KR101687477B1 - A Method for Providing Event Occurrence Information Using Big Data and A System for the Same - Google Patents
A Method for Providing Event Occurrence Information Using Big Data and A System for the SameDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101687477B1 KR101687477B1KR1020150027883AKR20150027883AKR101687477B1KR 101687477 B1KR101687477 B1KR 101687477B1KR 1020150027883 AKR1020150027883 AKR 1020150027883AKR 20150027883 AKR20150027883 AKR 20150027883AKR 101687477 B1KR101687477 B1KR 101687477B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- event
- information
- data
- occurrence
- risk
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B23/00—Alarms responsive to unspecified undesired or abnormal conditions
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q50/00—Information and communication technology [ICT] specially adapted for implementation of business processes of specific business sectors, e.g. utilities or tourism
- G06Q50/01—Social networking
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B21/00—Alarms responsive to a single specified undesired or abnormal condition and not otherwise provided for
- G08B21/02—Alarms for ensuring the safety of persons
- G08B21/04—Alarms for ensuring the safety of persons responsive to non-activity, e.g. of elderly persons
- G08B21/0438—Sensor means for detecting
- G08B21/0476—Cameras to detect unsafe condition, e.g. video cameras
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B21/00—Alarms responsive to a single specified undesired or abnormal condition and not otherwise provided for
- G08B21/02—Alarms for ensuring the safety of persons
- G08B21/10—Alarms for ensuring the safety of persons responsive to calamitous events, e.g. tornados or earthquakes
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B25/00—Alarm systems in which the location of the alarm condition is signalled to a central station, e.g. fire or police telegraphic systems
- G08B25/14—Central alarm receiver or annunciator arrangements
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B27/00—Alarm systems in which the alarm condition is signalled from a central station to a plurality of substations
Landscapes
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Emergency Management (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- General Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Gerontology & Geriatric Medicine (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Geology (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Alarm Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 빅데이터를 이용한 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 방법 및 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 시스템에 관한 것으로, 더욱 상세하게는 범죄 및 사건사고 등의 각종 이벤트 발생 상황을 수집하고 이에 기초한 각종 이벤트 발생 상황을 수집하고, 이에 기초한 위험 상황 정보를 사용자에게 제공하기 위한 방법 및 시스템에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method for providing event occurrence information using Big Data and an event occurrence information providing system. More particularly, the present invention collects various event occurrence situations such as crime and incidents, collects various event occurrence situations based thereon, And more particularly, to a method and system for providing risk-based risk information to a user.
빅데이터란 디지털 환경에서 생성되는 데이터로 그 규모가 방대하고, 생성 주기가 짧으며, 수치 데이터뿐 아니라 문자와 영상 데이터 등 다양한 형태를 포함하는 대규모의 데이터를 말한다. 빅데이터는 각종 센서와 인터넷의 발달로 데이터가 늘어나면서 등장하게 되었다. 컴퓨터 및 처리기술이 발달함에 따라 디지털 환경에서 생성되는 빅데이터를 기반으로 분석을 수행하게 되면 질병이나 사회현상의 변화 등에 관한 새로운 시각이나 법칙을 발견할 가능성이 커지게 되었다. 따라서, 빅데이터는 사회적인 문제를 해결하는데 사용될 수 있는데, 특히 범죄 사건이나 안전 사고 등의 예방에 활용될 수 있다.Big data refers to large-scale data that is generated in a digital environment, has a large size, has a short generation cycle, and includes not only numerical data but also various forms such as text and image data. Big Data has emerged with increasing data due to the development of various sensors and the Internet. As computers and processing technologies develop, analysis based on big data generated in the digital environment has increased the possibility of discovering new perspectives and laws about changes in diseases and social phenomena. Therefore, Big Data can be used to solve social problems, especially for preventing crime and safety accidents.
한편, 국가에서 서비스하고 있는 생활공감지도 서비스는 스마트안전귀가와 같은 서비스를 통해 사용자의 안전을 위한 위치 기반 서비스를 제공하고 있다. 스마트안전귀가는 모바일 중심의 서비스로 스마트폰 사용자가 귀가할 때 보호자에게 주기적으로 위치정보를 전송하는 서비스이다. 그러나 이러한 서비스는 시간, 장소, 환경 등에 따라 변화하는 안전요소를 실시간 적으로 반영하지 못하고, 공공안전 정책 수립 및 개인의 사건사고 예방 및 대응에는 활용하기 어려운 문제점이 있다.On the other hand, the living sympathy guidance service provided by the country provides location based service for user's safety through services such as smart safety return. Smart Safety Home is a mobile-oriented service that periodically sends location information to a guardian when a smartphone user returns home. However, these services do not reflect safety factors that change according to time, place, environment, etc., and they are difficult to be used for establishing public safety policies and preventing and responding to incidents of individuals.
본 발명은 다양한 수단을 통해 이벤트 발생 상황에 대한 정보를 수집하고, 이에 대한 분석 데이터를 사용자에게 제공함으로 사용자가 범죄 및 안전상황에 대하여 실시간으로 파악하고 후속 피해를 줄일 수 있도록 하기 위한 목적을 가지고 있다.The present invention aims at collecting information on the event occurrence status through various means and providing analysis data to the user so that the user can grasp the crime and safety situation in real time and reduce subsequent damage .
또한 본 발명은 사물 인터넷(Internet of Things, IoT)과 빅데이터 분석 기술을 함께 이용하여 사용자의 일상 생활에서의 안전도를 수치화하여 제공하고, 이를 통해 신뢰성 있는 공공안전 지원 서비스를 제공하기 위한 목적을 가지고 있다.The present invention also aims to provide a reliable public safety support service by digitizing and providing the degree of safety in daily life of a user by using the Internet of Things (IoT) and Big Data Analysis technology together have.
상기와 같은 과제를 해결하기 위해, 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 방법은 적어도 하나의 이벤트 감지 장치로부터 신규 이벤트 발생 정보를 나타내는 이벤트 데이터를 수신하는 단계; 상기 수신된 이벤트 데이터를 기 설정된 정형 데이터로 변환하는 단계, 상기 정형 데이터는 이벤트 종류 정보 및 이벤트 발생 장소 정보를 포함함; 제1 종류 이벤트의 발생시 제2 종류 이벤트가 발생할 확률에 대한 정보를 나타내는 이벤트 발생 전이확률 정보를 이용하여, 상기 발생된 신규 이벤트에 기초한 다른 종류의 이벤트의 발생 확률을 획득하는 단계; 상기 신규 이벤트 발생 정보 및 상기 획득된 다른 종류의 이벤트 발생 확률에 기초하여 상기 이벤트 발생 장소의 위험도를 판별하는 단계; 및 사용자에게 상기 판별 결과에 기초한 위험 상황 정보를 제공하는 단계;를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of providing event occurrence information, the method including: receiving event data representing new event occurrence information from at least one event detection apparatus; Converting the received event data into predetermined formatted data, the formatted data including event type information and event occurrence place information; Acquiring probability of occurrence of another kind of event based on the generated new event using event occurrence transition probability information indicating information about a probability of occurrence of a second kind event when a first kind event occurs; Determining a risk of the event occurrence place based on the new event occurrence information and the obtained other kind of event occurrence probability; And providing the risk status information based on the determination result to the user.
한편, 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 시스템은, 적어도 하나의 이벤트 감지 장치로부터 신규 이벤트 발생 정보를 나타내는 이벤트 데이터를 수신하는 통신부; 상기 수신된 이벤트 데이터를 저장하는 빅데이터 DB; 상기 이벤트 데이터를 이벤트 종류 정보 및 이벤트 발생 장소 정보를 포함하는 기 설정된 정형 데이터로 변환하고, 제1 종류 이벤트의 발생시 제2 종류 이벤트가 발생할 확률에 대한 정보를 나타내는 이벤트 발생 전이확률 정보를 이용하여, 상기 발생된 신규 이벤트에 기초한 다른 종류 이벤트의 발생 확률을 획득하는 이벤트 분석부; 및 상기 신규 이벤트 발생 정보 및 상기 획득된 다른 종류 이벤트 발생 확률에 기초하여 상기 이벤트 발생 장소의 위험도를 판별하고, 사용자에게 상기 판별 결과에 기초한 위험 상황 정보를 제공하는 위험 상황 정보 제공부;를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided an event occurrence information providing system including: a communication unit for receiving event data representing new event occurrence information from at least one event detection device; A big data DB for storing the received event data; The method of claim 1, further comprising: converting event data into predetermined format data including event type information and event occurrence place information, and using event occurrence transition probability information indicating information on a probability of occurrence of a second type event when a first type event occurs, An event analyzer for obtaining a probability of occurrence of another kind event based on the generated new event; And a risk situation information providing unit for determining a risk of the event occurrence place based on the new event occurrence information and the obtained other kind event occurrence probability and providing the risk situation information based on the determination result to the user, .
이때, 상기 이벤트 발생 전이확률 정보는 상기 정형 데이터에서의 각 이벤트 종류 간의 전이 확률을 나타내는 마르코프(Markov) 체인을 이용하여 획득되는 것을 특징으로 한다.In this case, the event occurrence transition probability information is acquired using a Markov chain indicating a transition probability between each event type in the fixed data.
또한, 상기 신규 이벤트 발생 장소의 위험도는 상기 신규 이벤트에 대한 위험도 값과 상기 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 추정 위험도 값의 합산 값에 기초하여 산출되며,Also, the risk level of the new event occurrence place is calculated based on the sum of the risk value for the new event and the estimated risk value for the different kind of event,
상기 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 추정 위험도 값은 상기 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 위험도 값과 상기 다른 종류의 이벤트 발생 확률의 곱에 의해 결정되는 것을 특징으로 한다.And the estimated risk value for the other kind of event is determined by the product of the risk value for the other kind of event and the probability of occurrence of the other kind of event.
본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 상기 이벤트 감지 장치는 영상 데이터를 이용하여 상기 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 판별하되, 상기 영상 데이터에서의 객체의 행위 분석, 객체들 간의 상호 행위 분석 및 특정 객체 검출 결과 중 적어도 하나에 기초하여 상기 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 판별하는 것을 특징으로 한다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the event detection device determines whether or not the new event is generated using the image data, and includes at least one of a behavior analysis of an object in the image data, a mutual behavior analysis between objects, And whether the new event is generated or not.
본 발명의 다른 실시예에 따르면, 상기 이벤트 데이터를 수신하는 단계는, 뉴스 데이터, SNS(Social Network Service) 데이터 및 웹 데이터 중 적어도 하나를 이용하여 상기 이벤트 데이터를 획득하는 것을 특징으로 한다.According to another embodiment of the present invention, the step of receiving the event data may include acquiring the event data using at least one of news data, social network service (SNS) data, and web data.
또한, 상기 판별된 위험도 정보를 지도상에 매핑하는 단계를 더 포함하며, 상기 사용자에게 제공되는 위험 상황 정보에는 상기 위험도 정보가 매핑된 지도 데이터가 더 포함되는 것을 특징으로 한다.The method may further include mapping the determined risk information on a map, and the risk information provided to the user further includes map data to which the risk information is mapped.
본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 이벤트 관련 빅데이터를 이용하여 이벤트 발생간의 연쇄성을 분석할 수 있으며, 이를 통해 다양한 종류의 이벤트 발생 가능성을 예측할 수 있다.According to the embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to analyze the concurrency between event occurrences by using the event-related big data, and thereby it is possible to predict the occurrence possibility of various kinds of events.
또한, 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면 이벤트 발생 데이터를 기초로 통계적으로 산출된 위험도 정보를 사용자에게 시각적으로 제공하여 실시간 대응 체계를 마련할 수 있고, 사건사고의 피해를 최소화할 수 있다.According to the embodiment of the present invention, the risk information statistically calculated on the basis of the event occurrence data can be visually provided to the user, so that a real-time response system can be provided and the damage of the incident accident can be minimized.
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 시스템을 도시한 블록도.
도 2는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 방법을 나타낸 순서도.
도 3은 서로 다른 종류의 이벤트 간의 전이 확률을 나타내는 마르코프(Markov) 체인의 일 실시예를 나타낸 도면.
도 4는 시각적으로 표현된 본 발명의 위험 상황 정보의 일 실시예를 나타낸 도면.
도 5는 사용자 단말에서 출력되는 위험 상황 정보의 일 실시예를 나타낸 도면.1 is a block diagram illustrating an event occurrence information providing system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
2 is a flowchart illustrating a method of providing event occurrence information according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Figure 3 shows an embodiment of a Markov chain representing the transition probabilities between different kinds of events;
Figure 4 illustrates one embodiment of the risk context information of the present invention visually represented;
5 is a diagram illustrating an example of the dangerous situation information output from a user terminal;
본 명세서에서 사용되는 용어는 본 발명에서의 기능을 고려하면서 가능한 현재 널리 사용되는 일반적인 용어를 선택하였으나, 이는 당 분야에 종사하는 기술자의 의도, 관례 또는 새로운 기술의 출현 등에 따라 달라질 수 있다. 또한 특정 경우는 출원인이 임의로 선정한 용어도 있으며, 이 경우 해당되는 발명의 설명 부분에서 그 의미를 기재할 것이다. 따라서 본 명세서에서 사용되는 용어는, 단순한 용어의 명칭이 아닌 그 용어가 가진 실질적인 의미와 본 명세서의 전반에 걸친 내용을 토대로 해석되어야 함을 밝혀두고자 한다.As used herein, terms used in the present invention are selected from general terms that are widely used in the present invention while taking into account the functions of the present invention. However, these terms may vary depending on the intention of a person skilled in the art, custom or the emergence of new technology. Also, in certain cases, there may be a term arbitrarily selected by the applicant, and in this case, the meaning thereof will be described in the description of the corresponding invention. Therefore, it is intended that the terminology used herein should be interpreted relative to the actual meaning of the term, rather than the nomenclature, and its content throughout the specification.
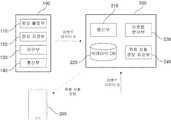
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 시스템을 도시한 블록도이다. 도시된 바와 같이 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 시스템은 이벤트 감지 장치(100), 서버(200) 및 사용자 단말(300)을 포함한다.1 is a block diagram illustrating an event occurrence information providing system according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the event occurrence information providing system according to the embodiment of the present invention includes an
본 발명의 이벤트 감지 장치(100)는 이벤트 발생 상황을 감지하고 이에 대한 데이터를 서버(200)에 전달한다. 본 발명에서 이벤트란 범죄, 사고, 재난 등의 다양한 사건을 총칭하는 개념의 용어로 사용된다. 일 실시예에 따르면 이벤트 감지 장치(100)는 CCTV(closed circuit television) 카메라, 적외선 카메라 등을 포함하는 영상 데이터 수집 장치일 수 있으며, 영상 촬영부(110), 영상 저장부(120), 제어부(130) 및 통신부(140)를 포함한다.The
먼저, 영상 촬영부(110)는 카메라 등의 촬상 장치를 이용하여 영상 데이터를 생성한다. 만약 이벤트 감지 장치(100)가 고정형 CCTV일 경우 영상 촬영부(110)는 기 설정된 영역을 촬영하여 영상 데이터를 생성할 수 있지만, 본 발명은 이에 한정하지 않는다.First, the
영상 저장부(120)는 영상 촬영부(110)에 의해 생성된 영상 데이터를 저장한다. 영상 저장부(120)는 하드디스크 드라이브, 플래시 메모리, RAM(Random Access Memory), SSD(Solid State Drive) 등의 다양한 디지털 데이터 저장 매체를 통해 구현될 수 있다.The
제어부(130)는 이벤트 감지 장치(100)의 각 부의 동작을 제어하며, 이벤트 감지 장치(100) 내부의 데이터를 프로세싱 할 수 있다. 또한, 제어부(130)는 이벤트 감지 장치(100)의 각 부 간의 데이터 송수신을 제어할 수 있다. 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 제어부(130)는 영상 촬영부(110)에 의해 생성된 영상 데이터를 이용하여 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 판별할 수 있다. 일 실시예에 따르면, 제어부(130)는 영상 데이터에서의 객체의 행위 분석, 객체들 간의 상호 행위 분석, 특정 객체 검출 결과 등에 기초하여 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 판별할 수 있으며, 구체적인 실시예는 후술하도록 한다. 신규 이벤트가 발생한 것으로 판별될 경우, 제어부(130)는 신규 이벤트 발생 정보를 나타내는 이벤트 데이터를 생성한다.The
통신부(140)는 외부 단말 또는 네트워크와 다양한 유선 또는 무선의 통신 방식을 사용하여 데이터를 송/수신할 수 있다. 이때, 사용 가능한 무선 통신 방식으로는 와이파이, LTE(Long Term Evolution), 블루투스, NFC(Near Field Communication), Zigbee, 적외선 통신 등이 있으며, 본 발명은 이에 한정하지 않는다. 본 발명의 실시예에 따라 신규 이벤트가 발생할 경우, 제어부(130)는 통신부(140)를 통해 이벤트 데이터를 서버(200)로 전송한다.The
한편, 본 발명의 서버(200)는 적어도 하나의 이벤트 감지 장치(100)로부터 이벤트 데이터를 수신하고, 수신된 이벤트 데이터에 기초하여 위험 상황 정보를 사용자 단말(300)에 제공한다. 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 서버(200)는 통신부(210), 빅데이터 DB(220), 이벤트 분석부(230) 및 위험 상황 정보 제공부(240)를 포함할 수 있다.Meanwhile, the
먼저, 통신부(210)는 외부 단말 또는 네트워크와 다양한 유선 또는 무선의 통신 방식을 사용하여 데이터를 송/수신할 수 있으며, 적어도 하나의 이벤트 감지 장치(100)로부터 이벤트 데이터를 수신할 수 있다. 또한, 후술하는 바와 같이 서버(200)에서 생성된 위험 상황 정보를 사용자 단말(300)로 전송할 수 있다.First, the
빅데이터 DB(220)는 다양한 디지털 데이터를 저장하며, 본 발명의 실시예에 따라 외부로부터 수신된 이벤트 데이터를 저장할 수 있다. 또한, 빅데이터 DB(220)는 서버(200)의 프로세싱에 따른 또는 프로세싱에 필요한 다양한 데이터를 저장할 수 있는데, 이를 테면 후술하는 이벤트 발생 전이확률 정보 등을 저장할 수 있다. 빅데이터 DB(220)는 하드디스크 드라이브, 플래시 메모리, RAM(Random Access Memory), SSD(Solid State Drive) 등의 다양한 디지털 데이터 저장 매체를 통해 구현될 수 있다.The big data DB 220 stores various digital data and can store event data received from outside according to an embodiment of the present invention. In addition, the
이벤트 분석부(230)는 수신된 이벤트 데이터를 기 설정된 정형 데이터로 변환하고, 이벤트 발생 전이확률 정보를 이용하여 다른 종류 이벤트의 발생 확률을 함께 산출한다. 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 정형 데이터는 이벤트 종류 정보 및 이벤트 발생 장소 정보를 포함한다. 따라서, 이벤트 분석부(230)는 다양한 형태로 수신된 이벤트 데이터에서 이벤트 종류 정보와 이벤트 발생 장소 정보를 추출하고, 추출된 이벤트 종류 정보 및 이벤트 발생 장소 정보에 기초하여 해당 이벤트 데이터를 분류 및 처리할 수 있다. 이벤트 발생 전이확률 정보는 특정 이벤트가 발생될 경우 다른 종류의 이벤트가 발생할 확률에 대한 정보를 나타내며, 이를 통해 특정 이벤트의 발생으로 인한 연쇄적인 이벤트의 발생 확률을 추정할 수 있다. 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 이벤트 발생 전이확률 정보는 정형 데이터에서 분류된 각 이벤트 종류 간의 전이 확률을 나타내는 마르코프(Markov) 체인을 이용하여 결정될 수 있으며, 이에 대한 구체적인 설명은 후술하도록 한다.The
위험 상황 정보 제공부(240)는 수신된 이벤트 데이터 및 획득된 다른 종류 이벤트들의 발생 확률에 기초하여 신규 이벤트가 발생한 장소의 위험도를 판별한다. 위험 상황 정보 제공부(240)는 상기 판별 결과에 기초하여 위험 상황 정보를 생성하고 이를 사용자에게 제공할 수 있다. 일 실시예에 따르면, 위험 상황 정보는 이벤트 발생 장소의 지도 정보를 포함할 수 있다. 즉, 위험 상황 정보 제공부(240)는 판별된 위험도 정보를 해당 이벤트 발생 장소의 지도상에 매핑하고, 위험도 정보가 매핑된 지도 데이터를 사용자에게 제공할 수 있다.The risk situation
한편, 본 발명의 서버(200)는 이벤트 감지 장치(100)로부터 수신된 이벤트 데이터(이벤트 데이터 A)뿐만 아니라 그 밖의 다양한 형태의 이벤트 데이터(이벤트 데이터 B)를 수신할 수 있다. 예를 들면, 이벤트 데이터는 뉴스 데이터, SNS(Social Network Service) 데이터, 웹 데이터 등을 포함할 수 있으며, 공공 기관에서 제공하는 이벤트 관련 데이터, 이벤트 관련 신고 접수 데이터 등을 포함할 수도 있다. 서버(200)는 다양한 형태의 이벤트 데이터를 정형화하여 분류할 수 있다. 즉, 서버(200)는 각 이벤트 데이터로부터 이벤트 종류 정보, 이벤트 발생 장소 정보 등의 항목을 추출하며, 추출된 항목 정보에 따라 각 이벤트 데이터를 분류하여 위험 상황 정보를 생성할 수 있다.Meanwhile, the
사용자 단말(300)은 서버(200)로부터 위험 상황 정보를 수신하고, 이를 영상 및/또는 음성 정보로 출력한다. 본 발명에서 사용자 단말(300)은 다양한 형태의 디지털 디바이스, 이를 테면 스마트폰, 데스크탑, 랩탑, 태블릿 피씨, PDA(Personal Digital Assistant), 스마트 워치, HMD(Head Mounted Display) 등을 포함할 수 있다.The
도 2는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 방법을 나타낸 순서도이다. 도 2의 각 단계는 도 1에 도시된 이벤트 감지 장치(100), 서버(200), 사용자 단말(300) 및 이들의 조합에 의해 수행될 수 있다.2 is a flowchart illustrating a method of providing event occurrence information according to an embodiment of the present invention. Each step of FIG. 2 may be performed by the
먼저, 본 발명의 이벤트 감지 장치는 영상 촬영부를 이용하여 영상을 촬영한다(S110).First, the event sensing apparatus of the present invention captures an image using an image capturing unit (S110).
다음으로, 이벤트 감지 장치는 촬영되는 영상 데이터를 실시간으로 분석하고, 이를 통해 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 감지한다(S112). 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 이벤트 감지 장치는 다양한 방법에 의해 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 판별할 수 있다. 일 실시예에 따르면 이벤트 감지 장치는 영상 데이터에서의 객체의 행위 분석 결과에 기초하여 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 판별할 수 있는데, 구체적으로 침입, 배회, 가상경계선 통과, 역방향 이동, 멈춤, 달리기, 쓰러짐, 도난, 방치 등의 기 설정된 행위가 검출될 경우 신규 이벤트가 발생한 것으로 판단할 수 있다. 또한, 이벤트 감지 장치는 영상 데이터에서의 객체들 간의 상호 행위 분석 결과에 기초하여 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 판별할 수 있는데, 구체적으로 군집, 폭력 등의 행위가 검출될 경우 신규 이벤트가 발생한 것으로 판단할 수 있다. 뿐만 아니라, 이벤트 감지 장치는 영상 데이터 내에서 특정 객체가 검출되는지 여부에 기초하여 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 판별할 수 있는데, 구체적으로 연기, 불꽃, 폭우, 낙뢰 등의 기 설정된 객체가 발견 될 경우 신규 이벤트가 발생한 것으로 판단할 수 있다.Next, the event detection device analyzes the captured image data in real time, and detects whether a new event is generated (S112). According to the embodiment of the present invention, the event detection apparatus can determine whether a new event is generated by various methods. According to an exemplary embodiment, the event detection device can determine whether a new event is generated based on a result of analyzing an action of an object in image data. Specifically, the event detection device can detect intrusion, wandering, virtual boundary passing, reverse movement, pause, running, It can be determined that a new event has occurred when a predetermined action such as theft, neglect, etc. is detected. In addition, the event detection apparatus can determine whether a new event has occurred based on a result of analysis of mutual behavior between objects in the image data. Specifically, when an action such as a cluster or violence is detected, have. In addition, the event detection device can determine whether a new event is generated based on whether or not a specific object is detected in the image data. Specifically, when a predetermined object such as smoke, flame, heavy rain, Can be determined to have occurred.
이와 같이 신규 이벤트가 발생한 것으로 판별될 경우, 이벤트 감지 장치는 신규 이벤트 발생 정보를 나타내는 이벤트 데이터를 생성하고 이를 서버에 전송한다(S114). 이벤트 감지 장치가 생성하는 이벤트 데이터는 자체적인 분석 결과에 따라 추정된 이벤트 종류 정보와 해당 이벤트의 발생 장소 정보를 포함하는 정형화된 데이터일 수 있으며, 또는 촬영된 영상 데이터 자체의 비정형 데이터일 수도 있다. 이벤트 감지 장치는 유/무선의 네트워크를 이용하여 이벤트 데이터를 서버로 전송한다. 일 실시예에 따르면, 이벤트 감지 장치는 사물 인터넷(Internet of Things, IoT) 방식을 이용하여 서버와 데이터를 송수신할 수 있으며, 신규 이벤트의 발생시 이벤트 데이터를 서버로 전송할 수 있다.If it is determined that a new event has occurred, the event detection apparatus generates event data indicating new event occurrence information and transmits it to the server (S114). The event data generated by the event detection device may be formatted data including the event type information estimated based on the analysis result of the event detection device and the generation location information of the event, or the atypical data of the captured image data itself. The event detection device transmits event data to the server using a wired / wireless network. According to one embodiment, the event detection device can transmit / receive data to / from a server using Internet of Things (IoT) method, and can transmit event data to a server when a new event occurs.
한편, 본 발명의 서버는 적어도 하나의 이벤트 감지 장치로부터 이벤트 데이터를 수신한다(S120). 전술한 바와 같이, 서버는 이벤트 감지 장치뿐만 아니라 다양한 소스를 통해 이벤트 데이터를 수신할 수 있는데, 이러한 이벤트 데이터에는 영상 데이터, 뉴스 데이터, SNS 데이터, 웹 데이터 등을 포함할 수 있으며, 공공 데이터, 신고 접수 데이터 등을 포함할 수도 있다.Meanwhile, the server of the present invention receives event data from at least one event detection device (S120). As described above, the server may receive event data through various sources as well as an event detection device. Such event data may include image data, news data, SNS data, web data, Reception data, and the like.
여기서, 영상 데이터는 본 발명의 이벤트 감지 장치 또는 개별 사용자가 촬영하여 전송한 영상 등을 포함하며, 뉴스 데이터는 신문사나 방송국 등에서 취재한 사건사고 관련 데이터를 포함한다. 또한, SNS 데이터는 트위터, 페이스북과 같은 SNS에서 사건사고와 관련하여 실시간으로 업데이트 되는 데이터이며, 웹 데이터는 인터넷 게시글이나 블로그 등의 웹 상에서 업로드 되는 다양한 종류의 데이터를 포함한다. 공공 데이터는 경찰서, 소방서, 기상청 등과 같은 공공기관에서 제공하는 사건사고 관련 데이터이며, 신고 접수 데이터는 경찰서, 소방서 등의 공공기관에서 사건사고 신고접수를 받은 데이터를 가리킨다.Here, the image data includes an event detection device of the present invention or an image captured by an individual user, and the news data includes incident incident related data collected by a newspaper company or a broadcasting station. In addition, SNS data is data that is updated in real time in relation to an incident event in SNS such as Twitter and Facebook, and the web data includes various kinds of data to be uploaded on the web such as an Internet post or a blog. Public data is data on incident incidents provided by public agencies such as police stations, fire stations, and meteorological offices, and data on the reported data refers to data received from public authorities such as police stations and fire stations.
한편, 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 서버는 다양한 언어의 뉴스 데이터, SNS 데이터 등을 이벤트 데이터로 수신할 수 있다. 서버는 해당 언어별로 각 이벤트 데이터를 분류하거나, 각 이벤트 데이터를 하나의 언어로 번역하여 이벤트 데이터 정형화에 사용할 수 있다.Meanwhile, according to the embodiment of the present invention, the server can receive news data, SNS data, etc. in various languages as event data. The server can classify each event data for each language or translate each event data into one language and use it for event data formatting.
다음으로, 서버는 수신된 이벤트 데이터를 정형화한다(S122). 본 발명의 실시예에서 정형 데이터는 각 이벤트의 종류 및 발생 장소에 대한 정보를 포함하는 데이터이며, 수신된 이벤트 데이터가 정형 데이터가 아닐 경우 서버는 해당 이벤트 데이터에서 상기 이벤트 종류 및 발생 장소 정보를 추출하여 이를 정형화한다. 본 발명의 정형 데이터는 이 외의 다른 항목 정보들도 포함할 수 있는데, 이를 테면 이벤트 발생 시간 정보를 더 포함할 수 있다. 이와 같이, 서버는 이벤트 데이터를 수집하여 발생 시간별, 발생 공간별, 발생 유형로 분류하여 사건사고 관련 데이터의 처리 및 분석이 용이하도록 정형화를 한다.Next, the server formalizes the received event data (S122). In the embodiment of the present invention, the formatted data is data including information on the type and location of each event, and when the received event data is not formatted data, the server extracts the event type and occurrence place information from the corresponding event data And formalizes it. The format data of the present invention may also include other item information, such as event occurrence time information. As described above, the server collects event data, classifies the event data according to occurrence time, occurrence space, and occurrence type, and shapes the event data to facilitate processing and analysis.
다음으로, 서버는 정형화된 이벤트 데이터를 이용하여 이벤트 상황을 판단하고 위험도를 산출한다(S124). 서버는 정형화된 이벤트 데이터의 이벤트 종류 정보, 이벤트 발생 장소 정보 등을 이용하여 해당 이벤트의 위험도를 추정할 수 있다. 이를 위해, 서버는 이벤트 종류별로 위험도 값을 매핑한 테이블을 구비할 수 있으며, 상기 테이블을 이용하여 해당 신규 이벤트의 위험도를 산출할 수 있다. 또한 서버는 이벤트 발생 시간대별로 해당 이벤트의 위험도 값에 대한 가중치를 차등할 수 있는데, 이를 테면 이벤트 발생 시점으로부터 시간이 지날수록 해당 이벤트에 대한 위험도를 낮출 수 있다.Next, the server determines the event situation using the formal event data and calculates the risk (S124). The server can estimate the risk level of the event using the event type information of the formal event data, the event occurrence place information, and the like. To this end, the server may have a table in which a risk value is mapped for each event type, and the risk of the new event can be calculated using the table. In addition, the server can differentiate the weight value of the risk value of the corresponding event according to the time of occurrence of the event, for example, the risk for the event can be lowered as time elapses from when the event occurs.
본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 서버는 이벤트 발생 전이확률 정보를 이용하여 해당 신규 이벤트 이외의 다른 종류 이벤트의 발생 확률을 획득한다. 이를 위해, 서버는 각 이벤트 종류 간의 전이 확률을 나타내는 마르코프(Markov) 체인에 기초하여 결정된 전이 확률 정보를 이용할 수 있다.According to the embodiment of the present invention, the server acquires probability of occurrence of a kind event other than the new event using the event occurrence transition probability information. To this end, the server may use the transition probability information determined based on the Markov chain indicating the transition probability between each event type.
서버는 신규 이벤트 발생 정보 및 다른 종류 이벤트의 발생 확률에 기초하여 신규 이벤트가 발생한 장소의 위험도를 산출한다. 더욱 구체적으로, 서버는 신규 이벤트에 대한 위험도 값과 다른 이벤트들에 대한 추정 위험도 값을 합산하여 해당 신규 이벤트가 발생한 장소의 위험도를 산출할 수 있다. 여기서, 다른 이벤트들에 대한 추정 위험도 값은 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 위험도 값과 상기 다른 종류의 이벤트 발생 확률의 곱에 의해 결정될 수 있다. 따라서, 신규 발생된 이벤트의 위험도 값이 높을수록, 그리고 다른 이벤트들의 전이 발생 확률이 높을수록 해당 이벤트 발생 장소의 위험도는 높게 산출된다.The server calculates the risk level of the place where the new event occurs based on the new event occurrence information and the probability of occurrence of other kinds of events. More specifically, the server may sum the risk value for the new event and the estimated risk value for other events to calculate the risk at the place where the new event occurred. Here, the estimated risk value for other events may be determined by multiplying the risk value for other types of events by the probability of occurrence of the other kind of events. Therefore, the higher the risk value of the newly generated event is, and the higher the probability of occurrence of the transition of the other events, the higher the risk of the event occurrence place is.
다음으로, 서버는 산출된 위험도에 기초하여 위험 상황 정보를 사용자에게 제공한다(S126). 일 실시예에 따르면, 서버는 이벤트 발생 장소의 위험도가 기 설정된 값 이상일 경우 위험 상황으로 판단하고, 해당 이벤트에 대응하는 위험 상황 정보를 사용자에게 제공할 수 있다. 서버는 다양한 형식의 위험 상황 정보를 생성하고 이를 사용자 단말로 전송할 수 있는데, 상기 위험 상황 정보는 영상 데이터, 텍스트 데이터, 음성 데이터 또는 이들의 조합으로 이루어질 수 있다. 일 실시예에 따르면, 서버는 이벤트가 발생한 지점의 지도 정보를 상기 위험도 정보와 조합하여 위험 상황 정보를 생성할 수 있다. 이때, 사용자 단말로 전송되는 위험 상황 정보에는 위험도 정보가 매핑된 지도 데이터가 포함될 수 있다.Next, the server provides risk status information to the user based on the calculated risk (S126). According to one embodiment, the server may determine that the event is a dangerous situation when the risk of the place where the event occurs is greater than a preset value, and provide the user with the dangerous situation information corresponding to the event. The server can generate various types of dangerous situation information and transmit it to the user terminal. The dangerous situation information can be image data, text data, voice data, or a combination thereof. According to one embodiment, the server can generate the dangerous situation information by combining the map information of the point where the event occurs with the risk information. At this time, the risk information transmitted to the user terminal may include map data to which the risk information is mapped.
사용자 단말은 서버로부터 위험 상황 정보를 수신한다(S130). 실시예에 따르면, 사용자 단말은 해당 단말의 위치 정보를 측정하여 서버에 전달할 수 있으며, 서버는 이벤트 발생 장소로부터 기 설정된 거리 이내에 위치한 사용자 단말로 해당 위험 상황 정보를 전송할 수 있다.The user terminal receives the dangerous situation information from the server (S130). According to the embodiment, the user terminal can measure the location information of the corresponding terminal and transmit it to the server, and the server can transmit the corresponding danger information to the user terminal located within a predetermined distance from the event occurrence place.
서버로부터 위험 상황 정보를 수신한 사용자 단말은 해당 위험 상황 정보를 출력한다(132). 이를 위해 사용자 단말은 디스플레이 유닛, 스피커 등의 영상 및/또는 음성 출력 장치를 구비할 수 있으며, 상기 출력 장치로 위험 상황 정보를 출력한다.The user terminal receiving the dangerous situation information from the server outputs the corresponding dangerous situation information (132). To this end, the user terminal may include a video and / or audio output device such as a display unit and a speaker, and outputs the dangerous situation information to the output device.
도 3은 서로 다른 종류의 이벤트 간의 전이 확률을 나타내는 마르코프(Markov) 체인의 일 실시예를 나타내고 있다. 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 마르코프 체인에 기초하여 결정된 전이 확률 정보를 이용하여 신규 이벤트 이외의 다른 종류 이벤트의 발생 확률이 획득될 수 있다. 마르코프 체인은 시간에 따른 상태의 변화를 나타내는 확률 모델로서, 특정한 상태에서 다른 상태로 전이될 확률은 반드시 현재의 상태에 의해서만 영향을 받는다.FIG. 3 shows an embodiment of a Markov chain representing the transition probabilities between different kinds of events. According to the embodiment of the present invention, probability of occurrence of a kind event other than a new event can be obtained by using the transition probability information determined based on the Markov chain. The Markov chain is a probability model that represents a change in state over time. The probability of transitioning from one state to another is necessarily influenced only by the current state.
도 3을 참조하면 S1은 이벤트 A의 발생 상태, S2는 이벤트 B의 발생 상태, S3는 이벤트 C의 발생 상태를 나타낸다. 또한, Pij는 이벤트 Si가 발생한 상태에서 이벤트 Sj가 발생할 전이확률을 나타낸다. 즉, P12는 이벤트 A(S1)가 발생한 상태에서 이벤트 B(S2)가 발생할 전이확률을 나타내며, P31은 이벤트 C(S3)가 발생한 상태에서 이벤트 A(S1)가 발생할 전이확률을 나타낸다. 또한, P11은 이벤트 A(S1)가 발생한 상태에서 이벤트 A(S1)가 또다시 발생할 확률을 나타낸다.Referring to FIG. 3, S1 represents the occurrence state of the event A, S2 represents the occurrence state of the event B, and S3 represents the occurrence state of the event C. In addition, Pij represents the transition probability of eventj S in a state in which the event occurred Si. That is, P12 is the event A (S1) shows a state event B (S2) is the transition probability from occurring, P31 is the event C (S3), the event A (S1) a transition occurs in the occurring state Probability. In addition, P11 is the event A (S1) that shows the status of the event A (S1) Also in the probability of re-occurred.
본 발명의 실시예에 따르면 전체 이벤트 종류의 개수를 n이라 할 때, 총 n개의 노드를 갖는 마르코프 체인을 이용하여 다음과 같은 이벤트 발생 전이확률 행렬 P를 획득할 수 있다. 행렬 P의 각 원소 Pij는 이벤트 Si가 발생한 상태에서 이벤트 Sj가 발생할 전이확률을 나타낸다.According to the embodiment of the present invention, when the number of all event types is n, the following event occurrence transition probability matrix P can be obtained using a Markov chain having a total of n nodes. Each element Pij of the matrix P represents the transition probability of the event, the event Si Sj in state has occurred.
여기서,이며, i 및 j는 1에서 n 사이의 자연수이다.here, And i and j are natural numbers between 1 and n.
본 발명의 서버는 상기 전이확률 행렬 P를 이용하여, 신규 발생 이벤트에 기초한 다른 종류의 이벤트 발생 확률을 획득할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 신규 이벤트 Si가 발생한 경우, 다른 종류의 이벤트 Sj가 발생할 확률은 Pij로 추정될 수 있다. 이때, 신규 이벤트 Si가 발생한 장소의 위험도 R(i)total은 다음과 같은 수식으로 산출될 수 있다.The server of the present invention can obtain another kind of event occurrence probability based on the new occurrence event using the transition probability matrix P. [ For example, when a new event Si occurs, the probability of occurrence of another kind of event Sj can be estimated as Pij . At this time, the risk R (i)total of the place where the new event Si occurs can be calculated by the following equation.
여기서, Rk는 이벤트 Sk에 대한 위험도 값.Here, Rk is the risk value for the event Sk.
즉, 위험도 R(i)total은 신규 이벤트에 대한 위험도 값 Ri와, 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 추정 위험도 값의 합산 값에 기초하여 산출될 수 있다. 이때, 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 추정 위험도 값은 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 위험도 값 Rk와 다른 종류의 이벤트 발생 확률 Pik의 곱에 의해 결정된다.That is, the risk R (i)total can be calculated based on the risk value Ri for the new event and the sum of the estimated risk values for different kinds of events. At this time, the estimated risk value for other types of events are determined by the different kind of risk value for the event Rk and another type of event product of the probability Pik.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 전이확률 행렬 P는 각 지역의 이벤트 발생 통계에 기초하여 서로 다른 행렬 값으로 결정될 수 있다. 즉, 서버는 누적된 이벤트 데이터를 이용하여 각 지역 또는 장소 별로 전이확률 행렬을 산출하고, 신규 이벤트가 발생한 경우 해당 이벤트가 발생한 장소에 대응하는 전이확률 행렬을 이용하여 위험도를 산출할 수 있다. 따라서, 위험도 정보는 신규 이벤트의 발생 장소에 기초하여 결정될 수 있다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, the transition probability matrix P may be determined as a different matrix value based on the event occurrence statistics of each region. That is, the server calculates a transition probability matrix for each region or place using the accumulated event data, and when a new event occurs, the server can calculate the risk using the transition probability matrix corresponding to the place where the event occurred. Therefore, the risk information can be determined based on the place where the new event occurs.
한편 본 발명의 다른 실시예에 따르면, 서버는 누적된 이벤트 데이터를 이용하여 각 이벤트 종류별로 통합된 발생 확률을 산출할 수 있다. 먼저, 서버는 기 설정된 시간 동안 발생한 이벤트 발생 빈도수를 이용하여, 각 이벤트 S1, S2, … , Sn이 발생할 초기 확률 P0를 다음과 같이 산출할 수 있다.Meanwhile, according to another embodiment of the present invention, the server can calculate the integrated occurrence probability for each event type using the accumulated event data. First, the server calculates the number of events S1 , S2 , ... , The initial probability P0 at which Sn occurs can be calculated as follows.
여기서, a, b, … , c는 기 설정된 시간 동안의 각 이벤트 S1, S2, … , Sn의 발생 빈도수이며, F는 상기 빈도수 a, b, … , c의 총 합이다. 또한, 상기 기 설정된 시간은 시스템 설정에 따라 결정될 수 있는데, 이를 테면 최근 3개월, 최근 6개월 등의 시간으로 결정될 수 있다.Here, a, b, ... , c is the number of each event S1 , S2 , ... , Sn , and F is the frequency of occurrence of a, b, ... , c. In addition, the preset time may be determined according to the system setting, for example, the last 3 months, the last 6 months, and so on.
다음으로, 서버는 각 이벤트의 초기 발생 확률 P0와, 이벤트 발생 전이확률 행렬 P를 이용하여 각 이벤트 별 통합 발생 확률을 다음과 같이 산출할 수 있다.Next, the server can calculate the integrated occurrence probability for each event as follows using the initial occurrence probability P0 of each event and the event occurrence transition probability matrix P as follows.
즉, 이벤트 Si의 통합 발생 확률 P(Si)는 각 이벤트 Sk의 초기 발생 확률 P0(Sk)와, 각 이벤트 Sk에서 Si로 전이될 전이확률 Pki를 곱한 값의 합산 값으로 결정될 수 있다. 이와 같이 결정된 각 이벤트 별 통합 발생 확률은 각 이벤트 별 위험도 정보로 이용될 수 있다. 서버는 각 이벤트 별로 산출된 통합 발생 확률이 기 설정된 값 이상일 경우, 위험 상황인 것으로 판단하고 해당 위험도 정보를 사용자에게 제공할 수 있다.That is, the integrated occurrence of an event Si the probability P (Si) is the summation of the product of the initial probability of occurrence P0 (Sk) and, Si transition probabilities Pki be transferred to in each event, Sk for each event Sk Value. ≪ / RTI > The integrated probability of each event thus determined can be used as risk information for each event. If the integrated occurrence probability calculated for each event is equal to or greater than a predetermined value, the server determines that the event is a dangerous situation and can provide the risk information to the user.
도 4는 시각적으로 표현된 본 발명의 위험 상황 정보의 일 실시예를 나타내고 있다. 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 서버는 적어도 하나의 위험도 정보(25a~25e)를 해당 이벤트의 발생 장소에 기초하여 지도상에 매핑하고, 매핑된 지도 데이터를 위험 상황 정보로 제공할 수 있다. 이때, 표시되는 위험도 정보(25a~25e)는 각 위험도 값에 따라 시각적으로 차등화 되어 표현될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 위험도가 높을수록 해당 위험도 정보(25a~25e)의 색을 진하게 표현할 수 있다. 이와 같이, 본 발명의 서버는 지도상에서 이벤트 발생 위험도가 높은 지역에 대한 정보를 시각적으로 표시하여 사용자에게 제공할 수 있다. 서버는 이와 같이 생성된 위험 상황 정보를 사용자 단말로 전송한다.FIG. 4 shows an embodiment of the risk situation information of the present invention expressed visually. According to the embodiment of the present invention, the server may map at least one of the
도 5는 사용자 단말에서 출력되는 위험 상황 정보의 일 실시예를 나타내고 있다. 사용자 단말(300)은 서버로부터 위험 상황 정보를 수신하고, 이를 영상 및/또는 음성으로 출력한다. 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 사용자 단말(300)은 GPS 신호, AP(Access Point) 신호, 비콘 신호 등을 이용하여 사용자의 위치 정보(10)를 측정할 수 있으며, 해당 사용자의 위치 주변의 위험도 정보(25)를 출력할 수 있다. 이러한 위험도 정보(25)는 지도 상에 매핑된 시각적 정보뿐만 아니라 텍스트 정보 등의 다양한 형태를 포함한다. 이때, 사용자 단말(300)은 해당 이벤트의 내용, 대응 방법, 위험도 및 이벤트 발생 위치 등을 알람 형태로 제공할 수 있다.5 shows an example of the dangerous situation information output from the user terminal. The
이상에서는 본 발명을 구체적인 실시예를 통하여 설명하였으나, 당업자라면 본 발명의 취지 및 범위를 벗어나지 않고 수정, 변경을 할 수 있다. 따라서 본 발명의 상세한 설명 및 실시예로부터 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에 속한 사람이 용이하게 유추할 수 있는 것은 본 발명의 권리범위에 속하는 것으로 해석된다.While the present invention has been described with reference to the particular embodiments, those skilled in the art will appreciate that various modifications, additions and substitutions are possible, without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention. Therefore, it is to be understood that those skilled in the art can easily deduce from the detailed description and the embodiments of the present invention that they fall within the scope of the present invention.
100: 이벤트 감지 장치200: 서버
300: 사용자 단말100: Event detection device 200: Server
300: user terminal
Claims (12)
Translated fromKorean상기 수신된 이벤트 데이터를 기 설정된 정형 데이터로 변환하는 단계, 상기 정형 데이터는 이벤트 종류 정보 및 이벤트 발생 장소 정보를 포함함;
제1 종류 이벤트의 발생시 제2 종류 이벤트가 발생할 확률에 대한 정보를 나타내는 이벤트 발생 전이확률 정보를 이용하여, 발생된 신규 이벤트에 기초한 다른 종류의 이벤트의 발생 확률을 획득하는 단계;
상기 신규 이벤트 발생 정보 및 상기 획득된 다른 종류의 이벤트 발생 확률에 기초하여 이벤트 발생 장소의 위험도를 판별하는 단계;
상기 판별된 위험도 정보를 지도상에 매핑하는 단계; 및
상기 위험도 정보가 매핑된 지도 데이터를 포함하는 위험 상황 정보를 사용자에게 제공하는 단계;
를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 방법.
Receiving event data representing new event occurrence information from at least one event detection device;
Converting the received event data into predetermined formatted data, the formatted data including event type information and event occurrence place information;
Acquiring a probability of occurrence of another kind of event based on the generated new event using the event occurrence transition probability information indicating information about a probability of occurrence of the second kind event upon occurrence of the first kind event;
Determining a risk of an event occurrence place based on the new event occurrence information and the obtained another kind of event occurrence probability;
Mapping the identified risk information onto a map; And
Providing the user with risk condition information including map data to which the risk information is mapped;
And generating the event occurrence information.
상기 이벤트 발생 전이확률 정보는 상기 정형 데이터에서의 각 이벤트 종류 간의 전이 확률을 나타내는 마르코프(Markov) 체인을 이용하여 획득되는 것을 특징으로 하는 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 방법.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the event occurrence transition probability information is acquired using a Markov chain indicating a transition probability between each event type in the fixed data.
신규 이벤트 발생 장소의 위험도는 상기 신규 이벤트에 대한 위험도 값과 상기 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 추정 위험도 값의 합산 값에 기초하여 산출되며,
상기 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 추정 위험도 값은 상기 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 위험도 값과 상기 다른 종류의 이벤트 발생 확률의 곱에 의해 결정되는 것을 특징으로 하는 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 방법.
The method according to claim 1,
The risk of the new event occurrence place is calculated based on the sum of the risk value for the new event and the estimated risk value for the other kind of event,
Wherein the estimated risk value for the different kind of event is determined by multiplying the risk value for the different kind of event by the probability of occurrence of the different kind of event.
상기 이벤트 감지 장치는 영상 데이터를 이용하여 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 판별하되,
상기 영상 데이터에서의 객체의 행위 분석, 객체들 간의 상호 행위 분석 및 특정 객체 검출 결과 중 적어도 하나에 기초하여 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 판별하는 것을 특징으로 하는 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 방법.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the event detection device determines whether a new event is generated using the image data,
Determining whether a new event is generated based on at least one of a behavior analysis of an object in the image data, a mutual behavior analysis between objects, and a specific object detection result.
상기 이벤트 데이터를 수신하는 단계는,
뉴스 데이터, SNS(Social Network Service) 데이터 및 웹 데이터 중 적어도 하나를 이용하여 상기 이벤트 데이터를 획득하는 것을 특징으로 하는 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 방법.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the step of receiving the event data comprises:
Wherein the event data is acquired using at least one of news data, social network service (SNS) data, and web data.
상기 수신된 이벤트 데이터를 저장하는 빅데이터 DB;
상기 이벤트 데이터를 이벤트 종류 정보 및 이벤트 발생 장소 정보를 포함하는 기 설정된 정형 데이터로 변환하고, 제1 종류 이벤트의 발생시 제2 종류 이벤트가 발생할 확률에 대한 정보를 나타내는 이벤트 발생 전이확률 정보를 이용하여, 발생된 신규 이벤트에 기초한 다른 종류 이벤트의 발생 확률을 획득하는 이벤트 분석부; 및
상기 신규 이벤트 발생 정보 및 상기 획득된 다른 종류 이벤트 발생 확률에 기초하여 이벤트 발생 장소의 위험도를 판별하고, 상기 판별된 위험도 정보를 지도상에 매핑하고, 상기 위험도 정보가 매핑된 지도 데이터를 포함하는 위험 상황 정보를 사용자에게 제공하는 위험 상황 정보 제공부;
를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 시스템.
A communication unit for receiving event data representing new event occurrence information from at least one event detection device;
A big data DB for storing the received event data;
The method of claim 1, further comprising: converting event data into predetermined format data including event type information and event occurrence place information, and using event occurrence transition probability information indicating information on a probability of occurrence of a second type event when a first type event occurs, An event analyzer for obtaining a probability of occurrence of another kind event based on the generated new event; And
Wherein the risk information includes at least one of a risk of generating an event on the basis of the new event occurrence information and a probability of occurrence of the different kind of event, mapping the determined risk information on a map, Providing risk information providing the user with the situation information;
The event generation information providing system comprising:
상기 이벤트 발생 전이확률 정보는 상기 정형 데이터에서의 각 이벤트 종류 간의 전이 확률을 나타내는 마르코프(Markov) 체인을 이용하여 획득되는 것을 특징으로 하는 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 시스템.
8. The method of claim 7,
Wherein the event occurrence transition probability information is acquired using a Markov chain indicating a transition probability between each event type in the fixed data.
신규 이벤트 발생 장소의 위험도는 상기 신규 이벤트에 대한 위험도 값과 상기 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 추정 위험도 값의 합산 값에 기초하여 산출되며,
상기 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 추정 위험도 값은 상기 다른 종류의 이벤트에 대한 위험도 값과 상기 다른 종류의 이벤트 발생 확률의 곱에 의해 결정되는 것을 특징으로 하는 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 시스템.
8. The method of claim 7,
The risk of the new event occurrence place is calculated based on the sum of the risk value for the new event and the estimated risk value for the other kind of event,
Wherein the estimated risk value for the different kind of event is determined by a product of the risk value for the different kind of event and the probability of occurrence of the different kind of event.
상기 이벤트 감지 장치는 영상 데이터를 수집하고, 수집된 영상 데이터를 이용하여 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 판별하되,
상기 영상 데이터에서의 객체의 행위 분석, 객체들 간의 상호 행위 분석 및 특정 객체 검출 결과 중 적어도 하나에 기초하여 신규 이벤트 발생 여부를 판별하는 것을 특징으로 하는 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 시스템.
8. The method of claim 7,
The event detection apparatus collects image data and determines whether a new event is generated using the collected image data,
Wherein the event occurrence information providing system determines whether a new event is generated based on at least one of a behavior analysis of an object in the image data, a mutual behavior analysis between objects, and a specific object detection result.
상기 이벤트 데이터는 뉴스 데이터, SNS(Social Network Service) 데이터 및 웹 데이터 중 적어도 하나를 이용하여 획득되는 것을 특징으로 하는 이벤트 발생 정보 제공 시스템.
8. The method of claim 7,
Wherein the event data is acquired using at least one of news data, social network service (SNS) data, and web data.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150027883AKR101687477B1 (en) | 2015-02-27 | 2015-02-27 | A Method for Providing Event Occurrence Information Using Big Data and A System for the Same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150027883AKR101687477B1 (en) | 2015-02-27 | 2015-02-27 | A Method for Providing Event Occurrence Information Using Big Data and A System for the Same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20160104940A KR20160104940A (en) | 2016-09-06 |
| KR101687477B1true KR101687477B1 (en) | 2016-12-16 |
Family
ID=56945867
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020150027883AActiveKR101687477B1 (en) | 2015-02-27 | 2015-02-27 | A Method for Providing Event Occurrence Information Using Big Data and A System for the Same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101687477B1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102172952B1 (en) | 2019-12-06 | 2020-11-02 | 이정무 | Method for video monitoring, Apparatus for video monitoring and Computer program for the same |
| KR20220019406A (en)* | 2020-08-10 | 2022-02-17 | 건국대학교 글로컬산학협력단 | apparatus and system for child safety education |
| KR20220072316A (en) | 2020-11-25 | 2022-06-02 | 주식회사 넥스트케이 | Image Analysis Apparatus for Detecting Multi-object Events and Driving Method Thereof |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101857988B1 (en)* | 2017-03-16 | 2018-05-16 | 주식회사 핸즈 | Method for providing possibility information of encounter and server thereof |
| KR102162065B1 (en)* | 2017-12-06 | 2020-10-14 | 주식회사 아세스 | Method for predicting water leisure safety and computer readable record-medium on which program for executing method therefor |
| JP7095312B2 (en)* | 2018-03-01 | 2022-07-05 | オムロン株式会社 | Hazard level detection device, risk level detection method, and risk level detection program |
| US11288509B2 (en)* | 2019-11-12 | 2022-03-29 | Toyota Research Institute, Inc. | Fall detection and assistance |
| KR102316610B1 (en)* | 2020-01-31 | 2021-10-25 | 조앤소프트 주식회사 | School safety accident management system and school safety accident prevention method using the same |
| US20220307709A1 (en)* | 2021-03-26 | 2022-09-29 | Asahi Kasei Microdevices Corporation | Risk information provision device, risk information provision system, risk information provision method, and computer-readable medium |
| KR102793872B1 (en)* | 2022-06-21 | 2025-04-11 | 대한민국 | Prediction method and system through social event criterion model including any one or more of terrorism, disaster, war and crime |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100907985B1 (en)* | 2007-03-21 | 2009-07-16 | 한국정보통신대학교 산학협력단 | Contextual Information Management System |
| KR101349763B1 (en)* | 2011-12-29 | 2014-01-10 | 전자부품연구원 | Method and apparatus for guiding car accident crisis |
| KR101747212B1 (en)* | 2012-04-02 | 2017-06-15 | 한화테크윈 주식회사 | System for monitoring image and thereof method |
| KR20140106883A (en)* | 2013-02-27 | 2014-09-04 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Apparatus and method for detecting a risk situation by analyzing a relation of object |
- 2015
- 2015-02-27KRKR1020150027883Apatent/KR101687477B1/enactiveActive
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102172952B1 (en) | 2019-12-06 | 2020-11-02 | 이정무 | Method for video monitoring, Apparatus for video monitoring and Computer program for the same |
| KR20220019406A (en)* | 2020-08-10 | 2022-02-17 | 건국대학교 글로컬산학협력단 | apparatus and system for child safety education |
| KR102494884B1 (en)* | 2020-08-10 | 2023-02-01 | 건국대학교 글로컬산학협력단 | apparatus and system for child safety education |
| KR20220072316A (en) | 2020-11-25 | 2022-06-02 | 주식회사 넥스트케이 | Image Analysis Apparatus for Detecting Multi-object Events and Driving Method Thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20160104940A (en) | 2016-09-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101687477B1 (en) | A Method for Providing Event Occurrence Information Using Big Data and A System for the Same | |
| US12079272B2 (en) | Distributed video storage and search with edge computing | |
| US11295405B2 (en) | Cognitive recommendations for first responders | |
| US9792434B1 (en) | Systems and methods for security data analysis and display | |
| US20170188216A1 (en) | Personal emergency saver system and method | |
| US20170089739A1 (en) | Sensor grouping for a sensor based detection system | |
| US20150100355A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for identifying early status | |
| US20150248275A1 (en) | Sensor Grouping for a Sensor Based Detection System | |
| US9622048B2 (en) | SNS based incident management | |
| US11610470B1 (en) | Systems and methods for crowdsourcing detected events | |
| US9881480B2 (en) | Mobile device loss prevention | |
| JP6631618B2 (en) | Image monitoring apparatus and image monitoring method | |
| JP2018526706A (en) | Method and apparatus for adaptively managing data collection devices in a distributed computing system | |
| KR101386591B1 (en) | Surveillance Camera Integrated Management System | |
| US20150379853A1 (en) | Method and system for sensor based messaging | |
| US20150379848A1 (en) | Alert system for sensor based detection system | |
| CN109831742A (en) | Monitoring method and system based on terminal detection | |
| KR101646733B1 (en) | Method and apparatus of classifying media data | |
| KR101864222B1 (en) | system and method for pedestrian traffic big data analysis | |
| KR20160104223A (en) | A Method for a Crime Prediction Using a Crime Pattern Analysis based on Big Data and A System for the Same | |
| CN115171007A (en) | Scene monitoring method, device and equipment based on edge calculation and storage medium | |
| KR101703116B1 (en) | System for generating disaster information, method of generating disaster information and apparatus for the same | |
| EP3698336B1 (en) | Intrusion detection methods and devices | |
| KR101660160B1 (en) | A Method for Estimating a Crime Risk Using Big Data and A System for Reporting the Crime Risk Using thereof | |
| JP2018174520A (en) | Bandwidth control apparatus, bandwidth control method, and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20150227 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20160421 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20161031 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20161212 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20161212 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20191202 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20191202 Start annual number:4 End annual number:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20211201 Start annual number:6 End annual number:6 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20221205 Start annual number:7 End annual number:7 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20230921 Start annual number:8 End annual number:8 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee |