JPWO2018220745A1 - Monitoring device - Google Patents
Monitoring deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JPWO2018220745A1 JPWO2018220745A1JP2019521598AJP2019521598AJPWO2018220745A1JP WO2018220745 A1JPWO2018220745 A1JP WO2018220745A1JP 2019521598 AJP2019521598 AJP 2019521598AJP 2019521598 AJP2019521598 AJP 2019521598AJP WO2018220745 A1JPWO2018220745 A1JP WO2018220745A1
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- target
- processing unit
- observation
- sensor
- image
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S13/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar systems; Analogous systems using reflection or reradiation of waves whose nature or wavelength is irrelevant or unspecified
- G01S13/86—Combinations of radar systems with non-radar systems, e.g. sonar, direction finder
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S13/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar systems; Analogous systems using reflection or reradiation of waves whose nature or wavelength is irrelevant or unspecified
- G01S13/88—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications
- G01S13/91—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications for traffic control
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
- Radar Systems Or Details Thereof (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromJapaneseDescription
Translated fromJapaneseこの発明は、観測センサにより観測された目標物と、画像センサの撮像画像内の目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する監視装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a monitoring device that determines whether or not a target observed by an observation sensor and a target in a captured image of an image sensor are the same.
例えば、観測諸元が異なるレーダ又はカメラなどの複数のセンサを用いて、航空機、船舶又は車両などの目標物を観測し、複数のセンサにより観測された目標物の同一性を判定する監視装置がある。
この監視装置は、例えば、画像センサから出力された撮像画像内の目標物と、或るレーダにより観測された目標物とが同一物であると判定すれば、或るレーダにより観測された目標物の識別情報を撮像画像上に重ねて表示する。For example, a monitoring device that observes a target such as an aircraft, a ship, or a vehicle using a plurality of sensors such as radars or cameras having different observation specifications and determines the identity of the target observed by the plurality of sensors. is there.
For example, if it is determined that the target in the captured image output from the image sensor and the target observed by a certain radar are the same, the monitoring apparatus detects the target observed by the certain radar. The identification information is superimposed on the captured image and displayed.
この監視装置を適用可能なシステムとして、例えば、目標物である航空機を観測する航空管制支援システムがある。
航空管制支援システムに適用される監視装置が備えるセンサとして、例えば、空港面探知レーダ(ASDE:Airport Surface Detection Equipment)、空港監視レーダ(ASR:Airport Surveillance Radar)がある。ASDEは目標物である航空機の距離や方位を探知することによって2次元位置を取得することができる。ASRは、例えば、一次監視レーダ(PSR:Primary Surveillance Radar)と、二次監視レーダ(SSR:Secondary Surveillance Radar)とを組み合わせたレーダである。PSRは、目標物である航空機の距離及び方位を探知する。SSRは、レーダのアンテナから送信された電波である質問信号に対して、航空機に搭載されたトランスポンダが応答することによって、目標物の航空機である距離及び方位を探知し、応答信号には、航空機の識別情報及び高度が含まれるため、距離及び方位に加えて、高度を知ることができる。
これらのセンサは、航空機の高度を取得できない場合、2次元位置として取得することになり、航空機の高度が取得できる場合、3次元位置として取得することができる。
また、監視装置が備えるセンサとして、マルチラテレーション(MLAT:MultirateLATion)、広域マルチラテレーション(WAM:Wide Area Multiratelation)、ADS-B(Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast)out/inなどがある。
これらのセンサは、目標物である航空機の3次元位置及び航空機の識別情報を取得することができる。As a system to which this monitoring apparatus can be applied, for example, there is an air traffic control support system for observing an aircraft as a target.
As sensors provided in a monitoring device applied to an air traffic control support system, for example, there are an airport surface detection radar (ASDE) and an airport surveillance radar (ASR: Aircraft Radar Radar). ASDE can acquire a two-dimensional position by detecting the distance and direction of the target aircraft. The ASR is, for example, a radar that combines a primary surveillance radar (PSR) and a secondary surveillance radar (SSR). The PSR detects the distance and direction of the target aircraft. The SSR detects the distance and azimuth of the target aircraft as a result of the transponder mounted on the aircraft responding to the interrogation signal transmitted from the radar antenna. In addition to the distance and direction, the altitude can be known.
These sensors are acquired as a two-dimensional position when the altitude of the aircraft cannot be acquired, and can be acquired as a three-dimensional position when the altitude of the aircraft can be acquired.
Also, sensors included in the monitoring device include multilateration (MLAT), wide area multilateration (WAM), ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Survey-Broadcast) out / in, and the like.
These sensors can acquire the three-dimensional position of the target aircraft and the identification information of the aircraft.
以下の特許文献1に開示されている監視装置は、観測センサとして、空港面探知レーダを使用して、空港面を移動する全ての目標物を観測し、全ての目標物の位置及び識別情報を取得するようにしている。目標物には、空港面を移動する航空機のほか、空港面を移動する車両なども含まれる。
また、この監視装置は、画像センサであるビデオカメラを用いて、目標物を撮影し、目標物が映っている撮像画像を取得するようにしている。
この監視装置は、撮像画像内の目標物を検出して、撮像画像上での目標物の位置と、空港面探知レーダにより取得された目標物の位置との相関の有無を判定することで、空港面探知レーダにより観測された目標物と、画像センサの撮像画像内の目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定している。The monitoring device disclosed in the following
In addition, this monitoring apparatus uses a video camera, which is an image sensor, to capture a target and acquire a captured image showing the target.
This monitoring device detects a target in a captured image and determines whether or not there is a correlation between the position of the target on the captured image and the position of the target acquired by the airport surface detection radar. It is determined whether or not the target observed by the airport surface detection radar is the same as the target in the captured image of the image sensor.
従来の監視装置は以上のように構成されているので、目標物が空港面を移動している航空機又は車両などであれば、目標物の同一性を判定することができる。しかし、目標物が飛行中の航空機である場合、撮像画像内の目標物の位置座標を解析しても、目標物の3次元位置を正確に求めることが困難であり、撮像画像上での目標物の3次元位置と、空港面探知レーダにより取得された目標物の3次元位置との相関の有無を判定することができない。このため、目標物が飛行中の航空機である場合、空港面探知レーダにより観測された目標物と、画像センサの撮像画像内の目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定することができないという課題があった。 Since the conventional monitoring apparatus is configured as described above, the identity of the target can be determined if the target is an aircraft or a vehicle moving on the airport surface. However, when the target is an aircraft in flight, it is difficult to accurately obtain the three-dimensional position of the target even if the position coordinates of the target in the captured image are analyzed. Whether or not there is a correlation between the three-dimensional position of the object and the three-dimensional position of the target acquired by the airport surface detection radar cannot be determined. For this reason, when the target is an aircraft in flight, it cannot be determined whether the target observed by the airport surface detection radar and the target in the image captured by the image sensor are the same. There was a problem.
この発明は上記のような課題を解決するためになされたもので、目標物が飛行中の航空機である場合でも、観測センサにより観測された目標物と、画像センサの撮像画像内の目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定することができる監視装置を得ることを目的とする。 The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems. Even when the target is an aircraft in flight, the target observed by the observation sensor, the target in the captured image of the image sensor, and the target It is an object to obtain a monitoring device that can determine whether or not the two are the same.
この発明に係る監視装置は、目標物が存在している領域を撮像して、その領域の撮像画像を出力する画像センサと、画像センサから出力された撮像画像内の目標物を検出し、検出した目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含画像領域を特定する目標検出部と、目標物を観測して、観測した目標物の識別情報及び観測した目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を出力する観測センサと、観測センサから出力された識別情報によって目標物の大きさを特定し、特定した目標物の大きさ及び観測センサから出力された目標物観測位置のそれぞれを画像センサの投影面に変換し、変換した目標物の大きさと、変換した目標物観測位置とから、画像センサの投影面上で、観測センサにより観測された目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含観測領域を特定する変換処理部とを設け、第1の判定処理部が、変換処理部により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、目標検出部により特定された目標物包含画像領域とを比較して、観測センサにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定するようにしたものである。 The monitoring apparatus according to the present invention images an area in which a target is present, outputs an image captured in the area, detects a target in the captured image output from the image sensor, and detects the target A target detection unit that identifies a target inclusion image area that is a range that includes the target, and observation of the target, identification information of the observed target, and target observation that is the position of the observed target The size of the target is specified by the observation sensor that outputs the position and the identification information output from the observation sensor, and each of the specified target size and the target observation position output from the observation sensor is determined by the image sensor. The target is included in the range including the target observed by the observation sensor on the projection plane of the image sensor from the converted target size and the converted target observation position. Observation area And a first determination processing unit comparing the target object inclusion observation area specified by the conversion processing part with the target object inclusion image area specified by the target detection part, It is determined whether or not the target observed by the observation sensor and the target detected by the target detector are the same.
この発明によれば、観測センサから出力された識別情報によって目標物の大きさを特定し、特定した目標物の大きさ及び観測センサから出力された目標物観測位置のそれぞれを画像センサの投影面に変換し、変換した目標物の大きさと、変換した目標物観測位置とから、画像センサの投影面上で、観測センサにより観測された目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含観測領域を特定する変換処理部を設け、第1の判定処理部が、変換処理部により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、目標検出部により特定された目標物包含画像領域とを比較して、観測センサにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定するように構成したので、目標物が飛行中の航空機である場合でも、観測センサにより観測された目標物と、画像センサの撮像画像内の目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定することができる効果がある。 According to this invention, the size of the target is specified by the identification information output from the observation sensor, and each of the specified target size and the target observation position output from the observation sensor is displayed on the projection plane of the image sensor. The target inclusion observation area, which is a range including the target observed by the observation sensor on the projection plane of the image sensor from the converted target size and the converted target observation position. And a first determination processing unit compares the target inclusion observation region specified by the conversion processing unit with the target inclusion image region specified by the target detection unit, and performs observation. Since it is configured to determine whether or not the target observed by the sensor and the target detected by the target detector are the same, the observation sensor even if the target is an aircraft in flight By And observed target, and the target in the captured image of the image sensor is effective which can be determined whether one and the same.
以下、この発明をより詳細に説明するために、この発明を実施するための形態について、添付の図面に従って説明する。 Hereinafter, in order to explain the present invention in more detail, modes for carrying out the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
実施の形態1.
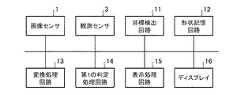
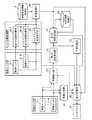
図1は、この発明の実施の形態1による監視装置を示す構成図である。図2は、この発明の実施の形態1による監視装置を示すハードウェア構成図である。
図1及び図2において、画像センサ1は、例えば、光学カメラ又は赤外カメラなどで実現される。
画像センサ1は、目標物が存在している領域として、例えば、移動体が交通する空港敷地内及び空港周辺の領域を撮像して、前記領域の撮像画像を目標検出部2及び表示処理部7に出力する。この目標物には、航空機のほか、地上を走行する車両なども含まれる。さらに、海が近い空港であれば船舶なども含まれ、また、鉄道があれば、鉄道車両なども含まれる。
1 is a block diagram showing a monitoring apparatus according to
1 and 2, the
The
目標検出部2は、例えば、図2に示す目標検出回路11で実現される。
目標検出部2は、画像センサ1から出力された撮像画像内の目標物を検出する処理を実施する。
目標検出部2は、撮像画像上での検出した目標物の位置である目標物画像位置及び撮像画像上で目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含画像領域のそれぞれを第1の判定処理部6及び表示処理部7に出力する処理を実施する。The
The
The
観測センサ3は、画像センサ1以外のセンサであり、例えば、ASR、ASDE、MLAT、WAM、ADS−Bout/inなどで実現される。
観測センサ3は、目標物を観測して、観測した目標物の識別情報及び目標物の3次元位置である目標物観測位置のそれぞれを変換処理部5に出力する。目標物の識別情報には、例えば、航空機の便名のほか、航空機の機体など、目標物の固有の識別番号が含まれている。
物体形状情報格納部4は、例えば、図2に示す形状記憶回路12で実現される。
物体形状情報格納部4は、各種の目標物の形状を示す形状情報を格納している。例えば、目標物の識別情報に対応する形状情報として、識別情報が示す目標物の全長、全幅及び高さなどを格納している。The
The
The object shape information storage unit 4 is realized by, for example, the
The object shape information storage unit 4 stores shape information indicating the shapes of various target objects. For example, as the shape information corresponding to the identification information of the target, the total length, full width, height, and the like of the target indicated by the identification information are stored.
変換処理部5は、例えば、図2に示す変換処理回路13で実現される。
変換処理部5は、物体形状情報格納部4から、観測センサ3から出力された識別情報に対応する形状情報を読み出し、形状情報を参照することで、観測センサ3により観測された目標物の大きさを特定する処理を実施する。
変換処理部5は、特定した目標物の大きさ及び観測センサ3から出力された目標物観測位置のそれぞれを画像センサ1の投影面に変換する処理を実施する。
変換処理部5は、変換した目標物の大きさと、変換した目標物観測位置とから、画像センサ1の投影面上で、観測センサ3により観測された目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含観測領域を特定する処理を実施する。
この実施の形態1では、変換処理部5が、観測センサ3から出力された識別情報に対応する形状情報を参照することで、観測センサ3により観測された目標物の大きさを特定し、特定した目標物の大きさを画像センサ1の投影面に変換する例を示しているが、これに限るものではない。
例えば、観測センサ3が目標物の識別情報を得ることが困難であるような場合、変換処理部5が、予め設定されている目標物の大きさを画像センサ1の投影面に変換するようにしてもよい。
予め設定されている目標物の大きさは、例えば、カタログ上の大きさなどが考えられる。The
The
The
The
In the first embodiment, the
For example, when it is difficult for the
As the size of the target set in advance, for example, the size on a catalog can be considered.
第1の判定処理部6は、例えば、図2に示す第1の判定処理回路14で実現される。
第1の判定処理部6は、変換処理部5により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、目標検出部2から出力された目標物包含画像領域とを比較して、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、目標検出部2により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する処理を実施する。
即ち、第1の判定処理部6は、画像センサ1の投影面上で、変換処理部5により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、目標検出部2から出力された目標物包含画像領域との重なり範囲を算出する処理を実施する。
また、第1の判定処理部6は、重なり範囲が閾値以上であれば、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、目標検出部2により検出された目標物とが同一物であると判定し、重なり範囲が閾値未満であれば、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、目標検出部2により検出された目標物とが同一物でないと判定する処理を実施する。The first
The first
That is, the first
The first
表示処理部7は、例えば、図2に示す表示処理回路15で実現される。
表示処理部7は、画像センサ1から出力された撮像画像をディスプレイ16に表示する処理を実施する。
表示処理部7は、第1の判定処理部6により同一物であると判定された場合、変換処理部5により画像センサ1の投影面に変換された目標物観測位置及び観測センサ3から出力された識別情報のそれぞれを撮像画像上に表示し、また、目標検出部2から出力された目標物包含画像領域を撮像画像上に表示する処理を実施する。
また、第1の判定処理部6により同一物であると判定されなかった場合でも、表示処理部7は、変換処理部5により画像センサ1の投影面に変換された目標物観測位置、観測センサ3から出力された識別情報、変換処理部5により特定された目標物包含観測領域、目標検出部2から出力された目標物画像位置、目標検出部2から出力された目標物包含画像領域のそれぞれを独立に撮像画像上に表示しても良いこととする。
ディスプレイ16は、例えば、液晶ディスプレイなどの表示装置である。The
The
When it is determined by the first
Even if the first
The
図1では、監視装置の構成要素である画像センサ1、目標検出部2、観測センサ3、物体形状情報格納部4、変換処理部5、第1の判定処理部6、表示処理部7及びディスプレイ16のそれぞれが、図2に示すような専用のハードウェアで実現されるものを想定している。即ち、画像センサ1、目標検出回路11、観測センサ3、形状記憶回路12、変換処理回路13、第1の判定処理回路14、表示処理回路15及びディスプレイ16で実現されるものを想定している。 In FIG. 1, an
ここで、形状記憶回路12は、例えば、RAM(Random Access Memory)、ROM(Read Only Memory)、フラッシュメモリ、EPROM(Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory)、EEPROM(Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory)などの不揮発性又は揮発性の半導体メモリや、磁気ディスク、フレキシブルディスク、光ディスク、コンパクトディスク、ミニディスク、DVD(Digital Versatile Disc)などが該当する。
また、目標検出回路11、変換処理回路13、第1の判定処理回路14及び表示処理回路15は、例えば、単一回路、複合回路、プログラム化したプロセッサ、並列プログラム化したプロセッサ、ASIC(Application Specific Integrated Circuit)、FPGA(Field−Programmable Gate Array)、または、これらを組み合わせたものが該当する。Here, the
The
監視装置の画像センサ1、観測センサ3及びディスプレイ16を除く構成要素は、専用のハードウェアで実現されるものに限るものではなく、ソフトウェア、ファームウェア、または、ソフトウェアとファームウェアとの組み合わせで実現されるものであってもよい。
ソフトウェア又はファームウェアはプログラムとして、コンピュータのメモリに格納される。コンピュータは、プログラムを実行するハードウェアを意味し、例えば、CPU(Central Processing Unit)、中央処理装置、処理装置、演算装置、マイクロプロセッサ、マイクロコンピュータ、プロセッサ、DSP(Digital Signal Processor)、GPU(Graphics Processing Unit)などが該当する。The components other than the
Software or firmware is stored as a program in the memory of a computer. The computer means hardware for executing a program. For example, a central processing unit (CPU), a central processing unit, a processing unit, a processing unit, a microprocessor, a microcomputer, a processor, a DSP (Digital Signal Processor), a GPU (Graphics) (Processing Unit).
図3は、監視装置の画像センサ1、観測センサ3及びディスプレイ16を除く構成要素がソフトウェア又はファームウェアなどで実現される場合のコンピュータのハードウェア構成図である。
監視装置の画像センサ1、観測センサ3及びディスプレイ16を除く構成要素がソフトウェア又はファームウェアなどで実現される場合、物体形状情報格納部4をコンピュータのメモリ21上に構成するとともに、目標検出部2、物体形状情報格納部4、変換処理部5、第1の判定処理部6及び表示処理部7の処理手順をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムをメモリ21に格納し、コンピュータのプロセッサ22がメモリ21に格納されているプログラムを実行するようにすればよい。FIG. 3 is a hardware configuration diagram of a computer when components other than the
When components other than the
図4は、監視装置の画像センサ1、観測センサ3及びディスプレイ16を除く構成要素がソフトウェア又はファームウェアなどで実現される場合の処理手順を示すフローチャートである。
また、図2では、監視装置の構成要素のそれぞれが専用のハードウェアで実現される例を示し、図3では、監視装置の画像センサ1、観測センサ3及びディスプレイ16を除く構成要素がソフトウェアやファームウェアなどで実現される例を示しているが、監視装置における一部の構成要素が専用のハードウェアで実現され、残りの構成要素がソフトウェアやファームウェアなどで実現されるものであってもよい。FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing a processing procedure when components other than the
2 shows an example in which each component of the monitoring device is realized by dedicated hardware. In FIG. 3, the components other than the
次に動作について説明する。
画像センサ1は、目標物が存在している領域として、例えば、移動体が交通する空港敷地内及び空港周辺の領域を撮像して、前記領域の撮像画像を目標検出部2及び表示処理部7に出力する。この目標物には、航空機のほか、地上を走行する車両なども含まれる。Next, the operation will be described.
The
目標検出部2は、画像センサ1から出力された撮像画像内の目標物を検出する処理を実施する(図4のステップST1)。
撮像画像内の目標物を検出する処理自体は、公知の技術であるため詳細な説明を省略する。
目標検出部2は、検出した目標物の撮像画像上での位置である目標物画像位置を第1の判定処理部6及び表示処理部7に出力する。
また、目標検出部2は、撮像画像上で目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含画像領域と、検出した目標物を識別するID(IDentification)とを第1の判定処理部6及び表示処理部7に出力する。このIDは、目標検出部2により任意に割り当てられた番号等である。
ここで、目標物包含画像領域は、例えば、撮像画像上で目標物を囲む矩形の枠、曲線と直線から構成する枠が該当する。
また、目標物画像位置は、例えば、目標物包含画像領域の中心に存在している画素の位置座標が該当する。The
Since the process itself for detecting the target in the captured image is a known technique, detailed description thereof is omitted.
The
In addition, the
Here, the target object including image region corresponds to, for example, a rectangular frame surrounding the target object on the captured image, or a frame formed of a curve and a straight line.
In addition, the target image position corresponds to, for example, the position coordinates of a pixel existing at the center of the target-including image area.
この実施の形態1では、監視装置が1つの画像センサ1を実装している例を想定しているが、監視装置が複数の画像センサ1を実装しているものであってもよい。
監視装置が複数の画像センサ1を実装している場合、目標検出部2が、画像センサ1毎に、独立して目標物を検出するようにしてもよいし、複数の画像センサ1により撮影された画像をパノラマ映像として1つの撮像画像に合成し、合成した撮像画像上で目標物を検出するようにしてもよい。また、複数の画像センサ1が、独立して目標物を検出すると同時に、他の画像センサ1と協調動作することで、複数の画像センサ1間を跨がって存在する同一の目標物について同一のIDを付与し、前記IDが同じ目標物については、ある画像センサ1で検出した目標物を他の画像センサ1で検出しない、もしくは後段の処理部へ出力しないようにしてもよい。In the first embodiment, an example in which the monitoring device is mounted with one
When the monitoring apparatus has a plurality of
観測センサ3は、目標物を観測して、観測した目標物の識別情報及び目標物の3次元位置である目標物観測位置(X1,Y1,Z1)のそれぞれを変換処理部5及び表示処理部7に出力する。また、前述した通り、単一の観測センサ3を扱う際に、センサによってはASRのように距離と方位、ASDEのように地上面の2次元位置のみ取得される場合がある。ASRの場合は、航空機の気圧高度、もしくは気圧高度に標準大気の補正を加えて海面からの高度に変換し、距離、方位、高度を3次元位置(X1,Y1,Z1)へ変換して出力しても良いこととする。ASDEの場合は、目標物の高度として、デフォルト値(航空管制のルール上、現実的にあり得る値)を設定して、3次元位置(X1,Y1,Z1)を出力しても良いこととする。
目標物の識別情報には、例えば、航空機の便名又は航空機の機体の情報など、目標物の固有の識別番号が含まれている。
また、観測センサ3は、目標物の推定速度を示す速度ベクトルを取得できる場合は変換処理部5に出力しても良いこととする。The
The identification information of the target includes, for example, a unique identification number of the target such as an aircraft flight number or aircraft fuselage information.
In addition, the
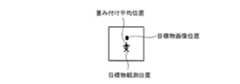
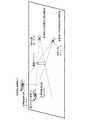
変換処理部5は、図5に示すように、観測センサ3から出力された目標物観測位置(X1,Y1,Z1)を画像センサ1の投影面に投影することで、目標物観測位置(X1,Y1,Z1)を画像センサ1の投影面の座標(u,v)に変換する(図4のステップST2)。
図5は、変換処理部5により画像センサ1の投影面に変換された目標物観測位置及び変換処理部5により特定された目標物包含観測領域を示す説明図である。
画像センサ1の投影面の座標(u,v)は、目標物包含観測領域における中心画素の座標に相当する。As shown in FIG. 5, the
FIG. 5 is an explanatory diagram showing the target observation position converted into the projection plane of the
The coordinates (u, v) of the projection plane of the
例えば、変換処理部5は、以下の式(1)を用いることで、目標物観測位置(X1,Y1,Z1)を画像センサ1の投影面の座標(u,v)に変換することができる。
式(1)において、Aは、画像センサ1の内部パラメータ、Rは、回転行列、Tは、平行移動ベクトルである。
Xworld,Yworld,Zworldは、目標物が存在している3次元直交座標系の各軸の座標値である。例えば、観測センサ3が設置されている位置を原点とする北基準直交座標系が考えられる。
uimage,vimageは、画像センサ1の投影面上での各軸の座標値である。
したがって、目標物観測位置(X1,Y1,Z1)を式(1)の座標値(Xworld,Yworld,Zworld)に代入すると、式(1)の画像センサ1の投影面上での座標値(uimage,vimage)が、画像センサ1の投影面の座標(u,v)となる。For example, the
In Expression (1), A is an internal parameter of the
Xworld , Yworld , and Zworld are coordinate values of each axis of the three-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system where the target is present. For example, a north reference orthogonal coordinate system whose origin is the position where the
uimage and vimage are the coordinate values of each axis on the projection plane of the
Therefore, if the target observation position (X1, Y1, Z1) is substituted into the coordinate values (Xworld , Yworld , Zworld ) of the equation (1), the coordinates on the projection plane of the
変換処理部5は、観測センサ3から目標物の識別情報を受けると、物体形状情報格納部4から識別情報に対応する形状情報の読み出しを行う。
変換処理部5は、形状情報を参照することで、目標物の全長、全幅及び高さを把握する。目標物の識別情報が入力されない場合は、例えば、一般的な全長、全幅及び高さをデフォルト値予め設定しておき、使用しても良いこととする。
また、変換処理部5は、観測センサ3から速度ベクトルを受けると、速度ベクトルから目標物の進行方向を把握する。速度ベクトルが入力されない場合は、例えば、航空管制のルール上、予め設定されているコース又は一般的な速度よって、速度ベクトルのデフォルト値を設定して、目標物の進行方向を把握しても良いこととする。
図6は、変換処理部5により特定される目標物包含観測領域を示す説明図である。
図6Aは、目標物の全長と全幅に対応する第1の矩形領域を示し、図6Bは、目標物の全幅と高さに対応する第2の矩形領域を示している。Upon receiving the target identification information from the
The
Further, when the
FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram showing the target inclusion observation area specified by the
6A shows a first rectangular area corresponding to the overall length and width of the target, and FIG. 6B shows a second rectangular area corresponding to the overall width and height of the target.
変換処理部5は、図6Aに示すように、目標物の進行方向に対応する辺の長さが目標物の全長であり、進行方向と直交する方向に対応する辺の長さが目標物の全幅である第1の矩形領域を生成する。
また、変換処理部5は、図6Bに示すように、高さ方向に対応する辺の長さが目標物の高さであり、水平方向に対応する辺の長さが目標物の全幅である第2の矩形領域を生成する。
ここで、目標物の進行方向が把握できない場合でも、予め設定しておいた進行方向や目標物の傾きよって、矩形領域を生成しても良いこととする。一方、目標物のピッチ、ヨー、ロールなどの詳細な情報が得られる場合は利用しても良いこととする。As shown in FIG. 6A, the
In addition, as shown in FIG. 6B, the
Here, even when the traveling direction of the target cannot be grasped, a rectangular region may be generated based on the previously set traveling direction and the inclination of the target. On the other hand, when detailed information such as the pitch, yaw and roll of the target can be obtained, it may be used.
次に、変換処理部5は、図6Aに示すように、第1の矩形領域における2つの対角線D1,D2のうち、画像センサ1の視線方向との角度が直角に近い方向の対角線D1を選択する。
変換処理部5は、選択した対角線D1の端点a1,a2を画像センサ1の投影面に投影することで、対角線D1の端点a1,a2を画像センサ1の投影面の座標a3,a4に変換する。Next, as illustrated in FIG. 6A, the
The
対角線D1の端点a1,a2を画像センサ1の投影面の座標a3,a4に変換するには、対角線D1の端点a1,a2における3次元直交座標系の座標を得る必要がある。
観測センサ3から出力された目標物観測位置(X1,Y1,Z1)が、第1の矩形領域の中心位置に対応していれば、目標物観測位置(X1,Y1,Z1)と第1の矩形領域の大きさとから、対角線D1の端点a1,a2における3次元直交座標系の座標を得ることができる。
しかし、一般的には、観測センサ3から出力された目標物観測位置(X1,Y1,Z1)は、第1の矩形領域の中心位置に対応しているとは限らない。
目標物観測位置(X1,Y1,Z1)が、第1の矩形領域の中心位置に対応していない場合、対角線D1の端点a1,a2における3次元直交座標系の座標を得ることが困難である。
そこで、この実施の形態1では、例えば、以下のようにして、対角線D1の端点a1,a2を画像センサ1の投影面の座標a3,a4に変換する。In order to convert the end points a1 and a2 of the diagonal line D1 into the coordinates a3 and a4 of the projection surface of the
If the target observation position (X1, Y1, Z1) output from the
However, generally, the target observation position (X1, Y1, Z1) output from the
When the target observation position (X1, Y1, Z1) does not correspond to the center position of the first rectangular area, it is difficult to obtain the coordinates of the three-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system at the end points a1, a2 of the diagonal line D1. .
Therefore, in the first embodiment, for example, the end points a1 and a2 of the diagonal line D1 are converted to the coordinates a3 and a4 on the projection surface of the
対角線D1の端点a1,a2は、第1の矩形領域に9おける対角線D1の端点であるため、端点a1と端点a2との距離を算出することができる。このため、例えば、端点a2における3次元直交座標系の座標を、端点a1における3次元直交座標系の座標で表すことができる。
端点a1の未知の座標を式(1)に代入することで、端点a1の座標を画像センサ1の投影面の座標a3に変換し、端点a1の座標で表した端点a2の座標を式(1)に代入することで、端点a2の座標を画像センサ1の投影面の座標a4に変換すれば、座標a3と座標a4との距離L1−2を求めることができる。
画像センサ1の投影面上での目標物観測位置である座標(u,v)は既に算出しているため、座標(u,v)と距離L1−2から、画像センサ1の投影面の座標a3,a4を算出することができる。Since the end points a1 and a2 of the diagonal line D1 are the end points of the diagonal line D1 in the first
By substituting the unknown coordinates of the end point a1 into the equation (1), the coordinates of the end point a1 are converted into the coordinates a3 of the projection surface of the
Since the coordinates (u, v) that are the target observation positions on the projection plane of the
また、変換処理部5は、図6Bに示すように、第2の矩形領域における2つの対角線D3,D4のうち、画像センサ1の視線方向との角度が直角に近い方向の対角線D3を選択する。
変換処理部5は、選択した対角線D3の端点b1,b2を画像センサ1の投影面に投影することで、対角線D3の端点b1,b2を画像センサ1の投影面の座標b3,b4に変換する。
対角線D3の端点b1,b2を画像センサ1の投影面の座標b3,b4に変換する処理も、対角線D1の端点b1,b2を画像センサ1の投影面の座標b3,b4に変換する処理と同様に行うことができる。Further, as illustrated in FIG. 6B, the
The
The process of converting the end points b1 and b2 of the diagonal line D3 into the coordinates b3 and b4 of the projection plane of the
変換処理部5は、変換した投影面の座標a3,a4及び座標b3,b4から、図5に示すように、画像センサ1の投影面上で、目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含観測領域を特定する(図4のステップST3)。
図5において、目標物包含観測領域の左上の端点の座標は、(a3,b3)であり、目標物包含観測領域の左下の端点の座標は、(a3,b4)である。
また、目標物包含観測領域の右上の端点の座標は、(a4,b3)であり、目標物包含観測領域の右下の端点の座標は、(a4,b4)である。As shown in FIG. 5, the
In FIG. 5, the coordinates of the upper left end point of the target object including observation area are (a3, b3), and the coordinates of the lower left end point of the target object including observation area are (a3, b4).
Also, the coordinates of the upper right end point of the target inclusion observation area are (a4, b3), and the coordinates of the lower right end point of the target inclusion observation area are (a4, b4).
第1の判定処理部6は、変換処理部5により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、目標検出部2から出力された目標物包含画像領域とを比較して、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、目標検出部2により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する。
即ち、第1の判定処理部6は、図7に示すように、画像センサ1の投影面上で、変換処理部5により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、目標検出部2から出力された目標物包含画像領域との重なり範囲Ovを算出する(図4のステップST4)。
図7は、目標物包含観測領域と目標物包含画像領域との重なり範囲Ovを示す説明図である。The first
That is, as shown in FIG. 7, the first
FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram showing an overlapping range Ov between the target object inclusion observation area and the target object inclusion image area.
第1の判定処理部6は、図7に示すように、算出した重なり範囲Ovと事前に設定された閾値Thとを比較する(図4のステップST5)。
第1の判定処理部6は、重なり範囲Ovが閾値Th以上であれば(図4のステップST5:YESの場合)、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、目標検出部2により検出された目標物とが同一物であると判定する(図4のステップST6)。
第1の判定処理部6は、重なり範囲Ovが閾値Th未満であれば(図4のステップST5:NOの場合)、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、目標検出部2により検出された目標物とが同一物でないと判定する(図4のステップST7)。As shown in FIG. 7, the first
The first
The first
表示処理部7は、画像センサ1から出力された撮像画像をディスプレイ16に表示する。
表示処理部7は、第1の判定処理部6により同一物であると判定された場合、変換処理部5により画像センサ1の投影面に変換された目標物観測位置及び観測センサ3から出力された識別情報のそれぞれを撮像画像上に表示し、また、目標検出部2から出力された目標物包含画像領域を撮像画像上に表示する(図4のステップST8)。The
When it is determined by the first
表示処理部7は、第1の判定処理部6により同一物でないと判定された場合、目標検出部2から出力された目標物画像位置、目標物包含画像領域及び目標物のIDとを撮像画像上に表示する(図4のステップST9)。
あるいは、表示処理部7は、第1の判定処理部6により同一物でないと判定された場合、観測センサ3から出力された識別情報と、変換処理部5により画像センサ1の投影面に変換された目標物観測位置及び変換処理部5により特定された目標物包含観測領域とを撮像画像上に表示する。When it is determined by the first
Alternatively, when the first
以上で明らかなように、この実施の形態1によれば、観測センサ3から出力された識別情報によって目標物の大きさを特定し、特定した目標物の大きさ及び観測センサ3から出力された目標物観測位置のそれぞれを画像センサ1の投影面に変換し、変換した目標物の大きさと、変換した目標物観測位置とから、画像センサ1の投影面上で、観測センサ3により観測された目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含観測領域を特定する変換処理部5を設け、第1の判定処理部6が、変換処理部5により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、目標検出部2により特定された目標物包含画像領域とを比較して、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、目標検出部2により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定するように構成している。これにより、目標物が飛行中の航空機である場合でも、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、画像センサ1の撮像画像内の目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定することができる効果を奏する。 As is apparent from the above, according to the first embodiment, the size of the target is specified by the identification information output from the
この実施の形態1では、目標検出部2により撮像画像上で1つの目標物が検出されている例を示しているが、例えば、1つの目標物の前方部分と後方部分が分離されて、2つの目標物として検出されることがある。
このような場合、目標検出部2は、図8に示すように、1つの目標物の前方部分を包含している範囲である目標物包含画像領域(以下、第1の目標物包含画像領域と称する)と、1つの目標物の後方部分を包含している範囲である目標物包含画像領域(以下、第2の目標物包含画像領域と称する)とを特定する。
図8は、目標物包含観測領域と第1及び第2の目標物包含画像領域との重なり範囲Ovを示す説明図である。In the first embodiment, an example is shown in which one target is detected on the captured image by the
In such a case, as shown in FIG. 8, the
FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram showing an overlapping range Ov between the target object inclusion observation area and the first and second target object inclusion image areas.
第1の判定処理部6は、画像センサ1の投影面上で、変換処理部5により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、第1の目標物包含画像領域との重なり範囲Ov1を算出し、また、変換処理部5により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、第2の目標物包含画像領域との重なり範囲Ov2を算出する。
第1の判定処理部6は、重なり範囲Ov1と重なり範囲Ov2の合計が閾値Th以上であれば、目標検出部2により検出された複数の目標物が1つの目標物の一部であり、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、1つの目標物とが同一物であると判定する。
第1の判定処理部6は、重なり範囲Ov1と重なり範囲Ov2の合計が閾値Th未満であれば、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、1つの目標物とが同一物でないと判定する。The first
If the sum of the overlapping range Ov1 and the overlapping range Ov2 is equal to or greater than the threshold Th, the first
If the sum of the overlapping range Ov1 and the overlapping range Ov2 is less than the threshold Th, the first
この実施の形態1では、表示処理部7が、目標検出部2から出力された目標物包含画像領域、あるいは、変換処理部5により特定された目標物包含観測領域を撮像画像上に表示する例を示している。
これは一例に過ぎず、例えば、表示処理部7が、目標物包含画像領域と目標物包含観測領域の双方を含む領域である双方包含領域を撮像画像上に表示するようにしてもよい。
図9は、この発明の実施の形態1による他の監視装置を示す構成図である。
図9において、包含領域特定部8は、例えば包含領域特定回路で実現される。
包含領域特定部8は、図10に示すように、画像センサの1投影面上で、変換処理部5により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、目標検出部2から出力された目標物包含画像領域との双方を含む領域である双方包含領域を特定する処理を実施する。
図10は、包含領域特定部8により特定される双方包含領域を示す説明図である。
表示処理部7は、画像センサ1から出力された撮像画像上に、包含領域特定部8により特定された双方包含領域を表示する。In the first embodiment, the
This is merely an example, and for example, the
FIG. 9 is a block diagram showing another monitoring apparatus according to
In FIG. 9, the inclusion
As shown in FIG. 10, the inclusion
FIG. 10 is an explanatory diagram showing both inclusion areas specified by the inclusion
The
この実施の形態1では、表示処理部7が、変換処理部5により画像センサ1の投影面に変換された目標物観測位置、あるいは、目標検出部2から出力された目標物画像位置を撮像画像上に表示する例を示している。
これは一例に過ぎず、例えば、表示処理部7が、目標物観測位置と目標物画像位置とを重み付け平均して、重み付け平均した位置を撮像画像上に表示するようにしてもよい。
図11は、この発明の実施の形態1による他の監視装置を示す構成図である。
図11において、平均位置出力部9は、例えば平均位置出力回路で実現される。
平均位置出力部9は、図12に示すように、変換処理部5により画像センサ1の投影面に変換された目標物観測位置と、目標検出部2から出力された目標物画像位置とを重み付け平均して、重み付け平均した位置を出力する処理を実施する。
図12は、重み付け平均した位置を示す説明図である。
表示処理部7は、画像センサ1から出力された撮像画像上に、平均位置出力部9から出力された位置を表示する。In the first embodiment, the
This is merely an example, and for example, the
FIG. 11 is a block diagram showing another monitoring apparatus according to
In FIG. 11, the average
As shown in FIG. 12, the average
FIG. 12 is an explanatory diagram showing a weighted average position.
The
実施の形態2.
上記実施の形態1では、変換処理部5が、目標物包含観測領域を特定する例を示している。
この実施の形態2では、変換処理部5が、目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲を示す観測誤差情報に従って目標物包含観測領域を補正する例を説明する。
この実施の形態2の監視装置の構成図は、上記実施の形態1の監視装置と同様に、図1、図9又は図11である。
In the said
In the second embodiment, an example will be described in which the
The configuration diagram of the monitoring device according to the second embodiment is FIG. 1, FIG. 9, or FIG. 11, similar to the monitoring device according to the first embodiment.
観測センサ3により観測された目標物の位置には観測誤差が含まれている。このため、図13に示すように、観測センサ3から出力された目標物観測位置と、目標検出部2から出力された目標物画像位置とが大きくずれていることがある。
図13は、観測センサ3に起因する目標物観測位置と目標物画像位置との位置ずれを示す説明図である。The position of the target observed by the
FIG. 13 is an explanatory diagram showing a positional shift between the target observation position and the target image position caused by the
この実施の形態2では、観測センサ3は、目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲を示す観測誤差情報として、3次元の観測誤差共分散行列を変換処理部5に出力する。
変換処理部5は、図14に示すように、観測センサ3から出力された観測誤差情報が示す目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲を画像センサ1の投影面に投影することで、目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲を画像センサ1の投影面の座標に変換する。
図14は、目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲及び画像センサ1の投影面上での観測誤差範囲を示す説明図である。
目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲は、幾何的には図14のような楕円体で表現される。
変換処理部5は、目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲における各々の点の位置を式(1)の座標値(Xworld,Yworld,Zworld)に代入することで、目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲を画像センサ1の投影面の座標に変換することができる。
目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲を画像センサ1の投影面の座標に変換する処理として、以下の処理を用いることもできる。In the second embodiment, the
As shown in FIG. 14, the
FIG. 14 is an explanatory diagram showing the observation error range of the target observation position and the observation error range on the projection plane of the
The observation error range of the target observation position is geometrically expressed by an ellipsoid as shown in FIG.
The
The following processing can also be used as processing for converting the observation error range of the target observation position into the coordinates of the projection plane of the
変換処理部5は、目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲である楕円体の固有値及び固有ベクトルから、楕円体の長軸の幅及び短軸の幅のそれぞれを算出する。
図15は、楕円体の固有ベクトルと長軸の幅との関係を示す説明図である。
そして、変換処理部5は、式(1)を用いて、楕円体における長軸の幅の端点及び短軸の幅の端点のそれぞれを画像センサ1の投影面の座標に変換することで、投影面上での観測誤差範囲を算出する。The
FIG. 15 is an explanatory diagram showing the relationship between the eigenvector of the ellipsoid and the width of the long axis.
Then, the
変換処理部5は、図16に示すように、投影面上での観測誤差範囲が、上記実施の形態1と同様の方法で特定した目標物包含観測領域を包含していない場合、投影面上での観測誤差範囲が目標物包含観測領域を包含するように、投影面上での観測誤差範囲を拡大する。
次に、変換処理部5は、目標物包含観測領域が、拡大した観測誤差範囲と一致するように、目標物包含観測領域を補正する。
即ち、変換処理部5は、図16に示すように、拡大した観測誤差範囲を補正後の目標物包含観測領域とする。
変換処理部5は、補正後の目標物包含観測領域を第1の判定処理部6に出力する。
図16は、補正前後の目標物包含観測領域及び投影面上での観測誤差範囲を示す説明図である。
第1の判定処理部6の処理内容は、上記実施の形態1と同様であるため、詳細な説明を省略する。As shown in FIG. 16, when the observation error range on the projection plane does not include the target inclusion inclusion observation area specified by the same method as in the first embodiment, the
Next, the
That is, as shown in FIG. 16, the
The
FIG. 16 is an explanatory diagram showing a target inclusion observation area before and after correction and an observation error range on the projection plane.
Since the processing content of the first
以上で明らかなように、この実施の形態2によれば、観測センサ3が、目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲を示す観測誤差情報を出力し、変換処理部5が、観測センサ3から出力された観測誤差情報に従って目標物包含観測領域を補正するように構成したので、観測センサ3の観測誤差が大きくても、同一物の判定精度の劣化を防止することができる効果を奏する。 As is apparent from the above, according to the second embodiment, the
実施の形態3.
この実施の形態3では、目標検出部2と第1の判定処理部6との間に第1の追尾処理部を備え、観測センサ3と変換処理部5との間に第2の追尾処理部を備えている例を説明する。
In the third embodiment, a first tracking processing unit is provided between the
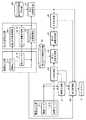
図17は、この発明の実施の形態3による監視装置を示す構成図である。図18は、この発明の実施の形態3による監視装置を示すハードウェア構成図である。
図17及び図18において、図1及び図2と同一符号は同一または相当部分を示すので説明を省略する。
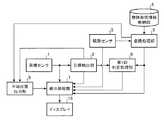
画像センサ1−1〜1−Nは、図1の画像センサ1と同様に、例えば、光学カメラ又は赤外カメラなどで実現される。
画像センサ1−1〜1−Nは、目標物が存在している領域として、例えば、移動体が交通する空港敷地内及び空港周辺の領域を撮像して、前記領域の撮像画像を映像生成部31及び目標検出部32に出力する。FIG. 17 is a block diagram showing a monitoring apparatus according to
17 and 18, the same reference numerals as those in FIGS. 1 and 2 indicate the same or corresponding parts, and thus description thereof is omitted.
The image sensors 1-1 to 1-N are realized by, for example, an optical camera or an infrared camera, similarly to the
The image sensors 1-1 to 1-N image, for example, an area in and around an airport site where a moving object is traveling as an area where the target is present, and a captured image of the area is generated as a video generation unit. 31 and the
映像生成部31は、例えば、図18に示す映像生成回路41で実現される。
映像生成部31は、画像センサ1−1〜1−Nから出力された撮像画像のそれぞれを表示処理部40に出力する。
また、映像生成部31は、画像センサ1−1〜1−Nから出力された撮像画像を合成することで、1つのパノラマ画像を生成し、パノラマ画像を撮像画像として目標検出部32及び表示処理部40に出力する。ここで、画像センサ1−1〜1−Nから出力された撮像画像を別々に、直接、撮像画像として目標検出部32及び表示処理部40に出力しても良いこととする。The
The
In addition, the
目標検出部32は、例えば、図18に示す目標検出回路42で実現される。
目標検出部32は、画像センサ1−n(n=1,2,・・・,N)から出力された撮像画像内の目標物、あるいは、映像生成部31から出力された撮像画像内の目標物を検出する処理を実施する。
目標検出部32は、撮像画像上で検出した目標物の位置である目標物画像位置及び撮像画像上で目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含画像領域のそれぞれを第1の追尾処理部33に出力する処理を実施する。The
The
The
第1の追尾処理部33は、例えば、図18に示す第1の追尾処理回路43で実現される。
第1の追尾処理部33は、目標検出部32により検出された目標物の追尾処理を実施して、追尾処理後の目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含画像領域を第1の判定処理部37に出力する処理を実施する。
第1の追尾処理部33が実施する目標物の追尾処理として、例えば、カルマンフィルタ、パーティクルフィルタなどを用いる公知の追尾処理を利用することができる。The first
The first
As the target tracking process performed by the first
観測センサ3−1〜3−Mは、図1の観測センサ3と同様に、例えば、ASR、MLAT、WAMなどで実現される。
観測センサ3−m(m=1,2,・・・,M)は、目標物を観測して、観測した目標物の識別情報及び目標物の3次元位置である目標物観測位置のそれぞれを第2の追尾処理部34−m及びマルチセンサ追尾処理部35に出力する。The observation sensors 3-1 to 3-M are realized by, for example, ASR, MLAT, WAM, and the like, similarly to the
The observation sensor 3-m (m = 1, 2,..., M) observes the target, and identifies the identification information of the observed target and the target observation position that is the three-dimensional position of the target. The data is output to the second tracking processing unit 34-m and the multi-sensor
第2の追尾処理部34−mは、例えば、図18に示す第2の追尾処理回路44で実現される。
第2の追尾処理部34−mは、観測センサ3−mから出力された目標物観測位置を用いて、目標物の追尾処理を実施し、追尾処理後の目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を変換処理部36に出力する処理を実施する。
また、第2の追尾処理部34−mは、観測センサ3−mから出力された目標物の識別情報を変換処理部36に出力する処理を実施する。
マルチセンサ追尾処理部35は、例えば、図18に示すマルチセンサ追尾処理回路45で実現される。
マルチセンサ追尾処理部35は、M個の観測センサ3−1〜3−Mから出力された目標物観測位置を用いて、目標物の追尾処理を実施し、追尾処理後の目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を変換処理部36に出力する処理を実施する。
マルチセンサ追尾処理部35は、第2の追尾処理部34−mと比べて、複数の目標物観測位置を用いる点でのみ相違している。
第2の追尾処理部34−m及びマルチセンサ追尾処理部35のそれぞれが実施する目標物の追尾処理として、例えば、カルマンフィルタ、パーティクルフィルタなどを用いる公知の追尾処理を利用することができる。The second tracking processing unit 34-m is realized by, for example, the second
The second tracking processing unit 34-m performs target tracking processing using the target observation position output from the observation sensor 3-m, and performs target observation that is the position of the target after the tracking processing. A process of outputting the position to the
In addition, the second tracking processing unit 34-m performs a process of outputting the identification information of the target output from the observation sensor 3-m to the
The multi-sensor
The multi-sensor
The multi-sensor
As the target tracking process performed by each of the second tracking processing unit 34-m and the multi-sensor
変換処理部36は、例えば、図18に示す変換処理回路46で実現される。
変換処理部36は、物体形状情報格納部4から、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された識別情報に対応する形状情報を読み出し、形状情報を参照することで、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物の大きさを特定する処理を実施する。
変換処理部36は、特定した目標物の大きさ及び第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測位置のそれぞれを画像センサ1−nの投影面に変換する処理を実施する。
変換処理部36は、変換した目標物の大きさと、変換した目標物観測位置とから、画像センサ1−nの投影面上で、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含観測領域を特定する処理を実施する。The
The
The
The
第1の判定処理部37は、例えば、図18に示す第1の判定処理回路47で実現される。
第1の判定処理部37は、変換処理部36により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、第1の追尾処理部33から出力された目標物包含画像領域とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する処理を実施する。
即ち、第1の判定処理部37は、画像センサ1−nの投影面上で、変換処理部36により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、第1の追尾処理部33から出力された目標物包含画像領域との重なり範囲を算出する処理を実施する。
また、第1の判定処理部37は、重なり範囲が閾値以上であれば、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32により検出された目標物とが同一物であると判定する処理を実施する。
第1の判定処理部37は、重なり範囲が閾値未満であれば、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32により検出された目標物とが同一物でないと判定する処理を実施する。
判定結果格納部38は、例えば、図18に示す判定結果記憶回路48で実現される。
判定結果格納部38は、第1の判定処理部37の判定結果を格納する。The first
The first
That is, the first
In addition, if the overlapping range is equal to or greater than the threshold, the first
If the overlapping range is less than the threshold value, the first
The determination
The determination
平滑処理部39は、例えば、図18に示す平滑処理回路49で実現される。
平滑処理部39は、第1の追尾処理部33から出力された目標物包含画像領域を時間方向に平滑化し、平滑化後の目標物包含画像領域を表示処理部40に出力する処理を実施する。
表示処理部40は、例えば、図2に示す表示処理回路50で実現される。
表示処理部40は、映像生成部31から出力された撮像画像をディスプレイ16に表示する処理を実施する。
表示処理部40は、第1の判定処理部37により同一物であると判定された場合、変換処理部36により画像センサ1−nの投影面に変換された目標物観測位置及び観測センサ3−mから出力された識別情報のそれぞれを撮像画像上に表示し、また、平滑処理部39から出力された平滑化後の目標物包含画像領域を撮像画像上に表示する処理を実施する。The smoothing
The smoothing
The
The
When the first
図17では、監視装置の構成要素である画像センサ1−n、観測センサ3−m、映像生成部31、目標検出部32、第1の追尾処理部33、第2の追尾処理部34−m、マルチセンサ追尾処理部35、変換処理部36、第1の判定処理部37、判定結果格納部38、平滑処理部39、表示処理部40及びディスプレイ16のそれぞれが、図18に示すような専用のハードウェアで実現されるものを想定している。即ち、画像センサ1−n、観測センサ3−m、映像生成回路41、目標検出回路42、第1の追尾処理回路43、第2の追尾処理回路44、マルチセンサ追尾処理回路45、変換処理回路46、第1の判定処理回路47、判定結果記憶回路48、平滑処理回路49、表示処理回路50及びディスプレイ16で実現されるものを想定している。 In FIG. 17, the image sensor 1-n, the observation sensor 3-m, the
ここで、形状記憶回路12及び判定結果記憶回路48は、例えば、RAM、ROM、フラッシュメモリ、EPROM、EEPROMなどの不揮発性又は揮発性の半導体メモリや、磁気ディスク、フレキシブルディスク、光ディスク、コンパクトディスク、ミニディスク、DVDなどが該当する。
また、映像生成回路41、目標検出回路42、第1の追尾処理回路43、第2の追尾処理回路44、マルチセンサ追尾処理回路45、変換処理回路46、第1の判定処理回路47、平滑処理回路49及び表示処理回路50は、例えば、単一回路、複合回路、プログラム化したプロセッサ、並列プログラム化したプロセッサ、ASIC、FPGA、または、これらを組み合わせたものが該当する。Here, the
The
監視装置の画像センサ1−n、観測センサ3−m及びディスプレイ16を除く構成要素は、専用のハードウェアで実現されるものに限るものではなく、ソフトウェア、ファームウェア、または、ソフトウェアとファームウェアとの組み合わせで実現されるものであってもよい。 The components other than the image sensor 1-n, the observation sensor 3-m, and the
監視装置の画像センサ1−n、観測センサ3−m及びディスプレイ16を除く構成要素がソフトウェア又はファームウェアなどで実現される場合、物体形状情報格納部4及び判定結果格納部38を図3に示すコンピュータのメモリ21上に構成するとともに、映像生成部31、目標検出部32、第1の追尾処理部33、第2の追尾処理部34−m、マルチセンサ追尾処理部35、変換処理部36、第1の判定処理部37、平滑処理部39及び表示処理部40の処理手順をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムをメモリ21に格納し、コンピュータのプロセッサ22がメモリ21に格納されているプログラムを実行するようにすればよい。 When components other than the image sensor 1-n, the observation sensor 3-m, and the
次に動作について説明する。
画像センサ1−n(n=1,2,・・・,N)は、目標物が存在している領域として、例えば、移動体が交通する空港敷地内及び空港周辺の領域を撮像して、前記領域の撮像画像を目標検出部32及び映像生成部31に出力する。
映像生成部31は、画像センサ1−nから出力された撮像画像を表示処理部40に出力する。
また、映像生成部31は、画像センサ1−1〜1−Nから出力されたN個の撮像画像を合成することで、1つのパノラマ画像を生成し、パノラマ画像を撮像画像として目標検出部32及び表示処理部40に出力する。Next, the operation will be described.
The image sensor 1-n (n = 1, 2,..., N), for example, images areas in and around the airport site where the mobile object is in traffic, The captured image of the area is output to the
The
In addition, the
目標検出部32は、画像センサ1−nから出力された撮像画像内の目標物、あるいは、映像生成部31から出力された撮像画像内の目標物を検出する処理を実施する。
撮像画像内の目標物を検出する処理自体は、公知の技術であるため詳細な説明を省略する。
この実施の形態3では、説明の簡単化のため、目標検出部32によって、1つの目標物が検出されるものとする。
目標検出部32は、撮像画像上で検出した目標物の位置である目標物画像位置と、検出した目標物を識別するIDとを第1の追尾処理部33及び表示処理部40に出力する。
また、目標検出部32は、撮像画像上で検出した目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含画像領域を第1の追尾処理部33に出力する。The
Since the process itself for detecting the target in the captured image is a known technique, detailed description thereof is omitted.
In the third embodiment, it is assumed that one target is detected by the
The
In addition, the
第1の追尾処理部33は、目標検出部32から出力された目標物画像位置を用いて、撮像画像内の目標物の追尾処理を実施し、追尾処理後の目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含画像領域を第1の判定処理部37及び平滑処理部39に出力する。
第1の追尾処理部33による目標物の追尾処理は、目標検出部32から出力された目標物画像位置の時系列方向の相関を取る処理であり、例えば、カルマンフィルタを用いることができる。
なお、第1の追尾処理部33は、目標物包含画像領域を平滑化し、平滑後の目標物包含画像領域を第1の判定処理部37に出力するようにしてもよい。目標物包含画像領域を平滑化することで、目標物包含画像領域の変動が抑えられるため、第1の判定処理部37の判定精度を高めることができる。The first
The target tracking process by the first
Note that the first
観測センサ3−m(m=1,2,・・・,M)は、目標物を観測して、観測した目標物の識別情報及び目標物の3次元位置である目標物観測位置を第2の追尾処理部34−m及びマルチセンサ追尾処理部35に出力する。
また、観測センサ3−mは、目標物の推定速度を示す速度ベクトルを第2の追尾処理部34−mに出力する。
この実施の形態3では、説明の簡単化のため、観測センサ3−mによって、1つの目標物が観測されるものとする。The observation sensor 3-m (m = 1, 2,..., M) observes the target, and secondly identifies the identification information of the observed target and the target observation position that is the three-dimensional position of the target. Output to the tracking processing unit 34-m and the multi-sensor
In addition, the observation sensor 3-m outputs a speed vector indicating the estimated speed of the target to the second tracking processing unit 34-m.
In the third embodiment, it is assumed that one target is observed by the observation sensor 3-m for simplification of description.
第2の追尾処理部34−mは、観測センサ3−mから出力された目標物観測位置及び速度ベクトルを用いて、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物の追尾処理を実施し、追尾処理後の目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を変換処理部36に出力する。
第2の追尾処理部34−mによる目標物の追尾処理は、観測センサ3−mから出力された目標物観測位置の時系列方向の相関を取る処理であり、例えば、カルマンフィルタを用いることができる。
また、第2の追尾処理部34−mは、観測センサ3−mから出力された目標物の識別情報及び追尾処理時に算出される推定誤差共分散行列などを変換処理部36に出力する。
推定誤差共分散行列は、目標物の追尾処理による推定誤差を示す推定誤差情報に相当する。The second tracking processing unit 34-m performs tracking processing of the target observed by the observation sensor 3-m using the target observation position and velocity vector output from the observation sensor 3-m. The target observation position, which is the position of the target after processing, is output to the
The target tracking process by the second tracking processing unit 34-m is a process for obtaining a correlation in the time series direction of the target observation position output from the observation sensor 3-m. For example, a Kalman filter can be used. .
In addition, the second tracking processing unit 34-m outputs the target identification information output from the observation sensor 3-m, the estimated error covariance matrix calculated during the tracking process, and the like to the
The estimation error covariance matrix corresponds to estimation error information indicating an estimation error due to the target tracking process.
マルチセンサ追尾処理部35は、M個の観測センサ3−1〜3−Mから出力された目標物観測位置及び速度ベクトルを用いて、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物の追尾処理を実施し、追尾処理後の目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を変換処理部36に出力する。
また、マルチセンサ追尾処理部35は、追尾処理時に算出される推定誤差共分散行列などを変換処理部36に出力する。
マルチセンサ追尾処理部35が目標物の追尾処理を実施することで、M個の観測センサ3−1〜3−Mのうち、いずれかの観測センサが目標物の識別情報を取得できない場合でも、マルチセンサ追尾処理部35は、他の観測センサにより取得された識別情報を追尾処理後の目標物に対応付けることができる。
このため、マルチセンサ追尾処理部35は、M個の観測センサ3−1〜3−Mの中に、目標物の識別情報を取得できない観測センサが存在していても、追尾処理後の目標物の識別情報を変換処理部36に出力することができる。The multi-sensor
In addition, the multi-sensor
Even when any one of the M observation sensors 3-1 to 3-M cannot acquire the identification information of the target, the multi-sensor
For this reason, the multi-sensor
変換処理部36は、物体形状情報格納部4から、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された識別情報に対応する形状情報を読み出し、形状情報を参照することで、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物の大きさを特定する。
変換処理部36は、特定した目標物の大きさ及び第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測位置のそれぞれを画像センサ1−nの投影面に変換する処理を実施する。
変換処理部36は、変換した目標物の大きさと、変換した目標物観測位置とから、画像センサ1−nの投影面上で、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含観測領域を特定する。
変換処理部36の処理内容は、概ね、上記実施の形態2における変換処理部5の処理内容と同様であるが、以下の点で相違している。The
The
The
The processing content of the
上記実施の形態2における変換処理部5は、目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲を示す観測誤差情報に従って目標物包含観測領域を補正している。
これに対して、この実施の形態3における変換処理部36は、目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲の代わりに、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された追尾処理による推定誤差を示す推定誤差共分散行列に従って目標物包含観測領域を補正する。
変換処理部36による目標物包含観測領域の補正処理自体は、変換処理部5による目標物包含観測領域の補正処理と同様であるため詳細な説明を省略するが、追尾処理による推定誤差の範囲は、目標物観測位置の観測誤差範囲と比べて狭い範囲となるため、上記実施の形態2よりも、更に同一物の判定精度を高めることができる。The
On the other hand, the
The correction process for the target inclusion observation area by the
第1の判定処理部37は、変換処理部36により補正された目標物包含観測領域と、第1の追尾処理部33から出力された目標物包含画像領域とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する。
即ち、第1の判定処理部37は、画像センサ1−nの投影面上で、変換処理部36により補正された目標物包含観測領域と、第1の追尾処理部33から出力された目標物包含画像領域との重なり範囲Ovを算出する。The first
In other words, the first
第1の判定処理部37は、算出した重なり範囲Ovと事前に設定された閾値Thとを比較する。
第1の判定処理部37は、重なり範囲Ovが閾値Th以上であれば、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32により検出された目標物とが同一物であると判定する。
第1の判定処理部37は、重なり範囲Ovが閾値Th未満であれば、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、目標検出部32により検出された目標物とが同一物でないと判定する。The first
If the overlap range Ov is equal to or greater than the threshold Th, the first
If the overlapping range Ov is less than the threshold Th, the first
第1の判定処理部37による判定処理の処理タイミングが、画像センサ1−nのフレームレートに対応している場合、第1の判定処理部37の処理負荷が大きくなり、画像センサ1−nのフレームレートで判定処理が終了しない場合がある。
そこで、第1の判定処理部37が、同一物であるか否かの判定結果を判定結果格納部38に格納し、一定期間中は、判定処理を実施せずに、判定結果格納部38に格納されている判定結果を読み出して、その判定結果を表示処理部40に出力するようにしてもよい。
また、第1の判定処理部37は、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、目標検出部32により検出された目標物とが同一物であると判定した場合、目標物のID、目標物の識別情報、目標物包含画像領域及び目標物包含観測領域などの情報を判定結果格納部38に格納する。
そして、第1の判定処理部37は、判定結果格納部38に格納されている情報を、判定結果と一緒に表示処理部40に出力するようにしてもよい。When the processing timing of the determination processing by the first
Therefore, the first
Further, when the first
Then, the first
平滑処理部39は、以下の式(2)に示すように、第1の追尾処理部33から出力された目標物包含画像領域を時間方向に平滑化し、平滑化後の目標物包含画像領域を表示処理部40に出力する。
式(2)において、Lkは、時刻tkにおける目標物包含画像領域の横幅(または縦幅)、Ls,k−1は、時刻tk−1における目標物包含画像領域の横幅推定値(または縦幅推定値)、Ls,kは、時刻tkにおける目標物包含画像領域の横幅推定値(または縦幅推定値)、aは係数である。
平滑処理部39が目標物包含画像領域を時間方向に平滑化することで、目標物包含画像領域の横幅又は縦幅の変動を抑えることができる。As shown in the following equation (2), the smoothing
In Equation (2), Lk is the horizontal width (or vertical width) of the target object including image area at time tk, and Ls, k−1 is the estimated horizontal width (or vertical width) of the target object including image area at time tk−1. (Estimated value), Ls, k is a lateral width estimated value (or vertical width estimated value) of the target object including image region at time tk, and a is a coefficient.
The smoothing
表示処理部40は、映像生成部31から出力された画像センサ1−nの撮像画像、または、パノラマ画像である撮像画像をディスプレイ16に表示する。
表示処理部40は、第1の判定処理部37により同一物であると判定された場合、変換処理部36により画像センサ1の投影面に変換された目標物観測位置及び観測センサ3−mから出力された識別情報のそれぞれを撮像画像上に表示し、また、平滑処理部39から出力された平滑化後の目標物包含画像領域を撮像画像上に表示する。The
When the first
表示処理部40は、第1の判定処理部37により同一物でないと判定された場合、目標検出部32から出力された目標物画像位置及び平滑処理部39から出力された平滑化後の目標物包含画像領域と、目標検出部32から出力された目標物のIDとを撮像画像上に表示する。
あるいは、表示処理部7は、第1の判定処理部37により同一物でないと判定された場合、観測センサ3−mから出力された識別情報と、変換処理部36により画像センサ1−nの投影面に変換された目標物観測位置及び変換処理部36により補正された目標物包含観測領域とを撮像画像上に表示する。When the first
Alternatively, when the first
この実施の形態3では、第1の判定処理部37が、変換処理部36により補正された目標物包含観測領域と、第1の追尾処理部33から出力された目標物包含画像領域とを比較する例を示している。
しかし、観測センサ3−mは、画像センサ1−nと比べて、更新レートが低いため、観測センサ3−mの観測時刻と、画像センサ1−nの撮像時刻との間に時刻差を生じることがある。上記の時刻差は、第1の判定処理部37の判定精度の劣化要因になる。
また、観測センサ3−mの観測時刻と、画像センサ1−nの撮像時刻とが同じ時刻であっても、観測センサ3−mと第1の判定処理部37間のデータ遅延時間と、画像センサ1−nと第1の判定処理部37間のデータ遅延時間との間に時間差を生じることがある。上記の時間差は、第1の判定処理部37の判定精度の劣化要因になる。In the third embodiment, the first
However, since the observation sensor 3-m has a lower update rate than the image sensor 1-n, a time difference is generated between the observation time of the observation sensor 3-m and the imaging time of the image sensor 1-n. Sometimes. The time difference is a cause of deterioration in the determination accuracy of the first
Even if the observation time of the observation sensor 3-m and the imaging time of the image sensor 1-n are the same time, the data delay time between the observation sensor 3-m and the first
そこで、第1の判定処理部37が、以下のようにして、判定精度の劣化要因を解消するようにしてもよい。
まず、第1の判定処理部37は、例えば、画像センサ1−nの更新レートに対応する更新時刻tを設定する。
第1の判定処理部37は、観測センサ3−mの観測時刻が更新時刻tよりも遅れている場合、更新時刻tと、第2の追尾処理部34−mから目標物観測位置が出力される時刻t’又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から目標物観測位置が出力される時刻t’との時刻差(t−t’)を算出する。Therefore, the first
First, the first
When the observation time of the observation sensor 3-m is behind the update time t, the first
次に、第1の判定処理部37は、時刻差(t−t’)によって、以下の式(3)に示すように、例えば、第2の追尾処理部34−mの追尾処理で算出される推定状態ベクトルxハットtを時間外挿する。明細書の文章中では、電子出願の関係上、xの文字の上に“^”の記号を付することができないので、「xハットt」のように表記している。推定状態ベクトルxハットtは、第2の追尾処理部34−m等による追尾処理後の時刻tの目標物観測位置に相当する。
式(3)におけるΦ(t−t’)は、例えば、以下の式(4)に示すように、等速直線運動モデルの状態推移行列として定義することができる。
式(4)において、In×nは、n行n列の単位行列、On×nは、n行n列の零行列である。Next, the first
Φ (t−t ′) in equation (3) can be defined as a state transition matrix of a constant velocity linear motion model, for example, as shown in equation (4) below.
In Expression (4), In × n is an n × n unit matrix, and On × n is an n × n zero matrix.
また、第1の判定処理部37は、時刻差(t−t’)によって、以下の式(5)に示すように、例えば、第2の追尾処理部34−mの追尾処理による推定誤差を示す推定誤差共分散行列Ptを時間外挿する。
式(5)において、Q(t−t’)は、駆動雑音共分散行列である。
第1の判定処理部37が、時間外挿した推定状態ベクトルxハットtである追尾処理後の目標物観測位置及び時間外挿した推定誤差共分散行列Ptを変換処理部36に出力することで、時刻差(t−t’)による判定精度の劣化要因が解消される。Further, the first
In Equation (5), Q (t−t ′) is a drive noise covariance matrix.
The first
以上で明らかなように、この実施の形態3によれば、目標検出部32により検出された目標物の追尾処理を実施して、追尾処理後の目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含画像領域を第1の判定処理部37に出力する第1の追尾処理部33と、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物の追尾処理を実施して、追尾処理後の目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を変換処理部36に出力する第2の追尾処理部34−mとを備えている。これにより、画像センサ1−nによる目標物の撮像誤差及び観測センサ3−mによる目標物の観測誤差のそれぞれが抑圧される。その結果、上記実施の形態1よりも、更に、同一物の判定精度を高めることができる効果を奏する。 As is apparent from the above, according to the third embodiment, the target that is the range including the target after the tracking process is performed by performing the tracking process of the target detected by the
実施の形態4.
上記実施の形態1〜3では、監視装置が第1の判定処理部6又は第1の判定処理部37を備えている例を示している。
この実施の形態4では、監視装置が第1の判定処理部37、第2の判定処理部62及び第3の判定処理部64を備えている例を説明する。
また、この実施の形態4では、上記実施の形態1〜3と異なり、同一物の判定に画像上ではなく、地図座標における位置を用いることを特徴としている。Embodiment 4 FIG.
In the first to third embodiments, an example in which the monitoring device includes the first
In the fourth embodiment, an example in which the monitoring device includes a first
Further, the fourth embodiment is characterized in that, unlike the first to third embodiments, the position in the map coordinates is used for determining the same object, not on the image.
図19は、この発明の実施の形態4による監視装置を示す構成図である。図20は、この発明の実施の形態4による監視装置を示すハードウェア構成図である。
図19及び図20において、図1、図2、図17及び図18と同一符号は同一または相当部分を示すので説明を省略する。
観測位置射影部61は、例えば、図20に示す観測位置射影回路71で実現される。
観測位置射影部61は、第2の追尾処理部34−mから出力された目標物観測位置又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測位置を、画像センサ1−nの視線方向に移動したときに、地上面と交差する位置を射影位置として算出する処理を実施する。FIG. 19 is a block diagram showing a monitoring apparatus according to Embodiment 4 of the present invention. FIG. 20 is a hardware configuration diagram showing a monitoring apparatus according to Embodiment 4 of the present invention.
19 and 20, the same reference numerals as those in FIGS. 1, 2, 17, and 18 indicate the same or corresponding parts, and thus description thereof is omitted.
The observation
The observation
第2の判定処理部62は、例えば、図20に示す第2の判定処理回路72で実現される。
第2の判定処理部62は、観測位置射影部61により算出された射影位置と目標検出部32bから出力された目標物地図座標位置とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する処理を実施する。
ここで、目標検出部32bは、図17の目標検出部32と同様に、目標物を検出する処理を実施する。
ただし、目標検出部32bが、目標物地図座標位置を算出する方法としては、画像上での目標物画素位置より、予め用意していた地図DBを用いて、地図上の座標位置と照合する方法でも良い。一方、飛行中の目標物については、地上を走行する目標物でないことから、地図との照合が困難であるため、図21のように、画像センサ視線方向ベクトルを延長し、水平面と交差する位置を目標物地図座標位置として出力しても良いこととする。The second
The second
Here, the
However, as a method for calculating the target map coordinate position by the
第3の追尾処理部63は、例えば、図20に示す第3の追尾処理回路73で実現される。
第3の追尾処理部63は、目標検出部32bにより検出された1つ以上の目標物のうち、第2の判定処理部62により同一物であると判定された目標物以外の目標物の追尾処理を実施して、追尾処理後の目標物の位置である目標物地図座標位置を出力する処理を実施する。The third
The third
第3の判定処理部64は、例えば、図20に示す第3の判定処理回路74で実現される。
第3の判定処理部64は、第2の追尾処理部34−mから出力された目標物観測位置又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測位置と、第3の追尾処理部63から出力された目標物包含画像領域とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する処理を実施する。
目標物選択部65は、例えば、図20に示す目標物選択回路75で実現される。
目標物選択部65は、第1の判定処理部37、第2の判定処理部62又は第3の判定処理部64により同一物であると判定された目標物の中から、1つ以上の目標物を選択する処理を実施する。The third
The third
The
The
図19の監視装置は、観測位置射影部61、第2の判定処理部62、第3の追尾処理部63、第3の判定処理部64及び目標物選択部65が図17の監視装置に適用されている例を示しているが、図1の監視装置に適用されているものであってもよい。
図19では、監視装置の構成要素である画像センサ1−n、観測センサ3−m、映像生成部31、目標検出部32b、第1の追尾処理部33、第2の追尾処理部34−m、マルチセンサ追尾処理部35、変換処理部36、第1の判定処理部37、判定結果格納部38、平滑処理部39、表示処理部40、観測位置射影部61、第2の判定処理部62、第3の追尾処理部63、第3の判定処理部64、目標物選択部65及びディスプレイ16のそれぞれが、図20に示すような専用のハードウェアで実現されるものを想定している。即ち、画像センサ1−n、観測センサ3−m、映像生成回路41、目標検出回路42、第1の追尾処理回路43、第2の追尾処理回路44、マルチセンサ追尾処理回路45、変換処理回路46、第1の判定処理回路47、判定結果記憶回路48、平滑処理回路49、表示処理回路50、観測位置射影回路71、第2の判定処理回路72、第3の追尾処理回路73、第3の判定処理回路74、目標物選択回路75及びディスプレイ16で実現されるものを想定している。In the monitoring device of FIG. 19, the observation
In FIG. 19, the image sensor 1-n, the observation sensor 3-m, the
映像生成回路41、目標検出回路42、第1の追尾処理回路43、第2の追尾処理回路44、マルチセンサ追尾処理回路45、変換処理回路46、第1の判定処理回路47、平滑処理回路49、表示処理回路50、観測位置射影回路71、第2の判定処理回路72、第3の追尾処理回路73、第3の判定処理回路74及び目標物選択回路75は、例えば、単一回路、複合回路、プログラム化したプロセッサ、並列プログラム化したプロセッサ、ASIC、FPGA、または、これらを組み合わせたものが該当する。
監視装置の画像センサ1−n、観測センサ3−m及びディスプレイ16を除く構成要素は、専用のハードウェアで実現されるものに限るものではなく、ソフトウェア、ファームウェア、または、ソフトウェアとファームウェアとの組み合わせで実現されるものであってもよい。
監視装置の画像センサ1−n、観測センサ3−m及びディスプレイ16を除く構成要素がソフトウェア又はファームウェアなどで実現される場合、物体形状情報格納部4及び判定結果格納部38を図3に示すコンピュータのメモリ21上に構成するとともに、映像生成部31、目標検出部32b、第1の追尾処理部33、第2の追尾処理部34−m、マルチセンサ追尾処理部35、変換処理部36、第1の判定処理部37、平滑処理部39、表示処理部40、観測位置射影部61、第2の判定処理部62、第3の追尾処理部63、第3の判定処理部64及び目標物選択部65の処理手順をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムをメモリ21に格納し、コンピュータのプロセッサ22がメモリ21に格納されているプログラムを実行するようにすればよい。The components other than the image sensor 1-n, the observation sensor 3-m, and the
When components other than the image sensor 1-n, the observation sensor 3-m, and the
次に動作について説明する。
観測位置射影部61は、図21に示すように、第2の追尾処理部34−mから出力された目標物観測位置又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測位置を、画像センサ1−nの視線方向に移動したときに、地上面と交差する位置を射影位置として算出する。
図21は、観測位置射影部61により算出される射影位置を示す説明図である。
図22は、観測位置射影部61により算出される射影位置と、目標検出部32bから出力される目標物地図座標位置との関係を示す説明図である。
観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物である撮像画像上の目標物とが同一物であれば、図22に示している射影位置と目標物地図座標位置との距離が短いが、同一物でなければ、射影位置と目標物地図座標位置との距離が長い。Next, the operation will be described.
As shown in FIG. 21, the observation
FIG. 21 is an explanatory diagram showing the projection position calculated by the observation
FIG. 22 is an explanatory diagram showing the relationship between the projection position calculated by the observation
If the target observed by the observation sensor 3-m and the target on the captured image, which is the target detected by the
第2の判定処理部62は、観測位置射影部61により算出された射影位置と、目標検出部32bから出力された目標物地図座標位置とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する。
図23は、第2の判定処理部62の処理内容を示すフローチャートである。
以下、図23を参照しながら、第2の判定処理部62の処理内容を具体的に説明する。
この実施の形態4では、目標検出部32bによって、I個の目標物が検出され、観測センサ3−mによって、J個の目標物が観測されているものとする。The second
FIG. 23 is a flowchart showing the processing contents of the second
Hereinafter, the processing content of the second
In the fourth embodiment, it is assumed that I target objects are detected by the
第2の判定処理部62は、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から目標物j(j=1,2,・・・,J)の目標物観測位置を受けると、目標物jの高度Zを認識する。
第2の判定処理部62は、目標物jの高度Zと事前に設定された閾値Zthとを比較する(図23のステップST11)。
第2の判定処理部62は、目標物jの高度Zが閾値Zth以上であれば(図23のステップST11:YESの場合)、目標物jが飛行中の移動体であると認識する(図23のステップST12)。
第2の判定処理部62は、目標物jの高度Zが閾値Zth未満であれば(図23のステップST11:NOの場合)、目標物jが地上に存在している移動体であると認識する(図23のステップST13)。地上に存在している移動体には、停止中の移動体も含まれる。When the second
The second
If the altitude Z of the target j is greater than or equal to the threshold Zth (step ST11 in FIG. 23: YES), the second
If the altitude Z of the target j is less than the threshold value Zth (step ST11 in FIG. 23: NO), the second
第2の判定処理部62は、目標物jが飛行中の移動体であると認識すると、飛行中の移動体である目標物jと、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物i(i=1,2,・・・,I)とが同一物であるか否かを判定する。
具体的には、第2の判定処理部62は、観測位置射影部61により算出された目標物jの射影位置を取得する(図23のステップST14)。When the second
Specifically, the second
次に、第2の判定処理部62は、例えば、以下の式(6)に示すように、観測位置射影部61により算出された目標物jの射影位置と、目標検出部32bから出力された目標物iの目標物地図座標位置とを用いて、カイ二乗検定の検定値εを算出する(図23のステップST15)。
式(6)において、
xハットxt,j,HETは、観測位置射影部61により算出された目標物jの時刻tにおける射影位置を示す推定位置ベクトル
xハットxt,j,CAMは、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物iの時刻tにおける目標物地図座標位置を示す推定位置ベクトル
Pt,j,HETは、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35の追尾処理による目標物jの時刻tにおける推定位置誤差を示す推定誤差共分散行列
Pt,i,CAMは、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物iの時刻tにおける推定位置誤差を示す推定誤差共分散行列Next, the second
In equation (6),
xhat xt, j, HET is an estimated position vector xhatxt, j, CAM indicating the projected position of the target j calculated at the time t calculated by the observation
次に、第2の判定処理部62は、以下の式(7)に示すように、カイ二乗検定の検定値εと事前に設定された閾値εthとを比較する(図23のステップST16)。
閾値εthは、所定の有意水準に基づいて、例えば、カイ二乗分布表から求めたものである。
例えば、有意水準を5%として検定すると、危険率5%で、本来同一である航跡が、同一でない航跡と誤った判定がなされることを意味する。
第2の判定処理部62は、カイ二乗検定の検定値εが閾値εth未満であれば(図23のステップST16:YESの場合)、飛行中の移動体である目標物jと、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物iとが同一物であると判定する(図23のステップST17)。
第2の判定処理部62は、カイ二乗検定の検定値εが閾値εth以上であれば(図23のステップST16:NOの場合)、飛行中の移動体である目標物jと、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物iとが同一物でないと判定する(図23のステップST18)。
第2の判定処理部62は、目標物iと同一物であると判定した目標物jの識別情報を第3の判定処理部64及び目標物選択部65に出力し、目標物jと同一物であると判定した目標物iのIDを第3の追尾処理部63に出力する。
第2の判定処理部62による飛行中の移動体である目標物jと、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物iとの同一物か否かの判定処理は、飛行中の移動体である目標物jと目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物iとの全ての組み合わせについて行われる。Next, as shown in the following equation (7), the second
The threshold value εth is obtained from, for example, a chi-square distribution table based on a predetermined significance level.
For example, a test with a significance level of 5% means that a wake that is originally the same with a risk rate of 5% is erroneously determined as a wake that is not the same.
If the test value ε of the chi-square test is less than the threshold value εth (in the case of step ST16: YES in FIG. 23), the second
If the test value ε of the chi-square test is equal to or greater than the threshold value εth (in the case of step ST16 in FIG. 23: NO), the second
The second
The determination process of whether or not the target object j which is a moving object in flight by the second
第3の追尾処理部63は、目標検出部32bから出力されたI個の目標物のIDと、第2の判定処理部62から出力された目標物iのIDとを比較し、I個の目標物の中から、目標物iのIDと異なるIDを有する目標物fを選択する。
第3の追尾処理部63は、目標検出部32bから出力されたI個の目標物の目標物地図座標位置のうち、選択した目標物fについての目標物地図座標位置を用いて、目標物fの追尾処理を実施する。
第3の追尾処理部63は、追尾処理後の目標物fの位置である目標物観測位置を第3の判定処理部64に出力する。
第3の追尾処理部63による目標物fの追尾処理は、選択した目標物fについての目標物地図座標位置の時系列方向の相関を取る処理であり、例えば、カルマンフィルタを用いることができる。The third
The third
The third
The tracking process of the target f by the third
第3の判定処理部64は、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力されたJ個の目標物の識別情報と、第2の判定処理部62から出力された目標物jの識別情報とを比較し、J個の目標物の中から、目標物jの識別情報と異なる識別情報を有する目標物gを選択する。
第3の判定処理部64は、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力されたJ個の目標物の目標物観測位置の中から、選択した目標物gの目標物観測位置を選択する。
第3の判定処理部64は、選択した目標物gの目標物観測位置と、第3の追尾処理部63から出力された目標物fの目標物地図座標位置とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物gと、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物fとが同一物であるか否かを判定する。
以下、第3の判定処理部64の処理内容を具体的に説明する。The third
The third
The third
Hereinafter, the processing content of the 3rd
第3の判定処理部64は、例えば、以下の式(8)に示すように、目標物gの目標物観測位置と、目標検出部32bから出力された目標物fの目標物地図座標位置とを用いて、カイ二乗検定の検定値εを算出する。
式(8)において、
xハットxt,g,HETは、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物gの時刻tにおける目標物観測位置及び速度を含む推定状態ベクトル
xハットxt,f,CAMは、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物iの時刻tにおける目標物観測位置及び速度を含む推定状態ベクトル
Pt,g,HETは、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35の追尾処理による目標物jの時刻tにおける推定誤差を示す推定誤差共分散行列
Pt,f,CAMは、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物iの時刻tにおける推定誤差を示す推定誤差共分散行列The third
In equation (8),
xhat xt, g, HET is an estimated state vector xhat xt including the target observation position and velocity at the time t of the target g output from the second tracking processing unit 34-m or the multi-sensor
次に、第3の判定処理部64は、以下の式(9)に示すように、カイ二乗検定の検定値εと事前に設定された閾値εthとを比較する。
第3の判定処理部64は、カイ二乗検定の検定値εが閾値εth未満であれば、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物gと、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物fとが同一物であると判定する。
第3の判定処理部64は、カイ二乗検定の検定値εが閾値εth以上であれば、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物gと、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物fとが同一物でないと判定する。
第3の判定処理部64は、目標物fと同一物であると判定した目標物gの識別情報を目標物選択部65に出力する。Next, as shown in the following equation (9), the third
If the test value ε of the chi-square test is less than the threshold value εth, the third
If the test value ε of the chi-square test is equal to or greater than the threshold value εth, the third
The third
目標物選択部65は、第1の判定処理部37、第2の判定処理部62又は第3の判定処理部64により同一物であると判定された目標物の中から、1つ以上の目標物を選択する。
例えば、目標物選択部65は、第2の判定処理部62から出力された識別情報が示す目標物の中から、いずれかの目標物を選択する。
次に、目標物選択部65は、第3の判定処理部64から出力された識別情報が示す目標物の中から、第2の判定処理部62から出力された識別情報と異なる識別情報を有する目標物を選択する。
次に、目標物選択部65は、第1の判定処理部37から出力された識別情報が示す目標物の中から、第2の判定処理部62から出力された識別情報及び第3の判定処理部64から出力された識別情報と異なる識別情報を有する目標物を選択する。
目標物選択部65は、目標物を選択すると、選択した目標物の識別情報と、選択した目標物の目標物観測位置及び目標物観測位置とを表示処理部40に出力する。The
For example, the
Next, the
Next, the
When the target is selected, the
表示処理部40は、映像生成部31から出力された画像センサ1−nの撮像画像、または、パノラマ画像である撮像画像をディスプレイ16に表示する。
表示処理部40は、第1の判定処理部37により同一物であると判定された場合、目標物選択部65から出力された目標物観測位置及び観測センサ3−mから出力された識別情報のそれぞれを撮像画像上に表示し、また、平滑処理部39から出力された平滑化後の目標物包含画像領域を撮像画像上に表示する。The
When the first
表示処理部40は、第1の判定処理部37により同一物でないと判定された場合、目標検出部32bから出力された目標物地図座標位置及び平滑処理部39から出力された平滑化後の目標物包含画像領域と、目標検出部32bから出力された目標物のIDとを撮像画像上に表示する。
あるいは、表示処理部7は、第1の判定処理部37により同一物でないと判定された場合、観測センサ3−mから出力された識別情報と、目標物選択部65から出力された目標物観測位置及び目標物包含観測領域とを撮像画像上に表示する。When it is determined by the first
Alternatively, the
以上で明らかなように、この実施の形態4によれば、第2の追尾処理部34−mから出力された目標物観測位置又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測位置を、画像センサ1−nの視線方向に移動したときに、地上面と交差する位置を射影位置として算出する観測位置射影部61と、観測位置射影部61により算出された射影位置と目標検出部32bから出力された目標物観測位置とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する第2の判定処理部62とを備えている。これにより、上記実施の形態1〜3よりも、更に、同一物の判定精度を高めることができる効果を奏する。 As apparent from the above, according to the fourth embodiment, the target observation position output from the second tracking processing unit 34-m or the target observation position output from the multi-sensor
また、この実施の形態4によれば、目標検出部32bにより検出された1つ以上の目標物のうち、第2の判定処理部62により同一物であると判定された目標物以外の目標物の追尾処理を実施して、追尾処理後の目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を出力する第3の追尾処理部63と、観測センサ3−mから出力された目標物観測位置と、第3の追尾処理部63から出力された目標物観測位置とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する第3の判定処理部64とを備えている。これにより、上記実施の形態1〜3よりも、更に、同一物の判定精度を高めることができる効果を奏する。 Further, according to the fourth embodiment, among the one or more targets detected by the
実施の形態5.
この実施の形態5では、第1の変換処理部82が、目標物地図座標位置を画像センサ1−nの基準位置を原点とする角度に変換し、第2の変換処理部85が、目標物観測位置を画像センサ1−nの基準位置を原点とする角度に変換し、判定処理部86が、双方の変換角度を比較する例を説明する。
In the fifth embodiment, the first
図24は、この発明の実施の形態5による監視装置を示す構成図である。図25は、この発明の実施の形態5による監視装置を示すハードウェア構成図である。
図24及び図25において、図1、図2、図17、図18、図19及び図20と同一符号は同一または相当部分を示すので説明を省略する。
第1の対応情報格納部81は、例えば、図25を示す第1の対応情報記憶回路91で実現される。
第1の対応情報格納部81は、画像センサ1−1〜1−Nの基準位置を原点とする角度である方位角及び仰角と、目標検出部32から出力された目標物地図座標位置との対応関係を格納しているデータベースである。
画像センサ1の個数が1つである場合には、第1の対応情報格納部81が、1つの画像センサ1の設置位置を原点とする方位角及び仰角と、目標物地図座標位置との対応関係を格納しているものであってもよい。FIG. 24 is a block diagram showing a monitoring apparatus according to
24 and 25, the same reference numerals as those in FIGS. 1, 2, 17, 18, 19, and 20 indicate the same or corresponding parts, and thus description thereof is omitted.
The first correspondence
The first correspondence
When the number of
第1の変換処理部82は、例えば、図25を示す第1の変換処理回路92で実現される。
第1の変換処理部82は、目標検出部32から出力された目標物地図座標位置を画像センサ1−1〜1−Nの基準位置を原点とする角度である方位角及び仰角に変換する処理を実施する。
即ち、第1の変換処理部82は、第1の対応情報格納部81に格納されている対応関係を参照して、目標検出部32から出力された目標物地図座標位置に対応する方位角及び仰角を取得する処理を実施する。The first
The first
That is, the first
第1の追尾処理部83は、例えば、図25に示す第1の追尾処理回路93で実現される。
第1の追尾処理部83は、第1の変換処理部82により変換された方位角及び仰角の追尾処理を実施して、追尾処理後の方位角及び仰角と、追尾処理後の方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度とを出力する処理を実施する。
第1の追尾処理部83による方位角及び仰角の追尾処理は、第1の変換処理部82により変換された方位角及び仰角の時系列方向の相関を取る処理であり、例えば、カルマンフィルタを用いることができる。The first
The first
The azimuth angle and elevation angle tracking process by the first
第2の対応情報格納部84は、例えば、図25を示す第2の対応情報記憶回路94で実現される。
第2の対応情報格納部84は、画像センサ1−1〜1−Nの基準位置を原点とする角度である方位角及び仰角と、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測位置及び目標物観測速度との対応関係を格納しているデータベースである。
画像センサ1の個数が1つである場合には、第2の対応情報格納部84が、1つの画像センサ1の設置位置を原点とする方位角及び仰角と、目標物観測位置及び目標物観測速度との対応関係を格納しているものであってもよい。The second correspondence
The second correspondence
When the number of
第2の変換処理部85は、例えば、図25を示す第2の変換処理回路95で実現される。
第2の変換処理部85は、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測位置を画像センサ1−1〜1−Nの基準位置を原点とする角度である方位角及び仰角に変換する処理を実施する。
即ち、第2の変換処理部85は、第2の対応情報格納部84に格納されている対応関係を参照して、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測位置に対応する方位角及び仰角を取得する処理を実施する。
また、第2の変換処理部85は、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測速度を画像センサ1−1〜1−Nの基準位置を原点とする方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度に変換する処理を実施する。
即ち、第2の変換処理部85は、第2の対応情報格納部84に格納されている対応関係を参照して、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測速度に対応する方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度とを取得する処理を実施する。The second
The second
That is, the second
In addition, the second
That is, the second
判定処理部86は、例えば、図25に示す判定処理回路96で実現される。
判定処理部86は、第1の追尾処理部83から出力された追尾処理後の方位角、仰角、方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度と、第2の変換処理部85により変換された方位角、仰角、方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する処理を実施する。The
The
図24では、監視装置の構成要素である画像センサ1−n、観測センサ3−m、映像生成部31、目標検出部32、第2の追尾処理部34−m、マルチセンサ追尾処理部35、表示処理部40、第1の対応情報格納部81、第1の変換処理部82、第1の追尾処理部83、第2の対応情報格納部84、第2の変換処理部85、判定処理部86及びディスプレイ16のそれぞれが、図25に示すような専用のハードウェアで実現されるものを想定している。即ち、画像センサ1−n、観測センサ3−m、映像生成回路41、目標検出回路42、第2の追尾処理回路44、マルチセンサ追尾処理回路45、表示処理回路50、第1の対応情報記憶回路91、第1の変換処理回路92、第1の追尾処理回路93、第2の対応情報記憶回路94、第2の変換処理回路95、判定処理回路96及びディスプレイ16で実現されるものを想定している。 In FIG. 24, the image sensor 1-n, the observation sensor 3-m, the
映像生成回路41、目標検出回路42、第2の追尾処理回路44、マルチセンサ追尾処理回路45、表示処理回路50、第1の変換処理回路92、第1の追尾処理回路93、第2の変換処理回路95及び判定処理回路96は、例えば、単一回路、複合回路、プログラム化したプロセッサ、並列プログラム化したプロセッサ、ASIC、FPGA、または、これらを組み合わせたものが該当する。
監視装置の画像センサ1−n、観測センサ3−m及びディスプレイ16を除く構成要素は、専用のハードウェアで実現されるものに限るものではなく、ソフトウェア、ファームウェア、または、ソフトウェアとファームウェアとの組み合わせで実現されるものであってもよい。 The components other than the image sensor 1-n, the observation sensor 3-m, and the
監視装置の画像センサ1−n、観測センサ3−m及びディスプレイ16を除く構成要素がソフトウェア又はファームウェアなどで実現される場合、第1の対応情報格納部81及び第2の対応情報格納部84を図3に示すコンピュータのメモリ21上に構成するとともに、映像生成部31、目標検出部32、第2の追尾処理部34−m、マルチセンサ追尾処理部35、表示処理部40、第1の変換処理部82、第1の追尾処理部83、第2の変換処理部85及び判定処理部86の処理手順をコンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムをメモリ21に格納し、コンピュータのプロセッサ22がメモリ21に格納されているプログラムを実行するようにすればよい。 When components other than the image sensor 1-n, the observation sensor 3-m, and the
次に動作について説明する。
この実施の形態5では、説明の簡単化のため、目標検出部32によって、1つの目標物が検出され、観測センサ3−mによって、1つの目標物が観測されるものとする。
図26は、画像センサ1−1〜1−Nの基準位置と、画像センサ1−1〜1−Nの角度とを示す説明図である。
第1の対応情報格納部81は、画像センサ1−1〜1−Nの基準位置を原点とする方位角及び仰角と、目標検出部32から出力された目標物地図座標位置との対応関係を格納している。Next, the operation will be described.
In the fifth embodiment, for simplification of description, it is assumed that one target is detected by the
FIG. 26 is an explanatory diagram illustrating the reference positions of the image sensors 1-1 to 1-N and the angles of the image sensors 1-1 to 1-N.
The first correspondence
第1の変換処理部82は、目標検出部32から出力された目標物地図座標位置を画像センサ1−1〜1−Nの基準位置を原点とする方位角及び仰角に変換する。
即ち、第1の変換処理部82は、第1の対応情報格納部81に格納されている対応関係を参照して、目標検出部32から出力された目標物地図座標位置に対応する方位角及び仰角を取得し、取得した方位角及び仰角を第1の追尾処理部83に出力する。
第1の追尾処理部83は、第1の変換処理部82から出力された方位角及び仰角の追尾処理を実施して、追尾処理後の方位角及び仰角と、追尾処理後の方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度とを判定処理部86に出力する。The first
That is, the first
The first
第2の追尾処理部34−m及びマルチセンサ追尾処理部35のそれぞれは、追尾処理後の目標物観測位置のほか、追尾処理後の目標物の速度である目標物観測速度を第2の変換処理部85に出力する。
第2の変換処理部85は、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測位置を画像センサ1−1〜1−Nの基準位置を原点とする方位角及び仰角に変換する。
即ち、第2の変換処理部85は、第2の対応情報格納部84に格納されている対応関係を参照して、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測位置に対応する方位角及び仰角を取得する。Each of the second tracking processing unit 34-m and the multi-sensor
The second
That is, the second
また、第2の変換処理部85は、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測速度を画像センサ1−1〜1−Nの基準位置を原点とする方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度に変換する。
即ち、第2の変換処理部85は、第2の対応情報格納部84に格納されている対応関係を参照して、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測速度に対応する方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度とを取得する。
第2の変換処理部85は、取得した方位角、仰角、方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度を判定処理部86に出力する。In addition, the second
That is, the second
The second
判定処理部86は、第1の追尾処理部83から出力された追尾処理後の方位角、仰角、方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度と、第2の変換処理部85から出力された方位角、仰角、方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する。
以下、判定処理部86の処理内容を具体的に説明する。The
Hereinafter, the processing content of the
判定処理部86は、以下の式(10)に示すように、第1の追尾処理部83から出力された追尾処理後の方位角、仰角、方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度と、第2の変換処理部85から出力された方位角、仰角、方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度とを用いて、カイ二乗検定の検定値εを算出する。
式(10)において、
xハットxt,HETは、第2の変換処理部85から出力された目標物の時刻tにおける方位角、仰角、方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度を含む推定状態ベクトル
xハットxt,CAMは、第1の追尾処理部83から出力された目標物の時刻tにおける方位角、仰角、方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度を含む推定状態ベクトル
Pt,HETは、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35の追尾処理による目標物の時刻tにおける推定誤差を示す推定誤差共分散行列
Pt,CAMは、目標検出部32により検出された目標物の時刻tにおける推定誤差を示す推定誤差共分散行列As shown in the following formula (10), the
In equation (10),
x hat xt, HET is the estimated state vector x hat xt, CAM including the azimuth angle, elevation angle, azimuth angular velocity, and elevation angular velocity of the target at time t output from the second
次に、判定処理部86は、以下の式(11)に示すように、カイ二乗検定の検定値εと事前に設定された閾値εthとを比較する。
判定処理部86は、カイ二乗検定の検定値εが閾値εth未満であれば、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32により検出された目標物とが同一物であると判定する。
判定処理部86は、カイ二乗検定の検定値εが閾値εth以上であれば、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32により検出された目標物とが同一物でないと判定する。Next, as shown in the following equation (11), the
If the test value ε of the chi-square test is less than the threshold value εth, the
If the test value ε of the chi-square test is equal to or greater than the threshold value εth, the
以上で明らかなように、第1の追尾処理部83から出力された追尾処理後の方位角、仰角、方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度と、第2の変換処理部85により変換された方位角、仰角、方位角の角速度及び仰角の角速度とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する判定処理部86を備えている。これにより、目標物が飛行中の航空機である場合でも、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、画像センサ1の撮像画像内の目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定することができる効果を奏する。 As is apparent from the above, the azimuth angle, elevation angle, angular velocity of the azimuth angle and angular velocity of the elevation angle output from the first
実施の形態6.
上記実施の形態5では、第1の変換処理部82の後段に第1の追尾処理部83が設けられている監視装置の例を示している。
しかし、これは一例に過ぎず、図27に示すように、第1の変換処理部82の前段に第1の追尾処理部33が設けられている監視装置であってもよい。
図27は、この発明の実施の形態6による監視装置を示す構成図である。
この実施の形態6の場合でも、上記実施の形態5と同様に、目標物が飛行中の航空機である場合でも、観測センサ3により観測された目標物と、画像センサ1の撮像画像内の目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定することができる。
In the fifth embodiment, an example of a monitoring device in which the first
However, this is only an example, and as shown in FIG. 27, a monitoring device in which the first
FIG. 27 is a block diagram showing a monitoring apparatus according to
Even in the case of the sixth embodiment, similarly to the fifth embodiment, even when the target is an aircraft in flight, the target observed by the
なお、本願発明はその発明の範囲内において、各実施の形態の自由な組み合わせ、あるいは各実施の形態の任意の構成要素の変形、もしくは各実施の形態において任意の構成要素の省略が可能である。 In the present invention, within the scope of the invention, any combination of the embodiments, any modification of any component in each embodiment, or omission of any component in each embodiment is possible. .
この発明は、観測センサにより観測された目標物と、画像センサの撮像画像内の目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する監視装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a monitoring device that determines whether or not a target observed by an observation sensor and a target in a captured image of an image sensor are the same.
1,1−1〜1−N 画像センサ、2 目標検出部、3,3−1〜3−M 観測センサ、4 物体形状情報格納部、5 変換処理部、6 第1の判定処理部、7 表示処理部、8 包含領域特定部、9 平均位置出力部、11 目標検出回路、12 形状記憶回路、13 変換処理回路、14 第1の判定処理回路、15 表示処理回路、16 ディスプレイ、21 メモリ、22 プロセッサ、31 映像生成部、32,32b 目標検出部、33 第1の追尾処理部、34−1〜34−M 第2の追尾処理部、35 マルチセンサ追尾処理部、36 変換処理部、37 第1の判定処理部、38 判定結果格納部、39 平滑処理部、40 表示処理部、41 映像生成回路、42 目標検出回路、43 第1の追尾処理回路、44 第2の追尾処理回路、45 マルチセンサ追尾処理回路、46 変換処理回路、47 第1の判定処理回路、48 判定結果記憶回路、49 平滑処理回路、50 表示処理回路、61 観測位置射影部、62 第2の判定処理部、63 第3の追尾処理部、64 第3の判定処理部、65 目標物選択部、71 観測位置射影回路、72 第2の判定処理回路、73 第3の追尾処理回路、74 第3の判定処理回路、75 目標物選択回路、81 第1の対応情報格納部、82 第1の変換処理部、83 第1の追尾処理部、84 第2の対応情報格納部、85 第2の変換処理部、86 判定処理部、91 第1の対応情報記憶回路、92 第1の変換処理回路、93 第1の追尾処理回路、94 第2の対応情報記憶回路、95 第2の変換処理回路、96 判定処理回路。 1, 1-1 to 1-N image sensor, 2 target detection unit, 3,3-1 to 3-M observation sensor, 4 object shape information storage unit, 5 conversion processing unit, 6 first determination processing unit, 7 Display processing unit, 8 inclusion region specifying unit, 9 average position output unit, 11 target detection circuit, 12 shape memory circuit, 13 conversion processing circuit, 14 first determination processing circuit, 15 display processing circuit, 16 display, 21 memory, 22 processors, 31 video generation units, 32, 32b target detection units, 33 first tracking processing units, 34-1 to 34-M second tracking processing units, 35 multi-sensor tracking processing units, 36 conversion processing units, 37 First determination processing unit, 38 determination result storage unit, 39 smoothing processing unit, 40 display processing unit, 41 video generation circuit, 42 target detection circuit, 43 first tracking processing circuit, 44 second tracking processing circuit, 4 Multi-sensor tracking processing circuit, 46 conversion processing circuit, 47 first determination processing circuit, 48 determination result storage circuit, 49 smoothing processing circuit, 50 display processing circuit, 61 observation position projection unit, 62 second determination processing unit, 63 Third tracking processing unit, 64 Third determination processing unit, 65 Target selection unit, 71 Observation position projection circuit, 72 Second determination processing circuit, 73 Third tracking processing circuit, 74 Third determination processing circuit 75 Target object selection circuit, 81 First correspondence information storage unit, 82 First conversion processing unit, 83 First tracking processing unit, 84 Second correspondence information storage unit, 85 Second conversion processing unit, 86 Determination processing unit, 91 first correspondence information storage circuit, 92 first conversion processing circuit, 93 first tracking processing circuit, 94 second correspondence information storage circuit, 95 second conversion processing circuit, 96 determination processing circuit .
第3の追尾処理部63は、例えば、図20に示す第3の追尾処理回路73で実現される。
第3の追尾処理部63は、目標検出部32bにより検出された1つ以上の目標物のうち、第2の判定処理部62により同一物であると判定された目標物以外の目標物の追尾処理を実施して、追尾処理後の目標物の位置を出力する処理を実施する。The third
The third
第3の判定処理部64は、例えば、図20に示す第3の判定処理回路74で実現される。
第3の判定処理部64は、第2の追尾処理部34−mから出力された目標物観測位置又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物観測位置と、第3の追尾処理部63から出力された追尾処理後の目標物の位置とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物と、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する処理を実施する。
目標物選択部65は、例えば、図20に示す目標物選択回路75で実現される。
目標物選択部65は、第1の判定処理部37、第2の判定処理部62又は第3の判定処理部64により同一物であると判定された目標物の中から、1つ以上の目標物を選択する処理を実施する。The third
The third
The
The
次に、第2の判定処理部62は、例えば、以下の式(6)に示すように、観測位置射影部61により算出された目標物jの射影位置と、目標検出部32bから出力された目標物iの目標物地図座標位置とを用いて、カイ二乗検定の検定値εを算出する(図23のステップST15)。
式(6)において、
xハットt,j,HETは、観測位置射影部61により算出された目標物jの時刻tにおける射影位置を示す推定位置ベクトル
xハットt,j,CAMは、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物iの時刻tにおける目標物地図座標位置を示す推定位置ベクトル
Pt,j,HETは、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35の追尾処理による目標物jの時刻tにおける推定位置誤差を示す推定誤差共分散行列
Pt,i,CAMは、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物iの時刻tにおける推定位置誤差を示す推定誤差共分散行列Next, the second
In equation (6),
xhatt, j, HET is an estimated position vector xhatt, j, CAM indicating the projected position of the target j calculated at the time t calculated by the observation
第3の判定処理部64は、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力されたJ個の目標物の識別情報と、第2の判定処理部62から出力された目標物jの識別情報とを比較し、J個の目標物の中から、目標物jの識別情報と異なる識別情報を有する目標物gを選択する。
第3の判定処理部64は、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力されたJ個の目標物の目標物観測位置の中から、選択した目標物gの目標物観測位置を選択する。
第3の判定処理部64は、選択した目標物gの目標物観測位置と、第3の追尾処理部63から出力された追尾処理後の目標物fの位置とを比較して、観測センサ3−mにより観測された目標物gと、目標検出部32bにより検出された目標物fとが同一物であるか否かを判定する。
以下、第3の判定処理部64の処理内容を具体的に説明する。The third
The third
The third
Hereinafter, the processing content of the 3rd
第3の判定処理部64は、例えば、以下の式(8)に示すように、目標物gの目標物観測位置と、第3の追尾処理部63から出力された追尾処理後の目標物fの位置とを用いて、カイ二乗検定の検定値εを算出する。
式(8)において、
xハットt,g,HETは、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35から出力された目標物gの時刻tにおける目標物観測位置及び速度を含む推定状態ベクトル
xハットt,f,CAMは、第3の追尾処理部63から出力された追尾処理後の時刻tにおける目標物fの位置及び速度を含む推定状態ベクトル
Pt,g,HETは、第2の追尾処理部34−m又はマルチセンサ追尾処理部35の追尾処理による目標物gの時刻tにおける推定位置誤差を示す推定誤差共分散行列
Pt,f,CAMは、第3の追尾処理部63の追尾処理による目標物fの時刻tにおける推定位置誤差を示す推定誤差共分散行列The third
In equation (8),
x hatt, g, HET is a second tracking processing unit 34-m, or multi-sensor target at time t of the output target g from the
Claims (18)
Translated fromJapanese前記画像センサから出力された撮像画像内の目標物を検出し、前記検出した目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含画像領域を特定する目標検出部と、
目標物を観測して、前記観測した目標物の識別情報及び前記観測した目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を出力する観測センサと、
前記観測センサから出力された識別情報によって目標物の大きさを特定し、前記特定した目標物の大きさ及び前記観測センサから出力された目標物観測位置のそれぞれを前記画像センサの投影面に変換し、前記変換した目標物の大きさと、前記変換した目標物観測位置とから、前記画像センサの投影面上で、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含観測領域を特定する変換処理部と、
前記変換処理部により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、前記目標検出部により特定された目標物包含画像領域とを比較して、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物と、前記目標検出部により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する第1の判定処理部と
を備えた監視装置。An image sensor that images a region where the target is present and outputs a captured image of the region;
A target detection unit that detects a target in a captured image output from the image sensor and identifies a target inclusion image area that is a range including the detected target;
An observation sensor that observes a target and outputs identification information of the observed target and a target observation position that is a position of the observed target;
The size of the target is specified by the identification information output from the observation sensor, and each of the specified target size and the target observation position output from the observation sensor is converted into a projection plane of the image sensor. Then, the target inclusion is a range including the target observed by the observation sensor on the projection plane of the image sensor from the size of the converted target and the converted target observation position. A conversion processing unit for identifying the observation region;
The target inclusion observation region specified by the conversion processing unit and the target inclusion image region specified by the target detection unit are compared, the target observed by the observation sensor, and the target detection unit And a first determination processing unit that determines whether or not the detected target is the same.
前記表示処理部は、前記画像センサから出力された撮像画像上に、前記包含領域特定部により特定された双方包含領域を表示することを特徴とする請求項2記載の監視装置。On the projection plane of the image sensor, a both-inclusion area that is an area including both the target-inclusion observation area specified by the conversion processing unit and the target-inclusion image area specified by the target detection unit is specified. Including an inclusion area specifying unit
The monitoring apparatus according to claim 2, wherein the display processing unit displays both inclusion areas specified by the inclusion area specification unit on the captured image output from the image sensor.
前記表示処理部は、前記画像センサから出力された撮像画像上に、前記平均位置出力部から出力された位置を表示することを特徴とする請求項2記載の監視装置。On the projection plane of the image sensor, the target observation position converted into the projection plane by the conversion processing unit and the position of the target in the captured image detected by the target detection unit are weighted and averaged. It has an average position output unit that outputs the averaged position,
The monitoring apparatus according to claim 2, wherein the display processing unit displays the position output from the average position output unit on the captured image output from the image sensor.
前記変換処理部は、前記観測センサから出力された観測誤差情報に従って前記特定した目標物包含観測領域を補正することを特徴とする請求項1記載の監視装置。The observation sensor outputs observation error information indicating an observation error range of the target observation position,
The monitoring apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the conversion processing unit corrects the identified target inclusion observation region in accordance with observation error information output from the observation sensor.
前記表示処理部は、前記画像センサから出力された撮像画像上に、前記平滑処理部により平滑化された目標物包含画像領域を表示することを特徴とする請求項2記載の監視装置。A smoothing processing unit that smoothes the target inclusion image area specified by the target detection unit in the time direction;
The monitoring apparatus according to claim 2, wherein the display processing unit displays the target object including image region smoothed by the smoothing processing unit on the captured image output from the image sensor.
前記観測センサにより観測された目標物の追尾処理を実施して、追尾処理後の目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を前記変換処理部に出力する第2の追尾処理部とを備え、
前記変換処理部は、前記特定した目標物の大きさ及び前記第2の追尾処理部から出力された目標物観測位置のそれぞれを前記画像センサの投影面に変換し、前記変換した目標物の大きさと、前記変換した目標物観測位置とから、前記画像センサの投影面上で、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含観測領域を特定し、
前記第1の判定処理部は、前記変換処理部により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、前記第1の追尾処理部から出力された目標物包含画像領域とを比較して、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物と、前記目標検出部により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定することを特徴とする請求項1記載の監視装置。A first tracking unit that performs tracking processing on the target detected by the target detection unit and outputs a target inclusion image area that is a range including the target after the tracking processing to the first determination processing unit. Tracking processing unit of
A second tracking processing unit that performs tracking processing of the target observed by the observation sensor and outputs a target observation position that is the position of the target after the tracking processing to the conversion processing unit;
The conversion processing unit converts each of the identified target size and the target observation position output from the second tracking processing unit to a projection plane of the image sensor, and converts the converted target size. And, from the converted target observation position, on the projection plane of the image sensor, specify a target inclusion observation area that is a range including the target observed by the observation sensor,
The first determination processing unit compares the target inclusion inclusion observation region specified by the conversion processing unit with the target inclusion inclusion image region output from the first tracking processing unit, and uses the observation sensor. The monitoring apparatus according to claim 1, wherein it is determined whether or not the observed target and the target detected by the target detection unit are the same.
前記変換処理部は、前記第2の追尾処理部から出力された推定誤差情報に従って前記特定した目標物包含観測領域を補正することを特徴とする請求項8記載の監視装置。The second tracking processing unit outputs estimation error information indicating an estimation error due to target tracking processing,
9. The monitoring apparatus according to claim 8, wherein the conversion processing unit corrects the identified target object inclusion observation region according to the estimation error information output from the second tracking processing unit.
前記画像センサの投影面上で、前記変換処理部により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、前記目標検出部により特定された目標物包含画像領域との重なり範囲を算出し、前記重なり範囲が閾値以上であれば、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物と、前記目標検出部により検出された目標物とが同一物であると判定し、前記重なり範囲が前記閾値未満であれば、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物と、前記目標検出部により検出された目標物とが同一物でないと判定することを特徴とする請求項1記載の監視装置。The first determination processing unit includes:
On the projection plane of the image sensor, an overlapping range between the target inclusion inclusion observation area specified by the conversion processing unit and the target inclusion inclusion image area specified by the target detection unit is calculated, and the overlapping range is a threshold value If so, it is determined that the target observed by the observation sensor and the target detected by the target detection unit are the same, and if the overlapping range is less than the threshold, the observation sensor 2. The monitoring apparatus according to claim 1, wherein it is determined that the target observed by the step and the target detected by the target detector are not the same.
前記目標検出部により複数の目標物が検出されており、前記目標検出部により各々の目標物の目標物包含画像領域が特定されていれば、前記画像センサの投影面上で、前記変換処理部により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、前記各々の目標物の目標物包含画像領域との重なり範囲をそれぞれ算出し、各々の重なり範囲の合計が閾値以上であれば、前記複数の目標物が1つの目標物の一部であり、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物と、前記1つの目標物とが同一物であると判定し、前記重なり範囲の合計が前記閾値未満であれば、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物と、前記1つの目標物とが同一物でないと判定することを特徴とする請求項1記載の監視装置。The first determination processing unit includes:
If a plurality of targets are detected by the target detection unit, and the target inclusion image area of each target is specified by the target detection unit, the conversion processing unit on the projection plane of the image sensor Calculating the overlapping range between the target inclusion observing area specified by the above and the target inclusion image area of each target, and if the total of the overlapping ranges is equal to or greater than a threshold, the plurality of targets are It is a part of one target, it is determined that the target observed by the observation sensor and the one target are the same, and if the sum of the overlapping ranges is less than the threshold, The monitoring apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the target observed by the observation sensor and the one target are determined not to be the same.
前記観測位置射影部により算出された射影位置と、前記目標検出部により検出された目標物の位置とを比較して、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物と、前記目標検出部により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する第2の判定処理部とを備えたことを特徴とする請求項1記載の監視装置。An observation position projection unit that calculates a position intersecting the ground surface as a projection position when the target observation position output from the observation sensor is moved in the line-of-sight direction of the image sensor;
The projection position calculated by the observation position projection unit is compared with the position of the target detected by the target detection unit, and the target observed by the observation sensor and detected by the target detection unit The monitoring apparatus according to claim 1, further comprising a second determination processing unit that determines whether or not the target is the same.
前記観測センサから出力された目標物観測位置と、前記第3の追尾処理部から出力された目標物観測位置とを比較して、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物と、前記目標検出部により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する第3の判定処理部と、
前記第1から第3の判定処理部により同一物であると判定された目標物の中から、1つ以上の目標物を選択する目標物選択部とを備えたことを特徴とする請求項12記載の監視装置。After the tracking process, the tracking process is performed on a target other than the target determined to be the same by the second determination processing unit among the one or more targets detected by the target detection unit. A third tracking processing unit that outputs a target observation position that is the position of the target of
The target observation position output from the observation sensor is compared with the target observation position output from the third tracking processing unit, and the target observed by the observation sensor is compared with the target detection unit. A third determination processing unit for determining whether or not the detected target is the same;
13. A target selection unit that selects one or more targets from the targets determined to be the same by the first to third determination processing units. The monitoring device described.
前記第2の判定処理部により同一物であると判定された目標物の中から、いずれかの目標物を選択し、
前記第3の判定処理部により同一物であると判定された目標物の中から、選択済みの目標物と異なる目標物を選択し、
前記第1の判定処理部により同一物であると判定された目標物の中から、選択済みの目標物と異なる目標物を選択することを特徴とする請求項13記載の監視装置。The target selection unit includes:
From the targets determined to be the same by the second determination processing unit, select any target,
From the targets determined to be the same by the third determination processing unit, select a target that is different from the selected target,
The monitoring apparatus according to claim 13, wherein a target different from the selected target is selected from the targets determined to be the same by the first determination processing unit.
前記画像センサから出力された撮像画像内の目標物を検出し、前記検出した目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含画像領域を特定する目標検出部と、
目標物を観測して、前記観測した目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を出力する観測センサと、
予め設定されている前記目標物の大きさ及び前記観測センサから出力された目標物観測位置のそれぞれを前記画像センサの投影面に変換し、前記変換した目標物の大きさと、前記変換した目標物観測位置とから、前記画像センサの投影面上で、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物を包含している範囲である目標物包含観測領域を特定する変換処理部と、
前記変換処理部により特定された目標物包含観測領域と、前記目標検出部により特定された目標物包含画像領域とを比較して、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物と、前記目標検出部により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する第1の判定処理部と
を備えた監視装置。An image sensor that images a region where the target is present and outputs a captured image of the region;
A target detection unit that detects a target in a captured image output from the image sensor and identifies a target inclusion image area that is a range including the detected target;
An observation sensor that observes the target and outputs a target observation position that is the position of the observed target;
Each of the size of the target set in advance and the target observation position output from the observation sensor is converted to the projection plane of the image sensor, and the converted size of the target and the converted target A conversion processing unit that identifies a target inclusion observation region that is a range including the target observed by the observation sensor on the projection plane of the image sensor from the observation position;
The target inclusion observation region specified by the conversion processing unit and the target inclusion image region specified by the target detection unit are compared, the target observed by the observation sensor, and the target detection unit And a first determination processing unit that determines whether or not the detected target is the same.
前記画像センサから出力された撮像画像内の目標物を検出して、前記検出した目標物の位置である目標物画像位置を出力する目標検出部と、
前記目標検出部から出力された目標物画像位置を前記画像センサの基準位置を原点とする角度に変換する第1の変換処理部と、
目標物を観測して、前記観測した目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を出力する観測センサと、
前記観測センサから出力された目標物観測位置を前記画像センサの基準位置を原点とする角度に変換する第2の変換処理部と、
前記第1の変換処理部により変換された角度と、前記第2の変換処理部により変換された角度とを比較して、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物と、前記目標検出部により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定する判定処理部と
を備えた監視装置。An image sensor that images a region where the target is present and outputs a captured image of the region;
A target detection unit that detects a target in a captured image output from the image sensor and outputs a target image position that is a position of the detected target;
A first conversion processing unit that converts a target image position output from the target detection unit into an angle with a reference position of the image sensor as an origin;
An observation sensor that observes the target and outputs a target observation position that is the position of the observed target;
A second conversion processing unit that converts the target observation position output from the observation sensor into an angle with a reference position of the image sensor as an origin;
The angle converted by the first conversion processing unit and the angle converted by the second conversion processing unit are compared, and the target observed by the observation sensor is detected by the target detection unit. And a determination processing unit that determines whether or not the target is the same.
前記観測センサから出力された目標物観測位置に従って目標物の追尾処理を実施して、追尾処理後の目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を前記第2の変換処理部に出力する第2の追尾処理部とを備え、
前記第2の変換処理部は、前記第2の追尾処理部から出力された目標物観測位置を前記画像センサの基準位置を原点とする角度に変換し、
前記判定処理部は、前記第1の追尾処理部から出力された角度と、前記第2の変換処理部により変換された角度とを比較して、前記観測センサにより観測された目標物と、前記目標検出部により検出された目標物とが同一物であるか否かを判定することを特徴とする請求項16記載の監視装置。A first tracking processing unit that performs tracking processing of the angle converted by the first conversion processing unit and outputs the angle after the tracking processing to the determination processing unit;
A target tracking process is performed according to the target observation position output from the observation sensor, and a target observation position that is the position of the target after the tracking process is output to the second conversion processing unit. A tracking processing unit,
The second conversion processing unit converts the target observation position output from the second tracking processing unit into an angle with a reference position of the image sensor as an origin,
The determination processing unit compares the angle output from the first tracking processing unit with the angle converted by the second conversion processing unit, and the target observed by the observation sensor, The monitoring apparatus according to claim 16, wherein it is determined whether or not the target detected by the target detection unit is the same.
前記観測センサにより観測された目標物の追尾処理を実施して、追尾処理後の目標物の位置である目標物観測位置を前記第2の変換処理部に出力する第2の追尾処理部とを備え、
前記第1の変換処理部は、前記第1の追尾処理部から出力された目標物画像位置を前記画像センサの基準位置を原点とする角度に変換し、
前記第2の変換処理部は、前記第2の追尾処理部から出力された目標物観測位置を前記画像センサの基準位置を原点とする角度に変換することを特徴とする請求項16記載の監視装置。A first tracking processing unit that performs tracking processing of the target detected by the target detection unit and outputs a target image position that is the position of the target after the tracking processing to the first conversion processing unit; ,
A second tracking processing unit that performs tracking processing of the target observed by the observation sensor and outputs a target observation position that is the position of the target after the tracking processing to the second conversion processing unit; Prepared,
The first conversion processing unit converts the target image position output from the first tracking processing unit into an angle with a reference position of the image sensor as an origin,
The monitoring according to claim 16, wherein the second conversion processing unit converts the target observation position output from the second tracking processing unit into an angle with a reference position of the image sensor as an origin. apparatus.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/020261WO2018220745A1 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2017-05-31 | Monitoring device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2018220745A1true JPWO2018220745A1 (en) | 2019-11-14 |
| JP6687296B2 JP6687296B2 (en) | 2020-04-22 |
Family
ID=64455810
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019521598AActiveJP6687296B2 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2017-05-31 | Monitoring device |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6687296B2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2018220745A1 (en) |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07229960A (en)* | 1994-02-16 | 1995-08-29 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | All-round visible display apparatus for aircraft |
| JPH08146130A (en)* | 1994-11-24 | 1996-06-07 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Airport surface ground control system |
| JPH08329393A (en)* | 1995-05-29 | 1996-12-13 | Daihatsu Motor Co Ltd | Preceding vehicle detector |
| JPH09264954A (en)* | 1996-03-29 | 1997-10-07 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | Image processing system using radar |
| JP2003132499A (en)* | 2001-10-24 | 2003-05-09 | Electronic Navigation Research Institute | Aircraft position display method in display device for air traffic control |
| JP2008215918A (en)* | 2007-03-01 | 2008-09-18 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Airport surface monitoring system and airport surface monitoring method |
| US20100002077A1 (en)* | 2005-01-13 | 2010-01-07 | Sensis Corporation | Method and system for tracking position of an object using imaging and non-imaging surveillance devices |
| JP2010032429A (en)* | 2008-07-30 | 2010-02-12 | Toyota Motor Corp | Object detector |
| JP2014122873A (en)* | 2012-11-22 | 2014-07-03 | Denso Corp | Target detection device |
- 2017
- 2017-05-31WOPCT/JP2017/020261patent/WO2018220745A1/ennot_activeCeased
- 2017-05-31JPJP2019521598Apatent/JP6687296B2/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07229960A (en)* | 1994-02-16 | 1995-08-29 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | All-round visible display apparatus for aircraft |
| JPH08146130A (en)* | 1994-11-24 | 1996-06-07 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Airport surface ground control system |
| JPH08329393A (en)* | 1995-05-29 | 1996-12-13 | Daihatsu Motor Co Ltd | Preceding vehicle detector |
| JPH09264954A (en)* | 1996-03-29 | 1997-10-07 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | Image processing system using radar |
| JP2003132499A (en)* | 2001-10-24 | 2003-05-09 | Electronic Navigation Research Institute | Aircraft position display method in display device for air traffic control |
| US20100002077A1 (en)* | 2005-01-13 | 2010-01-07 | Sensis Corporation | Method and system for tracking position of an object using imaging and non-imaging surveillance devices |
| JP2008215918A (en)* | 2007-03-01 | 2008-09-18 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Airport surface monitoring system and airport surface monitoring method |
| JP2010032429A (en)* | 2008-07-30 | 2010-02-12 | Toyota Motor Corp | Object detector |
| JP2014122873A (en)* | 2012-11-22 | 2014-07-03 | Denso Corp | Target detection device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6687296B2 (en) | 2020-04-22 |
| WO2018220745A1 (en) | 2018-12-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10782399B2 (en) | Object detecting method and apparatus using light detection and ranging (LIDAR) sensor and radar sensor | |
| JP5503578B2 (en) | Object detection apparatus and object detection method | |
| CN107305632B (en) | Monocular computer vision technology-based target object distance measuring method and system | |
| US11762071B2 (en) | Multi-mode multi-sensor calibration | |
| KR102054455B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for calibrating between heterogeneous sensors | |
| US9495750B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and storage medium for position and orientation measurement of a measurement target object | |
| JP5276721B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for identifying obstacles in an image | |
| US11954918B2 (en) | Object detection device, object detection method, and storage medium | |
| JP6396714B2 (en) | Object recognition device | |
| WO2018235300A1 (en) | Object detection apparatus, object detection method, and computer readable recording medium | |
| JP2018124787A (en) | Information processing device, data managing device, data managing system, method, and program | |
| US11993289B2 (en) | Vehicle control system and vehicle control method | |
| EP3361446A1 (en) | Imu-aided image registration | |
| EP3792874B1 (en) | Position estimation device, position estimation method, and computer program | |
| US12169135B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and storage medium | |
| EP3879810A1 (en) | Imaging device | |
| KR101907875B1 (en) | Fusion detection system, detection processor, radar device, and object detection method | |
| US20240312037A1 (en) | Slam device, computer readable medium, and autonomous mobility | |
| JP2014134856A (en) | Subject identification device, subject identification method, and subject identification program | |
| JP2006090957A (en) | Moving object surrounding object detection apparatus and moving object surrounding object detection method | |
| JP6687296B2 (en) | Monitoring device | |
| EP1307705A1 (en) | Height measurement apparatus | |
| JP2019179289A (en) | Processing device and program | |
| JP6818902B6 (en) | Vehicle detection system | |
| US20230046232A1 (en) | Automatic detection of lidar to vehicle alignment state using camera data |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20190617 | |
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20190617 | |
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date:20190617 | |
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date:20190703 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20190813 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20191002 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20191112 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20200106 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20200303 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20200331 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:6687296 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |