KR101565200B1 - New compound and organic light emitting device using the same - Google Patents
New compound and organic light emitting device using the sameDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101565200B1 KR101565200B1KR1020120037956AKR20120037956AKR101565200B1KR 101565200 B1KR101565200 B1KR 101565200B1KR 1020120037956 AKR1020120037956 AKR 1020120037956AKR 20120037956 AKR20120037956 AKR 20120037956AKR 101565200 B1KR101565200 B1KR 101565200B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- substituted
- group
- unsubstituted
- formula
- light emitting
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K85/00—Organic materials used in the body or electrodes of devices covered by this subclass
- H10K85/60—Organic compounds having low molecular weight
- H10K85/615—Polycyclic condensed aromatic hydrocarbons, e.g. anthracene
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/14—Carrier transporting layers
- H10K50/15—Hole transporting layers
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/14—Carrier transporting layers
- H10K50/16—Electron transporting layers
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/17—Carrier injection layers
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/17—Carrier injection layers
- H10K50/171—Electron injection layers
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K85/00—Organic materials used in the body or electrodes of devices covered by this subclass
- H10K85/60—Organic compounds having low molecular weight
- H10K85/631—Amine compounds having at least two aryl rest on at least one amine-nitrogen atom, e.g. triphenylamine
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K85/00—Organic materials used in the body or electrodes of devices covered by this subclass
- H10K85/60—Organic compounds having low molecular weight
- H10K85/649—Aromatic compounds comprising a hetero atom
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K2101/00—Properties of the organic materials covered by group H10K85/00
- H10K2101/27—Combination of fluorescent and phosphorescent emission
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 유기 발광 소자의 수명, 효율, 전기 화학적 안정성 및 열적 안정성을 크게 향상시킬 수 있는 신규한 화합물 및 상기 화합물이 유기물층에 함유되어 있는 유기 발광 소자에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a novel compound capable of greatly improving the lifetime, efficiency, electrochemical stability and thermal stability of an organic light emitting device, and an organic light emitting device in which the compound is contained in an organic material layer.
유기 발광 현상은 특정 유기 분자의 내부 프로세스에 의하여 전류가 가시광으로 전환되는 예의 하나이다. 유기 발광 현상의 원리는 다음과 같다. 양극과 음극 사이에 유기물층을 위치시켰을 때 두 전극 사이에 전압을 걸어주게 되면 음극과 양극으로부터 각각 전자와 정공이 유기물층으로 주입된다. 유기물층으로 주입된 전자와 정공은 재결합하여 엑시톤(exciton)을 형성하고, 이 엑시톤이 다시 바닥 상태로 떨어지면서 빛이 나게 된다. 이러한 원리를 이용하는 유기 발광 소자는 일반적으로 음극과 양극 및 그 사이에 위치한 유기물층, 예컨대 정공 주입층, 정공 수송층, 발광층, 전자 수송층을 포함하는 유기물층으로 구성될 수 있다.The organic light emission phenomenon is one example in which current is converted into visible light by an internal process of a specific organic molecule. The principle of organic luminescence phenomenon is as follows. When an organic layer is positioned between the anode and the cathode, when a voltage is applied between the two electrodes, electrons and holes are injected into the organic layer from the cathode and the anode, respectively. Electrons and holes injected into the organic material layer recombine to form an exciton, and the exciton falls back to the ground state to emit light. An organic light emitting device using such a principle may be generally composed of an organic material layer including a cathode, an anode, and an organic material layer disposed therebetween, for example, a hole injection layer, a hole transport layer, a light emitting layer, and an electron transport layer.
유기 발광 소자에서 사용되는 물질로는 순수 유기 물질 또는 유기 물질과 금속이 착물을 이루는 착화합물이 대부분을 차지하고 있으며, 용도에 따라 정공 주입 물질, 정공 수송 물질, 발광 물질, 전자 수송 물질, 전자 주입 물질 등으로 구분될 수 있다. 여기서, 정공 주입 물질이나 정공 수송 물질로는 p-타입의 성질을 가지는 유기 물질, 즉 쉽게 산화가 되고 산화시에 전기화학적으로 안정한 상태를 가지는 유기물이 주로 사용되고 있다. 한편, 전자 주입 물질이나 전자 수송 물질로는 n-타입 성질을 가지는 유기 물질, 즉 쉽게 환원이 되고 환원시에 전기화학적으로 안정한 상태를 가지는 유기물이 주로 사용되고 있다. 발광층 물질로는 p-타입 성질과 n-타입 성질을 동시에 가진 물질, 즉 산화와 환원 상태에서 모두 안정한 형태를 갖는 물질이 바람직하며, 엑시톤이 형성되었을 때 이를 빛으로 전환하는 발광 효율이 높은 물질이 바람직하다.As a material used in an organic light emitting device, a pure organic material or a complex in which an organic material and a metal form a complex is mostly used. Depending on the application, a hole injecting material, a hole transporting material, a light emitting material, an electron transporting material, . As the hole injecting material and the hole transporting material, an organic material having a p-type property, that is, an organic material that is easily oxidized and electrochemically stable at the time of oxidation is mainly used. On the other hand, as an electron injecting material or an electron transporting material, an organic material having an n-type property, that is, an organic material that is easily reduced and electrochemically stable when being reduced is mainly used. As the light emitting layer material, a material having both a p-type property and an n-type property, that is, a material having both a stable form in oxidation and in a reduced state is preferable, and a material having a high luminous efficiency for converting an exciton into light desirable.
위에서 언급한 외에, 유기 발광 소자에서 사용되는 물질은 다음과 같은 성질을 추가적으로 갖는 것이 바람직하다.In addition to the above, it is preferable that the material used in the organic light emitting device further has the following properties.
첫째로, 유기 발광 소자에서 사용되는 물질은 열적 안정성이 우수한 것이 바람직하다. 유기 발광 소자 내에서는 전하들의 이동에 의한 줄열(joule heating)이 발생하기 때문이다. 현재, 정공 수송층 물질로 주로 사용되는 NPB는 유리 전이 온도가 100℃ 이하의 값을 가지므로, 높은 전류를 필요로 하는 유기 발광 소자에서는 사용하기 힘든 문제가 있다.First, the material used in the organic light emitting device is preferably excellent in thermal stability. This is because joule heating occurs due to the movement of charges in the organic light emitting device. At present, NPB, which is mainly used as a hole transporting layer material, has a glass transition temperature of 100 DEG C or less, which makes it difficult to use in an organic light emitting device requiring a high current.
둘째로, 저전압 구동 가능한 고효율의 유기 발광 소자를 얻기 위해서는 유기 발광 소자 내로 주입된 정공 또는 전자들이 원활하게 발광층으로 전달되는 동시에, 주입된 정공과 전자들이 발광층 밖으로 빠져나가지 않도록 하여야 한다. 이를 위해서 유기 발광 소자에 사용되는 물질은 적절한 밴드갭(band gap)과 HOMO 또는 LUMO 에너지 준위를 가져야 한다. 현재 용액 도포법에 의해 제조되는 유기 발광 소자에서 정공 수송 물질로 사용되는 PEDOT:PSS의 경우, 발광층 물질로 사용되는 유기물의 LUMO 에너지 준위에 비하여 LUMO 에너지 준위가 낮기 때문에 고효율 장수명의 유기 발광 소자 제조에 어려움이 있다.Secondly, in order to obtain a highly efficient organic light emitting device capable of driving at a low voltage, holes or electrons injected into the organic light emitting element should be smoothly transferred to the light emitting layer, and injected holes and electrons should not escape from the light emitting layer. For this purpose, the material used in the organic light emitting device should have an appropriate band gap and a HOMO or LUMO energy level. In the case of PEDOT: PSS used as a hole transport material in the organic light emitting device manufactured by the solution coating method, since the LUMO energy level is lower than the LUMO energy level of the organic material used as the light emitting layer material, There is a difficulty.
이외에도 유기 발광 소자에서 사용되는 물질은 화학적 안정성, 전하이동도, 전극이나 인접한 층과의 계면 특성 등이 우수하여야 한다. 즉, 유기 발광소자에서 사용되는 물질은 수분이나 산소에 의한 물질의 변형이 적어야 한다. 또한, 적절한 정공 또는 전자 이동도를 가짐으로써 유기 발광 소자의 발광층에서 정공과 전자의 밀도가 균형을 이루도록 하여 엑시톤 형성을 극대화할 수 있어야 한다. 그리고, 소자의 안정성을 위해 금속 또는 금속 산화물을 포함한 전극과의 계면을 좋게 할 수 있어야 한다.In addition, materials used in organic light emitting devices should have excellent chemical stability, charge mobility, and interface characteristics with electrodes or adjacent layers. That is, the material used in the organic light emitting device should have little deformation of the material due to moisture or oxygen. In addition, by having appropriate hole or electron mobility, it is necessary to maximize the formation of excitons by balancing the density of holes and electrons in the light emitting layer of the organic light emitting device. And, for the stability of the device, the interface with the electrode including the metal or the metal oxide should be good.
따라서, 당 기술분야에서는 상기와 같은 요건을 갖춘 유기물의 개발이 요구되고 있다.Accordingly, there is a need in the art to develop organic materials having the above-mentioned requirements.
이에 본 발명자들은 유기 발광 소자에서 사용 가능한 물질에 요구되는 조건, 예컨대 적절한 에너지 준위, 전기 화학적 안정성 및 열적 안정성 등을 만족시킬 수 있으며, 치환기에 따라 유기 발광 소자에서 요구되는 다양한 역할을 할 수 있는 화학 구조를 갖는 화합물을 포함하는 유기 발광 소자를 제공하는 것을 목적으로 한다.Accordingly, the present inventors have found that a compound capable of satisfying the conditions required for a material usable in an organic light emitting device, for example, an appropriate energy level, electrochemical stability, and thermal stability, And a compound having a structure represented by the following formula (1).
본 발명은 하기 화학식 1로 표시되는 화합물을 제공한다.The present invention provides a compound represented by the following formula (1).
[화학식 1][Chemical Formula 1]
A-L-BA-L-B
상기 화학식 1에 있어서,In Formula 1,
L은 직접결합; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 6 내지 20의 아릴렌기; 또는 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 2 내지 20의 헤테로아릴렌기이고,L is a direct bond; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P An arylene group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms which is substituted or unsubstituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P as a hetero atom, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group substituted with a hetero atom, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, a substituted A substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S or A heteroarylene group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms which is substituted or unsubstituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms,
A는 하기 화학식 2로 표시되고,A is represented by the following formula (2)
[화학식 2](2)
상기 화학식 2에 있어서,In Formula 2,
R1 내지 R9는 각각 독립적으로 수소; 중수소; 할로겐기; 니트로기; 니트릴기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 1 내지 30의 알킬기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 1 내지 30의 알콕시기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 1 내지 30의 알킬티오기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 2 내지 20의 알케닐기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 2 내지 20의 알카이닐이기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 6 내지 60의 아릴기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 2 내지 50의 헤테로아릴기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 2 내지 50의 헤테로시클로알킬기; 또는 이웃한 치환기와 지방족, 헤테로 지방족, 방향족 또는 헤테로 방향족 고리를 형성할 수 있고,R 1 to R 9 are each independently hydrogen; heavy hydrogen; A halogen group; A nitro group; A nitrile group; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P An alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms which is unsubstituted or substituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P An alkoxy group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms which is substituted or unsubstituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P An alkylthio group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms which is unsubstituted or substituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P An alkenyl group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms which is substituted or unsubstituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P Alkenyl having 2 to 20 carbon atoms which is unsubstituted or substituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P An aryl group having 6 to 60 carbon atoms which is substituted or unsubstituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms; A halogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, A substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, A substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having O, N, S, or P as a hetero atom, Or an unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 2 to 50 carbon atoms; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, A substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, A substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having O, N, S, or P as a hetero atom, Or an unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having 2 to 50 carbon atoms; Or adjacent substituents to form an aliphatic, heteroaliphatic, aromatic or heteroaromatic ring,
R1 내지 R9 중 적어도 어느 하나는 화학식 1의 L로 대체되며,At least one of R 1 to R 9 is substituted with L of formula (1)
B는 하기 화학식 3으로 표시되고,B is represented by the following formula (3)
[화학식 3](3)
상기 화학식 3에 있어서,In Formula 3,
X는 O 또는 S이고,X is O or S,
E1 내지 E8은 각각 독립적으로 수소; 중수소; 할로겐기; 니트로기; 니트릴기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 1 내지 30의 알킬기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 1 내지 30의 알콕시기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 1 내지 30의 알킬티오기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 2 내지 20의 알케닐기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 2 내지 20의 알카이닐이기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 6 내지 60의 아릴기; 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티오기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 2 내지 50의 헤테로 아릴기; 또는 중수소, 니트로기, 니트릴기, 할로겐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로시클로알킬기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알콕시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬티옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴티옥시기, 치환 또는 비치환된 알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 시클로알케닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 실릴기, 치환 또는 비치환된 붕소기, 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴아민기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 2 내지 50의 헤테로 시클로알킬기이고,E1 to E8 each independently represent hydrogen; heavy hydrogen; A halogen group; A nitro group; A nitrile group; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P An alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms which is unsubstituted or substituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P An alkoxy group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms which is substituted or unsubstituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P An alkylthio group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms which is unsubstituted or substituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P An alkenyl group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms which is substituted or unsubstituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P Alkenyl having 2 to 20 carbon atoms which is unsubstituted or substituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms; A substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having O, N, S, or P, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group having a hetero atom, a nitro group, a nitrile group, A substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, An unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted boron group, a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a hetero atom, O, N, S, or P An aryl group having 6 to 60 carbon atoms which is substituted or unsubstituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms; A halogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkylthio group, A substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted arylthio group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, A substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having O, N, S, or P as a hetero atom, Or an unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 2 to 50 carbon atoms; A halogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heterocycloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl A substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted silyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, A substituted or unsubstituted arylamine group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having O, N, S, or P as a hetero atom, A substituted or unsubstituted C2-C50 heterocycloalkyl group,
E1 내지 E8 중 적어도 어느 하나는 화학식 1의 L로 대체된다.At least one of E1 to E8 is substituted with L in formula (1).
또한, 상기 화학식 1의 화합물을 포함하는 정공 전달 재료를 제공한다.Also, there is provided a hole transport material comprising the compound of Formula 1.
또한, 상기 화학식 1의 화합물을 포함하는 전자 저지 재료를 제공한다.Also provided is an electron blocking material comprising the compound of formula (1).
또한, 상기 화학식 1의 화합물을 포함하는 인광 발광 재료를 제공한다.Also provided is a phosphorescent material comprising the compound of formula (1).
또한, 본 발명은 제1 전극, 제2 전극, 및 상기 제1 전극과 제2 전극 사이에 배치된 1층 이상의 유기물층을 포함하는 유기 발광 소자로서, 상기 유기물층 중 1층 이상은 상기 화학식 1의 화합물 또는 상기 화학식 1의 화합물에 열경화성 또는 광경화성 작용기가 도입된 화합물을 포함하는 유기 발광 소자를 제공한다.Also, the present invention is an organic light emitting device comprising a first electrode, a second electrode, and at least one organic material layer disposed between the first electrode and the second electrode, wherein at least one of the organic material layers is a compound Or a compound having a thermosetting or photo-curable functional group introduced into the compound of formula (1).
본 발명의 화합물은 유기 발광 소자에서 유기물층 물질, 예컨대 정공 주입 물질, 정공 수송 물질, 발광 물질, 전자 수송 물질, 전자 주입 물질 등에 사용될 수 있으며, 본 발명의 화합물을 유기 발광 소자에 사용하는 경우 소자의 구동전압을 낮추고, 광효율을 향상시키며, 화합물의 열적 안정성에 의하여 소자의 수명 특성을 향상시킬 수 있다.The compound of the present invention can be used in an organic light emitting device such as a hole injecting material, a hole transporting material, a light emitting material, an electron transporting material, an electron injecting material, etc. When the compound of the present invention is used in an organic light emitting device, The driving voltage can be lowered, the light efficiency can be improved, and the lifetime characteristics of the device can be improved by the thermal stability of the compound.
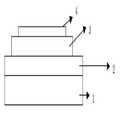
도 1은 기판(1), 제1 전극(2), 발광층(3) 및 제2 전극(4)로 이루어진 유기 발광 소자의 예를 도시한 것이다.
도 2는 기판(1), 제1 전극(2), 정공 주입층(5), 정공 수송층(6), 발광층(3), 전자 수송층(8) 및 제2 전극(4)으로 이루어진 유기 발광 소자의 예를 도시한 것이다.Fig. 1 shows an example of an organic light emitting element comprising a substrate 1, a
2 shows an organic light emitting device 1 including a substrate 1, a
이하에서 본 발명에 대하여 상세히 설명한다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail.
본 발명에 따른 화합물은 상기 화학식 1로 표시된다.The compound according to the present invention is represented by the above formula (1).
본 발명에 따른 화합물에 있어서, 상기 화학식 2는 하기 화학식 4 내지 6으로 표시될 수 있다.In the compound according to the present invention, the above-mentioned formula (2) may be represented by the following formulas (4) to (6).
[화학식 4][Chemical Formula 4]
[화학식 5][Chemical Formula 5]
[화학식 6][Chemical Formula 6]
상기 화학식 4 내지 6에 있어서, R1 내지 R9는 상기 화학식 2에서 정의한 바와 같다. In formulas (4) to (6), R 1 to R 9 are the same as defined in Formula (2).
본 발명에 따른 화합물에 있어서, 상기 화학식 1은 하기 화학식 7 내지 10으로 표시될 수 있다.In the compound according to the present invention, the formula (1) may be represented by the following formulas (7) to (10).
[화학식 7](7)
[화학식 8][Chemical Formula 8]
[화학식 9][Chemical Formula 9]
[화학식 10][Chemical formula 10]
상기 화학식 7 내지 10에 있어서, L, X, R1 내지 R8, 및 E1 내지 E8은 상기 화학식 1 내지 3에서 정의한 바와 같다.In Formulas 7 to 10, L, X, R 1 to
본 발명에 따른 화합물에 있어서, 상기 화학식 1은 하기 화학식 11 내지 14로 표시될 수 있다.In the compound according to the present invention, the formula (1) may be represented by the following formulas (11) to (14).
[화학식 11](11)
[화학식 12][Chemical Formula 12]
[화학식 13][Chemical Formula 13]
[화학식 14][Chemical Formula 14]
상기 화학식 11 내지 14에 있어서, L, X, R1 내지 R9, 및 E1 내지 E8은 상기 화학식 1 내지 3에서 정의한 바와 같다.In Formulas 11 to 14, L, X, R 1 to R 9, and E 1 to
상기 화학식 1에 있어서, 아릴렌기는 단환식 또는 다환식의 2가기로서, 탄소수는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 탄소수 6 내지 20인 것이 바람직하다. 구체적으로, 페닐렌기, 바이페닐렌기, 터페닐렌기, 스틸베닐렌기, 나프틸레닐기 및 하기와 같은 구조의 화합물이 될 수 있으나 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다. 하기 구조에서 2개 이상의 고리를 통과하는 직선은 통과하는 고리의 어떠한 치환 위치에 치환될 수 있음을 의미한다.In the above formula (1), the arylene group is a monocyclic or polycyclic divalent group, and the number of carbon atoms is not particularly limited, but is preferably 6 to 20 carbon atoms. Specifically, a phenylene group, a biphenylene group, a terphenylene group, a stilbene group, a naphthylenyl group, and a compound having the following structure may be used, but the present invention is not limited thereto. A straight line passing through two or more rings in the structure below means that it can be substituted at any substitution position of the passing ring.
상기 화학식 1에 있어서, 헤테로아릴렌기는 헤테로아릴기는 이종원자로 O, N 또는 S를 포함하는 2가기로서, 탄소수는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 탄소수 2 내지 20인 것이 바람직하다. 구체적으로, 하기와 같은 구조의 화합물이 될 수 있으나 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다. 하기 구조에서 2개 이상의 고리를 통과하는 직선은 통과하는 고리의 어떠한 치환 위치에 치환될 수 있음을 의미한다.In the above formula (1), the heteroarylene group is a divalent group containing O, N or S as a heteroatom, and the number of carbon atoms is not particularly limited, but preferably 2 to 20 carbon atoms. Specifically, it may be a compound having the following structure, but is not limited thereto. A straight line passing through two or more rings in the structure below means that it can be substituted at any substitution position of the passing ring.
상기 화학식 2 및 3에 있어서, 할로겐기는 불소, 염소, 브롬 또는 요오드가 될 수 있다.In the above formulas (2) and (3), the halogen group may be fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine.
상기 화학식 2 및 3에 있어서, 알킬기는 직쇄, 분지쇄 또는 고리쇄일 수 있다. 알킬기의 탄소수는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 탄소수 1 내지 30인 것이 바람직하다. 구체적으로, 메틸기, 에틸기, n-프로필기, iso-프로필기, n-부틸기, sec-부틸기, t-부틸기, n-펜틸기, iso-펜틸기, neo-펜틸기, n-헥실기, 시클로프로필기, 시클로부틸기, 시클로펜틸기, 시클로헥실기 등이 될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.In the general formulas (2) and (3), the alkyl group may be linear, branched or cyclic. The number of carbon atoms of the alkyl group is not particularly limited, but is preferably 1 to 30 carbon atoms. Specific examples thereof include a methyl group, ethyl group, n-propyl group, isopropyl group, n-butyl group, sec-butyl group, A cyclopropyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a cyclobutyl group, a cyclopentyl group, a cyclohexyl group, and the like, but is not limited thereto.
상기 화학식 2 및 3에 있어서, 알콕시기는 직쇄, 분지쇄 또는 고리쇄일 수 있다. 알콕시기의 탄소수는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 탄소수 1 내지 30인 것이 바람직하다. 구체적으로, 메톡시기, 에톡시기, n-프로필옥시기, iso-프로필옥시기, n-부틸옥시기,t-부틸옥시기, 옥시레인기, 옥시테인기, 테트라히드로퓨란기, 테트라히드로피란기 등이 될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.In the above formulas (2) and (3), the alkoxy group may be a straight chain, a branched chain or a cyclic chain. The number of carbon atoms of the alkoxy group is not particularly limited, but is preferably 1 to 30 carbon atoms. Specific examples thereof include a methoxy group, an ethoxy group, an n-propyloxy group, an iso-propyloxy group, a n-butyloxy group, at -butyloxy group, And the like, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
상기 화학식 2 및 3에 있어서, 알킬티오기는 직쇄, 분지쇄 또는 고리쇄일 수 있다. 알킬티오기의 탄소수는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 탄소수 1 내지 30인 것이 바람직하다. 구체적으로, 하기와 같은 구조의 화합물이 될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.In the formulas (2) and (3), the alkylthio group may be linear, branched or cyclic. The carbon number of the alkylthio group is not particularly limited, but is preferably 1 to 30 carbon atoms. Specifically, it may be a compound having the following structure, but is not limited thereto.
상기 화학식 2 및 3에 있어서, 알케닐기는 직쇄, 분지쇄 또는 고리쇄일 수 있다. 알케닐기의 탄소수는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 탄소수 1 내지 20인 것이 바람직하다. 알케닐기의 이중 결합 개수는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 이중 결합은 1 내지 10개를 가지는 것이 바람직하다. 구체적으로, 비닐기, 프로페닐기, 부테닐기, 펜테닐기, 헥세닐기, 부타디에닐기, 펜타디에닐기, 헥사디에닐기, 헥사트리에닐기, 시클로펜테닐기, 시클로헥세닐기, 시클로펜타디에닐기, 시클로헥사디에닐기 등이 될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.In the general formulas (2) and (3), the alkenyl group may be straight chain, branched chain or cyclic chain. The number of carbon atoms of the alkenyl group is not particularly limited, but is preferably 1 to 20 carbon atoms. The number of double bonds of the alkenyl group is not particularly limited, but it is preferable that the double bond has 1 to 10 bonds. Specific examples include a vinyl group, a propenyl group, a butenyl group, a pentenyl group, a hexenyl group, a butadienyl group, a pentadienyl group, a hexadienyl group, a hexatrienyl group, a cyclopentenyl group, a cyclohexenyl group, a cyclopentadienyl group, Cyclohexadienyl group, and the like, but is not limited thereto.
상기 화학식 2 및 3에 있어서, 알카이닐기는 직쇄, 분지쇄 또는 고리쇄일 수 있다. 알케닐기의 탄소수는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 탄소수 1 내지 20인 것이 바람직하다. 알카이닐기의 삼중 결합 개수는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 이중 결합은 1 내지 10개를 가지는 것이 바람직하다. 구체적으로, 에타인기, 프로파인기, 부타인기, 펜타인기, 헥사인기 등이 될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.In the above general formulas (2) and (3), the alkynyl group may be straight chain, branched chain or cyclic chain. The number of carbon atoms of the alkenyl group is not particularly limited, but is preferably 1 to 20 carbon atoms. The number of triple bonds of the alkynyl group is not particularly limited, but it is preferable that the double bond has 1 to 10 groups. Specifically, it may be, but not limited to, eta popular, propa popular, boot popular, penta popular, hexa popular, and the like.
상기 화학식 2 및 3에 있어서, 아릴기는 단환식 또는 다환식일 수 있고, 탄소수는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 탄소수 6 내지 60인 것이 바람직하다. 구체적으로, 단환식 아릴기로는 페닐기, 바이페닐기, 터페닐기, 스틸베닐기 등이 될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다. 다환식 아릴기로는 나프틸기, 안트릴기, 페난트릴기, 파이레닐기, 페릴레닐기, 크라이세닐기, 플루오레닐기 등이 될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.In the general formulas (2) and (3), the aryl group may be monocyclic or polycyclic, and the number of carbon atoms is not particularly limited, but is preferably 6 to 60 carbon atoms. Specific examples of the monocyclic aryl group include, but are not limited to, a phenyl group, a biphenyl group, a terphenyl group, a stilbenyl group, and the like. Examples of the polycyclic aryl group include, but are not limited to, naphthyl, anthryl, phenanthryl, pyrenyl, perylenyl, klycenyl,
상기 화학식 2 및 3에 있어서, 헤테로아릴기는 이종원자로 O, N 또는 S를 포함하는 고리기로서, 탄소수는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 탄소수 2 내지 50인 것이 바람직하다. 구체적으로, 퓨란기, 피롤기, 티오펜기, 이미다졸기, 옥사졸기, 티아졸기, 트리아졸기, 피리딜기, 피리다질기, 퀴놀리닐기, 아이소퀴놀리닐기, 아크리딜기 및 하기 구조식과 같은 화합물이 될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.In the general formulas (2) and (3), the heteroaryl group is a heterocyclic group containing O, N or S, and the number of carbon atoms is not particularly limited, but is preferably 2 to 50 carbon atoms. Specific examples of the substituent include a furan group, a pyrrolyl group, a thiophene group, an imidazole group, an oxazole group, a thiazole group, a triazole group, a pyridyl group, a pyridazyl group, a quinolinyl group, an isoquinolinyl group, But are not limited thereto.
상기 화학식 2 및 3에 있어서, 헤테로시클로알킬기는 이종원자로 O, N 또는 S를 포함하는 고리기로서, 탄소수는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 탄소수 2 내지 50인 것이 바람직하다. 구체적으로, 에폭시기, 옥시테인기, 테트라히드로퓨란기, 1,4-다이옥세인기, 1,3-다이옥세인기, 피롤리딘기, 피페리딘기, 테트라히드로티오펜기 등이 될 수 있으나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.In the general formulas (2) and (3), the heterocycloalkyl group is a heterocyclic group containing O, N or S, and the number of carbon atoms is not particularly limited, but is preferably 2 to 50 carbon atoms. Specific examples thereof include an epoxy group, an oxyethylene group, a tetrahydrofuran group, a 1,4-dioxolane group, a 1,3-dioxane group, a pyrrolidine group, a piperidine group and a tetrahydrothiophene group. But is not limited thereto.
상기 화학식 1에 있어서, "치환 또는 비치환"은 할로겐기, 니트릴기, 니트로기, 히드록시기, 알킬기, 시클로알킬기, 알케닐기, 알콕시기, 아릴옥시기, 티올기, 알킬티오기, 알릴티오기, 술폭시기, 알킬술폭시기, 아릴술폭시기, 실릴기, 붕소기, 아릴아민기, 아랄킬아민기, 알킬아민기, 아릴기, 플루오레닐기, 카바졸기, 아릴알킬기, 아릴알케닐기, 헤테로고리기 및 아세틸렌기로 이루어진 군에서 선택된 1개 이상의 치환기로 치환되었거나, 어떠한 치환기도 갖지 않는 것을 의미한다.In the above formula (1), the "substituted or unsubstituted" refers to a group selected from the group consisting of a halogen group, a nitrile group, a nitro group, a hydroxyl group, an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, an alkenyl group, an alkoxy group, An alkyl group, an aryl group, an aryl group, a fluorenyl group, a carbazole group, an arylalkyl group, an arylalkenyl group, a heterocyclic group, an arylalkoxy group, an arylalkoxy group, And an acetylene group, or does not have any substituent (s).
상기 화학식 4에 있어서, R3, R6 및 R9 중 어느 하나는 L인 것이 바람직하다.In Formula 4, it is preferable that any one of R3, R6, and R9 is L.
상기 화학식 6에 있어서, R6은 L인 것이 바람직하다.In the above formula (6), R6 is preferably L.
상기 화학식 1, 및 7 내지 14에 있어서, L은 직접결합 또는 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 6 내지 10의 아릴렌기가 바람직하며, 직접결합 또는 페닐렌기가 더욱 바람직하다.In Formulas 1 and 7 to 14, L is preferably a direct bond or a substituted or unsubstituted arylene group having 6 to 10 carbon atoms, more preferably a direct bond or a phenylene group.
화학식 2 및 3의 R1 내지 R9, 및 E1 내지 E8은 하기 [표 A-1]에 기재된 치환기로부터 선택되는 것이 바람직하나, 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.R 1 to R 9 and E 1 to
[표 A-1][Table A-1]
본 발명에 따른 화합물에 있어서, 상기 화학식 1은 하기 구조식 1 내지 48 중 어느 하나로 표시될 수 있으나, 이에만 한정되는 것은 아니다.In the compound according to the present invention, the above-mentioned formula (1) may be represented by any one of the following formulas (1) to (48), but is not limited thereto.
본 발명에 따른 화학식 1의 화합물은 다단계 화학반응으로 제조할 수 있다. 하기와 같이 일부 중간체 화합물이 먼저 제조되고, 그 중간체 화합물들로부터 화학식 1의 화합물들이 제조된다. 보다 구체적인 제조방법은 하기 실시예에 기재하였다.The compound of formula (I) according to the present invention can be prepared by a multistage chemical reaction. Some intermediate compounds are first prepared as follows, and the compounds of formula (1) are prepared from the intermediate compounds. More specific preparation methods are described in the following examples.
화합물의 컨쥬게이션 길이와 에너지 밴드갭은 밀접한 관계가 있다. 구체적으로, 화합물의 컨쥬게이션 길이가 길수록 에너지 밴드갭이 작아진다. 전술한 바와 같이, 상기 화학식 1의 화합물의 코어는 제한된 컨쥬게이션을 포함하고 있으므로, 이는 에너지 밴드 갭이 큰 성질을 갖는다.The conjugation length of the compound and the energy band gap are closely related. Specifically, the longer the conjugation length of the compound, the smaller the energy bandgap. As described above, since the core of the compound of Formula 1 contains limited conjugation, it has a large energy band gap.
본 발명에서는 상기와 같이 에너지 밴드 갭이 큰 코어 구조의 R1 내지 R9 및 E1 내지 E8 위치에 다양한 치환기를 도입함으로써 다양한 에너지 밴드 갭을 갖는 화합물을 합성할 수 있다. 통상 에너지 밴드 갭이 큰 코어 구조에 치환기를 도입하여 에너지 밴드 갭을 조절하는 것은 용이하나, 코어 구조가 에너지 밴드 갭이 작은 경우에는 치환기를 도입하여 에너지 밴드 갭을 크게 조절하기 어렵다.In the present invention, compounds having various energy bandgaps can be synthesized by introducing various substituents at positions R1 to R9 and E1 to E8 of the core structure having a large energy band gap as described above. Usually, it is easy to control the energy band gap by introducing a substituent to a core structure having a large energy band gap. However, when the core structure has a small energy band gap, it is difficult to control the energy band gap by introducing a substituent.
또한, 본 발명에서는 상기와 같은 구조의 코어 구조의 R1 내지 R9 및 E1 내지 E8 위치에 다양한 치환기를 도입함으로써 화합물의 HOMO 및 LUMO 에너지 준위도 조절할 수 있으며, 한편으로 유기물 사이에서의 계면에서의 특성을 향상되게 하며 물질의 용도를 다양하게 할 수 있다.In the present invention, the HOMO and LUMO energy levels of the compound can be controlled by introducing various substituents at the positions of R1 to R9 and E1 to E8 of the core structure having the above structure. On the other hand, And the use of the material can be varied.
또한, 상기와 같은 구조의 코어 구조에 다양한 치환기를 도입함으로써 도입된 치환기의 고유 특성을 갖는 화합물을 합성할 수 있다. 예컨대, 유기 발광 소자 제조시 사용되는 정공 주입층 물질, 정공 수송층 물질, 발광층 물질, 및 전자 수송층 물질에 주로 사용되는 치환기를 상기 코어 구조에 도입함으로써 각 유기물층에서 요구하는 조건들을 충족시키는 물질을 합성할 수 있다.Further, by introducing various substituents into the core structure having the above structure, it is possible to synthesize a compound having the intrinsic characteristics of the substituent introduced. For example, by introducing a substituent mainly used in a hole injection layer material, a hole transport layer material, a light emitting layer material, and an electron transport layer material used in the production of an organic light emitting device into the core structure, a material satisfying the conditions required in each organic layer is synthesized .
본 발명에서는 상기 화학식 1의 화합물 중 치환기에 따라 적절한 에너지 준위를 갖는 화합물을 선택하여 유기 발광 소자에 사용함으로써 구동 전압이 낮고 광효율이 높은 소자를 구현할 수 있다. 또한, 상기 코어 구조에 다양한 치환기를 도입함으로써 에너지 밴드 갭을 미세하게 조절이 가능하게 하며, 한편으로 유기물 사이에서의 계면에서의 특성을 향상되게 하며 물질의 용도를 다양하게 할 수 있다.In the present invention, a compound having an appropriate energy level according to the substituent among the compounds of the formula (1) is selected and used in an organic light emitting device, thereby realizing a device having a low driving voltage and a high light efficiency. Further, by introducing various substituent groups into the core structure, it is possible to finely control the energy band gap, and the characteristics at the interface between the organic materials can be improved and the use of the materials can be diversified.
한편, 상기 화학식 1의 화합물은 유리 전이 온도(Tg)가 높아 열적 안정성이 우수하다. 이러한 열적 안정성의 증가는 소자에 구동 안정성을 제공하는 중요한 요인이 된다.On the other hand, the compound of formula (1) has a high glass transition temperature (Tg) and is excellent in thermal stability. This increase in thermal stability is an important factor in providing drive stability to the device.
또한, 본 발명은 제1 전극, 제2 전극, 및 상기 제1 전극과 제2 전극 사이에 배치된 1층 이상의 유기물층을 포함하는 유기 발광 소자로서, 상기 유기물층 중 1층 이상은 상기 화학식 1의 화합물 또는 상기 화학식 1의 화합물에 열경화성 또는 광경화성 작용기가 도입된 화합물을 포함하는 유기 발광 소자를 제공한다.Also, the present invention is an organic light emitting device comprising a first electrode, a second electrode, and at least one organic material layer disposed between the first electrode and the second electrode, wherein at least one of the organic material layers is a compound Or a compound having a thermosetting or photo-curable functional group introduced into the compound of formula (1).
본 발명의 유기 발광 소자에서는 상기 화학식 1의 화합물 대신에 상기 화학식 1의 화합물에 열경화성 또는 광경화성 작용기를 도입한 화합물을 사용할 수도 있다. 이와 같은 화합물은 전술한 화학식 1의 화합물의 기본 물성을 유지하는 동시에, 소자의 제작시 용액 도포법에 의하여 박막으로 형성한 후 경화시키는 방법에 의하여 유기물층으로 형성될 수 있다.In the organic light emitting device of the present invention, a compound having a thermosetting or photo-curable functional group introduced into the compound of Formula 1 may be used in place of the compound of Formula 1. Such a compound may be formed into an organic layer by maintaining the basic physical properties of the compound of the above-mentioned formula (1), forming a thin film by solution coating method in manufacturing the device, and then curing it.
상기와 같이 유기 발광 소자의 제작시 유기물에 경화성 작용기를 도입하고, 용액 도포법에 의하여 상기 유기물의 박막을 형성한 후 경화하는 방법에 의하여 유기물층을 형성하는 방법은 미국 특허 공개 2003-0044518 및 유럽 특허 공개 1146574 A2 등에 기재되어 있다.As described above, a method of forming an organic material layer by introducing a curable functional group into an organic material and forming a thin film of the organic material by a solution coating method and then curing the organic material layer is disclosed in U.S. Patent Application Publication No. 2003-0044518 and European Patent Open No. 1146574 A2.
상기 문헌들에는 열경화 또는 광경화 가능한 비닐기 혹은 아크릴기를 가진 물질을 이용하여 상기와 같은 방법에 의하여 유기물층을 형성하여 유기 발광 소자를 제작하는 경우, 용액도포법에 의해 다층구조를 갖는 유기 발광 소자를 만들 수 있을 뿐 아니라 저전압 고휘도의 유기 발광 소자를 만들 수 있다고 기재되어 있다. 이와 같은 작용 원리는 본 발명의 화합물에도 적용될 수 있다.In the above documents, when an organic layer is formed by using a material having a thermosetting or photocurable vinyl group or an acrylic group to form an organic light emitting device, the organic light emitting device having a multilayer structure And can make an organic light emitting device having a low voltage and a high luminance. Such a working principle can also be applied to the compounds of the present invention.
본 발명에 있어서, 상기 열경화성 또는 광경화성 작용기는 비닐기, 아크릴기 등일 수 있다.In the present invention, the thermosetting or photocurable functional group may be a vinyl group, an acryl group, or the like.
도 1 및 2는 본 발명에 따른 유기 발광 소자의 일 예이며, 도 1은 기판(1), 제1 전극(2), 발광층(3) 및 제2 전극(4)으로 이루어진 유기 발광 소자의 예를 도시한 것이고, 도 2는 기판(1), 제1 전극(2), 정공 주입층(5), 정공 수송층(6), 발광층(3), 전자 수송층(8) 및 제2 전극(4)으로 이루어진 유기 발광 소자의 예를 도시한 것이다.1 and 2 show an example of an organic light emitting device according to the present invention. FIG. 1 shows an example of an organic light emitting device including a substrate 1, a
본 발명의 유기 발광 소자의 유기물층은 단층 구조로 이루어질 수도 있으나, 2층 이상의 유기물층이 적층된 다층 구조로 이루어질 수 있다.The organic material layer of the organic light emitting device of the present invention may have a single layer structure, but may have a multilayer structure in which two or more organic material layers are stacked.
예컨대, 본 발명의 유기 발광 소자는 유기물층으로서 정공 주입층, 정공 수송층, 발광층, 전자 수송층, 전자 주입층 등을 포함하는 구조를 가질 수 있다. 그러나, 유기 발광 소자의 구조는 이에 한정되지 않고 더 적은 수의 유기물층을 포함할 수 있다.For example, the organic light emitting device of the present invention may have a structure including a hole injecting layer, a hole transporting layer, a light emitting layer, an electron transporting layer, and an electron injecting layer as an organic material layer. However, the structure of the organic light emitting device is not limited thereto, and may include a smaller number of organic layers.
즉, 상기 유기 발광 소자에서, 상기 유기물층은 정공 주입층 및 정공 수송층 중 적어도 하나의 층을 포함하고, 이 정공 주입층 또는 정공 수송층이 상기 화학식 1로 표시되는 화합물을 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 상기 유기물층은 발광층을 포함하고, 이 발광층이 상기 화학식 1로 표시되는 화합물을 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 상기 유기물층은 전자 수송층을 포함하고, 상기 전자 수송층이 상기 화학식 1로 표시되는 화합물을 포함할 수 있다.That is, in the organic light emitting device, the organic material layer includes at least one of a hole injection layer and a hole transport layer, and the hole injection layer or the hole transport layer may include a compound represented by the above formula (1). In addition, the organic layer may include a light emitting layer, and the light emitting layer may include a compound represented by the general formula (1). In addition, the organic material layer may include an electron transporting layer, and the electron transporting layer may include a compound represented by the general formula (1).
상기 유기 발광 소자에서, 상기 발광층은 상기 화학식 1로 표시되는 화합물을 인광 발광 물질로 포함할 수 있다. 기존의 많은 소자가 형광 발광을 이용한 것이었지만, 삼중항 여기 상태로부터의 인광 발광을 이용하면, 기존의 일중항 여기 상태로부터의 인광 발광을 이용한 유기 발광 소자에 비하여 3배 정도의 발광 효율을 나타낸다.In the organic light emitting device, the light emitting layer may include the compound represented by Formula 1 as a phosphorescent light emitting material. Although many conventional devices use fluorescence emission, the use of phosphorescence emission from a triplet excited state exhibits a luminous efficiency of about three times that of an organic light emitting device using phosphorescence emission from a conventional singlet excited state.
기존의 인광 발광 재료들은 발광 특성 측면에서는 유리한 점이 있으나, 유리 전이 온도(Tg)가 낮아서 열적 안정성이 낮으므로, 진공 하에서 고온 증착 공정을 거치는 경우, 물질이 변성되는 등의 단점을 가지고 있다. 기존의 BAlq나 CBP 등의 인광 발광 재료를 사용하는 유기 발광 소자는 형광 발광 재료를 사용하는 유기 발광 소자에 비하여, 구동 전압이 높아서 전력 효율(lm/w)면에서 큰 이점이 없었다.Conventional phosphorescent materials are advantageous in terms of luminescent properties but have a disadvantage in that materials are denatured when they are subjected to a high temperature deposition process under vacuum because the glass transition temperature (Tg) is low and the thermal stability is low. The organic electroluminescent device using the phosphorescent material such as BAlq or CBP does not have a significant advantage in terms of power efficiency (lm / w) because the driving voltage is higher than that of the organic electroluminescent device using the fluorescent material.
상기 화학식 1로 표시되는 화합물은 유기 발광 소자의 제조시 진공 증착법 뿐만 아니라 용액 도포법에 의하여 유기물층으로 형성될 수 있다. 여기서, 용액 도포법이라 함은 스핀 코팅, 딥 코팅, 잉크젯 프린팅, 스크린 프린팅, 스프레이법, 롤 코팅 등을 의미하지만, 이들만으로 한정되는 것은 아니다.The compound represented by Formula 1 may be formed into an organic layer by a solution coating method as well as a vacuum deposition method in the production of an organic light emitting device. Here, the solution coating method refers to spin coating, dip coating, inkjet printing, screen printing, spraying, roll coating, and the like, but is not limited thereto.
본 발명의 유기 전기 소자는 유기물층 중 1층 이상이 본 발명의 화합물, 즉 상기 화학식 1로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 것을 제외하고는 당 기술분야에 알려져 있는 재료와 방법으로 제조될 수 있다.The organic electroluminescent device of the present invention can be manufactured by materials and methods known in the art, except that one or more of the organic layers includes the compound of the present invention, that is, the compound represented by the above formula (1).
본 발명의 유기 전기 소자는, 예컨대 기판 상에 제1 전극, 유기물층 및 제2 전극을 순차적으로 적층시킴으로써 제조할 수 있다. 이 때, 스퍼터링법(sputtering)이나 전자빔 증발법(e-beam evaporation)과 같은 PVD(Physical Vapor Deposition) 방법 등을 이용할 수 있으나, 이들 방법에만 한정되는 것은 아니다.The organic electroluminescent device of the present invention can be manufactured, for example, by sequentially laminating a first electrode, an organic material layer, and a second electrode on a substrate. In this case, a PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) method such as sputtering or e-beam evaporation may be used, but the present invention is not limited to these methods.
상기 양극 물질로는 통상 유기물층으로 정공 주입이 원활할 수 있도록 일함수가 큰 물질이 바람직하다. 본 발명에서 사용될 수 있는 양극 물질의 구체적인 예로는 바나듐, 크롬, 구리, 아연, 금과 같은 금속 또는 이들의 합금; 아연산화물, 인듐산화물, 인듐주석 산화물(ITO), 인듐아연산화물(IZO)과 같은 금속 산화물; ZnO:Al 또는 SnO2:Sb와 같은 금속과 산화물의 조합; 폴리(3-메틸티오펜), 폴리[3,4-(에틸렌-1,2-디옥시)티오펜](PEDT), 폴리피롤 및 폴리아닐린과 같은 전도성 고분자 등이 있으나, 이들에만 한정되는 것은 아니다.As the anode material, a material having a large work function is preferably used so that hole injection can be smoothly conducted into the organic material layer. Specific examples of the cathode material that can be used in the present invention include metals such as vanadium, chromium, copper, zinc, and gold, or alloys thereof; Metal oxides such as zinc oxide, indium oxide, indium tin oxide (ITO), and indium zinc oxide (IZO); ZnO: Al or SnO2: a combination of a metal and an oxide such as Sb; Conductive polymers such as poly (3-methylthiophene), poly [3,4- (ethylene-1,2-dioxy) thiophene] (PEDT), polypyrrole and polyaniline.
상기 음극 물질로는 통상 유기물층으로 전자 주입이 용이하도록 일함수가 작은 물질인 것이 바람직하다. 음극 물질의 구체적인 예로는 마그네슘, 칼슘, 나트륨, 칼륨, 타이타늄, 인듐, 이트륨, 리튬, 가돌리늄, 알루미늄, 은, 주석 및 납과 같은 금속 또는 이들의 합금; LiF/Al 또는 LiO2/Al과 같은 다층 구조 물질 등이 있으나, 이들에만 한정되는 것은 아니다.The negative electrode material is preferably a material having a small work function to facilitate electron injection into the organic material layer. Specific examples of the negative electrode material include metals such as magnesium, calcium, sodium, potassium, titanium, indium, yttrium, lithium, gadolinium, aluminum, silver, tin and lead or alloys thereof; Layer structure materials such as LiF / Al or LiO2 / Al, but are not limited thereto.
정공 주입 물질로는 낮은 전압에서 양극으로부터 정공을 잘 주입 받을 수 있는 물질로서, 정공 주입 물질의 HOMO(highest occupied molecular orbital)가 양극 물질의 일함수와 주변 유기물층의 HOMO 사이인 것이 바람직하다. 정공 주입 물질의 구체적인 예로는 금속 포피린(porphyrine), 올리고티오펜, 아릴아민 계열의 유기물, 헥사니트릴 헥사아자트리페닐렌, 퀴나크리돈(quinacridone) 계열의 유기물, 페릴렌(perylene) 계열의 유기물, 안트라퀴논 및 폴리아닐린과 폴리티오펜 계열의 전도성 고분자 등이 있으나, 이들에만 한정되는 것은 아니다.As the hole injecting material, it is preferable that the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) of the hole injecting material be between the work function of the anode material and the HOMO of the surrounding organic layer. Specific examples of the hole injecting material include metal porphyrine, oligothiophene, arylamine-based organic materials, hexanitrile hexaazatriphenylene, quinacridone-based organic materials, perylene-based organic materials, Anthraquinone, polyaniline and a polythiophene-based conductive polymer, but are not limited thereto.
정공 수송 물질로는 양극이나 정공 주입층으로부터 정공을 수송 받아 발광층으로 옮겨줄 수 있는 물질로 정공에 대한 이동성이 큰 물질이 적합하다. 구체적인 예로는 아릴아민 계열의 유기물, 전도성 고분자, 및 공액 부분과 비공액 부분이 함께 있는 블록 공중합체 등이 있으나, 이들에만 한정되는 것은 아니다.As the hole transporting material, a material capable of transporting holes from the anode or the hole injection layer to the light emitting layer and having high mobility to holes is suitable. Specific examples include arylamine-based organic materials, conductive polymers, and block copolymers having a conjugated portion and a non-conjugated portion together, but are not limited thereto.
발광 물질로는 정공 수송층과 전자 수송층으로부터 정공과 전자를 각각 수송받아 결합시킴으로써 가시광선 영역의 빛을 낼 수 있는 물질로서, 형광이나 인광에 대한 양자효율이 좋은 물질이 바람직하다. 구체적인 예로는 8-히드록시-퀴놀린 알루미늄 착물(Alq3); 카르바졸 계열 화합물; 이량체화 스티릴(dimerized styryl) 화합물; BAlq; 10-히드록시벤조 퀴놀린-금속 화합물; 벤족사졸, 벤즈티아졸 및 벤즈이미다졸 계열의 화합물; 폴리(p-페닐렌비닐렌)(PPV) 계열의 고분자; 스피로(spiro) 화합물; 폴리플루오렌, 루브렌 등이 있으나, 이들에만 한정되는 것은아니다.The light emitting material is preferably a material capable of emitting light in the visible light region by transporting and combining holes and electrons from the hole transporting layer and the electron transporting layer, respectively, and having a high quantum efficiency for fluorescence or phosphorescence. Specific examples include 8-hydroxy-quinoline aluminum complex (Alq3 ); Carbazole-based compounds; Dimerized styryl compounds; BAlq; 10-hydroxybenzoquinoline-metal compounds; Compounds of the benzoxazole, benzothiazole and benzimidazole series; Polymers of poly (p-phenylenevinylene) (PPV) series; Spiro compounds; Polyfluorene, rubrene, and the like, but are not limited thereto.
전자 수송 물질로는 음극으로부터 전자를 잘 주입 받아 발광층으로 옮겨줄 수 있는 물질로서, 전자에 대한 이동성이 큰 물질이 적합하다. 구체적인 예로는 8-히드록시퀴놀린의 Al 착물; Alq3를 포함한 착물; 유기 라디칼 화합물; 히드록시플라본-금속 착물 등이 있으나, 이들에만 한정되는 것은 아니다.As the electron transporting material, a material capable of transferring electrons from the cathode well into the light emitting layer, which is highly mobile, is suitable. Specific examples include an Al complex of 8-hydroxyquinoline; Complexes containing Alq3 ; Organic radical compounds; Hydroxyflavone-metal complexes, and the like, but are not limited thereto.
본 발명에 따른 유기 발광 소자는 사용되는 재료에 따라 전면 발광형, 후면 발광형 또는 양면 발광형일 수 있다.The organic light emitting device according to the present invention may be a front emission type, a back emission type, or a both-sided emission type, depending on the material used.
상기 화학식 1의 화합물의 제조방법 및 이들을 이용한 유기 발광 소자의 제조는 이하의 실시예에서 구체적으로 설명한다. 그러나, 하기 실시예는 본 발명을 예시하기 위한 것이며, 본 발명의 범위가 이들에 의하여 한정되는 것은 아니다.The method for preparing the compound of Formula 1 and the preparation of the organic light emitting device using the same will be described in detail in the following Examples. However, the following examples are intended to illustrate the present invention and the scope of the present invention is not limited thereto.
<<실시예Example>>
<<합성예Synthetic example 1> 구조식 1로 표시되는 화합물의 제조 1> Preparation of the compound represented by the structural formula 1
N-페닐-5-브로모벤조카바졸(10g, 26.9mmol)과 2-디벤조티에닐보론산(6.7g, 29.6mmol)을 테트라하이드로퓨란(150ml)에 녹인 후 탄산칼륨(K2CO3, potassium carbonate, 11.1g, 80.7mmol)을 물과 함께 반응 용액에 첨가한 뒤 한 시간 정도 질소 상태에서 가열 교반을 시켰다. 한 시간 가열 교반 후 테트라키스(트리페닐포스핀)팔라듐(0.62g, 0.54mmol)을 첨가한 뒤 4시간 동안 교반하면서 가열하였다. 반응 종료 후 상온으로 온도를 낮추고 테트라하이드로퓨란을 감압증류하여 제거한 후 클로로포름에 녹이고 무수 황산 마그네슘으로 건조하였다. 상기 용액을 감압 증류시키고 테트라하이드로퓨란과 에탄올로 재결정하여 구조식 1(8g, 수율 63%)을 얻었다.After the N- phenyl-5-bromo-benzo-carbazole (10g, 26.9mmol) and di-2-benzothienyl-boronic acid (6.7g, 29.6mmol) dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (150ml) of potassium carbonate (K2 CO3 , potassium carbonate, 11.1 g, 80.7 mmol) was added to the reaction solution together with water, followed by heating and stirring in a nitrogen state for about one hour. After stirring for one hour, tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0.62 g, 0.54 mmol) was added and the mixture was heated with stirring for 4 hours. After completion of the reaction, the temperature was lowered to room temperature, and tetrahydrofuran was removed by distillation under reduced pressure, followed by dissolving in chloroform and drying with anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solution was distilled under reduced pressure, and recrystallized from tetrahydrofuran and ethanol to obtain structural formula 1 (8 g, yield 63%).
MS: [M+H]+ = 476MS: [M + H] < + > = 476
<<합성예Synthetic example 2> 구조식 7로 표시되는 화합물의 제조 2> Preparation of the compound represented by the structural formula 7
상기 합성예 1의 구조식 1의 제조에 있어서, 2-디벤조티에닐보론산 대신 4-디벤조티에닐보론산(6.7g, 29.6mmol)을 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일한 방법으로 제조하여 구조식 7(8.6g, 67%)을 얻었다.Except that 4-dibenzothienylboronic acid (6.7 g, 29.6 mmol) was used instead of 2-dibenzothienylboronic acid in the preparation of the structural formula 1 of Synthesis Example 1, 8.6 g, 67%).
MS: [M+H]+ = 476MS: [M + H] < + > = 476
<<합성예Synthetic example 3> 구조식 2로 표시되는 화합물의 제조 3> Preparation of the compound represented by the
N-디페닐-5-브로모벤조카바졸(10g, 22.3mmol)과 2-디벤조티에닐보론산 (5.6g, 24.5mmol)을 테트라하이드로퓨란(150ml)에 녹인 후 탄산칼륨(K2CO3, potassium carbonate, 9.2g, 66.9mmol)을 물과 함께 반응 용액에 첨가한 뒤 한 시간 정도 질소 상태에서 가열 교반을 시켰다. 한 시간 가열 교반 후 테트라키스(트리페닐포스핀)팔라듐(0.51g, 0.45mmol)을 첨가한 뒤 4시간 동안 교반하면서 가열하였다. 반응 종료 후 상온으로 온도를 낮추고 테트라하이드로퓨란을 감압증류하여 제거한 후 클로로포름에 녹이고 무수 황산 마그네슘으로 건조하였다. 상기 용액을 감압 증류시키고 테트라하이드로퓨란과 에탄올로 재결정하여 구조식 2(8g, 수율 65%)을 얻었다.(10 g, 22.3 mmol) and 2-dibenzothienylboronic acid (5.6 g, 24.5 mmol) were dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (150 ml), potassium carbonate (K2 CO3 , potassium carbonate, 9.2 g, 66.9 mmol) was added to the reaction solution together with water, followed by heating and stirring in a nitrogen state for about one hour. After stirring for one hour, tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0.51 g, 0.45 mmol) was added and the mixture was heated with stirring for 4 hours. After completion of the reaction, the temperature was lowered to room temperature, and tetrahydrofuran was removed by distillation under reduced pressure, followed by dissolving in chloroform and drying with anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solution was distilled off under reduced pressure, and recrystallized from tetrahydrofuran and ethanol to obtain structural formula 2 (8 g, yield 65%).
MS: [M+H]+ = 552MS: [M + H] < + > = 552
<<합성예Synthetic example 4> 구조식 8로 표시되는 화합물의 제조 4> Preparation of the compound represented by the
상기 합성예 3의 구조식 2의 제조에 있어서, 2-디벤조티에닐보론산 대신 4-디벤조티에닐보론산(5.6g, 24.5mmol)을 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일한 방법으로 제조하여 구조식 8(7.8g, 63%)을 얻었다.Except that 4-dibenzothienylboronic acid (5.6 g, 24.5 mmol) was used instead of 2-dibenzothienylboronic acid in the preparation of the
MS: [M+H]+ = 552MS: [M + H] < + > = 552
<<합성예Synthetic example 5> 구조식 11로 표시되는 화합물의 제조 5> Preparation of the compound represented by the structural formula 11
N-페닐-8-브로모벤조카바졸(10g, 26.9mmol)과 2-디벤조티에닐보론산(6.7g, 29.6mmol)을 테트라하이드로퓨란(150ml)에 녹인 후 탄산칼륨(K2CO3, potassium carbonate, 11.1g, 80.7mmol)을 물과 함께 반응 용액에 첨가한 뒤 한 시간 정도 질소 상태에서 가열 교반을 시켰다. 한 시간 가열 교반 후 테트라키스(트리페닐포스핀)팔라듐(0.62g, 0.54mmol)을 첨가한 뒤 4시간 동안 교반하면서 가열하였다. 반응 종료 후 상온으로 온도를 낮추고 테트라하이드로퓨란을 감압증류하여 제거한 후 클로로포름에 녹이고 무수 황산 마그네슘으로 건조하였다. 상기 용액을 감압 증류시키고 테트라하이드로퓨란과 에탄올로 재결정하여 구조식 11(6.4g, 수율 50%)을 얻었다.After dissolving N-phenyl-8-bromobenzocarbazole (10 g, 26.9 mmol) and 2-dibenzothienyl boronic acid (6.7 g, 29.6 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (150 ml), potassium carbonate (K2 CO3 , potassium carbonate, 11.1 g, 80.7 mmol) was added to the reaction solution together with water, followed by heating and stirring in a nitrogen state for about one hour. After stirring for one hour, tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0.62 g, 0.54 mmol) was added and the mixture was heated with stirring for 4 hours. After completion of the reaction, the temperature was lowered to room temperature, and tetrahydrofuran was removed by distillation under reduced pressure, followed by dissolving in chloroform and drying with anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solution was distilled under reduced pressure, and recrystallized from tetrahydrofuran and ethanol to obtain the structural formula 11 (6.4 g, yield 50%).
MS: [M+H]+ = 476MS: [M + H] < + > = 476
<<합성예Synthetic example 6> 구조식 15로 표시되는 화합물의 제조 6> Preparation of the compound represented by the structural formula 15
상기 합성예 5의 구조식 11의 제조에 있어서, 2-디벤조티에닐보론산 대신 4-디벤조티에닐보론산(6.7g, 29.6mmol)을 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일한 방법으로 제조하여 구조식 15(6.8g, 53%)을 얻었다.Except that 4-dibenzothienylboronic acid (6.7 g, 29.6 mmol) was used instead of 2-dibenzothienylboronic acid in the preparation of the structural formula 11 of the above Synthesis Example 5 to obtain the compound represented by Structural Formula 15 6.8 g, 53%).
MS: [M+H]+ = 476MS: [M + H] < + > = 476
<<합성예Synthetic example 7> 구조식 12로 표시되는 화합물의 제조 7> Preparation of the compound represented by the structural formula 12
N-디페닐-8-브로모벤조카바졸(10g, 22.3mmol)과 2-디벤조티에닐보론산 (5.6g, 24.5mmol)을 테트라하이드로퓨란(150ml)에 녹인 후 탄산칼륨(K2CO3, potassium carbonate, 9.2g, 66.9mmol)을 물과 함께 반응 용액에 첨가한 뒤 한 시간 정도 질소 상태에서 가열 교반을 시켰다. 한 시간 가열 교반 후 테트라키스(트리페닐포스핀)팔라듐(0.51g, 0.45mmol)을 첨가한 뒤 4시간 동안 교반하면서 가열하였다. 반응 종료 후 상온으로 온도를 낮추고 테트라하이드로퓨란을 감압증류하여 제거한 후 클로로포름에 녹이고 무수 황산 마그네슘으로 건조하였다. 상기 용액을 감압 증류시키고 테트라하이드로퓨란과 에탄올로 재결정하여 구조식 12(6.8g, 수율 55%)을 얻었다.(5.6 g, 24.5 mmol) and 2-dibenzothienylboronic acid (10 g, 22.3 mmol) were dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (150 ml), and potassium carbonate (K2 CO3 , potassium carbonate, 9.2 g, 66.9 mmol) was added to the reaction solution together with water, followed by heating and stirring in a nitrogen state for about one hour. After stirring for one hour, tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0.51 g, 0.45 mmol) was added and the mixture was heated with stirring for 4 hours. After completion of the reaction, the temperature was lowered to room temperature, and tetrahydrofuran was removed by distillation under reduced pressure, followed by dissolving in chloroform and drying with anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solution was distilled under reduced pressure, and recrystallized from tetrahydrofuran and ethanol to obtain structural formula 12 (6.8 g, yield 55%).
MS: [M+H]+ = 552MS: [M + H] < + > = 552
<<합성예Synthetic example 8> 구조식 16으로 표시되는 화합물의 제조 8> Preparation of the compound represented by Structural Formula 16
상기 합성예 7의 구조식 12의 제조에 있어서, 2-디벤조티에닐보론산 대신 4-디벤조티에닐보론산 (5.6g, 24.5mmol)을 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일한 방법으로 제조하여 구조식 16(7.2g, 59%)을 얻었다.Except that 4-dibenzothienylboronic acid (5.6 g, 24.5 mmol) was used instead of 2-dibenzothienylboronic acid in the preparation of the structural formula 12 of the above Synthesis Example 7 to obtain the compound represented by Structural Formula 16 7.2 g, 59%).
MS: [M+H]+ = 552MS: [M + H] < + > = 552
<<실시예Example 1-1> 1-1>
ITO(인듐 주석 산화물)가 1,000Å 두께로 박막 코팅된 유리 기판(corning 7059 glass)을, 분산제를 녹인 증류수에 넣고 초음파로 세척하였다. 세제는 Fischer Co.의 제품을 사용하였으며, 증류수는 Millipore Co. 제품의 필터(Filter)로 2차 걸러진 증류수를 사용하였다. ITO를 30분간 세척한 후, 증류수로 2회 반복하여 초음파 세척을 10분간 진행하였다. 증류수 세척이 끝난 후 이소프로필알콜, 아세톤, 메탄올 용제 순서로 초음파 세척을 하고 건조시켰다.A glass substrate (corning 7059 glass) coated with ITO (indium tin oxide) at a thickness of 1,000 Å was immersed in distilled water containing a dispersing agent and washed with ultrasonic waves. The detergent was a product of Fischer Co. The distilled water was supplied by Millipore Co. Distilled water, which was secondly filtered with a filter of the product, was used. After the ITO was washed for 30 minutes, ultrasonic washing was repeated 10 times with distilled water twice. After the distilled water was washed, ultrasonic washing was performed in the order of isopropyl alcohol, acetone, and methanol solvent, followed by drying.
이렇게 준비된 ITO 투명 전극 위에 헥사니트릴 헥사아자트리페닐렌(hexanitrile hexaazatriphenylene)를 500Å의 두께로 열 진공 증착하여 정공 주입층을 형성하였다. 그 위에 정공을 수송하는 물질인 위 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1(400Å)을 진공증착한 후 발광층으로 호스트 H1과 도판트 D1 화합물을 300Å의 두께로 진공 증착하였다. 그 다음에 E1 화합물(300Å)을 전자 주입 및 수송층으로 순차적으로 열 진공 증착하였다. 상기 전자 수송층 위에 순차적으로 12Å 두께의 리튬 플루오라이드(LiF)와 2,000Å 두께의 알루미늄을 증착하여 음극을 형성하여, 유기 발광 소자를 제조하였다.Hexanitrile hexaazatriphenylene was thermally vacuum deposited on the prepared ITO transparent electrode to a thickness of 500 Å to form a hole injection layer. (400 Å) prepared in the above Synthesis Example 1, which is a material for transporting holes, was vacuum deposited, and a host H1 and a dopant D1 compound were vacuum deposited as a light emitting layer to a thickness of 300 Å. Then, an E1 compound (300 ANGSTROM) was sequentially vacuum-deposited by electron injection and transport layer. Lithium fluoride (LiF) having a thickness of 12 Å and aluminum having a thickness of 2,000 Å were sequentially deposited on the electron transporting layer to form a cathode, thereby preparing an organic light emitting device.
상기의 과정에서 유기물의 증착속도는 1 Å/sec를 유지하였고, 리튬플루라이드는 0.2 Å/sec, 알루미늄은 3 ~ 7 Å/sec의 증착속도를 유지하였다.In the above process, the deposition rate of the organic material was maintained at 1 Å / sec, the deposition rate of lithium fluoride was 0.2 Å / sec, and the deposition rate of aluminum was 3 to 7 Å / sec.
<<실시예Example 1-2> 1-2>
상기 실시예 1-1에서 정공 수송층으로 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 7을 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was carried out except that the hole transport layer in Example 1-1 was replaced by the structure 7 instead of the structure 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1. [
<<실시예Example 1-3> 1-3>
상기 실시예 1-1에서 정공 수송층으로 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 2를 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was carried out except that the hole transport layer in Example 1-1 was replaced by the
<<실시예Example 1-4> 1-4>
상기 실시예 1-1에서 정공 수송층으로 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 8을 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.In the same manner as in Example 1-1, except that the hole transport layer was replaced with the hole transport layer in place of the structure 1 of Synthesis Example 1.
<<실시예Example 1-5> 1-5>
상기 실시예 1-1에서 정공 수송층으로 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 11을 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.In the same manner as in Example 1-1, except that the hole transport layer was replaced with the hole transport layer in place of the hole transport layer in Synthesis Example 1,
<<실시예Example 1-6> 1-6>
상기 실시예 1-1에서 정공 수송층으로 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 15를 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was carried out except that the hole transport layer in Example 1-1 was replaced with the hole transport layer in place of the structure 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1.
<<실시예Example 1-7> 1-7>
상기 실시예 1-1에서 정공 수송층으로 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 12를 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was carried out as in Example 1-1 except that the hole transport layer was replaced by the structure 12 instead of the structure 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1.
<<실시예Example 1-8> 1-8>
상기 실시예 1-1에서 정공 수송층으로 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 16을 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was carried out except that the hole transport layer in Example 1-1 was replaced with the hole transport layer in place of the structure 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1.
<<비교예Comparative Example 1> 1>
상기 실시예 1-1에서 정공 수송층으로 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 HT1를 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was conducted except that HT1 was used instead of the structural formula 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1 as the hole transport layer in Example 1-1.
<<비교예Comparative Example 2> 2>
상기 실시예 1-1에서 정공 수송층으로 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 NPB를 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was conducted except that NPB was used instead of the structural formula 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1 as the hole transport layer in Example 1-1.
상기 실시예 1-1 ~ 1-8, 및 비교예 1 ~ 2와 같이 각각의 화합물을 정공 수송층 물질로 사용하여 제조한 유기 발광 소자를 실험한 결과를 표 1에 나타내었다.Table 1 shows the results of the organic light emitting device manufactured by using each compound as a hole transporting layer material as in Examples 1-1 to 1-8 and Comparative Examples 1 and 2.
[표 1][Table 1]
본 발명에 따른 화학식의 화합물 유도체는 유기 발광 소자를 비롯한 유기 전자 소자에서 정공 주입, 정공 수송 역할을 할 수 있으며, 본 발명에 따른 소자는 효율, 구동전압, 안정성 면에서 우수한 특성을 나타낸다.The compound represented by the chemical formula according to the present invention can perform hole injection and hole transport in an organic electronic device including an organic light emitting device, and the device according to the present invention exhibits excellent characteristics in terms of efficiency, driving voltage, and stability.
<<실시예Example 2-1> 2-1>
ITO(인듐 주석 산화물)가 1,000Å 두께로 박막 코팅된 유리 기판(corning 7059 glass)을, 분산제를 녹인 증류수에 넣고 초음파로 세척하였다. 세제는 Fischer Co.의 제품을 사용하였으며, 증류수는 Millipore Co. 제품의 필터(Filter)로 2차 걸러진 증류수를 사용하였다. ITO를 30분간 세척한 후, 증류수로 2회 반복하여 초음파 세척을 10분간 진행하였다. 증류수 세척이 끝난 후 이소프로필알콜, 아세톤, 메탄올 용제 순서로 초음파 세척을 하고 건조시켰다.A glass substrate (corning 7059 glass) coated with ITO (indium tin oxide) at a thickness of 1,000 Å was immersed in distilled water containing a dispersing agent and washed with ultrasonic waves. The detergent was a product of Fischer Co. The distilled water was supplied by Millipore Co. Distilled water, which was secondly filtered with a filter of the product, was used. After the ITO was washed for 30 minutes, ultrasonic washing was repeated 10 times with distilled water twice. After the distilled water was washed, ultrasonic washing was performed in the order of isopropyl alcohol, acetone, and methanol solvent, followed by drying.
이렇게 준비된 ITO 투명 전극 위에 헥사니트릴 헥사아자트리페닐렌(hexanitrile hexaazatriphenylene)를 500Å의 두께로 열 진공 증착하여 정공 주입층을 형성하였다. 그 위에 정공을 수송하는 물질인 HT1(200Å)을 진공증착한 후 이 막 상에 막두께 40nm의 인광호스트로서 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1, 및 인광 발광성의 도펀트로서 Iridium(III) tris(2-phenylpyridine) (Ir(ppy)3)를 각각 넣은 후, 두 물질을 다른 속도로 증발시켜 10% 중량으로 도핑되도록 발광층을 증착하였다.Hexanitrile hexaazatriphenylene was thermally vacuum deposited on the prepared ITO transparent electrode to a thickness of 500 Å to form a hole injection layer. HT1 (200 ANGSTROM), which is a material for transporting holes, was vacuum-deposited thereon. On this film, a phosphorescent host having a film thickness of 40 nm was formed by using the structural formula 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1 and the phosphorescent dopant Iridium (III) -phenylpyridine (Ir (ppy)3 ), and the two materials were evaporated at different rates to deposit a light emitting layer doped to 10% by weight.
그 다음에 E1 화합물(300Å)을 전자 주입 및 수송층으로 순차적으로 열 진공 증착하였다. 상기 전자 수송층 위에 순차적으로 12Å 두께의 리튬 플루오라이드(LiF)와 2,000Å 두께의 알루미늄을 증착하여 음극을 형성하여, 유기 발광 소자를 제조하였다.Then, an E1 compound (300 ANGSTROM) was sequentially vacuum-deposited by electron injection and transport layer. Lithium fluoride (LiF) having a thickness of 12 Å and aluminum having a thickness of 2,000 Å were sequentially deposited on the electron transporting layer to form a cathode, thereby preparing an organic light emitting device.
상기의 과정에서 유기물의 증착속도는 1 Å/sec를 유지하였고, 리튬플루라이드는 0.2 Å/sec, 알루미늄은 3 ~ 7 Å/sec의 증착속도를 유지하였다.In the above process, the deposition rate of the organic material was maintained at 1 Å / sec, the deposition rate of lithium fluoride was 0.2 Å / sec, and the deposition rate of aluminum was 3 to 7 Å / sec.
<<실시예Example 2-2> 2-2>
상기 실시예 2-1에서 인광호스트 재료로서 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 7을 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.Except that the phosphorescent host material in Example 2-1 was replaced by the structural formula 7 instead of the structural formula 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1.
<<실시예Example 2-3> 2-3>
상기 실시예 2-1에서 인광호스트 재료로서 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 2를 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was carried out except that the phosphorescent host material in Example 2-1 was replaced by the
<<실시예Example 2-4> 2-4>
상기 실시예 2-1에서 인광호스트 재료로서 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 8을 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was carried out except that the phosphorescent host material in Example 2-1 was replaced by the
<<실시예Example 2-5> 2-5>
상기 실시예 2-1에서 인광호스트 재료로서 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 11을 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was carried out as in Example 2-1 except that the phosphorescent host material was replaced by the structural formula 11 instead of the structural formula 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1.
<<실시예Example 2-6> 2-6>
상기 실시예 2-1에서 인광호스트 재료로서 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 15를 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was carried out except that the phosphorescent host material in Example 2-1 was replaced by the structural formula 15 instead of the structural formula 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1.
<<실시예Example 2-7> 2-7>
상기 실시예 2-1에서 인광호스트 재료로서 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 구조식 12를 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was carried out except that the phosphorescent host material in Example 2-1 was replaced by the structural formula 12 instead of the structural formula 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1.
<<실시예Example 2-8> 2-8>
상기 실시예 2-1에서 인광호스트 재료로서 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1대신 구조식 16을 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was carried out except that the phosphorescent host material in Example 2-1 was replaced by the structural formula 16 instead of the structural formula 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1.
<<비교예Comparative Example 3> 3>
상기 실시예 2-1에서 인광호스트 재료로서 합성예 1에서 제조한 구조식 1 대신 CBP를 사용한 것을 제외하고는 동일하게 실험하였다.The same experiment was conducted except that CBP was used instead of the structural formula 1 prepared in Synthesis Example 1 as the phosphorescent host material in Example 2-1.
상기 실시예 2-1 ~ 2-8 및 비교예 3과 같이 각각의 화합물을 인광호스트 물질로 사용하여 제조한 유기 발광 소자를 실험한 결과를 표 2에 나타내었다.Table 2 shows the results of experiments of organic light emitting devices manufactured using the respective compounds as phosphorescent host materials as in Examples 2-1 to 2-8 and Comparative Example 3. [
[표 2][Table 2]
본 발명에 따른 화학식의 화합물 유도체는 유기 발광 소자를 비롯한 유기 전자 소자에서 인광 발광층의 호스트 역할을 할 수 있으며, 본 발명에 따른 소자는 구동전압 및 효율면에서 우수한 특성을 나타낸다.The compound represented by the formula according to the present invention can serve as a host of a phosphorescent light emitting layer in an organic electronic device including an organic light emitting device, and the device according to the present invention exhibits excellent characteristics in driving voltage and efficiency.
Claims (15)
Translated fromKorean[화학식 1]
A-L-B
상기 화학식 1에 있어서,
L은 직접결합; 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 6 내지 20의 아릴렌기; 또는 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 2 내지 20의 헤테로아릴렌기이고,
A는 하기 화학식 2로 표시되고,
[화학식 2]
상기 화학식 2에 있어서,
R9는 아릴기이고,
R1 내지 R8은 각각 독립적으로 수소; 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 6 내지 60의 아릴기; 치환 또는 비치환된 퓨란기; 치환 또는 비치환된 피롤기; 치환 또는 비치환된 티오펜기; 치환 또는 비치환된 이미다졸기; 치환 또는 비치환된 옥사졸기; 치환 또는 비치환된 티아졸기; 치환 또는 비치환된 트리아졸기; 치환 또는 비치환된 피리딜기; 치환 또는 비치환된 피리다질기; 치환 또는 비치환된 퀴놀리닐기; 치환 또는 비치환된 아이소퀴놀리닐기; 치환 또는 비치환된 아크리딜기; 치환 또는 비치환된 하기 구조식의 화합물;
또는 이웃한 치환기와 지방족, 헤테로 지방족, 방향족 또는 헤테로 방향족 고리를 형성할 수 있고,
R1 내지 R8 중 적어도 어느 하나는 화학식 1의 L로 대체되며,
B는 하기 화학식 3으로 표시되고,
[화학식 3]
상기 화학식 3에 있어서,
X는 O 또는 S이고,
E1 내지 E8은 각각 독립적으로 수소; 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 6 내지 60의 아릴기; 또는 치환 또는 비치환된 플루오레닐기, 치환 또는 비치환된 아릴기, 또는 이종원소로 O, N, S 또는 P를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 헤테로아릴기로 치환 또는 비치환된 탄소수 2 내지 50의 헤테로 아릴기이고,
E1 내지 E8 중 적어도 어느 하나는 화학식 1의 L로 대체된다.A compound represented by the following formula (1):
[Chemical Formula 1]
ALB
In Formula 1,
L is a direct bond; A substituted or unsubstituted aryl group or a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 0, N, S, or P as a hetero atom, an arylene group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, which is substituted or unsubstituted; Or a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms, which is substituted or unsubstituted with a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having O, N, S, or P as a hetero atom Rengi,
A is represented by the following formula (2)
(2)
In Formula 2,
R9 is an aryl group,
R 1 to R 8 are each independently hydrogen; A substituted or unsubstituted aryl group or a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group having 6 to 60 carbon atoms, which is substituted or unsubstituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having O, N, S or P as a hetero atom; A substituted or unsubstituted furan group; A substituted or unsubstituted pyrrol group; A substituted or unsubstituted thiophene group; A substituted or unsubstituted imidazole group; A substituted or unsubstituted oxazole group; A substituted or unsubstituted thiazole group; A substituted or unsubstituted triazole group; A substituted or unsubstituted pyridyl group; A substituted or unsubstituted pyridyl group; A substituted or unsubstituted quinolinyl group; A substituted or unsubstituted isoquinolinyl group; A substituted or unsubstituted acridyl group; A substituted or unsubstituted compound of the following structural formula;
Or adjacent substituents to form an aliphatic, heteroaliphatic, aromatic or heteroaromatic ring,
At least one of R 1 to R 8 is substituted with L of formula (1)
B is represented by the following formula (3)
(3)
In Formula 3,
X is O or S,
E1 to E8 each independently represent hydrogen; A substituted or unsubstituted aryl group or a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group having 6 to 60 carbon atoms, which is substituted or unsubstituted with a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having O, N, S or P as a hetero atom; Or a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 2 to 50 carbon atoms substituted or unsubstituted with a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, or a heteroaryl group having O, N, S, or P as a hetero atom Lt; / RTI &
At least one of E1 to E8 is substituted with L in formula (1).
[화학식 4]
[화학식 5]
[화학식 6]
상기 화학식 4 내지 6에 있어서, R1 내지 R9는 상기 화학식 2에서 정의한 바와 같다.2. The compound according to claim 1, wherein the formula 2 is represented by any one of the following formulas 4 to 6:
[Chemical Formula 4]
[Chemical Formula 5]
[Chemical Formula 6]
In formulas (4) to (6), R 1 to R 9 are the same as defined in Formula (2).
[화학식 7]
[화학식 8]
[화학식 9]
[화학식 10]
상기 화학식 7 내지 10에 있어서, L, X, R1 내지 R8, 및 E1 내지 E8은 상기 화학식 1 내지 3에서 정의한 바와 같다.A compound represented by any one of the following formulas (7) to (10):
(7)
[Chemical Formula 8]
[Chemical Formula 9]
[Chemical formula 10]
In Formulas 7 to 10, L, X, R 1 to R 8, and E 1 to E 8 are as defined in Formulas 1 to 3.
[화학식 11]
[화학식 12]
[화학식 13]
[화학식 14]
상기 화학식 11 내지 14에 있어서, L, X, R1 내지 R9, 및 E1 내지 E8은 상기 화학식 1 내지 3에서 정의한 바와 같다.The compound according to claim 1, wherein the compound represented by formula (1) is represented by any one of the following formulas (11) to (14):
(11)
[Chemical Formula 12]
[Chemical Formula 13]
[Chemical Formula 14]
In Formulas 11 to 14, L, X, R 1 to R 9, and E 1 to E 8 are as defined in Formulas 1 to 3 above.
[표 A-1]
The compound according to claim 1, wherein R9 in the formula (2) is selected from the substituents described in the following Table A-1:
[Table A-1]
The compound according to claim 1, wherein the compound represented by Formula 1 is represented by any one of the following Formulas 1 to 48:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020120037956AKR101565200B1 (en) | 2012-04-12 | 2012-04-12 | New compound and organic light emitting device using the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020120037956AKR101565200B1 (en) | 2012-04-12 | 2012-04-12 | New compound and organic light emitting device using the same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20130115564A KR20130115564A (en) | 2013-10-22 |
| KR101565200B1true KR101565200B1 (en) | 2015-11-02 |
Family
ID=49635000
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020120037956AActiveKR101565200B1 (en) | 2012-04-12 | 2012-04-12 | New compound and organic light emitting device using the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101565200B1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10096777B2 (en) | 2016-12-22 | 2018-10-09 | Samsung Sdi Co., Ltd. | Composition for organic optoelectric device and organic optoelectric device and display device |
Families Citing this family (76)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101595697B1 (en)* | 2014-10-14 | 2016-02-26 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Multicyclic compound including nitrogen and organic light emitting device using the same |
| US9929361B2 (en) | 2015-02-16 | 2018-03-27 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11056657B2 (en) | 2015-02-27 | 2021-07-06 | University Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US9859510B2 (en) | 2015-05-15 | 2018-01-02 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US10418568B2 (en) | 2015-06-01 | 2019-09-17 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11127905B2 (en) | 2015-07-29 | 2021-09-21 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US10672996B2 (en) | 2015-09-03 | 2020-06-02 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20170125704A1 (en)* | 2015-10-30 | 2017-05-04 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Organic Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device |
| US20170229663A1 (en) | 2016-02-09 | 2017-08-10 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US10236456B2 (en) | 2016-04-11 | 2019-03-19 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11482683B2 (en) | 2016-06-20 | 2022-10-25 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US10672997B2 (en) | 2016-06-20 | 2020-06-02 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US10862054B2 (en) | 2016-06-20 | 2020-12-08 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US10608186B2 (en) | 2016-09-14 | 2020-03-31 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US10680187B2 (en) | 2016-09-23 | 2020-06-09 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11196010B2 (en) | 2016-10-03 | 2021-12-07 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11011709B2 (en) | 2016-10-07 | 2021-05-18 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US12317745B2 (en) | 2016-11-09 | 2025-05-27 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US10680188B2 (en) | 2016-11-11 | 2020-06-09 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11780865B2 (en) | 2017-01-09 | 2023-10-10 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US10844085B2 (en) | 2017-03-29 | 2020-11-24 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US10944060B2 (en) | 2017-05-11 | 2021-03-09 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US12098157B2 (en) | 2017-06-23 | 2024-09-24 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11228010B2 (en) | 2017-07-26 | 2022-01-18 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11744142B2 (en) | 2017-08-10 | 2023-08-29 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US12180230B2 (en) | 2017-11-28 | 2024-12-31 | University Of Southern California | Carbene compounds and organic electroluminescent devices |
| EP3492480B1 (en) | 2017-11-29 | 2021-10-20 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11937503B2 (en) | 2017-11-30 | 2024-03-19 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11542289B2 (en) | 2018-01-26 | 2023-01-03 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11165028B2 (en) | 2018-03-12 | 2021-11-02 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20200075870A1 (en) | 2018-08-22 | 2020-03-05 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11737349B2 (en) | 2018-12-12 | 2023-08-22 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US11780829B2 (en) | 2019-01-30 | 2023-10-10 | The University Of Southern California | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20200251664A1 (en) | 2019-02-01 | 2020-08-06 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US12082428B2 (en) | 2019-03-12 | 2024-09-03 | Universal Display Corporation | OLED with triplet emitter and excited state lifetime less than 200 ns |
| JP2020158491A (en) | 2019-03-26 | 2020-10-01 | ユニバーサル ディスプレイ コーポレイション | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US12281128B2 (en) | 2019-07-30 | 2025-04-22 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US12139501B2 (en) | 2019-08-16 | 2024-11-12 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20210135130A1 (en) | 2019-11-04 | 2021-05-06 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| JP7488091B2 (en) | 2019-11-14 | 2024-05-21 | ユニバーサル ディスプレイ コーポレイション | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20210217969A1 (en) | 2020-01-06 | 2021-07-15 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US12426495B2 (en) | 2020-01-28 | 2025-09-23 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| EP3937268B1 (en) | 2020-07-10 | 2025-05-07 | Universal Display Corporation | Plasmonic oleds and vertical dipole emitters |
| US12187748B2 (en) | 2020-11-02 | 2025-01-07 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20220158096A1 (en) | 2020-11-16 | 2022-05-19 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20220165967A1 (en) | 2020-11-24 | 2022-05-26 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US12325717B2 (en) | 2020-11-24 | 2025-06-10 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20220271241A1 (en) | 2021-02-03 | 2022-08-25 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| EP4059915A3 (en) | 2021-02-26 | 2022-12-28 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| EP4060758A3 (en) | 2021-02-26 | 2023-03-29 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20220298192A1 (en) | 2021-03-05 | 2022-09-22 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US12428599B2 (en) | 2021-03-09 | 2025-09-30 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20220298190A1 (en) | 2021-03-12 | 2022-09-22 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US12421262B2 (en) | 2021-03-15 | 2025-09-23 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20220340607A1 (en) | 2021-04-05 | 2022-10-27 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| EP4075531A1 (en) | 2021-04-13 | 2022-10-19 | Universal Display Corporation | Plasmonic oleds and vertical dipole emitters |
| US20220352478A1 (en) | 2021-04-14 | 2022-11-03 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic eletroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20220407020A1 (en) | 2021-04-23 | 2022-12-22 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20230006149A1 (en) | 2021-04-23 | 2023-01-05 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20230133787A1 (en) | 2021-06-08 | 2023-05-04 | University Of Southern California | Molecular Alignment of Homoleptic Iridium Phosphors |
| EP4151699A1 (en) | 2021-09-17 | 2023-03-22 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20240343970A1 (en) | 2021-12-16 | 2024-10-17 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20230292592A1 (en) | 2022-03-09 | 2023-09-14 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20230337516A1 (en) | 2022-04-18 | 2023-10-19 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20230389421A1 (en) | 2022-05-24 | 2023-11-30 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| EP4293001A1 (en) | 2022-06-08 | 2023-12-20 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20240016051A1 (en) | 2022-06-28 | 2024-01-11 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20240107880A1 (en) | 2022-08-17 | 2024-03-28 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20240180025A1 (en) | 2022-10-27 | 2024-05-30 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20240188316A1 (en) | 2022-10-27 | 2024-06-06 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20240196730A1 (en) | 2022-10-27 | 2024-06-13 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20240188419A1 (en) | 2022-10-27 | 2024-06-06 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20240188319A1 (en) | 2022-10-27 | 2024-06-06 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20240247017A1 (en) | 2022-12-14 | 2024-07-25 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20250204239A1 (en) | 2023-12-15 | 2025-06-19 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20250204238A1 (en) | 2023-12-15 | 2025-06-19 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminscent materials and devices |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2010110553A2 (en) | 2009-03-23 | 2010-09-30 | Dow Advanced Display Materials, Ltd. | Novel organic electroluminescent compounds and organic electroluminescent device using the same |
| WO2011019156A1 (en) | 2009-08-10 | 2011-02-17 | Rohm And Haas Electronic Materials Korea Ltd. | Novel organic electroluminescent compounds and organic electroluminescent device using the same |
- 2012
- 2012-04-12KRKR1020120037956Apatent/KR101565200B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2010110553A2 (en) | 2009-03-23 | 2010-09-30 | Dow Advanced Display Materials, Ltd. | Novel organic electroluminescent compounds and organic electroluminescent device using the same |
| WO2011019156A1 (en) | 2009-08-10 | 2011-02-17 | Rohm And Haas Electronic Materials Korea Ltd. | Novel organic electroluminescent compounds and organic electroluminescent device using the same |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10096777B2 (en) | 2016-12-22 | 2018-10-09 | Samsung Sdi Co., Ltd. | Composition for organic optoelectric device and organic optoelectric device and display device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20130115564A (en) | 2013-10-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101565200B1 (en) | New compound and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR101350581B1 (en) | New compounds and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR101575392B1 (en) | Organic light emitting device material and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR101412437B1 (en) | New compounds and organic electronic device using the same | |
| JP5638612B2 (en) | Novel heterocyclic derivative and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR101695063B1 (en) | Organic light emitting device and method for preparing the same | |
| KR101638665B1 (en) | New compound and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR101434018B1 (en) | New compounds and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR101592085B1 (en) | New compounds and organic electronic device using the same | |
| KR101512544B1 (en) | New compound and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR20130007441A (en) | New compounds and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR101647173B1 (en) | New compound and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR101680413B1 (en) | New compounds and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR101560028B1 (en) | New hetero-cyclic compound and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR20130135181A (en) | New compounds and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR101586531B1 (en) | New compounds and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR20150082156A (en) | New compounds and organic light emitting device comprising the same | |
| CN111212829A (en) | Spiro compound and organic light-emitting device comprising same | |
| KR101654960B1 (en) | New compound and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR20140063428A (en) | Amine compound and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR101671561B1 (en) | New compounds and organic light emitting device using the same | |
| KR101550485B1 (en) | New compounds and organic light emitting device comprising the same | |
| KR101640285B1 (en) | New compound and organic light emitting device using the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | St.27 status event code:A-1-1-Q10-Q12-nap-PG1501 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 Fee payment year number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20181016 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:4 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:6 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:7 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:8 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:9 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:10 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:11 |