KR102067629B1 - Learning method and apparatus for improved resolution of low resolution satellite images - Google Patents
Learning method and apparatus for improved resolution of low resolution satellite imagesDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102067629B1 KR102067629B1KR1020190130179AKR20190130179AKR102067629B1KR 102067629 B1KR102067629 B1KR 102067629B1KR 1020190130179 AKR1020190130179 AKR 1020190130179AKR 20190130179 AKR20190130179 AKR 20190130179AKR 102067629 B1KR102067629 B1KR 102067629B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- image
- generated
- resolution
- network
- learning
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T3/00—Geometric image transformations in the plane of the image
- G06T3/40—Scaling of whole images or parts thereof, e.g. expanding or contracting
- G06T3/4053—Scaling of whole images or parts thereof, e.g. expanding or contracting based on super-resolution, i.e. the output image resolution being higher than the sensor resolution
- G06T3/4076—Scaling of whole images or parts thereof, e.g. expanding or contracting based on super-resolution, i.e. the output image resolution being higher than the sensor resolution using the original low-resolution images to iteratively correct the high-resolution images
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N20/00—Machine learning
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/10—Image acquisition modality
- G06T2207/10032—Satellite or aerial image; Remote sensing
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20081—Training; Learning
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20084—Artificial neural networks [ANN]
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
- Image Processing (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 저해상도 위성영상의 해상도 향상을 위한 학습 방법 및 장치에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a learning method and apparatus for improving the resolution of low resolution satellite images.
최근 들어 지구 관측 위성 영상 기술의 발전에 의해 인공위성으로부터 고정밀, 대용량의 고해상도 위성 영상을 획득할 수 있게 되었다. 고해상도 위성 영상은 농작물 모니터링 및 분석, 국토 관리, 지도 제작, 국방 안보, 환경 관리, 입지 선정 등에 있어서 매우 유용한 자료가 되고 있다. 이와 같이 다양한 분야에서 고해상도 위성 영상의 활용도가 높아짐에 따라, 수신된 영상을 최대한 신속하게 획득하고자 하는 요구 또한 증가하고 있다.Recently, with the development of earth observation satellite imaging technology, it is possible to acquire high-resolution, high-resolution satellite images from satellites. High-resolution satellite images are very useful for crop monitoring and analysis, land management, mapping, defense security, environmental management, and location selection. As the utilization of high resolution satellite images increases in various fields, the demand for obtaining the received images as quickly as possible increases.
한편, 공공, 산업, 군사 등 분야를 막론하고 점차 실시간에 가까운 위성영상 수집 및 활용의 필요성이 증대되면서 여러 대의 초소형 위성 편대를 군집 운용하는 방식에 대한 관심이 증대되고 있다. 초소형 위성은 크기, 무게가 일반 대형위성에 비해 작아 상당한 비용절감 효과가 있으나, 이에 상응하게 촬영된 위성영상의 해상도 성능 저하가 발생하는 문제점이 있다.Meanwhile, as the necessity of collecting and utilizing near-real-time satellite images in public, industrial, and military fields is increasing, interest in a method of clustering and operating a plurality of ultra-small satellite squadrons is increasing. The ultra-small satellite has a considerable cost reduction effect due to its small size and weight compared to a general large satellite, but has a problem in that resolution performance of a satellite image corresponding to the satellite is reduced.
국방분야에서, 광학 위성영상 분석 과정은 숙련된 판독관이 수동으로 표적을 식별한다. 판독관의 표적 식별 정확도 향상 및 추후 판독과정의 자동화를 위해 위성영상 품질 향상이 반드시 필요한 과제이다. 한편, 광학 위성영상의 목표객체가 일반적으로 매우 작은 크기이기 때문에 물체 탐지 및 식별이 어렵고, 확대하게 되면 영상의 질이 떨어져 탐지 정확도가 떨어지는 문제점이 있다. 광학 영상 내 물체 식별 정확도는 광학 영상의 해상도와 질에 의존하기 때문에 초소형 위성에서 얻어진 저해상도의 광학 영상을 고해상도로 복원이 필요하다.In the field of defense, optical satellite image analysis procedures allow a skilled reader to manually identify the target. In order to improve the accuracy of the target identification of the reader and to automate the reading process later, the improvement of satellite image quality is an essential task. On the other hand, since the target object of the optical satellite image is generally a very small size, it is difficult to detect and identify the object, and when enlarged, the quality of the image is degraded and the detection accuracy is lowered. Since the accuracy of object identification in the optical image depends on the resolution and quality of the optical image, it is necessary to reconstruct the low resolution optical image obtained from the micro satellite at high resolution.
광학 위성영상은 매우 많은 물체가 들어있기에 일반 영상에 비해 복잡성이 크다. 따라서, 일반영상에서의 초해상도 기술을 그대로 광학 위성영상에 적용할 경우 복원되는 영상의 품질 향상도가 일반 영상에 비해 현저히 떨어지는 문제점이 있다.Optical satellite images are more complicated than ordinary images because they contain so many objects. Therefore, when the super resolution technology of the general image is applied to the optical satellite image as it is, the quality improvement of the reconstructed image is significantly lower than that of the general image.
현재 초소형 전술위성체계 구축을 위한 논의가 활발하게 이루어지고 있으며, 저비용의 초소형 위성을 군집으로 운용하여 짧은 재방문 주기 확보 가능하다. 적의 동태를 파악할 수 있는 실시간 감시정찰은 국방 분야에서 매우 중요한 과제이다. 예를 들면, 일례로, 미사일의 발사 징후 포착을 위해서는 수 시간 단위의 감시정찰이 필요하다.At present, discussions on the construction of a very small tactical satellite system are being actively conducted, and a short re-visit period can be secured by using a low-cost, compact satellite in a group. Real-time surveillance and reconnaissance of enemy dynamics is an important task in the defense sector. For example, several hours of surveillance and reconnaissance are needed to capture missile launch signs.
따라서, 초소형 위성체의 하드웨어 성능 한계를 극복하고 보완하기 위한 알고리듬이 필요하고, 위성영상의 해상도를 높이기 위해 지도학습 기반으로 많은 연구들이 수행되었으나, 데이터 쌍이 존재하지 않는 실제 위성영상의 해상도를 높이기에 적절하지 않다는 문제점이 있다.Therefore, algorithms are needed to overcome and supplement the hardware performance limitations of micro-satellite, and many studies have been conducted on the basis of supervised learning to increase the resolution of satellite images, but it is appropriate to increase the resolution of actual satellite images without data pairs. There is a problem that it does not.
[선행기술문헌번호][Prior art document number]
[특허문헌 1] KR 10-0991146호[Patent Document 1] KR 10-0991146
[특허문헌 2] KR 10-1986025호[Patent Document 2] KR 10-1986025
실시 예들은 초소형 위성에서 획득한 실제 저해상도 위성영상의 고해상화를 할 수 있으며, 그에 따라 위성영상 내 정보 증가 및 분석 능력을 향상시킬 수 있는 저해상도 영상의 해상도 향상을 위한 학습 방법 및 장치를 제공한다.Embodiments can provide a high resolution of a real low resolution satellite image obtained from a small satellite, and thus provide a learning method and apparatus for improving the resolution of a low resolution image that can improve information increase and analysis capability in the satellite image.
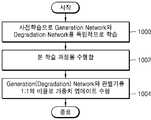
상기 과제를 해결하기 위한, 일 실시 예에 따른 저해상도 위성영상의 해상도를 향상시키기 위한 학습 방법으로서, 동일 영역을 촬영한 제1 해상도를 갖는 제1 영상 및 상기 제1 해상도보다 높은 제2 해상도를 갖는 제2 영상을 획득하는 단계; 상기 제1 영상을 제네레이션 네트워크(Generation Network)에 입력하여 상기 제2 해상도에 상응하는 제1-1 영상을 생성하고, 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상을 판별하는 단계; 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상을 디그라데이션 네트워크(Degaradation Network)에 입력하여 상기 제1 해상도에 상응하는 제1-2 영상을 생성하고, 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상을 판별하는 단계; 및 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상의 판별 결과 및 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상을 판별 결과를 기초로 상기 제네레이션 네트워크 및 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크를 학습하는 단계를 포함한다.In order to solve the problem, a learning method for improving the resolution of a low resolution satellite image according to an embodiment includes: a first image having a first resolution photographing the same region and a second resolution higher than the first resolution Obtaining a second image; Inputting the first image to a generation network to generate a first-first image corresponding to the second resolution, and determining the generated first-first image and the second image; The generated 1-1 image is input to a degaradation network to generate a 1-2 image corresponding to the first resolution, and the generated 1-2 image and the first image are discriminated. Doing; And learning the generation network and the degradation network based on a result of discriminating the generated first-first image and the second image and a result of discriminating the generated 1-2 image and the first image. Include.
상기 제네레이션 네트워크 및 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크는, 순환 대립 뉴럴 네트워크 구조인 것을 특징으로 한다.The generation network and the degradation network are characterized by a cyclically opposed neural network structure.
상기 학습 단계는, 상기 제네레이션 네트워크와 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상을 판별하는 판별기, 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크와 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상을 판별하는 판별기 각각을 1:1의 비율로 가중치 업데이트를 수행하는 것을 특징으로 한다.The learning step may include a discriminator for discriminating the generation network, the generated first-first image and the second image, and determining the discrimination network, the generated 1-2 image and the first image. Each weight is updated by a ratio of 1: 1.
상기 학습 단계는, 로스 함수를 계산하는 단계를 더 포함하고, 상기 로스 함수는, 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상 및 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상 각각의 소정의 가중치가 각각 곱해진, 대립적인 로스 값(Adverarial Loss)과 인지적인 로스 값(Perceptual Loss)의 합으로 구성되는 것을 특징으로 한다.The learning step may further include a step of calculating a loss function, wherein the loss function is an opposing, multiplied by a predetermined weight of each of the generated first-first image and the generated first-second image, respectively. It is characterized by consisting of the sum of the loss (Adverarial Loss) and the perceptual loss (Perceptual Loss).
상기 제1 영상을 업 샘플링하여 상기 제2 영상과 동일한 크기의 제3 영상을 생성하는 단계를 더 포함하고, 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상의 대립적인 로스 값은 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상 간의 차이에 따라 계산되고, 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상의 인지적인 로스 값은 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제3 영상 간의 차이에 따라 계산되고, 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상의 대립적인 로스 값은 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상 간의 차이에 따라 계산되고, 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상의 인지적인 로스 값은 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상 간의 차이에 따라 계산되는 것을 특징으로 한다. Generating a third image having the same size as that of the second image by upsampling the first image, wherein an opposite loss value of the generated first-first image is generated; Is calculated according to the difference between the second image and the perceived loss value of the generated first-first image is calculated according to the difference between the generated first-first image and the third image. The opposing loss value of the 1-2 image is calculated according to the difference between the generated 1-2 image and the first image, and the perceptual loss value of the generated 1-2 image is calculated in the generated first-first image. It is calculated according to the difference between the second image and the first image.
상기 로스 함수는를 사용하고, 다음 수학식 1 및 2에 의해 계산되는 것을 특징으로 하는 학습 방법.The loss function is Using, and is calculated by the following equations (1) and (2).
[수학식 1][Equation 1]
[수학식 2][Equation 2]
(여기서,는 사전학습된 VGG 모델의 4번 레이어의 피처 값()을 최소제곱법(MSE, mean square error)을 통해 계산하고, α와 β는 학습에 필요한 파라미터들이고, D는 촬영한 실제영상/생성영상을 판단하는 구분자이고, G는 저해상도 영상 입력을 받아 복원 영상을 생성하는 생성자를 의미함)(here, Is the feature value of
상기 제1 해상도는, GSD(Ground Sample Distance) 기준으로 4m이고, 상기 제2 해상도는, GSD 기준으로 0.5m인 것을 특징으로 한다.The first resolution is 4m on a GSD (Ground Sample Distance) basis, and the second resolution is 0.5m on a GSD basis.
상기 학습 방법은 상기 제네레이션 네트워크 및 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크를 독립적으로 사전 학습하는 것을 특징으로 한다.The learning method may be independently pre-learning the generation network and the degradation network.
다른 실시 예에 따른 저해상도 위성영상의 해상도를 향상시키기 위한 학습 방법을 수행하는 프로세서에 있어서, 상기 프로세서는 동일 영역을 촬영한 제1 해상도를 갖는 제1 영상 및 상기 제1 해상도보다 높은 제2 해상도를 갖는 제2 영상을 획득하고, 상기 제1 영상을 제네레이션 네트워크(Generation Network)에 입력하여 상기 제2 해상도에 상응하는 제1-1 영상을 생성하고, 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상을 판별하고, 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상을 디그라데이션 네트워크(Degaradation Network)에 입력하여 상기 제1 해상도에 상응하는 제1-2 영상을 생성하고, 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상을 판별하고, 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상의 판별 결과 및 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상을 판별 결과를 기초로 상기 제네레이션 네트워크 및 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크를 학습하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In a processor for performing a learning method for improving the resolution of a low resolution satellite image according to another embodiment, the processor may include a first image having a first resolution photographing the same area and a second resolution higher than the first resolution. Acquire a second image having the first image, input the first image to a generation network, generate a 1-1 image corresponding to the second resolution, and generate the generated 1-1 image and the second image. Determine the image, and input the generated 1-1 image to the degaradation network to generate a 1-2 image corresponding to the first resolution, the generated 1-2 image and the The first image is determined, and the generation network and the image are generated based on a result of discriminating the generated 1-1 image and the second image, and a result of discriminating the generated 1-2 image and the first image. Characterized in that the de-Learning Network gradient.
상기 제네레이션 네트워크 및 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크는, 순환 대립 뉴럴 네트워크 구조인 것을 특징으로 한다.The generation network and the degradation network are characterized by a cyclically opposed neural network structure.
상기 프로세서는, 상기 제네레이션 네트워크와 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상을 판별하는 판별기, 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크와 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상을 판별하는 판별기 각각을 1:1의 비율로 가중치 업데이트를 수행하는 것을 특징으로 한다.The processor may include a discriminator for discriminating the generation network, the generated 1-1 image and the second image, and a discriminator for discriminating the degradation network, the generated 1-2 image and the first image. Each of the weights may be updated at a ratio of 1: 1.
상기 프로세서는, 로스 함수를 계산하고, 상기 로스 함수는,The processor calculates a loss function, and the loss function is
상기 생성된 제1-1 영상 및 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상 각각의 소정의 가중치가 각각 곱해진, 대립적인 로스 값(Adverarial Loss)과 인지적인 로스 값(Perceptual Loss)의 합으로 구성되는 것을 특징으로 한다.A predetermined weight of each of the generated first-first image and the generated first-second image, respectively, is multiplied by a sum of an adversarial loss value and a perceptual loss value. It features.
또 다른 실시 예에 따른 저해상도 위성영상의 해상도 향상 방법에 있어서, 제1 해상도를 갖는 제1 위성영상을 획득하는 단계; 저해상도 위성영상의 해상도 향상을 위한 학습 방법에 의해 학습된 제너레이션 네트워크에 상기 제1 위성영상을 입력하는 단계; 및 제2 해상도에 상응하는 제2 위성영상을 생성하여 출력하는 단계를 포함한다.According to another embodiment, a method of improving resolution of a low resolution satellite image, the method comprising: obtaining a first satellite image having a first resolution; Inputting the first satellite image to a generation network learned by a learning method for improving the resolution of the low resolution satellite image; And generating and outputting a second satellite image corresponding to the second resolution.
또 다른 실시 예에 따른 저해상도 위성영상의 해상도 향상 장치에 있어서, 메모리; 및 프로세서를 포함하고, 상기 프로세서는, 저해상도 위성영상의 해상도 향상 방법을 수행하는 것을 특징으로 한다.According to another embodiment, an apparatus for improving resolution of a low resolution satellite image, the apparatus comprising: a memory; And a processor, wherein the processor is configured to perform a method for improving resolution of a low resolution satellite image.
또 다른 실시 예에 따른 저해상도 위성영상의 해상도를 향상시키기 위한 학습 방법을 컴퓨터에서 실행시키기 위한 프로그램을 기록한 기록매체를 포함한다.Another embodiment includes a recording medium on which a program for executing a learning method for improving the resolution of a low resolution satellite image is recorded on a computer.
실시 예들은 초소형 위성에서 획득한 실제 저해상도 위성영상의 고해상화를 할 수 있으며, 그에 따라 위성영상 내 정보 증가 및 분석 능력을 향상시킬 수 있다.Embodiments can achieve a high resolution of the actual low resolution satellite image obtained from the micro-satellite, thereby improving the information increase and analysis capabilities in the satellite image.
도 1은 일 실시예에 따른 뉴럴 네트워크의 아키텍처를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 2는 일 실시예에 따른 뉴럴 네트워크에서 입력 피처맵 및 출력 피처맵의 관계를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 3은 일 실시예에 따른 뉴럴 네트워크 장치의 하드웨어 구성을 도시한 블록도이다.
도 4는 뉴럴 네트워크의 컨볼루션 연산을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 5는 일 실시 예에 따른 학습 데이터의 예시 영상들이다.
도 6은 일 실시 예에 따른 순환 대립 뉴럴 네트워크 구조의 개략 도이다.
도 7은 일 실시 예에 따른 고해상도 영상의 로스 값을 도출하는 것을 설명하기 위한 예시 도이다.
도 8 내지 10은 일 실시 예에 따른 저해상도 영상의 해상도 향상 방법을 설명하기 위한 흐름도들이다.1 is a diagram illustrating an architecture of a neural network according to an embodiment.
2 is a diagram illustrating a relationship between an input feature map and an output feature map in a neural network, according to an exemplary embodiment.
3 is a block diagram illustrating a hardware configuration of a neural network device according to an embodiment.
4 is a diagram illustrating a convolution operation of a neural network.
5 illustrates example images of training data, according to an exemplary embodiment.
6 is a schematic diagram of a cyclically opposed neural network structure according to an embodiment.
7 illustrates an example of deriving a loss value of a high resolution image, according to an exemplary embodiment.
8 to 10 are flowcharts illustrating a method of improving the resolution of a low resolution image according to an exemplary embodiment.
본 실시 예들에서 사용되는 용어는 본 실시 예들에서의 기능을 고려하면서 가능한 현재 널리 사용되는 일반적인 용어들을 선택하였으나, 이는 당 기술분야에 종사하는 기술자의 의도 또는 판례, 새로운 기술의 출현 등에 따라 달라질 수 있다. 또한, 특정한 경우는 임의로 선정된 용어도 있으며, 이 경우 해당 실시 예의 설명 부분에서 상세히 그 의미를 기재할 것이다. 따라서, 본 실시 예들에서 사용되는 용어는 단순한 용어의 명칭이 아닌, 그 용어가 가지는 의미와 본 실시 예들의 전반에 걸친 내용을 토대로 정의되어야 한다.The terminology used in the present embodiments is a general term that is currently widely used as possible while considering the functions of the present embodiments, but may vary according to the intention or precedent of a person skilled in the art, the emergence of new technology, etc. . In addition, in certain cases, there is also a term arbitrarily selected, and in this case, the meaning thereof will be described in detail in the description of the corresponding embodiment. Therefore, the terms used in the present exemplary embodiments should be defined based on the meanings of the terms and the contents throughout the present exemplary embodiments, rather than simply names of the terms.
실시 예들에 대한 설명에서, 어떤 부분이 다른 부분과 연결되어 있다고 할 때, 이는 직접적으로 연결되어 있는 경우뿐 아니라, 그 중간에 다른 구성요소를 사이에 두고 전기적으로 연결되어 있는 경우도 포함한다. 또한, 어떤 부분이 어떤 구성요소를 포함한다고 할 때, 이는 특별히 반대되는 기재가 없는 한 다른 구성요소를 제외하는 것이 아니라 다른 구성요소를 더 포함할 수 있는 것을 의미한다. 또한, 실시 예들에 기재된 “...부”의 용어는 적어도 하나의 기능이나 동작을 처리하는 단위를 의미하며, 이는 하드웨어 또는 소프트웨어로 구현되거나 하드웨어와 소프트웨어의 결합으로 구현될 수 있다.In the description of the embodiments, when a part is connected to another part, this includes not only a case in which the part is directly connected, but also a case in which another part is electrically connected in between. In addition, when a part includes a certain component, this means that it may further include other components, without excluding other components unless otherwise stated. In addition, the term "... unit" described in the embodiments means a unit for processing at least one function or operation, which may be implemented in hardware or software, or a combination of hardware and software.
본 실시 예들에서 사용되는 “구성된다”또는“포함한다" 등의 용어는 명세서상에 기재된 여러 구성 요소들, 또는 여러 단계를 반드시 모두 포함하는 것으로 해석되지 않아야 하며, 그 중 일부 구성 요소들 또는 일부 단계들은 포함되지 않을 수도 있고, 또는 추가적인 구성 요소 또는 단계들을 더 포함할 수 있는 것으로 해석되어야 한다.Terms such as “consisting of” or “comprising” as used in the present embodiments should not be construed as necessarily including all of the various components or steps described in the specification, and some or some of them may be included. It is to be understood that the steps may not be included or may further include additional components or steps.
하기 실시 예들에 대한 설명은 권리범위를 제한하는 것으로 해석되지 말아야 하며, 해당 기술분야의 당업자가 용이하게 유추할 수 있는 것은 실시 예들의 권리범위에 속하는 것으로 해석되어야 할 것이다. 이하 첨부된 도면들을 참조하면서 오로지 예시를 위한 실시 예들을 상세히 설명하기로 한다.The description of the following embodiments should not be construed as limiting the scope of the right, it should be construed as belonging to the scope of the embodiments that can be easily inferred by those skilled in the art. Hereinafter, only exemplary embodiments will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
실시 예에서 사용된 해상도는 항공 또는 위성에서 촬영한 영상의 공간해상도(Ground Sample Distance, 이하 GSD라 한다)를 의미한다. GSD는 실제 픽셀의 사이즈, 즉 영상 내의 두 픽셀 사이의 실제 지구상에서의 거리를 의미한다.The resolution used in the embodiment refers to a spatial resolution (Ground Sample Distance, hereinafter referred to as GSD) of an image captured by air or satellite. GSD means the size of a real pixel, that is, the distance on the real earth between two pixels in an image.
실시 예에서 사용된 저해상도는 GSD기준으로 4m를 의미하고, 고해상도는 GSD 기준으로 0.5m를 의미한다. 실시 예에서 저해상도 위성영상의 해상도를 향상시키는 것은 위성에서 촬영된 GSD 4m급의 저해상도 영상을 비지도 뉴럴 네트워크로 학습된 모델을 통해 GSD 0.5m의 고해상도 영상으로 변환하는 것을 의미한다.The low resolution used in the embodiment means 4m on the basis of GSD, and the high resolution means 0.5m on the basis of GSD. Improving the resolution of the low resolution satellite image in the embodiment means converting the GSD 4m low resolution image captured by the satellite into a high resolution image of GSD 0.5m through a model trained by an unsupervised neural network.
실시 예에서 제1 해상도는 저해상도를 의미하고, 제2 해상도는 고해상도를 의미한다.In the embodiment, the first resolution means low resolution and the second resolution means high resolution.
실시 예에서, 제1 영상은 저해상도 영상, 제2 영상은 고해상도 영상을 의미하고, 실제 영상은 위성에서 촬영한 영상, 생성 영상은 이미지 처리를 통해 만든 영상을 의미한다.In an embodiment, the first image refers to a low resolution image, the second image refers to a high resolution image, the actual image refers to an image captured by a satellite, and the generated image refers to an image created through image processing.
실시 예에서, 제3 영상은 제1 영상을 업샘플링하여 제2 영상과 동일한 크기로 만든 영상을 의미한다.In an embodiment, the third image refers to an image made up to the same size as the second image by upsampling the first image.
실시 예에서, 1-1 영상, 1-2 영상은 학습 모델, 예를 들면 제네레이션 네트워크 또는 디그라데이션 네트워크에 입력되어 생성된 영상을 의미한다. 학습 모델의 입력 영상은 실제 저해상도 영상, 생성된 고해상도 영상을 포함한다.In an embodiment, the 1-1 image and the 1-2 image mean an image generated by being input to a learning model, for example, a generation network or a degradation network. The input image of the training model includes an actual low resolution image and a generated high resolution image.
실시 예에서, 학습은 사전학습, 본 학습을 포함하는 것으로, 사전학습은 일반적인 학습모델, 예를 들면, 16개 또는 19개 층으로 구성된 VGG모델을 사용할 수 있다. 여기서, 16층 또는 19층은 네트워크의 깊이를 의미한다. 여기서, VGG 모델을 예로서 설명하지만, 이에 한정되지 않고, 사전학습을 위한 다양한 CNN 알고리즘들 중에서 이미지 분류용 알고리즘을 사용할 수 있음은 물론이다.In an embodiment, the learning includes pre-learning, the main learning, and the pre-learning may use a general learning model, for example, a VGG model composed of 16 or 19 layers. Here, the 16th or 19th layer means the depth of the network. Here, the VGG model is described as an example, but the present invention is not limited thereto, and an image classification algorithm may be used among various CNN algorithms for pre-learning.
뉴럴 네트워크(neural network)는 생물학적 뇌를 모델링한 컴퓨터 과학적 아키텍쳐(computational architecture)를 참조한다. 최근 뉴럴 네트워크(neural network) 기술이 발전함에 따라, 다양한 종류의 전자 시스템에서 뉴럴 네트워크를 활용하여 입력 데이터를 분석하고 유효한 정보를 추출하는 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크를 처리하는 장치는 복잡한 입력 데이터에 대한 많은 양의 연산을 필요로 한다. 따라서, 뉴럴 네트워크를 이용하여 대량의 입력 데이터를 실시간으로 분석하여, 원하는 정보를 추출하기 위해서는 뉴럴 네트워크에 관한 연산을 효율적으로 처리할 수 있는 기술이 요구된다.Neural networks refer to a computer scientific computational architecture that models the biological brain. Recently, as neural network technology has developed, researches on analyzing input data and extracting valid information using neural networks in various kinds of electronic systems are being actively conducted. Devices that deal with neural networks require large amounts of computation on complex input data. Accordingly, in order to extract a desired information by analyzing a large amount of input data in real time using a neural network, a technology capable of efficiently processing a neural network is required.
도 1은 일 실시예에 따른 뉴럴 네트워크의 아키텍처를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.1 is a diagram illustrating an architecture of a neural network according to an embodiment.
도 1을 참고하면, 뉴럴 네트워크(1)는 딥 뉴럴 네트워크(Deep Neural Network, DNN) 또는 n-계층 뉴럴 네트워크(n-layers neural networks)의 아키텍처일 수 있다. DNN 또는 n-계층 뉴럴 네트워크는 컨볼루션 뉴럴 네트워크(Convolutional Neural Networks, CNN), 리커런트 뉴럴 네트워크(Recurrent Neural Networks, RNN), Deep Belief Networks, Restricted Boltzman Machines 등에 해당될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 뉴럴 네트워크(1)는 컨볼루션 뉴럴 네트워크(CNN)로 구현될 수 있으나, 이에 제한되지 않는다. 도 1에서는 뉴럴 네트워크(1)의 예시에 해당하는 컨볼루션 뉴럴 네트워크에서 일부의 컨볼루션 레이어가 도시되었지만, 컨볼루션 뉴럴 네트워크는 도시된 컨볼루션 레이어 외에도, 풀링 레이어(pooling layer), 풀리 커넥티드(fully connected) 레이어 등을 더 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 1, the
뉴럴 네트워크(1)는 입력 이미지, 피처맵들(feature maps) 및 출력을 포함하는 복수 레이어들을 갖는 아키텍처로 구현될 수 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크(1)에서 입력 이미지는 커널(kernel)이라 불리는 필터와의 컨볼루션 연산이 수행되고, 그 결과 피처맵들이 출력된다. 이때 생성된 출력 피처맵들은 입력 피처맵들로서 다시 커널과의 컨볼루션 연산이 수행되고, 새로운 피처맵들이 출력된다. 이와 같은 컨볼루션 연산이 반복적으로 수행된 결과, 최종적으로는 뉴럴 네트워크(1)를 통한 입력 이미지의 특징들에 대한 인식 결과가 출력될 수 있다.The
예를 들어, 도 1의 뉴럴 네트워크(1)에 24x24 픽셀 크기의 이미지가 입력된 경우, 입력 이미지는 커널과의 컨볼루션 연산을 통해 20x20 크기를 갖는 4채널의 피처맵들로 출력될 수 있다. 이후에도, 20x20 피처맵들은 커널과의 반복적인 컨볼루션 연산을 통해 크기가 줄어들면서, 최종적으로는 1x1 크기의 특징들이 출력될 수 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크(1)는 여러 레이어들에서 컨볼루션 연산 및 서브샘플링(또는 풀링) 연산을 반복적으로 수행함으로써 입력 이미지로부터 이미지 전체를 대표할 수 있는 강인한 특징들을 필터링하여 출력하고, 출력된 최종 특징들을 통해 입력 이미지의 인식 결과를 도출할 수 있다.For example, when an image of 24x24 pixel size is input to the
도 2는 일 실시예에 따른 뉴럴 네트워크에서 입력 피처맵 및 출력 피처맵의 관계를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.2 is a diagram illustrating a relationship between an input feature map and an output feature map in a neural network, according to an exemplary embodiment.
도 2를 참고하면, 뉴럴 네트워크의 어느 레이어(2)에서, 제1피처맵(FM1)은 입력 피처맵에 해당될 수 있고, 제2피처 맵(FM2)는 출력 피처맵에 해당될 수 있다. 피처맵은 입력 데이터의 다양한 특징들이 표현된 데이터 세트를 의미할 수 있다. 피처맵들(FM1, FM2)은 2차원 매트릭스의 엘리먼트들을 갖거나 또는 3차원 매트릭스의 엘리먼트들을 가질 수 있고, 각각의 엘리먼트에는 픽셀 값이 정의될 수 있다. 피처 맵들(FM1, FM2)은 너비(W)(또는 칼럼이라고 함), 높이(H)(또는 로우라고 함) 및 깊이(D)를 가진다. 이때, 깊이(D)는 채널들의 개수에 해당될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 2, in any
제1피처맵(FM1) 및 커널의 웨이트맵(WM)에 대한 컨볼루션 연산이 수행될 수 있고, 그 결과 제2피처맵(FM2)이 생성될 수 있다. 웨이트맵(WM)은 각 엘리먼트에 정의된 웨이트로 제1피처맵(FM1)과 컨볼루션 연산을 수행함으로써 제1피처맵(FM1)의 특징들을 필터링한다. 웨이트맵(WM)은 제1입력 피처맵(FM1)을 슬라이딩 윈도우 방식으로 시프트하면서 제1입력 피처맵(FM1)의 윈도우들(또는 타일이라고도 함)과 컨볼루션 연산을 수행한다. 각 시프트 동안, 웨이트맵(WM)에 포함된 웨이트들 각각은 제1피처맵(FM1) 내 중첩된 윈도우의 픽셀 값들 각각과 곱해지고 더해질 수 있다. 제1피처맵(FM1)과 웨이트맵(WM)이 컨볼루션됨에 따라, 제2피처맵(FM2)의 하나의 채널이 생성될 수 있다. 도 1에는 하나의 커널에 대한 웨이트맵(WM)이 도시되었으나, 실제로는 복수의 커널들의 웨이트 맵들이 제1피처맵(FM1)과 각각 컨볼루션되어, 복수의 채널들의 제2피처맵(FM2)이 생성될 수 있다. 제2피처맵(FM2)은 다음 레이어의 입력 피처맵에 해당될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 제2피처맵(FM2)은 풀링(또는 서브샘플링) 레이어의 입력 피처맵이 될 수 있다.A convolution operation may be performed on the first feature map FM1 and the kernel weight map WM, and as a result, a second feature map FM2 may be generated. The weight map WM filters the features of the first feature map FM1 by performing a convolution operation with the first feature map FM1 based on the weights defined for each element. The weight map WM performs a convolution operation with the windows (or tiles) of the first input feature map FM1 while shifting the first input feature map FM1 in a sliding window manner. During each shift, each of the weights included in the weight map WM may be multiplied and added with each of the pixel values of the overlapped window in the first feature map FM1. As the first feature map FM1 and the weight map WM are convolved, one channel of the second feature map FM2 may be generated. In FIG. 1, a weight map WM for one kernel is illustrated, but in reality, the weight maps of the plurality of kernels are convolved with the first feature map FM1, respectively, so that the second feature map FM2 of the plurality of channels is included. Can be generated. The second feature map FM2 may correspond to an input feature map of the next layer. For example, the second feature map FM2 may be an input feature map of the pooling (or subsampling) layer.
도 1 및 도 2에서는 설명의 편의를 위하여 뉴럴 네트워크(1)의 개략적인 아키텍처에 대해서만 도시되어 있다. 하지만, 뉴럴 네트워크(1)는 도시된 바와 달리, 보다 많거나 적은 개수의 레이어들, 피처맵들, 커널들 등으로 구현될 수 있고, 그 크기들 또한 다양하게 변형될 수 있음을 당해 기술분야의 통상의 기술자라면 이해할 수 있다.1 and 2 are shown only for the schematic architecture of the
도 3은 일 실시예에 따른 뉴럴 네트워크 장치의 하드웨어 구성을 도시한 블록도이다.3 is a block diagram illustrating a hardware configuration of a neural network device according to an embodiment.
뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10)는 PC(personal computer), 서버 디바이스, 모바일 디바이스, 임베디드 디바이스 등의 다양한 종류의 디바이스들로 구현될 수 있고, 구체적인 예로서 뉴럴 네트워크를 이용한 음성 인식, 영상 인식, 영상 분류 등을 수행하는 스마트폰, 태블릿 디바이스, AR(Augmented Reality) 디바이스, IoT(Internet of Things) 디바이스, 자율주행 자동차, 로보틱스, 의료기기 등에 해당될 수 있으나, 이에 제한되지 않는다. 나아가서, 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10)는 위와 같은 디바이스에 탑재되는 전용 하드웨어 가속기(HW accelerator)에 해당될 수 있고, 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10)는 뉴럴 네트워크 구동을 위한 전용 모듈인 NPU(neural processing unit), TPU(Tensor Processing Unit), Neural Engine 등과 같은 하드웨어 가속기일 수 있으나, 이에 제한되지 않는다.The
도 3을 참고하면, 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10)는 프로세서(110) 및 메모리(120)를 포함한다. 도 3에 도시된 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10)에는 본 실시예들와 관련된 구성요소들만이 도시되어 있다. 따라서, 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10)에는 도 3에 도시된 구성요소들 외에 다른 범용적인 구성요소들이 더 포함될 수 있음은 당해 기술분야의 통상의 기술자에게 자명하다.Referring to FIG. 3, the
프로세서(110)는 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10)를 실행하기 위한 전반적인 기능들을 제어하는 역할을 한다. 예를 들어, 프로세서(110)는 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10) 내의 메모리(120)에 저장된 프로그램들을 실행함으로써, 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10)를 전반적으로 제어한다. 프로세서(110)는 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10) 내에 구비된 CPU(central processing unit), GPU(graphics processing unit), AP(application processor) 등으로 구현될 수 있으나, 이에 제한되지 않는다.The
메모리(120)는 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10) 내에서 처리되는 각종 데이터들을 저장하는 하드웨어로서, 예를 들어, 메모리(120)는 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10)에서 처리된 데이터들 및 처리될 데이터들을 저장할 수 있다. 또한, 메모리(120)는 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10)에 의해 구동될 애플리케이션들, 드라이버들 등을 저장할 수 있다. 메모리(120)는 DRAM(dynamic random access memory), SRAM(static random access memory) 등과 같은 RAM(random access memory), ROM(read-only memory), EEPROM(electrically erasable programmable read-only memory), CD-ROM, 블루레이 또는 다른 광학 디스크 스토리지, HDD(hard disk drive), SSD(solid state drive), 또는 플래시 메모리를 포함할 수 있다.The
프로세서(110)는 메모리(120)로부터 뉴럴 네트워크 데이터, 예를 들어 이미지 데이터, 피처맵 데이터, 커널 데이터 등을 리드/라이트(read/write)하고, 리드/라이트된 데이터를 이용하여 뉴럴 네트워크를 실행한다. 뉴럴 네트워크가 실행될 때, 프로세서(110)는 출력 피처맵에 관한 데이터를 생성하기 위하여, 입력 피처맵과 커널 간의 컨볼루션 연산을 반복적으로 수행한다. 이때, 입력 피처맵의 채널 수, 커널의 채널 수, 입력 피처맵의 크기, 커널의 크기, 값의 정밀도(precision) 등의 다양한 팩터들에 의존하여 컨볼루션 연산의 연산량이 결정될 수 있다. 도 1에 도시된 뉴럴 네트워크(1)와 달리, 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10)에서 구동되는 실제 뉴럴 네트워크는 보다 복잡한 아키텍처로 구현될 수 있다. 이에 따라 프로세서(110)는 수억에서 수백억에 다다를 정도로 매우 많은 연산량(operation count)의 컨볼루션 연산들을 수행하게 되고, 프로세서(110)가 컨볼루션 연산을 위해 메모리(120)에 액세스하는 빈도가 함께 비약적으로 증가될 수 밖에 없다. 이와 같은 연산량 부담으로 인하여 비교적 처리 성능이 낮은 스마트폰, 태블릿, 웨어러블 디바이스 등과 같은 모바일 디바이스, 임베디드(embedded) 디바이스 등에서는 뉴럴 네트워크의 처리가 원활하지 않을 수 있다. 뉴럴 네트워크에서 커널은 부동 소수점(floating point) 타입의 웨이트 또는 고정 소수점(fixed point) 타입의 웨이트를 갖거나, 바이너리(binary)-웨이트 커널 또는 터너리(ternary)-웨이트 커널에 해당될 수도 있다. 즉, 뉴럴 네트워크에서 커널은 뉴럴 네트워크의 활용 목적, 디바이스의 성능 등 다양한 요인들을 고려하여 다양하게 정의될 수 있다. 여기서, 바이너리-웨이트 커널은 부동 소수점 웨이트 또는 고정 소수점 웨이트를 갖는 커널과 달리, 웨이트 값이 예를 들어 +1 또는 -1로 제한되어(constrained) 있는 커널을 의미할 수 있다. 그리고, 터너리-웨이트 커널은 웨이트 값이 +1, 0 또는 -1로 제한되어 있는 커널을 의미할 수 있다.The
이하에서, 프로세서(110)에 의해 실행되는 뉴럴 네트워크는 바이너리-웨이트 커널, 터너리-웨이트 커널 등과 같이 웨이트가 특정 레벨들로 양자화된 커널을 이용하여 컨볼루션 연산을 수행하는 경우를 가정하여 설명하겠으나, 본 실시예들은 이에 제한되지 않고 다른 종류의 커널을 이용한 컨볼루션 연산에도 적용이 가능하다.In the following description, a neural network executed by the
커널의 웨이트가 특정 레벨들로 양자화된 바이너리-웨이트 커널 또는 터너리-웨이트 커널이라 할지라도, 컨볼루션 연산은 뉴럴 네트워크의 처리에 있어서 전체 연산량 중에서 여전히 높은 비중을 차지한다. 따라서, 뉴럴 네트워크의 처리에 있어서 컨볼루션 연산의 연산량을 충분히 감소시키면서도 정확도 로스를 최소화하는 처리 방식이 요구된다.Although the weight of the kernel is a binary-weight kernel or a ternary-weight kernel quantized to certain levels, convolution operations still account for a high proportion of the total computation in the processing of the neural network. Therefore, in the processing of the neural network, there is a demand for a processing scheme that minimizes the accuracy loss while sufficiently reducing the amount of computation of the convolution operation.
바이너리-웨이트 커널의 경우, 웨이트가 2 종류(예를 들어 -1 또는 +1, 0 또는 1, -1 또는 0)로 제한되어 있기 때문에, 바이너리-웨이트 커널에서 임의로 두 개의 웨이트들을 선택했을 때 선택된 웨이트들은 서로 같을 확률이 높을 수 있다. 즉, 부동 소수점 또는 고정 소수점 타입의 커널에 비해, 뉴럴 네트워크의 어느 레이어 내 임의의 두 바이너리-웨이트 커널들은 유사할 확률이 높다. 이와 같은 유사할 확률을 활용하여, 뉴럴 네트워크의 커널들을, 커널들에 공통된 근사적인 서브 커널과, 에러를 보정해주는 서브 커널로 분해하여(decompose) 컨볼루션 연산이 수행된다면 컨볼루션 연산의 연산량이 효율적으로 줄어들 수 있다. 이하 본 실시예들의 설명에서는 이와 같이 뉴럴 네트워크의 커널들을 분해하여 컨볼루션 연산을 수행하는 방법들에 대해 상세하게 설명하도록 한다. 이하에서 설명된 방법들은 뉴럴 네트워크 장치(10)의 프로세서(110) 및 메모리(120)에 의해 수행될 수 있다.In the binary-weight kernel, since the weight is limited to two types (for example, -1 or +1, 0 or 1, -1 or 0), the binary-weight kernel is selected when two weights are arbitrarily selected. The weights are likely to be equal to each other. That is, compared to a floating point or fixed point type kernel, any two binary-weight kernels in any layer of the neural network are likely to be similar. Using this similar probability, the convolution operation is efficient if the convolution operation is performed by decomposing the kernels of the neural network into an approximate subkernel common to the kernels and a subkernel for error correction. Can be reduced. In the following description of the present embodiments, methods for performing a convolution operation by disassembling the kernels of the neural network are described in detail. The methods described below may be performed by the
도 4는 뉴럴 네트워크의 컨볼루션 연산을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.4 is a diagram illustrating a convolution operation of a neural network.
도 4의 예시에서, 입력 피처맵(410)은 6x6 크기이고, 원본 커널(420)은 3x3 크기이고, 출력 피처맵(430)은 4x4 크기인 것으로 가정하나, 이에 제한되지 않고 뉴럴 네트워크는 다양한 크기의 피처맵들 및 커널들로 구현될 수 있다. 또한, 입력 피처맵(410), 원본 커널(420) 및 출력 피처맵(430)에 정의된 값들은 모두 예시적인 값들일 뿐이고, 본 실시예들은 이에 제한되지 않는다. 한편, 원본 커널(420)은 앞서 설명된 바이너리-웨이트 커널에 해당된다.In the example of FIG. 4, it is assumed that the
원본 커널(420)은 입력 피처맵(410)에서 3x3 크기의 윈도우 단위로 슬라이딩하면서 컨볼루션 연산을 수행한다. 컨볼루션 연산은 입력 피처맵(410)의 어느 윈도우의 각 픽셀 값 및 원본 커널(420)에서 대응 위치의 각 엘리먼트의 웨이트 간의 곱셈을 하여 획득된 값들을 모두 합산하여, 출력 피처맵(430)의 각 픽셀 값을 구하는 연산을 의미한다. 구체적으로, 원본 커널(420)은 먼저 입력 피처맵(410)의 제1윈도우(411)와 컨볼루션 연산을 수행한다. 즉, 제1윈도우(411)의 각 픽셀 값 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9는 각각 원본 커널(420)의 각 엘리먼트의 웨이트 -1, -1, +1, +1, -1, -1, -1, +1, +1과 각각 곱해지고, 그 결과로서 -1, -2, 3, 4, -5, -6, -7, 8, 9가 획득된다. 다음으로, 획득된 값들 -1, -2, 3, 4, -5, -6, -7, 8, 9를 모두 더한 결과인 3이 계산되고, 출력 피처맵(430)의 1행1열의 픽셀 값(431)은 3으로 결정된다. 여기서, 출력 피처맵(430)의 1행1열의 픽셀 값(431)은 제1윈도우(411)에 대응된다. 마찬가지 방식으로, 입력 피처맵(410)의 제2윈도우(412)와 원본 커널(420) 간의 컨볼루션 연산이 수행됨으로써 출력 피처맵(430)의 1행2열의 픽셀 값(432)인 -3이 결정된다. 최종적으로, 입력 피처맵(410)의 마지막 윈도우인 제16윈도우(413)와 원본 커널(420) 간의 컨볼루션 연산이 수행됨으로써 출력 피처맵(430)의 4행4열의 픽셀 값(433)인 -13이 결정된다.The
즉, 하나의 입력 피처맵(410)과 하나의 원본 커널(420) 간의 컨볼루션 연산은 입력 피처맵(410) 및 원본 커널(420)에서 서로 대응하는 각 엘리먼트의 값들의 곱셈 및 곱셈 결과들의 합산을 반복적으로 수행함으로써 처리될 수 있고, 컨볼루션 연산의 결과로서 출력 피처맵(430)이 생성된다.That is, the convolution operation between one
하지만, 입력 피처맵(410)의 어느 한 윈도우와 원본 커널(420) 간의 컨볼루션 연산에서는 엘리먼트 개수만큼의 곱셈 및 곱셈 결과들의 합산이 필수적으로 요구되는바, 엘리먼트 개수가 많으면 많을수록 연산량이 높아질 수 있다. 나아가서, 입력 피처맵 내에 슬라이딩 횟수가 많거나 뉴럴 네트워크 내 많은 채널들의 입력 피처맵들이 존재하거나 많은 레이어들이 존재하는 경우에는, 연산량이 더욱 더 기하급수적으로 증가하게 된다. 본 실시예들에 따른 컨볼루션 연산은 원본 커널(420)을 여러 서브 커널들로 분해함으로써 연산량 감소를 이룰 수 있다.However, in a convolution operation between any one window of the
도 5는 일 실시 예에 따른 학습 데이터의 예시 영상들이다.5 illustrates example images of training data, according to an exemplary embodiment.
도 5를 참조하면, 3개의 학습 데이터 영상들이 도시되어 있다. 저해상도 영상, 고해상도 영상 및 업샘플링 영상을 포함한다. 3개의 영상을 모두 동일한 영역에 대한 영상들이지만, 서로 다른 해상도, 서로 다른 크기를 갖는다. 실시 예에서의 학습 데이터는 이미지 정합이 적용된 실제 저해상도, 고해상도 위성 영상과, 업샘플링 영상을 포함한다.Referring to FIG. 5, three learning data images are shown. Low resolution images, high resolution images and upsampling images. All three images are images for the same area, but have different resolutions and different sizes. The training data in the embodiment includes an actual low resolution, high resolution satellite image, and an upsampling image to which image matching is applied.
도 8을 참조하면, 단계 800에서, 동일 영역을 촬영한 실제 저해상도 및 고해상도 영상을 이미지 정합 기법을 통해 패치를 추출한다. 도 5에 도시된 것처럼, 동일한 영역을 촬영한 저해상도 영상과 고해상도 영상을 획득한다. 여기서, 2개의 영상에 대해 이미지 정합하여 영상 패치를 추출한다. 추출된 영상 패치 정보는 단계 802에서, 업샘플링 영상을 생성하는데 이용된다.Referring to FIG. 8, in
실시 예에서, 판별기(discriminator)가 학습을 하는데 있어 터무니 없이 영상 내용과 품질이 다른 경우 학습이 매우 어렵다. 하지만, 학습의 사전 준비로서 지구, 영상 좌표계와 GSD를 고려하여, 동일한 영역을 촬영한 저해상도 영상과 고해상도 영상에 대해 동일한 패치 쌍을 뽑아내어, 영상 내용을 최대한 유사하게 맞춰주어 판별기가 영상의 품질 차이 판단에 집중할 수 있도록 한다.In an embodiment, the learning is very difficult when the discriminator is ridiculously different from the image content. However, in preparation for learning, the same patch pairs are extracted for low-resolution and high-resolution images of the same area, taking into account the earth, the image coordinate system, and the GSD. Focus on judgment.
실시 예에서, 위성영상의 학습에 특화될 수 있도록, 지구, 영상 좌표계, GSD를 반영한 학습 데이터, 즉 동일한 영역을 촬영한 저해상도 위성영상과 고해상도 위성영상을 준비한다.In an exemplary embodiment, training data reflecting the earth, the image coordinate system, and the GSD, that is, the low resolution satellite image and the high resolution satellite image of the same region are prepared to be specialized in the satellite image learning.
단계 802에서, 실제 저해상도 영상을 샘플링을 통해 고해상도 영상과 동일한 크기의 업샘플링 영상을 생성한다. 여기서, 업샘플링은 bicubic 보간 알고리즘을 사용한다. 실시 예에서, bicubic 보간 알고리즘을 이용하여 업샘플링을 하였지만, 이에 한정되지 않고, bilinear 등 다양한 보간 알고리즘을 사용할 수 있음은 물론이다. 도 5에 도시된 것처럼, 실제 촬영된 저해상도 영상을 업샘플링하여 업샘플링 영상을 얻는다.In
도 6은 일 실시 예에 따른 순환 대립 뉴럴 네트워크 구조의 개략 도이다.6 is a schematic diagram of a cyclically opposed neural network structure according to an embodiment.
도 6을 참조하면, 순환 대립 뉴럴 네트워크는 제네레이션 네트워크(Generation Network, 110), 고해상도 판별기(115), 디그라데이션 네트워크(Degradation Network, 120), 저해상도 판별기(125)를 포함한다. 실시 예에서 본학습 과정에서는, 순환 대립 뉴럴 네트워크 구조를 통해, 제네레이션 네트워크(110), 디그라데이션 네트워크(120)를 배치하여 안정적인 비지도 학습 과정과 그에 따른 향상된 성능을 얻을 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 6, the cyclically opposed neural network includes a
여기서, 제네레이션 및 디그라데이션 네트워크(110 및 120)는 특정 영상(저해상도 영상 또는 고해상도 영상)을 입력으로 받고 생성하고자 하는 데이터와 같은 형태의 출력을 생성한다. 판별기(115 및 125)는 제네레이션 및 디그라데이션 네트워크(110 및 120)의 출력과 생성하고자 하는 데이터의 학습 데이터 셋을 식별한다. 이러한 학습 과정을 통해 제네레이션 및 디그라데이션 네트워크(110 및 120)는 보다 학습 데이터셋에 가깝게, 판별기(115 및 125)는 보다 정확히 식별하게 되며 보다 진짜에 가까운 데이터를 생성할 수 있다.Here, the generation and
도 6에 도시된 순환 대립 뉴럴 네트워크에 대해 본 학습을 수행하고 나서, 저해상도 위성영상의 해상도를 향상시키기 위한 네트워크로 제네레이션 네트워크(110)를 이용한다. 여기서, 제네레이션 네트워크(110)는 실시 예에 따른 비지도 뉴럴 네트워크를 통해 학습되었다.After performing the present learning on the cyclically opposed neural network shown in FIG. 6, the
실제 사용하는 단계에서는, 저해상도 위성영상을 제너레이션 네트워크(110)에 입력하면, 고해상도 영상 또는 고해상도에 상응하는 위성영상을 생성하여 출력한다.In the actual stage of use, when a low resolution satellite image is input to the
도 9를 참조하면, 단계 900에서, 저해상도 영상은 제네레이션 네트워크(110)의 입력으로 들어가서 고해상도 영상을 생성한다.Referring to FIG. 9, in
단계 902에서, 생성된 고해상도 영상과 실제 고해상도 영상이 HR 판별기(115)를 통해 실제 및 생성 영상간 판별된다. 영상간의 유사도 판단을 통해 생성된 고해상도 영상이 실제 고해상도 영상과 얼마나 유사한지를 판별한다. 영상간의 유사도 판단은 다양한 방법을 통해 수행할 수 있다.In
단계 904에서, 생성된 고해상도 영상은 디그라데이션 네트워크(120)의 입력으로 들어가서 저해상도 영상이 생성된다.In
단계 906에서, 생성된 저해상도 영상과 실제 저해상도 영상이 LR 판별기(125)를 통해 실제 및 생성 영상간 판별된다. 단계 902와 유사하게, 영상간의 유사도 판단을 통해 생성된 저해상도 영상이 실제 저해상도 영상과 얼마나 유사한지를 판별한다.In
도 7은 일 실시 예에 따른 고해상도 영상의 로스 값을 도출하는 것을 설명하기 위한 예시 도이다.7 is an exemplary diagram for describing obtaining a loss value of a high resolution image according to an exemplary embodiment.
도 7을 참조하면, 학습과정에서 로스 값은 생성된 고해상도 영상과 실제 고해상도 영상간의 대립적인 로스 값(Adverarial Loss)과 생성된 고해상도 영상과 업 샘플링 영상간의 인지적인 로스 값(Perceptual Loss)의 합으로 구성된다. 여기서, 인지적인 로스 값은 서로 크기가 다른 사물간에 구조적 연관성에 대한 손실 값을 의미한다. 또한, 각각의 로스 값에는 적절한 가중치가 곱해질 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 7, in the learning process, a loss value is a sum of an adversarial loss value between the generated high resolution image and the actual high resolution image and a perceptual loss value between the generated high resolution image and the upsampling image. It is composed. Here, the cognitive loss value means a loss value for structural association between objects having different sizes. In addition, each loss value may be multiplied by an appropriate weight.
도 7을 참조하여, 생성된 고해상도 영상에 대한 대립적인 로스 값과 인지적인 로스 값에 대해서 설명하였지만, 생성된 저해상도 영상에 대해서도 동일한 방식으로 로스 값을 계산할 수 있다. 즉, 생성된 저해상도 영상과 실제 저해상도 영상간의 대립적인 로스 값과, 생성된 저해상도 영상과 실제 저해상도 영상간의 인지적인 로스 값을 계산할 수 있다. , 예를 들면, 인지적인 로스는 위성영상 내의 structure(비행기, 구조물 등)를 유지하기 위한 수단인 반면에, 대립적인 로스 는 해상도, 흐림도, 노이즈 등 영상의 품질을 전이 시키기 위한 수단이다.Referring to FIG. 7, the opposing loss values and the cognitive loss values of the generated high resolution image have been described. However, the loss values may be calculated in the same manner with respect to the generated low resolution image. That is, the opposite loss value between the generated low resolution image and the actual low resolution image and the cognitive loss value between the generated low resolution image and the actual low resolution image may be calculated. For example, cognitive loss is a means for maintaining the structure (airplane, structure, etc.) in the satellite image, while alternative loss is a means for transferring the quality of the image, such as resolution, blurring, noise.
따라서, 생성된 제 1-1 영상은 실제로 제1 영상과 같은 구조를 지녀야 하므로, 인지적인 로스에서, 제 1-1영상과 제 1영상을 사용한다. 한편, 제1-2영상은 1-1영상에서 degradation 과정을 통해 만들어진 저해상도 영상이므로, 이상적으로 초기 입력 영상인 제 1 영상과 동일한 영상, 즉 구조(structure)와 영상 품질 모두 나와야 한다. 따라서, 이 경우에는 adversarial과 perceptual loss를 모두 제 1-2영상과 제 1영상을 입력으로 사용하는 것이 바람직하다.Therefore, since the generated 1-1 image should actually have the same structure as the first image, in the cognitive loss, the 1-1 image and the first image are used. On the other hand, since the 1-2-2 image is a low resolution image made through the degradation process in the 1-1 image, ideally, the same image as that of the first image, that is, the initial input image, that is, the structure and the image quality should all appear. Therefore, in this case, it is preferable to use the first and second images as the input for both the adversarial and the perceptual loss.
본 학습 과정에서 로스 함수는를 사용하고, 다음 수학식 1 내지 3에 의해 계산한다.In this lesson, the loss function Is calculated by the following equations (1) to (3).
[수학식 1][Equation 1]
[수학식 2][Equation 2]
[수학식 3][Equation 3]
여기서,는 generation에서 제 3 영상에 해당, degradation에서 제 1 영상에 해당하고,는 generation에서 제 1-1 영상에 해당하고, degradation에서 제 1-2 영상에 해당하고,는 VGG 4번 레이어의 피처 값에 해당한다.here, Corresponds to the third image in generation, corresponds to the first image in degradation, Corresponds to the 1-1 image in generation, corresponds to the 1-2 image in degradation, Corresponds to the feature value of the
여기서,는 사전학습된 VGG 모델의 4번 레이어의 피처 값()을 최소제곱법(MSE, mean square error)을 통해 계산하고, α와 β는 학습에 필요한 파라미터들이고, D는 촬영한 실제영상/생성영상을 판단하는 구분자이고, G는 저해상도 영상 입력을 받아 복원 영상을 생성하는 생성자를 의미한다.here, Is the feature value of
도 10을 참조하면, 단계 1000에서, 사전학습으로 제네레이션 네트워크, 디그라데이션 네트워크를 독립적으로 수행한다. 여기서, 네트워크의 학습 안정성을 확보하기 위해서, 각 네트워크 별로 사전학습을 수행할 수 있다. 사전 학습은 VGG 모델을 사용할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 10, in
단계 1002에서, 본 학습 과정을 수행한다.In
단계 1004에서, 제네레이션 네트워크, 디그라데이션 네트워크와 각각의 판결기를 1:1의 비율로 가중치 업데이트를 수행한다. 가중치 업데이트 과정은 다음 수학식 4에 의해 계산한다.In
[수학식 4][Equation 4]
여기서,는 각 컨볼루션 레이어의 가중치에 해당하고, L은 로스에 해당한다. Generation network와 degradation network에서 나온 loss를 번갈아서 1:1의 비율로 학습한다. 즉, 가중치 업데이트 과정을 수행한다. 이때, 위의 L(loss)은 Generation의 경우 제 2영상, 제 3영상, 제 1-1 영상으로부터 계산된이고, Degradation의 경우 제 1영상, 1-2 영상으로부터 계산된이다.here, Is the weight of each convolutional layer, and L is the loss. The loss from the generation network and the degradation network are alternately learned in a 1: 1 ratio. That is, the weight update process is performed. At this time, the L (loss) is calculated from the second image, the third image, the first image 1-1 in the case of Generation Degradation is calculated from the first image and the 1-2 image to be.
이상과 같이 본 발명은 비록 한정된 실시 예와 도면에 의해 설명되었으나, 본 발명은 상기의 실시 예에 한정되는 것은 아니며, 본 발명이 속하는 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 이러한 기재로부터 다양한 수정 및 변형 가능하다. 그러므로 본 발명의 범위는 실시 예에 국한되어 정해져서는 아니 되며, 후술하는 특허청구범위뿐만 아니라 이 특허청구범위와 균등한 것들에 의해 정해져야 한다.As described above, although the present invention has been described with reference to the limited embodiments and the drawings, the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments, and those skilled in the art to which the present invention pertains various modifications and variations from such descriptions. It is possible. Therefore, the scope of the present invention should not be limited to the embodiments, but should be determined not only by the claims below but also by the equivalents of the claims.
본 발명의 일 실시 예는 컴퓨터에 의해 실행되는 프로그램 모듈과 같은 컴퓨터에 의해 실행 가능한 명령어를 포함하는 기록 매체의 형태로도 구현될 수 있다. 컴퓨터 판독 가능 매체는 컴퓨터에 의해 액세스 될 수 있는 임의의 가용 매체일 수 있고, 휘발성 및 비휘발성 매체, 분리형 및 비 분리형 매체를 모두 포함한다. 또한, 컴퓨터 판독가능 매체는 컴퓨터 저장 매체 및 통신 매체를 모두 포함할 수 있다. 컴퓨터 저장 매체는 컴퓨터 판독가능 명령어, 데이터 구조, 프로그램 모듈 또는 기타 데이터와 같은 정보의 저장을 위한 임의의 방법 또는 기술로 구현된 휘발성 및 비휘발성, 분리형 및 비 분리형 매체를 모두 포함한다. 통신 매체는 전형적으로 컴퓨터 판독가능 명령어, 데이터 구조, 프로그램 모듈, 또는 반송파와 같은 변조된 데이터 신호의 기타 데이터, 또는 기타 전송 메커니즘을 포함하며, 임의의 정보 전달 매체를 포함한다.An embodiment of the present invention may also be implemented in the form of a recording medium including instructions executable by a computer, such as a program module executed by a computer. Computer readable media can be any available media that can be accessed by a computer and includes both volatile and nonvolatile media, removable and non-removable media. In addition, computer readable media may include both computer storage media and communication media. Computer storage media includes both volatile and nonvolatile, removable and non-removable media implemented in any method or technology for storage of information such as computer readable instructions, data structures, program modules or other data. Communication media typically includes computer readable instructions, data structures, program modules, or other data in a modulated data signal such as a carrier wave, or other transmission mechanism, and includes any information delivery media.
전술한 본 발명의 설명은 예시를 위한 것이며, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야의 통상의 지식을 가진 자는 본 발명의 기술적 사상이나 필수적인 특징을 변경하지 않고서 다른 구체적인 형태로 쉽게 변형 가능하다는 것을 이해할 수 있을 것이다. 그러므로 이상에서 기술한 실시 예들은 모든 면에서 예시적인 것이며 한정적이 아닌 것으로 이해해야만 한다. 예를 들어, 단일형으로 설명되어 있는 각 구성 요소는 분산되어 실시될 수도 있으며, 마찬가지로 분산된 것으로 설명되어 있는 구성 요소들도 결합된 형태로 실시될 수 있다.The foregoing description of the present invention is intended for illustration, and it will be understood by those skilled in the art that the present invention may be easily modified in other specific forms without changing the technical spirit or essential features of the present invention. . Therefore, it should be understood that the embodiments described above are exemplary in all respects and not restrictive. For example, each component described as a single type may be implemented in a distributed manner, and similarly, components described as distributed may be implemented in a combined form.
본 발명의 범위는 상기 상세한 설명보다는 후술하는 특허청구범위에 의하여 나타내어지며, 특허청구범위의 의미 및 범위 그리고 그 균등 개념으로부터 도출되는 모든 변경 또는 변형된 형태가 본 발명의 범위에 포함되는 것으로 해석되어야 한다.The scope of the present invention is shown by the following claims rather than the above description, and all changes or modifications derived from the meaning and scope of the claims and their equivalents should be construed as being included in the scope of the present invention. do.
Claims (15)
Translated fromKorean동일 영역을 촬영한 제1 해상도를 갖는 제1 영상 및 상기 제1 해상도보다 높은 제2 해상도를 갖는 제2 영상을 획득하는 단계;
상기 제1 영상을 제네레이션 네트워크(Generation Network)에 입력하여 상기 제2 해상도에 상응하는 제1-1 영상을 생성하고, 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상을 판별하는 단계;
상기 생성된 제1-1 영상을 디그라데이션 네트워크(Degaradation Network)에 입력하여 상기 제1 해상도에 상응하는 제1-2 영상을 생성하고, 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상을 판별하는 단계; 및
상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상의 판별 결과 및 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상을 판별 결과를 기초로 상기 제네레이션 네트워크 및 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크를 학습하는 단계를 포함하고,
상기 학습하는 단계는,
로스 함수를 계산하는 단계를 더 포함하고, 상기 로스 함수는,
상기 생성된 제1-1 영상 및 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상 각각의 소정의 가중치가 각각 곱해진, 대립적인 로스 값(Adverarial Loss)과 인지적인 로스 값(Perceptual Loss)의 합으로 구성되고,
상기 제1 영상을 업 샘플링하여 상기 제2 영상과 동일한 크기의 제3 영상을 생성하는 단계를 더 포함하고,
상기 생성된 제1-1 영상의 대립적인 로스 값은 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상 간의 차이에 따라 계산되고, 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상의 인지적인 로스 값은 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제3 영상 간의 차이에 따라 계산되고, 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상의 대립적인 로스 값은 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상 간의 차이에 따라 계산되고, 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상의 인지적인 로스 값은 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상 간의 차이에 따라 계산되는 것을 특징으로 하는 학습 방법.As a learning method to improve the resolution of low resolution satellite images,
Acquiring a first image having a first resolution of a same region and a second image having a second resolution higher than the first resolution;
Inputting the first image to a generation network to generate a 1-1 image corresponding to the second resolution, and determining the generated 1-1 image and the second image;
The generated 1-1 image is input to a degaradation network to generate a 1-2 image corresponding to the first resolution, and the generated 1-2 image and the first image are discriminated. Doing; And
Learning the generation network and the degradation network based on the generated discrimination result of the first-first image and the second image and the discriminating result of the generated 1-2 image and the first image. and,
The learning step,
Calculating a loss function, wherein the loss function comprises:
A predetermined weight of each of the generated first-first image and the generated first-second image, respectively, is multiplied by a sum of an adversarial loss value and a perceptual loss value,
Upsampling the first image to generate a third image having the same size as the second image;
An alternative loss value of the generated first-first image is calculated according to a difference between the generated first-first image and the second image, and a cognitive loss value of the generated first-first image is generated. Calculated based on the difference between the first-first image and the third image, and an alternative loss value of the generated 1-2 image is calculated according to the difference between the generated 1-2 image and the first image. And the perceptual loss value of the generated 1-2 image is calculated according to a difference between the generated 1-2 image and the first image.
상기 제네레이션 네트워크 및 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크는,
순환 대립 뉴럴 네트워크 구조인 것을 특징으로 하는 학습 방법.The method of claim 1,
The generation network and the degradation network,
Learning method characterized in that the cyclic alternative neural network structure.
상기 학습하는 단계는,
상기 제네레이션 네트워크와 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상을 판별하는 판별기, 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크와 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상을 판별하는 판별기 각각을 1:1의 비율로 가중치 업데이트를 수행하는 것을 특징으로 하는 학습 방법.The method of claim 2,
The learning step,
A discriminator for discriminating the generation network, the generated 1-1 image and the second image, and a discriminator for discriminating the degradation network, the generated 1-2 image and the first image, respectively; A learning method, characterized in that for performing a weight update at a ratio of one.
상기 로스 함수는를 사용하고, 다음 수학식 1 및 2에 의해 계산되는 것을 특징으로 하는 학습 방법.
[수학식 1]
[수학식 2]
(여기서,는 사전학습된 VGG 모델의 4번 레이어의 피처 값()을 최소제곱법(MSE, mean square error)을 통해 계산하고, α와 β는 학습에 필요한 파라미터들이고, D는 촬영한 실제영상/생성영상을 판단하는 구분자이고, G는 저해상도 영상 입력을 받아 복원 영상을 생성하는 생성자를 의미함)The method of claim 1,
The loss function is Using, and is calculated by the following equations (1) and (2).
[Equation 1]
[Equation 2]
(here, Is the feature value of layer 4 of the pre-learned VGG model ( ) Is calculated using the mean square error (MSE), α and β are necessary parameters for learning, D is an identifier for judging the actual image / production image, and G is a low resolution image input. Refers to the constructor that creates the image)
상기 제1 해상도는, GSD(Ground Sample Distance) 기준으로 4m이고,
상기 제2 해상도는, GSD 기준으로 0.5m인 것을 특징으로 하는 학습 방법.The method of claim 1,
The first resolution is 4m based on GSD (Ground Sample Distance),
The second resolution is a learning method, characterized in that 0.5m on the basis of the GSD.
상기 제네레이션 네트워크 및 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크를 독립적으로 사전 학습하는 것을 특징으로 하는 학습 방법.The method of claim 1,
Learning method, characterized in that the pre-learning of the generation network and the degradation network independently.
상기 프로세서에서,
동일 영역을 촬영한 제1 해상도를 갖는 제1 영상 및 상기 제1 해상도보다 높은 제2 해상도를 갖는 제2 영상을 획득하고,
상기 제1 영상을 제네레이션 네트워크(Generation Network)에 입력하여 상기 제2 해상도에 상응하는 제1-1 영상을 생성하고, 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상을 판별하고,
상기 생성된 제1-1 영상을 디그라데이션 네트워크(Degaradation Network)에 입력하여 상기 제1 해상도에 상응하는 제1-2 영상을 생성하고, 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상을 판별하고,
상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상의 판별 결과 및 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상을 판별 결과를 기초로 상기 제네레이션 네트워크 및 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크를 학습하고,
상기 프로세서는,
로스 함수를 계산하고, 상기 로스 함수는,
상기 생성된 제1-1 영상 및 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상 각각의 소정의 가중치가 각각 곱해진, 대립적인 로스 값(Adverarial Loss)과 인지적인 로스 값(Perceptual Loss)의 합으로 구성되고,
상기 프로세서는 상기 제1 영상을 업 샘플링하여 상기 제2 영상과 동일한 크기의 제3 영상을 생성하고,
상기 생성된 제1-1 영상의 대립적인 로스 값은 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상 간의 차이에 따라 계산되고, 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상의 인지적인 로스 값은 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제3 영상 간의 차이에 따라 계산되고, 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상의 대립적인 로스 값은 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상 간의 차이에 따라 계산되고, 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상의 인지적인 로스 값은 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상 간의 차이에 따라 계산되는 것을 특징으로 하는 프로세서.A processor for performing a learning method for improving the resolution of a low resolution satellite image,
In the processor,
Obtaining a first image having a first resolution of a same region and a second image having a second resolution higher than the first resolution,
Inputting the first image to a generation network to generate a 1-1 image corresponding to the second resolution, discriminating the generated 1-1 image and the second image,
The generated 1-1 image is input to the degaradation network to generate a 1-2 image corresponding to the first resolution, and the generated 1-2 image and the first image are discriminated. and,
Learn the generation network and the degradation network based on the generated discrimination result of the first-first image and the second image and the discrimination result of the generated 1-2 image and the first image;
The processor,
Calculate a loss function, and the loss function
And a sum of an alternative loss value and a perceptual loss value multiplied by a predetermined weight of each of the generated first-first image and the generated 1-2 image, respectively,
The processor upsamples the first image to generate a third image having the same size as the second image,
An alternative loss value of the generated first-first image is calculated according to a difference between the generated first-first image and the second image, and a cognitive loss value of the generated first-first image is generated. Calculated based on the difference between the first-first image and the third image, and an alternative loss value of the generated 1-2 image is calculated according to the difference between the generated 1-2 image and the first image. And the perceptual loss value of the generated 1-2 image is calculated according to a difference between the generated 1-2 image and the first image.
상기 제네레이션 네트워크 및 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크는,
순환 대립 뉴럴 네트워크 구조인 것을 특징으로 하는 프로세서.The method of claim 10,
The generation network and the degradation network,
And a cyclically opposed neural network structure.
상기 프로세서는,
상기 제네레이션 네트워크와 상기 생성된 제1-1 영상과 상기 제2 영상을 판별하는 판별기, 상기 디그라데이션 네트워크와 상기 생성된 제1-2 영상과 상기 제1 영상을 판별하는 판별기 각각을 1:1의 비율로 가중치 업데이트를 수행하는 것을 특징으로 하는 프로세서.The method of claim 11,
The processor,
A discriminator for discriminating the generation network, the generated 1-1 image and the second image, and a discriminator for discriminating the degradation network, the generated 1-2 image and the first image, respectively; And perform a weighted update at a rate of one.
제1 해상도를 갖는 제1 위성영상을 획득하는 단계;
제 1 항 내지 제 3 항, 제 6 항 내지 제 8 항 중 어느 한 항에 따른 학습 방법에 의해 학습된 제너레이션 네트워크에 상기 제1 위성영상을 입력하는 단계; 및
제2 해상도에 상응하는 제2 위성영상을 생성하여 출력하는 단계를 포함하는 저해상도 위성영상의 해상도 향상 방법.In the method of improving the resolution of low resolution satellite image,
Acquiring a first satellite image having a first resolution;
Inputting the first satellite image to a generation network learned by the learning method according to any one of claims 1 to 3 and 6 to 8; And
And generating and outputting a second satellite image corresponding to the second resolution.
메모리; 및
프로세서를 포함하고,
상기 프로세서는,
상기 제 14 항에 따른 방법을 수행하는 것을 특징으로 하는 저해상도 위성영상의 해상도 향상 장치.In the device for improving the resolution of a low resolution satellite image,
Memory; And
Includes a processor,
The processor,
An apparatus for improving the resolution of low resolution satellite images, comprising performing the method according to claim 14.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190130179AKR102067629B1 (en) | 2019-10-18 | 2019-10-18 | Learning method and apparatus for improved resolution of low resolution satellite images |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190130179AKR102067629B1 (en) | 2019-10-18 | 2019-10-18 | Learning method and apparatus for improved resolution of low resolution satellite images |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR102067629B1true KR102067629B1 (en) | 2020-01-17 |
Family
ID=69370180
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020190130179AActiveKR102067629B1 (en) | 2019-10-18 | 2019-10-18 | Learning method and apparatus for improved resolution of low resolution satellite images |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102067629B1 (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111915491A (en)* | 2020-08-14 | 2020-11-10 | 深圳清研智城科技有限公司 | Weak supervision super-resolution reconstruction model and method based on distant and close scenes |
| KR102188035B1 (en) | 2020-06-04 | 2020-12-07 | 국방과학연구소 | Learning method and apparatus for improved resolution of satellite images |
| CN114757859A (en)* | 2022-03-11 | 2022-07-15 | 理大产学研基地(深圳)有限公司 | Object-level space-time fusion method for remote sensing image data |
| KR20250044497A (en) | 2023-09-22 | 2025-04-01 | 서울대학교산학협력단 | Method and system for improving spatial resolution of past satellite images for long term vegetation monitoring using dual productive adversarial neural network model and cube satellite image |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101716082B1 (en)* | 2016-04-12 | 2017-03-14 | 연세대학교 산학협력단 | Method and apparatus for video quality measurement |
| KR20190114229A (en)* | 2018-03-29 | 2019-10-10 | 울산대학교 산학협력단 | Apparatus and method for processing image |
- 2019
- 2019-10-18KRKR1020190130179Apatent/KR102067629B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101716082B1 (en)* | 2016-04-12 | 2017-03-14 | 연세대학교 산학협력단 | Method and apparatus for video quality measurement |
| KR20190114229A (en)* | 2018-03-29 | 2019-10-10 | 울산대학교 산학협력단 | Apparatus and method for processing image |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| Jiang et al. GAN Based Multi level Mapping Network for Satellite Imagery Super Resolution. ICME, 2019년 7월, pp. 526-531. 1부.** |
| Zhao et al. Unsupervised degradation learning for single image super resolution. arXiv, 2018년, pp. 1-9. 1부.** |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102188035B1 (en) | 2020-06-04 | 2020-12-07 | 국방과학연구소 | Learning method and apparatus for improved resolution of satellite images |
| CN111915491A (en)* | 2020-08-14 | 2020-11-10 | 深圳清研智城科技有限公司 | Weak supervision super-resolution reconstruction model and method based on distant and close scenes |
| CN114757859A (en)* | 2022-03-11 | 2022-07-15 | 理大产学研基地(深圳)有限公司 | Object-level space-time fusion method for remote sensing image data |
| KR20250044497A (en) | 2023-09-22 | 2025-04-01 | 서울대학교산학협력단 | Method and system for improving spatial resolution of past satellite images for long term vegetation monitoring using dual productive adversarial neural network model and cube satellite image |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102141163B1 (en) | Neural network learning method and apparatus for generating synthetic aperture radar image | |
| KR102067629B1 (en) | Learning method and apparatus for improved resolution of low resolution satellite images | |
| CN110033003B (en) | Image segmentation method and image processing device | |
| KR102188035B1 (en) | Learning method and apparatus for improved resolution of satellite images | |
| CN112465828B (en) | Image semantic segmentation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| US11741581B2 (en) | Training method for image processing model, image processing method, network device, and storage medium | |
| JP7723159B2 (en) | Image Processing Using Self-Attention Based Neural Networks | |
| Zhou et al. | Scale adaptive image cropping for UAV object detection | |
| CN112287954B (en) | Image classification method, image classification model training method and device | |
| CN113591968A (en) | Infrared weak and small target detection method based on asymmetric attention feature fusion | |
| KR102140805B1 (en) | Neural network learning method and apparatus for object detection of satellite images | |
| Pashaei et al. | Deep learning-based single image super-resolution: an investigation for dense scene reconstruction with UAS photogrammetry | |
| Cui et al. | Exploring resolution and degradation clues as self-supervised signal for low quality object detection | |
| CN118762364A (en) | A method for infrared small target detection based on scene text information guidance | |
| Malav et al. | DHSGAN: An end to end dehazing network for fog and smoke | |
| CN116543161A (en) | Semantic segmentation method, semantic segmentation device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| Xu et al. | Extended non-local feature for visual saliency detection in low contrast images | |
| Yan et al. | RTHEN: Unsupervised deep homography estimation based on dynamic attention for repetitive texture image stitching | |
| US20250054115A1 (en) | Deep learning-based high resolution image inpainting | |
| CN116128727B (en) | Super-resolution method, system, equipment and medium for polarized radar image | |
| Rahunathan et al. | Prediction and Processing of Environment Geography Images Using Deep Learning Techniques | |
| CN115659836B (en) | Unmanned system vision self-positioning method based on end-to-end feature optimization model | |
| Palan et al. | Leveraging Super-Resolution Technology in Drone Imagery for Advanced Plant Disease Diagnosis and Prognosis | |
| CN113256556B (en) | Image selection method and device | |
| CN113487483A (en) | Training method and device for image segmentation network |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20191018 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0302 | Request for accelerated examination | Patent event date:20191021 Patent event code:PA03022R01D Comment text:Request for Accelerated Examination Patent event date:20191018 Patent event code:PA03021R01I Comment text:Patent Application | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20191226 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20200109 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20200113 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20200114 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20221223 Start annual number:4 End annual number:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20231220 Start annual number:5 End annual number:5 |