KR100714448B1 - Fast Distributed Pilot Synchronizer and Method in Digital Video Broadcasting Receiver - Google Patents
Fast Distributed Pilot Synchronizer and Method in Digital Video Broadcasting ReceiverDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100714448B1 KR100714448B1KR1020060030281AKR20060030281AKR100714448B1KR 100714448 B1KR100714448 B1KR 100714448B1KR 1020060030281 AKR1020060030281 AKR 1020060030281AKR 20060030281 AKR20060030281 AKR 20060030281AKR 100714448 B1KR100714448 B1KR 100714448B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- sprp
- symbol
- pattern
- subcarrier
- distributed pilot
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L27/00—Modulated-carrier systems
- H04L27/26—Systems using multi-frequency codes
- H04L27/2601—Multicarrier modulation systems
- H04L27/2647—Arrangements specific to the receiver only
- H04L27/2655—Synchronisation arrangements
- H04L27/2668—Details of algorithms
- H04L27/2673—Details of algorithms characterised by synchronisation parameters
- H04L27/2675—Pilot or known symbols
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F17/00—Digital computing or data processing equipment or methods, specially adapted for specific functions
- G06F17/10—Complex mathematical operations
- G06F17/14—Fourier, Walsh or analogous domain transformations, e.g. Laplace, Hilbert, Karhunen-Loeve, transforms
- G06F17/141—Discrete Fourier transforms
- G06F17/142—Fast Fourier transforms, e.g. using a Cooley-Tukey type algorithm
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03K—PULSE TECHNIQUE
- H03K19/00—Logic circuits, i.e. having at least two inputs acting on one output; Inverting circuits
- H03K19/20—Logic circuits, i.e. having at least two inputs acting on one output; Inverting circuits characterised by logic function, e.g. AND, OR, NOR, NOT circuits
- H03K19/21—EXCLUSIVE-OR circuits, i.e. giving output if input signal exists at only one input; COINCIDENCE circuits, i.e. giving output only if all input signals are identical
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04H—BROADCAST COMMUNICATION
- H04H2201/00—Aspects of broadcast communication
- H04H2201/10—Aspects of broadcast communication characterised by the type of broadcast system
- H04H2201/16—Aspects of broadcast communication characterised by the type of broadcast system digital video broadcasting - handhelds [DVB-H]
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Mathematical Analysis (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Pure & Applied Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Optimization (AREA)
- Computational Mathematics (AREA)
- Discrete Mathematics (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Algebra (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Synchronisation In Digital Transmission Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean도 1 은 본 발명에 따른 DVB-H/DVB-T의 주파수 영역에서 파일럿 및 TPS 신호에 대해 부반송파를 할당하는 방법에 대한 일실시예 설명도,1 is a diagram illustrating a method for allocating subcarriers for pilot and TPS signals in the frequency domain of DVB-H / DVB-T according to the present invention;
도 2 는 본 발명에 따른 DVB-H/DVB-T 수신기에서의 고속 분산 파일럿 동기 장치의 일실시예 구성도,2 is a block diagram of an embodiment of a fast distributed pilot synchronization device in a DVB-H / DVB-T receiver according to the present invention;
도 3 은 본 발명에 따른 DVB-H/DVB-T 수신기에서의 고속 분산 파일럿 동기 방법에 대한 일실시예 개념설명도,3 is a conceptual diagram illustrating an embodiment of a fast distributed pilot synchronization method in a DVB-H / DVB-T receiver according to the present invention;
도 4 는 시간 옵셋에 따른 파일럿 검출 오류 확률에 대한 비교분석도,4 is a comparative analysis of the probability of pilot detection error according to a time offset;
도 5 는 잡음 환경에서의 파일럿 검출 오류 확률에 대한 비교분석도,5 is a comparative analysis of the probability of pilot detection error in a noisy environment.
도 6a 및 도 6b 는 잡음 환경에서의 최소 보호율(MPR)에 대한 비교분석도,6a and 6b is a comparative analysis of the minimum protection rate (MPR) in the noise environment,
도 7a 내지 도 7c 는 다중 경로 페이딩 환경에서의 파일럿 검출 오류 확률에 대한 비교분석도,7A to 7C are comparative analysis diagrams of a pilot detection error probability in a multipath fading environment;
도 8 은 이동체 속도에 따른 최소 보호율(MPR)에 대한 비교분석도,8 is a comparative analysis of the minimum protection rate (MPR) according to the moving body speed,
도 9 는 SNR의 변화에 따른 최소 보호율(MPR)에 대한 비교분석도이다.9 is a comparative analysis of the minimum protection rate (MPR) according to the change of the SNR.
* 도면의 주요 부분에 대한 부호 설명* Explanation of symbols on the main parts of the drawing
201: FFT 변환부 202: 지연부201: FFT converter 202: delay unit
203, 207: SPRP 패턴 선택부 204: 기준 위상정보 제공부203 and 207: SPRP pattern selection unit 204: reference phase information providing unit
205: 위상 회전부 206: 상관기205: phase rotation unit 206: correlator
208: 분산 파일럿 패턴 추정부208: distributed pilot pattern estimation unit
본 발명은 디지털 비디오 방송 수신기에서의 고속 분산 파일럿 동기 장치 및 그 방법에 관한 것으로, 더욱 상세하게는 디지털 비디오 방송(DVB: Digital Video Broadcasting) 수신기에서 연속적으로 수신된 두 OFDM 수신심볼에 대하여 배치 가능한 분산 파일럿(scattered Pilot) 위치에서의 부반송파 심볼값 간의 상관값을 이용하여, 수신된 OFDM 심볼의 분산 파일럿 패턴을 추정함으로써, 신속/정확하게 분산 파일럿 동기를 수행하게 하는, 디지털 비디오 방송 수신기에서의 고속 분산 파일럿 동기 장치 및 그 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a fast distributed pilot synchronization device and method thereof in a digital video broadcasting receiver. More particularly, the present invention relates to a distributed scatterable signal for two OFDM reception symbols consecutively received in a digital video broadcasting (DVB) receiver. A fast distributed pilot in a digital video broadcast receiver, which makes distributed pilot synchronization fast and accurate by estimating a distributed pilot pattern of a received OFDM symbol using correlation values between subcarrier symbol values at a scattered pilot position. A synchronization device and a method thereof.
최근 디지털 방송과 이동 통신의 융합 추세 및 이동 통신 시스템의 비약적인 발전에 힘입어, 디지털 방송 시스템은 고정 수신만을 고려하여 설계되었던 초기 시스템에서 이동성뿐만 아니라 휴대성을 고려한 시스템으로 진화되어 가고 있다.With the recent convergence of digital broadcasting and mobile communication and the rapid development of mobile communication systems, digital broadcasting systems have evolved from the initial system designed for fixed reception only to the mobility as well as the mobile.
현재 국내에서는 위성 및 지상파 DMB(Digital Multimedia Broadcasting)를 통한 방송 서비스가 제공되고 있으며, 유럽에서는 기존의 DVB-T(Digital Video Broadcasting -Terrestrial) 표준을 기반으로 소형 휴대 단말기에 적합한 DVB-H(Digital Video Broadcasting - Handheld)의 표준화를 완료하였다. 또한, 미국에는 Qualcomm社의 자체 제작 표준인 MediaFLO를 기반으로 시스템을 개발하고 있는 중이다.Currently, broadcasting service through satellite and terrestrial Digital Multimedia Broadcasting (DMB) is provided in Korea, and in Europe, DVB-H (Digital Video Broadcasting-Terrestrial) standard based on the existing DVB-H (Digital Video Broadcasting) suitable for small portable devices Broadcasting-Handheld) is completed. In the United States, the company is developing a system based on Qualcomm's own production standard, MediaFLO.
휴대성을 고려한 방송 수신용 단말기는 단말의 소형화 및 전력 소모 감소가 필수적으로 요구된다. 특히 기존의 이동전화기와 융합된 단말을 이용하기 위해서는 디지털 방송 신호 모뎀 칩에 따른 전력 소모를 최소화해야만 한다.In consideration of portability, a broadcast receiving terminal is required to be smaller in size and to reduce power consumption. In particular, in order to use a terminal fused with an existing mobile phone, power consumption according to the digital broadcasting signal modem chip should be minimized.
DVB-H는 전력 소모를 최소화하기 위하여, 전송 데이터를 일정한 타임 슬롯(time slot)으로 구성한 후 각 타임 슬롯(time slot)에 패킷화된 방송신호(Burst)를 보내는 타임 슬라이스(Time-Slicing) 기술을 활용한다. 일정한 전송률을 가지고 지속적으로 전송(Streaming)되던 기존의 DVB-T 시스템과 달리, DVB-H는 향상된 압축 기술로 높은 전송률을 가지는 버스트(Burst)를 타임 슬라이스(Time-Slicing) 기법으로 일정 간격마다 전송하기 때문에, 방송 신호를 수신하지 않을 경우에는 수신 단말을 절전하여 전력 소모를 줄일 수 있다. 그러나 이 경우에는 각 버스트마다 수신 신호에 대한 빠른 동기가 요구되며, 동기 수행에 소요되는 시간이 길어지게 되면 수신기의 전력 소모가 증가하므로 동기 수행 시간을 최소화하는 것이 중요하다. 따라서, DVB-H 시스템의 전력 소모를 감소시키기 위해서는 고속의 동기 수행이 가능한 분산 파일럿 동기 방법이 필요하다.In order to minimize power consumption, DVB-H is a time-slicing technique in which transmission data is composed of a predetermined time slot and then a packetized broadcast signal is transmitted in each time slot. To utilize. Unlike the existing DVB-T system, which has been continuously streamed at a constant bit rate, DVB-H is an advanced compression technique that transmits bursts with a high rate at time intervals using a time-slicing technique. Therefore, when not receiving a broadcast signal, the power consumption can be reduced by saving the receiving terminal. In this case, however, it is important to minimize the synchronization execution time because fast synchronization of the received signal is required for each burst, and the power consumption of the receiver increases when the synchronization execution time becomes longer. Accordingly, in order to reduce power consumption of the DVB-H system, a distributed pilot synchronization method capable of high speed synchronization is required.
이와 관련된 종래 기술로는 TPS-bit(Transmission Parameter Signal-bit)를 이용한 동기 방식, 상관 기반의 분산 파일럿 동기 방식(CB_FSPS: Correlation Based Fast Scattered Pilot Synchronization), 전력 검출 기반 분산 파일럿 동기 방식(PB_FSPS: Power Based Fast Scattered Pilot Synchronization), 기준 신호 기반 방식(RB_FSPS: Reference Based Fast Scattered Pilot Synchronization) 등이 있다.The related arts include a synchronization method using a transmission parameter signal bit (TPS-bit), a correlation-based distributed pilot synchronization method (CB_FSPS), and a power detection-based distributed pilot synchronization method (PB_FSPS). Based Fast Scattered Pilot Synchronization (RB_FSPS) and Reference Based Fast Scattered Pilot Synchronization (RB_FSPS).
먼저, 'TPS-bit를 이용한 동기 방식'은 68개의 OFDM 심볼을 수신한 이후에 동기 수행이 가능하므로, Pre FFT & Post FFT 동기에 수행되는 총 7 심볼에 비하여 매우 많은 수의 심볼이 요구된다. 따라서, 이는 전력 소모의 최소화를 지향하는 DVB-H 시스템을 위한 고속 분산 파일럿 동기 방식으로는 적합하지 않다는 문제점이 있었다.First, since the 'synchronous method using TPS-bit' is capable of performing synchronization after receiving 68 OFDM symbols, a very large number of symbols are required as compared with a total of seven symbols performed for Pre FFT & Post FFT synchronization. Therefore, there is a problem that it is not suitable as a fast distributed pilot synchronization scheme for DVB-H system aimed at minimizing power consumption.
다음으로, '상관 기반의 분산 파일럿 동기 방식'(CB_FSPS)은 분산 파일럿의 위치를 결정하는데 5개의 OFDM 심볼이 소요되므로, 68 심볼이 소요되는 상기 TPS-bit를 이용한 동기 방식보다는 분산 파일럿 동기 수행 시간을 감소시킬 수 있는 장점이 있으나, 이 방식에서도 분산 파일럿 동기를 결정하는데 5개의 OFDM 심볼이 사용되고 이로 인하여 이전 수신 심볼을 저장하는 버퍼의 개수도 4개가 필요하기 때문에, 더욱 간단한 방식이 요구된다.Next, since the correlation-based distributed pilot synchronization method (CB_FSPS) takes 5 OFDM symbols to determine the location of the distributed pilot, distributed pilot synchronization execution time is more than the synchronization method using the TPS-bit, which requires 68 symbols. Although there is an advantage that can be reduced, even in this scheme, since five OFDM symbols are used to determine distributed pilot synchronization, and thus the number of buffers for storing previous received symbols is also required, a simpler scheme is required.
한편, '전력 검출 기반 분산 파일럿 동기 방식'(PB_FSPS)은 상관 기반의 분산 파일럿 동기 방식(CB_FSPS)과 달리 현재 심볼만을 이용하여 동기 수행을 최소화할 수 있으나, 서로 다른 신호의 상관을 통하여 잡음의 영향을 감소시킬 수 있는 상기 상관 기반의 분산 파일럿 동기 방식(CB_FSPS)에 비하여 동일한 신호의 전력을 이용하는 알고리즘이므로 잡음 환경에서 성능이 상대적으로 열화되는 문제점이 있었다.On the other hand, unlike the correlation-based distributed pilot synchronization method (CB_FSPS), the power detection-based distributed pilot synchronization method (PB_FSPS) can minimize synchronization using only current symbols, but the effect of noise through correlation of different signals Compared to the correlation-based distributed pilot synchronization method (CB_FSPS) that can reduce the power consumption of the same signal as the algorithm, there is a problem in that performance is relatively degraded in a noisy environment.
한편, '기준 신호 기반 방식'(RB_FSPS)은 기준 신호와 현재 신호의 상관으로 수행되므로, 동기에 소요되는 시간을 하나의 OFDM 심볼로 감소시킬 수 있다. 그러나, 이 방식은 주파수 영역의 기준 신호를 이용하게 되므로, 현재 수신 심볼에 대한 FFT 윈도우 위치 옵셋이 발생할 경우 상관 성능이 크게 열화 되어 실제 DVB-H의 분산 파일럿 동기로써 적합하지 않다는 문제점이 있었다.Meanwhile, since the 'reference signal based method' (RB_FSPS) is performed by correlation between the reference signal and the current signal, the time required for synchronization can be reduced to one OFDM symbol. However, since this method uses a reference signal in the frequency domain, the correlation performance is greatly degraded when the FFT window position offset occurs for the current received symbol, which is not suitable as a distributed pilot synchronization of the actual DVB-H.
본 발명은 상기 문제점을 해결하기 위하여 제안된 것으로, 디지털 비디오 방송(DVB) 수신기에서 연속적으로 수신된 두 OFDM 수신심볼에 대하여 배치 가능한 분산 파일럿(scattered Pilot) 위치에서의 부반송파 심볼값 간의 상관값을 이용하여, 수신된 OFDM 심볼의 분산 파일럿 패턴을 추정함으로써, 신속/정확하게 분산 파일럿 동기를 수행하게 하는, 디지털 비디오 방송 수신기에서의 고속 분산 파일럿 동기 장치 및 그 방법을 제공하는데 그 목적이 있다. The present invention has been proposed to solve the above problem, and uses a correlation value between subcarrier symbol values at a scattered pilot position that can be arranged for two OFDM reception symbols consecutively received at a digital video broadcasting (DVB) receiver. Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to provide a fast distributed pilot synchronization device and a method thereof in a digital video broadcasting receiver, which perform distributed pilot synchronization quickly and accurately by estimating a distributed pilot pattern of a received OFDM symbol.
본 발명의 다른 목적 및 장점들은 하기의 설명에 의해서 이해될 수 있으며, 본 발명의 실시예에 의해 보다 분명하게 알게 될 것이다. 또한, 본 발명의 목적 및 장점들은 특허청구범위에 나타낸 수단 및 그 조합에 의해 실현될 수 있음을 쉽게 알 수 있을 것이다.Other objects and advantages of the present invention can be understood by the following description, and will be more clearly understood by the embodiments of the present invention. It will also be appreciated that the objects and advantages of the present invention may be realized by the means and combinations thereof indicated in the claims.
상기 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명은, 디지털 비디오 방송 수신기에서의 고속 분산 파일럿 동기 장치에 있어서, OFDM 수신심볼에 대하여 고속푸리에변환(FFT)을 수행하기 위한 FFT 변환 수단; 상기 FFT 변환 수단에서 FFT 변환된 '현재 수신심볼'을 한 심볼구간 만큼 지연시켜 저장하고, 상기 '현재 수신심볼'보다 한 심볼 이전에 수신되어 FFT 변환되고 지연된 OFDM 수신심볼('이전 수신심볼')을 출력시키기 위한 지연 수단; 상기 지연 수단에서 출력되는 '이전 수신심볼'에 대한 SPRP(Scattered Pilot Raster Position)패턴으로 소정의 SPRP 패턴 집합에서 임의의 SPRP 패턴(제1 SPRP 패턴)을 선택하고, 상기 선택된 제1 SPRP 패턴의 분산 파일럿 위치에서의 부반송파 심볼값을 구하기 위한 복수의 제1 SPRP패턴 선택 수단; 상기 FFT 변환 수단에서 FFT 변환된 '현재 수신심볼'에 대한 SPRP 패턴으로, 송신측에서 상기 제1 SPRP패턴 다음으로 할당되는 인접 SPRP 패턴(제2 SPRP 패턴)을 선택하고, 상기 선택된 제2 SPRP 패턴의 분산 파일럿 위치에서의 부반송파 심볼값을 구하기 위한 복수의 제2 SPRP패턴 선택 수단; 상기 각각의 제1 SPRP패턴 선택 수단에서 구한 부반송파 심볼값을 위상 회전시키기 위한 위상회전 수단; 상기 각각의 위상회전된 부반송파 심볼값과 상기 각각의 제2 SPRP패턴 선택 수단에서 구한 부반송파 심볼값을 상관시키기 위한 상관 수단; 및 상기 상관 수단에서의 복수의 상관값 중에서 최대치를 검출하고, 상기 최대치 상관값을 가지는 제2 SPRP 패턴을 상기 '현재 수신심볼'의 분산 파일럿 패턴으로 추정하기 위한 분산 파일럿 패턴 추정 수 단을 포함한다.According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a fast distributed pilot synchronization device in a digital video broadcasting receiver, comprising: FFT conversion means for performing Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) on an OFDM reception symbol; The FFT converting means stores the FFT-converted 'current received symbol' by one symbol period and stores the received FFT-converted OFDM delay symbol ('previous received symbol') received one symbol before the 'current received symbol'. Delay means for outputting; A random SPRP pattern (first SPRP pattern) is selected from a set of SPRP patterns as a scattered pilot raster position (SPRP) pattern for the 'previous reception symbol' outputted from the delay means, and the dispersion of the selected first SPRP pattern A plurality of first SPRP pattern selection means for obtaining a subcarrier symbol value at a pilot position; As the SPRP pattern for the 'current reception symbol' FFT-converted by the FFT conversion means, a neighboring SPRP pattern (second SPRP pattern) allocated next to the first SPRP pattern is selected at the transmitting side, and the selected second SPRP pattern A plurality of second SPRP pattern selection means for obtaining a subcarrier symbol value at a distributed pilot position of the plurality of second SPRP patterns; Phase rotation means for phase-rotating the subcarrier symbol values obtained by the respective first SPRP pattern selection means; Correlating means for correlating the respective phase rotated subcarrier symbol values with the subcarrier symbol values obtained by the respective second SPRP pattern selection means; And a distributed pilot pattern estimation means for detecting a maximum value among a plurality of correlation values in the correlation means and estimating a second SPRP pattern having the maximum correlation value as a distributed pilot pattern of the 'current reception symbol'. .
한편, 본 발명은, 디지털 비디오 방송 수신기에서의 고속 분산 파일럿 동기화 방법에 있어서, 수신되는 OFDM 수신심볼에 대하여 심볼단위로 고속푸리에변환(FFT)을 수행하는 FFT 변환 단계; 상기 FFT 변환 단계에서 현재 FFT 변환된 OFDM 수신심볼('현재 수신심볼')보다 한 심볼 이전에 수신되어 FFT 변환된 OFDM 수신심볼('이전 수신심볼')에 대한 SPRP(Scattered Pilot Raster Position) 패턴으로 소정의 SPRP 패턴 집합 내의 각각의 SPRP 패턴(제1 SPRP 패턴)을 선택하고, 상기 각각의 제1 SPRP 패턴의 분산 파일럿 위치에서의 부반송파 심볼값을 구하는 제1 SPRP패턴 선택 단계; 상기 제1 SPRP패턴 선택 단계에서 구한 부반송파 심볼값을 위상 회전시키는 위상회전 단계; 상기 '현재 수신심볼'에 대한 SPRP 패턴으로, 송신측에서 상기 제1 SPRP패턴 다음으로 할당되는 인접 SPRP 패턴(제2 SPRP 패턴)을 선택하고, 상기 각각의 제2 SPRP 패턴의 분산 파일럿 위치에서의 부반송파 심볼값을 구하는 제2 SPRP패턴 선택 단계; 상기 위상회전 단계에서 위상회전된 각각의 부반송파 심볼값과 상기 제2 SPRP패턴 선택 단계에서 구한 각각의 부반송파 심볼값과의 상관값을 구하는 상관 단계; 및 상기 상관 단계에서의 구한 복수의 상관값 중에서 최대치를 검출하고, 상기 검출된 최대치 상관값을 가지는 제2 SPRP 패턴을 상기 '현재 수신심볼'의 분산 파일럿 패턴으로 추정하는 분산 파일럿 패턴 추정 단계를 포함한다.The present invention provides a fast distributed pilot synchronization method in a digital video broadcasting receiver, comprising: an FFT transform step of performing fast Fourier transform (FFT) on a symbol-by-symbol basis on a received OFDM reception symbol; In the FFT transforming step, as a scattered pilot raster position (SPRP) pattern for an OFDM reception symbol ('previous reception symbol') that is received one symbol before the current FFT transformed OFDM reception symbol ('current reception symbol'). A first SPRP pattern selection step of selecting each SPRP pattern (first SPRP pattern) in a predetermined set of SPRP patterns and obtaining a subcarrier symbol value at a distributed pilot position of each first SPRP pattern; A phase rotation step of phase-rotating the subcarrier symbol value obtained in the step of selecting the first SPRP pattern; As the SPRP pattern for the 'current reception symbol', a transmitting side selects an adjacent SPRP pattern (second SPRP pattern) allocated next to the first SPRP pattern, and at the distributed pilot position of each second SPRP pattern. A second SPRP pattern selection step of obtaining a subcarrier symbol value; A correlation step of obtaining a correlation value between each subcarrier symbol value phase rotated in the phase rotation step and each subcarrier symbol value obtained in the second SPRP pattern selection step; And a distributed pilot pattern estimating step of detecting a maximum value among the plurality of correlation values obtained in the correlation step and estimating a second SPRP pattern having the detected maximum correlation value as a distributed pilot pattern of the 'current reception symbol'. do.
상술한 목적, 특징 및 장점은 첨부된 도면과 관련한 다음의 상세한 설명을 통하여 보다 분명해 질 것이며, 그에 따라 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 본 발명의 기술적 사상을 용이하게 실시할 수 있을 것이다. 또한, 본 발명을 설명함에 있어서 본 발명과 관련된 공지 기술에 대한 구체적인 설명이 본 발명의 요지를 불필요하게 흐릴 수 있다고 판단되는 경우에 그 상세한 설명을 생략하기로 한다. 이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 본 발명에 따른 바람직한 일실시예를 상세히 설명하기로 한다.The above objects, features and advantages will become more apparent from the following detailed description taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, whereby those skilled in the art may easily implement the technical idea of the present invention. There will be. In addition, in describing the present invention, when it is determined that the detailed description of the known technology related to the present invention may unnecessarily obscure the gist of the present invention, the detailed description thereof will be omitted. Hereinafter, exemplary embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 1 은 본 발명에 따른 DVB-H/DVB-T의 주파수 영역에서 파일럿 및 TPS 신호에 대해 부반송파를 할당하는 방법에 대한 일실시예 설명도이다.1 is a diagram illustrating a method for allocating subcarriers for pilot and TPS signals in the frequency domain of DVB-H / DVB-T according to the present invention.
DVB-H/DVB-T 시스템에서는 데이터 심볼과 파일럿, 그리고 전송 파라미터 신호(TPS: Transmission Parameter Signal)를 각 부반송파에 할당하여 전송한다.In the DVB-H / DVB-T system, a data symbol, a pilot, and a transmission parameter signal (TPS) are allocated to each subcarrier and transmitted.
여기서, 파일럿은 모든 OFDM 심볼에서 고정된 위치로 전송되는 연속파일럿(Continual Pilot)과 네 개의 OFDM 심볼마다 위치가 주기적으로 변하는 분산 파일럿(Scattered Pilot)으로 구성된다. TPS는 현재 수신 신호의 전송 기법과 관련된 68개의 비트(bit) 정보를 전송하기 위해 사용되고, 68개의 OFDM 심볼에 나누어져서 전송된다.Here, the pilot is composed of a continuous pilot transmitted to a fixed position in all OFDM symbols and a scattered pilot whose position changes periodically every four OFDM symbols. TPS is used to transmit 68 bits of information related to the transmission scheme of the current received signal, and is divided into 68 OFDM symbols and transmitted.
분산 파일럿은 다음의 [수학식 1]에 따라, 네 개의 심볼마다, 할당되는 부반송파의 위치가 이동된다. 따라서, 채널 추정을 통한 데이터 복조를 위해서는 현재 수신된 심볼의 파일럿 패턴을 검출하는 분산 파일럿 동기가 요구된다.In the distributed pilot, the position of the allocated subcarrier is shifted every four symbols according to
여기서,,k와 n은 각각 분산 파일럿이 위치하는 부반송파 인덱스와 현재 수신된 OFDM 심볼(현재 수신심볼)의 인덱스를 의미하며, Kmin와 Kmax는 유효 부반송파 중에서 최소 부반송파 인덱스와 최대의 부반송파 인덱스를 나타낸다. Kmax는 FFT 크기에 따라서 2K 모드에서 "1704", 4K 모드에서 "6816", 8K 모드에서 "3408"의 값을 가진다.here, ,k and n represent the subcarrier index where the distributed pilot is located and the index of the currently received OFDM symbol (the current reception symbol), and Kmin and Kmax represent the minimum subcarrier index and the maximum subcarrier index among the valid subcarriers. Kmax has a value of "1704" in 2K mode, "6816" in 4K mode, and "3408" in 8K mode according to the FFT size.
고속 푸리에 변환(FFT) 모드에 따른 분산 파일럿의 개수(Nsp)는 2K 모드에서 142개, 4K 모드에서 284개, 8K 모드에서 568개를 가진다. 모든 파일럿은 BPSK로 변조되며 심볼의 값은 PRBS(Pseudo Random Binary Sequence)의 출력 비트에 의하여 결정된다.The number of distributed pilots Nsp according to the fast Fourier transform (FFT) mode has 142 in 2K mode, 284 in 4K mode, and 568 in 8K mode. All pilots are modulated with BPSK and the symbol value is determined by the output bits of the pseudo random binary sequence (PRBS).
도 2 는 본 발명에 따른 DVB-H/DVB-T 수신기에서의 고속 분산 파일럿 동기 장치의 일실시예 구성도이다.2 is a block diagram of an embodiment of a fast distributed pilot synchronization device in a DVB-H / DVB-T receiver according to the present invention.
본 발명에 따른 고속 분산 파일럿 동기 장치는, 도 2에 도시된 바와 같이, FFT 변환부(201), 지연부(D-1)(202), SPRP(Scattered Pilot Raster Position) 패턴 선택부(203, 207), 위상회전부(Phase Rotator)(205), 상관기(Correlator)(206), 분산 파일럿 패턴 추정부(208), 기준위상정보(Reference Phase Information) 제공부(204)를 포함하여 이루어진다.As shown in FIG. 2, the fast distributed pilot synchronization device according to the present invention includes an
FFT 변환부(201)는 수신된 1개의 OFDM 심볼에 대하여 고속 푸리에 변환(FFT)을 수행하며, 지연부(D-1)에서는 FFT 변환부(201)에서 FFT 변환되어 입력된 OFDM 심볼을 한 심볼구간 만큼 지연하여 저장하는 기능을 수행한다. 만약 n번째 OFDM 심볼(현재 수신심볼)이 수신되어 FFT 변환부(201)에서 고속 푸리에 변환(FFT)되어 SPRP 패턴 선택부(207)에 입력되는 경우, 지연부(D-1)(202)는 현재 OFDM 수신심볼을 입력받아 저장하면서 이미 저장하고 있던 '이전 OFDM 수신심볼'(즉, 현재 OFDM 수신심볼보다 한 심볼 이전의 심볼, n-1번째 심볼)을 SPRP 패턴 선택부(207)로 출력한다.The
SPRP 패턴 선택부(203, 207)는 배치 가능한 분산 파일럿 패턴(SPRP 패턴) 중에서 임의로 선택된 SPRP 패턴의 분산 파일럿 위치에서의 부반송파 심볼값을 구한다.The SPRP
즉, 예를 들어, "203"의 두번째 「SPRP 0 패턴 선택부」의 기능에 대하여 살펴보면, 「SPRP 0 패턴 선택부」는 지연부(202)로부터 입력되는 n-1번째 OFDM 수신심볼이 "SPRP 0"과 같은 파일럿 배치 구성(도 1 참조)을 가지고 있다고 가정한 후(즉, n-1번째 OFDM 수신심볼의 SPRP 패턴으로 "SPRP 0"으로 선택한 후), 그 가정한(선택된) "SPRP 0" 패턴을 기초로 하여 분산 파일럿 위치에서의 부반송파 심볼값을 구하는 기능을 수행한다.That is, for example, referring to the function of the second "
이와 동일한 방법으로,「SPRP 0 패턴 선택부」에 대응되는 「SPRP 1 패턴 선택부」(207 참조)는, n번째 OFDM 수신심볼이 "SPRP 1"과 같은 파일럿 배치 구성 (도 1 참조)을 가지고 있다고 가정한 후, 그 가정한 "SPRP 1" 패턴을 기초로 하여 분산 파일럿 위치에서의 부반송파 심볼값을 구하는 기능을 수행한다.In the same way, the "
여기서, SPRP는 [수학식 1]에 따라 4가지 패턴으로 구성되며, SPRP 0, SPRP 1, SPRP 2, SPRP 3의 패턴은 도 1과 같이 표현된다.Here, the SPRP is composed of four patterns according to [Equation 1], the pattern of
요컨대, SPRP 패턴 선택부(203, 207)는 OFDM 부반송파에서 각 SPRP n ∈{0, 1, 2, 3} 패턴에 해당되는 부반송파의 심볼값(SPRP n 패턴에 해당하는 분산 파일럿 위치에서의 부반송파 심볼값)을 구하는 기능을 수행한다.In other words, the
위상 회전부(Phase Rotator)(205)는 기준위상정보 제공부(204)가 제공하는 기준위상정보에 따라, 위상을 회전시키는 기능을 수행한다. 즉, 위상 회전부(Phase Rotator)(205)는 기준 위상정보 제공부(204)가 제공하는 기준 위상정보를 이용하여, 각각의 SPRP 패턴 선택부(203)에서 출력되는 n-1번째 심볼에 대한 부반송파 심볼값을, 각각의 SPRP패턴 선택부(207)에서 출력되는 n번째 심볼에 대한 부반송파 심볼값과 동위상이 되도록 위상 회전시킨다.The
여기서, 기준위상정보 제공부(204)가 제공하는 기준위상정보는, 송신측에서의 부반송파 할당 정보(도 1 참조)에 기초하여, 부반송파 3개 간격만큼 떨어진 두 개의 PRBS 출력 비트에 대하여 취해진 논리합(EX-OR) 연산 결과를 이용하여 생성한다.Here, the reference phase information provided by the reference phase
한편, 상관기(Correlator)(206)는 입력된 2개의 신호에 대한 상관값을 계산한다. 즉, 상관기(Correlator)(206)는 각각의 위상 회전부(205)에서 출력되는 각각의 위상회전된 부반송파 심볼값과, 각각의 SPRP패턴 선택부(207)에서 구한 부반송 파 심볼값을 상관시킴으로써, 4개의 상관값(PC1(n), PC22(n), PC3(n), PC4(n))을 획득하게 된다.Meanwhile, the
그러면, 분산 파일럿 패턴 추정부(208)는 4개의 상관기(206)로부터 입력된 4개의 상관값 중에서 가장 큰 값을 선택하여 분산 파일럿의 위치를 추정한다. 예를 들어, PC1(n) 값이 제일 클 경우에는 도 1에서의 SPRP 0의 패턴으로 부반송파가 있다고 판단하면 된다.Then, the distributed
도 3 은 본 발명에 따른 DVB-H/DVB-T 수신기에서의 고속 분산 파일럿 동기 방법에 대한 일실시예 개념설명도이다.3 is a conceptual diagram illustrating an embodiment of a fast distributed pilot synchronization method in a DVB-H / DVB-T receiver according to the present invention.
본 발명은, 도 3에 도시된 바와 같이, 현재 수신심볼과 한 심볼 이전에 수신된 심볼에 대하여, 분산 파일럿 위치에 수신된 인접한 신호 간의 상관을 통해 동기를 수행한다.As shown in FIG. 3, the present invention performs synchronization through a correlation between a current received symbol and an adjacent signal received at a distributed pilot position with respect to a symbol received one symbol before.
각 분산 파일럿은 부반송파 위치에 따라 서로 다른 변조 값을 가지므로, 인접한 파일럿의 위상 변화 정보를 기준 신호(기준 위상정보)로 이용하여 상관을 수행한다. 기준 신호 ph(p)(기준 위상정보)는 부반송파 3개 간격만큼 떨어진 두 개의 PRBS 출력 비트(bit)를 배타적 논리합(EX-OR) 연산하여 획득한 위상정보비트 φd, p를 통하여 생성된다. 여기서, p는 유효 부반송파 내에 할당된 파일럿의 전체 인덱스 중에서 해당 파일럿의 인덱스를 나타낸다. 모든 파일럿은 BPSK로 변조되므로, 파일럿의 위상 변화량은 다음의 [수학식 2]와 같이 동위상과 180 도의 두 가지로만 나타나게 된다.Since each distributed pilot has different modulation values according to subcarrier positions, correlation is performed by using phase change information of adjacent pilots as reference signals (reference phase information). The reference signal ph (p) (reference phase information) is generated through phase information bits φd and p obtained by performing an exclusive OR on two PRBS output bits spaced apart by three subcarriers. Here, p represents the index of the pilot among all the indexes of the pilot allocated in the effective subcarrier. Since all pilots are modulated with BPSK, the phase change amount of the pilot appears only in two phases and 180 degrees, as shown in
따라서, 기준위상정보 제공부(204)에서, 상기 발생 방법을 적용하여 위상 정보 비트 φd, p를 발생시킨다. 발생된 φd, p정보를 사용하여 위상 회전부(205)에서는 상기 [수학식 2]를 적용하여 위상 정보 ph(p)를 발생시킨 후, 곱 연산을 수행하여 위상을 회전시킨다.Accordingly, the reference phase
이하, 본 발명에 따른 고속 분산 파일럿 동기 장치에서 수행되는 고속 분산 파일럿 동기 방법에 대하여 전반적으로 설명하면, 다음과 같다.Hereinafter, a general description will be given of the fast distributed pilot synchronization method performed in the fast distributed pilot synchronization apparatus according to the present invention.
수신된 신호는 FFT 변환 과정을 통하여 OFDM 심볼 단위로, 부반송파 열로 변환된다. 변환된 OFDM 심볼은 지연부(D-1 )(202)에 저장되어 하나의 OFDM 심볼 구간 만큼 지연된 후, 각각의 SPRP 패턴 선택부(203)에 입력되어, 위상 회전부(205)를 거쳐 상관기(206)로 입력된다.The received signal is converted into a subcarrier sequence in units of OFDM symbols through an FFT conversion process. The converted OFDM symbol is stored in the delay unit (D-1 ) 202, delayed by one OFDM symbol interval, and then input to each SPRP pattern selector 203, and then passed through the
각각의 상관기(206)에 입력되는 신호는 2개가 되는데, 하나는 OFDM 심볼 구간 만큼 지연되어 입력되는 신호이고, 다른 하나 신호는 FFT 변환부(201)에서 FFT 수행된 후에 발생되는 부반송파 열을 SPRP 패턴 선택부(207)를 거쳐 입력되는 신호이다.There are two signals input to each correlator 206, one is a signal input delayed by an OFDM symbol interval, and the other is an SPRP pattern for a subcarrier string generated after the FFT is performed by the
각각의 상관기(206)는 2개의 입력된 신호에 대하여 상관을 수행한 후, 그 결과값(상관값)을 분산 파일럿 패턴 추정부(208)로 출력한다.Each
그러면, 분산 파일럿 패턴 추정부(208)는 각각의 상관기(206)로부터 입력되는 상관값들 중에서 최대치를 선택하여 분산 파일럿 위치를 추정한다.Then, the distributed
상기의 설명을 수학식으로 표현하면, 다음의 [수학식 3] 내지[수학식 5]와 같다.If the above description is expressed by a mathematical formula, it is as follows [Equation 3] to [Equation 5].
즉, [수학식 3] 내지[수학식 5]와 같이, 위상 정보 ph(p)를 이용하여, 한 개의 OFDM 심볼 이전의 수신 심볼(n-1 번째 수신 심볼)에 대한 부반송파 심볼값("203"에서 선택된 SPRP 패턴의 분산 파일럿 위치에서의 부반송파 심볼값)의 위상을, 현재 수신 심볼(n번째 수신 심볼)에 대한 부반송파 심볼값("207"에서 선택된 SPRP 패턴의 분산 파일럿 위치에서의 부반송파 심볼값)의 위상과 동위상으로 변화시킨다. 그리고 나서, 상관을 수행하고 추정된 상관값 중에서 최대치를 검출함으로써 분산 파일럿 패턴을 구하게 된다.That is, as shown in [Equations 3] to [Equation 5], using the phase information ph (p), the subcarrier symbol value ("203") for the received symbol (n-1 th received symbol) before one OFDM symbol is used. The subcarrier symbol value at the distributed pilot position of the SPRP pattern selected at "," the subcarrier symbol value for the current received symbol (nth received symbol) (the subcarrier symbol value at the distributed pilot position of the SPRP pattern selected at " 207 "). ) And change phase in phase. Then, the correlation is performed and the estimated correlation value The distributed pilot pattern is obtained by detecting the maximum value in the.
여기서, S[n, k]는 n번째 수신된 OFDM 심볼의 k번째 부반송파를 나타내고, Nsp는 분산 파일럿의 개수, p는 파일럿 인덱스, ps는 분산 파일럿 인덱스를 나타낸다. 그리고,는 가능한 네 개의 상관 결과를 나타내는데, 인덱스(index) 0의 경우 Kmin보다 앞선 부반송파 위치에 전송되는 파일럿이 존재하지 않으므로, [수학식 3]과 [수학식 4]와 같이 구분하여 나타내었다.Here, S [n, k] represents the k-th subcarrier of the nth received OFDM symbol, Nsp represents the number of distributed pilots, p represents a pilot index, and ps represents a distributed pilot index. And, Denotes four possible correlation results. In the case of
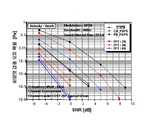
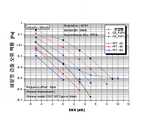
도 4 내지 도 9는 본 발명과 기존의 동기 방식들과의 성능을 비교하는 도면으로서, 도 4는 시간 옵셋에 따른 파일럿 검출 오류 확률, 도 5 는 잡음 환경에서의 파일럿 검출 오류 확률, 도 6a 및 도 6b는 잡음 환경에서의 최소 보호율(MPR), 도 7a 내지 도 7c는 다중 경로 페이딩 환경에서의 파일럿 검출 오류 확률, 도 8은 이동체 속도에 따른 최소 보호율(MPR), 도 9는 SNR의 변화에 따른 최소 보호율(MPR)에 대한 성능비교 결과를 나타낸다.4 to 9 are diagrams comparing the performance of the present invention and the conventional synchronization schemes. FIG. 4 is a pilot detection error probability according to a time offset, FIG. 5 is a pilot detection error probability in a noise environment, and FIGS. FIG. 6B is the minimum protection rate (MPR) in a noisy environment, FIGS. 7A-7C are the pilot detection error probabilities in a multipath fading environment, FIG. 8 is the minimum protection rate (MPR) depending on the vehicle speed, and FIG. Performance comparison results for the minimum protection rate (MPR) according to the change are shown.
본 발명과 종래의 파일럿(분산 파일럿) 동기 방식들 간의 성능 비교는 현재 수신된 심벌의 파일럿 패턴을 정확하게 검출하지 못할 확률, 즉 파일럿 검출 오류 확률(Pilot Detection Error Probability)과 출력 결과의 최소 보호율(MPR: Minimum Protection Ratio)을 기준으로 한다.The performance comparison between the present invention and the conventional pilot (distributed pilot) synchronization schemes is based on the probability of not correctly detecting the pilot pattern of the currently received symbol, that is, the pilot detection error probability and the minimum protection rate of the output result. It is based on MPR: Minimum Protection Ratio.
여기서, 보호율(PR: Protection Ratio)은 다음의 [수학식 6]과 같이 최대 출력값 대비 나머지 세 개의 파일럿 패턴의 출력값 간의 비율을 의미하며, 이에 사용되는 [수학식 6]은 CB_FSPS 방식을 기준으로 한 식이며, 다른 방식도 동일한 방식으로 PR 값을 구할 수 있다. 그리고, 최소 보호율(MPR)은 일정한 회수로 수행한 모의 실험 동안 최소의 PR을 가지는 값을 의미하며, 알고리즘의 강인성을 측정하는 요소가 된다.Here, the protection ratio (PR) refers to a ratio between the maximum output value and the output values of the remaining three pilot patterns as shown in
여기서, N0는 상관 비율의 관찰 회수로서 전체 성능 분석 과정에서 1000번으로 설정하였다.Here, N0 is set as 1000 times in the overall performance analysis as the number of observations of the correlation ratio.
그리고, 다음의 [표 1]은 모의 실험(Simulation)에 적용된 파라미 터(parameter)를 나타낸다.And the following [Table 1] shows the parameters (parameter) applied to the simulation (Simulation).
성능 분석의 기준이 되는 SNR은 데이터 심벌의 신호 전력 대비 잡음 전력의 비율로 설정한다. 성능 분석은 시간 옵셋에 따른 영향을 분석하고, 잡음 환경 및 다중 경로 페이딩 채널 환경에서 성능 분석을 수행하며, 분산 파일럿 동기는 주파수 동기 이후에 수행되므로 주파수 옵셋의 영향은 없다고 가정한다.The SNR, which is the basis of performance analysis, is set as the ratio of noise power to signal power of data symbols. Performance analysis analyzes the effects of time offset, performs performance analysis in noise environment and multipath fading channel environment, and assumes that there is no effect of frequency offset since distributed pilot synchronization is performed after frequency synchronization.
첫째, 시간 옵셋에 따른 동기 성능에 대하여 설명하면, 다음과 같다.First, the synchronization performance according to the time offset will be described.
일반적으로 미세 시간 동기는 모든 파일럿을 이용하여 수행되므로 분산 파일럿 동기 이후에 동작한다. 따라서 분산 파일럿 동기는 초기의 대략적인 시간 동기를 수행한 결과를 기준으로 FFT 윈도우의 위치가 결정되므로 시간 옵셋의 영향에 강인한 특성을 지녀야 한다.In general, since the fine time synchronization is performed using all pilots, it operates after distributed pilot synchronization. Therefore, since the position of the FFT window is determined based on the result of initial coarse time synchronization, the distributed pilot synchronization should be robust to the influence of the time offset.
도 4는 시간 옵셋만이 존재하는 이상적인 채널 환경에서 각 알고리즘의 파일럿 검출 오류 확률을 분석한 것으로서, 도 4를 살펴보면, 종래의 상관 방식(CB_FSPS) 및 전력 검출 방식(PB_FSPS)은 시간 옵셋에 따른 영향을 받지 않는 반면, 종래의 기준 신호를 이용한 방식(RB_FSPS)은 하나의 샘플 옵셋이 발생하여도 검출 오류가 나타나는 것을 알 수 있다. 이는 FFT 윈도우 위치 옵셋(샘플 옵셋)의 영향이 주파수 영역에서 위상 회전의 형태로 나타나서, 이상적인 채널 환경에서도 기준 신호와 수신 신호 간의 상관도를 저하시키는 요인으로 작용하기 때문이다.FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating analysis of a pilot detection error probability of each algorithm in an ideal channel environment in which only a time offset exists. Referring to FIG. 4, the conventional correlation method (CB_FSPS) and power detection method (PB_FSPS) are influenced by time offset. On the other hand, in the conventional method using the reference signal (RB_FSPS), even if one sample offset occurs, it can be seen that a detection error appears. This is because the influence of the FFT window position offset (sample offset) appears in the form of phase rotation in the frequency domain, which acts as a factor of reducing the correlation between the reference signal and the received signal even in an ideal channel environment.
따라서, 다음의 성능 분석 과정에서는 종래의 기준 신호 기반 방식(RB_FSPS) 알고리즘은 제외하고 성능 분석을 진행할 것이며, 나머지 방식들의 분산 파일럿 동기 성능을 중점적으로 분석하기 위하여 FFT 윈도우 위치 옵셋은 없다고 가정한다.Therefore, in the following performance analysis process, the performance analysis will be performed except for the conventional reference signal based method (RB_FSPS) algorithm, and it is assumed that there is no FFT window position offset in order to analyze the distributed pilot synchronization performance of the remaining methods.
둘째, 잡음 환경(AWGN Channel Environment)에서의 성능 분석 결과를 설명하면, 다음과 같다.Second, the results of the performance analysis in the AWGN channel environment are as follows.
도 5는 잡음 환경에서의 파일럿 검출 오류 확률을 분석한 것으로서, 세 가지 알고리즘 모두 FFT 크기가 증가함에 따라 상관 누적 크기가 증가하므로 성능이 향상되는 것을 알 수 있다. 상관 방식을 기본으로 하는 CB_FSPS와 본 발명의 성능은 FFT 크기가 증가함에 따라 약 1.7dB의 성능 향상이 있으며, PB_FSPS는 약 2dB의 성능 개선을 보임을 알 수 있다.FIG. 5 shows the analysis of the probability of pilot detection error in a noisy environment. As the FFT size increases, the correlation accumulation size increases in all three algorithms, and thus the performance is improved. The performance of the CB_FSPS based on the correlation method and the present invention is about 1.7 dB as the FFT size increases, and the PB_FSPS is about 2 dB.
그러나, 각 방식 간의 성능을 비교하여 볼 때, 종래의 CB_FSPS와 본 발명의 방식은 성능이 거의 유사한 반면에, PB_FSPS의 경우는 앞의 두 방식에 비하여 약 6dB의 성능 열화가 나타나고 있음을 알 수 있다. 이는 본 발명과 종래의 CB_FSPS에서는 서로 다른 잡음에 영향을 받은 두 신호를 상관함으로써 잡음의 영향을 감소시키기 때문이다.However, when comparing the performance of each method, it can be seen that the performance of the conventional CB_FSPS and the present invention is almost similar, whereas PB_FSPS shows a performance degradation of about 6dB compared to the previous two methods. . This is because the present invention and the conventional CB_FSPS reduces the influence of noise by correlating two signals affected by different noise.
한편, 도 6a 및 도 6b는 잡음 환경에서의 MPR 성능을 나타내는 것으로서, PB_FSPS의 MPR 성능이 SNR이 증가하여도 거의 1의 값을 가지며, 다른 알고리즘과 비교하여 가장 열화되어 나타남을 알 수 있다. PB_FSPS는 단순히 파일럿과 데이터 심볼의 전력 차이를 이용하므로 MPR 결과가 낮게 나오지만, 상관 특성을 이용하는 방식의 경우(본 발명과 종래의 CB_FSPS)에는 SNR이 증가함에 따라 상관 특성이 향상되어 MPR 성능도 크게 향상됨을 알 수 있다.6A and 6B show MPR performance in a noisy environment. The MPR performance of PB_FSPS has a value of almost 1 even when the SNR is increased, and is deteriorated compared to other algorithms. Since PB_FSPS simply uses the power difference between pilot and data symbols, the MPR result is low. However, in the case of using the correlation characteristic (the present invention and the conventional CB_FSPS), as the SNR increases, the correlation characteristic is improved and the MPR performance is greatly improved. It can be seen.
도 6b는 CB_FSPS와 본 발명의 성능을 보다 상세하게 비교한 것으로서, 모든 FFT 크기(2K, 4K. 8K)에서 SNR이 증가함에 따라 본 발명의 성능이 더 우수함을 알 수 있다.Figure 6b is a more detailed comparison of the performance of the present invention with CB_FSPS, it can be seen that the performance of the present invention is better as the SNR increases in all FFT sizes (2K, 4K, 8K).
셋째, 다음은 다중경로 페이딩 채널 환경에서의 성능 분석에 대하여 설명하면, 다음과 같다.Third, the following is a description of performance analysis in a multipath fading channel environment.
잡음 환경에서의 성능 분석 결과, 본 발명이 검출 오류 확률 및 MPR 성능 면에서 가장 우수한 성능을 가지고 있으며, 기존의 PB_FSPS 방식이 가장 열화된 성능 결과를 나타내는 것을 알 수 있다.As a result of the performance analysis in the noise environment, it can be seen that the present invention has the best performance in terms of detection error probability and MPR performance, and the conventional PB_FSPS scheme shows the most degraded performance result.
그러나, 잡음 환경이 아닌 다중 경로 페이딩 채널 환경에서는 잡음에 의한 요인 보다 이동체 속도나 FFT 크기가 성능에 미치는 영향이 크므로, 이하에서는 다중경로 페이딩 채널 환경에서의 성능 비교에 대하여 살펴보기로 한다.However, in the multipath fading channel environment, which is not a noise environment, the moving speed or the FFT size has a greater effect on the performance than the noise factor. Therefore, the performance comparison in the multipath fading channel environment will be described below.
도 7a 내지 도 7c는 다중 경로 페이딩 환경(Channel model COST 207 Typical Urban)에서 각 동기 방식 간의 검출 오류 확률에 대한 성능분석 결과를 나타내는 것으로서, 이를 살펴 보면, 모든 이동체 속도와 FFT 크기에 대하여 본 발명의 성능이 가장 우수함을 알 수 있다.7A to 7C show performance analysis results of detection error probabilities between synchronization methods in a multi-path fading environment (
먼저, 각각의 동기 방식에 대하여 이동체 속도에 따른 성능을 분석해 보면, 기존의 PB_FSPS의 경우에는 이동체 속도에 상관없이 거의 일정한 결과를 가지는 반면, 기존의 CB_FSPS 방식은 저속 환경에서는 FFT 크기가 큰 경우가 우수한 성능을 가지나 고속의 이동체 환경에서는 FFT 크기가 클수록 성능이 열화되는 것을 알 수 있다. 이러한 현상은 상관을 수행하는 두 OFDM 심볼 사이의 채널의 변화량으로부터 야기되므로, 한 심볼의 전력을 이용하는 PB_FSPS의 경우에는 성능의 변화가 나타나지 않는것이다.First, when analyzing the performance according to the moving speed for each synchronous method, the conventional PB_FSPS has almost constant result regardless of the moving speed, whereas the existing CB_FSPS method has a good FFT size in the low speed environment. In the high speed mobile environment, the larger the FFT size, the lower the performance. Since this phenomenon is caused by the amount of change in the channel between the two OFDM symbols performing correlation, the performance change does not appear in the case of PB_FSPS using the power of one symbol.
다음의 [표 2]는 다음의 [수학식 7]을 이용하여 이동체 속도 및 대역폭에 따른 코히어런스 시간(Coherence time)을 시간영역의 OFDM 샘플 단위로 나타낸 것이다.[Table 2] shows the coherence time according to the moving object speed and bandwidth in the OFDM sample unit of the time
여기서,Tc 는 코히어런스 시간(Coherence time),fm는 최대 도플러 주파수(Maximum Doppler Frequency)를 의미한다.Here,Tc denotes a coherence time andfm denotes a maximum Doppler frequency.
상기 [표 2]를 보면, 이동체 속도가 증가함에 따라서 코히어런스 시간(Coherence time) 내의 OFDM 샘플 수가 감소하는 것을 알 수 있다.[Table 2], it can be seen that the number of OFDM samples in the coherence time decreases as the moving speed increases.
따라서, 기본적으로 상관을 이용하는 동기 방식의 경우에는 이동체 속도가 증가하고 FFT 크기가 증가할수록 상관에 이용되는 두 OFDM 심볼 간의 채널의 변화폭이 증가하므로 성능이 열화된다. 특히, 4 심볼 이전의 심볼을 이용하는 기존의 CB_FSPS의 경우에는 이동체의 속도가 120km/h일 때 코히어런스 시간이 감소하므로, 잡음 환경 또는 저속의 이동체 속도에서와 달리 성능이 역전되는 현상을 보인다.Therefore, in the case of the synchronous method using the correlation, the performance is degraded because the variation of the channel between the two OFDM symbols used for correlation increases as the moving speed increases and the FFT size increases. In particular, in the conventional CB_FSPS using symbols before 4 symbols, since the coherence time is reduced when the speed of the moving object is 120 km / h, the performance is reversed unlike a noise environment or a low moving speed of the vehicle.
하지만, 본 발명은 인접한 두 심볼 간의 상관을 이용하기 때문에, 기존의 CB_FSPS 방식에 비하여 도플러(Doppler) 영향에 강인한 특성을 가짐을 알 수 있다.However, since the present invention uses the correlation between two adjacent symbols, it can be seen that the present invention is more robust to the Doppler effect than the conventional CB_FSPS scheme.
도 8 및 도 9는 이동체 속도 및 SNR의 변화에 따른 동기방식들 간의 MPR 성능을 비교한 결과를 나타낸다.8 and 9 show the results of comparing the MPR performance between the synchronization scheme according to the change of the moving speed and the SNR.
기존의 PB_FSPS의 경우에는 데이터 심볼과 파일럿 심볼의 전력 비율을 이용하므로, 이동체 속도에 상관없이 MPR이 대략 "1" 정도의 낮은 값을 가짐을 알 수 있다. SNR의 증가에 따라서는 잡음의 감소에 따른 미세한 성능 향상은 나타나지만 대략 1의 낮은 성능을 보인다.In the case of the conventional PB_FSPS, since the power ratio of the data symbol and the pilot symbol is used, the MPR has a low value of about "1" regardless of the moving speed. As the SNR increases, there is a slight performance improvement due to the reduction of the noise, but a low performance of about 1.
기본적으로 상관을 기반으로 하는 기존의 CB_FSPS와 본 발명은 검출 오류 확률의 성능 분석에서와 같이 이동체 속도가 증가할수록 상관도가 낮아지므로 성능이 다소 열화되지만, 동일한 이동체 환경에서는 SNR이 증가할수록 잡음 영향이 감소하므로 MPR 성능이 향상된다. 그리고, 기존의 CB_FSPS와 본 발명의 성능을 비교하면, 본 발명이 4 심볼 이전의 심볼을 이용하는 기존의 CB_FSPS보다, 이동체 속도 및 SNR의 변화에 따른 MPR 성능에 있어서 더욱 우수함을 알 수 있다.The CB_FSPS and the present invention which are basically based on correlation are degraded slightly as the correlation speed decreases as the moving speed increases, as in the performance analysis of the detection error probability. However, in the same moving environment, the noise effect increases as the SNR increases. This reduces the MPR performance. In addition, comparing the performance of the present invention with the conventional CB_FSPS, it can be seen that the present invention is superior to the conventional CB_FSPS using a symbol before four symbols in the MPR performance according to the change in the moving speed and SNR.
상기의 결과를 종합해 보면, 본 발명은 검출 오류 성능 및 MPR 측면에서, 기존의 어떠한 동기 방식보다도 우수한 성능을 가짐을 알 수 있다.In summary, it can be seen that the present invention has better performance than any conventional synchronization scheme in terms of detection error performance and MPR.
상술한 바와 같은 본 발명의 방법은 프로그램으로 구현되어 컴퓨터로 읽을 수 있는 형태로 기록매체(씨디롬, 램, 롬, 플로피 디스크, 하드 디스크, 광자기 디스크 등)에 저장될 수 있다. 이러한 과정은 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 용이하게 실시할 수 있으므로 더 이상 상세히 설명하지 않기로 한다.As described above, the method of the present invention may be implemented as a program and stored in a recording medium (CD-ROM, RAM, ROM, floppy disk, hard disk, magneto-optical disk, etc.) in a computer-readable form. Since this process can be easily implemented by those skilled in the art will not be described in more detail.
이상에서 설명한 본 발명은, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자에게 있어 본 발명의 기술적 사상을 벗어나지 않는 범위 내에서 여러 가지 치환, 변형 및 변경이 가능하므로 전술한 실시예 및 첨부된 도면에 의해 한정되는 것이 아니다.The present invention described above is capable of various substitutions, modifications, and changes without departing from the technical spirit of the present invention for those skilled in the art to which the present invention pertains. It is not limited by the drawings.
상기와 같은 본 발명은, 연속적으로 수신된 두 OFDM 심볼에 대하여 배치 가 능한 분산 파일럿 위치에서의 인접 부반송파 심볼값 간의 상관을 이용함으로써, DVB-T에 적용되는 'TPS-bit를 이용한 동기 방식'에 비하여 동기 수행 시간을 두 심볼로 현저히 줄일 수 있으며, 또한 기존의 DVB-H 시스템에 적용되는 '상관 기반의 분산 파일럿 동기 방식'(CB_FSPS), '전력 검출 기반 분산 파일럿 동기 방식'(PB_FSPS), 및 '기준 신호 기반 방식'(RB_FSPS)에 비하여 분산파일럿 동기의 신속성 및 정확성 측면에서 우수한 성능을 가지는 효과가 있다. As described above, the present invention utilizes the correlation between adjacent subcarrier symbol values at distributed pilot positions that can be allocated to two consecutively received OFDM symbols, thereby to the 'synchronous method using TPS-bit' applied to DVB-T. In comparison, the synchronization execution time can be significantly reduced to two symbols. Also, 'correlation based distributed pilot synchronization scheme' (CB_FSPS), 'power detection based distributed pilot synchronization scheme' (PB_FSPS), and Compared to the 'reference signal based method' (RB_FSPS), there is an effect of having excellent performance in terms of speed and accuracy of distributed pilot synchronization.
또한, 본 발명은, 파일럿 간의 상관을 이용하여 분산 파일럿 패턴을 검출한다는 점에서는 기존의 CB_FSPS 방식과 유사하나, 앞선 심볼과의 상관을 이용함으로써, 기존의 CB_FSPS 방식에 비하여 동기 수행 시간을 5개 OFDM 심볼에서 2개로 감소시킬 수 있으며, 또한 이전에 수신된 심볼을 저장하는 버퍼의 수도 4개에서 하나로 줄일 수 있는 효과가 있다.In addition, the present invention is similar to the conventional CB_FSPS scheme in that the distributed pilot pattern is detected using the correlation between pilots, but by using correlation with the preceding symbol, the synchronization execution time is 5 OFDM compared to the conventional CB_FSPS scheme. The number of symbols can be reduced from two, and the number of buffers for storing previously received symbols can be reduced from four to one.
요컨대, 본 발명은, 기존의 분산 파일럿 동기 방식들에 비하여 다양한 이동체 속도 및 FFT 크기에서 더욱 안정되고 우수한 성능을 보이면서도 동기 수행 시간을 감소시키는 효과가 있으며, 따라서, 소모 전력의 감소를 지향하는 DVB-H 시스템에 더욱 적합하다.In short, the present invention has a more stable and superior performance at various vehicle speeds and FFT sizes compared to the existing distributed pilot synchronization schemes, and has an effect of reducing the synchronization execution time, and thus, DVB which aims to reduce power consumption. More suitable for -H systems.
Claims (10)
Translated fromKoreanApplications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020050115026 | 2005-11-29 | ||
| KR20050115026 | 2005-11-29 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR100714448B1true KR100714448B1 (en) | 2007-05-04 |
Family
ID=38269680
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020060030281AExpired - Fee RelatedKR100714448B1 (en) | 2005-11-29 | 2006-04-03 | Fast Distributed Pilot Synchronizer and Method in Digital Video Broadcasting Receiver |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100714448B1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100864858B1 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2008-10-23 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Synchronization for Terrestrial DMB Receiver and Receiver using the same |
| KR101391398B1 (en) | 2009-12-21 | 2014-05-02 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Transmitter, receiver, transmitting method and receiving method in DVB-RCS system |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20000000689A (en)* | 1998-06-02 | 2000-01-15 | 윤종용 | Synchronizing method of high speed symbol timing |
| KR20040098989A (en)* | 2003-05-16 | 2004-11-26 | 삼성전자주식회사 | A robust timing recovery apparatus over frequency selsctive time-varying channels and a method timing recovering |
| KR20060068831A (en)* | 2004-12-17 | 2006-06-21 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Synchronous Capture Device and Method in Digital Receiver |
- 2006
- 2006-04-03KRKR1020060030281Apatent/KR100714448B1/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20000000689A (en)* | 1998-06-02 | 2000-01-15 | 윤종용 | Synchronizing method of high speed symbol timing |
| KR20040098989A (en)* | 2003-05-16 | 2004-11-26 | 삼성전자주식회사 | A robust timing recovery apparatus over frequency selsctive time-varying channels and a method timing recovering |
| KR20060068831A (en)* | 2004-12-17 | 2006-06-21 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Synchronous Capture Device and Method in Digital Receiver |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100864858B1 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2008-10-23 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Synchronization for Terrestrial DMB Receiver and Receiver using the same |
| KR101391398B1 (en) | 2009-12-21 | 2014-05-02 | 한국전자통신연구원 | Transmitter, receiver, transmitting method and receiving method in DVB-RCS system |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101375506B1 (en) | Time-frequency synchronization and frame number detection for dmb-t systems | |
| KR20090008330A (en) | Pilot Modulation Error Rate for Evaluating Transmitter Performance | |
| JP2004274722A (en) | Communication device | |
| KR20180112788A (en) | Signaling and Detection of Transmitter Identifiers in Broadcast Transmission Networks | |
| KR20070056881A (en) | Frequency Restoration Apparatus and Method in Orthogonal Frequency Multiple Access System | |
| CN100571236C (en) | Method, system and receiver for receiving multi-carrier transmissions | |
| EP1946505A2 (en) | Modulation type determination for evaluation of transmitter performance | |
| JP2019522929A (en) | Receiving apparatus and receiving method | |
| KR20070068821A (en) | Apparatus and Method for Estimating Initial Carrier Frequency Offset in Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Receiver | |
| TWI481220B (en) | Estimating method for maximum channel delay and cyclic prefix (cp) averaging method in ofdm receiver | |
| Lee et al. | Transmitter identification signal detection algorithm for ATSC 3.0 single frequency networks | |
| Yang et al. | Carrier phase tracking of OFDM-based DVB-T signals for precision ranging | |
| EP1706974B1 (en) | Method, system and receiver for receiving a multi-carrier transmission | |
| KR100714448B1 (en) | Fast Distributed Pilot Synchronizer and Method in Digital Video Broadcasting Receiver | |
| US20090103667A1 (en) | Methods for Modified Signal Acquisition for OFDM Schemes | |
| WO2007038554A2 (en) | Evaluation of transmitter performance | |
| Zou | Automatic Detection of the Guard Interval Length in OFDM System. | |
| KR100672304B1 (en) | Symbol Position Tracking Method in Broadcast Receiver | |
| CN102244627B (en) | Rough timing synchronization device of CMMB and realization method thereof | |
| Schexnayder et al. | Effects of oversampling and multipath on navigation using OFDM signals of opportunity | |
| Jung-Sun Um et al. | Fast and Robust Scattered Pilot Synchronization scheme for OFDM Systems | |
| Min et al. | Frequency synchronization for digital audio broadcasting | |
| Guoping et al. | Coarse Symbol Timing Synchronization Improved Algorithm for CMMB Mobile TV | |
| Zheng | Robust frame synchronization scheme for the Chinese TDS-OFDM-based DTTB systems | |
| Zheng | Frame Head Mode Detection for the Multiple-antenna Chinese DTTB System |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| D13-X000 | Search requested | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D13-srh-X000 | |
| D14-X000 | Search report completed | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D14-srh-X000 | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Fee payment year number:1 St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee | ||
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | Not in force date:20100427 Payment event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U13-oth-PC1903 | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | Ip right cessation event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE Not in force date:20100427 St.27 status event code:N-4-6-H10-H13-oth-PC1903 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 |