JP7618482B2 - Information processing device, program, and information processing method - Google Patents
Information processing device, program, and information processing methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7618482B2 JP7618482B2JP2021060194AJP2021060194AJP7618482B2JP 7618482 B2JP7618482 B2JP 7618482B2JP 2021060194 AJP2021060194 AJP 2021060194AJP 2021060194 AJP2021060194 AJP 2021060194AJP 7618482 B2JP7618482 B2JP 7618482B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- learner
- learning
- unit
- skills
- learning environment
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000010365information processingEffects0.000titleclaimsdescription18
- 238000003672processing methodMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription5
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000claimsdescription83
- 238000011156evaluationMethods0.000claimsdescription80
- 230000000007visual effectEffects0.000claimsdescription28
- 230000014509gene expressionEffects0.000claimsdescription12
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsdescription11
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000claimsdescription10
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000003340mental effectEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description15
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description13
- 238000000926separation methodMethods0.000description4
- 230000003542behavioural effectEffects0.000description3
- 239000012141concentrateSubstances0.000description3
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description3
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description3
- 208000021900auditory perceptual diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description2
- 238000005401electroluminescenceMethods0.000description2
- 230000001771impaired effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000013515scriptMethods0.000description2
- 208000012239Developmental diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-NGlycerineChemical compoundOCC(O)COPEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 210000004556brainAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000003925brain functionEffects0.000description1
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000019771cognitionEffects0.000description1
- 230000001149cognitive effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000018109developmental processEffects0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 239000004973liquid crystal related substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000description1
- 238000007726management methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000011218segmentationEffects0.000description1
- 210000000697sensory organAnatomy0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Electrically Operated Instructional Devices (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、情報処理装置、プログラム、および情報処理方法に関する。The present invention relates to an information processing device, a program, and an information processing method.
従来、学習方法や学習の支援方法を学習者ごとにカスタマイズして、学習者の学習への取り組みを支援する技術が存在する。下記特許文献1では、学習者の行動特性および学習履歴、ならびに脱退済みまたは継続中の状況を記憶し、脱退済みの学習者の行動特性および学習履歴に基づいて学習者の脱退に至る予測モデルを構築する学習継続システムが開示されている。また、このシステムでは、この構築した予測モデルに基づいて学習者に対して実行した施策(例えば、学習者および保護者の何れかへの「最近、学校の数学の授業はどうですか?」などの声かけ)を評価して、評価結果に基づいて取るべき施策を提示する。このようなシステムによれば、学習者ごとの学習の継続を促し得る適切な施策を提供可能となる。Conventionally, there exists technology that supports learners' efforts in learning by customizing learning methods and learning support methods for each learner. The following
ところで、近年、ICTを活用した学習ツールが普及している。しかしながら、WebサイトやアプリなどのICTを利用した学習ツールが、学習者全員に必ずしも合っているとは限らない。このような学習ツールに触れる際、学習者の特性によって、例えば、ある学習者はこの学習ツールの出題の表示が分かりづらく感じるために学習に集中できないとか、また別の学習者は読み上げた音声が意味を持って認識しにくいためにこの学習ツールで読み上げられる音声が聴き取りづらいといったことがある。このように、学習者の特性によっては、実際の学習そのものに至る以前に、学習に取り組むにあたっての困難が生じることがある。Recently, learning tools that utilize ICT have become widespread. However, ICT-based learning tools such as websites and apps are not necessarily suited to all learners. When using such learning tools, depending on the learner's characteristics, for example, some learners may find it difficult to understand the display of questions in the learning tool and therefore be unable to concentrate on their studies, while other learners may have difficulty recognizing the meaning of the audio being read aloud and therefore have difficulty hearing the audio being read aloud by the learning tool. In this way, depending on the learner's characteristics, difficulties may arise in engaging in learning even before the actual learning itself begins.
そこで、本発明のいくつかの態様は、ICTを利用する学習ツールにおいて学習者が学習に取り組むにあたっての困難を軽減できる情報処理装置、プログラム、および情報処理方法を提供することを目的とする。Therefore, some aspects of the present invention aim to provide an information processing device, program, and information processing method that can reduce the difficulties that learners face when learning with learning tools that utilize ICT.
本発明の一態様に係る情報処理装置は、学習者に対して、アセスメントテストを実施する実施部と、アセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、学習者がレッスンに取り組む際の学習環境と、学習者の発達特性を評価する評価部と、学習者がレッスンに取り組む際、評価部で評価された学習環境に基づいて設定された学習環境で、評価部で評価された発達特性に基づいて決定された学習コンテンツを、学習者に提供する提供部と、を備える。An information processing device according to one aspect of the present invention includes an implementation unit that administers an assessment test to a learner, an evaluation unit that evaluates the learning environment in which the learner works on a lesson and the developmental characteristics of the learner based on the results of the assessment test, and a provision unit that provides the learner with learning content determined based on the developmental characteristics evaluated by the evaluation unit in a learning environment set based on the learning environment evaluated by the evaluation unit when the learner works on a lesson.
本発明の一態様に係るプログラムは、コンピュータに、学習者に対して、アセスメントテストを実施する実施機能と、アセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、学習者がレッスンに取り組む際の学習環境と、学習者の発達特性を評価する評価機能と、学習者がレッスンに取り組む際、評価部で評価された学習環境に基づいて設定された学習環境で、評価部で評価された発達特性に基づいて決定された学習コンテンツを、学習者に提供する提供機能と、を実現させる。A program according to one aspect of the present invention causes a computer to realize an implementation function for administering an assessment test to a learner, an evaluation function for evaluating the learning environment in which the learner works on a lesson and the developmental characteristics of the learner based on the results of the assessment test, and a provision function for providing the learner with learning content determined based on the developmental characteristics evaluated by the evaluation unit in a learning environment set based on the learning environment evaluated by the evaluation unit when the learner works on a lesson.
本発明の一態様に係る情報処理方法は、コンピュータが、学習者に対して、アセスメントテストを実施し、アセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、学習者がレッスンに取り組む際の学習環境と、学習者の発達特性とを評価し、学習者がレッスンに取り組む際、評価部で評価された学習環境に基づいて設定された学習環境で、評価部で評価された発達特性に基づいて決定された学習コンテンツを、学習者に提供する。In one aspect of the information processing method of the present invention, a computer administers an assessment test to a learner, evaluates the learning environment in which the learner works on a lesson and the developmental characteristics of the learner based on the results of the assessment test, and provides the learner with learning content determined based on the developmental characteristics evaluated by the evaluation unit in a learning environment set based on the learning environment evaluated by the evaluation unit when the learner works on the lesson.
これらの態様によれば、アセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、学習者に最適な学習環境と、学習者の発達特性に合った学習コンテンツとを提供することができる。According to these aspects, it is possible to provide the learner with an optimal learning environment and learning content suited to the learner's developmental characteristics based on the results of the assessment test.
本発明のいくつかの態様によれば、ICTを利用する学習ツールにおいて学習者が学習に取り組むにあたっての困難を軽減できる。Some aspects of the present invention can reduce the difficulties that learners face when learning with learning tools that use ICT.
添付図面を参照して、本発明の一実施形態(以下、「本実施形態」という。)について説明する。なお、各図において、同一の符号を付したものは、同一又は同様の構成を有する。One embodiment of the present invention (hereinafter, referred to as "this embodiment") will be described with reference to the attached drawings. Note that in each drawing, parts with the same reference numerals have the same or similar configurations.
<1.システム構成>
図1を用いて、本実施形態に係る学習システム1のシステム構成の例を説明する。本実施形態では、学習システム1を用いて、読み書きや算数などの学習をするためのICTを利用する学習ツール(以下、単に「学習ツール」ともいう)をオンラインで提供する例を説明するが、本発明をこれに限る趣旨ではない。他の例として、端末のローカルにおいてオフラインで動作する学習ツールであってもよい。 1. System configuration
An example of the system configuration of a
図1に示すように、学習システム1は、サーバ装置100と、学習者が使用する学習者端末200と、を備える。サーバ装置100と学習者端末200とは、通信ネットワークNを介して接続される。As shown in FIG. 1, the
通信ネットワークNは、無線ネットワークや有線ネットワークにより構成される。通信ネットワークの一例としては、携帯電話網や、PHS(Personal Handy-phone System)網、無線LAN(Local Area Network)、3G(3rd Generation)、LTE(Long Term Evolution)、4G(4th Generation)、5G(5th Generation)、WiMax(登録商標)、赤外線通信、Bluetooth(登録商標)、有線LAN、電話線、電灯線ネットワーク、IEEE1394などに準拠したネットワークがある。The communication network N is composed of a wireless network and a wired network. Examples of communication networks include a mobile phone network, a PHS (Personal Handy-phone System) network, a wireless LAN (Local Area Network), 3G (3rd Generation), LTE (Long Term Evolution), 4G (4th Generation), 5G (5th Generation), WiMax (registered trademark), infrared communication, Bluetooth (registered trademark), a wired LAN, a telephone line, a power line network, and a network conforming to IEEE 1394, etc.
[サーバ装置]
サーバ装置100は、学習者端末200との通信が可能な情報処理装置である。サーバ装置100は、学習者に対して学習ツールを提供する。本実施形態では、サーバ装置100が学習ツールを提供するためのWebサイト(以下、「学習サイト」ともいう)を生成し、生成した学習サイトのWebページをこれらの端末に配信することで学習ツールの提供を実現させる例を説明する。サーバ装置100は、学習者端末200を介して学習者に学習サイトのURLを指定しログインさせることにより、許可された学習サイトのページにアクセスをさせることができる。このログインは、それぞれが学習システム1に予め登録したアカウント(ユーザIDとパスワード)によって行われる。 [Server device]
The
[学習者端末]
学習者端末200は、例えば、スマートフォンや携帯電話、ラップトップなどの汎用または専用の情報処理装置によって構成される。本実施形態では、学習者端末200に標準的に備わるWebブラウザを利用する例を説明する。学習者端末200は、サーバ装置100から配信されたWebページをWebブラウザから閲覧することで、サーバ装置100から学習ツールの提供を受けるものとする。なお、他の例として、学習者端末200は、家庭用ゲーム機器(携帯型ゲーム機を含む)、電子書籍リーダ、またはその他のコンピュータ機器により構成されてもよい。 [Student's device]
The
<2.システムの概要>
図2を用いて、本実施形態に係る学習システム1の概要を説明する。図2に示すように、学習システム1は、(1)アセスメント(2)学習環境の設定、(3)学習コンテンツの決定、(4)レッスンのサイクルを繰り返すことで学習者に最適な学習環境や学習コンテンツを作りあげることができる。 2. System Overview
An overview of the
「学習環境」は、学習者がレッスンに取り組む際の環境をいう。学習環境は、例えば、不正解のときの表現、または分かち書きの仕方のうち少なくともいずれかを含んでもよい。学習環境は、例えば、音声の入出力の仕方や画面の操作および表示の仕方であってもよい。画面の表示の仕方の一例として、不正解のときの表現において、不正解を表すマークとしてチェックマークを表示させたり「?」マークを表示させたりすることであってもよい。このような構成によれば、学習者の特性に合わせて細やかに学習環境を設定することができる。"Learning environment" refers to the environment in which a learner works on a lesson. The learning environment may include, for example, at least one of the expression for an incorrect answer or the way words are separated into words. The learning environment may also be, for example, the way voice is input and output, or the way a screen is operated and displayed. As an example of the way a screen is displayed, when an incorrect answer is given, a check mark or a "?" mark may be displayed as a mark indicating an incorrect answer. With this configuration, the learning environment can be carefully set to suit the characteristics of the learner.
「学習コンテンツ」とは、学習ツールで提供されるレッスン(以下、単に「レッスン」ともいう)の内容、ひいてはレッスンに関するデータである。学習コンテンツは、例えば、レッスンの内容を示すテキスト、音声データ、画像(静止画または動画)、プログラムなどのデータである。"Learning content" refers to the content of lessons (hereinafter simply referred to as "lessons") provided by a learning tool, and further, data related to the lessons. Learning content is, for example, data such as text, audio data, images (still images or videos), and programs that show the content of the lessons.
(1)学習システム1は、学習者に対するアセスメントを行う。学習システム1は、具体的には、学習者の特性を測るためのアセスメントテストを学習者に実施させ、このアセスメントテストの結果に基づいて学習環境や発達特性の評価を行う。ここで「学習者の特性」とは、発達特性、または読み書きもしくは算数の困り、読み書きもしくは算数の得意の傾向などをいう。(1) The
「発達特性」とは、生まれつきの脳機能の発達の偏りであり、行動や認知の特徴を示す。具体的には、発達特性は、五感を中心とした感覚器から入ってきた様々な情報を脳の中で「理解」「整理」「記憶」「表現」する能力、例えば、学習者の聴覚に関する能力または視覚に関する能力を表す。また、発達特性は、例えば、学習者の視覚に関する特性と聴覚に関する特性のうち優位な特性を表す。言い換えれば、発達特性は、学習者の視覚や聴覚による認知の仕方の得意不得意を表すものであってよい。"Developmental characteristics" are innate biases in the development of brain functions, and indicate behavioral and cognitive characteristics. Specifically, developmental characteristics represent the ability to "understand," "organize," "memorize," and "express" various pieces of information received through the sensory organs, mainly the five senses, in the brain, for example, a learner's auditory or visual abilities. Developmental characteristics also represent, for example, the dominant characteristic of a learner's visual or auditory characteristics. In other words, developmental characteristics may represent a learner's strengths and weaknesses in visual or auditory cognition.
「読み書きもしくは算数の困り」とは、読み書き学習や算数の学習に取り組む際の妨げとなりうる学習者の性質や能力、学習者が使用する方略を表す。読み書きの困りとしては、例えば、ひらがなの文字から音韻に変換する力が弱いなどが考えられる。"Difficulties with reading, writing, or mathematics" refers to the characteristics or abilities of a learner that may hinder learning to read, write, or learn mathematics, or the strategies used by the learner. An example of a difficulty with reading and writing would be a weak ability to convert hiragana characters into sounds.
「読み書きもしくは算数の得意の傾向」とは、読み書きもしくは算数の困りとは逆に、読み書き学習や算数の学習に取り組みを推進しうる学習者の性質や能力、学習者が使用する方略を表す。算数の得意の傾向として、例えば、暗記と演算が得意なため暗算の問題に取り掛かりやすいなどが考えられる。"Tendency to excel at reading, writing, or arithmetic" refers to the qualities and abilities of a learner that can promote learning to read, write, or learn arithmetic, as well as the strategies used by the learner, in contrast to difficulties with reading, writing, or arithmetic. For example, a tendency to excel at arithmetic might be that a learner is good at memorization and arithmetic, and therefore finds it easy to tackle problems with mental arithmetic.
(2)学習システム1は、上記(1)のアセスメントの結果に基づいて、学習者それぞれについて、学習環境を設定する。また、(3)学習システム1は、上記(1)のアセスメントの結果に基づいて、学習者それぞれについて、特性パターン別にひらがなの読み書きクイズや計算問題などの学習コンテンツを決定する。ここで「特性パターン」とは、学習者の特性のパターンであって、例えば、学習者が学習を取り組む際の困りを感じることのパターン(以下、「困りパターン」ともいう)と、視覚優位または聴覚優位のいずれかを表す発達特性のパターンとの組み合わせをいう。(2) The
(4)レッスンにおいて、学習システム1は、上記(2)で設定された学習環境で、上記(3)で決定された学習コンテンツを提供する。(4) During the lesson, the
学習システム1は、上記(1)のアセスメントを定期的(例えば、3か月に1回や半年に1回など)に実施し、このアセスメントの結果により上記(2)の学習環境の再設定や上記(3)の学習コンテンツの再決定をし、上記(4)のレッスンを行う。学習システム1は、このように上記(1)~(4)のサイクルを繰り返すことで、学習者ごとに、学習環境や学習コンテンツを最適化することができる。The
上記構成によれば、学習システム1は、アセスメントの結果に基づいて、学習者の発達特性や基礎学力など、学習者の特性に合った学習環境で学習者の発達特性に合った学習コンテンツを提供するこができる。このため、上記構成によれば、学習システム1は、ICTを利用する学習ツールにおいて、学習ツールの出題の表示が分かりづらく感じるために学習に集中できないとか、また別の学習者は読み上げた音声が意味を持って認識しにくいためにこの学習ツールで読み上げられる音声が聴き取りづらいといった学習に取り組むにあたっての困難を軽減することができる。さらに、上記構成によれば、学習システム1は、このように学習に取り組むにあたっての困難を軽減することで、学習者の自己肯定感を向上させ、前向きに学習に取り組ませることができる。According to the above configuration, the
<3.機能構成>
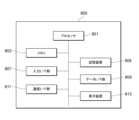
図3を参照して、本実施形態に係るサーバ装置100の機能構成を説明する。図3に示すように、サーバ装置100は、制御部110と、通信部120と、記憶部130と、を備える。 <3. Functional configuration>
The functional configuration of the
[制御部]
制御部110は、実施部111と、評価部112と、提供部113と、を備える。 [Control unit]
The
[実施部]
実施部111は、学習者に対して、アセスメントテストを実施する。実施部111は、例えば、まず、テスト情報に基づいて、アセスメントテストに関するコンテンツ(例えば、テストの出題内容を示すテキストや画像、スクリプトなど)を生成する。このテストコンテンツは、例えば、Webブラウザを介してアセスメントテストを配信するためのWebページ(HTMLファイル)である。ここで「テスト情報」とは、アセスメントテストに関する情報であり、テストの内容や出題形式などを示す情報である。次に、実施部111は、生成したテストコンテンツを学習者端末200に送信する。実施部111は、この送信したテストコンテンツにより学習者端末200にアセスメントテストを実施するためのテスト画面を表示させる。次に、実施部111は、学習者端末200を介して、この表示されたテスト画面の入力フォームに対して学習者から入力された回答の情報を受信する。 [Implementation Department]
The
実施部111は、実施したアセスメントの結果を学習者情報に記憶する。ここで「学習者情報」とは、学習者に関する情報であり、学習者それぞれのアセスメントの結果やレッスンの結果、学習者のスキルや学習環境、発達特性などの評価結果、設定された学習環境に関する情報(例えば、学習環境の設定項目ごとのパラメータなど)、決定された学習コンテンツに関する情報を含む。The
アセスメントテストは、例えば、発達特性、読み書きもしくは算数の困り、または読み書きもしくは算数の得意の傾向の少なくともいずれかに関するチェックテストのうち少なくともいずれかを含んでもよい。The assessment test may include, for example, at least one of a check test regarding developmental characteristics, difficulties with reading, writing or mathematics, or tendencies to excel in reading, writing or mathematics.
上記構成によれば、学習者において、この学習ツールの出題の表示が分かりづらく感じるために学習に集中できないとか、また読み上げた音声が意味を持って認識しにくいためにこの学習ツールで読み上げられる音声が聴き取りづらいといった学習の際の困りをチェックすることができる。The above configuration makes it possible to check for difficulties that a learner may have when studying, such as being unable to concentrate on their studies because they find the questions displayed in the learning tool difficult to understand, or having difficulty hearing the audio read out by the learning tool because they find it difficult to recognize the meaning of the audio being read out.
上記構成によれば、発達特性のチェックと読み書き計算の困りや得意の傾向のチェックそれぞれのチェックをすることができる。また、上記構成によれば、発達特性のチェックの結果と読み書き計算の困りや得意の傾向のチェックの結果とをクロスチェックすることもできる。このため、上記構成によれば、このクロスチェックの結果に基づいて学習者の特性を評価させることができる。したがって、上記構成によれば、いわゆる学力テストだけ、または知能検査だけでは評価できない学習の際に感じる困りごとや学習を推進する得意の傾向などの特性を、評価することができる。The above configuration makes it possible to check developmental characteristics and difficulties and strengths in reading, writing, and arithmetic. The above configuration also makes it possible to cross-check the results of the developmental characteristics check with the results of the difficulties and strengths in reading, writing, and arithmetic. Therefore, the above configuration makes it possible to evaluate the characteristics of the learner based on the results of this cross-check. Therefore, the above configuration makes it possible to evaluate characteristics such as difficulties felt during learning and strengths that promote learning, which cannot be evaluated by so-called academic ability tests or intelligence tests alone.
[評価部]
評価部112は、実施部111が実施したアセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、学習者がレッスンに取り組む際の学習環境と、学習者の発達特性とを評価する。この学習者の発達特性は、例えば、学習者の視覚に関する特性と聴覚に関する特性のうち優位な特性を示してもよい。以降、各学習者において、視覚に関する特性が優位なことを「視覚優位」、聴覚に関する特性が優位なことを「聴覚優位」ともいう。また、評価部112は、例えば、レッスンの結果に基づいて、学習環境と発達特性とを評価してもよい。評価部112は、これらの評価した結果を学習者情報に記憶する。 [Evaluation Department]
The
上記構成によれば、評価部112は、各学習者に対して、視覚優位か聴覚優位かを評価することができる。このため、上記構成によれば、評価部112は、学習者の優位な特性を評価することができるため、この優位な特性を活かせるような学習環境と学習コンテンツの提供を実現させ、ひいては学習者の自己肯定感の向上を図ることができる。According to the above configuration, the
評価部112は、第1評価部1121と、第2評価部1122と、を含む。The
第1評価部1121は、アセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、学習者の視覚に関するスキル、聴覚に関するスキル、読み書きに関するスキル、または算数に関するスキルの少なくともいずれかを示すスキル(以下、単に「スキル」ともいう)を評価する。第1評価部1121は、例えば、これらのスキルのレベルを、「1(◎)」「2(〇)」「3(△)」「4(×)」の4段階で評価してもよい。The
学習者のスキルは、例えば、語彙力、音節、数概念、数処理、暗算、または算数の文章題に関する能力のうち少なくともいずれかを含んでもよい。The learner's skills may include, for example, at least one of vocabulary, syllables, number concepts, number processing, mental arithmetic, or ability to solve mathematical word problems.
上記構成によれば、第1評価部1121は、読み書きに関するスキルや算数に関するスキルを細分化して評価することができる。このため、上記構成によれば、第1評価部1121は、学習者のスキルをより精度よく評価することができ、ひいては、学習環境や発達特性もより精度よく評価することができる。According to the above configuration, the
第1評価部1121は、例えば、アセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、学習者が学習に取り組む際の困りパターンを評価してもよい。言い換えれば、第1評価部1121は、例えば、アセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、該当する困りパターンに学習者を分類してもよい。困りパターンの詳細は、図5を用いて後述する。The
第2評価部1122は、第1評価部1121により評価されたスキルに基づいて、学習者がレッスンに取り組む際の学習環境と学習者の発達特性とを評価する。The
上記構成によれば、評価部112は、学習者のスキルを評価した上で、学習環境と発達特性とを評価することができる。このため、上記構成によれば、評価部112は、学習者の保護者や指導者などに対して、学習者のスキルと学習環境と発達特性の評価とを対応付けさせることができ、学習者のスキルをふまえた学習環境や発達特性を考えられるよう支援することができる。According to the above configuration, the
[提供部]
提供部113は、学習者がレッスンに取り組む際、評価部112で評価された学習環境に基づいて設定された学習環境で、評価部112で評価された発達特性に基づいて決定された学習コンテンツを、学習者に提供する。提供部113は、例えば、まず、学習者ごとに、評価部112で評価された学習環境に基づいて学習環境を設定する。また、提供部113は、学習者ごとに、評価部112で評価された発達特性に基づいて、学習者に提供する学習コンテンツを決定する。そして、提供部113は、この設定された学習環境で、決定された学習コンテンツを、学習者に提供する。提供部113は、設定した学習環境や決定した学習コンテンツを学習者情報に記憶する。 [Provision Department]
When a learner works on a lesson, the
提供部113は、例えば、まず、学習者情報に基づいて、レッスンに関する学習コンテンツ(例えば、レッスンの出題内容を示すテキストや画像、スクリプトなど)を生成する。この学習コンテンツは、例えば、Webブラウザを介してレッスンを配信するためのWebページである。次に、実施部111は、生成した学習コンテンツを学習者端末200に送信する。次に、実施部111は、この送信した学習コンテンツに基づいて学習者端末200にレッスンを実施するためのレッスン画面を表示させる。For example, the providing
上記構成によれば、提供部113は、アセスメントの結果に基づいて評価された学習者に合った学習環境で、学習者に合った学習コンテンツを提供することができる。このため、上記構成によれば、提供部113は、ICTを利用する学習ツールにおいて、出題の表示が分かりづらいとか、この読み上げられる音声が聴き取りづらいなどの学習に取り組むにあたっての学習者ごとの困難を軽減し、自己肯定感を向上させることができる。According to the above configuration, the
提供部113は、例えば、学習者の発達特性のうちが視覚に関する特性が優位な場合、視覚の強さを活かした学習コンテンツを学習者に提供してもよい。また、提供部113は、例えば、学習者の発達特性のうち聴覚に関する特性が優位な場合、聴覚の強さを活かした学習コンテンツを学習者に提供してもよい。For example, if visual characteristics are dominant among the developmental characteristics of the learner, the
上記構成によれば、提供部113は、学習者の視覚の強さや聴覚の強さを活かした学習コンテンツを提供することができる。このため、上記構成によれば、提供部113は、学習者の発達特性にあった学習コンテンツを提供することができる。したがって、上記構成によれば、提供部113は、例えば、聴覚記憶に障害をもつAPD(聴覚情報処理障害)の学習者の場合、視覚の強さを活かす学習コンテンツを提供することで、この学習者が聴覚記憶の障害による学習の際の困りごとを軽減することができる。According to the above configuration, the
<アセスメントテストと学習者のスキルと学習環境および学習コンテンツとの関係>
図4を用いて、アセスメントテストとスキルと学習環境および学習コンテンツとの関係の一例を説明する。 <Relationship between assessment tests, learner skills, learning environment, and learning content>
An example of the relationship between assessment tests, skills, learning environments, and learning contents will be described with reference to FIG.
図4に示すように、学習システム1が実施するアセスメントテストにおいて、例えば、学習者の発達特性を評価するためのテストと学習者の読み書きの困りや得意の傾向を評価するためのテストとを設けてもよい。学習システム1では、発達特性を評価するためのテストから、発達特性に関するスキルを評価する。また、学習システム1では、例えば、読み書きの困りや得意の傾向を評価するためのテストから、読み書きに関するスキルを評価する。As shown in FIG. 4, the assessment test conducted by the
第1評価部1121は、例えば、数字を聞いて覚えるクイズ(図4、6では、「数唱」と表記)のテスト3を学習者が実施した場合、このテスト3の結果に基づいて聴覚に関するスキル(例えば、聴覚記憶など)を評価する。また、第1評価部1121は、例えば、視覚を使ったテスト4を学習者が実施した場合、このテストの結果に基づいて視覚に関するスキル(例えば、視覚記憶など)のレベルを判定する。そして、第2評価部1122は、例えば、聴覚に関するスキルが視覚に関するスキルより上回る場合、学習者の発達特性は聴覚優位であると評価する。提供部113は、例えば、発達特性が聴覚優位の場合、聴覚の強さを活かした学習コンテンツ、例えば、漢字の書き順を学ぶレッスンであれば、絵描き歌のように発声させて覚えさせるような学習コンテンツに決定する。他方、提供部113は、例えば、発達特性が視覚優位の場合、視覚の強さを活かした学習コンテンツ、例えば、漢字の書き順を学ぶレッスンであれば、漢字にまつわるイラストと一緒に覚えさせるような学習コンテンツに決定する。For example, when the learner performs
<アセスメントテストと困りパターンとの関係>
ここで図5を用いて、アセスメントテストと学習者の困りパターンとの関係の一例を説明する。本例では、語彙力に関するアセスメントテストを例に説明する。図5に示すように第1評価部1121は、アセスメントテストの結果を、語彙力のスキルのレベルが「×」の場合と、語彙力のスキルのレベルが「△」か「〇」の場合とで大きく分類する。さらに第1評価部1121は、語彙力のスキルを細分化してそれぞれのレベルに応じて分類する。第1評価部1121は、このように分類した結果に応じて、学習に取り組む際の困りの種類とその度合いをパターン化した困りパターン別に学習者を分類する。例えば、音韻変換を苦手とする困りがあるため読みに関するスキルが低い疑いがある場合、第1評価部1121は、学習者の困りパターンを「読み書き低・音韻パターン(パターン3)」と分類する。この困りパターンに分類された場合、提供部113は、学習者に、音韻変換のレッスンを優先的にリコメンドするよう学習コンテンツを決定する。 <Relationship between assessment tests and problem patterns>
Here, an example of the relationship between the assessment test and the learner's difficulty pattern will be described with reference to FIG. 5. In this example, an assessment test on vocabulary will be described as an example. As shown in FIG. 5, the
第2評価部1122は、例えば、第1評価部1121が分類した困りパターンと発達特性における聴覚優位か視覚優位かのパターンとを組み合わせて、学習者を特性パターン別に分類してもよい。The
<アセスメントテストから学習コンテンツの提供までのプロセス>
ここで図6~9を用いて、学習者T(小2男児)と学習者X(小2男児)それぞれの場合におけるアセスメントテストから学習コンテンツの提供までのプロセスの一例を説明する。 <The process from assessment tests to providing learning content>
Here, an example of the process from the assessment test to the provision of learning content for each of learner T (a boy in the second grade of elementary school) and learner X (a boy in the second grade of elementary school) will be described with reference to FIGS.
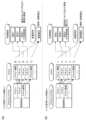
<(ア)発達特性に関するチェックテスト~スキル評価~学習環境・発達特性の評価>
図6(a)に示すように、学習環境のうち不正解のときの表現について、学習者Tの場合、第1評価部1121は、発達特性に関するチェックテストの結果に基づいて、正答率に関するスキル4のレベルを「〇」と評価する。第2評価部1122は、この評価されたスキル4のレベルに基づいて、誤答が少ないタイプとし、不正解の表現は標準の表現が学習者Tに合っていると評価する。 <(A) Developmental characteristic check test – Skills evaluation – Evaluation of learning environment and developmental characteristics>
6A, for the expressions when answers are incorrect in the learning environment, in the case of learner T, the
発達特性について、学習者Tの場合、第1評価部1121は、発達特性に関するチェックテストの結果に基づいて、視覚に関するスキルのレベルを「◎」、聴覚に関するレベルを「〇」と評価する。第2評価部1122は、視覚に関するスキルのレベルが聴覚に関するレベルを上回るため、学習者Tの発達特性を視覚優位と評価する。Regarding developmental characteristics, in the case of learner T, the
図6(b)に示すように、学習環境のうち不正解のときの表現について、学習者Xの場合、第1評価部1121は、発達特性に関するチェックテストの結果に基づいて、正答率に関するスキル4のレベルを「△」と評価する。第2評価部1122は、この評価されたスキル4のレベルに基づいて、誤答が多いタイプとし、不正解の表現は標準の表現よりも柔らかい表現が学習者Xに合っていると評価する。As shown in FIG. 6(b), for learner X, the
発達特性について、学習者Xの場合、第1評価部1121は、発達特性に関するチェックテストの結果に基づいて、視覚に関するスキルのレベルを「×」、聴覚に関するレベルを「〇」と評価する。第2評価部1122は、聴覚に関するレベルが視覚に関するスキルのレベルを上回るため、学習者Xの発達特性を視覚優位と評価する。Regarding the developmental characteristics of learner X, the
<(イ)読み書きに関するチェックテスト~スキル評価~学習コンテンツの決定>
図7(a)に示すように、学習コンテンツの決定をするため、学習者Tの場合、第1評価部1121は、読み書きに関するチェックテストの結果に基づいて、語彙力などの読み書きに関するスキルのレベルを評価する。第2評価部1122は、この評価されたスキルのレベルに基づいて、学習者Tの困りパターンを「読み書き低・音韻パターン(パターン3)」と評価する。 <(a) Reading and writing check test – skills evaluation – deciding on learning content>
7A, in order to determine learning content, in the case of learner T, the
図7(b)に示すように、学習者Xの場合も同様に、学習コンテンツの決定をするため、学習者Xの場合、第1評価部1121が語彙力などの読み書きに関するスキルのレベルを評価し、第2評価部1122がこの評価されたスキルのレベルに基づいて学習者Xの困りパターンを「語彙力低パターン(パターン1)」と評価する。As shown in FIG. 7(b), in the case of learner X, in order to determine the learning content, the
<(ウ)学習環境の設定>
図8(a)に示すように、学習者Tの場合、不正解の表現は標準の表現が合っているとの上記(ア)の評価に基づいて、提供部113は、不正解の表示を標準の画像(チェック画像)に設定する。また、学習者Tの場合、視覚優位とする上記(ア)の評価に基づいて、分かち書きの種類を標準のもの(本例では、分かち書きなしとする)に設定する。 (C) Setting up the learning environment
8A, in the case of learner T, the providing
図8(b)に示すように、学習者Xの場合、不正解の表現は標準の表現よりも柔らかい表現が合っているとの上記(ア)の評価に基づいて、提供部113は、不正解の表示を標準の画像ではなくやわらかい表現の画像(?マークの画像)に設定する。また、学習者Xの場合、聴覚優位とする上記(ア)の評価に基づいて、分かち書きの種類を明確なもの(本例では、スラッシュによる分かち書きありとする)に設定する。As shown in FIG. 8(b), in the case of learner X, based on the above evaluation (a) that a softer expression is more appropriate than a standard expression for the incorrect answer, the providing
<(エ)学習コンテンツの決定>
図9(a)に示すように、学習者Tの場合、上記(ア)の評価で発達特性が視覚優位と評価されているため、ひらがなの「つ」を覚えさせるコンテンツの場合、視覚の強さを活かすため、提供部113は、ひらがなの「つ」の説明と併せて「つ」にまつわるイラスト(図10では、月のイラスト画像)と併せて表示するものに決定する。また、学習者Tの場合、上記(イ)の評価で困りパターンが「読み書き低・音韻パターン(パターン3)」と評価されているため、学習者Tに提供する学習コンテンツとして、提供部113は、音韻に係わるレッスンのコンテンツを優先させる。さらに、学習者Tの場合、提供部113は、読みに関するレベルが低いため、この音韻に係わるレッスンのコンテンツのうち難易度を低くしたものにする。 (D) Determining learning content
As shown in FIG. 9A, in the case of learner T, the developmental characteristics are evaluated as being visually dominant in the evaluation (A) above, so in the case of content for memorizing the hiragana character "tsu", the
図9(b)に示すように、学習者Xの場合、視覚優位か聴覚優位かを示す発達特性については、上記(イ)の評価で困りパターンが「語彙力低パターン(パターン1)」評価されているため、視覚と聴覚どちらにも偏らない共通のものに決定する。また、学習者Xの場合、この困りパターンにより語彙力が低いと疑われるため、学習者Xに提供する学習コンテンツとして、難易度を最も低くしたものにする。As shown in Figure 9 (b), in the case of Learner X, the difficulty pattern was evaluated as "low vocabulary pattern (Pattern 1)" in the evaluation of (i) above, so a common pattern that is not biased towards either visual or auditory is decided upon for the developmental characteristics indicating whether Learner X is visually or auditorily dominant. Also, in the case of Learner X, this difficulty pattern suggests that he or she has low vocabulary, so the learning content to be provided to Learner X is set to the lowest level of difficulty.
[通信部]
図3に戻って説明を続ける。通信部120は、通信ネットワークNを介して、学習者端末200と、学習サイトのWebページなどの各種情報を送受信する。 [Communications Department]
Continuing the explanation by returning to Fig. 3, the
[記憶部]
記憶部130は、テスト情報や学習者情報を含む配送に関する各種情報を記憶する。記憶部130は、例えば、これらの情報を相互に関連付けて記憶してもよい。記憶部130は、データベースマネジメントシステム(DBMS)を利用して各種情報を記憶してもよいし、ファイルシステムを利用して各種情報を記憶してもよい。DBMSを利用する場合は、情報ごとにテーブルを設けて、このテーブル間を関連付けて各種情報を管理してもよい。 [Memory unit]
The
<4.動作例>
図10を参照して、サーバ装置100の動作例を説明する。なお、以下に示す処理の順番は一例であって、適宜、変更されてもよい。 <4. Operation example>
An example of the operation of the
図10に示すように、実施部111は、学習者に対して、アセスメントテストを実施する(S10)。次に、評価部112は、アセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、学習者がレッスンに取り組む際の学習環境と、学習者の発達特性とを評価する(S11)。次に、提供部113は、評価部112で評価された学習環境に基づいて学習者に適用する学習環境を設定する(S12)。そして、提供部113は、学習者がレッスンに取り組む際、この設定された学習環境で、評価部112で評価された発達特性に基づいて決定された学習コンテンツを、学習者に提供する(S13)。As shown in FIG. 10, the
<5.ハードウェア構成>
図11を参照して、上述してきたサーバ装置100をコンピュータ800により実現する場合のハードウェア構成の一例を説明する。なお、それぞれの装置の機能は、複数台の装置に分けて実現することもできる。 5. Hardware Configuration
11, an example of a hardware configuration in which the above-mentioned
図11に示すように、コンピュータ800は、プロセッサ801と、メモリ803と、記憶装置805と、入力I/F部807と、データI/F部809と、通信I/F部811、及び表示装置813を含む。As shown in FIG. 11, the
プロセッサ801は、メモリ803に記憶されているプログラムを実行することによりコンピュータ800における様々な処理を制御する。例えば、サーバ装置100の制御部110が備える各機能部などは、メモリ803に一時記憶されたプログラムを、プロセッサ801が実行することにより実現可能である。The
メモリ803は、例えばRAM(Random Access Memory)などの記憶媒体である。メモリ803は、プロセッサ801によって実行されるプログラムのプログラムコードや、プログラムの実行時に必要となるデータを一時的に記憶する。The
記憶装置805は、例えばハードディスクドライブ(HDD)やフラッシュメモリなどの不揮発性の記憶媒体である。記憶装置805は、オペレーティングシステムや、上記各構成を実現するための各種プログラムを記憶する。この他、記憶装置805は、テスト情報、学習者情報等の各種情報を登録するテーブルと、当該テーブルを管理するDBを記憶することも可能である。このようなプログラムやデータは、必要に応じてメモリ803にロードされることにより、プロセッサ801から参照される。The
入力I/F部807は、ユーザからの入力を受け付けるためのデバイスである。入力I/F部807の具体例としては、キーボードやマウス、タッチパネル、各種センサ、ウェアラブル・デバイスなどが挙げられる。入力I/F部807は、例えばUSB(Universal Serial Bus)などのインタフェースを介してコンピュータ800に接続されても良い。The input I/
データI/F部809は、コンピュータ800の外部からデータを入力するためのデバイスである。データI/F部809の具体例としては、各種記憶媒体に記憶されているデータを読み取るためのドライブ装置などがある。データI/F部809は、コンピュータ800の外部に設けられることも考えられる。その場合、データI/F部809は、例えばUSBなどのインタフェースを介してコンピュータ800へと接続される。The data I/
通信I/F部811は、コンピュータ800の外部の装置と有線または無線により、インターネットNを介したデータ通信を行うためのデバイスである。通信I/F部811は、コンピュータ800の外部に設けられることも考えられる。その場合、通信I/F部811は、例えばUSBなどのインタフェースを介してコンピュータ800に接続される。The communication I/
表示装置813は、各種情報を表示するためのデバイスである。表示装置813の具体例としては、例えば液晶ディスプレイや有機EL(Electro-Luminescence)ディスプレイ、ウェアラブル・デバイスのディスプレイなどが挙げられる。表示装置813は、コンピュータ800の外部に設けられても良い。その場合、表示装置813は、例えばディスプレイケーブルなどを介してコンピュータ800に接続される。また、入力I/F部807としてタッチパネルが採用される場合には、表示装置813は、入力I/F部807と一体化して構成することが可能である。The
なお、本実施形態は、本発明を説明するための例示であり、本発明をその実施の形態のみに限定する趣旨ではない。また、本発明は、その要旨を逸脱しない限り、さまざまな変形が可能である。さらに、当業者であれば、以下に述べる各要素を均などなものに置換した実施の形態を採用することが可能であり、かかる実施の形態も本発明の範囲に含まれる。Note that this embodiment is an example for explaining the present invention, and is not intended to limit the present invention to this embodiment alone. Furthermore, the present invention can be modified in various ways without departing from the gist of the invention. Furthermore, a person skilled in the art can adopt an embodiment in which each element described below is replaced with an equivalent one, and such an embodiment is also included in the scope of the present invention.
[変形例]
なお、本発明を上記実施の形態に基づいて説明してきたが、以下のような場合も本発明に含まれる。 [Modification]
Although the present invention has been described based on the above embodiment, the following cases are also included in the present invention.
[変形例1]
上記実施形態に係るサーバ装置100が備える各構成の少なくとも一部は、学習者端末200が備えていてもよい。学習者端末200は、例えば、学習システム1専用のアプリケーションプログラム(ネイティブアプリ)(以下、「学習アプリ」ともいう)をインストールしてこの学習アプリを実行することでこれらの構成を実現させてもよい。言い換えれば、学習システム1では、学習ツールとして、サーバ装置100が配信する学習サイトを利用することもでき、また代わりに学習アプリを利用することもできる。学習システムにおいて、学習アプリを利用する場合、学習者端末200がオフラインであっても、学習者は少なくとも一部の機能を利用することができる。 [Modification 1]
At least some of the components of the
[変形例2]
上記実施形態では示していないが、学習システム1は、学習者の保護者が使用する保護者端末と、学習者を指導する指導者が使用する指導者端末と、を備えてもよい。保護者と指導者とは、特に区別の必要がない場合、これらをまとめて「関係者」と総称する。また、保護者端末と指導者端末とは、特に区別の必要がない場合は、これらをまとめて「関係者端末」と総称する。なお、学習者と保護者とが使用する端末は同じ端末であってもよい。サーバ装置100と、学習者端末200と、関係者端末とは、通信ネットワークNを介して通信可能に接続されている。なお、学習者、保護者および指導者は、学習サイトに対してそれぞれ個別のアカウントを利用するようにしてもよいし、学習者(特に、未就学児や発達障害児など)と保護者とは、同一のアカウントを利用するようにしてもよい。 [Modification 2]
Although not shown in the above embodiment, the
関係者端末は、学習者端末200と同様に、例えば、スマートフォンや携帯電話、ラップトップなどの汎用の端末装置によって構成される。また、本例では、学習者端末200と同様に、関係者端末に標準的に備わるWebブラウザを利用する例を説明する。The related party terminal, like the
提供部113は、例えば、関係者から、学習環境の設定変更を受け付けてもよい。提供部113は、例えば、図12に示すような学習環境の設定変更をするための画面(以下、「学習設定画面」ともいう)を関係者端末に表示させてもよい。学習設定画面では、例えば、ふりがなのON/OFFを指定する入力フォーム(図12では、「漢字にふりがなは必要ですか?」のテキストとON/OFFのスライドボタンとを表記)、分かち書きの種類を指定するための入力フォーム(図12では、「文章はどの表示が一番よみやすいですか?」のテキストと「見本 です」「見本です」「見本/です」の3つのボタンを表記)などの複数の設定項目を備える。提供部113は、関係者端末から、この表示された学習設定画面を介して、学習環境の設定変更を受け付ける。そして、提供部113は、受け付けた設定変更に基づいて、学習者に適用する学習環境の設定を変更する。このような構成によれば、提供部113は、保護者や指導者の意向にそった学習環境に調整することができる。The providing
提供部113は、例えば、学習者が学習する場面ごとに、学習環境および学習コンテンツを設定してもよい。提供部113は、例えば、学習者が自宅で学習する場面で適用する自宅用学習環境と、学習者が学校で学習する場面で適用する指導用学習環境と、をそれぞれ設定してもよい。提供部113は、例えば、自宅用学習環境と指導用学習環境とは、それぞれ関係者から設定変更を受け付けてもよい。このような構成によれば、提供部113は、学習する場面に応じた適切な学習環境や学習コンテンツを提供することができる。The providing
提供部113は、例えば、関係者に、アセスメントテストの結果を提供してもよい。また、提供部113は、例えば、保護者と指導者それぞれに対して、アセスメントテストの結果の出力態様を変えて提供してもよい。例えば、図13に示すように、保護者に対するアセスメントテストの結果の表示態様は、指導者用と比較して、直接的な表現を避け、柔らかい表現としてもよい。具体的には、提供部113は、アセスメントテストの各テストの正答数は非表示にし、複数のスキルをまとめた指標を設け、この指標ごとにスキルのレベル(1~4の数値)を集計し、集計の結果をレーダーチャートなどのグラフ形式で表示してもよい。他方、指導者に対するアセスメントテストの結果の表示態様は、指導者用と比較して、直接的な表現としてもよい。例えば、図7に示すようなアセスメントテストの各テストそれぞれの正答数やそれに基づく各スキルそれぞれのレベルを表形式で表示させてもよい。このような構成によれば、提供部113は、保護者や指導者それぞれの立場に応じたアセスメント結果の表示とすることができる。The providing
1…学習システム、100…サーバ装置、110…制御部、111…実施部、112…評価部、113…提供部、800…コンピュータ、801…プロセッサ、803…メモリ、805…記憶装置、807…入力I/F部、809…データI/F部、811…通信I/F部、813…表示装置。1... learning system, 100... server device, 110... control unit, 111... implementation unit, 112... evaluation unit, 113... provision unit, 800... computer, 801... processor, 803... memory, 805... storage device, 807... input I/F unit, 809... data I/F unit, 811... communication I/F unit, 813... display device.
Claims (9)
Translated fromJapanese前記アセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、前記学習者がレッスンに取り組む際の音声の入出力の仕方、画面の操作の仕方、又は画面の表示の仕方の少なくともいずれかである学習環境と、前記学習者の発達特性とを評価する評価部と、
前記学習者がレッスンに取り組む際、前記評価部で評価された前記学習環境に基づいて設定された学習環境で、前記評価部で評価された前記発達特性に基づいて決定された学習コンテンツを、前記学習者に提供する提供部と、
を備える情報処理装置。 An implementation department that administers assessment tests to learners;
an evaluation unit that evaluates the learning environment,which is at least one of a manner of voice input/output, a manner of screen operation, and a manner of screen display when the learner engages in a lesson, and the developmental characteristics of the learner, basedon a result of the assessment test;
a provision unit that provides, when the learner works on a lesson, learning content determined based on the developmental characteristics evaluated by the evaluation unit in a learning environment set based on the learning environment evaluated by the evaluation unit to the learner;
An information processing device comprising:
請求項1に記載の情報処理装置。 The development characteristics indicate a dominant characteristic among the visual characteristics and the auditory characteristics of the learner.
The information processing device according to claim 1 .
前記発達特性のうち視覚に関する特性が優位な場合、視覚の強さを活かした学習コンテンツを前記学習者に提供し、
前記発達特性のうち聴覚に関する特性が優位な場合、聴覚の強さを活かした学習コンテンツを前記学習者に提供する、
請求項1から4のいずれか1項に記載の情報処理装置。 The providing unit is
If visual characteristics are dominant among the developmental characteristics, providing the learner with learning content that utilizes the learner's visual strengths;
If the hearing-related characteristic is dominant among the developmental characteristics, providing the learner with learning content that utilizes the strength of hearing;
The information processing device according to claim 1 .
前記アセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、前記学習者の視覚に関するスキル、聴覚に関するスキル、読み書きに関するスキル、または算数に関するスキルの少なくともいずれかを示すスキルを評価する第1評価部と、
前記評価されたスキルに基づいて、前記学習環境と前記発達特性とを評価する第2評価部とを含む、
請求項1から5のいずれか1項に記載の情報処理装置。 The evaluation unit is
a first evaluation unit that evaluates the learner's skills indicating at least one of visual skills, auditory skills, reading and writing skills, and arithmetic skills based on a result of the assessment test;
A second evaluation unit that evaluates the learning environment and the development characteristics based on the evaluated skills.
The information processing device according to claim 1 .
学習者に対して、アセスメントテストを実施する実施機能と、
前記アセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、前記学習者がレッスンに取り組む際の音声の入出力の仕方、画面の操作の仕方、又は画面の表示の仕方の少なくともいずれかである学習環境と、前記学習者の発達特性とを評価する評価機能と、
前記学習者がレッスンに取り組む際、前記評価機能で評価された前記学習環境に基づいて設定された学習環境で、前記評価機能で評価された前記発達特性に基づいて決定された学習コンテンツを、前記学習者に提供する提供機能と、を実現させる、
プログラム。 On the computer,
An assessment test implementation function for conducting assessment tests on learners;
an evaluation function for evaluating the learning environment, which is at least one of a manner of voice input/output, a manner of screen operation, and a manner of screen display when the learner works on the lesson, and the developmental characteristics of the learner, based on the result of the assessment test;
a provision function for providing the learner with learning content determined based on the developmental characteristics evaluated by the evaluation function in a learning environment set based on the learning environment evaluated by the evaluation function when the learner works on a lesson;
program.
学習者に対して、アセスメントテストを実施し、
前記アセスメントテストの結果に基づいて、前記学習者がレッスンに取り組む際の音声の入出力の仕方、画面の操作の仕方、又は画面の表示の仕方の少なくともいずれかである学習環境と、前記学習者の発達特性とを評価し、
前記学習者がレッスンに取り組む際、前記評価された前記学習環境に基づいて設定された学習環境で、前記評価された前記発達特性に基づいて決定された学習コンテンツを、前記学習者に提供する、
情報処理方法。 The computer
An assessment test is administered to students.
Based on the result of the assessment test, evaluating the learning environment, which is at least one of the manner of voice input/output, the manner of screen operation, and the manner of screen display when the learner engages in the lesson, and the developmental characteristics of the learner;
providing the learner with learning content determined based on the assessed developmental characteristics in a learning environment configured based on the assessed learning environment when the learner engages in a lesson;
Information processing methods.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021060194AJP7618482B2 (en) | 2021-03-31 | 2021-03-31 | Information processing device, program, and information processing method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021060194AJP7618482B2 (en) | 2021-03-31 | 2021-03-31 | Information processing device, program, and information processing method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2022156477A JP2022156477A (en) | 2022-10-14 |
| JP7618482B2true JP7618482B2 (en) | 2025-01-21 |
Family
ID=83559150
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021060194AActiveJP7618482B2 (en) | 2021-03-31 | 2021-03-31 | Information processing device, program, and information processing method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7618482B2 (en) |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001501320A (en) | 1996-09-25 | 2001-01-30 | シルバン ラーニング システムズ インコーポレイテッド | Automated system for exam and electronic command delivery and student management |
| JP2002221893A (en) | 2001-01-25 | 2002-08-09 | Takeshi Hashimoto | Learning support system |
| JP2003046980A (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2003-02-14 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Request response method, apparatus and program |
| JP2005321647A (en) | 2004-05-10 | 2005-11-17 | Ricoh Elemex Corp | Learning support method and learning support system |
| JP2014010499A (en) | 2012-06-27 | 2014-01-20 | Coach A Co Ltd | Communication support system and communication support program |
| JP2016212168A (en) | 2015-04-30 | 2016-12-15 | シナノケンシ株式会社 | Education support system and terminal |
| JP2017227780A (en) | 2016-06-23 | 2017-12-28 | ソニー株式会社 | Information processing device, information processing method, and program |
| JP2018514815A (en) | 2015-04-05 | 2018-06-07 | スマイラブルズ インコーポレイテッド | Presentation of customized learning content for infants based on developmental age, customized learning content based on parental preferences, customized educational playlists, and automated systems for detecting infant performance |
| JP2019179103A (en) | 2018-03-30 | 2019-10-17 | 特定非営利活動法人まなの樹 | Learning support program |
- 2021
- 2021-03-31JPJP2021060194Apatent/JP7618482B2/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001501320A (en) | 1996-09-25 | 2001-01-30 | シルバン ラーニング システムズ インコーポレイテッド | Automated system for exam and electronic command delivery and student management |
| JP2002221893A (en) | 2001-01-25 | 2002-08-09 | Takeshi Hashimoto | Learning support system |
| JP2003046980A (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2003-02-14 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Request response method, apparatus and program |
| JP2005321647A (en) | 2004-05-10 | 2005-11-17 | Ricoh Elemex Corp | Learning support method and learning support system |
| JP2014010499A (en) | 2012-06-27 | 2014-01-20 | Coach A Co Ltd | Communication support system and communication support program |
| JP2018514815A (en) | 2015-04-05 | 2018-06-07 | スマイラブルズ インコーポレイテッド | Presentation of customized learning content for infants based on developmental age, customized learning content based on parental preferences, customized educational playlists, and automated systems for detecting infant performance |
| JP2016212168A (en) | 2015-04-30 | 2016-12-15 | シナノケンシ株式会社 | Education support system and terminal |
| JP2017227780A (en) | 2016-06-23 | 2017-12-28 | ソニー株式会社 | Information processing device, information processing method, and program |
| JP2019179103A (en) | 2018-03-30 | 2019-10-17 | 特定非営利活動法人まなの樹 | Learning support program |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2022156477A (en) | 2022-10-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Dinehart | Handwriting in early childhood education: Current research and future implications | |
| Abdel Latif | Coping with COVID-19-related online English teaching challenges: teacher educators’ suggestions | |
| Rossing et al. | iLearning: The future of higher education? Student perceptions on learning with mobile tablets | |
| Salmon | Factors that affect emergent literacy development when engaging with electronic books | |
| Griffith et al. | Promoting metacognitive decision-making in teacher education | |
| Reinders | Learning analytics for language learning and teaching | |
| KR20170141264A (en) | Vertically integrated mobile computer system | |
| CN105070124A (en) | Interactive commercial law basic teaching system | |
| Casagrand et al. | Redesigning a course to help students achieve higher-order cognitive thinking skills: from goals and mechanics to student outcomes | |
| Li et al. | Pre-school children’s behavioral patterns and performances in learning numerical operations with a situation-based interactive e-book | |
| US12046157B1 (en) | Adaptive educational activities | |
| Chen et al. | Enhancement of English learning performance by using an attention-based diagnosing and review mechanism in paper-based learning context with digital pen support | |
| Chatziemmanouil et al. | Accessibility Academy: Interactive learning of the WCAG 2.1 web accessibility guidelines | |
| KR20170130222A (en) | A system for solving problems and using corresponding explanation contents and its systematic building method | |
| Rustan et al. | Teachers’ perspectives on technology-based learning for the kindergarten students | |
| WO2013105114A2 (en) | A computer implemented system and method for statistically assessing co-scholastic skills of a user | |
| JP7618482B2 (en) | Information processing device, program, and information processing method | |
| Lenci | Technology and language learning: from CALL to MALL | |
| US20170116871A1 (en) | Systems and methods for automated tailored methodology-driven instruction | |
| JP2021110773A (en) | Management equipment, methods and programs | |
| Carrió-Pastor et al. | Second language writing: Use of the World Wide Web to improve specific writing | |
| Eddy | Recent research in science teaching and learning | |
| Al Fadda et al. | International standards for e-learning ESL programs: A comparative study | |
| Gehrke | Creating more equitable rubrics to reduce discrimination and inequities in public-speaking courses | |
| Haryana et al. | Indonesian EFL Students’ Autonomus Learning Implementation in Online Learning |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20231214 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20240926 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20241002 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20241121 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20241219 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20250108 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:7618482 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |