing recognition target data such as image data using a convolution neural network (CNN) model. .
영상 데이터 혹은 텍스트 데이터 등의 인식 대상 데이터를 자동으로 분석하여, 상기 인식 대상 데이터를 유형별로 분류하거나 상기 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 정보를 추출해 내는 기술이 인공 지능(artificial intelligence, AI) 기술의 일종으로서 최근 각광받고 있다. 이와 같은 기술은 단순히 영상 데이터 내의 객체의 종류를 인식하는 것에 그치지 않고, 자율 주행, 의료 영상 판독, 보안 시스템 등 다양한 분야에서 이용될 수 있다.As a kind of artificial intelligence (AI) technology, a technology that automatically analyzes recognition data such as image data or text data, classifies the recognition data by type, or extracts information included in the recognition data. It has been spotlighted recently. Such a technology is not only recognizing the type of object in image data, but can be used in various fields such as autonomous driving, medical image reading, and security systems.
특히 최근에는 딥 러닝(deep learning)과 같은 기계 학습(machine learning) 기법이 데이터 인식 기술에 적용되고 있다. 이와 같은 딥 러닝 기법 중 널리 알려진 합성곱 신경망 기법은 영상 데이터 인식에 있어 높은 성능을 보이고 있다.In particular, recently, machine learning techniques such as deep learning have been applied to data recognition technology. Among these deep learning techniques, the well-known convolutional neural network technique has high performance in image data recognition.
다만, 합성곱 신경망 기법을 이용하여 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 정보를 인식하는 과정에서는, 곱셈과 덧셈의 조합으로 이루어지는 합성곱(convolution) 연산이 다수 회 수행된다. 이와 같이 거듭되어 수행되는 방대한 연산량의 합성곱 연산은 합성곱 신경망 기법을 통한 데이터 인식에 걸림돌로 작용할 수 있다. 특히, 앞서 언급한 자율 주행과 같이 신속한 연산이 중요한 영상 데이터 인식 분야에 있어서는, 합성곱 연산에 소요되는 시간은 큰 문제가 될 수 있다.However, in the process of recognizing information included in the data to be recognized using the convolutional neural network technique, a convolution operation consisting of a combination of multiplication and addition is performed multiple times. The convolution operation of a massive amount of computation performed repeatedly may act as an obstacle to data recognition through the convolutional neural network technique. In particular, in the field of image data recognition, in which rapid calculation is important, such as autonomous driving, the time required for the compositing operation can be a big problem.
본 발명이 해결하고자 하는 과제는, 합성곱 신경망 모델을 이용한 인식 대상 데이터의 인식 작업의 속도를 향상시키기 위한 장치 및 방법을 제공하는 것이다.The problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide an apparatus and a method for improving the speed of recognition work of recognition target data using a convolutional neural network model.
다만, 본 발명이 해결하고자 하는 과제는 이상에서 언급한 것으로 제한되지 않으며, 언급되지 않은 또 다른 해결하고자 하는 과제는 아래의 기재로부터 본 발명이 속하는 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 명확하게 이해될 수 있을 것이다.However, the problem to be solved by the present invention is not limited to those mentioned above, and another problem not to be solved can be clearly understood by those having ordinary knowledge to which the present invention belongs from the following description. will be.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 생성하는 서버 장치는, 학습용 데이터를 복수의 단위 데이터로 분할하는 데이터 분할부, 상기 각 단위 데이터를, 소정의 분류 기준에 따라 복수의 그룹 중 하나의 그룹에 속하도록 분류하고, 상기 복수의 그룹 중 같은 그룹에 속하는 단위 데이터를 동일한 값을 갖는 변환 데이터로 변환하는 전처리부, 상기 변환 데이터로 구성된 데이터 행렬(matrix)에, 소정의 차원(dimension)을 갖는 행렬인 특징 추출 필터를 적용하여 합성곱(convolution) 연산을 수행한 결과 및 상기 학습용 데이터에 포함된 정보 간의 관계에 기초하여 신경망 모델을 생성하는 모델 생성부 및 상기 데이터 행렬의 일부인 부분 행렬과, 상기 합성곱 연산 중 상기 부분 행렬에 대해 수행된 연산의 결과가 서로 매칭되어 저장됨으로써, 상기 신경망 모델을 통해 상기 학습용 데이터와는 다른 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 정보를 인식하는 데 이용되는 연산 테이블을 생성하는 테이블 생성부를 포함할 수 있다.A server apparatus for generating a neural network model to which computational acceleration has been applied according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a data division unit for dividing training data into a plurality of unit data, and each of the unit data is a plurality of groups according to a predetermined classification criterion A pre-processing unit that classifies the data to belong to one group and converts unit data belonging to the same group among the plurality of groups into transform data having the same value, and a predetermined dimension (a) in a data matrix consisting of the transform data A model generator that generates a neural network model based on a result of performing a convolution operation by applying a feature extraction filter that is a matrix having a dimension) and a part that is part of the data matrix The result of the operation performed on the matrix and the partial matrix among the convolution operation is matched and stored. Writing, with the training data through the neural network model may include a table generator which generates an operation table to be used to recognize the information contained in other recognition target data.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 이용하는 서버 장치는, 인식 대상 데이터를, 소정의 분할 기준에 따라 복수의 대상 단위 데이터로 분할하는 데이터 분할부, 상기 각 대상 단위 데이터를, 소정의 분류 기준에 따라 복수의 그룹 중 하나의 그룹에 속하도록 분류하고, 상기 복수의 그룹 중 같은 그룹에 속하는 대상 단위 데이터를 동일한 값을 갖는 변환 데이터로 변환하는 데이터 변환부 및 상기 변환 데이터로 구성된 대상 데이터 행렬에, 소정의 차원을 갖는 행렬인 특징 추출 필터를 적용하여 상기 인식 대상 데이터의 특징을 추출함으로써 상기 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 정보를 인식하되, 상기 대상 데이터 행렬의 일부인 대상 부분 행렬과 동일한 원소를 갖는 행렬과 상기 특징 추출 필터 간에 기 수행된 합성곱 연산의 결과가 기 저장된 연산 테이블로부터 상기 대상 부분 행렬과 상기 특징 추출 필터 간의 합성곱 연산의 결과를 획득하는 대상 인식부를 포함할 수 있다.A server device using a neural network model to which computational acceleration has been applied according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises: a data partitioning unit for dividing recognition target data into a plurality of target unit data according to a predetermined partitioning criterion, and each target unit data, A data conversion unit configured to classify data to belong to one of a plurality of groups according to a predetermined classification criterion, and to convert target unit data belonging to the same group among the plurality of groups into conversion data having the same value, and the conversion data The information included in the recognition target data is recognized by applying a feature extraction filter, which is a matrix having a predetermined dimension, to the target data matrix, and the same as the target sub-matrix that is part of the target data matrix. Between the matrix of elements and the feature extraction filter It may include a target recognition unit for obtaining a result of the result of the composite product between the target sub-matrix and the feature extraction filter from the calculation table in which the result is stored.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 생성하기 위한 방법은, 학습용 데이터를 복수의 단위 데이터로 분할하는 단계, 상기 각 단위 데이터를, 소정의 분류 기준에 따라 복수의 그룹 중 하나의 그룹에 속하도록 분류하고, 상기 복수의 그룹 중 같은 그룹에 속하는 단위 데이터를 동일한 값을 갖는 변환 데이터로 변환하는 단계, 상기 변환 데이터로 구성된 데이터 행렬에, 소정의 차원을 갖는 행렬인 특징 추출 필터를 적용하여 합성곱 연산을 수행한 결과 및 상기 학습용 데이터에 포함된 정보 간의 관계에 기초하여 신경망 모델을 생성하는 단계 및 상기 데이터 행렬의 일부인 부분 행렬과, 상기 합성곱 연산 중 상기 부분 행렬에 대해 수행된 연산의 결과가 서로 매칭되어 저장됨으로써, 상기 신경망 모델을 통해 상기 학습용 데이터와는 다른 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 정보를 인식하는 데 이용되는 연산 테이블을 생성하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.A method for generating a neural network model to which computational acceleration is applied according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises: dividing the training data into a plurality of unit data, and dividing the unit data into one of a plurality of groups according to a predetermined classification criterion Classifying to belong to a group of, and converting unit data belonging to the same group among the plurality of groups into transformed data having the same value, a feature extraction filter that is a matrix having a predetermined dimension in a data matrix composed of the transformed data Generating a neural network model based on a relationship between a result of performing a convolution operation and information included in the training data, and performing a partial matrix that is part of the data matrix and the partial matrix of the convolution operation The result of the calculated operation is matched with each other and stored, so that the learning is performed through the neural network model. Rotor and it may comprise the step of generating an operation table to be used to recognize the information contained in other recognition target data.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 이용한 데이터 인식 방법은, 인식 대상 데이터를, 소정의 분할 기준에 따라 복수의 대상 단위 데이터로 분할하는 단계, 상기 각 대상 단위 데이터를, 소정의 분류 기준에 따라 복수의 그룹 중 하나의 그룹에 속하도록 분류하고, 상기 복수의 그룹 중 같은 그룹에 속하는 대상 단위 데이터를 동일한 값을 갖는 변환 데이터로 변환하는 단계 및 상기 변환 데이터로 구성된 대상 데이터 행렬에, 소정의 차원을 갖는 행렬인 특징 추출 필터를 적용하여 상기 인식 대상 데이터의 특징을 추출함으로써 상기 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 정보를 인식하되, 상기 대상 데이터 행렬의 일부인 대상 부분 행렬과 동일한 원소를 갖는 행렬과 상기 특징 추출 필터 간에 기 수행된 합성곱 연산의 결과가 기 저장된 연산 테이블로부터 상기 대상 부분 행렬과 상기 특징 추출 필터 간의 합성곱 연산의 결과를 획득하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.A data recognition method using a neural network model to which computational acceleration is applied according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises: dividing the recognition target data into a plurality of target unit data according to a predetermined partitioning criterion, and each target unit data is predetermined Classifying to belong to one of a plurality of groups according to the classification criteria of, and converting the target unit data belonging to the same group of the plurality of groups into conversion data having the same value and a target data matrix composed of the conversion data In this example, information included in the recognition target data is recognized by applying a feature extraction filter, which is a matrix having a predetermined dimension, to extract the characteristics of the recognition target data, but having the same elements as the target sub-matrix that is part of the target data matrix. The result of the pre-combined convolution operation between the matrix and the feature extraction filter is A can from the calculation table can include the step of obtaining the results of the convolution operation between the matrix and the target portion of the feature extraction filter.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 합성곱 신경망 모델 생성 과정에서 입력 가능한 모든 데이터와 합성곱 신경망 간의 연산을 미리 수행하여 연산 테이블에 저장해 놓고, 인식 대상 데이터를 인식하는데 이를 이용할 수 있다. 이로써 인식 과정에서의 연산의 중복 수행이 방지될 수 있으며, 결과적으로 연산량이 획기적으로 줄어들어 신경망 모델을 이용하는 시스템의 효율이 증대될 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, in the process of generating a convolutional neural network model, all the data that can be input and the convolutional neural network are performed in advance and stored in an operation table, which can be used to recognize data to be recognized. As a result, it is possible to prevent duplication of operations in the recognition process, and as a result, the amount of computation is drastically reduced, so that the efficiency of a system using a neural network model can be increased.
특히, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 의하면, 신경망 모델 생성 과정에서의 학습용 데이터 혹은 신경망 모델 활용 과정에서의 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 데이터의 양 혹은 가짓수를 합리적인 수준으로 감소시킬 수 있다. 이를 통해 상기 연산 테이블과 같은 시스템에 저장되어야 하는 정보의 양이 감소될 수 있으며, 신경망 모델의 생성 및 활용에 있어서의 효율이 크게 향상될 수 있다.In particular, according to an embodiment of the present invention, the amount or false number of data included in the learning data in the process of generating the neural network model or the data to be recognized in the process of using the neural network model can be reduced to a reasonable level. Through this, the amount of information to be stored in the system such as the calculation table can be reduced, and the efficiency in generating and utilizing a neural network model can be greatly improved.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델의 생성 및 활용을 위한 서버 장치의 구성을 도시한 도면이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델의 생성 방법의 각 단계를 도시한 도면이다.
도 3a 및 3b는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 의한 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델의 생성 방법의 전처리 과정에 대해 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 4는 합성곱 신경망에서의 합성곱 연산에 대해 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델의 활용 방법의 각 단계를 도시한 도면이다.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델의 활용 방법의 효과를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.1 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of a server device for generating and utilizing a neural network model to which computational acceleration is applied according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating each step of a method of generating a neural network model to which computational acceleration is applied according to an embodiment of the present invention.
3A and 3B are diagrams for explaining a pre-processing process of a method for generating a neural network model to which computational acceleration is applied according to an embodiment of the present invention.
4 is a diagram for explaining a convolution operation in a convolutional neural network.
5 is a diagram illustrating each step of a method of utilizing a neural network model to which computational acceleration is applied according to an embodiment of the present invention.
6 is a view for explaining the effect of a method of utilizing a neural network model to which computational acceleration is applied according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명의 이점 및 특징, 그리고 그것들을 달성하는 방법은 첨부되는 도면과 함께 상세하게 후술되어 있는 실시예들을 참조하면 명확해질 것이다. 그러나 본 발명은 이하에서 개시되는 실시예들에 한정되는 것이 아니라 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 구현될 수 있으며, 단지 본 실시예들은 본 발명의 개시가 완전하도록 하고, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 발명의 범주를 완전하게 알려주기 위해 제공되는 것이며, 본 발명은 청구항의 범주에 의해 정의될 뿐이다.Advantages and features of the present invention, and methods for achieving them will be clarified with reference to embodiments described below in detail together with the accompanying drawings. However, the present invention is not limited to the embodiments disclosed below, but may be implemented in various different forms, and only the embodiments allow the disclosure of the present invention to be complete, and common knowledge in the art to which the present invention pertains It is provided to completely inform the person having the scope of the invention, and the present invention is only defined by the scope of the claims.
본 발명의 실시예들을 설명함에 있어서 공지 기능 또는 구성에 대한 구체적인 설명이 본 발명의 요지를 불필요하게 흐릴 수 있다고 판단되는 경우에는 그 상세한 설명을 생략할 것이다. 그리고 후술되는 용어들은 본 발명의 실시예에서의 기능을 고려하여 정의된 용어들로서 이는 사용자, 운용자의 의도 또는 관례 등에 따라 달라질 수 있다. 그러므로 그 정의는 본 명세서 전반에 걸친 내용을 토대로 내려져야 할 것이다.In describing embodiments of the present invention, when it is determined that a detailed description of known functions or configurations may unnecessarily obscure the subject matter of the present invention, the detailed description will be omitted. In addition, terms to be described later are terms defined in consideration of functions in an embodiment of the present invention, which may vary according to a user's or operator's intention or practice. Therefore, the definition should be made based on the contents throughout this specification.
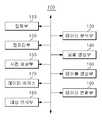
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델의 생성 및 활용을 위한 서버 장치의 구성을 도시한 도면이다. 도 1의 서버 장치(100)는 입력부(110), 데이터 분할부(120), 전처리부(130), 모델 생성부(140), 사전 생성부(150), 테이블 생성부(160), 데이터베이스(170), 데이터 변환부(180) 및 대상 인식부(190)를 포함할 수 있다. 다만, 도 1의 서버 장치(100)의 구성 요소는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 불과하므로, 도 1에 의해 본 발명의 기술적 사상이 한정 해석되는 것은 아니다.1 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of a server device for generating and utilizing a neural network model to which computational acceleration is applied according to an embodiment of the present invention. The
입력부(110)는 신경망 모델 생성 과정에서 이용될 학습용 데이터, 혹은 신경망 모델 활용 과정에서 이용될 인식 대상 데이터를 입력받을 수 있다. 상기 학습용 데이터 혹은 인식 대상 데이터는 복수의 부호로 구성된 것이라면 어느 것이든 될 수 있겠지만, 이하에서는 영상 데이터임을 가정하고 설명하도록 한다. 입력부(110)는 키보드(keyboard), 마우스(mouse) 등의 입력 장치, 데이터의 수신을 위한 데이터 버스, 혹은 유/무선 통신 모듈 등을 포함하여 구현될 수 있다.The
데이터 분할부(120)는 학습용 데이터 혹은 인식 대상 데이터를 소정의 분할 기준에 따라 분할할 수 있다. 예컨대, 영상 데이터인 학습용 데이터 혹은 인식 대상 데이터의 경우, 상기 분할 기준은 픽셀(pixel) 단위의 분할이 될 수 있다. 이하에서는 학습용 데이터가 분할되어 생성된 데이터를 단위 데이터, 인식 대상 데이터가 분할되어 생성된 데이터를 대상 단위 데이터라 칭하도록 한다. 따라서, 하나의 단위 데이터 혹은 대상 단위 데이터는 학습용 데이터 혹은 인식 대상 데이터의 하나의 픽셀에 대응될 수 있다.The
상기 데이터 분할부(120)는 마이크로프로세서(microprocessor)와 같은 연산 장치를 포함하여 구현될 수 있으며, 이는 후술할 다른 구성 요소인 전처리부(130), 모델 생성부(140), 사전 생성부(150), 테이블 생성부(160), 데이터 변환부(180) 및 대상 인식부(190)에 있어서도 같다.The
한편, 학습용 데이터에 속한 단위 데이터는 그 분량뿐 아니라 가질 수 있는 값의 가짓수가 매우 많을 수 있다. 예컨대, 영상 데이터의 각 픽셀은 R(red, 빨강), G(green, 초록), B(blue, 파랑)의 세 가지 색상을 각각 나타내기 위한 3개의 채널(channel)을 통해 표현될 수 있음은 주지된 바와 같다. 0 이상 255 이하의 정수를 이용하여 임의의 한 픽셀의 한 채널의 값을 나타낼 경우, 상기 픽셀의 픽셀 값(pixel value), 즉 상기 픽셀에 대응되는 하나의 단위 데이터가 가질 수 있는 값의 가짓수는 총 2563가지가 될 것이다. 게다가, 영상 데이터 내에는 매우 많은 수의 픽셀이 행렬(matrix)의 형태를 이루어 존재하고 있으므로, 영상 데이터로부터 생성되는 단위 데이터에 포함된 정보의 양 및 이들 단위 데이터들이 가질 수 있는 값의 조합의 총 가짓수는 천문학적인 수가 될 것이다.On the other hand, the unit data belonging to the learning data can have a very large number of possible values as well as the amount. For example, each pixel of the image data can be expressed through three channels for representing three colors: R (red, red), G (green, green), and B (blue, blue). As is well known. When an integer value of 0 or more and 255 or less is used to represent a channel value of any one pixel, a pixel value of the pixel, that is, a false number of values that one unit data corresponding to the pixel can have There will be a total of 256three . In addition, since a very large number of pixels exist in the form of a matrix in the image data, the total amount of information included in the unit data generated from the image data and the combination of values that these unit data can have. Gajitsu will be an astronomical number.
이에, 본 발명의 일 실시예에서의 전처리부(130)는 소정의 분류 기준에 따라, 단위 데이터(혹은 대상 단위 데이터)를 분류할 수 있다. 구체적으로, 전처리부(130)는 소정의 분류 기준에 따라 각 단위 데이터가 복수의 그룹 중 하나의 그룹에 속하도록 분류하고, 상기 복수의 그룹 중 같은 그룹에 속하는 단위 데이터는 서로 동일한 값을 갖는 변환 데이터로 변환되도록 할 수 있으며, 상이한 그룹에 속하는 단위 데이터는 상이한 변환 데이터로 변환되도록 할 수 있다. 즉, 같은 그룹에 속한 단위 데이터끼리는 신경망 모델의 생성 및 활용에 있어 서로 같은 입력 데이터로 여겨질 수 있게 되며, 상기 분류 기준의 구체적인 예시에 대해서는 후술하도록 한다.Accordingly, the
모델 생성부(140)는 단위 데이터로 분할되고 변환 데이터로 변환된 학습용 데이터를 학습함으로써, 학습용 데이터와는 다른 데이터로서 인식의 대상이 되는 인식 대상 데이터의 인식을 위한 신경망 모델을 생성할 수 있다. 이와 같은 신경망 모델은 인식 대상 데이터의 인식 과정에서 합성곱 연산을 활용하는 모델이라면 어떤 것이든 될 수 있다. 신경망 모델의 구체적인 생성 및 활용 방법에 대해서는 머신 러닝 분야의 통상의 기술자에게 용이한 것이므로 여기에서는 자세한 설명을 생략한다.The
사전 생성부(150)는 단위 데이터(혹은 대상 단위 데이터)를 분류하기 위한 분류 기준 및 분류된 단위 데이터를 변환 데이터로 변환하기 위한 변환 기준을 저장하는 사전(dictionary)을 생성할 수 있다. 상기 분류 기준 및 변환 기준은 신경망 모델 생성 과정을 거치며 최적화될 수 있으며, 이와 같은 최적화된 기준이 사전에 저장되어, 인식 대상 데이터로부터 생성된 대상 단위 데이터를 분류 및 변환하는 데 이용될 수 있다.The
테이블 생성부(160)는 모델 생성부(140)가 신경망 모델을 생성하는 과정에서 학습용 데이터에 대해 수행한 합성곱(convolution) 연산의 결과를 저장하는 연산 테이블을 생성할 수 있다. 이와 같이 연산 테이블에 신경망 모델 생성 과정에서의 합성곱 연산의 결과가 저장됨에 따라, 신경망 모델 활용 과정에서는 합성곱 연산을 일일이 수행하는 대신, 상기 연산 테이블로부터 동일한 상황에서의 합성곱 연산의 결과를 획득하여 사용하는 것이 가능해진다.The
데이터베이스(170)는 생성된 신경망 모델, 연산 테이블 및 사전 등을 저장할 수 있다. 물론 데이터베이스(170)가 저장할 수 있는 정보는 반드시 이에 한정되지 않고, 서버 장치(100)의 동작에 필요한 임시적 혹은 영구적 정보라면 어떤 것이든 될 수 있다. 데이터베이스(170)는 컴퓨터 판독 기록 매체로서 구현될 수 있으며, 상기 컴퓨터 판독 기록 매체의 예로는 하드 디스크, 플로피 디스크 및 자기 테이프와 같은 자기 매체(magnetic media), CD-ROM, DVD와 같은 광기록 매체(optical media), 플롭티컬 디스크(floptical disk)와 같은 자기-광 매체(magneto-optical media), 플래시 메모리(flash memory)와 같은 프로그램 명령어들을 저장하고 수행하도록 특별히 구성된 하드웨어 장치를 들 수 있다.The
데이터 변환부(180)는 인식 대상 데이터가 데이터 분할부(120)에 의해 분할되어 생성된 각 단위 데이터를, 변환 데이터 중 어느 하나로 각각 변환할 수 있다. 이와 같은 변환은 데이터베이스(170)에 저장된 사전을 이용하여 수행될 수 있다.The
대상 인식부(190)는 데이터베이스(170)에 저장된 신경망 모델을 이용하여 인식 대상 데이터의 특징을 추출하고, 이를 바탕으로 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 정보를 인식하여, 인식 대상 데이터의 분류 혹은 내용 파악 등의 작업을 수행할 수 있다. 이와 같은 대상 인식부(190)의 신경망 모델 이용 과정에서는 합성곱 연산이 수행될 수 있는데, 대상 인식부(190)는 합성곱 연산을 일일이 수행하는 대신, 데이터베이스(170)에 저장된 연산 테이블로부터 합성곱 연산의 결과를 획득하여 사용할 수 있다. 이와 같은 연산 테이블의 사용은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 대상 인식 과정의 효율을 비약적으로 증대시킬 수 있다.The
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델의 생성 방법의 각 단계를 도시한 도면이다. 도 2의 방법은 도 1을 참조하여 설명한 서버 장치(100)에 의해 수행될 수 있다. 단, 도 2에 도시된 방법은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 불과하므로 도 2에 의해 본 발명의 사상이 한정 해석되는 것은 아니며, 도 2에 도시된 방법의 각 단계는 경우에 따라 도면에 제시된 바와 그 순서를 달리하여 수행될 수 있음은 물론이다. 또한, 도 1과 중복되는 바에 대해서는 자세한 설명이 생략될 수 있다.FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating each step of a method of generating a neural network model to which computational acceleration is applied according to an embodiment of the present invention. The method of FIG. 2 may be performed by the
우선 데이터 분할부(120)는, 입력부(110)를 통해 입력된 학습용 데이터를 복수의 단위 데이터로 분할할 수 있다(S110). 이하에서는 학습용 데이터 및 인식 대상 데이터를 특정 객체를 촬영한 영상 데이터로 가정하도록 하겠지만, 본 발명의 적용 범위가 반드시 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.First, the
다음으로, 전처리부(130)는 상기 각 단위 데이터에 대한 분류 및 변환 데이터로의 변환을 수행할 수 있다(S120). 예컨대, 영상 데이터인 학습용 데이터에서 각 픽셀의 픽셀 값은 0 이상 255 이하의 정수로 총 256가지가 나올 수 있음은 앞서 말한 바와 같다. 이 때, 전처리부(130)는 양자화(quantization) 기법을 이용하여, 상기 픽셀 값이 가질 수 있는 수치의 범위를 복수의 구간으로 분할하고, 각 단위 데이터에 대응되는 픽셀의 픽셀 값이 상기 복수의 구간 중 어느 구간에 속하는지에 따라 상기 각 단위 데이터를 분류할 수 있다.Next, the
예컨대, 전처리부(130)는 상기 픽셀 값의 범위를 동일한 크기를 갖는 8개의 구간으로 분할할 수 있다. 그러면 하나의 구간에는 32종류의 픽셀 값이 속하게 된다. 이에 따라, 전처리부(130)는 상기 256종류의 픽셀 값에 의한 단위 데이터를, 8종류의 값을 갖는 변환 데이터로 변환할 수 있으며, 이에 따라 0 이상 255 이하의 정수로 표현되는 단위 데이터는 0 이상 7 이하의 정수로 표현되는 변환 데이터 중 어느 하나로 변환될 수 있을 것이다.For example, the
혹은, 전처리부(130)는 학습용 데이터의 각 픽셀에 대해, 서로 다른 색상에 관한 두 종류 이상의 픽셀 값을 평균한 값을 산출한 결과에 기초하여 상기 분류를 수행할 수도 있을 것이다. 예컨대, 각 픽셀이 위에서도 언급한 대로 R, G, B의 3개의 색상에 각각 대응되는 3종류의 픽셀 값을 가질 경우, 전처리부(130)는 이들 3종류의 각 픽셀 값을 모두 포함하는 단위 데이터를, 상기 3종류의 픽셀 값의 평균값 하나만을 포함하는 변환 데이터로 변환할 수 있다. 이는 컬러 영상을 그레이 스케일(gray scale)로 변환하여 취급하는 것과 유사하다 할 수 있다.Alternatively, the
경우에 따라, 전처리부(130)는 상기 평균값으로서 단순한 산술 평균 대신 픽셀 값의 각 종류별로 정해지는 가중치에 따라 가중평균(weighted mean)된 값을 이용할 수도 있다. 이에 따르면, 다른 종류의 픽셀 값에 비해 보다 인식 결과에 영향을 미친다고 판단되는 픽셀 값에 높은 가중치를 부여하여, 신경망 모델의 성능을 높이는 것이 가능하다.In some cases, the
전처리부(130)는 지금까지 설명한 분류 및 변환의 기준 중 하나만을 사용할 수도 있고, 두 개 이상의 기준을 혼합하여 사용할 수도 있다. 한편, 지금까지 설명한 분류 및 변환의 기준은 단지 예시적인 것일 뿐이며, 다른 기준이 적용될 수도 있음은 물론이다. 아울러, 상기 분류 및 변환의 기준은 사용자에 의해 직접 설정될 수도 있지만, 신경망 모델 생성 과정에서 최적화될 수도 있다. 이 경우, 전처리부(130)는 모델 생성부(140)와 상호 작용을 수행하며 동작하게 될 것이다. 상기 최적화에 의해, 신경망 모델에 의해 처리될 데이터의 양을 줄이면서도, 모델의 성능 감소는 최소화할 수 있는 기준을 설정할 수 있다.The
다음으로 모델 생성부(140)가 상기 각 변환 데이터를 이용하여, 신경망 모델을 생성할 수 있다(S130). 즉, 신경망 모델은 모델 생성부(140)가 학습용 데이터를 학습한 결과에 기초하여 생성된다. 아울러, 사전 생성부(150)는 상기 분류 및 변환의 기준을 저장하는 사전을 생성함으로써(S140), 신경망 모델 활용 단계에서 상기 사전을 참조하여 인식 대상 데이터가 분류 및 변환되도록 할 수 있다.Next, the
보다 구체적으로, 학습용 데이터로부터 생성된 각 변환 데이터는 대응되는 픽셀이 학습용 데이터에서 차지하는 위치에 기초하여, 하나의 데이터 행렬(matrix)를 구성할 수 있다. 모델 생성부(140)는 상기 데이터 행렬에 대해 소정의 차원(예컨대, 2x2 혹은 3x3)을 갖는 행렬인 특징 추출 필터를 적용하여 합성곱 연산을 수행한 결과와, 상기 학습용 데이터에 포함된 객체의 종류와 같은 정보 간의 관계에 기초하여, 인식 대상 데이터의 인식을 위한 신경망 모델을 생성할 수 있다.More specifically, each transformed data generated from the training data may form one data matrix based on the position of the corresponding pixel in the training data. The
또한, 신경망 모델을 생성하는 과정에서, 상기 특징 추출 필터 역시 학습에 의해 적응적으로 변화함으로써 최적화될 수 있다. 특징 추출 필터의 최적화 과정 및 특징 추출 필터에 의한 합성곱 연산의 결과를 활용하는 과정의 구체적인 사항에 대해서는 통상의 기술자에게 용이한 것이므로 여기에서는 자세한 설명을 생략한다.In addition, in the process of generating a neural network model, the feature extraction filter may also be optimized by adaptively changing by learning. The details of the optimization process of the feature extraction filter and the process of utilizing the result of the convolution operation by the feature extraction filter are easy for a person skilled in the art, and thus detailed description thereof will be omitted.
이하에서는 도 3a 내지 4를 참조하여, 전처리 과정 및 합성곱 연산의 결과 저장에 대해 상세히 설명하도록 한다. 도 3a 및 3b는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 의한 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델의 생성 방법의 전처리 과정에 대해 설명하기 위한 도면이다. 학습용 데이터 혹은 인식 대상 데이터로서 사용될 수 있는 영상 데이터(210)가 입력부(110)를 통해 입력되면, 데이터 분할부(120)는 픽셀 단위로 상기 영상 데이터(210)를 분할할 수 있음은 앞서 말한 바와 같다.Hereinafter, with reference to FIGS. 3A to 4, it will be described in detail about the pre-processing process and storage of the result of the composite product operation. 3A and 3B are diagrams for explaining a pre-processing process of a method for generating a neural network model to which computational acceleration is applied according to an embodiment of the present invention. As described above, when the
여기서, 전처리부(130)는 R, G, B 3개의 채널을 이용해 표현된 영상 데이터(210)각 픽셀의 픽셀 값을 평균함으로써, 도 3a와 같이 각 픽셀의 픽셀 값이 하나의 채널로 표현된 변환 영상 데이터(220)를 생성할 수 있다. 즉, 변환 영상 데이터(220)의 한 픽셀의 픽셀 값은 하나의 변환 데이터가 된다고 볼 수 있다.Here, the
또한 도 3b를 참조하면, 변환 영상 데이터(220)의 각 픽셀에서의 위치에 기초하여, 각 픽셀에 대응되는 변환 데이터(231)를 원소로 갖는 데이터 행렬(230)이 전처리부(130)에 의해 도출될 수 있음을 볼 수 있다. 본래의 영상 데이터(220)에는 하나의 픽셀당 R, G, B의 3종류의 값이 있었으나, 데이터 행렬(230)에서는 하나의 픽셀에 대응되는 변환 데이터(231)가 0 이상 255 이하의 값을 갖는 하나의 수치로서 표현될 수 있다.Also, referring to FIG. 3B, based on the position of each pixel of the transformed
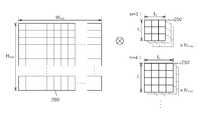
도 4는 합성곱 신경망에서의 합성곱 연산에 대해 설명하기 위한 도면이다. 모델 생성부(140)는 신경망 모델 생성 과정에서, 데이터 행렬(230)에 소정 차원(도 4의 예에서는 3x3)의 행렬 형태의 특징 추출 필터(250)를 적용하여 영상 데이터(210)의 특징을 추출할 수 있다. 특징 추출 필터(250)는 데이터 행렬(230)과 마찬가지로 소정 범위 내의 수치를 원소로 갖는 행렬일 수 있다. 또한, 상기 특징 추출 필터(250)는 바람직하게는 정사각 행렬(square matrix)일 수 있다.4 is a diagram for explaining a convolution operation in a convolutional neural network. The
보다 구체적으로, 신경망 모델 생성 과정에서 데이터 행렬(230)의 일부로서 특징 추출 필터(250)와 같은 차원을 갖는 부분 행렬(240, 진한 테두리 안의 부분)과 특징 추출 필터(250) 간의 합성곱 연산이 수행될 수 있다. 이와 같은 부분 행렬(240)에 대한 합성곱 연산에 의하면, 부분 행렬(240)의 원소와, 특징 추출 필터(250) 중 상기 부분 행렬(240)의 원소에 대응되는 위치의 원소를 곱하게 된다. 이와 같은 곱셈은 부분 행렬(240) 혹은 특징 추출 필터(250)의 원소의 개수만큼 수행될 수 있다. 그리고 나서, 상기 곱셈의 결과를 모두 더하게 된다.More specifically, in the process of generating a neural network model, a convergence operation between the partial matrix 240 (parts in a dark frame) having the same dimension as the
이와 같은 합성곱 연산은, 데이터 행렬(230)로부터 도출될 수 있는 각 부분 행렬(240)에 대해 반복하여 수행될 수 있다. 즉, 특징 추출 필터(250)는 데이터 행렬(230)의 모든(혹은 일부) 영역을 스캔함으로써, 상기 합성곱 연산이 수행되도록 할 수 있다. 또한, 이와 같은 특징 추출 필터(250)는 복수 개 존재할 수 있으며, 각 특징 추출 필터(250) 간에는 차원이 다를 수 있다.Such a convolution operation may be performed repeatedly for each sub-matrix 240 that may be derived from the
상기 합성곱 연산은 데이터 행렬(230)로부터 도출될 수 있는 각 부분 행렬(240)과 특징 추출 필터(250)의 각 원소 간의 곱셈 및 이들 곱셈의 결과에 대한 덧셈을 포함하므로, 그 연산의 양이 매우 많아 비효율적이다. 이와 같은 비효율의 방지를 위해, 본 발명의 일 실시예에서의 테이블 생성부(160)는, 합성곱 모델 생성 과정에서 부분 행렬(240)과 특징 추출 필터(250)간에 수행된 합성곱 연산의 결과가 상기 부분 행렬(240)과 매칭되어 저장된 연산 테이블을 생성할 수 있다(S150). 이 경우, 신경망 모델을 이용하여 인식 대상 데이터를 인식할 때에 수행될 합성곱 연산에 대해서는, 직접 합성곱 연산을 수행하는 대신, 상기 연산 테이블로부터 기 수행된 합성곱 연산의 결과만을 획득함으로써, 연산의 부담을 대폭 줄일 수 있다.The convolution operation includes multiplication between each element of each sub-matrix 240 and
한편, 상기 연산 테이블에는 어떤 하나의 부분 행렬(240)과 특징 추출 필터(250) 간의 합성곱 연산 결과가 전체로서 저장될 수도 있지만, 특징 추출 필터(250)의 특정 행(혹은 특정 열)과, 상기 특정 행(혹은 특정 열)에 대응되는 부분 행렬의 행(혹은 열) 간의 합성곱 연산 결과가 저장될 수도 있다. 예컨대, 도 4에서 특징 추출 필터(250)의 첫 번째 행인 (239, 94, 241)과 부분 행렬(240)의 첫 번째 행인 (6, 6, 6)의 합성곱 연산(실질적으로는 두 행 벡터의 내적) 결과가 저장될 수 있으며, 마찬가지로 특징 추출 필터(250)과 부분 행렬(240)의 두 번째 행끼리의 합성곱 연산 결과와 세 번째 행끼리의 합성곱 연산 결과도 각각 따로 저장될 수 있다.On the other hand, in the operation table, the result of the convolution operation between any one
이와 같이 특징 추출 필터(250)를 행 혹은 열 단위로 분해(decomposition)함으로써, 연산 결과를 보다 세분화하여 저장할 수 있다. 특징 추출 필터(250)를 어느 정도의 크기로 분해하는가에 따라 연산 테이블에 포함된 데이터의 양이 달라질 수 있기 때문에, 특징 추출 필터(250)의 분해 기준 역시 신경망 모델 생성 과정에서 적절히 최적화될 수 있다.In this way, the decomposition of the
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델의 활용 방법의 각 단계를 도시한 도면이다. 도 5의 방법은 도 1을 참조하여 설명한 서버 장치(100)에 의해 수행될 수 있다. 단, 도 5에 도시된 방법은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 불과하므로 도 5에 의해 본 발명의 사상이 한정 해석되는 것은 아니며, 도 5에 도시된 방법의 각 단계는 경우에 따라 도면에 제시된 바와 그 순서를 달리하여 수행될 수 있음은 물론이다. 또한, 도 1 내지 4와 중복되는 바에 대해서는 자세한 설명이 생략될 수 있다.5 is a diagram illustrating each step of a method of utilizing a neural network model to which computational acceleration is applied according to an embodiment of the present invention. The method of FIG. 5 may be performed by the
우선 데이터 분할부(120)는 입력부(110)에 의해 획득된 인식 대상 데이터를 대상 단위 데이터로 분할할 수 있다(S210). 그리고, 데이터 변환부(180)는 사전을 참고하여 각 대상 단위 데이터에 대한 분류 및 변환 데이터로의 변환을 수행할 수 있다(S220). 구체적으로, 데이터 변환부(180)는 각 대상 단위 데이터를 복수의 그룹 중 하나의 그룹에 속하도록 분류하고, 상기 복수의 그룹 중 같은 그룹에 속하는 대상 단위 데이터를 동일한 값을 갖는 변환 데이터로 변환할 수 있다. 이와 같은 분류 및 변환에는 데이터베이스(170)에 저장된 사전이 이용될 수 있으며, 이로써 인식 대상 데이터에도 학습용 데이터와 같은 기준의 전처리가 수행될 수 있다.First, the
다음으로, 대상 인식부(190)는 상기 대상 단위 데이터에 대한 합성곱 연산의 결과를 도출하여(S230), 인식 대상 데이터에 대한 인식 결과를 생성할 수 있다(S240). 요컨대, 대상 인식부(190)는 신경망 모델을 이용하여 인식 대상 데이터의 인식을 수행할 수 있는 것이다. 보다 구체적으로, 대상 인식부(190)는 상기 신경망 모델에 상기 각 대상 단위 데이터가 변환되어 생성된 각 변환 데이터로 구성된 대상 데이터 행렬을 입력할 경우의 출력에 기초하여 상기 인식을 수행할 수 있다.Next, the
다만, 전술한 바와 같이 대상 인식부(190)는 합성곱 연산을 일일이 수행하는 대신, 대상 데이터 행렬의 일부인 대상 부분 행렬과 동일한 원소를 갖는 행렬과 특징 추출 필터(250) 간에 기 수행된 합성곱 연산의 결과가 기 저장된 연산 테이블로부터 상기 대상 부분 행렬과 특징 추출 필터(250) 간의 합성곱 연산의 결과만을 추출하여 사용할 수 있다. 즉, 대상 부분 행렬의 각 원소와 특징 추출 필터(250)의 각 원소끼리의 곱셈 및 곱셈 결과에 대한 덧셈을 일일이 수행하지 않고도 합성곱 연산의 결과를 연산 테이블을 통해 쉽게 얻음으로써, 획기적인 연산 가속화가 달성될 수 있다.However, as described above, the
아울러, 상기 신경망 모델을 이용한 인식 과정에서는, 합성곱 연산의 결과 도출 이후에도 맥스 풀링(max pooling), 신경망을 통한 분류(classification) 등의 세부 과정이 수행될 수 있으며, 이에 대해서는 통상의 기술자에게 용이한 것이므로 자세한 설명은 생략한다.In addition, in the recognition process using the neural network model, detailed processes such as max pooling and classification through a neural network may be performed even after deriving the result of the convolution operation, which is easy for a person skilled in the art. Because it is, detailed description is omitted.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델의 활용 방법의 효과를 설명하기 위한 도면이다. 인식 대상 데이터로부터 생성된 대상 데이터 행렬(260)의 행의 개수를 Hseq, 열의 개수를 Wseq라 하도록 한다. 그리고 특징 추출 필터(250)는 크기(즉, 정사각 행렬에서의 행 혹은 열의 개수)별로 다양하게 마련될 수 있는데, 같은 크기(fn)를 갖는 특징 추출 필터(250)의 개수는 Nfilter라 하고, 이러한 특징 추출 필터(250)를 1 x fn 크기를 갖는 fn개의 필터로 분리하였다고 가정하도록 한다. 이 때, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 의해 줄어들게 되는 덧셈 연산의 횟수는 아래 수학식 1과 같다.6 is a view for explaining the effect of a method of utilizing a neural network model to which computational acceleration is applied according to an embodiment of the present invention. Let the number of rows of the
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 의해 줄어들게 되는 곱셈 연산의 횟수는 아래 수학식 2와 같다.In addition, the number of multiplication operations reduced by an embodiment of the present invention is as shown in Equation 2 below.
상기 수학식 1 및 2를 통해, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 의하면 비약적인 연산량 감소의 효과를 달성할 수 있다는 결론을 얻을 수 있다.Through Equations 1 and 2, it can be concluded that according to an embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to achieve an effect of dramatically reducing computational complexity.
지금까지 설명한 바와 같은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 합성곱 신경망이 적용된 특징 모델을 이용하여 인식 대상 데이터를 인식하는 과정에서의 연산의 중복 수행이 방지될 수 있으며, 이에 따라 연산량이 획기적으로 줄어들어 상기 신경망 모델을 이용하는 시스템의 효율이 증대될 수 있다. 특히 본 발명의 일 실시예에서는, 영상 데이터와 같이 입력 데이터의 양 및 가짓수가 매우 많은 경우에 있어서도, 전술한 전처리 과정을 통해 입력 데이터의 양 및 가짓수를 합리적인 수준으로 줄임으로써, 인식 과정에서의 효율성 증대 및 저장 공간의 절약 등의 효과를 달성할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention as described so far, it is possible to prevent duplication of operations in the process of recognizing data to be recognized using a feature model to which a convolutional neural network is applied, and accordingly, the amount of computation is significantly reduced. The efficiency of the system using the neural network model can be increased. In particular, in one embodiment of the present invention, even in a case where the amount and the number of input data are very large, such as image data, the efficiency in the recognition process is reduced by reducing the amount and the number of input data to a reasonable level through the aforementioned pre-processing process. Effects such as increase and saving of storage space can be achieved.
본 발명에 첨부된 블록도의 각 블록과 흐름도의 각 단계의 조합들은 컴퓨터 프로그램 인스트럭션들에 의해 수행될 수도 있다. 이들 컴퓨터 프로그램 인스트럭션들은 범용 컴퓨터, 특수용 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비의 인코딩 프로세서에 탑재될 수 있으므로, 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비의 인코딩 프로세서를 통해 수행되는 그 인스트럭션들이 블록도의 각 블록 또는 흐름도의 각 단계에서 설명된 기능들을 수행하는 수단을 생성하게 된다. 이들 컴퓨터 프로그램 인스트럭션들은 특정 방법으로 기능을 구현하기 위해 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비를 지향할 수 있는 컴퓨터 이용 가능 또는 컴퓨터 판독 가능 메모리에 저장되는 것도 가능하므로, 그 컴퓨터 이용가능 또는 컴퓨터 판독 가능 메모리에 저장된 인스트럭션들은 블록도의 각 블록 또는 흐름도 각 단계에서 설명된 기능을 수행하는 인스트럭션 수단을 내포하는 제조 품목을 생산하는 것도 가능하다. 컴퓨터 프로그램 인스트럭션들은 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비 상에 탑재되는 것도 가능하므로, 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비 상에서 일련의 동작 단계들이 수행되어 컴퓨터로 실행되는 프로세스를 생성해서 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비를 수행하는 인스트럭션들은 블록도의 각 블록 및 흐름도의 각 단계에서 설명된 기능들을 실행하기 위한 단계들을 제공하는 것도 가능하다.Combinations of each block in the block diagrams and respective steps in the flow diagrams attached to the present invention may be performed by computer program instructions. These computer program instructions may be mounted on an encoding processor of a general purpose computer, special purpose computer, or other programmable data processing equipment, so that the instructions performed through the encoding processor of a computer or other programmable data processing equipment may include each block in the block diagram or In each step of the flowchart, means are created to perform the functions described. These computer program instructions can also be stored in computer readable or computer readable memory that can be oriented to a computer or other programmable data processing equipment to implement a function in a particular way, so that computer readable or computer readable memory The instructions stored in it are also possible to produce an article of manufacture containing instructions means for performing the functions described in each block or flowchart step of the block diagram. Since computer program instructions may be mounted on a computer or other programmable data processing equipment, a series of operational steps are performed on the computer or other programmable data processing equipment to create a process that is executed by the computer to generate a computer or other programmable data. It is also possible for instructions to perform processing equipment to provide steps for executing the functions described in each block of the block diagram and in each step of the flowchart.
또한, 각 블록 또는 각 단계는 특정된 논리적 기능(들)을 실행하기 위한 하나 이상의 실행 가능한 인스트럭션들을 포함하는 모듈, 세그먼트 또는 코드의 일부를 나타낼 수 있다. 또, 몇 가지 대체 실시예들에서는 블록들 또는 단계들에서 언급된 기능들이 순서를 벗어나서 발생하는 것도 가능함을 주목해야 한다. 예컨대, 잇달아 도시되어 있는 두 개의 블록들 또는 단계들은 사실 실질적으로 동시에 수행되는 것도 가능하고 또는 그 블록들 또는 단계들이 때때로 해당하는 기능에 따라 역순으로 수행되는 것도 가능하다.Further, each block or each step may represent a module, segment, or portion of code that includes one or more executable instructions for executing the specified logical function (s). It should also be noted that in some alternative embodiments it is also possible that the functions mentioned in blocks or steps occur out of order. For example, two blocks or steps shown in succession may in fact be executed substantially simultaneously, or it is also possible that the blocks or steps are sometimes performed in reverse order depending on the corresponding function.
이상의 설명은 본 발명의 기술 사상을 예시적으로 설명한 것에 불과한 것으로서, 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 본 발명의 본질적인 품질에서 벗어나지 않는 범위에서 다양한 수정 및 변형이 가능할 것이다. 따라서, 본 발명에 개시된 실시예들은 본 발명의 기술 사상을 한정하기 위한 것이 아니라 설명하기 위한 것이고, 이러한 실시예에 의하여 본 발명의 기술 사상의 범위가 한정되는 것은 아니다. 본 발명의 보호 범위는 아래의 청구범위에 의하여 해석되어야 하며, 그와 균등한 범위 내에 있는 모든 기술사상은 본 발명의 권리범위에 포함되는 것으로 해석되어야 할 것이다.The above description is merely illustrative of the technical spirit of the present invention, and those of ordinary skill in the art to which the present invention pertains will be capable of various modifications and variations without departing from the essential quality of the present invention. Therefore, the embodiments disclosed in the present invention are not intended to limit the technical spirit of the present invention, but to explain, and the scope of the technical spirit of the present invention is not limited by these embodiments. The scope of protection of the present invention should be interpreted by the following claims, and all technical ideas within the scope equivalent thereto should be interpreted as being included in the scope of the present invention.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 합성곱 신경망이 적용된 특징 모델을 이용하여 인식 대상 데이터를 인식하는 과정에서의 연산의 중복 수행이 방지될 수 있으며, 이에 따라 연산량이 획기적으로 줄어들 수 있다. 또한, 상기 연산 테이블과 같은 시스템에 저장되어야 하는 정보의 양이 감소될 수 있으며, 신경망 모델의 생성 및 활용에 있어서의 효율이 크게 향상될 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, redundant execution of an operation in a process of recognizing data to be recognized may be prevented by using a feature model to which a convolutional neural network is applied, and accordingly, the computational amount may be significantly reduced. In addition, the amount of information to be stored in the system such as the operation table can be reduced, and the efficiency in generating and using a neural network model can be greatly improved.
100: 서버 장치
110: 입력부
120: 데이터 분할부
130: 전처리부
140: 모델 생성부
150: 사전 생성부
160: 테이블 생성부
170: 데이터베이스
180: 데이터 변환부
190: 대상 인식부100: server device
110: input unit
120: data division
130: pre-processing unit
140: model generation unit
150: dictionary generation unit
160: table creation unit
170: database
180: data conversion unit
190: target recognition unit
Claims (13)
Translated fromKorean상기 각 단위 데이터를, 소정의 분류 기준에 따라 복수의 그룹 중 하나의 그룹에 속하도록 분류하고, 상기 복수의 그룹 중 같은 그룹에 속하는 단위 데이터를 동일한 값을 갖는 변환 데이터로 변환하는 전처리부;
상기 변환 데이터로 구성된 데이터 행렬(matrix)에, 소정의 차원(dimension)을 갖는 행렬인 특징 추출 필터를 적용하여 합성곱(convolution) 연산을 수행한 결과 및 상기 학습용 데이터에 포함된 정보 간의 관계에 기초하여 신경망 모델을 생성하는 모델 생성부; 및
상기 데이터 행렬의 일부인 부분 행렬과, 상기 합성곱 연산 중 상기 부분 행렬에 대해 수행된 연산의 결과가 서로 매칭되어 저장됨으로써, 상기 신경망 모델을 통해 상기 학습용 데이터와는 다른 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 정보를 인식하는 데 이용되는 연산 테이블을 생성하는 테이블 생성부를 포함하는
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 생성하는 서버 장치.A data division unit for dividing the learning data into a plurality of unit data;
A pre-processing unit for classifying the unit data to belong to one of a plurality of groups according to a predetermined classification criterion, and converting unit data belonging to the same group among the plurality of groups into conversion data having the same value;
Based on the relationship between the result of performing a convolution operation by applying a feature extraction filter, which is a matrix having a predetermined dimension, to a data matrix composed of the transformed data and information included in the training data A model generator for generating a neural network model; And
The partial matrix which is a part of the data matrix and the result of the operation performed on the partial matrix among the convolution operations are matched and stored, so that information included in data to be recognized different from the training data through the neural network model is stored. It includes a table generator for generating a calculation table used to recognize
A server device that generates a neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
상기 학습용 데이터는, 영상(image) 데이터이며,
상기 데이터 분할부는, 상기 학습용 데이터의 하나의 픽셀(pixel)의 정보가 하나의 단위 데이터를 이루도록 상기 학습용 데이터를 분할하는
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 생성하는 서버 장치.According to claim 1,
The learning data is image data,
The data division unit divides the learning data so that information of one pixel of the learning data forms one unit data.
A server device that generates a neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
상기 전처리부는, 상기 학습용 데이터의 픽셀이 픽셀 값으로 가질 수 있는 수치의 범위를 복수의 구간으로 분할하고, 상기 학습용 데이터의 각 픽셀의 픽셀 값이 상기 복수의 구간 중 어느 구간에 속하는지에 기초하여 상기 각 단위 데이터를 분류하는
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 생성하는 서버 장치.According to claim 2,
The pre-processing unit divides a range of numerical values that a pixel of the learning data can have as a pixel value into a plurality of sections, and based on which section of the plurality of sections the pixel value of each pixel of the training data belongs to To classify each unit data
A server device that generates a neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
상기 전처리부는, 상기 학습용 데이터의 각 픽셀에 대해, 서로 다른 색상에 관한 두 종류 이상의 픽셀 값을 평균한 값을 산출한 결과에 기초하여 상기 각 단위 데이터를 분류하는
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 생성하는 서버 장치.According to claim 2,
The pre-processing unit classifies each unit data based on a result of calculating an average value of two or more types of pixel values for different colors for each pixel of the learning data.
A server device that generates a neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
상기 평균한 값은, 상기 픽셀 값의 종류별로 정해지는 가중치에 따라 가중평균(weighted mean)된 값인
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 생성하는 서버 장치.The method of claim 4,
The averaged value is a weighted mean value according to a weight determined for each type of the pixel value.
A server device that generates a neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
상기 부분 행렬은, 상기 특징 추출 필터와 같은 차원을 가지며,
상기 합성곱 연산 중 상기 부분 행렬에 대해 수행된 연산의 결과는, 상기 부분 행렬의 각 원소에 상기 특징 추출 필터에서 대응되는 위치의 원소를 곱한 결과를 모두 더함으로써 산출되는
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 생성하는 서버 장치.According to claim 1,
The sub-matrix has the same dimension as the feature extraction filter,
The result of the operation performed on the sub-matrix of the convolution operation is calculated by adding all the elements of the sub-matrix multiplied by the element at the corresponding position in the feature extraction filter.
A server device that generates a neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
상기 각 단위 데이터와 상기 각 변환 데이터 간의 변환 기준이 저장된 사전을 생성하는 사전 생성부를 더 포함하며,
상기 변환 기준은, 상기 복수의 그룹 중 상이한 그룹에 속한 단위 데이터는 상이한 변환 데이터로 변환되도록 정의되는
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 생성하는 서버 장치.According to claim 1,
Further comprising a dictionary generating unit for generating a dictionary storing the conversion criteria between each of the unit data and each of the conversion data,
The conversion criterion is defined such that unit data belonging to different groups among the plurality of groups are converted into different conversion data.
A server device that generates a neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
상기 데이터 분할부는, 상기 인식 대상 데이터를, 소정의 분할 기준에 따라 복수의 대상 단위 데이터로 분할하며,
상기 서버 장치는,
상기 각 대상 단위 데이터를, 상기 사전에 저장된 상기 변환 기준에 기초하여 상기 변환 데이터 중 어느 하나로 각각 변환하는 데이터 변환부; 및
상기 인식 대상 데이터로부터 생성된 각 변환 데이터로 구성된 대상 데이터 행렬을 상기 신경망 모델에 입력할 경우의 출력에 기초하여 상기 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 정보를 인식하되, 상기 대상 데이터 행렬에 대해 상기 특징 추출 필터를 적용할 경우 수행될 합성곱 연산의 결과를 상기 연산 테이블로부터 획득하는 대상 인식부를 더 포함하는
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 생성하는 서버 장치.The method of claim 7,
The data division unit divides the recognition target data into a plurality of target unit data according to a predetermined division criterion,
The server device,
A data conversion unit for converting the respective target unit data into any one of the conversion data based on the conversion criteria stored in the dictionary; And
Based on the output when inputting the target data matrix composed of each transformed data generated from the target data to the neural network model, information included in the target data is recognized, and the feature extraction filter is applied to the target data matrix When applying a further comprising a target recognition unit for obtaining the result of the convolution operation to be performed from the operation table
A server device that generates a neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
상기 각 대상 단위 데이터를, 소정의 분류 기준에 따라 복수의 그룹 중 하나의 그룹에 속하도록 분류하고, 상기 복수의 그룹 중 같은 그룹에 속하는 대상 단위 데이터를 동일한 값을 갖는 변환 데이터로 변환하는 데이터 변환부; 및
상기 변환 데이터로 구성된 대상 데이터 행렬에, 소정의 차원을 갖는 행렬인 특징 추출 필터를 적용하여 상기 인식 대상 데이터의 특징을 추출함으로써 상기 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 정보를 인식하되, 상기 대상 데이터 행렬의 일부인 대상 부분 행렬과 동일한 원소를 갖는 행렬과 상기 특징 추출 필터 간에 기 수행된 합성곱 연산의 결과가 기 저장된 연산 테이블로부터 상기 대상 부분 행렬과 상기 특징 추출 필터 간의 합성곱 연산의 결과를 획득하는 대상 인식부를 포함하는
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 이용하는 서버 장치.A data division unit for dividing the recognition target data into a plurality of target unit data according to a predetermined division criterion;
Data conversion for classifying the target unit data to belong to one of a plurality of groups according to a predetermined classification criterion, and converting the target unit data belonging to the same group among the plurality of groups into conversion data having the same value part; And
Recognizing information included in the recognition target data by applying a feature extraction filter, which is a matrix having a predetermined dimension, to a target data matrix composed of the transformed data, and extracting features of the recognition target data, but which is a part of the target data matrix. A target recognition unit that obtains a result of a convolution operation between the target sub-matrix and the feature extraction filter from an operation table in which a result of a pre-combined convolution operation between a matrix having the same element as a target sub-matrix and the feature extraction filter is pre-stored. Containing
Server device using neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
상기 부분 행렬은, 상기 특징 추출 필터와 같은 차원을 가지며,
상기 대상 부분 행렬과 상기 특징 추출 필터 간의 합성곱 연산은, 상기 대상 부분 행렬의 각 원소에 상기 특징 추출 필터에서 대응되는 위치의 원소를 곱한 결과를 모두 더하는 연산인
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 이용하는 서버 장치.The method of claim 9,
The sub-matrix has the same dimension as the feature extraction filter,
The convergence operation between the target sub-matrix and the feature extraction filter is an operation of adding all the results of multiplying each element of the target sub-matrix by the element at a corresponding position in the feature extraction filter.
Server device using neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
상기 데이터 변환부는, 상기 대상 단위 데이터와 상기 변환 데이터 간의 변환 기준이 기 저장된 사전을 이용하여 상기 각 대상 단위 데이터에 대한 변환을 수행하는
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 이용하는 서버 장치.The method of claim 9,
The data conversion unit performs conversion on each target unit data using a dictionary in which a conversion criterion between the target unit data and the conversion data is previously stored.
Server device using neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
학습용 데이터를 복수의 단위 데이터로 분할하는 단계;
상기 각 단위 데이터를, 소정의 분류 기준에 따라 복수의 그룹 중 하나의 그룹에 속하도록 분류하고, 상기 복수의 그룹 중 같은 그룹에 속하는 단위 데이터를 동일한 값을 갖는 변환 데이터로 변환하는 단계;
상기 변환 데이터로 구성된 데이터 행렬에, 소정의 차원을 갖는 행렬인 특징 추출 필터를 적용하여 합성곱 연산을 수행한 결과 및 상기 학습용 데이터에 포함된 정보 간의 관계에 기초하여 신경망 모델을 생성하는 단계; 및
상기 데이터 행렬의 일부인 부분 행렬과, 상기 합성곱 연산 중 상기 부분 행렬에 대해 수행된 연산의 결과가 서로 매칭되어 저장됨으로써, 상기 신경망 모델을 통해 상기 학습용 데이터와는 다른 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 정보를 인식하는 데 이용되는 연산 테이블을 생성하는 단계를 포함하는
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 생성하기 위한 방법.In the method for generating a neural network model is applied to the computational acceleration performed by the server device,
Dividing the learning data into a plurality of unit data;
Classifying each unit data to belong to one group of a plurality of groups according to a predetermined classification criterion, and converting unit data belonging to the same group among the plurality of groups into conversion data having the same value;
Generating a neural network model based on a relationship between a result of performing a multiplication operation by applying a feature extraction filter, which is a matrix having a predetermined dimension, to a data matrix composed of the transformed data and information included in the learning data; And
The partial matrix which is a part of the data matrix and the result of the operation performed on the partial matrix among the convolution operations are matched and stored, so that information included in data to be recognized different from the training data through the neural network model is stored. Generating an operation table used to recognize
Method for generating neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
인식 대상 데이터를, 소정의 분할 기준에 따라 복수의 대상 단위 데이터로 분할하는 단계;
상기 각 대상 단위 데이터를, 소정의 분류 기준에 따라 복수의 그룹 중 하나의 그룹에 속하도록 분류하고, 상기 복수의 그룹 중 같은 그룹에 속하는 대상 단위 데이터를 동일한 값을 갖는 변환 데이터로 변환하는 단계; 및
상기 변환 데이터로 구성된 대상 데이터 행렬에, 소정의 차원을 갖는 행렬인 특징 추출 필터를 적용하여 상기 인식 대상 데이터의 특징을 추출함으로써 상기 인식 대상 데이터에 포함된 정보를 인식하되, 상기 대상 데이터 행렬의 일부인 대상 부분 행렬과 동일한 원소를 갖는 행렬과 상기 특징 추출 필터 간에 기 수행된 합성곱 연산의 결과가 기 저장된 연산 테이블로부터 상기 대상 부분 행렬과 상기 특징 추출 필터 간의 합성곱 연산의 결과를 획득하는 단계를 포함하는
연산 가속화가 적용된 신경망 모델을 이용한 데이터 인식 방법.In the data recognition method using the neural network model to which the computational acceleration performed by the server device is applied,
Dividing the recognition target data into a plurality of target unit data according to a predetermined division criterion;
Classifying each target unit data to belong to one group of a plurality of groups according to a predetermined classification criterion, and converting target unit data belonging to the same group among the plurality of groups into conversion data having the same value; And
The information included in the recognition object data is recognized by applying a feature extraction filter, which is a matrix having a predetermined dimension, to the object data matrix composed of the transformed data to extract the features of the recognition object data. Obtaining a result of a convolution operation between the target sub-matrix and the feature extraction filter from an operation table in which a result of a pre-combined convolution operation between a matrix having the same element as a target sub-matrix and the feature extraction filter is pre-stored. doing
Data recognition method using neural network model with computational acceleration applied.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170152180AKR102095335B1 (en) | 2017-11-15 | 2017-11-15 | Apparatus and method for generating and using neural network model applying accelerated computation |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170152180AKR102095335B1 (en) | 2017-11-15 | 2017-11-15 | Apparatus and method for generating and using neural network model applying accelerated computation |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020200031002ADivisionKR102227437B1 (en) | 2020-03-12 | 2020-03-12 | Apparatus and method for generating and using neural network model applying accelerated computation |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20190055447A KR20190055447A (en) | 2019-05-23 |
| KR102095335B1true KR102095335B1 (en) | 2020-03-31 |
Family
ID=66681240
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170152180AActiveKR102095335B1 (en) | 2017-11-15 | 2017-11-15 | Apparatus and method for generating and using neural network model applying accelerated computation |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102095335B1 (en) |
Cited By (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102236615B1 (en) | 2020-07-31 | 2021-04-06 | 주식회사 웨이센 | Neural network model learning method and apparatus for complex characteristic classification and common localization |
| KR102243125B1 (en) | 2020-07-31 | 2021-04-22 | 주식회사 웨이센 | Method and apparatus for classifying complex characteristics of images using neural network model |
| KR20220018336A (en)* | 2020-08-06 | 2022-02-15 | 주식회사 영국전자 | Method of spectrum-space generation for image recognition |
| US11403069B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2022-08-02 | Tesla, Inc. | Accelerated mathematical engine |
| US11409692B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2022-08-09 | Tesla, Inc. | Vector computational unit |
| US11487288B2 (en) | 2017-03-23 | 2022-11-01 | Tesla, Inc. | Data synthesis for autonomous control systems |
| US11537811B2 (en) | 2018-12-04 | 2022-12-27 | Tesla, Inc. | Enhanced object detection for autonomous vehicles based on field view |
| US11562231B2 (en) | 2018-09-03 | 2023-01-24 | Tesla, Inc. | Neural networks for embedded devices |
| US11561791B2 (en) | 2018-02-01 | 2023-01-24 | Tesla, Inc. | Vector computational unit receiving data elements in parallel from a last row of a computational array |
| US11567514B2 (en) | 2019-02-11 | 2023-01-31 | Tesla, Inc. | Autonomous and user controlled vehicle summon to a target |
| US11610117B2 (en) | 2018-12-27 | 2023-03-21 | Tesla, Inc. | System and method for adapting a neural network model on a hardware platform |
| US11636333B2 (en) | 2018-07-26 | 2023-04-25 | Tesla, Inc. | Optimizing neural network structures for embedded systems |
| US11665108B2 (en) | 2018-10-25 | 2023-05-30 | Tesla, Inc. | QoS manager for system on a chip communications |
| US11681649B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2023-06-20 | Tesla, Inc. | Computational array microprocessor system using non-consecutive data formatting |
| US11734562B2 (en) | 2018-06-20 | 2023-08-22 | Tesla, Inc. | Data pipeline and deep learning system for autonomous driving |
| US11748620B2 (en) | 2019-02-01 | 2023-09-05 | Tesla, Inc. | Generating ground truth for machine learning from time series elements |
| US11790664B2 (en) | 2019-02-19 | 2023-10-17 | Tesla, Inc. | Estimating object properties using visual image data |
| US11816585B2 (en) | 2018-12-03 | 2023-11-14 | Tesla, Inc. | Machine learning models operating at different frequencies for autonomous vehicles |
| US11841434B2 (en) | 2018-07-20 | 2023-12-12 | Tesla, Inc. | Annotation cross-labeling for autonomous control systems |
| US11893393B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2024-02-06 | Tesla, Inc. | Computational array microprocessor system with hardware arbiter managing memory requests |
| US11893774B2 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2024-02-06 | Tesla, Inc. | Systems and methods for training machine models with augmented data |
| US12014553B2 (en) | 2019-02-01 | 2024-06-18 | Tesla, Inc. | Predicting three-dimensional features for autonomous driving |
| US12307350B2 (en) | 2018-01-04 | 2025-05-20 | Tesla, Inc. | Systems and methods for hardware-based pooling |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102372869B1 (en) | 2019-07-31 | 2022-03-08 | 한양대학교 산학협력단 | Matrix operator and matrix operation method for artificial neural network |
| CN112434781B (en)* | 2019-08-26 | 2024-09-10 | 上海寒武纪信息科技有限公司 | Method, apparatus and related products for processing data |
| CN113837923B (en)* | 2021-09-26 | 2024-08-06 | 安徽寒武纪信息科技有限公司 | Data processing device, data processing method and related products |
| CN118862963B (en)* | 2024-09-25 | 2025-01-21 | 杭州海康威视数字技术股份有限公司 | A data processing method, device and equipment |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10387773B2 (en)* | 2014-10-27 | 2019-08-20 | Ebay Inc. | Hierarchical deep convolutional neural network for image classification |
| EP3035204B1 (en)* | 2014-12-19 | 2018-08-15 | Intel Corporation | Storage device and method for performing convolution operations |
| KR101719278B1 (en) | 2015-04-14 | 2017-04-04 | (주)한국플랫폼서비스기술 | Deep learnig framework and image recognition method for content-based visual image recognition |
- 2017
- 2017-11-15KRKR1020170152180Apatent/KR102095335B1/enactiveActive
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| Aravind Vasudevan 외 2명. Parallel Multi Channel Convolution using General Matrix Multiplication. 2017.7.3. |
| Caiwen Ding 외 15명. CirCNN: Accelerating and Compressing Deep Neural Networks Using Block-Circulant Weight Matrices. 2017.8.29. |
Cited By (38)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11487288B2 (en) | 2017-03-23 | 2022-11-01 | Tesla, Inc. | Data synthesis for autonomous control systems |
| US12020476B2 (en) | 2017-03-23 | 2024-06-25 | Tesla, Inc. | Data synthesis for autonomous control systems |
| US11681649B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2023-06-20 | Tesla, Inc. | Computational array microprocessor system using non-consecutive data formatting |
| US12216610B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2025-02-04 | Tesla, Inc. | Computational array microprocessor system using non-consecutive data formatting |
| US12086097B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2024-09-10 | Tesla, Inc. | Vector computational unit |
| US11403069B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2022-08-02 | Tesla, Inc. | Accelerated mathematical engine |
| US11409692B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2022-08-09 | Tesla, Inc. | Vector computational unit |
| US11893393B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2024-02-06 | Tesla, Inc. | Computational array microprocessor system with hardware arbiter managing memory requests |
| US12307350B2 (en) | 2018-01-04 | 2025-05-20 | Tesla, Inc. | Systems and methods for hardware-based pooling |
| US11797304B2 (en) | 2018-02-01 | 2023-10-24 | Tesla, Inc. | Instruction set architecture for a vector computational unit |
| US11561791B2 (en) | 2018-02-01 | 2023-01-24 | Tesla, Inc. | Vector computational unit receiving data elements in parallel from a last row of a computational array |
| US11734562B2 (en) | 2018-06-20 | 2023-08-22 | Tesla, Inc. | Data pipeline and deep learning system for autonomous driving |
| US11841434B2 (en) | 2018-07-20 | 2023-12-12 | Tesla, Inc. | Annotation cross-labeling for autonomous control systems |
| US11636333B2 (en) | 2018-07-26 | 2023-04-25 | Tesla, Inc. | Optimizing neural network structures for embedded systems |
| US12079723B2 (en) | 2018-07-26 | 2024-09-03 | Tesla, Inc. | Optimizing neural network structures for embedded systems |
| US12346816B2 (en) | 2018-09-03 | 2025-07-01 | Tesla, Inc. | Neural networks for embedded devices |
| US11983630B2 (en) | 2018-09-03 | 2024-05-14 | Tesla, Inc. | Neural networks for embedded devices |
| US11562231B2 (en) | 2018-09-03 | 2023-01-24 | Tesla, Inc. | Neural networks for embedded devices |
| US11893774B2 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2024-02-06 | Tesla, Inc. | Systems and methods for training machine models with augmented data |
| US11665108B2 (en) | 2018-10-25 | 2023-05-30 | Tesla, Inc. | QoS manager for system on a chip communications |
| US12367405B2 (en) | 2018-12-03 | 2025-07-22 | Tesla, Inc. | Machine learning models operating at different frequencies for autonomous vehicles |
| US11816585B2 (en) | 2018-12-03 | 2023-11-14 | Tesla, Inc. | Machine learning models operating at different frequencies for autonomous vehicles |
| US12198396B2 (en) | 2018-12-04 | 2025-01-14 | Tesla, Inc. | Enhanced object detection for autonomous vehicles based on field view |
| US11537811B2 (en) | 2018-12-04 | 2022-12-27 | Tesla, Inc. | Enhanced object detection for autonomous vehicles based on field view |
| US11908171B2 (en) | 2018-12-04 | 2024-02-20 | Tesla, Inc. | Enhanced object detection for autonomous vehicles based on field view |
| US12136030B2 (en) | 2018-12-27 | 2024-11-05 | Tesla, Inc. | System and method for adapting a neural network model on a hardware platform |
| US11610117B2 (en) | 2018-12-27 | 2023-03-21 | Tesla, Inc. | System and method for adapting a neural network model on a hardware platform |
| US12014553B2 (en) | 2019-02-01 | 2024-06-18 | Tesla, Inc. | Predicting three-dimensional features for autonomous driving |
| US12223428B2 (en) | 2019-02-01 | 2025-02-11 | Tesla, Inc. | Generating ground truth for machine learning from time series elements |
| US11748620B2 (en) | 2019-02-01 | 2023-09-05 | Tesla, Inc. | Generating ground truth for machine learning from time series elements |
| US12164310B2 (en) | 2019-02-11 | 2024-12-10 | Tesla, Inc. | Autonomous and user controlled vehicle summon to a target |
| US11567514B2 (en) | 2019-02-11 | 2023-01-31 | Tesla, Inc. | Autonomous and user controlled vehicle summon to a target |
| US11790664B2 (en) | 2019-02-19 | 2023-10-17 | Tesla, Inc. | Estimating object properties using visual image data |
| US12236689B2 (en) | 2019-02-19 | 2025-02-25 | Tesla, Inc. | Estimating object properties using visual image data |
| KR102236615B1 (en) | 2020-07-31 | 2021-04-06 | 주식회사 웨이센 | Neural network model learning method and apparatus for complex characteristic classification and common localization |
| KR102243125B1 (en) | 2020-07-31 | 2021-04-22 | 주식회사 웨이센 | Method and apparatus for classifying complex characteristics of images using neural network model |
| KR102387437B1 (en)* | 2020-08-06 | 2022-04-15 | 주식회사 영국전자 | Method of spectrum-space generation for image recognition |
| KR20220018336A (en)* | 2020-08-06 | 2022-02-15 | 주식회사 영국전자 | Method of spectrum-space generation for image recognition |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20190055447A (en) | 2019-05-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102095335B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for generating and using neural network model applying accelerated computation | |
| Zhou et al. | Contextual ensemble network for semantic segmentation | |
| TWI806134B (en) | Method and system for hierarchical weight-sparse convolution processing and related non-transitory computer-readable storage medium | |
| Noman et al. | ELGC-Net: Efficient local–global context aggregation for remote sensing change detection | |
| CN107871306B (en) | A method and device for image denoising | |
| Carlucci et al. | $^ 2$ CO: Deep depth colorization | |
| JP4567660B2 (en) | A method for determining a segment of an object in an electronic image. | |
| CN106296681B (en) | A collaborative learning saliency detection method based on two-channel low-rank decomposition | |
| CN109886391B (en) | A Neural Network Compression Method Based on Spatial Forward and Anti-diagonal Convolution | |
| ES2284478T3 (en) | PROCEDURE AND APPARATUS FOR THE TREATMENT OF COLOR IMAGES. | |
| CN104966054B (en) | Detection method of small target in unmanned plane visible images | |
| KR20190140527A (en) | Method and apparatuis for acquaring feature data | |
| CN107480720B (en) | Human body posture model training method and device | |
| JP2016520897A (en) | System and method for describing an image outline | |
| JP7282474B2 (en) | Encryption mask determination method, encryption mask determination device, electronic device, storage medium, and computer program | |
| KR20210048281A (en) | Apparatus and method for generating video with background removed | |
| US20240104913A1 (en) | Extracting features from sensor data | |
| CN111667005A (en) | Human body interaction system adopting RGBD visual sensing | |
| CN112434731B (en) | Image recognition method, device and readable storage medium | |
| KR20200030524A (en) | Apparatus and method for generating and using neural network model applying accelerated computation | |
| CN112132253B (en) | 3D action recognition method, device, computer readable storage medium and equipment | |
| Wieluch et al. | Dropout induced noise for co-creative gan systems | |
| US20220270346A1 (en) | Image processing using self-attention | |
| KR20130132221A (en) | Method and apparatus for recognizing face | |
| KR100793285B1 (en) | Image noise elimination system, method and recording medium using filter matrix |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20171115 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20190722 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20191231 | |
| PA0107 | Divisional application | Comment text:Divisional Application of Patent Patent event date:20200312 Patent event code:PA01071R01D | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20200325 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20200326 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20241219 Start annual number:6 End annual number:6 |