KR100666452B1 - Diagnosis method of rotating machine and diagnostic system using the method - Google Patents
Diagnosis method of rotating machine and diagnostic system using the methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100666452B1 KR100666452B1KR1020050083230AKR20050083230AKR100666452B1KR 100666452 B1KR100666452 B1KR 100666452B1KR 1020050083230 AKR1020050083230 AKR 1020050083230AKR 20050083230 AKR20050083230 AKR 20050083230AKR 100666452 B1KR100666452 B1KR 100666452B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- state
- rotating machine
- vibration
- feature extraction
- vibration data
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01H—MEASUREMENT OF MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS OR ULTRASONIC, SONIC OR INFRASONIC WAVES
- G01H1/00—Measuring characteristics of vibrations in solids by using direct conduction to the detector
- G01H1/003—Measuring characteristics of vibrations in solids by using direct conduction to the detector of rotating machines
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F17/00—Digital computing or data processing equipment or methods, specially adapted for specific functions
- G06F17/10—Complex mathematical operations
- G06F17/14—Fourier, Walsh or analogous domain transformations, e.g. Laplace, Hilbert, Karhunen-Loeve, transforms
- G06F17/148—Wavelet transforms
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Computational Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Analysis (AREA)
- Mathematical Optimization (AREA)
- Pure & Applied Mathematics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Algebra (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Testing Of Devices, Machine Parts, Or Other Structures Thereof (AREA)
- Measurement Of Mechanical Vibrations Or Ultrasonic Waves (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean도1은 본 발명의 진단방법이 적용되는 유도전동기를 보여주는 분해사시도 사진이고1 is an exploded perspective view showing an induction motor to which the diagnostic method of the present invention is applied;
도2 내지 도5는 종래에 개시된 유도전동기의 정상 상태와 여러 가지 이상 상태의 진동 주파수 스펙트럼이고2 to 5 are vibration frequency spectrums of steady state and various abnormal states of the induction motor disclosed in the related art.
도6에서 원래의 시간 영역에서 샘플링된 진동신호의 통계치를 나타내고,6 shows statistical values of the vibration signal sampled in the original time domain,
도7과 도8은 각각 주파수 대역(4~8Khz)과 주파수 대역(0.5~1Khz)에서 웨이브릿 변환된 진동신호의 통계치를 나타내고7 and 8 show statistical values of the wavelet transformed vibration signal in the frequency band (4-8Khz) and the frequency band (0.5-1Khz), respectively.
도9는 본 발명에서 K-means clustering 알고리즘을 적용한 블록도이고9 is a block diagram to which the K-means clustering algorithm is applied in the present invention.
도10은 데이터 세트에 검출 오차 최소화 학습(minimum detection error training)을 적용하는 과정을 보여주는 개념도이고FIG. 10 is a conceptual diagram illustrating a process of applying minimum detection error training to a data set. FIG.
도11은 본 발명에서 검출 오차 최소화 학습(minimum detection error training)을 적용하는 블록도이다.
* 주요 도면 부호의 설명 *
1 : 모터 축 2 : 볼 베어링 3 : 로터
4 : 정류자 5 : 시동축전기 9 : 밀폐 내부하우징
10: 외부 팬 11: 환풍슬롯11 is a block diagram to apply minimum detection error training in the present invention.
Explanation of the Main References
1: motor shaft 2: ball bearing 3: rotor
4: commutator 5: starting capacitor 9: sealed internal housing
10: External Fan 11: Vent Slot
문 헌Moon Hun
(1) 양보석, 김광진, 한천, 2004, "진동 및 전류신호의 데이터 융합을 이용한 유도전동기의 결함 진단", 한국소음진동공학회논문집, 제14권, 제11호, pp.1091~1100. (1) Yang-Suk Yang, Kwang-Jin Kim, Hancheon, 2004, "Defect Diagnosis of Induction Motors Using Data Fusion of Vibration and Current Signals", Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, Vol. 14, No. 11, pp.1091 ~ 1100.
(2) 안경룡, 한천, 양보석, 전재진, 김원철, 2002, "ART- Kohonen 신경망을 이용한 회전기계의 결함진단 알고리듬의 제안", 한국소음진동공학회 논문집, 12권 10호, pp.799~807. (2) Ahn, Kyung-Ryong, Agar, Bo-Suk Yang, Jae-Jin Jeon, Won-Chul Kim, 2002, "Suggestion of Defect Diagnosis Algorithm for Rotating Machines Using Art-Khonen Neural Network", Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, Vol.
(3) 서동욱, 2000, "웨이브렛 분석을 이용한 회전기계 및 공구 상태 감지 및 진단", 서강대학교 석사학위 논문. (3) Seo Dong-wook, 2000, "Detection and Diagnosis of Rotating Machine and Tool Condition Using Wavelet Analysis," Master's Thesis, Sogang University.
(4) B.S. Yang, W.W. Hwang, D.J. Kim and A.C.C. Tan, 2003, "Condition Classification of Small Reciprocating Compressor for Refrigerators using Artificial Neural Networks and Support Vector Machines," Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing. Vol. 19, pp. 371~390. (4) B.S. Yang, W.W. Hwang, D.J. Kim and A.C.C. Tan, 2003, "Condition Classification of Small Reciprocating Compressor for Refrigerators using Artificial Neural Networks and Support Vector Machines," Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing. Vol. 19, pp. 371-390.
(5) A. M. Kondoz, 1998, "Digital Speech", Neural Networks for Signal Processing VIII, pp. 383~392. (5) A. M. Kondoz, 1998, "Digital Speech", Neural Networks for Signal Processing VIII, pp. 383-392.
(6) Hideyuki W., Yuji M., Satoru T., and Shigeru K., 1998, "Sound Monitoring based on the Generalized Probabilistic Descent Method," Neural Networks for Signal Processing VIII, pp. 383~392. (6) Hideyuki W., Yuji M., Satoru T., and Shigeru K., 1998, "Sound Monitoring based on the Generalized Probabilistic Descent Method," Neural Networks for Signal Processing VIII, pp. 383-392.
(7) 이충희, 2000, "회전 설비의 이상고장진단 시스템의 개발", 한양대학 교 석사학위 논문. (7) Lee, Chung Hee, 2000, "Development of an Error Diagnosis System for Rotating Equipment," Master's Thesis, Hanyang University.
(8) B.H. Juang and S. Katagiri, 1992, "Discriminant Learning for Minimum Error Classification," IEEE Trans. Signal Processing, Vol. 40, No. 12, pp. 3043~3054. (8) B.H. Juang and S. Katagiri, 1992, "Discriminant Learning for Minimum Error Classification," IEEE Trans. Signal Processing, Vol. 40, no. 12, pp. 3043-3054.
(9) 황원우, 양보석, 2004, "Multi-class SVM을 이용한 회전기계의 결함 진단," 한국소음진동공학회논문집, 제14권, 제12호, pp.1233~1240. (9) Won-Woo Hwang, Bo-Suk Yang, 2004, "Diagnosis of Rotating Machines Using Multi-class SVM," Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, Vol. 14, No. 12, pp.1233 ~ 1240.
본 발명은 회전기계의 상태 진단방법 및 그 방법을 사용하는 진단 시스템에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing a state of a rotating machine and a diagnostic system using the method.
회전기계에 이상이 발생했을 때, 막대한 경제적 손실이나 인명 피해를 가져올 수 있으므로 회전기계에 대한 이상 진단은 매우 중요하다. 다양한 종류의 회전기계에서 발생할 수 있는 여러 가지 이상 현상은 회전기계의 용도, 사양, 크기 등에 따라 각기 다른 특성을 가지지만, 회전기계라는 구조적 특성 때문에 공통적인 이상 원인과 특성을 가지기도 한다. 이런 일부 공통적인 이상 원인들에 대해 이상 진단을 할 때 많이 이용될 수 있는 것이 진동 신호이다. 진동 신호는 이상 진단을 위해 고려되는 전기적 특성이나, 회전 방향, 온도 등의 다른 자료들에 비해 주변 환경에 영향을 적게 받고 비슷한 구조의 회전기계들에 대해 공통적으로 적용될 수 있다는 장점이 있다.When an abnormality occurs in a rotary machine, it can cause enormous economic loss or human damage, so it is very important to diagnose the abnormality of the rotary machine. Various abnormalities that can occur in various kinds of rotary machines have different characteristics according to the purpose, specification, size, etc. of rotary machines, but they also have common causes and characteristics because of the structural characteristics of rotary machines. Vibration signals can be used to diagnose some of these common causes of abnormality. Vibration signal has the advantage that it is less affected by the surrounding environment and can be commonly applied to rotating machines of similar structure than other data such as electrical characteristics, rotation direction, temperature, etc. which are considered for abnormal diagnosis.
이론적으로는 동일 주기로 회전하는 회전기계는 주파수 영역에서 평균적인 진동 스펙트럼을 얻을 수 있고 이러한 진동 스펙트럼의 패턴에 의하여 회전기계의 운전 상태를 진단하는 것이 가능하다. 그러나 실시간으로 진동신호센서에 검출되는 신호에 의하여 일정 범위의 주파수 영역에서 진동 스펙트럼을 얻는 것은 어려울 뿐만 아니라 이러한 진동 스펙트럼의 해석에도 별도의 처리가 수행되어야 하기 때문에 굉장히 복잡하여 실질적으로 불가능하다.Theoretically, a rotating machine that rotates at the same cycle can obtain an average vibration spectrum in the frequency domain, and it is possible to diagnose the operating state of the rotating machine by the pattern of the vibration spectrum. However, it is difficult to obtain a vibration spectrum in a frequency range of a certain range by a signal detected by the vibration signal sensor in real time, and because it is very complicated because a separate process must be performed in the analysis of the vibration spectrum, it is practically impossible.
이상 진단을 위해 진동신호에 대해 신호의 평균값 등의 특징 데이터를 결정하고 그 데이터를 이용하여 패턴 인식 등의 방법으로 이상을 진단하는 기술이 많이 이용되어 왔다. 그러나 회전기계의 진동은 종류, 용도, 사양 등에 따라 각각 다르며 동일한 기계도 완전히 같은 진동을 갖지는 않으므로 단일 특징 데이터를 이용하는 것은 많은 제약이 따르고 또한 원하는 결과도 얻기 힘들다. In order to diagnose an abnormality, a technique of determining characteristic data such as an average value of a signal with respect to a vibration signal and using the data to diagnose an abnormality by a method such as pattern recognition has been widely used. However, the vibration of a rotating machine varies depending on the type, use, and specification, and since the same machine does not have exactly the same vibration, it is difficult to use a single feature data and obtain a desired result.
본 발명은 실시간으로 신뢰성이 있는 회전기계의 상태 진단방법 및 그 방법을 사용하는 진단 시스템을 제공하기 위한 것이다.The present invention is to provide a method for diagnosing a state of a rotating machine reliable in real time and a diagnostic system using the method.
또한 본 발명은 시간 영역데이터를 사용하여 경제적으로 구축할 수 있는 회전기계의 상태 진단방법 및 그 방법을 사용하는 진단 시스템을 제공하기 위한 것이다.The present invention also provides a method for diagnosing a state of a rotating machine which can be economically constructed using time domain data, and a diagnostic system using the method.
본 발명에 의하여 회전기계의 구성요소에 설치된 진동신호센서에 의하여 검출된 진동데이터를 입력하는 단계; 상기 진동데이터의 통계적 수치 값에 웨이브릿 변환을 적용하여 특징추출 벡터를 구성하는 단계; 상기 특징추출 벡터에 케이민즈클러스터링(K-means clustering) 알고리즘을 적용하여 얻어진 값과 미리 정해진 정 상 상태와 다수의 비정상 상태의 모델 값과 가장 적은 차이를 갖는 상태의 값으로 회전기계의 상태를 분류하는 단계로 이루어지는 회전기계의 상태 진단방법이 제공된다. 상기 미리 정해진 상태 모델의 값은 바람직하게는 정상 상태와 다수의 비정상 상태에 있는 회전기계의 구성요소에 설치된 진동신호센서에 의하여 검출된 각 상태의 진동데이터를 입력하는 단계; 상기 각 상태의 진동데이터의 통계적 수치 값에 웨이브릿 변환을 적용하여 각 특징추출 벡터를 구성하는 단계; 상기 각 상태의 특징추출 벡터에 K-means 클러스터링 알고리즘을 적용하는 단계; 및 검출오차 최소화 학습 단계로 이루어진 방법으로 얻어진다.Inputting vibration data detected by a vibration signal sensor installed in a component of a rotating machine according to the present invention; Constructing a feature extraction vector by applying a wavelet transform to statistical values of the vibration data; The state of the rotating machine is classified into a value obtained by applying the K-means clustering algorithm to the feature extraction vector and a state having the smallest difference between a predetermined normal state and a plurality of abnormal state model values. There is provided a method for diagnosing a state of a rotating machine. The value of the predetermined state model is preferably inputting vibration data of each state detected by a vibration signal sensor installed in a component of a rotating machine in a normal state and a plurality of abnormal states; Constructing each feature extraction vector by applying a wavelet transform to statistical values of vibration data of each state; Applying a K-means clustering algorithm to the feature extraction vector of each state; And a detection error minimization learning step.
회전기계 예를 들면, 유도 전동기에서 주로 이상이 발생하는 부분으로는 회전자축(shaft), 베어링(bearing), 회전자(rotor) 등이 있고, 이들 부분에서 질량 불평형(mass unbalance), 정렬 불량(misalignment), 베어링 결함(faulty bearing), 회전자봉 균열(broken rotor bar), 굽은 회전축(bowed rotor shaft) 등의 이상 현상들이 발생한다. 따라서 회전기계의 운전상태는 바람직하게는 정상상태와 상기 5개의 이상 상태로, 가장 바람직하게는, 정렬불량을 각 정렬 불량(angular misalignment)과 수평 정렬 불량(parallel misalignment)으로 세분하여 6개의 이상 상태로 분류할 수 있다. 각각의 이상 상태를 간단히 정리하면 다음과 같다.Rotating machines, for example, are the parts where the abnormality occurs in induction motors such as rotor shafts, bearings, and rotors, and in these parts, mass unbalance, misalignment ( Anomalies such as misalignment, faulty bearings, broken rotor bars, and bowed rotor shafts occur. Therefore, the operating state of the rotating machine is preferably in the normal state and the five abnormal states, and most preferably, the six or more states by subdividing the misalignment into angular misalignment and parallel misalignment. Can be classified as A summary of each abnormal state is as follows.
(1) 질량 불평형 (1) mass unbalance
질량 불평형은 회전체의 기하학적 중심축과 질량 중심이 일치하지 않는 경우에 발생하며 회전체의 제작시의 오류 또는 운전시의 마모나 부식이 원인이 되어 발생한다.Mass unbalance occurs when the geometric center of mass of the rotor and the center of mass do not coincide, and are caused by errors in the manufacture of the rotor, or wear and corrosion during operation.
(2) 회전축 정렬 불량 (2) Rotation axis misalignment
정렬 불량은 회전기계의 조립 시 또는 열 변형 등의 원인에 의해 발생하는 이상으로 회전축의 정렬이 평행하지 않은 상태이다. 경우에 따라서 두 가지 정렬 이상으로 분류할 수 있는데, 각 정렬 불량(angular misalignment)은 회전축이 평행한 방향으로 놓여있지 않고 서로 다른 각도를 가진 상태이고 수평 정렬 불량(parallel misalignment)는 회전축의 높이가 어긋난 상태를 말한다.Misalignment is a state in which the alignment of the rotation shafts is not parallel, more than that caused by the assembly of the rotary machine or due to thermal deformation. In some cases, it can be classified into two or more alignments, where each angular misalignment is not placed in a parallel direction, but at different angles, and a parallel misalignment is caused by an uneven height of the axis of rotation. Say the status.
(3) 베어링 결함 (3) bearing defect
베어링은 회전축의 회전 운동을 좀 더 원활하게 하고 회전축의 하중을 지탱하는 역할을 한다. 베어링 결함은 회전축을 지지하는 베어링이 오랜 운전으로 열과 마찰 등으로 마모되는 상태로서 회전기계에서 가장 일반적으로 발생하고 이는 회전자의 편심을 유도하므로 다른 고장을 일으킬 수 있다.The bearing serves to make the rotational movement of the rotating shaft more smooth and to support the load of the rotating shaft. Bearing defects are the most common occurrences in rotating machines because bearings supporting the rotating shaft are worn out due to heat and friction due to long operation, which can cause other failures as it induces eccentricity of the rotor.
(4) 굽은 회전축 (4) bent axis of rotation
기기를 장시간 가동 하지 않을 경우, 회전자 자체의 무게에 의해 회전축이 휘어지거나, 정렬불량의 상태로 운전했을 때 회전축이 강제적으로 굽혀지는 현상을 가져오게 되고 이것에 의해서 비정상적인 진동이 발생된다.If the machine is not operated for a long time, the rotating shaft may be bent due to the weight of the rotor itself, or the rotating shaft may be forcibly bent when operated in a misaligned state, thereby causing abnormal vibration.
(5) 회전자봉 균열 (5) rotor bar crack
유도 전동기의 회전자는 여러 개의 회전자봉(rotor bar)으로 구성되어 있는데, 이들 중 일부의 회전자봉에 손상 또는 균열이 생기게 되면 이상 진동이 발생하게 된다.The rotor of the induction motor is composed of a plurality of rotor bars (rotor bar), some of these rotor rods are damaged or cracks will cause abnormal vibration.
상기 진동신호센서는 바람직하게는 변위센서 또는 가속도 센서이고 가장 바 람직하게는 가속도 센서이다. 이러한 진동신호센서는 바람직하게는 회전축 베어링의 하우징에 부착된다.The vibration signal sensor is preferably a displacement sensor or an acceleration sensor and most preferably an acceleration sensor. This vibration signal sensor is preferably attached to the housing of the rotating shaft bearing.
상기 진동데이터는 0.1Hz 내지 40KHz의 범위, 바람직하게는 0.5 Hz 내지 8KHz의 범위이고 이의 통계적 수치 값은 바람직하게는 RMS 및/또는 표준편차이다. 일반적으로 사용되는 통계적 수치는 RMS(root mean square), 평균(mean), 표준편차(standard deviation), 왜도(skewness), 첨도(kurtosis) 등인데 특히 RMS(root mean square)와 표준편차가 유용하다.The vibration data is in the range of 0.1 Hz to 40 KHz, preferably in the range of 0.5 Hz to 8 KHz and its statistical numerical values are preferably RMS and / or standard deviation. Commonly used statistical values are root mean square (RMS), mean, standard deviation, skewness, kurtosis, etc. Especially, root mean square (RM) and standard deviation are useful. Do.
회전기계의 운전상태 별로 바람직하게는 상기 진동데이터의 통계적 수치 RMS와 표준편차에 대해서 4개 내지8 개 대역 주파수로 웨이브릿 변환을 적용하여 8차 내지 16차 특징추출 벡터를 구성한다.Preferably, the 8th to 16th order feature extraction vectors are constructed by applying wavelet transforms at 4 to 8 band frequencies with respect to the statistical values RMS and standard deviation of the vibration data.
상기 특징추출 벡터에 K-means 클러스터링 알고리즘을 적용하여 얻어진 값과 미리 정해진 정상 상태와 다수의 비정상 상태의 모델 값과 가장 적은 차이를 갖는 상태의 값으로 회전기계의 상태를 분류한다. 상기 미리 정해진 상태 모델의 값은 정상 상태와 다수의 비정상 상태에 있는 회전기계의 구성요소에 설치된 진동신호센서에 의하여 검출된 각 상태의 진동데이터를 진단 방법과 동일한 절차에 의하여 특징 추출벡터를 구성하고 상기 각 상태의 특징추출 벡터에 K-means 클러스터링 알고리즘을 적용하여 각 상태에 대하여 초기 모델의 값을 얻은 다음 검출오차 최소화 학습에 의하여 개선된 모델 값을 얻는다.The state of the rotating machine is classified into a value obtained by applying the K-means clustering algorithm to the feature extraction vector and a state having the smallest difference from a predetermined steady state and a plurality of abnormal state model values. The value of the predetermined state model constitutes a feature extraction vector by the same procedure as the method of diagnosing the vibration data of each state detected by the vibration signal sensor installed in the components of the rotating machine in a normal state and a plurality of abnormal states. By applying the K-means clustering algorithm to the feature extraction vector of each state, we obtain the initial model value for each state and then obtain the improved model value by minimizing the detection error.
또한 본 발명에 의하여 피진단 회전기계의 구성요소에 설치된 진동신호센서; 상기 진동신호센서에 의하여 검출된 진동데이터를 통계적 수치 값으로 변환하고, 상기 통계적 수치 값에 웨이브릿 변환을 적용하여 특징추출 벡터를 얻고, 상기 특징추출 벡터에 K-means 클러스터링 알고리즘을 적용하여 얻어진 값과 미리 정해진 정상 상태와 다수의 비정상 상태의 모델 값과 가장 적은 차이를 갖는 상태의 값으로 회전기계의 상태를 분류하는 컴퓨팅 수단;및 상기 분류된 회전기계의 상태를 표시하는 디스플레이수단을 포함하는 회전기계의 상태 진단 시스템이 제공된다. 상기 컴퓨팅 수단은 바람직하게는 정상 상태와 다수의 비정상 상태에 있는 회전기계의 구성요소에 설치된 진동신호센서에 의하여 검출된 각 상태의 진동데이터의 통계적 수치 값에 웨이브릿 변환을 적용하여 각 특징추출 벡터를 구성하고, 상기 각 상태의 특징추출 벡터에 K-means 클러스터링 알고리즘을 적용하여 상태 모델의 값을 1차로 얻은 다음 검출오차 최소화 학습화 단계를 거쳐 미리 정해진 상태 모델의 값을 얻는다. 상기 컴퓨팅 수단은 특별히 제한되지 않는다. 범용 워크스테이숀이면 본 발명에 사용될 수 있다. 디스플레이 수단은 예를 들면 CRT, LCD 또는 LED 등이다.The present invention also provides a vibration signal sensor installed in a component of a diagnosis rotating machine; The vibration data detected by the vibration signal sensor is converted into a statistical numerical value, a wavelet transform is applied to the statistical numerical value to obtain a feature extraction vector, and a value obtained by applying a K-means clustering algorithm to the feature extraction vector. And computing means for classifying a state of the rotating machine into a value of a state having a smallest difference from a predetermined steady state and a plurality of abnormal state model values; and a display means for displaying the classified state of the rotating machine. A state diagnosis system of the machine is provided. The computing means preferably applies wavelet transforms to the statistical numerical values of the vibration data of each state detected by vibration signal sensors installed in the components of the rotating machine in a steady state and a plurality of abnormal states. Then, by applying the K-means clustering algorithm to the feature extraction vector of each state to obtain the value of the state model first, and through the detection error minimization learning step to obtain the value of the predetermined state model. The computing means is not particularly limited. Any general workstation can be used in the present invention. The display means is for example a CRT, LCD or LED.
이하 도면에 의하여 본 발명을 상세히 설명한다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도1은 본 발명의 진단방법이 적용되는 유도전동기를 보여주는 분해사시도 사진이다. 유도 전동기에서 주로 이상이 발생하는 부분으로는 회전자축(shaft), 베어링(bearing), 회전자(rotor) 등이 있고, 이들 부분에서 질량 불평형(mass unbalance), 정렬 불량(misalignment), 베어링 결함(faulty bearing), 회전자봉 균열(broken rotor bar), 굽은 회전축(bowed rotor shaft) 등의 이상 현상들이 발생한다.1 is an exploded perspective view showing an induction motor to which the diagnostic method of the present invention is applied. The main parts of the induction motor where the abnormality occurs are the rotor shaft (bearing), the rotor (rotator), etc. In these areas, mass unbalance, misalignment, bearing defects ( Anomalies such as faulty bearings, broken rotor bars and bowed rotor shafts occur.
도2 내지 도5는 종래에 개시된 유도전동기의 정상 상태와 여러가지 이상 상태의 진동 주파수 스펙트럼(부경대학교 지능역학연구실 제공)을 보여준다. 도2에 보이는 바와 같이 60Hz 부근에서 회전주파수 성분이 크게 나타나고, 대부분의 성분들이 저주파 대역에 있음을 알 수 있다. 도3은 질량 불평형 상태의 주파수 스펙트럼을 보여준다. 정상 상태 스펙트럼과 비교해보면, 다른 주파수 성분들의 진폭 변화는 적지만 회전주파수 성분이 많이 증가했고, 조화성분(harmonics)들도 조금씩 증가하는 것을 알 수 있다. 각 정렬 불량 및 수평 정렬 불량 상태(도시 안됨)에서는 질량 불평형에 비해 회전주파수 성분은 조금 증가하고 그 이상의 조화 성분들 중에서 특히 3차 및 4차 조화성분들 크게 증가했으며, 그 이상의 조화 성분도 크게 증가한다. 도4의 베어링 결함 상태의 주파수 스펙트럼을 보면, 회전주파수가 약간 감소하고 정상상태에서는 발생하지 않았던 고주파수 성분이 전체적으로 크게 증가한 것을 알 수 있다. 굽은 회전축의 경우(도시 안됨) 회전주파수를 포함한 저주파수 성분이 전체적으로 많이 감소하고, 1kHz 이상의 고주파수 성분이 크게 증가한다. 도5의 회전자봉 균열 상태의 주파수 스펙트럼을 보면, 정상 상태에 비해 회전주파수 및 저주파수 성분이 전체적으로 조금씩 감소하는 것을 알 수 있다. 이상과 같이 이상 상태에 따라 다른 주파수 영역에서 특징이 쉽게 확인될 수 있고 시간 영역에서의 진동데이터를 주파수 대역 별로 변환할 필요가 있음을 알 수 있다. 그러나 진동신호에 의하여 일정 범위의 주파수 스펙트럼을 구하는 것은 높은 진동센서 감도와 많은 계산량을 수반하는 것이므로 실질적으로 불가능하고 이를 해석하는 솔루션을 만드는 것도 쉽지 않다.2 to 5 show vibration frequency spectra of a steady state and various abnormal states of an induction motor disclosed in the related art (provided by Pukyong National University). As shown in FIG. 2, the rotation frequency component appears large around 60 Hz, and it can be seen that most components are in the low frequency band. Figure 3 shows the frequency spectrum of mass unbalance. Compared with the steady-state spectrum, the amplitude change of the other frequency components is small but the rotation frequency component is increased, and the harmonics are also increased little by little. In each misalignment and horizontal misalignment (not shown), the rotational frequency component increased slightly compared to the mass unbalance, and among the higher harmonic components, especially the 3rd and 4th harmonic components, the higher harmonic components also increased significantly. Referring to the frequency spectrum of the bearing defect state of Fig. 4, it can be seen that the rotational frequency is slightly decreased and the high frequency component which is not generated in the steady state is greatly increased as a whole. In the case of a curved rotating shaft (not shown), the low frequency components including the rotation frequency are greatly reduced as a whole, and the high frequency components of 1 kHz or more are greatly increased. Looking at the frequency spectrum of the rotor bar crack state of Figure 5, it can be seen that the overall rotation frequency and low frequency components are slightly reduced as compared to the steady state. As described above, it can be seen that the characteristics can be easily identified in different frequency domains according to the abnormal state, and it is necessary to convert the vibration data in the time domain for each frequency band. However, obtaining a range of frequency spectrums by vibrating signals involves a high vibration sensor sensitivity and a large amount of computation, and thus it is practically impossible and it is not easy to make a solution to interpret them.
진동신호 시간 영역 데이터의 통계적 수치Statistical value of vibration signal time domain data
유도전동기의 이상 진단을 위해 취득된 진동 신호는 시간 영역의 데이터로써 서로 다른 진폭과 주파수를 가지는 많은 신호들의 조합으로 이루어져 있고 많은 특징 정보를 가지지만, 또한 잡음 성분과 같은 불필요한 부분이 많으므로 직관적인 특징을 얻기 어렵다. 따라서 효과적인 이상 진단을 위해서 신호 처리 기법을 이용하여 각 기계별 혹은 이상 종류별 고유한 특징을 찾아내는 것이 필요한데 이런 과정을 특징 추출(feature extraction)이라고 한다. 문헌(1)(양보석, 김광진, 한천, 2004, "진동 및 전류신호의 데이터 융합을 이용한 유도전동기의 결함 진단", 한국소음진동공학회논문집, 제14권, 제11호, pp.1091~1100)과 문헌(2)(안경룡, 한천, 양보석, 전재진, 김원철, 2002, "ART- Kohonen 신경망을 이용한 회전기계의 결함진단 알고리듬의 제안", 한국소음진동공학회 논문집, 12권 10호, pp.799~807.)를 참조한다.The vibration signal obtained for the fault diagnosis of the induction motor is composed of a combination of many signals having different amplitudes and frequencies as data in the time domain and has a lot of characteristic information, but it is also intuitive because there are many unnecessary parts such as noise components. Hard to get features Therefore, in order to effectively diagnose the abnormality, it is necessary to find out the unique features of each machine or type of error using signal processing techniques. This process is called feature extraction. Document (1) (Yang Bo-seok, Kim Kwang-jin, Hancheon, 2004, "Defect Diagnosis of Induction Motor Using Data Fusion of Vibration and Current Signal", Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, Vol. 14, No. 11, pp.1091 ~ 1100) And Literature (2) (Kyung-yong Ahn, Agar, Yang Bo-seok, Jeon-jin Jeon, Won-cheol Kim, 2002, "Proposal of Defect Diagnosis Algorithm for Rotating Machines Using ART-Khonen Neural Network", Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, Vol. ~ 807.).
특징 추출을 위한 진동신호 데이터는 평균(mean), 표준편차(STD;standard deviation), 왜도(skewness), 첨도(kurtosis) 등의 통계적 데이터들로 가공된다. 진동신호 데이터로서 바람직한 통계치는 표준편차와 RMS(root mean square)이다.The vibration signal data for feature extraction is processed into statistical data such as mean, standard deviation (STD), skewness, kurtosis and the like. Preferred statistics for vibration signal data are standard deviation and root mean square (RMS).
특징 데이터의 비교Comparison of feature data
유도 전동기(induction motor)에서 정상 및 각종 이상 상태의 조건을 발생시켜 측정한 데이터로 샘플링 주파수 8kHz의 시간 2.1333초 길이로 취득하였으며, 같 은 기계에 대해 여섯 번씩 측정하여 각 상태별 총 12.78초 길이를 갖는다. 실험에서는 전체 데이터를 0.35초 길이의 프레임으로 나누어 각 상태별 30개씩의 데이터 집합(data set)을 구성했다. 원래 시간 영역의 신호와 4단계 웨이브릿을 거쳐 d1(4~8kHz), d2(2~4kHz), d3(1~2kHz), d4(0.5~1kHz)로 나누었다. 도6에서 수평축은 입력 신호의 각 상태별 데이터 샘플을 나타내고, 수직축은 각각 데이터의 RMS, 평균, 표준편차, 왜도, 첨도를 나타낸다. 다른 특징 데이터들은 각 상태별 큰 차이가 나지 않고, RMS와 표준편차의 경우 베어링 결함, 굽은 회전축 상태가 다른 상태들과 차이가 나타난다.This data was generated by induction motors in normal and various abnormal conditions. The data was acquired with a sampling frequency of 8 kHz and 2.1333 seconds in length. Six measurements were taken for the same machine. Have In the experiment, the total data was divided into 0.35 second frames to form 30 data sets for each state. Originally, the signal was divided into d1 (4-8 kHz), d2 (2-4 kHz), d3 (1-2 kHz), and d4 (0.5-1 kHz) through a signal in the time domain and a four-step wavelet. In Fig. 6, the horizontal axis represents data samples for each state of the input signal, and the vertical axis represents RMS, average, standard deviation, skewness, and kurtosis of the data, respectively. The other characteristic data are not significantly different for each state, and the difference between the bearing defects and the state of the bent axis of rotation in the case of RMS and standard deviation is different.
도7과 도8을 비교해보면, 웨이브릿 변환을 거친 데이터의 대역별 신호 중에서 고주파수 영역 신호인 4~8kHz 대역의 신호에서는 RMS와 표준편차를 이용하여 베어링 결함, 굽은 회전축의 이상 상태를 알아낼 수 있다. 이상 상태의 주파수 특성에서 보았듯이, 베어링 결함과 굽은 회전축 상태는 정상 상태와 비교했을 때 고주파수 성분이 크게 나타나므로 다른 상태들과 구분이 잘 될 수 있다. 그러나 저주파수 대역인 0.5~1kHz 영역의 신호에서는 질량 불평형, 각 정렬 불량, 수평 정렬 불량, 회전자봉 균열 등의 이상 주파수 특성이 저주파수 대역에서 나타나는 이상 현상들을 더 잘 구분할 수 있다. 위와 같이 기본 시간 신호에서 찾을 수 없는 특징들을 각 대역별 신호에서 각각 찾아낼 수 있고 이런 대역별 신호의 특징들을 조합하여 여러 가지 상태들의 특징 추출 벡터를 구성할 수 있다.7 and 8, in the signals of the high frequency region signals of the 4 to 8 kHz band of the wavelet transformed data, the abnormal state of the bearing defects and the bent rotation axis can be detected using RMS and standard deviation. . As seen in the frequency characteristics of the abnormal state, the bearing defects and the bent axis state can be distinguished from other states because the high frequency components appear larger than the normal state. However, in the low frequency band 0.5 ~ 1kHz region, the abnormal frequency characteristics such as mass unbalance, angular misalignment, horizontal misalignment, and rotor rod crack can better distinguish abnormal phenomena in low frequency band. As described above, features not found in the basic time signal may be found in each band signal, and feature extraction vectors of various states may be configured by combining the features of the band-specific signals.
K-Means Clustering 알고리즘의 적용Application of K-Means Clustering Algorithm
위의 특징 데이터들에 정상 및 이상 상태의 분류를 위해, 패턴 인식의 간단한 알고리즘 중 하나인 K-means 클러스터링(clustering) 알고리즘에 적용하였고, 이 알고리즘을 요약하면 다음과 같다. 이 알고리즘에 대해서는 문헌(5)( A. M. Kondoz, 1998, "Digital Speech", Neural Networks for Signal Processing VIII, pp. 383~392.)에 기재되어 있다.In order to classify the normal and abnormal states in the above feature data, it is applied to the K-means clustering algorithm, which is one of simple algorithms of pattern recognition, and the algorithm is summarized as follows. This algorithm is described in Document (5) (A. M. Kondoz, 1998, "Digital Speech", Neural Networks for Signal Processing VIII, pp. 383-392.).
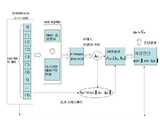
도9는 K-means 클러스터링(clustering) 알고리즘을 적용하여 각 상태 모델을 결정하고 상태 모델과 입력 데이터와 가장 적은 차이를 갖는 상태를 입력의 상태로 결정하여 정상 및 이상 상태를 진단하는 진단 시스템을 나타낸다.9 illustrates a diagnostic system for determining normal and abnormal states by determining each state model by applying a K-means clustering algorithm and determining a state having the least difference between the state model and the input data as the state of the input. .
검출 오차 최소화 학습Detection error minimization learning
4단계 4개 대역 웨이브릿 변환 신호와 6단계 8개 대역 웨이브릿 변환 신호에 대해 특징 벡터를 구성하기 위해 실험했던 5가지의 진동신호 통계치를 조합하여 K-means 알고리즘에 적용하였을 때, 정상 및 각종 이상 상태를 구분하는 정도를 식(1)과 같이 계산하였다.When applied to the K-means algorithm by combining the five vibration signal statistics that were experimented to construct the feature vector for the four-stage four-band wavelet transform signal and the six-stage eight-band wavelet transform signal, The degree to distinguish the abnormal state was calculated as in Equation (1).
Table 1은 프레임 길이를 0.4초로 하고 웨이브릿 변환을 4단계 4개 대역 신호로 두고 특징 데이터를 서로 바꿔 조합해 비교했을 때, K-means 클러스터링(clustering) 알고리즘에서 결정된 상태별 모델과 비교해서 이상 진단 결과의 진단율을 나타낸 것이다. 표의 결과에서 RMS값과 표준편차를 이상 진단의 특징 추출을 위한 특징 벡터로 사용하는 것이 유리하다는 것을 알 수 있다.Table 1 compares the state-specific model determined by the K-means clustering algorithm when the frame length is 0.4 seconds and the wavelet transform is four-stage four-band signal, and the feature data are interchanged and compared. The diagnostic rate of the results is shown. From the results of the table, it can be seen that it is advantageous to use the RMS value and standard deviation as a feature vector for feature extraction of the fault diagnosis.
Table 1 Detection rate for each feature dataTable 1 Detection rate for each feature data
검출 오차 최소화 학습은 각 상태의 클래스 모델을 기울기 강화(gradient descent)의 방법을 기반으로 만약 입력 데이터가 올바른 상태 클래스가 아닌 다른 상태 클래스에 분류되었다면 이것을 잘못된 검출(false alarm)로 두고, 올바른 상태 클래스로 분류되지 못했을 경우 검출 실패(detection failure)의 두 가지 상태 클래스 분류의 오차로 나누어 상태 클래스 모델과 임계 값의 오차가 적도록 수정하게 된다The detection error minimization learning is based on the method of gradient descent of the class model of each state, and if the input data is classified in a state class other than the correct state class, it is set as a false alarm and the correct state class. If it is not classified as, the error is divided into two state class classifications of detection failure, so that the error between the state class model and the threshold is small.
상태 모델과 임계 값은Λs =λs,hs 로 두어 MDE 훈련에 적용한다. 오차 함수를 식(2)와 같이 임계 값과 거리 함수의 차이로 두고,The state model and thresholds are applied to MDE training by placingΛs =λs ,hs . Let the error function be the difference between the threshold and the distance function, as shown in equation (2),
이 오차 함수를 Smoothed Zero-One 함수, 식(3)에 적용하여 기울기가 커지도록 학습하게 된다. 여기서 검출 실패(DF error)와 잘못된 검출(FA error)의 두 가지로 나누어 학습을 다르게 한다.This error function is applied to the Smoothed Zero-One function, Equation (3), to learn to increase the slope. Here, learning is divided into two types: detection failure (DF error) and false detection (FA error).
식(3)의 값을 미분을 통해 기울기를 구하여 기울기가 커지는 방향으로 학습하여 상태 모델과 임계 값이 이상 진단에서 오류가 적도록 수정하게 된다.The value of Equation (3) is derived from the derivative to learn the slope in the direction of increasing slope, so that the state model and the threshold value are modified to have fewer errors in the abnormal diagnosis.
식(4)의 ε은 학습률을 나타내고,Us는 임계값과 상태 모델로 구성된 학습 데이터에 대해 정의된 행렬이다.Ε in Equation (4) represents a learning rate, andUs is a matrix defined for training data composed of a threshold and a state model.
검출 오차 최소화 학습을 이상 진단에 다시 적용한 결과는 표 2와 3에서 알 수 있다. K-Means 클러스터링(Clustering) 알고리즘을 적용한 초기 상태와 검출 오차 최소화 학습을 적용한 후의 상태를 비교했을 때, 각 상태별 진단율에서는 정상 상태(N)와 질량 불평형(F1) 상태가 개선되었다. 따라서 전체 상태의 평균 진단율은 94.76%에서 96.19%로 약 1.43% 증가하였다.The results of applying the detection error minimization learning to the abnormal diagnosis can be seen in Tables 2 and 3. When comparing the initial state with the K-Means clustering algorithm and the state after the detection error minimization learning, the steady state (N) and mass unbalance (F1) states were improved in the diagnosis rate for each state. Therefore, the average diagnosis rate of the overall condition increased by 1.43% from 94.76% to 96.19%.
표 2 각 상태의 진단율Table2 Diagnostic Rate of Each Condition
표 3 평균진단율Table3 Average Diagnosis Rate
본 발명에 의하여 많은 하드웨어적인 투자 없이도 실시간으로 신뢰성이 있는 회전기계의 운전상태를 진단할 수 있는 진단 방법 및 진단 시스템이 제공된다.The present invention provides a diagnostic method and a diagnostic system capable of diagnosing an operating state of a reliable rotating machine in real time without a large hardware investment.
Claims (12)
Translated fromKoreanPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020050083230AKR100666452B1 (en) | 2005-09-07 | 2005-09-07 | Diagnosis method of rotating machine and diagnostic system using the method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020050083230AKR100666452B1 (en) | 2005-09-07 | 2005-09-07 | Diagnosis method of rotating machine and diagnostic system using the method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR100666452B1true KR100666452B1 (en) | 2007-01-09 |
Family
ID=37867395
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020050083230AExpired - Fee RelatedKR100666452B1 (en) | 2005-09-07 | 2005-09-07 | Diagnosis method of rotating machine and diagnostic system using the method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100666452B1 (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100963685B1 (en) | 2008-05-21 | 2010-06-15 | 울산대학교 산학협력단 | Fault diagnosis device and method through video signal conversion of machine operation sound and vibration signal |
| KR100993378B1 (en) | 2008-12-03 | 2010-11-09 | 서울대학교산학협력단 | Method and apparatus for judging combustion time of compression ignition engine |
| CN101968379A (en)* | 2010-09-30 | 2011-02-09 | 南昌航空大学 | Method for extracting characteristic information of operating condition vibration signal of aircraft engine rotor system |
| US10082520B2 (en) | 2016-03-18 | 2018-09-25 | Simmonds Precision Products, Inc. | Rotational frequency estimation from sensed vibrations based on a supervised learning method |
| KR20190000826A (en) | 2017-06-23 | 2019-01-03 | 퓨처메인 주식회사 | Automatic diagnosis method for rotating machinery using real-time vibration analysis |
| WO2021107342A1 (en)* | 2019-11-28 | 2021-06-03 | (주) 위세아이텍 | Device and method for monitoring state of vibration of rotating equipment using deep learning-based time series analysis |
| CN114742094A (en)* | 2022-03-17 | 2022-07-12 | 同济大学 | Vibration signal defect feature extraction method based on deep morphological convolution network |
| KR20230152470A (en)* | 2022-04-27 | 2023-11-03 | 한국해양과학기술원 | Apparatus and method for estimating RPM(revolutions per minute) of rotating machine |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR960028091A (en)* | 1994-12-23 | 1996-07-22 | 김광호 | Fax machine with memo function during call |
| KR20020074615A (en)* | 2001-03-21 | 2002-10-04 | 주식회사 캄코 | System and method for testing heating motor of vehicle |
| KR20050080005A (en)* | 2005-06-30 | 2005-08-11 | 강성환 | Wastewater treatment apparatus with supplying tank that supplies dissolved oxygen |
- 2005
- 2005-09-07KRKR1020050083230Apatent/KR100666452B1/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR960028091A (en)* | 1994-12-23 | 1996-07-22 | 김광호 | Fax machine with memo function during call |
| KR20020074615A (en)* | 2001-03-21 | 2002-10-04 | 주식회사 캄코 | System and method for testing heating motor of vehicle |
| KR20050080005A (en)* | 2005-06-30 | 2005-08-11 | 강성환 | Wastewater treatment apparatus with supplying tank that supplies dissolved oxygen |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100963685B1 (en) | 2008-05-21 | 2010-06-15 | 울산대학교 산학협력단 | Fault diagnosis device and method through video signal conversion of machine operation sound and vibration signal |
| KR100993378B1 (en) | 2008-12-03 | 2010-11-09 | 서울대학교산학협력단 | Method and apparatus for judging combustion time of compression ignition engine |
| CN101968379A (en)* | 2010-09-30 | 2011-02-09 | 南昌航空大学 | Method for extracting characteristic information of operating condition vibration signal of aircraft engine rotor system |
| US10082520B2 (en) | 2016-03-18 | 2018-09-25 | Simmonds Precision Products, Inc. | Rotational frequency estimation from sensed vibrations based on a supervised learning method |
| KR20190000826A (en) | 2017-06-23 | 2019-01-03 | 퓨처메인 주식회사 | Automatic diagnosis method for rotating machinery using real-time vibration analysis |
| WO2021107342A1 (en)* | 2019-11-28 | 2021-06-03 | (주) 위세아이텍 | Device and method for monitoring state of vibration of rotating equipment using deep learning-based time series analysis |
| CN114742094A (en)* | 2022-03-17 | 2022-07-12 | 同济大学 | Vibration signal defect feature extraction method based on deep morphological convolution network |
| KR20230152470A (en)* | 2022-04-27 | 2023-11-03 | 한국해양과학기술원 | Apparatus and method for estimating RPM(revolutions per minute) of rotating machine |
| KR102757991B1 (en) | 2022-04-27 | 2025-01-22 | 한국해양과학기술원 | Apparatus and method for estimating RPM(revolutions per minute) of rotating machine |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102393095B1 (en) | A system for predicting and diagnosing malfunctions in rotating equipment based on artificial intelligence using vibration, sound, and image data | |
| CN110276416B (en) | Rolling bearing fault prediction method | |
| EP3615899B1 (en) | Systems and methods for monitoring of mechanical and electrical machines | |
| US10520397B2 (en) | Methods and apparatuses for defect diagnosis in a mechanical system | |
| CN111122191B (en) | Equipment health alarm threshold setting method based on EWMA control | |
| JP2008014679A (en) | Equipment diagnostic method, equipment diagnostic system, and computer program | |
| KR100666452B1 (en) | Diagnosis method of rotating machine and diagnostic system using the method | |
| Kumar et al. | A brief review of condition monitoring techniques for the induction motor | |
| US11429900B1 (en) | Systems and methods for automatic detection of error conditions in mechanical machines | |
| US20200220525A1 (en) | Method For Automatic Detection of Physical Modes In A Modal Analysis Model | |
| KR20210006832A (en) | Method and apparatus for machine fault diagnosis | |
| KR20240076319A (en) | Fault Diagnosis Method for Electrical Rotating Equipment Using Machine Learning Classification Model | |
| Liu et al. | Fault diagnosis of ball bearing elements: A generic procedure based on time-frequency analysis | |
| CN117609869A (en) | Intelligent fault diagnosis and self-learning method and system for reducer | |
| Wang et al. | Multi-domain extreme learning machine for bearing failure detection based on variational modal decomposition and approximate cyclic correntropy | |
| JP4100413B2 (en) | Equipment monitoring method and equipment monitoring apparatus | |
| CN107305159A (en) | The method for diagnosing faults and device of a kind of main exhauster of sintering | |
| Giantomassi et al. | Signal based fault detection and diagnosis for rotating electrical machines: Issues and solutions | |
| Çaliş et al. | Artificial immunity-based induction motor bearing fault diagnosis | |
| Magadán et al. | Explainable and interpretable bearing fault classification and diagnosis under limited data | |
| JP2006300896A (en) | Facility monitoring method and facility monitoring device | |
| EP4194979A1 (en) | System and method for monitoring condition of an electromechanical system | |
| Hou et al. | Bearing fault diagnosis based on spatial features of 2.5 dimensional sound field | |
| CN118503926B (en) | Intelligent electromechanical comprehensive diagnosis, monitoring method and system based on industrial Internet | |
| CN107305238A (en) | The method for diagnosing faults and device of a kind of main exhauster of sintering |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| D13-X000 | Search requested | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D13-srh-X000 | |
| D14-X000 | Search report completed | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D14-srh-X000 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| E13-X000 | Pre-grant limitation requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-3-E10-E13-lim-X000 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | Fee payment year number:1 St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| P14-X000 | Amendment of ip right document requested | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-P10-P14-nap-X000 | |
| P16-X000 | Ip right document amended | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-P10-P16-nap-X000 | |
| Q16-X000 | A copy of ip right certificate issued | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q16-nap-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee | ||
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | Not in force date:20100104 Payment event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U13-oth-PC1903 | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | Ip right cessation event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE Not in force date:20100104 St.27 status event code:N-4-6-H10-H13-oth-PC1903 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 |