KR101708491B1 - Method for recognizing object using pressure sensor - Google Patents
Method for recognizing object using pressure sensorDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101708491B1 KR101708491B1KR1020150047621AKR20150047621AKR101708491B1KR 101708491 B1KR101708491 B1KR 101708491B1KR 1020150047621 AKR1020150047621 AKR 1020150047621AKR 20150047621 AKR20150047621 AKR 20150047621AKR 101708491 B1KR101708491 B1KR 101708491B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- data
- information
- pressure
- sensed
- metadata
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V20/00—Scenes; Scene-specific elements
- G06V20/50—Context or environment of the image
- G06V20/52—Surveillance or monitoring of activities, e.g. for recognising suspicious objects
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B13/00—Burglar, theft or intruder alarms
- G08B13/02—Mechanical actuation
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01L—MEASURING FORCE, STRESS, TORQUE, WORK, MECHANICAL POWER, MECHANICAL EFFICIENCY, OR FLUID PRESSURE
- G01L5/00—Apparatus for, or methods of, measuring force, work, mechanical power, or torque, specially adapted for specific purposes
- G06K9/6201—
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B13/00—Burglar, theft or intruder alarms
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B21/00—Alarms responsive to a single specified undesired or abnormal condition and not otherwise provided for
- G08B21/02—Alarms for ensuring the safety of persons
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Emergency Management (AREA)
- Alarm Systems (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법에 관한 것으로, 보다 상세하게는 감시 영역에 설치된 압력 센서로부터 센싱 데이터를 수신하고, 수신된 센싱 데이터를 이용하여 감시 영역을 지나는 객체의 유형을 인식할 수 있는 객체 인식 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method of recognizing an object using a pressure sensor, and more particularly to a method and apparatus for receiving sensing data from a pressure sensor installed in a surveillance area and recognizing a type of an object passing through the surveillance area using the received sensing data And an object recognition method.
감시 구역 내에 존재하는 객체를 감지하기 위한 방법으로 다양한 방법들이 활용되고 있다.Various methods are used to detect objects in the surveillance area.
예를 들어, 카메라 등과 같은 광학 장비를 이용하여 특정 영역을 촬영하거나, 초음파나 레이져 등의 비접촉식 센서를 이용함으로써 특정 구역 을 지나는 객체를 인식하는 방법들이 활용되어 왔다.For example, there have been used methods of photographing a specific area using an optical device such as a camera or recognizing an object passing through a specific area by using a non-contact type sensor such as an ultrasonic wave or a laser.
그러나, 종래 방법에 따른 객체 인식 방법의 경우 사각지대에 존재하는 객체를 인식할 수 없다는 점, 기상 변화나, 암전 등 외부 환경 변화에 영향을 받아 감시 영역을 효율적으로 관찰할 수 없다는데 문제점이 있었다.However, in the case of the object recognition method according to the conventional method, there is a problem in that it is not possible to efficiently recognize the surveillance region due to the fact that the object existing in the blind spot can not be recognized, the weather change, .
이에, 외부 환경의 영향을 최소화하여 감시 영역 내 객체의 출입을 감지할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 출입한 객체를 인식할 수 있는 기능을 갖춘 새로운 형태의 객체 인식 방법의 필요성이 대두되었다.Therefore, there is a need for a new type of object recognition method capable of not only detecting the access of objects in the surveillance area by minimizing the influence of the external environment but also recognizing the objects entering and exiting.
본 발명은 상술한 문제점을 해결하기 위해 안출된 것으로, 본 발명의 목적은 외부 환경에 의한 영향을 최소화하여 감시 영역 내에 존재하는 객체를 효율적으로 감시 및 인식할 수 있는 객체 인식 방법을 제공하는데 있다.An object of the present invention is to provide an object recognition method capable of efficiently monitoring and recognizing an object existing in a surveillance area by minimizing the influence of an external environment.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은 객체 인식의 결과로 객체의 이동 경로, 패턴 분석 등을 추가적으로 수행함으로써 그 분석 결과를 다양한 응용 분야에 접목할 수 있도록 하는 객체 인식 방법을 제공하는데 있다.It is still another object of the present invention to provide an object recognition method that can add an analysis result to various application fields by additionally performing an object movement path and a pattern analysis as a result of object recognition.
본 발명의 기술적 과제들은 이상에서 언급한 기술적 과제들로 제한되지 않으며, 언급되지 않은 또 다른 기술적 과제들은 아래의 기재로부터 본 발명이 속한 기술분야의 통상의 기술자에게 명확하게 이해될 수 있을 것이다.The technical objects of the present invention are not limited to the above-mentioned technical problems, and other technical subjects not mentioned can be clearly understood by those skilled in the art from the following description.
상술한 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법은 센서에서 감지된 센싱 데이터를 수신하는 단계, 상기 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 위치 정보를 포함하는 유효 데이터를 산출하는 단계, 상기 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 단계 및 상기 메타데이터에 포함된 정보와 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보를 비교하여 객체의 유형을 인식하는 단계를 포함한다.According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of recognizing an object using a pressure sensor, the method including sensing sensing data sensed by a sensor, sampling the sensed data at a predetermined time interval, Calculating valid data including the size information of the metadata and the sensed position information, converting the valid data into metadata having a predetermined data structure, and comparing the information included in the metadata and the pre- And comparing the object information to recognize the type of the object.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 상기 유효 데이터를 산출하는 단계는, 소정의 크기를 갖은 압력이 검출된 영역의 면적이 임계값 이상인 샘플링 데이터를 유효 데이터로 산출하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the step of calculating the valid data may include the step of calculating, as valid data, sampling data in which an area of a region where a pressure having a predetermined size is detected is equal to or greater than a threshold value.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 상기 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 검출된 영역의 면적이 임계값 이상인 샘플링 데이터가 복수개인 경우, 상기 검출된 영역의 면적이 최대값을 갖는 샘플링 데이터로 유효 데이터를 산출할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, when there are a plurality of pieces of the sampled data in which the area of the detected pressure having the predetermined size is equal to or greater than the threshold, the sampled data having the detected area has the maximum value, Can be calculated.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 상기 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 단계는, 추가적인 센싱 데이터를 수신하는 단계, 추가로 수신된 센싱 데이터에서 유효 데이터를 산출하고 식별자를 부가하는 단계 및 상기 식별자가 부가된 유효 데이터를 상기 메타데이터에 추가하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the step of converting the valid data into meta data having a predetermined data structure may include receiving additional sensing data, calculating valid data from the received sensing data, And adding valid data added with the identifier to the metadata.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 상기 메타데이터는, 상기 센싱 데이터가 수신된 시간 정보, 압력을 감지한 센서의 고유 정보, 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 센서의 위치 정보, 상기 압력이 감지된 영역의 넓이, 상기 압력이 감지된 영역의 외곽선 중 적어도 하나의 정보를 포함할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the metadata may include time information on the sensing data, unique information of the sensor that sensed the pressure, size information of the pressure, position information of the sensor that sensed the pressure, The width of the sensed area, and the outline of the sensed area.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 상기 객체의 유형을 인식하는 단계는, 상기 메타데이터를 이용하여 객체의 특징점을 추출하는 단계, 기 저장된 복수의 객체들의 특징점과 상기 메타데이터 추출된 특징점을 비교하는 단계 및 기 저장된 복수의 객체들의 특징점 중 상기 메타데이터에서 추출된 동일한 특징점을 가지는 객체가 감시 영역을 지나는 것이라고 인식하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the step of recognizing the type of the object may include extracting minutiae points of the object using the meta data, comparing the minutiae points of the plurality of previously stored objects with the extracted minutiae And recognizing that an object having the same minutiae extracted from the metadata among the minutiae points of the plurality of stored objects passes through the surveillance area.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 상기 메타데이터에서 추출된 동일한 특징점을 가지는 객체가 감시 영역을 지나는 것이라고 인식하는 단계는, 상기 기 저장된 복수의 객체들의 특징점 중 상기 메타데이터에서 추출된 동일한 특징점을 가지는 객체에 부여된 고유 번호를 선택하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the step of recognizing that an object having the same minutiae extracted from the meta data passes through a surveillance area may include recognizing that the same minutiae extracted from the meta data among the minutiae points of the previously stored plurality of objects And selecting a unique number assigned to the object.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 상기 메타데이터를 이용하여 객체의 특징점을 추출하는 단계는, 상기 메타데이터에 포함된 정보는 상기 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보, 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 검출되는 위치 정보, 압력이 검출된 영역의 외곽선 정보, 압력이 검출된 영역의 넓이 정보 중 적어도 하나를 이용하여 추출할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the step of extracting feature points of the object using the metadata may include extracting information on the size of the sensed pressure of the sensor, The area information of the area where the pressure is detected, the area information of the area where the pressure is detected, and the area information of the area where the pressure is detected.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 상기 메타데이터에서 추출된 특징점을 기초로 인식된 결과를 저장하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the method may further include storing the recognized result based on the minutiae extracted from the metadata.
본 발명의 또 다른 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 방법은, 센서에서 감지된 센싱 데이터를 수신하는 단계, 상기 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 0 내지 255 레벨 중 하나의 값을 갖는 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 2차원 좌표 정보를 포함하는 유효 데이터를 산출하는 단계, 상기 유효 데이터를 상기 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보, 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 검출되는 위치 정보, 압력이 검출된 영역의 외곽선 정보, 압력이 검출된 영역의 넓이 정보 중 적어도 하나의 정보를 포함하고 기 설정된 구조를 가지는 메타데이터로 변환하는 단계, 상기 메타데이터에 포함된 정보로 특징점을 추출하여, 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보와 비교하는 단계, 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보 중 상기 메타데이터에서 추출된 특징점과 동일한 특징점을 갖는 객체에 부여된 고유 번호를 선택하는 단계 및 상기 선택된 고유 번호에 대응되는 객체가 상기 센서가 감지된 감시 영역에 출입한 것으로 인식하는 단계를 포함한다.The method of recognizing an object according to another embodiment of the present invention includes receiving sensing data sensed by a sensor, sampling the sensed data at a predetermined time interval, storing the pressure magnitude information having one of 0 to 255 levels Dimensional coordinate information of the pressure detected; calculating valid data including the size information of the pressure sensed by the sensor, position information where a pressure having a predetermined size is detected, Extracting a feature point from the information included in the metadata, extracting feature points from the information included in the metadata, and extracting feature points from the information contained in the metadata, Comparing the extracted feature information with object information, comparing the feature information extracted from the stored plurality of pieces of object information with the feature information extracted from the metadata, Selecting the unique number assigned to an object and having a step for the object corresponding to the selected ID number recognized as the monitor area and out of the sensor is detected.
본 발명의 또 다른 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 장치는 센서에서 감지된 센싱 데이터를 수신하는 수신부, 상기 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 위치 정보를 포함하는 유효 데이터를 산출하는 전 처리부, 상기 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 메타데이터 생성부 및 상기 메타데이터에 포함된 정보와 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보를 비교하여 객체의 유형을 인식하는 객체 인식부를 포함한다.According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided an object recognition apparatus including a receiver for receiving sensing data sensed by a sensor, a controller for sampling the sensed data at predetermined time intervals, A metadata generating unit for converting the valid data into meta data having a predetermined data structure, and a memory for storing the object information by comparing the information contained in the meta data with a plurality of previously stored object information, And an object recognition unit for recognizing the type of the object.
본 발명의 또 다른 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 장치는, 하나 이상의 프로세서, 상기 프로세서에 의하여 수행되는 컴퓨터 프로그램을 로드(load)하는 메모리 및 복수의 객체 정보 및 감시 영역을 지나는 객체의 유형을 인식하는 컴퓨터 프로그램을 저장하는 스토리지를 포함하되, 상기 컴퓨터 프로그램은, 센서에서 감지된 센싱 데이터를 수신하는 오퍼레이션, 상기 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 위치 정보를 포함하는 유효 데이터를 산출하는 오퍼레이션, 상기 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 오퍼레이션 및 상기 메타데이터에 포함된 정보와 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보를 비교하여 객체의 유형을 인식하는 오퍼레이션을 포함한다.According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided an object recognition apparatus including at least one processor, a memory for loading a computer program executed by the processor, and a computer for recognizing a type of an object passing through a plurality of object information and a surveillance region And a storage for storing the program, wherein the computer program comprises: an operation of receiving sensing data sensed by a sensor; sampling the sensed data at a predetermined time interval to calculate size information of the sensed pressure of the sensor, An operation for calculating valid data including positional information, an operation for converting the valid data into metadata having a predetermined data structure, and an operation for comparing the information contained in the metadata with a plurality of previously stored object information, And includes an operation to recognize.
본 발명의 또 다른 실시예에 따른 컴퓨터 프로그램은 컴퓨팅 장치와 결합하여, 센서에서 감지된 센싱 데이터를 수신하는 단계, 상기 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 위치 정보를 포함하는 유효 데이터를 산출하는 단계, 상기 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 단계 및 상기 메타데이터에 포함된 정보와 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보를 비교하여 객체의 유형을 인식하는 단계를 실행시키기 위하여 기록 매체에 저장된다.According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a computer program for causing a computer to execute the steps of: receiving sensed data sensed by a sensor, sampling sensed data at predetermined time intervals, Converting valid data into metadata having a predetermined data structure, comparing the information included in the metadata with a plurality of pre-stored object information, And is stored in the recording medium to execute the step of recognizing the type of the object.
본 발명의 실시예들에 따른 객체 인식 방법에 따르면, 감시 영역에 설치된 압력 센서를 통해 해당 구역을 통과하는 객체의 유형을 인식하면 날씨, 조도 등과 같의 외부 환경의 영향을 최소화하여 인식률을 높일 수 있다는 효과를 달성할 수 있다.According to the object recognition method according to the embodiments of the present invention, when the type of the object passing through the corresponding area is recognized through the pressure sensor installed in the surveillance area, the influence of the external environment such as weather and illumination can be minimized, Can be achieved.
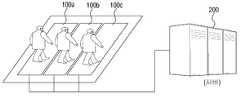
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 시스템을 설명하기 위한 개념도이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법을 설명하기 위한 흐름도이다.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 센서로부터 수신된 센싱 데이터를 소정의 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 유효 데이터를 산출하는 과정을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 유효 데이터가 변환되어 생성된 메타데이터의 구조를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 메타 데이터에 포함되는 정보가 업데이트 되는 과정을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 감시 영역에 차량이 출입하는 경우 유효 데이터를 산출하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 7은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 상술한 과정을 거쳐 생성된 메타데이터에 포함된 정보를 시각적으로 표시한 도면이다.
도 8은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 메타데이터를 이용하여 감시 영역에 출입한 객체를 인식하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 흐름도이다.
도 9는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 객체 인식 장치(200)에 기 저장된 복수의 객체들에 대한 정보를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 10은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 장치(200)를 설명하기 위한 기능 블록도이다.
도 11은 본 발명의 또 다른 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 장치(1110)을 설명하기 위한 기능 블록도이다.1 is a conceptual diagram illustrating an object recognition system using a pressure sensor according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a flowchart illustrating an object recognition method using a pressure sensor according to an embodiment of the present invention.
3 is a diagram illustrating a process of sampling valid data received from a sensor at predetermined time intervals and calculating valid data according to an embodiment of the present invention.
4 is a diagram for explaining a structure of metadata generated by transforming valid data according to an embodiment of the present invention.
5 is a diagram illustrating a process of updating information included in meta data according to an embodiment of the present invention.
6 is a diagram for explaining a method of calculating valid data when a vehicle enters and exits a monitoring area according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 7 is a diagram for visually displaying information included in the metadata generated through the above-described process according to an embodiment of the present invention.
8 is a flowchart illustrating a method of recognizing an object entering and exiting the surveillance area using metadata according to an embodiment of the present invention.
9 is a view for explaining information on a plurality of objects previously stored in the
10 is a functional block diagram illustrating an
11 is a functional block diagram illustrating an
이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예를 상세히 설명한다. 본 발명의 이점 및 특징, 그리고 그것들을 달성하는 방법은 첨부되는 도면과 함께 상세하게 후술되어 있는 실시예들을 참조하면 명확해질 것이다. 그러나 본 발명은 이하에서 게시되는 실시예들에 한정되는 것이 아니라 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 구현될 수 있으며, 단지 본 실시예들은 본 발명의 게시가 완전하도록 하고, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 발명의 범주를 완전하게 알려주기 위해 제공되는 것이며, 본 발명은 청구항의 범주에 의해 정의될 뿐이다. 명세서 전체에 걸쳐 동일 참조 부호는 동일 구성 요소를 지칭한다.Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The advantages and features of the present invention, and the manner of achieving them, will be apparent from and elucidated with reference to the embodiments described hereinafter in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. The present invention may, however, be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, and will fully convey the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art. To fully disclose the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art, and the invention is only defined by the scope of the claims. Like reference numerals refer to like elements throughout the specification.
다른 정의가 없다면, 본 명세서에서 사용되는 모든 용어(기술 및 과학적 용어를 포함)는 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 공통적으로 이해될 수 있는 의미로 사용될 수 있을 것이다. 또 일반적으로 사용되는 사전에 정의되어 있는 용어들은 명백하게 특별히 정의되어 있지 않는 한 이상적으로 또는 과도하게 해석되지 않는다.Unless defined otherwise, all terms (including technical and scientific terms) used herein may be used in a sense commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this invention belongs. Also, commonly used predefined terms are not ideally or excessively interpreted unless explicitly defined otherwise.
또한, 본 명세서에서 단수형은 문구에서 특별히 언급하지 않는 한 복수형도 포함될 수 있다. 명세서에서 사용되는 "포함한다(comprises)" 및/또는 "포함하는(comprising)"은 언급된 구성요소, 단계, 동작 및/또는 소자는 하나 이상의 다른 구성요소, 단계, 동작 및/또는 소자의 존재 또는 추가를 배제하지 않는다.Also, the singular forms herein may include plural forms unless specifically stated in the text. It is noted that the terms "comprises" and / or "comprising" used in the specification are intended to be inclusive in a manner similar to the components, steps, operations, and / Or additions.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 시스템을 설명하기 위한 개념도이다.1 is a conceptual diagram illustrating an object recognition system using a pressure sensor according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 시스템은 차량이나 사람의 통행을 감시하고자 하는 영역에 설치된 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c) 로부터 센싱 데이터를 수신하여 감시 영역을 지나는 객체를 인식하는 객체 인식 장치(200)를 포함한다.An object recognition system using a pressure sensor according to an embodiment of the present invention receives sensing data from a plurality of pressure sensors (100a, 100b, 100c) installed in an area for monitoring the passage of a vehicle or a person, And an
복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)는 감시 영역의 지면에 설치되어, 감시 영역을 지나는 차량이나 피감시자에 의해 압력이 가해지면 이를 센싱하여 객체 인식 장치(200)로 전송한다.The plurality of
구체적으로, 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)에서 전송되는 센싱 데이터에는 측정된 압력의 크기 정보 및 압력이 측정된 위치 정보가 포함될 수 있으나 이에 한정되지 않으며 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)에서 측정된 센싱 데이터가 순차적으로 객체 인식 장치(200)로 전송될 수 있다.Specifically, the sensing data transmitted from the plurality of
객체 인식 장치(200)는 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)로부터 센싱 데이터를 수신하고 이를 처리한 후, 기 저장된 객체 정보와 비교하여 감시 영역을 지나는 객체의 유형을 인식할 수 있다.The
예를 들어, 감시 영역을 지나는 객체가 사람인지 차량인지 여부 등을 판단할 수 있다. 더 나아가 처리된 센싱 데이터는 인식된 객체의 행동 패턴 분석, 이동 경로 추적하는데 활용할 수도 있다.For example, it can be determined whether the object passing through the surveillance region is a person or a vehicle. Furthermore, the processed sensed data may be used to analyze the behavior pattern of the recognized object and track the movement route.
복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)로부터 수신된 센싱 데이터를 이용하여 감시 영역을 지나는 객체를 인식하는 구체적인 방법은 이하에서 상세하게 설명하도록 한다.A specific method of recognizing an object passing through the surveillance region using the sensing data received from the plurality of
한편, 본 실시예에서는 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)가 객체 인식 장치(200)와 구별되는 독립적인 장치인 것으로 도시하였으나 이에 한정되지 않으며, 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)가 객체 인식 장치(200)에 포함되도록 구현할 수도 있다.Although the plurality of
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법을 설명하기 위한 흐름도이다.2 is a flowchart illustrating an object recognition method using a pressure sensor according to an embodiment of the present invention.
객체 인식 장치(200)는 감시 영역에 설치된 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)로부터 센싱 데이터를 수신한다(S210). 센싱 데이터에는 0~255 레벨값 중 하나의 레벨값을 갖는 압력의 크기 정보 및 압력이 감지된 위치 정보가 포함되어 있을 수 있다.The
센싱 데이터를 수신한 객체 인식 장치(200)는 센싱 데이터를 소정의 시간 간격으로 샘플링하고, 샘플링된 데이터 중 기 설정된 조건을 충족하는 데이터를 선택하여 유효 데이터를 산출한다(S220).The
여기서 유효 데이터란, 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)를 통해 수신된 데이터 중 실제 객체를 인식하는데 사용되는 데이터를 의미한다. 이때, 유효 데이터에는 감지된 압력의 크기 정보와 소정의 값을 갖는 압력이 감지된 감지된 위치 정보가 포함될 수 있다.Here, valid data means data used to recognize actual objects among data received through the plurality of
복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)로부터 수신된 센싱 데이터를 샘플링하여 유효 데이터를 산출하는 구체적인 방법은 도 3에서 설명하도록 한다.A concrete method of sampling the sensing data received from the plurality of
유효 데이터가 산출되면 객체 인식 장치(200)는 이를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환한다(S230). 메타데이터에는 센서에서 센싱 데이터가 수신된 시간, 압력의 크기 및 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 감지된 센서의 위치 정보 등이 포함될 수 있다.When valid data is calculated, the
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면 유효 데이터는 XML(Extensible Markup Language), JSON(JavaScript Object Notation), TXT 등과 같은 데이터 포맷 형태를 가지를 메타데이터로 변환될 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, valid data can be converted into metadata having a data format such as Extensible Markup Language (XML), JavaScript Object Notation (JSON), TXT, and the like.
이와 같이 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 이유는 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)로부터 수신되는 로우 데이터(Raw Data)를 객체 인식에 그대로 활용하는 경우 데이터들을 효율적으로 관리하기가 쉽지 않기 때문이다.The reason why the valid data is converted into the metadata having the predetermined data structure is that when the raw data received from the plurality of
즉, 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 형태를 가지는 메타데이터로 변환하고 이후에 센서들로부터 수신되는 데이터를 메타데이터에 반영하면, 데이터가 어떤 센서로부터 언제 수신되었는지 식별하는데 용이할 뿐만 아니라 이전에 수신된 데이터와 관련성을 판단하는데도 용이하다는 장점을 누릴 수 있다.That is, if the valid data is converted into metadata having a predetermined type and the data received from the sensors thereafter is reflected in the metadata, it is not only easy to identify when the data is received from which sensor, It is easy to judge the relevance.
예를 들어, 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)가 설치된 감시 영역에 피감시자가 들어오면, 피감시자의 발자국 모양으로 압력이 감지되고 이에 관한 센싱 데이터가 유효 데이터로 산출되어 기 설정된 구조의 메타데이터로 변환된다.For example, when a monitored person enters a monitoring area in which a plurality of
메타 데이터에는 피감시자 발자국 영역의 크기, 윤곽선 정보, 좌표 정보 등과 같은 세부 정보가 포함될 수 있다.The metadata may include detailed information such as the size of the subject's footprint area, contour information, coordinate information, and the like.
이후, 객체 인식 장치(200)는 메타 데이터에 포함된 정보와 기 저장된 객체의 특징 정보를 비교하여 감시 영역에 출입한 객체의 유형을 인식한다(S240).Thereafter, the
예를 들어, 메타 데이터에 포함된 정보, 예를 들어, 압력의 크기, 소정의 값을 가지는 압력이 검출된 영역의 형태, 영역의 외곽선의 형상 등의 정보로 추출한 특징점과 객체 인식 장치(200)에 기 저장된 객체의 특징점을 비교하여 감시 영역에 출입한 객체가 사람인지 혹은 차량인지 등을 인식할 수 있다.For example, the feature point extracted by the information included in the meta data, for example, information on the size of the pressure, the shape of the area where the pressure having a predetermined value is detected, the shape of the outline of the area, And compare the minutiae points of the previously stored objects to recognize whether the object entering or exiting the monitoring area is human or vehicle.
메타데이터로부터 추출된 특징점과 기 저장된 복수의 객체들에 대한 특징점을 비교하여 감시 영역에 출입한 객체를 인식하는 구체적인 방법은 이하에서 상세하게 설명하도록 한다.A concrete method of recognizing an object entering and exiting the surveillance area by comparing minutiae points extracted from the metadata with minutiae points of a plurality of pre-stored objects will be described in detail below.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 센서로부터 수신된 센싱 데이터를 소정의 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 유효 데이터를 산출하는 과정을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.3 is a diagram illustrating a process of sampling valid data received from a sensor at predetermined time intervals and calculating valid data according to an embodiment of the present invention.
구체적으로, 도 3은 센싱 데이터에 포함된 정보를 시각적으로 표시한 도면이다.Specifically, FIG. 3 is a diagram visually showing the information included in the sensing data.
상술한 바와 같이, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 장치(200)는 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 센서로부터 수신된 데이터를 샘플링한다. 예를 들어, 객체 인식 장치(200)가 100ms 마다 데이터를 샘플링한다면, 제1 샘플링 데이터(310)와 제2 샘플링 데이터(320)가 샘플링된 시간 간격은 100ms가 된다.As described above, the
마찬가지로, 제2 샘플링 데이터(320)와 제3 샘플링 데이터(330)의 간격 및 제3 샘플링 데이터(330)와 제4 샘플링 테이터(340)의 간격도 100ms가 됨을 알 수 있다.Similarly, the interval between the
제1 샘플링 데이터(310)에서 흑색으로 표시된 부분은 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력값이 측정된 영역을 의미한다.The portion indicated by black in the
압력 센서가 설치된 감시 영역에 피감시자가 발을 내딛을 경우 통상 피감시자의 발 뒷꿈치가 지면에 먼저 닿게 되므로 제1 샘플링 데이터(310)와 같은 데이터가 취득된다.When the monitored person puts his / her foot on the surveillance area where the pressure sensor is installed, the heel of the surveillance person first touches the ground, so that data such as the
이후, 시간이 지남에 따라 앞꿈치가 지면에 닿고 이후 뒷꿈치가 지면에서 떨어지게 되므로 제2 샘플링 데이터(320), 제3 샘플링 데이터(330), 제4 샘플링 데이터(340)와 같은 데이터가 샘플링 된다.Then, since the forearm comes into contact with the ground as time passes and then the heel falls from the ground, data such as the
도 3의 경우 복수의 샘플링 데이터(310, 320, 330, 340, 350) 중 샘플링된 데이터가 피감시자의 발자국임을 인식하기 위해서는 제3 샘플링 데이터(330)를 활용하는 것이 인식률을 높이는데 도움이 될 것이다.3, it is helpful to use the
제3 샘플링 데이터(330)에 포함된 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 검출된 영역이 발자국의 외형과 유사하기 때문이다.This is because the area in which the pressure having a predetermined size included in the
따라서, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 장치(200)는 샘플링 된 데이터 중 제3 데이터(330)를 유효 데이터로 산출하여 객체 인식을 하는데 사용할 수 있다.Accordingly, the
구체적으로, 샘플링된 데이터 중 압력값이 측정된 영역의 면적이 임계값 이상인 샘플링 데이터를 유효 데이터로 산출하여 객체를 인식하는데 사용할 수 있다.More specifically, the sampling data having the area of the measured area of the pressure value of the sampled data may be used as effective data to recognize the object.
제1 샘플링 데이터(310), 제2 샘플링 데이터(320), 제4 샘플링 데이터(340), 제5 샘플링 데이터(350) 모두 피감시자가 압력 센서를 밟고 지나감에 따라 생성된 데이터 이긴 하나, 제1 샘플링 데이터(310), 제2 샘플링 데이터(320), 제4 샘플링 데이터(340), 제5 샘플링 데이터(350)의 경우 발자국 모양의 특성을 나타내지 못하므로, 이를 활용하면 인식률이 떨어질 수 있기 때문이다.Although the
한편, 상술한 과정을 거쳐 유효 데이터를 산출하면, 압력값이 측정된 영역의 면적이 임계값 이상인 샘플링 데이터가 복수개 있는 경우가 발생될 수 있다.On the other hand, when valid data is calculated through the above-described process, there may be a case where a plurality of pieces of sampling data in which the area of the area where the pressure value is measured is equal to or larger than the threshold value may occur.
이때에는 압력값이 검출된 영역의 면적이 최대값을 갖는 샘플링 데이터를 유효 데이터로 산출함으로써 객체 인식률을 높일 수 있을 것이다.At this time, the object recognition rate can be increased by calculating the sampling data having the maximum value of the area where the pressure value is detected as valid data.
다만, 유효 데이터를 산출하는 방법은 이에 한정되지 않으며 인식하고자 하는 객체의 종류에 따라 다른 방법이 적용되도록 구현할 수 있음은 물론이다.However, the method of calculating valid data is not limited to this, and other methods may be applied according to the type of object to be recognized.
상술한 과정을 거쳐 산출된 유효 데이터는 기 설정된 형태의 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환된다.The valid data calculated through the above-described process is converted into the metadata having a predetermined type of structure.
도 4는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 유효 데이터가 변환되어 생성된 메타데이터의 구조를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.4 is a diagram for explaining a structure of metadata generated by transforming valid data according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 실시예에서는 피감시자의 발자국에 의해 센싱된 유효 데이터가 메타데이터로 변환되는 과정을 예로 들어 설명한다.In this embodiment, the process of converting the valid data sensed by the footprint of the monitored person into meta data will be described as an example.
상술한 바와 같이 유효 데이터에 포함된 다양한 정보를 효율적으로 관리하기 위해 산출된 유효 데이터는 기 설정된 형태의 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환된다.As described above, in order to efficiently manage various information included in valid data, the calculated valid data is converted into metadata having a predetermined type of structure.
도 4에 도시된 바와 같이 메타데이터에는 설치된 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)들로부터 센싱 데이터를 수신한 시간 정보, 압력을 감지한 센서의 고유 정보, 소정의 값을 가지는 압력이 감지된 영역의 크기 정보, 상술한 압력이 감지된 영역의 위치 정보 등이 포함될 수 있다.As shown in FIG. 4, in the meta data, time information of sensing data received from the plurality of
한편, 본 실시예에서는 하나의 메타데이터에 하나의 발자국에 의해 생성된 센싱 데이터가 포함되는 것으로 설명하였으나, 이에 한정되지 않으며 메타데이터가 업데이트되어 추가적인 정보가 포함되도록 할 수도 있다.In the present embodiment, one metadata includes the sensing data generated by one of the footsteps. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the metadata may be updated to include additional information.
예를 들어, 설치된 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)가 설치된 감시 구역에 사람이 출입하면, 이동 방향으로 복수개의 발자국이 형성될 수 있다. 이 경우, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 장치(200)는 각각의 발자국에 의해 형성된 센싱 데이터를 샘플링하여 유효 데이터를 산출하고, 이를 메타 데이터에 추가시킬 수 있다.For example, when a person enters or exits a monitoring area in which a plurality of installed
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 메타 데이터에 포함되는 정보가 업데이트 되는 과정을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.5 is a diagram illustrating a process of updating information included in meta data according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 실시예에서는 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)가 설치된 감시 영역에 피감시자가 출입하여 화살표가 도시된 방향으로 이동하는 것을 예로 들어 설명한다.In the present embodiment, it is assumed that the monitored person moves into and out of the monitoring area in which the plurality of
도 5에 도시된 도면은 샘플링을 통해 획득된 유효 데이터에 포함된 정보를 시각적으로 표현한 것을 의미한다.The figure shown in FIG. 5 means that the information included in the valid data obtained through sampling is visually expressed.
즉, 유효 데이터에는 압력의 크기 정보 및 소정의 크기의 값을 갖는 압력이 검출된 센서의 위치 정보 등이 포함되므로 이를 시각적으로 표현하면 도 5에 도시된 도면을 얻을 수 있다.That is, the valid data includes the pressure magnitude information and the position information of the sensor that detects the pressure having the predetermined magnitude value, etc., so that the graph shown in FIG. 5 can be obtained by visual representation thereof.
도 5에 도시된 실시예에서는 제1 유효 데이터(510)가 최초로 메타데이터로 변환된 이후에, 제2 유효 데이터(520) 및 제3 유효 데이터(530)가 메타데이터에 추가되도록 구현될 수 있다.In the embodiment shown in FIG. 5, the second
제2 유효 데이터(520)에 대응되는 발자국을 식별하기 위해 고유의 식별자를 제2 유효 데이터(520)에 부가하고, 식별자가 부가된 제2 유효 데이터(520)를 제1 유효 데이터(510)가 변환되어 생성된 메타데이터에 추가할 수 있다.A unique identifier is added to the second
제3 유효 데이터(530)도 마찬가지로, 피감시자의 이동에 의해 제3 유효 데이터(530)가 취득되면 이에 고유의 식별자를 부가한 후 기 생성된 메타데이터에 추가할 수 있다.Likewise, the
상술한 바와 같이 피감시자가 이동됨에 따라 발생되는 유효 데이터에 고유의 식별자를 부가한 후, 이를 메타데이터에 포함시키는 이유는 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링되어 수신되는 데이터들을 보다 용이하게 관리하고 동일한 피감시자에 의해 생성된 유효 데이이터들을 하나의 메타 데이터로 관리함으로써 객체 인식률을 높이 위함이다.The reason why the unique identifier is added to the valid data generated due to the movement of the subject as described above and included in the metadata is that the data sampled and received at a predetermined time interval are more easily managed, To manage the validity data generated by the metadata as a single metadata, thereby increasing the object recognition rate.
즉, 본 실시예에서는 한명의 피감시자가 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)가 설치된 감시 영역에 출입하는 것을 예로 들었으나 다수의 피감시자가 감시 영역에 출입하면 복수의 유효 데이터들이 산출되므로 피감시자 별로 메타데이터를 생성하여 그에 대응되는 데이터들을 관리해야 데이터들을 용이하게 관리할 수 있게 된다.That is, in this embodiment, it is assumed that one monitored person enters and exits the monitoring area in which the plurality of
상술한 과정을 거쳐 생성된 메타데이터는 개체 인식 장치(200)에 기 저장된 데이터와 비교되어 객체를 인식하는데 사용된다.The metadata generated through the above-described process is used to recognize the object by comparing it with the previously stored data in the
한편, 상술한 실시예에서는 피감시자가 사람인 경우를 예로 들어 유효 데이터를 산출하고 이를 이용하여 메타데이터를 생성하는 것을 예로 들어 설명하였으나, 사람이 아닌 다른 객체가 출입하더라도 동일한 알고리즘을 이용하여 메타데이터를 업데이트할 수 있다.Meanwhile, in the above-described embodiment, the case where the observer is a person is described as an example of generating valid data and generating the metadata using the valid data. However, even if an object other than a person enters or exits, You can update it.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 감시 영역에 차량이 출입하는 경우 유효 데이터를 산출하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.6 is a diagram for explaining a method of calculating valid data when a vehicle enters and exits a monitoring area according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 6에서는 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)가 설치된 감시 영역에 4륜 차량이 출입하는 경우를 예로 들어 설명한다.In Fig. 6, a case in which a four-wheel vehicle enters and exits a monitoring region in which a plurality of
4륜 차량이 감시 영역에 설치된 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)을 지남에 따라 수신되는 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하면 도 6에 도시된 바와 같은 데이터를 취득할 수 있다.The data as shown in FIG. 6 can be acquired by sampling the received data at a predetermined time interval as the four-wheel vehicle passes through the plurality of
즉, 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 검출되는 영역이 4군데에서 나타나며 시간이 지남에 따라 압력이 검출된 영역이 차량의 이동방향으로 이동되는 모습이 나타난다.That is, a region where a pressure having a predetermined size is detected appears in four places, and a region in which pressure is detected moves in a moving direction of the vehicle as time passes.
최초로 샘플링된 제6 샘플링 데이터(610)를 유효 데이터로 산출하고 이를 메타데이터로 변환한 후 이후에 수신되는 샘플링 데이터로 산출한 유효 데이터를 추가하여 메타데이터를 업데이트 할 수 있다.The
도 7은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 상술한 과정을 거쳐 생성된 메타데이터에 포함된 정보를 시각적으로 표시한 도면이다.FIG. 7 is a diagram for visually displaying information included in the metadata generated through the above-described process according to an embodiment of the present invention.
메타데이터에 차량이 이동됨에 따라 수신되는 각종 데이터를 반영하면 차량 바퀴에 의한 압력의 크기 정보, 압력이 감지된 센서의 위치 정보 및 압력이 감지된 시간 정보 등이 메타데이터에 포함될 수 있다.When the vehicle is moved to the meta data, the meta data may include information on the magnitude of the pressure of the vehicle wheel, the position information of the pressure sensor, and the time when the pressure is sensed.
이를 시각적으로 표시하면 도 7에 도시된 바와 같은 데이터를 얻을 수 있다. 즉, 차량이 이동됨에 따라 나타나는 바퀴 자국의 정보를 얻을 수 있다.If this is visually displayed, data as shown in FIG. 7 can be obtained. That is, the information of the wheel mark appearing as the vehicle is moved can be obtained.
물론 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하므로 도 7에 데이터와 같은 연속적인 데이터가 얻어지지 않을 수도 있으나, 센싱 데이터를 샘플링 하는 시간이 충분히 짧은 경우 시각적으로 도 7과 같은 데이터를 얻을 수 있다.Although continuous data such as data may not be obtained in FIG. 7 because the sensing data is sampled at predetermined time intervals, if the sampling time of the sensing data is sufficiently short, data as shown in FIG. 7 can be visually obtained.
이와 같은 데이터를 포함하는 메타데이터와 객체 인식 장치(200)에 기 저장된 객체 정보를 비교하여 일치하는 객체 정보를 검색하면, 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)가 설치된 감시 영역을 지나는 객체의 종류를 인식할 수 있다는 효과를 달성할 수 있다.When the metadata including such data is compared with the previously stored object information in the
상술한 과정을 거쳐 생성된 메타데이터와 객체 인식 장치(200)에 기 저장된 객체 정보를 비교하여 객체를 인식하는 구체적인 방법은 이하에서 상세하게 설명하도록 한다.A concrete method of recognizing the object by comparing the generated metadata with the object information stored in the
도 8은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 메타데이터를 이용하여 감시 영역에 출입한 객체를 인식하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 흐름도이다.8 is a flowchart illustrating a method of recognizing an object entering and exiting the surveillance area using metadata according to an embodiment of the present invention.
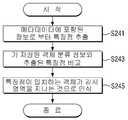
상술한 과정을 거쳐 메타데이터가 생성되면 메타데이터에 포함된 정보를 이용하여 감시 영역을 지나는 객체의 특징점이 생성된다(S241).When the metadata is generated through the above-described process, feature points of the object passing through the surveillance region are generated using the information included in the metadata (S241).
즉, 메타데이터를 통해 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)가 설치된 영역을 지나면서 센싱 데이터를 발생시킨 객체의 특징점이 생성된다.That is, the characteristic points of the object generating the sensing data are generated through the area where the plurality of
객체 인식 장치(200)는 압력이 감지된 영역의 크기, 압력의 크기 정보, 압력이 감지된 영역의 외곽선, 압력이 감지된 센서의 위치 정보 등을 이용하여 특징점을 생성할 수 있다.The
또한, 객체 인식 장치(200)는 복수의 객체들에 대한 특징점 정보들을 기 저장하고 있을 수 있다. 이에, 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)가 설치된 감시 영역을 지나는 객체로부터 메타데이터가 생성되면 객체 인식 장치(200)에 포함된 객체 인식 모듈이 메타데이터로부터 특징점을 생성하고, 메타데이터로부터 생성된 특징점과 기 저장된 복수의 객체들의 특징점을 비교한다(S243).In addition, the
이후, 특징점이 일치하는 객체가 감시 영역을 지나는 것이라고 인식한다(S245).Then, it is recognized that the object whose feature points coincide passes through the surveillance region (S245).
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 장치(200)는 메타데이터로부터 특징점을 생성하고, 생성된 특징점과 기 저장된 복수의 객체들의 특징점을 비교하는 객체 인식 모듈로 SVM(Support Vector Machine), NN(Neural Network) 중 어느 하나를 사용할 수 있다.The
다만, 상술한 객체 인식 모듈은 일 실시예에 불과한 것으로 발명을 구현하는 과정에 있어 상술한 분류기 외에 다른 분류기를 사용할 수 있음은 물론이다.However, it should be understood that the above-described object recognition module is merely an embodiment, and that a classifier other than the classifier described above can be used in the process of implementing the invention.
한편, 상술한 과정을 거쳐 감시 영역을 지나는 객체의 유형이 인식되면 인식 결과를 저장할 수도 있다.Meanwhile, if the type of the object passing through the surveillance region is recognized through the above-described process, the recognition result may be stored.
즉, 메타데이터로 생성된 특징점 및 그 특징점을 기초로 인식된 결과를 저장하면, 차후에 유사한 특징점이 생성된 객체를 인식할 때 인식 결과를 참고함으로써 인식률을 높일 수 있다는 효과를 달성할 수 있다.That is, by storing the minutiae created by the metadata and the recognized results based on the minutiae points, it is possible to increase the recognition rate by referring to the recognition results when recognizing the object in which similar minutiae are generated.
예를 들어, 메타데이터에서 추출된 특징점이 A인 객체를 사람의 발자국이라고 인식했다면 그 인식결과를 저장하고, 차후에 동일한 특징점 A가 추출된 객체 또는 그와 유사한 특징점 A’을 갖는 객체를 인식할 때 이전에 인식한 결과를 참고할 수 있다.For example, if an object having a minutiae extracted from the metadata is recognized as a human footprint, the recognition result is stored, and when an object having the same minutiae A or a minutiae point A 'similar thereto is recognized You can refer to the previously recognized results.
상술한 바와 같이, 객체 인식 장치(200)의 분류기가 메타데이터로부터 특징점을 추출하여 감시 영역을 지나는 객체를 인식하기 위해서는 복수의 객체들에 대한 특징점 정보를 미리 저장하고 있어야 한다.As described above, in order for the classifier of the
예를 들어, 피감시자가 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)를 밟고 지나갈 때 어떠한 형태의 데이터가 생성되는지 또는 차량이 지나갈 때 어떠한 형태의 데이터가 생성되는지에 대한 정보를 미리 가지고 있어야 한다.For example, information on what kind of data is generated when the monitored person steps on the plurality of
도 9는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 객체 인식 장치(200)에 기 저장된 복수의 객체들에 대한 정보를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.9 is a view for explaining information on a plurality of objects previously stored in the
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 장치(200)에는 도 9에 도시된 바와 같은 객체 정보들이 저장되어 있을 수 있다. 구체적으로, 객체의 고유 번호, 객체의 세부 번호 및 객체의 세부 정보 등이 저장되어 있을 수 있다.The
객체의 고유 번호란 임의의 객체에 부여된 고유 번호를 의미한다. 예를 들어, 사람의 발자국, 차량의 바퀴 자국 각각에 대해 부여된 고유 번호를 의미한다.A unique number of an object means a unique number assigned to an arbitrary object. For example, a footprint of a person, or a unique number assigned to each wheel of a vehicle.
세부 번호는 고유 번호가 부가된 임의의 객체를 구체적으로 식별하기 위해 부여된 번호를 의미한다.The detail number refers to a number assigned to specifically identify an arbitrary object to which a unique number is added.
예를 들어, 사람의 발자국에 고유 번호가 부가된 경우 바람의 발자국이 우측발에 의한 것인지 도는 좌측발에 의한 것인지 여부를 구분하기 위해 세부 번호가 추가적으로 더 부여될 수도 있다.For example, if a unique number is added to a person's footprint, an additional detail number may be added to distinguish whether the foot of the wind is due to the right foot or the left foot.
감시 영역에 출입하는 사람의 인원수를 파악하기 위해서는 좌측발 및 우측발에 의한 압력 정보를 한 쌍으로 관리하여야 하므로 세부 번호를 추가적으로 더 부가할 수도 있다.In order to know the number of persons entering and leaving the surveillance area, the pressure information by the left foot and the right foot must be managed in a pair, so that the detail number may be additionally added.
세부 정보는 특정 객체가 압력 센서 위를 지날 때 나타나는 압력의 크기, 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 검출되는 위치 정보, 압력이 검출된 영역의 외곽선 정보, 압력이 검출된 영역의 넓이 정보 등이 포함될 수 있다.The detailed information may include a magnitude of pressure appearing when a specific object passes over the pressure sensor, position information where a pressure having a predetermined magnitude is detected, outline information of a region where pressure is detected, have.
객체 인식 장치(200)의 객체 분류기는 메타데이터로부터 특징점을 생성한 후, 기 저장된 객체의 세부 정보들로부터 추출된 특징점과 비교하여 특징점이 일치하는 객체의 고유 번호 및 세부 번호 중 적어도 하나의 정보를 선택하고, 이와 같은 과정을 통해 감시 영역을 지나는 객체의 유형을 인식할 수 있다.The object classifier of the
추가적으로, 감시 영역을 지나는 객체의 이동 방향, 행동 패턴 등에 관한 정보도 얻을 수 있다.In addition, information on the direction of movement, behavior patterns, etc. of objects passing through the surveillance area can be obtained.
상술한 바와 같이, 감시 영역에 설치된 압력 센서를 통해 해당 구역을 통과하는 객체의 유형을 인식하면 날씨, 조도 등과 같의 외부 환경의 영향을 최소화함으로써 인식률을 높일 수 있다는 효과를 달성할 수 있다.As described above, when the type of the object passing through the area is recognized through the pressure sensor installed in the surveillance area, the effect that the recognition rate can be increased by minimizing the influence of the external environment such as weather, illumination and the like can be achieved.
도 10은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 장치(200)를 설명하기 위한 기능 블록도이다.10 is a functional block diagram illustrating an
도 10에 도시된 객체 인식 장치는 수신부(1010), 전 처리부(1020), 메타데이터 생성부(1030) 및 객체 인식부(1040)을 포함한다.10 includes a
도 10에 도시된 객체 인식 장치(200)에는 본 발명의 실시예들과 관련 있는 구성요소들만이 도시되어 있다. 따라서, 본 발명이 속한 기술분야의 통상의 기술자라면 도 10에 도시된 구성요소외에 다른 범용적인 구성요소들이 더 포함될 수 있음을 알 수 있다.Only the components related to the embodiments of the present invention are shown in the
수신부(1010)는 감시 영역에 설치된 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)들로부터 센싱 데이터를 수신한다. 센싱 데이터에는 0~255 레벨값 중 하나의 레벨값을 갖는 압력의 크기 정보와, 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 감지된 센서의 위치 정보가 포함될 수 있다.The receiving
전 처리부(1020)는 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보 및 압력이 감지된 위치 정보를 포함하는 유효 데이터를 산출한다. 센싱 데이터를 샘플링하여 유효 데이터를 산출하는 구체적인 방법은 도 3에서 상세하게 설명하였으므로 중복되는 설명은 생략하도록 한다.The preprocessing unit 1020 samples the sensed data at predetermined time intervals and calculates effective data including the pressure information of the sensed pressure in the sensor and the sensed position information. A detailed method of sampling sensed data to calculate effective data has been described in detail with reference to FIG. 3, and thus redundant description will be omitted.
메타데이터 생성부(1030)는 산출된 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환한다.The
산출된 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 이유는 센서로부터 수신되는 방대한 양의 데이터를 효율적으로 관리함으로써 객체 인식률을 높이기 위함이다.The reason for converting the calculated effective data into the metadata having the predetermined data structure is to increase the object recognition rate by efficiently managing the vast amount of data received from the sensor.
메타데이터에는 센서에서 센싱 데이터가 수신된 시간, 압력의 크기 정보, 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 감지된 센서의 위치 정보, 압력이 감지된 영역의 넓이, 압력이 감지된 영역의 외곽선 정보 등이 포함될 수 있다.The meta data includes the time at which the sensing data was received from the sensor, the size information of the pressure, the position information of the sensor that sensed a pressure having a predetermined size, the width of the sensed area, and the outline information of the sensed area .
객체 인식부(1040)는 메타데이터에 포함된 정보와 기 저장된 복수의 객체에 관한 정보를 비교하여 객체의 유형을 인식한다. 구체적으로, 메타데이터에 포함된 정보를 기초로 생성된 특징점과, 기 저장된 복수의 객체에 관한 정보를 기초로 산출된 특징점을 비교하여 동일한 특징점을 가진 객체가 감시 영역을 지나는 것으로 인식한다.The
추가적으로, 인식된 객체의 이동 경로를 추적하거나 행동 패턴 등을 감지하여 효율적으로 감시 영역을 관찰하는데 활용할 수도 있다.In addition, it may be used to efficiently track the surveillance region by tracking the movement path of the recognized object, detecting the behavior pattern, and the like.
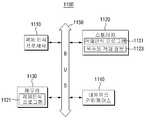
도 11은 본 발명의 또 다른 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 장치(1110)을 설명하기 위한 기능 블록도이다.11 is a functional block diagram illustrating an
본 발명의 또 다른 실시예에 따른 객체 인식 장치(1110)은 객체 인식 프로세서(1110), 스토리지(1120), 메모리(1130), 네트워크 인터페이스(1140) 및 버스(1150)을 포함한다.The
도 11에는 본 발명의 실시예와 관련된 구성요소들만이 도시되어 있다. 따라서, 본 발명이 속한 기술분야의 통상의 기술자라면 도 11에 도시된 구성요소들 외에 다른 범용적인 구성요소들이 더 포함될 수 있음을 알 수 있을 것이다.Fig. 11 shows only the components related to the embodiment of the present invention. Accordingly, those of ordinary skill in the art will recognize that other general-purpose components may be included in addition to those shown in FIG.
객체 인식 프로세서(1110)는 객체 인식 프로그램(1121)을 실행할 수 있는 프로세서이다. 그러나, 이에 한정되지 않으며 다른 프로그램을 실행하도록 구현할 수도 있다.The
스토리지(1120)는 객체 인식 프로그램(1121)의 데이터는 바이너리 실행 파일 및 기타 리소스 파일을 포함할 수 있다.The
객체 인식 프로그램(1121)은, 센서에서 감지된 센싱 데이터를 수신하는 단계, 상기 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 위치 정보를 포함하는 유효 데이터를 산출하는 단계, 상기 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 단계 및 상기 메타데이터에 포함된 정보와 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보를 비교하여 객체의 유형을 인식하는 단계를 수행하는 일련의 오퍼레이션을 포함할 수 있다.The
또한, 스토리지(1120)에는 감시 영역을 지나는 객체를 인식하는데 사용되는 복수의 객체들에 대한 정보가 포함될 수 있다.In addition, the
예를 들어, 사람의 발자국이 복수의 압력 센서(100a, 100b, 100c)가 설치된 감시영역을 지나는 경우, 감지되는 압력의 크기, 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 검출되는 센서의 위치 정보, 압력이 검출되는 크기의 넓이, 압력이 검출된 영역의 외곽선 정보 등이 미리 저장되어 있을 수 있다.For example, when a footprint of a person passes through a surveillance region in which a plurality of
메모리(1130)는 객체 인식 프로그램(1121)을 로딩한다. 메모리(1130)에 로딩된 객체 인식 프로그램(1121)은 객체 인식 프로세서(1110)에 의해 실행된다.The
네트워크 인터페이스(1140)에는 다른 컴퓨팅 장치가 연결될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 네트워크 인터페이스(1140)에 연결되는 다른 컴퓨팅 장치는 디스플레이 장치, 사용자 단말 등이 될 수 있다.The
또한, 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 네트워크 인터페이스(1140)는 이더넷, FireWire, USB 등으로 구현될 수 있다.Also, the
버스(1150)는 상술한 객체 인식 프로세서(1110), 스토리지(1120) 및 메모리(1130) 등이 연결되어 데이터 이동 통로로서의 역할을 수행한다.The
한편, 상술한 방법은 컴퓨터에서 실행될 수 있는 프로그램으로 작성 가능하고, 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 기록매체를 이용하여 상기 프로그램을 동작시키는 범용 디지털 컴퓨터에서 구현될 수 있다. 또한, 상술한 방법에서 사용된 데이터의 구조는 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 기록매체에 여러 수단을 통하여 기록될 수 있다. 상기 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 기록매체는 마그네틱 저장매체(예를 들면, 롬, 플로피 디스크, 하드 디스크 등), 광학적 판독 매체(예를 들면, 시디롬, 디브이디 등)와 같은 저장매체를 포함한다.Meanwhile, the above-described method can be implemented in a general-purpose digital computer that can be created as a program that can be executed by a computer and operates the program using a computer-readable recording medium. In addition, the structure of the data used in the above-described method can be recorded on a computer-readable recording medium through various means. The computer-readable recording medium includes a storage medium such as a magnetic storage medium (e.g., ROM, floppy disk, hard disk, etc.), optical reading medium (e.g., CD ROM,
본 실시예와 관련된 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자는 상기된 기재의 본질적인 특성에서 벗어나지 않는 범위에서 변형된 형태로 구현될 수 있음을 이해할 수 있을 것이다. 그러므로 개시된 방법들은 한정적인 관점이 아니라 설명적인 관점에서 고려되어야 한다. 본 발명의 범위는 전술한 설명이 아니라 특허청구범위에 나타나 있으며, 그와 동등한 범위 내에 있는 모든 차이점은 본 발명에 포함된 것으로 해석되어야 할 것이다.It will be understood by those skilled in the art that various changes in form and details may be made therein without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims. Therefore, the disclosed methods should be considered from an illustrative point of view, not from a restrictive point of view. The scope of the present invention is defined by the appended claims rather than by the foregoing description, and all differences within the scope of equivalents thereof should be construed as being included in the present invention.
Claims (13)
Translated fromKorean상기 객체 인식 장치가 상기 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 위치 정보를 포함하는 유효 데이터를 산출하는 단계;
상기 객체 인식 장치가 상기 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 단계; 및
상기 객체 인식 장치가 상기 메타데이터에 포함된 정보와 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보를 비교하여 객체의 유형을 인식하는 단계를 포함하는 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법.Receiving object sensing data from a sensor;
Sampling the sensed data at a predetermined time interval and calculating effective data including the sensed pressure magnitude information and the pressure sensed position information;
Converting the valid data into metadata having a predetermined data structure; And
Wherein the object recognition apparatus recognizes the type of the object by comparing information included in the metadata with a plurality of pre-stored object information.
상기 유효 데이터를 산출하는 단계는,
소정의 크기를 갖은 압력이 검출된 영역의 면적이 임계값 이상인 샘플링 데이터를 유효 데이터로 산출하는 단계를 포함하는 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the step of calculating the valid data comprises:
And calculating, as valid data, sampling data having an area of a region where a pressure having a predetermined size is detected is equal to or larger than a threshold value.
상기 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 검출된 영역의 면적이 임계값 이상인 샘플링 데이터가 복수개인 경우,
상기 검출된 영역의 면적이 최대값을 갖는 샘플링 데이터로 유효 데이터를 산출하는 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법.3. The method of claim 2,
When there are a plurality of pieces of the sampling data in which the area of the pressure detected region having the predetermined size is equal to or larger than the threshold value,
And the effective data is calculated from the sampling data having the maximum value of the area of the detected area.
상기 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 단계는,
추가적인 센싱 데이터를 수신하는 단계;
추가로 수신된 센싱 데이터에서 유효 데이터를 산출하고 식별자를 부가하는 단계; 및
상기 식별자가 부가된 유효 데이터를 상기 메타데이터에 추가하는 단계를 포함하는 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the converting the valid data into metadata having a predetermined data structure includes:
Receiving additional sensing data;
Calculating effective data from the further received sensing data and adding an identifier; And
And adding valid data added with the identifier to the meta data.
상기 메타데이터는,
상기 센싱 데이터가 수신된 시간 정보, 압력을 감지한 센서의 고유 정보, 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 센서의 위치 정보, 상기 압력이 감지된 영역의 넓이, 상기 압력이 감지된 영역의 외곽선 중 적어도 하나의 정보를 포함하는 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법.5. The method of claim 4,
The metadata includes:
The sensor information of the sensor that senses the pressure, the magnitude information of the pressure, the position information of the sensor where the pressure is sensed, the width of the sensed area, the outline of the sensed area, The method comprising the steps of: (a)
상기 객체의 유형을 인식하는 단계는,
상기 메타데이터를 이용하여 객체의 특징점을 생성하는 단계;
기 저장된 복수의 객체들의 특징점과 상기 메타데이터로 생성된 특징점을 비교하는 단계; 및
기 저장된 복수의 객체들의 특징점 중 상기 메타데이터로 생성된 특징점과 동일한 특징점을 가지는 객체가 감시 영역을 지나는 것이라고 인식하는 단계를 포함하는 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the step of recognizing the type of the object comprises:
Generating minutiae points of the object using the meta data;
Comparing minutiae points of a plurality of previously stored objects with minutiae generated by the meta data; And
And recognizing that an object having the same minutiae as the minutiae generated by the meta data among the minutiae of the plurality of previously stored objects passes through the surveillance area.
상기 메타데이터로 생성된 특징점과 동일한 특징점을 가지는 객체가 감시 영역을 지나는 것이라고 인식하는 단계는,
상기 기 저장된 복수의 객체들의 특징점 중 상기 메타데이터로 생성된 특징점과 동일한 특징점을 가지는 객체에 부여된 고유 번호를 선택하는 단계를 포함하는 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법.The method according to claim 6,
The step of recognizing that an object having the same minutiae as the minutiae created by the meta data passes through the surveillance area,
And selecting a unique number assigned to an object having the same minutiae as the minutiae created by the meta data among minutiae of the plurality of previously stored objects.
상기 메타데이터를 이용하여 객체의 특징점을 생성하는 단계는,
상기 메타데이터에 포함된 상기 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보, 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 검출되는 위치 정보, 압력이 검출된 영역의 외곽선 정보, 압력이 검출된 영역의 넓이 정보 중 적어도 하나를 이용하여 생성하는 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법.The method according to claim 6,
Wherein the generating of the feature point of the object using the metadata comprises:
At least one of size information of a pressure detected by the sensor included in the metadata, position information where a pressure having a predetermined size is detected, outline information of a region where pressure is detected, and width information of a region where pressure is detected A method for recognizing an object using a pressure sensor.
상기 메타데이터로 생성된 특징점을 기초로 인식된 결과를 저장하는 단계를 더 포함하는 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법.The method according to claim 6,
And storing the recognized result based on the minutiae created by the meta data.
상기 객체 인식 장치가, 상기 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 0 내지 255 레벨 중 하나의 값을 갖는 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 2차원 좌표 정보를 포함하는 유효 데이터를 산출하는 단계;
상기 객체 인식 장치가, 상기 유효 데이터를 상기 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보, 소정의 크기를 갖는 압력이 검출되는 위치 정보, 압력이 검출된 영역의 외곽선 정보, 압력이 검출된 영역의 넓이 정보 중 적어도 하나의 정보를 포함하고 기 설정된 구조를 가지는 메타데이터로 변환하는 단계;
상기 객체 인식 장치가, 상기 메타데이터에 포함된 정보로 특징점을 추출하여, 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보와 비교하는 단계;
상기 객체 인식 장치가, 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보 중 상기 메타데이터에서 추출된 특징점과 동일한 특징점을 갖는 객체에 부여된 고유 번호를 선택하는 단계; 및
상기 객체 인식 장치가, 상기 선택된 고유 번호에 대응되는 객체가 상기 센서가 감지된 감시 영역에 출입한 것으로 인식하는 단계를 포함하는 압력 센서를 이용한 객체 인식 방법.The object recognition apparatus comprising: receiving sensed sensing data from a sensor;
Wherein the object recognition apparatus samples the sensing data at a predetermined time interval and calculates validity data including pressure magnitude information having one of 0 to 255 levels and two-dimensional coordinate information in which the pressure is sensed ;
The object recognition apparatus may be configured to obtain the valid data from the information on the magnitude of the pressure sensed by the sensor, the positional information on which the pressure with a predetermined size is detected, the outline information on the region on which the pressure is detected, Converting at least one piece of information into metadata having a predetermined structure;
Extracting feature points from the information included in the metadata and comparing the extracted feature points with a plurality of previously stored object information;
Selecting the unique number assigned to the object having the same minutiae as the minutiae extracted from the meta data among the previously stored plurality of object information; And
Wherein the object recognizing device recognizes that an object corresponding to the selected inherent number enters and exits the surveillance area in which the sensor is sensed.
상기 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 위치 정보를 포함하는 유효 데이터를 산출하는 전 처리부;
상기 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 메타데이터 생성부; 및
상기 메타데이터에 포함된 정보와 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보를 비교하여 객체의 유형을 인식하는 객체 인식부를 포함하는 객체 인식 장치.A receiving unit for receiving sensing data sensed by a sensor;
A preprocessor for sampling the sensed data at a predetermined time interval and calculating effective data including magnitude information of the pressure sensed by the sensor and position information on which the pressure is sensed;
A metadata generating unit for converting the valid data into metadata having a predetermined data structure; And
And an object recognition unit for comparing the information included in the metadata with previously stored plurality of object information to recognize the type of the object.
상기 프로세서에 의하여 수행되는 컴퓨터 프로그램을 로드(load)하는 메모리; 및
복수의 객체 정보 및 감시 영역을 지나는 객체의 유형을 인식하는 컴퓨터 프로그램을 저장하는 스토리지를 포함하되,
상기 컴퓨터 프로그램은,
센서에서 감지된 센싱 데이터를 수신하는 오퍼레이션;
상기 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 위치 정보를 포함하는 유효 데이터를 산출하는 오퍼레이션;
상기 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 오퍼레이션; 및
상기 메타데이터에 포함된 정보와 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보를 비교하여 객체의 유형을 인식하는 오퍼레이션을 포함하는 객체 인식 장치.One or more processors;
A memory for loading a computer program executed by the processor; And
A storage for storing a computer program that recognizes a plurality of object information and a type of object passing through the surveillance area,
The computer program comprising:
Receiving sensing data sensed by the sensor;
Sampling the sensed data at a predetermined time interval to calculate effective data including magnitude of pressure sensed by the sensor and sensed position information;
An operation of converting the valid data into metadata having a predetermined data structure; And
And an operation of recognizing the type of the object by comparing the information included in the metadata with the previously stored plurality of object information.
센서에서 감지된 센싱 데이터를 수신하는 단계;
상기 센싱 데이터를 기 설정된 시간 간격으로 샘플링하여 센서에서 감지된 압력의 크기 정보 및 상기 압력이 감지된 위치 정보를 포함하는 유효 데이터를 산출하는 단계;
상기 유효 데이터를 기 설정된 데이터 구조를 갖는 메타데이터로 변환하는 단계; 및
상기 메타데이터에 포함된 정보와 기 저장된 복수의 객체 정보를 비교하여 객체의 유형을 인식하는 단계를 실행시키기 위하여 기록 매체에 저장된 컴퓨터 프로그램.In combination with the computing device,
Receiving sensed sensing data from a sensor;
Sampling the sensed data at a predetermined time interval to calculate effective data including magnitude information of the pressure sensed by the sensor and position information of the sensed pressure;
Converting the valid data into metadata having a predetermined data structure; And
Comparing the information included in the metadata with previously stored plurality of object information to recognize the type of the object;
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150047621AKR101708491B1 (en) | 2015-04-03 | 2015-04-03 | Method for recognizing object using pressure sensor |
| CN201610202237.7ACN106056034A (en) | 2015-04-03 | 2016-04-01 | Pressure sensor-based object identification method and object identification method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150047621AKR101708491B1 (en) | 2015-04-03 | 2015-04-03 | Method for recognizing object using pressure sensor |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20160118830A KR20160118830A (en) | 2016-10-12 |
| KR101708491B1true KR101708491B1 (en) | 2017-02-20 |
Family
ID=57173794
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150047621AExpired - Fee RelatedKR101708491B1 (en) | 2015-04-03 | 2015-04-03 | Method for recognizing object using pressure sensor |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101708491B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN106056034A (en) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106408865A (en)* | 2016-11-03 | 2017-02-15 | 上海斐讯数据通信技术有限公司 | Early warning device, system and early warning method |
| KR102073091B1 (en)* | 2017-05-08 | 2020-02-04 | 두산중공업 주식회사 | Object Location Tracking System |
| CN107610390A (en)* | 2017-10-23 | 2018-01-19 | 安吉艺科装饰材料科技有限公司 | A kind of intelligent doormat with anti-theft feature |
| CN108961447B (en)* | 2018-06-07 | 2019-12-27 | 京东方科技集团股份有限公司 | Method for judging whether seat is occupied or not, seat system and attendance checking method |
| TWI675331B (en)* | 2018-08-31 | 2019-10-21 | 財團法人工業技術研究院 | Storage device and storage method |
| KR102407723B1 (en)* | 2020-08-21 | 2022-06-15 | 이승환 | Personnel counting system using piezoelectric mat |
| KR102428899B1 (en)* | 2020-08-31 | 2022-08-02 | 한국로봇융합연구원 | Pressure distribution data acquisition and verification method |
| CN113315792B (en)* | 2021-07-30 | 2021-11-30 | 深圳市永达电子信息股份有限公司 | Object extraction method and device of network data, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4888581A (en) | 1988-04-06 | 1989-12-19 | Aritech Corporation | Pressure sensitive security system for tracking motion over a surface |
| US6818842B2 (en)* | 2002-12-19 | 2004-11-16 | Delphi Technologies, Inc. | Seat foam humidity compensation for vehicle seat occupant weight detection system |
| FI120605B (en)* | 2008-02-28 | 2009-12-15 | Elsi Technologies Oy | Procedures and systems for detecting events |
| KR101244940B1 (en)* | 2011-01-21 | 2013-03-18 | 주식회사 에스원 | method and apparatus for measuring activity state of moving object and device control system using them |
| KR101497106B1 (en)* | 2012-10-31 | 2015-03-03 | 전진홍 | Crime Prevention system |
| KR102029155B1 (en)* | 2013-03-25 | 2019-10-07 | 한화테크윈 주식회사 | Apparatus and method for recognizing pattern |
| CN203422765U (en)* | 2013-06-02 | 2014-02-05 | 广州腾浩电子科技有限公司 | Automatic identification system for vehicle type |
| CN103800016B (en)* | 2014-02-25 | 2015-11-04 | 河北工业大学 | Human identity gait recognition system and its recognition method based on the combination of visual and tactile senses |
- 2015
- 2015-04-03KRKR1020150047621Apatent/KR101708491B1/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
- 2016
- 2016-04-01CNCN201610202237.7Apatent/CN106056034A/enactivePending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20160118830A (en) | 2016-10-12 |
| CN106056034A (en) | 2016-10-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101708491B1 (en) | Method for recognizing object using pressure sensor | |
| CN107358149B (en) | Human body posture detection method and device | |
| US9904846B2 (en) | Pedestrian behavior predicting device and pedestrian behavior predicting method | |
| US11308315B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus, control method, and program | |
| KR101764845B1 (en) | A video surveillance apparatus for removing overlap and tracking multiple moving objects and method thereof | |
| EP2874098A1 (en) | Image recognition apparatus and data registration method for image recognition apparatus | |
| CN112016531A (en) | Model training method, object recognition method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| US20190370982A1 (en) | Movement learning device, skill discriminating device, and skill discriminating system | |
| JP2007334756A (en) | Abnormal operation detection device and abnormal operation detection method | |
| CN116129350B (en) | Intelligent monitoring method, device, equipment and medium for safety operation of data center | |
| KR20170077366A (en) | System and method for face recognition | |
| CN110728258B (en) | Step detection method and system based on front-back frame connected domain matching | |
| JP6988790B2 (en) | Crowd type identification system, crowd type identification method and crowd type identification program | |
| US20220172378A1 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method and non-transitory computer readable medium | |
| JP2012221162A (en) | Object detection device and program | |
| KR20170003348A (en) | Updating method and apparatus of registration database for user authentication | |
| CN111814510A (en) | Detection method and device for remnant body | |
| CN114419343A (en) | A multi-target identification and tracking method and identification and tracking system | |
| CN112541403A (en) | Indoor personnel falling detection method utilizing infrared camera | |
| JP2010231254A (en) | Image analysis apparatus, image analysis method, and program | |
| CN113723355A (en) | Target monitoring method and device, storage medium and electronic device | |
| US12380319B2 (en) | Computer-readable recording medium storing person identification machine learning program, person identification machine learning method, and information processing apparatus | |
| KR102821064B1 (en) | Prediction of the attitude of pedestrians in front based on deep learning technology using camera image and collision risk estimation technology using this | |
| EP3336746A1 (en) | System and method of video content filtering | |
| JP6077785B2 (en) | Object detection apparatus and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| D13-X000 | Search requested | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D13-srh-X000 | |
| D14-X000 | Search report completed | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D14-srh-X000 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| AMND | Amendment | ||
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | St.27 status event code:A-1-1-Q10-Q12-nap-PG1501 | |
| E601 | Decision to refuse application | ||
| PE0601 | Decision on rejection of patent | St.27 status event code:N-2-6-B10-B15-exm-PE0601 | |
| X091 | Application refused [patent] | ||
| AMND | Amendment | ||
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| PX0901 | Re-examination | St.27 status event code:A-2-3-E10-E12-rex-PX0901 | |
| PX0701 | Decision of registration after re-examination | St.27 status event code:A-3-4-F10-F13-rex-PX0701 | |
| X701 | Decision to grant (after re-examination) | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 Fee payment year number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| P14-X000 | Amendment of ip right document requested | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-P10-P14-nap-X000 | |
| P16-X000 | Ip right document amended | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-P10-P16-nap-X000 | |
| Q16-X000 | A copy of ip right certificate issued | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q16-nap-X000 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20200121 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:6 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U13-oth-PC1903 Not in force date:20230215 Payment event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | St.27 status event code:N-4-6-H10-H13-oth-PC1903 Ip right cessation event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE Not in force date:20230215 |