KR101800676B1 - Methane oxidation catalyst and method for oxidation of methane using a catalyst - Google Patents
Methane oxidation catalyst and method for oxidation of methane using a catalystDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101800676B1 KR101800676B1KR1020170110966AKR20170110966AKR101800676B1KR 101800676 B1KR101800676 B1KR 101800676B1KR 1020170110966 AKR1020170110966 AKR 1020170110966AKR 20170110966 AKR20170110966 AKR 20170110966AKR 101800676 B1KR101800676 B1KR 101800676B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- methane
- catalyst
- support
- methane oxidation
- present
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/34—Chemical or biological purification of waste gases
- B01D53/74—General processes for purification of waste gases; Apparatus or devices specially adapted therefor
- B01D53/86—Catalytic processes
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J29/00—Catalysts comprising molecular sieves
- B01J29/04—Catalysts comprising molecular sieves having base-exchange properties, e.g. crystalline zeolites
- B01J29/06—Crystalline aluminosilicate zeolites; Isomorphous compounds thereof
- B01J35/1061—
- B01J35/1066—
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J35/00—Catalysts, in general, characterised by their form or physical properties
- B01J35/60—Catalysts, in general, characterised by their form or physical properties characterised by their surface properties or porosity
- B01J35/64—Pore diameter
- B01J35/647—2-50 nm
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J35/00—Catalysts, in general, characterised by their form or physical properties
- B01J35/60—Catalysts, in general, characterised by their form or physical properties characterised by their surface properties or porosity
- B01J35/64—Pore diameter
- B01J35/651—50-500 nm
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Nanotechnology (AREA)
- Catalysts (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 자동차, 선박 등에서 발생하는 배기가스에 포함되어 있는 메탄을 산화시켜 제거하기 위한 제조방법에 관한 것으로서, 더 상세하게는 수증기가 공존하는 배기가스 조건에서도, 미연소 메탄을 400℃ 보다 낮은 저온에서 효율적으로 산화시켜 제거할 수 있는 메탄산화촉매 및 메탄의 산화 방법에 대한 것이다.BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates to a method for oxidizing and removing methane contained in exhaust gas generated from an automobile, a ship, and the like, and more particularly, And a method of oxidizing methane.
자동차, 선박 등에서 발생하는 배기가스에는 환경오염 물질인 메탄(CH4, methane)이 포함되어 있다. 메탄은 매우 안정한 구성으로서, 메탄을 선택적으로 산화시키기 위해서는 450℃ 이상의 높은 반응온도가 요구된다. 백금(Pt), 팔라듐(Pd), 코발트(Co), 로듐(Rh), 페르브스카이트(perovskite) 구조의 산화물 등과 같이 극히 제한된 금속 및 산화물 촉매들만이 메탄 산화반응에 활성을 나타내는 것으로 알려져 있다.Emissions from automobiles and ships contain methane (CH4 , methane), an environmental pollutant. Methane is a very stable constitution, and a high reaction temperature of 450 DEG C or more is required to selectively oxidize methane. It is known that only very limited metal and oxide catalysts, such as platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd), cobalt (Co), rhodium (Rh), perovskite structure oxides, .
특히 메탄을 산화제거하기 위해서는 백금(Pt), 팔라듐(Pd) 등이 담지된 귀금속 촉매가 매우 효과적이며, 그 활용 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있다. 이들 활성 귀금속을 알루미나(Al2O3), 실리카(Silica), 지르코니아(zirconia), 티타늄(Ti), 제올라이트(zeolite) 등과 같은 여러 가지 담체에 담지시켜 사용하고 있으나, 담체에 따라 반응온도 및 활성에 큰 차이를 나타내고 있다.Particularly, in order to oxidize and remove methane, noble metal catalysts carrying platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd), etc. are very effective, and their utilization studies are actively under way. These active noble metals are supported on various carriers such as alumina (Al2 O3 ), silica (silica), zirconia, titanium (Ti), zeolite, etc. However, .
즉, 알루미나, 실리카, 지르코니아, 티타늄 등과 같이 미세세공을 갖지 않는 담체에 담지된 촉매들의 경우 500℃ 이상의 높은 반응 온도가 요구됨과 동시에 담지된 활성 귀금속 촉매의 소결(sintering)이 일어나 반응활성 저하가 일어난다.That is, catalysts supported on a carrier having no fine pores such as alumina, silica, zirconia, titanium and the like require a high reaction temperature of 500 ° C or higher and sintering of the supported active noble metal catalyst, .
반면에, 일정한 크기의 미세세공을 갖는 제올라이트에 담지할 경우는 높은 메탄 산화활성을 갖는 우수한 산화특성을 나타낸다. 위에 언급한 귀금속 촉매 이외에도 열적으로 안정한 페르브스카이트 구조의 금속산화수증기 촉매가 사용되기도 하나, 메탄의 완전산화를 위해서는 550℃ 이상의 온도가 요구되고 있다.On the other hand, when supported on a zeolite having micropores of a certain size, it exhibits excellent oxidation characteristics having a high methane oxidation activity. In addition to the above-mentioned noble metal catalysts, a thermally stable perovskite-structured metal oxide vapor catalyst may be used, but a temperature of 550 ° C or more is required for complete oxidation of methane.
또한, 팔라듐(Pd)에 세륨(Ce), 란타륨(La), 네오디뮴(Nd), 사마륨(Sm) 등이 첨가된 이성분계 촉매를 알루미나, 실리카, 지르코니아 또는 타이타니아에 담지시킨 메탄 산화촉매를 단일담체(monolith)에 코팅하여 사용하였다. 이들 외에도, 금속산화수증기 촉매를 600℃ 내지 1400℃에서 가스터빈이나 보일러 등에서 배출되는 메탄 산화에 적용하였으며, 최근에는, 팔라듐(Pd)에 알카리 금속 또는 알카리 토금속(세륨(Ce), 란탄니아(La), 나이오비움(Nd) 그리고 사마리움(Sm)) 등이 첨가된 이성분계 금속산화수증기 촉매의 경우 메탄 산화반응에 매우 높은 활성을 나타내었다.A methane oxidation catalyst in which a binary catalyst having cerium (Ce), lanthanum (La), neodymium (Nd), and samarium (Sm) added to palladium (Pd) is supported on alumina, silica, zirconia or titania Coated on a monolith. In addition to these, a metal oxide vapor catalyst is applied to methane oxidation discharged from a gas turbine or a boiler at 600 ° C. to 1400 ° C. Recently, an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal such as cerium (Ce), lanthanum ), Niobium (Nd), and Samarium (Sm)) were added to the methane oxidation reaction.
상술한 바와 같이, 귀금속을 담지한 메탄 산화촉매들은 고온 또는 고압의 메탄 산화에는 효과적이나, 400℃ 이하의 저온에서 존재하는 메탄 산화반응에의 적용에는 한계가 있으며, 특히, 수증기가 공존하는 배기가스 조건에서도 낮은 온도에서 메탄을 산화시키는 것은 매우 어려운 것으로 알려져 있다.As described above, the noble metal-supported methane oxidation catalysts are effective for methane oxidation at a high temperature or a high pressure. However, application to the methane oxidation reaction at a low temperature of 400 ° C or lower is limited. Particularly, Oxidation of methane at low temperatures is known to be very difficult.
본 발명은 상기와 같은 문제점을 포함하여 여러 문제점들을 해결하기 위한 것으로서, 배기가스와 같이 수증기와 메탄이 공존하는 혼합가스 조건에서도, 종래에 비해 더 낮은 온도에서 미연소 메탄을 효율적으로 산화시킬 수 있는 방법 및 메탄산화촉매의 제공을 목적으로 한다. 전술한 과제는 예시적으로 제시되었고, 본 발명의 범위가 이러한 과제에 의해서 제한되는 것은 아니다.The present invention has been made to solve the above problems and it is an object of the present invention to provide a method of efficiently oxidizing unburned methane at a lower temperature than a conventional method even in a mixed gas condition in which steam and methane coexist, And to provide a methane oxidation catalyst. The foregoing problems have been presented by way of example and the scope of the present invention is not limited by these problems.
본 발명의 일 관점에 따르면, 산소, 수증기 및 메탄을 포함하는 혼합가스 내에서 촉매를 이용하여 상기 메탄을 산화시키는 방법이 제공된다. 이때 상기 촉매는 소수성 표면을 가지는 지지체 및 상기 지지체의 적어도 일부의 표면에 존재하는 활성촉매금속을 포함하되, 상기 메탄의 산화반응이 일어나는 온도는 300℃ 내지 400℃ 일 수 있다.According to one aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method for oxidizing methane using a catalyst in a mixed gas comprising oxygen, water vapor and methane. Wherein the catalyst comprises a support having a hydrophobic surface and an active catalyst metal present on the surface of at least a portion of the support, wherein the temperature at which the oxidation reaction of the methane occurs may be from 300 ° C to 400 ° C.
상기 촉매를 이용한 메탄의 산화 방법에 있어서, 상기 지지체는 Si과 Al의 몰 비율(Si/Al)이 10보다 크고 50보다 작은 알루미노실리케이트 제올라이트를 포함할 수 있다.In the method for the oxidation of methane using the catalyst, the support may include aluminosilicate zeolite having Si / Al molar ratio (Si / Al) of more than 10 and less than 50.
상기 촉매를 이용한 메탄의 산화 방법에 있어서, 상기 활성촉매금속은 상기 지지체의 적어도 일부에 이온교환되어 존재할 수 있다.In the method for the oxidation of methane using the catalyst, the active catalyst metal may be ion-exchanged to at least a portion of the support.
상기 촉매를 이용한 메탄의 산화 방법에 있어서, 상기 지지체는 규칙기공을 가지는 다공성 지지체일 수 있으며, 상기 다공성 지지체는 0보다 크고 10nm 이하의 평균 기공 크기를 가질 수 있다.In the method of oxidizing methane using the catalyst, the support may be a porous support having regular pores, and the porous support may have an average pore size of greater than 0 and less than 10 nm.
상기 촉매를 이용한 메탄의 산화 방법에 있어서, 상기 메탄의 전환율이 50%가 되는 온도범위가 300℃ 내지 400℃일 수 있다.In the methane oxidation method using the catalyst, the temperature range in which the conversion of methane is 50% may be 300 ° C to 400 ° C.
상기 촉매를 이용한 메탄의 산화 방법에 있어서, 상기 혼합가스 내에서의 수증기는 1 중량% 내지 20 중량% 범위로 존재할 수 있다.In the method of oxidizing methane using the catalyst, the water vapor in the mixed gas may be present in the range of 1 wt% to 20 wt%.
본 발명의 다른 관점에 따르면, 산소, 수증기 및 메탄을 포함하는 혼합가스 내에서 상기 메탄을 산화시키는 촉매가 제공된다. 상기 촉매는 소수성 표면을 가지는 지지체; 및 상기 지지체의 적어도 일부의 표면에 존재하는 활성촉매금속;을 포함을 포함하고, 상기 지지체는 Si과 Al의 몰 비율(Si/Al)이 10보다 크고 50보다 작은 알루미노실리케이트 제올라이트를 포함하며, 상기 활성촉매금속은 상기 지지체의 적어도 일부에 이온교환 되어 존재하고, 상기 메탄의 전환율이 90%가 되는 온도범위가 300℃ 내지 400℃일 수 있다.According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a catalyst for oxidizing methane in a mixed gas comprising oxygen, water vapor and methane. The catalyst comprising: a support having a hydrophobic surface; And an active catalyst metal present on at least a portion of the surface of the support, wherein the support comprises an aluminosilicate zeolite having a Si / Al molar ratio (Si / Al) greater than 10 and less than 50, The active catalyst metal is present in ion exchange on at least a portion of the support, and the temperature range at which the conversion of methane is 90% may be 300 ° C to 400 ° C.
상기 메탄산화촉매에 있어서, 상기 지지체는 규칙기공을 가지는 다공성 지지체이며, 상기 지지체는 0보다 크고 10nm 이하의 기공 크기를 가질 수 있다.In the methane oxidation catalyst, the support is a porous support having regular pores, and the support may have a pore size of greater than 0 and 10 nm or less.
상기한 바와 같이 이루어진 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 수증기가 공존하는 혼합가스 조건에서도, 미연소 메탄을 효율적으로 산화시킬 수 있으며, 메탄을 효율적으로 산화할 수 있는 메탄산화촉매 및 촉매를 이용한 메탄의 산화방법을 제공할 수 있다. 물론 이러한 효과에 의해 본 발명의 범위가 한정되는 것은 아니다.According to one embodiment of the present invention, the unburned methane can be efficiently oxidized even under a mixed gas condition in which water vapor coexists, and the methane oxidation catalyst capable of efficiently oxidizing methane and the methane oxidation catalyst Can be provided. Of course, the scope of the present invention is not limited by these effects.
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 메탄산화촉매 구조체를 개략적으로 도해하는 도면이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 메탄산화촉매의 촉매 부착특성을 측정한 결과이다.
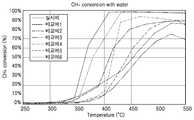
도 3은 본 발명의 실시예 및 비교예에 따른 수증기가 없는 상태에서 메탄산화촉매를 이용한 메탄 전환율 측정 결과이다.
도 4는 본 발명의 실시예 및 비교예에 따른 수증기가 있는 상태에서 메탄산화촉매를 이용한 메탄 전환율 측정 결과이다.1 is a schematic illustration of a methane oxidation catalyst structure according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a graph illustrating the results of measurement of catalyst adhesion characteristics of a methane oxidation catalyst according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 3 shows the results of methane conversion measurement using a methane oxidation catalyst in the absence of steam in Examples and Comparative Examples of the present invention.
4 is a graph showing the results of methane conversion measurement using a methane oxidation catalyst in the presence of water vapor according to Examples and Comparative Examples of the present invention.
이하, 첨부된 도면들을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예를 상세히 설명하면 다음과 같다. 그러나 본 발명은 이하에서 개시되는 실시예에 한정되는 것이 아니라 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 구현될 수 있는 것으로, 이하의 실시예는 본 발명의 개시가 완전하도록 하며, 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 발명의 범주를 완전하게 알려주기 위해 제공되는 것이다. 또한 설명의 편의를 위하여 도면에서는 구성 요소들이 그 크기가 과장 또는 축소될 수 있다.Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. It should be understood, however, that the invention is not limited to the disclosed embodiments, but may be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, Is provided to fully inform the user. Also, for convenience of explanation, the components may be exaggerated or reduced in size.
일반적으로 천연가스 엔진을 사용하는 자동차, 선박 등에서 발생하는 배기가스에 포함되어 있는 환경오염 물질을 제거하기 위해서, 귀금속을 이용한 촉매를 사용한다. 상기 환경오염 물질 중 대표적인 물질로는 메탄(CH4)이 있다. 메탄은 매우 안정한 물질로서, 저온에서 처리가 어려우며, 고온에서 산화촉매들을 이용하여 메탄을 제거하고 있다. 예를 들어, 귀금속을 담지한 메탄 산화촉매들은 고온 또는 고압의 메탄 산화에는 효과적이다. 그러나, 자동차, 선박 등에서 발생하는 배기가스는 400℃ 이하로 적용 온도가 낮아 종래의 촉매로는 메탄 산화반응에의 적용에는 한계가 있다. 이에 저온 촉매와 담체 소재 기술의 고성능화 고기능화가 필수적이다. 특히, 수증기가 공존하는 배기가스 조건에서도 낮은 온도에서 메탄을 산화시키는 촉매를 제조하는 것은 매우 어렵다.Generally, in order to remove environmental pollutants contained in exhaust gas generated from automobiles and ships using natural gas engines, a catalyst using a noble metal is used. Methane (CH4 ) is a representative example of the environmental pollutants. Methane is a very stable material that is difficult to treat at low temperatures and is removing methane using oxidation catalysts at high temperatures. For example, noble metal supported methane oxidation catalysts are effective for high temperature or high pressure methane oxidation. However, the exhaust gas generated from automobiles, ships, etc. has a low application temperature of 400 ° C or lower, which limits application to methane oxidation reaction with conventional catalysts. Therefore, high performance and high functionalization of low temperature catalyst and carrier material technology are essential. In particular, it is very difficult to produce a catalyst that oxidizes methane at low temperatures even under exhaust gas conditions where water vapor coexists.
이와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위해서, 본 발명에서는 지지체 표면이 소수성을 가지는 메탄산화촉매를 이용하여 종래에 비해 더 저온에서 메탄을 산화시키는 방법을 제공한다.In order to solve such problems, the present invention provides a method of oxidizing methane at a lower temperature than the conventional method using a methane oxidation catalyst having a hydrophobic surface on a support.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 메탄산화촉매는 지지체 및 상기 지지체의 적어도 일부의 표면에 활성촉매금속을 포함할 수 있다. 상기 지지체는 표면에 소수성을 가지며, 규칙기공을 갖는 다공성 지지체일 수 있다. 상기 다공성 지지체는 0보다 크고 10nm 이하의 평균 기공 크기를 가질 수 있다.The methane oxidation catalyst according to an embodiment of the present invention may include an active catalyst metal on the surface of at least a part of the support and the support. The support may be a porous support having hydrophobicity on the surface and having regular pores. The porous support may have an average pore size of greater than 0 and 10 nm or less.
일 예로서 상기 지지체는 표면의 특성이 소수성을 가지는 알루미노실리케이트 제올라이트(aluminosilicate zeolite)일 수 있다. 이러한 소수성을 가지는 알루미노실리케이트 제올라이트는 Si과 Al의 몰 비율(molar ratio) 즉, Si/Al(Si의 몰수를 Al의 몰수로 나눈 값)가 10 보다 더 크고, 50보다 작은 값을 가질 수 있다.As an example, the support may be an aluminosilicate zeolite whose surface characteristics are hydrophobic. The aluminosilicate zeolite having such hydrophobicity may have a molar ratio of Si to Al, that is, Si / Al (the number of moles of Si divided by the number of moles of Al) of more than 10 and less than 50 .
상기 알루미노실리케이트 제올라이트 이외에도 알루미나(Al2O3), 이산화규소(SiO2), 산화주석(SnO2) 및 산화티탄(TiO2) 등 다양한 물질이 사용될 수 있다. 이 중에서도 바람직하게는 산에 강하고 소수성의 성질을 갖는 재료를 사용할 수 있다.Various materials such as alumina (Al2 O3 ), silicon dioxide (SiO2 ), tin oxide (SnO2 ) and titanium oxide (TiO2 ) may be used in addition to the aluminosilicate zeolite. Among these, a material having a strong acid-base and hydrophobic nature can be used.
한편, 상기 활성촉매금속은 상기 지지체의 적어도 일부에 이온교환 되어 존재할 수 있다. 상기 활성촉매금속은 메탄산화 반응을 더욱 활성화하는 물질로서, 예를 들어, 팔라듐(Pd)과 백금(Pt)을 촉매로 사용할 수 있다. 팔라듐(Pd)의 경우, 메탄산화 반응에 가장 많이 사용되는 촉매재료 중의 하나로서 수증기가 없는 분위기에서는 400℃ 이하의 저온에서 매우 높은 메탄 전환율을 가진다.On the other hand, the active catalyst metal may be ion-exchanged with at least a part of the support. The active catalyst metal further activates the methane oxidation reaction. For example, palladium (Pd) and platinum (Pt) can be used as a catalyst. In the case of palladium (Pd), it is one of the most frequently used catalyst materials for methane oxidation reaction, and it has a very high methane conversion rate at a low temperature of 400 ° C or less in an atmosphere free of steam.
백금(Pt) 촉매의 경우, 팔라듐(Pd) 촉매와 비교하여 저온에서의 활성이 낮지만, 일산화탄소(CO)나 일산화질소(NO) 등의 물질에 의한 내피독성이 강하다. 따라서, 400℃ 이하의 저온에서 반응하는 촉매재료로는 팔라듐(Pd)을 주로 사용할 수 있으나, 경우에 따라 팔라듐(Pd)과 백금(Pt)을 혼합하여 사용할 수도 있다.In the case of the platinum (Pt) catalyst, the activity at low temperature is lower than that of the palladium (Pd) catalyst, but the endotoxicity due to the substances such as carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen monoxide (NO) is strong. Therefore, palladium (Pd) may be mainly used as a catalyst material reacting at a low temperature of 400 ° C or less, but palladium (Pd) and platinum (Pt) may be mixed in some cases.
본원 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 메탄산화촉매는 지지체의 적어도 일부에 이온교환법(ion exchange)을 이용하여 활성촉매금속을 형성한 것이다. 활성촉매금속을 지지체의 적어도 일부에 형성하는 단계는, 촉매금속의 염을 출발 물질로 이용하며, 상기 염을 용해시킨 수용액과 지지체 재료를 혼합해서 가열 교반하고, 지지체 내의 양이온과 상기 촉매금속을 이온교환함으로써 금속이온을 형성하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다. 여기서, 상기 이온교환법은 이미 공지된 기술로써 이에 대한 상세한 설명은 생략한다.The methane oxidation catalyst according to an embodiment of the present invention is formed by forming an active catalyst metal on at least a part of a support using an ion exchange method. The step of forming the active catalyst metal on at least a part of the support comprises the steps of using a salt of the catalyst metal as a starting material and mixing the solution and the support material with the salt dissolved therein, And forming metal ions by exchange. Here, the ion exchange method is a well-known technique, and a detailed description thereof will be omitted.
또한, 본 발명의 다른 실시예에 따른 메탄산화촉매는 볼밀(ball mill)을 이용하여 활성촉매금속을 슬러리(slurry)로 제조하고, 상기 슬러리를 모노리스(monolith) 담체에 코팅하여 제조할 수도 있다. 이렇게 제조된 메탄산화촉매는 지지체의 적어도 일부에 활성촉매금속이 형성됨으로써 지지체의 적어도 일부에 금속원자가 벌크(bulk)형태로 형성된 메탄산화촉매보다 상대적으로 더 낮은 온도에서 메탄을 제거할 수 있다.In addition, the methane oxidation catalyst according to another embodiment of the present invention may be manufactured by preparing an active catalyst metal as a slurry using a ball mill and coating the slurry on a monolith carrier. The methane oxidation catalyst thus prepared can remove methane at a relatively lower temperature than the methane oxidation catalyst in which metal atoms are formed in bulk in at least a portion of the support by forming an active catalyst metal on at least a portion of the support.
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 메탄산화촉매를 이용할 경우, 산소 및 수증기가 공존하는 분위기에서 메탄의 전환율이 50%가 되는 온도범위가 300℃ 내지 400℃이고, 상기 메탄의 전환율이 90%가 되는 온도범위도 300℃ 내지 400℃ 일 수 있다.In addition, when the methane oxidation catalyst according to an embodiment of the present invention is used, the temperature range in which the methane conversion rate is 50% in the atmosphere where oxygen and water vapor coexist is 300 ° C to 400 ° C, the methane conversion rate is 90% May also be 300 ° C to 400 ° C.
일예로, LNG(Liquefied Natural Gas) 또는 LPG(Liquefied Petroleum Gas) 등의 액화가스가 연소실에서 연소된 후 배출되는 혼합가스에는 미연소 된 메탄 이외에도 N2, O2, 수증기(H2O), NOx, CO 및 CO2 등 다양한 가스가 존재하는데, 상기 수증기의 경우, 전체 혼합가스의 양 대비 약 1중량% 내지 20중량%의 범위에서 존재한다.For example, in a mixed gas discharged after a liquefied gas such as LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) or LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) is combusted in a combustion chamber, N2 , O2 , water vapor (H2 O), NOx , CO and CO2. In the case of the steam, the gas is present in a range of about 1% by weight to about 20% by weight based on the total amount of the mixed gas.
일반적으로 종래의 알려진 메탄산화촉매의 경우에는 상기 수증기 성분에 의해 메탄산화촉매의 피독(불활성화)이 빠르게 진행됨으로써, 메탄산화촉매의 성능을 저하시키고, 메탄산화촉매의 효율이 매우 낮아지게 된다. 따라서 종래에는 메탄을 포함하는 혼합가스(대표적으로 탄화수소 계열의 연소 후 배출되는 가스) 내에 수증기가 공존할 경우에는 상기 혼합가스의 온도가 300℃ 내지 400℃의 저온에서는 메탄의 산화 촉매 특성이 크게 저하된 다는 문제점이 있었다.In general, in the case of the known methane oxidation catalysts, poisoning (deactivation) of the methane oxidation catalyst proceeds rapidly by the water vapor component, thereby deteriorating the performance of the methane oxidation catalyst and reducing the efficiency of the methane oxidation catalyst. Therefore, conventionally, when water vapor coexists in a mixed gas containing methane (typically, a gas discharged after combustion of a hydrocarbon series), the catalytic properties of the oxidation catalyst of methane are greatly deteriorated at a low temperature of 300 to 400 캜 There was a problem.
반면, 본 발명에 따른 메탄산화촉매와 같이, 지지체의 표면이 소수성을 갖게 되면, 상기 수증기 성분이 메탄산화촉매에 영향을 감소시킬 수 있게 된다. 즉, 지지체의 표면이 소수성을 가짐에 따라 지지체 표면에 접촉되는 수증기는 높은 접촉각을 가지는 액적(droplet)의 구조를 가지며, 지지체 표면의 넓게 분포하지 못하고 일부 영역에 국부적으로 존재할 확률이 높아지게 된다. 또한 지지체의 표면에 안정적으로 위치하지 못하고 외력 등에 의해 표면으로부터 다시 떨어져 나갈 확률도 높다. 따라서 지지체의 표면 상에 존재하는 활성촉매금속이 수증기와 접촉될 확률이 낮아지며, 이러한 이유로 활성촉매금속이 수증기에 의해 피독될 확률 또한 현저하게 감소하게 된다고 판단된다. 따라서 이러한 메탄산화촉매를 구성하는 지지체의 소수성 특성으로 인해 상기 수증기를 함유하는 분위기에서도 효율적으로 메탄을 제거할 수 있다.On the other hand, when the surface of the support has hydrophobicity like the methane oxidation catalyst according to the present invention, the influence of the water vapor component on the methane oxidation catalyst can be reduced. That is, since the surface of the support has hydrophobicity, the water vapor contacting the support surface has a droplet structure having a high contact angle, and the surface of the support can not be widely distributed, and the probability that the support surface exists locally in a certain region is increased. In addition, it is not stably positioned on the surface of the support, and there is a high probability of falling off from the surface due to an external force or the like. Thus, it is considered that the probability that the active catalyst metal present on the surface of the support is in contact with water vapor is lowered, and for this reason, the probability that the active catalyst metal is poisoned by water vapor is also remarkably reduced. Therefore, due to the hydrophobic nature of the support constituting the methane oxidation catalyst, it is possible to efficiently remove methane even in the atmosphere containing the steam.
이하, 본 발명의 이해를 돕기 위해서 상술한 기술적 사상을 적용한 실험예를 설명한다. 다만, 하기의 실험예는 본 발명의 이해를 돕기 위한 것일 뿐, 본 발명이 아래의 실험예에 의해서 한정되는 것은 아니다.Hereinafter, an experimental example to which the technical idea described above is applied will be described in order to facilitate understanding of the present invention. It should be understood, however, that the following examples are for the purpose of promoting understanding of the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 메탄산화촉매 구조체를 개략적으로 도해하는 도면이다.1 is a schematic illustration of a methane oxidation catalyst structure according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 1에는 메탄산화촉매 구조체(100)가 예시되어 있다. 메탄산화촉매 구조체(100)는 세라믹모노리스(110) 및 그 상부에 코팅된 메탄산화촉매(120)로 구성된다. 메탄산화촉매(120)는 활성촉매금속과 상기 활성촉매물질을 담지하는 지지체로 구분될 수 있다. 여기서, 상기 지지체는 규칙기공을 가지는 다공성이면서 소수성 표면을 가진다. 상기 지지체는 0보다 크고 10nm 이하의 기공 크기를 가질 수 있다.1, a methane
표 1은 본 발명의 실시예 및 여러 비교예에 따른 메탄산화촉매의 제조방법으로 제조한 메탄산화촉매 샘플의 지지체와 촉매를 정리한 것이다.Table 1 summarizes the supports and catalysts of the methane oxidation catalyst samples prepared by the method of the present invention and various comparative examples.
실시예의 경우, 원자비율로 Si에 대한 Al의 비율이 14.5인 제올라이트로 이루어진 지지체와 팔라듐 질산염(Pd nitrate) 수용액을 사용하여 이온교환법으로 메탄산화촉매 샘플을 제조하였다. 먼저, 팔라듐(Pd) 이온으로 이온교환하기 전 암모니아(NH4)로 이온교환을 먼저 진행하였다. 1M의 암모늄(NH4) 수용액을 제조한 후 암모늄 수용액 1L와 Si/Al ratio=14.5를 만족하는 지지체 10g의 비율로 핫플레이트에서 약 80℃에서 8시간동안 이온 교환하였다. 이후에 여과지를 사용하여 용액과 지지체 분말을 분리한다. 분리된 지지체 분말은 다시 암모늄 수용액에 주입하여 2회 더 이온교환을 진행하였다. 암모늄으로 이온 교환된 지지체에 팔라듐이 포함된 증류수를 1:100의 비율로 넣고, 약 80℃에서 24시간동안 핫플레이트에서 교반시켰다. 이후에 팔라듐으로 이온 교환된 지지체는 120℃에서 12시간동안 건조시켰다. 건조된 촉매는 덩어리이기 때문에 분말 믹서(powder mixer)와 체(sieve)를 이용하여 입자의 크기를 일정하게 제어하고, 약 600℃에서 3시간동안 소성하여 본 발명의 실시예에 의한 Pd를 2중량% 포함한 메탄산화촉매 샘플을 제조하였다.In the examples, a methane oxidation catalyst sample was prepared by ion exchange using a support made of zeolite having an Al ratio to Si of 14.5 by atomic ratio and an aqueous solution of palladium nitrate (Pd nitrate). First, ion exchange was performed with ammonia (NH4 ) before ion exchange with palladium (Pd) ion. 1M ammonium (NH4 ) aqueous solution was prepared and ion exchanged at a temperature of about 80 ° C for 8 hours on a hot plate at a ratio of 1L of the aqueous ammonium solution and 10g of the support satisfying Si / Al ratio = 14.5. Thereafter, the solution and the support powder are separated using a filter paper. The separated support powders were again injected into aqueous ammonium solution and ion exchange was carried out two more times. The support impregnated with ammonium was mixed with distilled water containing palladium at a ratio of 1: 100, and stirred on a hot plate at about 80 캜 for 24 hours. The palladium-ion-exchanged support was then dried at 120 DEG C for 12 hours. Since the dried catalyst is a lump, the particle size is controlled to be constant by using a powder mixer and a sieve, and fired at about 600 ° C for 3 hours to obtain Pd according to an embodiment of the present invention, % Of methane oxidation catalyst samples were prepared.
한편, 이와 비교하기 위해서, BEA35 및 ZSM5 지지체와 팔라듐 질산염 수용액을 각각 사용하여 이온교환법으로 메탄산화촉매 샘플을 제조하였다. 먼저, 팔라듐 이온으로 이온교환하기 전 암모늄으로 이온교환을 먼저 진행하였다. 1M의 암모늄 수용액을 제조한 후 암모늄 수용액 1L와 BEA35 및 ZSM5 지지체 10g의 비율로 핫플레이트에서 약 80℃에서 8시간동안 이온 교환하였다. 이후에 여과지를 사용하여 용액과 지지체 분말을 분리한다. 분리된 지지체 분말은 다시 암모늄 수용액에 주입하여 2회 더 이온교환을 진행하였다.On the other hand, for comparison, a methane oxidation catalyst sample was prepared by ion exchange using BEA35 and ZSM5 support and an aqueous solution of palladium nitrate, respectively. First, the ion exchange was carried out with ammonium before the ion exchange with the palladium ion. 1M aqueous ammonium solution was prepared and ion exchanged at a temperature of about 80 캜 for 8 hours on a hot plate at a ratio of 1 L of aqueous ammonium solution to 10 g of BEA35 and ZSM5 support. Thereafter, the solution and the support powder are separated using a filter paper. The separated support powders were again injected into aqueous ammonium solution and ion exchange was carried out two more times.
암모늄으로 이온 교환된 지지체에 팔라듐이 포함된 증류수를 1:100의 비율로 넣고, 약 80℃에서 24시간동안 핫플레이트에서 교반시켰다. 이후에 팔라듐으로 이온 교환된 지지체는 120℃에서 12시간동안 건조시켰다. 건조된 촉매는 덩어리이기 때문에 분말 믹서(powder mixer)와 체(sieve)를 이용하여 입자의 크기를 일정하게 제어하고, 약 600℃에서 3시간동안 소성하여 본 발명의 비교예1 및 비교예2에 의한 메탄산화촉매 샘플을 제조하였다.The support impregnated with ammonium was mixed with distilled water containing palladium at a ratio of 1: 100, and stirred on a hot plate at about 80 캜 for 24 hours. The palladium-ion-exchanged support was then dried at 120 DEG C for 12 hours. Since the dried catalyst is a lump, the particle size is controlled to be constant by using a powder mixer and a sieve, and the catalyst is calcined at about 600 ° C for 3 hours to give Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 2 Methane oxidation catalyst samples were prepared.
또한, 입도 크기 40㎚ 실리카(SiO2), 입도 크기 300㎚ 실리카(SiO2) 및 알루미나(Al2O3) 지지체와 팔라듐 질산염 수용액을 각각 사용하여 함침법(incipient wetness impregnation)으로 메탄산화촉매 샘플을 합성하였다. 촉매 합성에는 팔라듐 질산염 수용액과 알루미나(γ-Al2O3), 실리카(hollow SiO2)를 사용하였다. 촉매 합성을 위하여 알루미나와 실리카는 건조기에서 약 120℃에서 4시간동안 건조시켰다. 팔라듐 질산염 수용액을 목표치의 팔라듐 중량%가 되도록 건조시킨 촉매와 에틸 알코올(ethyl alcohol)을 함께 넣어 혼합액을 만들었다. 이때, 상기 에틸 알코올은 파우더의 약 10배 이상 주입하였다. 제조된 혼합액은 진공회전증발기(Rotary Evaporator)를 이용하여 상기 에틸 알코올을 증발 시킨 후 오븐에서 약 120℃에서 4시간동안 건조하고, 약 600℃에서 2시간동안 소성시켰다.Further, by using impregnation method (incipient wetness impregnation) using a 40 nm size particle size silica (SiO2 ), a 300 nm particle size silica (SiO2 ) and alumina (Al2 O3 ) Were synthesized. Palladium nitrate aqueous solution, alumina (γ-Al2 O3 ) and silica (hollow SiO2 ) were used for the catalyst synthesis. For catalyst synthesis, alumina and silica were dried in a dryer at about 120 ° C for 4 hours. A catalyst prepared by drying palladium nitrate aqueous solution to the target palladium weight% and ethyl alcohol were mixed together to prepare a mixed solution. At this time, the ethyl alcohol was injected at least ten times as much as the powder. The ethyl alcohol was evaporated using a rotary evaporator, dried in an oven at about 120 ° C for 4 hours, and fired at about 600 ° C for 2 hours.
실리카계 촉매는 입도 크기가 각각 40㎚(비교예3)와 300㎚(비교예4)로 하였으며, 이때, 팔라듐은 2중량%를 만족하였다. 완성된 알루미나계 촉매의 팔라듐 2중량%(비교예5), 5중량%(비교예6)를 만족하도록 각각 제조하여 촉매특성을 비교분석하였다.The silica-based catalysts had particle sizes of 40 nm (Comparative Example 3) and 300 nm (Comparative Example 4), respectively, and 2 mass% of palladium was satisfied. 2% by weight of palladium of the finished alumina catalyst (Comparative Example 5) and 5% by weight of Comparative Example 6 (Comparative Example 6).
상술한 바와 같이, 완성된 메탄산화촉매 샘플들은 세라믹 모노리스(ceramic monolith)에 코팅하기 위해 슬러리 형태로 제조하였다. 슬러리를 제조하기 위하여 촉매 파우더와 증류수를 사용한다. 슬러리의 농도가 너무 높으면 볼밀(ball mill)이 잘 진행되지 않기 때문에 알루미나 기준으로 약 25중량% 정도의 농도로 맞춰주며, 완성된 슬러리와 지르코니아(ZrO2) 볼을 볼밀용 통에 함께 넣어 슬러리의 평균입도(d50)가 약 1㎛ 내지 2㎛가 되도록 약 12시간동안 볼밀을 진행하였다.As described above, the finished methane oxidation catalyst samples were prepared in slurry form for coating on a ceramic monolith. Catalyst powder and distilled water are used to prepare the slurry. If the concentration of the slurry is too high, the ball mill does not proceed well, so the concentration of the slurry is adjusted to about 25% by weight based on alumina. The finished slurry and the zirconia (ZrO2 ) The ball mill was run for about 12 hours such that the average particle size (d50) was about 1 탆 to 2 탆.
또한, 세라믹 모노리스와 접착력을 높이기 위해 바인더(binder)를 넣어주며, 바인더는 증류수와 혼합하여 액상의 상태로 사용한다. 제조한 바인더는 하루가 지난 후 사용하며 촉매 기준으로 약 15중량%의 양을 사용한다. 볼밀이 완료된 슬러리와 혼합하여 약 1시간동안 교반하여 주며 교반이 완료된 슬러리를 사용하여 코팅을 진행하였다.In addition, a binder is added to improve the adhesion to the ceramic monolith, and the binder is mixed with distilled water and used in a liquid state. The prepared binder is used after one day and uses an amount of about 15% by weight based on the catalyst. The mixture was mixed with the slurry in which the ball mill was completed, and the slurry was stirred for about 1 hour.
촉매 코팅을 하기 전에 금속 모노리스(metal monolith)는 이소프로필 알코올(isopropyl alcohol)과 에틸 알코올(ethyl alcohol)을 사용하여 각각 5분씩 세척을 진행하였다. 이후에 세척이 완료된 모노리스는 건조기를 사용하여 건조 후 코팅에 사용하였다. 코팅에 사용하는 장치는 워시 코팅(wash coating) 장치로 진공챔버에서 진공을 잡은 후 밸브를 열 때 발생하는 공기의 흐름으로 슬러리를 빨아들여 코팅하는 장치로 압력과 밸브의 개폐 시간을 조절하여 코팅 정도를 조절하였다. 모노리스는 진공챔버와 연결된 지그 위에 장착하며, 그 위에 거름망과 슬러리를 올린 후 밸브 개폐시 발생한 공기의 흐름으로 빨려 들어가는 슬러리에 의해 균일하게 코팅되었다. 코딩된 모노리스는 오븐에 넣어 약 120℃에서 4시간동안 건조 시킨 후 약 600℃에서 2시간동안 소성시켰다.Prior to the catalyst coating, the metal monoliths were washed with isopropyl alcohol and ethyl alcohol for 5 minutes each. The monoliths which had been cleaned afterwards were dried and used for coating after drying. The equipment used for the coating is a device for coating the slurry by sucking the slurry by the air flow generated when the valve is opened after taking a vacuum in the vacuum chamber by a wash coating device and controlling the opening and closing time of the pressure and the valve, Respectively. The monolith was mounted on a jig connected to a vacuum chamber, on which the sieve and slurry were placed, and then uniformly coated with a slurry sucked into the flow of air generated upon opening and closing the valve. The cured monolith was placed in an oven, dried at about 120 ° C. for 4 hours, and then calcined at about 600 ° C. for 2 hours.
이후에지름 1인치 및 높이 1인치 크기의 메탄산화촉매가 코팅된 모노리스를 반응장치에 장착하여 촉매 특성을 테스트하였다. 공기(air)를 10L/min 주입한 상태에서 약 600℃에서 200℃까지 온도를 하강시키면서 촉매의 활성을 테스트하였다. 온도를 변화시키면서 10분마다 GC(gas chromatography)를 사용하여 분석하였으며, 반응에는 두 가지 가스조건으로 실험하였다. 첫 번째 가스조건은 메탄(CH4) 1중량%, 산소(O2) 10중량% 및 잔부가 질소(N2)로 이루어졌고, 두 번째 가스조건은 메탄(CH4) 1중량%, 산소(O2) 10중량%, 수증기(H2O) 5중량% 및 잔부가 질소(N2)로 이루어져있다. 이때, 공간속도(GHSV, Gas Hourly Space Velocity)는 50,000/h 이었고, 전체 가스의 유량은 10L/min으로 하였다.Since the Monoliths coated with methane oxidation catalysts of 1 inch in diameter and 1 inch in height were mounted on the reactor to test the catalyst characteristics. The activity of the catalyst was tested while the temperature was lowered from about 600 ° C to 200 ° C while air was being injected at 10 L / min. The gas was analyzed by GC (Gas Chromatography) every 10 minutes while changing the temperature. The reaction was carried out under two different gas conditions. The first gas condition consisted of 1 wt% of methane (CH4 ), 10 wt% of oxygen (O2 ) and the balance of nitrogen (N2 ) and the second gas condition was 1 wt% of methane (CH4 ) O2 ), 5% by weight of water vapor (H2 O), and the balance of nitrogen (N2 ). At this time, the gas hourly space velocity (GHSV) was 50,000 / h, and the total gas flow rate was 10 L / min.
하기 표 2는 표 1의 메탄산화촉매 샘플들을 이용하여 메탄 전환율(제거된 메탄 양) / (촉매에 들어가기 직전의 메탄 양, 즉 투입량) x 100 %)에 따른 각 온도를 측정한 결과를 정리한 것이다. 여기에서, T10, T50 및 T90은 각각 전환율 10%, 50% 및 90%일 때의 온도를 의미한다.Table 2 shows the results of measurement of the respective temperatures according to methane conversion rate (amount of removed methane) / (amount of methane just before entering the catalyst, i.e., amount of input) x 100%) using the methane oxidation catalyst samples in Table 1 will be. Here, T10, T50 and T90 mean the temperatures at conversion rates of 10%, 50% and 90%, respectively.
각 촉매별로 수증기(steam)의 영향을 확인하기 위하여 수증기를 주입한 조건과 주입하지 않은 조건으로 각각 실험을 진행하였다. Experiments were conducted under conditions of steam injection and no injection to check the effect of steam on each catalyst.
도 2는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 메탄산화촉매의 촉매 부착특성을 측정한 결과이다.2 is a graph illustrating the results of measurement of catalyst adhesion characteristics of a methane oxidation catalyst according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 2를 참조하면, 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 메탄산화촉매 샘플로서, 촉매의 로딩(loading) 양을 다르게 선정하여 초음파 분해기(sonicator)에서 약 120분 동안 부착력 테스트를 진행하였다. 여기서, 촉매의 로딩양은 각각 100g/L, 140g/L 및 180g/L로 제어하였다. 그 결과, 촉매의 로딩양이 적을수록 손실되는 코팅층이 적었으며, 100g/L 촉매의 경우 손실율이 약 2중량% 이하로 우수한 부착성능을 보였다. 일반적으로 메탄산화촉매로 사용하는 범위인 100g/L 내지 150g/L의 조건이 아닌 180g/L 조건의 촉매는 손실율이 최종적으로 약 14중량%였으며, 100g/L 조건 대비 손실율이 크게 증가하는 추세를 보였다.Referring to FIG. 2, as a sample of the methane oxidation catalyst according to an embodiment of the present invention, loading amount of the catalyst was selected differently, and the adhesion test was performed on an ultrasonic disintegrator for about 120 minutes. Here, the loading amounts of the catalyst were controlled to 100 g / L, 140 g / L and 180 g / L, respectively. As a result, the smaller the loading amount of the catalyst was, the less the coating layer was lost. In the case of the 100 g / L catalyst, the loss rate was about 2 wt% or less. Generally, the catalyst of 180 g / L, which is not the range of 100 g / L to 150 g / L, which is used as the methane oxidation catalyst, has a loss ratio of about 14 wt%, and the loss ratio of 100 g / L is greatly increased It looked.
도 3은 본 발명의 실시예 및 비교예에 따른 수증기가 없는 상태에서 메탄산화촉매를 이용한 메탄전환율 측정 결과이고, 도 4는 본 발명의 실시예 및 비교예에 따른 수증기가 있는 상태에서 메탄산화촉매를 이용한 메탄전환율 측정 결과이다.FIG. 3 shows the results of measurement of methane conversion using a methane oxidation catalyst in the absence of steam in Examples and Comparative Examples of the present invention. FIG. Methane conversion rate.
도 3, 도 4, 표 1 및 표 2를 참조하면, 수증기를 주입하지 않았을 경우, 비교예 1 샘플은 400℃에서 88% 정도의 촉매 활성을 나타낸다. 반면, 수증기를 주입하였을 경우, 비교예 1 샘플은 촉매의 활성이 매우 나빠지며, 메탄 전환율이 매우 불안정했다.3, 4, Table 1 and Table 2, when no steam is injected, the sample of Comparative Example 1 exhibits a catalytic activity of about 88% at 400 ° C. On the other hand, when the water vapor was injected, the activity of the catalyst of Comparative Example 1 was very poor, and the conversion of methane was very unstable.
비교예 2 샘플은 저온에서의 촉매활성이 매우 낮으며, 수증기를 주입하였을 경우, 다른 촉매와 비교하여 메탄 전환율이 최대 75%로 가장 낮은 성능을 나타냈다. 반면, 입도 크기가 각각 다른 두 종류의 SiO2를 지지체로 사용한 메탄산화촉매 샘플로서, 비교예 3 및 비교예 4의 샘플에 각각 수증기를 주입하였을 때와 주입하지 않았을 때 400℃ 이하에서 최대 80%의 메탄 전환율을 나타낸다. 이는 SiO2 자체의 열적 안정성이 높기 때문인 것으로 판단된다.Comparative Example 2 The sample had very low catalytic activity at low temperatures and showed the lowest methane conversion rate of 75% when compared to other catalysts when steam was injected. On the other hand, as a methane oxidation catalyst sample using two types of SiO2 having different particle sizes as a support, it was found that when steam was injected into each of the samples of Comparative Example 3 and Comparative Example 4, Methane conversion. This is because the thermal stability of SiO2 itself is high.
비교예 5 및 비교예 6 샘플 모두 수증기를 주입하지 않은 경우에는 400℃ 이하에서 메탄 전환율이 90% 이상으로 매우 높은 활성도를 보이나, 수증기를 주입하게 되면 400℃ 이하에서는 촉매의 활성이 매우 낮아진다.In all of the samples of Comparative Example 5 and Comparative Example 6, when the water vapor was not injected, the activity of methane conversion was as high as 90% or higher at 400 ° C or lower. However, when the water vapor was injected, the activity of the catalyst was very low at 400 ° C or lower.
한편, 본 발명의 실시예 샘플은 합성한 촉매 중에 가장 높은 촉매 활성을 나타내었다. 메탄 전환율은 수증기를 주입하지 않았을 경우 400℃ 미만의 온도에서 99% 이상의 메탄 전환율을 나타내었다. 또, 수증기를 주입하였을 경우에도 400℃ 에서 90%의 메탄 전환율을 나타내었다. 이는 비교예들과 비교할 때 수증기 분위기에서의 촉매 활성의 열화가 상대적으로 작게 일어났음을 의미한다.Meanwhile, the sample of the present invention exhibited the highest catalytic activity among the synthesized catalysts. Conversion rate of methane was 99% or more at a temperature below 400 ℃ when no water vapor was injected. Also, when the steam was injected, the methane conversion was 90% at 400 ° C. This means that the deterioration of the catalytic activity in the steam atmosphere is relatively small as compared with the comparative examples.
수증기를 주입하지 않은 경우, 비교예 5 및 실시예 샘플 촉매가 400℃ 이하에서 T90에 도달하였다. 상기 두 촉매 외에도 비교예 1 및 비교예 3 촉매가 양호한 촉매 활성을 보였다. 그러나 본 발명의 실시예 샘플 촉매의 경우, 수증기를 주입하였을 경우, T50이 364℃, T90이 396℃로 모두 400℃ 미만으로 나타났다. 본 발명의 실시예 샘플 촉매만이 400℃ 미만에서 T90에 도달하였으며, 실시예 샘플 촉매를 제외하면 400℃ 미만에서 T90에 도달한 촉매는 없었다.When no water vapor was injected, Comparative Example 5 and the sample catalyst of Example reached T90 at 400 占 폚 or lower. In addition to the two catalysts, Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 3 showed good catalytic activity. However, in the case of the sample catalyst of the present invention, when steam was injected, T50 was 364 ° C and T90 was 396 ° C, all of which were below 400 ° C. Only the sample catalyst of the present invention reached T90 at less than 400 DEG C and no catalyst reached T90 at less than 400 DEG C except for the sample catalyst of the Example.
특히, 비교예 6의 경우에는 활성촉매금속으로 Pd를 5중량% 함유하였으나, 단지 2중량%의 Pd를 포함하고 있는 실시예에 비해 더 열악한 촉매특성을 나타내었다.In particular, Comparative Example 6 contained 5 wt% of Pd as an active catalyst metal, but exhibited poorer catalytic properties than the example containing only 2 wt% of Pd.
이로부터 본 발명의 실시예 샘플은 다른 샘플들에 비해 저온메탄산화 반응 영역에서 매우 높은 활성을 가지며, 이는 수증기의 영향을 가장 적게 받기 때문으로 해석될 수 있다.From this it can be interpreted that the sample of the present invention has very high activity in the low temperature methane oxidation reaction zone compared to other samples, which is least influenced by water vapor.
본 발명은 도면에 도시된 일 실시예를 참고로 설명되었으나 이는 예시적인 것에 불과하며, 당해 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 이로부터 다양한 변형 및 균등한 다른 실시예가 가능하다는 점을 이해할 것이다. 따라서 본 발명의 진정한 기술적 보호 범위는 첨부된 특허청구범위의 기술적 사상에 의하여 정해져야 할 것이다.While the present invention has been particularly shown and described with reference to exemplary embodiments thereof, it is evident that many alternatives, modifications and variations will be apparent to those skilled in the art. Accordingly, the true scope of the present invention should be determined by the technical idea of the appended claims.
100 : 메탄산화촉매 구조체
110 : 세라믹모노리스
120 : 메탄산화촉매100: methane oxidation catalyst structure
110: Ceramic Monolith
120: methane oxidation catalyst
Claims (9)
Translated fromKorean상기 촉매는 소수성 표면을 가지는 지지체 및 상기 지지체의 적어도 일부의 표면에 존재하는 활성촉매금속을 포함하며,
상기 메탄의 전환율이 90%가 되는 온도범위가 300℃ 내지 400℃인,
촉매를 이용한 메탄의 산화 방법.A method for oxidizing methane using a catalyst in a mixed gas comprising oxygen, water vapor and methane,
Wherein the catalyst comprises a support having a hydrophobic surface and an active catalyst metal present on at least a portion of the surface of the support,
Wherein the temperature range at which the conversion of methane is 90% is 300 ° C to 400 ° C,
Methane oxidation method using catalyst.
상기 지지체는 Si과 Al의 몰 비율(Si/Al)이 10보다 크고 50보다 작은 알루미노실리케이트 제올라이트를 포함하는,
촉매를 이용한 메탄의 산화 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the support comprises an aluminosilicate zeolite having a Si / Al molar ratio (Si / Al) greater than 10 and less than 50,
Methane oxidation method using catalyst.
상기 활성촉매금속은 상기 지지체의 적어도 일부에 이온교환 되어 존재하는,
촉매를 이용한 메탄의 산화 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the active catalyst metal is present in ion exchange with at least a portion of the support,
Methane oxidation method using catalyst.
상기 지지체는 규칙기공을 가지는 다공성 지지체인,
촉매를 이용한 메탄의 산화 방법.The method according to claim 1,
The support is a porous support having regulatory pores,
Methane oxidation method using catalyst.
상기 메탄의 전환율이 50%가 되는 온도범위가 300℃ 내지 400℃인,
촉매를 이용한 메탄의 산화 방법.The method according to claim 1,
And a temperature range in which the methane conversion rate is 50% is 300 ° C to 400 ° C.
Methane oxidation method using catalyst.
상기 혼합가스 내에서의 수증기는 1 중량% 내지 20 중량% 범위로 존재하는,
촉매를 이용한 메탄의 산화 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein water vapor in the mixed gas is present in the range of 1 wt% to 20 wt%
Methane oxidation method using catalyst.
상기 촉매는 소수성 표면을 가지는 지지체; 및
상기 지지체의 적어도 일부의 표면에 존재하는 활성촉매금속;
을 포함하고,
상기 지지체는 Si과 Al의 몰 비율(Si/Al)이 10보다 크고 50보다 작은 알루미노실리케이트 제올라이트를 포함하며, 상기 활성촉매금속은 상기 지지체의 적어도 일부에 이온교환 되어 존재하고,
상기 메탄의 전환율이 90%가 되는 온도범위가 300℃ 내지 400℃인,
메탄산화촉매.A catalyst for the oxidation of methane in a mixed gas comprising oxygen, water vapor and methane,
The catalyst comprising: a support having a hydrophobic surface; And
An active catalyst metal present on the surface of at least a portion of the support;
/ RTI >
Wherein the support comprises an aluminosilicate zeolite with a Si / Al molar ratio (Si / Al) greater than 10 and less than 50, the active catalyst metal being present in ion exchange with at least a portion of the support,
Wherein the temperature range at which the conversion of methane is 90% is 300 ° C to 400 ° C,
Methane oxidation catalyst.
상기 지지체는 규칙기공을 가지는 다공성 지지체인,
메탄산화촉매.8. The method of claim 7,
The support is a porous support having regulatory pores,
Methane oxidation catalyst.
상기 지지체는 0보다 크고 10nm 이하의 기공 크기를 가지는,
메탄산화촉매.9. The method of claim 8,
Wherein the support has a pore size of greater than 0 and 10 nm or less,
Methane oxidation catalyst.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170110966AKR101800676B1 (en) | 2017-08-31 | 2017-08-31 | Methane oxidation catalyst and method for oxidation of methane using a catalyst |
| PCT/KR2018/009945WO2019045430A1 (en) | 2017-08-31 | 2018-08-29 | Methane oxidation catalyst and method for oxidizing methane by using catalyst |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170110966AKR101800676B1 (en) | 2017-08-31 | 2017-08-31 | Methane oxidation catalyst and method for oxidation of methane using a catalyst |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR101800676B1true KR101800676B1 (en) | 2017-12-20 |
Family
ID=60931339
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020170110966AActiveKR101800676B1 (en) | 2017-08-31 | 2017-08-31 | Methane oxidation catalyst and method for oxidation of methane using a catalyst |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101800676B1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2019045430A1 (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2019045430A1 (en)* | 2017-08-31 | 2019-03-07 | 한국기계연구원 | Methane oxidation catalyst and method for oxidizing methane by using catalyst |
| KR20210014510A (en)* | 2019-07-30 | 2021-02-09 | 한국조선해양 주식회사 | Regeneration system for methane oxidation catalyst and methane oxidation reactor comprising the same |
| KR20210014509A (en)* | 2019-07-30 | 2021-02-09 | 한국조선해양 주식회사 | Catalyst for methane oxidation reaction at low temperature |
| KR20210075543A (en) | 2019-12-13 | 2021-06-23 | 연세대학교 산학협력단 | Methane oxidation catalyst, preparation method thereof and partial oxidation of methane using the same |
| KR20230064301A (en) | 2021-11-03 | 2023-05-10 | 연세대학교 산학협력단 | Nanocatalyst for partial oxidation of methane, manufacturing method thereof, and method for partial oxidation of methane using the same |
| KR20230116335A (en)* | 2022-01-28 | 2023-08-04 | 한국화학연구원 | Catalyst for Methane Oxidation Reaction and Oxidation of Methane Using the Same |
| KR20230121281A (en)* | 2022-02-11 | 2023-08-18 | 한국화학연구원 | Bimetalic Catalyst for Methane Oxidation Reaction and Method for Preparing the Same |
| KR20250127429A (en) | 2024-02-19 | 2025-08-26 | 에스티엑스엔진 주식회사 | Ship exhaust gas treatment system using methane oxidation catalysts |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2593786B (en) | 2020-07-07 | 2023-01-25 | Daphne Tech Sa | Apparatus and method for electron irradiation scrubbing |
| CN113198490A (en)* | 2021-05-26 | 2021-08-03 | 华东理工大学 | Palladium-cobalt-loaded alloy catalyst for low-temperature combustion of methane and preparation method thereof |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008246473A (en) | 2007-03-08 | 2008-10-16 | Osaka Gas Co Ltd | Catalyst and method for cleaning exhaust gas |
| US20160310895A1 (en) | 2013-12-20 | 2016-10-27 | Clariant International Ltd. | Zeolite Catalysts Containing Titanium For The Oxidation Of Methane In Exhaust Gas Streams |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07241470A (en)* | 1994-03-01 | 1995-09-19 | Sakai Chem Ind Co Ltd | Methane combustion catalyst |
| JPH10337476A (en)* | 1997-06-05 | 1998-12-22 | Toho Gas Co Ltd | Methane oxidation catalyst |
| KR100908049B1 (en)* | 2007-10-31 | 2009-07-15 | 에스케이에너지 주식회사 | Catalyst for Purifying Natural Gas Automobile Exhaust |
| KR101800676B1 (en)* | 2017-08-31 | 2017-12-20 | 한국기계연구원 | Methane oxidation catalyst and method for oxidation of methane using a catalyst |
- 2017
- 2017-08-31KRKR1020170110966Apatent/KR101800676B1/enactiveActive
- 2018
- 2018-08-29WOPCT/KR2018/009945patent/WO2019045430A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008246473A (en) | 2007-03-08 | 2008-10-16 | Osaka Gas Co Ltd | Catalyst and method for cleaning exhaust gas |
| US20160310895A1 (en) | 2013-12-20 | 2016-10-27 | Clariant International Ltd. | Zeolite Catalysts Containing Titanium For The Oxidation Of Methane In Exhaust Gas Streams |
Cited By (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2019045430A1 (en)* | 2017-08-31 | 2019-03-07 | 한국기계연구원 | Methane oxidation catalyst and method for oxidizing methane by using catalyst |
| KR20210014510A (en)* | 2019-07-30 | 2021-02-09 | 한국조선해양 주식회사 | Regeneration system for methane oxidation catalyst and methane oxidation reactor comprising the same |
| KR20210014509A (en)* | 2019-07-30 | 2021-02-09 | 한국조선해양 주식회사 | Catalyst for methane oxidation reaction at low temperature |
| KR102305781B1 (en) | 2019-07-30 | 2021-09-30 | 한국조선해양 주식회사 | Regeneration system for methane oxidation catalyst and methane oxidation reactor comprising the same |
| KR102390017B1 (en)* | 2019-07-30 | 2022-04-26 | 한국조선해양 주식회사 | Catalyst for methane oxidation reaction at low temperature |
| KR20210075543A (en) | 2019-12-13 | 2021-06-23 | 연세대학교 산학협력단 | Methane oxidation catalyst, preparation method thereof and partial oxidation of methane using the same |
| KR20230064301A (en) | 2021-11-03 | 2023-05-10 | 연세대학교 산학협력단 | Nanocatalyst for partial oxidation of methane, manufacturing method thereof, and method for partial oxidation of methane using the same |
| US11878295B2 (en) | 2021-11-03 | 2024-01-23 | Industry-Academic Cooperation Foundation, Yonsei University | Nanocatalyst for partial oxidation of methane, method for preparing the nanocatalyst and method for partial oxidation of methane using the nanocatalyst |
| KR20230116335A (en)* | 2022-01-28 | 2023-08-04 | 한국화학연구원 | Catalyst for Methane Oxidation Reaction and Oxidation of Methane Using the Same |
| KR102687688B1 (en) | 2022-01-28 | 2024-07-23 | 한국화학연구원 | Catalyst for Methane Oxidation Reaction and Oxidation of Methane Using the Same |
| KR20230121281A (en)* | 2022-02-11 | 2023-08-18 | 한국화학연구원 | Bimetalic Catalyst for Methane Oxidation Reaction and Method for Preparing the Same |
| KR102722374B1 (en) | 2022-02-11 | 2024-10-25 | 한국화학연구원 | Bimetalic Catalyst for Methane Oxidation Reaction and Method for Preparing the Same |
| KR20250127429A (en) | 2024-02-19 | 2025-08-26 | 에스티엑스엔진 주식회사 | Ship exhaust gas treatment system using methane oxidation catalysts |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2019045430A1 (en) | 2019-03-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101800676B1 (en) | Methane oxidation catalyst and method for oxidation of methane using a catalyst | |
| JP6728289B2 (en) | Catalyst articles and methods for oxidizing nitric oxide | |
| CN113260454B (en) | Layered three-way conversion (TWC) catalyst and method of making the same | |
| CA1247074A (en) | Three-way catalysts of improved efficiency | |
| EP2969191B1 (en) | Catalyst materials for no oxidation | |
| WO2015081171A1 (en) | Oxygen storage capacity and thermal stability of synergized pgm catalyst systems | |
| US9707545B2 (en) | Three-way catalyst | |
| US9427730B2 (en) | Bimetallic synergized PGM catalyst systems for TWC application | |
| US20150238940A1 (en) | Synergized PGM Catalyst Systems Including Palladium for TWC Application | |
| WO2015080776A1 (en) | Method for improving lean performance of pgm catalyst systems: synergized pgm | |
| WO2015081183A1 (en) | Pgm and copper-manganese in three way catalyst systems | |
| KR20150008887A (en) | Base metal catalyst composition and methods of treating exhaust from a motorcycle | |
| KR20140110863A (en) | Supported noble metal catalyst for treating exhaust gas | |
| US10801384B2 (en) | Diesel oxidation catalyst containing manganese | |
| CN108472630B (en) | Oxidation catalyst for compressed natural gas combustion system exhaust gas | |
| JP4901366B2 (en) | Catalyst for oxidation removal of methane in exhaust gas and method for oxidation removal of methane in exhaust gas | |
| JP2006521203A (en) | Catalyst for low temperature oxidation of methane | |
| JPH11276907A (en) | Exhaust gas purification catalyst and method for producing the same | |
| JP3835436B2 (en) | Exhaust gas purification method and exhaust gas purification catalyst | |
| KR102843951B1 (en) | Adjustable NOx adsorbent | |
| EP0682975A1 (en) | Device and method for cleaning exhaust gas | |
| WO2016140641A1 (en) | Method for improving lean performance of pgm catalyst systesm: synergized pgm | |
| JP2007038155A (en) | Catalyst for selective reduction of nitrogen oxides with carbon monoxide and its preparation | |
| US20100008837A1 (en) | Metal ionic catalyst composition and a process thereof | |
| JP2005279371A (en) | Denitrification catalyst and denitrification method using the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| PA0302 | Request for accelerated examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D17-exm-PA0302 St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D16-exm-PA0302 | |
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 Fee payment year number:1 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:4 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R14-asn-PN2301 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:6 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:7 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:8 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:9 |