KR101515581B1 - Method for controling flow of mobile traffic - Google Patents
Method for controling flow of mobile trafficDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101515581B1 KR101515581B1KR1020130128945AKR20130128945AKR101515581B1KR 101515581 B1KR101515581 B1KR 101515581B1KR 1020130128945 AKR1020130128945 AKR 1020130128945AKR 20130128945 AKR20130128945 AKR 20130128945AKR 101515581 B1KR101515581 B1KR 101515581B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- flow
- router
- user terminal
- access
- class
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription66
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription53
- 239000000872bufferSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 230000003139buffering effectEffects0.000claims1
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description15
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description12
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description8
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description5
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description5
- 238000007726management methodMethods0.000description5
- 238000005111flow chemistry techniqueMethods0.000description3
- 230000004931aggregating effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description2
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description2
- 230000006855networkingEffects0.000description2
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description2
- 238000003491arrayMethods0.000description1
- 238000010295mobile communicationMethods0.000description1
- 230000035945sensitivityEffects0.000description1
- 239000010454slateSubstances0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/10—Flow control between communication endpoints
- H04W28/14—Flow control between communication endpoints using intermediate storage
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/0226—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control based on location or mobility
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/0268—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control using specific QoS parameters for wireless networks, e.g. QoS class identifier [QCI] or guaranteed bit rate [GBR]
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/16—Performing reselection for specific purposes
- H04W36/22—Performing reselection for specific purposes for handling the traffic
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/24—Reselection being triggered by specific parameters
- H04W36/30—Reselection being triggered by specific parameters by measured or perceived connection quality data
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 플로우 라우터가 플로우를 제어하는 방법 및 플로우 전송 경로를 제어하는 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method by which a flow router controls a flow and a method of controlling a flow transmission path.
현재 아이피(IP) 네트워크에는 웹 서비스, VoIP 서비스, 스트리밍 서비스 등 다양한 종류의 서비스가 공존하고 있다. 각 서비스는 시간지연, 손실률, 지터 (jitter) 등에서 서로 다른 서비스 품질(Quality of Service, QoS) 수준을 요구하지만, 일반적인 인터넷의 최선노력전송(best effort) 서비스 지원방식에서는 IP 패킷 단위의 라우팅 및 상태 비보존형 (stateless) 라우팅 방식을 사용하기 때문에 QoS를 제공하기 위한 접속 수락 제어, 스케줄링, 네트워크 가상화 서비스 등에서 트래픽 관리 성능에 제약이 있다.Currently, various kinds of services such as web service, VoIP service, and streaming service coexist in the IP network. Each service requires a different quality of service (QoS) level in terms of time delay, loss rate, jitter, etc. However, in a general best effort service support method of the Internet, Due to the use of stateless routing, traffic management performance is limited in connection admission control, scheduling, and network virtualization services to provide QoS.
이러한 한계를 극복하기 위해 IP 네트워크에서 플로우 기반의 트래픽 관리 기술이 제안되었다. 플로우 기반의 트래픽 관리 기술은 라우터에서 플로우의 상태 정보를 유지하는 보존형 (stateful) 라우팅 방식을 사용함으로써, 각 플로우에 포함된 모든 패킷들이 플로우의 QoS 요구사항에 따라 동일하게 처리될 수 있도록 하는 방법이다.To overcome these limitations, flow-based traffic management techniques have been proposed in IP networks. Flow-based traffic management technology uses a stateful routing method that maintains state information of flows in a router, so that all packets included in each flow can be handled the same according to the QoS requirements of the flow to be.
이와 관련하여, 공개특허공보 제 10-2011-0071770호(발명의 명칭: 플로우별 핸드오버를 수행하는 망 기반 IP 이동성 시스템 및 그 시스템에서의 플로우별 핸드오버 방법)에는 이동 단말의 이동이나 무선 환경의 변화에 따라 서비스 플로우별로 적합한 액세스 망으로 핸드오버시켜서 최적의 무선 환경에서 서비스 플로우가 제공될 수 있도록 하는 플로우별 핸드오버를 수행하는 망 기반 IP 이동성 시스템 및 그 시스템에서의 플로우별 핸드오버 방법이 개시되어 있다.In this connection, Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 10-2011-0071770 (entitled: Network-based IP mobility system for performing handover according to flows, and flow-by-flow handover method in the system) A network-based IP mobility system that performs handover for each flow that enables a service flow to be provided in an optimal wireless environment by performing handover to an access network appropriate for each service flow according to a change of the service flow, and a flow- Lt; / RTI >
한편, IP기반의 이동통신 네트워크의 액세스 단에서는 사용자 단말의 이동으로 인하여 데이터의 전달 경로의 변경이 빈번이 일어나기 때문에 개별적인 플로우 단위로 데이터 라우팅이 필요하다. 그러나, 코어 네트워크에서는 상대적으로 플로우 전달경로의 변경 빈도가 낮지만 라우터에서 관리해야 하는 플로우의 수가 많기 때문에 경계 라우터에서 각 플로우가 요구하는 QoS 조건들을 처리해야 하는 부담이 증가될 수 있다. 특히, IP 기반의 핸드오버 기술인 PMIP (Proxy Mobile IP)에서 LMA (Local Mobility Anchor)로 표시되는 이동성 관리 앵커 (Mobility Anchor)에 과도한 핸드오버 관련 관리제어 트래픽이 집중될 수 있다는 문제점이 있다.On the other hand, in an access terminal of an IP-based mobile communication network, data routing is required in individual flow units because frequent changes occur in data transmission paths due to movement of user terminals. However, in the core network, the frequency of change of the flow propagation route is relatively low, but since the number of flows to be managed by the router is large, the burden of processing the QoS conditions required by each flow in the border router may increase. In particular, there is a problem that excessive handover-related management control traffic may be concentrated on a mobility anchor indicated by LMA (Local Mobility Anchor) in Proxy Mobile IP (PMIP), which is an IP-based handover technology.
그러므로 코어 네트워크와 액세스 네트워크에서 단말의 핸드오버 관리를 위한 플로우 처리를 서로 다르게 차별적으로 관리하는 방법이 요구된다.Therefore, there is a need for a method for differentially managing the flow processing for handover management of the terminal in the core network and the access network differently.
본 발명은 전술한 종래 기술의 문제점을 해결하기 위한 것으로서, 본 발명의 일부 실시예는 이동 네트워크에서 핸드오버 발생 시 플로우에 요구되는 서비스 품질에 따라 플로우의 전달 경로를 제어한다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention has been made to solve the above-mentioned problems of the prior art, and it is an object of the present invention to control a delivery path of a flow according to a service quality required for a flow when a handover occurs in a mobile network.
또한, 본 발명의 일부 실시예는 액세스 라우터와 경계 라우터 사이에 크로스오버 라우터를 구현하여 핸드오버 절차를 수행하도록 함으로써 핸드오버 지연시간을 줄이고 각 플로우의 플로우 등급에 따라 차등적인 핸드오버 절차를 제공한다.In addition, some embodiments of the present invention implement a crossover router between an access router and a border router to perform a handover procedure, thereby reducing a handover delay time and providing a differential handover procedure according to the flow class of each flow .
상술한 기술적 과제를 달성하기 위한 기술적 수단으로서, 본 발명의 제 1 측면에 따른 플로우 라우터가 플로우를 제어하는 방법은, 사용자 단말 또는 다른 플로우 라우터로부터 플로우를 수신하는 단계; 플로우를 일정한 플로우 등급에 따라 분류하는 단계; 및 분류된 플로우를 사용자 단말 또는 다른 플로우 라우터로 전송하는 단계를 포함하되, 플로우 등급은, 플로우에 요구되는 서비스 품질에 따라 구분된다.As a technical means for achieving the above technical object, a method of a flow router for controlling a flow according to the first aspect of the present invention includes: receiving a flow from a user terminal or another flow router; Classifying the flows according to a constant flow class; And transmitting the classified flow to a user terminal or another flow router, wherein the flow class is classified according to the quality of service required for the flow.
또한, 본 발명의 제 2 측면에 따른 크로스오버 라우터가 플로우 전송 경로를 제어하는 방법에 있어서, 사용자 단말이 제 1 액세스 라우터로부터 제 2 액세스라우터로 핸드오버 되는 경우, 상기 사용자 단말에 서비스 중인 플로우의 등급에 따라 상기 제 1 액세스 라우터로부터 전송되는 핸드오버 준비 메시지를 상기 크로스오버 라우터가 가로채는 단계; 및 상기 사용자 단말에 서비스 중인 플로우의 등급에 따라, 상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 플로우의 전송경로를 설정하는 단계를 포함한다.Further, in a second aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of controlling a flow transmission path of a crossover router, the method comprising the steps of: when a user terminal is handed over from a first access router to a second access router, Intercepting a handover preparation message transmitted from the first access router according to a class; And setting the transmission path of the flow according to the class of the flow being serviced to the user terminal.
또한, 본 발명의 제 3 측면에 따른 플로우 라우터에 있어서, 플로우 라우터가 수신한 플로우가 속하는 플로우 등급을 검색하는 해싱모듈; 플로우의 전달 경로를 설정하는 라우팅 모듈; 및플로우 등급에 따른 전달 경로를 변경하는 서비스 제어모듈을 포함하되, 플로우 등급은, 수신한 플로우에 요구되는 서비스 품질에 따라 구분된다.According to a third aspect of the present invention, there is provided a flow router comprising: a hashing module for searching for a flow class to which a flow received by a flow router belongs; A routing module for setting a delivery path of the flow; And a service control module for changing a delivery path according to the flow class, wherein the flow class is classified according to the service quality required for the received flow.
전술한 본 발명의 과제 해결 수단에 의하면, 본 발명은 아이피(Internet Protocol, IP) 네트워크에서 계층별로 플로우를 분류하여 플로우에 요구되는 서비스 품질(Quality of Service, QoS)을 보장하면서 전송 경로를 제어하는 라우터 및 그 전송 경로 제어방법을 구현할 수 있다.According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of controlling a transmission path by classifying a flow for each layer in an Internet Protocol (IP) network to ensure quality of service (QoS) A router and its transmission path control method can be implemented.
또한, 전술한 본 발명의 과제 해결 수단에 의하면, 플로우 라우터가 플로우 등급에 따라 플로우 전송 경로를 달리함으로써, 경계 라우터의 전송 경로 제어 부담을 감소시키고, 사용자 단말이 다른 액세스 네트워크로 이동하는 경우에도 용이하게 전송 경로의 변경이 가능하다.Further, according to the above-mentioned object of the present invention, the flow router changes the flow transmission route according to the flow class, thereby reducing the transmission path control burden of the border router and facilitating the user terminal moving to another access network The transmission path can be changed.
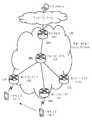
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 플로우 라우터가 구현된 네트워크 환경을 계층별로 도시한 일 예이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 액세스 라우터, 제 1 경계 라우터, 및 제 2 경계 라우터에서 플로우를 집합하고 분리하는 예시를 나타내는 도면이다.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 각 라우터에서 조합되는 플로우 헤더 필드에 관한 도면이다.
도 4는 플로우 등급의 일 예를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 각 플로우 라우터가 플로우 등급에 따라 수신한 플로우를 분류하는 프로세스에 대한 도면이다.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 엑세스 네트워크에 관한 도면이다.
도 7은 시간 지연 및 손실률에 대해 둔감한 등급(도 4의 제 1 등급)에 해당하는 플로우가 전송되는 경우 엑세스 네트워크에서 플로우의 전송 경로를 제어하는 방법에 대한 프로세스를 도시한다.
도 8은 시간 지연에는 둔감하지만 손실률에 대해 민감한 등급(도 4의 제 2 등급)에 해당하는 플로우가 전송되는 경우 엑세스 네트워크에서 플로우의 전송 경로를 제어하는 방법에 대한 프로세스를 도시한다.
도 9는 시간 지연에는 민감하지만 손실률에 대해 둔감한 등급(도 4의 제 3 등급)에 해당하는 플로우가 전송되는 경우 엑세스 네트워크에서 플로우의 전송 경로를 제어하는 방법에 대한 프로세스를 도시한다.
도 10은 시간 지연 및 손실률에 대해 모두 민감한 등급(도 4의 제 4 등급)에 해당하는 플로우가 전송되는 경우 엑세스 네트워크에서 플로우의 전송 경로를 제어하는 방법에 대한 프로세스를 도시한다.
도 11은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 플로우 라우터에 관한 블록도이다.1 is an example of a network environment in which a flow router according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention is implemented.
2 is a diagram illustrating an example of aggregating and separating flows in an access router, a first border router, and a second border router in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
3 is a diagram of a flow header field combined in each router according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Fig. 4 is a diagram for explaining an example of the flow grade.
5 is a diagram of a process for each flow router according to an embodiment of the present invention to classify received flows according to a flow class.
6 is a diagram of an access network according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 7 shows a process for a method of controlling a transmission path of a flow in an access network when a flow corresponding to an insensitive grade (first class in FIG. 4) for time delay and loss rate is transmitted.
Fig. 8 shows a process for a method of controlling a transmission path of a flow in an access network when a flow corresponding to a grade (second class in Fig. 4) sensitive to a loss rate is insensitive to a time delay is transmitted.
9 shows a process for a method of controlling a transmission path of a flow in an access network when a flow sensitive to a time delay but insensitive to a loss rate (corresponding to a third class in FIG. 4) is transmitted.
10 shows a process for a method for controlling the transmission path of a flow in an access network when a flow corresponding to a class (
11 is a block diagram of a flow router according to an embodiment of the present invention.
아래에서는 첨부한 도면을 참조하여 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 용이하게 실시할 수 있도록 본 발명의 실시예를 상세히 설명한다. 그러나 본 발명은 여러 가지 상이한 형태로 구현될 수 있으며 여기에서 설명하는 실시예에 한정되지 않는다. 그리고 도면에서 본 발명을 명확하게 설명하기 위해서 설명과 관계없는 부분은 생략하였으며, 명세서 전체를 통하여 유사한 부분에 대해서는 유사한 도면 부호를 붙였다.Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings, which will be readily apparent to those skilled in the art. The present invention may, however, be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein. In order to clearly illustrate the present invention, parts not related to the description are omitted, and similar parts are denoted by like reference characters throughout the specification.
명세서 전체에서, 어떤 부분이 다른 부분과 "연결"되어 있다고 할 때, 이는 "직접적으로 연결"되어 있는 경우뿐 아니라, 그 중간에 다른 소자를 사이에 두고 "전기적으로 연결"되어 있는 경우도 포함한다.Throughout the specification, when a part is referred to as being "connected" to another part, it includes not only "directly connected" but also "electrically connected" with another part in between .
본원 명세서 전체에서, 어떤 부재가 다른 부재 "상에" 위치하고 있다고 할 때, 이는 어떤 부재가 다른 부재에 접해 있는 경우뿐 아니라 두 부재 사이에 또 다른 부재가 존재하는 경우도 포함한다.Throughout this specification, when a member is "on " another member, it includes not only when the member is in contact with the other member, but also when there is another member between the two members.
본원 명세서 전체에서, 어떤 부분이 어떤 구성요소를 "포함" 한다고 할 때, 이는 특별히 반대되는 기재가 없는 한 다른 구성요소를 제외하는 것이 아니라 다른 구성 요소를 더 포함할 수 있는 것을 의미한다. 본원 명세서 전체에서 사용되는 정도의 용어 "~(하는) 단계" 또는 "~의 단계"는 "~ 를 위한 단계"를 의미하지 않는다.Throughout this specification, when an element is referred to as "including " an element, it is understood that the element may include other elements as well, without departing from the other elements unless specifically stated otherwise. The word " step (or step) "or" step "used to the extent that it is used throughout the specification does not mean" step for.
플로우는 데이터의 다른 전송 형태를 의미한다. 최근 인터넷 패킷 네트워크의 단점을 보완해서 서비스 품질을 높이려는 기술로서, 플로우 처리 기술은 오픈플로우와 관련하여 네트워크 관리방식으로 소프트웨어 정의 네트워킹(SDN), 클라우드(CLOUD)와 연계되어 새롭게 부각되고 있다. 오픈플로우는 소프트웨어정의네트워킹(이하, SDN)의 한 기술로서 사용자들이 프로그래밍된 소프트웨어로 네트워크 경로 설정, 제어, 관리할 수 있도록 구현된다.A flow refers to another form of transmission of data. As a technology to improve the service quality by complementing the disadvantages of the Internet packet network, the flow processing technology is newly emerging in connection with the open flow, in association with the software defined networking (SDN) and the cloud (CLOUD). Openflow is a technology of Software Defined Networking (SDN) that is implemented to allow users to route, control, and manage the network with programmed software.
본 발명은 이러한 플로우 처리 기술을 위한 플로우 제어방법, 플로우 전송 경로 제어방법, 및 플로우 라우터를 제안한다.The present invention proposes a flow control method, a flow transmission path control method, and a flow router for such a flow processing technique.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 플로우 라우터가 구현된 네트워크 환경을 계층별로 도시한 일 예이다.1 is an example of a network environment in which a flow router according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention is implemented.
도 1을 참조하면, 네트워크 계층은 액세스 네트워크 계층(115), 중간 네트워크 계층(125), 및 코어 네트워크 계층(135)으로 분류될 수 있고, 플로우 등급의 설정에 따라 네트워크 계층은 더욱 세분화되어 많아질 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 1, the network layer may be classified into an
각 네트워크 계층은 플로우 라우터를 통하여 다른 네트워크 계층과 연결된다. 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따르면, 플로우 라우터는 액세스 라우터(110)거나, 제 1 경계 라우터(120)거나, 또는 제 2 경계라우터(130)되, 반드시 이에 한정되지는 아니한다. 더 나아가, 플로우 라우터는 후술할 액세스 네트워크(115)에서 핸드오버 처리를 담당하는 크로스오버 라우터일 수 있는데, 이와 관련된 상세한 설명은 도 6과 관련하여 후술한다. 이하, 본 실시예에 따라 각 플로우 라우터의 제어 프로세스를 설명한다.Each network layer is connected to another network layer through a flow router. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the flow router is not necessarily limited to the
이때, 액세스 네트워크(115)는 사용자 단말이 접속하는 액세스 라우터 (110), 및 다음 계층인 중간 네트워크(125)를 연결하는 제 1 경계 라우터(120)를 통하여 다른 네트워크와 연결된다.At this time, the
중간 네트워크(125)는 이전 계층인 액세스 네트워크(115)를 연결하는 제 1 경계 라우터(120), 및 다음 계층인 코어 네트워크(135)를 연결하는 제 2 경계 라우터(130)를 통하여 다른 네트워크와 연결된다. 중간 네트워크(125)는 목적지 및 서비스 특성에 따라 다수가 존재할 수 있다.The
코어 네트워크(135)는 가장 큰 단위의 플로우를 관리하는 계층이다. 마찬가지로 제 2 경계 라우터(130)를 통하여 중간 네트워크(125)와 연결된다.The
이와 같은 계층적 네트워크를 구분하는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 플로우 라우터는 액세스 라우터(110), 및 경계 라우터(120, 130)를 포함하되 네트워크 계층화 특성에 따라 경계 라우터는 더 추가될 수 있다.The flow router according to an embodiment of the present invention for classifying such a hierarchical network includes an
네트워크는 근거리 통신망(Local Area Network; LAN), 광역 통신망(Wide Area Network; WAN) 또는 부가가치 통신망(Value Added Network; VAN) 등과 같은 유선 네트워크나 이동 통신망(mobile radio communication network) 또는 위성 통신망 등과 같이 플로우를 단위로 라우팅하는 모든 종류의 네트워크로 구현될 수 있다.The network may be a wired network such as a local area network (LAN), a wide area network (WAN) or a value added network (VAN), a mobile radio communication network, Lt; / RTI > can be implemented in any type of network that routes data in units of.
플로우 라우터는 사용자 단말 또는 다른 플로우 라우터로부터 플로우를 수신하고, 플로우에 요구되는 서비스 품질에 따라 일정한 플로우 등급으로 플로우를 분류(집합 또는 분리)한다. 이어서 분류된 플로우를 사용자 단말 또는 다른 플로우 라우터로 전송한다. 플로우 라우터는 상술한 액세스 라우터(110), 제 1 경계 라우터(120), 또는 제 2 경계 라우터(130)일 수 있다. 더 나아가, 후술할 크로스오버 라우터일 수도 있다. 크로스오버 라우터에 관련된 설명은 도 6과 관련하여 후술한다.The flow router receives flows from user terminals or other flow routers and classifies (aggregates or separates) the flows with a constant flow grade according to the quality of service required for the flows. And then sends the classified flow to the user terminal or another flow router. The flow router may be the
각 라우터는 수신한 플로우를 각자 독립적으로 설정된 기준변수를 이용하여 플로우 등급에 따라 분류(집합 또는 분리)시키는데, 이러한 플로우 등급은 각 라우터의 서비스 정책에 따라 다르게 설정될 수 있다. 이러한 플로우 등급과 관련된 상세한 설명은 후술한다.Each router classifies (aggregates or separates) the received flows according to the flow class by using independently set reference variables. Such a flow class can be set differently according to the service policy of each router. Details related to this flow grade will be described later.
이하, 각 라우터의 개별적인 특징과 관련하여 서술한다.Hereinafter, it will be described with respect to individual features of each router.
액세스 라우터(110)는 사용자 단말을 액세스 네트워크(115)에 접속시키는 라우터로서, 일정한 영역에 위치한 사용자 단말의 데이터를 송수신한다. 액세스 라우터(110)가 액세스 네트워크(115)를 통해 데이터를 송수신하는 경우, 데이터는 상술한 바와 같이 각 데이터에 요구되는 서비스 품질에 따라 플로우 형태로 송수신된다. 복수의 액세스 라우터(110)는 각각 독립된 영역을 관리하고, 각자의 영역에 존재하는 사용자 단말과 액세스 네트워크(115)를 연결시킨다.The
여기서 사용자 단말은 네트워크를 통해 액세스 라우터(110)에 접속할 수 있는 컴퓨터나 휴대용 단말기로 구현될 수 있다. 여기서, 컴퓨터는 예를 들어, 웹 브라우저(WEB Browser)가 탑재된 노트북, 데스크톱(desktop), 랩톱(laptop), 태블릿 PC, 슬레이트 PC 등을 포함하고, 휴대용 단말기는 예를 들어, 휴대성과 이동성이 보장되는 무선 통신 장치로서, PCS(Personal Communication System), GSM(Global System for Mobile communications), PDC(Personal Digital Cellular), PHS(Personal Handyphone System), PDA(Personal Digital Assistant), IMT(International Mobile Telecommunication)-2000, CDMA(Code Division Multiple Access)-2000, W-CDMA(W-Code Division Multiple Access), WiBro(Wireless Broadband Internet) 단말, 스마트 폰(Smart Phone) 등과 같은 모든 종류의 핸드헬드(Handheld) 기반의 무선 통신 장치를 포함할 수 있다.The user terminal may be implemented as a computer or a portable terminal capable of accessing the
경계 라우터(120, 130)는 계층별 네트워크 경계에서 접합하는 계층별 네트워크에서 정의하는 플로우의 특성 차이를 조정하기 위해 플로우를 집합하거나 분리하는 작업을 수행한다. 경계 라우터(120, 130)는 액세스 네트워크(115)와 중간 네트워크(125) 사이에 위치할 수 있고(제 1 경계 라우터, 120), 또한 중간 네트워크(125)와 코어 네트워크(135) 사이에 위치할 수도 있으며(제 2 경계 라우터, 130), 하나 이상의 경계 라우터(120, 130)가 각 네트워크의 계층을 구분할 수 있다.The
도 2는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 액세스 라우터, 제 1 경계 라우터, 및 제 2 경계 라우터에서 플로우를 집합하고 분리하는 예시를 나타내는 도면이다.2 is a diagram illustrating an example of aggregating and separating flows in an access router, a first border router, and a second border router in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
일 예에 따르면, 코어 네트워크로부터 멀리 떨어진 라우터일수록 수신한 플로우를 네트워크 계층 별로 세분화하여 집합시키거나 분리시키는데, 도 2를 참조하면, 제 2 경계 라우터보다 제 1 경계 라우터가 플로우를 더 세분화하여 플로우를 집합시키거나 분리시킨다. 즉, 코어 네트워크와 가까운 라우터일수록 플로우를 더 집적화시킨다. 따라서, 액세스 네트워크(115)를 통해 전달되는 플로우보다 중간 네트워크(125)를 통해 전달되는 플로우가 더 집적화되고, 중간 네트워크(125)를 통해 전달되는 플로우보다 코어 네트워크(135)를 통해 전달되는 플로우가 더 집적화된다.According to an example, the flows received from the core network are divided into sub-groups according to the network layers, and are collected or separated. Referring to FIG. 2, the first border router further subdivides the flow to the second border router Gathered or separated. That is, the closer the router is to the core network, the more integrated the flow. The flow delivered through the
도 2에 따르면, 사용자 단말로부터 업로딩되는 플로우는 액세스 라우터 1에 의해 요구되는 서비스 품질에 따라 플로우 a, 플로우 b, 플로우 c, 플로우 d, 플로우 e로 분류된다. 플로우 a, 플로우 b, 플로우 c, 플로우 d, 플로우 e로 분류된 플로우는 다음에 연결된 중간 라우터에 의해 플로우 f, 플로우 g로 집합된다. 이때, 도 2의 일 실시예에 따르면, 플로우 a, 플로우 b, 플로우 c는 제 1 경계 라우터에 의해 플로우 f로, 플로우 d, 플로우 e는 제 1 경계 라우터에 의해 플로우 g로 집합된다. 또한, 플로우 f, 플로우 g로 집합된 플로우는 제 2 경계 라우터에 의해 플로우 h로 집합된다.According to Fig. 2, the flow uploaded from the user terminal is classified into flow a, flow b, flow c, flow d and flow e according to the service quality required by the
마찬가지로, 사용자 단말로 다운로딩되는 플로우는 제 2경계 라우터에 의해 플로우 f, 플로우 g로 분리되고, 플로우 f는 제 1 경계 라우터에 의해 플로우 a, 플로우 b, 플로우 c로, 플로우 g는 플로우 d, 플로우 e로 분리된다. 분리된 플로우를 수신한 액세스 라우터는 사용자 단말에 플로우를 전송한다.Similarly, the flow downloaded to the user terminal is separated into the flow f and the flow g by the second border router, the flow f is divided into the flows a, b and c by the first border router, Flow e. The access router that has received the separated flow transmits the flow to the user terminal.
이와 같이 각 라우터 마다 독립적으로 분류된 플로우는 액세스 라우터, 제 1 경계 라우터, 및 제 2 경계 라우터에 의해 연결되어 하나의 전송 경로를 형성한다. 즉, 액세스 라우터, 제 1 경계 라우터, 및 제 2 경계 라우터가 각 라우터에 의해 분류된 플로우를 연결하여 하나의 전송 경로를 형성한다.Thus, the flow classified independently for each router is connected by the access router, the first border router, and the second border router to form one transmission path. That is, the access router, the first border router, and the second border router connect the flows classified by the respective routers to form one transmission path.
한편, 액세스 라우터, 제 1 경계 라우터, 및 제 2 경계 라우터는 사용자 단말의 이동으로 인해 발생하는 전송 경로 변경 비용을 최소화하기 위해 수신한 플로우를 각자 독립적으로 분류할 수 있는데, 이때, 상술한 바와 같이 각 플로우에 요구되는 서비스 품질에 따라 각 플로우 라우터가 단대 단 네트워크 전송 경로를 설정한다.Meanwhile, the access routers, the first border router, and the second border router can independently classify the received flows to minimize the transmission path change cost caused by the movement of the user terminal. At this time, Each flow router establishes a one-to-one network transmission path according to the quality of service required for each flow.
도 3은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따라 각 라우터에서 조합되는 플로우 헤더 필드에 관한 도면이다.3 is a diagram of a flow header field combined in each router according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 3에 따르면, 각 라우터는 독립적으로 플로우 헤더 필드를 조합하고, 조합한 헤더 필드를 상호 공유한다. 이때, 각 라우터는 계층 내에서 독립적으로 플로우에 요구되는 서비스 품질에 따라 플로우 헤더 필드를 조합하고, 공유할 수 있다.According to FIG. 3, each router independently combines flow header fields and mutually shares the combined header fields. At this time, each router can independently combine and share flow header fields according to the quality of service required in the flow in the layer.
도 1의 액세스 네트워크를 통해 전송되는 액세스 네트워크 헤더 필드는 송신자 맥 주소(MAC Src), 수신자 맥 주소(MAC Dst), 송신자 아이피 주소(IP Src), 수신자 아이피 주소(IP Dst), 송신자 포트넘버(PORT Src), 및 수신자 포트넘버(PORT Dst)를 포함한다. 따라서, 플로우가 업로딩되는 경우, 액세스 라우터가 액세스 네트워크 헤더 필드를 조합하고, 다운로딩 되는 경우, 제 1 경계 라우터가 액세스 네트워크 헤더 필드를 조합한다.The access network header field transmitted through the access network of FIG. 1 includes a sender MAC address MAC Src, a receiver MAC address MAC Dst, a sender IP address Src, a receiver IP address Dpst, PORT Src, and a recipient port number PORT Dst. Thus, when the flow is uploaded, the first border router combines the access network header fields if the access router combines the access network header fields and is downloaded.
도 1의 중간 네트워크를 통해 전송되는 중간 네트워크 헤더 필드는 송신자 아이피 주소(IP Src), 수신자 아이피 주소(IP Dst), 송신자 포트넘버(PORT Src), 및 수신자 포트넘버(PORT Dst)를 포함한다. 따라서, 플로우가 업로딩 되는 경우, 제 1 경계 라우터가 중간 네트워크 헤더 필드를 조합하고, 다운로딩 되는 경우, 제 2 경계 라우터가 중간 네트워크 헤더 필드를 조합한다.The intermediate network header field transmitted through the intermediate network of FIG. 1 includes a sender IP address (IP Src), a receiver IP address (IP Dst), a sender port number (PORT Src), and a receiver port number (PORT Dst). Thus, when a flow is uploaded, the first border router combines the intermediate network header fields and, if downloaded, the second border router combines the intermediate network header fields.
도 1의 코어 네트워크를 통해 전송되는 코어 네트워크 헤더 필드는 수신자 아이피 주소(IP Dst), 및 수신자 포트넘버(PORT Dst)를 포함한다. 따라서, 플로우가 업로딩 되는 경우 제 2 경계 라우터가 코어 네트워크 헤더 필드를 조합한다.The core network header field transmitted over the core network of FIG. 1 includes a recipient IP address (IP Dst), and a recipient port number (PORT Dst). Thus, if the flow is uploaded, the second border router combines the core network header fields.
도 4는 플로우 등급의 일 예를 설명하기 위한 도면이다.Fig. 4 is a diagram for explaining an example of the flow grade.
일 예로서, 플로우는 요구되는 서비스 품질(QoS)의 기준변수가 시간 지연 및 손실률인 경우 이에 따라 등급화될 수 있다. 각 라우터에 의해 분류된 데이터를 플로우라고 하는데, 일 실시예에 따르면 플로우 등급의 최대 개수는, 등급화 기준변수의 개수를 k라고 하는 경우 2k개로 설정할 수 있다. 위 예의 경우, 시간 지연 및 손실률이 기준변수가 되므로 22=4 이 플로우 등급의 최대 개수가 된다.As an example, the flow may be graded accordingly if the reference variable of the required quality of service (QoS) is time delay and loss rate. The data classified by each router is referred to as a flow. According to an embodiment, the maximum number of flow classes can be set to 2k when the number of ranking reference variables is k. In this case, 22 = 4 is the maximum number of flow classes since the time delay and loss rate are the reference variables.
도 4에 따르면, 플로우는 시간 지연 및 손실률 모두 둔감한 경우(Best Effort Service) 제 1 등급, 전자 메일과 같이 시간 지연에 둔감하되 손실률에 민감한 경우 제 2 등급, 동영상 재생 및 음성통화와 같이 시간 지연에 민감하되 손실률에 둔감한 경우 제 3 등급, 화상 통화와 같이 시간 지연 및 손실률 모두 민감한 경우 제 4 등급으로 분류될 수 있으나, 반드시 이에 한정되지 아니하고, 각 라우터는 네트워크 소유자 또는 운영자의 독립적인 서비스 정책(예를 들어, 기준 변수)에 따라 플로우 등급을 다르게 설정할 수 있다.According to FIG. 4, the flow is classified into a first grade when the time delay and a loss rate are both insensitive (Best Effort Service), a second grade when the delay is insensitive to a time delay such as an e-mail, But not necessarily limited to, a third class, where both the time delay and the loss rate are sensitive, such as video calls, may be categorized as a fourth class, but each router is independent of the network owner or operator, (For example, a reference variable).
이때, 민감 또는 둔감 여부는 기 설정된 임계값을 기준으로 판단할 수 있다. 따라서, 플로우는, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감한 제 1 등급, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감하고, 손실슐에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감한 제 2 등급, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감한 제 3 등급, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감한 제 4 등급으로 분류될 수 있다.At this time, the sensitivity or insensitivity can be judged based on a predetermined threshold value. Thus, the flow is a first class sensitive to less than a threshold value for time delay and less than a threshold value for loss rate, a second class sensitive for less than a threshold value for time delay, Class, a third class sensitive to a time delay greater than a threshold and sensitive to a loss rate less than a threshold, a fourth class sensitive to a time delay greater than a threshold and sensitive to a loss rate above a threshold .
도 5는 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 각 플로우 라우터가 플로우 등급에 따라 수신한 플로우를 분류하는 프로세스에 대한 도면이다.5 is a diagram of a process for each flow router according to an embodiment of the present invention to classify received flows according to a flow class.
도 5에 따르면, 플로우 라우터는 먼저 데이터(플로우) 수신 후 각 데이터에 요구되는 서비스 품질을 확인한다(S401). 이어서, 요구되는 서비스 품질인 시간 지연에 대해 민감한지 여부를 판단하고(S402), 이어서 손실률에 대해서 민감한지 여부를 판단한다(S403, S404). 시간 지연 및 손실률 모두에 민감한 경우 제 4 등급, 시간 지연에는 민감하되 손실률에는 둔감한 경우 제 3 등급, 시간 지연에는 둔감하되 손실률에는 민감한 경우 제 2 등급, 시간 지연 및 손실률 모두에 둔감한 경우 제 1 등급을 각 플로우에 부여한다.Referring to FIG. 5, the flow router first confirms the quality of service required for each data after receiving the data (flow) (S401). Subsequently, it is judged whether or not it is sensitive to the time delay which is a required quality of service (S402), and then it is judged whether or not it is sensitive to the loss rate (S403, S404).
종래에는 사용자 단말이 다른 액세스 네트워크로 이동하는 경우, 모든 플로우의전송 경로 변경이 동일한 경로와 절차로 이루어지고, 단 대 단의 전체 경로에 대한 경로 변경이 이루어져, 경계 라우터가 경로 제어를 새롭게 처리해야 하는 부담이 있었으나, 본 발명의 일 실시예와 같은 전송 경로 제어방법을 이용하는 경우, 네트워크를 계층화하여 플로우 등급에 따라 플로우 전송 경로를 달리 정의함으로써, 다른 액세스 네트워크로 이동하는 경우에도 플로우 경로 변경의 비용을 최소화하면서 동시에 서비스 품질을 만족시키도록 전송 경로의 변경이 가능하다.Conventionally, when a user terminal moves to another access network, a transmission path change of all flows is made by the same path and procedure, a path change is made to the entire path only, and a boundary router newly processes path control However, in the case of using the transmission path control method as in the embodiment of the present invention, by defining the flow transmission path according to the flow class by layering the network, even when moving to another access network, It is possible to change the transmission path so as to satisfy the service quality at the same time.
이를 위하여 본 발명의 일 실시예는 더 나아가 세부적으로 전송 경로를 제어하기 위한 엑세스 네트워크를 구현한다.To this end, an embodiment of the present invention further implements an access network for controlling a transmission path in detail.
도 6은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 액세스 네트워크에 관한 도면이다.6 is a diagram of an access network in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
상술한 바와 같이 엑세스 네트워크(115)에서는 액세스 라우터(110)와 경계 라우터(120)를 통하여 플로우 전송 경로가 제어되고, 플로우 라우터는 하나 이상의 액세스 라우터(111, 112, 113), 경계 라우터(120), 또는 크로스오버 라우터(300)일 수 있다.As described above, in the
액세스 라우터(111, 112, 113)는 도 1의 액세스 라우터(110)와 동일한 것으로, 앞서 상술한 바와 같이, 사용자 단말 및 액세스 네트워크(115)와 접속하고, 복수의 액세스 라우터(111, 112, 113)는 각자 독립된 영역을 관리한다. 도 1의 액세스 라우터(110)와 마찬가지로 플로우를 플로우 등급에 따라 집합시키거나 분리한다. 도 6은 사용자 단말이 제 1 액세스 라우터(111)가 관리하는 영역으로부터 제 2 액세스 라우터(112)가 관리하는 영역으로 이동하는 경우에 대하여 도시한다.The
경계 라우터(120)는 액세스 네트워크(115) 및 다른 네트워크와 접속하는 라우터로서, 액세스 네트워크(115)의 경계에 위치한다. 도 2의 경계 라우터(120)와 마찬가지로 플로우 등급에 따라 플로우를 집합시키거나 분리한다. 플로우 등급은 각 라우터의 서비스 정책에 따라 다르게 설정될 수 있다.The
크로스오버 라우터(300)는 종래의 액세스 네트워크(115)에는 없는 구성으로서, 경계 라우터(120)로 전송되는 핸드오버 준비 메시지 등을 가로채어 플로우 등급에 따라 플로우의 전송 경로를 제어한다. 즉, 액세스 네트워크(115) 내에서 이동 앵커와 같은 기능을 수행한다. 종래의 경계 라우터(120)의 경우, 모든 사용자 단말 플로우의 전송 경로를 제어하였으나, 크로스오버 라우터(300)를 설치함으로써, 경계 라우터(120)에 집중되는 핸드오버 부담을 줄일 수 있다. 또한, 사용자 단말과의 거리가 단축되어 핸드오버 지연 시간을 줄일 수 있다. 플로우 등급에 관하여는 도 4과 관련하여 상술한 바와 같고, 각 등급에 따른 플로우 전송경로의 제어에 관하여는 후술한다.The
도 7은 시간 지연 및 손실률에 대해 둔감한 등급(도 4의 제 1 등급)에 해당하는 플로우가 전송되는 경우 엑세스 네트워크에서 플로우의 전송 경로를 제어하는 방법에 대한 프로세스를 도시한다.FIG. 7 shows a process for a method of controlling a transmission path of a flow in an access network when a flow corresponding to an insensitive grade (first class in FIG. 4) for time delay and loss rate is transmitted.
도 7에 따르면, 먼저, 제 1 액세스 라우터의 영역에 위치한 사용자 단말이 제 2 액세스 라우터의 영역으로 이동하여 사용자 단말의 수신신호세기(Received Signal Strength, RSS)가 기설정된 임계값보다 낮아지면, 사용자 단말은 위치정보 및 핸드오버 트리거 메시지를 제 1 액세스 라우터에 전송한다(S510). 다만 제 1 등급의 경우, 제 1 액세스 라우터는 핸드오버 트리거 메시지를 무시한다. 이후, 제 2 액세스 라우터가 사용자 단말과 접속하면(S520) 제 2 액세스 라우터는 접속했음을 알리는 바인딩 메시지를 경계 라우터에 전송하고, 크로스 오버 라우터가 바인딩 메시지를 가로채어(수신하여) 제 2 액세스 라우터와의 바인딩 과정을 수행한다(S530). 그 이후의 플로우 전송은 변경된 경로를 통해 이뤄진다7, if the user terminal located in the area of the first access router moves to the area of the second access router and the received signal strength (RSS) of the user terminal becomes lower than a predetermined threshold value, The terminal transmits the location information and the handover trigger message to the first access router (S510). However, in the case of the first class, the first access router ignores the handover trigger message. Thereafter, when the second access router makes a connection with the user terminal (S520), the second access router transmits a binding message to the border router indicating that it is connected, and the crossover router intercepts (receives) the binding message, (S530). ≪ / RTI > Subsequent flow transfers take place via the modified path
도 8은 시간 지연에는 둔감하지만 손실률에 대해 민감한 등급(도 4의 제 2 등급)에 해당하는 플로우가 전송되는 경우 엑세스 네트워크에서 플로우의 전송 경로를 제어하는 방법에 대한 프로세스를 도시한다.Fig. 8 shows a process for a method of controlling a transmission path of a flow in an access network when a flow corresponding to a grade (second class in Fig. 4) sensitive to a loss rate is insensitive to a time delay is transmitted.
도 8에 따르면, 제 1 액세스 라우터의 영역에 위치한 사용자 단말이 제 2 액세스 라우터의 영역으로 이동하여 사용자 단말의 수신신호세기(Received Signal Strength, RSS)가 기설정된 임계값보다 낮아지면, 사용자 단말은 위치정보 및 핸드오버 트리거 메시지를 제 1 액세스 라우터에 전송하고(S610), 제 1 액세스 라우터는 핸드오버 트리거 메시지를 수신하여 경계 라우터에 핸드오버 준비 메시지를 전송한다(S620). 이때, 크로스오버 라우터는 경계 라우터로 전송된 핸드오버 준비 메시지를 가로채어(수신하여) 미리 플로우를 버퍼링(저장)한다(S630). 이후, 사용자 단말과 접속한(S640) 제 2 액세스 라우터는 사용자 단말과 접속했음을 알리는 바인딩 메시지를 경계 라우터에 전송하고, 크로스오버 라우터가 바인딩 메시지를 가로채어(수신하여) 제 2 액세스 라우터와의 바인딩 과정을 수행한다(S650). 그 이후의 통신은 변경된 경로를 통해 이뤄진다.Referring to FIG. 8, if the user terminal located in the area of the first access router moves to the area of the second access router and the received signal strength (RSS) of the user terminal becomes lower than a predetermined threshold value, In step S610, the first access router receives the handover trigger message and transmits a handover preparation message to the border router in step S620. At this time, the crossover router intercepts (receives) the handover preparation message transmitted to the border router and buffers (stores) the flow in advance (S630). Then, the second access router connected to the user terminal (S640) transmits a binding message to the border router indicating that the user terminal is connected, and when the crossover router intercepts (receives) the binding message and binds to the second access router (S650). Subsequent communications take place via the modified path.
도 9는 시간 지연에는 민감하지만 손실률에 대해 둔감한 등급(도 4의 제 3 등급)에 해당하는 플로우가 전송되는 경우 엑세스 네트워크에서 플로우의 전송 경로를 제어하는 방법에 대한 프로세스를 도시한다.9 shows a process for a method of controlling a transmission path of a flow in an access network when a flow sensitive to a time delay but insensitive to a loss rate (corresponding to a third class in FIG. 4) is transmitted.
도 9에 따르면, 제 1 액세스 라우터의 영역에 위치한 사용자 단말이 제 2 액세스 라우터의 영역으로 이동하여 사용자 단말의 수신신호세기(Received Signal Strength, RSS)가 기설정된 임계값보다 낮아지면, 사용자 단말은 위치정보 및 핸드오버 트리거 메시지를 제 1 액세스 라우터에 전송하고(S710), 제 1 액세스 라우터는 핸드오버 트리거 메시지를 수신하여 경계 라우터에 핸드오버 준비 메시지를 전송한다(S720). 크로스오버 라우터는 경계 라우터로 전송된 핸드오버 준비 메시지를 가로채어(수신하여) 현재 사용자 단말이 접속 가능한 하나 이상의 액세스 라우터가 플로우의 엔트리를 미리 생성하도록 한다(S730). 제 2 액세스 네트워크는 이러한 하나 이상의 액세스 네트워크 중 하나이다. 시간적 공백 없이 바로 다음 액세스 라우터로 연결되기 위함이다. 이후, 사용자 단말과 접속한(S740) 제 2 액세스 라우터는 사용자 단말과 접속했음을 알리는 바인딩 메시지를 경계 라우터에 전송하고, 크로스오버 라우터가 바인딩 메시지를 가로채어(수신하여) 제 2 액세스 라우터와의 바인딩 과정을 수행한다(S750). 그 이후의 통신은 변경된 경로를 통해 이뤄진다.Referring to FIG. 9, when the user terminal located in the area of the first access router moves to the area of the second access router and the received signal strength (RSS) of the user terminal becomes lower than a predetermined threshold value, The location information and the handover trigger message are transmitted to the first access router (S710). The first access router receives the handover trigger message and transmits a handover preparation message to the border router (S720). The crossover router intercepts (receives) the handover preparation message sent to the border router so that one or more access routers to which the current user terminal is connectable may generate an entry of the flow in advance (S730). The second access network is one of these one or more access networks. To connect to the next access router immediately without any time gap. Then, the second access router connected to the user terminal (S740) transmits a binding message to the border router indicating that the user terminal is connected, and when the crossover router intercepts (receives) the binding message and binds to the second access router (S750). Subsequent communications take place via the modified path.
도 10은 시간 지연 및 손실률에 대해 모두 민감한 등급(도 4의 제 4 등급)에 해당하는 플로우가 전송되는 경우 엑세스 네트워크에서 플로우의 전송 경로를 제어하는 방법에 대한 프로세스를 도시한다.10 shows a process for a method for controlling the transmission path of a flow in an access network when a flow corresponding to a class (
도 10에 따르면, 제 1 액세스 라우터의 영역에 위치한 사용자 단말이 제 2 액세스 라우터의 영역으로 이동하여 사용자 단말의 수신신호세기(Received Signal Strength, RSS)가 기설정된 임계값보다 낮아지면, 사용자 단말은 제 1 액세스 라우터에 위치정보 및 핸드오버 트리거 메시지를 전송하고(S810), 제 1 액세스 라우터는 핸드오버 트리거 메시지를 수신하여 경계 라우터에 핸드오버 준비 메시지를 전송한다(S820). 크로스오버 라우터는 경계 라우터로 전송된 핸드오버 준비 메시지를 가로채어(수신하여) 현재 사용자 단말이 접속 가능한 하나 이상의 액세스 라우터가 플로우의 엔트리를 미리 생성하도록 하고, 전송할 플로우를 미리 사용자 단말이 접속 가능한 하나 이상의 라우터에 전송한다(S830). 사용자 단말이 접속 가능한 하나 이상의 액세스 라우터는 플로우를 미리 버퍼링한다(S840). 이후, 사용자 단말과 접속한(S850) 제 2 액세스 라우터는 버퍼링된 플로우를 사용자 단말에 전송하고(S860), 바인딩 메시지를 경계 라우터에 전송한다. 이어서, 크로스오버 라우터가 바인딩 메시지를 가로채어(수신하여) 제 2 액세스 라우터와의 바인딩 과정을 수행한다(S870). 그 이후의 통신은 변경된 경로를 통해 이뤄진다Referring to FIG. 10, when the user terminal located in the area of the first access router moves to the area of the second access router and the received signal strength (RSS) of the user terminal becomes lower than a predetermined threshold value, The first access router transmits the handover trigger message to the first access router (S810). The first access router receives the handover trigger message and transmits a handover preparation message to the border router (S820). The crossover router intercepts (receives) the handover preparation message sent to the border router so that one or more access routers to which the current user terminal is connectable can generate an entry of the flow in advance, (S830). One or more access routers connectable to the user terminal buffer the flow in advance (S840). Thereafter, the second access router connected to the user terminal (S850) transmits the buffered flow to the user terminal (S860), and transmits the binding message to the border router. Then, the crossover router intercepts (receives) the binding message and performs a binding process with the second access router (S870). Subsequent communications take place via the modified path
종래에는 사용자 단말이 다른 액세스 네트워크로 이동하는 경우, 플로우 등급과 관계없이 전송 경로 변경이 이루어져, 경계 라우터가 경로 제어를 새롭게 처리해야 하는 부담이 있었으나, 본 발명의 일 실시예와 같은 크로스오버 라우터가 플로우 등급에 따라 플로우 전송 경로를 달리함으로써, 다른 액세스 네트워크로 이동하는 경우에도 용이하게 전송 경로의 변경이 가능하다.Conventionally, when a user terminal moves to another access network, a transmission path is changed regardless of a flow class, and a border router has to handle a new path control. However, a crossover router like the embodiment of the present invention By changing the flow transmission path according to the flow class, it is possible to easily change the transmission path even when moving to another access network.
도 11은 본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 플로우 라우터의 블록도를 도시한다.11 shows a block diagram of a flow router according to an embodiment of the invention.
본 발명의 일 실시예에 따른 플로우 라우터는 액세스 라우터, 제 1 경계 라우터, 제 2 경계 라우터, 또는 크로스오버 라우터로서, 각 라우터는 공통적으로 해싱모듈(310), 라우팅모듈(320), 및 서비스 제어모듈(330)을 포함하되, 크로스오버 라우터 및 경계 라우터(제 1 경계 라우터 및 제 2 경계 라우터를 포함함)의 경우 핸드오버 제어모듈(340)을 더 포함할 수 있다.The flow router according to an embodiment of the present invention is an access router, a first border router, a second border router, or a crossover router, and each router commonly includes a
먼저, 해싱모듈(310)은 수신한 플로우가 속하는 플로우 등급을 검색한다. 플로우 등급에 관하여는 도 4와 관련하여 상술한 바 생략한다.First, the
이어서, 라우팅모듈(320)은 플로우의 전달 경로를 설정하는 모듈로서, 서비스 제어모듈의 신호에 따라 플로우 등급에 기반하여 플로우의 전송 경로를 설정한다. 본 실시예에 따른 라우팅모듈(320)은 일반적인 라우팅모듈과 동일하되, 서비스 제어모듈(330) 및 핸드오버 제어모듈(340)의 제어에 기반하여 플로우 전송 경로를 설정한다는 점에 차이가 있다.Next, the
이어서, 서비스 제어모듈(330)은 플로우 등급에 따른 경로 변경을 라우팅모듈에 알린다. 플로우 등급과 관련해서는 마찬가지로 도 4과 관련하여 상술한 바 생략한다. 플로우는 서비스 제어모듈(330)에 의해 도 4와 같이 제 1 등급, 제 2 등급, 제 3 등급, 및 제 4 등급으로 분류될 수 있다.Then, the
마지막으로, 플로우 라우터 중 크로스오버 라우터, 및 경계 라우터(제 1 경계 라우터 또는 제 2 경계 라우터)는 핸드오버 제어모듈(340)을 더 포함할 수 있는데, 사용자 단말의 핸드오버를 처리하고 핸드오버에 따른 경로변경을 라우팅모듈에 전달한다. 핸드오버를 처리하는 과정과 관련해서는 도 7 내지 도 11와 관련하여 상술한 바와 동일하나, 핸드오버를 처리하는 주체가 크로스오버 라우터의 "핸드오버 제어모듈(340)"이라는 점에 차이가 있다. 상술한 바와 같이, 핸드오버 제어모듈(340)은 플로우 라우터가 제 2 액세스 라우터로부터 전송된 바인딩 메시지를 수신하면 제 2 액세스 라우터로 상기 사용자 단말의 플로우 전송 경로를 변경한다.Finally, the crossover router and the border router (first border router or second border router) among the flow routers may further include a
다만, 제 2 내지 제 4 등급의 경우, 핸드오버 제어모듈(340)은 제 1 액세스 라우터로부터 전송되는 핸드오버 준비 메시지를 크로스오버 라우터가 수신하면, 사용자 단말에 서비스 중인 플로우의 등급에 따라, 사용자 단말로 전송되는 데이터를 크로스오버 라우터가 버퍼링하도록 하거나(제 2 등급), 사용자 단말과 접속 가능한 라우터에 사용자 단말의 엔트리를 미리 생성하도록 지시하거나(제 3 등급), 사용자에게 전송될 데이터를 사용자 단말과 접속 가능한 라우터로 전송하도록 지시한다(제 4 등급). 더욱 상세한 설명은 도 7 내지 도 11와 관련하여 상술한 바와 동일한 바 생략한다.However, in the case of the second through fourth classes, when the crossover router receives the handover preparation message transmitted from the first access router, the
참고로, 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 도 1, 도 6, 및 도 11에 도시된 시스템의 구성 요소들은 소프트웨어 또는 FPGA(Field Programmable Gate Array) 또는 ASIC(Application Specific Integrated Circuit)와 같은 하드웨어 구성 요소를 의미하며, 소정의 역할들을 수행한다.1, 6, and 11 according to an embodiment of the present invention may include hardware components such as software or an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) or ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) And performs certain roles.
그렇지만 '구성 요소들'은 소프트웨어 또는 하드웨어에 한정되는 의미는 아니며, 각 구성 요소는 어드레싱할 수 있는 저장 매체에 있도록 구성될 수도 있고 하나 또는 그 이상의 프로세서들을 재생시키도록 구성될 수도 있다.However, 'components' are not meant to be limited to software or hardware, and each component may be configured to reside on an addressable storage medium and configured to play one or more processors.
따라서, 일 예로서 구성 요소는 소프트웨어 구성 요소들, 객체지향 소프트웨어 구성 요소들, 클래스 구성 요소들 및 태스크 구성 요소들과 같은 구성 요소들과, 프로세스들, 함수들, 속성들, 프로시저들, 서브루틴들, 프로그램 코드의 세그먼트들, 드라이버들, 펌웨어, 마이크로 코드, 회로, 데이터, 데이터베이스, 데이터 구조들, 테이블들, 어레이들 및 변수들을 포함한다.Thus, by way of example, an element may comprise components such as software components, object-oriented software components, class components and task components, processes, functions, attributes, procedures, Routines, segments of program code, drivers, firmware, microcode, circuitry, data, databases, data structures, tables, arrays, and variables.
구성 요소들과 해당 구성 요소들 안에서 제공되는 기능은 더 작은 수의 구성 요소들로 결합되거나 추가적인 구성 요소들로 더 분리될 수 있다.The components and functions provided within those components may be combined into a smaller number of components or further separated into additional components.
본 발명의 방법 및 장치는 특정 실시예와 관련하여 설명되었지만, 그것들의 구성 요소 또는 동작의 일부 또는 전부는 범용 하드웨어 아키텍쳐를 갖는 컴퓨터 시스템을 사용하여 구현될 수 있다.While the methods and apparatus of the present invention have been described with reference to particular embodiments, some or all of those elements or operations may be implemented using a computer system having a general purpose hardware architecture.
전술한 본 발명의 설명은 예시를 위한 것이며, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야의 통상의 지식을 가진 자는 본 발명의 기술적 사상이나 필수적인 특징을 변경하지 않고서 다른 구체적인 형태로 쉽게 변형이 가능하다는 것을 이해할 수 있을 것이다. 그러므로 이상에서 기술한 실시예들은 모든 면에서 예시적인 것이며 한정적이 아닌 것으로 이해해야만 한다. 예를 들어, 단일형으로 설명되어 있는 각 구성 요소는 분산되어 실시될 수도 있으며, 마찬가지로 분산된 것으로 설명되어 있는 구성 요소들도 결합된 형태로 실시될 수 있다.It will be understood by those skilled in the art that the foregoing description of the present invention is for illustrative purposes only and that those of ordinary skill in the art can readily understand that various changes and modifications may be made without departing from the spirit or essential characteristics of the present invention. will be. It is therefore to be understood that the above-described embodiments are illustrative in all aspects and not restrictive. For example, each component described as a single entity may be distributed and implemented, and components described as being distributed may also be implemented in a combined form.
본 발명의 범위는 상기 상세한 설명보다는 후술하는 특허청구범위에 의하여 나타내어지며, 특허청구범위의 의미 및 범위 그리고 그 균등 개념으로부터 도출되는 모든 변경 또는 변형된 형태가 본 발명의 범위에 포함되는 것으로 해석되어야 한다.The scope of the present invention is defined by the appended claims rather than the detailed description and all changes or modifications derived from the meaning and scope of the claims and their equivalents are to be construed as being included within the scope of the present invention do.
110: 액세스 라우터
115: 액세스 네트워크
120: 제 1 경계 라우터
125: 중간 네트워크
130: 제 2 경계 네트워크
135: 코어 네트워크110: Access router
115: Access network
120: first border router
125: Intermediate network
130: second boundary network
135: Core Network
Claims (20)
Translated fromKorean사용자 단말 또는 다른 플로우 라우터로부터 플로우를 수신하는 단계;
상기 플로우를 소정의 플로우 등급에 따라 분류하되, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감한지 여부와 손실률에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감한지 여부에 따라 분류하는 단계; 및
상기 분류된 플로우를 상기 사용자 단말 또는 상기 다른 플로우 라우터로 전송하는 단계를 포함하되,
상기 수신된 플로우는
상기 사용자 단말의 이동으로 인해 발생되는 것인, 플로우 제어방법.In a method for a flow router to control a flow,
Receiving a flow from a user terminal or another flow router;
Classifying the flow according to a predetermined flow class, classifying the flow according to whether it is sensitive to less than a threshold value for a time delay and whether it is less than a threshold value for a loss rate; And
And transmitting the classified flow to the user terminal or the other flow router,
The received flow
And wherein the user terminal is caused by movement of the user terminal.
상기 플로우 라우터는,
상기 사용자 단말 및 액세스 네트워크와 접속하는 액세스 라우터이거나,
상기 액세스 네트워크 및 중간 네트워크와 접속하는 제 1 경계 라우터이거나, 또는
상기 중간 네트워크 및 코어 네트워크와 접속하는 제 2 경계 라우터이되,
상기 액세스 라우터, 상기 제 1 경계 라우터, 및 상기 제 2 경계 라우터는,
수신한 플로우를 각자 독립적으로 상기 플로우 등급에 따라 분류하는 플로우 제어방법.The method according to claim 1,
The flow router includes:
An access router connected to the user terminal and the access network,
A first border router connecting to the access network and the intermediate network, or
A second border router connected to the intermediate network and the core network,
The access router, the first border router, and the second border router,
And classifying the received flows independently according to the flow class.
상기 플로우를 소정의 플로우 등급으로 분류하는 단계에서,
상기 플로우는 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감한 제 1 등급, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감한 제 2 등급, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감한 제 3 등급, 및 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감한 제 4 등급으로 분류되는 플로우 제어방법.The method according to claim 1,
In the step of classifying the flow into a predetermined flow class,
Said flow being sensitive to less than a threshold value for a time delay and being sensitive to less than a threshold value for a loss rate, a second rate sensitive for less than a threshold value for a time delay and more than a threshold value for a loss rate, A third class sensitive to a delay greater than a threshold value and sensitive to less than a threshold value for a loss rate and a flow control classed as a fourth class sensitive to a delay greater than a threshold value for a time delay, Way.
상기 액세스 라우터, 상기 제 1 경계 라우터, 및 상기 제 2 경계 라우터는,
네트워크 계층별로 상기 코어 네트워크와 가까운 라우터일수록 상기 수신한 플로우를 집적화시키는 플로우 제어방법.3. The method of claim 2,
The access router, the first border router, and the second border router,
And integrating the received flows in a router closer to the core network in each network layer.
상기 액세스 라우터, 상기 제 1 경계 라우터, 및 상기 제 2 경계 라우터는,
각 라우터 마다 독립적으로 분류된 플로우를 연결하여 하나의 전송 경로를 형성하는 플로우 제어방법.The method according to claim 2 or 4,
The access router, the first border router, and the second border router,
A flow control method for forming a single transmission path by connecting independently classified flows to each router.
상기 액세스 라우터, 상기 제 1 경계 라우터, 및 상기 제 2 경계 라우터는,
각자 독립적으로 상기 수신한 플로우의 플로우 헤더 필드를 조합하고, 조합한 플로우 헤더 필드를 상호 공유하는 플로우 제어방법.3. The method of claim 2,
The access router, the first border router, and the second border router,
And combining the flow header fields of the received flows independently and sharing the combined flow header fields with each other.
상기 액세스 라우터, 상기 제 1 경계 라우터, 및 상기 제 2 경계 라우터는,
각자 계층 내에서 독립적으로 플로우에 요구되는 서비스 품질에 따라 플로우 헤더 필드를 조합하고, 공유하는 플로우 제어방법.The method according to claim 6,
The access router, the first border router, and the second border router,
A flow control method for combining and sharing flow header fields according to service quality required for a flow independently in each layer.
사용자 단말이 제 1 액세스 라우터로부터 제 2 액세스라우터로 핸드오버 되는 경우, 상기 사용자 단말에 서비스 중인 플로우의 등급에 따라 상기 제 1 액세스 라우터로부터 전송되는 핸드오버 준비 메시지를 상기 크로스오버 라우터가 가로채는 단계; 및
상기 사용자 단말에 서비스 중인 플로우의 등급에 따라, 상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 플로우의 전송경로를 설정하는 단계를 포함하는 전송 경로 제어방법.A method for controlling a flow transmission path when a crossover router generates a handover,
When the user terminal is handed over from the first access router to the second access router, interrupting the handover preparation message transmitted from the first access router according to the class of the service flow to the user terminal; And
Wherein the crossover router sets the transmission path of the flow according to the class of the service being served to the user terminal.
상기 전송경로를 설정하는 단계는,
상기 사용자 단말에 서비스 중인 플로우의 등급에 따라, 상기 사용자 단말로 전송되는 플로우를 버퍼링하거나, 상기 사용자 단말과 접속 가능한 라우터에 상기 사용자 단말의 엔트리를 미리 생성하도록 지시하거나, 상기 사용자에게 전송될 플로우를 상기 사용자 단말과 접속 가능한 라우터로 전송하는 단계;
상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 제 2 액세스 라우터로부터 전송된 바인딩 메시지를 수신하는 단계; 및
상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 제 2 액세스라우터로 상기 사용자 단말의 플로우 전송 경로를 변경하는 단계를 포함하는 전송 경로 제어방법.9. The method of claim 8,
Wherein the setting of the transmission path comprises:
Wherein the control unit instructs the user terminal to buffer the flow to be transmitted to the user terminal according to the class of the flow being serviced or to generate an entry of the user terminal in advance in a router connectable with the user terminal, To a router connectable to the user terminal;
The crossover router receiving a binding message transmitted from the second access router; And
And the crossover router changes the flow transmission path of the user terminal to the second access router.
상기 제 1 액세스 라우터, 상기 제 2 액세스 라우터, 및 상기 크로스오버 라우터는 상기 플로우를 각자 독립적으로 일정한 플로우 등급에 따라 분류하되,
상기 플로우는,
시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감한 제 1 등급, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감한 제 2 등급, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감한 제 3 등급, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감한 제 4 등급으로 분류되는 전송 경로 제어방법.9. The method of claim 8,
Wherein the first access router, the second access router, and the crossover router sort the flows according to a flow rate independently of each other,
The above-
A first class that is sensitive to less than a threshold value for a time delay and is less sensitive than a threshold value for a loss rate, a second class that is sensitive to less than a threshold value for a time delay and more than a threshold value for a loss rate, A third class that is sensitive to more than a threshold value and is sensitive to a loss rate less than a threshold value; and a fourth class that is sensitive to a loss rate by more than a threshold value.
상기 제 1 등급에 해당하는 플로우가 전송되는 경우,
상기 전송경로를 설정하는 단계는,
상기 사용자 단말이 핸드오버 트리거 메시지를 상기 제 1 액세스 라우터에 전송하면, 상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 제 2 액세스 라우터로부터 전송된 바인딩 메시지를 수신하는 단계; 및
상기 크로스오버 라우터가 제 2 액세스 라우터로 상기 플로우의 전송 경로를 변경하는 단계를 포함하는 전송 경로 제어방법.11. The method of claim 10,
When a flow corresponding to the first rank is transmitted,
Wherein the setting of the transmission path comprises:
Receiving, by the crossover router, a binding message transmitted from the second access router when the user terminal transmits a handover trigger message to the first access router; And
And the crossover router changes the transmission path of the flow to the second access router.
상기 제 2 등급에 해당하는 플로우가 전송되는 경우,
상기 전송경로를 설정하는 단계는,
상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 플로우를 버퍼링하는 단계;
상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 제 2 액세스 라우터로부터 전송된 바인딩 메시지를 수신하는 단계; 및
상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 제 2 액세스라우터로 상기 사용자 단말의 플로우 전송 경로를 변경하는 단계를 포함하는 전송 경로 제어방법.11. The method of claim 10,
When the flow corresponding to the second rank is transmitted,
Wherein the setting of the transmission path comprises:
Buffering the flow by the crossover router;
The crossover router receiving a binding message transmitted from the second access router; And
And the crossover router changes the flow transmission path of the user terminal to the second access router.
상기 제 3 등급에 해당하는 플로우가 전송되는 경우,
상기 전송경로를 설정하는 단계는,
상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 사용자 단말이 접속 가능한 하나 이상의 액세스 라우터에게 플로우의 엔트리를 생성하도록 하는 단계;
상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 제 2 액세스 라우터로부터 전송된 바인딩 메시지를 수신하는 단계; 및
상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 제 2 액세스라우터로 상기 사용자 단말의 플로우 전송 경로를 변경하는 단계를 포함하는 전송 경로 제어방법.11. The method of claim 10,
When a flow corresponding to the third rank is transmitted,
Wherein the setting of the transmission path comprises:
Causing the crossover router to generate an entry of a flow to one or more access routers to which the user terminal is connectable;
The crossover router receiving a binding message transmitted from the second access router; And
And the crossover router changes the flow transmission path of the user terminal to the second access router.
상기 제 4 등급에 해당하는 플로우가 전송되는 경우,
상기 전송경로를 설정하는 단계는,
상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 사용자 단말이 접속 가능한 하나 이상의 액세스 라우터에게 플로우의 엔트리를 생성하도록 하고, 전송할 플로우를 미리 상기 사용자 단말이 접속 가능한 하나 이상의 라우터에 전송하도록 하는 단계;
상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 제 2 액세스 라우터로부터 전송된 바인딩 메시지를 수신하는 단계; 및
상기 크로스오버 라우터가 상기 제 2 액세스라우터로 상기 사용자 단말의 플로우 전송 경로를 변경하는 단계를 포함하는 전송 경로 제어방법.11. The method of claim 10,
When the flow corresponding to the fourth rank is transmitted,
Wherein the setting of the transmission path comprises:
Causing the crossover router to generate an entry of a flow to one or more access routers to which the user terminal is connectable and causing the flow to be transmitted to be forwarded to one or more routers to which the user terminal is connectable in advance;
The crossover router receiving a binding message transmitted from the second access router; And
And the crossover router changes the flow transmission path of the user terminal to the second access router.
수신된 플로우가 속하는 플로우 등급을 검색하되, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감한지 여부와 손실률에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감한지 여부에 따라 검색하는 해싱모듈;
상기 플로우의 전달 경로를 설정하는 라우팅 모듈; 및
상기 플로우 등급에 따른 상기 전달 경로를 변경하는 서비스 제어모듈을 포함하되,
상기 플로우는,
사용자 단말의 이동으로 인해 발생되는 것인, 플로우 라우터.In a flow router,
A hashing module for searching for a flow class to which the received flow belongs and searching for whether the received flow is sensitive to less than a threshold value for a time delay and whether it is less than a threshold value for a loss rate;
A routing module for setting a delivery path of the flow; And
And a service control module for changing the delivery path according to the flow class,
The above-
Lt; RTI ID = 0.0 > user terminal. ≪ / RTI >
상기 플로우 라우터는,
네트워크 계층별로 코어 네트워크와 가까운 라우터일수록 상기 수신한 플로우를 집적화시키는 플로우 라우터.16. The method of claim 15,
The flow router includes:
And a flow router for integrating the received flows as a router closer to the core network for each network layer.
상기 플로우 라우터는,
사용자 단말 및 액세스 네트워크와 접속하는 액세스 라우터이거나,
상기 액세스 네트워크 및 중간 네트워크와 접속하는 경계 라우터이거나, 또는
상기 경계 라우터 대신 상기 사용자 단말의 핸드오버를 제어하는 크로스오버 라우터인 플로우 라우터.16. The method of claim 15,
The flow router includes:
An access router connecting with a user terminal and an access network,
A border router connecting to the access network and the intermediate network, or
And a crossover router that controls handover of the user terminal instead of the border router.
상기 서비스 제어모듈은,
상기 플로우를 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감한 제 1 등급, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감한 제 2 등급, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감하고, 손실률에 대하여 임계값 미만으로 민감한 제 3 등급, 시간 지연에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감하고, 및 손실률에 대하여 임계값 이상으로 민감한 제 4 등급으로 분류하는 플로우 라우터.18. The method according to claim 15 or 17,
The service control module includes:
A first class sensitive to less than a threshold value for time delay and sensitive to less than a threshold value for a loss rate, a second class sensitive for less than a threshold value for a time delay and more than a threshold value for a loss rate, A third class sensitive to a delay greater than a threshold and sensitive to less than a threshold for a loss rate, a flow classifier classifying a fourth class that is more sensitive than a threshold value for a time delay and more sensitive than a threshold value for a loss rate .
상기 사용자 단말의 핸드오버를 처리하고 핸드오버에 따른 플로우의 전달 경로를 변경하는 핸드오버 제어모듈을 더 포함하되,
상기 사용자 단말이 제 1 액세스 라우터로부터 제 2 액세스 라우터로 핸드오버 되는 경우,
상기 핸드오버 제어모듈은,
상기 플로우 라우터가 상기 제 2 액세스 라우터로부터 전송된 바인딩 메시지를 수신하면 상기 제 2 액세스 라우터로 상기 사용자 단말의 플로우 전송 경로를 변경하는 플로우 라우터.18. The method of claim 17,
Further comprising: a handover control module that handles the handover of the user terminal and changes the delivery path of the handover-related flow,
When the user terminal is handed over from the first access router to the second access router,
Wherein the handover control module comprises:
And when the flow router receives the binding message transmitted from the second access router, changes the flow transmission path of the user terminal to the second access router.
상기 핸드오버 제어모듈은,
상기 사용자 단말에 서비스 중인 플로우의 등급에 따라 상기 제 1 액세스 라우터로부터 전송되는 핸드오버 준비 메시지를 상기 크로스오버 라우터가 수신하면, 상기 사용자 단말에 서비스 중인 플로우의 등급에 따라, 상기 사용자 단말로 전송되는 데이터를 상기 크로스오버 라우터가 버퍼링하도록 하거나, 상기 사용자 단말과 접속 가능한 라우터에 상기 사용자 단말의 엔트리를 미리 생성하도록 지시하거나, 상기 사용자에게 전송될 데이터를 상기 사용자 단말과 접속 가능한 라우터로 전송하도록 지시하는 플로우 라우터.20. The method of claim 19,
Wherein the handover control module comprises:
When the crossover router receives a handover preparation message transmitted from the first access router according to the class of the service flow in the user terminal, the crossover router transmits the handover preparation message to the user terminal according to the class of the flow being serviced to the user terminal Instructs the crossover router to buffer data or to generate an entry of the user terminal in advance in a router connectable with the user terminal or instructs the user to transmit data to be transmitted to the user to a router connectable with the user terminal Flow router.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020130128945AKR101515581B1 (en) | 2013-10-29 | 2013-10-29 | Method for controling flow of mobile traffic |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020130128945AKR101515581B1 (en) | 2013-10-29 | 2013-10-29 | Method for controling flow of mobile traffic |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR101515581B1true KR101515581B1 (en) | 2015-05-04 |
Family
ID=53393270
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020130128945AActiveKR101515581B1 (en) | 2013-10-29 | 2013-10-29 | Method for controling flow of mobile traffic |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101515581B1 (en) |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20030089747A (en)* | 2002-05-18 | 2003-11-28 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Router providing differentiated quality-of-service and fast internet protocol packet classification method for the same |
| KR20040027175A (en)* | 2002-09-27 | 2004-04-01 | 주식회사 케이티 | Traffic processing method on a edge router in TCP/IP network |
| KR20050037933A (en)* | 2003-10-20 | 2005-04-25 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method for searching crossover router and reservating resource in the mobile network, and resorce reservation system thereof |
- 2013
- 2013-10-29KRKR1020130128945Apatent/KR101515581B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20030089747A (en)* | 2002-05-18 | 2003-11-28 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Router providing differentiated quality-of-service and fast internet protocol packet classification method for the same |
| KR20040027175A (en)* | 2002-09-27 | 2004-04-01 | 주식회사 케이티 | Traffic processing method on a edge router in TCP/IP network |
| KR20050037933A (en)* | 2003-10-20 | 2005-04-25 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method for searching crossover router and reservating resource in the mobile network, and resorce reservation system thereof |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6561204B2 (en) | Dual connectivity and carrier aggregation in IP layer | |
| US12381818B2 (en) | Data routing in communications systems | |
| KR102087226B1 (en) | Method for sharing network based on software defined network to support multiple operator | |
| US8811329B2 (en) | System and method for mobility with a split home agent architecture using MPTCP | |
| US7245917B2 (en) | System and method for IP handoff | |
| US20160119165A1 (en) | Methods and systems to manage network connections | |
| US20090168701A1 (en) | Multi-access terminal with capability for simultaneous connectivity to multiple communication channels | |
| JP2014531859A (en) | Self-adjusting mobile platform policy enforcement agent to control network access, mobility, efficient use of local resources and network resources | |
| US9713077B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for distributing handoff control in wireless networks via programmable black and white lists | |
| US20250176056A1 (en) | Configuration and Reporting for Deterministic Networks | |
| US20250267023A1 (en) | Deterministic Networks | |
| Nagaraj et al. | Procel: Smart traffic handling for a scalable software epc | |
| US20240291752A1 (en) | Application-Aware BGP Path Selection And Forwarding | |
| US10939331B2 (en) | Information centric network heterogenous wireless switching | |
| CN110839261A (en) | Data transmission method and device | |
| US20150072701A1 (en) | Wireless system control device and control method | |
| Yap et al. | Software-defined networking techniques to improve mobile network connectivity: technical review | |
| KR101515581B1 (en) | Method for controling flow of mobile traffic | |
| I. Meneguette et al. | Vehicle-to-infrastructure communication | |
| De Schepper et al. | ORCHESTRA: Supercharging wireless backhaul networks through multi-technology management | |
| GB2539677A (en) | Multi-path telecommunications networks | |
| Lee et al. | Host-based distributed mobility management: Example of traffic offloading | |
| US20220334861A1 (en) | Self-assembly and self-optimization of virtual network functions | |
| Lee et al. | An enhanced buffer management for handover in WiMedia WLP-based mobile IP networks | |
| Battulga et al. | Handover with buffering for distributed mobility management in software defined mobile networks |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20131029 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20140925 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20150410 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20150421 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20150422 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20180406 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20180406 Start annual number:4 End annual number:4 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20190411 Year of fee payment:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20190411 Start annual number:5 End annual number:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20200401 Start annual number:6 End annual number:6 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20210412 Start annual number:7 End annual number:7 |