KR101986497B1 - Method for selecting data packet transmission path in mobile ad-hoc network - Google Patents
Method for selecting data packet transmission path in mobile ad-hoc networkDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101986497B1 KR101986497B1KR1020180126134AKR20180126134AKR101986497B1KR 101986497 B1KR101986497 B1KR 101986497B1KR 1020180126134 AKR1020180126134 AKR 1020180126134AKR 20180126134 AKR20180126134 AKR 20180126134AKR 101986497 B1KR101986497 B1KR 101986497B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- path
- node
- data packet
- quality
- packet transmission
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription27
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription26
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description15
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000description8
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description8
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description3
- 230000014509gene expressionEffects0.000description3
- 238000010187selection methodMethods0.000description3
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description2
- 238000013507mappingMethods0.000description2
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description2
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description2
- 238000003491arrayMethods0.000description1
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 230000006872improvementEffects0.000description1
- 230000002452interceptive effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000007726management methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000010295mobile communicationMethods0.000description1
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description1
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W40/00—Communication routing or communication path finding
- H04W40/02—Communication route or path selection, e.g. power-based or shortest path routing
- H04W40/12—Communication route or path selection, e.g. power-based or shortest path routing based on transmission quality or channel quality
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W40/00—Communication routing or communication path finding
- H04W40/24—Connectivity information management, e.g. connectivity discovery or connectivity update
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W84/00—Network topologies
- H04W84/18—Self-organising networks, e.g. ad-hoc networks or sensor networks
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 모바일 애드혹 네트워크에서 데이터 패킷 송신 경로 선택 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method of selecting a data packet transmission path in a mobile ad hoc network.
디지털 무전기는 기지국 또는 액세스 포인트 등과 같은 기반 망 없이 디지털 무전기 간 패킷 통신을 이용하여 자율적으로 애드혹 망을 구성한다. 애드혹 망은 디지털 무전기의 이동과 지형/지물에 의해 토폴로지가 변경된다. 이러한 환경에서 신뢰성 있는 데이터 패킷 송수신을 위해서는 신속한 토폴로지 변화 인지와 신뢰성 높은 경로를 통한 데이터 패킷 송수신 기술이 필요하다. 종래에는 데이터 패킷을 수신하여 헤더 내의 경로를 이용하여 토폴로지를 갱신하거나, 별도의 프레임을 이용하여 갱신하였다. 전자는 단일 경로 정보만을 업데이트 가능하고, 후자는 토폴로지 갱신을 위한 오버헤드가 발생한다. 그리고 최소홉(minimum hop) 우선 정책을 이용한 링크 품질을 적용하여 데이터 패킷 전송 경로를 선택하였다. 최소홉 기반의 링크 품질 방법은 최소홉의 경로들이 모두 품질이 떨어지는 경우 데이터 패킷 송수신의 신뢰성을 보장하기 힘들다.Digital radios autonomously configure an ad hoc network using packet communications between digital radios without a base network such as a base station or an access point. The ad hoc network changes the topology by the movement of the digital radio and the terrain / ground. In order to transmit and receive reliable data packets in this environment, there is a need for a rapid topology change and a technology for transmitting and receiving data packets through a reliable path. Conventionally, a data packet is received and the topology is updated using the path in the header, or updated using a separate frame. The former can only update single path information, and the latter generates overhead for topology update. And we choose the data packet transmission path by applying the link quality using the minimum hop priority policy. The minimum hop-based link quality method can not guarantee the reliability of data packet transmission and reception if the quality of all the paths of the minimum hop is low.
본 발명의 목적은 모바일 애드혹 네트워크에서 신뢰성 높은 데이터 패킷 송신 경로 선택 방법을 제공하는 데 있다.It is an object of the present invention to provide a reliable data packet transmission path selection method in a mobile ad hoc network.
본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 모바일 애드혹 네트워크에서 데이터 패킷 송신 경로 선택 방법은: 제 1 노드에서 데이터 패킷을 수신하는 단계; 상기 수신된 데이터 패킷의 목적 노드에 대응하는 경로 품질에 따라 데이터 패킷 송신 경로를 선택하는 단계; 및 상기 선택된 데이터 패킷 송신 경로로 상기 데이터 패킷의 헤더를 구성하는 단계; 및 상기 구성된 헤더를 갖는 데이터 패킷을 제 2 노드로 전송하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.A method for selecting a data packet transmission path in a mobile ad hoc network according to an embodiment of the present invention includes: receiving a data packet at a first node; Selecting a data packet transmission path according to a path quality corresponding to a destination node of the received data packet; And configuring a header of the data packet with the selected data packet transmission path; And transmitting the data packet having the configured header to a second node.
실시 예에 있어서, 상기 데이터 패킷 송신 경로를 선택하는 단계는, 라우팅 테이블에서 목적 노드까지의 경로를 탐색하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.In the embodiment, the step of selecting the data packet transmission path may further include searching for a path from the routing table to the destination node.
실시 예에 있어서, 상기 탐색 결과로써 상기 목적 노드까지 단일 경로인 지를 판별하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.The method may further include determining whether the path is a single path to the destination node as the search result.
실시 예에 있어서, 상기 목적 노드까지 상기 단일 경로가 아닐 때, 모든 후보 경로에 대한 상기 경로 품질을 계산하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.In an embodiment, the method may further comprise calculating the path quality for all candidate paths when the destination path is not the single path.
실시 예에 있어서, 상기 데이터 패킷 송신 경로를 선택하는 단계는, 상기 모든 후보 경로 중에서 상기 경로 품질이 가장 높은 경로를 상기 데이터 패킷 송신 경로로 선택하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In the embodiment, the step of selecting the data packet transmission path may include a step of selecting, as the data packet transmission path, a path having the highest path quality among all the candidate paths.
실시 예에 있어서, 상기 경로 품질을 계산하는 단계는, 링크 품질과 홉의 가중치를 이용하여 상기 경로 품질을 계산하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In an embodiment, calculating the path quality may include calculating the path quality using a link quality and a weight of the hop.
실시 예에 있어서, 상기 링크 품질은 WSNR(weighted signal to noise ratio)과 PDR(packet delivery ratio)을 이용하여 계산되는 것을 특징으로 한다.In an embodiment, the link quality is calculated using weighted signal to noise ratio (WSNR) and packet delivery ratio (PDR).
실시 예에 있어서, 상기 링크 품질은,을 만족하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In an embodiment, Is satisfied.
실시 예에 있어서, 상기 WSNR은, WSNRt = α * SNRt + (1-α) * WSNRt-1,0.5 < α < 1을 만족하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In an embodiment, the WSNR satisfies WSNRt = α * SNRt + (1-α) * WSNRt-1, 0.5 <α <1.
실시 예에 있어서, 상기 PDR은,을 만족하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In an embodiment, the PDR comprises: Is satisfied.
본 발명에 따르면, 첫째, 노드들은 모든 무선 데이터 패킷을 엿듣기로 수신하여 패킷 내 포함된 이웃 노드 정보를 이용하여 라우팅 테이블을 업데이트 한다. 그래서 망 변화 정보를 빠르게 라우팅 테이블에 적용할 수 있다. 둘째, 경로 선택 시에 link quality에 HOP 가중치를 적용한 경로 품질을 통해 경로를 선택하여 최소홉 우선 방식에서 발생할 수 있는 부작용을 줄인다. 셋째, 중계노드에서 품질이 더 좋은 경로를 재탐색하여 패킷을 전달하므로 데이터 전송 신뢰성을 높인다.According to the present invention, first, the nodes receive all wireless data packets by eavesdropping and update the routing table using neighbor node information included in the packet. Thus, the network change information can be quickly applied to the routing table. Second, by selecting path through path quality with HOP weight applied to link quality in path selection, it reduces side effects that may occur in minimum hop priority scheme. Third, it improves the reliability of data transmission because the relay node searches for the better path and transmits the packet.
이하에 첨부되는 도들은 본 실시 예에 관한 이해를 돕기 위한 것으로, 상세한 설명과 함께 실시 예들을 제공한다. 다만, 본 실시예의 기술적 특징이 특정 도에 한정되는 것은 아니며, 각 도에서 개시하는 특징들은 서로 조합되어 새로운 실시 예로 구성될 수 있다.
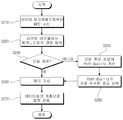
도 1은 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 노드 장치에서 다른 노드로 송신할 데이터의 내부 처리 과정을 예시적으로 보여주는 흐름도이다.
도 2는 중계노드가 데이터 패킷을 수신하고 중계를 수행하는 과정을 나타내는 흐름도이다.
도 3은 노드 A의 라우팅 테이블 정보를 예시적으로 보여주는 그래프이다.
도 4는 도 3의 토폴로지 구성에서 노드 A에서 노드 D로 데이터 송신 시 노드 A에서 경로 품질을 계산하는 실시 예를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다.
도 5는 노드 A의 라우팅 테이블 정보를 예시적으로 보여주는 그래프이다.
도 6은 노드 C의 라우팅 테이블 정보를 예시적으로 보여주는 그래프이다.
도 7은 노드 A에서 노드 E로 전송할 패킷에 대한 경로 품질 계산 실시 예를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다.
도 8은 노드 A로부터 전송 받은 패킷에 대해 노드 C에서 다음 중계노드를 선택하기 위한 경로 품질 계산 실시 예를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다.
도 9는 데이터 패킷을 이용한 라우팅 테이블 업데이트 과정을 설명하기 위한 토폴로지를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다.
도 10은 노드 A의 최초 라우팅 테이블 정보를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다.
도 11은 노드B의 데이터에 포함된 이웃 노드 정보를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다.
도 12는 노드 A의 변경된 라우팅 테이블 정보를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다.
도 13은 LQE 계산 결과에 따른 링크 품질 등급을 매핑한 테이블이다.
도 14는 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 중계 노드의 데이터 전송 방법에 예시적으로 보여주는 흐름도이다.BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The accompanying drawings, which are included to provide a further understanding of the present invention, are provided to illustrate embodiments of the invention and, together with the description, serve to explain the principles of the invention. However, the technical features of the present embodiment are not limited to the specific diagrams, and the features disclosed in the drawings may be combined with each other to constitute a new embodiment.
1 is a flowchart illustrating an exemplary internal process of data to be transmitted from a node device to another node according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a flowchart illustrating a process in which a relay node receives a data packet and performs relaying.
FIG. 3 is a graph illustrating an exemplary routing table information of node A. FIG.
4 is an exemplary diagram illustrating an embodiment for calculating path quality at node A when transmitting data from node A to node D in the topology configuration of FIG.
FIG. 5 is a graph illustrating an exemplary routing table information of node A. FIG.
FIG. 6 is a graph illustrating an exemplary routing table information of a node C. FIG.
FIG. 7 is an exemplary diagram illustrating an embodiment of path quality calculation for a packet to be transmitted from node A to node E. FIG.
8 is a diagram illustrating an exemplary path quality calculation for selecting a next relay node at a node C for a packet received from the node A. In FIG.
9 is a diagram illustrating a topology for explaining a routing table update process using a data packet.
FIG. 10 is an exemplary diagram illustrating initial routing table information of node A. FIG.
11 is an exemplary diagram showing neighbor node information included in data of a node B. FIG.
12 is an exemplary diagram illustrating the modified routing table information of node A. FIG.
13 is a table mapping the link quality class according to the LQE calculation result.
14 is a flowchart illustrating an exemplary method of transmitting data to a relay node according to an embodiment of the present invention.
아래에서는 도면들을 이용하여 본 발명의 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 용이하게 실시할 수 있을 정도로 본 발명의 내용을 명확하고 상세하게 기재할 것이다.BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The above and other objects, features and advantages of the present invention will be more apparent from the following detailed description taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, in which: FIG.
본 발명은 다양한 변경을 가할 수 있고 여러 가지 형태를 가질 수 있는바, 특정 실시 예들을 도에 예시하고 본문에 상세하게 설명하고자 한다. 그러나 이는 본 발명을 특정한 개시 형태에 대해 한정하려는 것이 아니며, 본 발명의 사상 및 기술 범위에 포함되는 모든 변경, 균등물 내지 대체물을 포함하는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. 제 1, 제 2 등의 용어는 다양한 구성요소들을 설명하는데 사용될 수 있지만, 상기 구성요소들은 상기 용어들에 의해 한정되어서는 안 된다.While the invention is susceptible to various modifications and alternative forms, specific embodiments thereof are shown by way of example in the drawings and will herein be described in detail. It is to be understood, however, that the invention is not intended to be limited to the particular forms disclosed, but on the contrary, is intended to cover all modifications, equivalents, and alternatives falling within the spirit and scope of the invention. The terms first, second, etc. may be used to describe various components, but the components should not be limited by the terms.
상기 용어들은 하나의 구성요소를 다른 구성요소로부터 구별하는 목적으로 사용될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 본 발명의 권리 범위로부터 이탈되지 않은 채 제 1 구성요소는 제 2 구성요소로 명명될 수 있고, 유사하게 제 2 구성요소도 제 1 구성요소로 명명될 수 있다. 어떤 구성요소가 다른 구성요소에 "연결되어" 있다거나 "접속되어" 있다고 언급된 때에는, 그 다른 구성요소에 직접적으로 연결되어 있거나 혹은 접속되어 있을 수도 있지만, 중간에 다른 구성요소가 존재할 수도 있다고 이해되어야 할 것이다. 반면에, 어떤 구성요소가 다른 구성요소에 "직접 연결되어" 있다거나 "직접 접속되어" 있다고 언급된 때에는, 중간에 다른 구성요소가 존재하지 않는 것으로 이해되어야 할 것이다.The terms may be used for the purpose of distinguishing one component from another. For example, without departing from the scope of the present invention, the first component may be referred to as a second component, and similarly, the second component may also be referred to as a first component. It is to be understood that when an element is referred to as being "connected" or "connected" to another element, it may be directly connected or connected to the other element, . On the other hand, when an element is referred to as being "directly connected" or "directly connected" to another element, it should be understood that there are no other elements in between.
구성요소들 간의 관계를 설명하는 다른 표현들, 즉 "~사이에"와 "바로 ~사이에" 혹은 "~에 이웃하는"과 "~에 직접 이웃하는" 등도 마찬가지로 해석되어야 한다. 본 출원에서 사용한 용어는 단지 특정한 실시 예를 설명하기 위해 사용된 것으로, 본 발명을 한정하려는 의도가 아니다. 단수의 표현은 문맥상 명백하게 다르게 뜻하지 않는 한, 복수의 표현을 포함한다.Other expressions that describe the relationship between components, such as "between" and "between" or "neighboring to" and "directly adjacent to" should be interpreted as well. The terminology used in this application is used only to describe a specific embodiment and is not intended to limit the invention. The singular expressions include plural expressions unless the context clearly dictates otherwise.
본 출원에서, "포함하다" 혹은 "가지다" 등의 용어는 실시된 특징, 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부분품 혹은 이들을 조합한 것이 존재함을 지정하려는 것이지, 하나 혹은 그 이상의 다른 특징들이나 숫자, 단계, 동작, 구성요소, 부분품 혹은 이들을 조합한 것들의 존재 혹은 부가 가능성을 미리 배제하지 않는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. 다르게 정의되지 않는 한, 기술적이거나 과학적인 용어를 포함해서 여기서 사용되는 모든 용어들은 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 일반적으로 이해되는 것과 동일한 의미이다. 일반적으로 사용되는 사전에 정의되어 있는 것과 같은 용어들은 관련 기술의 문맥상 가지는 의미와 일치하는 의미인 것으로 해석되어야 하며, 본 출원에서 명백하게 정의하지 않는 한, 이상적이거나 과도하게 형식적인 의미로 해석되지 않는다.In this application, the terms "comprises" or "having" are intended to specify the presence of stated features, integers, steps, operations, components, parts, or combinations thereof, wherein one or more other features, , Steps, operations, components, parts, or combinations thereof, as a matter of course. Unless otherwise defined, all terms used herein, including technical or scientific terms, have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this invention belongs. Terms such as those defined in commonly used dictionaries should be construed as meaning consistent with meaning in the context of the relevant art and are not to be construed as ideal or overly formal in meaning unless expressly defined in the present application .
본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 모바일 애드혹 네트워크에서 노드 장치의 동작 방법은, Hello 및 패킷 엿듣기를 이용한 토폴로지 업데이트 방법, 데이터 패킷 수신 시 라우팅 테이블에서 경로 탐색 및 선택 방법, 및 중계 노드에서 경로 재탐색 방법으로 구성될 수 있다.A method of operating a node device in a mobile ad hoc network according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a topology update method using Hello and packet eavesdropping, a route search and selection method in a routing table in receiving a data packet, and a route re- Lt; / RTI >
첫째로, Hello 및 패킷 엿듣기를 이용한 토폴로지 업데이트 방법은 다음과 같다. 실시 예에 있어서, 모든 노드는 30초 간격으로 1/2-hop 이웃 노드 정보를 담은 Hello 패킷 송신할 수 있다. 여기서 30초 간격은 본 발명을 제한하지 않는다고 이해되어야 할 것이다. 실시 예에 있어서, 모든 노드는 Hello를 제외한 모든 데이터 패킷에 1-hop 이웃 노드 정보를 담아 송신할 수 있다. 실시 예에 있어서, 모든 노드는 이웃 노드의 Hello 패킷을 수신 및 데이터 패킷 엿듣기를 이용하여 토폴로지 업데이트 수행할 수 있다.First, the topology update method using Hello and packet eavesdropping is as follows. In an embodiment, all nodes may transmit a Hello packet containing the 1/2-hop neighbor node information every 30 seconds. It should be understood that the 30 second interval does not limit the present invention. In the embodiment, all nodes can transmit 1-hop neighbor node information to all data packets except hello. In an embodiment, all nodes may receive Hello packets of neighboring nodes and perform topology updates using data packet eavesdropping.
둘째로, 데이터 패킷 수신 시 라우팅 테이블에서 경로 탐색 및 선택 방법은 다음과 같다. 실시 예에 있어서, 송신 데이터가 발생하면, 라우팅 테이블에서 전송 가능한 모든 경로 탐색이 수행될 수 있다. 실시 예에 있어서, 모든 후보 경로에 대해 경로 품질(path quality)을 계산하여 가장 우수한 경로가 선택될 수 있다.Second, the path search and selection method in the routing table when receiving a data packet is as follows. In the embodiment, when transmission data is generated, all transmittable route searches in the routing table can be performed. In an embodiment, the best path may be selected by calculating the path quality for all candidate paths.
실시 예에 있어서, 경로 품질은 링크 품질(link quality)를 이용하여 다음의 수식으로 계산될 수 있다.In an embodiment, the path quality may be calculated using the link quality with the following equation:
여기서, Link Quality(LQ)는 LQE(Link Quality Estimation) 계산 값을 15단계로Here, the Link Quality (LQ) has 15 values of LQE (Link Quality Estimation)
등급화한 결과이다.This is the result of grading.
한편, LQE(Link Quality Estimation)는 Weighted SNR(WSNR)과 패킷 전달 성공률(PDR)을 이용하여 다음과 같이 계산될 수 있다.Meanwhile, LQE (Link Quality Estimation) can be calculated as follows using Weighted SNR (WSNR) and Packet Delivery Success Rate (PDR).
여기서, WSNR의 α 값은 최신 SNR 값에 더 가중치를 주기 위한 계수로써 망의 변화가 심할수록 1에 가까운 값을 할당될 수 있다. 또한, SNR(signal to noise ratio)은 신호 대 잡음비로 데이터 수신 시 측정되는 신호세기이다. SNR은 1~10 사이의 값을 가지며, 10 이상으로 측정된 경우 10으로 변환하여 WSNR 계산식에 적용될 수 있다. 또한, PDR(Packet Delivery Ratio)에서 latest send packet numbers는 최근에 송신한 패킷 수를 의미하며, receive ACK packet numbers 수신 노드가 데이터 수신 후 ACK 패킷 수를 의미한다. 그리고 PDR에서는 오래된 정보를 배제하기 위해 마지막으로 전송한 20개의 데이터에 대해서만 성공률 계산에 이용한다.Here, the a value of WSNR is a coefficient for giving more weight to the latest SNR value, and can be assigned a value closer to 1 as the network change becomes greater. Also, the signal to noise ratio (SNR) is the signal strength measured at the time of data reception with a signal-to-noise ratio. The SNR has a value between 1 and 10, and when it is measured above 10, it can be converted to 10 and applied to the WSNR calculation formula. In PDR (Packet Delivery Ratio), latest send packet numbers means the number of recently transmitted packets, and receive ACK packet numbers means the number of ACK packets after receiving data from the receiving node. In the PDR, only the last 20 data transmitted to exclude the old information is used for the success rate calculation.
셋째로, 중계 노드에서 경로 재탐색 방법은 다음과 같다. 실시 예에 있어서, 중계 노드는 데이터 패킷을 수신하면 자신의 라우팅 테이블을 이용하여 목적 노드로의 경로 탐색을 수행할 수 있다. 실시 예에 있어서, 헤더의 경로와 비교하여 더 우수한 경로가 있으면 경로를 교체하여 송신 데이터가 전송될 수 있다.Third, the route re-search method at the relay node is as follows. In an embodiment, the relay node may perform a route search to a destination node using its routing table upon receipt of a data packet. In an embodiment, if there is a better path compared to the path of the header, the transmission data may be transmitted by replacing the path.
도 1은 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 노드 장치에서 다른 노드로 송신할 데이터의 내부 처리 과정을 예시적으로 보여주는 흐름도이다. 도 1을 참조하면, 노드 장치의 데이터 처리 과정은 다음과 같다. 노드 장치는 IP 계층으로부터 다른 노드로 송신할 IP 데이터 패킷을 수신할 수 있다(S110). 노드 장치는 IP 패킷 헤더의 목적지 주소를 기반으로 라우팅 테이블을 탐색하여 패킷 전송 가능한 모든 경로 정보를 확보할 수 있다(S120). 탐색된 경로가 한 개가 아니라면, 최종 경로 선택을 위한 작업이 수행될 수 있다. 단일 경로인 경우에는 경로 정보를 기반으로 헤더 구성 작업이 수행될 수 있다(S130).1 is a flowchart illustrating an exemplary internal process of data to be transmitted from a node device to another node according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 1, a data processing process of a node device is as follows. The node device may receive an IP data packet to be transmitted from the IP layer to another node (S110). The node device searches the routing table based on the destination address of the IP packet header and obtains all route information that can be transmitted in the packet (S120). If the path is not one, an operation for final path selection may be performed. In case of a single path, the header configuration operation may be performed based on the path information (S130).
다수 경로의 경우에는 각 경로 별로 경로 품질이 계산될 수 있다(S150). 경로 품질은 다음의 수학식을 통해 계산될 수 있다.In case of multiple paths, the path quality may be calculated for each path (S150). The path quality can be calculated by the following equation.
Path Quality = (LQ1-hop / 15) * (LQ2-hop /15) * … * (LQn-hop/15).Path Quality = (LQ1-hop / 15) * (LQ2-hop / 15) * ... * (LQn-hop / 15).
LQ(link quality)는 전체 15단계로 구분되며, 값이 높을 수록 좋은 경로를 의미한다. LQn-hop은 전체 경로에서 n번째 홉의 경로 품질을 뜻한다. 각 홉의 링크 품질은 15로 나누어져 1 이하의 값으로 변환되며, 링크 별로 변환된 값을 곱하여 최종 경로 품질이 계산될 수 있다. 각 링크 품질 변환값이 1이하여서 곱해질 수록 값이 더 작아지므로 짧은 경로에 대한 높은 가중치가 부여될 수 있다. 모든 경로에 대한 경로 품질 계산이 끝나면, 가장 높은 경로 품질을 전송 경로로 선택될 수 있다(S160). 최종 경로가 선택되면, 다음 중계노드와 목적노드 주소가 헤더에 기록될 수 있다(S170). 헤더 구성이 완료되면, 무선링크를 통해 전송될 수 있도록 데이터링크 계층으로 패킷이 전달될 수 있다(S170).LQ (link quality) is divided into 15 steps, and the higher the value, the better the path. LQn-hop means the path quality of the nth hop in the entire path. The link quality of each hop is divided by 15 and converted into a value of 1 or less, and the final path quality can be calculated by multiplying the converted value for each link. Since each link quality conversion value is less than 1 and multiplied, the value becomes smaller, so a high weight for a short path can be given. After calculating the path quality for all the paths, the highest path quality can be selected as the transmission path (S160). When the final path is selected, the next relay node and the destination node address can be recorded in the header (S170). When the header configuration is completed, the packet may be transmitted to the data link layer so as to be transmitted over the wireless link (S170).
도 2는 중계노드가 데이터 패킷을 수신하고 중계를 수행하는 과정을 나타내는 흐름도이다. 도 2를 참조하면, 중계노드에서 중계를 수행하는 과정은 다음과 같이 진행될 수 있다. 중계노드는 데이터링크 계층으로부터 패킷이 수신될 수 있다(S210). 이후의 S220, S230, S240, S250, S260은, 도 1에 도시된 S120, S130, S140, S150, S160와 동일할 수 있다.2 is a flowchart illustrating a process in which a relay node receives a data packet and performs relaying. Referring to FIG. 2, the process of relaying at the relay node may proceed as follows. The relay node may receive a packet from the data link layer (S210). Subsequent steps S220, S230, S240, S250, and S260 may be the same as S120, S130, S140, S150, and S160 shown in FIG.
도 3은 노드 A의 라우팅 테이블 정보를 예시적으로 보여주는 그래프이다. 도 3을 참조하면, A, B, C, D는 망을 구성하는 노드이며, 연결선은 노드 간 무선 링크가 존재함을 의미한다. 선상의 숫자는 무선 링크의 품질이다.FIG. 3 is a graph illustrating an exemplary routing table information of node A. FIG. Referring to FIG. 3, A, B, C, and D are nodes constituting a network, and a connection line means that there is a wireless link between nodes. The number on the line is the quality of the wireless link.
도 4는 도 3의 토폴로지 구성에서 노드 A에서 노드 D로 데이터 송신 시 노드 A에서 경로 품질을 계산하는 실시 예를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다.4 is an exemplary diagram illustrating an embodiment for calculating path quality at node A when transmitting data from node A to node D in the topology configuration of FIG.
도 3에 도시된 토폴로지에서 노드A에서 노드D로 전송이 가능한 경로는 총 5개이다. 5개의 경로에 대해서 도 1에서 설명한 바와 같이 경로 품질을 계산하면 노드 B를 이용한 2 hop 경로가 가장 품질이 우수한 경로이다. 따라서 노드A는 헤더에 다음 중계노드 노드 B와, 목적노드 노드 D를 기록하여 무선으로 송신할 수 있다.In the topology shown in FIG. 3, there are five routes that can be transmitted from the node A to the node D in total. As described above with reference to FIG. 1, the path quality is calculated for five paths, and the two hop route using the node B is the best route. Therefore, the node A can record the next relay node B and the destination node D in the header, and transmit it wirelessly.
도 5는 노드 A의 라우팅 테이블 정보를 예시적으로 보여주는 그래프이다. 도 5를 참조하면, 노드 A에서 노드 E로의 전송 가능한 경로는, A → B → E, A → C → D → E, A → C → B → E가 있다.FIG. 5 is a graph illustrating an exemplary routing table information of node A. FIG. Referring to FIG. 5, paths that can be transmitted from the node A to the node E are A? B? E, A? C? D? E, A? C? B? E.
도 6은 노드 C의 라우팅 테이블 정보를 예시적으로 보여주는 그래프이다. 도 6을 참조하면, 노드 B의 라우팅 테이블에는 노드 A에는 아직 업데이트 되지 않은 노드 E로의 직접 연결이 가능한 무선 링크 정보와 노드 D의 망이탈 정보가 이미 업데이트 되어 있다.FIG. 6 is a graph illustrating an exemplary routing table information of a node C. FIG. Referring to FIG. 6, in the routing table of the node B, the wireless link information capable of direct connection to the node E that has not yet been updated to the node A and the network deviation information of the node D have already been updated.
도 7은 노드 A에서 노드 E로 전송할 패킷에 대한 경로 품질 계산 실시 예를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다. 도 7에서 도시된 바와 같이, 노드 A에서 노드 E로 전송이 가능한 경로는 3개이며, 그 중에서 경로 품질이 가장 높은 A → C → D → E가 우선적으로 경로 선택될 가능성이 높다.FIG. 7 is an exemplary diagram illustrating an embodiment of path quality calculation for a packet to be transmitted from node A to node E. FIG. As shown in FIG. 7, there are three paths that can be transmitted from the node A to the node E, and it is highly likely that the path quality of the path A → C → D → E is preferentially selected.
도 8은 노드 A로부터 전송 받은 패킷에 대해 노드 C에서 다음 중계노드를 선택하기 위한 경로 품질 계산 실시 예를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다. 도 8을 참조하면, 노드 B에서 노드 E로 전송이 가능한 경로들의 경로 품질을 계산해보면 C → E의 경로가 선택될 수 있다.8 is a diagram illustrating an exemplary path quality calculation for selecting a next relay node at a node C for a packet received from the node A. In FIG. Referring to FIG. 8, the path quality of the paths that can be transmitted from the node B to the node E can be calculated, so that the path C → E can be selected.
종래의 소스 직접 릴레이(source directed relay) 방식을 적용하면 송신 노드가 결정한 A → C → D → E의 경로가 변경되지 않고 전송되어 망을 이탈한 노드 D로 중계를 시도한다. 반면에, 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 중계 방식은 중계노드에서 최신 정보를 이용한 경로 재탐색을 통하여 해당 문제를 회피할 수 있다.When a conventional source directed relay scheme is applied, the path of A → C → D → E determined by the transmitting node is transmitted unchanged, and relay is attempted to the node D which has left the network. On the other hand, the relaying method according to the embodiment of the present invention can avoid the problem by searching the route using the latest information at the relay node.
도 9는 데이터 패킷을 이용한 라우팅 테이블 업데이트 과정을 설명하기 위한 토폴로지를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다. 도 9에 도시된 바와 같이, 노드 B가 노드 C로 전송하는 데이터 패킷이 발생하면, 패킷 내에 최신 1-hop 이웃 노드 정보가 전송될 수 있다. 해당 패킷은 노드 A로 전송하는 패킷은 아니지만, 노드 A는 데이터 패킷 엿듣기를 통해 패킷 내의 이웃 노드 정보를 읽고, 자신의 라우팅 테이블을 업데이트 할 수 있다.9 is a diagram illustrating a topology for explaining a routing table update process using a data packet. As shown in FIG. 9, when a data packet is transmitted from the node B to the node C, the latest 1-hop neighbor node information can be transmitted in the packet. The packet is not a packet to be transmitted to node A, but node A can read neighbor node information in the packet through eavesdropping of data packets and update its routing table.
도 10은 노드 A의 최초 라우팅 테이블 정보를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다. 도 10에 도시된 노드 A의 라우팅 테이블은 노드 B와 노드 G 간의 링크 정보를 포함하지 않는다. 해당 링크 정보는 노드 B로부터의 Hello 패킷 수신으로 획득 가능하다. 최대 Hello 패킷 송신 주기만큼의 시간 후에 노드 A가 B-G 링크 정보를 얻을 수 있다. 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 중계 방식은 링크 정보 업데이트를 빠르게 수행하기 위해 데이터 패킷에도 이웃 노드 정보를 포함할 수 있다.FIG. 10 is an exemplary diagram illustrating initial routing table information of node A. FIG. The routing table of node A shown in Fig. 10 does not include link information between node B and node G. [ The link information is obtainable by receiving a Hello packet from the node B. After the maximum Hello packet transmission period, the node A can obtain the B-G link information. The relaying method according to the embodiment of the present invention may include the neighbor node information in the data packet to quickly perform the link information update.
도 11은 노드B의 데이터에 포함된 이웃 노드 정보를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다.11 is an exemplary diagram showing neighbor node information included in data of a node B. FIG.
도 12는 노드 A의 변경된 라우팅 테이블 정보를 예시적으로 보여주는 도면이다. 도 12을 참조하면, 노드 B에서 노드 C로 전송하는 데이터 패킷 내의 이웃 노드 정보를 기반으로 업데이트된 노드 A의 라우팅 테이블이 도시된다.12 is an exemplary diagram illustrating the modified routing table information of node A. FIG. Referring to FIG. 12, a routing table of node A updated based on neighbor node information in a data packet transmitted from node B to node C is shown.
도 13은 LQE 계산 결과에 따른 링크 품질 등급을 매핑한 테이블이다.13 is a table mapping the link quality class according to the LQE calculation result.
도 14는 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 중계 노드의 데이터 전송 방법에 예시적으로 보여주는 흐름도이다. 도 1 내지 도 14를 참조하면, 중계 노드의 데이터 전송 방법은 다음과 같이 진행될 수 있다.14 is a flowchart illustrating an exemplary method of transmitting data to a relay node according to an embodiment of the present invention. 1 to 14, a data transmission method of a relay node may proceed as follows.
제 1 노드에서 중계를 위한 데이터 패킷이 수신될 수 있다(S310). 데이터 패킷의 목적 노드에 대응하는 경로들에 대한 경로 품질이 계산될 수 있다. 계산된 경로 품질 중에서 가장 높은 경로가 선택될 수 있다(S320). 선택된 경로는 상기 데이터 패킷의 헤더에 업데이트 하도록 데이터 패킷이 새롭게 구성될 수 있다(S330). 선택된 경로에 대응하는 제 2 노드로 새롭게 구성된 데이터 패킷이 전송될 수 있다(S340).A data packet for relaying at the first node may be received (S310). The path quality for the paths corresponding to the destination node of the data packet can be calculated. The highest path among the calculated path qualities may be selected (S320). The data packet may be newly configured to update the selected path in the header of the data packet (S330). A newly configured data packet may be transmitted to the second node corresponding to the selected path (S340).
본 발명에 따른 단계들 및/또는 동작들은 기술분야의 통상의 기술자에 의해 이해될 수 있는 것과 같이, 다른 순서로, 또는 병렬적으로, 또는 다른 에포크(epoch) 등을 위해 다른 실시 예들에서 동시에 일어날 수 있다.The steps and / or operations in accordance with the present invention may occur in different orders, in parallel, or concurrently in other embodiments for other epochs or the like, as may be understood by one of ordinary skill in the art .
실시 예에 따라서는, 단계들 및/또는 동작들의 일부 또는 전부는 하나 이상의 비-일시적 컴퓨터-판독가능 매체에 저장된 명령, 프로그램, 상호작용 데이터 구조(interactive data structure), 클라이언트 및/또는 서버를 구동하는 하나 이상의 프로세서들을 사용하여 적어도 일부가 구현되거나 또는 수행될 수 있다. 하나 이상의 비-일시적 컴퓨터-판독가능 매체는 예시적으로 소프트웨어, 펌웨어, 하드웨어, 및/또는 그것들의 어떠한 조합일 수 있다. 또한, 본 명세서에서 논의된 "모듈"의 기능은 소프트웨어, 펌웨어, 하드웨어, 및/또는 그것들의 어떠한 조합으로 구현될 수 있다.Depending on the embodiment, some or all of the steps and / or operations may be performed on one or more non-transitory computer-readable media, including instructions, programs, interactive data structures, At least some of which may be implemented or performed using one or more processors. The one or more non-transitory computer-readable media can be, by way of example, software, firmware, hardware, and / or any combination thereof. Further, the functions of the "module" discussed herein may be implemented in software, firmware, hardware, and / or any combination thereof.
본 발명의 실시 예들의 하나 이상의 동작들/단계들/모듈들을 구현/수행하기 위한 하나 이상의 비-일시적 컴퓨터-판독가능 매체 및/또는 수단들은 ASICs(application-specific integrated circuits), 표준 집적 회로들, 마이크로 컨트롤러를 포함하는, 적절한 명령들을 수행하는 컨트롤러, 및/또는 임베디드 컨트롤러, FPGAs(field-programmable gate arrays), CPLDs(complex programmable logic devices), 및 그와 같은 것들을 포함할 수 있지만, 여기에 한정되지는 않는다.One or more non-transitory computer-readable media and / or means for implementing / performing one or more operations / steps / modules of embodiments of the present invention may be implemented as application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), standard integrated circuits, But are not limited to, controllers that perform appropriate instructions, including microcontrollers, and / or embedded controllers, field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), complex programmable logic devices (CPLDs) .
한편, 상술 된 본 발명의 내용은 발명을 실시하기 위한 구체적인 실시 예들에 불과하다. 본 발명은 구체적이고 실제로 이용할 수 있는 수단 자체뿐 아니라, 장차 기술로 활용할 수 있는 추상적이고 개념적인 아이디어인 기술적 사상을 포함할 것이다.The above-described contents of the present invention are only specific examples for carrying out the invention. The present invention will include not only concrete and practical means themselves, but also technical ideas which are abstract and conceptual ideas that can be utilized as future technologies.
A, B, C, D, E: 노드
PQ: 경로 품질
LQ: 링크 품질A, B, C, D, E: node
PQ: Path quality
LQ: Link quality
Claims (10)
Translated fromKorean제 1 노드에서 데이터 패킷을 수신하는 단계;
상기 수신된 데이터 패킷의 목적 노드에 대응하는 경로 품질에 따라 데이터 패킷 송신 경로를 선택하는 단계; 및
상기 선택된 데이터 패킷 송신 경로로 상기 데이터 패킷의 헤더를 구성하는 단계; 및
상기 구성된 헤더를 갖는 데이터 패킷을 제 2 노드로 전송하는 단계를 포함하고,
상기 데이터 패킷 송신 경로를 선택하는 단계는, 라우팅 테이블에서 목적 노드까지의 경로를 탐색하는 단계를 더 포함하고,
상기 탐색 결과로써 상기 목적 노드까지 단일 경로인 지를 판별하는 단계를 더 포함하고,
상기 목적 노드까지 상기 단일 경로가 아닐 때, 모든 후보 경로에 대한 상기 경로 품질을 계산하는 단계를 더 포함하고,
상기 경로 품질을 계산하는 단계는, 링크 품질과 홉의 가중치를 이용하여 상기 경로 품질을 계산하는 단계를 포함하고,
상기 링크 품질은 WSNR(weighted signal to noise ratio)과 PDR(packet delivery ratio)을 이용하여 계산되고,
상기 링크 품질은,을 만족하는 것을 특징으로 하는 방법.A method for selecting a data packet transmission path in a mobile ad hoc network, comprising:
Receiving a data packet at a first node;
Selecting a data packet transmission path according to a path quality corresponding to a destination node of the received data packet; And
Configuring a header of the data packet with the selected data packet transmission path; And
And sending a data packet having the configured header to a second node,
Wherein the step of selecting the data packet transmission path further comprises the step of searching for a path from the routing table to the destination node,
Further comprising the step of determining whether the path is a single path to the destination node as the search result,
Further comprising calculating the path quality for all candidate paths when the destination path is not the single path to the destination node,
Wherein calculating the path quality comprises calculating the path quality using link quality and a weight of the hop,
The link quality is calculated using weighted signal to noise ratio (WSNR) and packet delivery ratio (PDR)
The link quality, ≪ / RTI >
상기 데이터 패킷 송신 경로를 선택하는 단계는,
상기 모든 후보 경로 중에서 상기 경로 품질이 가장 높은 경로를 상기 데이터 패킷 송신 경로로 선택하는 단계를 포함하는 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the step of selecting the data packet transmission path comprises:
And selecting the path having the highest path quality among all the candidate paths as the data packet transmission path.
상기 PDR은,
을 만족하는 것을 특징으로 하는 방법.The method according to claim 1,
The PDR includes:
≪ / RTI >
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180126134AKR101986497B1 (en) | 2018-10-22 | 2018-10-22 | Method for selecting data packet transmission path in mobile ad-hoc network |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180126134AKR101986497B1 (en) | 2018-10-22 | 2018-10-22 | Method for selecting data packet transmission path in mobile ad-hoc network |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR101986497B1true KR101986497B1 (en) | 2019-06-07 |
Family
ID=66849692
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020180126134AActiveKR101986497B1 (en) | 2018-10-22 | 2018-10-22 | Method for selecting data packet transmission path in mobile ad-hoc network |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101986497B1 (en) |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20050116852A (en)* | 2004-06-08 | 2005-12-13 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method and apparatus for configuring routing path in a wireless ad hoc network |
| KR100895621B1 (en) | 2008-03-27 | 2009-05-06 | 국방과학연구소 | Topology Management in Wireless Mobile Ad-Hoc Network |
| KR20120067883A (en)* | 2010-12-16 | 2012-06-26 | 한국전자통신연구원 | A multi hop routing apparatus and a multi hop routing method |
- 2018
- 2018-10-22KRKR1020180126134Apatent/KR101986497B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20050116852A (en)* | 2004-06-08 | 2005-12-13 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method and apparatus for configuring routing path in a wireless ad hoc network |
| KR100895621B1 (en) | 2008-03-27 | 2009-05-06 | 국방과학연구소 | Topology Management in Wireless Mobile Ad-Hoc Network |
| KR20120067883A (en)* | 2010-12-16 | 2012-06-26 | 한국전자통신연구원 | A multi hop routing apparatus and a multi hop routing method |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 등록특허: 10-0766869, 등록일: 2007년 10월 8일, 제목: Ad-Hoc 이동 통신망에서 TEST 프레임을 이용한 토폴로지 갱신 기능 향상 방법. |
| 등록특허: 10-1369992, 등록일: 2014년 2월 26일, 제목: MIL-STD-188-220 프로토콜에서 DTR 비트를 활용한 서비스 품질 적용 방법. |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8243603B2 (en) | Method and system for improving a wireless communication route | |
| CN102113404B (en) | Relay apparatus, control method, and program | |
| RU2423010C2 (en) | Index of routing based on data along radio communication and band, letting through for multi-channel multiple-hop wireless networks with multiple radio stations | |
| CN101617549B (en) | Method and device for selecting access point or relay node in multi-hop wireless network | |
| JP4672452B2 (en) | System and method for link quality routing using weighted cumulative expected transmission time metrics | |
| US7911962B2 (en) | Integrating local congestion and path interference into QoS routing for wireless mobile AD HOC networks | |
| JP4023681B2 (en) | Multi-hop wireless communication system and route selection method thereof | |
| KR101269234B1 (en) | Method and apparatus transmitting data based on link quality in wireless network | |
| KR20130016156A (en) | Wireless communication method and system for routing packets via intra-mesh and extra-mesh routes | |
| JP5851020B2 (en) | Communication system and communication method | |
| KR101986497B1 (en) | Method for selecting data packet transmission path in mobile ad-hoc network | |
| KR102148981B1 (en) | Method for reducing routing overhead in cognitive radio adhoc networks | |
| JP5474861B2 (en) | Wireless communication apparatus and wireless communication method | |
| JP5431416B2 (en) | Wireless communication system and wireless communication method | |
| JP2014138215A (en) | Node | |
| JP5541380B1 (en) | Wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication system, and wireless communication program | |
| JP5420599B2 (en) | Wireless communication system and wireless communication method | |
| JP4851511B2 (en) | Routing method and transceiver base station and computer program for executing the method | |
| Xu et al. | Finding the fastest path in wireless networks | |
| Clausen et al. | A depth first forwarding (dff) extension for the loadng routing protocol | |
| JP5483489B2 (en) | Radio and bandwidth aware routing metrics for multi-radio, multi-channel and multi-hop wireless networks | |
| JP4385926B2 (en) | Wireless communication system | |
| KR20090062277A (en) | Communication method in mesh network system, client node, mesh node of mesh network system, Communication method in client node | |
| Toham et al. | OLSR enhancement for multi-interface multi-channel ad hoc networks | |
| AU2015213041B2 (en) | Relay method implemented in a radio communication network and terminal for implementing said method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20181022 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0302 | Request for accelerated examination | Patent event date:20181121 Patent event code:PA03022R01D Comment text:Request for Accelerated Examination Patent event date:20181022 Patent event code:PA03021R01I Comment text:Patent Application | |
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20190212 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20190524 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20190531 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20190531 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20220406 Start annual number:4 End annual number:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20240319 Start annual number:6 End annual number:6 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20250218 Start annual number:7 End annual number:7 |