KR100920273B1 - A method, a device and a system for duplex communications - Google Patents
A method, a device and a system for duplex communicationsDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100920273B1 KR100920273B1KR1020067019083AKR20067019083AKR100920273B1KR 100920273 B1KR100920273 B1KR 100920273B1KR 1020067019083 AKR1020067019083 AKR 1020067019083AKR 20067019083 AKR20067019083 AKR 20067019083AKR 100920273 B1KR100920273 B1KR 100920273B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- information
- time
- transmission
- frequency
- channel
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L5/00—Arrangements affording multiple use of the transmission path
- H04L5/14—Two-way operation using the same type of signal, i.e. duplex
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B1/00—Details of transmission systems, not covered by a single one of groups H04B3/00 - H04B13/00; Details of transmission systems not characterised by the medium used for transmission
- H04B1/38—Transceivers, i.e. devices in which transmitter and receiver form a structural unit and in which at least one part is used for functions of transmitting and receiving
- H04B1/40—Circuits
- H04B1/50—Circuits using different frequencies for the two directions of communication
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B1/00—Details of transmission systems, not covered by a single one of groups H04B3/00 - H04B13/00; Details of transmission systems not characterised by the medium used for transmission
- H04B1/69—Spread spectrum techniques
- H04B1/713—Spread spectrum techniques using frequency hopping
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B7/00—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field
- H04B7/24—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts
- H04B7/26—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts at least one of which is mobile
- H04B7/2643—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts at least one of which is mobile using time-division multiple access [TDMA]
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean본 발명은 일반적으로 통신 시스템들에 관한 것이다. 특히, 본 발명은 무선 통신 네트워크들의 대기 인터페이스들(air interfaces) 및 이들의 듀플렉싱 방법들(duplexing methods)과 관련된다.The present invention relates generally to communication systems. In particular, the present invention relates to air interfaces and their duplexing methods of wireless communication networks.
유럽 제 3 세대 이동 통신 표준으로서 선택된 UMTS(범용 이동 통신 시스템) 및 GSM(이동 통신용 글로벌 시스템)과 같은 현대의 무선 통신 시스템들은 기지국 및 이동 단말기와 같은 네트워크 요소들간에서 대기 인터페이스를 통해 다양한 타입의 데이터를 전송할 수 있다. 이를 위해, GSM 및 UMTS 모두는 FDD(주파수 분할 듀플렉스)로 불리는 선진(mature) 듀플렉스 전송 방법을 이용하는데, 여기서 업링크 및 다운링크 전송 방향들은 2개의 서로다른 주파수 대역들(~쌍 대역들(paired bands)) 을 통해 구현된다. 따라서, FDD는 전송 방향들의 주파수 도메인 분리를 이용하며, 연속적인 2-방향 전송을 가능하게 한다. 전형적으로 마크로셀들 및 마이크로셀들에 할당된 FDD에 추가하여, UMTS 사양은 또한 홑(unpaired) 주파수 대역들과 함께 사용되는 전송 방향들의 시간 도메인 분리를 위한 보다 최신의 TDD(시분할 듀플렉스) 기술을 지원함과 아울러 보다 높은 사용자 밀도를 갖는 피코셀들 등에 관 하여 주로 근거리 액세스를 제공하는 모드를 포함한다. UMTS 주파수 대역들에서, 1920 내지 1980㎒(업링크) 및 2110 내지 2170㎒(다운링크)가 FDD 동작에 대해 쌍을 이루고 있는 동안에, 1900 내지 1920㎒ 및 2010 내지 2025㎒ 주파수 범위들은 TDD 동작에 목적을 두고 있다.Modern wireless communication systems, such as UMTS (Universal Mobile Communication System) and GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication), selected as the European third generation mobile communication standard, provide various types of data through standby interfaces between network elements such as base stations and mobile terminals. Can be transmitted. To this end, both GSM and UMTS use a feature duplex transmission method called FDD (Frequency Division Duplex), where the uplink and downlink transmission directions are paired with two different frequency bands (~ paired bands). bands)). Thus, FDD utilizes frequency domain separation of transmission directions and enables continuous two-way transmission. In addition to the FDD typically assigned to macrocells and microcells, the UMTS specification also introduces a more recent time division duplex (TDD) technique for time domain separation of transmission directions used with unpaired frequency bands. In addition to supporting, it includes a mode mainly providing near-field access for picocells having a higher user density. In the UMTS frequency bands, while 1920 to 1980 MHz (uplink) and 2110 to 2170 MHz (downlink) are paired for FDD operation, the 1900 to 1920 MHz and 2010 to 2025 MHz frequency ranges are intended for TDD operation. Leave.
FDD 및 TDD 개념들은 도 1의 도움으로 더욱 분명하게 되는데, 도 1에서 이동 단말기 또는 통신 인에이블(enable) PDA(개인용 디지털 어시스턴트)(102)와 같은 무선 통신 디바이스는 UMTS에서와 같이 내부적으로 무선 액세스 네트워크 및 코어 네트워크로 분리될 수 있는 이동 네트워크에 접속되어 있다. 무선 통신 디바이스(102)와 직접적으로 통신하는 네트워크 요소가 본 예에서 기지국(104)으로 불리는데, 여기서 기지국은 예를 들어, GPRS(범용 패킷 무선 서비스)의 경우에 본래 GGSN(게이트웨이 GPRS 지원 노드)로부터 전송된, SGSN(서빙 GPRS 지원 노드)로부터 수신된 데이터를 활성 DL(다운링크) 접속을 이용함으로써 대기 인터페이스를 통해 무선 통신 디바이스(102)로 전송한다. 따라서, 무선 통신 디바이스(102)는 설정된 UL(업링크) 접속을 이용함으로써 네트워크 측에 데이터를 송신할 수 있다.FDD and TDD concepts become more apparent with the aid of FIG. 1, where a wireless communication device such as a mobile terminal or a communication enabled PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) 102 is internally accessed as in UMTS. It is connected to a mobile network that can be separated into a network and a core network. The network element that directly communicates with the
발신된 UL/DL 데이터 전송은 FDD 및 TDD 기법들 모두를 통해 구현될 수 있다. FDD가 선택된 경우에, UL(112) 및 DL(110) 전송 방향들은 이들의 반송파 주파수들에 대해 분리된다. 따라서, 보호 주파수대로 불리는 필요한 분리를 갖는 동일하거나 서로다른 대역폭들을 갖는 이들 2개의 대역들은 듀플렉스 데이터 전송에 사용된다. 쌍 대역들 솔루션이 보이스(voice) 통신들 및 비디오 컨퍼런싱과 같은 대칭 트래픽에 대해 이상적이지만, 하향측(downside)으로서, UL 및 DL 전송 자원들간 의 진정으로 유연성있는. 동적인 대역폭 할당을 수행하는 것이 불가능하거나 비교적 복잡하게 된다.The sent UL / DL data transmission can be implemented via both FDD and TDD techniques. If FDD is selected, the
FDD 또는 TDD 기반 네트워크에서 다중 액세스를 지원하기 위해, 예를 들어 GSM 시스템에서의 TDMA(시분할 다중 접속) 기법 또는 UMTS 시스템에서의 (W)CDMA((광대역) 코드분할 다중 접속) 기법, 또는 동시에 이들 모두(예를 들어, UMTS TDD)가 사용될 수 있다. 더욱이, 전송 방향에 복수의 반송파들이 존재하는 때에, FDMA(주파수 분할 다중 접속)이 적용될 수 있다.To support multiple access in an FDD or TDD based network, for example, the TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) scheme in GSM systems or the (W) CDMA ((Wideband) Code Division Multiple Access) scheme in UMTS systems, or simultaneously All (eg, UMTS TDD) can be used. Moreover, when there are a plurality of carriers in the transmission direction, FDMA (frequency division multiple access) can be applied.
TDD 접근방식은 UL/DL 용량의 상대적인 변경 및 이러한 방식으로 FDD보다 용이한 비대칭 트래픽을 지원하는데, 이는 타임 슬롯들의 2개의 개별 세트들에 하나의 반송파를 할당(각 방향에 대해 하나씩 할당)함으로써, 요구되는 분리가 시간 도메인에서 발생함과 아울러 UL 및 DL 방향들이 동일 주파수를 공유하기 때문이다. 타임 슬롯들은 대칭 트래픽(114)에 대해 동일한 방식으로, 대안적으로, 예를 들어 전형적인 인터넷 트래픽(웹 서핑 어플리케이션: 헤비(heavy) 다운링크 트래픽, 거의 비-존재의 업링크 제어 데이터)에 대해 불균형 방식(116)으로 동적으로 할당되는데, 후자의 경우에 UL 또는 DL 방향은 시간 사용에 관하여 다른 것을 지배할 수 있다. 따라서, 주파수 자원들은 비활성 전송 방향에 대해 의미없이 예비되지 않는다. 결점으로서, TDD는 두 접속 단들에 대해 불연속 전송을 내포하며, 가능한 UL/DL 전송 오버랩으로 인해, 전송 방향들간에서 도입되는 간섭 위험이 발생한다. 오버랩을 피하기 위해, (단지 설명 목적으로 도면에서 예시된 하나의 UL 타임 슬롯에 대한) 보호 종료(guard period)(118)가 전형적으로 각 슬롯의 종료점에서 사용 된다.The TDD approach supports relative changes in UL / DL capacity and asymmetric traffic that is easier than FDD in this way, by assigning one carrier to two separate sets of time slots (one for each direction), This is because the required separation occurs in the time domain as well as the UL and DL directions share the same frequency. The time slots are unbalanced in the same way for
국제공개 제 99/38343호는 다중-셀 환경들에서 스펙트럼 사용을 개선하기 위한 시분할 및 주파수 분할 듀플렉스 기법들 모두를 지원하는 구성을 개시한다. 인접 셀들에 위치되지만, 지리적으로 분리된 2개의 기지국들은 동일 주파수들을 사용할 수 있는데, 이는 제 1 이동국에 접속된 제 1 기지국이 제 1 주파수를 이용함으로써 일정 시간 순간에서 송신하는 동안에, 제 2 이동국에 접속된 제 2 기지국이 제 2 주파수를 이용함으로써 송신(또는 수신)하는 방식으로 된다. 이후에, 제 1 기지국은 제 2 주파수를 통해 데이터를 수신하는 동안에, 제 2 기지국은 제 1 주파수를 통해 데이터를 수신(또는 송신)한다. 이후에, 상기 사이클이 재시작된다.International Publication No. 99/38343 discloses a configuration that supports both time division and frequency division duplex techniques for improving spectrum use in multi-cell environments. Two base stations located in adjacent cells, but geographically separated, may use the same frequencies, which means that while the first base station connected to the first mobile station transmits at a certain time instant by using the first frequency, it transmits to the second mobile station. The second base station to be connected is transmitted (or received) by using the second frequency. Thereafter, while the first base station receives data on the second frequency, the second base station receives (or transmits) data on the first frequency. After that, the cycle is restarted.
어느 정도까지 서로다른 타입들의 데이터 접속들 및 듀플렉스 방법들을 이용할 수 있는 다양한 기존의 데이터 전송 구성들에 있어서도, 어떤 종래기술 방법들이 특정적으로 적합하지 않게 되는 상황들이 여전히 발생한다. 반면에, TDD 및 FDD도 시스템에 상술한 바와같은 순수한 이점들을 제공하지 않는다.With various existing data transfer configurations that can to some extent use different types of data connections and duplex methods, situations still arise that some prior art methods are not particularly suitable. On the other hand, TDD and FDD also do not provide the system with the pure advantages as described above.
본 발명의 목적은 종래기술 구성들에서 발견된 결함들을 완화함과 아울러 공지된 TDD 및 FDD 솔루션들의 환경 주변에 위치되는 새로운 방법, 디바이스 및 시스템을 제공하는 것이다. 이는 TDD 및 FDD 기법들 모두의 많은 이점을 결합 및 강화하는 방식으로 2개 이상의 송수신기 유닛들간에 듀플렉스 통신을 가능하게 한다.It is an object of the present invention to provide new methods, devices and systems that are located around the environment of known TDD and FDD solutions as well as mitigating deficiencies found in prior art configurations. This enables duplex communication between two or more transceiver units in a manner that combines and enhances many of the advantages of both TDD and FDD techniques.
본 발명의 기본 사상에서, 2개의 송수신기 유닛들은 서로 통신하며, 업링크 및 다운링크 주파수들은 일 시간 순간에서, 일정 반송파 주파수가 업링크(다운링크) 전송에 사용되며, 다른 시간 순간에서 다운링크(업링크) 전송에 사용되는 직교 방식으로 할당된다. 대응적으로, 상기 일 시간 순간에서 제 2 반송파 주파수가 다운링크(업링크) 전송에 사용되며, 상기 다른 시간 순간에서 선택적으로 업링크(다운링크) 전송에 사용된다. 듀플렉스 통신은 임의 종류의 2-방향 정보 전송(스피치(speech) 또는 다른 진정한 페이로드 데이터, 시그널링, 파일롯 신호들 등)을 가리킨다.In the basic idea of the present invention, two transceiver units communicate with each other, the uplink and downlink frequencies are used at one time instant, a constant carrier frequency is used for uplink (downlink) transmission, and at another time instant the downlink ( Uplink) in the orthogonal manner used for transmission. Correspondingly, a second carrier frequency is used for downlink (uplink) transmission at said one time instant and optionally for uplink (downlink) transmission at said other time instant. Duplex communication refers to any kind of two-way information transmission (speech or other true payload data, signaling, pilot signals, etc.).
본 발명의 이용에 관하여, 이는 FDD 또는 그 "주파수 홉핑" 양상으로 인해 충분한 전송 다이버시티(diversity)를 제공한다. 더욱이, 일부에 대한 TDD 양상으로 인해, 최신 채널 상태 정보에 따라 전송 유닛들을 제어하는 수단이 제공된다. 예를 들어, 종래 FDD 솔루션에서, 송신기에 전송 채널에 관한 정보 및 다른 관련 정보를 제공하는데 피드백 채널이 필요하다. 본 발명을 이용함으로써, 전송 제어를 위한 이러한 채널 정보는 동일 주파수를 통해 수신된 정보로부터 도출될 수 있다. 당연하게, 또한 명시적 피드백 데이터가 수신 당사자에 의해 주기적으로 또는 소정의 이벤트의 필요 또는 발생하에서 TDD에 기반하여 본래 전송 채널로부터 도출된 피드백 채널을 통해 송신기에 송신될 수 있다. 간섭 상황은 통신 링크의 서로다른 단들에서 여전히 서로 다르며, 따라서 명시적 피드백 데이터의 이용은 무모하게 생략되지 않아야 한다. 내재적 또는 명시적 전송 제어 데이터는 높은 오버헤드(overhead)로 피드백 채널들을 정의할 필요없이 예를 들어, 전송 코딩, 빔 형성, 변조, 전력 제어, 속도 제어, (다중-사용자) 스케줄링, 채널 선택, 임의 개수의 송신 및 수신 안테나 구성들을 위한 기타 유닛들을 조정하는데 사용될 수 있다. 또한 추가적으로, 개선된 용량과 같은 많은 현재 TDD 특정 이점들이 또한 FDD 쌍 대역들에 적용가능하게 되었다.With regard to the use of the present invention, this provides sufficient transmit diversity due to FDD or its “frequency hopping” aspect. Moreover, due to the TDD aspect for some, means are provided for controlling the transmission units in accordance with the latest channel state information. For example, in a conventional FDD solution, a feedback channel is needed to provide the transmitter with information about the transport channel and other related information. By using the present invention, such channel information for transmission control can be derived from information received over the same frequency. Naturally, explicit feedback data may also be transmitted to the transmitter periodically by the receiving party or through a feedback channel derived from the original transmission channel based on TDD based on the need or occurrence of a predetermined event. The interference situation is still different at the different ends of the communication link, so the use of explicit feedback data should not be recklessly omitted. Intrinsic or explicit transmission control data can be used for example in transmission coding, beamforming, modulation, power control, rate control, (multi-user) scheduling, channel selection, without having to define feedback channels with high overhead. It can be used to coordinate other units for any number of transmit and receive antenna configurations. In addition, many current TDD specific advantages, such as improved capacity, have also become applicable to FDD pair bands.
본 발명의 일 양상에서, 정보 전송을 위해 2개 이상의 주파수들을 할당하는 단계 및 상기 2개 이상의 주파수들에 속하는 제 1 주파수들을 통해 제 1 방향으로, 그리고 상기 2개 이상의 주파수들에 속하지만 상기 제 1 주파수들과 다른 제 2 주파수들을 통해 제 2 방향으로 정보를 전송하는 단계를 포함하는 듀플렉스 통신용 방법은:In one aspect of the invention, the step of assigning two or more frequencies for information transmission and through first frequencies belonging to the two or more frequencies in a first direction and belonging to the two or more frequencies but belonging to the second A method for duplex communication comprising transmitting information in a second direction via second frequencies different from one frequency:
-일정 시간 순간에서 상기 제 1 주파수들에 속하는 제 1 주파수를 통해 상기 제 2 전송 방향으로 정보를 전송하는 단계를 더 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.-Transmitting the information in the second transmission direction over a first frequency belonging to the first frequencies at a certain time instant.
본 발명의 다른 양상에서, 제 1 및 제 2 송수신기 유닛간의 듀플렉스 통신용 방법은:In another aspect of the invention, a method for duplex communication between a first and a second transceiver unit is:
-제 1 시간 기간 동안 제 1 반송파 주파수를 통해 상기 제 1 및 제 2 송수신기 유닛들간의 제 1 전송 방향으로 정보를 전송하는 단계와;-Transmitting information in a first transmission direction between the first and second transceiver units over a first carrier frequency for a first time period;
-상기 제 1 시간 기간 동안 제 2 반송파 주파수를 통해 상기 제 1 및 제 2 송수신기 유닛들간의 제 2 전송 방향으로 정보를 전송하는 단계와; 그리고-Transmitting information in a second transmission direction between the first and second transceiver units over a second carrier frequency during the first time period; And
-제 2 시간 기간 동안 대체적으로 상기 제 1 반송파 주파수를 통해 상기 제 1 및 제 2 송수신기 유닛들간의 제 2 전송 방향으로 정보를 전송하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.-Transmitting information in a second transmission direction between the first and second transceiver units over the first carrier frequency, generally during a second time period.
단어 "대체적으로"는 반송파 주파수들(또는 주파수 대역들)이 완전히 동일하지 않지만 적어도 부분적으로 오버랩함을 강조한다.The word “alternatively” emphasizes that the carrier frequencies (or frequency bands) are not completely identical but at least partially overlap.
용어 "전송"은 본원에서 보다 낮은 송신 또는 수신 과정 또는 집합체로서 송신 및 수신을 가리킨다. 송신 및 수신 당사자를 포함하는 시스템의 관점에서, 2개의 양상들은 하나의 단계를 가리키거나 그렇지 않을 수 있으며, 하나의 통신 디바이스의 견지에서, 한 번에 하나의(송신/수신) 양상만이 적용가능하다.The term "transmission" herein refers to transmission and reception as a lower transmission or reception process or aggregate. In view of a system comprising a transmitting and receiving party, the two aspects may or may not indicate one step, and in terms of one communication device, only one (transmit / receive) aspect is applied at a time It is possible.
본 발명의 추가적인 양상에서, 무선 듀플렉스 통신용 송수신기를 포함하며, 명령들 및 데이터를 프로세싱하고 저장하는 프로세싱 및 메모리 수단을 추가적으로 포함하는 통신 디바이스는:In a further aspect of the invention, a communication device comprising a transceiver for wireless duplex communication, further comprising processing and memory means for processing and storing instructions and data:
-제 1 시간 기간 동안 제 1 반송파 주파수를 통해 제 1 전송 방향으로 정보를 전송하며,-Transmit information in a first transmission direction on a first carrier frequency for a first time period,
-상기 제 1 시간 기간 동안 제 2 반송파 주파수를 통해 제 2 전송 방향으로 정보를 전송하며, 그리고Transmit information in a second transmission direction on a second carrier frequency during the first time period, and
-제 2 시간 기간 동안 대체적으로 상기 제 1 반송파 주파수를 통해 상기 제 2 전송 방향으로 정보를 전송하는 것을 특징으로 한다.-Transmit information in said second transmission direction generally over said first carrier frequency during a second time period.
또한 본 발명의 추가적인 양상에서, 듀플렉스 데이터 전송을 수행할 수 있는 하나 이상의 송수신기들을 포함하는 시스템- 상기 시스템은 명령들 및 데이터를 프로세싱하며 저장하는 프로세싱 및 메모리 수단을 더 포함하며, 상기 시스템은 정보 전송을 위해 2개 이상의 반송파 주파수들을 할당한다 -에 있어서, 상기 시스템은 제 1 시간 기간 동안, 제 1 반송파 주파수가 제 1 방향으로의 정보 전송을 위해 할당되며, 제 2 반송파 주파수가 제 2 방향으로의 정보 전송을 위해 할당되며, 제 2 시간 기간 동안, 상기 제 1 반송파 주파수가 상기 제 2 방향으로의 정보 전송을 위해 할당되는 것을 특징으로 한다.In a further aspect of the invention, there is also provided a system comprising one or more transceivers capable of performing duplex data transmission, the system further comprising processing and memory means for processing and storing instructions and data, the system transmitting information Wherein the system allocates two or more carrier frequencies for the first time period, the first carrier frequency being allocated for information transmission in the first direction, and the second carrier frequency in the second direction. And is allocated for information transmission, and during the second time period, the first carrier frequency is allocated for information transmission in the second direction.
상기 제 1 방향은 전형적인 통신 시스템의 경우에서 업링크 또는 다운링크 방향으로 해석될 수 있음을 주목해야 한다. 마찬가지로, 상기 제 2 방향은 이러한 순서로 다운링크 또는 업링크 방향으로 해석될 것이다.It should be noted that the first direction may be interpreted as an uplink or downlink direction in the case of a typical communication system. Similarly, the second direction will be interpreted in this order as the downlink or uplink direction.
하기에서, 본 발명은 첨부 도면들을 참조하여 더욱 상세히 설명된다.In the following, the invention is explained in more detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 1은 FDD 및 TDD 접근방식들을 갖는 인용된 종래기술 솔루션들을 도시한다.1 illustrates the cited prior art solutions with FDD and TDD approaches.
도 2A, 2B 및 2C는 FDD 및 TDD 기법들 모두가 정교한 방식으로 사용되는 상술한 본 발명의 사상을 예시한다.2A, 2B and 2C illustrate the idea of the invention described above where both FDD and TDD techniques are used in a sophisticated manner.
도 3은 본 발명의 방법의 흐름도이다.3 is a flow chart of the method of the present invention.
도 4는 본 발명의 방법의 보충적인 흐름도이다.4 is a supplementary flowchart of the method of the present invention.
도 5는 본 발명의 디바이스의 블록도이다.5 is a block diagram of the device of the present invention.
도 6은 본 발명의 다른 디바이스의 블록도이다.6 is a block diagram of another device of the present invention.
도 7A 및 7B는 하나의 가능한 사용 경우에서 표준 FDD 및 듀플렉스 홉핑 기법들간의 비교를 도시한다.7A and 7B show a comparison between standard FDD and duplex hopping techniques in one possible use case.
도 1은 관련 종래기술의 설명과 관련하여 이미 설명되었다.1 has already been described in connection with the description of the related prior art.
본 발명의 단지 예시적인 서로다른 시나리오들이 도 2A, 2B 및 2C에서 도시된다.Only exemplary different scenarios of the present invention are shown in FIGS. 2A, 2B and 2C.
도 2A는 가장 단순한 듀플렉스 홉핑 경우를 나타내는데, 본 발명의 FDD 양상에 따라, 정보(스피치 또는 다른 데이터, 제어 정보 등) 전송을 위해 2개의 개별 주파수들(또는, 실제상 주파수 대역들)이 할당되며, 일정 기간(T1) 내에서 일 반송파 주파수(대역)가 UL 방향에서, 다른 반송파 주파수가 DL 방향에서 이용된다. 본 발명의 TDD 양상에 따른 제 2 시간 기간(T2) 내에서, 기간(T1) 동안 UL 방향에서 이용된 반송파 주파수는 이제 DL 방향에서 이용되며, 그리고 선택적으로(optionally), 대응적으로, 기간(T1) 동안 DL 방향에서 이용된 반송파 주파수는 역으로 UL 방향에서 이용된다. 보호 주파수대(guard band)가 도면에서 참조부호(G)로 표시된다.2A illustrates the simplest duplex hopping case, in which two separate frequencies (or in fact frequency bands) are allocated for transmitting information (speech or other data, control information, etc.) in accordance with the FDD aspect of the present invention. In one period T1, one carrier frequency (band) is used in the UL direction, and another carrier frequency is used in the DL direction. Within the second time period T2 according to the TDD aspect of the present invention, the carrier frequency used in the UL direction during the period T1 is now used in the DL direction, and optionally, correspondingly, the period ( The carrier frequency used in the DL direction during T1) is inversely used in the UL direction. The guard band is indicated by the reference sign G in the figure.
본원에서 언급되는 시간 기간은 임의의 다른 시간적으로 제한된, 대체적으로 연속적인 세그먼트들에 추가하여 예를 들어, 다수의 타임 슬롯들을 가리키거나 이들로서 구체화될 수 있다. 많은 기존의 통신 시스템들에서, UL 및 DL 정보 전송 방향들은 예를 들어, 타임 슬롯 경계들에 대한 상호 타이밍 오프셋(mutual timing offset)을 가지며, 따라서 본 명세서에서 사용된 바와같은 시간 기간 정의는 실제 타임 슬롯 경계들에 대한 정의와 다를 수 있다. 또한, 정보 전송을 위해 할당된 일정 시간 기간 동안에, 실제 전송은 전체 기간이 아니라 여전히 기간의 일부만을 취할 수 있다는 사실을 인식할 것이다.The time period referred to herein may, for example, point to or be embodied as a number of time slots in addition to any other time limited, generally contiguous segments. In many existing communication systems, the UL and DL information transmission directions have mutual timing offsets, for example with respect to time slot boundaries, so that the time period definition as used herein may be a real time. It may differ from the definition for slot boundaries. It will also be appreciated that during a certain time period allocated for information transmission, the actual transmission may still take only part of the period, not the entire period.
데이터 수신에 대한 반송파 역할을 한 동일 주파수(채널)가 시간 코히어런시(time coherence) 내에 있으며, 또한 정보 전송을 위해 재사용되기 때문에, 송신기에 채널 상태 정보를 제공하는 종래 피드백 채널들이 필요하지 않게 된다. 송신 기는 금방 수신된 정보에 기초하여 공제(deduct)될 수 있는데, 이러한 정보는 유용한 트레이닝(~파일롯) 시퀀스들 등, 적당한 전송 파라메터들(전력, 빔 (형성) 계수들 등)을 포함한다. 결과적으로, 송신기는 TDD 접근 방법 이후에 채널 정보를 갖추게 되며, 주파수 홉핑 접근은 전체적인 의미에서 전송에 다이버시티를 제공한다.Since the same frequency (channel) that served as a carrier for data reception is within time coherence and is reused for information transmission, there is no need for conventional feedback channels that provide channel state information to the transmitter. do. The transmitter can be deducted based on the information received immediately, which includes appropriate transmission parameters (power, beam (forming) coefficients, etc.), such as useful training (~ pilot) sequences. As a result, the transmitter is equipped with channel information after the TDD approach, and the frequency hopping approach provides diversity for transmission in the overall sense.
추가적으로, 적어도 부분적으로 동일한 (소스) 정보(즉, 송신 정보 블록들은 대체로 예를 들어, 적용된 채널 코딩으로 인한 리던던시(redundancy)를 포함한다)는 복수의 주파수들을 통해 송신되어, 예를 들어 까다로운 또는 미지의 채널 조건들의 경우에 원단(far-end)에서 성공적인 수신의 가능성을 증가시킬 수 있다. 채널 조건들은 수신 정보에 기초하여 분석될 수 있다.Additionally, at least partially identical (source) information (ie, transmission information blocks generally include redundancy due to, for example, applied channel coding) is transmitted over a plurality of frequencies, for example tricky or unknown In the case of channel conditions, the probability of successful reception at the far-end can be increased. Channel conditions may be analyzed based on the received information.
도 2B에서, 듀플렉스 홉핑이 도 2A의 환경과 일치하는 환경에서 수행되지만, UL 방향은 적어도 시간적으로 비활성(트래픽이 없음)이다. 따라서, DL 방향 데이터 전송은 주기적인 방식으로 주파수들을 통해 홉핑하지만, 또한 DL 전송들간의 미사용 UL 시간을 이용하여 예를 들어, (트레이닝 시퀀스들과 같은 채널을 분석하기 위한 채널 정보 또는 테스트 데이터와 같은) 제어 또는 파라메터 데이터를 종종 송신한다(202). 이러한 주기적인 제어 또는 파라메터 전송들은 예를 들어, 원단에서 가변 채널 조건들을 분석할 수 있게 하기 위해 일반적인 홉핑 원리에 따라 서로다른 주파수들로 송신될 수 있다.In FIG. 2B, duplex hopping is performed in an environment consistent with the environment of FIG. 2A, but the UL direction is at least temporally inactive (no traffic). Thus, DL directional data transmissions hop through frequencies in a periodic manner, but also utilize unused UL time between DL transmissions, e.g., such as channel information or test data for analyzing a channel such as training sequences. Control or parameter data is often transmitted (202). Such periodic control or parameter transmissions may be transmitted at different frequencies according to general hopping principles, for example, to enable the analysis of variable channel conditions at the far end.
도 2C는 전형적인 FDD 할당 과정이 발생하였으며, 적어도 하나의 반송파 주파수가 UL 방향에 대해, 다른 주파수가 DL 방향에 대해 예비되어 있는 추가적인 시나리오를 개시한다. 2개의 방향들은 과거에 활성(데이터 전송의 발생)이었거나 그 렇지 않을 수 있지만, 도 2C에 의해 시각화되는 시간 창 내에서, UL은 비활성이며, 이에 따라 어떤 진정한 페이로드 데이터 또는 시그널링이 이 방향으로 전송되지 않는다. 이후에, 만일 동일 주파수를 통한 UL/DL 전송들간의 간섭을 피하기 위해 필요한 보호 기간들이 적당하게 정의되어 있는 경우에, DL 수신에 관한 보고들 또는 일부 다른 보다 적은량의 데이터가 DL 대역에서 UL 방향으로 주기적으로 송신될 수 있으며(204), 통신 링크의 양 단들은 간헐적인 보고들을 인식하고 있다(예를 들어, 이전 DL 전송 유닛이 미래 타임 슬롯에서 송신될 보고를 요구하였을 수 있다).2C discloses an additional scenario in which a typical FDD allocation process has occurred and at least one carrier frequency is reserved for the UL direction and another frequency is reserved for the DL direction. The two directions may or may not have been active in the past (occurrence of data transmission), but within the time window visualized by FIG. 2C, the UL is inactive, so any true payload data or signaling is transmitted in this direction. It doesn't work. Later, if the guard periods necessary to avoid interference between UL / DL transmissions on the same frequency are properly defined, reports on DL reception or some other lesser amount of data may be sent from the DL band to the UL direction. It may be sent 204 periodically, and both ends of the communication link are aware of intermittent reports (eg, a previous DL transmission unit may have requested a report to be sent in a future time slot).
상기 예들의 관점에서, 본 발명을 이용하는 방법의 일반적인 흐름도가 도 3에서 도시된다. 단계(302)에서, 방법이 시작되어, 정보를 송신/수신하는 통신 디바이스들이 부팅되며, 필요한 코드가 메모리들에 적재된 이후에 (개인용) 통신 디바이스들이 네트워크 등에 등록할 수 있다. 단계(304)에서, 전송 자원들이 할당되는데, 이는 시작 단계 이후에 자동으로 되거나, 예를 들어 다수의 반송파들을 이를 이용하는 다수의 디바이스들과 관련시킴으로써 데이터 전송 접속 요구의 수신하에서 발생할 수 있다. 게다가, 본 발명의 TDD 양상에 따르면, 일정 시간 기간들, 예를 들어 타임 슬롯들이 디바이스들의 개수에 할당될 수 있다. 더욱이, 본 발명의 사상에서, 예를 들어, 반송파 주파수-시간 기간(예를 들어, 타임 슬롯) 쌍들에서 적용된 듀플렉스 홉핑 시퀀스들을 정의하는 (UMTS에서 스크램블링 코드들과 같은) 필요한 시퀀스 리스팅들은 디바이스들과 관련되며 디바이스들에 전달될 수 있다. 이는 또한 이후의 스테이지에서 동적으로 발생할 수 있다. 단계(306)에서, 적어도 2개의 디바이스들, 보다 정확하게는 송수신기 유닛들 또는 개별 송신기 및 수신기 회로들(이에 따라, 사상적 의미에서 송수신기를 형성함)간의 정보 전송은 정의된 듀플렉스 홉핑 시퀀스에 따라 일정 시간 기간 동안 전용 주파수 대역에서 정보를 전송(~송신) 및/또는 수신함으로써 개시된다. 단계(308)에서, 데이터 전송 동작들과 관련된 디바이스들은 듀플렉스 홉핑 시퀀스들에 따라 자신의 수신/송신 주파수 및/또는 타이밍 정보를 갱신하며, 이후에 새로운 주파수/타임 슬롯 구성으로 스위칭한다. 전송될 더 이상의 데이터가 없을 때까지(310), 단계들(306 및 308)에 따라 데이터 전송은 계속된다. 방법은 단계(312)에서 종료된다.In view of the above examples, a general flow diagram of a method using the present invention is shown in FIG. 3. At
도 4는 하나의 통신 디바이스의 관점으로부터 도 3의 정보 전송 단계(306)를 수행하는 더욱 상세한 선택사항을 개시하는데, 상기 디바이스는 본 발명의 원리들을 적용하는 통신 링크의 일 단에 있게 된다.4 discloses a more detailed option of performing the
단계(402)에서, 전송 방향에 기반하여 시간 기간 동안에 정보가 전송(송신 또는 수신)되어야 하는지가 체크된다. 만일 그러한 경우에, 정보의 송신(406) 또는 수신(407)을 위한 적당한 타이밍(예를 들어, 전파 지연들 등으로 인해 가능한 오프세들을 갖는 기간 내의 적당한 타임 슬롯)이 결정된다(404). 수신 정보로부터, 예를 들어 수신 트레이닝 시퀀스로 인해, 동일(또는 인접) 주파수를 통한 데이터 전송 동안에 사용하기 위해 채널 파라메터들이 획득될 수 있다. 마지막으로, 송신/수신을 위한 명시적 피드백 정보가 예기되는 경우에(408), 이러한 정보는 단계(410)에서 (예를 들어, 시퀀스의 최근 데이터 전송 또는 후속 전송에서와 동일한) 소정의 주파수를 통한 소정의 시간 기간 동안에 선택적으로 수신/송신될 수 있다.In
일반적으로, 정보 전송은 분명한 바로서 무선 통신 디바이스와 기지국과 같 은 적어도 2개의 디바이스들간에서 발생할 수 있다. 게다가, 이러한 구성은 적어도 2개의 기지국들과 2개의 무선 통신 디바이스들로 특징되는 다중 셀 시나리오에서 발생할 수 있다. 이러한 보다 복잡한 경우에서, 복수의 인접 기지국들간의 예를 들어, 부분적으로 공통 듀플렉스 시퀀스들에 기초할 수 있는 일종의 동기화가 동일 주파수를 통한 동시적인 전송들을 피하기 위해 셀들간에서 필요하다. 대안적으로, 듀플렉스 홉핑의 사용을 기지국들의 바로 근접에서 한계를 정하는 것이 가능하지만, 종래 FDD는 보다 큰 거리들에서의 "소프트 핸드오버(soft handover)" 영역들에서 이용될 것이다. 예를 들어, 다수의 부-반송파들이 듀플렉스 홉핑에 할당될 수 있으며, 다른 것들은 종래 FDD에서 사용된다. 무선 전송의 의미에서, "바로 근접(immediate proximity)"은 경로 손실, 채널 상태, 요구 전송 전력 등 또는 이들의 조합과 같은 다수의 서로다른 문제들을 의미할 수 있다.In general, information transmission can occur between at least two devices, such as a wireless communication device and a base station, as is apparent. In addition, this configuration may occur in a multi-cell scenario characterized by at least two base stations and two wireless communication devices. In this more complex case, some sort of synchronization between multiple adjacent base stations, for example based in part on common duplex sequences, is needed between cells to avoid simultaneous transmissions over the same frequency. Alternatively, it is possible to delimit the use of duplex hopping in the immediate proximity of base stations, but conventional FDD would be used in “soft handover” areas at larger distances. For example, multiple sub-carriers can be assigned for duplex hopping, others are used in conventional FDD. In the sense of wireless transmission, "immediate proximity" can mean a number of different problems such as path loss, channel conditions, required transmit power, or the like, or a combination thereof.
도 2A 내지 2C의 예들에 의해 암시되는 바와같이, 듀플렉스 홉핑은 가변적인 사용 결정(varying usage resolution)에서 실행가능하며, 즉 모든 통신에 적용가능한 연속적인 홉핑이 가능하지만, 또한 종래 FDD 모드가 사용될 수 있는데, 예를 들어 99%의 시간, 및 피드백/트레이닝(~파일롯) 시퀀스들만이 무선 통신 디바이스에 의해 "다운링크" 주파수를 통해 업링크 방향으로 기지국에 송신된 일부 소정의 이벤트(급격하게 변경된 채널 파라메터 등)의 발생하에서 또는 주기적으로 될 수 있는데, 이는 예를 들어, 접속의 양 단들이 소정의 개수의 계속적인 시간 기간들 동안 (앞서 언급한 듀플렉스 시퀀스들과 같은) 주파수-시간 할당들을 인식하는 한에서 그러하다. 당연하게, 이러한 할당들은 적응되며 동적으로 변경될 수 있는데, 즉 기지국은 제어 채널을 통해 변경에 의해 영향받은 대응하는 무선 통신 디바이스들에 갱신 메시지를 송신함으로써 예를 들어, 새로운 정보 전송 접속들의 활성화로 인해 시퀀스들을 갱신한다.As implied by the examples of Figures 2A-2C, duplex hopping is feasible at varying usage resolution, i.e., continuous hopping applicable to all communications, but conventional FDD mode may also be used. For example, only 99% of the time, and only some feedback / training (~ pilot) sequences are sent by the wireless communication device to the base station in the uplink direction via the "downlink" frequency (a radically altered channel). Parameters, etc.) or periodically, such that both ends of the connection, for example, recognize frequency-time assignments (such as the aforementioned duplex sequences) for a predetermined number of successive time periods. So in one. Naturally, these assignments are adapted and can be changed dynamically, i.e., the base station sends an update message to the corresponding wireless communication devices affected by the change over the control channel, for example, by activation of new information transmission connections. Update the sequences.
명백하게, 만일 반송파들이 오버랩하지 않는 경우에, 직교성 요건은 보존된다. 시간에 대한 적합한 반송파 주파수 할당들(듀플렉스 홉핑 시퀀스들)이 예를 들어, Walsh (-Hadamard), Gold, 또는 직교 특성들을 갖는 다른 공지의 시퀀스들을 이용함으로써 구성될 수 있다.Clearly, if the carriers do not overlap, the orthogonality requirement is preserved. Suitable carrier frequency assignments (duplex hopping sequences) over time can be configured, for example, by using Walsh (-Hadamard), Gold, or other known sequences with orthogonal characteristics.
종종, 이러한 사상에서, 구현 불완전성으로 인해, 반송파들간의 보호 주파수대가 바람직하며, 또한 서로다른 전송 방향들과 관련된 시간 기간들간의 보호 기간(~보호 시간)이 바람직하다. 보호 기간들을 제어하는 수단은 TDD 통신 문헌(또한, 예를 들어 UMTS WCDMA 참조)들로부터 자체로서 공지되며, 보호 주파수대들을 정의하는 수단(종종 보호 주파수들 또는 듀플렉스 거리로서 지칭됨)은 전형적인 조정 또는 구현 문제들로서 여겨질 수 있다.Often, in this idea, due to implementation imperfections, a guard band between carriers is preferred, and also a guard period (~ guard time) between time periods associated with different transmission directions. The means for controlling the guard periods are known per se from the TDD communication literature (also see UMTS WCDMA, for example), and the means for defining guard bands (often referred to as guard frequencies or duplex distances) are typical adjustments or implementations. It can be considered as a problem.
업링크 및 다운링크 주파수들 모두에서 여러 부-반송파들이 있다. 이와같은 사상은 임의의 특정 디지털 또는 아날로그 변조 개념 또는 다중 액세스 프로토콜과는 독립적이다. 이는 셀룰러, 코드리스(cordless), ad-hoc 네트워크들, 무선 LAN, 3G/4G 네트워크들 등과 같은 임의의 무선 또는 유선 통신 네트워크들에서 사용될 수 있다.There are several sub-carriers at both uplink and downlink frequencies. This idea is independent of any particular digital or analog modulation concept or multiple access protocol. It can be used in any wireless or wired communication networks such as cellular, cordless, ad-hoc networks, wireless LANs, 3G / 4G networks, and the like.
본 발명의 이점들과 관련하여, 듀플렉스 타임들이 (시간 코히어런시 내에서) 충분히 짧으며, 전송이 정보가 상기 코히어런시 시간 내에서 수신된 주파수를 통해 발생하는 경우에, 고유 채널 상호관계(channel reciprocity)는 예를 들어, 프리-레이크 결합(pre-rake combining) 또는 빔 형성이 송신기에서 정확하게 수행되는 때에 수신 복잡도를 단순화하기 위해, 그리고 제어 채널 용량 요건들(TDD 대 FDD 폐쇄-루프 송신 다이버시티 참조)을 감소하기 위해 전송을 위한 전송 파라메터(또는 통신 파라메터)들(빔 계수들, 코딩/변조 선택사항들, 전력 제어, 속도 제어, 스케줄링 등)을 결정하는데 사용될 수 있다. 실용적인 관점에서, 공개문헌 [1]은 예를 들어, 스케줄링을 위해 다중-사용자 시스템에서 CQI(채널 품질 표시기)를 통해 채널 정보를 어떻게 적용하는지를 제안한다.With respect to the advantages of the present invention, the duplex times are short enough (within time coherency), and if the transmission occurs over a frequency received within the coherency time, the unique channel mutual The channel reciprocity is for example to simplify reception complexity when pre-rake combining or beamforming is performed correctly at the transmitter, and to control channel capacity requirements (TDD vs. FDD closed-loop). It can be used to determine transmission parameters (or communication parameters) (beam coefficients, coding / modulation options, power control, rate control, scheduling, etc.) for transmission to reduce transmit diversity (see transmit diversity). From a practical point of view, Publication [1] proposes how to apply channel information via CQI (Channel Quality Indicator) in a multi-user system, for example, for scheduling.
듀플렉스(주파수) 거리가 충분히 크며, 연속적인 슬롯들이 서로다른 주파수들로 송신되는 때의 개선된 다이버시티(diversity)는 본 발명의 다른 명백한 이점이다. 다이버시티 이점은 예를 들어, 연속적인 슬롯들로 2개의 서로다른 듀플렉스 대역들을 통해 코드화된 정보 스트림의 서로다른 부분들을 예를 들어, 송신함으로써 사용될 수 있다. 따라서, 심지어 일 듀플렉스 대역이 깊은 페이드(deep fade)인 경우에도, 채널 디코더(Turbo 디코더, 콘볼루션 디코더 등)가 전송된 정보를 재구성할 수 있다.The duplex (frequency) distance is large enough, and the improved diversity when successive slots are transmitted at different frequencies is another obvious advantage of the present invention. Diversity benefit can be used, for example, by transmitting different portions of the coded information stream over two different duplex bands in consecutive slots. Thus, even when the one duplex band is a deep fade, the channel decoder (Turbo decoder, convolution decoder, etc.) can reconstruct the transmitted information.
본 발명은 또한 결합된 이점들을 제공한다. 예를 들어, 송신기는 채널 상호관계로 인해 각 슬롯에 대한 빔들을 최적화할 수 있다(송신 전력 등을 최소화할 수 있다). 추가적인 참조를 위해, 빔 형성과 관련하여 TDD 시스템에서의 채널 정보 이용은 공개문헌 US6584302에서 설명된다. 동시에, 다이버시티를 획득하기 위해 서로다른 슬롯들은 서로다른 주파수들로 송신된다. 더욱이, 시스템은 요구 송신 전력이 최소가 되는 주파수들(예를 들어, 2개의 주파수들 중 양호한 것만이 사용됨)로 전송을 스케줄/라우팅할 수 있다. 따라서, 공간-주파수-시간 자원 할당이 단순화되는데, 이는 명시적 피드백 채널들이 더 이상 의무적이지 않기 때문이다.The present invention also provides combined advantages. For example, the transmitter may optimize the beams for each slot due to channel interrelationships (minimizing transmit power, etc.). For further reference, the use of channel information in a TDD system in connection with beam forming is described in publication US6584302. At the same time, different slots are transmitted on different frequencies to achieve diversity. Moreover, the system can schedule / route the transmission at frequencies at which the required transmit power is minimal (eg, only the better of the two frequencies is used). Thus, space-frequency-time resource allocation is simplified because explicit feedback channels are no longer mandatory.
당연하게, 채널 상호관계를 사용하기 위해, 수신기는 서로다른 주파수 채널을 통해 가능한 동시적으로 전송하는 동안에 다운링크/업링크 채널을 측정해야 한다. 채널 추정을 가능하게 하는 수단(또는 보다 일반적인 채널 관련 정보를 획득하는 방법들) 및 대응하는 채널 등화 방법들이 기술분야(파일롯 시퀀스들, 매칭된 필터, 추정 이론, 등화 필터들 등)에서 공지되어 있다. 따라서, 이러한 측정들은 수신 및 송신 모두에 사용되는데, 달성된 채널 추정은 공지 기법들을 사용하여 소정의 채널에서 송신 방법을 최적화하는데 사용된다.Naturally, in order to use channel correlation, the receiver must measure the downlink / uplink channel during the simultaneous transmission possible over different frequency channels. Means for enabling channel estimation (or methods for obtaining more general channel related information) and corresponding channel equalization methods are known in the art (pilot sequences, matched filter, estimation theory, equalization filters, etc.). . Thus, these measurements are used for both reception and transmission, where the channel estimation achieved is used to optimize the transmission method on a given channel using known techniques.
TDD에서, 송수신기는 송신 모드 또는 수신 모드의 일정 순간에서 동작하지만, 본원에서는 2개의 모드에서 가능한한 동시에 동작하며, 이에 따라 전송 지연을 감소시킨다. 그러나, 2개의 (업링크/다운링크) 주파수들은 동시에 활성이 되지 않는다. 더욱이, TDD에서와 같이 (비록 이것이 듀얼 전송 체인들을 요구하지만은), 예를 들어 단순히 소정의 시간 구간/부분 동안 2개의 듀플렉스 주파수들을 하나의 듀플렉스 방향에 할당함으로써 UL과 DL간의(또는, 일반적으로 2개의 듀플렉스 방향들에 대한) 비대칭 용량 공유에 대한 어떤 제약들이 없게 된다.In TDD, the transceivers operate at some instant in the transmit mode or receive mode, but here they operate simultaneously in the two modes as possible, thus reducing the transmission delay. However, the two (uplink / downlink) frequencies are not active at the same time. Moreover, as in TDD (although this requires dual transmission chains), for example between UL and DL (or, in general, simply by assigning two duplex frequencies to one duplex direction for a given time period / part) There are no restrictions on asymmetric capacity sharing (for two duplex directions).
이하에서, 본 발명이 어떻게 기존의 시스템들에 적합화될 수 있는지를 명확하게 하기 위한 몇가지 사용 사례들이 제공된다.In the following, several use cases are provided to clarify how the present invention can be adapted to existing systems.
CDMA2000CDMA2000
WCDMA와 대조적인 CDMA2000 시스템은 TDD 요소를 갖지 않는다. 본 발명의 방법은 CDMA2000 네트워크들의 용량을 강화하는데 사용될 수 있는데, 이는 TDD가 WCDMA를 강화하는데 사용되는 것과 같다. 이를 위해, 개별 TDD 대역을 정의할 필요가 없지만, 예를 들어 개별 반송파(쌍)가 사용될 수 있다. 현재에, HDR(cdma2000-1×DO) 사양은 개별 반송파를 사용하며, 동기화된 네트워크 동작과 결합되며, 심지어, 타이밍 제어를 위한 과도한 추가적인 측정들 없이 다중-셀 서비스가 실현가능하다.In contrast to WCDMA, a CDMA2000 system does not have a TDD element. The method of the present invention can be used to enhance the capacity of CDMA2000 networks, as TDD is used to enhance WCDMA. For this purpose, it is not necessary to define individual TDD bands, but for example individual carriers (pairs) can be used. Currently, the HDR (cdma2000-1 × DO) specification uses separate carriers, is combined with synchronized network operation, and even multi-cell service is feasible without undue additional measurements for timing control.
GSM/EDGE(Enhanced Data rates for GSM/Global Evolution)Enhanced Data rates for GSM / Global Evolution (GSM / EDGE)
TDMA 네트워크들에 내재하는 주파수 재사용 거리는 부정확한 타이밍 제어 효과를 완화하게 한다. 반면에, TDMA 네트워크들은 이미 타이밍 제어 메커니즘들을 포함하며, 이들은 또한 필요한 경우에 본 발명과 함께 사용될 수 있다. TDMA 시스템들에서 본 발명 방법의 직접적인 사용은 조정의 관점에서 단순하지 않을 수 있지만, 본 발명은 현재에 사양들에 의해 커버되지 않는 다른 주파수 대역들에 대해 GSM/EDGE의 고속 시스템 구현을 가능하게 할 것이다.The frequency reuse distance inherent in TDMA networks allows to mitigate incorrect timing control effects. On the other hand, TDMA networks already include timing control mechanisms, which can also be used with the present invention where necessary. The direct use of the method of the present invention in TDMA systems may not be simple in terms of coordination, but the present invention will enable high speed system implementation of GSM / EDGE for other frequency bands not currently covered by the specifications. will be.
UMTS/WCDMAUMTS / WCDMA
UMTS는 TDD 모드를 가지며, 타이밍을 조정하는 관련 수단을 갖는다. 이들은 만일 필요한 경우에, 예를 들어 다중-셀 경우에서 또한 본 발명과 함께 사용될 수 있다. 적어도 TDD가 적용가능한 경우에 본 발명이 적용가능하며, 따라서 본 발명은 홑 대역들(unpaired bands)에서 동작할 필요없이 UMTS의 내부 셀들(indoor cells)의 용량을 더 증가시키는데 사용될 수 있다. 네트워크는 소정의 셀/반송파 쌍이 듀 플렉스 홉핑 모드에서 동작하도록 지시할 수 있다. 용량 증가는 추가적인 스펙트럼(쌍 대역들)의 이용가능성에 기인하며, 특히 효율적인 자원 제어 알고리즘들이 실현가능하다는 사실에 기인한다.UMTS has a TDD mode and has associated means for adjusting timing. They can also be used with the invention if necessary, for example in multi-cell cases. The invention is applicable where at least TDD is applicable, and thus the invention can be used to further increase the capacity of the indoor cells of the UMTS without having to operate in unpaired bands. The network may instruct a given cell / carrier pair to operate in duplex hopping mode. The capacity increase is due to the availability of additional spectrum (pair bands), especially due to the fact that efficient resource control algorithms are feasible.
예를 들어, 정확한 빔 형성이 용량을 개선함과 아울러 수신기 복잡도를 완화한다. 만일 제안된 사상이 사용되지 않는 경우에, 높은 용량의 피드백 채널들을 정의하여 (명시적 시그널링을 통해 채널 상태 정보를 제공함으로써) 유사한 성능에 도달할 필요가 있게 된다. 따라서, 본 발명은 쌍 대역들에서 동작하는 때에 송신기에 채널 상태 정보를 전달하는 새로운 방법을 제공한다. 채널 상태 정보(CSI)는 다중-입력 다중-출력(MIMO) 채널을 위한 송신기를 고안하는데 사용될 수 있는데, 여기서 최적 또는 개선된 다중-빔 형성 및 전력 및 속도 할당이 사용된다. CSI는 적당한 a)전송 포맷(코딩, 변조 방법), b)MIMO 시스템에서 사용될 스트림들의 개수, 및 관련 전력들/속도들/빔들의 선택, c)일반적으로, MIMO/MISO/SIMO/SISO(단일-입력 단일-출력) 전송 방법의 선택, d)서비스(들) 및/또는 사용자(들)의 선택 또는 우선화 등에 사용될 수 있다.For example, accurate beamforming improves capacity while mitigating receiver complexity. If the proposed idea is not used, it is necessary to define high capacity feedback channels to reach similar performance (by providing channel state information via explicit signaling). Accordingly, the present invention provides a new method of conveying channel state information to a transmitter when operating in pair bands. Channel state information (CSI) can be used to design a transmitter for a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) channel, where optimal or improved multi-beam shaping and power and speed allocation are used. The CSI may be adapted to a) the transmission format (coding, modulation method), b) the number of streams to be used in the MIMO system, and the selection of associated powers / speeds / beams, c) in general, MIMO / MISO / SIMO / SISO (single Input single-output) transmission method, d) selection or prioritization of service (s) and / or user (s).
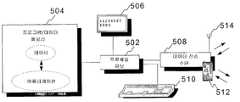
본 발명을 더욱 상세히 수행하는 장비를 고려한다면, 도 5는 기지국과 같은 통신 디바이스를 위한 기본 요소들의 블록도를 개시한다. 프로세싱 유닛(502)은 또한 현재의 주파수-시간 할당들과 같은 데이터를 선택적으로 포함하는 메모리(504)에 저장된 명령들에 따라 동작들의 실행(예를 들어, 데이터 전송 제어 어플리케이션)을 제어한다. 데이터 전송 수단(508)은 무선/적외선 송수신기 또는 무선 네트워크(WLAN 등) 어댑터들과 같은 무선 접속 수단(514), 또는 예를 들어, 종래 네트워 크 어댑터(이더넷 카드 등) 또는 TDMA 인터페이스 카드와 같은 고정 접속 수단(512)을 포함할 수 있다. 명백하게, 선택 키보드 또는 다른 데이터 입력 수단(510) 및 디스플레이(506)가 사용자에게 디바이스를 관리 및 제어하는 인터페이스를 제공하는데 유용하게 된다.Considering the equipment for carrying out the invention in more detail, FIG. 5 discloses a block diagram of the basic elements for a communication device, such as a base station.
본 발명의 방법을 수행하는 소프트웨어가 예를 들어, 플로피 디스크, CD-ROM, 및 메모리 카드와 같은 운송 매체(carrier medium)상에 제공될 수 있다.Software for performing the method of the present invention may be provided on a carrier medium such as, for example, floppy disks, CD-ROMs, and memory cards.
마찬가지로, 그 블록도가 도 6에서 도시되는 본 발명에서 이용될 수 있는 무선 통신 디바이스는 프로세싱 수단(602), 메모리 수단(604), 예를 들어 도 5의 기지국을 통해 무선 통신 디바이스들을 무선 네트워크 또는 다른 디바이스에 접속시킬 수 있는 송수신기(612)와 같은 데이터 전송 수단(608)을 포함하며, 선택적으로 충분한 UI를 수행하기 위해 키패드(610)에 추가하여 디스플레이(606)를 포함한다.Likewise, a wireless communication device that can be used in the present invention, whose block diagram is shown in FIG. 6, can be used to process wireless communication devices via a processing means 602, a memory means 604, for example the base station of FIG. Data transmission means 608, such as
상기 2개의 통신 디바이스들은 하나 이상의 송신 또는 수신 안테나들을 포함할 수 있다.The two communication devices can include one or more transmit or receive antennas.
MIMO를 갖는 현대의 통신들에서의 듀플렉스 홉핑 효과, 가능한 다중-사용자 특성들을 구체화하기 위해, 도 7A 및 7B는 표준 FDD와 하나의 가능한 시나리오와 관련된 듀플렉스 홉핑 경우들간의 차이를 도시한다. 본원에서 사용되는 표준 신호 모델[2]은:To specify the duplex hopping effect, possible multi-user characteristics in modern communications with MIMO, FIGS. 7A and 7B show the differences between the duplex hopping cases associated with standard FDD and one possible scenario. As used herein, the standard signal model [2] is:
Y=XWH +noiseY =XWH +noise
이며, 여기서Y는 수신 신호에 대응하는 매트릭스를 나타내며,X는 변조 매트릭스이며,W는 빔-형성 매트릭스이며,H는 채널 매트릭스이며,noise는 전송 과정 동안 에 신호에 도입된 잡음을 나타낸다.WhereY represents the matrix corresponding to the received signal,X is the modulation matrix,W is the beam-forming matrix,H is the channel matrix, andnoise represents the noise introduced into the signal during the transmission process.
자원 할당 및 스케줄링 목적들을 위해, 송신기에는 송신 자원들의 등급을 매기는 수단이 제공된다. 관련 정보는 송신기와 반대되는 것으로서 전형적으로 수신기에 상주하며, 따라서 대응하는 송신 유닛에 신호화될 필요가 있다. 예외는 듀플렉스 홉핑의 경우인데, 여기서 채널 상호관계로 인해, CQI는 단지 수신기로부터 신호화된 (다른 사용자들 및 잡음으로 인한) 가능한 간섭 전력과 함께 송신기에서 계산될 수 있다. 종래 FDD 시스템 내의 신호화 기반 방식에서, 각 수신기는 예를 들어, 공통 또는 전용 파일롯 채널들로부터의 측정들을 사용하여 MIMO 채널 매트릭스(H)를 알고 있는 것으로 가정된다. 수신기는 실현가능한 빔 형성 매트릭스들{W} 세트에 대한 조건부 채널 품질 표시기를 결정함과 아울러 전력 할당, 속도 할당 등을 결정한다. 듀플렉스 홉핑 기반 FDD 방식에서, 기지국이 채널(H)을 추정하게 하는 신호들을 송신하는 것으로 가정하면, 채널(H)은 송신기에서 공지된다. 선택된 CQI를 최대화하는 선택된 사용자 특정(W)은 스케줄러에 의해 선택될 때까지 송신기에서 사용되지 않는다. 역으로, 비록 다른 스케줄링, 우선화 및 다중화 선택들이 또한 명백하게 가능하지만은, 열망하는(greedy) 스케줄러가 최고 채널 품질을 갖는 사용자를 선택한다. 특히, 듀플렉스 홉핑에 있어서, 다운링크 전송이 모든 사용자들에 대해 함께 최적화될 수 있다.For resource allocation and scheduling purposes, the transmitter is provided with means for ranking transmission resources. The relevant information typically resides in the receiver as opposed to the transmitter and therefore needs to be signaled to the corresponding transmitting unit. An exception is the case of duplex hopping, where due to channel correlation, the CQI can only be calculated at the transmitter with possible interference power signaled from the receiver (due to other users and noise). In a signaling based scheme in a conventional FDD system, it is assumed that each receiver knows the MIMO channel matrixH using, for example, measurements from common or dedicated pilot channels. The receiver determines the conditional channel quality indicator for a set of feasible beamforming matrices {W } as well as determining power allocation, speed allocation, and the like. In the duplex hopping based FDD scheme, assuming that the base station transmits signals that cause channelH to be estimated, channelH is known at the transmitter. The selected user specificW that maximizes the selected CQI is not used at the transmitter until it is selected by the scheduler. Conversely, although other scheduling, prioritization and multiplexing choices are also clearly possible, the greedy scheduler selects the user with the highest channel quality. In particular, for duplex hopping, the downlink transmission can be optimized together for all users.
마지막으로, 듀플렉스 홉핑 이점들을 시각화하기 위해, 2개의 실험이 수행되는데, 일 실험은 듀플렉스 홉핑 사상에서의 경우이며(도 7B 참조), 다른 실험은 명시적 피드백 신호화를 사용하는 종래의 사상이다(도 7A 참조). BER 비율들은 채널 사용당 일 수신기 안테나당 잡음 전력에 대한 채널 사용당 비트당 송신 신호 전력의 함수로서 도시된다. 사용된 변조들은 4bps/Hz에 도달한다. 송신기들은 8개의 안테나들을 구비하고 있지만, 수신기들은 2개의 안테나를 갖고 있다. 듀플렉스 홉핑 기반 피드백은 30 피드백 비트들을 포함하는 피드백 방식에 대해 대략 1.5 내지 2dB의 성능을 개선하고 있음이 주목된다. 범례 "i-Th"을 갖는 커브들은 i-Threaded 2×2 매트릭스 변조[3]를 갖는 2개의 QPSK 변조 스트림들로부터 발생되는 반면에, TX-AA는 단일-스트림 16-QAM 전송을 가리킨다. 또한, 도면들은 CQI를 통한 채널 상태 정보를 사용하여 선택되는 바와같이, 보다 양호한 듀플렉스 주파수에서 전송이 수행되는 경우의 성능을 표시한다. 따라서, 듀플렉스 주파수 선택(범례들 "S-TXAA" 및 "S-iTh")은 2명의 사용자를 갖는 다중-사용자 다이버시티와 유사하며, 성능 증가를 촉진한다.Finally, to visualize the duplex hopping advantages, two experiments are performed, one for the duplex hopping event (see FIG. 7B) and the other for the conventional idea using explicit feedback signaling ( See FIG. 7A). The BER rates are shown as a function of transmit signal power per bit per channel use versus noise power per receiver antenna per channel use. The modulations used reach 4bps / Hz. The transmitters have eight antennas, but the receivers have two antennas. It is noted that duplex hopping based feedback improves performance of approximately 1.5 to 2 dB over a feedback scheme including 30 feedback bits. Curves with the legend "i-Th" are generated from two QPSK modulation streams with i-Threaded 2x2 matrix modulation [3], while TX-AA indicates a single-stream 16-QAM transmission. The figures also indicate the performance when transmission is performed at a better duplex frequency, as selected using channel state information over CQI. Thus, duplex frequency selection (legends “S-TXAA” and “S-iTh”) is similar to multi-user diversity with two users and promotes increased performance.
당연하게, 상기 시나리오는 단지 명확화를 위해 의도된 것이며, 달성된 실제 결과들은 우세한 채널 조건들, 사용된 전송 파라메터들, 안테나 파라메터들 및 구성들 등에 따라 크게 변할 수 있다.Of course, the scenario is only intended for clarity, and the actual results achieved may vary greatly depending on the prevailing channel conditions, transmission parameters used, antenna parameters and configurations, and the like.
본 발명에 따라 정보 전송에서 이용되는 하드웨어 계층 요소들뿐만 아니라 프로토콜들 및 프로토콜 스택들은 기존의 것들로부터 선택될 수 있는데, 이는 본 발명의 일 이점으로부터 알 수 있는 바와같이, 본 발명을 수행하는데 요구되는 전송 성능들이 특정적으로 복잡하거나 특수하지 않기 때문이다. 본 발명은, 추가적인 소프트웨어/하드웨어 모듈 또는 이들의 조합이 데이터 전송을 요구하는 디바이스에 포함되거나 적어도 연결되도록 구현될 수 있다.The protocols and protocol stacks as well as the hardware layer elements used in the information transmission in accordance with the present invention can be selected from existing ones, as can be seen from one advantage of the present invention, as required to carry out the present invention. This is because the transmission capabilities are not particularly complex or special. The invention may be implemented such that additional software / hardware modules or combinations thereof are included or at least coupled to the device requiring data transfer.
청구범위에 의해 한정된 본 발명의 범주를 벗어남이 없이 본원에서 개시된 본 발명에 대한 서로다른 변형들이 이루질 수 있음이 기술분야의 당업자에게 자명할 것이다. 예를 들어, 이용된 디바이스들 및 방법 단계들 또는 이들의 상호 순서는 변할 수 있지만, 이들은 여전히 본 발명의 기본 사상에 수렴한다. 하나의 결과로서, 본 발명의 무선 통신 디바이스는 실제상으로 예를 들어, 이동 전화기, PDA, 통신 인에이블 핸드헬드 게임 콘솔/엔터테인먼트 디바이스 등으로서 목록화 될 수 있다.It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that different modifications may be made to the invention disclosed herein without departing from the scope of the invention as defined by the claims. For example, the devices and method steps used or their mutual order may vary, but they still converge on the basic idea of the present invention. As one result, the wireless communication device of the present invention may be practically listed as, for example, a mobile phone, a PDA, a communication enabled handheld game console / entertainment device, and the like.
참조문헌들:References :
[1] Ari Hottinen: Multiuser scheduling with matrix modulation, Proceedings of IEEE ISSPIT 2003, Dec 2003 Darmstadt Germany[1] Ari Hottinen: Multiuser scheduling with matrix modulation, Proceedings of IEEE ISSPIT 2003, Dec 2003 Darmstadt Germany
[2] A. Hottinen, O. Tirkkonen, R. Wichman: Multi-antenna transceiver techniques for 3G and beyond, John Wiley & Sons, 2003[2] A. Hottinen, O. Tirkkonen, R. Wichman: Multi-antenna transceiver techniques for 3G and beyond, John Wiley & Sons, 2003
[3] A. Hottinen, O. Tirkkonen: Precoder designs for high rate space-time block codes, Proceedings of CISS 2004, March 2004 Princeton USA[3] A. Hottinen, O. Tirkkonen: Precoder designs for high rate space-time block codes, Proceedings of CISS 2004, March 2004 Princeton USA
Claims (63)
Translated fromKoreanPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020067019083AKR100920273B1 (en) | 2006-09-15 | 2004-03-16 | A method, a device and a system for duplex communications |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020067019083AKR100920273B1 (en) | 2006-09-15 | 2004-03-16 | A method, a device and a system for duplex communications |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20060123638A KR20060123638A (en) | 2006-12-01 |
| KR100920273B1true KR100920273B1 (en) | 2009-10-08 |
Family
ID=37728587
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020067019083AExpired - Fee RelatedKR100920273B1 (en) | 2006-09-15 | 2004-03-16 | A method, a device and a system for duplex communications |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100920273B1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022092836A1 (en)* | 2020-11-02 | 2022-05-05 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | Method for multi-band communication and electronic device therefor |
| US11909435B2 (en) | 2020-11-02 | 2024-02-20 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method for multi-band communication and electronic device thereof |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080198837A1 (en)* | 2007-02-02 | 2008-08-21 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | System and method for transmitting and receiving signal in communication system |
| KR102314623B1 (en)* | 2014-12-30 | 2021-10-19 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Inter-beam interference avoiding apparatus and method for avoiding inter-beam interference in a communication system of time division duplex using multi-beam |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1999026437A1 (en)* | 1997-11-14 | 1999-05-27 | Ericsson Inc. | Flexible frequency-time division duplex in radio communications systems |
| KR20020087873A (en)* | 2001-05-16 | 2002-11-23 | 가부시키가이샤 엔티티 도코모 | Mobile communication system |
- 2004
- 2004-03-16KRKR1020067019083Apatent/KR100920273B1/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1999026437A1 (en)* | 1997-11-14 | 1999-05-27 | Ericsson Inc. | Flexible frequency-time division duplex in radio communications systems |
| KR20020087873A (en)* | 2001-05-16 | 2002-11-23 | 가부시키가이샤 엔티티 도코모 | Mobile communication system |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022092836A1 (en)* | 2020-11-02 | 2022-05-05 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | Method for multi-band communication and electronic device therefor |
| US11909435B2 (en) | 2020-11-02 | 2024-02-20 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method for multi-band communication and electronic device thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20060123638A (en) | 2006-12-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8842581B2 (en) | Method, a device and a system for duplex communications | |
| KR101188396B1 (en) | Methods and apparatus of enhancing performance in wireless communication systems | |
| US6925095B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for communication | |
| JP4562091B2 (en) | Communication system using relay base station with asymmetric data link | |
| US9049722B2 (en) | Methods and apparatus of enhancing performance in wireless communication systems | |
| JP4937357B2 (en) | Link adaptation in wireless communication systems | |
| US8588053B2 (en) | Transmitting apparatus, transmission control method, and communication apparatus | |
| KR20030084957A (en) | System and method for wireless code division multiple access communication | |
| EP1249092A1 (en) | Adaptive frame structures for hybrid cdma / tdma system | |
| JP3652837B2 (en) | TDMA communication system | |
| WO2006062368A1 (en) | Orthogonal frequency and code hopping multiplexing communications method | |
| EP2260587B1 (en) | Timeslot hopping for transmitting call data | |
| US7873055B2 (en) | Scheduling user transmissions of mobile stations on a reverse link of a spread spectrum cellular system | |
| JP2007074737A (en) | Duplex communication method with alternating frequency time division | |
| KR100920273B1 (en) | A method, a device and a system for duplex communications | |
| RU2358385C2 (en) | Method, device and system for duplex communication | |
| EP3122087B1 (en) | Method and device for transmitting downlink multiframe | |
| HK1102040B (en) | A method, a device and a system for duplex communications |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| E13-X000 | Pre-grant limitation requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-3-E10-E13-lim-X000 | |
| PA0105 | International application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A15-nap-PA0105 | |
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | St.27 status event code:A-1-1-Q10-Q12-nap-PG1501 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| T11-X000 | Administrative time limit extension requested | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T11-oth-X000 | |
| T11-X000 | Administrative time limit extension requested | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T11-oth-X000 | |
| T11-X000 | Administrative time limit extension requested | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T11-oth-X000 | |
| E13-X000 | Pre-grant limitation requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-3-E10-E13-lim-X000 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| T11-X000 | Administrative time limit extension requested | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T11-oth-X000 | |
| T11-X000 | Administrative time limit extension requested | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T11-oth-X000 | |
| T11-X000 | Administrative time limit extension requested | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T11-oth-X000 | |
| T11-X000 | Administrative time limit extension requested | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T11-oth-X000 | |
| T11-X000 | Administrative time limit extension requested | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T11-oth-X000 | |
| T11-X000 | Administrative time limit extension requested | St.27 status event code:U-3-3-T10-T11-oth-X000 | |
| E13-X000 | Pre-grant limitation requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-3-E10-E13-lim-X000 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| R17-X000 | Change to representative recorded | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R17-oth-X000 | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U12-oth-PR1002 Fee payment year number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20120907 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:4 | |
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee | ||
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U13-oth-PC1903 Not in force date:20130929 Payment event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | St.27 status event code:N-4-6-H10-H13-oth-PC1903 Ip right cessation event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE Not in force date:20130929 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 |