KR101855395B1 - Screening method of lung tumor using near-infrared light - Google Patents
Screening method of lung tumor using near-infrared lightDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101855395B1 KR101855395B1KR1020160123392AKR20160123392AKR101855395B1KR 101855395 B1KR101855395 B1KR 101855395B1KR 1020160123392 AKR1020160123392 AKR 1020160123392AKR 20160123392 AKR20160123392 AKR 20160123392AKR 101855395 B1KR101855395 B1KR 101855395B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- infrared rays
- chest wall
- tumor
- near infrared
- present
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/0059—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence
- A61B5/0071—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence by measuring fluorescence emission
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N21/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, i.e. using sub-millimetre waves, infrared, visible or ultraviolet light
- G01N21/17—Systems in which incident light is modified in accordance with the properties of the material investigated
- G01N21/25—Colour; Spectral properties, i.e. comparison of effect of material on the light at two or more different wavelengths or wavelength bands
- G01N21/31—Investigating relative effect of material at wavelengths characteristic of specific elements or molecules, e.g. atomic absorption spectrometry
- G01N21/35—Investigating relative effect of material at wavelengths characteristic of specific elements or molecules, e.g. atomic absorption spectrometry using infrared light
- G01N21/359—Investigating relative effect of material at wavelengths characteristic of specific elements or molecules, e.g. atomic absorption spectrometry using infrared light using near infrared light
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/48—Biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Haemocytometers
- G01N33/50—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing
- G01N33/53—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor
- G01N33/574—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor for cancer
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/48—Biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Haemocytometers
- G01N33/50—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing
- G01N33/53—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor
- G01N33/574—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor for cancer
- G01N33/57407—Specifically defined cancers
- G01N33/57423—Specifically defined cancers of lung
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Apparatus For Radiation Diagnosis (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법에 관한 것으로서, 상세히는 흉벽 종양까지 조사되는 근적외선 또는 복수의 근적외선이 체내에서 체외를 통해 흉벽을 통과하여 투영 입사되도록 한 후, 상기 흉벽 종양으로부터 투영 입사되는 근적외선을 카메라로 검출하여 음영으로 영상화하거나, 혈관을 통해 주입된 형광염료와 함께 카메라로 검출하여 영상화하거나, 또는 분광기로 복수 파장의 근적외선의 흡수도의 차이를 통해 영상화하여 흉벽 종양의 유무 및 퍼짐 정도를 확인하도록 한 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법에 관한 것이다.More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for screening lung tumors using near infrared rays. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for screening lung tumors using near infrared rays. More specifically, near infrared rays or near infrared rays irradiated to chest wall tumors are projected through a chest wall, Or by imaging with a camera in conjunction with a fluorescent dye injected through a blood vessel, or by imaging with a spectroscope through the difference in the absorbance of multiple wavelengths of near-infrared light to determine the presence and extent of chest wall tumors And to a lung tumor screening method using near-infrared rays.
세계보건기구 산하 국제암연구소(WHO/IARC)에서 1급 발암물질로 분류하고 있는 석면은 흉막에 발생하는 폐종양인 악성중피종의 대표적인 원인물질 중 하나로, 상기 악성중피종은 석면에 처음 노출된 후 약 15∼40년의 잠복기를 가진다.Asbestos classified as a primary carcinogen in the International Agency for Research on Cancer (WHO / IARC) under the World Health Organization is one of the leading causes of malignant mesothelioma, a pulmonary tumor that occurs in the pleura. It has a latency period of 15 to 40 years.
한편 도 1에서 보는 바와 같이, 흉막은 벽측 흉막(parietal pleura)과 장측 흉막(visceral pleura)으로 구성되며, 상기 흉막에 발생하는 흉막반(pleural plaques)도 석면노출에 의해 발생하고 있다. 그러나 이러한 흉막반은 결핵에 의해서도 발생하므로 국내의 높은 결핵 유병률과 흉막반의 임상적 증상에 대한 근거 부족으로 석면 유래 흉막반과 결핵 유래 흉막반의 차이를 규명하지 못하고 있어 석면관련 보상 근거가 부족하다.On the other hand, as shown in FIG. 1, the pleura consists of a parietal pleura and a visceral pleura. Pleural plaques occurring in the pleura are also caused by exposure to asbestos. However, because these tuberculosis is also caused by tuberculosis, there is a lack of reason for asbestos-related compensation because of the high prevalence of tuberculosis in Korea and lack of evidence on the clinical symptoms of pleura.
또한 악성중피종은 치료면에서 예후가 불량(진단 후 생존율 1년 미만)하고, 발생율과 사망률은 지속적 증가하고 있는 상태에 있는데, 이렇게 되는 이유는 조기진단이 매우 어렵기 때문이다.In addition, malignant mesothelioma has poor prognosis (less than 1 year survival rate after diagnosis), and incidence and mortality rate are continuously increasing. This is because early diagnosis is very difficult.
현재 실시되는 X선 흉부검사는 보통 암의 크기가 5∼10mm 이상 되어야 이상 부위를 확인할 수 있으며, 갈비뼈에 의해 보호되고 있고 심장의 위치와 겹쳐있는 폐의 특성상 다른 장기들에 의해 가려져 이상 부위를 확인할 수 없는 경우가 많은 한계점이 있다. 또한 X선 흉부검사에 의해 이상 부위가 확인된다고 하여도 폐 조직은 공기와 직접 접촉하면서 혈관과 밀접하게 연결되어 있어 이미 전이가 이루어지고 있는 등 악성화 되어 있을 가능성이 높다. 따라서 X선 흉부검사는 폐종양의 조기진단법으로서의 효용성이 매우 낮은 상태에 있다.The current X-ray chest examination usually requires the size of the cancer to be 5 to 10 mm or more to identify the abnormal region. It is protected by the ribs, and the lung is overlapped with the position of the heart. There are many limitations that can not be achieved. In addition, even if the abnormality is confirmed by X-ray chest examination, the lung tissue is in direct contact with the air and is closely connected with the blood vessel, so that it is highly likely that the lung is already metastasized. Therefore, X-ray chest examination is very ineffective as an early diagnostic method for lung tumors.
특히 얇은 흉막 또는 복막중피에 발생하는 악성중피종의 특성상 도 2에서 보는 바와 같이, 전산단층 촬영이나 PET-CT의 해상도가 충분치 못하여 이들은 조기 진단에 도움이 되지 않고 있다.Especially, as shown in Fig. 2, malignant mesothelioma that occurs in the thin pleura or peritoneum is not helpful for early diagnosis because of insufficient resolution of computed tomography or PET-CT.
한편 조기 진단을 위한 혈액 내의 암 바이오마커에 대한 연구가 있었지만, 비특이도를 극복하기 어려워 진단율의 향상이 잘 이뤄지지 않고 있는 실정에 있다. 최근 도 2에서 보는 바와 같이, 흉강경이나 복강경 기술이 발전함에 따라 이들을 이용한 최소 침습적 악성중피종 검사에 대한 연구가 동물을 대상으로 진행되고 있으나, 이들은 침습적 방법이므로 조기 진단용으로 사용되기에는 한계가 있다.On the other hand, there have been studies on cancer biomarkers in blood for early diagnosis, but it is difficult to overcome nonspecificity and improvement of diagnosis rate is not done well. As shown in FIG. 2, studies on minimally invasive malignant mesothelioma using these techniques have been conducted on animals. However, since they are invasive methods, they are limited to be used for early diagnosis.
본 발명은 상기한 바와 같은 제반 문제점을 개선하기 위해 안출된 것으로서, 그 목적은 흉막의 흉벽 종양의 위치까지 조사되는 근적외선을 체내에서 체외로 흉벽을 통과하여 투영 입사한 후, 이를 검출하여 음영으로 영상화함으로써 흉벽 종양의 유무 및 퍼짐 정도를 확인하도록 한 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 제공함에 있다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention has been made in order to solve all of the above problems, and it is an object of the present invention to provide a method and apparatus for detecting near-infrared rays irradiated up to the position of a chest wall tumor of a pleura through a chest wall, The present invention provides a method for screening lung tumors using near-infrared rays, in which the presence or absence and extent of chest wall tumors are confirmed.
다른 목적은 형광염료를 혈관에 주입하여 흉벽 종양에 침착되면, 흉막의 흉벽 종양 위치까지 조사되는 근적외선이 상기 형광염료에 의해 흉벽 종양에서 형광을 방출함에 따라 이를 검출하여 흉벽 종양의 신생 혈관을 영상화함으로써, 흉벽 종양의 유무를 확인하도록 한 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 제공함에 있다.Another objective is to detect the neovascularization of the chest wall tumors when the fluorescent dye emits fluorescence from the chest wall tumor by the fluorescent dye, which is irradiated to the chest wall tumor site when the fluorescent dye is deposited in the chest wall tumor by injecting the fluorescent dye into the blood vessel And a method for screening lung tumors using near-infrared rays to confirm the presence or absence of chest wall tumors.
또 다른 목적은 흉막의 흉벽 종양 위치까지 동시에 또는 순차적으로 조사되는 서로 다른 파장대의 다수의 근적외선의 빛의 세기를 측정하거나 영상화하여 흡수도의 차이를 통해 흉벽 종양의 유무를 확인하도록 한 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 제공함에 있다.Another goal was to measure the intensity of light from multiple near-infrared rays of different wavelengths simultaneously or sequentially to the chest wall tumors of the pleura and to measure the intensity of the light by using near- Thereby providing a tumor screening method.
상기한 바와 같은 목적을 달성하기 위해 본 발명의 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법은, 흉벽 종양의 위치까지 조사되는 근적외선을 체내에서 체외로 상기 흉벽을 통과해서 투영 입사시키는 단계와, 이를 검출하여 상기 흉벽 종양의 음영을 영상화하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하고 있다.In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a method for screening lung tumors using near-infrared rays, comprising: projecting near-infrared rays irradiated to a chest wall tumor through a chest wall through a body; And imaging the shadow of the tumor.
또 상기 근적외선의 투영 입사 단계에서 흉벽 종양의 위치까지 삽입되는 광섬유를 통해 상기 근적외선을 조사하고, 투영 입사되는 상기 근적외선을 검출하는 단계에서 근적외선 검출 카메라에 의해 검출하는 것이 바람직하다.In addition, it is preferable that the near-infrared ray camera irradiates the near-infrared rays through the optical fiber inserted to the position of the chest wall tumor in the projection of the near-infrared rays, and detects the near-infrared rays in the projection.
또 상기 광섬유의 삽입 이후 근적외선의 조사 단계 이전에, 기관지경의 작업채널로 내로 가이드 시스를 흉벽 종양의 위치까지 삽입하는 단계를 더 포함하여, 상기 가이드 시스 내로 광섬유를 삽입하는 것이 바람직하다.In addition, it is preferable to insert the optical fiber into the guide sheath, further comprising inserting the guide sheath into the working channel of the bronchoscope to the position of the chest wall tumor before the irradiation of the near infrared rays after the insertion of the optical fiber.
또 상기 근적외선은 780∼2000nm 영역 파장대의 근적외선인 것이 바람직하다.Further, the near-infrared rays are preferably near-infrared rays in the wavelength region of 780 to 2000 nm.
또 상기 근적외선의 조사 단계 이전에, 형광염료를 혈관에 주입하는 단계를 더 포함하여, 상기 형광염료가 흉벽 종양 주변의 미성숙 혈관에서 누출되면서 상기 ??벽 종양에 침착되는 것을 통해, 상기 근적외선의 조사로 형광을 방출하는 흉벽 종양의 신생혈관을 영상화하는 것을 다른 특징으로 하고 있다.Further, it is preferable that the method further comprises a step of injecting a fluorescent dye into a blood vessel prior to the step of irradiating near-infrared rays, wherein the fluorescent dye leaks from immature blood vessels around the chest wall tumors and is deposited on the wall tumor, , Which is characterized by the imaging of new blood vessels of chest wall tumors that emit fluorescence.
또 상기 형광염료는 인도시아닌 그린(Indocyanine green:ICG)인 것이 바람직하다.The fluorescent dye is preferably indocyanine green (ICG).
또 상기 근적외선 검출 카메라의 전면에 배치되는 방사 필터를 더 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.And a radiation filter disposed on the front surface of the near-infrared ray detecting camera.
또 상기 근적외선 광원 전면에 배치되는 여기 필터를 더 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.And an excitation filter disposed on the front surface of the near-infrared light source.
또 상기 근적외선은 서로 다른 다수의 파장대의 근적외선으로 조사되어, 흉벽을 통과한 각각의 근적외선의 빛의 세기를 측정하거나 영상화하여 흡수도의 차이를 통해 흉벽 종양의 유무를 확인하는 것을 또 다른 특징으로 하고 있다.Further, the near-infrared rays are irradiated with near-infrared rays of a plurality of different wavelength ranges, and the intensity of light of each of the near-infrared rays passing through the chest wall is measured or imaged to confirm the presence or absence of a chest wall tumor through the difference in absorbency have.
또 상기한 흡수도의 차이를 통해 흉벽 종양의 유무를 확인하는 것은 분광기나 하이퍼스펙트럼 카메라에 의해 수행되는 것이 바람직하다.In addition, it is preferable that the presence of the chest wall tumor is confirmed by the difference in absorbency by the spectroscope or the hyper-spectral camera.
본 발명의 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법에 의하면, 흉벽 종양으로써 악성종피종을 조기 진단하기 위해서 석면 노출 전력이 있는 고위험군에 대하여 정기적으로 스크리닝을 할 필요가 있는데, 본 발명에 의한 스크리닝 방법으로 악성중피종의 조기 진단이 가능해지는 효과가 있다.According to the present invention, it is necessary to regularly screen a high-risk group having asbestos exposure power for early diagnosis of malignant hereditary species as a chest wall tumor. In the screening method according to the present invention, malignant mesothelioma It is possible to perform early diagnosis.
도 1은 벽측 흉막(parietal pleura)과 장측 흉막(visceral pleura)으로 구성되는 흉막을 보여주는 해부이미지
도 2는 PET/CT에서는 정상소견 결과를 보였지만 흉강경(thoracoscopy)을 사용해서는 악성중피종임의 확진을 보여주는 PET/CT 사진 및 내시경 사진 (Roca E, Laroumagne S, Vandemoortele T, Berdah S, Dutau H, Maldonado F, Astoul P., "18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography fused imaging in malignant mesothelioma patients: looking from outside is not enough", Lung Cancer. 2013 Feb;79(2):187-90. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.10.017. Epub 2012 Dec 1.)
도 3은 본 발명의 제1 실시예에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 보여주는 개념도
도 4는 상기 도 3의 주요부 확대도
도 5는 본 발명의 제2 실시예에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 보여주는 개념도
도 6은 본 발명의 제3 실시예에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 보여주는 개념도
도 7은 본 발명에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 동물모델에 적용한 예
도 8은 본 발명에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 동물모델에 적용하여 정상 흉벽을 나타낸 예를 보여주는 이미지
도 9는 본 발명에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 동물모델에 적용하여 흉벽 종양을 나타낸 예를 보여주는 이미지Figure 1 shows an anatomical image showing a pleura consisting of a parietal pleura and a visceral pleura.
Figure 2 shows normal findings on PET / CT. However, PET / CT and endoscopic photographs (Roca E, Laroumagne S, Vandemoortele T, Berdah S, Dutau H, Maldonado F , Astoul P., "18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography / computed tomography fused imaging in malignant mesothelioma patients: Lung cancer" 2013 Feb; 79 (2): 187 -90. Doi: 10.1016 / j.lungcan.2012.10.017. Epub 2012 Dec 1.)
FIG. 3 is a conceptual diagram showing a lung tumor screening method using near-infrared rays according to the first embodiment of the present invention
4 is an enlarged view of the main part of Fig. 3
5 is a conceptual diagram showing a lung tumor screening method using near-infrared rays according to a second embodiment of the present invention
6 is a conceptual diagram showing a lung tumor screening method using near-infrared rays according to a third embodiment of the present invention
FIG. 7 shows an example of applying a lung tumor screening method using near-infrared rays to an animal model according to the present invention
8 is an image showing an example of a normal chest wall by applying a lung tumor screening method using near-infrared rays according to the present invention to an animal model
9 is an image showing an example of a chest wall tumor by applying a lung tumor screening method using near-infrared rays according to the present invention to an animal model
이하, 본 발명에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법의 바람직한 실시예를 첨부한 도면을 참조로 하여 상세히 설명한다. 본 발명은 이하에서 개시되는 실시예에 한정되는 것이 아니라 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 구현될 수 있으며, 단지 본 실시예는 본 발명의 개시가 완전하도록 하며 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 발명의 범주를 완전하게 알려주기 위하여 제공되는 것이다.Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of a lung tumor screening method using near-infrared rays according to the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. It is to be understood that the present invention is not limited to the disclosed embodiments, but may be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, It is provided to inform.
도 3은 본 발명의 제1 실시예에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 보여주는 개념도이고, 도 4는 상기 도 3의 주요부 확대도를 도시한 것이다. FIG. 3 is a conceptual view showing a lung tumor screening method using near-infrared rays according to the first embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 4 is an enlarged view of the main part of FIG.
본 발명의 제1 실시예에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법은, 흉벽 종양을 간단히 스크리닝(screening)하여 진단하기 위해 근적외선을 이용한 투영법을 사용하여 흉벽 종양의 영상을 획득하는 방법을 제시한 것이다. 근적외선은 780∼2000nm 영역의 파장을 가진 전자기파로서 조직 내 투과도가 높아 생체진단용으로 흔히 사용되고 있다.The near-infrared ray lung tumor screening method according to the first embodiment of the present invention proposes a method of acquiring an image of a chest wall tumor using a projection method using near-infrared rays to simply diagnose screening of chest wall tumors. Near-infrared rays are electromagnetic waves having wavelengths in the range of 780 to 2000 nm, and have high permeability in tissues and are often used for biomedical diagnosis.
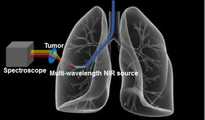
이러한 근적외선 투영법에 의한 흉벽 종양의 스크리닝은 도 3에서 보는 바와 같이, 근적외선(NIR source)을 흉벽 종양(tumor)의 위치까지 조사하고, 조사된 근적외선이 체내에서 체외로 흉벽을 통과하여 투영 입사될 때, 이렇게 흉벽을 통과한 근적외선을 체외에 위치시킨 근적외선 검출 카메라(camera)로 검출하여 영상화하도록 한 것이다. 이때 근적외선을 검출한 영상에서 흉벽 종양의 음영이 상기 근적외선 검출 카메라에 의해 획득되어 상기 흉벽 종양의 유무 및 퍼짐 정도를 알 수 있게 된다.As shown in FIG. 3, the NIR source is irradiated to the site of the chest wall tumor. When the irradiated near-infrared ray is projected from the body through the chest wall and projected, , And the near infrared ray that has passed through the chest wall is detected and imaged by a near infrared ray camera located outside the body. At this time, the shade of the chest wall tumor in the near-infrared ray-detected image is acquired by the near-infrared ray detecting camera, so that the presence and spread of the chest wall tumor can be known.
상기 근적외선은 광섬유에 의해 흉벽 종양의 위치에 조사되는데, 도 4에서 보는 바와 같이, 기관지경(endoscope)의 작업 채널(working channel) 내로 가이드 시스(guide sheath)를 삽입하여 흉벽 종양이 있는 부분의 투영하고자 하는 위치를 정한 후, 상기 가이드 시스 내부로 광섬유를 삽입하여 상기 광섬유를 통해 근적외선을 흉벽 종양의 위치에 조사하고 체내에서 체외로 흉벽을 통과해서 투영 입사시키게 된다. 이렇게 흉벽을 통과한 근적외선은 상기한 바와 같은 과정을 거쳐 흉벽 종양의 유무 및 퍼짐정도를 확인하게 된다.As shown in FIG. 4, the guide sheath is inserted into a working channel of an endoscope, and the projection of the portion having the chest wall tumor is inserted into the working channel of the endoscope, The optical fiber is inserted into the guide sheath, and the near infrared rays are irradiated through the optical fiber to the site of the chest wall tumor and projected through the chest wall to the outside of the body. The near-infrared rays passing through the chest wall are checked for the presence and spread of chest wall tumors through the above-described process.
도 5는 본 발명의 제2 실시예에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 보여주는 개념도를 도시한 것이다.FIG. 5 is a conceptual diagram showing a lung tumor screening method using near-infrared rays according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명의 제2 실시예에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법은, 근적외선에 의해 형광을 방출하는 형광염료인 인도시아닌 그린(Indocyanine green:ICG)을 이용한 형광 이미징을 이용하는 방법을 제시한 것이다. 인도시아닌 그린(ICG)은 혈장 단백질에 쉽게 결합하여 혈관 이미징에 흔히 사용되고, 780nm의 빛을 최대로 흡수하여 820nm의 형광을 방출하는 특성이 있다.The method for screening lung tumors using near infrared rays according to the second embodiment of the present invention is a method of using fluorescence imaging using fluorescent dye Indocyanine green (ICG) that emits fluorescence by near infrared rays. Indocyanine green (ICG) binds readily to plasma proteins and is commonly used in vascular imaging, and has the property of absorbing maximum 780 nm light and emitting 820 nm fluorescence.
본 발명에서는 도 5에서 보는 바와 같이, 흉벽 종양이 진행되면 종양 주변에 신생혈관이 발생하게 되는데, 이런 경우에 상기 ICG와 같은 형광염료를 혈관으로 주입하여 흉벽 종양 주변의 미성숙 혈관에서 새어나온 형광염료가 상기 흉벽 종양에 침착되는 것을 이용하는 것으로, 상기한 바와 같이 흉벽 종양의 위치로 조사된 후 체내에서 체외로 통과하는 근적외선에 의해 형광을 방출하는 흉벽 종양의 신생혈관을 근적외선 검출 카메라로 영상화하여 상기 흉벽 종양의 유무와 퍼짐정도를 확인하게 된다. 이때 흉벽 종양으로부터 방출하는 형광을 영상화하기 위해 상기 근적외선 검출 카메라의 전면에는 820nm의 방사 필터(emission filter)를 배치하고 근적외선 광원 전면에는 780 nm의 여기 필터(excitation filter)를 배치하도록 한다.As shown in FIG. 5, when the chest wall tumor progresses, neovascularization occurs around the tumor. In such a case, a fluorescent dye such as ICG is injected into the blood vessel and the fluorescent dye leaking from the immature blood vessel around the chest wall tumor The neovascularization of a chest wall tumor which emits fluorescence by the near-infrared rays passing through the body in the body after being irradiated to the position of the chest wall tumor as described above is imaged by a near-infrared ray detection camera, The presence or absence of the tumor and the extent of spread. At this time, in order to image fluorescence emitted from the chest wall tumor, an 820 nm emission filter is arranged on the front face of the near-infrared ray camera and an excitation filter of 780 nm is arranged on the front face of the near-infrared light source.
본 발명의 제2 실시예에서 근적외선의 조사는 상기한 바와 같은 광섬유에 의해 이루어지며, 상기 광섬유가 작업채널의 가이드 시스 내로 삽입되어 흉벽 종양의 위치를 정하는 것은 상기한 바와 동일하다.In the second embodiment of the present invention, irradiation of the near-infrared rays is performed by the optical fiber as described above, and the optical fiber is inserted into the guide sheath of the working channel to position the chest wall tumor.
도 6은 본 발명의 제3 실시예에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 보여주는 개념도를 도시한 것이다.FIG. 6 is a conceptual diagram illustrating a lung tumor screening method using near-infrared rays according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
도 6에서 보는 바와 같이, 본 발명의 제3 실시예에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법은, 근적외선 대의 서로 다른 두 파장 또는 다수의 파장의 근적외선(Multi-wavelength NIR source)을 동시에 또는 순차적으로 상기한 바와 같은 내시경적 방법으로 조사한 후, 체내에서 체외로 흉벽을 통과한 각각의 근적외선 빛의 세기를 측정하거나 영상화하여 흡수도의 차이를 통하여 종양의 유무를 확인하는 근적외선 분광 방법을 제시한 것이다. 이때 상기 근적외선 빛의 세기를 측정하거나 영상화하여 흡수도를 차이를 구하는 것은 체외의 위치하고 있는 분광기(Spectroscope)나 하이퍼스펙트럼 카메라 (Hyperspectral camera)등의 근적외선 검출기에 의해 이루어진다.6, a method for screening lung tumors using near-infrared rays according to a third embodiment of the present invention includes the steps of simultaneously or sequentially applying two different wavelengths of a near-infrared ray band or a multi-wavelength NIR source of a plurality of wavelengths, The present invention proposes a near-infrared spectroscopy method for confirming the presence or absence of a tumor by measuring the intensity of near-infrared light passing through the chest wall in vitro, and measuring the intensity of the near-infrared light passing through the body. At this time, the intensity of the near-infrared light is measured or imaged to obtain a difference in absorbance by a near-infrared ray detector such as a spectroscope or a hyperspectral camera located outside the body.
도 7은 본 발명에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법을 동물모델에 적용한 것으로 내시경적 방법으로 체내에서 체외로 근적외선을 흉벽을 통과해서 투영 입사시키는 예를 보여주는 이미지이다.FIG. 7 is an image showing an example in which near infrared rays are projected through a chest wall and extruded in vitro from the body by an endoscopic method, using a near-infrared ray lung-based screening method according to the present invention.
도 7에서 보는 바와 같이, 동물 모델로 실험 토끼인 정상 뉴질랜드 백색가토를 이용하여 상기한 제1 실시예의 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법으로 흉벽 근적외선 투영법을 실시하여 나타낸 결과 이미지이다. 이 이미지에서 보면 적색으로 보이는 부분에서 상당량의 근적외선이 흉벽을 통과하여 외부로 투영되고 있음을 잘 알 수 있다.As shown in FIG. 7, the result is an image showing the chest wall near-infrared projection method using the near-infrared ray lung screening method of the first embodiment using the normal New Zealand white rabbit as the experimental animal as the animal model. In this image, it can be seen that a considerable amount of near-infrared rays are projected through the chest wall and projected to the outside in the red visible portion.
도 8은 뉴질랜드 백색가토의 정상 흉벽을 통과하여 투영되는 근적외선을 보여주는 이미지이며 도 9는 종양 흉벽을 통과하여 투영되는 근적외선을 보여주는 이미지이다.FIG. 8 is an image showing near infrared rays projected through the normal chest wall of New Zealand white rabbit; and FIG. 9 is an image showing near infrared rays projected through the tumor chest wall.
도 8과 도 9에서 보는 바와 같이, 정상 흉벽 투영이미지는 흉골을 따라 음영이 평행하게 발생하지만 종양 흉벽 투영이미지는 종양의 음영이 추가됨에 따라 어둡게 보이고 있음을 잘 알 수 있다.As can be seen from FIGS. 8 and 9, the normal chest wall projection image shows shadows parallel to the sternum but the tumor chest wall projection image is darker as the tumor shade is added.
이상과 같이 본 발명에 따른 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법에 대해서 예시한 도면을 참조로 하여 설명하였으나, 본 명세서에 개시된 실시예와 도면에 의해 본 발명이 한정되는 것은 아니며, 본 발명의 기술사상의 범위 내에서 당업자에 의해 다양한 변형이 이루어질 수 있음은 물론이다.As described above, the method for screening pulmonary tumor using near-infrared rays according to the present invention has been described with reference to the drawings. However, the present invention is not limited to the embodiments and drawings disclosed in the present specification, It is needless to say that various modifications can be made by those skilled in the art within the scope of the present invention.
Claims (9)
Translated fromKorean상기 근적외선의 투영 입사 단계에서 흉벽 종양의 위치까지 삽입되는 광섬유를 통해 상기 근적외선을 조사하고, 투영 입사되는 상기 근적외선을 검출하는 단계에서 근적외선 검출 카메라에 의해 검출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the near infrared rays are irradiated through an optical fiber inserted to the position of the chest wall tumor in the projecting step of the near infrared rays and the near infrared rays are detected by the near infrared ray camera in the step of detecting the near infrared rays projected into the projection, Way.
상기 광섬유의 삽입 이후 근적외선의 조사 단계 이전에, 기관지경의 작업채널로 내로 가이드 시스를 흉벽 종양의 위치까지 삽입하는 단계를 더 포함하여, 상기 가이드 시스 내로 광섬유를 삽입하는 것을 특징으로 하는 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법.3. The method of claim 2,
Further comprising the step of inserting the guide sheath into the working channel of the bronchoscope to the position of the chest wall tumor before the irradiation of the near infrared rays after the insertion of the optical fiber, wherein the optical fiber is inserted into the guide sheath Lung tumor screening method.
상기 근적외선은 780∼2000nm 영역 파장대의 근적외선인 것을 특징으로 하는 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the near-infrared rays are near-infrared rays in a wavelength range of 780 to 2000 nm.
상기 근적외선의 조사 단계 이전에, 형광염료를 혈관에 주입하는 단계를 더 포함하여, 상기 형광염료가 흉벽 종양 주변의 미성숙 혈관에서 누출되면서 상기 흉벽 종양에 침착되는 것을 통해, 상기 근적외선의 조사로 형광을 방출하는 흉벽 종양의 신생혈관을 영상화하는 것을 특징으로 하는 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법.The method according to claim 3 or 4,
The method of claim 1, further comprising injecting a fluorescent dye into a blood vessel prior to the step of irradiating near infrared rays, wherein the fluorescent dye leaks from immature blood vessels around the chest wall tumor and is deposited on the chest wall tumor, A method for screening pulmonary tumors using near-infrared light, characterized by imaging neovascularization of a chest wall tumor releasing.
상기 형광염료는 인도시아닌 그린(Indocyanine green:ICG)인 것을 특징으로 하는 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법.6. The method of claim 5,
Wherein the fluorescent dye is indocyanine green (ICG).
상기 근적외선 검출 카메라의 전면에 배치되는 방사 필터와 근적외선 광원 전면에 배치되는 여기 필터를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법.6. The method of claim 5,
Further comprising a radiation filter disposed on a front surface of the near-infrared ray detecting camera and an excitation filter disposed on a front surface of the near-infrared ray light source.
상기 근적외선은 서로 다른 다수의 파장대의 근적외선으로 조사되어, 흉벽을 통과한 각각의 근적외선의 빛의 세기를 측정하거나 영상화하여 흡수도의 차이를 통해 흉벽 종양의 유무를 확인하는 것을 특징으로 하는 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the near-infrared rays are irradiated with near-infrared rays of a plurality of different wavelength ranges, and the intensity of light of each of the near-infrared rays passing through the chest wall is measured or imaged to confirm presence or absence of chest wall tumors through a difference in absorption degree. Lung tumor screening method.
상기한 흡수도의 차이를 통해 흉벽 종양의 유무를 확인하는 것은 분광기에 의해 수행되는 것을 특징으로 하는 근적외선을 이용한 폐종양 스크리닝 방법.9. The method of claim 8,
Wherein the presence or absence of the chest wall tumor is confirmed by the difference in absorbency by the spectroscope.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160123392AKR101855395B1 (en) | 2016-09-26 | 2016-09-26 | Screening method of lung tumor using near-infrared light |
| PCT/KR2017/008771WO2018056574A1 (en) | 2016-09-26 | 2017-08-11 | Pulmonary tumor screening method using near infrared rays |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160123392AKR101855395B1 (en) | 2016-09-26 | 2016-09-26 | Screening method of lung tumor using near-infrared light |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20180033878A KR20180033878A (en) | 2018-04-04 |
| KR101855395B1true KR101855395B1 (en) | 2018-05-09 |
Family
ID=61690475
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160123392AExpired - Fee RelatedKR101855395B1 (en) | 2016-09-26 | 2016-09-26 | Screening method of lung tumor using near-infrared light |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101855395B1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2018056574A1 (en) |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101460908B1 (en) | 2013-08-09 | 2014-11-17 | 서울여자대학교 산학협력단 | Lung tumor tracking system and the method in 4D CT images |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE4445065A1 (en)* | 1994-12-07 | 1996-06-13 | Diagnostikforschung Inst | Methods for in-vivo diagnostics using NIR radiation |
| WO2007016048A2 (en)* | 2005-07-27 | 2007-02-08 | University Of Massachusetts Lowell | Infrared scanner for biological applications |
| CN102770071B (en)* | 2009-12-15 | 2015-03-25 | 爱默蕾大学 | Systems and methods for providing real-time anatomical guidance during diagnostic or therapeutic procedures |
| US20130211246A1 (en)* | 2011-12-27 | 2013-08-15 | Vinod PARASHER | METHODS AND DEVICES FOR GASTROINTESTINAL SURGICAL PROCEDURES USING NEAR INFRARED (nIR) IMAGING TECHNIQUES |
| US10517483B2 (en)* | 2012-12-05 | 2019-12-31 | Accuvein, Inc. | System for detecting fluorescence and projecting a representative image |
- 2016
- 2016-09-26KRKR1020160123392Apatent/KR101855395B1/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
- 2017
- 2017-08-11WOPCT/KR2017/008771patent/WO2018056574A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101460908B1 (en) | 2013-08-09 | 2014-11-17 | 서울여자대학교 산학협력단 | Lung tumor tracking system and the method in 4D CT images |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20180033878A (en) | 2018-04-04 |
| WO2018056574A1 (en) | 2018-03-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10314490B2 (en) | Method and device for multi-spectral photonic imaging | |
| EP1824379B1 (en) | System and method for normalized fluorescence or bioluminescence imaging | |
| JP2024037188A (en) | Devices, systems, and methods for tumor visualization and removal | |
| Grootendorst et al. | Cerenkov luminescence imaging (CLI) for image-guided cancer surgery | |
| CA2373299C (en) | Laser imaging apparatus using biomedical markers that bind to cancer cells | |
| JP5406205B2 (en) | Method for detecting the presence of heterogeneity inside a turbid medium and apparatus for imaging the inside of a turbid medium | |
| US20160263402A1 (en) | Cherenkov imaging systems and methods to monitor beam profiles and radiation dose while avoiding interference from room lighting | |
| US10413619B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| US20150359525A1 (en) | Optical guided vacuum assisted biopsy device | |
| KR101710902B1 (en) | An astral lamp and astral lamp system about projection for near infrared fluoresence diagnosis | |
| Boykoff et al. | Current clinical applications of Cerenkov luminescence for intraoperative molecular imaging | |
| Sterkenburg et al. | Standardization and implementation of fluorescence molecular endoscopy in the clinic | |
| Fernandes et al. | Fibre-based fluorescence-lifetime imaging microscopy: a real-time biopsy guidance tool for suspected lung cancer | |
| WO2013111053A1 (en) | An apparatus for optical analysis of an associated tissue | |
| Leiloglou et al. | Tissue texture extraction in indocyanine green fluorescence imaging for breast-conserving surgery | |
| KR101855395B1 (en) | Screening method of lung tumor using near-infrared light | |
| Kang et al. | A feasibility study of an integrated NIR/gamma/visible imaging system for endoscopic sentinel lymph node mapping | |
| Park et al. | Ultra-low-dose intraoperative X-ray imager for minimally invasive surgery: a pilot imaging study | |
| KR101630539B1 (en) | Apparatus and method of registering multiple fluorescent images in real time for surgical microscope | |
| KR102392593B1 (en) | Multi-modal endoscopy system comprising radiation image | |
| KR101865657B1 (en) | Diagnostic apparatus for laryngeal cancer detection | |
| ř í Votruba et al. | Non-Contrast Radiation Free NIR Lung Imaging | |
| Patel | Assessment of optical transmission and image contrast at infrared wavelengths using tissue simulating phantoms and biological tissues | |
| Koenig et al. | Validation of an XCT/fDOT System on Mice | |
| Kuo et al. | In vivo bioluminescence tomography using multi-spectral and multiple-perspective image data |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| R15-X000 | Change to inventor requested | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R15-oth-X000 | |
| R16-X000 | Change to inventor recorded | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R16-oth-X000 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | St.27 status event code:A-1-1-Q10-Q12-nap-PG1501 | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Fee payment year number:1 St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Fee payment year number:4 St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Fee payment year number:5 St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Fee payment year number:6 St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | Not in force date:20240501 Payment event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U13-oth-PC1903 | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | Ip right cessation event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE Not in force date:20240501 St.27 status event code:N-4-6-H10-H13-oth-PC1903 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 |