KR100650718B1 - Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method - Google Patents
Phase change memory device and its manufacturing methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100650718B1 KR100650718B1KR1020040050069AKR20040050069AKR100650718B1KR 100650718 B1KR100650718 B1KR 100650718B1KR 1020040050069 AKR1020040050069 AKR 1020040050069AKR 20040050069 AKR20040050069 AKR 20040050069AKR 100650718 B1KR100650718 B1KR 100650718B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- film
- upper electrode
- interlayer insulating
- phase change
- insulating film
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N70/00—Solid-state devices having no potential barriers, and specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching
- H10N70/20—Multistable switching devices, e.g. memristors
- H10N70/231—Multistable switching devices, e.g. memristors based on solid-state phase change, e.g. between amorphous and crystalline phases, Ovshinsky effect
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N70/00—Solid-state devices having no potential barriers, and specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching
- H10N70/801—Constructional details of multistable switching devices
- H10N70/821—Device geometry
- H10N70/826—Device geometry adapted for essentially vertical current flow, e.g. sandwich or pillar type devices
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N70/00—Solid-state devices having no potential barriers, and specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching
- H10N70/801—Constructional details of multistable switching devices
- H10N70/841—Electrodes
- H10N70/8416—Electrodes adapted for supplying ionic species
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N70/00—Solid-state devices having no potential barriers, and specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching
- H10N70/801—Constructional details of multistable switching devices
- H10N70/881—Switching materials
- H10N70/882—Compounds of sulfur, selenium or tellurium, e.g. chalcogenides
Landscapes
- Semiconductor Memories (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean도 1은 상변환 메모리 셀을 프로그램 및 소거시키는 방법을 설명하기 위한 도면.1 is a diagram for explaining a method of programming and erasing a phase change memory cell.
도 2는 종래 상변환 메모리 셀을 설명하기 위한 도면.2 is a diagram for explaining a conventional phase change memory cell.
도 3은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 상변환 기억 소자를 설명하기 위한 단면도.3 is a cross-sectional view illustrating a phase change memory device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 4a 내지 도 4d는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 상변환 기억 소자의 제조방법을 설명하기 위한 공정별 단면도.4A to 4D are cross-sectional views of steps for explaining a method of manufacturing a phase change memory device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
* 도면의 주요 부분에 대한 부호의 설명 *Explanation of symbols on the main parts of the drawings
21 : 반도체 기판22 : 층간절연막21
23 : 제1콘택홀24 : 콘택플러그23: first contact hole 24: contact plug
25 : 하부전극26 : 상부전극25: lower electrode 26: upper electrode
27 : 상변환막28 : 산화막27: phase change film 28: oxide film
29 : 제2콘택홀30 : 금속막29: second contact hole 30: metal film
본 발명은 상변환 기억 소자 및 그 제조방법에 관한 것으로, 보다 상세하게는, 하부전극과 상변환막과의 접촉면적을 줄여 전류량을 감소시킬 수 있는 상변환 기억 소자 및 그 제조방법에 관한 것이다.BACKGROUND OF THE
최근, 전원이 차단되더라도 저장된 데이터가 소멸되지 않는 특징을 갖는 플래쉬 메모리 소자들이 채택되고 있다. 이러한 플래쉬 메로리 소자들은 채널 상에 차례로 적층된 터널산화막, 부유게이트, 게이트 층간 유전체막(Inter-Gate Dielectric Layer) 및 컨트롤 게이트 전극을 포함한다. 따라서, 상기 플래쉬 메모리 소자들의 신뢰성 및 프로그램 효율을 향상시키기 위해서는 터널산화막의 막질이 개선되어야 하고 셀의 커플링 비율이 증가되어야 한다.Recently, flash memory devices having a feature in which stored data are not destroyed even when a power supply is cut off have been adopted. Such flash memory devices include a tunnel oxide film, a floating gate, an inter-gate dielectric layer, and a control gate electrode, which are sequentially stacked on a channel. Therefore, in order to improve the reliability and program efficiency of the flash memory devices, the film quality of the tunnel oxide film should be improved and the coupling ratio of the cell should be increased.
또한, 플래쉬 메모리 소자들 대신에 새로운 비휘발성 메모리 소자들이 최근에 제안되었다. 예를 들면, 상변환 메모리(Phase-Change Memory) 소자들이며, 상변환에 따른 전기저항 차이를 이용하여 정보를 저장하고, 찰코젠나이드(Chalcogenide) 합금재료(Ge2Sb2Te5) 박막이 비정질 상태에서 결정질 상태로 상변환을 하여 결정질 상태일 때 저항 및 활성화 에너지가 낮아지고, 장거리 원자질서와 자유전자 밀도는 높아진다. 상기 상변환 기억 소자의 장점은 Soc(System On Chip)으로 제작하기 쉬우며, 차세대 메모리 반도체 중에서 생산가격이 낮은 편이다. 상기 상변환 기억 소자의 처리속도는 5ns로 매우 빠르며, 소비전력이 낮고 동작온도의 범위는 -196∼180℃로 넓은영역을 가지고 있다.In addition, new nonvolatile memory devices have recently been proposed in place of flash memory devices. For example, these devices are phase-change memory devices, and store information by using electric resistance difference according to a phase change, and the chalcogenide alloy material (Ge2Sb2Te5) thin film is changed from an amorphous state to a crystalline state. Phase transformation results in lower resistance and activation energy when in the crystalline state, and higher long-range atomic order and free electron density. The advantages of the phase change memory device are easy to fabricate with Soc (System On Chip), and low production cost among next generation memory semiconductors. The processing speed of the phase change memory device is very fast, 5ns, low power consumption, and a wide range of operating temperature of -196 to 180 ° C.
도 1은 상변환 메모리 셀을 프로그램 및 소거시키는 방법을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.1 is a diagram for describing a method of programming and erasing a phase change memory cell.
도 1에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 상변환 박막을 용융온도(Melting Temperature : Tm)보다 높은 온도에서 제 1 동작(First Operation; T1)동안 가열한 후에 냉각시키면, 상기 상변환 박막은 비정질 상태(Amorphous State)로 변한다(A). 반면에, 상기 상변환 박막을 상기 용융온도(Tm)보다 낮고 결정화온도(Crystallization Temperature : Tc)보다 높은 온도에서 상기 제 1 동작(T1)보다 긴 제 2 동작(Second Operation : T2)동안 가열한 후에 냉각시키면, 상기 상변환 물질막은 결정상태(Crystalline State)로 변한다(B). 여기에서, 비정질 상태를 갖는 상변환 박막의 비저항은 결정질 상태를 갖는 상변환 박막의 비저항보다 높다.As shown in FIG. 1, when the phase conversion thin film is heated after cooling during a first operation (T1) at a temperature higher than a melting temperature (Tm), the phase conversion thin film is in an amorphous state. State) (A). On the other hand, after the phase conversion thin film is heated for a second operation longer than the first operation T1 at a temperature lower than the melting temperature Tm and higher than the crystallization temperature Tc, the second operation T2 is performed. Upon cooling, the phase change material film changes to a crystalline state (B). Here, the specific resistance of the phase change thin film having an amorphous state is higher than that of the phase change thin film having a crystalline state.
따라서, 읽기(Read) 모드에서 상기 상변환 박막을 통하여 흐르는 전류를 감지(Detection)함으로써, 상기 상변환 메모리 셀에 저장된 정보가 논리 '1'인지 또는 논리 '0'인지를 판별할 수 있다. 상기 상변환 박막으로는 게르마늄(Ge), 스티비움(Stibium : Sb), 텔루리움(Tellurium : Te)을 함유하는 화합물막(Compound Material Layer; 이하 GST막이라 함)이 널리 사용된다.Accordingly, by detecting the current flowing through the phase change thin film in a read mode, it is possible to determine whether the information stored in the phase change memory cell is logic '1' or logic '0'. As the phase change thin film, a compound film containing a germanium (Ge), stevilium (Sb), and tellurium (Te) (Compound Material Layer; hereinafter referred to as a GST film) is widely used.
도 2는 종래 상변환 메모리 셀을 설명하기 위한 도면이다.2 is a diagram for describing a conventional phase change memory cell.
도 2에 도시된 바와 같이, 종래 상변환 기억 소자는 하부전극(3)을 포함하는 반도체 기판(1) 상에 층간절연막(5)을 형성한다. 그 다음, 상기 층간 절연막(5)을 식각하여 소오스 영역들과 전기적으로 연결되는 콘택플러그(7)를 형성한 후에 콘택플러그(7)를 포함한 기판 결과물 상에 상변환막(9)을 형성한다. 이어서, 상기 상변환막(9) 상에 상부전극(11)을 형성한다.As shown in FIG. 2, the conventional phase change memory device forms an
상기 상변환 메모리 셀을 프로그램하기 위해 전압을 인가하면, 상기 상변환막(9)과 콘택플러그(7) 사이의 계면에서 열이 발생하여 상변환막의 일부분(9a)이 비정질 상태로 변한다. 상기 상변환막(9)과 콘택플러그(7)의 가장자리(C)의 열은 주변의 층간절연막(7)으로 확산되어 상태변화에 필요한 온도가 되지 않을 수 있다. 이로 인해, 상기 상변환막을 비정질화시킬때 상기 가장자리의 상변환막(9)이 비정질화되지 않은 비정상적 영역이 생성될 수 있다.When a voltage is applied to program the phase change memory cell, heat is generated at the interface between the
또한, 상변화 메모리 소자의 읽기(Read) 및 쓰기(Write) 동작시 상기 하부전극과 상변환막의 접촉면적이 크기 때문에 상변화에 필요한 전류량이 증가하게 되고, 이로 인해 상변환 기억 소자의 속도에도 영향을 주게된다.In addition, since the contact area between the lower electrode and the phase conversion film is large during read and write operations of the phase change memory device, the amount of current required for phase change increases, thereby affecting the speed of the phase change memory device. Will give.
따라서, 본 발명은 상기와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위해 안출된 것으로서, 하부전극과 상변환막과의 접촉면적을 줄여 전류량을 감소시킬 수 있는 상변환 기억 소자 및 그 제조방법을 제공하는데 그 목적이 있다.Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to provide a phase change memory device and a method of manufacturing the same, which reduce the amount of current by reducing the contact area between the lower electrode and the phase conversion film. .
상기 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명은, 하부패턴이 구비된 반도체 기판; 상기 하부패턴을 덮도록 반도체 기판 상에 형성된 층간절연막; 상기 층간절연막 내에 형성된 수 개의 콘택플러그; 상기 각 콘택플러그 및 이에 인접한 층간절연막 부분 상에 형성된 하부전극; 상기 하부전극들 사이의 층간절연막 부분 상에 형성된 상부전극; 상기 하부전극과 상부전극 사이의 층간절연막 부분 상에 상기 전극들과의 접하도록 형성된 상변환막; 상기 하부전극과 상부전극 및 상변환막 상에 형성되며 상 기 상부전극을 노출시키는 콘택홀이 구비된 산화막; 및 상기 상부전극과 콘택하도록 콘택홀 내부 및 산화막 상에 형성된 금속배선을 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.The present invention for achieving the above object is a semiconductor substrate provided with a lower pattern; An interlayer insulating film formed on the semiconductor substrate to cover the lower pattern; Several contact plugs formed in said interlayer insulating film; A lower electrode formed on each of the contact plugs and an interlayer insulating film portion adjacent thereto; An upper electrode formed on an interlayer insulating film portion between the lower electrodes; A phase conversion film formed on the interlayer insulating film portion between the lower electrode and the upper electrode to be in contact with the electrodes; An oxide layer formed on the lower electrode, the upper electrode, and the phase change layer and having a contact hole exposing the upper electrode; And a metal wiring formed in the contact hole and on the oxide layer to contact the upper electrode.
여기에서, 상기 하부전극은 단축 방향의 바(Bar)형태로 형성된 것을 특징으로 한다.Here, the lower electrode is characterized in that formed in the form of a bar (Bar) in the short axis direction.
또한, 본 발명은 하부패턴을 구비한 반도체 기판을 제공하는 단계; 상기 하부패턴을 덮도록 반도체 기판 상에 층간절연막을 형성하는 단계; 상기 층간절연막 내에 수 개의 콘택플러그를 형성하는 단계; 상기 콘택플러그를 포함한 층간절연막 상에 도전막을 형성하는 단계; 상기 도전막을 식각하여 각 콘택플러그와 콘택되는 하부전극들과 이웃하는 하부전극들 사이에 배치되는 상부전극을 동시에 형성하는 단계; 상기 하부전극과 상부전극을 포함한 층간절연막 상에 상변환막을 형성하는 단계; 상기 하부전극과 상부전극 사이에만 잔류되도록 상변환막을 에치백하는 단계; 상기 하부전극과 상변환막 및 상부전극 상에 산화막을 형성하는 단계; 상기 산화막을 식각하여 상부전극을 노출시키는 콘택홀을 형성하는 단계; 상기 콘택홀을 매립하도록 산화막 상에 금속막을 증착하는 단계; 및 상기 금속막을 식각하여 상부전극과 콘택되는 금속배선을 형성하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In addition, the present invention provides a semiconductor substrate having a lower pattern; Forming an interlayer insulating film on the semiconductor substrate so as to cover the lower pattern; Forming several contact plugs in the interlayer insulating film; Forming a conductive film on the interlayer insulating film including the contact plug; Etching the conductive layer to simultaneously form an upper electrode disposed between each of the contact plugs and lower electrodes contacted with neighboring lower electrodes; Forming a phase conversion film on the interlayer insulating film including the lower electrode and the upper electrode; Etching back a phase conversion film so as to remain only between the lower electrode and the upper electrode; Forming an oxide film on the lower electrode, the phase conversion film, and the upper electrode; Etching the oxide layer to form a contact hole exposing an upper electrode; Depositing a metal film on an oxide film to fill the contact hole; And etching the metal film to form a metal wire in contact with the upper electrode.
여기에서, 상기 도전막은 폴리실리콘막 또는 금속막인 것을 특징으로 한다.Here, the conductive film is characterized in that the polysilicon film or a metal film.
상기 산화막은 SOG, PSG, TEOS, BPSG, USG, HLD 및 HDP 산화막으로 구성된 그룹으로부터 선택되는 어느 하나로 이루어진 것을 특징으로 한다.The oxide film is characterized in that it is made of any one selected from the group consisting of SOG, PSG, TEOS, BPSG, USG, HLD and HDP oxide film.
(실시예)(Example)
이하, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예에 대해 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 상세하게 설명한다.Hereinafter, exemplary embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
도 3은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 상변환 기억 소자를 설명하기 위한 단면도이다.3 is a cross-sectional view illustrating a phase change memory device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
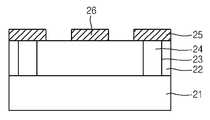
도 3에 도시된 바와 같이, 본 발명의 상변환 기억 소자는 하부패턴(미도시)이 구비된 반도체 기판(21) 상에 하부패턴을 덮도록 층간절연막(22)을 포함한다. 상기 층간절연막(22) 내에 콘택플러그(24)가 형성되어 있으며, 상기 각 콘택플러그(24) 및 이에 인접한 층간절연막(22) 부분 상에 하부전극(25)이 형성된다. 상기 하부전극들(25) 사이의 층간절연막(22) 부분 상에 상부전극(26)이 형성된다. 상기 하부전극(25)과 상부전극(26)사이의 층간절연막(22) 부분 상에 상기 전극들과 접하도록 상변환막(27)이 형성된다.As shown in FIG. 3, the phase change memory device of the present invention includes an
상기 하부전극(25)과 상부전극(26) 및 상변화막(27) 상에 형성되며, 상기 상부전극(26)을 노출시키는 콘택홀(29)이 구비된 산화막(28)이 형성된다. 상기 상부전극(26)과 콘택하도록 콘택홀(29) 내부 및 산화막(28) 상에 금속배선(30)이 형성된다.An
상기 하부전극(25)과 상부전극(26)은 동시에 형성되며, 상기 하부전극(25)은 단축방향의 바(Basr)형태로 형성된다. 또한, 하부전극(25)은 폴리실리콘막 또는 금속막으로 형성하는 것이 바람직하다. 상기 산화막(28)은 SOG, PSG, TEOS, BPSG, USG, HLD 및 HDP 산화막으로 구성된 그룹으로부터 선택되는 어느 하나로 이루어진다. 상기 상변환막(27)은 Ge1Sb2Te4 및 Ge2Sb2Te로 형성하는 것이 바람직하다.The
상기 상변화 메모리 소자의 읽기(Read) 및 쓰기(Write) 동작시 상기 상변환 막(27)의 접촉면에서 열이 발생하면 상기 상변화막의 상태가 비정질 상태 또는 결정질 상태로 변한다. 본 발명의 상변환 기억 소자는 상변환막이 하부전극의 측벽(D)에만 접촉하도록 형성함으로써 하부전극과 상변환막과의 접촉면적을 줄일 수 있으며, 이로 인해 상변화에 필요한 전류량을 감소시킬 수 있다.When heat is generated at the contact surface of the
도 4a 내지 도 4d는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 상변환 기억 소자의 제조방법을 설명하기 위한 공정별 단면도이다.4A through 4D are cross-sectional views illustrating processes of manufacturing a phase change memory device according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention.
도 4a에 도시된 바와 같이, 하부패턴(미도시)을 구비한 반도체 기판(21)을 제공하고, 상기 하부패턴을 덮도록 층간절연막(22)을 형성한다. 그 다음, 상기 층간절연막(22)을 식각하여 제1콘택홀(23)을 형성한 후에 상기 제1콘택홀(23)을 매립하여 콘택플러그(24)를 형성한다.As shown in FIG. 4A, a
도 4b에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 콘택플러그(24)를 포함한 층간절연막(22) 상에 도전막을 형성한다. 상기 도전막을 식각하여 각 콘택플러그(24)와 콘택되는 하부전극들(25)과 이웃하는 하부전극들(25) 사이에 배치되는 상부전극(26)을 동시에 형성한다. 이때, 상기 도전막은 폴리실리콘막 또는 금속막으로 형성한다. 여기에서, 상기 하부전극(25)은 단축 방향의 바(Bar) 형태로 형성한다.As shown in FIG. 4B, a conductive film is formed on the
또한, 도전막을 식각하여 하부전극(25) 및 상부전극(26)을 동시에 형성함으로써, 상부전극을 형성하기 위한 공정이 필요하지 않으며, 이로 인해 공정 단순화를 얻을 수 있다.In addition, by forming the
도 4c에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 하부전극(25)과 상부전극(26)을 포함한 층간절연막(22) 상에 상변환막(27)을 형성한다. 이어서, 상기 하부전극(25) 및 상부 전극(26) 사이에만 상변환막(27)이 잔류되도록 상변환막(27)을 에치백(Etch Back) 한다. 그 다음, 상기 하부전극(25)과 상변환막(27) 및 상부전극(26) 상에 산화막(28)을 형성한다. 이때, 상기 하부전극(25)과 상변환막(27)이 접촉하고 있는 계면(E)에서 상변화가 일어난다.As shown in FIG. 4C, a
도 4d에 도시된 바와 같이, 상기 산화막(28)을 식각하여 상부전극(26)을 노출시키는 제2콘택홀(29)을 형성한다. 이어서, 상기 제2콘택홀(29)을 매립하도록 산화막(28) 상에 금속막(30)을 증착한다.As shown in FIG. 4D, the
도면에 도시되지 않았지만, 상기 금속막(30)을 식각하여 상부전극과 콘택되는 금속배선을 형성한다.Although not shown in the drawing, the
전술한 바와 같이, 본 발명은 상변환 기억 소자 제조시 하부전극과 상부전극을 동시에 형성하고 상변환막이 하부전극의 측벽에만 접촉하도록 형성함으로써 하부전극과 상변환막과의 접촉면적을 줄일 수 있으며, 이로 인해 상변화에 필요한 전류량을 감소시킬 수 있다.As described above, the present invention can reduce the contact area between the lower electrode and the phase change film by forming the lower electrode and the upper electrode at the same time and forming the phase change film to contact only the sidewalls of the lower electrode when the phase change memory device is manufactured. This can reduce the amount of current required for phase change.
이상, 본 발명을 몇 가지 예를 들어 설명하였으나, 본 발명은 이에 한정되는 것은 아니며, 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 본 발명의 사상에서 벗어나지 않으면서 많은 수정과 변형을 가할 수 있음을 이해할 것이다.In the above, the present invention has been described with reference to some examples, but the present invention is not limited thereto, and a person of ordinary skill in the art may make many modifications and variations without departing from the spirit of the present invention. I will understand.
이상에서와 같이, 본 발명은 상변화막의 상변화가 용이하게 일어나도록 하기 위해 상변환막이 하부전극의 측벽에만 접촉하도록 형성함으로써 하부전극과 상변환 막과의 접촉면적을 줄일 수 있으며, 이로 인해 상변화에 필요한 전류량을 감소시킬 수 있다.As described above, the present invention can reduce the contact area between the lower electrode and the phase change film by forming the phase change film to contact only the sidewall of the lower electrode in order to facilitate the phase change of the phase change film. The amount of current required for change can be reduced.
또한, 본 발명은 하부전극과 상부전극을 동시에 형성함으로써 상부전극을 형성하기 위한 공정이 필요하지 않으며, 이로 인해 공정 단순화를 얻을 수 있다.In addition, the present invention does not require a process for forming the upper electrode by forming the lower electrode and the upper electrode at the same time, thereby obtaining a process simplification.
Claims (5)
Translated fromKoreanPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020040050069AKR100650718B1 (en) | 2004-06-30 | 2004-06-30 | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020040050069AKR100650718B1 (en) | 2004-06-30 | 2004-06-30 | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20060001052A KR20060001052A (en) | 2006-01-06 |
| KR100650718B1true KR100650718B1 (en) | 2006-11-27 |
Family
ID=37104250
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020040050069AExpired - Fee RelatedKR100650718B1 (en) | 2004-06-30 | 2004-06-30 | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100650718B1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101006517B1 (en)* | 2004-06-30 | 2011-01-07 | 주식회사 하이닉스반도체 | Phase change memory device and manufacturing method thereof |
| KR101006515B1 (en)* | 2004-06-30 | 2011-01-10 | 주식회사 하이닉스반도체 | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method |
- 2004
- 2004-06-30KRKR1020040050069Apatent/KR100650718B1/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20060001052A (en) | 2006-01-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100639206B1 (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| KR100668823B1 (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| KR100668824B1 (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| US7989796B2 (en) | Nonvolatile memory cell with concentric phase change material formed around a pillar arrangement | |
| US8686393B2 (en) | Integrated circuit semiconductor devices including channel trenches and related methods of manufacturing | |
| JP2004158852A (en) | Phase change storage element and method of manufacturing the same | |
| KR101052860B1 (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| KR100650718B1 (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| JP4955218B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| KR100437457B1 (en) | Phase changeable memory cells having voids and methods of fabricating the same | |
| CN106298481A (en) | Phase transition storage and forming method thereof | |
| KR101052861B1 (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| KR100650719B1 (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| KR100997785B1 (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| KR101052862B1 (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| KR101052859B1 (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| KR20060001049A (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| KR20060001050A (en) | Manufacturing method of phase change memory device | |
| KR100650720B1 (en) | Phase change memory device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR101006515B1 (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| KR20060001088A (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| KR20060001101A (en) | Phase change memory device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR20070036939A (en) | Phase change memory device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR20060001090A (en) | Phase change memory device and its manufacturing method | |
| KR20070063810A (en) | Phase change memory device and manufacturing method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | St.27 status event code:A-1-1-Q10-Q12-nap-PG1501 | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 Fee payment year number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:4 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20101025 Year of fee payment:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:5 | |
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee | ||
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U13-oth-PC1903 Not in force date:20111122 Payment event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | St.27 status event code:N-4-6-H10-H13-oth-PC1903 Ip right cessation event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE Not in force date:20111122 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 | |
| P22-X000 | Classification modified | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-P10-P22-nap-X000 |