KR100761912B1 - Method and system for extracting document information based on body identification - Google Patents
Method and system for extracting document information based on body identificationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100761912B1 KR100761912B1KR1020060030795AKR20060030795AKR100761912B1KR 100761912 B1KR100761912 B1KR 100761912B1KR 1020060030795 AKR1020060030795 AKR 1020060030795AKR 20060030795 AKR20060030795 AKR 20060030795AKR 100761912 B1KR100761912 B1KR 100761912B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- title
- document
- information
- area
- region
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F40/00—Handling natural language data
- G06F40/20—Natural language analysis
- G06F40/258—Heading extraction; Automatic titling; Numbering
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F40/00—Handling natural language data
- G06F40/10—Text processing
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Audiology, Speech & Language Pathology (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean도 1은 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예에 따른 문서의 제목추출 방법을 구체적으로 도시한 작업 흐름도이다.1 is a flowchart illustrating a method of extracting a title of a document according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention in detail.
도 2a는 본 발명의 실시예에 의하여 문서가 영역들로 구획된 결과의 한 예를 나타내는 도면이다.2A is a diagram illustrating an example of a result of dividing a document into regions according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 2b는 본 발명의 실시예에 의하여 문서에서 제목후보구의 위치가 식별된 결과를 나타내는 도면이다.2B is a diagram illustrating a result of identifying a position of a title candidate in a document according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 3은 본 발명의 실시예에 의하여 본문영역 외에서 제목이 선정된 결과를 예시한 도면이다.3 is a diagram illustrating a result of selecting a title outside the body region according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 4는 본 발명에 따른 문서 정보추출방법을 구현하기 위한 시스템의 구성도 이다.4 is a block diagram of a system for implementing a document information extraction method according to the present invention.
본 발명은 문서로부터 정보를 추출하는 방법에 관한 것으로서, 더욱 상세하게는 문서 내에서 본문영역 또는 본문내용의 위치를 식별하고, 본문영역의 기준위치와의 상대위치 등에 기반으로 식별된 제목후보들 중에서 해당 문서의 제목을 결정하는 문서정보 추출방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method of extracting information from a document, and more particularly, to identify the position of a body region or body content in a document, and among the title candidates identified based on a relative position with respect to a reference position of the body region. A document information extraction method for determining a title of a document.
인터넷상에 수많은 문서들이 존재하게 됨에 따라, 검색엔진이 주요한 정보원으로 활용되고 있으며, 검색엔진의 이용에 있어서, 질의어와 관련된 검색결과 리스트로부터 사용자가 원하는 문서들을 재선택하는 데에는 해당 문서의 제목 및 요약정보가 중요한 역할을 하게 된다.As a large number of documents exist on the Internet, search engines are being used as a major source of information, and in the use of search engines, the title and summary of the documents are necessary for reselecting the desired documents from the list of search results related to the query. Information plays an important role.
그러나 웹 문서들의 경우 문서의 작성 시에 그 내부에 해당 문서의 제목을 메타정보로서 포함할 수 있음에도 불구하고, 단순히 문서가 존재하는 사이트명 내지는 상위분류 정보만을 메타정보로 포함하고 있는 경우가 많으며, 문서 작성자의 부주의로 인하여 해당 문서와는 전혀 상관성을 가지지 않는 정보가 메타정보로 포함되기도 한다.However, in the case of web documents, although the title of the document may be included as meta information when the document is created, in many cases, only the site name or upper classification information where the document exists is included as meta information. Due to the inattention of the document author, information that has nothing to do with the document at all may be included as meta information.
따라서 검색서비스가 그 검색결과를 리스팅하는 데 있어서 html 문서의 <title> 태그내의 정보만을 활용하여 제목정보로 제공하는 것은 사용자를 만족시킬 수 없으며, 이는 문서의 제목에 국한된 문제가 아니어서 문서의 요약정보를 제공함에 있어서도 단순히 질의어가 나타나는 부분을 예시하는 것은 문서의 전체 내용을 반영하지 못해 결과적으로 사용자를 불만족을 초래하기도 한다.Therefore, it is not enough for the search service to provide the title information using only the information in the <title> tag of the html document in listing the search results, which is not limited to the title of the document. Even in providing information, simply exemplifying the parts of the query that do not reflect the entire contents of the document may result in user dissatisfaction.
이를 개선하기 위하여, 해당 문서 내에서 눈에 띄는 속성을 가진 텍스트를 제목으로 반영한다거나, 학습 알고리즘을 사용하여 해당 문서의 내용을 반영하는 제목 내지는 요약정보를 생성하는 방법 등이 시도되어 왔다.In order to improve this, a method of reflecting text having prominent attributes in the document as a title or generating a title or summary information reflecting the content of the document by using a learning algorithm has been attempted.
그러나 현재의 웹 문서들의 경우에는 광고정보, 각종 링크정보 등이 한 문서내에 병존한다거나. 클릭율을 높이기 위하여 이러한 부가정보들이 더욱 강조되어 표시되는 경향 등으로 인해 성과가 만족스럽지 못하다는 문제가 있다.However, in the case of current web documents, advertisement information, various link information, etc. coexist in one document. There is a problem that the performance is not satisfactory due to the tendency of such additional information to be highlighted in order to increase the click rate.
본 발명은 상기와 같은 문제점들을 해결하기 위하여 안출된 것으로서, 본 발명은 문서를 영역별로 구획하고 그 영역들 중에서 본문정보를 포함하는 영역을 식별하고 그에 포함된 본문내용의 위치를 식별하는 것을 목적으로 한다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention has been made to solve the above problems, and the present invention aims to partition a document by area, identify a region including body information among the regions, and identify a location of the body content contained therein. do.
또한, 본 발명의 목적은 상기 식별된 본문영역 또는 본문내용의 위치를 기준으로 문서의 제목을 탐색할 영역을 설정함으로써 한 문서 내에 여러 부가정보가 혼재되어 있는 경우에도, 해당 문서에 대한 제목정보 등을 정확하게 추출하는 데에 있다.In addition, an object of the present invention is to set the area to search for the title of the document based on the identified body region or the position of the body content, so that even if several additional information is mixed in one document, the title information of the document, etc. To extract exactly.
상기의 목적을 이루기 위한 본 발명의 한 실시예에 따라, 문서를 파싱하는 단계; 상기 파싱결과를 이용하여 웹 문서를 영역별로 구획하는 단계; 소정의 기준에 따라 본문영역을 식별하는 단계; 상기 식별된 본문영역의 위치 등을 기준으로 제목정보 탐지영역을 설정하는 단계; 상기 제목정보 탐지영역에서 제목후보구를 선정하는 단계; 및 상기 제목후보구들을 대상으로 제목적합도를 산정하고 그를 기준 으로 상기 문서의 제목정보를 식별하는 단계를 포함하는 정보추출방법에 의해 달성된다.In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention for achieving the above object, parsing a document; Partitioning the web document into regions using the parsing result; Identifying a body region according to a predetermined criterion; Setting a title information detection area based on the location of the identified body area; Selecting a title candidate in the title information detection area; And calculating title suitability for the title candidates and identifying title information of the document based on the title candidates.
한편, 본 발명의 다른 분야에 의하면, 상기 기술적 과제는 문서를 파싱하는 문서해석부; 상기 파싱결과를 이용하여 문서를 영역별로 구획하는 문서구획부; 소정의 기준에 따라 본문영역을 식별하는 본문영역 식별부; 상기 본문영역의 위치 등을 기준으로 본문정보 탐색영역을 설정하는 탐색영역 설정부; 및 상기 제목후보구들을 대상으로 산출한 제목적합도를 기준으로 상기 문서의 제목정보를 식별하는 제목정보 식별부를 포함하는 정보추출 시스템에 의하여도 달성된다.On the other hand, according to another field of the present invention, the technical problem is a document interpretation unit for parsing a document; A document partitioner for partitioning a document into areas using the parsing result; A body region identification unit for identifying a body region according to a predetermined criterion; A search area setting unit for setting a text information search area based on the position of the text area; And a title information identification unit for identifying title information of the document based on the title suitability calculated for the title candidates.
본 명세서에서 지속적으로 사용되는 용어로서 문서라 함은 전자적인 방법으로 기록된 문서를 의미하는 것으로, 특정한 파일의 형식이나 확장자에 한정되는 것은 아니라 할 것이며, 인터넷 상에서 브라우저를 통해 보이는 웹 페이지의 개념을 포함한다.As used herein, the term document refers to a document recorded electronically, and is not limited to a specific file format or extension, and refers to the concept of a web page viewed through a browser on the Internet. Include.
이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 웹 문서의 정보추출방법 및 시스템에 대하여 설명한다.Hereinafter, a method and a system for extracting information of a web document will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 1은 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예에 따른 웹 문서의 제목추출 방법을 구체적으로 도시한 작업 흐름도이다.1 is a flowchart illustrating a method of extracting a title of a web document according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention.
문서를 파싱하는 단계(110)는 문서를 영역별로 구획하기 위한 사전 단계로서 문서들에서 문서가 전달하고자 하는 실질적인 정보를 가진 텍스트와 그 정보 텍스트에 부가되는 속성값들을 구문 분석하는 과정이다.Parsing the document 110 is a preliminary step for dividing the document into regions, and is a process of parsing text having substantial information to be conveyed by the document in the documents and attribute values added to the information text.
한 예로 html로 구성된 문서의 경우를 보자면, <title>, <p> 등의 태그 사이에 존재하는 이너텍스트(inner text)들을 문서의 구성요소(element)로 보고, 그 각각의 글씨체, 글씨의 크기, 표현되는 위치, 메타태그의 의미 등이 부가되는 속성으로 파악될 수 있다. 또한, 바람직하게는 파싱과 관련하여 출원 전에 공지된 파이어폭스(firefox) 등의 프로그램이 활용될 수 있다.For example, in the case of a document composed of html, inner texts existing between tags such as <title> and <p> are regarded as elements of the document, and their fonts and font sizes are described. , The expressed position, the meaning of the meta tag, etc. may be identified as an added attribute. In addition, a program such as Firefox, which is known before application, may be preferably used in connection with parsing.
문서를 영역별로 구획하는 단계(S120)는 문서를 파싱한 정보를 이용하여 문서들을 하나 이상의 영역으로 나누는 단계로서 문서를 파싱하는 단계(S110)에서 얻어진 정보를 활용하여 문서의 구성요소가 문서에서 표현되는 위치와 그 표현되는 폭(width) 등을 기준으로 하여 하나 이상의 구성요소를 포함하는 영역을 구성할 수 있다. 일반적으로 구획되는 영역의 형태는 사각형의 형태가 될 것이나, 각 영역의 병합, 분할 등으로 인해 변경될 수 있다.The step S120 of dividing the document into regions divides the documents into one or more regions by using the information parsed from the document, and the components of the document are represented in the document by using the information obtained in the process of parsing the document (S110). An area including one or more components may be configured based on the location and the expressed width. In general, the shape of the region to be partitioned will be in the form of a rectangle, but may be changed due to merging, division, etc. of each region.
바람직하게는 위치의 인접성 등을 기준으로 영역들을 병합하거나 하나의 영역을 분할하는 과정이 추가로 포함될 수 있으며 상기 재구성과정에서는 추후 계산과정에서의 효율성을 위해 하나의 문서 내에 포함될 수 있는 영역의 최소, 최대치를 한정하는 조건이 추가로 부가될 수 있다.Preferably, the process may further include a process of merging regions or dividing one region based on the positional proximity, etc. In the reconstruction process, the minimum of the regions that can be included in one document for efficiency in the later calculation process, Conditions that define the maximum may be added further.
본문영역을 식별하는 단계(S130)는 하나 이상의 영역으로 구획된 문서에서 어떤 영역이 문서의 주 내용을 포함하는 본문영역에 해당하는지 여부를 평가하기 위한 단계이다.Identifying the body region (S130) is a step for evaluating which region in the document divided into one or more regions corresponds to the body region including the main content of the document.
본문영역을 판정하기 위한 판단 인자로서는 영역의 폭과 높이, 문서대비 영역 폭과 높이의 비율, 영역의 문서내 위치, 영역들 간의 유기적 위치 관계, 각 영역의 전체 텍스트 분량 및 해당 영역 내의 링크속성을 가지지 아니한 텍스트의 비 율 등이 있으며, 특히, 웹 문서 등에서는 광고정보 내지는 사용자의 내비게이션을 보조하기 위한 링크속성을 가진 앵커 텍스트는 해당문서가 아닌 그 링크가 참조하는 문서를 대표하는 정보를 가지고 있을 확률이 크기에 각 영역에 포함된 텍스트 중에 링크 속성을 가지지 않는 텍스트의 비율이 중요한 판단 기준이 될 수 있다.Determinants for determining the body region include the width and height of the region, the ratio of the region width and height to the document, the position of the region in the document, the organic positional relationship between the regions, the total amount of text in each region, and the link attributes within the region. In particular, in web documents, the anchor text with link attributes to assist the navigation of the user may have information representing the document referenced by the link, not the corresponding document. Probability is large and the ratio of the text which does not have a link attribute among the text included in each area may be an important criterion.
상기 링크속성이란 해당 구성요소에 대한 사용자의 클릭 등에 의하여 이벤트가 발생하는 경우를 지칭하는 것으로, 바람직하게는 상기 이벤트에 의하여 수행되는 일련의 동작들이 다른 문서를 참조하기 위한 것인지 또는 해다 구성요소에 대한 단순한 부가 설명을 위해 존재하는 것인지 등에 따라 달리 취급하는 것이 필요하다.The link attribute refers to a case in which an event occurs due to a user's click on the corresponding component, and preferably, a series of operations performed by the event refer to another document or a reference to another component. It is necessary to treat it differently depending on whether or not it exists for a simple additional explanation.
문서로부터 구획된 하나 이상의 영역 중에서 본문영역을 결정하기 위해서는 여러 가지 방법이 사용될 수 있다. 바람직하게는 각 영역별로 상기 판단인자를 사용하여 본문적합도를 산출하고 그 산출된 결과를 기준으로 하여 본문영역을 선정할 수 있으며, 상기 본문적합도를 평가치를 산출하는 방법으로는 각 인자들에 가중치를 부여하여 하나의 수식으로 산출하는 방법, 상기 인자들로 신경회로망을 구성하여 학습시키는 방법 및 결정트리를 사용하는 방법 등이 활용될 수 있다.Various methods may be used to determine the text area among one or more areas partitioned from the document. Preferably, the body suitability may be calculated using the determination factor for each region, and a body region may be selected based on the calculated result. The method of calculating the body suitability may include weighting factors. The method of assigning and calculating a single equation, a method of constructing and learning a neural network using the factors, and a method of using a decision tree may be utilized.
제목정보 탐지 영역을 설정하는 단계(S140)는 문서의 제목을 추출하는 데 있어서, 해당 문서의 내용을 표현하고 있는 부분 외의 정보들이 문서 제목추출 과정에 개입하는 것을 방지하기 위한 단계로서 제목후보구가 선정될 영역을 문서의 일부로 제한하는 단계이다.In the setting of the title information detection area (S140), in extracting the title of the document, the title candidate is a step for preventing information other than the part expressing the content of the document from intervening in the document title extraction process. This step limits the area to be selected to be part of the document.
일반적인 경우에 문장의 작성은 위에서 아래로 이루어지게 되고, 제목은 본문내용에 위쪽에 본문내용의 시작점과 인접하여 위치한다.In the general case, the writing of the sentence should be made from top to bottom, and the title should be located above the body content and adjacent to the start point of the body content.
따라서 본문영역 자체에 포함된 모든 문자열을 대상으로 제목적합도를 평가하는 방법이 보다 보수적이고 안정적일 수도 있으나, 본문영역 내에서도 본문내용이 시작되는 위치를 식별하여 제목을 탐색할 영역을 본문내용이 시작하는 위치보다 상부로 한정하는 것이 효율적인 방안이 될 수 있다.Therefore, the method of evaluating the title conformity for all the texts included in the text area itself may be more conservative and stable.However, even in the text area, the area where the text content starts is identified by identifying the location where the text content starts. Confining above the location may be an efficient solution.
다만, 문서의 제목이 언제나 본문영역 내부에 위치하는 것은 아니므로 바람직하게는 본문영역보다 상부에 위치하는 영역까지도 그 제목 탐색 대상 영역으로 추가하는 것이 바람직하며, 본문영역이나 그 상부영역에 드러나지 아니하더라도 문서에 포함된 메타정보들을 활용하는 것도 추가로 고려될 수 있다. 한 예로 html 문서들의 경우에는 <title></title> 태그 등의 메타정보가 포함되며, 그 내용이 문서의 진정한 제목인가 여부는 별론으로 적어도 제목의 후보로서는 고려될 가치는 있다.However, since the title of the document is not always located inside the body area, it is preferable to add the area located above the body area as the subject search area, even if it is not revealed in the body area or the upper area. Utilization of meta-information contained in the document may also be considered further. For example, in the case of html documents, meta information such as <title> </ title> tags is included, and whether or not the content is the true title of the document is separately worth considering at least as a candidate for the title.
상기 본문내용 위치의 식별과 관하여 좀더 구체적으로 살펴보자면, 일반적인 문서 작성의 경우에서 있어서, 본문내용은 밑줄, 기울임 등의 속성의 부여가 상대적으로 적으며, 두 줄 이상으로 작성되어 문서 전체에서 상대적으로 많은 분량을 차지하는 등의 경향을 보인다. 따라서, 유사한 속성을 가지는 구성요소(element) 내지는 텍스트 군집이 본문영역에서 차지하는 상대적 비율이 높다거나, 텍스트의 폭이 본문영역의 폭에 근접하거나 본문영역의 폭 이상이어서 줄 바뀜이 나타난다거나 하는 경우에는 해당 구성요소(element)가 본문내용일 확률이 높은 것으로 판단할 수 있고, 밑줄, bold, 기울임 등의 속성이 빈번히 나타난다거나 해당 구성요소가 표시되는 폭이 본문영역의 폭에 비해 상대적으로 좁은 경우 등에는 해당 구성요소가 본문내용일 확률이 낮은 것으로 판단할 수 있다.In more detail with regard to the identification of the location of the text content, in the case of general document writing, the text content has relatively little provision of attributes such as underlining and italicity, and is written in two or more lines and is relatively relatively in the entire document. It tends to take up a large amount. Therefore, when a component or a text cluster having similar properties occupies a large proportion in the body region, or when a line break appears because the width of the text is close to or larger than the width of the body region. It can be judged that the element is likely to be the body content, and the properties such as underline, bold, and italic appear frequently, or when the width of the element is displayed is relatively narrow compared to the width of the body area. Can be determined that the component is less likely to be the content of the body.
일 예로 본문영역 내에서 줄바뀜이 반복적으로 일어나는 첫 단락을 본문내용의 시작점으로서 식별한다거나, 본문영역 내에서 최대의 폭을 가진 텍스트 내지 본문영역 내의 가장 긴 단락은 본문내용의 일부로 간주한다는 등의 기준에 의해서도 문서의 실질적인 본문내용이 시작하는 위치로 파악될 수 있다.For example, the first paragraph that causes repeated line breaks in the body area is identified as the starting point of the body content, or the text having the maximum width in the body area or the longest paragraph in the body area is regarded as part of the body content. Can also be identified as the starting point of the actual body content of the document.
다만, 본문영역의 위치로 의심되는 위치가 두 곳 이상인 경우, 상대적으로 아래에 있는 부분을 기준으로 하여 제목 탐지영역을 한정하는 것이 좀더 보수적이고 안정적인 방법일 수 있다.However, when there are two or more locations suspected as the location of the body area, it may be a more conservative and stable method to limit the title detection area based on the relatively lower part.
제목후보구를 선정하는 단계(S150)는 상기 설정된 제목탐지 영역 내에서 제목후보구들을 선정하는 단계이다.Selecting the title candidates (S150) is a step of selecting title candidates within the set title detection area.
상기 제목탐지 영역을 한정하는 단계(S140)를 통해 제목을 탐색하는 영역을 문서의 일부분으로 한정함으로써 문서 전체에 포함된 모든 구성요소를 대상으로 하여 제목적합도를 평가하는 등의 비효율은 상당부분 개선될 것이며, 그 계산과정에 무리가 없다면, 상기 탐색영역 내의 모든 구성요소에 대하여 제목적합도를 산정하여 제목을 선정하는 방법으로도 제목정보 추출이라는 목적을 달성할 수 있다.By limiting the title detection area (S140), the area for searching the title is limited to a part of the document, and thus the inefficiency such as evaluating the title suitability for all the components included in the entire document can be substantially improved. If the calculation process is not overwhelming, the purpose of extracting title information may be achieved by calculating title suitability for all components in the search area and selecting a title.
그러나 계산과정에서의 부담이 개선을 위해 바람직하게는 상기 한정된 제목 탐색영역내에서 1차적으로 제목후보구를 선정하는 단계를 추가적으로 포함할 수 있다. 한 예로 제목적합도에 산출에 사용되는 속성들 중에서 일부만을 고려하여 제목 탐색영역에 포함된 구성요소 중에서 제목일 가능성이 매우 낮은 것들을 배제할 수 있다.However, in order to reduce the burden in the calculation process, the method may further include selecting a title candidate first in the limited title search area. For example, considering only some of the attributes used in the calculation of title suitability, it is possible to exclude those that are very unlikely to be the title from the elements included in the title search area.
또한, 제목후보구를 선정하는 단계(S150)는 유사한 위치정보를 가진 문서들에서 반복여부를 고려하여 제목후보구를 조정하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다.In addition, selecting the title candidates (S150) may include adjusting the title candidates in consideration of repetition in documents having similar location information.
유사한 위치정보를 가진 문서들이란, 로컬영역에서는 그 위치한 경로정보가 유사한 문서들을 의미하고, 웹 문서들의 경우에 있어서는 URL의 정보가 유사한 문서들을 의미한다. 문서의 파일명을 제외한 최하위 경로정보까지 동일한 문서들을 의미하는 것으로 국한되어 해석할 것은 아니며, 동일한 템플릿 등에 의하여 작성되어 사용자에게 보이는 문서의 구조가 유사한 문서들에 까지 확대 해석될 수 있다.Documents having similar location information mean documents in which local route information is similar, and documents in which URL information is similar in the case of web documents. The lowermost path information except the file name of the document is not limited to the same document and is not interpreted. The structure of the document created by the same template and displayed to the user may be extended to similar documents.
예를 들어, 이러한 문서들에서 완전히 동일한 형태로 반복되는 문자열의 경우에는 해당 문서만의 내용 또는 특징을 대변한다기보다는 그 그룹의 특징을 나타내는 것으로서 해석될 가능성이 잇는데, 예로서, 웹 문서의 경우 사이트 맵에서의 해당문서의 위치에 대응하는 경로 정보가 문서에 노출되어 반복되는 경우라든지, <title>태그 내에 해당 웹사이트의 최상위 주소만이 동일하게 반복되는 경우가 이에 해당한다.For example, a string that repeats in exactly the same form in these documents is likely to be interpreted as representing the group's characteristics, rather than representing the content or characteristics of that document alone. This is the case when the path information corresponding to the position of the document in the site map is exposed and repeated in the document, or only the top address of the website is identically repeated in the <title> tag.
유사한 위치정보를 가지는 문서들에서 반복되는 문자열을 참고하는 것은 단순히, 상기의 무의미한 후보구를 배제하는 목적으로만 활용되는 것은 아니며, 제목적합도를 산출하고 문서의 제목을 결정하는 단계(S160)에도 그 결과가 반영될 수 있다. 한 예로 한 문서에서 "한국근대사 - part.1 1950년대"가 제목으로 추출되고 동일한 경로에 위치하는 또 다른 문서에서 같은 위치에 "한국근대사 - part.2 1960년대" 라는 나타나는 경우에는 그 문자열의 일부가 반복된다는 이유만으로 제목후보구에서 배제되어서는 아니 되며, 오히려 제목을 결정하는 단계(S160)서 제목적합도의 산출에 있어서 가중되는 요인으로 반영될 수 있다.Referencing the repeated character strings in documents having similar location information is not merely used for the purpose of excluding the meaningless candidate phrase, but also in calculating the title suitability and determining the title of the document (S160). The results can be reflected. For example, if one document "Korean Modern History-part.1 1950s" is extracted as the title and another document is located in the same path and "Korean Modern History-part.2 1960s" appears in the same location, it is part of the string. It should not be excluded from the title candidate only because it is repeated, but rather may be reflected as a weighting factor in the calculation of title conformity at the step S160.
제목후보구들에 대해 제목적합도를 산출하고 그를 기준으로 제목을 결정하는 단계(S160)는 상기 단계들에 의하여 추출된 제목후보구들을 평가하여 문서의 제목을 선택하는 과정이다.Calculating the title suitability for the title candidates and determining the title based on the title candidates (S160) is a process of selecting the title of the document by evaluating the title candidates extracted by the above steps.
제목적합도의 평가는 각 제목후보구의 속성들에 가중치를 부여하여 합산하는 방법으로 산출될 수 있으며, 바람직하게는 학습알고리즘을 사용하여 상기 가중치들을 튜닝하는 과정이 추가로 사용될 수도 있다. 또한, 결정트리 등을 사용하여 최적의 트리구조를 학습하는 방법 등도 고려될 수 있다.The evaluation of the title suitability may be calculated by weighting and adding the attributes of each title candidate. Preferably, the process of tuning the weights using a learning algorithm may be further used. In addition, a method of learning an optimal tree structure using a decision tree or the like may also be considered.
일 예로서 웹 문서의 경우에 상기 산출과정에서 고려될 수 있는 속성치들에 관해 살펴보자면, 제목후보구의 문서상 절대위치, 문서 전체에서의 상대위치, 문자열이 브라우징 될 경우의 그 문단의 절대적 크기, 폰트의 크기, 폰트 웨이트(font weight), 속해 있는 영역 또는 전체 문서의 크기에 대한 폰트의 상대적 크기, 문서내에서의 각 제목후보구가 가지는 폰트의 크기의 순서, 해당 문구가 여러 줄에 걸쳐있는지 여부, 수평 및 수직으로 같은 DOM(Document Object Model)의 개수, 문자열에 붙어 있는 태그명, 제목후보구가 문서에서 출현하는 문단의 순서, 후보문구의 문자열의 길이, 문서내에서 문자열의 foreground color의 빈도의 역순서, 문서 내에서 문자열의 배경색(background color)의 빈도의 역순서 및 문자열의 문서내 발생 확률을 로그값으로 정규화한 값들 중 적어도 하나 이상이 사용될 수 있다.As an example, in the case of a web document, the attribute values that may be considered in the calculation process may include: an absolute position in a document of a title candidate, a relative position in the entire document, an absolute size of a paragraph when a string is browsed, and a font. The font size, font weight, relative size of the font to the size of the region or entire document to which it belongs, the order of the font size of each title candidate in the document, and whether the text spans multiple lines The number of Document Object Models (DOMs) that are the same horizontally and vertically, the name of the tag attached to the string, the order in which paragraphs the title candidate appears in the document, the length of the candidate text string, and the frequency of the foreground color of the string in the document. The reverse order of, the reverse order of the frequency of the background color of the string in the document, and the probability of occurrence of the string in the document in logarithm. There is more than one can be used.
또한, 웹 문서들이 아니라 일반적인 전자적 문서들의 경우에도 상기 열거된 속성들에 대응하는 값들이 제목적합도의 평가에 사용될 수 있다.In addition, in the case of general electronic documents, not web documents, values corresponding to the above-listed attributes may be used for the evaluation of title conformance.
또한, 각각의 제목후보구가 문서 전체의 내용 또는 본문내용에 포함된 정보들과의 내용적 관련성을 평가하여 제목적합도에 반영할 수 있다. 한 예로 상기 내용적 관련성은 제목후보구에 포함된 단어들과 본문내용에 속한 단어들 간의 상호정보(mutual information)를 활용하거나 또는 (query)-(query)값 등을 사용하여 평가될 수 있다.In addition, each title candidate can evaluate the content relevance with the contents of the entire document or the contents of the document and reflect it in the title conformance. For example, the content relevance may be evaluated using mutual information between words included in the title candidate phrase and words belonging to the text content, or by using a (query)-(query) value.
또한 바람직하게는 상기 제목적합도가 최상위인 제목후보구들 중에서 하나만을 선택하는 것이 부적당하다고 여겨질 만큼. 제목적합도의 차이가 근소한 경우라든가, 최상위 제목후보구의 길이가 너무 짧아서 그 대표성이 떨어지는 것으로 판단되는 경우에는 차상위 제목후보구 중 하나가 병기되어 문서의 제목을 형성할 수도 있다.Also preferably, it is considered inadequate to select only one of the title candidates whose title suitability is the highest. If the difference in title suitability is small or the length of the top title candidate is too short to determine its representativeness, one of the next higher title candidates may be written together to form the title of the document.
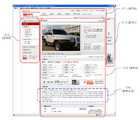
도 2a는 본 발명의 실시예에 의하여 문서가 영역들로 구획된 결과의 한 예를 나타내는 도면이다.2A is a diagram illustrating an example of a result of dividing a document into regions according to an embodiment of the present invention.
예시된 문서는 인터넷 상의 중고차 매매사이트인 SK엔카(www.skencar.com)의 한 페이지로서 해당 페이지는 문서게시자가 작성시에 판매하고자 하는 차량에 대한 정보 이외에도 각종 광고정보 및 해당사이트의 관련정보 등이 병기되어 화면에 표시되어 있다. 이 문서를 구문분석하면, 문서 내에 포함된 각 구성요소(element)들과 그 속성을 파악할 수 있다.The illustrated document is a page of SK Enka (www.skencar.com), a used car trading site on the Internet, and the page includes various advertisement information and related information on the site as well as information on the vehicle that the document publisher wants to sell at the time of writing. This is written together and displayed on the screen. By parsing this document, you can identify each of the elements contained in the document and their attributes.
한 예로서 상기 구문분석 결과에 의하여 파악된 구성요소들의 브라우징 되는 폭과 위치를 고려하여 문서를 영역별로 구획하면, 예시된 문서는 도 2a에 도시된 바와 같이 여러 영역으로 구획될 수 있다.As an example, if a document is divided into regions in consideration of the width and position of the elements identified by the parse result, the illustrated document may be divided into several regions as illustrated in FIG. 2A.
상기 영역들을 살펴보자면. 영역A(211)와 영역B(212)는 해당사이트에서 다른 정보들을 보여주는 등이 사용자 편의를 제공하기 위해 구성되는 영역이고, 영역C(213)는 해당 웹사이트에서 광고가 노출되는 영역이다. 영역D(214)는 게시자가 자신이 판매하고자 하는 중고차의 정보 등을 기재한 영역이며, 도면에 도시되지는 않았지만 관계법령에 따라 사이트의 운영주체에 대한 정보가 노출되는 영역이 영역D(214)의 이하에 별도로 존재한다.Looking at the above areas. The area A 211 and the
본 발명의 한 실시예에 따라서 상기 영역들 중에서 본문영역을 식별하는 과정을 살펴보자면, 영역D (214)가 상대적으로 폭이 넓고, 전체문서에서 차지하는 위치가 가운데이며, 영역의 면적 및 높이 또한 크고, 다른 영역들은 광고라거나, 해당 사이트내에서의 네비게이션을 도와주기 위한 링크 정보들이 많이 포함되어 있는데 반하여 영역D(210)는 게시자가 자신이 판매하고자하는 중고차량에 대한 설명을 일반 텍스트(plain text)로 기술하고 있으므로, 영역 내의 링크 속성을 가지고 있지 않은 텍스트의 비율이 높게 나타난다. 따라서 결과적으로는 영역D(210)가 본문영역으로 식별된다.According to an embodiment of the present invention, a process of identifying a main body region among the above-mentioned regions may include a region D 214 having a relatively large width, a position occupying the entire document, and having a large area and height. Other areas are advertisements or contain a lot of link information to help navigation within the site, whereas area D 210 provides a plain text description of the used vehicle the publisher wants to sell. Because of this, the proportion of text that does not have link attributes in the region is high. As a result, area D 210 is identified as the body area.
도 2b는 본 발명의 실시예에 의하여 문서에서 제목후보구의 위치가 식별된 결과를 나타내는 도면이다. 제목탐지영역을 한정하기 위한 기준으로서 본문영역으로 식별된 영역D(214)내에서 본문내용의 위치를 식별하는 과정이 수행된다. 한 예로 본문영역(210)의 폭과 유사하고 별다른 속성이 없는 텍스트로서 줄바뀜이 일어나는 경우를 찾아보면 본문내용(220)의 위치는 파악될 수 있다.2B is a diagram illustrating a result of identifying a position of a title candidate in a document according to an embodiment of the present invention. As a criterion for limiting the title detection area, a process of identifying the position of the body content in the area D 214 identified as the body area is performed. As an example, looking for a case in which line breaks occur as text similar to the width of the body region 210 and without any special attributes, the position of the
따라서 본문영역으로 식별된 영역D(214)내에서도 본문내용(220)상단이 제목탐지영역이 되며, 추가적으로는 본문영역보다 상단인 영역A(211)가 제목탐지영역이 될 수 있다.Accordingly, even in the area D 214 identified as the body area, the upper portion of the
단순히 본문영역만을 인식하여, 그 영역 내부에 있는 문자열들 모두에 대해 제목적합도를 평가하는 방법도 가능하나. 계산과정의 부담이 증가하며, 더욱이 이러한 계산과정에서의 부담은 유사한 위치정보를 가진 다른 문서들의 정보를 활용하는 과정에서 기하급수적으로 증가할 수 있다.It is also possible to simply recognize the body area and evaluate the title suitability for all the strings in the area. The burden of the calculation process increases, and moreover, the burden of this calculation process can increase exponentially in the process of utilizing the information of other documents with similar location information.
따라서 바람직하게는 본문영역 내에서 본문내용(220)의 위치를 기준으로 하여 그 상부의 영역에서 1차적으로 구성요소의 폰트 크기, 폰트 색깔, 본문영역과의 거리 등 제목적합도의 평가에 사용되는 속성중 일부만을 사용하여 제목후보구를 추출하면 본문영역의 다른 문자열들에 비해 그 폰트가 크고, bold 속성을 가진 4개의 제목후보구가 선정된다.Therefore, preferably, the attribute used for evaluating the title suitability such as the font size, font color, and distance from the main body of the element is primarily in the upper region based on the position of the
이들 후보구 모두에 있어 제목적합도를 산출하는 경우에는 후보구2(232)가 가장 폰트사이즈가 크고 폰트의 색깔이 대비되는 속성을 가지고 있으므로 제목으로 선정될 확률이 크다 할 것이다.In the case of calculating title suitability in all of these candidate phrases, candidate phrase 2 (232) is most likely to be selected as the title since the font size has the largest attribute and the color of the font is contrasted.
또한, 4개의 후보구들 중 후보구2(232)를 제외한 나머지 3개의 후보구들은 해당 중고차 판매사이트에서의 일정한 템플릿에 따라 표기되는 문자열로서, 다른 문서들에서도 동일한 위치에 동일한 형태로 반복되는 정보에 불과하다. 따라서 제목후보구로부터 이들을 배제하거나. 제목적합도 산출에 부정적으로 반영함으로써 후보구2(232)가 문서의 제목으로 선정되는 과정이 보다 명확해 질 수 있다.In addition, among the four candidate phrases, the remaining three candidate phrases except for candidate phrase 2 (232) are strings written according to a predetermined template in the used car sales site, and the information is repeated in the same position in the same position in other documents. It is only. So exclude them from the title candidate. By negatively reflecting the title suitability, the process of selecting candidate phrase 2 232 as the title of the document may be more clearly defined.
도 3은 본 발명의 실시예에 의하여 본문영역 외에서 제목이 선정된 결과를 예시한 도면이다.3 is a diagram illustrating a result of selecting a title outside the body region according to an embodiment of the present invention.
예시된 웹 문서는 '태리'라는 예명을 가진 가수의 '섹시가이(sexy guy)'제목의 곡에 대한 정보를 보여주는 웹 페이지이다. 상기 페이지에서의 영역의 위치, 영역의 폭 및 그 영역 내에서 링크 속성을 가지지 않는 텍스트의 비율등을 고려하여 보면 본문영역은 영역A(310)로 결정된다.The illustrated web document is a web page showing information about a song of the title 'sexy guy' of a singer entitled 'Tary'. In view of the position of the region on the page, the width of the region, and the proportion of text having no link attribute within the region, the body region is determined as region A 310.
상기 영역A(310)의 내부에서도 '섹시가이(sexy guy)'라는 형태로 그 곡명이나. '아티스트: 태리'라는 형태로 가수명이 노출되지만, 그 현출되는 형태가 다른 정보를 가진 텍스트에 비하여 현격한 차이를 보이지는 못하는바, 단순히 이들을 대상으로 제목 적합도를 평가하는 경우에는 그 적합도의 차이가 크게 구별되지 않을 수 있다. 이 경우 본문영역 내에서 그 제목적합도를 산출하는 방식을 최적화하는 것보다는 제목 탐지영역을 본문영역의 상단에 위치하는 영역B(311)이나 영역C(312)가지 확대하여 탐색하는 것이 문제를 해결하는 효율적일 수 있으며, 이 경우 영역B(311)에 게시된 '태리싱글 - 섹시가이(Sexy Guy)'가 제목으로 결정되는 것이 바람작하다.The name of the song in the form of 'sexy guy' also in the area A (310). The artist's name is exposed in the form of 'Artist: Tarry', but the manifestation of the artist does not show a significant difference compared to the text with other information. It may not be largely distinguished. In this case, rather than optimizing the method of calculating the title suitability in the text area, it is possible to solve the problem by enlarging and searching the title detection area by the area B 311 or C 312 located at the top of the text area. It may be efficient, and in this case, it is preferable that the title 'Tari Single-Sexy Guy' posted in the area B 311 is determined.
도 4는 본 발명에 따른 문서 정보추출방법을 구현하기 위한 시스템의 구성도 이다.4 is a block diagram of a system for implementing a document information extraction method according to the present invention.
문서를 파싱하는 문서해석부(410)는 문서를 구성요소별로 속성치를 해석하여 영역구획과 제목적합도를 산정하는 기초 자료를 생성한다. 또한, html 문서들에서 제목속성 즉, <title>태그 내의 정보를 제목후보구 선정부로 전달하는 역할을 수행한다.The
문서구획부(420)는 상기 문서해석부(410)에서 파싱한 결과를 이용하여 소정의 기준에 따라 하나 이상의 영역으로 구획하는 역할을 수행하며, 본문영역 식별부(430)는 각 영역의 위치, 폭 및 링크속성을 가지지 않는 텍스트의 비율에 의하여 해당문서의 본문을 가지고 있다고 생각되는 영역을 선정하는 기능을 수행한다.The
본문내용 식별부(440)는 본문영역 내에서 줄바뀜 위치 등을 기준으로 하여 해당문서에서 중심이 되는 내용을 포함하는 문서의 구성요소를 식별한다. 식별된 본문내용은 제목정보를 탐지하는 영역을 제한하는 용도로 사용될 수도 있다. 또한 바람직하게는 문서검색 시스템 등에서 검색결과를 표현함에 있어 그 문서의 내용을 요약한 정보로서 상기본문내용이 제공될 수 있다.The body
탐지영역 식별부(450)는 문서전체에서 제목후보구를 추출하여 제목적합도를 산정하는 비효율을 제거하기 위해 일반적으로 제목정보가 노출되는 것이 일반적이라고 생각되는 영역으로 그 탐지영역을 한정하는 과정이다.The detection
제목 후보구 선정부(460)는 제목탐지영역 내에서 제목적합도를 평가받을 제목후보구를 선정하는 과정이다. 계산과정 자체의 부담이 없다면 제목탐지영역 내의 모든 구성요소만을 제목후보구로 고려하는 것이 안정적일 수 있으나, 1차적으로 간단한 몇몇의 속성을 고려하여 제목후보구를 적당한 수로 설정하는 것이 효율적일 수 있다.The title candidate
제목정보 식별부(470)는 소정의 기준에 의하여 제목적합도를 산출하고 그를 기준으로 하여 해당 문서의 제목을 선정한다. 다만, 경우에 따라서는 최상위의 제목후보구 하나만을 제목으로서 선택할 뿐만 아니라 상위의 제목적합도를 가지는 제목후보구를 병기하여 제목정보를 생성하는 역할을 수행하기도 한다.The title
본 발명의 실시예들은 다양한 컴퓨터로 구현되는 동작을 수행하기 위한 프로그램 명령을 포함하는 컴퓨터 판독가능 매체를 포함한다. 상기 컴퓨터 판독 가능 매체는 프로그램 명령, 데이터 파일, 데이터 구조 등을 단독으로 또는 조합하여 포함할 수 있다. 상기 매체는 본 발명을 위하여 특별히 설계되고 구성된 것들이거나 컴퓨터 소프트웨어 당업자에게 공지되어 사용 가능한 것일 수도 있다. 컴퓨터 판독 가능 기록 매체의 예에는 하드 디스크, 플로피 디스크 및 자기 테이프와 같은 자기 매체, CD-ROM, DVD와 같은 광기록 매체, 자기-광 매체 및 롬, 램, 플래시 메모리 등과 같은 프로그램 명령을 저장하고 수행하도록 특별히 구성된 하드웨어 장치가 포함된다. 프로그램 명령의 예에는 컴파일러에 의해 만들어지는 것과 같은 기계어 코드뿐만 아니라 인터프리터등을 사용해서 컴퓨터에 의해서 실행될 수 있는 고급 언어 코드를 포함한다.Embodiments of the invention include a computer readable medium containing program instructions for performing various computer-implemented operations. The computer readable medium may include program instructions, data files, data structures, etc. alone or in combination. The media may be those specially designed and constructed for the purposes of the present invention, or they may be of the kind well-known and available to those having skill in the computer software arts. Examples of computer readable recording media include magnetic media such as hard disks, floppy disks, and magnetic tape, optical recording media such as CD-ROMs, DVDs, magnetic-optical media, and program instructions such as ROM, RAM, flash memory, and the like. Hardware devices specifically configured to perform are included. Examples of program instructions include machine language code, such as produced by a compiler, as well as high-level language code that can be executed by a computer using an interpreter.
지금까지 본 발명에 따른 구체적인 실시예에 관하여 설명하였으나, 본 발명 의 범위에서 벗어나지 않는 한도 내에서는 여러 가지 변형이 가능하므로, 본 발명의 범위는 설명된 실시예에 국한되어 정해져서는 안되며, 후술하는 특허청구범위뿐만이 아니라 특허청구범위와 균등한 것들에 의해 정해져야 한다.Although specific embodiments of the present invention have been described so far, various modifications may be made without departing from the scope of the present invention, and the scope of the present invention should not be limited to the described embodiments, and the patents described below. It should be determined not only by the claims but also by the claims and their equivalents.
이상과 같이 한정된 실시예와 도면에 의해 설명하였으나, 본 발명은 상기의 실시예에 한정되는 것은 아니며, 이는 본 발명이 속하는 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 이러한 기재로부터 다양한 수정 및 변형이 가능하다. 따라서, 본 발명 사상은 아래에 기재된 특허청구범위에 의해 파악되어야 하고, 이의 균등 또는 등가적 변형 모두는 본 발명사상의 범주에 속한다고 할 것이다.Although described by the limited embodiments and drawings as described above, the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments, which can be variously modified and modified by those skilled in the art to which the present invention pertains. . Accordingly, the spirit of the present invention should be grasped by the claims set forth below, and all equivalent or equivalent modifications thereof shall fall within the scope of the present invention.
이상의 설명에서 알 수 있는 바와 같이 본 발명에 따르면 문서에서 사용자가 본문으로 인식할 영역의 위치를 식별할 수 있으며, 본문영역과의 상대적 위치를 기준으로 하여 제목후보구를 선정하고,As can be seen from the above description, according to the present invention, the position of a region to be recognized by the user in the document can be identified, the title candidate is selected based on the relative position with the body region,
또한 본 발명에 따르면 유사한 위치정보를 가지는 문서들의 집합에서 반복되어 나타날 뿐 본문을 대표하는 정보를 가지지 못하는 문구들을 제목후보구에서 배제함으로서 웹 문서의 작성자의 의도와는 상관없는 문자열이 웹 문서의 제목으로서 표현되는 것을 차단할 수 있는 효과가 있다.In addition, according to the present invention, by removing the phrases that appear repeatedly in a set of documents having similar location information and do not have information representing the text from the title candidate, the character string of the web document is irrelevant to the intention of the creator of the web document. There is an effect that can block what is represented as.
Claims (18)
Translated fromKoreanPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020060030795AKR100761912B1 (en) | 2006-04-05 | 2006-04-05 | Method and system for extracting document information based on body identification |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020060030795AKR100761912B1 (en) | 2006-04-05 | 2006-04-05 | Method and system for extracting document information based on body identification |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020070043587ADivisionKR100791580B1 (en) | 2007-05-04 | 2007-05-04 | Method and system for extracting document information based on body identification |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR100761912B1true KR100761912B1 (en) | 2007-09-28 |
Family
ID=38738753
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020060030795AActiveKR100761912B1 (en) | 2006-04-05 | 2006-04-05 | Method and system for extracting document information based on body identification |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100761912B1 (en) |
Cited By (32)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2010096193A3 (en)* | 2009-02-18 | 2010-10-28 | Exbiblio B.V. | Identifying a document by performing spectral analysis on the contents of the document |
| US7990556B2 (en) | 2004-12-03 | 2011-08-02 | Google Inc. | Association of a portable scanner with input/output and storage devices |
| US8005720B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2011-08-23 | Google Inc. | Applying scanned information to identify content |
| US8081849B2 (en) | 2004-12-03 | 2011-12-20 | Google Inc. | Portable scanning and memory device |
| US8146156B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2012-03-27 | Google Inc. | Archive of text captures from rendered documents |
| US8179563B2 (en) | 2004-08-23 | 2012-05-15 | Google Inc. | Portable scanning device |
| US8261094B2 (en) | 2004-04-19 | 2012-09-04 | Google Inc. | Secure data gathering from rendered documents |
| US8442331B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2013-05-14 | Google Inc. | Capturing text from rendered documents using supplemental information |
| US8447111B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2013-05-21 | Google Inc. | Triggering actions in response to optically or acoustically capturing keywords from a rendered document |
| US8447066B2 (en) | 2009-03-12 | 2013-05-21 | Google Inc. | Performing actions based on capturing information from rendered documents, such as documents under copyright |
| US8489624B2 (en) | 2004-05-17 | 2013-07-16 | Google, Inc. | Processing techniques for text capture from a rendered document |
| US8600196B2 (en) | 2006-09-08 | 2013-12-03 | Google Inc. | Optical scanners, such as hand-held optical scanners |
| US8619287B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2013-12-31 | Google Inc. | System and method for information gathering utilizing form identifiers |
| US8621349B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2013-12-31 | Google Inc. | Publishing techniques for adding value to a rendered document |
| US8620083B2 (en) | 2004-12-03 | 2013-12-31 | Google Inc. | Method and system for character recognition |
| US8619147B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2013-12-31 | Google Inc. | Handheld device for capturing text from both a document printed on paper and a document displayed on a dynamic display device |
| US8713418B2 (en) | 2004-04-12 | 2014-04-29 | Google Inc. | Adding value to a rendered document |
| US8793162B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2014-07-29 | Google Inc. | Adding information or functionality to a rendered document via association with an electronic counterpart |
| US8799303B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2014-08-05 | Google Inc. | Establishing an interactive environment for rendered documents |
| US8874504B2 (en) | 2004-12-03 | 2014-10-28 | Google Inc. | Processing techniques for visual capture data from a rendered document |
| US8903759B2 (en) | 2004-12-03 | 2014-12-02 | Google Inc. | Determining actions involving captured information and electronic content associated with rendered documents |
| US8990235B2 (en) | 2009-03-12 | 2015-03-24 | Google Inc. | Automatically providing content associated with captured information, such as information captured in real-time |
| US9081799B2 (en) | 2009-12-04 | 2015-07-14 | Google Inc. | Using gestalt information to identify locations in printed information |
| US9116890B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2015-08-25 | Google Inc. | Triggering actions in response to optically or acoustically capturing keywords from a rendered document |
| US9143638B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2015-09-22 | Google Inc. | Data capture from rendered documents using handheld device |
| US9268852B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2016-02-23 | Google Inc. | Search engines and systems with handheld document data capture devices |
| US9275051B2 (en) | 2004-07-19 | 2016-03-01 | Google Inc. | Automatic modification of web pages |
| US9323784B2 (en) | 2009-12-09 | 2016-04-26 | Google Inc. | Image search using text-based elements within the contents of images |
| US9454764B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2016-09-27 | Google Inc. | Contextual dynamic advertising based upon captured rendered text |
| US10769431B2 (en) | 2004-09-27 | 2020-09-08 | Google Llc | Handheld device for capturing text from both a document printed on paper and a document displayed on a dynamic display device |
| CN112668581A (en)* | 2020-12-29 | 2021-04-16 | 北京声智科技有限公司 | Document title identification method and device |
| CN114239689A (en)* | 2021-11-19 | 2022-03-25 | 厦门市美亚柏科信息股份有限公司 | Multi-mode-based website type judgment method and device |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11203285A (en) | 1998-01-14 | 1999-07-30 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Document structure analysis device and its method, and recording medium |
| KR20010075874A (en)* | 2000-01-21 | 2001-08-11 | 오길록 | Method for analyzing structure of treatise typed of document image |
| JP2003248690A (en) | 2003-02-13 | 2003-09-05 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | Document processing device and method |
| JP2005234761A (en) | 2004-02-18 | 2005-09-02 | Seiko Epson Corp | Title determining apparatus, title determining method and program thereof |
- 2006
- 2006-04-05KRKR1020060030795Apatent/KR100761912B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11203285A (en) | 1998-01-14 | 1999-07-30 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Document structure analysis device and its method, and recording medium |
| KR20010075874A (en)* | 2000-01-21 | 2001-08-11 | 오길록 | Method for analyzing structure of treatise typed of document image |
| JP2003248690A (en) | 2003-02-13 | 2003-09-05 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | Document processing device and method |
| JP2005234761A (en) | 2004-02-18 | 2005-09-02 | Seiko Epson Corp | Title determining apparatus, title determining method and program thereof |
Cited By (48)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8442331B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2013-05-14 | Google Inc. | Capturing text from rendered documents using supplemental information |
| US8619147B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2013-12-31 | Google Inc. | Handheld device for capturing text from both a document printed on paper and a document displayed on a dynamic display device |
| US8005720B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2011-08-23 | Google Inc. | Applying scanned information to identify content |
| US8019648B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2011-09-13 | Google Inc. | Search engines and systems with handheld document data capture devices |
| US8799303B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2014-08-05 | Google Inc. | Establishing an interactive environment for rendered documents |
| US8515816B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2013-08-20 | Google Inc. | Aggregate analysis of text captures performed by multiple users from rendered documents |
| US8831365B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2014-09-09 | Google Inc. | Capturing text from rendered documents using supplement information |
| US8214387B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2012-07-03 | Google Inc. | Document enhancement system and method |
| US9268852B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2016-02-23 | Google Inc. | Search engines and systems with handheld document data capture devices |
| US8447144B2 (en) | 2004-02-15 | 2013-05-21 | Google Inc. | Data capture from rendered documents using handheld device |
| US8146156B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2012-03-27 | Google Inc. | Archive of text captures from rendered documents |
| US8447111B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2013-05-21 | Google Inc. | Triggering actions in response to optically or acoustically capturing keywords from a rendered document |
| US9143638B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2015-09-22 | Google Inc. | Data capture from rendered documents using handheld device |
| US9116890B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2015-08-25 | Google Inc. | Triggering actions in response to optically or acoustically capturing keywords from a rendered document |
| US9454764B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2016-09-27 | Google Inc. | Contextual dynamic advertising based upon captured rendered text |
| US8505090B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2013-08-06 | Google Inc. | Archive of text captures from rendered documents |
| US8781228B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2014-07-15 | Google Inc. | Triggering actions in response to optically or acoustically capturing keywords from a rendered document |
| US9514134B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2016-12-06 | Google Inc. | Triggering actions in response to optically or acoustically capturing keywords from a rendered document |
| US8619287B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2013-12-31 | Google Inc. | System and method for information gathering utilizing form identifiers |
| US8621349B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2013-12-31 | Google Inc. | Publishing techniques for adding value to a rendered document |
| US8793162B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2014-07-29 | Google Inc. | Adding information or functionality to a rendered document via association with an electronic counterpart |
| US8620760B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2013-12-31 | Google Inc. | Methods and systems for initiating application processes by data capture from rendered documents |
| US9633013B2 (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2017-04-25 | Google Inc. | Triggering actions in response to optically or acoustically capturing keywords from a rendered document |
| US8713418B2 (en) | 2004-04-12 | 2014-04-29 | Google Inc. | Adding value to a rendered document |
| US9030699B2 (en) | 2004-04-19 | 2015-05-12 | Google Inc. | Association of a portable scanner with input/output and storage devices |
| US8261094B2 (en) | 2004-04-19 | 2012-09-04 | Google Inc. | Secure data gathering from rendered documents |
| US8799099B2 (en) | 2004-05-17 | 2014-08-05 | Google Inc. | Processing techniques for text capture from a rendered document |
| US8489624B2 (en) | 2004-05-17 | 2013-07-16 | Google, Inc. | Processing techniques for text capture from a rendered document |
| US9275051B2 (en) | 2004-07-19 | 2016-03-01 | Google Inc. | Automatic modification of web pages |
| US8179563B2 (en) | 2004-08-23 | 2012-05-15 | Google Inc. | Portable scanning device |
| US10769431B2 (en) | 2004-09-27 | 2020-09-08 | Google Llc | Handheld device for capturing text from both a document printed on paper and a document displayed on a dynamic display device |
| US8874504B2 (en) | 2004-12-03 | 2014-10-28 | Google Inc. | Processing techniques for visual capture data from a rendered document |
| US8953886B2 (en) | 2004-12-03 | 2015-02-10 | Google Inc. | Method and system for character recognition |
| US7990556B2 (en) | 2004-12-03 | 2011-08-02 | Google Inc. | Association of a portable scanner with input/output and storage devices |
| US8903759B2 (en) | 2004-12-03 | 2014-12-02 | Google Inc. | Determining actions involving captured information and electronic content associated with rendered documents |
| US8081849B2 (en) | 2004-12-03 | 2011-12-20 | Google Inc. | Portable scanning and memory device |
| US8620083B2 (en) | 2004-12-03 | 2013-12-31 | Google Inc. | Method and system for character recognition |
| US8600196B2 (en) | 2006-09-08 | 2013-12-03 | Google Inc. | Optical scanners, such as hand-held optical scanners |
| US8418055B2 (en) | 2009-02-18 | 2013-04-09 | Google Inc. | Identifying a document by performing spectral analysis on the contents of the document |
| WO2010096193A3 (en)* | 2009-02-18 | 2010-10-28 | Exbiblio B.V. | Identifying a document by performing spectral analysis on the contents of the document |
| US8638363B2 (en) | 2009-02-18 | 2014-01-28 | Google Inc. | Automatically capturing information, such as capturing information using a document-aware device |
| US8447066B2 (en) | 2009-03-12 | 2013-05-21 | Google Inc. | Performing actions based on capturing information from rendered documents, such as documents under copyright |
| US9075779B2 (en) | 2009-03-12 | 2015-07-07 | Google Inc. | Performing actions based on capturing information from rendered documents, such as documents under copyright |
| US8990235B2 (en) | 2009-03-12 | 2015-03-24 | Google Inc. | Automatically providing content associated with captured information, such as information captured in real-time |
| US9081799B2 (en) | 2009-12-04 | 2015-07-14 | Google Inc. | Using gestalt information to identify locations in printed information |
| US9323784B2 (en) | 2009-12-09 | 2016-04-26 | Google Inc. | Image search using text-based elements within the contents of images |
| CN112668581A (en)* | 2020-12-29 | 2021-04-16 | 北京声智科技有限公司 | Document title identification method and device |
| CN114239689A (en)* | 2021-11-19 | 2022-03-25 | 厦门市美亚柏科信息股份有限公司 | Multi-mode-based website type judgment method and device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100761912B1 (en) | Method and system for extracting document information based on body identification | |
| US9483460B2 (en) | Automated formation of specialized dictionaries | |
| US8630972B2 (en) | Providing context for web articles | |
| US7065707B2 (en) | Segmenting and indexing web pages using function-based object models | |
| CN103309862B (en) | Webpage type recognition method and system | |
| US7458017B2 (en) | Function-based object model for use in website adaptation | |
| JPWO2009096523A1 (en) | Information analysis apparatus, search system, information analysis method, and information analysis program | |
| US20130339840A1 (en) | System and method for logical chunking and restructuring websites | |
| US9268878B2 (en) | Entity category extraction for an entity that is the subject of pre-labeled data | |
| US10810245B2 (en) | Hybrid method of building topic ontologies for publisher and marketer content and ad recommendations | |
| US20190392209A1 (en) | Document Analyzer, Document Analysis Method, and Computer-Readable Storage Medium Storing Program | |
| CN103810251A (en) | Method and device for extracting text | |
| CN103942211B (en) | A kind of recognition methods of text page and device | |
| Wu | Language independent web news extraction system based on text detection framework | |
| KR101050013B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for ranking search results using representative reliability | |
| CN109165373B (en) | Data processing method and device | |
| KR101086550B1 (en) | Japanese automatic recommendation system and method using roman conversion | |
| KR100791580B1 (en) | Method and system for extracting document information based on body identification | |
| CN115757760A (en) | Text abstract extraction method and system, computing device and storage medium | |
| CN115391711B (en) | Webpage text information extraction method, device, equipment and medium | |
| JP4959032B1 (en) | Web page analysis apparatus and web page analysis program | |
| CN115017430A (en) | List page determination method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| Bing et al. | Primary content extraction with mountain model | |
| KR20070067058A (en) | Web document title extraction method and device thereof | |
| Matosevic | Using anchor text to improve web page title in process of search engine optimization |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0109 | Patent application | Patent event code:PA01091R01D Comment text:Patent Application Patent event date:20060405 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | Comment text:Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date:20070314 Patent event code:PE09021S01D | |
| A107 | Divisional application of patent | ||
| PA0107 | Divisional application | Comment text:Divisional Application of Patent Patent event date:20070504 Patent event code:PA01071R01D | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | Patent event code:PE07011S01D Comment text:Decision to Grant Registration Patent event date:20070907 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | Comment text:Registration of Establishment Patent event date:20070919 Patent event code:PR07011E01D | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Payment date:20070920 End annual number:3 Start annual number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | ||
| G170 | Re-publication after modification of scope of protection [patent] | ||
| PG1701 | Publication of correction | ||
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20100628 Start annual number:4 End annual number:5 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20120705 Year of fee payment:6 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20120705 Start annual number:6 End annual number:6 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20130626 Year of fee payment:7 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20130626 Start annual number:7 End annual number:7 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20140725 Year of fee payment:8 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20140725 Start annual number:8 End annual number:8 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20150722 Year of fee payment:9 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20150722 Start annual number:9 End annual number:9 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20160817 Year of fee payment:10 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20160817 Start annual number:10 End annual number:10 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20170726 Year of fee payment:11 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20170726 Start annual number:11 End annual number:11 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20180702 Year of fee payment:12 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20180702 Start annual number:12 End annual number:12 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20190819 Year of fee payment:13 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20190819 Start annual number:13 End annual number:13 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20200727 Start annual number:14 End annual number:14 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20210818 Start annual number:15 End annual number:15 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20230620 Start annual number:17 End annual number:17 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20240624 Start annual number:18 End annual number:18 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | Payment date:20250623 Start annual number:19 End annual number:19 |