KR102084948B1 - A super-water-repellent solution for fibers having a capability of preventing fine dust from being adsorbed and absorbed on a fabric, and a method for manufacturing an super-water-repellent fabric using the same - Google Patents
A super-water-repellent solution for fibers having a capability of preventing fine dust from being adsorbed and absorbed on a fabric, and a method for manufacturing an super-water-repellent fabric using the sameDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102084948B1 KR102084948B1KR1020190108734AKR20190108734AKR102084948B1KR 102084948 B1KR102084948 B1KR 102084948B1KR 1020190108734 AKR1020190108734 AKR 1020190108734AKR 20190108734 AKR20190108734 AKR 20190108734AKR 102084948 B1KR102084948 B1KR 102084948B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- repellent
- water
- fabric
- super
- acid
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000005871repellentSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription117
- 239000004744fabricSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription102
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription24
- 239000000835fiberSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription22
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription21
- 239000000428dustSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription18
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription54
- -1silicon alkoxideChemical class0.000claimsabstractdescription52
- 230000002940repellentEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription34
- 229910052782aluminiumInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription19
- 229910052710siliconInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription18
- 239000010703siliconSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription18
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription15
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription38
- 239000003795chemical substances by applicationSubstances0.000claimsdescription37
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-NMethanolChemical compoundOCOKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription30
- 239000002245particleSubstances0.000claimsdescription28
- 238000010306acid treatmentMethods0.000claimsdescription16
- 238000001035dryingMethods0.000claimsdescription14
- 238000004078waterproofingMethods0.000claimsdescription13
- BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-Nmethanoic acidNatural productsOC=OBDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription12
- 239000004094surface-active agentSubstances0.000claimsdescription12
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-NOxalic acidChemical compoundOC(=O)C(O)=OMUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription9
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncitric acidChemical compoundOC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=OKRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000claimsdescription9
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-LSulfateChemical compound[O-]S([O-])(=O)=OQAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000claimsdescription8
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000claimsdescription7
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000claimsdescription7
- 229910021645metal ionInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription7
- 238000003756stirringMethods0.000claimsdescription7
- 238000003860storageMethods0.000claimsdescription7
- OSWFIVFLDKOXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N4-(3-methoxyphenyl)anilineChemical compoundCOC1=CC=CC(C=2C=CC(N)=CC=2)=C1OSWFIVFLDKOXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-NAcetic acidChemical compoundCC(O)=OQTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-ND-gluconic acidChemical compoundOC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=ORGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-NPhosphoric acidChemical compoundOP(O)(O)=ONBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-NSulfuric acidChemical compoundOS(O)(=O)=OQAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000010521absorption reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000002253acidSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000003929acidic solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 235000019253formic acidNutrition0.000claimsdescription6
- 229920000858CyclodextrinPolymers0.000claimsdescription5
- SFNALCNOMXIBKG-UHFFFAOYSA-Nethylene glycol monododecyl etherChemical compoundCCCCCCCCCCCCOCCOSFNALCNOMXIBKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000010438heat treatmentMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000000944linseed oilSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 235000021388linseed oilNutrition0.000claimsdescription5
- HFHDHCJBZVLPGP-UHFFFAOYSA-Nschardinger α-dextrinChemical compoundO1C(C(C2O)O)C(CO)OC2OC(C(C2O)O)C(CO)OC2OC(C(C2O)O)C(CO)OC2OC(C(O)C2O)C(CO)OC2OC(C(C2O)O)C(CO)OC2OC2C(O)C(O)C1OC2COHFHDHCJBZVLPGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription5
- 229910019142PO4Inorganic materials0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000003945anionic surfactantSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 235000014113dietary fatty acidsNutrition0.000claimsdescription4
- 229940047642disodium cocoamphodiacetateDrugs0.000claimsdescription4
- SMVRDGHCVNAOIN-UHFFFAOYSA-Ldisodium;1-dodecoxydodecane;sulfateChemical compound[Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCOCCCCCCCCCCCCSMVRDGHCVNAOIN-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000claimsdescription4
- 229930195729fatty acidNatural products0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000000194fatty acidSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000002265preventionEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910052708sodiumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000011734sodiumSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- QJZYHAIUNVAGQP-UHFFFAOYSA-N3-nitrobicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-ene-2,3-dicarboxylic acidChemical compoundC1C2C=CC1C(C(=O)O)C2(C(O)=O)[N+]([O-])=OQJZYHAIUNVAGQP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-UHFFFAOYSA-ND-gluconic acidNatural productsOCC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)=ORGHNJXZEOKUKBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000001293FEMA 3089Substances0.000claimsdescription3
- 229960000583acetic acidDrugs0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000032683agingEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- 229910000147aluminium phosphateInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription3
- 235000013871bee waxNutrition0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000012166beeswaxSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 235000019438castor oilNutrition0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000004359castor oilSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- KRVSOGSZCMJSLX-UHFFFAOYSA-Lchromic acidSubstancesO[Cr](O)(=O)=OKRVSOGSZCMJSLX-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000claimsdescription3
- 235000019820disodium diphosphateNutrition0.000claimsdescription3
- GYQBBRRVRKFJRG-UHFFFAOYSA-Ldisodium pyrophosphateChemical compound[Na+].[Na+].OP([O-])(=O)OP(O)([O-])=OGYQBBRRVRKFJRG-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000claimsdescription3
- 229940038485disodium pyrophosphateDrugs0.000claimsdescription3
- AWJWCTOOIBYHON-UHFFFAOYSA-Nfuro[3,4-b]pyrazine-5,7-dioneChemical compoundC1=CN=C2C(=O)OC(=O)C2=N1AWJWCTOOIBYHON-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000012362glacial acetic acidSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000000174gluconic acidSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 235000012208gluconic acidNutrition0.000claimsdescription3
- ZEMPKEQAKRGZGQ-XOQCFJPHSA-Nglycerol triricinoleateNatural productsCCCCCC[C@@H](O)CC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](COC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CC[C@@H](O)CCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CC[C@H](O)CCCCCCZEMPKEQAKRGZGQ-XOQCFJPHSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000004021humic acidSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- CMTSCLKCQBPLSH-UHFFFAOYSA-Nisoindole-1,3-dithioneChemical compoundC1=CC=C2C(=S)NC(=S)C2=C1CMTSCLKCQBPLSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- 235000006408oxalic acidNutrition0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000003002pH adjusting agentSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-KphosphateChemical compound[O-]P([O-])([O-])=ONBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000010452phosphateSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000001993waxSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 235000021317phosphateNutrition0.000claims2
- 238000001179sorption measurementMethods0.000claims2
- 238000013019agitationMethods0.000claims1
- 230000001153anti-wrinkle effectEffects0.000claims1
- 238000004090dissolutionMethods0.000claims1
- 150000003013phosphoric acid derivativesChemical class0.000claims1
- 150000003839saltsChemical class0.000claims1
- 238000011109contaminationMethods0.000abstractdescription6
- 229920000742CottonPolymers0.000abstractdescription4
- 229920000728polyesterPolymers0.000abstractdescription4
- 244000025254Cannabis sativaSpecies0.000abstractdescription3
- 235000012766Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa var. sativaNutrition0.000abstractdescription3
- 235000012765Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa var. spontaneaNutrition0.000abstractdescription3
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical compoundCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription3
- 239000004677NylonSubstances0.000abstractdescription3
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-Nacrylic acid groupChemical groupC(C=C)(=O)ONIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription3
- 235000009120camoNutrition0.000abstractdescription3
- 235000005607chanvre indienNutrition0.000abstractdescription3
- 239000011487hempSubstances0.000abstractdescription3
- 239000002105nanoparticleSubstances0.000abstractdescription3
- 229920001778nylonPolymers0.000abstractdescription3
- 229910052719titaniumInorganic materials0.000abstractdescription3
- 239000010936titaniumSubstances0.000abstractdescription3
- 229910052726zirconiumInorganic materials0.000abstractdescription3
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-NTitaniumChemical compound[Ti]RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription2
- 150000001875compoundsChemical class0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000000052comparative effectEffects0.000description37
- 238000005406washingMethods0.000description12
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description11
- 239000003921oilSubstances0.000description11
- 235000019198oilsNutrition0.000description11
- 230000003373anti-fouling effectEffects0.000description6
- 239000004615ingredientSubstances0.000description6
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description4
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description4
- 239000000758substrateSubstances0.000description4
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000description3
- 239000000356contaminantSubstances0.000description3
- 230000007423decreaseEffects0.000description3
- 230000003247decreasing effectEffects0.000description3
- 239000000178monomerSubstances0.000description3
- 230000003075superhydrophobic effectEffects0.000description3
- 238000010998test methodMethods0.000description3
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-MAcetateChemical compoundCC([O-])=OQTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description2
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-MAcrylateChemical compound[O-]C(=O)C=CNIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description2
- YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-NFluorine atomChemical compound[F]YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 239000004952PolyamideSubstances0.000description2
- 229920000297RayonPolymers0.000description2
- 125000000217alkyl groupChemical group0.000description2
- 239000004760aramidSubstances0.000description2
- 229920003235aromatic polyamidePolymers0.000description2
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000description2
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description2
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description2
- 229910052731fluorineInorganic materials0.000description2
- 239000011737fluorineSubstances0.000description2
- 150000002222fluorine compoundsChemical class0.000description2
- 150000002430hydrocarbonsChemical class0.000description2
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000description2
- 238000002156mixingMethods0.000description2
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description2
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description2
- SNGREZUHAYWORS-UHFFFAOYSA-Nperfluorooctanoic acidChemical compoundOC(=O)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)FSNGREZUHAYWORS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 230000035699permeabilityEffects0.000description2
- 229920000747poly(lactic acid)Polymers0.000description2
- 229920002647polyamidePolymers0.000description2
- 239000004626polylactic acidSubstances0.000description2
- 229920001296polysiloxanePolymers0.000description2
- 229920002635polyurethanePolymers0.000description2
- 239000004814polyurethaneSubstances0.000description2
- 239000002964rayonSubstances0.000description2
- 231100000331toxicToxicity0.000description2
- 230000002588toxic effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000004804windingMethods0.000description2
- 210000002268woolAnatomy0.000description2
- 239000004215Carbon black (E152)Substances0.000description1
- IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthylene oxideChemical groupC1CO1IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-MMethacrylateChemical compoundCC(=C)C([O-])=OCERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description1
- 240000002853Nelumbo nuciferaSpecies0.000description1
- 235000006508Nelumbo nuciferaNutrition0.000description1
- 235000006510Nelumbo pentapetalaNutrition0.000description1
- BLRPTPMANUNPDV-UHFFFAOYSA-NSilaneChemical compound[SiH4]BLRPTPMANUNPDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 238000007792additionMethods0.000description1
- 230000002411adverseEffects0.000description1
- 238000005054agglomerationMethods0.000description1
- 230000002776aggregationEffects0.000description1
- 230000000903blocking effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000002131composite materialSubstances0.000description1
- 239000012153distilled waterSubstances0.000description1
- 239000000839emulsionSubstances0.000description1
- 125000000524functional groupChemical group0.000description1
- 230000014509gene expressionEffects0.000description1
- 229930195733hydrocarbonNatural products0.000description1
- 230000005661hydrophobic surfaceEffects0.000description1
- 230000001771impaired effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000description1
- 239000012528membraneSubstances0.000description1
- 239000002086nanomaterialSubstances0.000description1
- 239000004745nonwoven fabricSubstances0.000description1
- 239000005022packaging materialSubstances0.000description1
- 230000000149penetrating effectEffects0.000description1
- YFSUTJLHUFNCNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-Nperfluorooctane-1-sulfonic acidChemical classOS(=O)(=O)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)FYFSUTJLHUFNCNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000000704physical effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000005554picklingMethods0.000description1
- 231100000614poisonToxicity0.000description1
- 229920000642polymerPolymers0.000description1
- 239000011148porous materialSubstances0.000description1
- 238000007781pre-processingMethods0.000description1
- 238000002203pretreatmentMethods0.000description1
- 238000010526radical polymerization reactionMethods0.000description1
- 230000008707rearrangementEffects0.000description1
- 238000007670refiningMethods0.000description1
- 230000001172regenerating effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000001846repelling effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description1
- 238000012827research and developmentMethods0.000description1
- 229910000077silaneInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000007787solidSubstances0.000description1
- 239000004753textileSubstances0.000description1
- 239000003440toxic substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 238000009736wettingMethods0.000description1
- 239000002759woven fabricSubstances0.000description1
- 230000037303wrinklesEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06M—TREATMENT, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE IN CLASS D06, OF FIBRES, THREADS, YARNS, FABRICS, FEATHERS OR FIBROUS GOODS MADE FROM SUCH MATERIALS
- D06M13/00—Treating fibres, threads, yarns, fabrics or fibrous goods made from such materials, with non-macromolecular organic compounds; Such treatment combined with mechanical treatment
- D06M13/50—Treating fibres, threads, yarns, fabrics or fibrous goods made from such materials, with non-macromolecular organic compounds; Such treatment combined with mechanical treatment with organometallic compounds; with organic compounds containing boron, silicon, selenium or tellurium atoms
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06M—TREATMENT, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE IN CLASS D06, OF FIBRES, THREADS, YARNS, FABRICS, FEATHERS OR FIBROUS GOODS MADE FROM SUCH MATERIALS
- D06M13/00—Treating fibres, threads, yarns, fabrics or fibrous goods made from such materials, with non-macromolecular organic compounds; Such treatment combined with mechanical treatment
- D06M13/10—Treating fibres, threads, yarns, fabrics or fibrous goods made from such materials, with non-macromolecular organic compounds; Such treatment combined with mechanical treatment with compounds containing oxygen
- D06M13/184—Carboxylic acids; Anhydrides, halides or salts thereof
- D06M13/188—Monocarboxylic acids; Anhydrides, halides or salts thereof
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06M—TREATMENT, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE IN CLASS D06, OF FIBRES, THREADS, YARNS, FABRICS, FEATHERS OR FIBROUS GOODS MADE FROM SUCH MATERIALS
- D06M15/00—Treating fibres, threads, yarns, fabrics, or fibrous goods made from such materials, with macromolecular compounds; Such treatment combined with mechanical treatment
- D06M15/01—Treating fibres, threads, yarns, fabrics, or fibrous goods made from such materials, with macromolecular compounds; Such treatment combined with mechanical treatment with natural macromolecular compounds or derivatives thereof
- D06M15/03—Polysaccharides or derivatives thereof
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06M—TREATMENT, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE IN CLASS D06, OF FIBRES, THREADS, YARNS, FABRICS, FEATHERS OR FIBROUS GOODS MADE FROM SUCH MATERIALS
- D06M15/00—Treating fibres, threads, yarns, fabrics, or fibrous goods made from such materials, with macromolecular compounds; Such treatment combined with mechanical treatment
- D06M15/01—Treating fibres, threads, yarns, fabrics, or fibrous goods made from such materials, with macromolecular compounds; Such treatment combined with mechanical treatment with natural macromolecular compounds or derivatives thereof
- D06M15/17—Natural resins, resinous alcohols, resinous acids, or derivatives thereof
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06M—TREATMENT, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE IN CLASS D06, OF FIBRES, THREADS, YARNS, FABRICS, FEATHERS OR FIBROUS GOODS MADE FROM SUCH MATERIALS
- D06M2200/00—Functionality of the treatment composition and/or properties imparted to the textile material
- D06M2200/10—Repellency against liquids
- D06M2200/12—Hydrophobic properties
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Treatments For Attaching Organic Compounds To Fibrous Goods (AREA)
- Chemical Or Physical Treatment Of Fibers (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromKorean이 발명은 원단에 미세먼지가 흡착 및 흡수되는 것을 방지하는 성능을 가지는 섬유용 초발수 용액과 이를 이용한 초발수 원단의 제조 방법에 관한 것으로, 더욱 자세하게 설명하자면, 오물로 인한 오염의 제거 및 사용에 의해 저하되는 초발수성을 재생하는 방법을 포함하는 초발수 용액과 이를 이용한 초발수 원단에 대한 것이다.The present invention relates to a super-water-repellent solution for fibers having a performance of preventing fine dust from being adsorbed and absorbed on a fabric and a method of manufacturing a super-water-repellent fabric using the same, to be described in more detail, to remove and use contamination caused by dirt. It relates to a super water-repellent solution and a super-water-repellent fabric using the same, including a method of regenerating the super water-repellent property deteriorated by.
초발수 표면기술은 표면의 젖음(wetting)현상을 조절하기 위한 표면 개질(surface modification) 기술의 한 분야로, 고체 표면상에서 이루어지는 물방울의 접촉각이 150° 이상인 것을 의미하며, 이러한 발수성은 대체로 표면의 거칠기와 표면 에너지로 인해 결정된다. 이는 연잎효과(Lotus effect)를 통해 익히 알려져 있으며, 레저 및 아웃도어, 스포츠 의류 시장의 확대로 인해 발수성 직물의 필요성이 증가하면서 발수성 구현에 관한 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있는 실정이다.Super water-repellent surface technology is a field of surface modification technology for controlling the wetting phenomenon of a surface, which means that the contact angle of water droplets formed on a solid surface is 150 ° or more, and such water repellency is generally roughness of the surface. And surface energy. This is well-known through the Lotus effect, and the need for water repellent fabrics has increased due to the expansion of the leisure, outdoor, and sports apparel markets, and research on implementing water repellency has been actively conducted.
지금까지 각종 소재의 표면에 초발수 표면을 구현하기 위하여 표면의 에너지가 낮은 불소화합물을 사용하였다. 대한민국특허출원 제 10-2001-0065617호는 표면 프렉탈 구조(fractal structure)를 갖고 ㎚ ∼ ㎛ 크기의 세공을 갖는 무기 지지체 표면에 아조계 염화실란을 고착화 한 후, 불소계 단량체를 주요 단량체로 하여 기능성 단량체를 표면으로부터 라디칼 중합함으로써 표면에 초발수 효과와 같은 표면 특성을 지니는 유/무기 복합막에 대한 것으로 이 또한 불소화합물을 사용하는 좋은 예로 들 수 있다.To date, fluorine compounds with low energy on the surface have been used to realize super water-repellent surfaces on the surfaces of various materials. Republic of Korea Patent Application No. 10-2001-0065617 is a functional monomer using a fluorine-based monomer as a main monomer after the azo-based silane is fixed on the surface of an inorganic support having a surface fractional structure and pores having a size of ㎚ to µm. By radical polymerization from the surface of the organic / inorganic composite membrane having a surface property such as a super water-repellent effect, this is also a good example of using a fluorine compound.
불소계 화합물은 비교적 고가임에도 불구하고 저농도, 소량 사용만으로도 그 성능이 우수하고, 타 재료인 실리콘 혹은 탄화수소계 화합물이 구현할 수 없는 탁월한 초발수성을 발휘하기 때문에 외부의 액상 오염과 접촉했을 때 매우 큰 접촉각을 나타내 초기 오염방지성이 매우 우수한 것으로 알려져 있다. 그러나 시간이 지남에 따라 물리적으로 침적되는 오염물질 때문에 최외곽 표면이 오염물질로 채워지게 되면서, 세정 시 소수성인 표면은 물과 반발력을 가지게 되어 부착된 오염물질의 제거가 용이하지 않게 되는 문제점이 발생한다.Although the fluorine-based compound is relatively expensive, its performance is excellent even at low concentrations and in small amounts, and it has a very large contact angle when it comes into contact with external liquid contamination because it exhibits excellent superhydrophobicity that other materials such as silicone or hydrocarbon compounds cannot realize. It is known that the initial anti-pollution property is very excellent. However, as the outermost surface is filled with contaminants due to contaminants that are physically deposited over time, a hydrophobic surface has a repelling force with water, and thus, it is difficult to remove the attached contaminants. do.
이러한 문제점을 해결하기 위하여 과불소알킬기를 함유하는 아크릴레트 또는 메타크릴레이트와 에틸렌옥사이드기가 부가된 탄화수소계 아크릴레이트 구조를 이용한 양성 고분자를 코팅하여 초기 오염방지성을 유지하며, 물로 세정 시 표면에서의 환경 대응형 관능기의 재배치가 발생하여 오염을 쉽게 제거하려는 연구 개발 노력이 있었으나, 상기한 방법으로 제조된 재료는 에멀젼 입자의 크기가 2~3㎛로 비교적 크기 때문에 기재와의 혼합 시 사용성 및 기재에 대한 침투성이 떨어진다는 문제가 존재하였다.In order to solve this problem, a coating of a positive polymer using an acrylate or methacrylate containing a perfluorinated alkyl group and a hydrocarbon-based acrylate structure added with an ethylene oxide group maintains the initial contamination prevention property, and when washed with water, There has been a research and development effort to easily remove the contamination due to the rearrangement of functional groups corresponding to the environment, but the material produced by the above-described method has a relatively large size of the emulsion particles of 2 to 3 μm, so it is useful in mixing with the substrate and the substrate. There was a problem of poor permeability to Korea.
또한 과불소알킬기 함유 코팅제의 경우 퍼플루오르옥탄술폰산(Perfluorooctane sulfonates, PFOS), 퍼플루오로옥탄산(Perfluorooctanoic acid, PFOA) 등 인체 및 환경에 유독한 물질이 포함되어있을 수 있다는 문제점이 존재하였다.In addition, in the case of the perfluorinated alkyl group-containing coating agent, there existed a problem that substances toxic to the human body and the environment, such as perfluorooctane sulfonates (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), may be included.
이에 이 발명은 종래의 문제점을 해결하기 위한 것으로, 기재와의 혼합 시 침투가 용이하고, 인체 및 환경에 유독한 물질을 포함하지 않으면서도 초발수성을 지니며 원단 내부에 미세먼지가 흡수되는 것을 방지하는 기능을 지니는 섬유용 초발수 용액과의 이를 이용한 초발수 원단의 제조 방법을 제공하는 데 그 목적이 있다.Accordingly, the present invention is to solve the conventional problems, it is easy to infiltrate when mixed with the substrate, it has a super water repellency without containing toxic substances in the human body and the environment and prevents the absorption of fine dust inside the fabric An object of the present invention is to provide a method for manufacturing a super water-repellent fabric using the same as a super-water-repellent solution for fibers having a function to be performed.
상기의 목적을 달성하기 위한 수단으로 이 발명의 구성은, 발수제 60~70 중량부, 방수제 53~66 중량부, 유연제 8~15 중량부 및 계면활성제 0.3~0.7 중량부를 포함하여 이루어지며, 상기 발수제는 실리콘알콕사이드, 알루미늄알콕사이드, 지르코니움알콕사이드, 티타늄알콕사이드 중에서 선택되는 이들의 혼합물로 이루어지며, 상기 방수제는 밀랍, 왁스, 아마인유, 테레빈유, 피마자유 중에서 선택되는 하나 또는 이들의 혼합물로 이루어진다.As a means for achieving the above object, the composition of the present invention comprises 60 to 70 parts by weight of a water repellent agent, 53 to 66 parts by weight of a waterproofing agent, 8 to 15 parts by weight of a softener and 0.3 to 0.7 parts by weight of a surfactant, and the water repellent agent. Is made of a mixture of silicon alkoxide, aluminum alkoxide, zirconium alkoxide and titanium alkoxide, and the waterproofing agent is one or a mixture selected from beeswax, wax, linseed oil, turpentine oil, and castor oil.
또한, 상기 발수제는, 평균 입경이 5~100nm인 것과 평균 입경이 300~500nm인 것을 동시에 포함하여 이루어진다.In addition, the water repellent agent is composed of an average particle diameter of 5 to 100 nm and an average particle diameter of 300 to 500 nm simultaneously.
또한, 상기 발수제는, 평균 입경이 5~100nm인 것과 평균 입경이 300~500nm인 것의 비율이 1:2, 1:1, 2:1로 이루어진다.In addition, the water-repellent agent, the ratio of the average particle diameter of 5 to 100nm and the average particle diameter of 300 to 500nm is 1: 2, 1: 1, 2: 1.
또한, 상기 계면활성제는, 음이온 계면활성제로, 라우레스설포욱시
네이트, 소듐라우릴에테르설페이트, 디소듐코코암포디아세테이트, 지방산나트륨, 모노알킬황산염, 알킬폴리옥시에틸렌황산염, 알킬벤젠술폰산염, 모노알킬인산염으로 구성된 군에서 선택되는 어느 하나를 포함하여 이루어진다.In addition, the surfactant is an anionic surfactant, laureth sulfowooksi
Nate, sodium lauryl ether sulfate, disodium cocoamphodiacetate, sodium fatty acid, monoalkyl sulfate, alkylpolyoxyethylene sulfate, alkylbenzene sulfonate, monoalkyl phosphate.
또한, 상기 초발수 용액은, 발수제에 방수제가 첨가되어 이루어지며, 40~45℃의 온도로 교반되어 이루어진다.In addition, the super water repellent solution is made by adding a water repellent agent to the water repellent agent, and is made by stirring at a temperature of 40 to 45 ° C.
또한, 상기 초발수 용액은, 10~15℃의 저온저장고에서 숙성되어 이루어진다.In addition, the super water-repellent solution is made by aging in a cold storage at 10-15 ° C.
또한 상기 초발수 용액은, 금속이온봉쇄제를 더 포함할 수 있으며, 글루코닉에씨드, 디소듐파이로포스페이트, 사이클로덱스트린, 이디티에이, 시트릭에씨드, 하이드록시프로필사이클로텍스트린, 휴믹애씨드로 이루어진 군에서 선택되는 어느 하나를 포함하여 이루어진다.In addition, the super water-repellent solution may further include a metal ion blocker, gluconic acid, disodium pyrophosphate, cyclodextrin, IDT, citric acid, hydroxypropyl cyclotextrin, and humic acid It consists of any one selected from the group consisting of.
또한, 이 발명의 방법의 구성으로, 제 1항에서 제조된 초발수 용액을 이용한 초발수 원단의 제조 방법에 있어서, 원단을 산성용액에 침지하여 산처리하는 단계, 상기 산처리를 마친 원단을 초발수 용액에 침지하여 약제처리하는 단계, 상기 약제처리를 거친 원단을 건조하여 수분을 제거하는 단계, 상기 건조를 마친 원단을 가열하여 원단에 초발수성분을 고착시키는 단계로 이루어진다.In addition, with the configuration of the method of the present invention, in the method of manufacturing a super water-repellent fabric using the super-water-repellent solution prepared in
또한, 이 발명의 방법의 구성으로 상기 원단은, 폴리에스테르, 나일론, 아크릴, 폴리우레탄, 아세테이트, 레이온, 폴리젖산, 아라미드, 폴리아미드의 화학섬유 및 면, 마, 견, 양모의 천연 섬유의 혼섬, 혼방, 교직품으로 구성된 군에서 적어도 하나 선택되어 이루어진다.In addition, the composition of the method of the present invention, the fabric, polyester, nylon, acrylic, polyurethane, acetate, rayon, polylactic acid, aramid, a mixture of chemical fibers of polyamide and natural fibers of cotton, hemp, silk, wool It is made of at least one selected from the group consisting of, blend, and teaching products.
또한, 이 발명의 방법의 구성으로 상기 산성용액은, 포름산, 빙초산, 황산, 수산, 크롬산, 인산으로 이루어진 군에서 선택된 어느 하나로 구성되어 이루어지며, 산도가 4.0~5.0인 것을 특징으로 이루어진다.In addition, as the composition of the method of the present invention, the acid solution is composed of any one selected from the group consisting of formic acid, glacial acetic acid, sulfuric acid, oxalic acid, chromic acid, and phosphoric acid, and is characterized in that the acidity is 4.0 to 5.0.
또한, 이 발명의 방법의 구성으로 상기 산성용액의 산도를 맞추기 위해 pH 조절제를 더 첨가하는 것을 특징으로 이루어진다.In addition, in order to adjust the acidity of the acidic solution with the configuration of the method of the present invention, it is further characterized in that a pH adjusting agent is further added.
또한, 이 발명의 방법의 구성으로 상기 산처리를 마친 원단은, 5.5~6.5의 산도를 지니는 특징으로 이루어진다.In addition, the fabric of the acid treatment in the configuration of the method of the present invention is made of a feature having an acidity of 5.5 to 6.5.
또한, 이 발명의 방법의 구성으로 상기 약제처리를 거친 원단을 건조하는 단계는, 110~150℃의 온도로 이루어지는 특징이 있으며, 상기 건조 단계를 마친 원단의 수분율은 50~60%인 것을 특징으로 이루어진다.In addition, the step of drying the fabric subjected to the drug treatment with the configuration of the method of the present invention is characterized by having a temperature of 110 to 150 ° C, and the moisture content of the fabric after the drying step is 50 to 60%. Is done.
또한, 이 발명의 방법의 구성으로 상기 건조를 마친 원단을 가열하여 원단에 초발수성분을 고착시키는 단계는, 140~160℃의 온도로 1~2분 동안 이루어진다.In addition, the step of fixing the super water-repellent component to the fabric by heating the dried fabric with the configuration of the method of the present invention is performed for 1 to 2 minutes at a temperature of 140 to 160 ° C.
또한, 이 발명의 방법의 구성으로 상기 고착단계를 거쳐 완성된 원단은, 구김방지, 수분 제어, 얼룩 방지, 얼룩 제거, 오염 방지, 미세먼지 흡수 방지, 발수, 발유, 자외선 차단의 표면 효과를 지니며, 상기한 미세먼지는 PM 2.5~10의 미세한 먼지인 것을 특징으로 이루어진다.In addition, the fabric finished through the fixing step with the composition of the method of the present invention has a surface effect of preventing wrinkles, controlling moisture, preventing stains, removing stains, preventing contamination, absorbing fine dust, water repellent, oil repellent, and blocking UV rays. The fine dust is characterized in that it is a fine dust of PM 2.5 ~ 10.
이 발명의 제조 방법에 따라 완성된 섬유용 초발수 용액은 나노사이즈의 발수제를 사용하여 기재와의 혼합 시 침투성이 좋으며, 이를 이용하여 제작된 초발수 원단은 인체 및 환경에 유독한 물질을 포함하지 않으면서도 초발수성이 뛰어나며 원단에 미세먼지가 흡수되는 것을 방지하는다는 효과가 있다.The super water-repellent solution for textiles prepared according to the manufacturing method of the present invention uses a nano-sized water repellent agent and has good permeability when mixed with a substrate, and the super-water-repellent fabric produced by using this does not contain substances toxic to the human body and the environment. It is excellent in super water repellency, but also has the effect of preventing the absorption of fine dust into the fabric.
도 1은 이 발명 실시예에 따른 초발수 원단의 제조 방법 흐름도이다.
도 2는 이 발명 실시예에 따른 초발수 용액의 제조 방법 흐름도이다.
도 3은 이 발명 실시예에 따른 초발수 원단의 제조 공정에 대한 개략도이다.
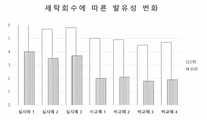
도 4는 이 발명 실험예 2에 따른 세탁횟수에 따른 발수성의 변화를 표기한 도표이다.
도 5는 이 발명 실험예 3에 따른 세탁횟수에 따른 발유성의 변화를 표기한 도표이다.
도 6은 이 발명 실험예 4에 따른 세탁횟수에 따른 방오성의 변화에 표기한 도표이다.1 is a flowchart of a method for manufacturing a super water-repellent fabric according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Figure 2 is a flow chart of a method for producing a super water-repellent solution according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of the manufacturing process of the super water-repellent fabric according to an embodiment of the present invention.
4 is a chart showing the change in water repellency according to the number of washings according to Experimental Example 2 of the present invention.
5 is a diagram showing the change in oil repellency according to the number of washings according to Experimental Example 3 of the present invention.
6 is a diagram showing the change in antifouling properties according to the number of washings according to Experimental Example 4 of the present invention.
이하, 이 발명에 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 이 발명을 용이하게 실시할 수 있을 정도로 상세히 설명하기 위하여, 이 발명의 바람직한 실시예를 첨부된 도면을 참조로 하여 상세히 설명하기로 한다. 이 발명의 목적, 작용, 효과에 대한 이점이 바람직한 실시예의 설명에 의해 보다 명확해질 것이다.Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings in order to describe in detail that a person skilled in the art pertaining to the present invention can easily implement the present invention. Advantages of the objects, actions, and effects of this invention will become more apparent by the description of preferred embodiments.
참고로, 여기에서 개시되는 실시예는 실시 가능한 예 중에서 당업자의 이해를 돕기 위하여 가장 바람직한 실시예를 선정하여 제시한 것일 뿐, 이 발명의 기술적 사상이 반드시 제시된 실시예에 의해서 한정되거나 제한되는 것이 아니고, 이 발명의 기술적 사상을 벗어나지 않는 범위 내에서 균등물 내지 대체물들을 포함하는 다양한 변화, 부가 및 변경이 가능하다.For reference, the embodiments disclosed herein are only selected and presented as the most preferred embodiments to assist the skilled person in understanding among the possible examples, and the technical spirit of the present invention is not necessarily limited or limited by the presented embodiments , Various changes, additions, and modifications including equivalents or substitutes are possible without departing from the technical spirit of the present invention.
또한, 본원의 명세서 및 청구범위에 사용된 용어나 단어의 표현은, 발명자가 그 자신의 발명을 가장 최선의 방법으로 설명하기 위하여 용어의 개념을 적절하게 정의할 수 있다는 원칙에 입각하여 정의된 것으로서, 통상적이거나 사전적인 의미로만 한정해서 해석되어서는 아니되며, 이 발명의 기술적 사상에 부합하는 의미와 개념으로 해석되어야만 한다.In addition, the expressions of terms or words used in the specification and claims of the present application are defined based on the principle that the inventor can appropriately define the concept of terms in order to explain his or her invention in the best way. However, it should not be interpreted as being limited to ordinary or dictionary meanings, but should be interpreted as meanings and concepts consistent with the technical spirit of the present invention.
도 1은 이 발명 실시예에 따른 초발수 원단의 제조 방법 흐름도이다.1 is a flowchart of a method for manufacturing a super water-repellent fabric according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 1에 도시된 것과 같이 초발수 원단은 원단을 산처리하는 단계(S100), 상기 산처리를 마친 원단을 약제처리하는 단계(S200), 상기 약제처리를 거친 원단을 건조하는 단계(S300), 상기 건조를 마친 원단을 가열하여 원단에 초발수성분을 고착시키는 단계(S400)를 포함하여 이루어지면 바람직하다.As illustrated in FIG. 1, the super water-repellent fabric includes acid treatment of the fabric (S100), chemical treatment of the acid-treated fabric (S200), and drying of the fabric subjected to the chemical treatment (S300), It is preferable to include the step (S400) of fixing the super water-repellent component to the fabric by heating the dried fabric.
이 때 사용되는 원단은 폴리에스테르, 나일론, 아크릴, 폴리우레탄, 아세테이트, 레이온, 폴리젖산, 아라미드, 폴리아미드의 화학섬유 및 면, 마, 견, 양모의 천연 섬유의 혼섬, 혼방, 교직품 중 하나이며, 직물, 편물, 부직포 등 어떠한 형태이어도 좋다. 그러나 원단은 깨끗한 상태여야 하며, 어떠한 유연제나 정련제 및 다른 케미컬을 포함하지 않는 것이 바람직하며, 그렇지 않은 경우 발수기능이 저하될 수 있으며, 욕조의 안정성에도 영향을 줄 수있어 바람직하지 않다.The fabric used at this time is one of polyester fiber, nylon, acrylic, polyurethane, acetate, rayon, polylactic acid, aramid, polyamide, chemical fiber and natural fiber of cotton, hemp, silk and wool. , And may be in any form such as woven fabric, knitted fabric, and non-woven fabric. However, the fabric should be in a clean state, and it is preferable not to include any softener, refining agent, and other chemicals, otherwise the water repellent function may be deteriorated, and it may also affect the stability of the bath, which is undesirable.
또한 원단을 산처리하는 단계(S100)는 포름산, 빙초산, 황산, 수산, 크롬산, 인산으로 이루어진 군에서 선택된 어느 하나로 구성된 욕조에서 이루어지며, 특히 포름산(Formic acid)을 이용하는 것이 바람직하다.In addition, the step (S100) of acid treatment of the fabric is made in a bath composed of any one selected from the group consisting of formic acid, glacial acetic acid, sulfuric acid, oxalic acid, chromic acid, and phosphoric acid, and it is particularly preferable to use formic acid.
또한 상기 욕조는 4.0~5.0의 산도로 이루어지면 바람직하며, 산도가 4.0 미만으로 떨어질 경우 원단의 산처리가 과하게 되어 원단의 수명이 극도로 짧아질 수 있어 바람직하지 않고, 산도가 5.0를 초과할 경우 산처리가 미비하여 원단 내에 이물질이 남아있을 수 있기 때문에 초발수 용액의 코팅이 바람직하게 이루어지지 않는 문제점이 있을 수 있어 바람직하지 않다. 또한 상기 산처리를 마친 원단은 5.5~6.5의 산도로 이루어지는 것이 바람직하며, 해당 산도를 만족하지 못할 경우 약제처리 단계(S200)에 영향을 미칠 수 있으므로 산처리 단계(S100)를 반복하여 실시할 수 있다.In addition, the bath is preferably made of an acidity of 4.0 to 5.0, and if the acidity falls below 4.0, the acid treatment of the fabric is excessive, and the life of the fabric may be extremely short, which is undesirable, and the acidity exceeds 5.0. Since the acid treatment is insufficient, foreign matter may remain in the fabric, which is undesirable because there may be a problem in that the coating of the super water-repellent solution is not preferably performed. In addition, it is preferable that the acid-treated fabric is made of an acidity of 5.5 to 6.5, and if the acidity is not satisfied, it may affect the drug treatment step (S200), so that the acid treatment step (S100) can be repeated. have.
또한 상기 약제처리를 거친 원단을 건조하는 단계(S300)는 110~150℃의 온도로 가열된 텐터기에서 이루어지는 것이 바람직하며, 온도가 110℃ 미만일 경우 충분한 건조가 이루어지지 않을 수 있어 바람직하지 않으며, 온도가 150℃를 초과할 경우 건조가 과하게 이루어지기 때문에 고착 단계(S400)를 거친 후 원단의 수명이 극도로 짧아질 수 있으므로 바람직하지 않다. 또한 상기 건조 단계(S300)를 마친 원단의 수분율은 50~60%인 것이 바람직하며, 해당 수분율을 만족하지 못할 경우, 원단 경화 시 원단의 수명에 영향을 미치거나, 충분한 경화가 이루어지지 않아 원단의 초발수성이 약화될 수 있어 바람직하지 않다.In addition, the step (S300) of drying the fabric subjected to the pharmaceutical treatment is preferably performed in a tenter machine heated to a temperature of 110 to 150 ° C, and when the temperature is less than 110 ° C, sufficient drying may not be performed, which is not preferable. When the temperature exceeds 150 ° C, drying is excessively performed, so after the fixing step (S400), the life of the fabric may be extremely short, which is not preferable. In addition, the moisture content of the fabric that has completed the drying step (S300) is preferably 50 to 60%, and if the moisture content is not satisfied, it affects the life of the fabric when curing the fabric, or sufficient curing is not performed, so that It is not preferable because superhydrophobicity may be weakened.
또한 상기 건조를 마친 원단을 가열하여 원단에 초발수성분을 고착시키는 단계(S400)는, 140~160℃의 온도로 가열된 텐더기에서 1~2분동안 이루어지는 것이 바람직하며, 더 바람직하게는 145~155℃, 더더욱 바람직하게는 148~152℃에서 이루어지는 것이 바람직하다. 140℃ 미만의 온도로 경화가 이루어질 경우, 초발수 용액의 경화가 충분하지 않아 초발수성이 떨어지는 문제가 있을 수 있어 바람직하지 않으며, 160℃를 초과하는 온도로 경화가 이루어질 경우 원단의 수명에 영향을 미칠 수 있어 바람직하지 않다. 또한 텐더기에서 원단이 경화되는 시간은 2분을 넘기지 않는 것이 바람직하며, 2분을 넘길 경우 원단의 수분률이 급감하면서, 초발수 용액과 원단 사이의 결합을 저하하므로 바람직하지 않다.In addition, the step of fixing the super water-repellent component to the fabric by heating the dried fabric (S400) is preferably made for 1 to 2 minutes in a tender machine heated to a temperature of 140 to 160 ° C, more preferably 145 It is preferably made at ~ 155 ° C, even more preferably at 148 ~ 152 ° C. When curing is performed at a temperature of less than 140 ° C, the superhydrophobic solution may not be sufficiently cured, which may cause a problem of poor water repellency, which is undesirable, and when curing at a temperature exceeding 160 ° C affects the life of the fabric. It is not desirable because it can be crazy In addition, it is preferable that the time for the fabric to cure in a tender machine does not exceed 2 minutes, and if it exceeds 2 minutes, the moisture content of the fabric decreases rapidly, and the bonding between the super water-repellent solution and the fabric decreases.
도 2는 이 발명 실시예에 따른 초발수 용액의 제조 방법 흐름도이다.Figure 2 is a flow chart of a method for producing a super water-repellent solution according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 2에 도시된 것과 같이 초발수 용액은 평균입경이 다른 두 발수제에 메탄올을 첨가하며 고르게 교반하는 단계(S201), 상기 발수제에 방수제를 첨가하여 40~45℃의 온도에서 교반하여 완전히 용해하는 단계(S202), 상기 용액에 유연제 8~15 중량부와 계면활성제 0.3~0.7 중량부를 첨가하여 용해하는 단계(S203), 상기 용액을 10~15℃의 저온저장고에서 숙성하는 단계(S204)를 포함하여 이루어지면 바람직하다.As shown in Figure 2, the super water-repellent solution is stirred evenly by adding methanol to two water-repellent agents having different average particle diameters (S201), and completely dissolving by adding a waterproofing agent to the water-repellent agent and stirring at a temperature of 40 to 45 ° C. (S202), including the step of dissolving by adding 8 to 15 parts by weight of a softener and 0.3 to 0.7 parts by weight of a surfactant to the solution (S203), including the step of aging the solution in a cold storage at 10 ~ 15 ℃ (S204) It is desirable if done.
이 때 사용되는 발수제는 원단 안으로 물이 침투하는 것을 방지하는 역할을 하며 이 발명에서 사용되는 발수제로는 알콕사이드 화합물인 것이 바람직하며, 특히 실리콘 알콜사이드, 알루미늄알콕사이드, 지르코니움알콕사이드, 티타늄알콜사이드 중에서 선택되는 이들의 혼합물로 이루어지는 것이 바람직하다. 또한, 서로 다른 입경의 나노입자를 혼합하였을 때 듀얼스케일의 나노구조물을 잘 형성하게 되어 소수성이 증가하므로, 발수제는 평균 입경이 다른 두 물질을 혼합하여 사용하는 것이 바람직하다.The water-repellent agent used at this time serves to prevent water from penetrating into the fabric, and the water-repellent agent used in the present invention is preferably an alkoxide compound, particularly among silicone alcohol, aluminum alkoxide, zirconium alkoxide, and titanium alcohol. It is preferably made of a mixture of these selected. In addition, when nanoparticles of different particle diameters are mixed, the dual-scale nanostructures are well formed and hydrophobicity increases. Therefore, it is preferable to use water repellents by mixing two materials having different average particle diameters.
또한 발수제에 방수제를 첨가하고 교반하여 완전히 용해하는 단계(S202)에서 발수제와 방수제를 섞어 용해하는 온도는 40~45℃가 바람직하며, 40℃ 미만의 온도에서 해당 단계가 지속될 경우 교반시간이 길어져 경제적이지 못하고, 45℃를 초과하는 온도에서 해당 단계가 지속될 경우 발수제 또는 방수제의 뭉침이 일어날 수 있어 바람직하지 못하다.In addition, in the step of completely dissolving by adding a waterproofing agent to the water-repellent agent and stirring (S202), the temperature at which the water-repellent agent and the waterproofing agent are mixed and dissolved is preferably 40 to 45 ° C. If the step continues at a temperature below 40 ° C, the stirring time becomes longer and economical If it does not, and if the corresponding step is continued at a temperature exceeding 45 ° C., it is not preferable because agglomeration of the water repellent or waterproofing agent may occur.
또한 유연제와 계면활성제를 첨가하는 단계(S203)에서 유연제는 원단에 부드러운 촉감을 부여하기 위해 사용되며, 이는 발수제 또는 방수제로 인해 원단의 촉감이 경화되는 것을 방지한다. 상기 유연제는 8~15 중량부 첨가되는 것이 바람직하며, 8 중량부 미만으로 첨가될 경우 유연 효과가 충분히 발휘되지 않아 바람직하지 않으며, 15 중량부를 초과하여 첨가될 경우 발수제의 성능을 저해할 수 있어 바람직하지 않다. 또한 완성된 용액은 저온저장고에서 숙성(S204)되는 것이 바람직하며 저온저장고의 온도는 10~15℃로 이루어지는 것이 바람직하다.In addition, in the step (S203) of adding a softener and a surfactant, the softener is used to impart a soft touch to the fabric, which prevents the texture of the fabric from curing due to a water repellent or waterproofing agent. The softener is preferably added in an amount of 8 to 15 parts by weight, and when added in an amount of less than 8 parts by weight, the softening effect is not sufficiently exhibited, which is undesirable, and when added in excess of 15 parts by weight, the performance of the water repellent agent may be impaired. Do not. In addition, the completed solution is preferably aged (S204) in a low temperature storage room, and the temperature of the low temperature storage room is preferably 10 to 15 ° C.
또한 유연제와 계면활성제를 첨가하는 단계(S203)에서 계면활성제는
특히 음이온 계면활성제로, 라우레스설포욱시네이트, 소듐라우릴에테르설페이트, 디소듐코코암포디아세테이트, 지방산나트륨, 모노알킬황산염, 알킬폴리옥시에틸렌황산염, 알킬벤젠술폰산염, 모노알킬인산염으로 구성된 군에서 선택되는 어느 하나로 이루어지며, 0.3~0.7 중량부 첨가되어 이루어지면 바람직하다.In addition, in the step (S203) of adding a softener and a surfactant, the surfactant
In particular, as anionic surfactants, the group consisting of laureth sulfouccinate, sodium lauryl ether sulfate, disodium cocoamphodiacetate, sodium fatty acid, monoalkyl sulfate, alkylpolyoxyethylene sulfate, alkylbenzenesulfonate, and monoalkyl phosphate It is made of any one selected from, and is preferably made by adding 0.3 to 0.7 parts by weight.
또한 유연제와 계면활성제를 첨가하는 단계(S203)에서 금속이온봉쇄제를 포함할 수 있다. 금속이온봉쇄제는 용액의 안정성 또는 성상에 악영향을 끼치는 금속성이온과 결합하여 불활성화시키는 성분으로, 글루코닉에씨드, 디소듐파이로포스페이트, 사이클로덱스트린, 이디티에이, 시트릭에씨드, 하이드록시프로필사이클로텍스트린, 휴믹애씨드로 이루어진 군에서 선택되는 어느 하나로 이루어지면 바람직하다.In addition, in the step (S203) of adding a softener and a surfactant, a metal ion blocker may be included. Metal ion blocker is a component that inactivates by combining with metal ions, which adversely affect the stability or properties of the solution, gluconic acid, disodium pyrophosphate, cyclodextrin, IDT, citric acid, hydroxypropyl cyclo It is preferable to use any one selected from the group consisting of textrin and humic acid.
도 3은 이 발명 실시예에 따른 초발수 원단의 제조 공정에 대한 개략도이다.Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of the manufacturing process of the super water-repellent fabric according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 3에 도시된 것과 같이 초발수 원단의 제조는 원단공급부(1), 상기 원단의 텐션을 유지하기 위한 다수 개의 텐션부(2), 상기 원단을 산세 처리하여 원단 표면을 정련하는 전처리부(3), 상기 표면이 정련된 원단에 초발수성을 부여하는 약제처리부(4), 상기 약제처리된 원단을 건조하는 건조부(5), 상기 건조된 원단을 경화하는 경화부(6), 경화된 원단이 권취되는 권취부(7)를 포함하여 이루어진다.As shown in Figure 3, the manufacture of the super water-repellent fabric includes a fabric supply unit (1), a plurality of tension units (2) for maintaining the tension of the fabric, and a pre-treatment unit (3) for pickling the fabric to refine the fabric surface. ), A chemical treatment unit (4) for imparting super water repellency to the fabric having the surface refined, a drying unit (5) for drying the drug-treated fabric, a curing unit (6) for curing the dried fabric, and a cured fabric It comprises the winding part 7 to be wound up.
상기한 구성에 의한 초발수 원단에 대하여 설명하면 다음과 같다.When explaining the super water-repellent fabric by the above configuration is as follows.
(실시예 1)(Example 1)
발수제로서 평균입경이 50nm인 실리콘알콕사이드 20중량부와 평균입경이 350nm인 알루미늄알콕사이드 20 중량부에 메탄올 40중량부를 첨가하면서 고르게 교반하고, 방수제로서 아마인유 53 중량부를 상기 발수제에 첨가한 후, 40℃의 온도에서 교반하여 완전히 용해한다. 그리고 유연제 10 중량부, 계면활성제인 라우레스설포욱시네이트 0.5 중량부, 금속이온봉쇄제인 사이클로덱스트린 3 중량부를 첨가하여 용해한 후, 15℃가 유지되는 저온저장고에서 약 3일간 숙성하여 섬유용 초발수 용액을 제조하였다. 상기 초발수 용액을 제조하는 데 첨가된 성분을 하기의 표 1에 표기하였다.20 parts by weight of silicon alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 50 nm and 20 parts by weight of aluminum alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 350 nm as a water repellent agent were evenly stirred while adding 40 parts by weight of methanol, and 53 parts by weight of linseed oil as a water repellent was added to the water repellent agent, and then 40 ° C. Stir at the temperature to dissolve completely. And 10 parts by weight of the softener, 0.5 parts by weight of the surfactant laureth sulfouccinate, and 3 parts by weight of the metal ion blocker cyclodextrin are dissolved and aged for about 3 days in a low-temperature storage room maintained at 15 ° C for super water repellent for fibers. The solution was prepared. The components added to prepare the super water-repellent solution are listed in Table 1 below.
상기 초발수 용액을 이용하여 초발수 원단을 제조하는 방법은 다음과 같다.A method of manufacturing a super water-repellent fabric using the super water-repellent solution is as follows.
먼저 포름산과 ph 조절제를 이용하여 제작한 산도가 4.5인 산성용액에 원단을 침지하여 원단의 산도를 6으로 조절한 후, 상기 초발수 용액에 픽업률 60%로 약재처리한다. 이어서 상기 원단에 포함된 수분을 제거하기 위하여 120℃로 가열된 텐터기에 통과시켜 건조하고, 약재를 원단에 고착시키기 위하여 150℃로 가열된 텐터기에서 1분간 큐어하여 초발수 원단을 완성하였다.First, the acidity of the fabric is adjusted to 6 by immersing the fabric in an acidic solution having an acidity of 4.5 produced using formic acid and a ph-adjusting agent, and then treated with a pick-up rate of 60% in the superhydrophobic solution. Subsequently, in order to remove moisture contained in the fabric, it was dried by passing through a tenter heated to 120 ° C, and cured for 1 minute in a tenter heated to 150 ° C to fix the medicine to the fabric, thereby completing the super water-repellent fabric.
(실시예 2)(Example 2)
제조 방법은 실시예 1과 동일하되, 평균입경이 50nm인 실리콘알콕사이드 30중량부와 평균입경이 350nm인 알루미늄알콕사이드 30 중량부에 메탄올 40중량부를 첨가하며 고르게 교반한 발수제를 사용하여 초발수 원단을 완성하였다.The manufacturing method is the same as in Example 1, but 30 parts by weight of silicon alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 50 nm and 30 parts by weight of aluminum alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 40 parts by weight are added with 40 parts by weight of methanol, and a super water-repellent fabric is completed using a water-repellent agent evenly stirred. Did.
(실시예 3)(Example 3)
제조 방법은 실시예 1과 동일하되, 평균입경이 50nm인 실리콘알콕사이드 40중량부와 평균입경이 350nm인 알루미늄알콕사이드 20 중량부에 메탄올 40중량부를 첨가하며 고르게 교반한 발수제를 사용하여 초발수 원단을 완성하였다.The manufacturing method is the same as in Example 1, but 40 parts by weight of silicon alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 50 nm and 20 parts by weight of aluminum alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 40 nm are added to 40 parts by weight of methanol and a super water-repellent fabric is completed using a water-repellent agent evenly stirred. Did.
(비교예 1)(Comparative Example 1)
제조 방법은 실시예 1과 동일하되, 평균입경이 350nm인 알루미늄알콕사이드 60 중량부에 메탄올 40 중량부를 첨가하며 고르게 교반한 발수제를 사용하여 초발수 원단을 완성하였다.The manufacturing method was the same as in Example 1, but the super water-repellent fabric was completed by using 40 parts by weight of methanol and 60 parts by weight of aluminum alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 350 nm, and evenly stirred water repellent.
(비교예 2)(Comparative Example 2)
제조 방법은 실시예 1과 동일하되, 평균입경이 50nm인 실리콘알콕사이드 10중량부와 평균입경이 350nm인 알루미늄알콕사이드 50 중량부에 메탄올 40 중량부를 첨가하며 고르게 교반한 발수제를 사용하여 초발수 원단을 완성하였다.The manufacturing method is the same as in Example 1, but adding 10 parts by weight of silicon alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 50 nm and 50 parts by weight of aluminum alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 40 nm, and adding 40 parts by weight of methanol to complete the super water-repellent fabric by using an evenly stirred water repellent agent. Did.
(비교예 3)(Comparative Example 3)
제조 방법은 실시예 1과 동일하되, 평균입경이 50nm인 실리콘알콕사이드 50중량부와 평균입경이 350nm인 알루미늄알콕사이드 10 중량부에 메탄올 40중량부를 첨가하며 고르게 교반한 발수제를 사용하여 초발수 원단을 완성하였다.The manufacturing method is the same as in Example 1, but 50 parts by weight of silicon alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 50 nm and 10 parts by weight of aluminum alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 40 nm are added to 40 parts by weight of methanol, and a super water-repellent fabric is completed using a water-repellent agent evenly stirred. Did.
(비교예 4)(Comparative Example 4)
제조 방법은 실시예 1과 동일하되, 평균입경이 50nm인 실리콘알콕사이드 60중량부에 메탄올 40중량부를 첨가하며 고르게 교반한 발수제를 사용하여 초발수 원단을 완성하였다.The manufacturing method was the same as in Example 1, but the super water-repellent fabric was completed by using 40 parts by weight of methanol and 60 parts by weight of silicon alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 50 nm, and evenly stirred water repellent.
상기 실시예 1~3 및 비교예 1~4에 포함된 발수제의 함량은 하기의 표 2와 같다.The contents of the water repellent agent included in Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Examples 1 to 4 are shown in Table 2 below.
(실험예 1) 접촉각측정(Experimental Example 1) Measurement of contact angle
상기 실시예 1~3 및 비교예 1~4로 제조된 초발수 원단의 접촉각을 측정하였다. 접촉각을 측정함으로서 초발수 처리된 직물의 표면 성상 및 물리적 특성변화, 즉, 표면자유에너지 또는 표면장력의 변화를 확인할 수 있으며, 이는 접촉각측정기를 이용하여 측정되었다. 증류수 10㎕를 원단에 떨어뜨려 접촉각을 측정하고, 3회 반복 측정 한 후 평균값을 구하여 하기의 표 3에 서술하였다.The contact angles of the superhydrophobic fabrics prepared in Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Examples 1 to 4 were measured. By measuring the contact angle, it is possible to confirm the change in the surface properties and physical properties of the super water-repellent treated fabric, that is, the change in surface free energy or surface tension, which was measured using a contact angle meter. 10 µl of distilled water was dropped on the fabric to measure the contact angle, and after 3 measurements, the average value was obtained and described in Table 3 below.
(°)Contact angle
( °)
표 3에 따르면 평균입경이 50nm인 실리콘알콕사이드와 평균입경이 350nm인 알루미늄알콕사이드의 비율이 1:2일 때 가장 접촉각이 높았으며, 이 값을 벗어날 경우 접촉각이 감소하는 것을 알 수 있었으며, 따라서, 평균 입경에 차이가 나는 두 성분을 섞어 발수제로 이용하는 것이 바람직하며, 그 비율은 1:2, 1:1, 2:1이 가장 바람직함을 알 수 있었다.According to Table 3, when the ratio of silicon alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 50 nm and aluminum alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 350 nm is 1: 2, the contact angle is highest, and it can be seen that the contact angle decreases when it exceeds this value. It was found that it is preferable to mix two components having different particle diameters and use them as a water repellent, and the ratio is 1: 2, 1: 1, and 2: 1 being the most preferable.
(실험예 2) 세탁횟수에 따른 발수성의 변화(Experimental Example 2) Change in water repellency according to the number of washes
상기 실시예 1~3 및 비교예 1~4로 처리된 원단의 세탁횟수별 발수성의 변화에 대해 실험하였다. 원단은 폴리에스테르와 면이 혼섬된 것으로 모든 실시예 및 비교예에서 동일한 것을 이용하였으며, 산도가 4.0인 포름산으로 산처리를 진행한 후, 약제처리를 하고, 수분 제거 및 고착 단계를 거쳐 완성되었다. 또한 발수/방수성은 AATCC 22 테스트 방법으로 측정되었으며, 그 결과는 하기의 표 4 및 도 4 와 동일하다.Experiments were conducted on the change in water repellency for each washing number of the fabrics treated with Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Examples 1 to 4. The fabric was a mixture of polyester and cotton, and the same was used in all examples and comparative examples. After the acid treatment was performed with formic acid having an acidity of 4.0, the agent was treated and completed through a water removal and fixation step. In addition, water repellency / water repellency was measured by the AATCC 22 test method, and the results are the same as in Table 4 and FIG. 4 below.
(50nm)(50nm)
(%)(%)
표 4에 따르면 세탁횟수가 0회인 경우 발수성을 띠던 실시예 및 비교예가 세탁 횟수가 30회일 때는 전체적으로 발수/방수성이 하락한 것을 알 수 있었으며, 실시예 1, 2, 3의 경우 하락률이 30% 미만인 것을 알 수 있으나, 비교예 1, 2, 3, 4의 하락률은 50%를 초과하는 것을 알 수 있었다.According to Table 4, when the number of washings was 0, it was found that the water repellent / water-repellent properties were decreased when the number of washes was 30 and the Examples and Comparative Examples that had water repellency were less than 30% in Examples 1, 2, and 3. As can be seen, it was found that the drop rates of Comparative Examples 1, 2, 3, and 4 exceeded 50%.
(실험예 3) 세탁횟수에 따른 발유성의 변화(Experimental Example 3) Change in oil repellency according to the number of washes
상기 실시예 1~3 및 비교예 1~4에 대한 세탁횟수별 발유성의 변화에 대해 실험하였다. 사용된 원단의 실험예 2의 방법과 동일하게 제작되었으며, 발유성은 AATCC 118 테스트 방법으로 측정되었고, 그 결과는 하기의 표 5 및 도 5와 동일하다.Experiments were conducted on the changes in oil repellency according to the number of washes for Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Examples 1 to 4. The fabric used was produced in the same way as in Experimental Example 2, and the oil repellency was measured by the AATCC 118 test method, and the results are the same as in Table 5 and FIG. 5 below.
(50nm)(50nm)
(%)(%)
표 5에 따르면 세탁횟수가 0회인 경우 발유성을 띠던 실시예 및 비교예가 세탁 횟수가 30회 일때는 전체적으로 발유성이 하락한 것을 알 수 있었으며, 실시예 1, 2, 3의 경우 하락률이 40% 미만이었지만, 비교예 1, 2, 3, 4의 하락률이 60%에 가까운 것을 알 수 있었다.According to Table 5, when the number of washings was 0, it was found that in the Examples and Comparative Examples that had oil repellency, when the number of washings was 30, the overall oil repellency decreased, and in Examples 1, 2, and 3, the drop rate was less than 40%. However, it was found that the drop rates of Comparative Examples 1, 2, 3, and 4 were close to 60%.
(실험예 4) 세탁횟수에 따른 방오성의 변화(Experimental Example 4) Change of antifouling property according to the number of washing
상기 실시예 1~3 및 비교예 1~4에 대한 세탁횟수별 방오성의 변화에 대해 실험하였다. 사용된 원단의 실험예 2의 방법과 동일하게 제작되었으며, 방오성은 AATCC 193 테스트 방법으로 측정되었고, 그 결과는 하기의 표 6 및 도 6과 동일하다.The anti-fouling properties of each of Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Examples 1 to 4 according to the number of washings were tested. The fabric used was manufactured in the same manner as in Experimental Example 2, and the antifouling property was measured by the AATCC 193 test method, and the results are the same as in Table 6 and FIG. 6 below.
(50nm)(50nm)
(%)(%)
표 6에 따르면 세탁횟수가 0회인 경우 발유성을 띠던 실시예 및 비교예가 세탁 횟수가 30회 일때는 전체적으로 발유성이 하락한 것을 알 수 있었으며, 실시예 1, 2, 3의 경우 하락률이 40% 미만이었지만, 비교예 1, 2, 3, 4의 하락률이 60%를 초과하는 것을 알 수 있었다.According to Table 6, when the number of washings was 0, it was found that in the Examples and Comparative Examples that had oil repellency, when the number of washings was 30, the overall oil repellency decreased, and in Examples 1, 2, and 3, the drop rate was less than 40%. However, it was found that the drop rates of Comparative Examples 1, 2, 3, and 4 exceeded 60%.
상기 실험예 2, 3, 4에 따르면 평균 입경에 차이가 나는 두 성분을 섞어 발수제로 이용하는 경우 그 비율이 1:2, 1:1, 2:1이 가장 바람직하며, 해당 비율을 지키지 않은 비교예 1, 2, 3, 4의 경우 발수성, 발유성 및 방오성이 미미하게 떨어지며, 특히 30회 이상 세탁한 후에는 실시예 1, 2, 3보다 현저하게 그 성질이 떨어지는 것을 알 수 있다.According to Experimental Examples 2, 3, and 4, when two components having differences in average particle diameters are used as a water repellent, the ratios of 1: 2, 1: 1, and 2: 1 are most preferable, and comparative examples in which the ratios are not observed. In the case of 1, 2, 3, 4, the water repellency, oil repellency, and antifouling properties are insignificantly lowered. In particular, it can be seen that the properties are significantly lower than those of Examples 1, 2, and 3 after washing 30 times or more.
1 : 원단공급부
2 : 텐션부
3 : 전처리부
4 : 약제처리부
5 : 건조부
6 : 경화부
7 : 권취부1: Fabric supply part
2: Tension part
3: Pre-processing part
4: Pharmaceutical treatment unit
5: drying section
6: Hardened part
7: winding part
Claims (15)
Translated fromKorean발수제 60 중량부에 대하여 방수제 53~66 중량부, 유연제 8~15 중량부 및
계면활성제 0.3~0.7 중량부를 포함하여 이루어지되,
금속이온봉쇄제를 더 포함할 수 있으며,
상기 발수제는,
평균 입경이 5~100nm인 실리콘알콕사이드와 평균 입경이 300~500nm인 알루미늄알콕사이드의 혼합물로 이루어지며,
상기 실리콘알콕사이드와 상기 알루미늄알콕사이드의 비율은 1:2로 이루어지고,
상기 방수제는,
밀랍, 왁스, 아마인유, 테레빈유, 피마자유 중에서 선택되는 하나 또는 이들의 혼합물로 이루어지며,
상기 계면활성제는,
음이온 계면활성제로, 라우레스설포욱시네이트, 소듐라우릴에테르설페이트, 디소듐코코암포디아세테이트, 지방산나트륨, 모노알킬황산염, 알킬폴리옥시에틸렌황산염, 알킬벤젠술폰산염, 모노알킬인산염으로 구성된 군에서 선택되는 어느 하나로 이루어지며,
상기 금속이온봉쇄제는,
글루코닉에씨드, 디소듐파이로포스페이트, 사이클로덱스트린, 이디티에이, 시트릭에씨드, 하이드록시프로필사이클로텍스트린, 휴믹애씨드로 이루어진 군에서 선택되는 어느 하나로 이루어지는 특징이 있는 원단에 미세먼지가 흡착 및 흡수되는 것을 방지하는 성능을 가지는 섬유용 초발수 용액.In the super water-repellent solution for fibers,
53 to 66 parts by weight of waterproofing agent, 8 to 15 parts by weight of softener and 60 parts by weight of water repellent
It consists of 0.3 to 0.7 parts by weight of surfactant,
It may further include a metal ion blocker,
The water repellent,
It consists of a mixture of silicon alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 5 to 100 nm and aluminum alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 300 to 500 nm.
The ratio of the silicon alkoxide and the aluminum alkoxide is 1: 2,
The repellent,
It consists of one or a mixture of beeswax, wax, linseed oil, turpentine oil, castor oil,
The surfactant,
As an anionic surfactant, in the group consisting of laureth sulfouccinate, sodium lauryl ether sulfate, disodium cocoamphodiacetate, sodium fatty acid, monoalkyl sulfate, alkylpolyoxyethylene sulfate, alkylbenzenesulfonate, monoalkyl phosphate It is made of any one selected,
The metal ion blocker,
Fine dust is adsorbed and adsorbed on the fabric having the characteristic of any one selected from the group consisting of gluconic acid, disodium pyrophosphate, cyclodextrin, IDT, citric acid, hydroxypropyl cyclotextrin, and humic acid. Super water-repellent solution for fibers having the performance of preventing absorption.
상기 초발수 용액은,
발수제에 방수제가 첨가되어 이루어지며,
40~45℃의 온도로 교반되어 이루어지는 특징이 있는 원단에 미세먼지가 흡착 및 흡수되는 것을 방지하는 성능을 가지는 섬유용 초발수 용액.According to claim 1,
The super water-repellent solution,
Made by adding water repellent to water repellent,
A super water-repellent solution for fibers having the performance of preventing fine dust from being adsorbed and absorbed on a fabric having a characteristic of being stirred at a temperature of 40 to 45 ° C.
상기 초발수 용액은,
10~15℃의 저온저장고에서 숙성되어 이루어지는 특징이 있는 원단에 미세먼지가 흡착 및 흡수되는 것을 방지하는 성능을 가지는 섬유용 초발수 용액.According to claim 1,
The super water-repellent solution,
A super water-repellent solution for fibers having the performance of preventing fine dust from being adsorbed and absorbed on a fabric having characteristics characterized by being aged in a cold storage at 10 ~ 15 ℃.
(b) 상기 교반 단계 후에 발수제 60 중량부기준으로 방수제 53~66 중량부를 첨가하여 40~45℃의 온도에서 교반하여 완전히 용해하는 방수제첨가 단계;
(c) 상기 방수제첨가 단계 후에 유연제 8~15 중량부와 계면활성제 0.3~0.7 중량부를 첨가하여 용해하는 용해 단계;
(d) 상기 용해 단계 후에 10~15℃의 저온저장고에서 숙성하여 초발수 용액이 완성되는 초발수용액 완성 단계;
(e) 원단을 산성용액에 침지하여 산처리하는 산처리 단계;
(f) 상기 산처리 단계에서 산처리를 마친 원단을 상기 초발수 용액에 침지하여 약제처리하는 약제처리 단계;
(g) 상기 약제처리 단계에서 약제처리를 거친 원단을 110~150℃의 온도로 건조하여 수분율이 50~60%가 되도록 수분을 제거하는 건조 단계;
(h) 상기 건조 단계에서 건조를 마친 원단을 가열하여 원단에 초발수성분을 고착시키는 고착 단계;로 이루어지되,
상기 방수제첨가 단계에서 방수제는 밀랍, 왁스, 아마인유, 테레빈유, 피마자유 중에서 선택되는 하나 또는 이들의 혼합물로 이루어지고,
상기 용해 단계에서 상기 계면활성제는, 음이온 계면활성제로, 라우레스설포욱시네이트, 소듐라우릴에테르설페이트, 디소듐코코암포디아세테이트, 지방산나트륨, 모노알킬황산염, 알킬폴리옥시에틸렌황산염, 알킬벤젠술폰산염, 모노알킬인산염으로 구성된 군에서 선택되는 어느 하나로 이루어지고,
상기 산처리 단계에서 산성용액은, 포름산, 빙초산, 황산, 수산, 크롬산, 인산으로 이루어진 군에서 선택된 어느 하나로 구성되어 이루어지며, 상기 산성용액의 산도가 4.0~5.0인 것을 특징으로 하고,
상기 산처리 단계에서 산처리를 마친 원단은, 5.5~6.5의 산도를 지니는 특징이 있는 미세먼지가 흡착 및 흡수되는 것을 방지하는 성능을 가지는 섬유용 초발수 용액을 이용한 초발수 원단의 제조방법.(a) agitation step of adding 40 parts by weight of methanol and stirring based on 60 parts by weight of a water repellent agent in which the ratio of silicon alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 5 to 100 nm and aluminum alkoxide having an average particle diameter of 300 to 500 nm is 1: 2;
(b) after the stirring step, adding a waterproofing agent 53 to 66 parts by weight based on 60 parts by weight of the water repellent, followed by stirring at a temperature of 40 to 45 ° C. to completely dissolve the waterproofing agent;
(c) a dissolution step of adding and dissolving 8 to 15 parts by weight of a softener and 0.3 to 0.7 parts by weight of a surfactant after the step of adding the waterproofing agent;
(d) after the dissolving step, a super water-repellent solution completion step of aging in a cold storage at 10-15 ° C. to complete the super-water-repellent solution;
(e) acid treatment step of acid treatment by immersing the fabric in an acidic solution;
(f) a chemical treatment step of immersing the fabric that has been acid-treated in the acid treatment step in the super water-repellent solution to treat the medicine;
(g) a drying step of removing the water so that the water content is 50 to 60% by drying the fabric that has undergone the drug treatment at a temperature of 110 to 150 ° C in the drug treatment step;
(h) a fixing step of fixing the super water-repellent component to the fabric by heating the fabric that has been dried in the drying step;
In the step of adding the waterproofing agent, the waterproofing agent is made of one or a mixture selected from beeswax, wax, linseed oil, turpentine oil, and castor oil,
In the dissolving step, the surfactant is an anionic surfactant, laurethsulfouxinate, sodium lauryl ether sulfate, disodium cocoamphodiacetate, sodium fatty acid, monoalkyl sulfate, alkylpolyoxyethylene sulfate, alkylbenzenesulfonic acid It is made of any one selected from the group consisting of salts and monoalkyl phosphates,
In the acid treatment step, the acidic solution is made of any one selected from the group consisting of formic acid, glacial acetic acid, sulfuric acid, oxalic acid, chromic acid, and phosphoric acid, and the acidic solution has an acidity of 4.0 to 5.0,
In the acid treatment step, the fabric which has been subjected to the acid treatment is a method for producing a super water-repellent fabric using a super-water-repellent solution for fibers having a function of preventing adsorption and absorption of fine dust having a characteristic having an acidity of 5.5 to 6.5.
상기 산처리 단계에서,
상기 산성용액의 산도를 맞추기 위해 pH 조절제를 더 첨가하는 것을 특징으로 이루어지는 미세먼지가 흡착 및 흡수되는 것을 방지하는 성능을 가지는 섬유용 초발수 용액을 이용한 초발수 원단의 제조방법.The method of claim 8,
In the acid treatment step,
Method for manufacturing a super water-repellent fabric using a super water-repellent solution for fibers having the performance of preventing the fine dust is adsorbed and absorbed, characterized in that a pH adjuster is further added to adjust the acidity of the acid solution.
상기 고착 단계는,
140~160℃의 온도로 1~2분 동안 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 미세먼지가 흡착 및 흡수되는 것을 방지하는 성능을 가지는 섬유용 초발수 용액을 이용한 초발수 원단의 제조방법.The method of claim 8,
The fixing step,
Method for manufacturing a super water-repellent fabric using a super-water-repellent solution for fibers having a function of preventing adsorption and absorption of fine dust, characterized in that it is made for 1 to 2 minutes at a temperature of 140 to 160 ° C.
상기 고착단계를 거쳐 완성된 원단은,
구김방지, 수분 제어, 얼룩 방지, 얼룩 제거, 오염 방지, 미세먼지 흡수 방지, 발수, 발유, 자외선 차단의 표면 효과를 지니며,
상기한 미세먼지는 PM 2.5~10의 미세한 먼지인 특징이 있는 미세먼지가 흡착 및 흡수되는 것을 방지하는 성능을 가지는 섬유용 초발수 용액을 이용한 초발수 원단의 제조방법.The method of claim 8,
The fabric completed through the fixing step,
Anti-wrinkle, moisture control, stain prevention, stain removal, pollution prevention, fine dust absorption prevention, water-repellent, oil-repellent, UV-blocking surface effect,
The fine dust is a method of manufacturing a super water-repellent fabric using a super-water-repellent solution for fibers having the performance of preventing the fine dust having the characteristic of fine dust of PM 2.5 to 10 from being adsorbed and absorbed.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190108734AKR102084948B1 (en) | 2019-09-03 | 2019-09-03 | A super-water-repellent solution for fibers having a capability of preventing fine dust from being adsorbed and absorbed on a fabric, and a method for manufacturing an super-water-repellent fabric using the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190108734AKR102084948B1 (en) | 2019-09-03 | 2019-09-03 | A super-water-repellent solution for fibers having a capability of preventing fine dust from being adsorbed and absorbed on a fabric, and a method for manufacturing an super-water-repellent fabric using the same |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR102084948B1true KR102084948B1 (en) | 2020-04-24 |
Family
ID=70466154
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190108734AActiveKR102084948B1 (en) | 2019-09-03 | 2019-09-03 | A super-water-repellent solution for fibers having a capability of preventing fine dust from being adsorbed and absorbed on a fabric, and a method for manufacturing an super-water-repellent fabric using the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102084948B1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102273201B1 (en) | 2021-01-12 | 2021-07-06 | 주식회사 삼흥글로벌텍스 | Manufacturing method of functional mesh fabric and functional mesh fabric manufactured by the same |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20010065617A (en) | 1999-12-30 | 2001-07-11 | 박종섭 | Structure of semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same |
| KR20050096183A (en)* | 2003-02-07 | 2005-10-05 | 아사히 가라스 가부시키가이샤 | Water repellent oil repellent agent water base composition |
| JP2007056126A (en)* | 2005-08-24 | 2007-03-08 | Lion Corp | Water repellent composition |
| KR20100109236A (en)* | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-08 | 코오롱글로텍주식회사 | Compositions having water-repellent and antistatic property, manufacturing method thereof and polyester fabrics treated thereby |
| JP2013541649A (en)* | 2010-09-20 | 2013-11-14 | ザ プロクター アンド ギャンブル カンパニー | Fabric care formulations and methods |
| KR20180024722A (en)* | 2016-08-31 | 2018-03-08 | (주)브리즈텍스 | Eco―Friendly Water―Repellent Treatment Having Excellent Water―Repellent And Wash Durability |
- 2019
- 2019-09-03KRKR1020190108734Apatent/KR102084948B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20010065617A (en) | 1999-12-30 | 2001-07-11 | 박종섭 | Structure of semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same |
| KR20050096183A (en)* | 2003-02-07 | 2005-10-05 | 아사히 가라스 가부시키가이샤 | Water repellent oil repellent agent water base composition |
| JP2007056126A (en)* | 2005-08-24 | 2007-03-08 | Lion Corp | Water repellent composition |
| KR20100109236A (en)* | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-08 | 코오롱글로텍주식회사 | Compositions having water-repellent and antistatic property, manufacturing method thereof and polyester fabrics treated thereby |
| JP2013541649A (en)* | 2010-09-20 | 2013-11-14 | ザ プロクター アンド ギャンブル カンパニー | Fabric care formulations and methods |
| KR20180024722A (en)* | 2016-08-31 | 2018-03-08 | (주)브리즈텍스 | Eco―Friendly Water―Repellent Treatment Having Excellent Water―Repellent And Wash Durability |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102273201B1 (en) | 2021-01-12 | 2021-07-06 | 주식회사 삼흥글로벌텍스 | Manufacturing method of functional mesh fabric and functional mesh fabric manufactured by the same |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1475426B1 (en) | Process for the production of removable soil- and water-resistant surface coatings | |
| EP2510074B1 (en) | Use of soil repellency aqueous dispersions, soil repellant soft articles, and methods of making the same | |
| CA2219894A1 (en) | Improved aqueous anti-soiling composition | |
| CN109923180B (en) | Non-Fluorinated Paints and Finishes | |
| Ali et al. | Novel, Self-Assembled Antimicrobial Textile Coating Containing Chitosan Nanoparticles. | |
| Ceria et al. | Atmospheric plasma treatment to improve durability of a water and oil repellent finishing for acrylic fabrics | |
| ES2390123T3 (en) | Water-based composition and a water and oil repellent agent | |
| Rahmatinejad et al. | Polyester hydrophobicity enhancement via UV-Ozone irradiation, chemical pre-treatment and fluorocarbon finishing combination | |
| Shen et al. | Development of durable shrink-resist coating of wool with sol-gel polymer processing | |
| EP4039714A1 (en) | Organic fine particle | |
| KR102084948B1 (en) | A super-water-repellent solution for fibers having a capability of preventing fine dust from being adsorbed and absorbed on a fabric, and a method for manufacturing an super-water-repellent fabric using the same | |
| CN110512428B (en) | Durable fluoride-free super-hydrophobic fabric finishing liquid and method for finishing fabric by using same | |
| CN113214703B (en) | A kind of water-based photocurable superhydrophobic coating and preparation method and application thereof | |
| WO2019076823A1 (en) | METHOD FOR PRODUCING A TEXTILE ARTICLE WITH HYDROPHOBIZED TEXTILE SURFACE BY PLASMA TREATMENT AND WET CHEMICAL TREATMENT | |
| Ma et al. | Fabricating durable, fluoride‐free, water repellency cotton fabrics with CPDMS | |
| Gashti et al. | Ultrasound for efficient emulsification and uniform coating of an anionic lubricant on cotton | |
| Tragoonwichian et al. | Double coating via repeat admicellar polymerization for preparation of bifunctional cotton fabric: ultraviolet protection and water repellence | |
| EP3498910A1 (en) | Superhydrophobic coatings for the treatment of textiles | |
| DE10135157A1 (en) | Process for applying a self-cleaning coating to textiles | |
| CN106758215A (en) | A kind of bafta hydrophobic finishing method based on the modified silicon ball electron beam technology of esters of acrylic acid | |
| US20150072171A1 (en) | Hydrophobic surface treatment compositions comprising titanium precursors | |
| CN115538169B (en) | Durable superhydrophobic cotton fabric and preparation method thereof | |
| KR102359633B1 (en) | Antifouling fabric and producing method thereof | |
| CN105780448A (en) | Waterproof, antifouling and antibacterial functional fabric | |
| KR102054867B1 (en) | Method of manufacturing for superhydrophobic polymer fabric comprising fluorine-free polymer |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20190903 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0302 | Request for accelerated examination | Patent event date:20190905 Patent event code:PA03022R01D Comment text:Request for Accelerated Examination Patent event date:20190903 Patent event code:PA03021R01I Comment text:Patent Application | |
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20191022 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20200227 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20200228 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20200228 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20230328 Start annual number:4 End annual number:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20240214 Start annual number:5 End annual number:5 |