KR102014359B1 - Method and apparatus for providing camera location using surgical video - Google Patents
Method and apparatus for providing camera location using surgical videoDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102014359B1 KR102014359B1KR1020180098359AKR20180098359AKR102014359B1KR 102014359 B1KR102014359 B1KR 102014359B1KR 1020180098359 AKR1020180098359 AKR 1020180098359AKR 20180098359 AKR20180098359 AKR 20180098359AKR 102014359 B1KR102014359 B1KR 102014359B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- body model
- surgical
- camera position
- position information
- camera
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/36—Image-producing devices or illumination devices not otherwise provided for
- A61B90/37—Surgical systems with images on a monitor during operation
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/10—Computer-aided planning, simulation or modelling of surgical operations
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/20—Surgical navigation systems; Devices for tracking or guiding surgical instruments, e.g. for frameless stereotaxis
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/25—User interfaces for surgical systems
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/30—Surgical robots
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/70—Manipulators specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/76—Manipulators having means for providing feel, e.g. force or tactile feedback
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/36—Image-producing devices or illumination devices not otherwise provided for
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/36—Image-producing devices or illumination devices not otherwise provided for
- A61B90/361—Image-producing devices, e.g. surgical cameras
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N20/00—Machine learning
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T17/00—Three dimensional [3D] modelling, e.g. data description of 3D objects
- G06T17/20—Finite element generation, e.g. wire-frame surface description, tesselation
- G06T3/0068—
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H30/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images
- G16H30/40—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images for processing medical images, e.g. editing
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/10—Computer-aided planning, simulation or modelling of surgical operations
- A61B2034/101—Computer-aided simulation of surgical operations
- A61B2034/105—Modelling of the patient, e.g. for ligaments or bones
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/20—Surgical navigation systems; Devices for tracking or guiding surgical instruments, e.g. for frameless stereotaxis
- A61B2034/2046—Tracking techniques
- A61B2034/2065—Tracking using image or pattern recognition
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/25—User interfaces for surgical systems
- A61B2034/252—User interfaces for surgical systems indicating steps of a surgical procedure
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/36—Image-producing devices or illumination devices not otherwise provided for
- A61B2090/364—Correlation of different images or relation of image positions in respect to the body
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Robotics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Computer Graphics (AREA)
- Gynecology & Obstetrics (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
- Apparatus For Radiation Diagnosis (AREA)
- Processing Or Creating Images (AREA)
- Image Generation (AREA)
- Surgical Instruments (AREA)
- Image Processing (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법 및 장치에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for providing a surgical image based camera position.
최근에는 가상현실을 의료수술 시뮬레이션 분야에 적용하고자 하는 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있다.Recently, researches on applying virtual reality to the field of medical surgery simulation have been actively conducted.
의료수술은 개복수술(open surgery), 복강경 수술 및 로봇 수술을 포함하는 최소침습수술(MIS: Minimally Invasive Surgery), 방사선수술(radio surgery) 등으로 분류할 수 있다. 개복수술은 치료되어야 할 부분을 의료진이 직접 보고 만지며 시행하는 수술을 말하며, 최소침습수술은 키홀 수술(keyhole surgery)이라고도 하는데 복강경 수술과 로봇 수술이 대표적이다. 복강경 수술은 개복을 하지 않고 필요한 부분에 작은 구멍을 내어 특수 카메라가 부착된 복강경과 수술 도구를 몸속에 삽입하여 비디오 모니터를 통해서 관측하며 레이저나 특수기구를 이용하여 미세수술을 한다. 또한, 로봇수술은 수술로봇을 이용하여 최소 침습수술을 수행하는 것이다. 나아가 방사선 수술은 체외에서 방사선이나 레이저 광으로 수술 치료를 하는 것을 말한다.Medical surgery can be classified into open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, minimally invasive surgery (MIS) including radio surgery, radio surgery, and the like. Laparoscopic surgery refers to surgery performed by medical staff to see and touch the part to be treated. Minimally invasive surgery is also known as keyhole surgery, and laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery are typical. In laparoscopic surgery, a small hole is made in a necessary part without opening, and a laparoscopic with a special camera is attached and a surgical tool is inserted into the body and observed through a video monitor. Microsurgery is performed using a laser or a special instrument. In addition, robot surgery is to perform minimally invasive surgery using a surgical robot. Furthermore, radiation surgery refers to surgical treatment with radiation or laser light outside the body.
이러한 의료수술의 경우, 수술경로 상에서 현재 수술이 진행되고 있는 수술부위 및 수술도구의 위치를 파악하는 것이 중요하다. 이를 위해 수술영상을 이용하여 카메라의 위치를 파악함으로써 현재 수술이 진행되고 있는 수술부위 및 수술도구의 위치를 파악할 수 있는 방법을 제공한다.In the case of such medical surgery, it is important to identify the location of the surgical site and the surgical tool that is currently undergoing surgery on the surgical path. To this end, by using the surgical image to determine the location of the camera provides a method to determine the location of the surgical site and surgical instruments that are currently undergoing surgery.
본 발명이 해결하고자 하는 과제는 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법 및 장치를 제공하는 것이다.The problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide a surgical image-based camera position providing method and apparatus.
본 발명이 해결하고자 하는 과제들은 이상에서 언급된 과제로 제한되지 않으며, 언급되지 않은 또 다른 과제들은 아래의 기재로부터 통상의 기술자에게 명확하게 이해될 수 있을 것이다.Problems to be solved by the present invention are not limited to the above-mentioned problems, and other problems not mentioned will be clearly understood by those skilled in the art from the following description.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 컴퓨터에 의해 수행되는 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법은, 카메라가 신체내부로 진입하여 수술경로를 이동함에 따라 촬영한 수술영상을 획득하는 단계, 상기 수술영상을 기초로 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 단계, 및 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기반으로 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 제공하는 단계를 포함한다.Surgical image-based camera position providing method performed by a computer according to an embodiment of the present invention, obtaining a surgical image taken as the camera enters the body and moves the surgical path, based on the surgical image Deriving camera position information on the standard body model, and providing camera position information on the virtual body model of the current surgical subject based on the camera position information on the standard body model.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 있어서, 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 단계는, 상기 수술영상으로부터 상기 수술경로 상에서 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상을 지정하는 단계, 상기 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상을 이용하여 상기 표준신체모델 상에서 대응하는 지점에 매핑하는 단계, 및 상기 표준신체모델 상에서 대응하는 지점에 대한 좌표 정보를 산출하여 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보로 도출하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In one embodiment of the present invention, deriving the camera position information on the standard body model, the step of specifying a surgical image corresponding to at least one reference point on the surgical path from the surgical image, the at least one Mapping to a corresponding point on the standard body model using a surgical image corresponding to a reference point of the; and calculating coordinate information of a corresponding point on the standard body model to obtain camera position information on the standard body model. It may include the step of deriving.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 있어서, 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 단계는, 상기 수술영상으로부터 상기 수술경로 상에서 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상을 지정하는 단계, 상기 수술영상에 대응하는 가상신체모델을 획득하여, 상기 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상을 상기 가상신체모델 상에 매핑하는 단계, 및 상기 가상신체모델 상에 매핑된 지점을 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보로 변환하여 도출하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In one embodiment of the present invention, the step of deriving the camera position information on the standard body model, specifying a surgical image corresponding to at least one reference point on the surgical path from the surgical image, the surgical image Acquiring a virtual body model corresponding to the at least one reference point, mapping a surgical image corresponding to the at least one reference point onto the virtual body model, and mapping a point mapped on the virtual body model to the camera on the standard body model. And converting the location information into a location information.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 있어서, 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 단계는, 딥러닝 기반의 CNN(Convolutional Neural Network)을 이용한 학습을 통해 상기 수술영상을 기초로 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출할 수 있다.In one embodiment of the present invention, the step of deriving the camera position information on the standard body model, based on the surgical image through the learning using the deep learning-based convolutional neural network (CNN) on the standard body model Camera position information can be derived.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 있어서, 상기 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 제공하는 단계는, 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보를 상기 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 단계, 및 상기 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로부터 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보에 대응하는 대응 위치를 산출하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In one embodiment of the present invention, the step of providing the camera position information on the virtual body model of the current surgery subject, the coordinate information on the standard body model to the coordinate information on the virtual body model of the current surgery subject And converting the corresponding position corresponding to the camera position information on the standard body model from the coordinate information on the virtual body model.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 있어서, 상기 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 단계는, 상기 표준신체모델 상에서 레퍼런스 위치를 추출하는 단계, 상기 레퍼런스 위치에 대응하는 상기 가상신체모델 상에서 대응 레퍼런스 위치를 추출하여 변환 매트릭스(Transformation Matrix)를 적용하는 단계, 및 상기 변환 매트릭스를 기반으로 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보를 상기 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In one embodiment of the present invention, the step of converting the coordinate information on the virtual body model of the current surgery subject, extracting a reference position on the standard body model, on the virtual body model corresponding to the reference position Extracting a corresponding reference position to apply a transformation matrix, and converting coordinate information on the standard body model into coordinate information on the virtual body model based on the transformation matrix. .
본 발명의 일 실시예에 있어서, 상기 현재 수술 대상자에 대한 수술 시, 상기 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기초로 상기 현재 수술 대상자의 실제신체 내 카메라 위치 정보를 산출하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.In one embodiment of the present invention, during the operation on the current surgery subject, the method may further include calculating the camera position information in the actual body of the current surgery subject based on the camera position information on the virtual body model. have.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 있어서, 상기 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기초로 상기 현재 수술 대상자의 수술경로 상에서 상기 카메라의 이동 경로를 가이드하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.In one embodiment of the present invention, the method may further include guiding a movement path of the camera on a surgical path of the current surgery subject based on camera position information on the virtual body model.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 있어서, 상기 카메라의 이동 경로를 가이드하는 단계는, 상기 현재 수술 대상자의 수술경로 상에서 제1 영역의 수술이 종료됨을 인식하는 단계, 및 상기 제1 영역에서 제2 영역으로 수술이 진행됨에 따라 상기 제2 영역에 대한 위치 정보를 상기 카메라의 이동 경로로 가이드하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In one embodiment of the present invention, the step of guiding the movement path of the camera, the step of recognizing that the operation of the first area on the operation path of the current surgery subject, and from the first area to the second area As the surgery progresses, the method may include guiding position information of the second area to a movement path of the camera.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 있어서, 상기 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델은, 상기 현재 수술 대상자의 신체내부를 촬영한 의료영상데이터를 기반으로 생성된 3차원 모델링 데이터이며, 상기 표준신체모델은, 신체의 해부학적 특징을 표준화하여 생성한 3차원 신체모델일 수 있다.In one embodiment of the present invention, the virtual body model of the current surgery subject is three-dimensional modeling data generated based on the medical image data taken inside the body of the current surgery subject, the standard body model, the body It may be a three-dimensional body model generated by standardizing the anatomical features of the.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 장치는, 하나 이상의 인스트럭션을 저장하는 메모리, 및 상기 메모리에 저장된 상기 하나 이상의 인스트럭션을 실행하는 프로세서를 포함하며, 상기 프로세서는 상기 하나 이상의 인스트럭션을 실행함으로써, 카메라가 신체내부로 진입하여 수술경로를 이동함에 따라 촬영한 수술영상을 획득하는 단계, 상기 수술영상을 기초로 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 단계, 및 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기반으로 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 제공하는 단계를 수행한다.An apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a memory for storing one or more instructions, and a processor for executing the one or more instructions stored in the memory, the processor executing the one or more instructions, such that Acquiring a surgical image taken as the inside is moved and moving a surgical path, deriving camera position information on a standard body model based on the surgical image, and based on camera position information on the standard body model It provides a step of providing the camera position information on the virtual body model of the current surgery subject.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 컴퓨터프로그램은 하드웨어인 컴퓨터와 결합되어, 상기 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법을 수행할 수 있도록 컴퓨터에서 독출가능한 기록매체에 저장된다.A computer program according to an embodiment of the present invention is combined with a computer, which is hardware, and stored in a computer-readable recording medium to perform the method for providing a surgical image-based camera position.
본 발명에 따르면, 수술영상의 카메라 시점을 검출함으로써 3차원 모델링된 신체모델 내에서 동일 시점으로 보이는 3차원 상의 카메라 위치 정보를 효과적으로 산출할 수 있다.According to the present invention, by detecting the camera viewpoint of the surgical image it is possible to effectively calculate the camera position information on the three-dimensional image seen in the same viewpoint in the three-dimensional modeled body model.
본 발명에 따르면, 실제 수술시에 카메라의 위치를 파악하기 위해서 별도의 장치를 구비하지 않더라도, 수술영상만 가지고 효율적으로 3차원 공간상의 카메라 좌표 정보를 제공할 수 있다.According to the present invention, even if a separate device is not provided to determine the position of the camera during the actual surgery, the camera coordinate information in the three-dimensional space can be efficiently provided with only the surgical image.
본 발명에 따르면, 수술경로 상에서의 기준 위치에 해당하는 지점에 대한 카메라 위치 정보를 도출함으로써, 수술 전에 미리 카메라가 위치하여야 할 지점을 제공할 수 있다.According to the present invention, by deriving the camera position information for a point corresponding to the reference position on the surgical path, it is possible to provide a point to be located before the operation of the camera.
본 발명의 효과들은 이상에서 언급된 효과로 제한되지 않으며, 언급되지 않은 또 다른 효과들은 아래의 기재로부터 통상의 기술자에게 명확하게 이해될 수 있을 것이다.Effects of the present invention are not limited to the effects mentioned above, and other effects not mentioned will be clearly understood by those skilled in the art from the following description.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법을 도시한 흐름도이다.
도 2는 특정 수술에 대한 각 환자마다 수술경로를 도시한 도면이다.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 수술영상으로부터 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 과정의 일례를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 환자의 가상신체모델의 좌표 정보를 표준신체모델의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 과정의 일례를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 표준신체모델의 좌표 정보를 현재 수술 대상자에 대한 가상신체모델의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 과정을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 6 및 도 7은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 학습을 통해 수술영상으로부터 표준신체모델 상에서의 위치 정보를 도출하는 과정을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 8은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 로봇수술을 수행할 수 있는 시스템을 간략하게 도식화한 도면이다.
도 9는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법을 수행하는 장치(500)의 구성을 개략적으로 나타내는 도면이다.1 is a flowchart illustrating a method for providing a surgical image based camera position according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
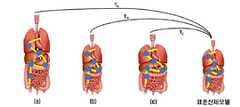
2 is a diagram illustrating a surgical path for each patient for a specific surgery.
3 is a view for explaining an example of a process of deriving the camera position information on the standard body model from the surgical image according to an embodiment of the present invention.
4 is a diagram illustrating an example of a process of converting coordinate information of a virtual body model of a patient into coordinate information of a standard body model according to an embodiment of the present invention.
5 is a view for explaining a process of converting the coordinate information of the standard body model according to an embodiment of the present invention to the coordinate information of the virtual body model for the current surgery subject.
6 and 7 are diagrams for explaining a process of deriving the position information on the standard body model from the surgical image through the learning according to an embodiment of the present invention.
8 is a schematic diagram of a system capable of performing robot surgery according to an embodiment of the present invention.
9 is a diagram schematically illustrating a configuration of an
본 발명의 이점 및 특징, 그리고 그것들을 달성하는 방법은 첨부되는 도면과 함께 상세하게 후술되어 있는 실시예들을 참조하면 명확해질 것이다. 그러나, 본 발명은 이하에서 개시되는 실시예들에 제한되는 것이 아니라 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 구현될 수 있으며, 단지 본 실시예들은 본 발명의 개시가 완전하도록 하고, 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야의 통상의 기술자에게 본 발명의 범주를 완전하게 알려주기 위해 제공되는 것이며, 본 발명은 청구항의 범주에 의해 정의될 뿐이다.Advantages and features of the present invention and methods for achieving them will be apparent with reference to the embodiments described below in detail with the accompanying drawings. However, the present invention is not limited to the embodiments disclosed below, but can be embodied in various different forms, and the present embodiments only make the disclosure of the present invention complete, and those of ordinary skill in the art to which the present invention belongs. It is provided to fully inform the skilled worker of the scope of the invention, which is defined only by the scope of the claims.
본 명세서에서 사용된 용어는 실시예들을 설명하기 위한 것이며 본 발명을 제한하고자 하는 것은 아니다. 본 명세서에서, 단수형은 문구에서 특별히 언급하지 않는 한 복수형도 포함한다. 명세서에서 사용되는 "포함한다(comprises)" 및/또는 "포함하는(comprising)"은 언급된 구성요소 외에 하나 이상의 다른 구성요소의 존재 또는 추가를 배제하지 않는다. 명세서 전체에 걸쳐 동일한 도면 부호는 동일한 구성 요소를 지칭하며, "및/또는"은 언급된 구성요소들의 각각 및 하나 이상의 모든 조합을 포함한다. 비록 "제1", "제2" 등이 다양한 구성요소들을 서술하기 위해서 사용되나, 이들 구성요소들은 이들 용어에 의해 제한되지 않음은 물론이다. 이들 용어들은 단지 하나의 구성요소를 다른 구성요소와 구별하기 위하여 사용하는 것이다. 따라서, 이하에서 언급되는 제1 구성요소는 본 발명의 기술적 사상 내에서 제2 구성요소일 수도 있음은 물론이다.The terminology used herein is for the purpose of describing particular embodiments only and is not intended to be limiting of the invention. In this specification, the singular also includes the plural unless specifically stated otherwise in the phrase. As used herein, "comprises" and / or "comprising" does not exclude the presence or addition of one or more other components in addition to the mentioned components. Like reference numerals refer to like elements throughout, and "and / or" includes each and all combinations of one or more of the mentioned components. Although "first", "second", etc. are used to describe various components, these components are of course not limited by these terms. These terms are only used to distinguish one component from another. Therefore, of course, the first component mentioned below may be a second component within the technical spirit of the present invention.
다른 정의가 없다면, 본 명세서에서 사용되는 모든 용어(기술 및 과학적 용어를 포함)는 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야의 통상의 기술자에게 공통적으로 이해될 수 있는 의미로 사용될 수 있을 것이다. 또한, 일반적으로 사용되는 사전에 정의되어 있는 용어들은 명백하게 특별히 정의되어 있지 않는 한 이상적으로 또는 과도하게 해석되지 않는다.Unless otherwise defined, all terms used in the present specification (including technical and scientific terms) may be used in a sense that can be commonly understood by those skilled in the art. In addition, terms that are defined in a commonly used dictionary are not ideally or excessively interpreted unless they are specifically defined clearly.
명세서에서 사용되는 "부" 또는 “모듈”이라는 용어는 소프트웨어, FPGA 또는 ASIC과 같은 하드웨어 구성요소를 의미하며, "부" 또는 “모듈”은 어떤 역할들을 수행한다. 그렇지만 "부" 또는 “모듈”은 소프트웨어 또는 하드웨어에 한정되는 의미는 아니다. "부" 또는 “모듈”은 어드레싱할 수 있는 저장 매체에 있도록 구성될 수도 있고 하나 또는 그 이상의 프로세서들을 재생시키도록 구성될 수도 있다. 따라서, 일 예로서 "부" 또는 “모듈”은 소프트웨어 구성요소들, 객체지향 소프트웨어 구성요소들, 클래스 구성요소들 및 태스크 구성요소들과 같은 구성요소들과, 프로세스들, 함수들, 속성들, 프로시저들, 서브루틴들, 프로그램 코드의 세그먼트들, 드라이버들, 펌웨어, 마이크로 코드, 회로, 데이터, 데이터베이스, 데이터구조들, 테이블들, 어레이들 및 변수들을 포함한다. 구성요소들과 "부" 또는 “모듈”들 안에서 제공되는 기능은 더 작은 수의 구성요소들 및 "부" 또는 “모듈”들로 결합되거나 추가적인 구성요소들과 "부" 또는 “모듈”들로 더 분리될 수 있다.As used herein, the term "part" or "module" refers to a hardware component such as software, FPGA, or ASIC, and the "part" or "module" plays certain roles. However, "part" or "module" is not meant to be limited to software or hardware. The “unit” or “module” may be configured to be in an addressable storage medium or may be configured to play one or more processors. Thus, as an example, a "part" or "module" may include components such as software components, object-oriented software components, class components, and task components, processes, functions, properties, Procedures, subroutines, segments of program code, drivers, firmware, microcode, circuitry, data, databases, data structures, tables, arrays, and variables. Functions provided within components and "parts" or "modules" may be combined into smaller numbers of components and "parts" or "modules" or into additional components and "parts" or "modules". Can be further separated.
의료수술을 수행할 때, 수술과정에서 촬영된 수술영상 또는 수술과정에서 발생하는 다양한 수술정보를 포함하는 데이터를 획득할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 복강경 수술이나 로봇수술과 같은 최소침습수술의 경우, 환자의 신체 내부로 수술도구와 함께 카메라가 진입하여 카메라에 의해 수술부위를 촬영한 수술영상을 관측하면서 미세수술을 진행한다. 이에, 본 발명에서는 이와 같이 수술 과정에서 획득할 수 있는 수술정보(즉, 수술영상)를 활용할 수 있는 방법을 제안하고자 한다. 이하에서는, 본 발명에서 제안하고자 하는 방법으로서, 수술영상을 기초로 특정 환자에 대해 현재 수행되고 있는 수술에서 카메라의 실제 위치 정보를 제공하는 방법을 설명한다.When performing a medical operation, it is possible to obtain data including a surgical image taken in the operation process or a variety of surgical information generated during the operation. For example, in the case of minimally invasive surgery such as laparoscopic surgery or robotic surgery, the camera enters the patient's body together with the surgical tool and proceeds with microscopic surgery while observing a surgical image of the surgical site by the camera. Thus, the present invention is to propose a method that can utilize the surgical information (that is, surgical image) that can be obtained in the surgical process as described above. Hereinafter, as a method proposed by the present invention, a method of providing actual position information of a camera in a surgery currently performed on a specific patient based on a surgical image will be described.
또한, 이하에서는 설명의 편의를 위해 “컴퓨터”가 본 명세서에서 개시되는 실시예들을 수행하는 것으로 설명한다. “컴퓨터”는 컴퓨팅 처리를 수행할 수 있는 장치를 포괄하는 의미로 사용될 수 있다. 예를 들어, "컴퓨터"는 연산처리를 수행하여 사용자에게 결과를 제공할 수 있는 다양한 장치로, 데스크 탑 PC, 노트북(Note Book) 뿐만 아니라 스마트폰(Smart phone), 태블릿 PC, 셀룰러폰(Cellular phone), 피씨에스폰(PCS phone; Personal Communication Service phone), 동기식/비동기식 IMT-2000(International Mobile Telecommunication-2000)의 이동 단말기, 팜 PC(Palm Personal Computer), 개인용 디지털 보조기(PDA; Personal Digital Assistant) 등도 해당될 수 있다. 또한, 헤드마운트 디스플레이(Head Mounted Display; HMD) 장치가 컴퓨팅 기능을 포함하는 경우, HMD장치가 컴퓨터가 될 수 있다. 또한, 컴퓨터는 클라이언트로부터 요청을 수신하여 정보처리를 수행하는 서버가 해당될 수 있다.In addition, hereinafter, for convenience of description, a "computer" is described as performing the embodiments disclosed herein. "Computer" may be used to encompass any device capable of performing computing processing. For example, a "computer" is a variety of devices that can perform computational processing and provide results to users, as well as smart phones, tablet PCs, and cellular phones as well as desktop PCs and notebooks. phone, PCS (Personal Communication Service Phone), synchronous / asynchronous mobile terminal of International Mobile Telecommunication-2000 (IMT-2000), Palm Personal Computer (PDA), Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) ) May also be applicable. In addition, when a head mounted display (HMD) device includes a computing function, the HMD device may be a computer. Also, the computer may correspond to a server that receives a request from a client and performs information processing.
이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예를 상세하게 설명한다.Hereinafter, exemplary embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법을 도시한 흐름도이다.1 is a flowchart illustrating a method for providing a surgical image based camera position according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
도 1을 참조하면, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 컴퓨터에 의해 수행되는 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법은, 카메라가 신체내부로 진입하여 수술경로를 이동함에 따라 촬영한 수술영상을 획득하는 단계(S100), 수술영상을 기초로 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 단계(S110), 및 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기반으로 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 제공하는 단계(S120)를 포함할 수 있다. 이하, 각 단계에 대한 상세한 설명을 기재한다.Referring to Figure 1, the method for providing a surgical image-based camera position performed by a computer according to an embodiment of the present invention, the step of acquiring a surgical image taken as the camera enters the body and moves the surgical path ( S100), deriving camera position information on the standard body model based on the surgical image (S110), and providing camera position information on the virtual body model of the current surgical subject based on the camera position information on the standard body model. It may include the step (S120). Hereinafter, a detailed description of each step will be described.
컴퓨터는 카메라가 신체내부로 진입하여 수술경로를 이동함에 따라 촬영한 수술영상을 획득할 수 있다(S100).The computer may acquire a surgical image taken as the camera enters the body and moves the surgical path (S100).
일 실시예로, 컴퓨터는 실제수술을 수행함에 따른 실제수술영상을 획득할 수 있다. 예컨대 컴퓨터는 로봇 수술이나 복강경 수술 등과 같은 최소침습수술이 수행되는 경우에 촬영된 실제수술영상을 획득할 수도 있고, 또는 실제 의료진이 수술을 수행함에 따라 획득되는 데이터일 수도 있다.In one embodiment, the computer may acquire the actual surgery image according to the actual surgery. For example, the computer may acquire a real surgical image photographed when a minimally invasive surgery such as robotic surgery or laparoscopic surgery is performed, or may be data obtained as the actual medical staff performs the surgery.
이때, 수술영상은 적어도 하나의 환자에 대해 수술을 수행하여 획득된 수술영상일 수 있다. 일반적으로 외과 수술의 경우, 의사나 환자가 달라지더라도 동일한 종류의 수술은 유사한 수술과정으로 진행된다. 따라서, 수술이 동일하다면 여러 명의 임의의 환자에 대해 획득한 수술영상은 유사한 수술동작이나 수술경로를 포함하고 있다. 이에, 컴퓨터는 적어도 하나의 환자로부터 수술영상을 획득하고, 이를 학습을 위한 학습 데이터로 사용할 수 있다. 또한 컴퓨터는 후술할 표준신체모델에 학습 데이터를 이용하여 학습을 시킬수 있다. 이에 대한 구체적인 과정은 후술하도록 한다.In this case, the surgical image may be a surgical image obtained by performing surgery on at least one patient. In general, in the case of a surgical operation, the same type of surgery is performed in a similar surgical process even if the doctor or the patient is different. Thus, if the surgery is the same, the surgical images obtained for any number of patients include similar surgical movements or surgical routes. Thus, the computer may obtain a surgical image from at least one patient, and use it as learning data for learning. In addition, the computer can be trained using the training data in the standard body model to be described later. A detailed process thereof will be described later.
도 2는 특정 수술에 대한 각 환자마다 수술경로를 도시한 도면이다. 도 2의 (a), (b), (c)에 도시된 각 환자마다 3차원 모델링된 신체모델(예컨대, 가상신체모델)은 서로 상이하지만, 수술이 진행되는 수술경로(200, 210, 220)는 서로 유사하다는 것을 알 수 있다. 따라서, 이러한 수술경로를 따라 수술이 진행될 경우, (a), (b), (c)에 도시된 각 환자에 대해 유사한 수술경로를 포함하는 수술영상을 획득할 수 있다.2 is a diagram illustrating a surgical path for each patient for a specific surgery. Although the three-dimensional modeled body models (eg, virtual body models) for each patient illustrated in FIGS. 2A, 2B, and 3C are different from each other, the
다시 도 1을 참조하면, 컴퓨터는 수술영상을 기초로 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출할 수 있다(S110).Referring back to FIG. 1, the computer may derive camera position information on a standard body model based on the surgical image (S110).
여기서, 표준신체모델이란, 신체의 해부학적 특징을 표준화하여 생성한 3차원 신체모델일 수 있다. 예를 들어, 각 신체부위(예: 간, 심장, 자궁, 뇌, 유방, 복부 등의 장기, 및 혈관 등)에 대한 외형, 크기, 위치 등과 같은 해부학적 특징들을 표준화하여 각 신체부위를 3차원 모델링하여 구축된 신체모델일 수 있다. 또한, 표준신체모델은 성별, 나이, 외형 조건 등과 같은 다양한 조건에 따라 각 신체의 해부학적 특징을 표준화하여 생성된 신체모델일 수 있으며, 이러한 여러가지 조건에 따라 적어도 하나 이상의 표준신체모델로 구현될 수도 있다.Here, the standard body model may be a three-dimensional body model generated by standardizing the anatomical features of the body. For example, each body part is three-dimensional by standardizing anatomical features such as shape, size, and location for each part of the body (e.g. liver, heart, uterus, brain, breast, abdomen, and blood vessels, etc.). It may be a body model constructed by modeling. In addition, the standard body model may be a body model generated by standardizing the anatomical characteristics of each body according to various conditions such as gender, age, appearance conditions, etc., may be implemented as at least one standard body model according to these various conditions have.
일 실시예로, 컴퓨터는 수술영상으로부터 수술경로 상에서 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상을 지정할 수 있다. 기준 지점은 카메라가 신체내부로 진입하여 수술경로를 따라 이동하는 지점들 중 정해진 조건을 만족하는 적어도 하나의 지점일 수 있다. 예를 들어, 수술경로 상에서 카메라가 소정의 시간동안 이동하지 않는 지점을 기준 지점으로 정할 수 있다. 또는, 소정의 시간간격을 기초로 수술경로 상에서 카메라가 위치할 수 있는 지점을 기준 지점으로 정할 수도 있다. 다음으로, 컴퓨터는 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상을 이용하여 표준신체모델 상에서 대응하는 지점에 매핑할 수 있다. 그리고, 컴퓨터는 표준신체모델 상에서 대응하는 지점에 대한 좌표 정보를 산출하고, 이를 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보로 도출할 수 있다. 이때, 카메라 위치 정보라함은, 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상과 동일한 시점으로 보이도록 하는 표준신체모델 내 3차원 공간상의 좌표 정보를 의미할 수 있다.In an embodiment, the computer may designate a surgical image corresponding to at least one reference point on the surgical path from the surgical image. The reference point may be at least one point that satisfies a predetermined condition among points where the camera enters the body and moves along the surgical path. For example, a reference point may be defined as a point where the camera does not move for a predetermined time on the surgical path. Alternatively, a point at which the camera may be positioned on the surgical path may be determined as a reference point based on a predetermined time interval. Next, the computer may map to a corresponding point on the standard body model using a surgical image corresponding to at least one reference point. In addition, the computer may calculate coordinate information of a corresponding point on the standard body model and derive it as camera position information on the standard body model. In this case, the camera position information may refer to coordinate information on a three-dimensional space in the standard body model to be viewed at the same viewpoint as the surgical image corresponding to at least one reference point.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 수술영상으로부터 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 과정의 일례를 설명하기 위한 도면이다. 도 3을 참조하면, 컴퓨터는 수술영상(300)을 획득할 수 있고, 획득된 수술영상(300)에서 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상(310, 320)을 검출할 수 있다. 일 실시예로, 환자의 신체내부의 수술경로 상에서 카메라의 이동이 발생하지 않는 지점(예컨대, 특정 영역에서 수술을 수행하고 있는 경우일 수 있음)을 기준 지점으로 지정할 수 있다. 이 경우, 컴퓨터는 수술영상(300) 중에서 카메라의 이동이 발생하지 않는 시점의 수술영상, 즉 동일한 배경이미지가 연속적으로 등장하는 수술영상들에 해당하는 지점을 기준 지점으로 인식할 수 있다. 따라서, 컴퓨터는 카메라의 이동이 발생하지 않는 시점의 수술영상들 중에서 마지막 시점의 수술영상(310, 320), 다시 말해 카메라의 이동이 발생하는 시점에 해당하는 수술영상(310, 320)을 전체 수술영상(300)으로부터 검출할 수 있다. 이후, 컴퓨터는 검출된 수술영상(310, 320)에 해당하는 지점을 표준신체모델의 수술경로 상(330)에 매핑할 수 있고, 매핑된 지점의 위치 정보를 표준신체모델의 좌표 정보로 산출할 수 있다. 예컨대, 표준신체모델이 3차원 모델링된 데이터인 경우, 3차원 공간에 대한 좌표 정보로 산출될 수 있다. 도 3의 실시예는 학습을 통해 구현될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 학습 방법은 지도학습, 비지도학습, 강화학습 등의 기계학습 방법을 사용할 수 있으며, 예컨대 딥러닝 기반의 CNN(Convolutional neural network)을 이용할 수 있다. 또는 사람(예: 의사 등)이 기준 시점에 해당하는 수술영상을 검출하여 표준신체모델 상에 대응하는 지점에 레이블링하는 방법으로 학습을 수행할 수도 있다.3 is a view for explaining an example of a process of deriving the camera position information on the standard body model from the surgical image according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 3, the computer may acquire the
단계 S110의 다른 실시예로, 컴퓨터는 수술영상으로부터 수술경로 상에서 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상을 지정할 수 있다. 또한, 컴퓨터는 수술영상에 대응하는 환자의 가상신체모델을 획득하고, 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상을 환자의 가상신체모델 상에 매핑할 수 있다. 이는 상술한 도 3의 과정과 유사하게 진행될 수 있다. 이후, 컴퓨터는 환자의 가상신체모델 상에 매핑된 지점을 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보로 변환하여 도출할 수 있다. 이때, 컴퓨터는 가상신체모델의 좌표 정보를 표준신체모델의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 과정을 수행할 수 있으며, 예를 들어 변환 매트릭스(Transformation Matrix)를 이용하여 상호 간의 좌표 정보를 매칭할 수 있다.In another embodiment of step S110, the computer may designate a surgical image corresponding to at least one reference point on the surgical path from the surgical image. In addition, the computer may acquire a virtual body model of the patient corresponding to the surgical image, and map the surgical image corresponding to the at least one reference point on the virtual body model of the patient. This may be similar to the process of FIG. 3 described above. Then, the computer may derive the point mapped on the virtual body model of the patient by converting the camera position information on the standard body model. In this case, the computer may perform a process of converting the coordinate information of the virtual body model to the coordinate information of the standard body model, for example, to match the coordinate information between each other using a transformation matrix.
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 환자의 가상신체모델의 좌표 정보를 표준신체모델의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 과정의 일례를 설명하기 위한 도면이다. 도 4의 (a), (b), (c)에 도시된 각 환자에 대한 가상신체모델에 변환 매트릭스(TA, TB, TC)를 이용하여 변환시킴으로써 표준신체모델의 좌표 정보를 도출할 수 있다. 컴퓨터는 최종적으로 도 4의 (a), (b), (c)에 도시된 각 환자에 대해 획득된 수술영상으로부터 표준신체모델 공간으로 변형된 좌표 정보를 산출할 수 있다.4 is a diagram illustrating an example of a process of converting coordinate information of a virtual body model of a patient into coordinate information of a standard body model according to an embodiment of the present invention. Coordinate information of the standard body model is derived by converting the virtual body model for each patient shown in FIGS. 4A,4B , and4C by using a transformation matrix (TA , TB , TC ). can do. The computer can finally calculate the coordinate information transformed into the standard body model space from the surgical image obtained for each patient shown in (a), (b), (c) of FIG.
상술한 단계 S110의 실시예에서, 컴퓨터는 수술영상을 학습 데이터로 구성하여 학습을 통해 표준신체모델 상에서의 위치 정보를 도출할 수 있다. 이러한 학습 과정은 도 6 및 도 7을 참조하여 설명하도록 한다.In the above-described embodiment of step S110, the computer may derive the positional information on the standard body model through learning by configuring the surgical image as the training data. This learning process will be described with reference to FIGS. 6 and 7.
다시 도 1을 참조하면, 컴퓨터는 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기반으로 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 제공할 수 있다(S120).Referring back to FIG. 1, the computer may provide the camera position information on the virtual body model of the current surgery subject based on the camera position information on the standard body model (S120).
여기서, 현재 수술 대상자는 상술한 단계 S100에서 획득된 수술영상에 대응하는 환자와 상이할 수 있으며, 현재 실제수술이 수행될 환자를 의미할 수 있다. 또한, 현재 수술 대상자에 대해 사전에 확보한 수술영상을 이용할 수도 있다.Here, the current surgical subject may be different from the patient corresponding to the surgical image obtained in the above-described step S100, and may mean a patient currently performing the actual surgery. In addition, it is also possible to use a surgical image obtained in advance for the current surgical subject.
일 실시예로, 컴퓨터는 표준신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보를 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로 변환할 수 있다. 그리고, 컴퓨터는 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보에 대응하는 대응 위치를 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서 변환된 좌표 정보로부터 산출할 수 있다. 즉, 표준신체모델과 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 간의 대응하는 카메라 위치에서는 동일한 카메라 시점을 가질 수 있고, 따라서 최종적으로는 단계 S100에서 획득된 수술영상의 카메라 시점과 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 내 카메라 시점이 동일하게 매핑될 수 있다. 다시 말해, 컴퓨터는 단계 S100에서 획득된 수술영상을 기초로 표준신체모델과의 매핑을 통해 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 현재 카메라의 위치 정보를 파악할 수 있다.In one embodiment, the computer may convert the coordinate information on the standard body model to the coordinate information on the virtual body model of the current surgical subject. The computer may calculate a corresponding position corresponding to the camera position information on the standard body model from coordinate information converted on the virtual body model of the current surgery subject. That is, at the corresponding camera position between the standard body model and the virtual body model of the current surgery subject, the camera may have the same camera viewpoint. Therefore, the camera view of the surgical image acquired in step S100 and the virtual body model of the current surgery subject are finally obtained. Camera viewpoints may be mapped identically. In other words, the computer may grasp the location information of the current camera on the virtual body model of the current surgical subject through the mapping with the standard body model based on the surgical image acquired in step S100.
표준신체모델과 가상신체모델 간의 변환을 수행함에 있어서, 신체 전체에 대해 변환을 수행할 수도 있고 신체 내부의 각 장기별로 변환을 수행할 수도 있다. 또한, 변환 시에는 선형 변환을 적용할 수도 있고 비선형 변환을 적용할 수도 있다. 예를 들어, 컴퓨터는 표준신체모델 상에서 레퍼런스 위치를 추출하고, 추출된 레퍼런스 위치에 대응하는 가상신체모델 상에서 대응 레퍼런스 위치를 추출할 수 있다. 그리고 서로 대응하는 레퍼런스 위치를 매칭하여 변환 매트릭스를 적용함으로써, 표준신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보를 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로 변환할 수 있다. 이후, 컴퓨터는 가상신체모델 상에서의 변환된 좌표 정보로부터 카메라 위치 정보를 도출할 수 있다. 여기서, 레퍼런스 위치는 신체내부의 특정 장기를 추출하여 그 위치를 레퍼런스 위치로 정할 수도 있고, 또는 신체내부의 각 장기를 추출하여 각 장기의 기준 위치(예: 장기의 중심점)를 레퍼런스 위치로 정할 수도 있다. 예컨대, 신체 전체에 대해 변환을 수행할 경우, 특정한 장기를 레퍼런스로 추출하여 해당 위치를 기준으로 변환 매트릭스를 적용하여 변환을 수행할 수 있다. 또는 각 장기별로 변환을 수행할 경우, 각 장기별로 기준 위치를 추출하고 추출된 각 기준 위치를 기준으로 변환 매트릭스를 적용하여 변환을 수행할 수도 있다.In performing the transformation between the standard body model and the virtual body model, the transformation may be performed for the whole body or for each organ in the body. In addition, a linear transformation may be applied or a nonlinear transformation may be applied. For example, the computer may extract the reference position on the standard body model, and extract the corresponding reference position on the virtual body model corresponding to the extracted reference position. By applying a transformation matrix by matching the corresponding reference positions, the coordinate information on the standard body model can be converted into the coordinate information on the virtual body model. The computer can then derive the camera position information from the transformed coordinate information on the virtual body model. Here, the reference position may be determined by extracting a specific organ in the body as a reference position, or by extracting each organ in the body to determine the reference position of each organ (for example, the center point of the organ) as a reference position. have. For example, when the transformation is performed on the entire body, the transformation may be performed by extracting a specific organ as a reference and applying a transformation matrix based on the corresponding position. Alternatively, when the transformation is performed for each organ, the transformation may be performed by extracting a reference position for each organ and applying a transformation matrix based on each extracted reference position.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 표준신체모델의 좌표 정보를 현재 수술 대상자에 대한 가상신체모델의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 과정을 설명하기 위한 도면이다. 일 실시예로, 도 5에 도시된 바와 같이, 컴퓨터는 표준신체모델에 대해 세그먼테이션(segmentation)을 적용하여 각 장기를 추출하고, 각 장기에 대한 레퍼런스 위치를 산출할 수 있다. 또한, 컴퓨터는 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델에 대해서도 세그먼테이션을 적용하여 각 장기를 추출하고, 각 장기에 대한 레퍼런스 위치를 산출할 수 있다. 컴퓨터는 표준신체모델과 가상신체모델 간의 대응하는 각 장기의 레퍼런스 위치를 매칭하여 변환 매트릭스(T)를 적용할 수 있다. 이때, 변환 매트릭스는 실시예에 따라 선형 변환도 가능하고 비선형 변환도 가능하다. 컴퓨터는 변환 매트릭스를 적용함으로써 표준신체모델과 가상신체모델 간의 좌표 정보를 변환시킬 수 있다. 따라서, 최종적으로 컴퓨터는 가상신체모델 상의 좌표 정보로 변환된 카메라 위치 정보를 도출할 수 있다.5 is a view for explaining a process of converting the coordinate information of the standard body model according to an embodiment of the present invention to the coordinate information of the virtual body model for the current surgery subject. As an example, as shown in FIG. 5, the computer may apply segmentation to a standard body model to extract each organ and calculate a reference position for each organ. In addition, the computer may apply segmentation to the virtual body model of the current surgical subject, extract each organ, and calculate a reference position for each organ. The computer may apply the transformation matrix T by matching the reference positions of the corresponding organs between the standard body model and the virtual body model. In this case, the transformation matrix may be linearly transformed or non-linearly transformed according to an embodiment. The computer can transform the coordinate information between the standard body model and the virtual body model by applying the transformation matrix. Therefore, the computer can finally derive the camera position information converted into coordinate information on the virtual body model.
도 6 및 도 7은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 학습을 통해 수술영상으로부터 표준신체모델 상에서의 위치 정보를 도출하는 과정을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.6 and 7 are diagrams for explaining a process of deriving the position information on the standard body model from the surgical image through the learning according to an embodiment of the present invention.
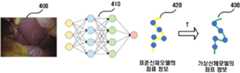
도 6을 참조하면, 컴퓨터는 수술영상(400)을 입력으로 하여 표준신체모델 공간상에서의 카메라 위치 정보(x, y, z, rx, ry, rz)를 출력으로 하는 딥러닝 기반의 CNN 방식으로 학습을 수행할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 컴퓨터는 신규 환자에 대한 수술영상(400)을 입력 값으로 획득할 수 있다. 이때 수술영상(400)은 신규 환자의 신체내부의 특정 위치에 해당하는 영상일 수 있다. 이에 따라, 컴퓨터는 입력된 수술영상(400)에 대해 CNN 학습 모델(410)을 통해 표준신체모델 상에서의 위치 정보(x, y, z, rx, ry, rz)를 탐색할 수 있다. 이러한 학습 모델의 경우, 기존 환자의 수술영상과 이 수술영상에 대응되는 표준신체모델 상에서의 위치 정보가 학습 데이터셋으로 사용될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 6, the computer uses the deep learning based on the
또한, 상술한 도 4의 실시예로서, 컴퓨터가 수술영상으로부터 환자의 가상신체모델을 통해 표준신체모델 상에서의 위치 정보를 도출하는 경우에도 상술한 CNN 방식의 학습을 수행할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 컴퓨터는 수술영상(400)을 입력으로 하여 환자의 가상신체모델 공간상에서의 카메라 위치 정보(x, y, z, rx, ry, rz)를 출력으로 하는 딥러닝 기반의 CNN 방식으로 학습을 수행할 수 있다. 또한, 컴퓨터는 환자의 가상신체모델과 표준모델 간의 변환 매트릭스를 적용하여, 환자의 가상신체모델 공간상에서의 카메라 위치 정보(x, y, z, rx, ry, rz)를 표준신체모델 상에서의 위치로 변환할 수 있으며, 이 과정 역시 CNN 학습을 적용할 수 있다. 이와 같은 학습 모델의 경우, 기존 환자의 수술영상, 환자의 가상신체모델 상의 위치 정보, 표준신체모델과 가상신체모델 간의 변환 매트릭스를 학습 데이터셋으로 사용할 수 있고, 또한 표준신체모델과 가상신체모델 간의 변환 매트릭스를 통한 가상신체모델 상의 위치와 표준신체모델 상의 위치를 최종 학습 데이터셋으로 구축할 수 있다.In addition, in the embodiment of FIG. 4 described above, even when the computer derives the position information on the standard body model through the virtual body model of the patient from the surgical image, the above-described CNN type learning may be performed. For example, the computer uses the deep learning-based output of the camera position information (x, y, z, rx , ry , rz ) in the virtual body model space of the patient as the input of the
또한, 본 발명의 실시예에서는 도 6과 같은 방법으로 훈련을 하고 훈련에 대한 테스트 과정을 수행할 수도 있다. 도 7을 참조하면, 컴퓨터는 CNN(410)을 통해 수술영상(400)을 입력으로 받고 표준신체모델 공간상에서의 좌표 정보(420)를 출력할 수 있다. 그리고, 컴퓨터는 출력된 표준신체모델 공간상에서의 좌표 정보(420)를 변환 매트릭스(T)를 이용하여 환자의 가상신체모델에 대한 좌표 정보(430)로 변환할 수 있다. 즉, 컴퓨터는 훈련 및 테스트 과정을 수행하여 학습 데이터로부터 최종적으로 예측하고자 하는 값이 정확하게 유추되었는지 여부를 판단할 수 있다.In addition, in the embodiment of the present invention can be trained by the method as shown in Figure 6 and may perform a test process for training. Referring to FIG. 7, the computer may receive the
한편, 본 발명에서의 가상신체모델이라함은, 사전에 수술 대상자의 신체내부를 촬영한 의료영상데이터를 기반으로 생성된 3D 모델링 데이터일 수 있다. 예컨대, 수술 대상자의 신체와 부합하게 모델링된 것으로서, 실제 수술 상태와 동일한 상태로 보정된 것일 수도 있다.Meanwhile, the virtual body model in the present invention may be 3D modeling data generated based on medical image data previously photographed inside the body of the patient. For example, the model may be modeled in accordance with the body of the surgical subject, and may be corrected to the same state as the actual surgical state.
본 발명의 실시예에 있어서, 컴퓨터는 현재 수술 대상자에 대한 수술 시에 단계 S120에서 도출된 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기초로 현재 수술 대상자의 실제신체 내 카메라 위치 정보를 산출할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 컴퓨터가 현재 수술 대상자에 대한 실제 수술 시, 현재 수술 장면을 촬영한 현재수술영상을 입력 받는 경우, 컴퓨터는 상술한 단계 S100 내지 S120을 수행하여 입력받은 현재수술영상의 시점에 대응하는 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 산출할 수 있다. 가상신체모델은 현재 수술 대상자의 신체와 부합하게 모델링되어 실제 수술시와 동일한 상태로 구현된 것이므로, 컴퓨터는 가상신체모델 상에서의 현재 카메라의 위치 정보를 파악하면 현재 수술 대상자의 실제신체 내에서 카메라가 위치하는 지점의 정보를 산출할 수 있다.In an embodiment of the present invention, the computer may calculate the camera position information in the actual body of the current surgery subject based on the camera position information on the virtual body model derived in step S120 at the time of surgery on the current surgery subject. For example, when the computer receives a current surgical image photographing the current surgical scene during the actual surgery on the current surgical subject, the computer performs the above-described steps S100 to S120 to correspond to the viewpoint of the current surgical image received. Camera position information on the virtual body model can be calculated. Since the virtual body model is modeled according to the current operation subject's body and implemented in the same state as during the actual operation, the computer recognizes the position information of the current camera on the virtual body model. Information on the location of the location can be calculated.
또한 본 발명의 실시예에 있어서, 컴퓨터는 단계 S120에서 도출된 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기초로 현재 수술 대상자의 수술경로 상에서 카메라의 이동 경로를 가이드할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 컴퓨터는 현재 수술 대상자의 수술경로 상에서 제1 영역의 수술이 종료됨을 인식할 수 있다. 그리고, 컴퓨터는 제1 영역의 다음 수술 영역인 제2 영역으로 수술이 진행됨을 인식하고, 이에 따라 제2 영역에 대한 위치 정보를 가이드할 수 있다. 예컨대, 현재 수술영상이 화면을 통해 출력되는 경우, 현재 수술영상의 화면상에서 카메라의 이동 경로(예컨대, 카메라의 이동 시점 및 이동 방향)를 표시하는 정보를 함께 출력할 수 있다.In addition, in the embodiment of the present invention, the computer may guide the movement path of the camera on the surgical path of the current surgical subject based on the camera position information on the virtual body model derived in step S120. For example, the computer may recognize that the surgery of the first area is terminated on the surgical path of the current surgical subject. In addition, the computer may recognize that the surgery is performed to the second region, which is the next surgical region of the first region, and thus guide the position information of the second region. For example, when the current surgical image is output through the screen, information indicating the moving path of the camera (for example, the moving time and the moving direction of the camera) may be output together on the screen of the current surgical image.
이때, 제1 영역의 수술이 종료되고 제2 영역으로 수술이 진행됨을 인식함에 있어서, 컴퓨터는 이미지 인식으로 해당 영역(지점)에서의 수술의 종료를 인식할 수도 있고, 수술영상 이외의 보조 정보로서 큐시트데이터를 활용할 수도 있다. 큐시트데이터는 최소 수술동작 단위를 기초로 실제수술 과정을 시간에 따라 순서대로 나열한 데이터로 구성되는 것으로, 최소 수술동작 단위에 대응하는 수술정보를 포함할 수 있다. 따라서, 컴퓨터는 큐시트데이터로부터 해당 수술영역의 수술동작 정보를 파악하고 이를 기초로 수술동작의 종료를 인식할 수 있다. 또한, 큐시트데이트는 상위수술동작에서 하위수술동작으로 분류된 계층적 구조로 구성되어 있기 때문에, 동일한 수술동작이 여러 번 등장하더라도 큐시트데이터를 이용하면 계층구조 상에서 해당 수술동작이 어디에 속하는지 파악할 수 있어서 비교적 정확하게 수술동작의 종료 시를 인식할 수 있다.At this time, in recognizing that the operation of the first region is terminated and the operation is proceeded to the second region, the computer may recognize the end of the operation in the corresponding region (point) by image recognition, or as auxiliary information other than the surgical image. You can also use cuesheet data. The cue sheet data includes data in which the actual surgery process is arranged in order according to time based on the minimum surgical operation unit, and may include surgical information corresponding to the minimum surgical operation unit. Therefore, the computer can recognize the operation operation information of the corresponding surgery area from the cue sheet data and recognize the end of the operation operation based on this. In addition, since the cue sheet data is composed of a hierarchical structure classified from the upper surgical operation to the lower surgical operation, even if the same surgical operation appears several times, the cue sheet data can be used to determine where the surgical operation belongs in the hierarchy. It is possible to recognize the end of the surgical operation relatively accurately.
또한 본 발명의 실시예에 있어서, 컴퓨터는 가상신체모델 상에서 카메라의 이동 경로를 표시할 수 있다. 예컨대, 현재 수술 대상자의 수술경로 상에서 제1 수술영역에서 제2 수술영역으로 단계적으로 이동하는 이동 경로를 가상신체 모델 상에서 표시해 줄 수 있다. 이 경우, 컴퓨터는 수술 시 다음 수술영역(수술 단계)으로 이동하기 직전의 행위들을 수술영상으로부터 인식함으로써 카메라의 이동 시점을 파악할 수 있다. 또한, 상술한 바와 같이, 컴퓨터는 큐시트데이터로부터 다음 수술영역(수술 단계)으로 이동하기 직전의 행위들을 인식하여 카메라이 이동 시점을 파악할 수도 있다.In addition, in an embodiment of the present invention, the computer may display the movement path of the camera on the virtual body model. For example, a movement path that is gradually moved from the first surgical region to the second surgical region on the surgical path of the current surgical subject may be displayed on the virtual body model. In this case, the computer can recognize the movement time of the camera by recognizing the behavior just before moving to the next surgery area (surgery step) from the surgery image. In addition, as described above, the computer may recognize the action just before moving to the next surgery area (surgery step) from the cue sheet data, so that the camera may grasp the movement time.
또한 본 발명의 실시예에 있어서, 복강경 수술이나 로봇수술과 같은 최소침습수술을 수행하는 경우, 복강경이나 수술로봇에 카메라의 이동 경로와 관련된 기능을 추가할 수도 있다. 예컨대, 현재 수술 대상자의 수술경로 상에서 제1 수술영역에서의 수술행위가 종료되었을 때, 컴퓨터는 다음 수술영역(수술 단계)으로 카메라의 위치를 자동으로 이동하도록 설정하는 기능을 제공하여 줄 수 있다.In addition, in the embodiment of the present invention, when performing a minimally invasive surgery such as laparoscopic surgery or robot surgery, it is possible to add a function related to the movement path of the camera to the laparoscopic or surgical robot. For example, when the operation in the first surgical area is terminated on the surgical path of the current surgical subject, the computer may provide a function of automatically setting the position of the camera to the next surgical area (surgery step).
본 발명에 따르면, 실제 수술시에 카메라의 위치를 파악하기 위해서 별도의 장치를 구비하지 않더라도, 수술영상만 가지고 효율적으로 3차원 공간상의 카메라 좌표 정보를 제공할 수 있다.According to the present invention, even if a separate device is not provided to determine the position of the camera during the actual surgery, the camera coordinate information in the three-dimensional space can be efficiently provided with only the surgical image.
또한, 수술 시에 실제 수술을 수행하는 있는 영역에서의 카메라 위치를 제공하는 것이 중요하다. 따라서, 본 발명에서는 수술경로 상에서의 기준 위치에 해당하는 지점에 대한 카메라 위치 정보를 도출함으로써, 수술 전에 미리 카메라가 위치하여야 할 지점을 제공할 수 있다.In addition, it is important to provide a camera position in the area where the actual surgery is performed at the time of the surgery. Therefore, in the present invention, by deriving the camera position information for the point corresponding to the reference position on the surgical path, it is possible to provide a point to be located before the operation of the camera.
본 발명에 따르면, 학습 모델을 각 환자마다 개별적으로 구축하여 학습을 시킬 필요 없이 표준신체모델에 대해서만 학습 모델을 구축하면 되므로, 학습 모델을 구축하고 학습을 수행하는 과정이 효율적으로 이루어질 수 있다.According to the present invention, since the learning model only needs to be constructed for the standard body model without having to build and learn the learning model for each patient individually, the process of building the learning model and performing the learning can be efficiently performed.
도 8은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 로봇수술을 수행할 수 있는 시스템을 간략하게 도식화한 도면이다.8 is a schematic diagram of a system capable of performing robot surgery according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 8에 따르면, 로봇수술 시스템은 의료영상 촬영장비(10), 서버(100) 및 수술실에 구비된 제어부(30), 디스플레이(32) 및 수술로봇(34)을 포함한다. 실시 예에 따라서, 의료영상 촬영장비(10)는 개시된 실시 예에 따른 로봇수술 시스템에서 생략될 수 있다.According to FIG. 8, the robotic surgical system includes a
일 실시 예에서, 수술로봇(34)은 촬영장치(36) 및 수술도구(38)를 포함한다.In one embodiment,
일 실시 예에서, 로봇수술은 사용자가 제어부(30)를 이용하여 수술용 로봇(34)을 제어함으로써 수행된다. 일 실시 예에서, 로봇수술은 사용자의 제어 없이 제어부(30)에 의하여 자동으로 수행될 수도 있다.In one embodiment, the robot surgery is performed by the user controlling the
서버(100)는 적어도 하나의 프로세서와 통신부를 포함하는 컴퓨팅 장치이다.The
제어부(30)는 적어도 하나의 프로세서와 통신부를 포함하는 컴퓨팅 장치를 포함한다. 일 실시 예에서, 제어부(30)는 수술용 로봇(34)을 제어하기 위한 하드웨어 및 소프트웨어 인터페이스를 포함한다.The
촬영장치(36)는 적어도 하나의 이미지 센서를 포함한다. 즉, 촬영장치(36)는 적어도 하나의 카메라 장치를 포함하여, 대상체, 즉 수술부위를 촬영하는 데 이용된다. 일 실시 예에서, 촬영장치(36)는 수술로봇(34)의 수술 암(arm)과 결합된 적어도 하나의 카메라를 포함한다.The
일 실시 예에서, 촬영장치(36)에서 촬영된 영상은 디스플레이(340)에 표시된다.In an embodiment, the image photographed by the photographing
일 실시 예에서, 수술로봇(34)은 수술부위의 절단, 클리핑, 고정, 잡기 동작 등을 수행할 수 있는 하나 이상의 수술도구(38)를 포함한다. 수술도구(38)는 수술로봇(34)의 수술 암과 결합되어 이용된다.In one embodiment,
제어부(30)는 서버(100)로부터 수술에 필요한 정보를 수신하거나, 수술에 필요한 정보를 생성하여 사용자에게 제공한다. 예를 들어, 제어부(30)는 생성 또는 수신된, 수술에 필요한 정보를 디스플레이(32)에 표시한다.The
예를 들어, 사용자는 디스플레이(32)를 보면서 제어부(30)를 조작하여 수술로봇(34)의 움직임을 제어함으로써 로봇수술을 수행한다.For example, the user performs the robot surgery by controlling the movement of the
서버(100)는 의료영상 촬영장비(10)로부터 사전에 촬영된 대상체의 의료영상데이터를 이용하여 로봇수술에 필요한 정보를 생성하고, 생성된 정보를 제어부(30)에 제공한다.The
제어부(30)는 서버(100)로부터 수신된 정보를 디스플레이(32)에 표시함으로써 사용자에게 제공하거나, 서버(100)로부터 수신된 정보를 이용하여 수술로봇(34)을 제어한다.The
일 실시 예에서, 의료영상 촬영장비(10)에서 사용될 수 있는 수단은 제한되지 않으며, 예를 들어 CT, X-Ray, PET, MRI 등 다른 다양한 의료영상 획득수단이 사용될 수 있다.In one embodiment, the means that can be used in the
상술한 바와 같이, 로봇수술을 수행할 경우 수술 과정에서 촬영된 수술영상 또는 수술로봇의 제어과정에서 다양한 수술정보를 포함하는 데이터를 획득할 수 있다. 이에, 본 발명에서는 이와 같이 수술 과정에서 수술정보(즉, 수술영상)를 획득하고, 이를 기초로 특정 환자에 대해 현재 수행되고 있는 수술에서 카메라의 실제 위치 정보를 제공할 수 있다. 이에 대해서는 도 1 내지 도 7의 실시예를 통해 상세히 설명한 바 있으므로, 여기서는 설명을 생략하도록 한다. 물론, 상술한 도 1 내지 도 7의 실시예들이 도 8에 도시된 로봇수술 시스템과 연관되어서만 적용될 수 있는 것은 아니고, 본 발명이 적용될 수 있는 모든 종류의 실시예들에서 다양한 형태로 구현 가능하다.As described above, when performing a robot operation, it is possible to obtain data including various surgical information in the surgical image taken during the surgical procedure or the control of the surgical robot. Thus, in the present invention, as described above, the surgical information (ie, the surgical image) may be obtained during the surgical procedure, and the actual position information of the camera may be provided in the surgery currently being performed on the specific patient. This has been described in detail with reference to the embodiment of FIGS. 1 to 7, and thus description thereof will be omitted. Of course, the above-described embodiments of FIGS. 1 to 7 may not be applicable only in connection with the robotic surgery system illustrated in FIG. 8, and may be implemented in various forms in all kinds of embodiments to which the present invention may be applied. .
도 9는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법을 수행하는 장치(500)의 구성을 개략적으로 나타내는 도면이다.9 is a diagram schematically illustrating a configuration of an
도 9를 참조하면, 프로세서(510)는 하나 이상의 코어(core, 미도시) 및 그래픽 처리부(미도시) 및/또는 다른 구성 요소와 신호를 송수신하는 연결 통로(예를 들어, 버스(bus) 등)를 포함할 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 9, the processor 510 may include a connection passage (eg, a bus or the like) that transmits and receives a signal with one or more cores (not shown) and a graphic processor (not shown) and / or other components. ) May be included.
일 실시예에 따른 프로세서(510)는 메모리(520)에 저장된 하나 이상의 인스트럭션을 실행함으로써, 도 1 내지 도 7과 관련하여 설명된 수술영상을 기반으로 한 카메라 위치 제공 방법을 수행한다.The processor 510 according to an exemplary embodiment executes one or more instructions stored in the
예를 들어, 프로세서(510)는 메모리(520)에 저장된 하나 이상의 인스트럭션을 실행함으로써 카메라가 신체내부로 진입하여 수술경로를 이동함에 따라 촬영한 수술영상을 획득하고, 상기 수술영상을 기초로 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하고, 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기반으로 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 제공할 수 있다.For example, the processor 510 executes one or more instructions stored in the
한편, 프로세서(510)는 프로세서(510) 내부에서 처리되는 신호(또는, 데이터)를 일시적 및/또는 영구적으로 저장하는 램(RAM: Random Access Memory, 미도시) 및 롬(ROM: Read-Only Memory, 미도시)을 더 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 프로세서(510)는 그래픽 처리부, 램 및 롬 중 적어도 하나를 포함하는 시스템온칩(SoC: system on chip) 형태로 구현될 수 있다.Meanwhile, the processor 510 may include random access memory (RAM) and read-only memory (ROM) for temporarily and / or permanently storing a signal (or data) processed in the processor 510. , Not shown) may be further included. In addition, the processor 510 may be implemented in the form of a system on chip (SoC) including at least one of a graphic processor, a RAM, and a ROM.
메모리(520)에는 프로세서(510)의 처리 및 제어를 위한 프로그램들(하나 이상의 인스트럭션들)을 저장할 수 있다. 메모리(520)에 저장된 프로그램들은 기능에 따라 복수 개의 모듈들로 구분될 수 있다.The
이상에서 전술한 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법은, 하드웨어인 컴퓨터와 결합되어 실행되기 위해 프로그램(또는 어플리케이션)으로 구현되어 매체에 저장될 수 있다.The method for providing a surgical image-based camera position according to an embodiment of the present invention described above may be implemented as a program (or an application) and stored in a medium in order to be executed in combination with a computer which is hardware.
상기 전술한 프로그램은, 상기 컴퓨터가 프로그램을 읽어 들여 프로그램으로 구현된 상기 방법들을 실행시키기 위하여, 상기 컴퓨터의 프로세서(CPU)가 상기 컴퓨터의 장치 인터페이스를 통해 읽힐 수 있는 C, C++, JAVA, 기계어 등의 컴퓨터 언어로 코드화된 코드(Code)를 포함할 수 있다. 이러한 코드는 상기 방법들을 실행하는 필요한 기능들을 정의한 함수 등과 관련된 기능적인 코드(Functional Code)를 포함할 수 있고, 상기 기능들을 상기 컴퓨터의 프로세서가 소정의 절차대로 실행시키는데 필요한 실행 절차 관련 제어 코드를 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 이러한 코드는 상기 기능들을 상기 컴퓨터의 프로세서가 실행시키는데 필요한 추가 정보나 미디어가 상기 컴퓨터의 내부 또는 외부 메모리의 어느 위치(주소 번지)에서 참조되어야 하는지에 대한 메모리 참조관련 코드를 더 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 상기 컴퓨터의 프로세서가 상기 기능들을 실행시키기 위하여 원격(Remote)에 있는 어떠한 다른 컴퓨터나 서버 등과 통신이 필요한 경우, 코드는 상기 컴퓨터의 통신 모듈을 이용하여 원격에 있는 어떠한 다른 컴퓨터나 서버 등과 어떻게 통신해야 하는지, 통신 시 어떠한 정보나 미디어를 송수신해야 하는지 등에 대한 통신 관련 코드를 더 포함할 수 있다.The above-described program includes C, C ++, JAVA, machine language, etc. which can be read by the computer's processor (CPU) through the computer's device interface so that the computer reads the program and executes the methods implemented as the program. Code may be coded in the computer language of. Such code may include functional code associated with a function or the like that defines the necessary functions for executing the methods, and includes control procedures related to execution procedures necessary for the computer's processor to execute the functions according to a predetermined procedure. can do. In addition, the code may further include memory reference code for additional information or media required for the computer's processor to execute the functions at which location (address address) of the computer's internal or external memory should be referenced. have. Also, if the processor of the computer needs to communicate with any other computer or server remotely in order to execute the functions, the code may be used to communicate with any other computer or server remotely using the communication module of the computer. It may further include a communication related code for whether to communicate, what information or media should be transmitted and received during communication.
상기 저장되는 매체는, 레지스터, 캐쉬, 메모리 등과 같이 짧은 순간 동안 데이터를 저장하는 매체가 아니라 반영구적으로 데이터를 저장하며, 기기에 의해 판독(reading)이 가능한 매체를 의미한다. 구체적으로는, 상기 저장되는 매체의 예로는 ROM, RAM, CD-ROM, 자기 테이프, 플로피디스크, 광 데이터 저장장치 등이 있지만, 이에 제한되지 않는다. 즉, 상기 프로그램은 상기 컴퓨터가 접속할 수 있는 다양한 서버 상의 다양한 기록매체 또는 사용자의 상기 컴퓨터상의 다양한 기록매체에 저장될 수 있다. 또한, 상기 매체는 네트워크로 연결된 컴퓨터 시스템에 분산되어, 분산방식으로 컴퓨터가 읽을 수 있는 코드가 저장될 수 있다.The stored medium is not a medium for storing data for a short time such as a register, a cache, a memory, but semi-permanently, and means a medium that can be read by the device. Specifically, examples of the storage medium include, but are not limited to, a ROM, a RAM, a CD-ROM, a magnetic tape, a floppy disk, an optical data storage device, and the like. That is, the program may be stored in various recording media on various servers to which the computer can access or various recording media on the computer of the user. The media may also be distributed over network coupled computer systems so that the computer readable code is stored in a distributed fashion.
본 발명의 실시예와 관련하여 설명된 방법 또는 알고리즘의 단계들은 하드웨어로 직접 구현되거나, 하드웨어에 의해 실행되는 소프트웨어 모듈로 구현되거나, 또는 이들의 결합에 의해 구현될 수 있다. 소프트웨어 모듈은 RAM(Random Access Memory), ROM(Read Only Memory), EPROM(Erasable Programmable ROM), EEPROM(Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM), 플래시 메모리(Flash Memory), 하드 디스크, 착탈형 디스크, CD-ROM, 또는 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 잘 알려진 임의의 형태의 컴퓨터 판독가능 기록매체에 상주할 수도 있다.The steps of a method or algorithm described in connection with an embodiment of the present invention may be implemented directly in hardware, in a software module executed by hardware, or by a combination thereof. Software modules may include random access memory (RAM), read only memory (ROM), erasable programmable ROM (EPROM), electrically erasable programmable ROM (EEPROM), flash memory, hard disk, removable disk, CD-ROM, or It may reside in any form of computer readable recording medium well known in the art.
이상, 첨부된 도면을 참조로 하여 본 발명의 실시예를 설명하였지만, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야의 통상의 기술자는 본 발명이 그 기술적 사상이나 필수적인 특징을 변경하지 않고서 다른 구체적인 형태로 실시될 수 있다는 것을 이해할 수 있을 것이다. 그러므로, 이상에서 기술한 실시예들은 모든 면에서 예시적인 것이며, 제한적이 아닌 것으로 이해해야만 한다.In the above, embodiments of the present invention have been described with reference to the accompanying drawings, but those skilled in the art to which the present invention pertains may implement the present invention in other specific forms without changing the technical spirit or essential features. I can understand that. Therefore, it should be understood that the embodiments described above are exemplary in all respects and not restrictive.
Claims (12)
Translated fromKorean카메라가 신체내부로 진입하여 수술경로를 이동함에 따라 촬영한 수술영상을 획득하는 단계;
상기 수술영상을 기초로 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 단계; 및
상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기반으로 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 제공하는 단계를 포함하며,
상기 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 제공하는 단계는,
상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보를 상기 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 단계; 및
상기 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로부터 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보에 대응하는 대응 위치를 산출하는 단계를 포함하되,
상기 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 단계는,
상기 표준신체모델 상에서 레퍼런스 위치를 추출하는 단계;
상기 레퍼런스 위치에 대응하는 상기 가상신체모델 상에서 대응 레퍼런스 위치를 추출하여 변환 매트릭스(Transformation Matrix)를 적용하는 단계; 및
상기 변환 매트릭스를 기반으로 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보를 상기 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 단계를 포함하며,
상기 표준신체모델은,
일반적인 신체로부터 이미 생성된 3차원 신체모델로서, 적어도 하나의 신체로부터 획득된 해부학적 특징을 표준화하여 생성한 3차원 모델링된 데이터인 것을 특징으로 하는 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법.In the surgical image based camera position providing method performed by a computer,
Obtaining a surgical image taken as the camera enters the body and moves the surgical path;
Deriving camera position information on a standard body model based on the surgical image; And
Providing camera position information on the virtual body model of the current surgical subject based on the camera position information on the standard body model,
Providing the camera position information on the virtual body model of the current surgery subject,
Converting coordinate information on the standard body model to coordinate information on the virtual body model of the current surgery subject; And
Calculating a corresponding position corresponding to camera position information on the standard body model from coordinate information on the virtual body model,
Converting the coordinate information on the virtual body model of the current surgery subject,
Extracting a reference position on the standard body model;
Extracting a corresponding reference position on the virtual body model corresponding to the reference position and applying a transformation matrix; And
Converting coordinate information on the standard body model to coordinate information on the virtual body model based on the transformation matrix,
The standard body model,
Surgical image-based camera position providing method characterized in that the three-dimensional body model already generated from the general body, the three-dimensional modeled data generated by standardizing the anatomical features obtained from at least one body.
상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 단계는,
상기 수술영상으로부터 상기 수술경로 상에서 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상을 지정하는 단계;
상기 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상을 이용하여 상기 표준신체모델 상에서 대응하는 지점에 매핑하는 단계; 및
상기 표준신체모델 상에서 대응하는 지점에 대한 좌표 정보를 산출하여 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보로 도출하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법.The method of claim 1,
Deriving the camera position information on the standard body model,
Designating a surgical image corresponding to at least one reference point on the surgical path from the surgical image;
Mapping to a corresponding point on the standard body model using a surgical image corresponding to the at least one reference point; And
And calculating coordinate information of a corresponding point on the standard body model and deriving it as camera position information on the standard body model.
상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 단계는,
상기 수술영상으로부터 상기 수술경로 상에서 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상을 지정하는 단계;
상기 수술영상에 대응하는 가상신체모델을 획득하여, 상기 적어도 하나의 기준 지점에 해당하는 수술영상을 상기 가상신체모델 상에 매핑하는 단계; 및
상기 가상신체모델 상에 매핑된 지점을 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보로 변환하여 도출하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법.The method of claim 1,
Deriving the camera position information on the standard body model,
Designating a surgical image corresponding to at least one reference point on the surgical path from the surgical image;
Obtaining a virtual body model corresponding to the surgical image and mapping a surgical image corresponding to the at least one reference point on the virtual body model; And
And converting the point mapped on the virtual body model into camera position information on the standard body model, and deriving it.
상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 단계는,
딥러닝 기반의 CNN(Convolutional Neural Network)을 이용한 학습을 통해 상기 수술영상을 기초로 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법.The method of claim 1,
Deriving the camera position information on the standard body model,
Surgical image-based camera position providing method comprising deriving the camera position information on the standard body model based on the surgical image through learning using deep learning-based convolutional neural network (CNN).
상기 현재 수술 대상자에 대한 수술 시, 상기 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기초로 상기 현재 수술 대상자의 실제신체 내 카메라 위치 정보를 산출하는 단계를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법.The method of claim 1,
Providing a surgical image-based camera position further comprising the step of calculating the camera position information in the actual body of the current surgery subject based on the camera position information on the virtual body model during the surgery on the current surgery subject Way.
상기 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기초로 상기 현재 수술 대상자의 수술경로 상에서 상기 카메라의 이동 경로를 가이드하는 단계를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법.The method of claim 1,
And guiding a moving path of the camera on a surgical path of the current surgery subject based on the camera position information on the virtual body model.
상기 카메라의 이동 경로를 가이드하는 단계는,
상기 현재 수술 대상자의 수술경로 상에서 제1 영역의 수술이 종료됨을 인식하는 단계; 및
상기 제1 영역에서 제2 영역으로 수술이 진행됨에 따라 상기 제2 영역에 대한 위치 정보를 상기 카메라의 이동 경로로 가이드하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법.The method of claim 8,
Guide the moving path of the camera,
Recognizing that the surgery of the first region is terminated on the surgery path of the current surgery subject; And
And guiding position information on the second region as a movement path of the camera as the surgery progresses from the first region to the second region.
상기 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델은,
상기 현재 수술 대상자의 신체내부를 촬영한 의료영상데이터를 기반으로 생성된 3차원 모델링 데이터인 것을 특징으로 하는 수술영상 기반 카메라 위치 제공 방법.The method of claim 1,
The virtual body model of the current surgery subject,
Surgical image-based camera position providing method characterized in that the three-dimensional modeling data generated based on the medical image data taken inside the body of the current surgery subject.
상기 메모리에 저장된 상기 하나 이상의 인스트럭션을 실행하는 프로세서를 포함하며,
상기 프로세서는 상기 하나 이상의 인스트럭션을 실행함으로써,
카메라가 신체내부로 진입하여 수술경로를 이동함에 따라 촬영한 수술영상을 획득하는 단계;
상기 수술영상을 기초로 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 도출하는 단계; 및
상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 기반으로 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 제공하는 단계를 수행하며,
상기 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보를 제공하는 단계는,
상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보를 상기 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 단계; 및
상기 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로부터 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 카메라 위치 정보에 대응하는 대응 위치를 산출하는 단계를 포함하되,
상기 현재 수술 대상자의 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 단계는,
상기 표준신체모델 상에서 레퍼런스 위치를 추출하는 단계;
상기 레퍼런스 위치에 대응하는 상기 가상신체모델 상에서 대응 레퍼런스 위치를 추출하여 변환 매트릭스(Transformation Matrix)를 적용하는 단계; 및
상기 변환 매트릭스를 기반으로 상기 표준신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보를 상기 가상신체모델 상에서의 좌표 정보로 변환하는 단계를 수행하며,
상기 표준신체모델은,
일반적인 신체로부터 이미 생성된 3차원 신체모델로서, 적어도 하나의 신체로부터 획득된 해부학적 특징을 표준화하여 생성한 3차원 모델링된 데이터인 것을 특징으로 하는 장치.Memory for storing one or more instructions; And
A processor for executing the one or more instructions stored in the memory,
The processor executes the one or more instructions,
Obtaining a surgical image taken as the camera enters the body and moves the surgical path;
Deriving camera position information on a standard body model based on the surgical image; And
Providing camera position information on the virtual body model of the current surgical subject based on the camera position information on the standard body model,
Providing the camera position information on the virtual body model of the current surgery subject,
Converting coordinate information on the standard body model to coordinate information on the virtual body model of the current surgery subject; And
Calculating a corresponding position corresponding to camera position information on the standard body model from coordinate information on the virtual body model,
Converting the coordinate information on the virtual body model of the current surgery subject,
Extracting a reference position on the standard body model;
Extracting a corresponding reference position on the virtual body model corresponding to the reference position and applying a transformation matrix; And
Converting coordinate information on the standard body model to coordinate information on the virtual body model based on the transformation matrix,
The standard body model,
A three-dimensional body model already generated from a general body, characterized in that the three-dimensional modeled data generated by standardizing the anatomical features obtained from at least one body.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/KR2019/002093WO2019164275A1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2019-02-20 | Method and device for recognizing position of surgical instrument and camera |
Applications Claiming Priority (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180019866 | 2018-02-20 | ||
| KR20180019867 | 2018-02-20 | ||
| KR20180019866 | 2018-02-20 | ||
| KR1020180019867 | 2018-02-20 | ||
| KR1020180019868 | 2018-02-20 | ||
| KR20180019868 | 2018-02-20 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR102014359B1true KR102014359B1 (en) | 2019-08-26 |
Family
ID=67763730
Family Applications (21)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180098359AActiveKR102014359B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-08-23 | Method and apparatus for providing camera location using surgical video |
| KR1020180098413AActiveKR102018565B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-08-23 | Method, apparatus and program for constructing surgical simulation information |
| KR1020180098358AActiveKR102014385B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-08-23 | Method and apparatus for learning surgical image and recognizing surgical action based on learning |
| KR1020180098360AActiveKR102014355B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-08-23 | Method and apparatus for calculating location information of surgical device |
| KR1020180109204AActiveKR102014377B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-09-12 | Method and apparatus for surgical action recognition based on learning |
| KR1020180115328AActiveKR102013868B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-09-27 | Method and apparatus for optimization of surgical process |
| KR1020180122454AActiveKR102014351B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-10-15 | Method and apparatus for constructing surgical information |
| KR1020180122949AActiveKR102013806B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-10-16 | Method and apparatus for generating artificial data |
| KR1020180129709AActiveKR102014364B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-10-29 | Method and apparatus for evaluating bleeding using surgical video |
| KR1020180130229AActiveKR102013866B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-10-29 | Method and apparatus for calculating camera location using surgical video |
| KR1020180131478AActiveKR102013837B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-10-31 | Method and apparatus for providing surgical video |
| KR1020180135590AActiveKR102016959B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-07 | Method and apparatus for generating blood vessel model |
| KR1020180135578ACeasedKR20190100004A (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-07 | Method and apparatus for using surgical information |
| KR1020180140050ACeasedKR20190100009A (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-14 | Method and apparatus for providing surgical video |
| KR1020180143367AActiveKR102013857B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-20 | Method and apparatus for generating learning data based on surgical video |
| KR1020180145157AActiveKR102013828B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-22 | Method and apparatus for predicting surgical duration based on surgical video |
| KR1020180145177ACeasedKR20190100011A (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-22 | Method and apparatus for providing surgical information using surgical video |
| KR1020180147015AActiveKR102014371B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-26 | Method and apparatus for estimating recognition of surgical video |
| KR1020180149293AActiveKR102013848B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-28 | Method and apparatus for providing blood vessel information using blood vessel model |
| KR1020180153569AActiveKR102013814B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-12-03 | Method and apparatus for generating virtual model using surgical video |
| KR1020180155562AActiveKR102013863B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-12-05 | Method and program for creating a virtual body model |
Family Applications After (20)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180098413AActiveKR102018565B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-08-23 | Method, apparatus and program for constructing surgical simulation information |
| KR1020180098358AActiveKR102014385B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-08-23 | Method and apparatus for learning surgical image and recognizing surgical action based on learning |
| KR1020180098360AActiveKR102014355B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-08-23 | Method and apparatus for calculating location information of surgical device |
| KR1020180109204AActiveKR102014377B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-09-12 | Method and apparatus for surgical action recognition based on learning |
| KR1020180115328AActiveKR102013868B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-09-27 | Method and apparatus for optimization of surgical process |
| KR1020180122454AActiveKR102014351B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-10-15 | Method and apparatus for constructing surgical information |
| KR1020180122949AActiveKR102013806B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-10-16 | Method and apparatus for generating artificial data |
| KR1020180129709AActiveKR102014364B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-10-29 | Method and apparatus for evaluating bleeding using surgical video |
| KR1020180130229AActiveKR102013866B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-10-29 | Method and apparatus for calculating camera location using surgical video |
| KR1020180131478AActiveKR102013837B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-10-31 | Method and apparatus for providing surgical video |
| KR1020180135590AActiveKR102016959B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-07 | Method and apparatus for generating blood vessel model |
| KR1020180135578ACeasedKR20190100004A (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-07 | Method and apparatus for using surgical information |
| KR1020180140050ACeasedKR20190100009A (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-14 | Method and apparatus for providing surgical video |
| KR1020180143367AActiveKR102013857B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-20 | Method and apparatus for generating learning data based on surgical video |
| KR1020180145157AActiveKR102013828B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-22 | Method and apparatus for predicting surgical duration based on surgical video |
| KR1020180145177ACeasedKR20190100011A (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-22 | Method and apparatus for providing surgical information using surgical video |
| KR1020180147015AActiveKR102014371B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-26 | Method and apparatus for estimating recognition of surgical video |
| KR1020180149293AActiveKR102013848B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-11-28 | Method and apparatus for providing blood vessel information using blood vessel model |
| KR1020180153569AActiveKR102013814B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-12-03 | Method and apparatus for generating virtual model using surgical video |
| KR1020180155562AActiveKR102013863B1 (en) | 2018-02-20 | 2018-12-05 | Method and program for creating a virtual body model |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (21) | KR102014359B1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (43)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102301234B1 (en)* | 2019-09-20 | 2021-09-09 | 울산대학교 산학협력단 | System for providing surgical video and method thereof |
| US11992373B2 (en)* | 2019-12-10 | 2024-05-28 | Globus Medical, Inc | Augmented reality headset with varied opacity for navigated robotic surgery |
| KR102246966B1 (en) | 2020-01-29 | 2021-04-30 | 주식회사 아티큐 | Method for Recognizing Object Target of Body |
| KR102321157B1 (en)* | 2020-04-10 | 2021-11-04 | (주)휴톰 | Method and system for analysing phases of surgical procedure after surgery |
| WO2021235804A1 (en)* | 2020-05-18 | 2021-11-25 | 주식회사 루닛 | Method and system for determining abnormality of medical device |
| KR102348368B1 (en)* | 2020-05-21 | 2022-01-11 | 주식회사 누아 | Device, method, system and computer readable storage medium for generating training data of machine learing model and generating fake image using machine learning model |
| KR102395873B1 (en) | 2020-06-02 | 2022-05-10 | 주식회사 메디픽셀 | Method and apparatus for processing vascular image automatically |
| KR102426925B1 (en)* | 2020-06-23 | 2022-07-29 | (주)휴톰 | Method and program for acquiring motion information of a surgical robot using 3d simulation |
| KR102505016B1 (en)* | 2020-08-03 | 2023-03-02 | (주)휴톰 | System for generating descriptive information of unit movement in surgical images and method thereof |
| WO2022035237A1 (en)* | 2020-08-11 | 2022-02-17 | (주)휴톰 | Learning data collection apparatus and method for training surgical tool and organ recognition learning |
| KR102517398B1 (en)* | 2020-11-20 | 2023-04-04 | 주식회사 엔가든 | Lock screw insertion hole detection method |
| CN112712878B (en)* | 2020-12-30 | 2024-09-06 | 四川桑瑞思环境技术工程有限公司 | Digital operating room system and control method |
| KR102511938B1 (en)* | 2021-01-06 | 2023-03-17 | 가톨릭대학교 산학협력단 | Apparatus for measuring vaginal health care index |
| KR102464091B1 (en)* | 2021-01-14 | 2022-11-04 | 고지환 | Apparatus and Method for Large Intestine Examination Using an Endoscope |
| US11883245B2 (en) | 2021-03-22 | 2024-01-30 | Verb Surgical Inc. | Deep-learning-based real-time remaining surgery duration (RSD) estimation |
| KR102640314B1 (en) | 2021-07-12 | 2024-02-23 | (주)휴톰 | Artificial intelligence surgery system amd method for controlling the same |
| KR102606249B1 (en)* | 2021-07-15 | 2023-11-24 | 사회복지법인 삼성생명공익재단 | Lesion analysis method using cerebrovascular modeling and apparatus thereof |
| KR102667464B1 (en)* | 2021-07-21 | 2024-05-20 | (주)휴톰 | Apparatus and Method for Determining the Insertion Position of a Trocar on a Patient's three-dimensional Virtual Pneumoperitoneum Model |
| US11986248B2 (en)* | 2021-07-29 | 2024-05-21 | Hutom Co., Ltd. | Apparatus and method for matching the real surgical image with the 3D-based virtual simulated surgical image based on POI definition and phase recognition |
| KR102709930B1 (en)* | 2021-08-10 | 2024-09-26 | (주)휴톰 | Apparatus and Method for Generating a Virtual Pneumoperitoneum Model |
| KR20230039932A (en) | 2021-09-15 | 2023-03-22 | 안명천 | System and method for detecting bleeding |
| CN113813053A (en)* | 2021-09-18 | 2021-12-21 | 长春理工大学 | A method for analyzing surgical progress based on laparoscopic endoscopic images |
| KR102827068B1 (en) | 2021-12-13 | 2025-06-30 | (주)휴톰 | Method and apparatus for providing virtual blood vessel model based on artificial intelligence |
| CN114391947B (en)* | 2021-12-15 | 2024-03-01 | 深圳爱博合创医疗机器人有限公司 | Hierarchical control type interventional operation robot |
| KR102841693B1 (en)* | 2022-01-12 | 2025-08-04 | (주)휴톰 | System and method for providing a virtual reality based surgical environment for each surgical situation |
| KR102694614B1 (en)* | 2022-01-17 | 2024-08-13 | (주)휴톰 | Apparatus and method for generating a virtual lung model of a patient |
| WO2023172109A1 (en)* | 2022-03-11 | 2023-09-14 | 주식회사 림사이언스 | Method and system for managing path of needle by using digital twin, and non-transitory computer-readable recording medium |
| US12279837B2 (en)* | 2022-05-18 | 2025-04-22 | Cilag Gmbh International | Identification of images shapes based on situational awareness of a surgical image and annotation of shapes or pixels |
| KR102690712B1 (en)* | 2022-07-29 | 2024-08-05 | 주식회사 로브로스 | Method for estimation of remaining motion time of robot system using observational learning |
| KR20240022047A (en)* | 2022-08-10 | 2024-02-20 | 주식회사 엠티이지 | A methods and a device for providing scenarios for surgery |
| KR102815219B1 (en)* | 2022-11-21 | 2025-05-30 | (주)휴톰 | Method and device for automatically classifying blood vessel types in the entire blood vessel area for each operation |
| KR102807689B1 (en)* | 2022-11-22 | 2025-05-20 | (주)휴톰 | Method and device for detecting intraoperative bleeding through spatiotemporal feature fusion mode |
| KR102794031B1 (en)* | 2022-11-23 | 2025-04-14 | (주)휴톰 | Apparatus and method for segmentation of blood vessel based on artificial intelligence model |
| KR102807918B1 (en)* | 2023-01-25 | 2025-05-16 | (주)휴톰 | Method for acquiring vessel information through learned neural network and computing device performing the same method |
| KR102628690B1 (en)* | 2023-07-04 | 2024-01-25 | 주식회사 클레버러스 | A system of detecting abnormal action |
| KR102806707B1 (en)* | 2023-09-06 | 2025-05-20 | 주식회사 메디픽셀 | Method for generating aneurysm region and electronic device thereof |
| KR20250080982A (en)* | 2023-11-29 | 2025-06-05 | (주)휴톰 | Apparatus and method for generating virtual pneumoperitoneum model based on semi-automatic process |
| KR20250100472A (en) | 2023-12-26 | 2025-07-03 | 주식회사 퍼즐에이아이 | System for generating automatic surgical records through surgical video analysis and integrating them into electronic medical records |
| KR20250107482A (en) | 2024-01-05 | 2025-07-14 | 서울대학교산학협력단 | Apparatus and method for generating mucosal texture for virtual endoscopy simulator |
| KR20250108891A (en) | 2024-01-09 | 2025-07-16 | 서울대학교산학협력단 | Method and device for predicting bleeding volume of patient in surgical |
| KR20250115250A (en) | 2024-01-23 | 2025-07-30 | 한림대학교 산학협력단 | Electronic device, control method, and computer program generating learning data for artificial intelligence model about laparoscopic surgery by generating virtual surgery images based on laparoscopic surgery images and surgical tool images |
| KR20250120635A (en) | 2024-02-02 | 2025-08-11 | 주식회사 스킬웨이브 | A surgical training method using similarity analysis of surgical videos |
| KR102779994B1 (en)* | 2024-02-07 | 2025-03-13 | 주식회사 스피나이 | Human body structure and hemorrhage recognition system using real-time artificial intelligence based image analysis and optical flow method for endoscopic spine surgery |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20120046439A (en)* | 2010-11-02 | 2012-05-10 | 서울대학교병원 (분사무소) | Method of operation simulation and automatic operation device using 3d modelling |
| KR20120111871A (en)* | 2011-03-29 | 2012-10-11 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method and apparatus for creating medical image using 3d deformable model |
| KR20140020071A (en)* | 2012-08-07 | 2014-02-18 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Surgical robot system and control method thereof |
| KR20150043245A (en)* | 2012-08-14 | 2015-04-22 | 인튜어티브 서지컬 오퍼레이션즈 인코포레이티드 | Systems and methods for registration of multiple vision systems |
Family Cites Families (30)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002207832A (en)* | 2000-12-28 | 2002-07-26 | Atsushi Takahashi | Distribution system of internet technology instruction education, and instruction system using communication network |
| US20080133602A1 (en)* | 2005-01-19 | 2008-06-05 | Koichi Tashiro | Operation Data Management Device, Operation Control Device, and Operation Data Processing Method |
| JP4767591B2 (en)* | 2005-06-01 | 2011-09-07 | オリンパスメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Endoscope diagnosis support method, endoscope diagnosis support device, and endoscope diagnosis support program |
| JP4781085B2 (en)* | 2005-10-25 | 2011-09-28 | オリンパスメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Surgical schedule display system |
| US9718190B2 (en)* | 2006-06-29 | 2017-08-01 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Tool position and identification indicator displayed in a boundary area of a computer display screen |
| JP4762160B2 (en)* | 2007-01-16 | 2011-08-31 | 株式会社日立メディコ | Surgery support system |
| US20100217991A1 (en)* | 2008-08-14 | 2010-08-26 | Seung Wook Choi | Surgery robot system of server and client type |
| KR101049507B1 (en)* | 2009-02-27 | 2011-07-15 | 한국과학기술원 | Image-guided Surgery System and Its Control Method |
| KR101114226B1 (en)* | 2009-05-19 | 2012-03-05 | 주식회사 이턴 | Surgical robot system using history information and control method thereof |
| KR101108927B1 (en)* | 2009-03-24 | 2012-02-09 | 주식회사 이턴 | Surgical Robot System Using Augmented Reality and Its Control Method |
| KR101152177B1 (en)* | 2009-04-09 | 2012-06-18 | 의료법인 우리들의료재단 | Method and System for Automatic Leading Surgery Position and Apparatus Having Surgery Position Leading Function |
| GB0913930D0 (en)* | 2009-08-07 | 2009-09-16 | Ucl Business Plc | Apparatus and method for registering two medical images |
| JP2011036371A (en)* | 2009-08-10 | 2011-02-24 | Tohoku Otas Kk | Medical image recording apparatus |
| KR101181613B1 (en)* | 2011-02-21 | 2012-09-10 | 윤상진 | Surgical robot system for performing surgery based on displacement information determined by user designation and control method therefor |
| KR101795720B1 (en)* | 2011-05-12 | 2017-11-09 | 주식회사 미래컴퍼니 | Control method of surgical robot system, recording medium thereof, and surgical robot system |
| KR20130015146A (en)* | 2011-08-02 | 2013-02-13 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method and apparatus for processing medical image, robotic surgery system using image guidance |
| US20150127031A1 (en)* | 2011-08-26 | 2015-05-07 | EBM Corporation | Bloodstream simulation system for simulating blood vessel treatment effect, method therefor, and computer software program |
| KR101175065B1 (en)* | 2011-11-04 | 2012-10-12 | 주식회사 아폴로엠 | Method for bleeding scanning during operation using image processing apparatus for surgery |
| KR101302595B1 (en)* | 2012-07-03 | 2013-08-30 | 한국과학기술연구원 | System and method for predict to surgery progress step |
| KR20140112207A (en)* | 2013-03-13 | 2014-09-23 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Augmented reality imaging display system and surgical robot system comprising the same |
| KR101572487B1 (en)* | 2013-08-13 | 2015-12-02 | 한국과학기술연구원 | System and Method For Non-Invasive Patient-Image Registration |
| KR101538041B1 (en)* | 2013-10-15 | 2015-07-23 | 한국과학기술원 | Device for positioning of surgical tool and sergical robot system including the same |
| US10314656B2 (en)* | 2014-02-04 | 2019-06-11 | Intuitive Surgical Operations, Inc. | Systems and methods for non-rigid deformation of tissue for virtual navigation of interventional tools |
| JP6254053B2 (en)* | 2014-08-13 | 2017-12-27 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Endoscopic image diagnosis support apparatus, system and program, and operation method of endoscopic image diagnosis support apparatus |
| JP6104288B2 (en)* | 2015-01-06 | 2017-03-29 | 三菱プレシジョン株式会社 | Method for generating surgical simulation model, surgical simulation method, and surgical simulator |
| KR20160086629A (en)* | 2015-01-12 | 2016-07-20 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Method and Apparatus for Coordinating Position of Surgery Region and Surgical Tool During Image Guided Surgery |
| JP6594133B2 (en)* | 2015-09-16 | 2019-10-23 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Endoscope position specifying device, operation method of endoscope position specifying device, and endoscope position specifying program |
| US20170132510A1 (en)* | 2015-11-05 | 2017-05-11 | Facebook, Inc. | Identifying Content Items Using a Deep-Learning Model |
| KR101740286B1 (en)* | 2015-12-17 | 2017-05-29 | (주)미래컴퍼니 | Surgical robot system and adaptive control method thereof |
| KR20180010721A (en)* | 2016-07-22 | 2018-01-31 | 한국전자통신연구원 | System for supporting intelligent surgery and method for using the same |
- 2018
- 2018-08-23KRKR1020180098359Apatent/KR102014359B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-08-23KRKR1020180098413Apatent/KR102018565B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-08-23KRKR1020180098358Apatent/KR102014385B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-08-23KRKR1020180098360Apatent/KR102014355B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-09-12KRKR1020180109204Apatent/KR102014377B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-09-27KRKR1020180115328Apatent/KR102013868B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-10-15KRKR1020180122454Apatent/KR102014351B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-10-16KRKR1020180122949Apatent/KR102013806B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-10-29KRKR1020180129709Apatent/KR102014364B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-10-29KRKR1020180130229Apatent/KR102013866B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-10-31KRKR1020180131478Apatent/KR102013837B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-11-07KRKR1020180135590Apatent/KR102016959B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-11-07KRKR1020180135578Apatent/KR20190100004A/ennot_activeCeased
- 2018-11-14KRKR1020180140050Apatent/KR20190100009A/ennot_activeCeased
- 2018-11-20KRKR1020180143367Apatent/KR102013857B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-11-22KRKR1020180145157Apatent/KR102013828B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-11-22KRKR1020180145177Apatent/KR20190100011A/ennot_activeCeased
- 2018-11-26KRKR1020180147015Apatent/KR102014371B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-11-28KRKR1020180149293Apatent/KR102013848B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-12-03KRKR1020180153569Apatent/KR102013814B1/enactiveActive
- 2018-12-05KRKR1020180155562Apatent/KR102013863B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20120046439A (en)* | 2010-11-02 | 2012-05-10 | 서울대학교병원 (분사무소) | Method of operation simulation and automatic operation device using 3d modelling |
| KR20120111871A (en)* | 2011-03-29 | 2012-10-11 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method and apparatus for creating medical image using 3d deformable model |
| KR20140020071A (en)* | 2012-08-07 | 2014-02-18 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Surgical robot system and control method thereof |
| KR20150043245A (en)* | 2012-08-14 | 2015-04-22 | 인튜어티브 서지컬 오퍼레이션즈 인코포레이티드 | Systems and methods for registration of multiple vision systems |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20190100005A (en) | 2019-08-28 |
| KR102018565B1 (en) | 2019-09-05 |
| KR102013806B1 (en) | 2019-08-23 |
| KR102014385B1 (en) | 2019-08-26 |
| KR20190099999A (en) | 2019-08-28 |
| KR102016959B1 (en) | 2019-09-02 |
| KR102014351B1 (en) | 2019-08-26 |
| KR102013828B1 (en) | 2019-08-23 |
| KR102013863B1 (en) | 2019-08-23 |
| KR102013848B1 (en) | 2019-08-23 |
| KR102013814B1 (en) | 2019-08-23 |
| KR20190100011A (en) | 2019-08-28 |
| KR20190100009A (en) | 2019-08-28 |
| KR102014377B1 (en) | 2019-08-26 |
| KR102013857B1 (en) | 2019-08-23 |
| KR102013837B1 (en) | 2019-10-21 |
| KR102014364B1 (en) | 2019-08-26 |
| KR102013868B1 (en) | 2019-08-23 |
| KR102014355B1 (en) | 2019-08-26 |
| KR102014371B1 (en) | 2019-08-26 |
| KR20190100004A (en) | 2019-08-28 |
| KR102013866B1 (en) | 2019-08-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102014359B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing camera location using surgical video | |
| KR102298412B1 (en) | Surgical image data learning system | |
| KR101864380B1 (en) | Surgical image data learning system | |
| US11660142B2 (en) | Method for generating surgical simulation information and program | |
| KR102457585B1 (en) | Method and system for navigating vascular during surgery | |
| KR102146672B1 (en) | Program and method for providing feedback about result of surgery | |
| CN115429430A (en) | Registration method, information display method, surgical navigation system, device and equipment | |
| KR102803773B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing information related to surgery via display screen | |
| US20230215059A1 (en) | Three-dimensional model reconstruction | |
| KR20200096155A (en) | Method for analysis and recognition of medical image | |
| KR102213412B1 (en) | Method, apparatus and program for generating a pneumoperitoneum model | |
| KR102298417B1 (en) | Program and method for generating surgical simulation information | |
| KR20190133423A (en) | Program and method for generating surgical simulation information | |
| KR101940706B1 (en) | Program and method for generating surgical simulation information | |
| KR102802633B1 (en) | Apparatus and Method for matching the Real Surgical Image with the 3D based Virtual Simulated Surgical Image | |
| KR20190133424A (en) | Program and method for providing feedback about result of surgery | |
| KR20250065077A (en) | Method for implementing object behavior based on hand gestures in mixed reality and device therefor | |
| KR20190100010A (en) | Method and apparatus for providing optimum surgical equipment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| PA0302 | Request for accelerated examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D17-exm-PA0302 St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D16-exm-PA0302 | |
| D13-X000 | Search requested | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D13-srh-X000 | |
| D14-X000 | Search report completed | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D14-srh-X000 | |
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| T11-X000 | Administrative time limit extension requested | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T11-oth-X000 | |
| E13-X000 | Pre-grant limitation requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-3-E10-E13-lim-X000 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 Fee payment year number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| R17-X000 | Change to representative recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R17-oth-X000 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:4 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:5 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:6 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:7 |