KR100650406B1 - Method of transmitting / receiving frame of MAC protocol in ad-hoc network using CSM / CA method - Google Patents
Method of transmitting / receiving frame of MAC protocol in ad-hoc network using CSM / CA methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100650406B1 KR100650406B1KR1020050060652AKR20050060652AKR100650406B1KR 100650406 B1KR100650406 B1KR 100650406B1KR 1020050060652 AKR1020050060652 AKR 1020050060652AKR 20050060652 AKR20050060652 AKR 20050060652AKR 100650406 B1KR100650406 B1KR 100650406B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- frame
- station
- identification
- network
- stations
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B7/00—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field
- H04B7/24—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts
- H04B7/26—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts at least one of which is mobile
- H04B7/2612—Arrangements for wireless medium access control, e.g. by allocating physical layer transmission capacity
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W74/00—Wireless channel access
- H04W74/08—Non-scheduled access, e.g. ALOHA
- H04W74/0808—Non-scheduled access, e.g. ALOHA using carrier sensing, e.g. carrier sense multiple access [CSMA]
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W84/00—Network topologies
- H04W84/18—Self-organising networks, e.g. ad-hoc networks or sensor networks
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromKoreanDescription
Translated fromKorean도 1은 본 발명이 적용되는 애드-혹 네트워크에서 인접한 지역에 여러 논리망(logical network)이 공존하는 상태를 나타낸 도면,1 is a view illustrating a state in which several logical networks coexist in an adjacent area in an ad-hoc network to which the present invention is applied;
도 2는 본 발명에 따라 하나의 논리망(logical network)이 구성된 상태와, 각 스테이션(station)이 저장하고 있는 라우팅 테이블의 예를 나타낸 도면,2 is a diagram illustrating an example of a state in which one logical network is configured and a routing table stored by each station according to the present invention;
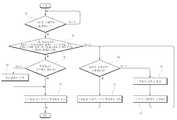
도 3은 본 발명에 따른 애드-혹 네트워크를 형성하는 논리망 내의 스테이션에서 프레임 송신시 맥 프로토콜 통신 방법의 순서도,3 is a flowchart of a MAC protocol communication method when transmitting a frame at a station in a logical network forming an ad-hoc network according to the present invention;
도 4는 본 발명에 따른 애드-혹 네트워크의 스테이션에서 사용되는 맥 프로토콜 프레임 구조도,4 is a diagram of a MAC protocol frame structure used in a station of an ad-hoc network according to the present invention;
도 5는 본 발명에 따라 두 개의 논리망 사이에 브릿지 스테이션(bridge station)이 정의된 상태를 나타낸 예와 라우팅 테이블의 구성 예를 나타낸 도면,5 is a diagram illustrating an example in which a bridge station is defined between two logical networks and a configuration example of a routing table according to the present invention;
도 6은 본 발명을 전력선 통신에 적용하여 주거지역에서 억세스 네트워크(access network) 및 홈 네트워크(home network)를 구축한 예를 나타낸 도면,6 is a view showing an example of building an access network and a home network in a residential area by applying the present invention to power line communication;
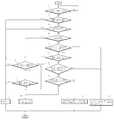
도 7은 본 발명에 따른 애드-혹 네트워크의 스테이션에서 프레임 수신시 맥 프로토콜 통신 방법의 순서도,7 is a flowchart of a MAC protocol communication method when receiving a frame at a station of an ad-hoc network according to the present invention;
< 도면의 주요부분에 대한 부호의 설명 ><Description of Symbols for Major Parts of Drawings>
1, 3, 5, 7, 50, 60 : 논리망 11~15, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29 : 스테이션1, 3, 5, 7, 50, 60: logical network 11 ~ 15, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29: station
22, 24, 22, 26, 28 : 라우팅 테이블22, 24, 22, 26, 28: routing table
51 : 브릿지 스테이션 75~78, 82~83 : 수용가51:
본 발명은 CSMA/CA 방식을 사용하는 애드-혹 네트워크에 관한 것으로서, 보다 상세하게는 애드-혹 네트워크에서 맥 프로토콜의 통신 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to an ad-hoc network using a CSMA / CA scheme, and more particularly, to a communication method of a Mac protocol in an ad-hoc network.
기존의 맥(매체접근제어, MAC) 프로토콜 중에서 CSMA/CA방식을 사용하는 것으로는 무선 랜의 기본적인 맥 프로토콜인 DCF(Distributed Coordination Function)등이 있다.Among the existing MAC protocols, the CSMA / CA method includes DCF (Distributed Coordination Function), which is a basic MAC protocol of wireless LAN.
CSMA/CA 방식의 맥 프로토콜은 프레임 전송시 신뢰성 있는 통신을 보장하기 위해 전송된 데이터에 대한 응답(Acknowledgment)을 제한된 시간 안에 수신토록 하는 ARQ (Automatic Repeat reQuest) 방식을 사용한다.CSMA / CA MAC protocol uses ARQ (Automatic Repeat reQuest) method to receive acknowledgment for transmitted data within limited time to ensure reliable communication during frame transmission.
이러한 시스템에서 브로드캐스트 프레임(broadcast frame)을 전송하고자 할 경우 모든 스테이션(station)들에 대한 응답을 동시에 수신할 수 없으므로 브로드캐스트 프레임을 수신할 스테이션 중 하나를 프록시 스테이션(proxy station)으로 삼아서 그 스테이션만이 응답을 하는 partial ARQ방식을 사용한다. 따라서, 프록시 스테이션의 존재는 CSMA/CA 방식의 맥 프로토콜이 신뢰성 있는 데이터 통신을 보장하기 위한 최소한의 조건이다.In such a system, if a broadcast frame is to be transmitted, a response to all stations cannot be received at the same time. Therefore, one of the stations to receive the broadcast frame is used as a proxy station. Only partial ARQ response is used. Therefore, the presence of the proxy station is a minimum condition for the CSMA / CA type MAC protocol to ensure reliable data communication.
CSMA/CA 방식의 맥 프로토콜을 사용하는 스테이션은 물리적 반송파감지(physical carrier sense)를 통해 채널 상에 다른 스테이션이 전송한 프레임이 있는지를 항상 관찰한다. 프레임의 전송이 감지될 경우 해당 프레임을 해석해 자신이 수신할 프레임이 아니라면 프레임이 전송되는 시간동안 가상적 반송파감지(virtual carrier sense)를 수행한다. 이러한 반송파감지 과정을 통해 전송 프레임들 간의 충돌(collision)을 최소화한다. 전송할 프레임이 있는 경우에는 백오프 절차(backoff procedure)를 통해 프레임들 간의 충돌을 최소화하여 채널을 효율적으로 사용할 수 있도록 한다. 전송을 하고자 하는 스테이션은 랜덤 백오프 타임(Random backoff time)을 설정하고 매체를 감지(sensing)하게 되는데, 매체가 idle 한 경우라면 백오프 타임(backoff time)을 줄인다. 백오프 타임이 만료되면 바로 전송을 시작한다.A station using the MAC protocol of the CSMA / CA method always observes a frame transmitted by another station on a channel through a physical carrier sense. When the transmission of a frame is detected, the frame is interpreted, and if it is not a frame to be received, the virtual carrier sense is performed during the time when the frame is transmitted. Through such a carrier detection process, collision between transmission frames is minimized. If there is a frame to be transmitted, a backoff procedure is used to minimize the collision between the frames so that the channel can be used efficiently. The station wishing to transmit sets a random backoff time and senses the medium. If the medium is idle, the station reduces the backoff time. The transmission starts as soon as the backoff time expires.
또한, 대부분의 통신기술에서 스테이션은 프레임을 전송할 때, 브로드캐스트 방식과 유니캐스트 방식을 사용한다. 브로드캐스트 방식은 동일 논리망(logical network) 내의 모든 스테이션들이 수신할 수 있도록 전송하는 방법이고, 유니캐스트 방식은 하나의 스테이션이 수신할 수 있도록 전송하는 방법이다.In addition, in most communication technologies, a station uses a broadcast method and a unicast method when transmitting a frame. The broadcast method is a method of transmitting for reception by all stations in the same logical network, and the unicast method is a method of transmitting for reception by one station.
그런데, 유니캐스트 방식을 사용하여 프레임을 전송하고자 할 때, 경우에 따라 OSI(Open Systems Interconnection) 7계층 중 물리 계층(physical layer)에서 채널 측정(channel estimation)이나 하드웨어의 메모리 할당 등 유니캐스트 통신을 위한 특별한 작업이 선행되어야 하는데, 이러한 선행작업이 완료된 상태를 통신 링크가 구축되었다고 표현한다. 실례로 전력선통신 등의 통신기술에서는 유니캐스트 통신을 위해서 스테이션(station) 사이의 각 링크마다 실시간으로 주파수특성을 파악하기 위해 채널측정을 실시해야 한다.However, when a frame is to be transmitted using the unicast method, unicast communication such as channel estimation or memory allocation is performed at the physical layer of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) layer in some cases. Special work must be done in advance, which indicates that the communication link has been established. For example, in communication technology such as power line communication, channel measurement must be performed to grasp frequency characteristics in real time for each link between stations for unicast communication.
기존의 CSMA/CA 방식의 맥 프로토콜은 모든 스테이션들의 통신신호가 서로 보이는 경우를 가정하므로 통신신호의 전송거리에 따르는 제약을 받는다. 게다가, 마스터/슬래이브(Master/Slave)의 계층구조가 맥 프로토콜에 포함되어 있을 경우, 논리적인 계층구조가 고정되어 있기 때문에 네트워크 토폴로지(topology)를 유연하게 변화시키기 어렵다. 따라서, 기존의 CSMA/CA 방식의 맥 프로토콜은 사용자의 다양한 요구에 맞추어 네트워크를 구성하기 어렵다는 단점이 있다.The conventional CSMA / CA MAC protocol assumes a case in which communication signals of all stations are seen from each other, and thus is limited by the transmission distance of the communication signals. In addition, when the Master / Slave hierarchy is included in the Mac protocol, it is difficult to flexibly change the network topology because the logical hierarchy is fixed. Therefore, the conventional MAC protocol of the CSMA / CA method has a disadvantage that it is difficult to configure the network to meet the various needs of the user.
이에 본 발명은 상기와 같은 문제점을 해소하기 위해 안출된 것으로, 물리적 네트워크에 두 개 이상의 논리망을 형성하여 공존할 수 있도록 한다. 또한, 유니캐스트 전송이 필요한 경우에만 통신 링크를 구축하기 때문에 그에 수반되는 오버헤드를 최소화하고 채널을 효율적으로 사용할 수 있는 애드-혹 네트워크의 맥 프로토콜의 프레임 송수신 방법을 제공함에 그 목적이 있다.Accordingly, the present invention has been made to solve the above problems, it is possible to coexist by forming two or more logical networks in the physical network. In addition, since a communication link is established only when unicast transmission is required, an object of the present invention is to provide a frame transmission / reception method of the MAC protocol of an ad-hoc network that can minimize the overhead and efficiently use a channel.
상기와 같은 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명은, CSMA/CA 방식을 사용하는 애드-혹 네트워크에서 맥 프로토콜의 프레임 송신 방법에 있어서, 각각이 식별 아이디를 갖는 적어도 두 개 이상의 스테이션이 상호 통신 가능하도록 이루어진 논리망에서, 스테이션이 프레임 전송시, 전송할 프레임에 포함된 목적 어드레스와 대응하는 식별 아이디가 라우팅 테이블에 존재하는지 판단하는 과정과; 상기 식별 아이디가 상기 라우팅 테이블에 존재하면 통신 링크가 구축되어 있는지 판단하는 과정과; 상기 통신 링크가 구축되어 있으면 프레임을 유니캐스트 방식으로 전송하는 과정과; 상기 식별 아이디가 상기 라우팅 테이블에 존재하지 않으면 소정의 스테이션을 프록시 스테이션으로 설정하여 상기 프레임을 브로드캐스트 방식으로 전송하는 과정으로 구성된다.In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a frame transmission method of a MAC protocol in an ad-hoc network using a CSMA / CA scheme, in which at least two stations each having an identification ID are configured to communicate with each other. In the logical network, when the station transmits a frame, determining whether an identification ID corresponding to a destination address included in a frame to be transmitted exists in the routing table; Determining whether a communication link is established if the identification ID exists in the routing table; Transmitting a frame in a unicast manner if the communication link is established; If the identification ID does not exist in the routing table, the process consists of setting a predetermined station as a proxy station and transmitting the frame in a broadcast manner.
여기서, 상기 라우팅 테이블은 사용자의 요구에 따라 수동으로 설정 및 저장하여 생성하거나, 상기 스테이션이 매 프레임 수신시 송신측 스테이션의 식별 아이디와 프레임의 목적지 어드레스를 추출하여 스테이션 식별 아이디와 목적지 어드레스의 대응관계를 자동으로 저장하여 생성하는 것이 바람직하다.Here, the routing table may be manually set and stored according to a user's request, or the station may extract the identification ID of the transmitting station and the destination address of the frame when receiving each frame, and correspond to the correspondence between the station identification ID and the destination address. It is desirable to automatically save and generate the.
상기 식별아이디가 상기 라우팅 테이블에 존재하지 않을 경우 상기 프록시 스테이션을 설정하는 과정은, 상기 프록시 스테이션이 존재하는지 판단하는 과정과; 상기 프록시 스테이션이 존재하면 프레임을 브로드캐스트 방식으로 전송하는 과정과; 상기 프록시 스테이션이 존재하지 않으면 프록시 디맨드 맥 관리 프레임을 주기적으로 전송하여 동일 논리망 내의 다른 스테이션에 자신의 존재를 알리고 응답을 요구하는 과정을 포함하는 맥 프로토콜을 사용하는 것이 바람직하다.The setting of the proxy station when the identification ID does not exist in the routing table comprises: determining whether the proxy station exists; If the proxy station exists, transmitting a frame in a broadcast manner; If the proxy station does not exist, it is preferable to use a MAC protocol including periodically transmitting a proxy demand MAC management frame to notify another station in the same logical network of its existence and requesting a response.
또한, 상기 스테이션이 프록시 서플라이 맥 관리 프레임을 수신하는 과정과; 상기 스테이션이 상기 프록시 서플라이 맥 관리 프레임을 전송한 스테이션을 프록시 스테이션으로 설정하는 과정과; 부분 ARQ(partial Automatic Repeat reQuest)를 수행하여 브로드캐스트 프레임을 전송하는 과정을 더 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.In addition, the station receives a proxy supply MAC management frame; Setting the station to which the station has transmitted the proxy supply MAC management frame as a proxy station; The method may further include transmitting a broadcast frame by performing a partial automatic repeat request (ARQ).
상기 라우팅 테이블에는 상기 프레임의 목적지 어드레스와 목적지 스테이션의 식별 아이디의 대응관계가 저장되어 있는 것이 바람직하다.Preferably, the routing table stores a correspondence between the destination address of the frame and the identification ID of the destination station.
상기 프레임은 목적지 스테이션의 식별 아이디와 소스 스테이션의 식별 아이디를 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.The frame preferably includes an identification ID of the destination station and an identification ID of the source station.
한편, 본 발명의 다른 견지에 따르면, 상기 목적은, CSMA/CA 방식을 사용하는 애드-혹 네트워크에서 맥 프로토콜의 프레임 송수신 방법에 있어서, 각각 식별 아이디를 갖는 적어도 두 개 이상의 스테이션이 상호 통신 가능하도록 구성되며, 각각이 그룹 아이디를 갖는 다수의 논리망 중에서 두 개의 논리망에 속하는 브릿지 스테이션을 설정하는 과정과; 상기 브릿지 스테이션이 소정의 스테이션으로부터 전송된 프레임을 수신하는 과정과; 상기 브릿지 스테이션이 수신된 프레임으로부터 그룹 아이디와 소스 스테이션 및 목적지 스테이션의 식별 아이디를 추출하는 과정과; 상기 브릿지 스테이션이 상기 추출한 그룹 아이디와 자신의 그룹 아이디를 비교하여 양측 논리망 중 어느 논리망에 해당하는지 판단하는 과정과; 상기 판단결과에 따라 해당 논리망에 프레임을 송신하여 두 개의 논리망 사이에 통신로를 형성하는 과정을 포함하는, CSMA/CA 방식을 사용하는 맥 프로토콜의 프레임 수신방법에 의해서 달성된다.On the other hand, according to another aspect of the present invention, in the method of transmitting and receiving the frame of the MAC protocol in the ad-hoc network using the CSMA / CA scheme, so that at least two or more stations each having an identification ID can communicate with each other Configuring a bridge station belonging to two logical networks from among a plurality of logical networks each having a group ID; The bridge station receiving a frame transmitted from a predetermined station; Extracting, by the bridge station, a group ID and identification IDs of a source station and a destination station from the received frame; Determining, by the bridge station, which logical network corresponds to both logical networks by comparing the extracted group ID with its group ID; According to the result of the determination is achieved by the frame receiving method of the MAC protocol using the CSMA / CA method comprising the step of forming a communication path between the two logical networks by transmitting a frame to the logical network.
여기서, 상기 수신된 프레임이 브로드캐스트 방식으로 전송된 것인지 유니캐스트 방식으로 전송된 것인지 판단하는 과정과; 상기 유니캐스트 방식으로 전송된 경우, 상기 프레임의 목적 어드레스에 대응하는 식별 아이디를 자신의 식별 아이디와 비교하여 일치하면, 상기 프레임을 수신하여 상위계층으로 전달하는 과정과, 상기 브로드캐스트 방식으로 전송된 경우, 곧바로 상기 프레임을 수신하여 상위계층으로 전달하는 과정을 더 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.Determining whether the received frame is transmitted by broadcast or unicast; When the transmission is transmitted by the unicast method, if the identification ID corresponding to the destination address of the frame matches with the identification ID of the frame, receiving the frame and transmitting the received ID to a higher layer; In this case, it is preferable to further include the step of immediately receiving the frame to pass to the upper layer.
상기 스테이션은 사용자의 요구에 따라 링크 허용된 스테이션들의 식별 아이디를 링크 허용 테이블로 저장하여 통신허용된 스테이션과 선별적으로 통신하게 하는 링크 제한 기능을 가지며; 상기 스테이션은 프레임 수신시 상기 링크 허용 테이블에 기초하여 식별 아이디의 스테이션에서 전송된 프레임만을 처리하는 것이 바람직하다.The station has a link restriction function for storing identification IDs of the stations allowed to link according to a user's request in a link permission table to selectively communicate with the communication allowed stations; Preferably, the station processes only the frames transmitted from the station of the identification ID based on the link grant table upon receiving the frame.
한편, 본 발명의 또 다른 견지에 따르면, 상기 목적은, CSMA/CA 방식을 사용하는 애드-혹 네트워크에서 맥 프로토콜의 프레임 송수신 방법에 있어서, 각각 식별 아이디를 갖는 적어도 두 개 이상의 스테이션이 상호 통신 가능하도록 구성되며, 각각이 그룹 아이디를 갖는 다수의 논리망 중에서 두 개의 논리망에 속하는 브릿지 스테이션을 설정하는 과정과; 상기 브릿지 스테이션이 소정의 스테이션으로부터 전송된 프레임을 수신하는 과정과; 상기 브릿지 스테이션이 수신된 프레임으로부터 그룹 아이디 및 식별 아이디를 추출하는 과정과; 상기 브릿지 스테이션이 상기 추출한 그룹 아이디 및 식별 아이디와 미리 저장된 라우팅 테이블을 비교하여 상기 수신한 프레임이 양측 논리망 중 어느 논리망에 해당하는지 판단하는 과정과; 상기 판단결과에 따라 해당 논리망에 프레임을 송신하여 두 개의 논리망 사이에 통신로를 형성하는 과정을 포함하여 달성될 수 있다.On the other hand, according to another aspect of the present invention, the object is, in the ad-hoc network using the CSMA / CA scheme in the frame transmission and reception method of the MAC protocol, at least two or more stations each having an identification ID can communicate with each other Configuring a bridge station belonging to two logical networks from among a plurality of logical networks each having a group ID; The bridge station receiving a frame transmitted from a predetermined station; Extracting, by the bridge station, a group ID and an identification ID from the received frame; Determining, by the bridge station, which logical network the received frame corresponds to by comparing the extracted group ID and identification ID with a previously stored routing table; And forming a communication path between the two logical networks by transmitting a frame to the logical network according to the determination result.
상기 브릿지 스테이션은 두 개의 그룹 아이디를 가짐으로써 양측의 논리망 내의 스테이션과 모두 통신가능한 것이 바람직하다.The bridge station preferably has two group IDs so that it can communicate with stations in both logical networks.
상기 브릿지 스테이션이 소정의 스테이션으로부터 전송된 프레임을 수신하여 재전송하는 과정은, 상기 프레임이 브로드캐스트 프레임으로 전송된 것인지 유니캐스트로 전송된 것인지 판단하는 제1과정과; 상기 판단결과 유니캐스트로 전송된 프레임이면 상기 프레임의 목적지 스테이션의 식별 아이디가 자신의 식별 아이디와 일치하는지 판단하는 제2과정과; 상기 목적지 스테이션의 식별 아이디가 자신의 식별 아이디와 일치하면, 최종 목적지 스테이션을 찾기 위해, 수신된 프레임에 대응하는 식별 아이디와 그룹 아이디가 라우팅 테이블에 존재하는지 검색하는 제3과정과; 상기 판단결과 상기 라우팅 테이블에 존재하면, 상기 라우팅 테이블에서 검색한 그룹 아이디가 상기 수신한 프레임의 그룹 아이디와 일치하는 지 판단하여 일치하면 프레임을 수신하여 상위 계층으로 전달하는 과정을 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.Receiving and retransmitting a frame transmitted from a predetermined station by the bridge station includes: a first step of determining whether the frame is transmitted in a broadcast frame or unicast; A second step of determining whether the identification ID of the destination station of the frame matches the identification ID of the frame if the frame is transmitted through unicast as a result of the determination; If the identification ID of the destination station matches its identification ID, searching for whether an identification ID and a group ID corresponding to the received frame exist in the routing table to find a final destination station; If the determination result is present in the routing table, determining whether the group ID searched from the routing table matches the group ID of the received frame, and if it matches, receiving the frame and delivering the frame to a higher layer. .
여기서, 상기 제2과정의 판단결과 수신된 프레임의 그룹 아이디와 상기 라우팅 테이블에서 검색한 그룹 아이디가 일치하지 않으면, 상기 라우팅 테이블에서 검색한 식별 아이디와 그룹 아이디로 프레임을 유니캐스트로 전송하는 과정을 더 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.Here, if the group ID of the received frame and the group ID searched from the routing table do not match as a result of the determination of the second process, transmitting the frame by unicast with the identification ID and the group ID searched from the routing table. It is preferable to further include.
또한, 상기 제1과정의 판단결과, 수신된 프레임이 브로드캐스트로 전송된 것 이면, 상기 프레임을 상위계층으로 전달함과 동시에 다른 논리망으로 프레임을 브로드캐스트 방식으로 재전송하는 과정을 더 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.The method may further include transmitting the frame to a higher layer and retransmitting the frame to another logical network in a broadcast manner when the received frame is transmitted by broadcast. desirable.
또한, 상기 제2과정의 판단결과, 수신된 프레임에 대응되는 식별 아이디와 그룹 아이디가 라우팅 테이블에 존재하지 않으면, 상기 프레임을 상위계층으로 전달함과 동시에 다른 논리망으로 프레임을 브로드캐스트 방식으로 재전송하는 과정을 더 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.In addition, if the identification ID and the group ID corresponding to the received frame do not exist in the routing table as a result of the determination of the second process, the frame is transmitted to a higher layer and the frame is retransmitted to another logical network in a broadcast manner. It is preferable to further include a process.
여기서, 상기 브릿지 스테이션의 라우팅 테이블에는 상위 계층의 어드레스와 식별 아이디의 대응관계와, 스테이션의 식별 아이디와 그 스테이션이 속한 논리망의 그룹 아이디의 대응관계가 저장되어 있는 것이 바람직하다.Here, it is preferable that the correspondence relationship between the address of the upper layer and the identification ID and the correspondence relationship between the identification ID of the station and the group ID of the logical network to which the station belongs are stored in the routing table of the bridge station.
상기 스테이션은 사용자의 요구에 따라 링크 허용된 스테이션들의 식별 아이디를 링크 허용 테이블로 저장하여 통신허용된 스테이션과 선별적으로 통신하게 하는 링크 제한 기능을 가지며; 상기 스테이션은 프레임 수신시 상기 링크 허용 테이블에 기초하여 식별 아이디의 스테이션에서 전송된 프레임만을 처리하는 것이 바람직하다.The station has a link restriction function for storing identification IDs of the stations allowed to link according to a user's request in a link permission table to selectively communicate with the communication allowed stations; Preferably, the station processes only the frames transmitted from the station of the identification ID based on the link grant table upon receiving the frame.
이하 본 발명을 첨부된 예시도면에 의거 상세히 설명한다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
본 발명은 맥 프로토콜(매체접근제어, MAC)의 일종으로 충돌회피기능 부착 반송파감지 다중접속(CSMA/CA)을 그 기반으로 한다.The present invention is based on a carrier detection multiple access (CSMA / CA) with collision avoidance function as a kind of MAC protocol (media access control, MAC).
애드-혹 방식이란 모든 스테이션들이 제어기능의 차이나 논리적 계층의 차이 없이 동등한 입장에서 서로 네트워크를 구성하여 통신하는 네트워크의 구조를 말한다. 애드-혹 방식은 마스터 스테이션(master station)이나 억세스 포인트(access point)와 같은 배타적인 권한을 가진 제어 스테이션(control station)없이 개별 스테이션들이 필요에 따라 통신 링크를 구축하므로 다양한 네트워크 토폴로지(network topology)에 적용될 수 있다. 즉 통신 링크 구축의 대상이 제한되어 있지 않으므로 유연한 네트워크 구성이 가능하다.The ad-hoc method is a network structure in which all stations communicate with each other by forming a network in an equal position without difference in control functions or logical layer differences. The ad-hoc approach uses a variety of network topologies, as individual stations establish communication links as needed, without the need for exclusive control stations such as master stations or access points. Can be applied to That is, since the target of communication link establishment is not limited, flexible network configuration is possible.
다중 논리 그룹(multiple logical group)의 공존이란 하나의 물리망(physical network)에 둘 이상의 논리망(logical network)이 공존할 수 있도록 하는 기능이다. 다중 논리 그룹의 공존을 이용해 채널을 물리적으로 분리하지 않고도 서로 다른 네트워크를 동시에 같은 장소에서 구성할 수 있기 때문에, 전체 네트워크를 다양한 토폴로지에 맞추어 구축할 수 있다. 이는 전력선통신이나 무선 랜 등과 같이 전달매체를 공유하는 통신기술에서 매우 유용하게 쓰일 수 있는 기술이다.Coexistence of multiple logical groups is a function that allows two or more logical networks to coexist in one physical network. With the coexistence of multiple logical groups, different networks can be configured in the same place at the same time without physically separating channels, allowing the entire network to be built for a variety of topologies. This is a technology that can be very useful in communication technology sharing the transmission medium, such as power line communication or wireless LAN.
리피터(repeater) 기능은 전송된 프레임을 다른 스테이션이 수신한 후 다시 전송하는 기능이다. 리피터 기능을 사용할 경우 하나의 스테이션에서 전송된 신호가 도달할 수 있는 거리의 제약을 극복할 수 있다. 따라서, 멀리 떨어져 있는 스테이션도 리피터를 반복적으로 사용하면 통신이 가능하다.The repeater function is a function of transmitting a transmitted frame again after another station receives it. The repeater function overcomes the limitation of the distance that a transmitted signal can reach from one station. Therefore, even distant stations can communicate by using repeaters repeatedly.
본 발명은 위와 같은 기술적 과제들을 효율적으로 수행할 수 있는 방법을 제시하여 어떠한 토폴로지의 통신망(communication network)에도 효과적으로 적용될 수 있는 맥 프로토콜을 구현한다.The present invention proposes a method that can efficiently perform the above technical problems to implement a Mac protocol that can be effectively applied to any communication network (communication network) of any topology.
본 발명에서 제시된 맥 프로토콜에서 각각의 스테이션(station)은 스테이션 ID(이하 'SID'라 칭함)와 그룹 ID(이하 'GID'라 칭함)를 가진다. SID는 스테이션마다 고유하게 부여되는 식별자로서 하나의 스테이션을 다른 스테이션들과 구분하는 기준이 된다. SID에 따른 기능의 차이는 허용되지 않으며, 모든 스테이션은 동등한 입장에서 동일한 기능으로 서로 통신을 한다. GID는 하나의 논리망(logical network)에 부여되는 식별자로서, 논리망은 서로 통신 가능한 둘 이상의 스테이션들이 모여 구성한다. 브릿지 스테이션을 제외한 모든 스테이션은 동일한 GID를 가지는 스테이션들과만 통신할 수 있다.In the MAC protocol proposed in the present invention, each station has a station ID (hereinafter referred to as 'SID') and a group ID (hereinafter referred to as 'GID'). SID is an identifier uniquely assigned to each station, and serves as a criterion for distinguishing one station from other stations. Function differences according to SIDs are not allowed, and all stations communicate with each other with the same function on the same side. GID is an identifier given to one logical network, and a logical network is composed of two or more stations that can communicate with each other. All stations except the bridge station can communicate only with stations having the same GID.
각각의 스테이션은 수신하는 프레임의 GID를 확인하여 자신의 GID와 동일한 경우에만 이를 처리하여 상위 계층으로 전달하고 그렇지 않은 경우에는 수신한 프레임을 무시한다. 이러한 과정을 통해 서로 다른 GID로 구분된 다수의 논리망들이 간섭하거나 통신하지 않고 동일한 물리망(physical network)에 공존할 수 있다. 이렇게 정의된 논리망을 본 발명에서는 셀(Cell)이라고 칭한다. 이는 독립적으로 존재하며 통신의 개별적인 단위가 되는 각각의 논리망의 특성을 강조하여 표현한 말이다.Each station checks the GID of the received frame, processes it only if it is identical to its own GID, and delivers it to the upper layer. Otherwise, the station ignores the received frame. Through this process, multiple logical networks separated by different GIDs can coexist in the same physical network without interfering or communicating. The logical network defined as described above is called a cell in the present invention. It is an expression that emphasizes the characteristics of each logical network that exists independently and becomes a separate unit of communication.
이와 같이, 본 발명은 계층구조가 없는 애드-혹(ad-hoc) 방식을 기본으로 하여 동작하고 다중 논리 그룹(multiple logical group)의 공존과 리피터 기능을 지원함으로써 다양한 토폴로지(topology)로 유연하게 네트워크를 구성할 수 있는 효율적인 맥 프로토콜을 구현한 것이다.As described above, the present invention operates on the basis of a hierarchical ad-hoc method and supports network coexistence and repeater functions of multiple logical groups, thereby flexibly networking in various topologies. It is an efficient Mac protocol that can be configured.
도 1은 인접한 지역에 여러 논리망이 공존하는 상태를 나타낸 도면이다. 도 1에 나타난 각각의 스테이션(station)들은 SID와 GID를 가지며, 동일한 GID를 가진 스테이션들만이 서로 통신할 수 있다. 도 1에서 통신 가능한 스테이션들 사이에 구축되는 통신 링크를 실선 및 점선으로 표현하였다. 실선은 실제로 통신 링크가 구 축되었음을 나타내고, 점선은 통신 링크가 구축되지는 않았지만 서로 통신 가능하여 필요에 따라 통신 링크가 구축될 수 있음을 나타낸다. 동일한 논리망에 속하는 모든 스테이션들이 실선 및 점선으로 연결되어 있는 것은 동일한 논리망에 속하는 스테이션들이 상대에 대한 제약 없이 모두 서로 통신 가능하다는 것을 보여주고 있다.1 is a diagram illustrating a state in which several logical networks coexist in an adjacent region. Each station shown in FIG. 1 has an SID and a GID, and only stations with the same GID can communicate with each other. In FIG. 1, a communication link established between communicable stations is represented by a solid line and a dotted line. The solid line actually indicates that the communication link is established, and the dotted line indicates that although the communication link is not established, it can communicate with each other so that the communication link can be established as necessary. The connection of all the stations belonging to the same logical network with solid and dashed lines shows that the stations belonging to the same logical network can communicate with each other without restriction of the other party.
또한, 각각의 스테이션은 라우팅 테이블(routing table)이라는 어드레스 맵핑 테이블(address mapping table)을 가진다. 라우팅 테이블은 상위 계층의 어드레스(address)와 맥 프로토콜의 SID의 대응관계를 저장하는 맵핑 테이블(mapping table)로서, 한 스테이션 내의 맥 프로토콜이 상위 계층에서 전달받은 프레임을 전송하고자 할 때 수신할 스테이션(station)을 결정하는 기준이 된다.Each station also has an address mapping table called a routing table. The routing table is a mapping table that stores the correspondence between the address of the upper layer and the SID of the MAC protocol. The routing table is a station to receive when the MAC protocol in one station wants to transmit a frame received from the upper layer. It is a standard for determining a station.
라우팅 테이블은 수동으로 설정 및 저장되어 생성되거나 매 프레임 수신시 소스 스테이션(source station)의 SID와, 전달된 프레임에 포함된 상위 프레임의 소스 어드레스(source address)를 자동으로 저장하는 동적인 방식으로 SID와 상위 계층의 어드레스의 대응관계를 저장한다. 프레임을 송신하고자 하는 스테이션(station)은 상위 계층에서 전달받은 프레임의 목적지 어드레스(destination address)를 확인하고 이와 대응되는 SID를 라우팅 테이블(routing table)에서 검색함으로써 프레임의 목적지 스테이션(destination station)을 확인한다. 이는 본 발명에서 애드-혹 네트워크를 구현하기 위해 사용한 방법으로, 각각의 스테이션이 능동적으로 프레임을 수신할 스테이션을 확인함으로써 한 스테이션이 미리 정해지지 않은 임의의 스테이션과 통신이 가능하도록 한다.The routing table is created and stored manually, or the SID in a dynamic manner that automatically stores the source station's SID and the source address of the upper frame included in the delivered frame upon receipt of each frame. And the correspondence between the addresses of the upper layer and the upper layer. The station to which the frame is to be transmitted checks the destination address of the frame received from the upper layer and the destination station of the frame by retrieving the corresponding SID from the routing table. do. This is the method used to implement the ad-hoc network in the present invention, whereby each station actively identifies a station to receive a frame, so that one station can communicate with any station that is not predetermined.
라우팅 테이블을 이용한 애드-혹 네트워크의 구현에 있어, 각 스테이션이 프레임을 전송할 때 이루어지는 자세한 과정은 다음과 같다.In the implementation of the ad-hoc network using the routing table, the detailed process performed when each station transmits a frame is as follows.
스테이션이 전송할 프레임을 상위 계층으로부터 전달받은 경우 프레임의 목적지 어드레스(destination address)를 살펴보고 자신의 라우팅 테이블(routing table)에서 그 목적지 어드레스와 대응하는 SID가 존재하는지 확인한다. 라우팅 테이블에 프레임이 전달될 SID가 존재하지 않을 경우 전송 스테이션은 프레임을 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 전송하고, 라우팅 테이블에 SID가 존재할 경우 해당 스테이션으로 프레임을 유니캐스트 방식으로 전송한다. 이때, 프레임을 유니캐스트 방식으로 전송하려면 통신 링크가 구축되어야 하므로, 프레임을 수신할 스테이션과의 통신 링크가 구축되지 않은 상태라면 통신 링크 구축과정을 마친 후 전송한다.When a station receives a frame to be transmitted from a higher layer, the station looks at a destination address of the frame and checks whether a corresponding SID exists in its routing table. If there is no SID to which a frame is to be delivered in the routing table, the transmitting station transmits the frame in a broadcast manner. If the SID exists in the routing table, the transmitting station transmits the frame to the corresponding station in a unicast manner. At this time, since the communication link must be established in order to transmit the frame in the unicast method, if the communication link with the station to receive the frame is not established, the communication link is completed and then transmitted.
이와 같이 통신상대가 정해진 상황에서는 유니캐스트 방식으로 통신을 하고 통신 상대가 정해지지 않은 상황에서는 브로드캐스트 방식으로 통신을 하므로, 각 스테이션(station)은 불특정한 상대와도 서로 통신할 수 있다.As described above, since communication is performed in a unicast manner when a communication partner is determined, and in a broadcast manner when a communication partner is not determined, each station can communicate with an unspecified partner.
또한, 데이터를 전송할 필요가 있는 스테이션에만 통신 링크를 구축함으로써 통신 링크 구축에 수반되는 오버헤드(overhead)를 최소화 할 수 있고, 이는 채널의 효율적인 사용을 보장한다.In addition, establishing a communication link only to stations that need to transmit data can minimize the overhead involved in establishing the communication link, which ensures efficient use of the channel.
도 2는 하나의 논리망(20)이 구성된 상태와, 각 스테이션이 저장하고 있는 라우팅 테이블(22, 24, 26, 28, 30)의 예를 나타낸 도면이다. 각각의 스테이션(station)(21, 23, 25. 27, 29)은 GID와 SID를 가지고 있고, 자신과 대응되는 상위 계층의 어드레스(address)를 가지고 있다. 또한, 각 스테이션(21, 23, 25. 27, 29) 은 자신과 통신하는 스테이션들에 대한 어드레스 정보를 자신의 라우팅 테이블에 저장하고 있다.FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a state where one
모든 스테이션(21, 23, 25, 27, 29)은 각각 SID로 S1~S5를 가지며, 모두 GID로 G1을 가지므로 동일한 논리망에 속한다.All
도2에서 나타난 바에 따르면 스테이션 사이의 실선은 이미 구축된 통신 링크를 나타내므로, 스테이션 S1은 스테이션 S3, S4, S5와 통신 링크가 구축되어 있고, 스테이션 S2는 스테이션 S4와만 통신 링크가 구축되어 있다는 것을 알 수 있다. 마찬가지로 스테이션 S3은 스테이션 S1과만 통신 링크가 구축되어 있고, 스테이션 S4는 스테이션 S1, S2, S5와 통신 링크가 구축되어 있으며, 스테이션 S5는 스테이션 S1과 스테이션 S4와 통신 링크가 구축되어 있는 것을 알 수 있다. 덧붙여, 스테이션 사이의 점선은 각 스테이션이 필요에 따라 통신 링크를 구축할 수 있다는 것을 나타낸 것이다.As shown in Fig. 2, since the solid line between stations represents an already established communication link, station S1 has a communication link established with stations S3, S4, and S5, and station S2 has only a communication link established with station S4. Able to know. Similarly, it can be seen that station S3 has a communication link established only with station S1, station S4 has a communication link established with stations S1, S2, and S5, and station S5 has a communication link established with stations S1, S4. . In addition, dashed lines between stations indicate that each station can establish a communication link as needed.
스테이션 S1(21)의 기준에서 프레임의 전송 과정을 살펴보면, 스테이션 S1(21)이 상위계층에서 프레임을 전달받고 그 프레임의 목적지 어드레스(destination address)를 추출한다. 이 때의 목적지 어드레스가 D인 경우, 스테이션 S1은 자신의 라우팅 테이블에서 D에 대응하는 스테이션이 S4임을 찾을 수 있다. 따라서 이 경우에는 스테이션 S4로 프레임을 유니캐스트 방식으로 전송하여 스테이션 S4가 프레임을 수신하도록 한다.Looking at the transmission process of the frame in the reference of the station S1 (21), the station S1 (21) receives the frame from the upper layer and extracts the destination address (destination address) of the frame. If the destination address at this time is D, the station S1 may find that the station corresponding to D is S4 in its routing table. In this case, therefore, the frame is transmitted to the station S4 in a unicast manner so that the station S4 receives the frame.
반면, 상위에서 전달받은 프레임의 목적지 어드레스가 B라면, 스테이션 S1은 자신의 라우팅 테이블에서 어드레스(B)와 대응하는 SID(S2)를 찾을 수 없게 된다. 이 경우에 S1은 프레임을 브로드캐스트 방식으로 전송하여 스테이션 S2가 프레임을 수신할 수 있도록 한다.On the other hand, if the destination address of the frame received from the upper layer is B, the station S1 cannot find the SID S2 corresponding to the address B in its routing table. In this case, S1 transmits the frame in a broadcast manner so that station S2 can receive the frame.
만약, 프레임을 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 전달하고자 할 때 프록시 스테이션(proxy station)이 설정되어 있지 않으면 partial ARQ를 사용할 수 없다. 따라서, 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 전송하는 프레임의 신뢰성이 보장되지 않는다. 여기서, partial ARQ는 브로드캐스트 프레임을 수신할 스테이션 중 하나를 프록시 스테이션(proxy station)으로 삼아서 그 스테이션만이 응답을 하는 것이다.If a proxy station is not set when the frame is to be broadcasted, partial ARQ cannot be used. Therefore, the reliability of the frame transmitted by the broadcast method is not guaranteed. In this case, the partial ARQ uses one of the stations to receive the broadcast frame as a proxy station so that only the station responds.
이 경우 먼저, 스테이션은 프록시 디맨드(proxy demand)라는 본 맥 프로토콜 고유의 맥 관리 프레임(MAC management frame)을 주기적으로 전송해 동일한 논리망 내의 다른 스테이션에게 자신의 존재를 알리고 그 응답을 요구한다.In this case, first, the station periodically transmits a MAC management frame unique to this MAC protocol called proxy demand to inform other stations in the same logical network of its existence and request a response.
프록시 디맨드(proxy demand)라는 맥 관리 프레임(MAC management frame)을 수신한 소정의 스테이션(station)은 프록시 서플라이(proxy supply)라는 맥 관리 프레임(MAC management frame)을 전송함으로써 프록시 디맨드(proxy demand)를 전송한 스테이션(station)에게 자신의 존재를 알린다.A station that receives a MAC management frame called proxy demand sends a MAC management frame called proxy supply to establish a proxy demand. Inform the transmitting station of its existence.
프록시 서플라이(proxy supply)를 수신한 스테이션은 그 스테이션을 프록시 스테이션(proxy station)으로 삼게 되며, 결과적으로 partial ARQ를 수행하여 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 프레임을 전송할 수 있게 된다.A station receiving a proxy supply makes the station a proxy station, and as a result, performs a partial ARQ to transmit a frame in a broadcast manner.
맥 관리 프레임(MAC management frame)은 맥 프로토콜의 프레임 구조에서 프레임 타입(Frame Type) 영역에 '프록시 디맨드(proxy demand)' 또는 '프록시 서플라이(proxy supply)'를 표시하고 프레임 바디(Frame Body) 영역을 'NULL' 로 표시 한 것이다.The MAC management frame indicates 'proxy demand' or 'proxy supply' in the frame type area of the frame structure of the MAC protocol, and the frame body area. Is marked as 'NULL'.
이와 같이, 본 발명은 프록시 디맨드/서플라이(proxy demand/supply) 프레임을 송수신하는 과정과 라우팅 테이블을 이용하여, 하나의 스테이션이 기존 네트워크의 구성정보를 모르는 상태에서도 최소한의 신뢰성을 보장하는 데이터 통신을 제공하고, 결과적으로 임의의 스테이션이 임의의 스테이션과 통신할 수 있는 애드-혹 네트워크를 구현한다.As described above, the present invention uses a process for transmitting and receiving proxy demand / supply frames and a routing table to provide data communication that guarantees minimum reliability even when one station does not know configuration information of an existing network. Provide an ad-hoc network in which any station can communicate with any station.
또한, 본 발명에서는 두개의 논리망 사이에 서로 통신을 가능하게 하는 브릿지 스테이션을 정의한다. 브릿지 스테이션은 두개의 논리망에 동시에 속하는 하나의 스테이션으로서, 양쪽 논리망에서 모두 송수신이 가능하다. 따라서, 브릿지 스테이션은 한쪽 논리망에서 수신한 프레임을 자신의 상위 계층 혹은 다른 쪽 논리망에 송신해 줌으로써 서로 다른 두 개의 논리망이 서로 통신을 할 수 있도록 한다.In addition, the present invention defines a bridge station that enables communication between two logical networks. The bridge station is a station belonging to two logical networks at the same time, and both the logical networks can transmit and receive. Therefore, the bridge station transmits a frame received from one logical network to its upper layer or the other logical network so that two different logical networks can communicate with each other.
브릿지 스테이션은 두 개의 논리망에 속하므로 두 개의 GID를 가진다. 각각의 논리망에서 브릿지 스테이션은 다른 스테이션과 동일한 방식으로 동작을 한다. 즉, 브릿지 스테이션은 프레임을 수신할 때에는 프레임의 GID와 자신의 GID를 비교하여 일치하는 것만을 수신하고, 프레임을 송신할 때에는 프록시 스테이션(proxy station)의 설정, 라우팅 테이블의 검색, 검색결과에 따라 브로드 캐스트 방식 혹은 유니 캐스트 방식으로 송신하는 일련의 과정을 거친다.The bridge station belongs to two logical networks and therefore has two GIDs. In each logical network, the bridge station behaves in the same way as other stations. In other words, when receiving a frame, the bridge station compares the GID of the frame with its own GID and receives only the match. When the frame is transmitted, the bridge station is set according to the proxy station setting, the routing table search, and the search result. It goes through a series of processes to transmit by broadcast or unicast.
브릿지 스테이션이 다른 스테이션들과 다른 것은, 두 개의 서로 다른 네트워크에 속해 있으므로 이러한 일련의 과정들을 각각의 논리망마다 독립적으로 수행한다는 데 있다. 즉, 프록시 스테이션도 각 논리망마다 하나씩 지정하고, 프레임을 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 전송할 시에는 각 논리망 별로 한번씩 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 전송한다.The difference between a bridge station and other stations is that since it belongs to two different networks, this series of processes is performed independently for each logical network. In other words, one proxy station is designated for each logical network, and when a frame is transmitted in a broadcast manner, the proxy station is transmitted once for each logical network.
브릿지 스테이션은, 일측 논리망 내에서 소정의 스테이션으로부터 전송된 프레임을 수신하면, 수신된 프레임에서 목적지 스테이션의 식별 아이디를 추출하여 미리 저장된 링크 허용 테이블에 존재하면, 소스 스테이션과 목적지 스테이션의 관계를 저장한 후, 상위 계층으로 전달하여 프레임을 처리한다. 마찬가지로 타측 논리망 내에서도 목적지 스테이션의 식별 아이디가 링크 허용 테이블에 존재하면 소스 스테이션과 목적지 스테이션의 관계를 저장하여, 일측 논리망의 소정 스테이션에서 타측 논리망의 스테이션으로 프레임을 전달하였을 때 프레임을 수신가능한 스테이션의 SID를 라우팅 테이블에 저장한다.When the bridge station receives a frame transmitted from a predetermined station in one logical network, the bridge station extracts an identification ID of the destination station from the received frame and stores the relationship between the source station and the destination station if it exists in the pre-stored link permission table. After that, the frame is delivered to the upper layer. Similarly, if the identification ID of the destination station exists in the link permission table in the other logical network, the relationship between the source station and the destination station is stored, and the frame can be received when the frame is transferred from the predetermined station of one logical network to the station of the other logical network. Store the SID of the station in the routing table.
즉, 브릿지 스테이션의 라우팅 테이블에는 상위 계층의 어드레스와 SID의 대응관계 뿐만이 아니라, 스테이션의 SID와 그 스테이션이 속한 논리망의 GID의 대응관계가 저장된다. 이에 따라, 브릿지 스테이션은 수신된 프레임을 분석하여 적절한 논리망으로 전달하게 된다.That is, not only the correspondence between the address of the upper layer and the SID, but also the correspondence between the SID of the station and the GID of the logical network to which the station belongs is stored in the routing table of the bridge station. Accordingly, the bridge station analyzes the received frame and delivers it to the appropriate logical network.
또한, 본 발명에서는 스테이션이 다른 스테이션과 선별적으로 통신하는 링크 제한(link restriction) 기능을 지원한다. 링크 제한기능은 한 스테이션이 지정된 스테이션들과만 통신할 수 있도록 통신 링크를 제한하는 기능으로서, 동일한 논리망 내의 모든 스테이션과 통신할 수 있는 애드-혹 네트워크의 기반 위에, 통신 가능한 상대 스테이션을 제한해 두는 기능이다. 제한된 스테이션들과만 통신을 하도록 지정해 줌으로써 억세스 네트워크를 구축하는 등 사용자의 요구에 맞게 네트워 크를 구축할 수 있으며, 스테이션 사이에 원하지 않는 통신이 이루어져 발생할 수 있는 보안문제를 해결할 수 있다.In addition, the present invention supports a link restriction function in which a station selectively communicates with another station. Link limiting is a feature that limits a communication link so that a station can only communicate with designated stations. It can limit the other stations that can communicate on the basis of an ad-hoc network that can communicate with all stations within the same logical network. Putting function is. By designating communication only with limited stations, it is possible to build a network to meet the needs of users, such as building an access network, and to solve security problems that may occur due to unwanted communication between stations.
본 발명을 억세스 네트워크(access network)에 적용하고자 할 때에는, 각 수용가에 설치된 스테이션(station) 사이의 통신 링크를 제한하여 서로 통신하지 못하도록 하는 것이 바람직하다. 이는 링크 제한(link restriction) 기능을 적용하는 좋은 예다. 통신 링크의 제한은 사용자의 요구에 따라 통신 링크의 구축이 허용된 스테이션들의 SID 정보를 별도의 링크 허용 테이블에 저장하여 원하지 않은 스테이션으로부터 통신 링크 구축을 요청 받으면 링크 허용 테이블에 기초하여 통신 링크를 구축하지 않고, 수신한 프레임을 무시한다.When the present invention is to be applied to an access network, it is desirable to restrict communication links between stations installed in each customer to prevent communication with each other. This is a good example of applying the link restriction feature. Restriction of communication link saves SID information of stations allowed to establish communication link in a separate link allowance table according to user's request, and establishes communication link based on link allowance table when requested to establish communication link from undesired station. The received frame is ignored.
도 3은 본 발명에 따른 애드-혹 네트워크의 스테이션(station)에서 프레임 송신시 맥 프로토콜의 통신 방법의 순서도이다. 본 실시예는 기존의 스테이션 및 브릿지 스테이션이 프레임을 송신하는 방법에 대한 것이다.3 is a flow chart of a method of communication of the Mac protocol in frame transmission at a station of an ad-hoc network in accordance with the present invention. This embodiment is directed to a method by which existing stations and bridge stations transmit frames.
S1단계에서 소정의 논리망 내의 스테이션은 전송할 프레임이 존재하는지 판단한다. S2단계에서 상위 계층의 목적 어드레스와 대응하는 SID가 라우팅 테이블에 존재하는지 판단한다. 자신이 브릿지 스테이션일 경우에는 SID와 더불어 GID도 라우팅 테이블에 저장되므로 SID와 GID의 존재 여부를 동시에 판단한다. 목적 어드레스와 대응하는 SID가 라우팅 테이블에 존재하면, S3단계에서 통신 링크가 구축되어 있는지 판단한다. 스테이션은 통신 링크가 구축되어 있으면, S5단계에서 프레임을 유니 캐스트 방식으로 전송한다. 그러나, 통신 링크가 구축되어 있지 않으면 S4단계에서 통신 링크를 구축한 후 S5단계에서 프레임을 유니 캐스트 방식으로 전송한 다.In step S1, the station in the predetermined logical network determines whether there is a frame to transmit. In step S2, it is determined whether the SID corresponding to the destination address of the upper layer exists in the routing table. If it is a bridge station, the GID is stored in the routing table together with the SID, and thus the existence of the SID and the GID is simultaneously determined. If the SID corresponding to the destination address exists in the routing table, it is determined in step S3 whether a communication link is established. If the communication link is established, the station transmits the frame in a unicast manner in step S5. However, if the communication link is not established, the communication link is established in step S4 and the frame is transmitted in the unicast method in step S5.
한편, S2단계의 판단결과 목적 어드레스와 대응하는 SID가 라우팅 테이블에 존재하지 않으면, S6단계에서 프록시 스테이션이 존재하는지 판단한다. 프록시 스테이션이 존재하면 S7단계에서 프레임을 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 전송한다. 이 때, 브릿지 스테이션의 경우 자신이 속한 논리망 별로 해당 프레임을 브로드캐스트로 각각 전송한다. 그러나, 프록시 스테이션이 존재하지 않으면 S8단계에서 프록시 디맨드(proxy demand)를 포함하는 프레임을 동일 논리망의 다수의 스테이션에 전송한다. S9단계에서 소정의 스테이션이 프록시 디맨드 프레임에 응답하여 송신하는 프록시 서플라이(proxy supply) 프레임을 수신할 때까지 대기한다. 이후에 프록시 서플라이 프레임을 전송한 소정의 스테이션을 프록시 스테이션으로 설정하여 프레임을 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 전송한다.On the other hand, if it is determined in step S2 that the SID corresponding to the destination address does not exist in the routing table, it is determined in step S6 whether a proxy station exists. If there is a proxy station, the frame is broadcasted in step S7. In this case, the bridge station transmits the corresponding frame by broadcasting for each logical network to which the bridge station belongs. However, if there is no proxy station, in step S8, the frame including the proxy demand (proxy demand) is transmitted to multiple stations of the same logical network. In step S9, the predetermined station waits until it receives a proxy supply frame that transmits in response to the proxy demand frame. Thereafter, a predetermined station that has transmitted the proxy supply frame is set as a proxy station to transmit the frame in a broadcast manner.
도 4는 본 발명에 따른 애드-혹 네트워크의 스테이션에서 사용될 수 있는 맥 프로토콜 프레임 구조도의 한 예이다. 도 4에서 FT(Frame Type)는 프레임 타입을 나타내고, CI(Control Information)는 제어 정보, FL(Frame Length)은 프레임의 길이, GID는 그룹 아이디(ID), DSID는 목적지 스테이션의 SID, SSID는 소스 스테이션의 SID, 프레임 바디(Frame Body)는 상위 계층의 프레임 등 맥 프로토콜이 전달하고자 하는 데이터, FCS(Frame Check Sequence)는 전달 과정에서 발생하는 에러를 검출하기 위한 프레임 체크 시퀀스이다.4 is an example of a Mac protocol frame structure diagram that may be used at a station of an ad-hoc network in accordance with the present invention. In Figure 4, FT (Frame Type) represents a frame type, CI (Control Information) is control information, FL (Frame Length) is the length of the frame, GID is the group ID (ID), DSID is the SID of the destination station, SSID is The SID and frame body of the source station are data to be delivered by the MAC protocol, such as a frame of a higher layer, and the frame check sequence (FCS) is a frame check sequence for detecting an error occurring in the delivery process.
하나의 셀 내의 스테이션에서 다른 스테이션으로 프레임을 전송 시에, 송신측 스테이션은 목적 어드레스와 대응하는 SID가 라우팅 테이블에 존재하지 않는 경 우에 프록시 스테이션을 설정해야 하므로, 도 4의 FT(Frame Type) 영역에 프록시 디맨드(proxy demand)를 삽입하고, 프레임 바디(Frame Body) 영역에는 'NULL'값을 삽입하여 송신한다. 그리고, 프록시 디맨드 프레임을 수신한 스테이션에서는 도 4의 FT(Frame Type)영역에 프록시 서플라이(proxy supply)를 삽입하고, 프레임 바디(Frame Body)영역에는 'NULL'값을 삽입하여 프록시 서플라이 프레임을 생성하여 송신한다.When transmitting a frame from a station in one cell to another station, the transmitting station needs to set a proxy station when the SID corresponding to the destination address does not exist in the routing table. Proxy demand is inserted into the frame and 'NULL' value is inserted into the frame body area. The station receiving the proxy demand frame inserts a proxy supply into the FT (Frame Type) region of FIG. 4 and inserts a NULL value into the frame body region to generate a proxy supply frame. Send it.
도 5는 본 발명에 따라 두 개의 논리망 사이에 브릿지 스테이션(bridge station)(51)이 정의된 상태를 나타낸 예와 라우팅 테이블의 구성 예를 나타낸 도면이다. 도 5의 예에서는 브릿지가 사용될 경우 라우팅 테이블이 어떻게 구성되는지 나타내기 위해 모든 스테이션(station)의 라우팅 테이블이 전체 네트워크의 라우팅 정보를 모두 저장하고 있음을 가정하고 있다.5 is a diagram illustrating an example in which a
스테이션 S1~S5는 GID로 모두 G1을 가지고 있어 하나의 논리망(50)을 구성하고, 스테이션 S5~S8은 GID로 모두 G2를 가지고 있어 다른 하나의 논리망(60)을 구성한다. 스테이션 S5(51)는 브릿지로서 GID로 G1과 G2를 모두 가지고 있으며, 양쪽 논리망에 동시에 속해 있어 모든 스테이션과 통신이 가능하다.Stations S1 to S5 have all G1s as GIDs to form one
브릿지의 라우팅 테이블에는 일측 논리망의 스테이션으로부터 전송된 프레임을 타측 논리망의 스테이션으로 전달시, 최종적으로 프레임을 수신할 목적지 스테이션의 식별 아이디와 그룹 아이디가 저장되어 있다. 라우팅 테이블에 최종 목적지의 스테이션의 식별 아이디와 그룹 아이디를 생성하여 저장하는 것은 다음의 구성에 의해 이루어진다. 일예로, 두 개의 논리망에 속하는 브릿지 스테이션을 설정한 상태에서, 일측의 논리망의 스테이션에서 타측 논리망의 스테이션으로 브로드캐스트 방식으로 프레임을 전송하는 과정을 수행함으로써 송수신된 프레임의 목적지 스테이션의 SID와 GID가 라우팅 테이블에 저장될 수 있다.In the bridge's routing table, when a frame transmitted from a station of one logical network is transferred to a station of the other logical network, an identification ID and a group ID of a destination station that will finally receive the frame are stored. Generating and storing the identification ID and the group ID of the station of the final destination in the routing table is performed by the following configuration. For example, in a state in which a bridge station belonging to two logical networks is set, a SID of a destination station of a transmitted / received frame is transmitted by performing a process of transmitting a frame in a broadcast manner from a station of one logical network to a station of another logical network. And GID may be stored in the routing table.
브릿지를 통해 두 개의 논리망이 서로 데이터를 주고받는 과정은 다음과 같다. 스테이션 S1(53)의 입장에서 봤을 때, 상위 계층에서 전달받은 프레임의 목적 어드레스가 F인 경우, S1은 자신의 라우팅 테이블에서 F와 대응하는 SID가 S5(51)임을 찾을 수 있다. 따라서 프레임을 유니 캐스트 방식으로 S5에게 전송한다. 브릿지 스테이션인 S5는 자신이 수신한 프레임의 GID(G1)가 자신이 속한 논리망의 GID(G1/G2)중 하나이므로 프레임을 처리하고, 프레임에 의해 전달된 프레임의 목적 어드레스를 추출하여 그것이 F임을 확인한다. S5는 다시 F를 자신의 라우팅 테이블에서 검색하여 그와 대응하는 SID가 S6(61)이고, 그 스테이션이 속한 논리망(60)의 GID가 G2임을 확인할 수 있다. S5는 전달받은 프레임을 다시 S6로 유니 캐스트 방식으로 전송하고, 따라서 프레임은 브릿지(S5)를 통해 최종목적지인 S6까지 전달된다.The process of two logical networks exchanging data with each other is as follows. From the standpoint of the
만약 S1이 자신의 라우팅 테이블에서 해당 SID를 찾을 수 없을 경우에는 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 전송을 하여 브릿지(51)에게 프레임을 전달하고, 브릿지가 자신의 라우팅 테이블에서 해당 SID를 찾을 수 없을 경우에는 다른 논리망(60)으로 프레임을 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 전송을 하여 다른 논리망(60)에 존재하는 스테이션이 프레임을 전달받을 수 있도록 한다. 이러한 과정을 통해, 서로 다른 두 개의 논리망이 브릿지 스테이션을 통하여 통신을 할 수 있다.If S1 cannot find the corresponding SID in its routing table, it transmits the frame to the
상기한 바와 같이, 하나의 논리망(50)에서 수신한 프레임을 적절히 판단하여 다른 논리망(60)으로 송신해 주는 브릿지의 기능을 통해 브릿지 스테이션(51)은 리피터로도 이용될 수 있다. 즉, 하나의 스테이션(station)에서 송신된 신호를 브릿지 스테이션(51)이 수신하여 재전송해 줌으로써 신호를 더 멀리 전송해 줄 수 있는 것이다.As described above, the
이와 같은 브릿지의 특성을 이용해 여러 개의 논리망을 서로 통신 가능하게 연결할 수 있고, 스테이션(station)이 갖는 물리적 거리의 한계를 이론적으로 무한히 확장할 수 있다. 본 발명은 이상과 같은 방법으로 브릿지를 정의함으로써 리피터 기능을 간단하고 효율적으로 구현하였다.By using the characteristics of such a bridge, several logical networks can be communicatively connected to each other, and the limits of physical distances of stations can be extended in theory infinitely. The present invention simply and efficiently implements a repeater function by defining a bridge in the manner described above.
상술한 바와 같이 본 발명은 다중 논리망(multiple logical network)의 공존, 애드-혹 네트워크 구성방식, 라우팅 테이블을 이용한 프레임 포워딩(forwarding) 기능, 프록시 디맨드/서플라이(proxy demand/supply) 기능, 브릿지 기능 및 링크 제한 기능 등을 이용하여 사용자가 요구할 수 있는 다양한 형태의 네트워크에 유연하게 적용할 수 있다.As described above, the present invention provides a coexistence of multiple logical networks, an ad hoc network configuration method, a frame forwarding function using a routing table, a proxy demand / supply function, and a bridge function. And it can be flexibly applied to various types of networks that can be requested by the user by using a link restriction function.
도 6은 본 발명을 전력선 통신에 적용하여 주거지역에서 억세스 네트워크(access network) 및 홈 네트워크(home network)를 구축한 예를 나타낸 도면이다.FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating an example in which an access network and a home network are constructed in a residential area by applying the present invention to power line communication.
도 6에서는 두 개의 전봇대(71, 72)에서 전력을 공급하는 수용가들에 인터넷 억세스 네트워크(internet access network)를 구축했으며, 그 중 하나의 수용가(78)에서 억세스 네트워크(access network) 없이, 수용가의 스테이션간에만 통신하는 홈 네트워크(home network)를 구축했다. 이는 같은 종류의 매체(media)에서 다 양한 형태의 네트워크가 본 발명의 다중 논리망(multiple logical network)의 공존기능을 통해 서로 간섭 없이 공존할 수 있음을 나타내고 있다.In FIG. 6, an internet access network was established for consumers powered by two
또한, 인터넷 억세스망은 인터넷 백본 망(internet backbone network)이 좌측 전봇대(71)에 설치된 스테이션(81)과 연결되고, 상기 스테이션(81)을 통해 각 수용가(82, 83, 84)까지 연결되어 형성된다. 여기서, 각 수용가에 설치된 브릿지 스테이션은 인터넷 억세스(internet access)를 위한 홈 게이트웨이(home gateway)의 역할을, 우측 전봇대(72)에 설치된 브리지 스테이션(80)은 억세스 네트워크를 위한 리피터의 역할을, 좌측 전봇대(71)에 설치된 스테이션(81)은 억세스 포인트(access point)의 역할을 한다.In addition, the Internet access network is formed by connecting an Internet backbone network to a
우측 전봇대(72)에 연결된 각 수용가(74~78)내의 브릿지 스테이션은 역시 해당 수용가의 홈 게이트웨이 역할을 하며, 우측 전봇대(72)에 설치된 리피터 스테이션(80)과 수용가내의 스테이션을 연결하는 기능을 한다.The bridge station in each
도 6에서는 브릿지들간의 논리망을 구분을 해놓지 않았는데, 실선으로 바로 연결된 스테이션들은 같은 논리망에 포함되어 있음을 함의하고 있다.In FIG. 6, logical networks between the bridges are not distinguished, meaning that stations directly connected by solid lines are included in the same logical network.
여기서, 각 수용가에 연결된 브릿지들 사이에 실선으로나 점선으로 통신 링크에 대한 표시를 하지 않았다. 이는 억세스 네트워크에서 링크 제한(link restriction) 기능을 사용하여 모든 스테이션(station)들이 억세스 포인트(access point)기능을 하는 좌측 전봇대(71)의 스테이션(81)을 향한 링크와만 통신할 수 있음을 보여주고 있는 것이다.Here, the communication link is not indicated by the solid line or the dotted line between the bridges connected to each customer. This shows that using the link restriction function in the access network, all stations can only communicate with the link to the
도 7은 본 발명에 따른 애드-혹 네트워크의 스테이션에서, 프레임을 수신한 스테이션이, 하나의 논리망내의 일반 스테이션인 경우와, 두 개의 논리망 사이에 존재하는 브릿지 스테이션인 경우에 프레임을 수신시 맥 프로토콜의 통신 방법의 순서도이다. P1단계에서 스테이션은 수신한 프레임이 있는지 판단한다. P2단계에서 프레임의 GID가 자신의 GID와 일치하는지 판단한다. P3단계에서 프레임의 SSID(소스 스테이션의 SID)가 링크 허용 리스트에 있는지 판단한다. 프레임이 링크 허용 리스트에 존재하면, P4단계에서 자신이 브릿지 스테이션인지 판단한다. 판단결과 브릿지 스테이션이 아니면 P11단계에서 수신된 프레임이 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 전송된 프레임인지 유니 캐스트 방식으로 전송된 프레임인지 판단한다. P12단계에서 유니 캐스트 방식으로 전송된 프레임이면, 프레임의 DSID(목적지 스테이션의 SID)가 자신의 SID와 일치하는지 판단하여, 일치하면 P13단계에서 프레임을 수신하고 상위계층으로 전달한다. 그러나, P11단계의 판단결과 수신된 프레임이 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 전송된 프레임이면 P13단계에서 프레임을 수신하여 곧바로 상위계층으로 전달한다.7 is a diagram of a station in an ad-hoc network according to the present invention, when receiving a frame is a normal station in one logical network and a bridge station existing between two logical networks. This is a flowchart of communication method of Mac protocol. In step P1, the station determines whether there is a received frame. In step P2, it is determined whether the GID of the frame matches its own GID. In step P3, it is determined whether the SSID of the frame (SID of the source station) is in the link allow list. If the frame exists in the link allow list, it is determined in step P4 whether it is a bridge station. As a result of the determination, if it is not the bridge station, it is determined whether the frame received in step P11 is a frame transmitted by a broadcast method or a frame transmitted by a unicast method. If the frame is transmitted in a unicast manner in step P12, it is determined whether the frame's DSID (SID of the destination station) matches its SID. If the frame is matched, the frame is received and transmitted to the upper layer in step P13. However, if the received frame is a frame transmitted in a broadcast manner as a result of the determination in step P11, the frame is received in step P13 and immediately transferred to the upper layer.
한편, P4단계의 판단결과 자신의 스테이션이 브릿지 스테이션인 경우에는, P5단계에서 수신된 프레임이 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 송신된 프레임인지 유니캐스트로 송신된 프레임인지 판단한다. 판단결과 유니캐스트 방식으로 송신된 프레임이면 P6단계에서 프레임의 DSID(목적지 스테이션의 SID)가 자신의 SID와 일치하는지 판단한다. 일치하면, P7단계에서 해당 프레임에 대응하는 SID와 GID가 라우팅 테이블에 존재하는지 판단한다. 여기서, 라우팅 테이블에는 브릿지 스테이션을 통해 두 개의 논리망 간에 프레임을 송수신할 때의 브릿징 정보가 미리 생성되어 저장되어 있으므로, 수신된 프레임에 대응하는 최종 스테이션의 SID와 GID를 검색할 수 있다.On the other hand, if it is determined that the station is a bridge station in step P4, it is determined whether the frame received in step P5 is a frame transmitted in a broadcast manner or a unicast frame. As a result of the determination, if the frame is transmitted by the unicast method, it is determined in step P6 whether the frame's DSID (SID of the destination station) matches its own SID. If there is a match, it is determined in step P7 whether the SID and the GID corresponding to the frame exist in the routing table. In this case, since the bridging information for transmitting and receiving frames between two logical networks through the bridge station is generated and stored in advance, the SID and the GID of the last station corresponding to the received frame can be retrieved.
P7단계의 판단결과 존재하면, P8단계에서 라우팅 테이블에서 검색한 GID가 프레임의 GID와 일치하는지 판단한다. 이는 프레임을 송신한 스테이션이 속하는 동일 논리망의 스테이션으로 전송할 것인지, 타 논리망의 스테이션으로 전송할 것인지를 판단하기 위함이다. 판단결과 일치하면, P13단계에서 프레임을 수신하고 상위계층으로 전달한다. 그러나, P8단계의 판단결과 라우팅 테이블에서 검색한 GID와 프레임의 GID가 일치하지 않으면 P9단계에서 라우팅 테이블에서 검색한 SID와 GID로 프레임을 유니캐스트로 전송한다.If the determination result of step P7 exists, it is determined whether the GID retrieved from the routing table in step P8 matches the GID of the frame. This is to determine whether to transmit a frame to a station of the same logical network to which the transmitting station belongs or to a station of another logical network. If the result of the determination matches, the frame is received in step P13 and transmitted to the upper layer. However, if the GID retrieved from the routing table and the GID of the frame do not coincide with the determination result of step P8, the frame is transmitted in unicast with the SID and GID retrieved from the routing table in step P9.
또한, P7단계의 판단결과, 해당 프레임에 대응하는 SID와 GID가 라우팅 테이블에 존재하지 않으면 P10단계에서 프레임을 수신하여 곧바로 상위계층으로 전달하여 다른 논리망으로 프레임을 브로드 캐스트로 전송한다.If the SID and the GID corresponding to the frame do not exist in the routing table, the frame is received in step P10 and immediately transmitted to the upper layer to transmit the frame to another logical network through broadcast.
한편, P5단계의 판단결과 자신이 브릿지 스테이션이고, 수신된 프레임이 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 송신된 경우에는 P10단계에서 프레임을 수신하여 상위 계층으로 전달한 후 다른 논리망으로 프레임을 브로드 캐스트 방식으로 전송한다.On the other hand, if it is determined that the step P5 is a bridge station and the received frame is transmitted in a broadcast manner, the frame is received in step P10 and transmitted to the upper layer, and then the frame is transmitted to another logical network in a broadcast manner.
이러한 구성에 의하여, 애드-혹 방식의 구현, 다중 논리 그룹(multiple logical group)의 공존, 리피터 기능을 구현할 수 있게 된다. 그리고, 거리의 제한, 목표 네트워크(target network)의 토폴로지 제한, 또는 통신 링크의 수 제한 없이 유연하고 효과적으로 네트워크를 구성할 수 있게 된다.By such a configuration, it is possible to implement an ad-hoc method, coexistence of multiple logical groups, and repeater functions. In addition, it is possible to flexibly and effectively configure the network without limiting distance, limiting topology of a target network, or limiting the number of communication links.
본 발명이 제공하는 이러한 기능들을 통해 네트워크 구성자는 어떠한 형태의 네트워크라도 필요에 맞게 구성할 수 있으며, 이는 기존 MAC 방식이 내재적으로 가지는 네트워크 구성의 제한을 해결할 수 있다.Through these functions provided by the present invention, the network configurator can configure any type of network as needed, which can solve the limitation of the network configuration inherent in the existing MAC scheme.
이상 설명한 바와 같이 본 발명에 의하면, 물리적 네트워크에 두 개 이상의 논리망을 형성하여 공존하도록 할 수 있게 된다. 또한, 유니캐스트 전송이 필요한 경우에만 통신 링크를 수행하기 때문에 그에 수반되는 오버헤드를 최소화하고 채널을 효율적으로 사용할 수 있게 된다. 또한, 두 개의 논리망에 공존하는 스테이션에 의한 브릿지 기능에 의해 두 개의 논리망을 서로 통신이 가능하도록 연결해 주는 동시에 프레임을 수신 및 재전송 해주기 때문에, 리피터 기능을 구현하여 거리의 제한을 극복할 수 있다.As described above, according to the present invention, two or more logical networks can be formed in a physical network to coexist. In addition, since the communication link is performed only when unicast transmission is required, the overhead accompanying it can be minimized and the channel can be efficiently used. In addition, since the bridge function by the station coexisting in the two logical networks connects the two logical networks so that they can communicate with each other, and receives and retransmits the frames, the repeater function can be implemented to overcome the limitation of distance. .
Claims (17)
Translated fromKoreanPriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020050060652AKR100650406B1 (en) | 2005-07-06 | 2005-07-06 | Method of transmitting / receiving frame of MAC protocol in ad-hoc network using CSM / CA method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020050060652AKR100650406B1 (en) | 2005-07-06 | 2005-07-06 | Method of transmitting / receiving frame of MAC protocol in ad-hoc network using CSM / CA method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR100650406B1true KR100650406B1 (en) | 2006-11-27 |
Family
ID=37713759
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020050060652AExpired - Fee RelatedKR100650406B1 (en) | 2005-07-06 | 2005-07-06 | Method of transmitting / receiving frame of MAC protocol in ad-hoc network using CSM / CA method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100650406B1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2010025586A1 (en)* | 2008-09-05 | 2010-03-11 | 上海贝尔股份有限公司 | A method for coexisting among networks using different wireless access technologies and the apparatus thereof |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20010048718A (en)* | 1999-11-29 | 2001-06-15 | 오길록 | Packet switch system structure for reducing to reduce a blocking problem of broadcast packets |
| US6522650B1 (en) | 2000-08-04 | 2003-02-18 | Intellon Corporation | Multicast and broadcast transmission with partial ARQ |
| KR20050062299A (en)* | 2003-12-20 | 2005-06-23 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method for communication between optical network units in broadband passive optical network |
| KR20060003401A (en)* | 2004-07-06 | 2006-01-11 | 한국과학기술원 | Optimal Protocol Design for Low Power Routing in Multi-hop Wireless Networks with Power Control |
- 2005
- 2005-07-06KRKR1020050060652Apatent/KR100650406B1/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20010048718A (en)* | 1999-11-29 | 2001-06-15 | 오길록 | Packet switch system structure for reducing to reduce a blocking problem of broadcast packets |
| US6522650B1 (en) | 2000-08-04 | 2003-02-18 | Intellon Corporation | Multicast and broadcast transmission with partial ARQ |
| KR20050062299A (en)* | 2003-12-20 | 2005-06-23 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method for communication between optical network units in broadband passive optical network |
| KR20060003401A (en)* | 2004-07-06 | 2006-01-11 | 한국과학기술원 | Optimal Protocol Design for Low Power Routing in Multi-hop Wireless Networks with Power Control |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2010025586A1 (en)* | 2008-09-05 | 2010-03-11 | 上海贝尔股份有限公司 | A method for coexisting among networks using different wireless access technologies and the apparatus thereof |
| CN102067710A (en)* | 2008-09-05 | 2011-05-18 | 上海贝尔股份有限公司 | Method and device for coexistence between networks using different radio access technologies |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110856194B (en) | Dual-mode fusion networking method and communication method | |
| US5331634A (en) | Technique for bridging local area networks having non-unique node addresses | |
| JP4298651B2 (en) | Message routing method, wireless network and master node | |
| EP1982201B1 (en) | System and method for multihop packet forwarding | |
| US7016336B2 (en) | Administrative domains for personal area networks | |
| US6928061B1 (en) | Transmission-scheduling coordination among collocated internet radios | |
| US20040167988A1 (en) | Bridging between a Bluetooth scatternet and an Ethernet LAN | |
| US20040141511A1 (en) | Bridging between a bluetooth scatternet and an ethernet LAN | |
| US20040151193A1 (en) | Bridging between a Bluetooth scatternet and an Ethernet LAN | |
| WO2009032648A1 (en) | Method and device for providing a bridge in a network | |
| CN101809944A (en) | Redundantly connected wireless sensor networking method | |
| US6873603B1 (en) | MAC address population protocol | |
| WO1995012942A1 (en) | A communication network providing wireless and hard-wired dynamic routing | |
| CN101939923A (en) | Method, system, integrated circuit, communication module, and computer readable medium for obtaining resource sharing including spatial and temporal reuse in a power line communication system | |
| US20040156318A1 (en) | Bridging between a Bluetooth scatternet and an Ethernet LAN | |
| JP2010524360A (en) | Frequency scanning to form a communication network | |
| US20040153520A1 (en) | Bridging between a bluetooth scatternet and an ethernet LAN | |
| WO2020035159A1 (en) | Independent redundant path discovery for bluetooth mesh | |
| US20040156384A1 (en) | Bridging between a Bluetooth scatternet and an Ethernet LAN | |
| CN101395857B (en) | Method for multi-hop data transmission in an ad-hoc network comprising concealed nodes | |
| CN111262787B (en) | Data transmission method and electronic equipment | |
| JP3599032B2 (en) | Wireless communication system, wireless communication method, and wireless station | |
| WO2007126231A1 (en) | Method of assigning address in wireless personal area network | |
| KR100650406B1 (en) | Method of transmitting / receiving frame of MAC protocol in ad-hoc network using CSM / CA method | |
| RU2758593C1 (en) | Detecting critical links in bluetooth mesh networks |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0109 | Patent application | St.27 status event code:A-0-1-A10-A12-nap-PA0109 | |
| PA0201 | Request for examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D11-exm-PA0201 | |
| A302 | Request for accelerated examination | ||
| PA0302 | Request for accelerated examination | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D17-exm-PA0302 St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D16-exm-PA0302 | |
| D13-X000 | Search requested | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D13-srh-X000 | |
| D14-X000 | Search report completed | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D14-srh-X000 | |
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D21-exm-PE0902 | |
| P11-X000 | Amendment of application requested | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P11-nap-X000 | |
| P13-X000 | Application amended | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-P10-P13-nap-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-3-3-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| PE0701 | Decision of registration | St.27 status event code:A-1-2-D10-D22-exm-PE0701 | |
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| PR0701 | Registration of establishment | St.27 status event code:A-2-4-F10-F11-exm-PR0701 | |
| PR1002 | Payment of registration fee | St.27 status event code:A-2-2-U10-U11-oth-PR1002 Fee payment year number:1 | |
| PG1601 | Publication of registration | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-Q10-Q13-nap-PG1601 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:4 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:5 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:6 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20130522 Year of fee payment:7 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:7 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20131118 Year of fee payment:8 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:8 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| S17-X000 | Non-exclusive voluntary license recorded | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-S10-S17-lic-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R14-asn-PN2301 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| S17-X000 | Non-exclusive voluntary license recorded | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-S10-S17-lic-X000 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20141103 Year of fee payment:9 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:9 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20151008 Year of fee payment:10 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:10 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| PN2301 | Change of applicant | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R13-asn-PN2301 St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R11-asn-PN2301 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20161102 Year of fee payment:11 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:11 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20171018 Year of fee payment:12 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:12 | |
| FPAY | Annual fee payment | Payment date:20181031 Year of fee payment:13 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:13 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:14 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:15 | |
| J206 | Request for trial to confirm the scope of a patent right | ||
| PJ0206 | Trial to confirm the scope of a patent | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-V10-V11-apl-PJ0206 | |
| J206 | Request for trial to confirm the scope of a patent right | ||
| PJ0206 | Trial to confirm the scope of a patent | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-V10-V11-apl-PJ0206 | |
| PJ1201 | Withdrawal of trial | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-V10-V13-apl-PJ1201 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:16 | |
| R18-X000 | Changes to party contact information recorded | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-R10-R18-oth-X000 | |
| J301 | Trial decision | Free format text:TRIAL NUMBER: 2021100002046; TRIAL DECISION FOR CONFIRMATION OF THE SCOPE OF RIGHT_DEFENSIVE REQUESTED 20210706 Effective date:20221011 | |
| PJ1301 | Trial decision | St.27 status event code:A-5-5-V10-V15-crt-PJ1301 Decision date:20221011 Appeal event data comment text:Appeal Kind Category : Confirmation of the scope of right_defensive, Appeal Ground Text : 0650406 Appeal request date:20210706 Appellate body name:Patent Examination Board Decision authority category:Office appeal board Decision identifier:2021100002046 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:17 | |
| PR1001 | Payment of annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U11-oth-PR1001 Fee payment year number:18 | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | St.27 status event code:A-4-4-U10-U13-oth-PC1903 Not in force date:20241122 Payment event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE | |
| PC1903 | Unpaid annual fee | St.27 status event code:N-4-6-H10-H13-oth-PC1903 Ip right cessation event data comment text:Termination Category : DEFAULT_OF_REGISTRATION_FEE Not in force date:20241122 |