KR101460048B1 - Method and apparatus for control of dynamic service chaining by using tagging - Google Patents
Method and apparatus for control of dynamic service chaining by using taggingDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101460048B1 KR101460048B1KR20130127146AKR20130127146AKR101460048B1KR 101460048 B1KR101460048 B1KR 101460048B1KR 20130127146 AKR20130127146 AKR 20130127146AKR 20130127146 AKR20130127146 AKR 20130127146AKR 101460048 B1KR101460048 B1KR 101460048B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- sdn
- service
- traffic
- tagging
- service chaining
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L49/00—Packet switching elements
- H04L49/25—Routing or path finding in a switch fabric
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L45/00—Routing or path finding of packets in data switching networks
- H04L45/12—Shortest path evaluation
- H04L45/122—Shortest path evaluation by minimising distances, e.g. by selecting a route with minimum of number of hops
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L49/00—Packet switching elements
- H04L49/30—Peripheral units, e.g. input or output ports
- H04L49/3009—Header conversion, routing tables or routing tags
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 태깅(tagging)을 이용한 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝(dynamic service chaining) 제어 방법 및 장치에 관한 것으로, 더욱 상세하게는 SDN(Software-Defined Networking) 기반의 태깅을 이용하는 서비스 체이닝 제어 방법 및 장치에 관한 것이다.BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates to a dynamic service chaining control method and apparatus using tagging, and more particularly, to a service chaining control method and apparatus using tagging based on SDN (Software-Defined Networking) .
주지하는 바와 같이, 이동통신 서비스 분야에서 모바일 부가가치 서비스는 차세대 네트워크의 수익화를 위한 기회의 장으로 여겨지고 있으며, 이러한 모바일 부가가치 서비스는 서비스 체이닝을 통하여 제공될 수 있다.As will be appreciated, mobile value added services in the field of mobile communication services are considered as opportunities for profitability of next generation networks, and such mobile value added services can be provided through service chaining.
이처럼, 이동통신 서비스 분야에서 서비스 체이닝을 통해 제공되는 모바일 부가가치 서비스들로는 모바일 비디오 최적화, WAN(Wide Area Network) 가속, 웹 최적화, 시큐리티(security), 방화벽 등의 서비스들이 있다. 그러므로, 이동통신 서비스 분야에서의 서비스 체이닝은 고객 경험 향상과 망 최적화를 위하여 코어 네트워크에서 제공하는 각종 서비스들의 조합을 의미한다고 할 수 있다.Mobile services such as mobile video optimization, WAN (Wide Area Network) acceleration, web optimization, security, and firewall are services that are provided through service chaining in the mobile communication service field. Therefore, service chaining in the field of mobile communication service can be said to mean a combination of various services provided by the core network for improving the customer experience and network optimization.
한편, 종래 기술에 따른 이동통신 서비스 분야의 서비스 체이닝은 가입자 정보와 트래픽 유형에 따라 수동적(statically) 또는 정적(manually)으로 설정되고 있었다.On the other hand, service chaining in the field of mobile communication service according to the related art has been set to be statically or manually manually according to subscriber information and traffic type.
따라서, 서비스의 형태가 다양해지고 서비스간의 조합의 수가 증대함에 따라 서비스 체이닝을 관리하거나 변경 또는 확장하는 데에 있어서 어려움이 따르는 문제점이 있었다.Accordingly, there has been a problem in that it is difficult to manage, change, or expand service chaining as the types of services are varied and the number of combinations of services increases.
본 발명은 전술한 바와 같은 종래 기술의 문제점을 해결하기 위해 제안한 것으로서, 서비스 체이닝에 SDN을 적용하여 리디자인(re-design)을 함으로써 가입자별, 트래픽 유형별 또는 망 상황별 자동 설정이나 다이나믹한 설정이 가능하도록 한다. 여기서, SDN은 하드웨어에 의존하던 네트워크 체계에서 속도, 안정성, 에너지 효율, 보안 등을 소프트웨어적으로 개선하기 위해 개발된 기술로 오픈 플로우(open flow)라는 개념을 바탕으로 하며, 오픈 플로우는 네트워크 스위치의 패킷 포워딩 기능과 제어 기능을 분리하여 두 기능 간의 통신을 위한 프로토콜을 제공하는 기술이다.The present invention has been proposed in order to solve the problems of the related art as described above, and it is possible to perform automatic setting or dynamic setting according to subscriber, traffic type or network situation by applying SDN to service chaining and re- . Here, SDN is a technology developed to improve software, such as speed, stability, energy efficiency, and security, in a network system dependent on hardware. It is based on the concept of open flow. It is a technology that provides protocol for communication between two functions by separating packet forwarding function and control function.
이를 위한 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 스위칭 동작에 따라 변화하는 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝(dynamic service chaining)을 제공하는 복수의 SDN 스위치에 인입되는 트래픽을 분류하여 서비스 노드들로 전달하기 위한 라우팅 규칙을 제공하는 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 방법 및 장치를 제공한다.According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a routing rule for classifying traffic that is introduced into a plurality of SDN switches providing dynamic service chaining that changes according to a switching operation, A dynamic service chaining control method and apparatus are provided.
본 발명의 해결하고자 하는 과제는 이상에서 언급한 것으로 제한되지 않으며, 언급되지 않은 또 다른 해결하고자 하는 과제는 아래의 기재로부터 본 발명이 속하는 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 명확하게 이해될 수 있을 것이다.The problems to be solved by the present invention are not limited to those mentioned above, and another problem to be solved can be clearly understood by those skilled in the art from the following description.
본 발명의 일 관점에 따른 태깅을 이용한 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 방법은, 스위칭 동작에 따라 변화하는 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝을 제공하는 복수의 SDN 스위치 중에서 어느 하나로 인입되는 트래픽에 제공할 서비스 목록을 도출하는 단계와, 도출된 상기 서비스 목록에 따른 서비스를 제공할 수 있는 홉 바이 홉(hop by hop) 라우팅 경로를 위한 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 설정하는 단계와, 상기 서비스 목록이 도출된 트래픽에 식별정보를 태깅하기 위한 태깅 규칙을 상기 복수의 SDN 스위치 중에서 상기 트래픽이 인입되는 SDN 스위치에게 제공하는 단계와, 상기 식별정보가 태깅된 트래픽의 라우팅 처리를 위한 상기 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 상기 복수의 SDN 스위치에게 제공하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a dynamic service chaining control method using tagging, comprising the steps of: deriving a service list to be provided to traffic that is introduced into any one of a plurality of SDN switches providing dynamic service chaining that changes according to a switching operation; Setting an SDN routing rule for a hop-by-hop routing path capable of providing a service according to the derived service list; setting a tagging rule for tagging the identification information in the traffic derived from the service list; To the SDN switch from which the traffic is received from among the plurality of SDN switches; and providing the SDN routing rules for the routing processing of the tagged traffic to the plurality of SDN switches have.
본 발명의 다른 관점에 따른 태깅을 이용한 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치는, 스위칭 동작에 따라 변화하는 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝을 제공하는 복수의 SDN 스위치 중에서 어느 하나로 인입되는 트래픽에 제공할 서비스 목록을 도출하며, 도출된 상기 서비스 목록에 따른 서비스를 제공할 수 있는 홉 바이 홉 라우팅 경로를 위한 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 설정하는 서비스 체이닝 처리부와, 상기 서비스 목록이 도출된 트래픽에 식별정보를 태깅하기 위한 태깅 규칙을 상기 복수의 SDN 스위치 중에서 상기 트래픽이 인입되는 SDN 스위치에게 제공하며, 상기 식별정보가 태깅된 트래픽의 라우팅 처리를 위한 상기 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 상기 복수의 SDN 스위치에게 제공하는 SDN 제어부를 포함할 수 있다.The dynamic service chaining control apparatus using tagging according to another aspect of the present invention derives a service list to be provided to traffic that is introduced into any one of a plurality of SDN switches providing dynamic service chaining varying according to a switching operation, A service chaining processor configured to set an SDN routing rule for a hop-by-hop routing path capable of providing a service according to the service list; and a tagging rule for tagging identification information in traffic derived from the service list, And an SDN control unit for providing the SDN routing rule to the SDN switch for providing the SDN routing rule for the routing processing of the tagged identification information.
본 발명의 실시예에 따르면, 스위칭 동작에 따라 변화하는 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝을 제공하는 복수의 SDN 스위치에 인입되는 트래픽을 분류하여 서비스 노드들로 전달하기 위한 라우팅 규칙을 제공할 수 있으며, 이러한 본 발명을 이동통신 서비스 분야의 서비스 체이닝에 적용하면 가입자별, 트래픽 유형별 또는 망 상황별(망 혼잡 상황 등) 자동 설정이나 다이나믹한 설정이 가능하도록 한다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to provide a routing rule for classifying traffic that is introduced into a plurality of SDN switches providing dynamic service chaining varying according to a switching operation and delivering the traffic to service nodes. When applied to service chaining in the field of mobile communication service, automatic setting or dynamic setting for each subscriber, traffic type, or network situation (network congestion situation, etc.) is enabled.
따라서, 트래픽 유형별로 데이터 오프로딩(offloading)이 가능하다. 예컨대, 비디오 최적화, 소프트웨어 업데이트, WAN 가속, 웹 최적화, 시큐리티, 방화벽 등의 여러 가지 서비스 중에서 특정 서비스가 불필요한 대용량 트래픽을 선별하고, 해당하는 서비스를 제공하는 서비스 노드를 바이패스(bypass)시켜서 자원을 절약할 수 있다.Therefore, data offloading is possible for each traffic type. For example, among various services such as video optimization, software update, WAN acceleration, web optimization, security, firewall, and the like, it is possible to select a large amount of unnecessary traffic, bypass the service node providing the corresponding service, You can save.
그리고, 트래픽 유형별로 시큐리티 서비스를 제공할 수 있다. 예컨대, 트래픽 검사(traffic inspection), 위협 방어(threat prevention), 로깅(logging) 등의 시큐리티 서비스를 모든 트래픽에 대해 항시 적용하는 것이 아닌 특정 조건 하에서 SDN을 이용해 인에이블(enable) 함으로써 비용 효율이 높으면서도 스케일러블(scalable)한 서비스를 구현할 수 있다.Then, the security service can be provided for each traffic type. For example, security services such as traffic inspection, threat prevention, logging, and the like are enabled by using SDN under certain conditions, not always for all traffic, A scalable service can be realized.
또, 컨텐츠 위치별 트래픽 스티어링(steering)이 가능하다. 예컨대, DPI(Deep Packet Inspection)를 통해 특정 컨텐츠에 대한 데이터 요청 지연 시간을 감시할 수 있으며, 지리적으로 멀리 떨어져 있어 지연 시간이 긴 컨텐츠를 요청하는 경우에 해당 플로우를 TIC(Transparent Internet Cache)를 통해 서빙(serving)함으로써 지연 시간을 단축할 수 있다.In addition, traffic steering by content location is possible. For example, it is possible to monitor a data request delay time for specific contents through DPI (Deep Packet Inspection). When requesting contents with a long delay time from geographically distant, the flow is transmitted through TIC (Transparent Internet Cache) The delay time can be shortened by serving.
아울러, 셀(cell)별 혼잡 여부를 DPI를 이용해 판단함으로써 망 혼잡 발생 시에 QoS(Quality of Service) 제어, 비디오 최적화 작업 등을 수행하도록 서비스 체인을 동적으로 설정할 수 있다.In addition, it is possible to dynamically set the service chain to perform Quality of Service (QoS) control and video optimization in case of network congestion by determining the congestion per cell using DPI.
또한, BYOD(Bring Your Own Device) 차등 네트워크 서비스를 제공할 수 있다. 예컨대, 비즈니스 클라우드 트래픽 등과 같은 엔터프라이즈 어플리케이션에 대해서는 무선 접속 우선권, 클라우드 가속, 시그널링 최적화, QoS 제어 등의 차별화된 품질의 네트워크 서비스를 제공할 수 있다.It can also provide Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) differential network services. For example, enterprise applications such as business cloud traffic can provide differentiated quality network services such as wireless access priority, cloud acceleration, signaling optimization, and QoS control.
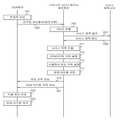
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치를 포함하는 SDN 기반 서비스 체이닝 네트워크의 구성도이다.
도 2는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치를 포함하는 SDN 기반 서비스 체이닝 네트워크에 의한 트래픽 라우팅 처리 과정을 설명하기 위한 흐름도이다.1 is a block diagram of an SDN-based service chaining network including a dynamic service chaining control apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a flowchart illustrating a traffic routing process performed by an SDN-based service chaining network including a dynamic service chaining control apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명의 이점 및 특징, 그리고 그것들을 달성하는 방법은 첨부되는 도면과 함께 상세하게 후술되어 있는 실시예들을 참조하면 명확해질 것이다. 그러나 본 발명은 이하에서 개시되는 실시예들에 한정되는 것이 아니라 서로 다른 다양한 형태로 구현될 수 있으며, 단지 본 실시예들은 본 발명의 개시가 완전하도록 하고, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 발명의 범주를 완전하게 알려주기 위해 제공되는 것이며, 본 발명은 청구항의 범주에 의해 정의될 뿐이다.BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The advantages and features of the present invention and the manner of achieving them will become apparent with reference to the embodiments described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings. The present invention may, however, be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, and will fully convey the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art. To fully disclose the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art, and the invention is only defined by the scope of the claims.
본 발명의 실시예들을 설명함에 있어서 공지 기능 또는 구성에 대한 구체적인 설명이 본 발명의 요지를 불필요하게 흐릴 수 있다고 판단되는 경우에는 그 상세한 설명을 생략할 것이다. 그리고 후술되는 용어들은 본 발명의 실시예에서의 기능을 고려하여 정의된 용어들로서 이는 사용자, 운용자의 의도 또는 관례 등에 따라 달라질 수 있다. 그러므로 그 정의는 본 명세서 전반에 걸친 내용을 토대로 내려져야 할 것이다.In the following description of the present invention, a detailed description of known functions and configurations incorporated herein will be omitted when it may make the subject matter of the present invention rather unclear. The following terms are defined in consideration of the functions in the embodiments of the present invention, which may vary depending on the intention of the user, the intention or the custom of the operator. Therefore, the definition should be based on the contents throughout this specification.
이하, 첨부된 도면들을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예들에 대해 살펴보기로 한다.Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치를 포함하는 SDN 기반 서비스 체이닝 네트워크의 구성도이다.1 is a block diagram of an SDN-based service chaining network including a dynamic service chaining control apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention.
이에 나타낸 바와 같이 실시예에 따른 SDN 기반 서비스 체이닝 네트워크는, SDN 장치(10), 서비스 체이닝 장치(20), 서비스 정책 서버(30), 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치(100) 등을 포함한다.As shown, the SDN-based service chaining network according to the embodiment includes the
SDN 장치(10)는 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치(100)로부터 제공되는 태깅 규칙에 따라 인입 트래픽에 식별정보를 태깅하며, 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치(100)로부터 제공되는 SDN 라우팅 규칙에 따라 인입 트래픽을 라우팅 처리하여 서비스 체이닝 장치(20)의 서비스 노드로 전달한다. 이러한 SDN 장치(10)는 복수의 SDN 스위치(11, 12, 13)를 포함하며, 도 1에 예시한 SDN 스위치(11, 12, 13)의 개수는 예시에 불과하다.The
서비스 체이닝 장치(20)는 SDN 장치(10)에 의해 전달되는 트래픽에 대해 모바일 비디오 최적화, WAN 가속, 웹 최적화, 시큐리티, 방화벽 등과 같은 여러 가지의 부가가치 서비스를 제공한다. 이러한 서비스 체이닝 장치(20)는 각각 개별의 부가가치 서비스를 제공하는 서비스 노드인 복수의 서비스 장치(21, 22, 23)를 포함하며, 도 1에 예시된 서비스 장치(21, 22, 23)의 개수는 예시에 불과하다.The
서비스 정책 서버(30)는 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치(100)의 질의에 응답하여 서비스 정책을 회신한다. 예컨대, 서비스 정책 서버(30)는 PCRF(Policy and Charging Rules Function), DPI, OSS(Operation Support System) 등으로 구현될 수 있다. PCRF는 서비스 정책으로서 이동통신 서비스에 가입된 가입자의 정보를 제공할 수 있으며, DPI는 서비스 정책으로서 가입자의 사용 서비스 정보를 제공할 수 있고, OSS는 가입자 정책으로서 망 상황 정보를 제공할 수 있다.The
다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치(100)는 서비스 체이닝 처리부(110)와 SDN 제어부(120)를 포함하며, 서비스 체이닝 처리부(110)는 서비스 체이닝 응용프로그램 구동부(111)와 매핑 테이블 저장부(112)를 포함한다.The dynamic service
서비스 체이닝 처리부(110)는 스위칭 동작에 따라 변화하는 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝을 제공하는 복수의 SDN 스위치(11, 12, 13) 중에서 어느 하나로 인입되는 트래픽에 제공할 서비스 목록을 도출하며, 도출된 서비스 목록에 따른 서비스를 제공할 수 있는 홉 바이 홉(hop by hop) 라우팅 경로를 위한 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 설정한다.The service
이러한 서비스 체이닝 처리부(110)는 서비스 체이닝 응용프로그램을 구동하여 SDN 장치(10)에게 제공할 태깅 규칙과 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 설정하는 서비스 체이닝 응용프로그램 구동부(111)를 포함한다. 또, 트래픽에 의한 플로우와 태깅을 위한 식별정보의 매핑 테이블이 저장되는 매핑 테이블 저장부(112)를 포함한다.The
SDN 제어부(120)는 서비스 체이닝 처리부(110)에 의해 서비스 목록이 도출된 트래픽에 식별정보를 태깅하기 위한 태깅 규칙을 복수의 SDN 스위치(11, 12, 13) 중에서 트래픽이 인입되는 SDN 스위치에게 제공하며, 식별정보가 태깅된 트래픽의 라우팅 처리를 위한 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 복수의 SDN 스위치(11, 12, 13)에게 제공한다.The
도 2는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치를 포함하는 SDN 기반 서비스 체이닝 네트워크에 의한 트래픽 라우팅 처리 과정을 설명하기 위한 흐름도이다.2 is a flowchart illustrating a traffic routing process performed by an SDN-based service chaining network including a dynamic service chaining control apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention.
이에 나타낸 바와 같이 실시예에 따른 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 방법은, 스위칭 동작에 따라 변화하는 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝을 제공하는 복수의 SDN 스위치를 포함하는 SDN 장치에 의해 인입 트래픽의 라우팅 처리에 대한 질의가 발생하면 가입자를 판별한 후에 판별된 가입자에 대한 서비스 정책을 획득하는 단계(201 내지 209)를 포함한다.As shown in the figure, the dynamic service chaining control method according to an embodiment of the present invention is a method of controlling a dynamic service chaining control according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention when an inquiry about a routing process of an incoming traffic is made by an SDN device including a plurality of SDN switches that provide dynamic service chaining, And a
그리고, 획득된 서비스 정책에 의거하여 인입 트래픽에 제공할 서비스 목록을 도출하는 단계(211)를 더 포함한다.And deriving a
아울러, 도출된 서비스 목록에 따른 서비스를 제공할 수 있는 홉 바이 홉(hop by hop) 라우팅 경로를 위한 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 설정하는 단계(213)를 더 포함한다.The method further includes setting (213) an SDN routing rule for a hop-by-hop routing path capable of providing a service according to the derived service list.
또, 서비스 목록이 도출된 인입 트래픽에 식별정보를 태깅하기 위한 태깅 규칙을 설정하는 단계(215)를 더 포함한다.The method further includes setting (215) a tagging rule for tagging the identification information to the incoming traffic derived from the service list.
이어서, 트래픽에 의한 플로우와 태깅을 위한 식별정보, 태깅 규칙 및 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 매핑 테이블에 저장하는 단계(217)를 더 포함한다.Next, the method further includes a
또한, SDN 장치를 구성하는 복수의 SDN 스위치 중에서 트래픽이 인입되는 SDN 스위치에게 태깅 규칙을 전송하는 단계(219)를 더 포함한다.In addition, the method further includes a step (219) of transmitting a tagging rule to an SDN switch in which traffic is received among a plurality of SDN switches constituting the SDN apparatus.
아울러, SDN 장치를 구성하는 복수의 SDN 스위치들에게 태깅 규칙에 따라 식별정보가 태깅된 트래픽의 라우팅 처리를 위한 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 전송하는 단계(221)를 더 포함한다.The method further includes transmitting (221) an SDN routing rule for routing processing of the tagged identification information to a plurality of SDN switches constituting the SDN apparatus according to the tagging rule.
이러한 단계 201 내지 221을 통해 태깅 규칙 및 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 제공받은 SDN 장치는 인입 트래픽에 식별정보를 태깅(223)하며, 식별정보가 태깅된 인입 트래픽에 대해 SDN 라우팅 규칙에 따른 라우팅 처리(225)를 수행하여 서비스 체이닝 장치(20)에게 전달한다.The SDN apparatuses provided with the tagging rule and the SDN routing rule through the
이하, 도 1 및 도 2를 참조하여 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치를 포함하는 SDN 기반 서비스 체이닝 네트워크에 의한 트래픽 라우팅 처리 과정에 대해 더 자세히 살펴보기로 한다.Hereinafter, the traffic routing process by the SDN-based service chaining network including the dynamic service chaining control apparatus will be described in more detail with reference to FIG. 1 and FIG.
먼저, SDN 장치(10)를 구성하는 복수의 SDN 스위치(11, 12, 13) 중에서 어느 하나의 스위치로 트래픽이 인입(201)되면 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치(100)에게 라우팅 처리에 대한 질의 메시지를 전송(203)한다. 이때, 트래픽의 패킷이 질의 메시지에 포함되어 전송된다.First, when a traffic is input (201) to any one of a plurality of SDN switches (11, 12, 13) constituting the
이에, 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치(100)의 서비스 체이닝 응용프로그램 구동부(111)가 서비스 체이닝 응용프로그램을 구동하며, 서비스 체이닝 응용프로그램의 구동에 따라 서비스 체이닝 처리부(110)가 트래픽을 발생시킨 가입자를 판별(205)한 후에 서비스 정책 서버(30)에게 서비스 정책 질의 메시지를 송신(207)한다.Accordingly, the service chaining application
여기서, 서비스 정책 서버(30)는 서비스 정책 질의 메시지에 따라 해당 가입자에 대한 서비스 정책, 예컨대 이동통신 서비스에 가입된 가입자의 정보, 가입자의 사용 서비스 정보, 망 상황 정보 등을 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치(100)에게 회신(209)한다.In this case, the
그러면, 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치(100)의 서비스 체이닝 처리부(110)는 서비스 정책 서버(30)로부터 획득된 서비스 정책에 의거하여 인입 트래픽에 제공할 서비스 목록을 도출(211)한다. 예컨대, 모바일 비디오 최적화, WAN 가속, 웹 최적화, 시큐리티, 방화벽 등과 같은 여러 가지의 부가가치 서비스 중에서 현재의 인입 트래픽에 제공할 서비스들을 결정하는 것이다.The service
아울러, 서비스 체이닝 처리부(110)는 도출된 서비스 목록에 따른 서비스를 제공할 수 있는 홉 바이 홉(hop by hop) 라우팅 경로를 위한 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 설정(213)한다. 즉, 서비스 체이닝 장치(20)를 구성하는 서비스 노드들 중에서 단계 211에서 결정된 부가가치 서비스들을 제공하는 서비스 노드들에게 트래픽을 전달할 수 있는 홉 바이 홉 라우팅 경로를 파악하는 것이다.In addition, the
그리고, 서비스 체이닝 처리부(110)에 의해 서비스 목록이 도출된 인입 트래픽에 고유의 식별정보를 태깅하기 위한 태깅 규칙을 설정(215)한다.Then, a tagging rule for tagging identification information unique to the incoming traffic derived from the service list by the service
여기서, 매핑 테이블 저장부(112)에는 인입 트래픽에 의한 플로우와 태깅을 위한 식별정보, 태깅 규칙 및 SDN 라우팅 규칙이 매핑 테이블에 저장(217)된다. 이는 추후에 동일한 트래픽에 대해서는 단계 205 내지 215의 과정을 생략할 수 있도록 하기 위함이다.In the mapping
다음으로, SDN 제어부(120)는 SDN 장치(10)를 구성하는 복수의 SDN 스위치(11, 12, 13) 중에서 트래픽이 인입되는 SDN 스위치에게 태깅 규칙을 전송(219)하며, SDN 장치(10)를 구성하는 복수의 SDN 스위치(11, 12, 13)에게 태깅 규칙에 따라 식별정보가 태깅된 트래픽의 라우팅 처리를 위한 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 전송(221)한다.Next, the
이후, 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치(100)로부터 태깅 규칙 및 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 제공받은 SDN 장치(10)는 인입 트래픽에 식별정보를 태깅(223)한다. 즉 SDN 장치(10)를 구성하는 복수의 SDN 스위치(11, 12, 13) 중에서 트래픽이 인입되는 스위치가 해당 트래픽에게 고유의 식별정보를 태깅하여 구별되도록 하는 것이다. 예컨대, SDN 장치(10)는 특정 포트로 인입되는 트래픽이 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치(100)로부터 제공받은 태깅 규칙에 해당하는 경우(예를 들어, 요금제 X를 사용하고 금일 데이터 사용량이 Y인 가입자가 망 혼잡 상황에 포트 0번을 통해 비디오 트래픽을 인입한 경우)에 식별정보 'A'를 태깅할 수 있다.Thereafter, the
그러면, SDN 장치(10)를 구성하는 모든 SDN 스위치(11, 12, 13)는 단계 223에 의해 식별정보가 태깅된 트래픽을 분별할 수 있으며, 식별정보가 태깅된 트래픽에 대해서 단계 221을 통해 제공받은 SDN 라우팅 규칙에 따른 라우팅 처리를 수행(225)한다. 예컨대, 식별정보 'A' 태깅되어 있고 이전 홉이 '널(null)'인 경우에 '비디오 최적화'인 서비스를 제공하는 서비스 노드로 트래픽이 전달되도록 라우팅 처리할 수 있다. 그리고, 식별정보 'A' 태깅되어 있고 이전 홉이 'QoS 제어' 서비스를 제공하는 서비스 노드로 트래픽이 전달되도록 라우팅 처리할 수 있다. 또는, 식별정보 'A'가 태깅되어 있고 이전 홉이 'QoS 제어'인 경우에 PE(provide edge) 라우터로 트래픽이 전달되도록 라우팅 처리하여 부가가치 서비스가 종료되도록 할 수 있다.Then, all the SDN switches 11, 12, and 13 constituting the
이로써, 서비스 체이닝 장치(20)를 구성하는 복수의 서비스 장치(21, 22, 23) 중에서 단계 211에서 결정된 부가가치 서비스들을 제공하는 서비스 노드들에게 트래픽이 전달되며, 복수의 서비스 장치(21, 22, 23) 중에서 트래픽을 전달받은 서비스 장치에 의해 해당하는 부가가치 서비스가 제공된다.Thus, traffic is delivered to the service nodes providing the added value services determined in
지금까지 설명한 바와 같이, 본 발명의 실시예에 따르면 스위칭 동작에 따라 변화하는 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝을 제공하는 복수의 SDN 스위치에 인입되는 트래픽을 분류하여 서비스 노드들로 전달하기 위한 라우팅 규칙을 제공할 수 있으며, 이동통신 서비스 분야의 서비스 체이닝에 적용하면 가입자별, 트래픽 유형별 또는 망 상황별(망 혼잡 상황 등) 자동 설정이나 다이나믹한 설정이 가능하도록 한다. 예컨대, 이동통신 서비스 시스템에서 코어 네트워크와 패킷 데이터 네트워크 사이에 배치되는 SGi/Gi 인터페이스 장치에 적용할 수 있으며, SDN 장치(10) 및 서비스 체이닝 장치(20)는 SGi/Gi 인터페이스에서 스위칭 상태에 따라 변화되는 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝을 제공할 수 있다.As described above, according to the embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to provide a routing rule for classifying traffic that is input to a plurality of SDN switches providing dynamic service chaining varying according to a switching operation and delivering the classified traffic to service nodes , And service chaining in the field of mobile communication services, it is possible to automatically or dynamically set by subscriber, traffic type, or network situation (network congestion situation, etc.). For example, the
따라서, 트래픽 유형별로 데이터 오프로딩(offloading)이 가능하다. 예컨대, 비디오 최적화, 소프트웨어 업데이트, WAN 가속, 웹 최적화, 시큐리티, 방화벽 등의 여러 가지 서비스 중에서 특정 서비스가 불필요한 대용량 트래픽을 선별하고, 해당하는 서비스를 제공하는 서비스 노드를 바이패스(bypass)시켜서 자원을 절약할 수 있다.Therefore, data offloading is possible for each traffic type. For example, among various services such as video optimization, software update, WAN acceleration, web optimization, security, firewall, and the like, it is possible to select a large amount of unnecessary traffic, bypass the service node providing the corresponding service, You can save.
그리고, 트래픽 유형별로 시큐리티 서비스를 제공할 수 있다. 예컨대, 트래픽 검사(traffic inspection), 위협 방어(threat prevention), 로깅(logging) 등의 시큐리티 서비스를 모든 트래픽에 대해 항시 적용하는 것이 아닌 특정 조건 하에서 SDN을 이용해 인에이블(enable) 함으로써 비용 효율이 높으면서도 스케일러블(scalable)한 서비스를 구현할 수 있다.Then, the security service can be provided for each traffic type. For example, security services such as traffic inspection, threat prevention, logging, and the like are enabled by using SDN under certain conditions, not always for all traffic, A scalable service can be realized.
또, 컨텐츠 위치별 트래픽 스티어링(steering)이 가능하다. 예컨대, DPI(Deep Packet Inspection)를 통해 특정 컨텐츠에 대한 데이터 요청 지연 시간을 감시할 수 있으며, 지리적으로 멀리 떨어져 있어 지연 시간이 긴 컨텐츠를 요청하는 경우에 해당 플로우를 TIC(Transparent Internet Cache)를 통해 서빙(serving)함으로써 지연 시간을 단축할 수 있다.In addition, traffic steering by content location is possible. For example, it is possible to monitor a data request delay time for specific contents through DPI (Deep Packet Inspection). When requesting contents with a long delay time from geographically distant, the flow is transmitted through TIC (Transparent Internet Cache) The delay time can be shortened by serving.
아울러, 셀(cell)별 혼잡 여부를 DPI를 이용해 판단함으로써 망 혼잡 발생 시에 QoS(Quality of Service) 제어, 비디오 최적화 작업 등을 수행하도록 서비스 체인을 동적으로 설정할 수 있다.In addition, it is possible to dynamically set the service chain to perform Quality of Service (QoS) control and video optimization in case of network congestion by determining the congestion per cell using DPI.
또한, BYOD(Bring Your Own Device) 차등 네트워크 서비스를 제공할 수 있다. 예컨대, 비즈니스 클라우드 트래픽 등과 같은 엔터프라이즈 어플리케이션에 대해서는 무선 접속 우선권, 클라우드 가속, 시그널링 최적화, QoS 제어 등의 차별화된 품질의 네트워크 서비스를 제공할 수 있다.It can also provide Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) differential network services. For example, enterprise applications such as business cloud traffic can provide differentiated quality network services such as wireless access priority, cloud acceleration, signaling optimization, and QoS control.
본 명세서에 첨부된 블록도의 각 블록과 흐름도의 각 단계의 조합들은 컴퓨터 프로그램 인스트럭션들에 의해 수행될 수도 있다. 이들 컴퓨터 프로그램 인스트럭션들은 범용 컴퓨터, 특수용 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비의 프로세서에 탑재될 수 있으므로, 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비의 프로세서를 통해 수행되는 그 인스트럭션들이 블록도의 각 블록 또는 흐름도의 각 단계에서 설명된 기능들을 수행하는 수단을 생성하게 된다. 이들 컴퓨터 프로그램 인스트럭션들은 특정 방식으로 기능을 구현하기 위해 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비를 지향할 수 있는 컴퓨터 이용 가능 또는 컴퓨터 판독 가능 메모리에 저장되는 것도 가능하므로, 그 컴퓨터 이용가능 또는 컴퓨터 판독 가능 메모리에 저장된 인스트럭션들은 블록도의 각 블록 또는 흐름도 각 단계에서 설명된 기능을 수행하는 인스트럭션 수단을 내포하는 제조 품목을 생산하는 것도 가능하다. 컴퓨터 프로그램 인스트럭션들은 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비 상에 탑재되는 것도 가능하므로, 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비 상에서 일련의 동작 단계들이 수행되어 컴퓨터로 실행되는 프로세스를 생성해서 컴퓨터 또는 기타 프로그램 가능한 데이터 프로세싱 장비를 수행하는 인스트럭션들은 블록도의 각 블록 및 흐름도의 각 단계에서 설명된 기능들을 실행하기 위한 단계들을 제공하는 것도 가능하다.Each block of the block diagrams attached hereto and combinations of steps of the flowchart diagrams may be performed by computer program instructions. These computer program instructions may be loaded into a processor of a general purpose computer, special purpose computer, or other programmable data processing apparatus so that the instructions, which may be executed by a processor of a computer or other programmable data processing apparatus, And means for performing the functions described in each step are created. These computer program instructions may also be stored in a computer usable or computer readable memory capable of directing a computer or other programmable data processing apparatus to implement the functionality in a particular manner so that the computer usable or computer readable memory It is also possible for the instructions stored in the block diagram to produce a manufacturing item containing instruction means for performing the functions described in each block or flowchart of the block diagram. Computer program instructions may also be stored on a computer or other programmable data processing equipment so that a series of operating steps may be performed on a computer or other programmable data processing equipment to create a computer- It is also possible that the instructions that perform the processing equipment provide the steps for executing the functions described in each block of the block diagram and at each step of the flowchart.
또한, 각 블록 또는 각 단계는 특정된 논리적 기능(들)을 실행하기 위한 하나 이상의 실행 가능한 인스트럭션들을 포함하는 모듈, 세그먼트 또는 코드의 일부를 나타낼 수 있다. 또, 몇 가지 대체 실시예들에서는 블록들 또는 단계들에서 언급된 기능들이 순서를 벗어나서 발생하는 것도 가능함을 주목해야 한다. 예컨대, 잇달아 도시되어 있는 두 개의 블록들 또는 단계들은 사실 실질적으로 동시에 수행되는 것도 가능하고 또는 그 블록들 또는 단계들이 때때로 해당하는 기능에 따라 역순으로 수행되는 것도 가능하다.Also, each block or each step may represent a module, segment, or portion of code that includes one or more executable instructions for executing the specified logical function (s). It should also be noted that in some alternative embodiments, the functions mentioned in the blocks or steps may occur out of order. For example, two blocks or steps shown in succession may in fact be performed substantially concurrently, or the blocks or steps may sometimes be performed in reverse order according to the corresponding function.
이상의 설명은 본 발명의 기술 사상을 예시적으로 설명한 것에 불과한 것으로서, 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 본 발명의 본질적인 특성에서 벗어나지 않는 범위에서 다양한 수정 및 변형이 가능할 것이다. 따라서, 본 발명에 개시된 실시예들은 본 발명의 기술 사상을 한정하기 위한 것이 아니라 설명하기 위한 것이고, 이러한 실시예에 의하여 본 발명의 기술 사상의 범위가 한정되는 것은 아니다. 본 발명의 보호 범위는 아래의 청구범위에 의하여 해석되어야 하며, 그와 동등한 범위 내에 있는 모든 기술사상은 본 발명의 권리범위에 포함되는 것으로 해석되어야 할 것이다.The foregoing description is merely illustrative of the technical idea of the present invention, and various changes and modifications may be made by those skilled in the art without departing from the essential characteristics of the present invention. Therefore, the embodiments disclosed in the present invention are intended to illustrate rather than limit the scope of the present invention, and the scope of the technical idea of the present invention is not limited by these embodiments. The scope of protection of the present invention should be construed according to the following claims, and all technical ideas within the scope of equivalents should be construed as falling within the scope of the present invention.
본 발명의 실시예에 의하면, 스위칭 동작에 따라 변화하는 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝을 제공하는 복수의 SDN 스위치에 인입되는 트래픽을 분류하여 서비스 노드들로 전달하기 위한 라우팅 규칙을 제공할 수 있다.According to the embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to provide a routing rule for classifying traffic that is introduced into a plurality of SDN switches providing dynamic service chaining varying according to a switching operation and delivering the classified traffic to service nodes.
이러한 본 발명은 이동통신 서비스 분야의 서비스 체이닝에 적용할 수 있다. 예컨대, 코어 네트워크와 패킷 데이터 네트워크 사이의 SGi 인터페이스 또는 Gi 인터페이스 등을 구현할 때에 이용할 수 있다.The present invention can be applied to service chaining in the field of mobile communication service. For example, it can be used when implementing an SGi interface or a Gi interface between a core network and a packet data network.
100 : 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치
110 : 서비스 체이닝 처리부
111 : 서비스 체이닝 응용프로그램 구동부
112 : 매핑 테이블 저장부
120 : SDN 제어부100: Dynamic service chaining control device
110: Service Chaining Processor
111: service chaining application program driving section
112: mapping table storage unit
120: SDN control unit
Claims (6)
Translated fromKorean도출된 상기 서비스 목록에 따른 서비스를 제공할 수 있는 홉 바이 홉(hop by hop) 라우팅 경로를 위한 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 설정하는 단계와,
상기 서비스 목록이 도출된 트래픽에 식별정보를 태깅하기 위한 태깅 규칙을 상기 복수의 SDN 스위치 중에서 상기 트래픽이 인입되는 SDN 스위치에게 제공하는 단계와,
상기 식별정보가 태깅된 트래픽의 라우팅 처리를 위한 상기 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 상기 복수의 SDN 스위치에게 제공하는 단계를 포함하는 태깅을 이용한 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 방법.Deriving a service list to be provided to traffic that is introduced into any one of a plurality of SDN (Software-Defined Networking) switches that provide dynamic service chaining that varies according to a switching operation;
Setting an SDN routing rule for a hop-by-hop routing path capable of providing a service according to the derived service list;
Providing a tagging rule for tagging identification information to traffic derived from the service list to the SDN switch in which the traffic is received from among the plurality of SDN switches;
And providing the SDN routing rule for routing processing of the tagged identification traffic to the plurality of SDN switches.
상기 복수의 SDN 스위치는, 이동통신 서비스를 위한 코어 네트워크와 패킷 데이터 네트워크 사이의 인터페이스에서 상기 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝을 제공하는 것을 특징으로 하는 태깅을 이용한 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the plurality of SDN switches provide the dynamic service chaining at an interface between a core network for a mobile communication service and a packet data network.
상기 서비스 목록은, 이동통신 서비스에 가입된 가입자의 정보, 사용 서비스 정보 또는 망 상황 정보 중에서 적어도 하나 이상을 이용하여 도출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 태깅을 이용한 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 방법.The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the service list is derived using at least one of information of a subscriber subscribed to a mobile communication service, service information or network context information.
상기 서비스 목록이 도출된 트래픽에 식별정보를 태깅하기 위한 태깅 규칙을 상기 복수의 SDN 스위치 중에서 상기 트래픽이 인입되는 SDN 스위치에게 제공하며, 상기 식별정보가 태깅된 트래픽의 라우팅 처리를 위한 상기 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 상기 복수의 SDN 스위치에게 제공하는 SDN 제어부를 포함하는 태깅을 이용한 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치.A plurality of SDN (Software-Defined Networking) switches providing dynamic service chaining varying according to a switching operation, deriving a list of services to be provided to traffic that is introduced into any one of the plurality of SDNs, A service chaining processor for setting an SDN routing rule for a hop-by-hop routing path capable of providing an SDN routing rule,
A tagging rule for tagging identification information to the traffic derived from the service list is provided to an SDN switch in which the traffic is received from among the plurality of SDN switches, and the SDN routing rule for routing the tagged traffic, And an SDN control unit for providing the plurality of SDN switches to the plurality of SDN switches.
상기 서비스 체이닝 처리부는, 서비스 체이닝 응용프로그램을 구동하여 상기 SDN 스위치에게 제공할 상기 태깅 규칙과 상기 SDN 라우팅 규칙을 설정하는 서비스 체이닝 응용프로그램 구동부와,
상기 트래픽에 의한 플로우와 상기 태깅을 위한 상기 식별정보의 매핑 테이블이 저장되는 매핑 테이블 저장부를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 태깅을 이용한 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치.5. The method of claim 4,
The service chaining processor includes a service chaining application program driver for driving the service chaining application program and setting the tagging rule and the SDN routing rule to be provided to the SDN switch,
And a mapping table storage unit for storing a mapping table of the flow caused by the traffic and the identification information for the tagging.
상기 서비스 목록은, 이동통신 서비스에 가입된 가입자의 정보, 사용 서비스 정보 또는 망 상황 정보 중에서 적어도 하나 이상을 이용하여 도출하는 것을 특징으로 하는 태깅을 이용한 다이나믹 서비스 체이닝 제어 장치.
5. The method of claim 4,
Wherein the service list is derived using at least one of information of a subscriber subscribed to a mobile communication service, service information or network context information.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR20130127146AKR101460048B1 (en) | 2013-10-24 | 2013-10-24 | Method and apparatus for control of dynamic service chaining by using tagging |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR20130127146AKR101460048B1 (en) | 2013-10-24 | 2013-10-24 | Method and apparatus for control of dynamic service chaining by using tagging |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR101460048B1true KR101460048B1 (en) | 2014-11-11 |
Family
ID=52287630
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR20130127146AActiveKR101460048B1 (en) | 2013-10-24 | 2013-10-24 | Method and apparatus for control of dynamic service chaining by using tagging |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101460048B1 (en) |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105591967A (en)* | 2014-11-12 | 2016-05-18 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and apparatus |
| KR20160105223A (en)* | 2015-02-27 | 2016-09-06 | 에스케이텔레콤 주식회사 | Service chaining control apparatus and method, service chaining executive method by using the same |
| KR101739100B1 (en)* | 2015-03-30 | 2017-05-24 | 쿨클라우드(주) | Method of controlling openflow switch capable of service chaining and controller thereof |
| KR101739097B1 (en) | 2015-03-30 | 2017-05-24 | 쿨클라우드(주) | Service chaining method in openflow switch |
| KR101746105B1 (en)* | 2015-03-30 | 2017-06-27 | 쿨클라우드(주) | Openflow switch capable of service chaining |
| WO2017131259A1 (en)* | 2016-01-29 | 2017-08-03 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method by which network nodes calculate optimum path for virtualized service functions |
| KR101800145B1 (en) | 2017-02-22 | 2017-11-21 | 한국과학기술원 | Software switch for providng network service and method for operating software switch |
| US9929945B2 (en) | 2015-07-14 | 2018-03-27 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Highly available service chains for network services |
| CN111953600A (en)* | 2020-08-24 | 2020-11-17 | 国网湖南省电力有限公司 | SDN-based business traffic scheduling method for energy storage data center |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20130099221A (en)* | 2010-12-28 | 2013-09-05 | 닛본 덴끼 가부시끼가이샤 | Information system, control device, virtual network provision method and program |
- 2013
- 2013-10-24KRKR20130127146Apatent/KR101460048B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20130099221A (en)* | 2010-12-28 | 2013-09-05 | 닛본 덴끼 가부시끼가이샤 | Information system, control device, virtual network provision method and program |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105591967A (en)* | 2014-11-12 | 2016-05-18 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and apparatus |
| CN105591967B (en)* | 2014-11-12 | 2019-06-28 | 华为技术有限公司 | A kind of data transmission method and device |
| KR20160105223A (en)* | 2015-02-27 | 2016-09-06 | 에스케이텔레콤 주식회사 | Service chaining control apparatus and method, service chaining executive method by using the same |
| KR102203734B1 (en)* | 2015-02-27 | 2021-01-15 | 에스케이텔레콤 주식회사 | Service chaining control apparatus and method, service chaining executive method by using the same |
| KR101739100B1 (en)* | 2015-03-30 | 2017-05-24 | 쿨클라우드(주) | Method of controlling openflow switch capable of service chaining and controller thereof |
| KR101739097B1 (en) | 2015-03-30 | 2017-05-24 | 쿨클라우드(주) | Service chaining method in openflow switch |
| KR101746105B1 (en)* | 2015-03-30 | 2017-06-27 | 쿨클라우드(주) | Openflow switch capable of service chaining |
| US9929945B2 (en) | 2015-07-14 | 2018-03-27 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Highly available service chains for network services |
| WO2017131259A1 (en)* | 2016-01-29 | 2017-08-03 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method by which network nodes calculate optimum path for virtualized service functions |
| US10575212B2 (en) | 2016-01-29 | 2020-02-25 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method by which network nodes calculate optimum path for virtualized service functions |
| KR101800145B1 (en) | 2017-02-22 | 2017-11-21 | 한국과학기술원 | Software switch for providng network service and method for operating software switch |
| CN111953600A (en)* | 2020-08-24 | 2020-11-17 | 国网湖南省电力有限公司 | SDN-based business traffic scheduling method for energy storage data center |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101473783B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for control of dynamic service chaining by using tunneling | |
| KR101460048B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for control of dynamic service chaining by using tagging | |
| US12328253B2 (en) | Scalable network slice based queuing using segment routing flexible algorithm | |
| US10742556B2 (en) | Tactical traffic engineering based on segment routing policies | |
| US10938727B2 (en) | Method and device for offloading processing of data flows | |
| RU2734895C2 (en) | Time-sensitive program-determined network | |
| CN104104718B (en) | User autonomous routing customization system based on software-defined network | |
| EP2880829B1 (en) | Adaptive infrastructure for distributed virtual switch | |
| EP3213546B1 (en) | System and method for placing virtual serving gateways for mobility management | |
| EP3085148B1 (en) | A method and apparatus for performing flexible service chaining | |
| CA2944566C (en) | Handling of traffic flows in a communications system | |
| EP3142303A1 (en) | Network control method and apparatus | |
| CN104904166A (en) | Intelligent routing of network packets on telecommunication devices | |
| US10321352B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for traffic steering | |
| CN101841487A (en) | Configuration method for aggregating link service flow and packet switching device | |
| KR20160041631A (en) | Apparatus and method for quality of service aware routing control | |
| US11146477B2 (en) | Discovery and admission control of forwarding boxes in a software-defined network | |
| KR101478944B1 (en) | Switch migration method for software-defined-networks with a plurality of controllers | |
| KR102055686B1 (en) | Method and apparatus to implement virtual networks using open flow switches and controller | |
| US20200036642A1 (en) | System and method for reactive path selection | |
| CN110958185B (en) | QoS configuration method and device based on service | |
| EP3217610B1 (en) | Network communication method and device, and internet system | |
| US20190238455A1 (en) | Multipath adjustments | |
| KR101739100B1 (en) | Method of controlling openflow switch capable of service chaining and controller thereof | |
| Patil et al. | Optimizing MPLS Tunnel Creation Performance by Using SDN |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20131024 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20140818 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20141104 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20141105 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20171031 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20171031 Start annual number:4 End annual number:4 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20181101 Year of fee payment:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20181101 Start annual number:5 End annual number:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20200928 Start annual number:7 End annual number:7 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20240919 Start annual number:11 End annual number:11 |