KR100876798B1 - Apparatus and method for determining delay value of common control information channel in code division multiple access communication system applying high speed forward packet access method - Google Patents
Apparatus and method for determining delay value of common control information channel in code division multiple access communication system applying high speed forward packet access methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100876798B1 KR100876798B1KR1020020009405AKR20020009405AKR100876798B1KR 100876798 B1KR100876798 B1KR 100876798B1KR 1020020009405 AKR1020020009405 AKR 1020020009405AKR 20020009405 AKR20020009405 AKR 20020009405AKR 100876798 B1KR100876798 B1KR 100876798B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- control information
- channel
- common control
- information channel
- common
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B7/00—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field
- H04B7/24—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts
- H04B7/26—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts at least one of which is mobile
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W88/00—Devices specially adapted for wireless communication networks, e.g. terminals, base stations or access point devices
- H04W88/08—Access point devices
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean도 1은 통상적인 비동기 부호분할다중접속 이동통신시스템의 개괄적인 구조를 도시한 도면.1 is a schematic block diagram of a conventional asynchronous code division multiple access mobile communication system.
도 2는 고속 순방향 패킷접속을 위해 사용되는 통상적인 OVSF 코드의 일 예를 도시한 도면.2 illustrates an example of a typical OVSF code used for high speed forward packet access.
도 3은 HSDPA를 위해 운용되는 채널들 간의 시간 관계를 도시한 도면.3 is a diagram illustrating a time relationship between channels operated for HSDPA.
도 4는 HI(HS-DSCH Indicator)의 QPSK 심볼을 이용한 코딩 방식을 도시한 도면.4 is a diagram illustrating a coding scheme using a QPSK symbol of an HI (HS-DSCH Indicator).
도 5는 HS-PDSCH 채널을 위한 제어정보를 전송하는 HS-SCCH 채널의 구조를 도시한 도면.5 is a diagram illustrating a structure of an HS-SCCH channel for transmitting control information for an HS-PDSCH channel.
도 6은 하향 물리 채널들 간의 시간 관계를 도시한 도면.6 illustrates the time relationship between downlink physical channels.
도 7은 종래 기술에 따른 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay) 설정을 도시한 도면.7 is a diagram illustrating a delay setting of an HS-SCCH channel according to the prior art.
도 8은 본 발명에 따른 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay) 설정을 도시한 도면.8 illustrates a delay setting of an HS-SCCH channel according to the present invention.
도 9는 본 발명에 따른 기지국 송신 장치의 일 예를 도시한 도면.9 is a diagram illustrating an example of an apparatus for transmitting a base station according to the present invention;
도 10은 본 발명에 따른 단말기 수신 장치의 일 예를 도시한 도면.10 is a diagram illustrating an example of a terminal receiving apparatus according to the present invention.
도 11은 본 발명의 일 실시 예에 의해 RNC가 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay) 설정시 기지국과 RNC간의 cell setup 관련 메시지를 이용한 시그널링 방법을 도시한 도면.11 is a diagram illustrating a signaling method using a cell setup related message between a base station and an RNC when an RNC sets a delay of an HS-SCCH channel according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 12는 본 발명의 다른 실시 예에 의해 RNC가 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay) 설정시 기지국과 RNC간의 common transport channel setup 관련 메시지를 이용한 시그널링 방법을 도시한 도면.12 is a diagram illustrating a signaling method using a common transport channel setup related message between a base station and an RNC when an RNC sets a delay of an HS-SCCH channel according to another embodiment of the present invention;
도 13은 본 발명의 또 다른 실시 예에 의해 기지국이 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay) 설정시 기지국과 RNC간의 cell setup 관련 메시지를 이용한 시그널링 방법을 도시한 도면.FIG. 13 illustrates a signaling method using a cell setup related message between a base station and an RNC when a base station sets a delay of an HS-SCCH channel according to another embodiment of the present invention; FIG.
도 14는 본 발명의 또 다른 실시 예에 의해 기지국이 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay) 설정시 기지국과 RNC간의 common transport channel setup 관련 메시지를 이용한 시그널링 방법을 도시한 도면.FIG. 14 illustrates a signaling method using a message related to common transport channel setup between a base station and an RNC when a base station sets a delay of an HS-SCCH channel according to another embodiment of the present invention; FIG.
도 15는 본 발명에 따른 단말기와 RNC간의 BCH 채널을 이용한 시그널링 방법을 도시한 도면.15 illustrates a signaling method using a BCH channel between a terminal and an RNC according to the present invention.
도 16은 본 발명에 따른 단말기와 RNC간의 RRC 메시지를 이용한 시그널링 방법을 도시한 도면.16 illustrates a signaling method using an RRC message between a terminal and an RNC according to the present invention.
도 17은 본 발명의 일 실시 예에 의해 RNC가 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay)를 설정할 때 기지국의 동작흐름도를 도시한 도면.17 is a flowchart illustrating an operation of a base station when the RNC sets a delay of an HS-SCCH channel according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 18은 본 발명의 일 실시 예에 의해 RNC가 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay)를 설정할 때 RNC의 동작흐름도를 도시한 도면.FIG. 18 is a flowchart illustrating an operation of an RNC when the RNC sets a delay of an HS-SCCH channel according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 19는 본 발명에 따른 단말기의 동작 흐름도를 도시한 도면.19 is a flowchart illustrating an operation of a terminal according to the present invention.
도 20은 본 발명의 일 실시 예에 의해 기지국이 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay)을 설정할 때 기지국의 동작 흐름도를 도시한 도면.20 is a flowchart illustrating an operation of a base station when the base station sets a delay of the HS-SCCH channel according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 21은 본 발명의 일 실시 예에 의해 기지국이 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay)을 설정할 때 RNC의 동작흐름도를 도시한 도면.
21 is a flowchart illustrating an operation of an RNC when a base station sets a delay of an HS-SCCH channel according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명은 고속순방향패킷접속 이동통신시스템에서 제어정보를 전송하는 장치 및 방법에 관한 것으로, 특히 기지국이 이동단말로 제어정보를 전송하는 공통제어정보채널의 타이밍을 조절하는 장치 및 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for transmitting control information in a high speed forward packet access mobile communication system, and more particularly, to an apparatus and method for adjusting a timing of a common control information channel for transmitting control information to a mobile station by a base station.
통상적으로 고속순방향패킷접속(High Speed Downlink Packet Access, 이하 "HSDPA"라 칭함)은 비동기방식의 부호분할다중접속 이동통신시스템(이하 "UMTS 이동통신시스템"이라 칭함)에서 고속의 순방향 데이터 전송을 위한 기술의 집합들로 3GPP에서 현재 표준화 작업이 진행되고 있다.In general, High Speed Downlink Packet Access (hereinafter referred to as "HSDPA") is used for high-speed forward data transmission in an asynchronous code division multiple access mobile communication system (hereinafter referred to as "UMTS mobile communication system"). A set of technologies is currently being standardized in 3GPP.
도 1은 통상적인 UMTS 이동통신시스템의 개괄적인 구조를 도시하고 있는 도면이다.1 is a diagram illustrating a general structure of a conventional UMTS mobile communication system.
상기 도 1을 참조하면, 상기 UMTS 이동통신시스템은 코어 망(Core Network: 100)과 복수개의 무선 망 서브 시스템들(Radio Network Subsystem: 이하 "RNS"라 칭함: 110, 120)과 이동단말(User Equipment, 이하 "UE"라 칭함: 130)로 구성된다. 상기 RNS(110)는 하나의 무선 망 제어기(Radio Network Controller: 이하 "RNC"라 함)(111) 및 복수개의 기지국들(115, 113)로 구성된다. 또한, 상기 RNS(120)는 하나의 RNC(111) 및 복수개의 기지국들(114, 116)로 구성된다. 상기 기지국(115, 113, 114, 116)은 "Node B" 또는 "셀"이라는 용어로서 사용될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 1, the UMTS mobile communication system includes a core network (100), a plurality of radio network subsystems (hereinafter referred to as "RNS": 110, 120), and a mobile terminal (User). Equipment, hereinafter referred to as "UE": 130). The RNS 110 is composed of one Radio Network Controller (hereinafter referred to as "RNC") 111 and a plurality of
상기 RNC(111, 1112)는 그 역할에 따라 서빙 RNC(Serving RNC, 이하 "SRNC"라 칭함), 드리프트 RNC(Drift RNC, 이하 "DRNC"라 칭함) 또는 컨트롤링 RNC(Controlling RNC, 이하 "CRNC"라 칭함)로 나누어진다. 상기 SRNC와 DRNC는 각 UE들의 정보를 관리하며, 각각의 UE들에 대한 역할에 따라 분류된다. 즉, 상기 코어 망(100)과의 데이터 전송을 담당하는 RNC를 해당 UE(130)의 SRNC라 칭하며, 상기 UE(130)로부터의 데이터가 상기 SRNC로 전달되기 위해 거치게되는 RNC를 상기 UE의 DRNC라 칭한다. 상기 CRNC는 각각의 Node B들을 제어하는 RNC를 각 Node B들의 CRNC라 칭한다.The
상기 도 1을 참조하여 설명하면, RNC(111)은 UE(130)의 정보를 관리함에 따라 상기 RNC(111)은 상기 UE(130)의 SRNC가 된다. 만약, 상기 UE(130)가 이동하여 RNC(112)로의 데이터를 송신 및 수신하는 경우 상기 RNC(112)는 상기 UE(130)의 DRNC가 된다. 그리고, 상기 RNC(111)는 자신이 제어하고 있는 Node B(115), Node B(113)에 대한 CRNC가 된다.Referring to FIG. 1, as the RNC 111 manages information of the UE 130, the RNC 111 becomes an SRNC of the UE 130. If the UE 130 moves to transmit and receive data to the
상기 HSDPA 기술은 구체적으로 다수의 직교코드(OVSF) 코드들의 사용과 적응 적 채널 코딩 기법 및 복합재전송 기법(Hybrid Automatic Re-transmission Request, 이하 "HARQ"라 칭함)을 사용한다. 상기 HARQ 기법은 빠른 재전송과 소프트 컴바이닝(soft combining) 기술을 포함한다. 상기 HSDPA에서 한 사용자에게 할당할 수 있는 최대 OVSF 코드의 개수는 15개이며, 변조 방식으로는 채널 상황에 따라 QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM 등이 적응적으로 선택되어 사용된다. 한편, 오류가 발생한 데이터에 대해서, UE와 Node B사이에서 재전송이 수행되고, 재전송된 데이터들을 소프트 컴바이닝을 통해 전체적인 통신 효율을 향상시킨다. 상기 재전송에 관한 방식들을 총체적으로 n-channel SAW HARQ(Stop And Wait Hybrid Automatic Re-transmission Request)라고 명명한다.Specifically, the HSDPA technology uses a plurality of orthogonal code (OVSF) codes, an adaptive channel coding technique, and a hybrid automatic re-transmission request (hereinafter referred to as "HARQ"). The HARQ scheme includes fast retransmission and soft combining techniques. The maximum number of OVSF codes that can be assigned to a user in the HSDPA is 15. QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, etc. are adaptively selected and used according to channel conditions as a modulation scheme. Meanwhile, retransmission is performed between the UE and the Node B with respect to the data having an error, and the overall communication efficiency is improved through soft combining the retransmitted data. The retransmission schemes are collectively referred to as n-channel SAW HARQ (Stop And Wait Hybrid Automatic Re-transmission Request).
이하 상기 n-channel SAW HARQ에 대해서 살펴보면 다음과 같다.Hereinafter, the n-channel SAW HARQ will be described.
상기 HSDPA에서 n-channel SAW HARQ 방식은 통상적인 SAW ARQ(Stop And Wait Automatic Re-transmission Request) 방식의 효율을 높이기 위해 다음 2가지 방안을 새롭게 도입한 방식이다.In the HSDPA, the n-channel SAW HARQ scheme newly introduces the following two schemes to increase the efficiency of a typical SAW ARQ (Stop And Wait Automatic Re-transmission Request) scheme.
첫 번째로, 수신측은 오류가 발생한 데이터를 일시적으로 저장하였다가 재전송되는 해당 데이터와의 결합에 의해 오류 발생 확률을 줄여 준다. 상기 과정을 소프트 컴바이닝(soft combining) 이라고 한다. 상기 소프트 컴바이닝에는 체이스 컴바이닝 기법(Chase Combining: 이하 "CC"라 칭함) 과 중복분 증가 기법(Incremental Redundancy: 이하 "IR"이라 칭함)이라는 2 가지 기법이 존재한다.First, the receiver temporarily stores the data in error and then reduces the probability of error by combining the data with the retransmitted data. This process is called soft combining. There are two types of soft combining, a chase combining technique (hereinafter referred to as "CC") and an incremental redundancy technique (hereinafter referred to as "IR").
상기 CC 기법을 사용하는 경우 송신측은 최초 전송과 재전송시 동일한 전송 포맷을 사용한다. 예컨대, 최초 전송과 재 전송 시 동일한 데이터를 전송한다. 만약, 최초 전송에 m개의 부호화 심벌들이 하나의 부호블록으로 전송되었다면, 재 전송시에도 동일한 m 개의 부호화 심벌들이 하나의 부호블록으로 전송된다. 따라서, 최초 전송과 재 전송시에 동일한 부호율(coding rate)이 적용되어야 한다. 한편, 수신측은 최초 전송된 부호블록과 재 전송된 부호블록을 결합하고, 상기 결합된 부호블록을 이용해서 CRC 연산을 통해 오류 발생 여부를 확인한다.When using the CC scheme, the sender uses the same transmission format for initial transmission and retransmission. For example, the same data is transmitted during initial transmission and retransmission. If m coded symbols are transmitted in one code block in the first transmission, the same m coded symbols are transmitted in one code block even when retransmitted. Therefore, the same coding rate should be applied at the first transmission and retransmission. Meanwhile, the receiving side combines the first transmitted code block and the retransmitted code block and checks whether an error has occurred through the CRC operation using the combined code block.
상기 IR 기법을 사용하는 경우 송신측은 최초 전송과 재 전송시에 서로 상이한 전송 포맷을 사용한다. 예컨대, n 비트의 사용자 데이터가 채널 부호화를 거쳐 m 개의 부호화 심벌들이 되었다면, 송신측은 최초 전송에서 상기 m 부호화 심벌들 중 일부만 전송하고, 재 전송시 순차적으로 나머지 부호화 심벌들을 전송한다. 따라서, 최초 전송과 재전송시에 상이한 부호율이 적용되어야 한다. 한편, 수신측은 최초 전송된 부호블록의 뒷부분에 재 전송된 부호블록들을 붙여서, 부호율이 높은 부호블록을 구성한 후 오류 정정 (error correction)을 실행한다. 상기 IR에서 상기 최초 전송과 각각의 재전송들을 중복분 버전(Redundancy Version, 이하 "RV"라 칭함)으로 구분한다. 최초 전송이 RV 1, 다음 재전송이 RV 2, 그 다음 재전송이 RV 3 등으로 명명된다. 수신측은 상기 RV 정보를 이용해서 최초 전송된 부호블록과 재 전송된 부호블록을 올바르게 결합할 수 있다.In the case of using the IR scheme, the transmitter uses different transmission formats for initial transmission and retransmission. For example, if n bits of user data are channel coded and become m coded symbols, the transmitter transmits only some of the m coded symbols in the first transmission, and sequentially transmits the remaining coded symbols upon retransmission. Therefore, different code rates should be applied during initial transmission and retransmission. Meanwhile, the receiving side attaches the retransmitted code blocks to the rear part of the first transmitted code block, forms a code block having a high code rate, and then executes error correction. In the IR, the initial transmission and each retransmission are divided into a redundancy version (hereinafter referred to as "RV"). The first transmission is named
두 번째로, 통상적인 SAW ARQ 방식에서는 이전 패킷의 ACK을 받아야만 다음 패킷을 전송할 수 있지만, n-channel SAW HARQ에서는 이전 패킷의 ACK를 받지 않은 상태에서도 다수의 패킷을 연속적으로 전송함으로서 무선 링크의 사용 효율을 높일 수 있도록 한다. 상기 n-channel SAW HARQ는 UE와 Node B간에 n 개의 논리적인 채널을 설정하고, 명시적인 채널 번호로 그 채널들을 식별한다. 따라서, 수신측인 UE는 임의의 시점에서 수신한 패킷이 어느 채널에 속한 패킷인지를 알 수 있다. 또한, 수신되어야 할 순서대로 패킷들을 재구성하거나, 해당 패킷을 소프트 컴바이닝하는 등 필요한 조치를 취할 수 있다.Second, in the conventional SAW ARQ method, the next packet can be transmitted only after receiving the ACK of the previous packet, but in the n-channel SAW HARQ, the radio link is used by continuously transmitting a plurality of packets without receiving the acknowledgment of the previous packet. Increase efficiency The n-channel SAW HARQ establishes n logical channels between the UE and the Node B, and identifies the channels by an explicit channel number. Accordingly, the UE on the receiving side can know which channel the packet received at any time point belongs to. In addition, necessary steps may be taken, such as reconfiguring the packets in the order in which they should be received, or soft combining the packets.
상기 n-channel SAW HARQ의 동작을 상기 도 1을 참조하여 구체적으로 설명하면 다음과 같다. 이때, 임의의 UE(130)와 임의의 Node B(113)사이에 4-channel SAW HARQ가 진행되고 있으며, 각 채널은 1에서 4까지 논리적 식별자를 부여받았다고 가정한다. 상기 UE(130)와 Node B(113)의 물리계층에는 각 채널에 대응되는 HARQ 프로세서를 구비한다. 상기 Node B(113)는 최초 전송하는 부호블록 (coded block: 한 TTI동안 전송되는 사용자 데이터를 의미함)에 1이라는 채널 식별자를 부여 상기 UE(130)로 전송한다. 상기 부호블록에 오류가 발생하였다면, 상기 UE(130)는 채널 식별자를 통해 채널 1과 대응되는 HARQ 프로세서 1로 상기 부호블록을 전달하고 채널 1에 대한 부정적 인지신호(NACK)를 전송한다. 상기 Node B(113)는 채널 1의 부호블록에 대한 인지신호의 도착 여부와 관계없이 후속 부호블록을 채널 2를 통하여 전송할 수 있다. 만약, 상기 후속되는 부호블록에도 오류가 발생하였다면, 상기 후속된 부호블록도 대응되는 HARQ 프로세서로 전달된다. 상기 Node B(113)는 채널 1의 부호블록에 대한 부정적 인지신호를 상기 UE(130)로부터 수신하면, 채널 1로 해당 부호블록을 재전송한다. 이에 대응하여 상기 UE(130)는 상기 부호블록의 채널 식별자를 통해, HARQ 프로세서 1로 상기 부호블록을 전달한다. 상기 HARQ 프로세서 1은 앞서 저장하고 있던 부호블록들과 상기 재 전송된 부호블록을 소프트 컴바이닝 한다. 이와 같이 n-channel SAW HARQ에서는 채널 식별자와 HARQ 프로세서를 일대일 대응시키는 방식으로, 인지신호가 수신될 때까지 사용자 데이터 전송을 지연시키지 않고도, 최초 전송 부호블록과 재 전송된 부호블록들을 적절하게 대응시킬 수 있다.The operation of the n-channel SAW HARQ will be described in detail with reference to FIG. 1. At this time, it is assumed that 4-channel SAW HARQ is in progress between any
도 2는 통상적인 HSDPA에서 사용되는 OVSF 코드들의 일 예를 보이고 있는 도면이다. 상기 도 2에서는 확산 계수가 16인 경우(SF = 16)를 일 예로서 보이고 있다. 상기 HSDPA에서 사용 가능한 다수개의 OVSF 코드들은 특정 동일시간에 다수의 UE들이 동시에 사용하는 것이 가능하다. 즉 특정 동일시간에서 다수의 UE들간에 OVSF 코드 다중화가 가능하다.2 is a diagram illustrating an example of OVSF codes used in a conventional HSDPA. 2 illustrates an example in which the diffusion coefficient is 16 (SF = 16). Multiple OVSF codes available in the HSDPA may be simultaneously used by multiple UEs at a particular time. That is, OVSF code multiplexing is possible between multiple UEs at a particular same time.
이를 도 2를 참조하여 설명하면, 각 OVSF 코드들은 코드 트리(code tree)의 위치에 따라 C(i,j)로 도시되어 있다. 상기 C(i,j)에서 상기 변수 i는 확산계수를 나타내며, 상기 변수 j는 상기 OVSF 코드 트리에서 맨 좌측부터 존재하는 순서를 나타낸 것이다. 예를 들면, C(16,0)은 상기 확산 계수가 16이며, 상기 확산 계수가 16인 OVSF 코드들 중 좌측으로부터 첫 번째 위치에 존재한다는 것을 나타낸다. 상기 도 2는 상기 확산 계수가 16일 경우 상기 OVSF 코드 트리에서 첫 번째부터 열 다섯 번째까지, 즉 C(16,0)에서 C(16,14)까지 15개의 OVSF 코드들을 HSDPA 이동통신시스템에 할당하는 경우를 도시하고 있다. 상기 15개의 OVSF 코드들은 다수의 UE들에게 다중화될 수 있는데, 예를 들어 하기 <표 1>과 같이 OVSF 코드들이 다중화될 수 있다.2, each OVSF code is shown as C (i, j) according to the location of the code tree. In C (i, j), the variable i represents a diffusion coefficient, and the variable j represents an order of existence from the far left in the OVSF code tree. For example, C (16,0) indicates that the spreading factor is 16 and is present at the first position from the left of the OVSF codes with the spreading factor 16. FIG. 2 shows that when the spreading factor is 16, 15 OVSF codes are allocated to an HSDPA mobile communication system from first to fifteenth, that is, C (16,0) to C (16,14) in the OVSF code tree. The case is shown. The 15 OVSF codes may be multiplexed to multiple UEs. For example, the OVSF codes may be multiplexed as shown in Table 1 below.
상기 <표 1>에서, 상기 A, B, C는 상기 HSDPA 이동통신시스템을 사용하고 있는 임의의 사용자들, 즉 임의의 UE들을 지정한다. 상기 <표 1>에 나타낸 바와 같이, 임의의 시점 T0, T1, T2에서 상기 사용자 A, B, C는 상기 HSDPA 이동통신시스템에 할당된 OVSF 코드들을 이용해서 코드 다중화된다. 상기 각 UE들에게 할당할 OVSF 코드의 개수와 OVSF 코드 트리 상의 위치는 상기 Node B가 결정하며, 이는 상기 Node B에 저장되어 있는 UE들 각각의 사용자 데이터(user data) 양과, 상기 Node B와 UE들 각각에 설정되어 있는 채널 상황 등을 고려해서 결정하는 것이다. 즉, 상기 UE들와 상기 Node B가 주고받는 제어 정보들로는 임의의 UE가 사용할 OVSF 코드의 개수와 코드 트리 상의 위치를 지정하는 상기 코드 정보, 변조 방식을 채널 상황에 적응적으로 결정하기 위해 필요한 채널 품질 정보와 변조 방식 정보 및 n-channel SAW HARQ를 지원하기 위해 필요한 채널 번호 정보와 ACK/NACK 정보 등이 있다.In Table 1, A, B, and C designate arbitrary users, that is, arbitrary UEs, using the HSDPA mobile communication system. As shown in Table 1, at arbitrary time points T0, T1, and T2, the users A, B, and C are code multiplexed using OVSF codes assigned to the HSDPA mobile communication system. The number of OVSF codes to be allocated to each of the UEs and the location on the OVSF code tree are determined by the Node B, which is the amount of user data of each of the UEs stored in the Node B, and the Node B and the UE. The decision is made in consideration of the channel conditions set in each of these. That is, the control information exchanged between the UEs and the Node B includes channel information necessary for adaptively determining the number of OVSF codes to be used by a UE, the code information for designating a location on a code tree, and a modulation scheme according to channel conditions. Information, modulation scheme information, channel number information and ACK / NACK information necessary to support n-channel SAW HARQ.
이하 상기 제어 정보들과 사용자 데이터를 전송하기 위해 사용되는 채널들에 대해서 설명한다.Hereinafter, channels used for transmitting the control information and user data will be described.
HSDPA에서 사용되는 채널의 종류를 순방향 채널과 역방향 채널로 구분해서 나열하면 다음과 같다. 상기 순방향 채널로는 순방향 공통제어정보채널(High Speed-Shared Control Channel, 이하 "HS-SCCH"라 칭함), 관련 순방향 전용채널(Associated Dedicated Physical Channel, 이하 "Associated DPCH"라 칭함), 고속 순방향 공통채널(High Speed-Physical Downlink Shared Channel, 이하 "HS-PDSCH"라 칭함)이 있다. 상기 역방향 채널로는 역방향 전용 부채널(Dedicated Physical Channel, 이하 "Secondary DPCH"라 칭함)이 있다.The types of channels used in HSDPA are classified into forward channel and reverse channel as follows. As the forward channel, a forward common control information channel (hereinafter referred to as "HS-SCCH"), an associated forward dedicated channel (hereinafter referred to as "Associated DPCH"), a high speed forward common There is a channel (High Speed-Physical Downlink Shared Channel, hereinafter referred to as "HS-PDSCH"). The reverse channel includes a reverse dedicated subchannel (hereinafter referred to as a "secondary DPCH").
상기한 각 채널들간의 시간(Timing) 관계는 도 3에 도시하고 있다.The timing relationship between the channels is shown in FIG. 3.
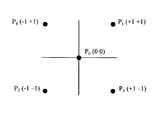
상기 도 3을 참조하면, UE는 제1공통파일럿채널(Primary-Common Pilot Channel, 이하 "P-CPICH"라 칭함) 등을 이용해서 자신과 Node B 사이의 채널 품질을 측정하고, 그 결과를 채널품질리포트(Channel Quality Report, 이하 "CQR"이라 칭함)를 이용해서 상기 Node B에게 통보한다. 상기 CQR은 Secondary DPCH를 통해 전송된다. 기타 자세한 사항 즉, 어떤 항목에 대한 측정을 수행하고, 어떤 빈도로 CQR을 전송하며, CQR에 구체적으로 어떤 정보를 담을 지에 대해서는 현재 표준회의에서 논의 중이다. 상기 Node B는 상기 CQR을 이용해서 스케줄링을 수행한다. 즉, 동일한 셀에서 HSDPA 서비스를 제공받고 있는 다수의 UE들 중, 다음 전송시간간격(Transmission Time Interval, 이하 "TTI"라 칭함)에 실제 데이터를 전송 받을 UE를 결정하고, 그 데이터 전송에 사용될 변조 방식과 할당될 코드의 개수 등을 결정하는 것을 말한다. 임의의 UE에 대하여 데이터 전송이 결정되면, 상기 Node B는 상기 UE와의 사이에 설정되어 있는 Associated DPCH를 통해서 소정 식별자 HI를 전송한다. 상기 HI는 HS-PDSCH를 통해서 해당 UE에게 패킷 데이터가 전송될 것이라는 사실과, 상기 패킷 데이터를 수신할 때 필요한 제어 정보들을 전송하는 HS-SCCH의 식별자를 담고 있다. 상기 UE는 복잡도 등을 고려하여 최대 4개의 HS-SCCH만을 수신할 수 있다. 반면, 상기 Node B는 4개 이상의 HS-SCCH를 운영하여 패킷 데이타의 스케줄링을 용이하게 할 수 있다. 따라서, 상기 HI는 도 4에서 예시하듯이 하나의 QPSK 심볼을 이용하여 전송할 수 있다. 즉, 상기 도 4에서 P1(+1 +1), P2(-1 1), P3 (+1 1), P4(-1 +1)이 각 하나의 HS-SCCH를 지시하도록 설정될 수 있다. 상기 HI가 전송되지 않는다면, 즉, DTX(P0(0 0))라면, 다음 TTI에 해당 UE로 데이터가 전송되지 않음을 의미할 수 있다. 임의의 한 UE에게 할당된 HS-SCCH 채널들의 집합을 "serving HS-SCCH set"이라고 한다. 상기 serving HS-SCCH set은 UE 별로 개별적으로 지정될 수 있다.Referring to FIG. 3, the UE measures a channel quality between itself and a Node B using a first common pilot channel (hereinafter, referred to as a "P-CPICH"), and the result is a channel. The Node B is notified using a Quality Report (hereinafter referred to as "CQR"). The CQR is transmitted on the secondary DPCH. Other details, such as what measures to take, how often to send a CQR, and what information to include in the CQR, are currently being discussed at the Standard Meeting. The Node B performs scheduling using the CQR. That is, among a plurality of UEs receiving HSDPA service in the same cell, a UE to receive actual data is transmitted at a next transmission time interval (hereinafter referred to as “TTI”), and modulation to be used for the data transmission. Determining the type and number of codes to be allocated. If data transmission is determined for a certain UE, the Node B transmits a predetermined identifier HI through an Associated DPCH established with the UE. The HI contains the fact that packet data will be transmitted to the corresponding UE through the HS-PDSCH, and an identifier of the HS-SCCH for transmitting control information necessary for receiving the packet data. The UE may receive only up to four HS-SCCHs in consideration of complexity and the like. On the other hand, the Node B may operate four or more HS-SCCHs to facilitate scheduling of packet data. Therefore, the HI may be transmitted using one QPSK symbol as illustrated in FIG. 4. That is, in FIG. 4, P1 (+1 +1), P2 (-1 1), P3 (+1 1), and P4 (-1 +1) may be set to indicate one HS-SCCH. If the HI is not transmitted, that is, DTX (P0 (0 0)), this may mean that data is not transmitted to the UE in the next TTI. The set of HS-SCCH channels assigned to any one UE is called a "serving HS-SCCH set". The serving HS-SCCH set may be individually designated for each UE.
한편, 상기 Node B는 상기 HI 송신과 동시에, 제어 정보를 HS-SCCH를 통해 전송한다. 상기 HS-SCCH에 포함되는 제어 정보들은 HS-PDSCH에 사용될 OVSF 코드들에 대한 정보(이하 "code 정보"라 칭함) 7 bit, HS-PDSCH에 적용될 변조 방식에 대한 정보 1 bit, HS-PDSCH를 통해 전송되는 데이터의 크기에 대한 정보 6 bit, 그리고 HARQ 관련 정보들이 있다.Meanwhile, the Node B transmits control information through the HS-SCCH simultaneously with the HI transmission. The control information included in the HS-SCCH includes information about OVSF codes to be used for the HS-PDSCH (hereinafter referred to as "code information") 7 bits, information about 1 bit about the modulation scheme to be applied to the HS-PDSCH, and HS-PDSCH. There are 6 bits of information on the size of data transmitted through the HARQ information.
상기 HARQ 관련 정보들의 종류는 다음과 같다. HS-PDSCH를 통해 전송될 데이터가 새로운 데이터인지 아닌지를 나타내는 새로운 데이터 식별자(new data indicator)가 1 bit, HS-PDSCH를 통해 전송될 데이터의 리던던시 버젼(Redundancy Version, 이하 "RV"라 칭함)에 대한 정보 2 bit, HS-PDSCH를 통해 전송될 데이터의 n-channel SAW HARQ 상에서의 채널 번호가 3 bit, 이렇게 총 6 bit로 HARQ 정보를 구성한다.The types of HARQ related information are as follows. A new data indicator indicating whether data to be transmitted through the HS-PDSCH is new data is 1 bit, and a redundancy version (hereinafter referred to as "RV") of data to be transmitted through the HS-PDSCH. 2 bits of information, the channel number on the n-channel SAW HARQ of the data to be transmitted through the HS-PDSCH is 3 bits, so that the HARQ information is composed of a total of 6 bits.
도 5에는 상기 HS-SCCH의 구조를 도시하고 있다. 도 5에서 보는 바와 같이 HS-SCCH은 확산계수 128인 OVSF 코드를 사용해서 전송되며, Part 1, CRC-1, Part 2, CRC-2의 4개의 부분으로 나누어진다. 상기 Part 1에는 해당 UE가 사용할 OVSF 코드의 코드 트리 상에서의 위치와 코드의 개수를 나타내는 코드 정보와 변조 방식이 포함된다. 상기 CRC-1에는 상기 Part 1의 정보들과 UE의 식별자에 대한 CRC 연산 결과가 들어간다. 상기 UE 식별자는 10 bit가 사용될 것으로 예상되며, 실제로 전송되지는 않지만, 전송측에서 CRC-1을 계산함에 있어서 상기 UE 식별자를 함께 계산한다. 한편, 수신측에서도 상기 CRC-1을 계산할 때 상기 UE 식별자를 함께 계산하는 용도로 사용된다. 이렇게 함으로써, 상기 UE는 임의의 HS-SCCH에 들어 있는 정보가 자신의 정보인지 아닌지를 판단할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 임의의 UE a에게 HS-SCCH를 이용해서 제어 정보를 전송하는 경우, Node B는 상기 Part 1과 상기 UE a의 식별자를 이용해서 상기 CRC-1을 산출한다. 상기 UE a는 자신의 serving HS-SCCH set에 속해있는 HS-SCCH들 중, 자신의 UE 식별자와 Part-1을 함께 계산했을 때, 상기 CRC-1에 대해서 오류가 발생하지 않은 HS-SCCH에 포함되어 있는 제어 정보들이, 자신에 대한 제어 정보인 것으로 판단한다. 상기 Part-2에는 HS-PDSCH를 통해 전송되는 데이터의 크기를 의미하는 전송블록(Transport Block, 이하 "TB"라 칭함) 크기 정보와, n-channel SAW HARQ의 채널 번호와, 해당 데이터가 새로운 데이터인지 재 전송되는 데이터인지를 알려주는 새로운 데이터 식별자(New data indicator)와, 해당 데이터가 IR 상에서 몇 번째 버젼(version)인지를 알려주는 리던던시 버젼(Redundancy Version)이 포함된다. 상기 Part-2 정보에 대한 CRC 결과는 CRC-2를 통해 전송된다.5 shows the structure of the HS-SCCH. As shown in FIG. 5, the HS-SCCH is transmitted using an OVSF code having a spreading factor of 128, and is divided into four parts,
상기 Part-1의 제어정보와 상기 CRC-1의 총 20 비트는 상기 도 5에서 도시하듯이 40비트로 부호화되어 1 슬롯(slot)구간 동안에 전송되며, 상기 Part-2의 제어정보와 상기 CRC-2의 총 20비트는 80비트로 부호화되어 2 슬롯구간 동안에 전송된다. 이와 같이, (Part-1 + CRC-1)과 (Part-2 + CRC-2)를 따로 부호화하는 이유는 HS-PDSCH의 역확산 및 복조를 위해 필요한 Part-1의 정보를 해당하는 HS-PDSCH TTI의 수신 전에 확보하기 위해서 이다.The control information of Part-1 and a total of 20 bits of the CRC-1 are encoded into 40 bits as shown in FIG. 5 and transmitted during one slot period, and the control information of Part-2 and the CRC-2. A total of 20 bits of are encoded into 80 bits and transmitted during the two slot periods. As such, the reason for separately encoding (Part-1 + CRC-1) and (Part-2 + CRC-2) is that HS-PDSCH corresponding to information of Part-1 necessary for despreading and demodulating the HS-PDSCH. This is to ensure before receiving the TTI.
UE는 HS-SCCH를 통해 수신한 상기 정보들을 바탕으로 HS-PDSCH를 통해 전송되는 데이터를 수신해서 복조 등 필요한 조치를 취한다. 이 때 code 정보를 통해서, 어떤 OVSF 코드를 통해 전송되는 HS-PDSCH를 수신할 지를 결정하고, 변조 정보를 통해서 어떻게 복조할 지를 결정한다. 상기 과정을 완료한 후 CRC 연산을 통해 해당 데이터의 오류 발생 여부를 판단한 뒤, 이에 대한 ACK/NACK 정보를 송신한다. 오류가 발생하지 않았다면 ACK을, 발생하였다면 NACK을 전송한다.The UE receives data transmitted through the HS-PDSCH based on the information received through the HS-SCCH and takes necessary measures such as demodulation. At this time, through the code information, it is determined through which OVSF code the HS-PDSCH transmitted, and how to demodulate through the modulation information. After the process is completed, it is determined whether an error occurs in the corresponding data through a CRC operation, and then ACK / NACK information is transmitted. If no error occurs, an ACK is sent. If an error occurs, a NACK is sent.
이상 HSDPA에 대한 개략적인 설명을 마치고, HS-SCCH의 타이밍 문제에 관하여 자세히 설명하고자 한다.After the brief description of the HSDPA, the timing problem of the HS-SCCH will be described in detail.
상기 HS-SCCH는 상기 도 5에서 도시하고 있듯이, 3 슬롯(1 TTI) 중 첫 번째 슬롯(slot)에 20비트(8bit의 제어정보 + 12bit의 CRC-1)를 40비트로 부호화하여 전송하고, 두 번째와 세 번째의 2 슬롯 구간 동안에 20비트(12bit의 제어정보 + 8bit의 CRC-2)를 80비트로 부호화하여 전송한다. 따라서 앞의 1 슬롯과 뒤의 2 슬롯들에 전송되는 데이터 양 및 부호화에 의한 이득이 달라질 수밖에 없다. 한편, Part-1 혹은 Part-2 제어정보 중 어느 한 곳이라도 에러가 발생하게 되면, 해당하는 HS- PDSCH TTI를 수신할 수 없게 되어 시스템의 효율(throughput)을 저하시키게 된다. 따라서, Part-1과 Part-2 정보 중 어느 한 곳만 채널 에러에 강인한 것보다는 양쪽의 채널에 대한 강인도가 비슷하게 유지되어야 시스템 효율을 향상시킬 수 있다. 이를 위해서는 부호화 이득이 다르기 때문에 전송 파워가 서로 다르게 배정되어야 한다. 즉, 앞의 1 슬롯에 뒤의 2 슬롯들 보다 더 큰 전송 파워를 할당해야 한다.As shown in FIG. 5, the HS-SCCH encodes and transmits 20 bits (8 bits of control information + 12 bits of CRC-1) into 40 bits in the first slot among 3 slots (1 TTI), 20 bits (12 bits of control information + 8 bits of CRC-2) are encoded into 80 bits during the 2nd and 3rd slot periods. Therefore, the amount of data transmitted in the first one slot and the second two slots and the gain due to the coding are inevitably changed. On the other hand, if an error occurs in any one of Part-1 or Part-2 control information, the corresponding HS-PDSCH TTI cannot be received, thereby reducing the efficiency of the system. Therefore, rather than any one of Part-1 and Part-2 information is robust to channel error, the robustness for both channels should be maintained similarly to improve system efficiency. To this end, transmission powers must be allocated differently because coding gains are different. That is, one transmit slot should be allocated larger than the latter two slots.
또한, HI는 단말기와 기지국의 처리 시간을 보장하고 스케줄링 지연을 감소시키기 위해서 상기 도 3에서 도시하듯이 HS-SCCH 채널의 앞의 1 슬롯 내에 HI를 전송한다. 상기 HI는 하나의 QPSK 심볼을 이용하여 전송하기 때문에 신뢰도를 높이기 위해서 전송 파워를 크게 할당해야 한다.In addition, the HI transmits the HI in one slot in front of the HS-SCCH channel as shown in FIG. 3 in order to ensure processing time of the terminal and the base station and reduce the scheduling delay. Since the HI is transmitted using one QPSK symbol, a large transmission power must be allocated to increase reliability.
상기의 이유들로 인해서 상기 도 5에서 도시하고 있듯이 HS-SCCH 채널의 앞의 1 슬롯 구간 동안의 전송전력 크기가 뒤의 2 슬롯구간 동안의 전송전력의 크기보다 커지는 문제가 발생한다.For the above reasons, as shown in FIG. 5, a problem arises in that the size of the transmit power during the first slot section of the HS-SCCH channel is larger than the size of the transmit power during the second slot section.
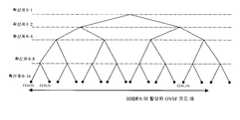
도 6에서는 하향 링크에서 각종 채널간의 시간(Timing) 관계를 도시하고 있다.상기 도 6에서 보이고 있는 바와 같이 HS-SCCH가 CPICH를 기준으로 하여 고정된 타이밍 오프셋을 갖게 할 수 있다. 그러나, 도 7에서 도시하고 있듯이 하나의 기지국내에 여러 셀들이 존재하는 경우, CPICH를 기준으로 하여 일정한 시간 차이로 정렬되어 있는 HS-SCCH로 인하여 앞에서 언급한 HS-SCCH TTI들 중 전송 전력이 더 큰 앞의 1 슬롯이 정렬되어, Node b에서의 전송 전력이 세 슬롯마다 한 슬롯에 집중되는 문제가 발생할 수 있다. 이는 여러 셀들간의 핸드오버(handover) 영역에서 하향 링크 간섭량을 증가시켜서, 핸드오버 영역에 위치한 UE들의 패킷 데이터 수신 성능 을 떨어뜨리게 될 뿐만 아니라 전체적인 시스템 효율을 감소시키게 된다.
6 illustrates a timing relationship between various channels in the downlink. As illustrated in FIG. 6, the HS-SCCH may have a fixed timing offset based on the CPICH. However, as shown in FIG. 7, when there are several cells in one base station, the transmission power of the aforementioned HS-SCCH TTIs is higher due to the HS-SCCH arranged at a constant time difference based on the CPICH. A large first one slot is aligned, which may cause a problem that transmit power in Node b is concentrated in one slot every three slots. This increases the amount of downlink interference in the handover area between several cells, thereby reducing the packet data reception performance of UEs located in the handover area, as well as reducing the overall system efficiency.
따라서, 상기한 바와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위한 본 발명의 목적은 고속 순방향 패킷 접속 통신 시스템에서, 기지국이 사용자 단말로 제어 정보를 전송하는 공통 제어 정보 채널의 타이밍을 조절하여 기지국 최대 송신 전력 및 하향 링크 간섭을 줄임으로써 고속 순방향 패킷 접속 통신 시스템의 효율을 높이는 데 있다.Accordingly, an object of the present invention for solving the above problems is to adjust the timing of the common control information channel through which the base station transmits control information to the user terminal in a high speed forward packet access communication system, the base station maximum transmission power and downlink Reducing the interference is to increase the efficiency of the high speed forward packet access communication system.
본 발명의 일 측면은 기지국으로부터의 송신 전력이 HS-SCCH 채널의 3 술롯들 중에서 첫 번째 슬롯에 집중됨으로써 하향 링크 간섭량이 증가하는 등의 문제점을 해결하여 시스템 효율을 향상시키는 것이다.One aspect of the present invention is to improve the system efficiency by solving a problem such that the amount of downlink interference is increased by concentrating the transmission power from the base station to the first slot among the three slots of the HS-SCCH channel.
본 발명의 또 다른 측면은 HS-SCCH의 시작점을 CPICH에 대하여 고정된 타이밍 옵셋 값을 갖지 않고, 셀별로 다른 타이밍 옵셋 값을 갖도록 하여 특정 시간 구간 동안에 기지국 송신 전력이 증가하여 하향 링크 간섭이 증가하여 시스템 효율이 저하되는 것을 방지할 수 있는 장치 및 방법을 제공하는 것이다.According to another aspect of the present invention, the start point of the HS-SCCH does not have a fixed timing offset value for the CPICH, but has a different timing offset value for each cell so that the base station transmit power is increased during a specific time interval, thereby increasing downlink interference. It is an object of the present invention to provide an apparatus and a method capable of preventing a decrease in system efficiency.
따라서 본 발명에서 제공하는 셀들 각각은 고유의 타이밍 옵셋에 의해 기지국과의 공통파일럿채널을 전송하고, 상기 공통파일럿채널에 대해 소정 지연 값을 가지고 상기 기지국과의 공통제어정보채널을 전송하는 고속순방향패킷접속 이동통신시스템에서 무선망 제어부에 의해 상기 셀별로 상기 공통파일럿채널에 대한 상기 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값을 결정하는 방법은, 상기 셀들 각각에 대응하여 상기 공통파일럿채널의 타이밍 옵셋을 설정하는 과정과, 상기 각 셀들별로 전송하게될 상기 공통제어정보채널의 전송시간간격에 대응하는 세 개의 슬롯들 중 첫 번째 슬롯들이 겹치는 구간이 최소가 되도록 상기 공통파일럿채널의 타이밍 옵셋을 감안하여 상기 셀들 각각에 대응하는 상기 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값들을 설정하는 과정과, 상기 설정한 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값들을 상기 이동단말과 상기 기지국으로 전송하는 과정을 포함한다.Accordingly, each of the cells provided by the present invention transmits a common pilot channel with the base station by a unique timing offset, and transmits a common control information channel with the base station with a predetermined delay value for the common pilot channel. The method for determining a delay value of the common control information channel for the common pilot channel for each cell by a wireless network controller in an access mobile communication system includes: setting a timing offset of the common pilot channel corresponding to each of the cells; And a timing offset of the common pilot channel to minimize the interval where the first slots among the three slots corresponding to the transmission time interval of the common control information channel to be transmitted for each cell are minimized. Setting delay values of the corresponding common control information channel; It comprises the step of transmitting a delay value of a common control information channel to the mobile station and the base station.
또한 본 발명에서 제공하는 셀들 각각은 고유의 타이밍 옵셋에 의해 기지국과의 공통파일럿채널을 전송하고, 상기 공통파일럿채널에 대해 소정 지연 값을 가지고 상기 기지국과의 공통제어정보채널을 전송하는 고속순방향패킷접속 이동통신시스템에서 상기 기지국에 의해 상기 셀별로 상기 공통파일럿채널에 대한 상기 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값을 결정하는 방법은 상기 무선망 제어부로부터 셀들 각각에 대응하는 공통파일럿채널의 타이밍 옵셋들을 수신하는 과정과, 상기 각 셀들별로 전송하게될 상기 공통제어정보채널의 전송시간간격에 대응하는 세 개의 슬롯들 중 첫 번째 슬롯들이 겹치는 구간이 최소가 되도록 상기 공통파일럿채널의 타이밍 옵셋을 감안하여 상기 셀들 각각에 대응하는 상기 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값들을 설정하는 과정과, 상기 설정한 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값들을 상기 무선망 제어부로 전송하는 과정을 포함한다.In addition, each cell provided by the present invention transmits a common pilot channel with the base station by a unique timing offset, and a high speed forward packet for transmitting a common control information channel with the base station with a predetermined delay value for the common pilot channel A method of determining a delay value of the common control information channel for the common pilot channel for each cell by the base station in an access mobile communication system includes receiving timing offsets of the common pilot channel corresponding to each of the cells from the radio network controller. And each of the cells in consideration of the timing offset of the common pilot channel such that a section in which the first slots of the three slots corresponding to the transmission time interval of the common control information channel to be transmitted for each cell overlap with each other is minimized. Setting delay values of the common control information channel corresponding to And includes the step of transmitting a delay value of the common control information channel, wherein the set to the radio network controller.
또한 본 발명에서 제공하는 셀들 각각은 고유의 타이밍 옵셋에 의해 기지국과의 공통파일럿채널을 전송하고, 상기 공통파일럿채널에 대해 소정 지연 값을 가지고 상기 기지국과의 공통제어정보채널을 전송하는 고속순방향패킷접속 이동통신시스템에서 상기 셀별로 상기 공통파일럿채널에 대한 상기 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값을 결정하는 장치는 상기 셀들 각각에 대응하여 상기 공통파일럿채널의 타이밍 옵셋을 설정하고, 상기 각 셀들별로 전송하게될 상기 공통제어정보채널의 전송시간간격에 대응하는 세 개의 슬롯들 중 첫 번째 슬롯들이 겹치는 구간이 최소가 되도록 상기 공통파일럿채널의 타이밍 옵셋을 감안하여 상기 셀들 각각에 대응하는 상기 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값들을 설정하여 전송하는 무선망 제어부와, 상기 무선망 제어부로부터 상기 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값을 수신하고, 상기 셀들 각각에 대응하는 지연 값에 의해 상기 공통제어정보채널을 송신하는 상기 기지국과, 상기 무선망 제어부로부터 상기 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값을 수신하고, 상기 지연 값에 의해 상기 기지국으로부터의 상기 공통제어정보채널을 수신하는 이동단말을 포함한다.In addition, each cell provided by the present invention transmits a common pilot channel with the base station by a unique timing offset, and a high speed forward packet for transmitting a common control information channel with the base station with a predetermined delay value for the common pilot channel An apparatus for determining a delay value of the common control information channel for the common pilot channel for each cell in an access mobile communication system sets a timing offset of the common pilot channel corresponding to each of the cells, and transmits each of the cells. In consideration of the timing offset of the common pilot channel so that the first overlapping interval of the first slots among the three slots corresponding to the transmission time interval of the common control information channel to be minimized, To the wireless network controller for setting and transmitting delay values, and to the wireless network controller. Receiving a delay value of the common control information channel from the base station and transmitting the common control information channel by a delay value corresponding to each of the cells, and receiving a delay value of the common control information channel from the radio network controller. And a mobile terminal for receiving the common control information channel from the base station by the delay value.
또한 본 발명에서 제공하는 셀들 각각은 고유의 타이밍 옵셋에 의해 기지국과의 공통파일럿채널을 전송하고, 상기 공통파일럿채널에 대해 소정 지연 값을 가지고 상기 기지국과의 공통제어정보채널을 전송하는 고속순방향패킷접속 이동통신시스템에서 상기 셀별로 상기 공통파일럿채널에 대한 상기 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값을 결정하는 장치는 상기 셀들 각각에 대응하는 공통파일럿채널의 타이밍 옵셋들을 설정하여 상기 기지국으로 전송하고, 상기 기지국으로부터의 상기 셀들 각각에 대응하는 상기 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값들을 수신하여 이동단말로 전송하는 무선망 제어부와, 상기 무선망 제어부로부터 셀들 각각에 대응하는 공통파일럿채널의 타이밍 옵셋들을 수신하고, 상기 각 셀들별로 전송하게될 상기 공통제어정보채널의 전송시간간격에 대응하는 세 개의 슬롯들 중 첫 번째 슬롯들이 겹치는 구간이 최소가 되도록 상기 공통파일럿채널의 타이밍 옵셋을 감안하여 상기 셀들 각각에 대응하는 상기 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값들을 설정하여 전송하며, 상기 셀들 각각에 대응하는 지연 값에 의해 상기 공통제어정보채널을 송신하는 상기 기지국과, 상기 무선망 제어부로부터 상기 공통제어정보채널의 지연 값을 수신하고, 상기 지연 값에 의해 상기 기지국으로부터의 상기 공통제어정보채널을 수신하는 이동단말을 포함한다.In addition, each cell provided by the present invention transmits a common pilot channel with the base station by a unique timing offset, and a high speed forward packet for transmitting a common control information channel with the base station with a predetermined delay value for the common pilot channel The apparatus for determining a delay value of the common control information channel for the common pilot channel for each cell in an access mobile communication system sets timing offsets of the common pilot channel corresponding to each of the cells, and transmits them to the base station. A wireless network controller for receiving delay values of the common control information channel corresponding to each of the cells from the mobile station and transmitting the delay values of the common pilot channel corresponding to each of the cells from the wireless network controller; When transmitting the common control information channel to be transmitted for each cell The delay value of the common control information channel corresponding to each of the cells is set and transmitted in consideration of the timing offset of the common pilot channel such that the interval of overlapping of the first slots among the three slots corresponding to the interval is minimized. Receiving the delay value of the common control information channel from the base station transmitting the common control information channel with a delay value corresponding to each of the cells, and from the radio network controller, and the common control from the base station with the delay value. It includes a mobile terminal for receiving the information channel.
이하 본 발명의 실시 예를 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 설명하면 다음과 같다.Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
후술될 상세한 설명에서는 상술한 기술적 과제를 이루기 위해 본 발명에 있어 한 개의 대표적인 실시 예를 제시할 것이다. 그리고 본 발명으로 제시될 수 있는 다른 실시 예들은 본 발명의 구성에서 설명으로 대체한다. 또한, 본 발명에서 제안하고자 하는 HSDPA는 UMTS 이동통신시스템에서 고속의 순방향 데이터 전송을 위한 기술의 집합들로서 3GPP에서 현재 표준화 작업이 진행되고 있다. 그러므로 본 발명에서는 아직 결정되지 않은 사항에 대해서는 지금까지의 논의 결과를 바탕으로 HSDPA를 설명하도록 한다.DETAILED DESCRIPTION In the following detailed description, one representative embodiment of the present invention is set forth in order to achieve the above technical problem. And other embodiments that can be presented with the present invention are replaced by the description in the configuration of the present invention. In addition, the HSDPA proposed by the present invention is a set of techniques for high speed forward data transmission in a UMTS mobile communication system. Therefore, in the present invention, the matters that have not yet been determined will be described based on the results of the discussion so far HSDPA.
우선 후술될 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 동작을 설명함에 있어 사용되는 HS- SCCH를 위한 타이밍 오프셋 값을 τhs-scch로 칭한다. 상기 τhs-scch는 256×N chip 값을 가질 수 있으며, 상기 N값은 0, 1, 2, ... , 30 값을 취할 수 있다. 따라서, 상기 τhs-scch는 최대 3 slot(=2560×3 chips)에 해당할 수 있다. Node B는 상기 τhs-scch 값에 따라 CPICH 프레임의 시작점에서 상기 τhs-scch 값 이후를 HS-SCCH TTI 시작점으로 하여 HS-SCCH 전송을 수행한다.First, a timing offset value for HS-SCCH used in describing an operation according to an embodiment of the present invention to be described below isreferred to as τhs -scch . The τhs-scch may have a 256 × N chip value, and the N value may take a value of 0, 1, 2, ..., 30. Therefore, τhs-scch may correspond to a maximum of 3 slots (= 2560 × 3 chips). Node B performs the HS-SCCH transmitted by thehs-scch Since the τ value to the HS-SCCH TTI starting point from the start point of the CPICH frame according to theτ-hs scch value.
도 8은 본 발명의 실시 예에 따라 각 셀들에서 HS-SCCH를 송신하기 위한 타이밍 오프셋 값 τhs-scch를 서로 겹치지 않도록 하는 일 예를 보이고 있는 도면이다.FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating an example in which timing offsets τhs -scch for transmitting an HS-SCCH in each cell do not overlap each other according to an embodiment of the present invention.
상기 도 8을 참조하면, 각 셀별로 τhs-scch가 다른 값을 갖도록 하여 큰 전송전력이 필요한 상기 각 셀들의 HS-SCCH TTI 중 첫 번째 슬롯이 서로 겹치지 않도록 하여 Node B의 최대 전송 전력이 증가하는 것을 방지하고, 하향 링크 간섭량의 증가를 방지할 수 있다. 또한 큰 전송 전력을 필요로 하는 HI 또한 HS-SCCH TTI 중 첫 번째 슬롯에서 전송되는데 HI가 전송되는 위치가 각 셀 별로 달라짐으로써 하향 링크 간섭량을 줄일 수 있게 된다.Referring to FIG. 8, τhs-scch has a different value for each cell so that the first slot of HS-SCCH TTI of each cell requiring a large transmit power does not overlap each other so that the maximum transmit power of Node B is increased. Can be prevented and an increase in the amount of downlink interference can be prevented. In addition, HI, which requires a large transmission power, is also transmitted in the first slot of the HS-SCCH TTI, and the amount of downlink interference can be reduced by changing the location where the HI is transmitted for each cell.
한편, 상향 링크로 전송되는 ACK/NACK 및 하향채널상태정보(CQR)의 전송시점 역시 상기 도 3에서 도시하듯이 HS-SCCH 타이밍에 의해 정해지는데, 각 셀별로 HS-SCCH 타이밍을 달리 함으로써 ACK/NACK 및 CQR의 전송시점 역시 달라지게 되어 상향 링크에서의 최대 간섭량을 줄일 수 있게 된다.On the other hand, the transmission time of the ACK / NACK and the downlink channel state information (CQR) transmitted on the uplink is also determined by the HS-SCCH timing, as shown in Figure 3, by varying the HS-SCCH timing for each cell ACK / The transmission time of the NACK and CQR is also changed to reduce the maximum amount of interference in the uplink.
전술한 바와 같이 상기 셀들 각각에 대응하는 서로 다른 τhs-scch를 사용하도 록 결정하는 방법은 크게 두 가지로 제안될 수 있다. 그 첫 번째가 상기 각 셀별 τhs-scch를 RNC가 결정하여 해당 Node B로 통보하는 방안이며, 그 두 번째가 상기 각 셀별 τhs-scch를 RNC의 요청에 의해 해당 Node B가 결정하여 상기 RNC로 통보하는 방안이다.As described above, two methods for determining to use different τhs-scch corresponding to each of the cells may be proposed. The first is amethod for the RNC to determine τhs-scch for each cell and notify the corresponding Node B. The second is for the RNC to determine τhs-scch for each cell by the RNC's request. This is to inform.
먼저, 상기 첫 번째 방안에 따른 상기 RNC와 Node B간의 신호 처리 절차는 도 11과 도 12에서 보이고 있는 바와 같다. 상기 도 11에서 보이고 있는 신호 처리 절차는 셀 셋업 단계에서 상기 τhs-scch를 결정하는 예이며. 상기 도 12에서 보이고 있는 신호 처리 절차는 공통전송채널을 셋업하는 단계에서 상기 τhs-scch를 결정하는 예이다.First, the signal processing procedure between the RNC and the Node B according to the first scheme is as shown in FIGS. 11 and 12. The signal processing procedure shown in FIG. 11 is an example of determining τhs -scch in a cell setup step. The signal processing procedure shown in FIG. 12 is an example of determining τhs -scch in setting up a common transport channel.
상기 도 11을 참조하면, 상기 RNC는 셀 셋업을 수행할 대상 Node B에 대응하여 셀 셋업 요청 메시지(Cell setup Request message)를 전송한다. 이때 상기 셀 셋업 메시지는 HS-SCCH에 사용할 코드, HS-DSCH에 사용할 코드 및 CPICH의 타이밍 옵셋 값 등의 정보를 함께 전송할 수 있다. 또한, 상기 RNC는 상기 셋 셋업 요청 메시지에 상기 Node B에 대응한 τhs-scch를 설정하여 전송한다. 상기 Node B는 상기 셀 셋업 요청 메시지에 대한 응답으로 셀 셋업 응답 메시지(cell setup response message)를 상기 RNC에게 전송한다.Referring to FIG. 11, the RNC transmits a cell setup request message corresponding to a target Node B to perform cell setup. In this case, the cell setup message may transmit information such as a code for HS-SCCH, a code for HS-DSCH and a timing offset value of CPICH. In addition, the RNC sets τhs-scch corresponding to the Node B in the set setup request message and transmits it. The Node B sends a cell setup response message to the RNC in response to the cell setup request message.
상기 도 12를 참조하면, 상기 RNC는 공통전송채널의 셋업을 수행할 대상 Node B에 대응하여 공통전송채널 셋업 요청 메시지(Common Transport Channel setup Request message)를 전송한다. 이때 상기 공통전송채널 셋업 요청 메시지는 HS-SCCH에 사용할 코드, HS-DSCH에 사용할 코드 등의 정보를 함께 전송할 수 있다. 또한, 상기 RNC는 상기 공통전송채널 셋업 요청 메시지에 상기 Node B에 대응한 τhs-scch를 설정하여 전송한다. 상기 Node B는 상기 셀 셋업 요청 메시지에 대한 응답으로 공통전송채널 셋업 응답 메시지(common transport channel setup response)를 상기 RNC에게 전송한다.Referring to FIG. 12, the RNC transmits a common transport channel setup request message corresponding to a target node B to perform setup of a common transport channel. In this case, the common transport channel setup request message may transmit information such as a code for HS-SCCH and a code for HS-DSCH. The RNC sets τhs -scch corresponding to the Node B in the common transport channel setup request message and transmits the same. The Node B sends a common transport channel setup response message to the RNC in response to the cell setup request message.
다음으로, 상기 두 번째 방안에 따른 상기 RNC와 Node B간의 신호 처리 절차는 도 13과 도 14에서 보이고 있는 바와 같다. 상기 두 번째 방안은 같은 Node B에 속한 셀들의 CPICH 채널들간의 타이밍 차이만 고려하여 상기 τhs-scch를 조정하고자 하는 경우에는 적용될 수 있다. 상기 도 13에서 보이고 있는 신호 처리 절차는 셀 셋업 단계에서 상기 Node B가 상기 τhs-scch를 결정하는 예이며. 상기 도 14에서 보이고 있는 신호 처리 절차는 공통전송채널을 셋업하는 단계에서 상기 Node B가 상기 τhs-scch를 결정하는 예이다.Next, the signal processing procedure between the RNC and Node B according to the second scheme is as shown in Figs. The second method may be applied when the τhs-scch is to be adjusted by considering only timing differences between CPICH channels of cells belonging to the same Node B. The signal processing procedure shown in FIG. 13 is an example in which the Node B determines τhs -scch in a cell setup step. The signal processing procedure shown in FIG. 14 is an example in which the Node B determines τhs -scch in setting up a common transport channel.
상기 도 13을 참조하면, 상기 RNC는 셀 셋업을 수행할 대상 Node B에 대응하여 셀 셋업 요청 메시지(Cell setup Request message)를 전송한다. 이때 상기 셀 셋업 메시지는 HS-SCCH에 사용할 코드, HS-DSCH에 사용할 코드 및 CPICH의 타이밍 옵셋 값 등의 정보를 함께 전송할 수 있다. 상기 Node B는 상기 셀 셋업 요청 메시지가 수신되면 셀들간의 CPICH 타이밍 차이를 고려하여 상기 τhs-scch를 설정한다. 한편, 상기 Node B는 상기 τhs-scch를 상기 셀 셋업 요청 메시지에 대응한 셀 셋업 응답 메시지(cell setup response message)에 포함시켜 상기 RNC에게 전송한다.Referring to FIG. 13, the RNC transmits a cell setup request message corresponding to a target Node B to perform cell setup. In this case, the cell setup message may transmit information such as a code for HS-SCCH, a code for HS-DSCH and a timing offset value of CPICH. When the cell setup request message is received, the Node B sets τhs-scch in consideration of CPICH timing differences between cells. Meanwhile, the Node B includes the τhs-scch in a cell setup response message corresponding to the cell setup request message and transmits it to the RNC.
상기 도 14를 참조하면, 상기 RNC는 공통전송채널의 셋업을 수행할 대상 Node B에 대응하여 공통전송채널 셋업 요청 메시지(Common Transport Channel setup Request message)를 전송한다. 이때 상기 공통전송채널 셋업 요청 메시지는 HS-SCCH에 사용할 코드, HS-DSCH에 사용할 코드 등의 정보를 함께 전송할 수 있다. 상기 Node B는 상기 공통전송채널 셋업 요청 메시지가 수신되면 셀들간의 CPICH 타이밍 차이를 고려하여 상기 τhs-scch를 설정한다. 한편, 상기 Node B는 상기 τhs-scch를 상기 공통전송채널 셋업 요청 메시지에 대응한 공통전송채널 셋업 응답 메시지(common transport channel setup response)에 포함시켜 상기 RNC에게 전송한다.Referring to FIG. 14, the RNC transmits a common transport channel setup request message corresponding to a target node B to perform setup of a common transport channel. In this case, the common transport channel setup request message may transmit information such as a code for HS-SCCH and a code for HS-DSCH. When the Node B receives the common transport channel setup request message, the Node B sets τhs-scch in consideration of CPICH timing differences between cells. Meanwhile, the Node B includes the τhs-scch in a common transport channel setup response message corresponding to the common transport channel setup request message and transmits it to the RNC.
한편, 상기 첫 번째 방안과 상기 두 번째 방안에 의해 결정된 τhs-scch는 HS-SCCH의 사용을 위해 해당하는 UE들에게 전달되어야 한다. 상기 상기 RNC가 상기 τhs-scch를 해당하는 UE들로 전달하는 신호 처리 절차는 도 15와 도 16에서 보이고 있는 바와 같다. 상기 도 15에서 보이고 있는 신호 처리 절차는 방송채널(Broadcasting Channel, 이하 "BCH"라 칭함)을 통해 상기 τhs-scch를 전달하는 예이며. 상기 도 16에서 보이고 있는 신호 처리 절차는 무선 베어러 셋업(Radio Bearer setup, 이하 "RB 셋업"이라 칭함) 등 RRC 메시지를 통해 상기 τhs-scch를 전 달하는 예이다.Meanwhile, τhs-scch determined by the first scheme and the second scheme should be delivered to the corresponding UEs for use of the HS-SCCH. The signal processing procedure for transmitting the τhs-scch to the corresponding UEs by the RNC is as shown in FIGS. 15 and 16. The signal processing procedure illustrated in FIG. 15 is an example of transmitting the τhs-scch through a broadcasting channel (hereinafter, referred to as a “BCH”). The signal processing procedure shown in FIG. 16 is an example of transmitting the τhs-scch through an RRC message such as a radio bearer setup (hereinafter referred to as “RB setup”).
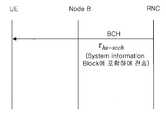
상기 도 15를 참조하면, 상기 RNC는 방송채널(Broadcasting Channel, 이하 "BCH"라 칭함)를 통해 시스템 정보 블록(System Information Block, 이하 "SIB"라 칭함)에 τhs-scch를 담아 특정 셀 전체를 대상으로 하여 송신한다.Referring to FIG. 15, the RNC includes τhs-scch in a system information block (hereinafter referred to as "SIB") through a broadcasting channel (hereinafter, referred to as "BCH") andincludes a specific cell as a whole. Send to the target.
상기 도 16을 참조하면, 상기 RNC는 무선 베어러 셋업(Radio Bearer setup, 이하 "RB 셋업"이라 칭함) 등 RRC 메시지를 이용하여 코드 정보 등을 포함한 HS-SCCH 정보를 전송할 때 상기 τhs-scch를 UE로 전송한다. 이 경우, 상기 UE는 이에 대한 응답으로 RB 셋업 완료메시지(RB setup complete message)를 상기 RNC로 전송한다.Referring to FIG. 16, when the RNC transmits HS-SCCH information including code information by using an RRC message such as a radio bearer setup (hereinafter, referred to as “RB setup”), the τhs-scch is used. Send to the UE. In this case, the UE sends an RB setup complete message to the RNC in response.
이하 전술한 바와 같이 각 셀별로 τhs-scch를 할당하고, 이를 이용하여 HS-SCCH를 송신 및 수신하는 동작을 도 17 내지 21을 참조하여 상세히 설명하면 다음과 같다. 상기 도 17 내지 상기 도 19에서는 RNC에 의해 각 셀들별 τhs-scch를 설정하는 실시 예에 따른 RNC, Node B 및 UE에서 수행하는 제어 흐름을 보이고 있는 도면이다. 상기 도 20 내지 상기 도 21은 Bpde B에 의해 각 셀들별 τhs-scch를 설정하는 실시 예에 따른 Node B와 RNC에서 수행하는 제어 흐름을 보이고 있는 도면이다.Hereinafter, an operation of allocating τhs-scch for each cell and transmitting and receiving the HS-SCCH using the same will be described in detail with reference to FIGS. 17 to 21. 17 to 19 illustrate control flows performed by an RNC, a Node B, and a UE according to an embodiment of configuring τhs-scch for each cell by the RNC. 20 to 21 illustrate control flows performed by Node B and RNC according to an embodiment of setting τhs-scch for each cell by Bpde B.
먼저, 도 17과 도 19를 참조하여 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay) 정보인 τhs-scch를 RNC가 결정하는 경우의 Node B와 RNC 및 UE에서의 동작을 각각 설명한다.First, operations in Node B, RNC, and UE when the RNC determines τhs-scch, that is, delay information of the HS-SCCH channel, will be described with reference to FIGS. 17 and 19, respectively.
상기 도 18을 참조하면, RNC는 1801단계에서 각 셀들별로 CPICH의 타이밍 옵 셋을 설정한다. 상기 각 셀들별로 CPICH의 타이밍 옵셋을 설정하는 과정은 셀 셋업과정에서 이루어진다. 상기 CPICH의 타이밍 옵셋의 설정이 완료되면 상기 RNC는 1803단계로 진행하여 각 셀들별로 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay) 정보인 τhs-scch를 설정한다. 이때, 상기 RNC는 상기 τhs-scch를 설정함에 있어 각 셀들별로 전송하게 될 HS-SCCH 채널들의 TTI 중 송신전력이 큰 첫 번째 슬롯들이 겹치는 구간이 최소화 되도록 하여야 한다.Referring to FIG. 18, in
예컨대, 세 개의 셀에 대해 상기 τhs-scch를 설정하는 구체적인 동작을 살펴보면 다음과 같다. 이때, cell 1의 CPICH 프레임 시작점을 기준으로 하여, cell 2의 CPICH 프레임은 Tcell,2 = 256 ×Tc 만큼 지연된다. 그리고, cell 3의 CPICH 프레임은 상기 cell 1의 CPICH 프레임 시작점을 기준으로 Tcell,3 = 768 ×Tc 만큼 지연되어 있다고 가정하자. 상기 Tc는 한 칩에 해당하는 시간 구간이다. 이러한 가정은 셀들간의 타이밍 차이가 256 chip의 배수이어야 한다는 3GPP(3rd Generation Partner Project) 규격에 따른 것이다. 이 경우, τhs-scch,1 = 0, τhs-scch,2 = 2304 ×Tc, τhs-scch,3 = 4352 ×Tc로 정하면, cell 1의 CPICH 프레임 시작점에 대한 각 cell의 HS-SCCH TTI의 시작점의 시간 지연은 cell 1의 경우 Ths-scch,1 = Tcell,1 + τhs-scch,1 = 0, cell 2의 경우 Ths-scch,2 = Tcell,2 + τhs-scch,2 = 2560 ×Tc, cell 3의 경우 Ths-scch,3 = Tcell,3 + τhs-scch,3 = 5120 ×Tc가 된다. 따라서, 각 cell의 HS-SCCH 채널 의 TTI 중 첫 번째 슬롯은 겹치지 않거나 최소로 겹쳐지도록 함으로서 Node B의 최대 송신전력 및 하향링크 간섭을 줄일 수 있게 된다.For example, a detailed operation of setting τhs-scch for three cells is as follows. At this time, the CPICH frame ofcell 2 is delayed by Tcell, 2 = 256 × Tc based on the CPICH frame start point of
상기 RNC는 상기와 같은 과정을 거쳐 상기 τhs-scch가 설정되면 1805단계로 진행하여 상기 설정된 τhs-scch를 각 Node B 및 UE에게 전송한다. 이때, 상기 τhs-scch를 상기 Node B로 전송하는 시그널링은 전술한 도 11 또는 도 12에서 제안한 바에 의해 이루어지며, 상기τhs-scch를 상기 UE로 전송하는 시그널링은 전술한 도 15 또는 도 16에서 제안한 바에 의해 이루어진다.When the τhs-scch is set through the above process, the RNC proceeds to step 1805 and transmits the τhs-scch to each Node B and the UE. In this case, the signaling for transmitting the τhs-scch to the Node B is performed by the proposal of FIG. 11 or 12, and the signaling for transmitting the τhs-scch to the UE is described with reference to FIG. 15 or 16. As suggested by
상기 도 17을 참조하면, Node B는 1701단계에서 상기 RNC로부터 HS-SCCH 지연(delay) 정보 τhs-scch를 수신한다. 상기 Node B는 1703단계에서 HS-SCCH로 전송할 제어정보를 생성한 후 1705단계로 진행한다. 상기 1705단계로 진행한 상기 Node B는 상기 수신한 τhs-scch에 따라 상기 HS-SCCH의 송신 시점을 조절하고, 상기 조절된 송신시점에서 상기 HS-SCCH를 통해 상기 생성한 제어정보를 해당 UE로 송신한다. 한편, 상기 Node B는 1707단계에서 전송할 HSDPA 패킷 데이터가 존재하는지를 판단한다. 전송할 HSDPA 패킷 데이터가 존재한다고 판단될 시 상기 Node B는 상기 1703단계로 진행하여 전술한 과정을 반복하여 수행한다.Referring to FIG. 17, in
상기 도 19를 참조하면, UE는 1901단계에서 상기 RNC로부터 HS-SCCH 채널 지연(delay) 정보 τhs-scch를 수신한다. 상기 UE는 1903단계에서 상기 수신한 τhs-scch에 따라 설정된 수신시점에서 HS-SCCH를 상기 Node B로부터 수신한다. 상기 UE는 1905 단계로 진행하여 상기 수신한 HS-SCCH로부터 제어정보를 추출한 후 1907단계로 진행한다. 상기 제어정보는 HS-PDSCH로부터 HSDPA 패킷 데이터를 수신하기 위해 요구되는 제어정보이다. 상기 1907단계로 진행한 상기 UE는 수신할 패킷 데이터가 존재하는지 여부를 판단한다. 상기 1907단계에서 수신할 HSDPA 패킷 데이터가 존재한다고 판단될 시 상기 UE는 상기 1903단계로 진행하여 전술한 과정을 반복하여 수행한다.Referring to FIG. 19, the UE receives HS-SCCH channel delay information τhs -scch from the RNC in
다음으로, 도 20과 도 21을 참조하여 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay) 정보인 τhs-scch를 Node B가 결정하는 경우의 Node B와 RNC에서의 동작을 각각 설명한다.Next, operations in Node B and RNC in the case where Node B determines τhs -scch , which is delay information of the HS-SCCH channel, will be described with reference to FIGS. 20 and 21, respectively.
상기 도 21을 참조하면, RNC는 2101단계에서 Node B에 속하는 각 셀들별로 CPICH의 타이밍 옵셋을 설정한 후 상기 Node B로 상기 설정한 CPICH의 타이밍 옵셋을 전송한다. 상기 CPICH의 타이밍 옵셋을 상기 Node B로 전송하는 시그널링은 도 13에서 보이고 있는 바와 같다. 즉, 상기 RNC는 상기 CPICH의 타이밍 옵셋을 셀 셋업 시 셀 셋업 요청 메시지(cell setup request message)를 통해 상기 Node B로 전송한다. 상기 Node B는 후술될 절차에 의해 각 셀별로 설정된 HS-SCCH 지연 값(delay) 정보 τhs-scch를 상기 RNC로 전송할 것이다. 상기 RNC는 상기 Node B로부터의 τhs-scch를 2103단계에서 수신한다. 상기 τhs-scch를 수신하기 위한 시그널링은 상기 도 13 및 도 14에서 보이고 있는 절차에 의해 이루어진다. 상기 RNC는 2105단계에서 상기 Node B로부터 수신한 상기 τhs-scch를 UE로 전송한다, 상기 τhs-scch를 상기 UE로 전송하기 위한 시그널링은 상기 도 15 및 상기 도 16에서 도시한 시그널링 절차에 의해 이루어진다.Referring to FIG. 21, in
상기 도 20을 참조하면, Node B는 2001단계에서 RNC로부터 각 셀별로 CPICH의 타이밍 옵셋 값을 수신한다. 상기 CPICH의 타이밍 옵셋의 수신이 완료되면 상기 Node B는 2003단계에서 상기 CPICH의 타이밍 옵셋을 이용하여 각 셀들별로 HS-SCCH 채널의 지연(delay) 정보인 τhs-scch를 설정한다. 이때, 상기 RNC는 상기 τhs-scch를 설정함에 있어 각 셀들별로 전송하게 될 HS-SCCH 채널들의 TTI 중 송신전력이 큰 첫 번째 슬롯들이 겹치는 구간이 최소화 되도록 하여야 한다. 상기 τhs-scch를 설정하는 구체적인 예는 상기 도 18을 참조하여 전술한 바와 같다. 상기 Node B는 상기와 같은 과정을 거쳐 상기 τhs-scch가 설정되면 2005단계로 진행하여 상기 설정된 τhs-scch를 상기 RNC로 전송한다. 이때, 상기 τhs-scch를 상기 RNC로 전송하는 시그널링은 전술한 도 13 또는 도 14에서 제안한 바에 의해 이루어진다. 상기 Node B는 2007단계에서 HS-SCCH로 전송할 제어정보를 생성한 후 2009단계로 진행한다. 상기 2009단계로 진행한 상기 Node B는 상기 설정된 τhs-scch에 따라 상기 HS-SCCH의 송신 시점을 조절하고, 상기 조절된 송신시점에서 상기 HS-SCCH를 통해 상기 생성한 제어정보를 해당 UE로 송신한다. 한편, 상기 Node B는 2011단계에서 전송할 HSDPA 패킷 데이터가 존재하는지를 판단한다. 전송할 HSDPA 패킷 데이터가 존재한다고 판단될 시 상기 Node B는 상기 2007단계로 진행하여 전술한 과정을 반복하여 수행한다.Referring to FIG. 20, in
한편, 전술한 Node B에서 상기 τhs-scch를 설정하는 경우라고 하더라도 상기 UE에서 수행되는 동작은 첫 번째 방안에서의 동작(도 19)과 동일하다. 즉, 상기 UE는 상기 τhs-scch를 상기 Node B에서 설정하거나 상기 RNC에서 설정하는데 관계없이 동일한 절차를 수행하게 된다.Meanwhile, even when the above-described Node B configures the τhs-scch , the operation performed by the UE is the same as the operation in the first scheme (FIG. 19). That is, the UE performs the same procedure regardless of setting the τhs-scch in the Node B or the RNC.
이하 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 Node B와 UE의 구성과 그 구성에 따른 동작을 상세히 설명하면 다음과 같다.Hereinafter, the configuration of the Node B and the UE according to an embodiment of the present invention and the operation according to the configuration will be described in detail.
도 9는 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 HSDPA 이동통신시스템에서 Node B의 상세 구성을 보이고 있는 도면이며, 도 10은 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 HSDPA 이동통신시스템에서 UE의 상세 구성을 보이고 있는 도면이다.9 is a diagram illustrating a detailed configuration of a Node B in an HSDPA mobile communication system according to an embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 10 is a diagram showing a detailed configuration of a UE in an HSDPA mobile communication system according to an embodiment of the present invention. .
먼저, 상기 도 9를 참조하면, HS-SCCH 제어정보는 상기에서 설명한 바와 같이 HS-PDSCH 채널을 통해 전송되는 패킷 데이터를 지연 없이 추출하기 위해 HS-SCCH TTI의 3 슬롯들 중 첫 번째 슬롯을 통해 먼저 전송되어야 하는 MS(Modulation Scheme), HS-DSCH OVSF code 정보로 구성되는 Part-1 정보와 나머지 뒤쪽 2개의 slot으로 전송되는 전송블록 크기와 HARQ 관련 정보로 구성되는 Part-2 정보로 나누어진다. 상기 Part-1 정보는 다중화기(932)에서 다중화된다. CRC 코더(930)에서는 상기 Part-1 정보와 UE-ID를 이용하여 UE-specific CRC (CRC-1)을 만든다. 채널 코딩부(928)에서는 상기 Part-1정보와 상기 CRC-1이 함께 채널 부호화되며, 레이트 매칭부(926)에서는 채널 부호화 출력이 첫 번째 슬롯에서 실제 전송 가능한 비트수인 40비트에 맞추어지는 레이트 매칭(rate matching)이 수행된다. 인터리빙부(924)에서는 상기 레이트 매칭이 이루어진 비트들에 대해 인터리빙을 수행한다. 상기 Part-2 정보는 CRC 코더(940)에서 CRC-2를 만들 때 UE-ID가 이용되지 않는다는 점만을 제외하고는 상기 930 내지 924와 동일한 구성을 통해서 HS-SCCH TTI 중 나머지 두 번째 및 세 번째 슬롯으로 전송되는 80비트로 할당된다. 상기 인터리빙부(924, 934)의 출력은 다중화기(922)에서 다중화된다. 상기 다중화기(922)로부터 다중화된 출력은 직병렬 변환부(920)를 거쳐 I, Q 비트열로 나누어지며, 확산부(916, 918)에서 확산된다. 상기 확산된 신호는 결합기(914)에서 복소수 심볼열로 변환되어 스크램블링부(912)에서 스크램블링된다. 지연 제어부(910)에서는 RNC에서 수신하거나 혹은 기지국 자체에서 설정한 τhs-scch에 따라 지연 인가부(908)를 제어한다. HS-SCCH 채널 신호는 상기 지연 인가부(908)에 의해 CPICH 프레임 신호에 비해 HS-SCCH TTI 시작점이 τhs-scch만큼 지연된 후 변조부(906)로 인가되어 RF부(904)에서 RF 신호로 변환되어 안테나(902)를 통해 송신된다.First, referring to FIG. 9, the HS-SCCH control information is transmitted through a first slot of three slots of the HS-SCCH TTI in order to extract packet data transmitted through the HS-PDSCH channel without delay as described above. Part-1 information consisting of MS (Modulation Scheme), HS-DSCH OVSF code information to be transmitted first, and Part-2 information consisting of transport block size and HARQ related information transmitted to the remaining two slots. The Part-1 information is multiplexed by the
다음으로, 상기 도 10을 참조하면, 안테나(1002)에 의해 수신된 HS-SCCH 신호는 RF부(1004)에 의해 기저대역 신호로 변환된 후, 복조부(1006)에 의해 복조된다. 지연 제어부(1010)는 도 15, 도 16에서 도시되어 있는 시그널링 방법에 의해 UE에게 전달된 τhs-scch에 따라 지연 보상부(1008)를 제어한다. 상기 지연 보상부(1008)는 HS-SCCH TTI가 CPICH 프레임의 디스크램블링으로부터 τhs-scch 이후에 디스크램블링이 시작될 수 있도록 시간 지연을 조정한다. 상기 디스크램블링부(1012), 복소심볼열의 I, Q 비트열로의 분리(1014), 역확산부(1016, 1018), 채널 보상부(1019), I, Q 비트열의 하나의 비트열로의 변환(1020), 역다중화부(1022) 과정을 거쳐서 HS-SCCH 채널을 통해 전송된 제어 정보는 Part-1 정보와 Part-2 정보로 분리된다. Part-1 정보는 디인터리버(1024), 역 레이트 매칭부(1026), 채널 디코딩부(1028)를 거친 후, 1030에서 UE-ID를 같이 이용하여 CRC-1에 대한 CRC 검사를 수행하고, HI에 의해 지정된 HS-SCCH 채널이 실제로 상기 단말기에게 할당된 HS-SCCH 채널인지 여부를 확인한다. 지정된 HS-SCCH 채널이 실제로 상기 단말기에게 할당되었다고 확인되면, 역다중화기(1032)에 의해 Part-1 정보는 역다중화 되어서 MS 정보와 HS-DSCH OVSF 코드 정보를 출력하게 된다. Part-2 정보의 추출 역시 상기 1034 내지 1042를 거치면서 동일한 동작에 의해 이루어진다. 단, Part-1 정보에 대한 동작과의 차이점은 1040에서의 CRC-2에 대한 CRC check시 1030과 달리 UE-ID가 이용되지 않는다는 점이다.
Next, referring to FIG. 10, the HS-SCCH signal received by the
본 발명을 적용할 경우, 여러 셀들로부터 송신되는 HS-SCCH 채널들의 3 슬롯 TTI 중 송신전력이 큰 첫 번째 슬롯들이 겹치는 현상을 방지하여 하향 링크의 간섭량을 줄임으로써 슬롯 앤드오버 영역에 있는 단말기의 수신효율을 향상시킬 수 있다. 따라서 전체 시스템의 효율을 향상시킬 수 있다.When the present invention is applied, the reception of the terminal in the slot and over area by reducing the amount of interference in the downlink by preventing the overlapping of the first slots having a large transmit power among the three slot TTIs of the HS-SCCH channels transmitted from several cells The efficiency can be improved. Therefore, the efficiency of the entire system can be improved.
Claims (21)
Translated fromKoreanPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020020009405AKR100876798B1 (en) | 2002-02-10 | 2002-02-10 | Apparatus and method for determining delay value of common control information channel in code division multiple access communication system applying high speed forward packet access method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020020009405AKR100876798B1 (en) | 2002-02-10 | 2002-02-10 | Apparatus and method for determining delay value of common control information channel in code division multiple access communication system applying high speed forward packet access method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20030068348A KR20030068348A (en) | 2003-08-21 |
| KR100876798B1true KR100876798B1 (en) | 2009-01-07 |
Family
ID=32222192
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020020009405AExpired - Fee RelatedKR100876798B1 (en) | 2002-02-10 | 2002-02-10 | Apparatus and method for determining delay value of common control information channel in code division multiple access communication system applying high speed forward packet access method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100876798B1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100499503B1 (en)* | 2003-02-18 | 2005-07-05 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | structure of physical transmission channel, and method for operating physical transmission channel |
| CN101146118B (en)* | 2006-09-12 | 2010-08-18 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Control method for getting scheduled time in floating radio network controller |
| KR20080086384A (en)* | 2007-03-21 | 2008-09-25 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Transmission and reception method of broadcasting and multicast service data in packet based mobile communication system |
| CN102984794B (en)* | 2011-09-05 | 2017-11-07 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method, system, base station and terminal that a kind of multicast system data are sent |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1993021697A1 (en)* | 1992-04-10 | 1993-10-28 | Nokia Telecommunications Oy | Signalling method for a radio system |
| JPH1013928A (en)* | 1996-06-20 | 1998-01-16 | Fujitsu Ltd | Channel data transmission method for individual cells |
| KR19990084445A (en)* | 1998-05-06 | 1999-12-06 | 구자홍 | Medium access control sublayer (MAC) of mobile communication system and communication control method using same |
| KR20010108441A (en)* | 2000-02-02 | 2001-12-07 | 추후보정 | Single-carrier/ds-cdma packet transmitting method, uplink packet transmitting method in multicarrier/ds-cdma mobile communication system, and structrue of downlink channel in multicarrier/ds-cdma mobile communication system |
| KR100365599B1 (en)* | 1999-05-12 | 2002-12-26 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | Method of providing burst timing for high-speed data transmission in a base station transceiver system of a mobile communication system |
- 2002
- 2002-02-10KRKR1020020009405Apatent/KR100876798B1/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1993021697A1 (en)* | 1992-04-10 | 1993-10-28 | Nokia Telecommunications Oy | Signalling method for a radio system |
| JPH1013928A (en)* | 1996-06-20 | 1998-01-16 | Fujitsu Ltd | Channel data transmission method for individual cells |
| KR19990084445A (en)* | 1998-05-06 | 1999-12-06 | 구자홍 | Medium access control sublayer (MAC) of mobile communication system and communication control method using same |
| KR100365599B1 (en)* | 1999-05-12 | 2002-12-26 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | Method of providing burst timing for high-speed data transmission in a base station transceiver system of a mobile communication system |
| KR20010108441A (en)* | 2000-02-02 | 2001-12-07 | 추후보정 | Single-carrier/ds-cdma packet transmitting method, uplink packet transmitting method in multicarrier/ds-cdma mobile communication system, and structrue of downlink channel in multicarrier/ds-cdma mobile communication system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20030068348A (en) | 2003-08-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100630128B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for determining pilot signal field position information for reverse power control in mobile communication system using high speed forward packet access method | |
| KR100810940B1 (en) | Adapting a diversity transmission mode in a wireless communication system | |
| JP4870128B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for signaling terminal state information for uplink packet transmission in soft handover region | |
| KR100832117B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving reverse transmission power offset information in mobile communication system using high speed forward packet access method | |
| KR100438432B1 (en) | Methode of transmitting control data in cdma mobile communication system | |
| US8514832B2 (en) | Methods and apparatus enabling increased throughput on the reverse link | |
| EP2501193B1 (en) | Base station for downlink signaling for high speed uplink packet access | |
| US9769843B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for transmitting, receiving and/or processing control information and/or data | |
| JP4309117B2 (en) | HS-SCCH transmission power control method in UMTS system | |
| US8194618B2 (en) | Radio base station device, communication terminal device, and control information transmission method | |
| US7403513B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for coding and decoding CQI information in communication system using high speed downlink packet access | |
| US7227851B1 (en) | Transport channel multiplexing system and method | |
| KR100596169B1 (en) | Transmission power control method and base station device | |
| EP1540983B1 (en) | Method and system for a data transmission in a communication system | |
| US20050053035A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing uplink packet data service on uplink dedicated channels in an asynchronous wideband code division multiple access communication system | |
| US20040179469A1 (en) | Method and system for a data transmission in a communication system | |
| AU2004221069C1 (en) | Method and system for a data transmission in a communication system | |
| US20040100918A1 (en) | Method and system for forwarding a control information | |
| KR100876798B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for determining delay value of common control information channel in code division multiple access communication system applying high speed forward packet access method | |
| KR100754668B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for determining slot format of forward dedicated physical channel in mobile communication system using high speed forward packet access method | |
| KR20090102594A (en) | Method and apparatus for transmission and reception of control information in mobile telecommunication system supporting hsdpa | |
| KR100856262B1 (en) | A method for transmitting and receiving serving high speed common control channel set information in a communication system using a high speed forward packet access method | |
| HK1078387A (en) | Dsch power control method for wcdma |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | St.27 status event code:A-1-1-Q10-Q12-nap-PG1501 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| D13-X000 | Search requested | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D13-srh-X000 | |
| D14-X000 | Search report completed | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D14-srh-X000 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| E90F | Notification of reason for final refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 Fee payment year number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:4 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20121129 Year of fee payment:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:5 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20131128 Year of fee payment:6 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:6 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20141127 Year of fee payment:7 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:7 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20151127 Year of fee payment:8 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:8 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20161129 Year of fee payment:9 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:9 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20171129 Year of fee payment:10 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:10 | |
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee | ||
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U13-oth-PC1903 Not in force date:20181224 Payment event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | St.27 status event code:N-4-6-H10-H13-oth-PC1903 Ip right cessation event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE Not in force date:20181224 |